Page 1

EP350
Portable Radios
Detailed Service Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Technical Information Updates
As we continue to make engineering enhancements to our products, the information in our
Service Manuals need to be updated accordingly. If you wish to be informed of these
updates, kindly fill in and fax us your details.
Fax to: 6-04-6124944
The Technical Publications Coordinator,
Global Customer Documentation,
R&D Department,
Motorola Penang.
Your Details
N a m e / C o n t a c t P e r s o n :
Company Name:
Address:
Telephone No. :
Fax No.:
Email Address:
How would you like to receive the update notification?
Through: mail email fax
Manual No.: 6878422A01
Kindly complete the Service Manual Feedback Form on the next page to help us ensure
that you receive the most accurate and complete information.
Page 4
Service Manual Feedback Form
We believe that reports from users provide valuable information for producing quality
manuals. Kindly take a few moments to provide feedback on this manual. Thank you for
your cooperation.
Fax to: 6-04-6124944
The Technical Publications Coordinator,
Global Customer Documentation,
R&D Department,
Motorola Penang.
1. Please check all the appropriate boxes:
Complete
Disassembly
Procedures
Alignment
Procedures
Exploded
Views
Schematic
Diagrams
Circuit Board
Details
Electrical Parts
List
Exploded View
Parts List
Incomplete
Correct
Incorrect
Clear
Confusing
Size
Adequate
Size
Too Small
Not Covered
in this Manual
2. How do you rate this particular Service Manual?
excellent very good good fair poor
3. Did this Service manual provide you with the information necessary to service and
maintain the specific equipment?
very much so generally yes to some extent no
4. We would appreciate any corrections or recommendations for improving this manual.
Please include the specific page number(s) of the diagram or procedure in question.
5. General comments/suggestions:
Manual No.: 6878422A01
Page 5

COPYRIGHT
Copyrights
© 2009 by Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into
any language or computer language, in any form or by any means, without the prior written
permission of Motorola Inc.
Computer Software Copyrights
The Motorola products described in this manual may include copyrighted Motorola computer
programs stored in semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the United States and other
countries preserve for Motorola certain exclusive rights for copyrighted computer programs including,
but not limited to, the exclusive right to copy or reproduce in any form the copyrighted computer
program. Accordingly, any copyrighted Motorola computer programs contained in the Motorola
products described in this manual may not be copied, reproduced, modified, reverse-engineered, or
distributed in any manner without the express written permission of Motorola. Furthermore, the
purchase of Motorola products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel,
or otherwise, any license under the copyrights, patents or patent applications of Motorola, except for
the normal non-exclusive royalty-free license to use that arises by operation of law in the sale of a
product.
i
Trademarks
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the U.S.Patent and Trademark Office. All
other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Page 6

ii
SAFETY INFORMATION
Product Safety and RF Energy Exposure Compliance
These servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To
reduce the risk of electric shock, do not perform any servicing other than that
contained in the Operating Instructions unless you are qualified to do so.
Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
Before using this product, read the operating instructions for safe usage
contained in the Product Safety and RF Exposure booklet enclosed with your
radio.
ATTENTION!
This is restricted to occupational use only to satisfy ICNIRP RF energy exposure
requirements. Before using this product, read the RF energy awareness information and
operating instructions in the Product Safety and RF Exposure booklet enclosed with your
(Motorola Publication part number 68007024010) to ensure compliance with RF energy
exposure limits.
For a list of Motorola-approved antennas, and other accessories, visit the following web site
which lists approved accessories: http://www.motorola.com/radiosolutions
Page 7
DOCUMENT HISTORY
The following major changes have been implemented in this manual since the previous edition:
Edition Description Date
6878422A01-A Initial edition Mar, 2009
iii
6878422A01-B Added VHF and UHF1 band information (Chapter 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13)
August, 2009
Page 8

iv
Notes
Page 9

Table of Contents v
Table of Contents
Copyright ........................................................................................................ i
Safety Information......................................................................................... ii
Document History ........................................................................................ iii
Chapter 1 Maintenance ........................................................................ 1-1
1.1 Preventive Maintenance ................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 Inspection ...................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.3 Cleaning......................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.4 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS............................................................................................ 1-2
1.5 General Repair Procedures and Techniques ................................................................................ 1-2
Chapter 2 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools........... 2-1
2.1 Test Equipment.............................................................................................................................. 2-1
2.2 Service Aids................................................................................................................................... 2-2
Chapter 3 DC Power Distribution........................................................ 3-1
3.1 DC Regulation and Distribution ..................................................................................................... 3-1
Chapter 4 Controller Theory of Operation.......................................... 4-1
4.1 RX Audio Circuit ............................................................................................................................ 4-1
4.1.1 Audio processor IC (U102) ............................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.1.1 RX Audio Processing......................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.1.2 RX Tone PL/Digital PL Decode Filtering............................................................ 4-2
4.1.2 Audio Amp ........................................................................................................................ 4-2
4.1.3 Internal and External Speaker .......................................................................................... 4-2
4.2 TX Audio Circuit............................................................................................................................. 4-3
4.2.1 MIC and External MIC ...................................................................................................... 4-3
4.2.2 4-order 4 kHz Low-Pass Filter (U501-C, D) ...................................................................... 4-3
4.2.3 Audio processor IC (U102) ............................................................................................... 4-3
4.2.3.1 TX Audio Processing ......................................................................................... 4-3
4.2.3.2 Tx Tone PL/Digital PL Encode Filtering............................................................. 4-4
4.2.4 TX audio amplifier and 6 order 3 kHz Low-Pass filter....................................................... 4-4
4.2.5 TX modulation Adjustment................................................................................................ 4-4
4.3 Microprocessor Circuitry ................................................................................................................ 4-4
4.3.1 Memory Usage ................................................................................................................. 4-5
4.3.2 Control and Indicator Interface ......................................................................................... 4-5
4.3.3 Interface to USB programming ......................................................................................... 4-5
4.3.4 Storage of Customer-Specific Information........................................................................ 4-5
4.3.5 Sensing of VOX operating ................................................................................................ 4-5
4.3.6 Microprocessor Power-on reset Routine .......................................................................... 4-5
4.3.7 Microprocessor 7.3728 MHz Clock................................................................................... 4-5
Page 10

vi Table of Contents
4.3.8 Battery indicator ................................................................................................................ 4-5
Chapter 5 435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation ....................... 5-1
5.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 UHF2 Receiver .............................................................................................................................. 5-1
5.2.1 Receiver Front End ...........................................................................................................5-2
5.2.2 Receiver Back End ........................................................................................................... 5-2
5.3 UHF2 Transmitter .......................................................................................................................... 5-3
5.3.1 Power Amplifier................................................................................................................. 5-3
5.3.2 Antenna Switch ................................................................................................................. 5-3
5.3.3 Harmonic Filter..................................................................................................................5-3
5.3.4 Auto Power Control........................................................................................................... 5-4
5.4 UHF2 Frequency Generation Circuitry........................................................................................... 5-4
5.4.1 Reference Oscillator (12.8 MHz VCTCXO)....................................................................... 5-4
5.4.2 PLL IC Prescaler and Comparator.................................................................................... 5-5
5.4.3 Voltage Doubler and Charge Pump .................................................................................. 5-5
5.4.4 Loop Filter ......................................................................................................................... 5-5
5.4.5 Dual VCO.......................................................................................................................... 5-5
5.5 Keypad........................................................................................................................................... 5-6
Chapter 6 UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables........................................... 6-1
6.1 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF2) .................................................................................6-1
6.2 Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF2) ............................................................................ 6-2
6.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF2) .............................................................................6-3
6.4 Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2) ............................................................. 6-4
Chapter 7 UHF2 Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists ... 7-1
7.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 7-1
7.1.1 Notes For All Schematics and Circuit Boards ...................................................................7-1
7.1.2 Four Layer Circuit Board...................................................................................................7-3
7.2 Speaker and Microphone Schematic .............................................................................................7-3
7.2.1 Speaker and Microphone Parts List.................................................................................. 7-3
7.3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)...................................... 7-4
7.3.1 Parts List ......................................................................................................................... 7-16
Chapter 8 136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation.......................... 8-1
8.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 8-1
8.2 VHF Receiver................................................................................................................................. 8-1
8.2.1 Receiver Front End ...........................................................................................................8-2
8.2.2 Receiver Back End ........................................................................................................... 8-2
8.3 VHF Transmitter............................................................................................................................. 8-3
8.3.1 Power Amplifier................................................................................................................. 8-3
8.3.2 Antenna Switch ................................................................................................................. 8-3
8.3.3 Harmonic Filter..................................................................................................................8-3
8.3.4 Auto Power Control........................................................................................................... 8-4
8.4 VHF Frequency Generation Circuitry............................................................................................. 8-4
8.4.1 Reference Oscillator (12.8 MHz VCTCXO)....................................................................... 8-4
8.4.2 PLL IC Prescaler and Comparator.................................................................................... 8-5
Page 11

Table of Contents vii
8.4.3 Voltage Doubler and Charge Pump.................................................................................. 8-5
8.4.4 Loop Filter......................................................................................................................... 8-5
8.4.5 Dual VCO.......................................................................................................................... 8-5
8.5 Keypad........................................................................................................................................... 8-6
Chapter 9 VHF Troubleshooting Tables ............................................. 9-1
9.1 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (VHF) ................................................................................... 9-1
9.2 Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (VHF) .............................................................................. 9-2
9.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (VHF) ............................................................................... 9-3
9.4 Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF) ............................................................... 9-4
Chapter 10 VHF Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists.... 10-1
10.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................. 10-1
10.1.1 Notes For All Schematics and Circuit Boards ................................................................. 10-1
10.1.2 Four Layer Circuit Board................................................................................................. 10-3
10.2 Speaker and Microphone Schematic........................................................................................... 10-3
10.2.1 Speaker and Microphone Parts List................................................................................ 10-3
10.3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)...................................... 10-1
10.3.1 Parts List....................................................................................................................... 10-14
Chapter 11 403 – 447 MHz UHF1 Theory Of Operation ..................... 11-1
11.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................. 11-1
11.2 UHF1 Receiver ............................................................................................................................ 11-1
11.2.1 Receiver Front End......................................................................................................... 11-2
11.2.2 Receiver Back End .........................................................................................................11-2
11.3 UHF1 Transmitter ........................................................................................................................ 11-3
11.3.1 Power Amplifier............................................................................................................... 11-3
11.3.2 Antenna Switch............................................................................................................... 11-3
11.3.3 Harmonic Filter ............................................................................................................... 11-3
11.3.4 Auto Power Control......................................................................................................... 11-4
11.4 UHF1 Frequency Generation Circuitry ........................................................................................ 11-4
11.4.1 Reference Oscillator (12.8 MHz VCTCXO) .................................................................... 11-4
11.4.2 PLL IC Prescaler and Comparator.................................................................................. 11-5
11.4.3 Voltage Doubler and Charge Pump ................................................................................ 11-5
11.4.4 Loop Filter....................................................................................................................... 11-5
11.4.5 Dual VCO........................................................................................................................ 11-5
11.5 Keypad......................................................................................................................................... 11-6
Chapter 12 UHF1 Troubleshooting Tables......................................... 12-1
12.1 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF1) ............................................................................... 12-1
12.2 Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF1) .......................................................................... 12-2
12.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF1) ........................................................................... 12-3
12.4 Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF1) ........................................................... 12-4
Chapter 13 UHF1 Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists . 13-1
13.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................. 13-1
Page 12

viii Table of Contents
13.1.1 Notes For All Schematics and Circuit Boards ................................................................. 13-1
13.1.2 Four Layer Circuit Board................................................................................................. 13-3
13.2 Speaker and Microphone Schematic........................................................................................... 13-3
13.2.1 Speaker and Microphone Parts List ................................................................................ 13-3
13.3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF1: 403–447 MHz).................................... 13-1
13.3.1 Parts List ....................................................................................................................... 13-13
Appendix A Warranty, Service Support, and Replacement Parts .......A-1
A.1 Scope of Manual ............................................................................................................................A-1
A.2 Warranty ........................................................................................................................................A-1
A.2.1 Warranty Period and Return Instructions..........................................................................A-1
A.2.2 After Warranty Period .......................................................................................................A-1
A.2.3 Piece Parts........................................................................................................................A-2
Page 13

List of Figures ix
List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Programming/Test Cable (PMDN4077_R)....................................................................... 2-3
Figure 2-2. Cloning Cable (PMDN4076_R) ........................................................................................ 2-3
Figure 2-3. Wiring of the Connectors.................................................................................................. 2-3
Figure 3-1. DC Power Distribution Block Diagram.............................................................................. 3-1
Figure 4-1. RX Audio Circuit ............................................................................................................... 4-1
Figure 4-2. TX Audio Circuit ............................................................................................................... 4-3
Figure 5-1. UHF2 Receiver Block Diagram ........................................................................................ 5-1
Figure 5-2. UHF2 Transmitter Block Diagram .................................................................................... 5-3
Figure 5-3. UHF2 Frequency Generation Unit Block Diagram ........................................................... 5-4
Figure 5-4. Keypad Block Diagram..................................................................................................... 5-6
Figure 7-1. Four–Layer Circuit Board: Copper Steps in Layer Sequence .......................................... 7-3
Figure 7-2. Speaker and Microphone Schematic ............................................................................... 7-3
Figure 7-3. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Receiver Schematic Diagram....................................................... 7-4
Figure 7-4. VCO and PLL Schematic Diagram................................................................................... 7-5
Figure 7-5. Transmitter Schematic Diagram....................................................................................... 7-6
Figure 7-6. Microprocessor and Keypad Schematic Diagram ............................................................ 7-7
Figure 7-7. Audio Power Amplifier and External Audio Schematic Diagram ...................................... 7-8
Figure 7-8. Switches and Battery Schematic Diagram ....................................................................... 7-9
Figure 7-9. Transmitter Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram ........................................... 7-10
Figure 7-10. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Mainboard Top Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON200..................... 7-11
Figure 7-11. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Mainboard Bottom Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON200 ............... 7-12
Figure 7-12. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Top View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100......... 7-13
Figure 7-13. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Bottom View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100.... 7-14
Figure 7-14. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Keypad Board: PCB No. 8422BEACON100 .............................. 7-15
Figure 8-1. VHF Receiver Block Diagram...........................................................................................8-1
Figure 8-2. VHF Transmitter Block Diagram....................................................................................... 8-3
Figure 8-3. VHF Frequency Generation Unit Block Diagram.............................................................. 8-4
Figure 8-4. Keypad Block Diagram..................................................................................................... 8-6
Figure 10-1. Four–Layer Circuit Board: Copper Steps in Layer Sequence ........................................ 10-3
Figure 10-2. Speaker and Microphone Schematic ............................................................................. 10-3
Figure 10-3. VHF (136–174 MHz) Receiver Schematic Diagram....................................................... 10-1
Figure 10-4. VCO and PLL Schematic Diagram................................................................................. 10-2
Figure 10-5. Transmitter Schematic Diagram..................................................................................... 10-3
Figure 10-6. Microprocessor and Keypad Schematic Diagram .......................................................... 10-4
Figure 10-7. Audio Power Amplifier and External Audio Schematic Diagram .................................... 10-5
Figure 10-8. Switches and Battery Schematic Diagram ..................................................................... 10-6
Figure 10-9. Transmitter Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram ........................................... 10-7
Figure 10-10. Receiver Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram ............................................... 10-8
Figure 10-11. VHF (136–174 MHz) Mainboard Top Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON400....................... 10-9
Figure 10-12. VHF (136–174 MHz) Mainboard Bottom Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON400................ 10-10
Figure 10-13. VHF (136–174 MHz)Sub Circuit Board Top View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100 .......... 10-11
Figure 10-14. VHF (136–174 MHz)Sub Circuit Board Bottom View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100 ..... 10-12
Figure 10-15. VHF (136–174 MHz) Keypad Board: PCB No. 8422BEACON100 .............................. 10-13
Figure 11-1. UHF1 Receiver Block Diagram ...................................................................................... 11-1
Figure 11-2. UHF1 Transmitter Block Diagram .................................................................................. 11-3
Figure 11-3. UHF1 Frequency Generation Unit Block Diagram ......................................................... 11-4
Figure 11-4. Keypad Block Diagram................................................................................................... 11-6
Figure 13-1. Four–Layer Circuit Board: Copper Steps in Layer Sequence ........................................ 13-3
Figure 13-2. Speaker and Microphone Schematic ............................................................................. 13-3
Figure 13-3. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Receiver Schematic Diagram..................................................... 13-1
Page 14

x List of Figures
Figure 13-4. VCO and PLL Schematic Diagram ................................................................................. 13-2
Figure 13-5. Transmitter Schematic Diagram ..................................................................................... 13-3
Figure 13-6. Microprocessor and Keypad Schematic Diagram .......................................................... 13-4
Figure 13-7. Audio Power Amplifier and External Audio Schematic Diagram .................................... 13-5
Figure 13-8. Switches and Battery Schematic Diagram ..................................................................... 13-6
Figure 13-9. Transmitter Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram ........................................... 13-7
Figure 13-10. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Mainboard Top Side: PCB No. 8431BEAUHF300 .....................13-8
Figure 13-11. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Mainboard Bottom Side: PCB No. 8431BEAUHF300 ................13-9
Figure 13-12. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Top View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100 ....... 13-10
Figure 13-13. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Bottom View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100.. 13-11
Figure 13-14. UHF1 (403–447 MHz) Keypad Board: PCB No. 8422BEACON100 ............................ 13-12
Page 15

List of Tables xi
List of Tables
Table 1-1. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List ......................................................................... 1-3
Table 1-2. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List ....................................................................... 1-3
Table 2-1. Recommended Test Equipment....................................................................................... 2-1
Table 2-2. Service Aids ..................................................................................................................... 2-2
Table 3-1. Voltage Regulators........................................................................................................... 3-2
Table 4-1. Radio Memory Requirements........................................................................................... 4-4
Table 6-1. Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF2) .................................................................... 6-1
Table 6-2. Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF2)................................................................ 6-2
Table 6-3. Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF2) ................................................................ 6-3
Table 6-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2)................................................. 6-4
Table 9-1. Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (VHF)....................................................................... 9-1
Table 9-2. Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (VHF) .................................................................. 9-2
Table 9-3. Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (VHF)................................................................... 9-3
Table 9-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF)................................................... 9-4
Table 12-1. Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF1) .................................................................. 12-1
Table 12-2. Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF1).............................................................. 12-2
Table 12-3. Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF1) .............................................................. 12-3
Table 12-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF1)............................................... 12-4
Page 16

xii Notations Used in This Manual
Notations Used in This Manual
Throughout the text in this publication, you will notice the use of the following notations. These notations are
used to emphasize that safety hazards exist, and due care must be taken and observed.
Note
An operational procedure, practice, or condition that isessential to emphasize.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
might result in equipment damage.
Page 17
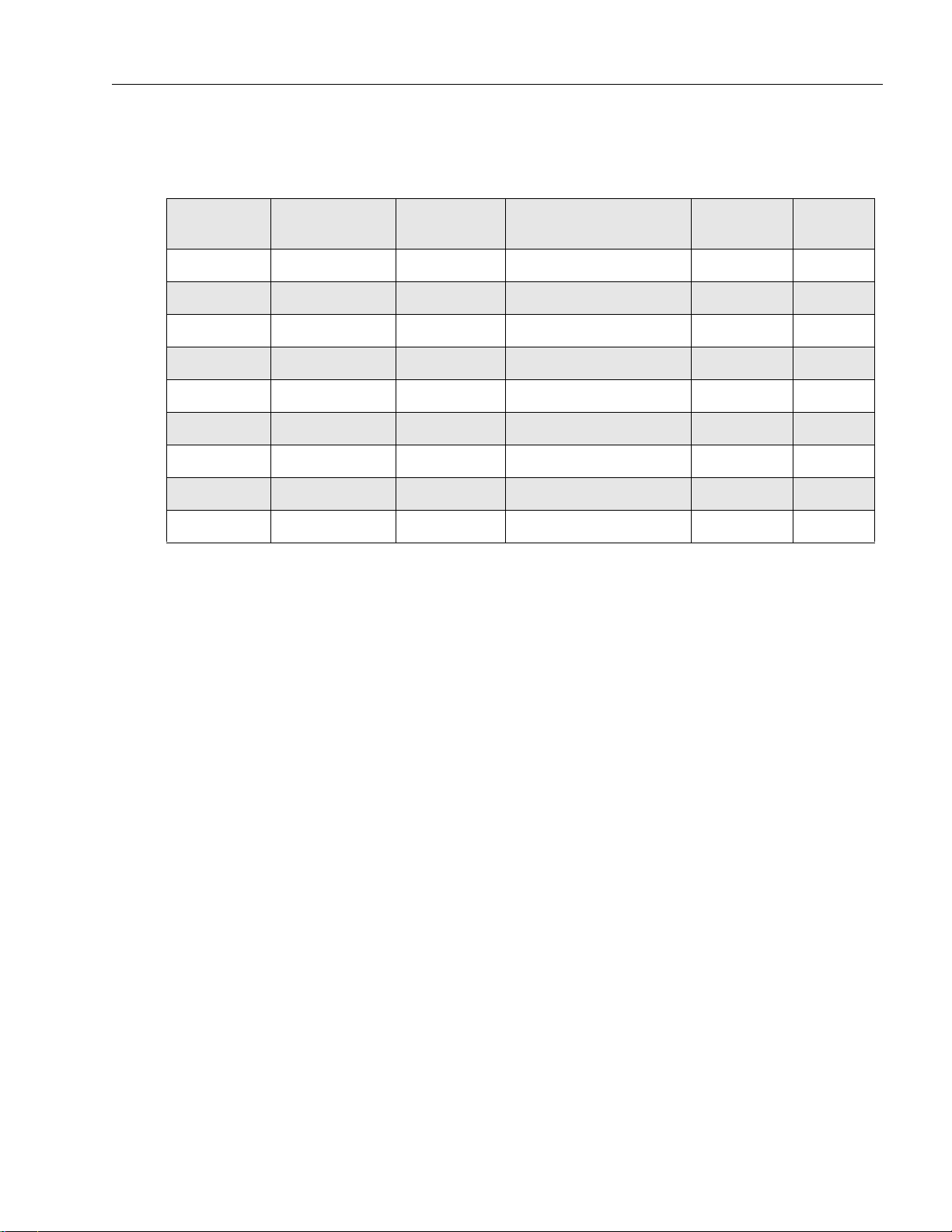
Summary of Printed Circuit Boards and Bands Available xiii
Summary of Printed Circuit Boards and Bands Available
Table below lists all the bands available in this manual.
Frequency
Band
UHF2 435 – 480 MHz 1W or 4W
UHF2 – –
UHF2 – –
VHF 136 – 162 MHz 1W or 5W
VHF – –
VHF – –
UHF1 403 – 447 MHz 1W or 4W
UHF1 – –
UHF1 – –
Bandwidth Power Level PC Board Part Number Board
8431BEACON200
8421BEACON100
8422BEACON100
8431BEACON400
8421BEACON100
8422BEACON100
8431BEAUHF300
8421BEACON100
8422BEACON100
Chapter
Revision
27
1 7
17
4 10
110
1 10
313
1 13
113
Page 18

xiv
Notes
Page 19

Chapter 1 Maintenance
1.0 Introduction
This chapter of the manual describes:
• Preventive maintenance
• Safe handling of CMOS devices
• Repair procedures and techniques
NOTE
The Servicing of your Intrinsically Safe Radios.
In order to maintain compliance, radios that are FM Approved to intrinsically safe
standards MUST be repaired at FM audited service centers. See Further Assistance From
Motorola on page 1-2 for more information.
1.1 Preventive Maintenance
Periodic visual inspection and cleaning is recommended.
1.2 Inspection
Check that the external surfaces of the radio are clean, and that all external controls and switches
are functional. It is not recommended to inspect the interior electronic circuitry.
1.3 Cleaning
The following procedures describe the recommended cleaning agents and the methods to be
used when cleaning the external and internal surfaces of the radio. External surfaces include the
front cover, housing assembly, and battery case. These surfaces should be cleaned whenever a
periodic visual inspection reveals the presence of smudges, grease, and/or grime.
NOTE
The only recommended agent for cleaning the external radio surfaces is a 0.5% solution of a mild
dishwashing detergent in water. The only factory recommended liquid for cleaning the printed
circuit boards and their components is isopropyl alcohol (100% by volume).
Internal surfaces should be cleaned only when the radio is disassembled for servicing or
repair.
CAUTION: The effects of certain chemicals and their vapors can have harmful results on
certain plastics. Aerosol sprays, tuner cleaners, and other chemicals should be avoided.
1. Cleaning External Plastic Surfaces
The detergent-water solution should be applied sparingly with a stiff, non-metallic, shortbristled brush to work all loose dirt away from the radio. A soft, absorbent, lintless cloth or
tissue should be used to remove the solution and dry the radio. Make sure that no water
remains entrapped near the connectors, cracks, or crevices.
Page 20
1-2 Introduction
2. Cleaning Internal Circuit Boards and Components
Isopropyl alcohol may be applied with a stiff, non-metallic, short-bristled brush to dislodge
embedded or caked materials located in hard-to-reach areas. The brush stroke should
direct the dislodged material out and away from the inside of the radio. Make sure that
controls or tunable components are not soaked with alcohol. Do not use high-pressure
air to hasten the drying process since this could cause the liquid to collect in unwanted
places. Upon completion of the cleaning process, use a soft, absorbent, lintless cloth to
dry the area. Do not brush or apply any isopropyl alcohol to the frame, front cover, or
back cover.
NOTE Always use a fresh supply of alcohol and a clean container to prevent contamination by
dissolved material (from previous usage).
1.4 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS
Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices are used in this family of radios.
CMOS characteristics make them susceptible to damage by electrostatic or high voltage charges.
Damage can be latent, resulting in failures occurring weeks or months later. Therefore, special
precautions must be taken to prevent device damage during disassembly, troubleshooting, and
repair.
Handling precautions are mandatory for CMOS circuits and are especially important in low
humidity conditions. DO NOT attempt to disassemble the radio without first referring to the CMOS
CAUTION paragraph in the Disassembly and Reassembly section of the manual.
1.5 General Repair Procedures and Techniques
NOTE
Environmentally Preferred Products (EPP) (refer to the marking on the printed circuit
boards - examples shown below) were developed and assembled using environmentally
preferred components and solder assembly techniques that meet or exceed compliance
to the European Union’s ROHS and WEEE directives (Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment (WEEE) Directive 2002/96/EC and Restriction of Hazardous Subtances
(ROHS) Directive 2002/95/EC). To maintain product compliance and reliability, use only
the Motorola specified parts in this manual.
For the identification of lead (Pb) free assemblies, all EPP products will carry the EPP
Marking, shown below, on the printed circuit board (PCB). This marking provides
information to those performing assembly, servicing and recycling operation on this
product, adhering to the JEDEC standard #97. The EPP Marking takes the form of a
label or marking on the PCB.
Page 21
Introduction 1-3
Any rework or repair on Environmentally Preferred Products must be done using the appropriate
lead-free solder wire and solder paste as stated in the following tables:
Table 1-1. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List
Motorola
Part
Number
1088929Y01 95.5Sn/3.8Ag/0.7Cu RMA Version 2.7-3.2% 217C 52171 0.015” 1lb spool
Alloy Flux Type
Flux
Content by
Weight
Melting
Point
Supplier
Part
number
Diamet
er
Weight
Table 1-2. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List
Motorola
Part Number
1085674C03 NC-SMQ230 900-1000KCPs
Manufacturer
Part Number
Viscosity Type Composition & Percent Metal
Brookfield (5rpm)
Type 3
(-325/+500)
(95.5%Sn-3.8%Ag-0.7%Cu)
89.3%
Liquid
Temperatur
e
217°C
Parts Replacement and Substitution
When damaged parts are replaced, identical parts should be used. If the identical replacement
component is not locally available, check the parts list for the proper Motorola part number and
order the component from the nearest Motorola Communications parts center listed in the “Piece
Parts” section of this manual.
Rigid Circuit Boards
The family of radios uses bonded, multi-layer, printed circuit boards. Since the inner layers are
not accessible, some special considerations are required when soldering and unsoldering
components. The through-plated holes may interconnect multiple layers of the printed circuit.
Therefore, care should be exercised to avoid pulling the plated circuit out of the hole.
When soldering near the connector pins:
• Avoid accidentally getting solder in the connector.
• Be careful not to form solder bridges between the connector pins
• Closely examine your work for shorts due to solder bridges.
Chip Components
Use the RLN4062 Hot-Air Repair Station for chip component replacement. Adjust the
temperature control to 390 °C (735 °F), and adjust the airflow to a minimum setting. Airflow can
vary due to component density.
• To remove a chip component:
1. Use a hot-air hand piece and position the nozzle of the hand piece approximately 0.3 cm
(1/8") above the component to be removed.
2. Begin applying the hot air. Once the solder reflows, remove the component using a pair
of tweezers.
3. Using a solder wick and a soldering iron or a power desoldering station, remove the
excess solder from the pads.
Page 22

1-4 Introduction
• To replace a chip component using a soldering iron:
1. Select the appropriate micro-tipped soldering iron and apply fresh solder to one of the
solder pads.
2. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new chip component in place while heating the
fresh solder.
3. Once solder wicks onto the new component, remove the heat from the solder.
4. Heat the remaining pad with the soldering iron and apply solder until it wicks to the
component. If necessary, touch up the first side. All solder joints should be smooth and
shiny.
• To replace a chip component using hot air:
1. Use the hot-air hand piece and reflow the solder on the solder pads to smooth it.
2. Apply a drop of solder paste flux to each pad.
3. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new component in place.
4. Position the hot-air hand piece approximately 0.3 cm (1/8”) above the component and
begin applying heat.
5. Once the solder wicks to the component, remove the heat and inspect the repair. All
joints should be smooth and shiny.
Shields
Removing and replacing shields is recommended to be done with the Air Blower,
BOSCH GHG 603 or equivalent.
• To remove the shield:
1. Place the circuit board in the circuit board holder.
2. Add solder paste flux around the base of the shield.
3. Position the heat-focus head onto the shield.
4. Turn on the heater and wait until the shield lifts off the circuit board.
5. Once the shield is off, turn off the heat, and grab the part with a pair of tweezers.
6. Remove the circuit board from the circuit board holder.
• To replace the shield:
1. Add solder to the shield if necessary, using a micro-tipped soldering iron.
2. Next, rub the soldering iron tip along the edge of the shield to smooth out any excess
solder. Use solder wick and a soldering iron to remove excess solder from the solder
pads on the circuit board.
3. Place the circuit board back in the circuit board holder.
4. Place the shield on the circuit board using a pair of tweezers.
5. Position the heat-focus head over the shield.
6. Turn on the heater and wait for the solder to reflow.
7. Once complete, turn off the heat, raise the heat-focus head and wait approximately one
minute for the part to cool.
8. Remove the circuit board and inspect the repair. No cleaning should be necessary.
Page 23
Chapter 2 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service
Tools
2.1 Test Equipment
Table 2-1 lists test equipment required to service the radios.
Table 2-1. Recommended Test Equipment
Motorola Part No. Description Characteristics Application
R2600 series or
HP 8920A
*R1074A Fluke 87 digital
*R1377A AC voltmeter 1 mV to 300 mV, 10 mega-
R1611A Dual channel
S1339A RF millivolt meter 100 μV to 3V RF, 10 kHz to
*R1013B or
*R1370A
System analyzer This item will substitute for
items with an asterisk (*)
True RMS metering,
multi-meter
Fluke 85 RF probe 500 MHz, 30 VAC max Use with Fluke 87 digital
100 MHz
oscilloscope
(Agillent)
SINAD meter or
SINAD meter with
RMS
200 kHz frequency
counter, 32-segment bar
graph with backlit display
Ohm input impedance
Two-channel, 100 MHz
bandwidth, 200 M sample
rate/sec, 2 MB memory/
channel
1 GHz frequency range
Without RMS audio
voltmeter or
With RMS audio voltmeter
Frequency/Deviation meter and
signal generator for wide-range
troubleshooting and alignment
Digital voltmeter is recommended
for AC/DC voltage and current
measurements
multi-meter for RF voltage
measurements.
Audio voltage measurements
Waveform measurements
RF level measurements
Receiver sensitivity
measurements
Page 24
2-2 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids
2.2 Service Aids
Table 2-2 lists the service aids recommended for working on the EP350 Series Radios. While all of
these items are available from Motorola, most are standard shop equipment items, and any
equivalent item capable of the same performance may be substituted for the item listed.
Table 2-2. Service Aids
Motorola Part
No.
PMDN4026_R Flat Ceramic Tuning Tools
(1.8mm)
PMDN4038_R Knob Remover/Chassis Opener Used to remove the front cover assembly.
PMDN4039_R Crab Eye Nut Opener Used to remove the crab eye nut.
1
PMDN4040_R
PMDN4041_R RF Adapter Adapts radio’s antenna port to BNC cabling of test
PMDN4044_R T-Head Ceramic Tuning Tool Used for tuning the VCO.
PMDN4053_R Flat Ceramic Tuning Tools
PMDN4076_R Radio to Radio Cloning Cable Allows a radio to be duplicated from a master radio by
PMDN4077_R Programming Cable Used to program the radio through Customer
PMDN4079_R GND Plate Interconnects radio’s chassis to RF Adaptor.
Radio Test Box Enables communication between the radio, test
(0.9mm)
Description Application
Used for tuning the VCO.
equipment and the computer's USB port.
equipment.
Used for tuning the VCO.
transferring programmed data from the master radio to
the other.
Programming Software and Radio Tuner.
PMDN4080_R Battery Eliminator Interconnects radio to power supply.
PMVN4161_ Customer Programming
Software on CD Rom
PMVN4165_ Tuner on CD Rom Only Motorola Service Centers or Authorized Motorola
Note: 1.Use PMDN4040BR or higher for tuning the EP350 Series radios as PMDN4040AR cannot be used to
perform this function.
Program customer option and channel data.
Service Dealers can perform this function.
Page 25
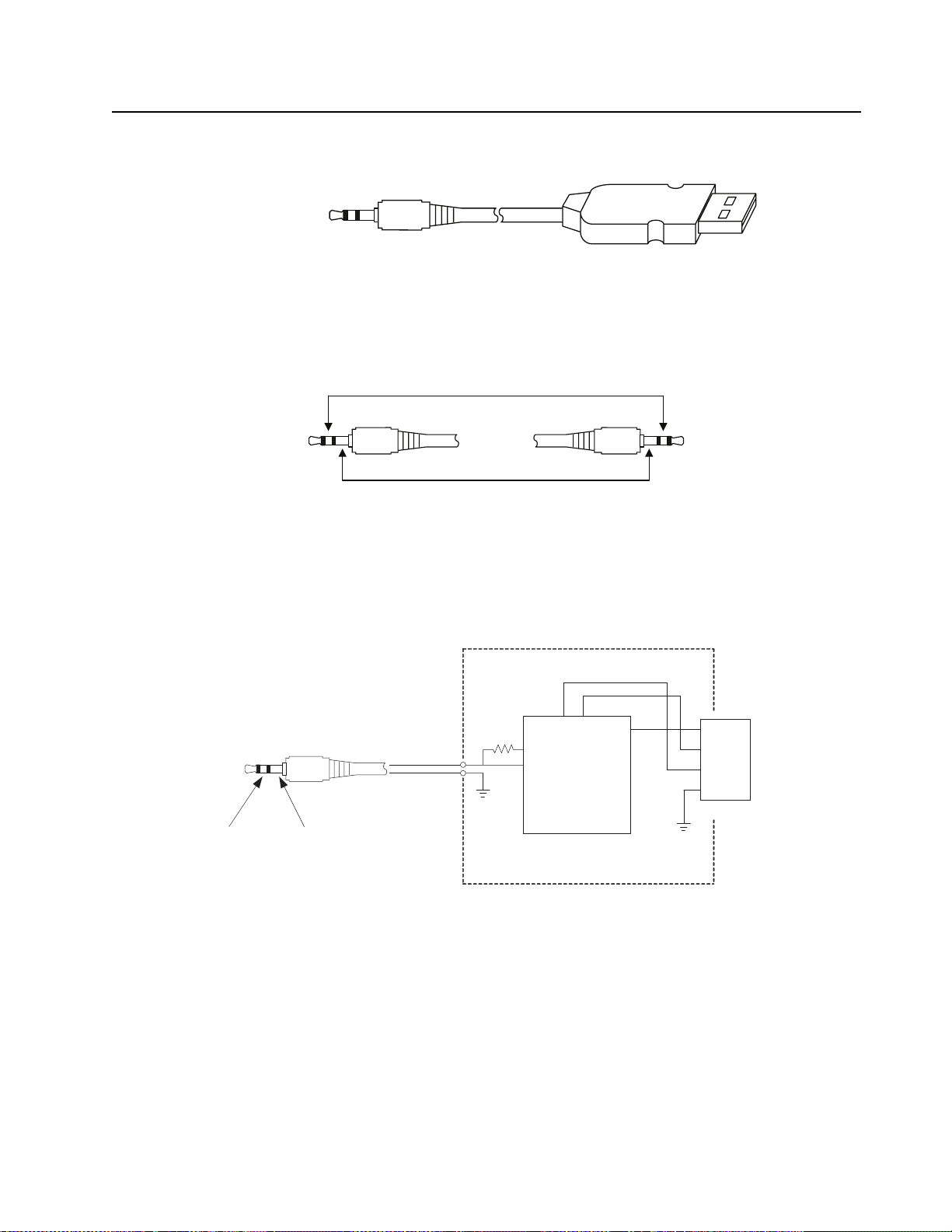
Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids 2-3
t
Programming/Test Cable
2.5mm stereo
USB connection
Figure 2-1. Programming/Test Cable (PMDN4077_R)
2.5mm stereo
2.5mm stereo >
12
RX / TX data GND
~
Figure 2-2. Cloning Cable (PMDN4076_R)
D-D+
VBUS
1
2
GND
TX_D
RX_D
IC : CP2102
2.5mm stereo
1
VBUS
2
D-
3
D+
GND
4, 5, 6
To Computor
USB_CONNECTOR
Figure 2-3. Wiring of the Connectors
Page 26

2-4 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids
Notes
Page 27
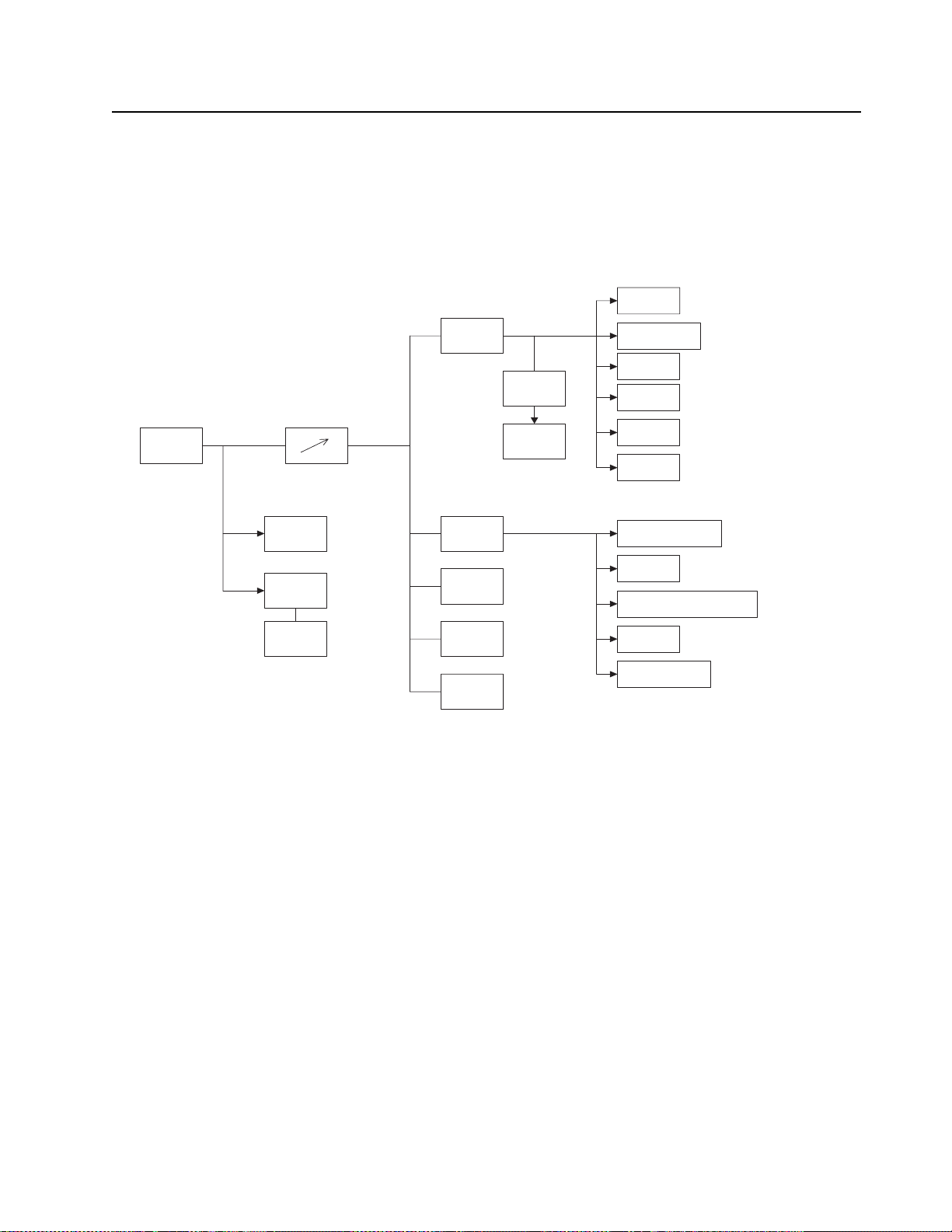
Chapter 3 DC Power Distribution
3.1 DC Regulation and Distribution
A block diagram of the DC power distribution throughout the radio is shown in Figure 3-1.
VCTCXO
Voltage
Doubler
10V
Charge
5V
Pump
3.3V
Audio filter
½ Vcc
VCO
RX B+
TXVB
MCU, EEPROM
PLL IC
Digital potent iometer
DTMF IC
LCD Driver
7.5V
Battery
Mech SW1
PA
APC
Driv er,
Pre-driver
SWB+
Vdd
Regulat or
Vdd
Regulat or
Key PC B
Low Batt.
detect or
Audio
Amplifier
Figure 3-1. DC Power Distribution Block Diagram
Battery voltage enters at connector J602 and is routed through SW/VOL1 to become SWB+.
This voltage is routed to:
•SW/VOL1
• TX power amplifier Q403 (via R417)
• APC circuit U401
• RX audio power amplifier U601
• 5V regulator (U505)
• 3.3V regulator (U506)
• Voltage divider R153/R154, a microprocessor A/D input which measures battery voltage
•Key PCB
Page 28
3-2 DC Power Distribution: DC Regulation and Distribution
The following regulators are used:
Table 3-1. Voltage Regulators
Reference No. Description Type
U505 5V regulator TK11250
U506 3.3V regulator TK11233
U507 Voltage Doubler (10V) TC12140
The 5 V source from U505 is applied to:
• RX back end circuitry
• RX/TX audio filters
• 1/2 VCC generator
• VCO power source (Q705, Q706)
• RX B+ (Q304)
• TXVB (Q407)
• VCTCXO
The 5 V source is also applied to transistor switches Q304 and Q407. Q304 is turned on by Q305
when RX_EN (from U101 Pin 71) is high, and supplies the source to mixer, IF IC and LNA. Q407 is
turned on by Q408 when TX_EN2 (from U101 Pin 85) is high, and supplies the "TXVB" source to the
first transmitter stage Q401 base, Q402 gate, APC power source (U401 Pin 8) and ANT switch
(CR401).
The 3.3 V regulated source from U506 is applied to:
• MCU IC U101
• EEProm IC U104
• DTMF IC U103
• Audio processor IC U102
• Microphone bias circuitry
• And applied to Key PCB (LCD driver power source)
The 10 V source from U507 is applied to Charge Pump.
Page 29
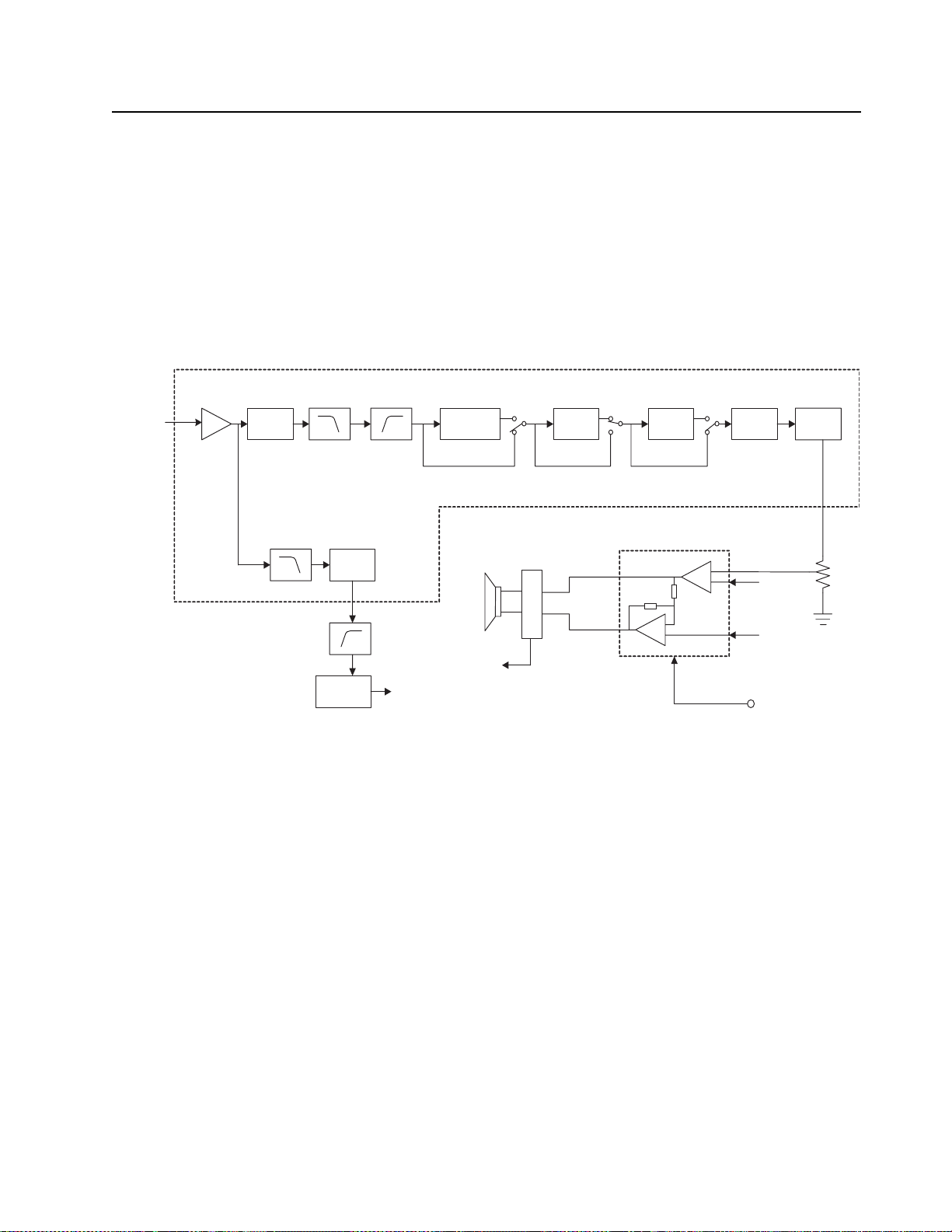
Chapter 4 Controller Theory of Operation
4.1 RX Audio Circuit
The RX audio circuit consists of Audio Processor IC, Audio Amplifier, Internal (INT)/External (EXT)
speaker and Sub-Audio Tones System.
Audio Processor IC (AK2347)
Audio IN
(from IF IC)
pin24
RXA1
VR3
-4 to +3.5dB/
0.5dB
Sub audio
Programmable
RX LPF TX/RX HPF
LPF
Sub audio
-6 to +6dB/
HPF
Comparator
U105-C
0.5dB
VR5
pin18
U105-A,B
(tone detect)
Figure 4-1. RX Audio Circuit
4.1.1 Audio processor IC (U102)
The RX audio from Pin 9 of U201 enters to Pin 24 of Audio processor IC.
To CPU
Scrambler/
Descrambler
U102
INT SPK.
EXT SPK.
J601
De-
emphasis
Expander VR4 SMF
-18, -4.5 to +4.5dB/
0.25dB
Audio Amp.
OUT-
OUT+
U601
IN-
IN+
SVR
Audio Mute
pin21
Vol1
control
• RX A: An operational amplifier used for gain adjustment of the receive demodulation signal
from Pin 9 of U201. The gain is unity and it acts as a buffer amplifier.
4.1.1.1 RX Audio Processing
•VR3: This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the input level of receive demodulation
signal. Adjustment range: -4.0dB to +3.5dB in 0.5dB steps.
• RX LPF: Low-pass filter to eliminate high-frequency components higher than 3 kHz which are
included in the receive demodulation signal.
• TX/RX HPF: High-pass filter to eliminate low-frequency components lower than 250 Hz which
are included in receive audio signal. This circuit is turned on and off by control register of Audio
processor IC.
• Descrambler: This circuit inverts the spectrum distribution of receive audio signals with respect
to the carrier frequency. The carrier frequency is 3.388 kHz or 3.290 kHz.
Page 30

4-2 Controller Theory of Operation: RX Audio Circuit
• De-emphasis: This circuit restores the original state of signal of which high-frequency
component has been emphasized by the pre-emphasis.
• Expander: This circuit expands the signal compressed twice by the Compressor in dB scale to
restore the original signal state.
•VR4: This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the RX output level.
Adjustment range: -18.0dB, -4.5dB to +4.5dB in 0.25dB steps.
•SMF: Smoothing filter to eliminate the high-frequency and clock components generated in the
Audio processor IC.
4.1.1.2 RX Tone PL/Digital PL Decode Filtering
• Sub-audio Programmable LPF: Low-pass filter to eliminate components of the RXA1 signal.
This circuit is controlled by the internal registers and by the audio processor IC for cut-off
frequency.
•VR5: This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the output level from the sub-audio LPF
signal. Adjustment range: -6.0dB, +6.0dB in 0.5dB steps
The sub-audio tone of U102 Pin 18 output pass through switchable high-pass filter U105. This filter
(U105-A, B) has 4 different high pass cut-off frequencies which can be selected accordingly to the
sub-tone audio. This filter (U105-A, B) filters the unwanted sub-tone. The tone of U105-B output
passed through U105-C comparator, which acts as a squaring circuit. This output signal is then sent
to microprocessor Pin 3. The micro-processor then decodes CTCSS and CDCSS from this square
signal.
4.1.2 Audio Amp
The de-emphasized audio signal from Pin 21 of audio processor IC passes through volume control
(SW/VOL1) and is amplified by U601BTL audio amplifier to a sufficient level to drive a loud speaker.
U601 has mute/un-mute function controlled by audio-mute control (Pin 83) of CPU. When U601
Pin 1 is low, the audio amp goes to active (un-mute) mode. When U601 Pin 1 is high, the audio amp
goes to mute mode.
4.1.3 Internal and External Speaker
When no external speaker is plugged into J601, the RX audio is passed through to the internal
speaker. When an external speaker is plugged into J601, the internal speaker is cut-off from the
rest of the circuit and RX audio is passed through the external speaker.
Page 31

Controller Theory of Operation: TX Audio Circuit 4-3
4.2 TX Audio Circuit
The TX audio circuit consists of MIC/External MIC, LPF, Audio processor IC, and TX Sub-tone
system. For UHF1 and UHF2, refer to Figure 4-2. For VHF, refer to Figure 4-3.
4 Order LPF
(Fc=4KHz)
Mic
(Audio IN)
U501-C,D
Audio Processor IC (AK2347)
pin4
TXA1
-6 to +4.5dB/
Tone IN
(from CPU)
4 Order LPF
(Fc=4KHz)
U501-C,D
VR1
(HPF)
1.5dB
Com-
pressor
pin19
Mic
(Audio IN)
TX/RX HPF
Pre-
Emphasis
Scrambler/
Descrambler
Limiter
Fc=300Hz
U102
DTA1
Sub audio
Programmable
LPF
-6 to +6dB/
0.5dB
2 Order LPF
(Fc=300Hz)
VR5
pin17
U502-A
To VCO &
VCTC XO
Figure 4-2. TX Audio Circuit (UHF1 and UHF2)
Audio Processor IC (AK2347)
-9.6 to +3dB/
6 Order LPF
(Fc=3KHz)
U501-A,B
VR2
0.2dB
Splatter SMF
Fc=2.55KHz/
3KHz
Mod.Adj,
U508
pin8
TX AF Amp.
U502-C
pin4
TXA1
-6 to +4.5dB/
(from CPU)
VR1
(HPF)
1.5dB
Tone IN
Com-
pressor
pin19
DTA1
TX/RX HPF
pin17
Scrambler/
Descrambler
U102
2 Order LPF
(Fc=300Hz)
U502-A
Pre-
Emphasis
Sub audio
Programmable
LPF
Fc=300Hz
-6 to +6dB/
0.5dB
VR5
Figure 4-3. TX Audio Circuit (VHF)
Limiter
To VCO &
VCTC XO
-9.6 to +3dB/
6 Order LPF
(Fc=3KHz)
U501-A,B
VR2
0.2dB
Splatter SMF
Fc=2.55KHz/
3KHz
U502-C
pin8
TX AF Amp.
Mod.Adj,
U508
Page 32

4-4 Controller Theory of Operation: TX Audio Circuit
4.2.1 MIC and External MIC
The TX audio enters the radio via the internal MIC or the external MIC jack. When using
the internal MIC, the audio passes through the external jack then rest of the circuits. When using the
external jack, the audio from the internal MIC is cut-off from the rest of the circuits and the external
MIC audio is passed to the rest of the circuits.
4.2.2 4-order 4 kHz Low-Pass Filter (U501-C, D)
4-order 4 kHz Low-pass filter to prevent aliasing noise of the ASIC switching cut-off frequency.
4.2.3 Audio processor IC (U102)
4.2.3.1 TX Audio Processing
Tx Audio from Pin 14 of U501-D enters the ASIC at Pin 3, 4 (Internal TX AMP).
• TX A1: Operational amplifier for gain adjustment of TX audio signal. R102, R103, C102, C103
are used to set the gain.
• VR1 (HPF): This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the input level of TX audio signal.
Adjustment range: -6.0dB, +4.5dB in 1.5dB steps
• Compressor: This circuit compresses the amplitude of transmit audio signal by 1/2 in dB scale.
• Pre-emphasis: This circuit emphasizes the high-pass frequency component of TX audio signal
to improve the S/N ratio of the modulation signal.
• TX/RX HPF: High-pass filter to eliminate low-frequency components lower than 250 Hz which
are included in transmitter audio signal. This circuit is turned on and off by control register of
Audio Processor IC.
• Scrambler: This circuit inverts the spectrum distribution of transmitter audio signals with
respect to the carrier frequency. The carrier frequency is 3.388 kHz or 3.290 kHz.
• Limiter: Amplitude limiting circuit to suppress frequency deviation in the modulation signal. The
limit level can be adjusted by applying a DC voltage the LIMLV Pin 7. When the pin is left open,
the level predetermined within the device is output.
• VR2: This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the output level on the MOD Pin 8.
Adjustment range: -9.6dB to +3.0dB in 0.2dB steps.
• Splatter: Low-pass filter to eliminate high-frequency components higher than 3 kHz which are
included in the limiter output signal. The cut-off frequency is 3 kHz.
• SMF: Smoothing filter to eliminate the high-frequency and clock components generated in the
ASIC.
4.2.3.2 Tx Tone PL/Digital PL Encode Filtering
The encode circuit of CTCSS and CDCSS mixes signals from 4 ports of microprocessor. This mixed
signal passes through ASIC Pin 19, 20 (U102).
• DTA1: Amplifier for gain adjustment of sub-audio signal which generated from CPU. Use
external resistor and capacitor to set the gain.
• Sub-audio Programmable LPF: Low-pass Filter to eliminate components of DAT1 signal in the
transmitter. This circuit is controlled cut-off frequency by the internal ASIC registers.
• VR5: This circuit controls the volume for adjusting the output level from the Sub-Audio LPF
signal. Adjustment range: -6.0dB to +6.0dB in 0.5 steps.
Page 33

Controller Theory of Operation: Microprocessor Circuitry 4-5
4.2.4 TX audio amplifier and 6 order 3 kHz Low-Pass filter
The TX audio signal from ASIC Pin 8 (UHF1, UHF2) or U508 Pin 4 (VHF) is linked by TX audio amp
(U502-C) to increase limiting range. The limited audio signal is adjusted to a proper level by U508
and passes through 6 order 3 kHz low pass filter (U501-A,B) before being modulated.
4.2.5 TX modulation Adjustment
TX audio signal from Pin 8 of U502-C (UHF1, UHF2) or Pin 8 of ASIC (VHF) is linked TX modulation
adjustment IC (U508). The TX modulation is tuned in the factory. If any of the TX part is replaced, the
TX modulation must be tuned using Tuner.
4.3 Microprocessor Circuitry
The microprocessor circuitry includes microprocessor (U101) and associated EEPROM.
Table 4-1. Radio Memory Requirements
Reference No. Description Size
U101 Microprocessor Flash ROM 128 Kbyte * 8
RAM 5 Kbyte * 8
U104 Serial EEPROM 8 Kbit * 8
4.3.1 Memory Usage
Radio operation is controlled by software that is stored in internal Flash ROM memory. Radio
parameters and customer specific information is stored in External EEPROM (U104). The operating
status of the radio is maintained in RAM located within the microprocessor. When the radio is turned
off, the operating status of the radio is written to EEPROM before operating voltage is removed from
the microprocessor.
4.3.2 Control and Indicator Interface
Ports Pin 35 and 36 are outputs which control the Sub-PCB mounted LED indicator. When Pin 35 is
high, the indicator is green. When Pin 36 is high, the indicator is red. When both are high, the
indicator is amber. When both are low, the indicator id is off.
Pressing the side-mounted PTT button (PB501) provides a low to port Pin 44, which indicates PTT is
asserted. Side-mounted function buttons 1 & 2 (PB502 and PB503) are connected to port Pin 21 and
Pin 32, respectively.
4.3.3 Interface to USB programming
The radio can be programmed, or the programmed information can be read, using a computer with
CPS (Customer Programming Software) connected to the radio via a USB Programming cable
(PMDN4077A). Connection to the radio is made via the microphone connector (part of accessory
connector J601). The line connects the programming connect (J601 Pin 6) to port PRG/CLONE_RX
(data into uP, Pin 34) and PRG/CLONE_TX(data out of uP, Pin 33).
4.3.4 Storage of Customer-Specific Information
Information that has been programmed using CPS, such as channel frequencies or selective
signaling codes, etc, are stored in the external EEPROM, where it is retained permanently (unless
reprogrammed) without needing DC power applied to the microprocessor.
Page 34

4-6 Controller Theory of Operation: Microprocessor Circuitry
4.3.5 Sensing of VOX operating
Port PTT2 (Pin 68) is used to detect the presence of VOX operating when externally connected
accessories with VOX enabled. When port PTT2 is low, the VOX will start to operate.
4.3.6 Microprocessor Power-on reset Routine
On power-up, the microprocessor is held in reset until the digital 3.3V regulator (U506 Pin 4)
provides a stable supply voltage. Once the digital supply reaches steady state and releases the reset
line (U107 Pin 2), the microprocessor begins to start up. After reset release by all circuit, the software
within the microprocessor begins executing port assignment, RAM checking, and initialization.
4.3.7 Microprocessor 7.3728 MHz Clock
The 7.3728 MHz clock signal (Pin 13, X-in) is provided from the FL101.
4.3.8 Battery indicator
Various battery types are available having different capacities. The radio can select different battery
type by FPP (Front Panel Programming) or CPS. A voltage divided by R153 and R154. And
EEPROM have a data for each battery types.
Page 35

Chapter 5 435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation
A
5.1 Introduction
This chapter provides a detailed theory of operation for the radio components. Schematic diagrams
for the circuits described in the following paragraphs are located in Chapter 7 of this manual.
5.2 UHF2 Receiver
The UHF2 receiver design covers the frequency range of 435 – 480 MHz and it is a double
conversion super heterodyne with 1st IF 45.1 MHz and 2nd IF 455 kHz. The receiver is divided into
two major blocks, Front End and Back End as shown in Figure 5-1.
Preselector
Filter
RF
Amp
Postselector
Filter
1st Mixer
Crystal
Filter
IF
Amp
RX from
ntenna Switch
Inj Filter
First LO
from Synthesizer
N/S_SW
Ceramic
Descriminator
455C24
Recovered Audio
LPF
Quadrature
Detector
Filter
IF
Amp
455FW
455HW
RSSI
Figure 5-1. UHF2 Receiver Block Diagram
Crystal
44.645MHz
Page 36

5-2 435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation: UHF2 Receiver
5.2.1 Receiver Front End
Incoming RF signals from antenna are first routed through the harmonic filter (L409, L410, L411,
C426, C427, C428, C429, C445, C446) and antenna switch (CR301), part of the transmitter circuitry,
before being applied to the receiver front end. The receiver front end consists of preselector filter,
RF amplifier, post-selector filter and a single-balanced mixer.
The preselector filter is a varactor-tuned 2-pole design using discrete elements (L320, L324, C351,
C352, C353, C354, C355, C356, C357, C358, C359, C360, C361) in a series/shunt resonator
configuration. It is a band-shift filter and the frequency shift is controlled by varactor diodes CR314
and CR307, which are connected to the microprocessor. It is configured to provide steeper
attenuation above the passband for improved spurious rejection when low-side local injection is used.
The frequency is separated into 8 steps and controlled by CPU (435 – 480 MHz).
The output of this filter is matched to the base of RF amplifier Q301 which provides 13dB of gain.
The output of the RF amplifier is applied to the post-selector filter. The post-selector filter designed
using discrete elements (L322, L323, L328, C379, C354, C355) in a series/shunt resonator
configuration. It is a band-shift filter and the frequency shift is controlled by varactor diodes CR313,
CR304 and CR305, which are connected to the microprocessor. It is configured to provide steeper
attenuation above the passband for improved spurious rejection when low-side local injection is used.
The frequency is separated into 8 steps and controlled by CPU (435 – 480 MHz).
The output of the post selector is connected to the single-balanced mixer consisting of components
L329, L333, Q306 and Q307. 1st local signal generated from VCO is filtered by injection filter (L310,
L331, C325, C326, C327) to remove second harmonics. The converted 1st IF frequency at mixer
passes through L331 and matches the 45.1 MHz IF signal to pair crystal filter (FL301).
5.2.2 Receiver Back End
The 1st IF signal is amplified about 15 dB by IF amp Q303. The output of the IF amp is connected to
IF IC (U201). 1st IF frequency (45.1 MHz) and 2nd LO frequency (44.645 MHz) are mixed in U201.
The second mixer converts the 45.1 MHz high IF frequency to 2nd IF frequency (455 kHz).
Additional IF selectivity is provided by two ceramic filters (CF1, CF2). The wider filter 455 FW is used
for 25 kHz channel spacing, and the narrower filter 455 HW is used for 12.5 kHz channel spacing.
These two ceramic filters may eliminate undesired signal and demodulated by demodulator in U201.
N/S_SW which connected to microprocessor is used to select the wide and narrow band.
The mute (squelch) circuit switches off the audio amplifier when no audio is present. The squelch
circuit consists of U201 and U202 and their associated components. The noise signal from Pin 9 of
U201 is used to control the squelch circuit sensitivity of U202. The noise passes through filter, and is
amplified by internal amp of U201. The amplified noise act as a DC voltage to control the mute
system. So if the noise level is under the threshold voltage, the microprocessor (U101) un-mutes the
radio. If the noise level is over the threshold voltage, the microprocessor mutes the radio.
The squelch level is tuned in the factory. When a component or a part in the RX system is replaced,
the squelch must be re-tuned using the Tuner.
Page 37

435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation: UHF2 Transmitter 5-3
5.3 UHF2 Transmitter
The UHF2 transmitter covers the range of 435 – 480 MHz. Depending on model, the output power of
the transmitter is switchable on a per-channel basis between high power (4 Watts) and low
power (1 Watt). The transmitter is divided into four major blocks as shown in Figure 5-2.
• Power Amplifier
• Harmonic Filter
• Antenna Matching Network
• Power Control.
From VCO
Attenuator
Circuit
5.3.1 Power Amplifier
The transmitter power amplifier has three stages of amplification – Pre Driver (Q401), Driver
Amp (Q402) and Final Amp (Q403). Signal from TX VCO is applied to the pre driver via an attenuator
circuit. The attenuator is pie style resistor attenuator, and is used as isolation between VCO and the
power amps. The -4dBm TX RF signal from attenuator is then amplified by pre driver and driver amp
to around +25dBm and is applied to the final amp. The final amp (Q403) is an enhancement-mode
N-channel MOSFET device providing a gain of 12dB. The device drain current is drawn directly from
the DC battery supply voltage input via L413. A matching network consisting of C416 to C420 and a
strip line, transforms the impedance to approximately 50 Ohm.
SWB+
Power Control
Pre Driver
Amp
Driver
Amp
BAT+
Current Detect
Strip Line
Final
Amp
To Receiver
Figure 5-2. UHF2 Transmitter Block Diagram
CR401
Antenna
Switch
Antenna
Harmonic
Filter
5.3.2 Antenna Switch
An antenna switch works mainly as a switching device between transmit and receive paths. In
transmit mode (PTT), Q407 is turned on and both PIN diodes (CR401, CR301) are forward biased
into conduction. This enables the RF signal to pass to the harmonic filter and then to the antenna. In
the receiver mode, both diodes are off. Signals applied to the antenna jack are routed via the LPF
(harmonic filter), through network L409 to L411, to the receiver input.
5.3.3 Harmonic Filter
The harmonic filter consists of components L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C430, C445
and C446. The harmonic filter is a seven-pole Chebychev filter.
Page 38

5-4 435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation: UHF2 Frequency Generation Circuitry
5.3.4 Auto Power Control
The APC keeps the current supply constant to the final amp (Q403). The drain current of Q403 (final
amp) is sensed across resistor R417. The voltage difference across R417 is amplified through U401
by the ratio of R423 to R417. The differential signal at the output of U401 (Pin 7) is passed to Q404
and Q405 that produces a constant power output to the antenna. If the current is changed due to
change of battery voltage or load, APC controls gate voltage of Q403 and collector voltage of Q401
and drain voltage of Q402 to keep TX power stable. This circuit stabilizes TX power at a
pre-determined level adjusted by U402. This bias voltage is tuned in the factory. If the transistor
(Q403) is replaced, the RF Output Power must be tuned. By tuning the RF output power, the bias
voltage will be tuned through U402. Extra care has to be taken during the tuning process. Do not
exceed the maximum allowed bias voltage.
5.4 UHF2 Frequency Generation Circuitry
The PLL synthesizer subsystem consists of the reference oscillator (VCTCXO), VCO, PLL IC, Charge
Pump and Loop Filter.
Modulating
Signal
FL701
12.8MHz
Ref.OSC.
Synthesizer
U701
PLL Data
from μP
Charge
Pump
Voltage
Doubler
Figure 5-3. UHF2 Frequency Generation Unit Block Diagram
5.4.1 Reference Oscillator (12.8 MHz VCTCXO)
The reference oscillator is powered by regulated 5V provided by U505. The reference frequency
12.8 MHz VCTCXO (Voltage Controlled Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator) is applied to
the PLL IC (U701) via Pin 1. Main frequency can be adjusted by chip trimmer of VCTCXO. This
frequency provides reference to the PLL IC and has a frequency stability of +/-2.5PPM (max) at the
temperature ranging from -30 to +60 Degree Celsius.
Loop
Filter
TX VCO
Circuit
TX Out
RX VCO
Circuit
RX Out
To PA Driver
To Mixer
Page 39

435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation: UHF2 Frequency Generation Circuitry 5-5
5.4.2 PLL IC Prescaler and Comparator
The reference frequency from VCTCXO is divided to 6.25 kHz or 5 kHz by reference counter, R. The
RF signal input from the VCO is divided to by prescaler (1/64), divided by N and A counters in PLL IC
to determine frequency steps and then supplied to the comparator. The comparison frequency is
6.25/5 kHz. The internal phase comparator compares the phase difference between the reference
and VCO signal. When the phase of the reference frequency is leading, Pin15 (R) is the output.
When VCO frequency is leading, Pin 16 (P) is the output. When P=R, small pulses are the output of
the phase detector.
5.4.3 Voltage Doubler and Charge Pump
The voltage doubler (U507) converts 5V to 10V and is applied to the charge pump circuitry. The
charge pump is used for charging output signals P, R supplied by PLL IC from 0-3.3V to 0-10V. This
voltage is used to drive the VCO.
5.4.4 Loop Filter
The loop filter contains C751, C752, C753, C754, R726, R727, R728. It reduces the residual sideband noise to get the best signal-to-noise ratio. The output signal from loop filter is applied to VCO.
5.4.5 Dual VCO
The dual VCO module contains a RX VCO and a TX VCO. They are configured as colpitts oscillators
and connected to power up through transistor switches. Only one VCO is selected at a time. A
steering line voltage between 0.35V and 9.7V at varactor CR701 tunes the full RX frequency range
from 389.9MHz to 434.9MHz, and varactor CR702 tunes the full TX frequency range from 435MHz
to 480MHz.
In Receiver mode, high signal of RX_EN from Pin 71, U101 activates Q305. When Q305 is activated,
current flows through the base of Q304 and thus activates the Q705. The varactor CR701 sets the
resonance frequency. When there is a change in voltage supplied by loop filter, there is a change in
the resonance frequency. L703 is the resonating coil, which forms the tank circuit together with
variable cap C710.
In Transmit mode, high signal of TX_EN1 from Pin 84, U101 enables current flows through collector
of Q503 and thus activates Q706. The varactor CR702 sets the resonance frequency. When there is
a change in voltage supplied by loop filter, there is a change in the resonance frequency. L706 is the
resonating tuning coil, which forms the tank circuit together with variable cap C722.
Page 40

5-6 435 – 480 MHz UHF2 Theory Of Operation: Keypad
5.5 Keypad
Left, Right and P1 to P3 keys are directly connected to microprocessor via 22 pin connector. When
any of these keys is pressed, the voltage goes "low" and microprocessor detects it.
For full keypad models, the number keys are in matrix type which consisted of 3 rows and 4 columns.
When any of these keys is pressed, the voltage goes "low" and microprocessor interprets the voltage
for each key press.
KEYPAD
Left
Right
P1 P2 P3
NUMBERS
Key
detect
Key row
Keypad board
Key
22pin connector
column
Figure 5-4. Keypad Block Diagram
MCP
Main board
22pin connector
Page 41

Chapter 6 UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables
6.1 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF2)
Table 6-1. Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (UHF2)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
Radio Dead (no
turn–on beep, no
LED indication)
No RX Audio (with
LED indication)
1. Battery dead or
defective
2. Defective battery
contacts
3. Microprocessor not
starting up
4. Regulator fault Verify U506 Pin 4 is 3.3V
5. Flexible Cable fault Check connection of the 12 pin
1. Speaker dead or
defective
2. Audio Processor IC
not starting up
3. Audio Amp IC not
starting up
Substitute good battery or battery
eliminator
Inspect battery contacts for
corrosion or bent terminals
Verify clock input to U101 Pin 13 is
7.3728 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify U101 Pin10(reset) is high.
Verify U505 Pin 4 is 5.0V
flexible cable between J104 & J105
Substitute a good housing (with
speaker)
Verify J603 connection
Verify clock input U102 Pin 14 is
3.5795 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify U601 Pin 6 is battery voltage.
Change or replace battery.
Clean/Repair/Replace J602
Troubleshoot/Replace FL101.
If reset is Low, troubleshoot
regulator U506 or U107.
Check for shorts on outputs
Troubleshoot/Repair as
needed, replace faulty regulator
Re–assemble or replace flexible
cable
Change the housing (with
accessory)
Change the housing (with
accessory)
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Troubleshoot/Replace U601
If battery voltage is being supplied to
Pin 6, then verify audio output at
Pin 5 & 8.
No Receive (with
no LED indication)
No RX 1. RX–B+ Verify Q304’s collector voltage is
1. IF IC dead or fault Verify clock input to U201 Pin 1 & 2
is 44.645Mhz using high impedance
probe.
4.8V when RX–EN is high.
Troubleshoot/Replace FL201
Check/Replace Q304
Page 42

6-2 UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF2)
6.2 Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF2)
Table 6-2. Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (UHF2)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
Synthesizer Out of
Lock (No RX
Mode)
Synthesizer Out of
Lock (No TX Mode)
1. Defective 12.8 MHz
VCTCXO
2. 1/2VCC defective Verify FL701 Pin 1, U502–B Pin 5 &
3. No RX–Enable Verify U101 Pin 71 (RX–EN1) is
4. Check PLL–LD port Verify U101 Pin 27 is Low (Normal
1. Defective 12.8 MHz
VCTCXO
2. 1/2VCC defective Verify FL701 Pin 1, U502–B Pin 5 &
3. No TX–Enable Verify U101 Pin 84(TX–EN1) is high
Verify clock output FL701 Pin 3 is
12.8 MHz using high impedance
probe.
U502–D Pin 14 voltage is 1.9V.
high.
Verify Q304 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V in RX mode
Mode)
Verify U101 Pin 27 is swept from low
to high (Power Save Mode)
Verify clock output FL701 Pin 3 is
12.8 MHz using high impedance
probe.
U502–D Pin 14 voltage is 1.9V.
when PTT is pressed.
Repair/Replace FL701
Troubleshoot: 1/2VCC circuitry
Check U101 operating
Troubleshoot: Q304 & Q305
circuitry
Troubleshoot: PLL circuitry.
Repair/Replace U701
Repair/Replace FL701
Troubleshoot: 1/2VCC circuitry
Check U101 operating
Verify Q407 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V when PTT is
pressed (TX–EN2).
4. Check PLL–LD port Verify U101 Pin 27 is Low (Normal
Mode)
Verify U101 Pin 27 is swept from low
to high (Power Save Mode)
Check U101–Pin 85 is high/
Replace Q407/check LK2 is
short
Troubleshoot: PLL circuitry
Repair/Replace U701
Page 43

UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF2) 6-3
6.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF2)
Table 6-3. Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (UHF2)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
No internal Mic
audio
No EXT. Mic audio 1. J601 defective Check connection with EXT mic Check/Replace J601
No transmit (No TX
LED indication)
No transmit (TX
LED indication OK)
Low Power
1. Mic dead or defective Verify audio present (~10mV rms)
when speaking into Mic.
Check bias of R194 (3.3V).
2. Mic bias fault Verify U101 Pin 78 is 1.1V when
PTT button is pressed.
3. Audio Processor IC
not starting up
2. Audio Processor IC
not starting up
1.PTT switch defective Verify U101 Pin 44 is low when PTT
1. Synthesizer out of lock
2. No TX–Enable Verify U101 Pin 84 (TX–EN1) is high
1. Low TX injection Check the RF level at Q409 & C449
Verify clock input U102 Pin 14 is
3.5795 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify clock input U102 Pin 14 is
3.579545 MHz using high
impedance probe.
is pressed.
Refer to Table 6-2.
when PTT is pressed.
Verify Q407 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V when PTT is
pressed (TX–EN2).
per schematic.
Replace Mic.
Check/Replace U101
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Replace PTT switch PB501
Check U101 operating
Check U101 Pin 85 is high/
Replace Q407/Check LK2 is
short
Troubleshoot Q409 circuitry &
VCO bias
Poor TX range
(Conducted power
OK)
2. R417 defective Verify resistance is 0.1 Ohm Replace R417.
3. Incorrect control
voltage
4. Q403 defective (High
current)
5. Antenna switch defect Verify CR401 anode voltage is
6. Harmonic filter
defective
7. Incorrect power tuning
(this has to be performed
only after item 1-6 has
been checked)
1. Defective or wrong
Antenna.
Verify Q404 collector voltage is
approximately 5.5V in low frequency
& high power.
Verify U401 Pin 7 is near 0V Replace Q403
approximately 1.4V
Visually inspect components
C426 – C429, C445, C446, C430
Check conducted power Re-tune power using tuner.
Verify correct antenna is installed.
Try using another antenna.
Troubleshoot APC circuitry
Replace Q404
Check/replace CR401 & CR301
Repair/Replace if necessary
Replace antenna
Page 44

6-4 UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2)
6.4 Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2)
Table 6-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
U201(IF IC) 1 Osc1 3.9 44.645 MHz input
2Osc2 3.3
4 VCC 4.7
9 Audio frequency 1.2
12 RSSI out Approximately 1 At –47dBm(with conducted)
13 N–DET(BUSY) Low At busy
15 GND 0
16 RF input 1 45.1 MHz input
U701(PLL IC)
1 Reference OSC input 1.4 12.8 MHz input
4VCC 3.3
6 GND 0
7XF IN 2.2
8 F IN 2.2
12 Power save High
13 GND 0
14 LD_out High If pll unlock is low
15 @P 2.4
16 @R Low
U601 1 Mode (Mute con) 0
(Audio Amp.) 2 SVR 3.8
3 IN+ 3.8
4IN- 3.8
5 OUT- 3.8
6 VCC 7.5 This voltage depends on Battery
7 GND 0
8OUT+ 3.8
U103 1 IN+ 1.6
Page 45
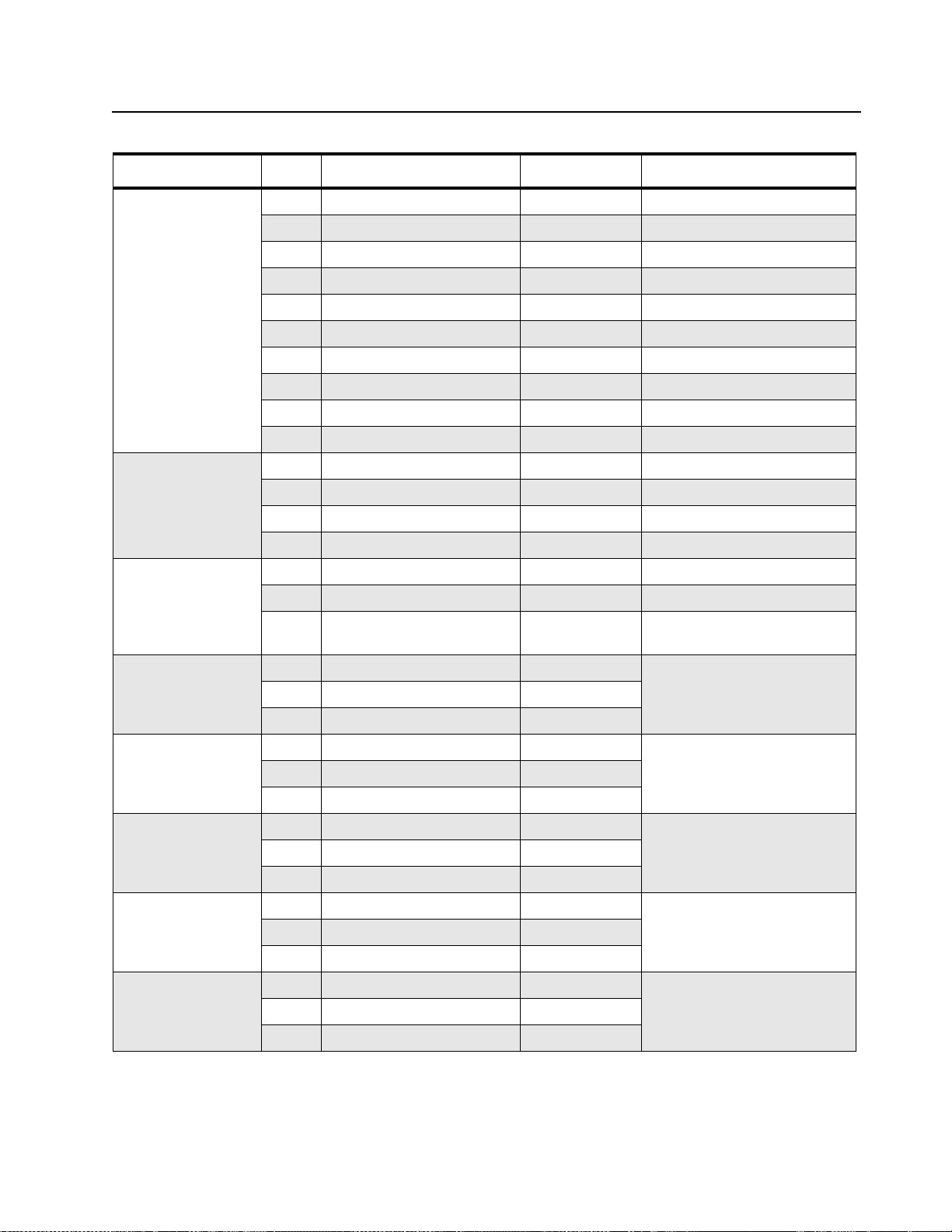
UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2) 6-5
Table 6-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2) (Continued)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
(DTMF decoder) 2 IN- 1.6
3 GS 1.6
4Vref 1.6
8 OSC1 1.6 3.579545 MHz input
10 VSS 0
11 TOE 3.3
17 STD High At DTMF detecting
18 EST 3.3
19 ST/GT 3.3
20 VDD 3.3
FL701(VCTCXO) 1 VCON 1.9
2 GND 0
3 OSC out osc Generate the 12.8 MHz
4 VCC 5
Q206(N/S SW) E GND 0
B N/S SW 12.5 kHz: Low
C Collector 12.5 kHz: High
25 kHz: Low
Q304 E +5V 5 At RX Mode
B To Q305 collector Low
C RX_B+ 4.7
Q305 E GND 0 At RX Mode
B RX_EN High
C To Q304 base Low
Q503 E GND 0 At TX Mode
B TX_EN1 High
C To Q706 base Low
Q407 E +5V 5 At TX Mode
B To Q408 collector Low
C TXVB 4.7
Q408 E GND 0 At TX Mode
B TX_EN2 High
C To Q 40 7 Low
Page 46

6-6 UHF2 Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2)
Table 6-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (UHF2) (Continued)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
Q601 E GND 0
B Audio_MUTE_CON Mute: Low
None Mute: High
C Mode Mute: High
None Mute: Low
1. All voltages are measured with a high-impedance digital voltmeter and expressed in volts DC relative to ground (0V).
2. Voltages are measured with a DC input voltage of 7.50 + .02 volts DC applied to the battery connector (J602).
3. All voltages are measured in the squelched receive mode, unless otherwise indicated.
4. Voltages are identical for VHF and UHF models unless otherwise indicated.
Page 47

Chapter 7 UHF2 Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and
Parts Lists
7.1 Introduction
This section provides schematic diagrams, overlays, and parts lists for the radio circuit boards and
interface connections.
7.1.1 Notes For All Schematics and Circuit Boards
* Component is frequency sensitive. Refer to the Electrical Parts List for value and usage.
1. Unless otherwise stated, resistance values are in Ohms (K = 1000), capacitance values are in
nanofarads (nF), picofarads (pF) or microfarads (µF), and inductance values are in
nanohenries (nH) or microhenries (µH).
2. DC voltages are measured from point indicated to chassis ground using a Motorola DC
multimeter or equivalent. If the board has been removed from the chassis, the transmitter
module mounting screws may be used for ground connection. (Note: The antenna nut
bracket is connected to ground.) Operating mode dependent voltages are followed by (RX)
for receive mode, (TX) for transmit mode, (UNSQ) for unsquelched mode, etc.
3. RF voltages on VHF models are measured with a Fluke model 85 RF probe. The indicated
voltages expressed in mV (RF) are DC level readings which correspond approximately 1:1 to
the RF voltage level in mV rms. RF voltages in the Receiver Front End and Receiver Back
End circuits are measured with an on-channel 1mV (-47dBm) RF signal applied to the
antenna jack ANT1/ANT.
4. RF voltages on UHF models are measured both with a high–impedance RF voltmeter having
a bandwidth in excess of 500 MHz (levels are expressed in dBm) and with a Fluke model 85
RF probe [levels are expressed in mV (RF)]. These indicated voltages are DC level readings
which correspond approximately 1:1 to the RF voltage level in mV rms, and are only
approximate for UHF frequency measurements. RF voltages in the Receiver Front End and
Receiver Back End circuits are measured with an on-channel 1mV (-47dBm) RF signal
applied to the antenna jack ANT1/ANT.
5. Audio voltages are measured with a high-impedance AC rms voltmeter. The indicated
voltages are expressed in mV rms. Receive mode voltages are followed by (RX) and are
measured with an on-channel signal with 1 kHz modulation at 60% deviation (3 kHz for 25
kHz channels, or 1.5 kHz for 12.5 kHz channels). Transmit mode voltages are followed by
(TX) and are measured with a 1 kHz, 10 mV rms signal present at the external microphone
input (accessory connector J601).
Page 48

7-2 UHF2 Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists: Introduction
6. Reference Designators are assigned in the following manner:
Ref. No. Series Circuit Block
101 – 199
Microprocessor & audio control
circuits
1001 – 1099 Microprocessor & audio control
circuits
201 – 299 IF IC circuit
301 – 399 Front-end and 1st Mixer
401– 499 Transmit RF stage & Auto power
control
501 – 599 Base band & generating circuit
601– 699 Audio amplifier
701– 799 VCO & PLL Synthesizer
7. Circuit Block Interconnection Legend:
Name Description
+5V 5 Volts (Regulated)
+3.3V 3.3 Volts (Regulated)
SWB+ Switched Battery Voltage
BAT+ Unswitched Battery voltage
+10V Digital 10V(Regulated)
RESET Low-line reset signal fromU107 to U101 Pin 10
TX_EN1 Transmit enable signal from U101 Pin 84
TX_EN2 Transmit enable signal from U101 Pin 85
TXVB TX operating voltage
TX_AF3 TX audio signal from audio processor IC to TX Audio
filter
TX_SUB_TONE TX sub tone signal from audio processor IC to TX
modulation.
RX_B+ RX operating voltage
RSSI RX signal strength indication from IF IC to U101
Busy RX detect signal from IF IC to U101
FTV RX frequency shift voltage
RX_AF1 RX audio signal from IF IC to Audio processor IC
PLL_LD PLL lock detect signal from PLL IC to U101
N/S SW Channel space selectable Switch (12.5 kHz/25 kHz)
1/2VCC 1.9 volts (divided by U502-D)
Page 49

UHF2 Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists: Speaker and Microphone Schematic 7-3
7.1.2 Four Layer Circuit Board
Plating (Au)
PSR ink
Copper Plate
Copper
PrePreg.
Copper
CCL (core)
Copper
PrePreg.
Copper
Copper Plate
PSR ink
Figure 7-1. Four–Layer Circuit Board: Copper Steps in Layer Sequence
7.2 Speaker and Microphone Schematic
MIC1
1
2
SPK1
Figure 7-2. Speaker and Microphone Schematic
7.2.1 Speaker and Microphone Parts List
Reference
Designator
MIC1 PMDN4139_R Microphone
SPK1
Motorola Part No. Description
PMDN4067BR
MATES WITH J103 ON
RADIO BOARD
1
MATES WITH J603 ON
RADIO BOARD
2
Speaker & Cable
Page 50

7-4 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
7.3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
FROM_HARMONIC_FILTER
C301
5pF
L325
220nH(1608)
C357
56pF
C303
3pF
CR314
KDV154E
L324
22nH
C361
22pF
EJPS
R323
100K
C360
4pF
L330
33nH
CR307
KDV154E
C325
33pF
L331
OR
L320
22nH
C351
10pF
C365
27pF
RX_B +
EJPS
CR309
KDS114E
R330
100K
L310
18nH
EJPS
6
4
L329
B4F(1667)
C326
3pF
C327
12pF
C307
18pF
C364
33pF
L334
8.2nH
R320
100R
CR310
KDS114E
3
2
1
Q301
2SC4226
R336
1K
R337
00R
1
L304
39nH
R302
56K
C309
3pF
RX_B +
Q306
2SK711
C367
220pF
FROM_RX_VCD
C368
10nF
C312
15pF
C369
NA
Q307
2SK711
C370
NA
C310
0.1uF
L321
N / A
R309
100R
820nH
C356
NA
CR313
KDV154E
L306
EJPS
R335
2.2K
L328
18nH
C363
NA
1
2
3
L333
B4F(1664)
C328
2pF
RX_B +
1
C332
10pF
L323
18nH
523
C318
15pF
C355
15pF
CR305
KDV154E
EJPS
4
FTV
R311
330R
C376
0.1uF
C358
15pF
C377
NA
R312
150K
Q303
2SC4
R314
100R
C378
10uF / 16V(A)
R315
100R
L327
820nH (1608)
226
C362
10pF
EJPS
4
6
C379
20pF
R334
100K
R310
4.7K
C372
33pF
C373
20pF
CR304
KDV154E
C329
10nF
R338
100R
L332
820nH (1608)
L340
820nH(1608)
C304ORC374
L322
EJPS
22nH
C375
NA
C354
10p
F
R332
100K
C330
39pF
C331
9pF
10pF
R333
100K
FL301
45.1MHz(SMF - 1) 8.5K
C320
10uF / 16V(A)
+
C319
10nF
C380
47pF
+
C334
1nF
CR312
KDS160E
C204
0.1uF
Q305
KRC404
C337
nF
10
C
E
C347
0.1uF
KRA305
Q304
B
R316
100K
C338
47nF
FL201
44.645MHz
C343
0.1uF
CR315
KDS160E
U201
TA31136
CR201
KDS181
C382
0.1uF
C344
470pF
16
C203
120pF
C339
0.1uF(K)
RF_IN
OSC1
1
C201
47pF
CR306
KDS160E
R317
180K
C340
0.1uF(K)
15
GND
OSC2
2
R258
1.5K
R206
10K
+5V
RX_EN
455FW
CF1
R217
10K
N_REC
MXOUT
C213
0.1uF(K)
BUSY
R318
3.3K
DEC1
455 C24(LCP)
C341
56pF
11 1 09
12
13
RSSI
N_DET
VCC
IF_IN
5
4143
C206
0.1uF(K)
R203
22K
R216 10k
R204
22K
CF2
455HW
R207
22K
6
CR202
KDS181
C208
0.1uF
IF_OUT
DECO
C207
0.1uF(K)
QUAD
FIL_O
87
R250
10K
Q206
KRC404
AF_OUT
FIL_IN
R210
120K
C209
330pF
C210
330pF
R319
3.3K
R342
NA
R211
15K
C214
0.1uF
R212
33K
RT201
10K(TH)
R220
5.6K
Q207
KRC404
C342
0.1uF(K)
C211
0.1uF(K)
+3.3V
C381
NA
R208
12K
MCP
R213
3.3K
1
2
3
4
4011(502)
VDD
VSS
A
W
U202
Q201
KRC404
Q202
NA
8
U/D
7
NC
6
B
5
CS/
RSSI
RX_AF1
N/S_SW
20KHZ_SEL
SQ_U/D
SQ_CS
Figure 7-3. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Receiver Schematic Diagram
Page 51

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-5
PLL_STB
PLL_DATA
PLL_CLK
PLL_PS
+3.3V
R732
10K
R731
10R
C741
0.1uF
RX_EN
VCO_OUT(RX)
TX_EN1
VCO_OUT(TX)
R7351KR736
9
CLK
FIN
87
C756
1nF
+5V
C731
2pF
R715
56R
Q711
KRA304
R730
33K
Q705
KRA305
E
C730
2pF
+
C538
C539
10nF
10uF / 16V(A)
14 15
LD_FOUT
VP
3
+3.3V
C755
1uF(K)
0.
16
@P
@R
OSCIN
OSCOUT
2
1
C738
7pF
R733
0R
L709
22nH
C747
10pF
R737
1K
1K
11
10
LE
DATA
U701
MB15E03L
GND
XFIN
6
C746
10pF
12
13
ZC
PS
DO
VCC
4
5
Q706
KRA305
B
R729
100K
R714
56R
C701
22uF / 10V(A)
C728
4pF
R706
100R
C
C715
22uF / 10V(A)
PLL_LD
R701
56R
+3.3V
C729
6pF
+
+
C716
470pF
L707
220nH(1608)
C714
1nF
R710
220R
C702
1nF
C704
1nF
L708
27nH
Q704
2SC4226
R720
R722
Q701
2SC4226
Q702
2SC4226
L704
220nH(1608)
Q703
2SC4226
C717
3pF
C718
4pF
C719
7pF
C748
0.1uF
R718
7.5K
R719
1K
R721
10K
C750
0.1uF
R705
220R
150R
150R
R716
300R
R723
1K
L701
27nH
C707
9pF
R707
1.5K
R708
4.7K (1%)
R709
6.8K (1%)
Q707
KTC4075
Q709
KTA2014
R724
390R
C705
2pF
+10V
C706
3pF
C721
3pF
L706
30103TL
R717
10R
R704
4.7K (1%)
TZY02
Q708
KTA2014
R725
100R
R702
1.5K
R703
4.7K (1%)
R713
30K
Q710
KTC4075
C709
4pF
L703
30113TL
C722
6pF
C723
0.5pF
R712
100K
R740
1.5K
C749
uF(1608)
1
C751
1uF / 35V
TZY02
CR703
KDV154E
C727
2pF
R711
100K
C710
F
6p
C711
13pF
CR701
KDV154E
C724
11pF
C726
1pF
CR702
KDV154E
R726
3K
+
C712
470pF
L705
2.2uH(1608)
R727
2.7K
C752
0.1uF(K)
C725
470pF
L702
2.2uH(1608)
C753
47nF(3216)
R728
2.7K
SH101
C754
47nF(3216)
+
C516
10uF / 16(A)
SH102
R734
+5V
10R
C740
0.1uF
C739
1nF
12.8MHZ
4
VCC
VCON GND
FL701
VCXO
OUT
3
21
U502-B
NJM324
R503
56K
5
7
6
C515
0.1uF
R506
10K
C575
47pF
1 / 2VCC
R504
47K
R505
12K
Figure 7-4. VCO and PLL Schematic Diagram
Page 52

7-6 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
A
A
TO_RX
R407
4.7K
A
W
C462
33F
C405
56pF
C437
0.1uF
2
3
4
R406
22R
TXVB
C464
47pF
C463
470pF
+
R441
0R
R413
8.2K
C403
470pF
L402
22nH(1608)
C438
NA
C439
1nF
C404
56pF
C
SWB+
C406
0.1uF
Q407
KRA305
B
LK2
L401 27nH(1608)
Q408
KRC404
Q401
PBR951
R405
1.5K
E
C471
0.1uF
C469
0.1uF
C402
10nF
C444
NA
C472
470pF
C470
47pF
C401
3pF
R404
8.2K
+5V
C473
47pF
TX_PWR_CS
TX_PWR_U/D
R403
180R
C467
470pF
TX_EN2
+3.3V
R402
39R
R401
180R
C440
470pF
C449 3pF
C448
10nF
R436
100R
L407
33nH
R434
33K
Q409
2SC4226
R435
150R
C465
470pF
C447
3pF
TX_VCO_B+
FROM_VCO
R412
R431
10K
Q404
STB1188
R409
10R
1
R408
2.2K
8
+
4
R440
15K
1K
C408
10nF
R432
27K
U402
8 1
VDD
U/D
7
VSS
NC
6
B
5
CS/
MCP4011(502)
Q405
Zo = 50
0.8t * 1.4(W)
CR401
C423
NA(1608)
C460
47pF
CR311
NA
R417
RLC63 0R1
C461
220pF
C422
12pF(1608)
L412
220nH(1068)
R415
220R(2012)
C432
1nF
C420 10pF(1608)
C466
470pF
R418
220K(0.5%)
R419
220K(0.5%)
R420
4.7M
15pF(1608)
C419 NA(1608) C451 3pF(1608) C417 12pF(1608)
C468
0.5pF
C453
470pF
C433
NA
R421
68K(0.5%)
C418
2
3
R422
68K(0.5%)
33pF(1608)
L413
35167L
+
C454
22uF/16V(B)
R423
3.9M
-
+
U401-A
KIA358
C452
C416 7pF(1608)
1
SH103
Q403
2SK3476
L406
220nH(1608)
R424
12K
R425
3.9K
C434
470pF
L405
6.8nH(1608)
C413
27pF(1608)
R430
100R
R429
3.6K
R426
4.7K
Q406
KRC404
CR301
L301
45145TL
C428
L409
451443TL
C427
4pF(1608)
C426
6pF(1608)
C431
NT1
1nF(1608)
NT
1
2
R416
47K(1608)
C430
NA
SH105
L410
45143TL
C429
5pF(1608)
6pF(1608)
L411
45143TL
C445
3pF(1608)
4pF(1608)
C446
060031MA005G500PL
KDS114
MA4P7001F-1072
BAT+
BAT+
J602
GND
KTC4075
R414
1K
C411
NA
C410
27pF(1608)
C409
NA(1608)
R428
100R
47nF C435
R427 220K
6
-
5
+
U401-B
KIA358
7
R411
560R
C436
0.1uF
R410
10R
U401-C
KIA358
R433
0R
L403
33nH(1608)
Q402
2SK3078
3
2
Figure 7-5. Transmitter Schematic Diagram
TX_PWR_LOW
Page 53

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-7
1
R139
10K
2
N1
SW_I
SW_IN
51
52
CLK
SW_IN3
DTMF_CON
PLL_
SW_SCAN1
SW_SC
SW_SCAN3
SW_SCAN4
PTT1
LED(RED)
LED(GREEN)
FUN_KEY2
AK_DATA
AK_CLK
AK_CSN
CS
T2
CON_
MOD_
TONE_IN
24
25
8
VCC
7
OC
6
SCL
5 4
SDA
VSS
U104
24LC64
U102_SDATA
U102_SCLK
U102_CSN
50
49
48
47
AN2
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
R195
33
R152
32
31
30
29
VOX_EN
D
28
U/
27
PLL_LD
CON_
DTMF_OUT
26
MOD_
A0
2
A1
3
A2
100R
680R
VOX_EN
DTMF_OUT
LCD101
+3.3V
SWB+
0pF
0pF
0pF
22
22
22
78
61
79
C1
C1
C1
0pF
0pF
22
22
70
71
C1
C1
0pF
0pF
22
22
67
66
C1
C1
TONE_IN
LCD_BEACON
pF
0pF
0
22
0pF
22
77
C1
0pF
0pF
22
22
73
72
C1
C1
0pF
0pF
22
22
68
69
C1
C1
22
88
89
C1
C1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
1S
J102
A0
22
05004HR_
MIC1
0pF
22
65
C1
0pF
0pF
0pF
22
22
22
62
63
64
C1
C1
C1
pF
47
5
03
C1
1
2
4
3
6
7
5
LCD Flex.PCB
J101
1
2
3
4
0pF
1uF
0.
22
76
75
PCB
C1
C1
ex.
Fl
B to B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
pF
47
034
C1
22
J103
0pF
22
00-800+
-0
292-022
04-6
018
C1
pF
47
036
C1
pF
47
1
01
C1
2
1
MIC1
0B27P40(2.8mm)
pF
pF
47
47
015
014
C1
C1
F
p
pF
47
47
009
010
C1
C1
pF
47
013
C1
R11
10K
05004HR_07C01S(G)
6
5
7
0pF
0.1uF
22
87
74
C1
C1
pF
47
012
C1
R193
5
10K
KRC104
Q110
47K
47K
9
R15
R160
pF
47
47pF
006
007
C1
C1
CR110 CR111
CR114
CR110~CR115 : BL-HG036
47K
47K
47K
47K
R197
R196
R161
R198
pF
pF
47
47
47pF
1
2
00
00
003
C1
C1
C1
pF
47
008
C1
R108
R109
R112
R119
+3.3V
TP
3
TP
9
TP
6
TP1
0
TP5
TP2
TP
4
TP
8
TP1
TP
7
47K
R199
47pF
004
C1
4.7K
4.7K
4.7K
4.7K
R155
470R
R156
1K
CR113 CR112
R157
1K
R158
CR115
1K
+3.3V
47K
R147
L_ARROW
P1
pF
47
5
00
C1
1
4
7
*
P2
R_ARROW
2
5
8
0
SH201
P3
3
6
9
#
+3.3V
BEEP
TX_AF1
FTV
C571
15nF
R1005
10nF
R1006
NA
+5V
R174 100K
R175 51K
R176 24K
C143
0.1uF
R507
10K
RT501
10K(TH)
+3.3V
C141
NA
R177
20K
+3.3V
R1004
10K
C198
NA
C140
47nF
R194
10K
C1017
470pF
R167
100K
R168
100K
C142
470pF
R171
10K
Q120
KRC404
C1016
0.1uF
KTA 2014
Q112
R172
10K
Q121
KRC404
C
B
R163
100K
CON
F_
DTM
E
MIC1
R173
10K
Q122
KRC404
KTA2014
Q111
R165
3K
SWB+
X_PWR_LOW
T
TX_PWR_CS
TX_PWR_U/D
C
BUSY
PLL_CLK
PLL_STB
PLL_DATA
RX_EN
SQ_CS
SQ_U/D
+3.3V
DTMF_OUT
R169
1.2K
E
B
R164
100K
P_CON
BEE
C195
220pF
+
C194
10uF / 16V
AUDIO_MUTE_CON
TX_EN1
TX_EN2
N/S_SW
RSSI
U107
1
KIA7027AT
R153
68K(1%)
R154
47K(1%)
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
STD
U106_SW
PTT2
20KHZ_SEL
PLL_PS
75
74
72
73
71
70
68
TX_PWR_U/D
BEEP_CON
MIC_MUTE2
PWDN
RX_TONE_CON1
RX_TONE_CON
2
VOX
LOW_BATT
+3.3V
R113
RX_TONE_EN
47K
C124
C123
1uF
0.1uF
R178
100K
2
3
CR101
NA
C144
0.1uF(K)
LOW_BATT
+3.3V
CS
R_
77
PW
78
TX_
79
DTMF_DEC_EN
80
FREQ_CON3
81
FREQ_CON2
82
FREQ_CON1
83
AUDIO_MUTE_CON
84
TX_EN1
85
TX_EN2
86
N/S_SW
87
RX_TONE_CON1
88
RX_TONE_CON2
89
90
ANL_SUBTONE_IN
91
VOX_IN
92
LOW_BATT_IN
93
TEMP_IN
94
A_GND
95
RSSI_IN
96
V_REF
97
A_VCC
98
LCD_CS
99
LCD_CLK
100
TONE4
1
100K
R180
R190
15K
R_LOW
PW
TX_
TONE3
2
3
K
51
R179
R184
15K
RX_TONE_EN
76
69
EER
U / D
ST
RX_EN
SQ_
F_
DTM
T3
VSS
TONE1
TONE2
TONE_IN
7
6
5
4
NA
200K
R183
R182
C145
15pF
FL101
7.372MHZ
C146
15pF
67
SEL
_SEL
PTT2
DCS
20KHZ_
A
T
SS
P
CNV
BEE
LCD_DA
8
9
FUN_KEY1
MOD_CON_CS
MOD_CON_U/D
FUN_KEY2
PROGRAM_DATA
LED(GREEN)
LED(RED)
66
10
65
2
1
F_Q
F_Q
DTM
DTM
SET
RE
11
B_S2
B_S1
A_S2
A_
PLL_LD
PTT1
UT
X_O
R185
0R
R148
1M
S3
64
F_Q3
DTM
U101
GND
12
63
F_Q4
DTM
13
X_IN
62
VSS
VCC1
14
+3.3V
61
60
59
58
57
A
T
CS
_CLK
VCC2
_DA
T_CON
SQ_
EPP
EPP
LIGH
M30302FCPGP
T1
B_S2
B_S2
TONE_IN
16
17
15
18
19
R114
10k
S2
A_
C147
0.1uF(K)
56
Y
BUS
S3
A_
20
54
53
55
A
T
STB
PLL_
PLL_DA
PGM_BUTTON1
PGM_BUTTON2
PGM_BUTTON3
LEFT_BUTTON
RIGHT_BUTTON
PRG / CLONE_RX
PRG / CLONE_TX
1
POP_CON
FUN_KEY
22
23
21
POP_CON
Figure 7-6. Microprocessor and Keypad Schematic Diagram
Page 54

7-8 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
+3.3V
C1038
47pF
R131 10R
C100
1uF(1608)
12
13
CSN
TEST
14
SCLK
XIN
15
SDATA
XOUT
VSS
16
VDD
10
11
12
J105
05504HR-12B01S(G)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
EXTINO
20
C1026
47pF
EXTIN
DIN0
21
TXIN
RXOUT
TXINO
FILO
22
AGND
RXINO
23
AGNDIN
U102
RXIN
24
AK2347
BEEP
C602
0.22uF(K)
C623
47pF
MOD
LIMLV
TSAOUT
RSAOUT
DIN
17
18
19
10
11
12
J104
XF2M-1215-1A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
SW/VOL1
RY8418
RX_AF1
C112
10uF/16V
+
R1003 10K
R1001
10K
C113
560pF
C114
220pF
R1002
9.1K
AUDIO_MUTE_CON
POP_CON
Q602
KRC404
C620
330pF
R623 560R
Q601
KRC404
R619
10K
R609 1K
R608
NA
C615
0.22uF (K)(1608)
R613
15K(1608)
R622 0R
C605
4.7uF (2012)
R621
39K
+
R620
33K
C619 33pF
390K(1608)
R614
4
3
2
1
C618
4.7uF / 16V(A)
U601
IN-
IN+
SVR
MODE
TDA8541
OUT-
VCC
GND
OUT+
C606
0.1uF
R616
0R
J603
53047-0210
L601 2.2uH(1608)
C621
330pF
R615
2R2
C616
5
6
7
8
0.1uF(K)
R610
2R2
SWB+
C601
0.1uF
C617
0.1uF(K)
C609
0.1uF(K)
SPK1
SM3624X1
+
-
L602 2.2uH(
C622
47pF
1608)
J601
0980683Z01
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
Figure 7-7. Audio Power Amplifier and External Audio Schematic Diagram
Page 55

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-9
J602
GND
060031MA005G500PL
BAT+
B_S2
B_S1
A_S2
A_S3
SWB+
BAT+
LED(GREEN)
LED(RED)
C460
C461
47pF
220pF
+3.3V
10K
R532
47pF
C579
BAT+
10K
R533
47pF
C580
10K
10K
R534
R535
47pF
47pF
C582
C581
R417
RLC63 0R1
220pF
C540
C432
1nF
J105
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
R418
220K(0.5%)
R419
220K(0.5%)
R420
4.7M
L413
C433
NA
R421
68K(0.5%)
1 / 2VCC
14
SWB+
U505
TK112 50AMTL
VIN
C
VOUT
C503
0.1uF
C507
22uF / 16V(B)
Q405
KTC4075
R411
560K
1
2
3
R412
1K
Q404
STB1188
R440
15K
C506
470pF
R414
1K
6
5
4
+
C501
470pF
SW/VOL1
RY8418
J104
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
47pF
C564
47pF
C562
47pF
C563
B
Q501
KRC404
A
BC
1
7
4
8
5
2
9
6
3
SW1
RY8487
2
R501
220R
Q502
KRC404
4
1
3
R502
220R
47pF
47pF
C560
C561
C
E
47pF
47pF
C566
C565
SWB+
BL-HEIG033B
CR501
+
APC(U401_PIN7)
C502
22uF / 16V(B)
C545
22uF
/ 10V(A)
C572
0.1uF
C462
33pF
+
C464
47pF
C531
0.1uF
U507
TC1240
1
VIN
2
VOUT
GND
3
SHDN
C-
C510
4.7uF(2012)
R413
8.2K
C463
470pF
NJM324
U502-D
6
C+
5
4
C406
0.1uF
+
SWB+
C619 33pF
C615
2
-
3
+
U401-A
KIA358
R422
68K(0.5%)
R423
3.9M
0.22uF(K)(1608)
R619
10K
R609
1K
MUTE_CON
Q601
KRC404
1
R424
R608
NA
C605
4.7uF(2012)
R621
39K
SWB+
U506
TK112 33AMTL
6
5
4
VIN
VOUT
C
C541
0.1uF
1
2
3
+
R613
15K(1608)
R622 OR
+
C509
470pF
C508
10uF / 16V(A)
R614 390K(1608)
U601
4
OUT-
IN-
3
VCC
IN+
2
SVR GND
1
MODE
OUT+
TDA8541
C618
4.7uF / 16V(A)
R620
33K
C606
0.1uF
5
6
7
8
C601
0.1uF
13
-`
12
+`
R523
30K(1%)
C511
22uF / 16V(B)
DRIVE_CON
AF_OUT1
AF_OUT2
R524
47K(1%)
+10V
C512
470pF
+3.3V
C533
0.1uF
R716,717
+10V
+5V
C529
0.1uF
R734
U501_pin4
Q705,706
Q304
Q407
R171~173
U105_pin4
U502_pin4
C530
10nF
+3.3V
pin1
U107_
+3.3V
U106_pin4
+3.3V
R131
+3.3V
R150
+3.3V
U103_pin11,20
+3.3V
U104_pin8
+3.3V
J102_pin16
+3.3V
U101_pin14,96,97
+3.3V
U104_pin1
+3.3V
Q711
+3.3V
R719,722
+3.3V
R507
+3.3V
U508_pin1
+3.3V
R537
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
Figure 7-8. Switches and Battery Schematic Diagram
Page 56

7-10 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
TO_VCTCXO & VCO
+3.3V
C517
15nF
R508
3.6K
R509
2.2K
R529
R530
R531
R540
47K
+3.3V
R194
10K
C140
C142
470pF
-
+
C525
2.2nF
47nF
L603
2.2uH(1608)
C141
NA
C625
47pF(1608)
C544
NA
C524
47nF
2
3
Q504
KRC404
C548
NA
R516
2.2K
Q505
KRA305
PTT1
FUN_KEY1
FUN_KEY2
PTT2
1 / 2VCC
CR502
NA
R517
15K
R537
1K
C542
10nF
2
1
MIC1
0B27P40(2.8mm)
C543
2.2nF
C522
15nF
6
R514
7
5
NJM324
U501-B
47K
47K
47K
C573
1
47pF
2
PB501
PTT
EVQPUD02K
1
2
15K
C523
470pF
PB502
R515
20K
1
NJM324
U501-A
C570
47pF
FUN1
EVQPUD02K
C574
47pF
1
2
PB503
FUN2
EVQPUD02K
C1032
47pF
R136
100K
C547
2.2nF
R135
0.1uF(K)
R111
NA
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
L604
2.2uH(1608)
TX_AF2
J601
0980683Z01
R538
10K
R536
330K
C139
10K
C136
0.1uF
Q114
KRC404
+3.3V
R526
47K
C527
18nF
C583
47pF
13
12
C624
47pF
R137
4.7M
+
-
PROGRAM_DATA
7
6
5
MCP4011(503)
1
NJM324
U502-A
C135
47pF
14
NJM324
U105-D
R120
47K
C546
0.1uF(K)
1 / 2V
CC
C576
47pF(1608)
MOD_CON_U /D
MOD_CON_CS
U508
U/D
VDD
VSSNC
B
A
W
CS/
2
-
3
+
C137
0.1uF(K)
+3.3V
VOX_EN
R511
8.2K
C191
220pF
C518
5.6nF
R510
15K
C550
560pF
C528
R520
18nF
1M
C579
47pF
U101_PIN31(SDATA)
U101_PIN30(CLK)
U101_PIN29(CSN)
C1038
47pF
U106
TC7S66FU
1
C577
47pF
4
C519
1.2nF
13
12
C3
47pF
2
C1029
47pF
-
+
NJM324
U501-D
C100
1uF(1608)
C125
47nF
R126
15K
14
C1031
47pF
C111
1uF(K)
R107
3.9K
R104
47K
10R R131
C1024
47pF
C1020
47
C126
33nF
R105
47K
pF
R162
820R
C1037
47pF
R106
47K
Q101
KRC413
C127
47nF
C101
R101
1uF(K)
10K
C1019
47pF(1608)
12
CSN
TEST
13141415151616171718181919202021222324
R146
0R
FL102
3.5795MHz
R145
C115
27pF
C1021
47pF
C156
0.22uF
C1030
C110
47pF
22nF
Q103
KRC413
C520
6.8nF
R513
R512
10K
20K
R539
330K
C549
560pF
+3.3V
18
2
R518
4.7K
3
4
1 / 2_VCC
C536
15nF
R527
82K
C537
2.2nF
CR117
KDS160E
CR116
KDS160E
9
-
10
+
NJM324
U501-C
C521
1.2nF
R519
4.7M
9
-
8
10
+
NJM324
U502-C
R521
330K
R541
330K
R528
82K
U101_PIN79(DTMF_DEC_EN)
VOX
C138
0.22uF1608)
R138
220K
8
+3.3V
+
C551
10uF / 10V(A)
C1025
47pF
R103
150K
C103
R102
33pF
47K
C102
2.2nF
C106
R117
C119
10nF
Q1
KRC413
C109
22nF
C154
1uF(K)
02
+3.3V
R150
10K(1%)
RX_AF2
8.2K
C104
150pF
R151
12K(1%)
R141
100K
U101_PIN79
RX_TONE_CON2
C157
0.22uF
R121
330K
RX_TONE_CON1
6
5
C1039
47pF
R140
68K
129
R
150K
-
+
NJM324
U105-B
Q113
KRC404
R110
270K
C1023
C1022
47pF
47pF
1
101111
VSS
MOD
SCLK
LIMLV
SDATA
XIN
VDD
XOUT
TSAOUT
RSAOUT
1M
C116
27pF
R127
33K
2
-
1
3
+
NJM324
U105-A
R122
330K
233445566778899
AGND
RXINO
C118
10uF / 16V
+
AGNDIN
U102
RXIN
C1028
47pF
AK2347
C1026
47pF
Q104
KRC413
C120
15pF
C130
33nF
C153
1uF(K)
TXIN
EXTIN
TXINO
EXTINO
DIN
FILO
DIN0
RXOUT
C1027
47pF
C117
1.2nF
R143
100K
R144
100K
C129
47nF
C128
47nF
R128
3.9K
R118
47K
C105
15nF
+3.3V
1
VDD
IN+
2
ST/GT
IN-
EST
GS
STD
VREF
NC
INH
PWDN
Q4
Q3
NC
13
OSC1
Q2
12
OSC2
Q1
10
TOE
VSS
U103
MT88L70
R180
100K
R179
51K
R182
200K
R183
NA
+5V
4
+
U105-E
-
NJM324
11
C158
0.22uF
7
R149
470K
C1033
47pF
47nF
1 / 2 VCC
R142
330K
TONE4
TONE3
TONE2
TONE1
R116
1.2K
C107
0.1uF(K)
R132
1K
R133
680K
U101_PIN26(DTMF_IN)
C121
33nF
U101_PIN72
U101_PIN63
U101_PIN64
U101_PIN65
U101_PIN66
R134
3.9M
9
10
C134
0.22uF(K)
U101_PIN100(RX_TONE_EN)
-
+
NJM324
U105-C
8
U101_PIN3_16_23
Figure 7-9. Transmitter Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram
Page 57

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-11
C622
Q407
R149
R135C139
L602
L601
L604
L603
R419
R421
R420 C433
R423
U401
R432
C436
R431
R427
R426
C435
R425
C438
C380
Q101
Q113Q104
Q103
C156
C110
R122
C128
C135
R137
C137
J102
CR117
C1030
R127
C126
C127
C125
R126
C1029
C136
R111
R136
Q114
CR116
C1031
TP1
C432
R424
C437
C1028
J601
R417
R418
R422
RT501
R730
R722
R723
C750
R724
R725
R140
U103
C577
C583
L413
SH102
R732
C752
R141
R142
C515
R506
Q404
R721
R727
C121
C528
Q709
Q710
R411
R440
SH103
Q403
C463
C462
C465
C746
L709
C747
C756
U701
C738
C741
R720
R731
R733
R719
C748
R718
Q707
C749
R716
Q708
R717
R740R726
R728
C754
TP11
C512
U507
R503
R520
C511
R504
C551
C578
R505
U502
C572
C510
R734
C739
C740
C516
R526
R528
C536
R527
C537
C530
R523
R524
C533
C545
C531
R541R521R519
C468
C453
C454
R507
C571
C411
R414
Q405
R412
C464
C406R413
C538
C539
Q503
R735
Q711
R736
C755R729
R737
C751
C753
C119
C120
C576
C621
PB501
PB502
PB503
C574
C573
Q202
C116
C115
J603
R616
C570
FL102
FL101
C214
Q206
C617
TP9
C616
R615
R623
R609
R608
R619
Q601Q602
R433
C473
DEC1
R318
R317
R342C381
C339
CR306
R316
C211
R208
R210
C209
C210
Q207
C213
C206
R216
CR202
C204
R203
R250
C208
R206
R207
R1005
R1006
C198
R168
C1027
C1026
R110
C1025
R145
R117
C105
R146
C107
C106
R116
C1038
C1024
R115
TP8
C145
R185
R148
C146
TP2
TP5
TP7
C623
C601
R213
RT201
R212
R211
R220
R1004
TP6
U402
R167
C104
R118
C624
Q408
C469
C470
C378
U202
CR201
R204 R217
C1016
R165
Q112
C1022
Q111
C1023
TP4
TP10
J105
C602
C625
C460
C461
C439
LK2
C471
C472
R441
Q406
C334
C320
R314
C382
C1017
Q102
C157
C109
R128
R121
C129
C130
R129
C158
U105
C134
R163
R133
R134
R169
R132
R164
C138
TP3
R138
C1021
C1019
C1037
C1039
U101
Figure 7-10. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Mainboard Top Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON200
Page 58

7-12 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
ANT4
ANT3
ANT1
ANT2
C430
C431 R416
L410
C428 C427
SH105
C429
CR301
C440
L407
R436
C426
C446
C423
CR703
R434
C727
R712
C717
R708
L409
C445
L411
CR401
C422
C420
C452
C413
C449
Q409
C447
L708
R707
R711
R713
C718
R709
C721
Q703
Q704
C723
C726
L705
CR311
C303
L325
C301
C466
C417
R409
R410
R406
C444
R405
SH101
C451
Q401
R429
R428
R107
C519
C550
C529
C548
C525
C516
C524
C544
C357
Q301
C312
C309
L321
C356
L328
L322
C372
C304
C373
C375
C374C362
L323
C318
C358
C364
L334
L330
C365
L329
C325
L331
C408
L310
Q701
U501
Q702
L703
C712
C518
R515
R715
C728
R537
Q505
C546
R510
C326
C327
C343
C702
L701
R701
C704
C701
Q705
C707
L704
R705
C710
CR701
Q504
R540
U104
R513
C520
R511
R539
R512
C521
C549
C523
R509
R508
C517
C543
C522
R514
C403
C402
L401
C731
R70
2
C705
R703
C706
C709
C704
C711
C702
CR502
L301
R415
L412
C419
C418
C416
C434
R430
L405
L406
C409
C410
L403
L402
Q402
C404
C405
R408
R407
C467
R402
R404
R403
R401
C401
C448
R435
C730C729
R714
R706
Q706
C714
C716
C715
L707
R710
C719
L706
C724
C722
CR702
C725
FL701
C575
R536
C547
C542
C527
R517
R538
R518
U508
CR314
C361C351
L324
C360
R323
L320
R330
C307
CR310
R302
CR309
C310
L304
R320
C363
C379
R334
CR313
C354
CR304
R332
C355
R333
CR305
R336
Q306
Q307
C368
R337
C367
C344
Q305
R171
C143
R177
R174
Q121
Q120
C1033
C1032
C111
R162
C101
U106
CR101
C147
C502
C503
R139
U505
C506
C507
C161
C178
C168
C179
C167
C177
C166
C165
C581
C582
C580
C579
C615
C540
R613
C619
CR307
R610
C609
J602
C369
R335
L333
C328
R310
C370
L306
R309
C377
C376
C319
Q304
R315
L327
R173
CR315
R176
R175
R172
CR312
Q122
CF1CF2
C153
C154
C103
R101
R103
R102
C102
R151
R150
R104
R105
R106
C1020
R154
C501
C194
U506
C541
C509
C508
C1036
C1035
R193
C1034
C172
C169
C173
C170
C189
C188
C171
C620
R153
C195
R194
R614
FL201
C164
C329
C191
TP15
TP16
TP14
C606
TP13
Q303
R621
R620
R120
U102
C347
C203
R113
C124
C123
R114
R532
R533
C162
C163
R534
R535
U601
R312
C337
R258
C201
R530
R531
R529
R152
R195
C142
R622
R338
R311
L340
C140
R178
ANT5
U1
L332
U201
C605
C618
C330
C331
C332
FL301
C340
C338
C341
C342R319
C207
Q201
C112
R1003
R1002
R1001
C114
C113
C117
R143
R144
C100
R131
R184
C118
R180
R179
R182
R183
R190
C144
07
C141
Figure 7-11. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Mainboard Bottom Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON200
Page 59

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-13
R501 R502
Q501 Q502
C563
CR501
C564
C562
C560
C561
C565
C566
Figure 7-12. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Top View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100
Page 60

7-14 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
SW1
SW / VOL1
J104
Figure 7-13. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Bottom View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100
Page 61

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-15
MIC1
CR110 CR111
SH201
C174
C187
R155
R196
R197
R198
R161
R160
R159
J101
Q110
C1004
C1011
C1018
C176
C175
R199
R147
C1005
C1009
C1010
J103
CR114 CR115
CR112 C R11 3
C1001
C1008
R156
R158
R157
C1007
R108
C1012
R109
C1013
C1014
R112
15
C10
R119
C1006
C1002
C1003
Figure 7-14. UHF2 (435–480 MHz) Keypad Board: PCB No. 8422BEACON100
Page 62

7-16 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
7.3.1 Parts List
Circuit
Ref.
C100 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 Z 1μF
C101 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1μF
C102 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 2200PF
C103 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C104 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 150PF
C105 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 153PF
C106 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C107 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C109 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 223PF
C110 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 223PF
C111 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1μF
C112 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
C113 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 560PF
C114 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C115 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 27PF
C116 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 27PF
C117 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 122PF
C118 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
C119 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C120 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C121 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 333PF
C123 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C124 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C125 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C126 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 333PF
C127 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C128 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C129 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
16V(A)
16V(A)
Circuit
Ref.
C130 TDK – Chip Cap,1005 K 333PF
C134 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.22μF
C135 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C136 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C137 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C138 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 K 0.22μF
C139 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
C140 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C142 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C143 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C144 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C145 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C146 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C147 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C153 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1μF
C154 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1μF
C156 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.22μF
C157 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.22μF
C158 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.22μF
C161 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C162 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C163 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C164 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C165 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C166 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C167 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C168 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C169 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C170 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C171 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
Circuit
Ref.
C172 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C173 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C174 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C175 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C176 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C177 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C178 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C179 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C187 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C188 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C189 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C191 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C194 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
C195 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C201 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C203 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 120PF
C204 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C206 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C207 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C208 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C209 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 330PF
C210 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 330PF
C211 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C213 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C214 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C301 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 5PF
C303 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C304 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
C307 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 18PF
C309 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
16V(A)
Page 63

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-17
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C310 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C312 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C318 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C319 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C320 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
16V(A)
C325 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C326 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C327 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 12PF
C328 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 2PF
C329 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C330 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 39PF
C331 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 9PF
C332 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C334 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C337 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C338 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C339 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C340 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C362 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C364 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C365 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 27PF
C367 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C368 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C372 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C373 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 20PF
C374 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C376 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C378 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
16V(A)
C379 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 20PF
C380 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C382 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C401 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C402 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C403 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C404 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 56PF
C405 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 56PF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C429 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 5PF
C431 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 K 1000PF
C432 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C434 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C435 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C436 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C437 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C439 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C440 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C445 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 3PF
C446 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 4PF
C447 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C448 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C449 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C451 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 3PF
C452 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 33PF
C453 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C454 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
16V(B)
C341 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 56PF
C342 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C343 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C344 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C347 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C351 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C354 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C355 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C357 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 56PF
C358 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 15PF
C360 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 4PF
C361 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 22PF
C406 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C408 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C410 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 27PF
C413 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 27PF
C416 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 D 7PF
C417 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 12PF
C418 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 15PF
C420 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 D 10PF
C422 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 12PF
C426 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 6PF
C427 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 4PF
C428 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 C 6PF
C460 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C461 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C462 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C463 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C464 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C465 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C466 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C467 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C468 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 0.5PF
C469 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C470 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C471 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
Page 64

7-18 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C472 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C473 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C501 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C502 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
16V(B)
C503 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C506 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C507 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
16V(B)
C508 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
16V(A)
C509 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C510 TDK – Chip Cap, 2012 Z 475PF
C511 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
16V(B)
C512 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C515 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C516 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
16V(A)
C517 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 153PF
C518 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 562PF
C519 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 122PF
C520 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 682PF
C521 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 122PF
C522 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 153PF
C523 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C524 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 473PF
C525 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 2200PF
C527 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 183PF
C528 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 183PF
C529 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C530 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C531 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C533 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C536 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 153PF
C537 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 2200PF
C538 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C539 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
16V(A)
C540 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 220PF
C541 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C542 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
C543 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 2200PF
C545 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
10V(A)
C546 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C547 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 2200PF
C549 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 560PF
C550 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 560PF
C551 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 10uF–M/
10V(A)
C560 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C561 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C562 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C563 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C564 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C565 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C566 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C570 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C571 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 153PF
C572 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C573 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C574 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C575 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C576 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 47PF
C577 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C578 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C579 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C580 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C581 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C582 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C583 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C601 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C602 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.22μF
C605 TDK – Chip Cap, 2012 Z 475PF
C606 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C609 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C615 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 K 0.22μF
C616 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C617 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C618 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 4.7uF–M/
16V(A)
C619 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 33PF
C620 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 330PF
C621 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 330PF
C622 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C623 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C624 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C625 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 J 47PF
C701 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
10V(A)
C702 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C704 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C705 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 2PF
Page 65

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-19
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C706 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C707 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 9PF
C709 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 4PF
C710 MURATA – Chip Trimmer Cap, 2PIE
6PF
C711 MURATA – Chip Cap, 1005 J 13PF
10V
C712 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C714 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C715 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 22uF–M/
10V(A)
C716 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C717 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C718 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 4PF
C719 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 7PF
C721 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 3PF
C722 MURATA – Chip Trimmer Cap, 2PIE
6PF
C723 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 0.5PF
C724 MURATA – Chip Cap, 1005 J 11PF
10V
C725 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
C726 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 0.5PF
C727 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 2PF
C728 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 4PF
C729 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 6PF
C730 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 2PF
C731 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 C 2PF
C738 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 7PF
C739 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C740 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C741 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C746 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C747 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 D 10PF
C748 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C749 TDK – Chip Cap, 1608 Z 1μF
C750 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C751 HITACH – Chip Tantal, 1uF–M/
35V(A)
C752 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C753 PANASINIC – Film Chip Cap, 3216 J
473PF
C754 PANASINIC – Film Chip Cap, 3216 J
473PF
C755 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 0.1μF
C756 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 1000PF
C1001 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1002 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1003 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1004 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1005 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1006 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1007 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1008 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1009 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1010 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1011 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1012 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1013 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1014 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1015 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1016 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 Z 0.1μF
C1017 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 470PF
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
C1018 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 220PF
C1019 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1020 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1021 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1022 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1023 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1024 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1025 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1026 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1027 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1028 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1029 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1030 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1031 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1032 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1033 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1034 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1035 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1036 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1037 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1038 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
C1039 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 J 47PF
CF1 BGTech 8286045500120 TOKO, Ceramic Filter,
ELFY455F
CF2 BGTech 8286045500220 TOKO, Ceramic Filter,
ELFY455H
CR110 BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
CR111 BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
CR112
2
BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
Page 66

7-20 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
Circuit
Ref.
CR113
2
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
CR114
2
BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
CR115
2
BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-HG036D-
TR
CR116 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
160E (ESM)
CR117 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
160E (ESM)
CR201 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS
181
CR202 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS
181
CR301 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
114
CR304 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR305 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR306 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
160E (ESM)
CR307 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR309 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
114E (ESM)
CR310 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
114E (ESM)
CR312 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
160E (ESM)
CR313 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR314 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR315 KEC – SWITCH DIODE, KDS–
160E (ESM)
CR401 M/A COM – PIN DIODE, MA4P7001F–
1072T
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
CR501 BRIGHT LED – LED DIODE, BL-
HEIG033B-TR
CR701 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR702 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
CR703 KEC – VARIABLE DIODE, KDV–
154E (ESM)
DEC1 BGTech 8287455C24010 CQ, Descriminator,
JTBC455C24 (LCP)
FL101 BGTech 82827R3728M00 SHINSUNG, Crystal,
7.3728MHz (H: 2.8mm)
FL102 BGTech 82823R5795M00 SHINSUNG, Crystal,
3.5795MHz (H: 2.8mm)
FL201 BGTech 828244R645M00 SHINSUNG, Crystal,
44.645MHz (SMD)
FL301 BGTech 828645R100220 SHINSUNG, Crystal Filter,
MCF 45.15S12.B (8.5
kHz)
FL701 BGTech 8289012R80010 SHINSUNG, VCTCXO,
12.8 MHZ
F–
CABLE
1
F–
CABLE
2
BGTech 8560228005000 SNAGGWA, BEACON
FLAT CABLE, FF12–
22N080XXA
BGTech 8560124005000 SNAGGWA, , BEACON
FLAT CABLE, FF12–
12N040XXA
J101 BGTech 851607C01S110 YUNHO, FPC
CONNECTOR, 05004HR07C01S(G)
J102 BGTech 851622A01S110 YUNHO, FPC
CONNECTOR, 05004HR–
22A01S
J103 BGTech 8516220005020 KYOCERA, FPC
CONNECTOR, 04-6292022-000-800+
J104 BGTech 851612151A110 OMIRON, FPC
CONNECTOR, XF2M1215-1A
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
J105 BGTech 851612A01S110 YUNHO, FPC
CONNECTOR, 05004HR–
12B01S(G)
J601 BGTech 8500031009800 CHI CHENG, SPK MIC
JACK, 0980683Z01–D
J602 BGTech 85100G500PL00 SUYIN, BATTERY
CONNECTOR,
060031MA005G500PL
J603 BGTech 8510530470210 MOLEX, CONNECTOR,
53047–0210
L301 DEARIM – Coil Air, 0.45–1.4–5TL
L304 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 39N
L306 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 820NH
(Tolerance: 5%)
L310 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 18NH
L320 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 22nH
L322 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 18NH
L323 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 18NH
L324 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 22nH
L325 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 220nH J
L327 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 820NH
L328 DELTA – Chip Ind, 2012 18NH
L329 BGTech 8920PT1667020 TOKO, #617PT–1667
L330 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 33nH
L331 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
L332 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 820NH
L333 BGTech 8920PT1664020 TOKO, #617PT–1664
L334 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 8.2nH
L340 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 820NH
L401 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 J 27nH
L402 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 J 22nH
L403 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 33NJ
L405 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 J 6.8nH
Page 67

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-21
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
L406 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 220nH J
L407 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 33nH
L409 DEARIM – Coil Air, 0.45–1.4–3TL
L410 DEARIM – Coil Air, 0.45–1.4–3TL
L411 DEARIM – Coil Air, 0.45–1.4–3TL
L412 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 220nH J
L413 DEARIM – Coil Air, 0.35–1.6–7TL
L601 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
L602 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
L603 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
L604 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
L701 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 27N
L702 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
L703 DAERIM – Coil Air, 0.3–1.1–3TL
L704 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 220nH J
L705 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 K 2.2uH
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
Q102 KEC – KRC 413 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q103 KEC – KRC 413 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q104 KEC – KRC 413 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q110 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q111 KEC – KTA 2014 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q112 KEC – KTA 2014 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q113 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q114 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q120 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q121 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
Q307 BGTech 81492SK711020 2SK711 TOSHIBA FET N–
Channel Transistor
Q401 BGTech 8142000951120 PBR 951LT1 PHILIPS BJT
NPN Transistor
Q402 BGTech 8149003078021 2SK3078 TOSHIBA FET
N–Channel Transistor
Q403 BGTech 8149003476021 2SK3476 TOSHIBA FET
N–Channel Transistor
Q404 BGTech 8145001188021 STB 1188 AUK BJT NPN
Transistor
Q405 KEC – KTC 4075 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q406 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q407 KEC – KRA 305 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q408 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q409 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
L706 DAERIM – Coil Air, 0.3–1.0–3TL
L707 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1608 220nH J
L708 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 27N
L709 TAIYOYUDEN – Chip Ind, 1005 J 22N
LCD101 BGTech 86343208A2020 EVERRVIEW,VBS3208A2
–7FWLYA,REV4.0
MIC1 BGTech 8420063215000 BSE, C-MIC, 6.0*2.7/
2.2KΩ,2V,-44±3dB, Pin
type
PB501 BGTech 8466PUD02K020 PANASONIC, Tack
Switch, EVQPUD02K
PB502 BGTech 8466PUD02K020 PANASONIC, Tack
Switch, EVQPUD02K
PB503 BGTech 8466PUD02K020 PANASONIC, Tack
Switch, EVQPUD02K
Q101 KEC – KRC 413 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q122 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q201 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q206 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q207 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q301 KEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q303 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q304 KEC – KRA 305 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q305 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q306 BGTech 81492SK711020 2SK711 TOSHIBA FET N–
Channel Transistor
Q501 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q502 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q503 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q504 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q505 KEC – KRA 305 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q601 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q602 KEC – KRC 404 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q701 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q702 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Page 68

7-22 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
Q703 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q704 NEC – 2SC4226 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q705 KEC – KRA 305 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q706 KEC – KRA 305 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q707 KEC – KTC 4075 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q708 KEC – KTA 2014 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q709 KEC – KTA 2014 BJT PNP
Transistor
Q710 KEC – KTC 4075 BJT NPN
Transistor
Q711 KEC – KRA 304 BJT PNP
Transistor
R101 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R102 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R103 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150KΩ
R104 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R105 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R106 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R107 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.9KΩ
2
R108
R109
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
2
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R110 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 270KΩ
2
R112
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R113 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R114 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R115 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R116 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.2KΩ
R117 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 8.2KΩ
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R118 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
2
R119
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R120 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R121 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R122 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R126 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R127 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 33KΩ
R128 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.9KΩ
R129 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150KΩ
R131 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R132 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R133 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 680KΩ
R134 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.9MΩ
R135 TDK – Chip Cap,1005 K 0.1μF
R136 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R137 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7MΩ
R138 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220KΩ
R139 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R140 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 68KΩ
R141 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R142 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R143 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R144 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R145 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1MΩ
R146 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R147 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R148 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1MΩ
R149 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 470KΩ
R150 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 10KΩ
R151 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 12KΩ
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R152 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 680Ω
R153 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 68KΩ
R154 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 47KΩ
R155 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 470Ω
R156 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
2
R157
R158
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KW
2
KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R159 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R160 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R161 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R162 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 820Ω
R163 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R164 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R165 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3KΩ
R167 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R168 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R169 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.2KΩ
R171 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R172 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R173 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R174 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R175 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 51KΩ
R176 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 24KΩ
R177 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 20KΩ
R178 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R179 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 51KΩ
R180 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R182 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 200KΩ
R184 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R185 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
Page 69

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-23
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R190 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R193 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R194 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R195 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R196 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R197 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R198 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R199 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R203 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 22KΩ
R204 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 22KΩ
R206 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R207 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 22KΩ
R208 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 12KΩ
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R317 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 180KΩ
R318 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.3KΩ
R319 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.3KΩ
R320 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R323 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R330 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R332 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R333 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R334 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R335 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2KΩ
R336 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R337 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R338 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R418 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1608 D 220KΩ
R419 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1608 D 220KΩ
R420 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7MΩ
R421 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1608 D 68KΩ
R422 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1608 D 68KΩ
R423 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.9MΩ
R424 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 12KΩ
R425 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.9KΩ
R426 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R427 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220KΩ
R428 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R429 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.6KΩ
R430 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R210 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 120KΩ
R211 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R212 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 33KΩ
R213 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.3KΩ
R216 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R217 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R220 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 5.6KΩ
R250 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R258 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.5KΩ
R302 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 56KΩ
R309 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R310 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R311 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330Ω
R312 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150KΩ
R314 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R315 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R316 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R401 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 180Ω
R402 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 39Ω
R403 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 180Ω
R404 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 8.2KΩ
R405 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.5KΩ
R406 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 22Ω
R407 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R408 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2KΩ
R409 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R410 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R411 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 560Ω
R412 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R413 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 8.2KΩ
R414 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R415 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 2012 J 220Ω
R416 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1608 J 47KΩ
R417 ROHM – Chip Res, 1W J 2512 0.1Ω
R431 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R432 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 27KΩ
R433 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R434 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 33KΩ
R435 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150Ω
R436 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R440 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R441 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R501 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220Ω
R502 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220Ω
R503 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 56KΩ
R504 NOBLE – Chip Semi V.R, 3PIE 47
KΩ
R505 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 12KΩ
R506 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R507 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R508 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3.6KΩ
R509 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2KΩ
Page 70

7-24 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz)
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R510 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R511 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 8.2KΩ
R512 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 20KΩ
R513 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R514 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R515 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 20KΩ
R516 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2KΩ
R517 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R518 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7KΩ
R519 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 4.7MΩ
R520 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1MΩ
R521 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R523 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 30KΩ
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R609 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R610 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2Ω
R613 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 15KΩ
R614 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 390KΩ
R615 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.2Ω
R616 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R619 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R620 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 33KΩ
R621 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 39KΩ
R622 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R623 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 560Ω
R701 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 56Ω
R702 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.5KΩ
Circuit
Ref.
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
R720 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150Ω
R721 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 150Ω
R722 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R723 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R724 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 390Ω
R725 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R726 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 3KΩ
R727 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.7KΩ
R728 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 2.7KΩ
R729 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R730 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 33KΩ
R731 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R732 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R524 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 47KΩ
R526 NOBLE – Chip Semi V.R, 2PIE 47
KΩ
R527 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 82KΩ
R528 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 82KΩ
R529 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R530 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R531 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R532 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R533 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R534 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R535 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R536 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R537 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R538 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R539 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R540 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 47KΩ
R541 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 330KΩ
R703 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 4.7KΩ
R704 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 4.7KΩ
R705 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220Ω
R706 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100Ω
R707 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.5KΩ
R708 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 4.7KΩ
R709 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 F 6.8KΩ
R710 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 220Ω
R711 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R712 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 100KΩ
R713 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 30KΩ
R714 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 56Ω
R715 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 56Ω
R716 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 300Ω
R717 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R718 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 7.5KΩ
R719 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R733 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 0Ω
R734 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10Ω
R735 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R736 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R737 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1KΩ
R740 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 1.5KΩ
R1001 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R1002 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 9.1KΩ
R1003 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R1004 KAMAYA – Chip Res, 1005 J 10KΩ
R1005 TDK – Chip Cap, 1005 K 10nF
RT201 TAIYOYUDEN – Thermistor, 103K
RT501 TAIYOYUDEN – Thermistor, 103K
SH101
SH102
SH103
SH105 MOTOROLA PMDN4149AR Finger Strip TX
BGTech
BGTech
BGTech
8860BEACA1010 Shield CAN, VCO
8860BEAC93010 Shield CAN, PLL
8660BEACA4010 Shield CAN, PA
Page 71

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (UHF2: 435–480 MHz) 7-25
Circuit
Ref.
SH201 MOTOROLA PMDN4151AR Finger Strip–Pair
SPK1 BGTech 8400362424100 SHINMYUNG, Speaker,
SW/
VOL1
U101 BGTech 81100303RF020 RENESAS, CPU IC,
U102 BGTech 8116AK2347020 ASAHI KASEL, AUDIO
U103 BGTech 8192088L70020 ZERLINK, DTMF
U104 BGTech 811324LC64020 MIRCO CHIP, EEPROM
U105 JRC – OP AMP, NJM324
U106 BGTech 8135TC7S66020 TOSHIBA, Analog SW IC,
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
24Ω 1.0W 36θ(Connector
type)
BGTech 84766N992N151 TOKOS, Switch Volume,
RY-8418 Rev1
M3030RFCPGP
LSI, AK2347
RECEIVER, MT88L70
IC, 24LC64
TC7S66FU
Circuit
Ref.
U508 BGTech 8191401150320 MIRCO CHIP,DIGITAL
U601 BGTech 811608541T020 PHILIPS, AUDIO
U701 BGTech 810415E03S020 FUJISU, PLL IC,
PCB1 BGTech 8431BEACON200 CAFSYSTEM, Main PCB,
KEY
PCB1
Supplier Supplier Part No. Description
POTENTIOMETER,
MCP4011(503)
AMP,TDA8541
MB15E03SLPFV1–G–
BND–EF–6
FR4 4 Layer PCB Rev.#P4
BGTech 8422BEACON100 CAFSYSTEM, Key PCB,
1.2T 2Layer
Note:
2: Not for PMUE3144AAL
U107 BGTech 81287027AT020 VOLTAGE DETECTOR,
KIA7027AT
U201 BGTech 8125311360020 TOSHIBA, FM IC,
TA31136
U202 BGTech 8191401150220 MIRCOCHIP, DIGITAL
POTENTIOMETER,
MCP4011(502)
U401 KEC – OP AMP (DUAL), KIA358
U402 BGTech 8191401150220 MIRCOCHIP, DIGITAL
POTENTIOMETER,
MCP4011(502)
U501 JRC – JRC, OP AMP, NJM324
U502 JRC – JRC, OP AMP, NJM324
U505 BGTech 8123011250021 TOKO, REGULATOR IC,
TK11250AMTL
U506 BGTech 8123112330020 TOKO, REGULATOR IC,
TK11233AMTL
U507 BGTech 8128TC1240020 MICRO CHIP, VOLTAGE
DOUBLER, TC1240
Page 72

7-26
Notes
Page 73

Chapter 8 136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation
A
8.1 Introduction
This chapter provides a detailed theory of operation for the radio components. Schematic diagrams
for the circuits described in the following paragraphs are located in Chapter 10 of this manual.
8.2 VHF Receiver
The VHF receiver design covers the frequency range of 136 – 174 MHz and it is a double
conversion super heterodyne with 1st IF 45.1 MHz and 2nd IF 455 kHz. The receiver is divided into
two major blocks, Front End and Back End as shown in Figure 8-1.
Preselector
Filter
RF
Amp
Postselector
Filter
1st Mixer
Crystal
Filter
IF
Amp
RX from
ntenna Switch
Inj Filter
First LO
from Synthesizer
N/S_SW
Ceramic
Descriminator
455C24
Recovered Audio
LPF
Quadrature
Detector
Filter
IF
Amp
455FW
455HW
RSSI
Figure 8-1. VHF Receiver Block Diagram
Crystal
44.645MHz
Page 74

8-2 136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation: VHF Receiver
8.2.1 Receiver Front End
Incoming RF signals from antenna are first routed through the harmonic filter (L409, L410, L411,
C426, C427, C428, C429, C445, C446) and antenna switch (CR301), part of the transmitter circuitry,
before being applied to the receiver front end. The receiver front end consists of preselector filter, RF
amplifier, post-selector filter and a single-balanced mixer.
The preselector filter is a varactor-tuned 2-pole design using discrete elements (L301, L302, L303,
L304, C301, C304, C305, C307) in a shunt or series resonator configuration. It is a band-shift filter
and the frequency shift is controlled by varactor diodes CR302 and CR303, which are connected to
the microprocessor. It is configured to provide steeper attenuation above the passband for improved
spurious rejection when high-side local injection is used. The frequency is separated into 6 steps and
controlled by CPU (136 – 174 MHz).
The output of this filter is matched to the base of RF amplifier Q301 which provides 15dB of gain.
The output of the RF amplifier is applied to the post-selector filter. The post-selector filter designed
using discrete elements (L307, L308, L309, L311, C315 and C354) in a series/shunt resonator
configuration. It is a band-shift filter and the frequency shift is controlled by varactor diodes CR305
and CR307, which are connected to the microprocessor. It is configured to provide steeper
attenuation above the passband for improved spurious rejection when low-side local injection is used.
The frequency is separated into 6 steps and controlled by CPU (136 – 174 MHz).
The output of the post selector is connected to the single-balanced mixer consisting of components
L329, L333, Q306 and Q307. 1st local signal generated from VCO is filtered by injection
filter (L310, L331, C325, C326, C327, C333 and C365) to remove second harmonics. The converted
1st IF frequency at mixer passes through L331 and matches the 45.1 MHz IF signal to pair crystal
filter (FL301).
8.2.2 Receiver Back End
The 1st IF signal is amplified about 15 dB by IF amp Q303. The output of the IF amp is connected to
IF IC (U201). 1st IF frequency (45.1 MHz) and 2nd LO frequency (44.645 MHz) are mixed in U201.
The second mixer converts the 45.1 MHz high IF frequency to 2nd IF frequency (455 kHz).
Additional IF selectivity is provided by two ceramic filters (CF1, CF2). The wider filter 455 FW is used
for 25 kHz channel spacing, and the narrower filter 455 HW is used for 12.5 kHz channel spacing.
These two ceramic filters may eliminate undesired signal and demodulated by demodulator in U201.
N/S_SW which connected to microprocessor is used to select the wide and narrow band.
The mute (squelch) circuit switches off the audio amplifier when no audio is present. The squelch
circuit consists of U201 and U202 and their associated components. The noise signal from pin 9 of
U201 is used to control the squelch circuit sensitivity of U202. The noise passes through filter, and is
amplified by internal amp of U201. The amplified noise act as a DC voltage to control the mute
system. So if the noise level is under the threshold voltage, the microprocessor (U101) un-mutes the
radio. If the noise level is over the threshold voltage, the microprocessor mutes the radio. The
squelch level is tuned in the factory. When a component or a part in the RX system is replaced, the
squelch must be re-tuned using the Tuner.
Page 75

136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation: VHF Transmitter 8-3
8.3 VHF Transmitter
The VHF transmitter covers the range of 136 – 174 MHz. Depending on model, the output power of
the transmitter is switchable on a per-channel basis between high power (5 Watts) and low
power (1 Watt). The transmitter is divided into four major blocks as shown in Figure 8-2.
• Power Amplifier
• Harmonic Filter
• Power Control
From VCO
Attenuator
Circuit
8.3.1 Power Amplifier
The transmitter power amplifier has three stages of amplification – Pre Driver (Q401), Driver Amp
(Q402) and Final Amp (Q403). Signal from TX VCO is applied to the pre driver via an attenuator
circuit. The attenuator is pie style resistor attenuator, and is used as isolation between VCO and the
power amps. The -3dBm TX RF signal from attenuator is then amplified by pre driver and driver amp
to around +28dBm and is applied to the final amp. The final amp (Q403) is an enhancement-mode
N-channel MOSFET device providing a gain of 12dB. The device drain current is drawn directly from
the DC battery supply voltage input via L413. A matching network consisting of C417, C418, C419,
C420, C455 and a strip line, transforms the impedance to approximately 50 Ohm.
SWB+
Power Control
Pre Driver
Amp
Driver
Amp
BAT+
Current Detect
Strip Line
Final
Amp
To Receiver
Figure 8-2. VHF Transmitter Block Diagram
CR401
Antenna
Switch
Antenna
Harmonic
Filter
8.3.2 Antenna Switch
An antenna switch works mainly as a switching device between transmit and receive paths. In
transmit mode (PTT), Q407 is turned on and both PIN diodes (CR401, CR301) are forward biased
into conduction. This enables the RF signal to pass to the harmonic filter and then to the antenna. In
the receiver mode, both diodes are off. Signals applied to the antenna jack are routed via the LPF
(harmonic filter), through a TX Low Pass Filter (L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C430,
C445 and C446), to the receiver input.
8.3.3 Harmonic Filter
The harmonic filter consists of components L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C430, C445
and C446. The harmonic filter is a seven-pole Chebychev filter.
Page 76

8-4 136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation: VHF Frequency Generation Circuitry
8.3.4 Auto Power Control
The APC keeps the current supply constant to the final amp (Q403). The drain current of Q403 (final
amp) is sensed across resistor R417. The voltage difference across R417. The differential signal at
the output of U401 (pin 7) is passed to Q404 and Q405 that produces a constant power output to the
antenna. If the current is changed due to change of battery voltage or load, APC controls gate voltage
of Q403 and collector voltage of Q401 and drain voltage of Q402 to keep TX power stable. This circuit
stabilizes TX power at a pre-determined level adjusted by U402. This bias voltage is tuned in the
factory. If the transistor (Q403) is replaced, the RF Output Power must be tuned. By tuning the RF
output power, the bias voltage will be tuned through U402. Extra care has to be taken during the
tuning process. Do not exceed the maximum allowed bias voltage.
8.4 VHF Frequency Generation Circuitry
The PLL synthesizer subsystem consists of the reference oscillator (VCTCXO), VCO, PLL IC, Charge
Pump and Loop Filter.
Modulating
Signal
FL701
12.8MHz
Ref.OSC.
Synthesizer
U701
PLL Data
from μP
Charge
Pump
Voltage
Doubler
Figure 8-3. VHF Frequency Generation Unit Block Diagram
8.4.1 Reference Oscillator (12.8 MHz VCTCXO)
The reference oscillator is powered by regulated 5V provided by U505. The reference frequency
12.8 MHz VCTCXO (Voltage Controlled Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator) is applied to
the PLL IC (U701) via pin 1. Main frequency can be adjusted by chip trimmer of VCTCXO. This
frequency provides reference to the PLL IC and has a frequency stability of +/-2.5PPM (max) at the
temperature ranging from -30 to +60 Degree Celsius.
Loop
Filter
TX VCO
Circuit
TX Out
RX VCO
Circuit
RX Out
To PA Driver
To Mixer
Page 77

136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation: VHF Frequency Generation Circuitry 8-5
8.4.2 PLL IC Prescaler and Comparator
The reference frequency from VCTCXO is divided to 6.25 kHz or 5 kHz by reference counter, R. The
RF signal input from the VCO is divided to by prescaler (1/64), divided by N and A counters in PLL IC
to determine frequency steps and then supplied to the comparator. The comparison frequency is
6.25/5 kHz. The internal phase comparator compares the phase difference between the reference
and VCO signal. When the phase of the reference frequency is leading, Pin15 (R) is the output.
When VCO frequency is leading, Pin16 (P) is the output. When P=R, small pulses are the output of
the phase detector.
8.4.3 Voltage Doubler and Charge Pump
The voltage doubler (U507) converts 5V to 10V and is applied to the charge pump circuitry. The
charge pump is used for charging output signals P, R supplied by PLL IC from 0-3.3V to 0-10V. This
voltage is used to drive the VCO.
8.4.4 Loop Filter
The loop filter contains C751, C752, C753, C754, R726, R727, R728. It reduces the residual sideband noise to get the best signal-to-noise ratio. The output signal from loop filter is applied to VCO.
8.4.5 Dual VCO
The dual VCO module contains a RX VCO and a TX VCO. They are configured as colpitts oscillators
and connected to power up through transistor switches. Only one VCO is selected at a time. A
steering line voltage between 0.35V and 9.7V at varactor CR701 tunes the full RX frequency range
from 181.1 MHz to 219.1 MHz, and varactor CR703 tunes the full TX frequency range from 136 MHz
to 174 MHz.
In Receiver mode, high signal of RX_EN from pin 71, U101 activates Q305. When Q305 is activated,
current flows through the base of Q304 and thus activates the Q705. The varactor CR701 sets the
resonance frequency. When there is a change in voltage supplied by loop filter, there is a change in
the resonance frequency. L703 is the resonating coil, which forms the tank circuit together with
variable cap C710.
In Transmit mode, high signal of TX_EN1 from pin 84, U101 enables current flows through collector
of Q503 and thus activates Q706. The varactor CR703 sets the resonance frequency. When there is
a change in voltage supplied by loop filter, there is a change in the resonance frequency. L706 is the
resonating tuning coil, which forms the tank circuit together with variable cap C722.
Page 78

8-6 136 – 174 MHz VHF Theory Of Operation: Keypad
8.5 Keypad
Left, Right and P1 to P3 keys are directly connected to microprocessor via 22 pin connector. When
any of these keys is pressed, the voltage goes "low" and microprocessor detects it.
For full keypad models, the number keys are in matrix type which consisted of 3 rows and 4 columns.
When any of these keys is pressed, the voltage goes "low" and microprocessor interprets the voltage
for each key press.
KEYPAD
Left
Right
P1 P2 P3
NUMBERS
Key
detect
Key row
Keypad board
Key
22pin connector
column
Figure 8-4. Keypad Block Diagram
MCP
Main board
22pin connector
Page 79

Chapter 9 VHF Troubleshooting Tables
9.1 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (VHF)
Table 9-1. Troubleshooting Table for Receiver (VHF)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
Radio Dead (no
turn–on beep, no
LED indication)
No RX Audio (with
LED indication)
1. Battery dead or
defective
2. Defective battery
contacts
3. Microprocessor not
starting up
4. Regulator fault Verify U506 pin 4 is 3.3V
5. Flexible Cable fault Check connection of the 12 pin
1. Speaker dead or
defective
2. Audio Processor IC
not starting up
3. Audio Amp IC not
starting up right
Substitute good battery or battery
eliminator
Inspect battery contacts for
corrosion or bent terminals
Verify clock input to U101 pin 13 is
7.3728 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify U101 pin10(reset) is high.
Verify U505 pin 4 is 5.0V
flexible cable between J104 & J105
Substitute a good housing (with
speaker)
Verify J603 connection
Verify clock input U102 pin 14 is
3.5795 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify U601 pin 6 is battery voltage.
Change or replace battery.
Clean/Repair/Replace J602
Troubleshoot/Replace FL101.
If reset is Low, troubleshoot
regulator U506 or U107.
Check for shorts on outputs
Troubleshoot/Repair as
needed, replace faulty regulator
Re–assemble or replace flexible
cable
Change the housing (with
accessory)
Change the housing (with
accessory)
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Troubleshoot/Replace U601
If battery voltage is being supplied to
pin 6, then verify audio output at
pin5&8.
No Receive (with
no LED indication)
No RX 1. RX–B+ Verify Q304’s collector voltage is
1. IF IC dead or fault Verify clock input to U201 pin 1&2 is
44.645 Mhz using high impedance
probe.
4.8V when RX–EN is high.
Troubleshoot/Replace FL201
Check/Replace Q304
Page 80

9-2 VHF Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (VHF)
9.2 Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (VHF)
Table 9-2. Troubleshooting Table for Synthesizer (VHF)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
Synthesizer Out of
Lock (No RX
Mode)
Synthesizer Out of
Lock (No TX Mode)
1. Defective 12.8 MHz
VCTCXO
2. 1/2VCC defective Verify FL701 pin 1, U502–B pin 5&
3. No RX–Enable Verify U101 pin 71 (RX–EN1) is
4. Check PLL–LD port Verify U101 pin 27 is Low (Normal
1. Defective 12.8 MHz
VCTCXO
2. 1/2VCC defective Verify FL701 pin 1, U502–B pin 5 &
3. No TX–Enable Verify U101 pin 84(TX–EN1) is high
Verify clock output FL701 pin 3 is
12.8 MHz using high impedance
probe.
U502–D pin 14 voltage is 1.9V.
high.
Verify Q304 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V in RX mode
Mode)
Verify U101 pin 27 is swept from low
to high (Power Save Mode)
Verify clock output FL701 pin 3 is
12.8 MHz using high impedance
probe.
U502–D pin 14 voltage is 1.9V.
when PTT is pressed.
Repair/Replace FL701
Troubleshoot: 1/2VCC circuitry
Check U101 operating
Troubleshoot: Q304 & Q305
circuitry
Troubleshoot: PLL circuitry.
Repair/Replace U701
Repair/replace FL701
Troubleshoot: 1/2VCC circuitry
Check U101 operating
Verify Q407 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V when PTT is
pressed (TX–EN2).
4. Check PLL–LD port Verify U101 pin 27 is Low (Normal
Mode)
Verify U101 pin 27 is swept from low
to high (Power Save Mode)
Check U101–pin 85 is high/
Replace Q407/check LK2 is
short
Troubleshoot: PLL circuitry
Repair/Replace U701
Page 81

VHF Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (VHF) 9-3
9.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (VHF)
Table 9-3. Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter (VHF)
Symptom Possible Causes Procedure Corrective Action
No internal Mic
audio
No EXT. Mic audio 1. J601 defective Check connection with EXT mic Check/Replace J601
No transmit (No TX
LED indication)
No transmit (TX
LED indication OK)
Low Power
1. Mic dead or defective Verify audio present (~10mV rms)
when speaking into Mic.
Check bias of R194 (3.3V).
2. Mic bias fault Verify U101 pin 78 is 1.1V when PTT
button is pressed.
3. Audio Processor IC
not starting up right
2. Audio Processor IC
not starting up right
1.PTT switch defective Verify U101 pin 44 is low when PTT
1. Synthesizer out of lock Refer to Table 9-2 Check U101 operating
2. No TX–Enable Verify U101 pin 84 (TX–EN1) is high
1. Low TX injection Check the RF level at Q7 & C449
2. R417 defective Verify resistance is 0.1 Ohm Replace R417.
3. Incorrect control
voltage
4. Q403 defective (High
current)
5. Antenna switch defect Verify CR401 anode voltage is
Verify clock input U102 pin 14 is
3.5795 MHz using high impedance
probe.
Verify clock input U102 pin 14 is
3.579545 MHz using high
impedance probe.
is pressed.
when PTT is pressed.
Verify Q407 collector voltage is
approximately 4.7V when PTT is
pressed (TX–EN2).
per schematic.
Verify Q404 collector voltage is
approximately 5.5V in low frequency
& high power.
Verify U401 pin 7 is near 0V Replace Q403
approximately 1.4V
Replace Mic.
Check/Replace U101
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Troubleshoot/Replace FL102
Replace PTT switch PB501
Check U101 pin 85 is high/
Replace Q407/Check LK2 is
short
Troubleshoot Q409 circuitry &
VCO bias
Troubleshoot APC circuitry
Replace Q404
Check/replace CR401 & CR301
Poor TX range
(Conducted power
OK)
6. Harmonic filter
defective
7. Incorrect power tuning
(this has to be performed
only after item 1-6 has
been checked)
1. Defective or wrong
Antenna.
Visually inspect components
C426 – C429, C445, C446, C430
Check conducted power Re–tune power using tuner.
Verify correct antenna is installed.
Try using another antenna.
Repair/Replace if necessary
Replace antenna
Page 82

9-4 VHF Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF)
9.4 Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF)
Table 9-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
U201(IF IC) 1 Osc1 3.9 44.645 MHz input
2Osc2 3.3
4 VCC 4.7
9 Audio frequency 1.2
12 RSSI out Approximately 1 At –47dBm(with conducted)
13 N–DET(BUSY) Low At busy
15 GND 0
16 RF input 1 45.1 MHz input
U701(PLL IC)
1 Reference OSC input 1.4 12.8 MHz input
4VCC 3.3
6 GND 0
7XF IN 2.2
8 F IN 2.2
12 Power save High
13 GND 0
14 LD_out High If pll unlock is low
15 @P 2.4
16 @R Low
U601 1 Mode (Mute con) 0
(Audio Amp.) 2 SVR 3.8
3 IN+ 3.8
4IN- 3.8
5 OUT- 3.8
6 VCC 7.5 This voltage depends on Battery
7 GND 0
8OUT+ 3.8
U103 1 IN+ 1.6
Page 83

VHF Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF) 9-5
Table 9-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF) (Continued)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
(DTMF decoder) 2 IN- 1.6
3 GS 1.6
4Vref 1.6
8 OSC1 1.6 3.579545 MHz input
10 VSS 0
11 TOE 3.3
17 STD High At DTMF detecting
18 EST 3.3
19 ST/GT 3.3
20 VDD 3.3
FL701(VCTCXO) 1 VCON 1.9
2 GND 0
3 OSC out osc Generate the 12.8 MHz
4 VCC 5
Q206(N/S SW) E GND 0
B N/S SW 12.5 kHz: Low
C Collector 12.5 kHz: High
25 kHz: Low
Q304 E +5V 5 At RX Mode
B To Q305 collector Low
C RX_B+ 4.7
Q305 E GND 0 At RX Mode
B RX_EN High
C To Q304 base Low
Q503 E GND 0 At TX Mode
B TX_EN1 High
C To Q706 base Low
Q407 E +5V 5 At TX Mode
B To Q408 collector Low
C TXVB 4.7
Q408 E GND 0 At TX Mode
B TX_EN2 High
C To Q 40 7 Low
Page 84

9-6 VHF Troubleshooting Tables: Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF)
Table 9-4. Troubleshooting Table for Board and IC Signals (VHF) (Continued)
IC Designator Pin Pin Function DC Voltage (V) Comments (Condition)
Q601 E GND 0
B Audio_MUTE_CON Mute: Low
None Mute: High
C Mode Mute: High
None Mute: Low
1. All voltages are measured with a high-impedance digital voltmeter and expressed in volts DC relative to ground (0V).
2. Voltages are measured with a DC input voltage of 7.50 + .02 volts DC applied to the battery connector (J602).
3. All voltages are measured in the squelched receive mode, unless otherwise indicated.
4. Voltages are identical for VHF and UHF models unless otherwise indicated.
Page 85

Chapter 10 VHF Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and
Parts Lists
10.1 Introduction
This section provides schematic diagrams, overlays, and parts lists for the radio circuit boards and
interface connections.
10.1.1 Notes For All Schematics and Circuit Boards
* Component is frequency sensitive. Refer to the Electrical Parts List for value and usage.
1. Unless otherwise stated, resistance values are in Ohms (K = 1000), capacitance values are in
nanofarads (nF), picofarads (pF) or microfarads (µF), and inductance values are in
nanohenries (nH) or microhenries (µH).
2. DC voltages are measured from point indicated to chassis ground using a Motorola DC
multimeter or equivalent. If the board has been removed from the chassis, the transmitter
module mounting screws may be used for ground connection. (Note: The antenna nut
bracket is connected to ground.) Operating mode dependent voltages are followed by (RX)
for receive mode, (TX) for transmit mode, (UNSQ) for unsquelched mode, etc.
3. RF voltages on VHF models are measured with a Fluke model 85 RF probe. The indicated
voltages expressed in mV (RF) are DC level readings which correspond approximately 1:1 to
the RF voltage level in mV rms. RF voltages in the Receiver Front End and Receiver Back
End circuits are measured with an on-channel 1mV (-47dBm) RF signal applied to the
antenna jack ANT1/ANT.
4. RF voltages on UHF models are measured both with a high–impedance RF voltmeter having
a bandwidth in excess of 500 MHz (levels are expressed in dBm) and with a Fluke model 85
RF probe [levels are expressed in mV (RF)]. These indicated voltages are DC level readings
which correspond approximately 1:1 to the RF voltage level in mV rms, and are only
approximate for UHF frequency measurements. RF voltages in the Receiver Front End and
Receiver Back End circuits are measured with an on-channel 1mV (-47dBm) RF signal
applied to the antenna jack ANT1/ANT.
5. Audio voltages are measured with a high-impedance AC rms voltmeter. The indicated
voltages are expressed in mV rms. Receive mode voltages are followed by (RX) and are
measured with an on-channel signal with 1 kHz modulation at 60% deviation (3 kHz for 25
kHz channels, or 1.5 kHz for 12.5 kHz channels). Transmit mode voltages are followed by
(TX) and are measured with a 1 kHz, 10 mV rms signal present at the external microphone
input (accessory connector J601).
Page 86

10-2 VHF Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists: Introduction
6. Reference Designators are assigned in the following manner:
Ref. No. Series Circuit Block
101 – 199
Microprocessor & audio control
circuits
1001 – 1099 Microprocessor & audio control
circuits
201 – 299 IF IC circuit
301 – 399 Front-end and 1st Mixer
401– 499 Transmit RF stage & Auto power
control
501 – 599 Base band & generating circuit
601– 699 Audio amplifier
701– 799 VCO & PLL Synthesizer
7. Circuit Block Interconnection Legend:
Name Description
+5V 5 Volts (Regulated)
+3.3V 3.3 Volts (Regulated)
SWB+ Switched Battery Voltage
BAT+ Unswitched Battery voltage
+10V Digital 10V(Regulated)
RESET Low-line reset signal fromU107 to U101 Pin 10
TX_EN1 Transmit enable signal from U101 Pin 84
TX_EN2 Transmit enable signal from U101 Pin 85
TXVB TX operating voltage
TX_AF3 TX audio signal from audio processor IC to TX Audio
filter
TX_SUB_TONE TX sub tone signal from audio processor IC to TX
modulation.
RX_B+ RX operating voltage
RSSI RX signal strength indication from IF IC to U101
Busy RX detect signal from IF IC to U101
FTV RX frequency shift voltage
RX_AF1 RX audio signal from IF IC to Audio processor IC
PLL_LD PLL lock detect signal from PLL IC to U101
N/S SW Channel space selectable Switch (12.5 kHz/25 kHz)
1/2VCC 1.9 volts (divided by U502-D)
Page 87

VHF Schematic Diagrams, Overlays, and Parts Lists: Speaker and Microphone Schematic 10-3
10.1.2 Four Layer Circuit Board
Plating (Au)
PSR ink
Copper Plate
Copper
PrePreg.
Copper
CCL (core)
Copper
PrePreg.
Copper
Copper Plate
PSR ink
Figure 10-1. Four–Layer Circuit Board: Copper Steps in Layer Sequence
10.2 Speaker and Microphone Schematic
MIC1
1
2
SPK1
Figure 10-2. Speaker and Microphone Schematic
10.2.1 Speaker and Microphone Parts List
Reference
Designator
MIC1 PMDN4139_R Microphone
SPK1
Motorola Part No. Description
PMDN4067BR
MATES WITH J103 ON
RADIO BOARD
1
MATES WITH J603 ON
RADIO BOARD
2
Speaker & Cable
Page 88

10-1 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
10.3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
FROM_HARMONIC_FILTER
L326
220nH
C359
10P
C301
47P
L302
27nH
C321
NA
L303
12nH
C317
1nF
KDV269E
CR302
R301
100K
C334
1nF
C337
10nF
CR312
KDS160E
R316 100K
C204
0.1uF
FL201
44.645MHZ
C338
47nF
C347
0.1uF
KDS160E
CR315
U201
TA31136
CR201
KDS181
16
1
C203
120pF
OSC1
C201
47pF
RF-IN
CR306
KDS160E
C339
0.1uF(K)
C340
0.1uF(K)
15
2
GND
OSC2
C213
0.1uF(K)
R258
1.5K
R206
10K
R217
10K
14
3
455FW
CF1
BUSY
SSI
R318
N-DET
C206
0.1uF(K)
R203
22K
455HW
R207
22K
1213
5 6
R204
22K
IF-IN
RSSI
11
CR202
KDS181
C208
0.1uF
2.2K
C341
47pF
IF-OUT
DECO
C207
0.1uF(K)
DEC1
455 C24
10
9
QUAD
AF-OUT
FIL-IN
FIL-O
8
7
C209
560pF
R210
120K
C210
560pF
R250
10K
Q207
KRC404
Q206
KRC404
R319
3.9K
R342
6.8K
R211
15K
C214
0.1uF
R222
1.2K
R212
100K
C342
0.1uF(K)
C381
0.1uF(K)
C211
0.1uF(K)
RT201
10K(TH)
+3.3V
TIGHT_SQ
R317
120k
N-REC
VCC
MXOUT
4
R216
4.7K
CF2
R208
2K
R213
20K
U202
1
VDD
2
VSS
3
A
4
W
MCP4011(503)
RX_AF1
Q201
KRC404
Q202
KRC404
8
U/D
7
NC
6
B
5
CS/
R
N/S_SW
20KHZ_SEL
SQ_U/D
SQ_CS
R311
560R
R314 100R
L327
820nH(1608)
R312
220K
Q303
2SC4226
C378
10UF/16V
+
L309
22nH
Q306
2SK711
L307
12nH
C367
220pF
KDV269E
CR305
C313
1nF
C368
10nF
C369
NA
C314
15P
C322
NA
R306
100K
C315
15P
R309
10R
L306
820nH EJPS
R335
NA
C370
NA
L308
68nH
CR307
KDV269E
FTV
1
2
3
L333
B4F(1664)
R307
100K
C328
6P
L335
27nH
C316
L336
15P
7nH
2
C318
10nF
C329
10nF
R310
1K
L340
R338
1P
L332
820nH
820nH
4
6
C330
7p
C331
5P
RX_B+
FL301
45.1MHZ(SMF-1)
1
5
C332
10pF
R315
100R
C376
C377
0.1uF
NA
C335 20pF
4
2
3
C309
N/F
R358
1R
R308
150R
6
4
L329
B4F(1667)
C326
12P
C327
10nH
L305
220nH
C310
0.1U
3
C312
10P
L311
220nH
C354
9P
C311
1nF
GND
RX_B+
RX_B+
2
1
Q307
2SK711
R336
1K
L337
22nH
R399
68R
R337
10R
R305
39k
C304
20P
C305
10P
FTV
C308
10nF
L304
68nH
CR303
KDV269E
C307
15P
R302
100K
C333
27P
L330
82nH
L331
47nH
Q301
2SC4226
C356
10nF
C365
47nH
C325
39P
R357
1R
L310
47nH
Figure 10-3. VHF (136–174 MHz) Receiver Schematic Diagram
VCO_OUT (RX)
Page 89

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-2
SH102
+5V
VCO_OUT(RX)
TX_EN1
VCO_OUT(TX)
Q503
KRC404
C538
10nF
+
C447 5pF
C539
10uF/16V(A)
C731
4pF
R715
100R
Q705
KRA305
C730
4pF
RX_B+
Q706
KRA305
R701
100R
C701
22uF / 10V(A)
C728
10pF
R706
47R
C715
22uF / 10V(A)
R714
100R
C319
10nF
C380
470pF
+
C729
3pF
+
C716
470pF
C320
10uF/16V(A)
+
L707
1uH(1608)
C714
1nF
R710
180R
C702
1nF
C704
470pF
C
E
L708
220nH
KRA305
Q304
Q305
KRC404
B
C343
0.1uF
Q701
2SC4226
L704
1uH(1608)
Q703
2SC4226
C717
12pF
Q704
2SC4226
C718
12pF
Q702
2SC4226
R705
180R
C719
27pF
+5V
L701
100nH
C707
27pF
R708
12K(1%)
C344
470pF
R707
4.7K(1%)
R709
12K(1%)
C705
6p
C706
10pF
F
R704
10K(1%)
C721
12pF
L706
30146TL
RX_EN
R702
3K(1%)
R703
10K(1%)
C722
TZY02 10pF
R713
10K
C709
10pF
L703
28116TL
C723
3pF
R712
100K
C
KDV300E
C727
3pF
R711
100K
R703
C710
TZY02 10pF
C711 33pF
CR701
KDV300E
C724
56pF
C726
6pF
CR702
KDV300E
SH10
L702
2.2uH(1608)
C712
470pF
L705
2.7uH(1608)
C725
470pF
TX_AUDIO_AND_SUB_T
1
ONE
1/2VCC
PLL_STB
PLL_DATA
PLL_CLK
PLL_PS
+3.3V
+5V
C515
0.1uF
R732
10K
R506
10K
R731
10R
C741
0.1uF
C747
33pF
R503
100K
C756
1nF
R734
10R
9
8
R753
1K
CLK
FIN
5
6
L709
47nH
C740
0.1uF
+
C746
20pF
R752
1K
10
DATAXFIN
U502-B
NJM324
-
R522
30K
+3.3V
C755
0.1uF(K)
R751
1K
11 12 13
LE
U701
MB15E03L
GND
C739
1nF
7
RT502
47K(TH)
R504
47K
PSDO
VCC ZC
4567
12.8MHz VCXO
4
VCC
VCON
FL701
R505
10K
14 15
LD_FOUT
VP
OUT
GND
Q711
KRA304
R730
33K
3
21
R729
100K
16
@ROSCIN
OSCOUT @P
+
C516
10uF / 16V(A)
PLL_LD
R716
680R
R723
1.2K
+10V
Q707
KTC4075
Q709
KTA2014
R724
820R
R717
56R
Q708
KTA2014
Q710
KTC4075
R725
220R
R740
1.8K
C749
1uF(1608)
C751
1uF / 35V
R728
R727
2.7K
2.7K
R726
2.4K
C752
0.1uF(K)
+
C753
47nF(3216)
C754
47nF(3216)
C748
0.1uF
R718
20K
R719
123
C738
7pF
R733
0R
+3.3V
1K
R720 270R
R721 270R
R722
22K
C750
0.1uF
Figure 10-4. VCO and PLL Schematic Diagram
Page 90

10-3 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
A
TO_RX
R412
Q404
STB1188
C415
20K
R409
10R
L403
220nH(1608)
Q402
2SK3078
1
R408
2.2K
C416
0.1uF
GND
8
4
R431
47K
3.9K
R432
47K
8
U/D
7
NC
6
B
5
CS/
MCP4011(502)
Q405
R414
4.7K
R428
100R
U401-B
KIA358
KTC4075
C411
NA
L404
22nH
C409
8P
7
R411
3.3K
R410
10R
C436
0.1uF
R433
0R
3
2
KIA358
U401-C
CR3002
NA
Zo = 50
0.8t * 1.4(W)
CR311
CR401
C423
NA
BAT+
BAT+
GND
NA
C462
0.1uF
C460
0.1uF
C422
270P
C419
18P
L412
1UH(1608)
C463
470P
R417
RLC63 OR1
C464
0.1uF
C461
470P
L408
28116TL
C420
5P
R415
220R(2012)
Land
C425
1nF(1608)
R418
220K(0.5%)
R419
220K(0.5%)
C432
0.1uF
R420
4.7M
C455
12P
L416
45143TL
C417
15P
C433
NA
R421
68K(0.5%)
C418
56P
C453
470pF
R422
68K(0.5%)
L415
45143TL
SH104
2
3
KIA358
R423
3.9M
U401-A
L413 351
B402
MPZ1608D101B
SH103
4
C45
22uF / 16V(B)
1
67TL
R424
12K
B401
MPZ1608D101B
Q403
2SK3476
L406
220nH(1608)
C434
470pF
R425
2.4K
L405
22nH
R430
100R
C413
30pF
R429
3.6K
R426
3.9K
C410
56pF
C421
47pF
Q406
KRC404
C435 10nF
R427 47K
6
5
CR301
MA2S077
L301
NT 1
ANT
1
C431
2
1nF(1608)
R416
47K(1608)
C430
12pF(1608)
SH105
L410
35166TL
C429
10pF(1608)
C428
22pF(1608)
L409
35166TL
C427
12pF(1608)
C426
27pF(1608)
L411
35166TL
C445
9pF(1
C446
22pF(1608)
608)
68nH(2520)
MA4P7001F - 1072
J602
060031MA005G500PL
C408
NA
U402
VDD
VSS
R407
8.2K
A
W
C405
20pF
C437
0.1uF
1
2
3
4
R413
8.2K
C406
0.1uF
R406
10R
TXVB
R499 1.5K
SWB+
C403
NA
L402
NA
C438
NA
C439
1nF
C404
15pF
C
L401
220nH
Q407
KRA305
B
LK2
Q401
PBR951
R405
2.7K
Q408
KRC404
C402
NA
C444
NA
+5V
R404
10K
C401
5pF
R403
180R
R402
39R
R401
180R
TX_EN2
+3.3V
TX_PWR_CS
TX_PWR_U/D
R436
47R
C440
470pF
C449 5pF
C448
10nF
L407
220nH
R434
33K
Q7
2SC4226
R435
80R
1
TX_VCO_B+
C447 5pF
FROM_VCO
Figure 10-5. Transmitter Schematic Diagram
TX_PWR_LOW
Page 91
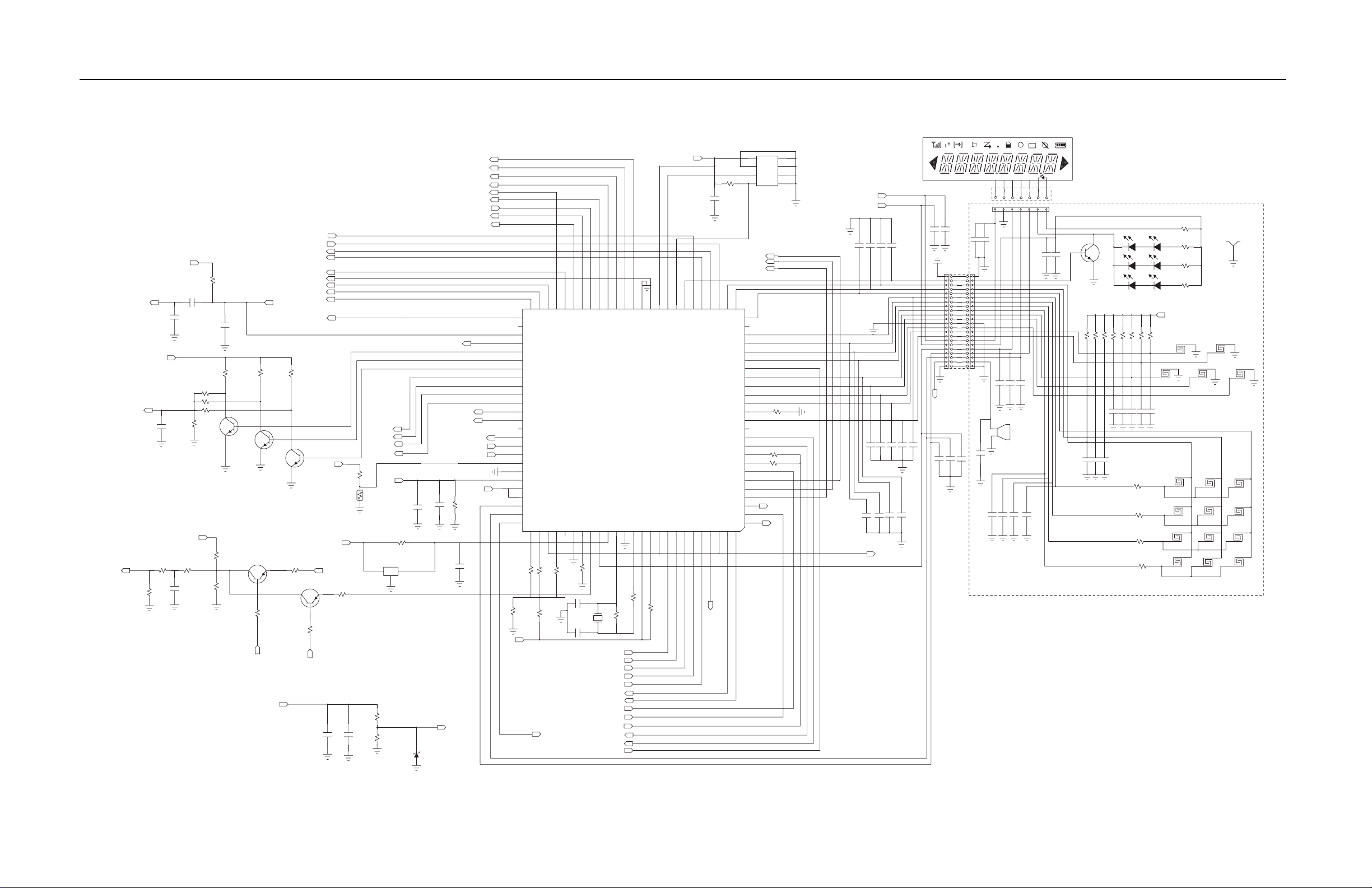
Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-4
1
R139
10K
U102_SDATA
SW_IN2
SW_IN1
PLL_CLK
53
52
51
SW_IN3
DTMF_CON
SW_SCAN1
SW_SCAN2
SW_SCAN3
SW_SCAN4
PTT1
LED(RED)
FUN_KEY2
AK_DATA
AK_CLK
AK_CSN
VOX_EN
PLL_LD
TONE_INT2
24
25
MOD_CON_CS
MOD_CON_U/D
8
7
6
5
U102_SCLK
U102_CSN
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
DTMF_OUT
VCC A0
A1
OC
A2
SCL
VSS
SDA
U104
C64
24L
R193 10K
R195 100R
R152 680R
VOX_EN
2
3
4
+3.3V
SWB+
C161 220pF
C178 220pF
C179 220pF
C171 220pF
C170 220pF
C167 220pF
C166 220pF
TONE_IN
LCD101
LCD_BEACON
C188 220pF
C189 220pF
C177 220pF
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
05004HR-22A01S
J102
MIC1
C165 220pF
C173 220pF
C172 220pF
C164 220pF
C163 220pF
C162 220pF
C169 220pF
C168 220pF
1
2
4
7
6
3
5
LCD Flex.PCB
J101
1
2
3
C176 220pF
C175 0.1uF
B to B Flex. PCB
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
C1011 47pF
C1010 47pF
04-6292-022-000-800+
J103
2
1
MIC1
0B27P40
C1018 220pF
C1015 47pF
C1013 47pF
C1014 47pF
05004HR - 0701S(G)
4
7
6
5
CR110
Q110
C187 0.1uF
C174 220pF
KRC104
R159 47K
R160 47K
C1009 47pF
006 47pF
C1
C1007 47pF
CR112
CR114 CR115
CR110~CR115 : BL - HG036
R161 47K
R196 47K
R197 47K
R198 47K
C1003 47pF
C1001 47pF
C1002 47pF
C1008 47pF
R108 4.7K
R199 47K
C1004 47pF
R109 4.7K
C1012 47pF
R112 4.7K
R119 4.7K
R155
470R
R156
CR111
1K
R157
CR113
1K
R158
1K
+3.3V
R147 47K
L_ARROW R_ARROW
P1
C1005 47pF
P2
1
4
5 6
7 8 9
SH201
P3
3 2
# 0 *
BEEP
TX_AF1
FTV
R1005
10nF
NA
R1006
+3.3V
C140
47nF
+5V
R174 120K
R175 47K
R176 30K
C143
0.1uF
R1004
10K
C198
NA
C141
NA
R177
56K
+3.3V
R194
6.8K
R167
100K
R168
100K
C142
470pF
R171
10K
Q120
KRC404
Q
KRC404
KTA2014
Q112
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
STD
U106_SW
PTT2
20KHZ_SEL
PLL_PS
BUSY
PLL_CLK
PLL_STB
PLL_DATA
RX_EN
SQ_CS
SQ_U/D
TX_PWR_LOW
TX_PWR_CS
MIC1
TIGHT_SQ
LOW_BATT
+3.3V
R113
47K
TX_PWR_U/D
BEEP_CON
MIC_MUTE2
VOX
LCD_CLK
RX_TONE_EN
TX_PWR_U/D
PWDN
R173
R172
10K
10K
RX_TONE_CON1
C124
1nF
CR101
NA
RX_TONE_CON2
C144
0.1uF(K)
LOW_BATT
AUDIO_MUTE_CON
TX_EN1
R507
10K
RT501
10K (TH)
KIA 7027AT
C194
0.1U
TX_EN2
N/S_SW
RSSI
U107
1
R153
68K(1%)
R154
47K(1%)
C123
0.1uF
R178
100K
2
3
121
Q122
KRC404
R165
3K
E
C
B
KTA2014
Q111
R163
100K
DTMF_CON
SWB+
+3.3V
+3.3V
DTMF_OUT
R169
1.2K
E
C
B
R164
100K
BEEP_CON
C195
220pF
75
76
77
78
TX_PWR_CS
79
DTMF_DEC_EN
80
FREQ_CON3
81
FREQ_CON2
82
FREQ_CON1
83
AUDIO_MUTE_CON
84
TX_EN1
85
TX_EN2
86
N/S_SW
87
RX_TONE_CON1
88
RX_TONE_CON2
89
90
TIGHT_SQ
91
VOX_IN
92
LOW_BATT_IN
93
TEMP_IN
94
A_GND
95
RSSI_IN
96
V_REF
97
A_VCC
98
LCD_CS
99
100
TONE4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
R179 51K
R180 100K
R190
15K
+3.3V
74
73
72
SQ_U/D
DTMF_STEER
TX_PWR_LOW
TONE3
TONE_INT3
TONE2
R182 200K
R184
15K
RX_TONE_EN
70
71
RX_EN
VSS
TONE1
FL101
7.3728MHZ
69
68
20KHZ_SEL
CNVSS
R115 10K
C145
15pF
C146
15pF
MOD_CON_U/D
PROGRAM_DATA
67
66
65
PTT2
DCS_SEL
DTMF_Q1
BEEP
LCD_DATA
RESET
11
10
B_S2
B_S1
A_S2
A_S3
FUN_KEY1
MOD_CON_CS
FUN_KEY2
PLL_LD
LED(GREEN)
LED(RED)
PTT1
DTMF_Q2
X_OUT
R185
0R
R148
1M
64
12
DTMF_Q3
GND
13
63
62
VSS
DTMF_Q4
U101
M30302FCPGP
X_IN
VCC1
14
+3.3V
C147
0.1uF(K)
60
59
58
57
56
55
61
VCC2
SQ_CS
EPP_CLK
TONE_INT1
B_S2
15
16
17
18
R114
10K
54
BUSY
PLL_STB
PLL_DATA
EPP_DATA
LIGHT_CON
PGM_BUTTON1
PGM_BUTTON2
PGM_BUTTON3
LEFT_BUTTON
RIGHT_BUTTON
LED(GREEN)
PRG/CLONE_RX
PRG/CLONE_TX
A_S2
A_S2
B_S2
POP_CON
FUN_KEY1
19
20
21
22
23
POP_CON
Figure 10-6. Microprocessor and Keypad Schematic Diagram
Page 92

10-5 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
A
AUDIO_IN
C615
0.22uF (K) (1608)
C619 33pF
UDIO_MUTE_CON
POP_CON
Q610
KRC404
R636
560R
Q601
KRC404
R619
10K
R609
1K
R608
NA
C605
R621
39K
R613
15K
R635 0R
4.7uF (2012)
R620
33K
R614 560K
4
IN- OUT-
3
2
SVR GND
1
+
TDA 8541
C618
4.7uF / 16V(A)
U601
VCCIN+
OUT+MODE
C606
0.1uF
R615
2R2
5
6
7
8
+
C601
10uF / 16V(A)
C616
0.1uF(K)
R610
2R2
SWB+
C617
0.1uF(K)
R616
0R
C609
0.1uF(K)
J603
53047-0210
C621
470pF
C622
47pF
SPK1
SM3624X1
+
-
L601
2.2uH(1608)
L602
2.2uH(1608)
J601
0980683Z01
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
Figure 10-7. Audio Power Amplifier and External Audio Schematic Diagram
Page 93

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-6
J602
GND
060031MA005G500PL
BAT+
B_S2
B_S1
A_S2
A_S3
SWB+
BAT+
RX_AUDIO
BEEP
LED(GREEN)
LED(RED)
C461
C460
470pF
0.1uF
RX_AF2
+3.3V
R532 10K
C620 470P
BAT +
C464
0.1uF
R533 10K
R535 10K
R534 10K
C540 0.1uF
R417
RLC63 0R1
C432
0.1uF
C602 0.22uF(k)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
J105
R418
220K(0.5%)
R419
220K(0.5%)
R420
4.7M
J104
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
L413
C433
NA
R421
68K(0.5%)
C564 47pF
2
-
3
+
R422
68K(0.5%)
C563 47pF
R423
3.9M
U401-A
KIA358
1
SW / VOL1
RY8418
C562 47pF
C561 47pF
B
Q501
KRC404
1/2 VCC
13
-
14
12
+
SWB+
U505
TK11250AMTL
1
2365
BCCA
47
8
9
SW1
RY8487
C506
470pF
6
5
4
+
C501
470pF
C565 47pF
C566 47pF
+
C502
22uF/16V(B)
VIN C
VOUT
C507
22uF/16V(B)
1
2
3
C503
0.1uF
SWB+
43
12
CR501
C560 47pF
R501 220R
E
Q502
KRC404
R502
220R
BL-HEIG033B
R412
3.9K
Q404
STB1188
C415
20K
APC(U401_PIN7)
R414 4.7K
C411
NA
Q405
KTC4075
R411
3.3K
+
C545
22uF/10V(A)
C531
0.1uF
U507
TC1240
VIN
2
GND
3
C510
4.7uF(2012)
R413
8.2K
NJM324
U502-D
61
C+
5
VOUT
4
SHDN
C-
+
C406
0.1uF
C511
22uF/16V(B)
DRIVE_CON
SWB +
RX_AUDIO
C619 33pF
C615
R424
POP_CON
Q610
KRC404
SWB +
R636
560R
MUTE_CON
Q601
KRC404
R619
10K
R609
1K
R608
NA
U506
TK112 33AMTL
6
VIN
5
4
VOUT
C
1
2
3
C541
0.1uF
0.22uF(K)(1608)
R635 0R
C605
4.7uF(2012)
R621
39K
+
R613
15K
+
C509
470pF
C508
10uF/16V(A)
R614 560K
U601
4
IN-
3
IN+
2
SVR
1
MODE OUT+
TDA8541
C618
4.7uF/16V(A)
R620
33K
OUT-
VCC
GND
C606
0.1uF
5
6
7
8
+
C601
10uF/16V(A)
AF_OUT1
AF_OUT2
R523
30K(1%)
+10V
C512
470pF
+3.3V
R524
47K(1%)
R716,717
C533
0.1uF
+10V
+5V
R734
U501_pin4
Q705,706
Q304
Q407
R171-173
U105_pin4
U502_pin4
+3.3V
U107_pin1
+3.3V
U106_pin4
+3.3V
R131
+3.3V
R150
+3.3V
U103_pin11,20
+3.3V
U104_pin8
+3.3V
J102_pin16
+3.3V
U101_pin14,96,97
+3.3V
U104_pin1
+3.3V
Q711
+3.3V
R719,722
+3.3V
R507
+3.3V
U508_pin1
+3.3V
R537
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
+5V
Figure 10-8. Switches and Battery Schematic Diagram
Page 94

10-7 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
R137
4.7M
C135 47pF
MIC1
0B27P40(2.8mm)
C139
R135
10K
0.1uF(K)
1/2VCC
+3.3V
R194
6.8K
C140
2
1
C142
470pF
47nF
2.2uH(1608)
L603
1
C14
NA
J601
0980683Z01
1
3
2
4
5
6
7
L604
2.2uH(1608)
CR601
KDZ5.1V
PROGRAM_DATA
C546
0.1uF
1/2VCC
R513
10K
R539
330K
C549
560pF
R512
20K
C520
4.7nF
R136
100K
R111
NA
9
-
1
0
+
NJM324
U501-C
C521
1.2nF
C136
0.1uF
Q114
KRC404
8
R511
8.2K
13
12
-
+
NJM324
105-D
C518
5.6nF
R510
15K
C550
60pF
5
R120
47K
-
+
NJM324
U501-D
CR117
KDS160E
CR116
KDS160E
C138
0.22U(K)(1608)
C111
1uF(K)
14
R162
820R
R107
3.9K
14
C137
0.1uF(K)
+3.3V
VOX_EN
13
12
C519
1.2nF
C101
1uF(K)
VOX
R138
220K
R101
10K
R102
47K
C102
2.2nF
R103
150K
C103
47pF
TO_VCTCXO&VCO
C568
10nF
R117
8.2K
U101_PIN79
R140
R110
270K
68K
C119
10nF
R181
150R
C153
1uF(K)
C154
1uF(K)
+3.3V
R150
10K(1%)
R151
12K(1%)
R141
100K
RX_AF2
C104
150pF
+5V
Q505
KRA305
C529
0.1uF
C547
NA
PTT1
FUN_KEY1
FUN_KEY2
PTT2
C543
1.2nF
C522
5.6nF
R508
1K
C517
22nF
GND
R509
2.2K
+3.3V
7
NJM324
U501-B
6
-
5
+
R529 47K
R530 47K
R531 47K
R540 47K
R514
24K
C523
1nF
PB501
R515
12K
R597
4.7K
1
2
PTT
DHT1114S
-
1
+
NJM324
U501-A
C525
330P
C570
1
47pF
2
FUN1
PB502
DHT1114S
C544
NA
C524
33nF
2
3
C548
NA
1
2
FUN2
PB503
DHT1114S
R516
12K
R517
15K
C542
10nF
Q504
KRC404
R536
330K
R538
8.2K
R537
1K
C530
10nF
NJM324
R518
5.6K
4
+
-
11
1/2VCC
TX_AF2
NJM324
U501-E
U502-E
R519
2M
8
NJM324
U502-C
R526
100R
MOD_CON_U/D
MOD_CON_CS
R541
330K
+3.3V
+
C567
10uF / 10V(A)
C191
220pF
+
C190
10uF / 16V
U101_PIN31(SDATA)
U101_PIN30(CLK)
U101_PIN2
9(CSN)
C199
470pF
C100
1uF(1608)
9
12
11
R104
R105
R106
47K
47K
47K
10R R131
10
VSS
CSNTEST
SCLK
SDATA
XIN
VDD
XOUT
13
14
151617181920212223
R146
0R
FL102
3.5795MHz
R145
1M
C115
C116
27pF
27pF
MOD
LIMLV
RSAOUT
TSAOUT
+3.3V
U508
8
1
C528
R520
18nF
560K
9
-
10
+
R521
330K
1/2VCC
R545
4.7k
+3.3V
1
NJM324
U502-A
R598
20K
+
U/DVDO
2
7
VSS
NC
3
6
A
B
4
5
W
CS/
MCP4011(503)
C536
10nF
2
R527
-
100K
3
C537
2.2nF
R599
NA
R528
82K
EXTINO
DIN
DIN0 EXTIN
C117 1.2nF
R143 91K
R144 100K
2345678
TXIN
TXIN0
AGND
AGNDIN
U102
AK2347
FIL0
RXIN
RXIN0
RXOUT
24 1
C120
15pF
C118
10uF / 16V
+
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C105
15nF
1
2
VREF
PWDN
OSC1
OSC2
U103
MT88L70
R118
C106
47K
47nF
+3.3V
20
VDD
IN+
19
ST/GT
IN-
18
EST
GS
17
STD
16
NC
INH
15
Q4
14
NC
Q3
13
Q2
12
Q1
11
VSS
TOE
R180
100K
R1
79
51K
R182
200K
R183
NA
R142
330K
R116
1.2K
C1
0.1uF(K)
TONE 4
TONE 3
TONE 2
TONE 1
07
U101-PIN26(DTMF_IN)
C121
33nF
U101_PIN72
U101_PIN63
U101_PIN64
U101_PIN65
U101_PIN66
Figure 10-9. Transmitter Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram
Page 95

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-8
A
+3.3V
UDIO_IN
+3.3V
C602
0.22uF(K)
C620
470P
C191
220pF
J105
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
R131
10R
C190
+
10uF/16V
SW/VOL1
RY8418
RX_AF1
B to B flex. PCB
XF2M-1215-1A
J104
52745-1297
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
C199
470P
C112
10uF/16V
+
C100
1uF(1608)
R1003
10K
C113
560pF
R104
47K
R105
47K
R1001
10K
R1002
9.1K
R106
47K
C114
220pF
SDATA
SCLK
CSN
12
TEST CSN
13
R146
0R
FL102
3.5795MHz
C115
27pF
14
SCLK
XIN
R145
1M
VSS
MOD
SDATA
XOUT
TSAOUT
VDD
181716
15
C116
27pF
TXIN
20
EXTIN
DINO
RXOUT
21
C125
47nF
AGND
TXINO
RXINO
FILO
23
22
DCS_SEL
LIMLV
EXTINO
DIN
RSAOUT
19
AGNDIN
RXIN
24
C126
33nF
R126
15K
AK2347
U102
U106
TC7S66FU
1
4
C153
1uF
2
103
Q
KRC413
1
2
3
4
5
6
789
10
11
R181
150R
C154
1uF
Q101
KRC413
C127
47nF
C110
22nF
R150
10K(1%)
R151
12K(1%)
C156
0.22uF(K)
2
3
R122
330K
R127 33K
-
+
NJM324
U105-A
RX_TONE_CON2
+5V
Q102
KRC413
C129
47nF
C128
47nF
1
R191
R128
15K
3.9K
C130
33nF
Q104
KRC413
C109
22nF
C157
0.22uF(K)
R121
330K
R129 150K
6
-
5
+
NJM324
U105-B
4
+
U105-E
NJM324
11
C158
R192
15K
Q113
KRC404
0.22uF(K)
R149
1
00K
7
R132 10K
R133 470K
1/2VCC
R134 4.7M
9
-
10
+
C134
0.22uF(K)
NJM324
U105-C
8
TONE_INT
RX_TONE_EN
RX_TONE_CON1
Figure 10-10. Receiver Audio Filter and Sub-tone Schematic Diagram
Page 96

10-9 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
C621
PB501
PB502
PB503
R616
J603
C570
Q202
FL102
TP9
FL101
C617
C214
Q206
Q407
R431
Q113
R149
R122
C139
R135
C128
U105
C135
R137
C137
C436
R426
J102
R420
R432
CR117
C622
L602
L601
L604
L603
R419R421
R423C433
U401
R427
C435
R425
C438
C380
Q101
Q103
C110
C156
R127
C126
C127
R126
C125
C136
R111
R136
Q114
CR116
C432
R424
J601
R417
R422
R418
R729
C454
Q503
C119
C120
R507
Q711
R412
C755
C753
R413
C406
C538
C751
R414
Q405
R730
RT501
R722
R723
C750
R724
R725
U103
L413
C411
R411
C415
Q404
SH102
R732
R721R720
Q709
C752
Q710
R726R740
R727
R141
R140
R142
C121
C515
R506
B401
B402
Q403
SH103
C746
L709
C747
C756
U701
C738
C741
R731
R733
R719
C748
R718
Q707
C749
R716
Q708
R717
R728
C754
TP11
C512
U507
C511
C510
R734
R505
R504
U502
C739
C740
C516
R526
R545
R528
C536
R527
C537
C530
C533
R523
R524
C545
C531
R541R521R519
C567
R503
R522
RT502
C437
C453
C539
R753
R752
R751
TP1
C616
R615
R636
R609
R608
R619
Q610
Q601
R433
DEC1
R318
R317
R342
C339
C381
CR306
R316
RT201
C211
R208
R210
C209
C210
R222
Q207
C213
C206
R216
CR202
R203
C204
R250
C208
R206
R207
R1005
R1004
C198
R1006
R168
R110
C116
R117
C105
R146R145
C115
C106
R116
C107
R115
TP8
C145C146
R185
R148
TP5
TP7
R213
J105
C602
C601
U402
C378
R212
R211
CR201
R204
R165
R167
C104
R118
TP2
TP6
Q111
TP3
R128
R192
R217
Q112
C461
C460
C439
LK2
Q408
R499
Q406
C334
C320
R314
U202
Q102
Q104
C109
C157
C129
R121
C130
R129
C158
C134
R163
R133
R134
R169
R132
R164
C138
R138
TP4
TP10
U101
Figure 10-11. VHF (136–174 MHz) Mainboard Top Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON400
Page 97

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-10
ANT4
ANT3
ANT1
ANT2
L410
C428 C427
C429
L409
C426
C445
L411
C446
CR401
C423
C422
SH104SH105
C419
L415
C413
C440
C449
L407
R436
R434
Q7
C447
L708
R707
Q703
C717
R708
Q704
R711
C718
R709
CR703
C721
C723
C726
C727
R712
L705
R713
R598
C421
C528R520
L405
Q402
C724
C410
R408
R402
R401
C448
R435
C729
C719
FL701
L406
C716
R599
L412
L408
R407
R403
C703
R706
C725
U508
CR301
C418
L707
C431
C430
L301
L706
R536
R538
R518
C405
C401
R714
C417
L404
C714
R710
CR702
C409
C722
R429
R430
L402
R404
Q706
C547
C542
R517
CR311
R415
C420
L403
C404
SH101
C715
C455
R410
R409
C444
R405
R416
Q401
C434
R428
R406
C425
R107
C519
C550
C529
C548
C525
R516
C524
C544
ANT5
R635
C541
C462
R310
R309
R315
C154
R103
R102
R151
R150
R104
R105
R106
CR101
R193
C172
C169
C620
C540
C463
C319
CR315
CR312
U506
C173
C328
L327
C153
R181
C190
C615
L333
C376
C609
C103
L306
C377
C509
C508
C188
R613
C619
R610
R154
C189
R614
Q303
FL201
R153
C195
C194
R194
C606
R621
R620
C605
C618
U601
R338
L332
L340
C330
C331
U107
C332
FL301
C340
C338
R319
C341
C342
C207
Q201
C112
R1003
R1002
C114
R1001
C113
R143
C117
R144
C100
R131
C199
R184
R180
C118
R179
R182
R183
R190
C144
CR601
C141
C329
C335R311
R312
C337
C347
R258
C203
U201
C201
CF2
U102
C191
R113
C124
C123
R178
TP12
TP13
R114
R532
R533
R534
TP14
R535
TP15
R530
R531
R529
R120
R152
R195
C162
C163
C142
C164
C140
CR3002
C301
C304
C305
R357
R358
Q301
C356
C464
C354
L305
L311
C314
C416
C315
L416
C408
C403
C402
L401
R715
R702
Q701
C705
R703
C706
C709
R704
C711
L702
R597
Q702
U501
C712
C518
C731
C728
L703
Q505
R537
R515
C546
R510
L308
L335
C316 L336
L330 C365
C333 C325 C326 C327
L331 L310
C702
L701
R701
C701
C704
Q705
C707
L704
R705
C710
CR701
Q504
U104
R513
R539
C520
R511
R512
C521
C549
C523
R509
R508
R514
C522
C543
C312
CR305
L329
C368
C343
R540
CR302
C307
CR307
C367
C147
R139
C517
C568
L309
R305
C310
R336
R337
Q120
L303
C321
C161
C178
C179
C177
C311
R399
C344
L304
L307
C322
C143
R177
R308
R307
C502
C503
C317
R301 R302
C308
CR303
C313
R306
C318
C369
Q306 Q307
R335
C370
L337
Q304
Q305
R173
R176
R175
R172
R171
R174
Q121
Q122
R191
CF1
R162
C111
R101
C101
C102
U106
C501
U505
C506
C507
C168
C167
C166
C170
C171
C165
C359
L302
L326
Figure 10-12. VHF (136–174 MHz) Mainboard Bottom Side: PCB No. 8431BEACON400
Page 98

10-11 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
R501 R502
C565
CR501
C566
Q501 Q502
C563
C564
C560
C562
C561
Figure 10-13. VHF (136–174 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Top View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100
Page 99

Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz) 10-12
SW1
SW / VOL1
J104
Figure 10-14. VHF (136–174 MHz) Sub Circuit Board Bottom View: PCB No. 8421BEACON100
Page 100
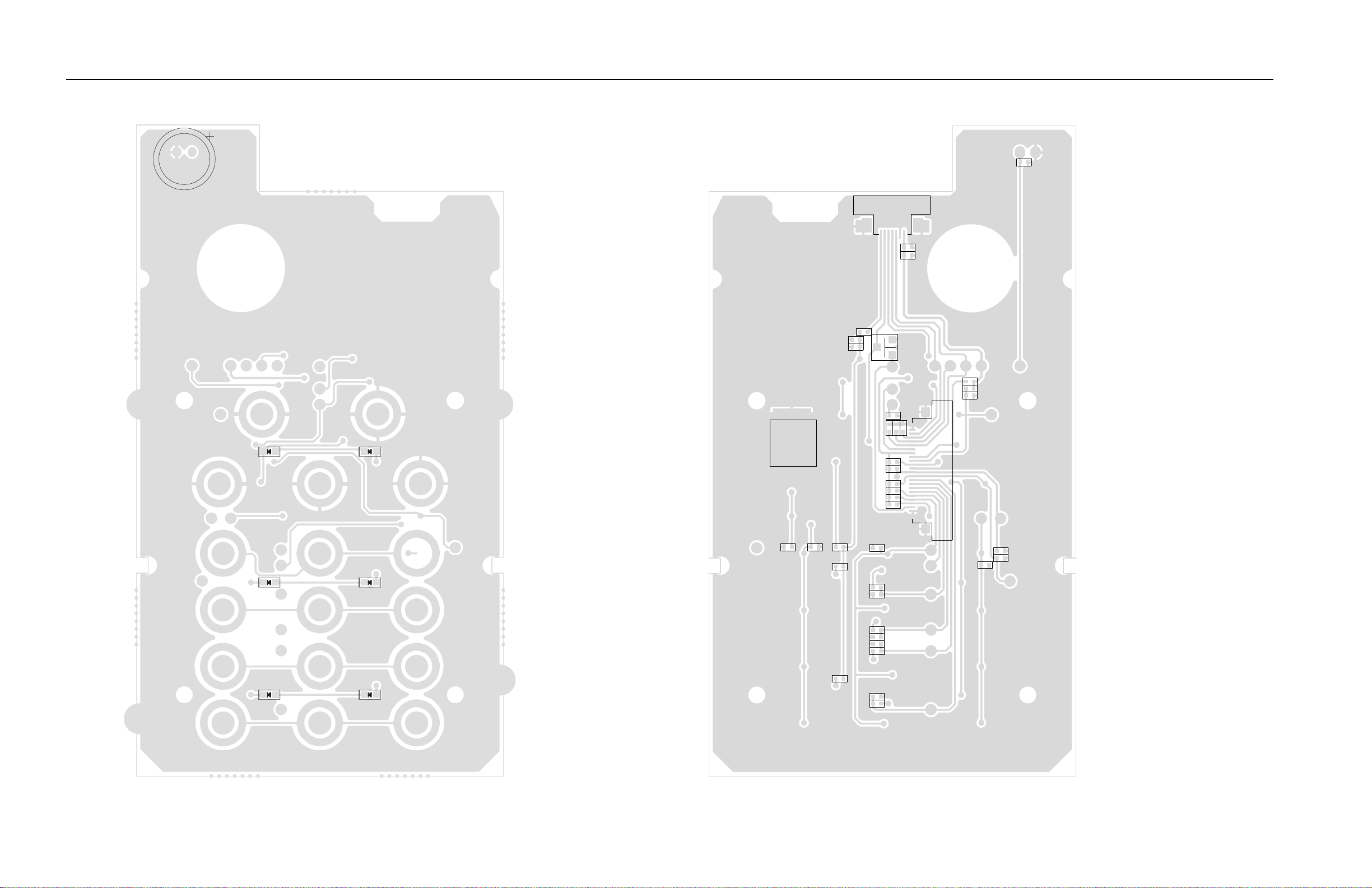
10-13 Circuit Board/Schematic Diagram and Parts List (VHF: 136–174 MHz)
MIC1
CR110 CR111
SH201
C174
C187
R155
R196
R197
R198
R161
R160
R159
J101
Q110
C1004
C1011
C1018
C176
C175
R199
R147
C1005
C1009
C1010
J103
CR114 CR115
CR112 C R11 3
Figure 10-15. VHF (136–174 MHz) Keypad Board: PCB No. 8422BEACON100
C1001
C1008
R156
R158
R157
C1007
R108
C1012
R109
C1013
C1014
R112
15
C10
R119
C1006
C1002
C1003
 Loading...
Loading...