

MELDAS and MELSEC are registered trademarks of Mitsubishi Electric Corporation.
Microsoft
States and/or other countries.
Intel
subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Other company and product names that appear in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of the
respective company.
®
and Windows® are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
®
, Pentium® and Celeron® are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation and its
Introduction
This manual describes the specifications of MITSUBISHI CNC 700/70 Series.
To safely use this CNC unit, thoroughly study the "Precautions for Safety" on the next page
before use.
Details described in this manual
At the beginning of each item, a table indicating it’s specification according to the model.
{
: Standard
U : Option
: Selection
: Special option
CAUTION
The items that are not described in this manual must be interpreted as "not possible".
This manual is written on the assumption that all option functions are added.
Some functions may differ or some functions may not be usable depending on the NC
system (software) version.
General precautions
(1) When the contents of this manual is updated, the version (A, B, …) on the cover will be
incremented.
Precautions for Safety
Always read this manual, related manuals and attached documents before installation, operation,
programming, maintenance or inspection to ensure correct use.
Understand all the conditions described in this manual before using the unit.
We rank the safety precautions into "DANGER", "WARNING" and "CAUTION" for the manuals issued
by Mitsubishi, including this manual.
DANGER
WARNING
CAUTION
Note that even items ranked as " CAUTION", may lead to major results depending on the situation.
In any case, important information that must always be observed is described.
Not applicable in this manual.
When there is a great risk that the user could be subject to
fatalities or serious injuries if handling is mistaken.
When the user could be subject to fatalities or serious injuries
if handling is mistaken.
When the user could be subject to injuries or when physical
damage could occur if handling is mistaken.
DANGER
Not applicable in this manual.
1. Items related to product and manual
The items that are not described in this manual must be interpreted as "not possible".
This manual is written on the assumption that all option functions are added.
Some functions may differ or some functions may not be usable depending on the NC
system (software) version.
2. Items related to start up and maintenance
Follow the power specifications (input voltage range, frequency range, momentary
power failure time range) described in this manual.
Follow the environment conditions (ambient temperature, humidity, vibration,
atmosphere) described in this manual.
!
Follow the remote type machine contact input/output interface described in this manual.
(Connect a diode in parallel with the inductive load or connect a protective resistor in
serial with the capacitive load, etc.)
WARNING
CAUTION
If the parameter is used to set the temperature rise detection function to invalid,
overheating may occur, thereby disabling control and possibly resulting in the axes
running out of control, which in turn may result in machine damage and/or bodily injury
or destruction of the unit. It is for this reason that the detection function is normally left
"valid" for operation.
The parameter for the temperature rise detection function will be validated forcibly
when the NC unit is turned ON.

CONTENTS
1. Control Axes................................................................................................................................1
1.1 Control Axes .........................................................................................................................1
1.1.1 Number of Basic Control Axes (NC Axes)...................................................................1
1.1.2 Max. Number of Axes (NC Axes + Spindles + PLC Axes)..........................................1
1.1.3 Max. Number of Auxiliary Axes (MR-J2-CT) ...............................................................2
1.1.4 Number of Simultaneous Contouring Control Axes.....................................................2
1.1.5 Max. Number of NC Axes in a Part System ................................................................2
1.2 Control Part System..............................................................................................................2
1.2.1 Standard Number of Part Systems..............................................................................2
1.2.2 Max. Number of Part Systems.....................................................................................2
1.3 Control Axes and Operation Modes.....................................................................................3
1.3.1 Tape (RS-232C Input) Mode .......................................................................................3
1.3.2 Memory Mode..............................................................................................................3
1.3.3 MDI Mode.....................................................................................................................3
1.3.4 High-Speed Program Server Mode (CF Card in Control Unit)....................................3
1.3.5 Front IC Card Mode.....................................................................................................4
1.3.6 Hard Disk Mode ...........................................................................................................4
2. Input Command ..........................................................................................................................5
2.1 Data Increment .....................................................................................................................5
2.1.1 Least Command Increment .........................................................................................5
2.1.2 Least Control Increment...............................................................................................6
2.1.3 Indexing Increment.......................................................................................................6
2.2 Unit System...........................................................................................................................7
2.2.1 Inch/Metric Changeover...............................................................................................7
2.2.2 Input Command Increment Tenfold.............................................................................8
2.3 Program Format....................................................................................................................9
2.3.1 Program Format...........................................................................................................9
2.3.1.1 Format 1 for Lathe (G-code List 2, 3)..............................................................9
2.3.1.2 Format 2 for Lathe (G-code List 4, 5)..............................................................9
2.3.1.3 Special Format for Lathe (G-code List 6, 7)....................................................9
2.3.1.4 Format 1 for Machining Center (G-code List 1)..............................................9
2.3.1.5 Format 2 for Machining Center (M2 Format)..................................................9
2.3.1.6 MITSUBISHI CNC Special Format .................................................................9
2.4 Command Value.................................................................................................................10
2.4.1 Decimal Point Input I, II..............................................................................................10
2.4.2 Absolute/Incremental Command ...............................................................................11
2.4.3 Diameter/Radius Designation....................................................................................13
3. Positioning/Interpolation .........................................................................................................14
3.1 Positioning...........................................................................................................................14
3.1.1 Positioning..................................................................................................................14
3.1.2 Unidirectional Positioning...........................................................................................15
3.2 Linear/Circular Interpolation................................................................................................16
3.2.1 Linear Interpolation ....................................................................................................16
3.2.2 Circular Interpolation (Center/Radius Designation)...................................................17
3.2.3 Helical Interpolation....................................................................................................19
3.2.4 Spiral/Conical Interpolation........................................................................................21
3.2.5 Cylindrical Interpolation..............................................................................................23
3.2.6 Polar Coordinate Interpolation...................................................................................24
3.2.7 Milling Interpolation....................................................................................................25
3.2.8 Hypothetical Axis Interpolation...................................................................................26
3.3 Curve Interpolation..............................................................................................................27
3.3.2 Exponential Interpolation ...........................................................................................27
3.3.3 Spline Interpolation ....................................................................................................28
i

3.3.4 NURBS Interpolation..................................................................................................28
3.3.5 3-Dimensional Circular Interpolation..........................................................................29
4. Feed............................................................................................................................................30
4.1 Feed Rate...........................................................................................................................30
4.1.1 Rapid Traverse Rate (m/min) ....................................................................................30
4.1.2 Cutting Feed Rate (m/min).........................................................................................31
4.1.3 Manual Feed Rate (m/min)........................................................................................32
4.1.4 Rotary Axis Command Speed Tenfold......................................................................32
4.2 Feed Rate Input Methods...................................................................................................33
4.2.1 Feed per Minute (Asynchronous Feed).....................................................................33
4.2.2 Feed per Revolution (Synchronous Feed).................................................................35
4.2.3 Inverse Time Feed.....................................................................................................36
4.2.4 F 1-digit Feed.............................................................................................................37
4.2.5 Manual Speed Command..........................................................................................37
4.3 Override ..............................................................................................................................38
4.3.1 Rapid Traverse Override............................................................................................38
4.3.2 Cutting Feed Override................................................................................................38
4.3.3 2nd Cutting Feed Override.........................................................................................38
4.3.4 Override Cancel.........................................................................................................39
4.4 Acceleration/Deceleration...................................................................................................40
4.4.1 Automatic Acceleration/Deceleration after Interpolation ...........................................40
4.4.2 Rapid Traverse Constant Inclination Acceleration/Deceleration...............................42
4.5 Thread Cutting....................................................................................................................44
4.5.1 Thread Cutting (Lead/Thread Number Designation).................................................44
4.5.2 Variable Lead Thread Cutting....................................................................................46
4.5.3 Synchronous Tapping................................................................................................47
4.5.3.1 Synchronous Tapping Cycle.........................................................................47
4.5.3.2 Pecking Tapping Cycle .................................................................................49
4.5.3.3 Deep-hole Tapping Cycle..............................................................................51
4.5.4 Chamfering.................................................................................................................53
4.5.6 Circular Thread Cutting..............................................................................................54
4.6 Manual Feed.......................................................................................................................55
4.6.1 Manual Rapid Traverse..............................................................................................55
4.6.2 Jog Feed ....................................................................................................................55
4.6.3 Incremental Feed.......................................................................................................56
4.6.4 Handle Feed...............................................................................................................56
4.6.5 Manual Feed Rate B..................................................................................................57
4.6.6 Manual Feed Rate B Surface Speed Control............................................................58
4.7 Dwell ...................................................................................................................................59
4.7.1 Dwell (Time-based Designation)................................................................................59
5. Program Memory/Editing.........................................................................................................60
5.1 Memory Capacity................................................................................................................60
5.1.1 Memory Capacity (Number of Programs Stored)......................................................60
5.2 Editing.................................................................................................................................61
5.2.1 Program Editing .........................................................................................................61
5.2.2 Background Editing....................................................................................................62
5.2.3 Buffer Correction........................................................................................................63
6. Operation and Display..............................................................................................................64
6.1 Structure of Operation/Display Panel.................................................................................64
6.1.1 Color display (8.4-type LCD TFT)..............................................................................64
6.1.2 Color display (10.4-type LCD TFT)............................................................................64
6.1.3 Color display (10.4-type LCD TFT/WindowsXPe).....................................................64
6.1.4 Color display (15-type LCD TFT/WindowsXPe)........................................................64
6.1.5 Color touch-panel display (10.4-type LCD TFT/WIndowsXPe).................................64
6.1.6 Color touch-panel display (10.4-type LCD TFT)........................................................64
ii

6.2 Operation Methods and Functions.....................................................................................65
6.2.1 Operation Input ..........................................................................................................65
6.2.2 Absolute/Incremental Setting.....................................................................................65
6.2.5 Displayed Part System Switch...................................................................................65
6.2.6 Menu List....................................................................................................................66
6.2.7 Display Switch by Operation Mode............................................................................66
6.2.8 External Signal Display Switch..................................................................................66
6.2.10 Screen Saver ...........................................................................................................66
6.2.11 Parameter/Operation Guidance...............................................................................67
6.2.12 Alarm Guidance .......................................................................................................67
6.2.13 Machining Program Input Mistake Check Warning.................................................67
6.3 Display Methods and Contents...........................................................................................68
6.3.1 Status Display........................................................................................................... .68
6.3.2 Clock Display .............................................................................................................68
6.3.3 Operation Screen Display..........................................................................................68
6.3.4 Preparation Screen Display.......................................................................................69
6.3.5 Edit Screen Display....................................................................................................69
6.3.6 Diagnosis Screen Display..........................................................................................69
6.3.7 Maintenance Screen Display.....................................................................................69
6.3.8 Additional Language..................................................................................................70
6.3.8.1 Japanese.......................................................................................................70
6.3.8.2 English...........................................................................................................70
6.3.8.3 German..........................................................................................................70
6.3.8.4 Italian.............................................................................................................70
6.3.8.5 French ...........................................................................................................70
6.3.8.6 Spanish..........................................................................................................70
6.3.8.7 Chinese .........................................................................................................70
6.3.8.8 Korean...........................................................................................................71
6.3.8.9 Portuguese....................................................................................................71
6.3.8.10 Hungarian....................................................................................................71
6.3.8.11 Dutch...........................................................................................................71
6.3.8.12 Swedish.......................................................................................................71
6.3.8.13 Turkish.........................................................................................................71
7. Input/Output Functions and Devices .....................................................................................72
7.1 Input/Output Data................................................................................................................72
7.2 Input/Output I/F...................................................................................................................73
7.2.1 RS-232C I/F...............................................................................................................73
7.2.2 IC Card I/F..................................................................................................................74
7.2.2.1 I/F for CF Card in Control Unit................................................................................74
7.2.2.2 Front IC Card I/F.....................................................................................................74
7.2.3 Ethernet I/F.................................................................................................................74
7.2.4 Hard Disk I/F..............................................................................................................74
7.2.5 Floppy Disk I/F...........................................................................................................74
7.3 Computer Link.....................................................................................................................75
7.3.1 Computer Link B ........................................................................................................75
7.4 Others .................................................................................................................................76
7.4.1 Handy Terminal Connection......................................................................................76
8. Spindle, Tool and Miscellaneous Functions .........................................................................77
8.1 Spindle Functions (S) .........................................................................................................77
8.1.1 Spindle Control Functions..........................................................................................77
8.1.1.1 Spindle Digital I/F ..........................................................................................78
8.1.1.2 Spindle Analog I/F.........................................................................................78
8.1.1.3 Coil Switch.....................................................................................................78
8.1.1.4 Automatic Coil Switch....................................................................................78
8.1.1.5 Encoder Input I/F...........................................................................................79
iii

8.1.2 S Code Output ...........................................................................................................80
8.1.3 Constant Surface Speed Control...............................................................................81
8.1.4 Spindle Override ........................................................................................................82
8.1.5 Multiple-spindle Control .............................................................................................82
8.1.5.1 Multiple-spindle Control I...............................................................................83
8.1.5.2 Multiple-spindle Control II..............................................................................83
8.1.6 Spindle Orientation.....................................................................................................84
8.1.7 Spindle Position Control (Spindle/C Axis Control).....................................................85
8.1.8 Spindle Synchronization ............................................................................................86
8.1.8.1 Spindle Synchronization I..............................................................................86
8.1.8.2 Spindle Synchronization II.............................................................................87
8.1.9 Tool Spindle Synchronization I (Polygon)..................................................................88
8.1.9.1 Tool Spindle Synchronization IA (Spindle-Spindle Polygon)........................88
8.1.9.2 Tool Spindle Synchronization IB (Spindle-Spindle Polygon)........................89
8.1.9.3 Tool Spindle Synchronization IC (Spindle-NC Axis Polygon).......................90
8.2 Tool Functions (T)...............................................................................................................91
8.2.1 Tool Functions (T Command)....................................................................................91
8.3 Miscellaneous Functions (M)..............................................................................................92
8.3.1 Miscellaneous Functions............................................................................................92
8.3.2 Multiple M Codes in 1 Block.......................................................................................93
8.3.3 M Code Independent Output .....................................................................................93
8.3.4 Miscellaneous Function Finish...................................................................................94
8.3.5 M Code Output during Axis Traveling........................................................................95
8.4 2nd Miscellaneous Functions (B) .......................................................................................96
8.4.1 2nd Miscellaneous Functions...........................................................................96
9. Tool Compensation..................................................................................................................97
9.1 Tool Length/Tool Position...................................................................................................97
9.1.1 Tool Length Compensation........................................................................................97
9.1.2 Tool Position Offset..................................................................................................100
9.1.3 Tool Compensation for Additional Axes ..................................................................100
9.2 Tool Radius.......................................................................................................................101
9.2.1 Tool Radius Compensation .....................................................................................101
9.2.2 3-dimensional Tool Radius Compensation..............................................................103
9.2.3 Tool Nose Radius Compensation (G40/41/42) .......................................................104
9.2.4 Automatic Decision of Nose Radius Compensation Direction (G46/40).................105
9.2.5 Tool Radius Compensation Diameter Designation........................................105
9.3 Tool Compensation Amount.............................................................................................106
9.3.1 Number of Tool Compensation Sets .......................................................................106
9.3.1.1 Number of tool compensation sets 20 Sets..............................................107
9.3.1.2 Number of tool compensation sets 40 Sets..............................................107
9.3.1.3 Number of tool compensation sets 80 Sets..............................................107
9.3.1.4 Number of tool compensation sets 200 Sets............................................107
9.3.1.5 Number of tool compensation sets 400 Sets............................................107
9.3.1.6 Number of tool compensation sets 999 Sets............................................107
9.3.2 Compensation Memory............................................................................................108
9.3.2.1 Tool Shape/Wear Compensation Amount..................................................108
10. Coordinate System...............................................................................................................111
10.1 Coordinate System Type and Setting.............................................................................111
10.1.1 Machine Coordinate System..................................................................................112
10.1.2 Coordinate System Setting....................................................................................113
10.1.3 Automatic Coordinate System Setting...................................................................114
10.1.4 Workpiece Coordinate System Selection..............................................................115
10.1.5 External Workpiece Coordinate Offset..................................................................117
10.1.6 Workpiece Coordinate System Preset (G92.1).....................................................118
10.1.7 Local Coordinate System.......................................................................................119
iv

10.1.8 Coordinate System for Rotary Axis........................................................................120
10.1.9 Plane Selection......................................................................................................121
10.1.10 Origin Set/Origin Cancel......................................................................................122
10.1.11 Counter Set..........................................................................................................124
10.2 Return .............................................................................................................................125
10.2.1 Manual Reference Position Return........................................................................125
10.2.2 Automatic 1st Reference Position Return..............................................................126
10.2.3 2nd, 3rd, 4th Reference Position Return...............................................................128
10.2.4 Reference Position Check.....................................................................................129
10.2.5 Absolute Position Detection...................................................................................130
10.2.6 Tool Change Position Return.................................................................................131
11. Operation Support Functions .............................................................................................132
11.1 Program Control..............................................................................................................132
11.1.1 Optional Block Skip................................................................................................132
11.1.2 Single Block ...........................................................................................................133
11.2 Program Test..................................................................................................................134
11.2.1 Dry Run..................................................................................................................134
11.2.2 Machine Lock.........................................................................................................134
11.2.3 Miscellaneous Function Lock.................................................................................134
11.2.4 Graphic Check .......................................................................................................135
11.2.4.1 Graphic Check....................................................................................................135
11.2.4.2 3D Solid Program Check....................................................................................135
11.2.5 Graphic Trace ........................................................................................................136
11.2.6 Machining Time Computation................................................................................136
11.3 Program Search/Start/Stop ............................................................................................137
11.3.1 Program Search.....................................................................................................137
11.3.2 Sequence Number Search ....................................................................................137
11.3.3 Verification Stop.....................................................................................................138
11.3.4 Program Restart.....................................................................................................139
11.3.5 Automatic Operation Start......................................................................................139
11.3.6 NC Reset................................................................................................................140
11.3.7 Feed Hold...............................................................................................................140
11.3.8 Search & Start........................................................................................................141
11.4 Interrupt Operation..........................................................................................................142
11.4.1 Manual Interruption................................................................................................142
11.4.2 Automatic Operation Handle Interruption..............................................................142
11.4.3 Manual Absolute Switch.........................................................................................143
11.4.4 Thread Cutting Cycle Retract ................................................................................144
11.4.5 Tapping Retract......................................................................................................145
11.4.6 Manual Numerical Value Command......................................................................146
11.4.8 MDI Interruption .....................................................................................................146
11.4.9 Simultaneous Operation of Manual and Automatic Modes...................................147
11.4.10 Simultaneous Operation of JOG and Handle Modes..........................................147
11.4.11 Reference Position Retract..................................................................................148
11.4.12 Tool Escape and Return......................................................................................149
11.4.13 Skip Retract..........................................................................................................149
11.4.14 PLC Interruption...................................................................................................149
12. Program Support Functions................................................................................................150
12.1 Machining Method Support Functions............................................................................150
12.1.1 Program..................................................................................................................150
12.1.1.1 Subprogram Control..................................................................................150
12.1.1.2 Figure Rotation..........................................................................................152
12.1.1.3 Scaling.......................................................................................................154
12.1.2 Macro Program ......................................................................................................155
12.1.2.1 User Macro................................................................................................155
v

12.1.2.2 Machine Tool Builder Macro .....................................................................158
12.1.2.3 Macro Interruption.....................................................................................159
12.1.2.4 Variable Command ...................................................................................160
12.1.2.4.1 100 Sets.....................................................................................161
12.1.2.4.2 200 Sets.....................................................................................161
12.1.2.4.3 300 Sets.....................................................................................161
12.1.2.4.4 600 Sets.....................................................................................161
12.1.2.4.5 (50+50 ´ Number of Part Systems) Sets...................................161
12.1.2.4.6 (100+100 ´ Number of Part Systems) Sets...............................161
12.1.2.4.7 (200+100 ´ Number of Part Systems) Sets...............................161
12.1.2.4.8 (400+100 ´ Number of Part Systems) Sets...............................161
12.1.3 Fixed Cycle ............................................................................................................162
12.1.3.1 Fixed Cycle for Drilling ..............................................................................163
12.1.3.2 Fixed Cycle for Drilling (Type II)................................................................170
12.1.3.3 Special Fixed Cycle...................................................................................171
12.1.3.4 Fixed Cycle for Turning Machining ...........................................................175
12.1.3.5 Compound Type Fixed Cycle for Turning Machining ...............................180
12.1.3.6 Compound Type Fixed Cycle for Turning Machining (Type II).................188
12.1.3.7 Small-diameter Deep-hole Drilling Cycle..................................................189
12.1.4 Mirror Image...........................................................................................................190
12.1.4.1 Mirror Image by Parameter Setting...........................................................190
12.1.4.2 Mirror Image by External Input..................................................................190
12.1.4.3 Mirror Image by G Code............................................................................191
12.1.4.4 Mirror Image for Facing Tool Posts...........................................................192
12.1.4.5 T Code Mirror Image for Facing Tool Posts..............................................192
12.1.5 Coordinate System Operation ...............................................................................193
12.1.5.1 Coordinate Rotation by Program ..............................................................193
12.1.5.2 Coordinate Rotation by Parameter ...........................................................195
12.1.5.3 3-dimensional Coordinate Conversion......................................................196
12.1.6 Dimension Input.....................................................................................................197
12.1.6.1 Corner Chamfering/Corner R....................................................................197
12.1.6.2 Linear Angle Command ............................................................................203
12.1.6.3 Geometric Command................................................................................204
12.1.6.4 Polar Coordinate Command .....................................................................208
12.1.7 Axis Control............................................................................................................209
12.1.7.1 Chopping...................................................................................................209
12.1.7.1.1 Chopping....................................................................................209
12.1.7.2 Normal Line Control ..................................................................................210
12.1.7.3 Circular Cutting..........................................................................................211
12.1.8 Multi-part System Control ......................................................................................212
12.1.8.1 Timing Synchronization between Part Systems.......................................212
12.1.8.2 Start Point Designation Timing Synchronization ......................................213
12.1.8.3 Mixed Synchronization Control.................................................................215
12.1.8.5 Control Axis Synchronization across Part Systems..................................216
12.1.8.6 Balance Cut...............................................................................................217
12.1.8.7 Common Memory for Part Systems..........................................................218
12.1.9 Data Input by Program...........................................................................................219
12.1.9.1 Parameter Input by Program.....................................................................219
12.1.9.2 Compensation Data Input by Program .....................................................220
12.1.10 Machining Modal..................................................................................................222
12.1.10.1 Tapping Mode .........................................................................................222
12.1.10.2 Cutting Mode...........................................................................................222
12.2 Machining Accuracy Support Functions.........................................................................223
12.2.1 Automatic Corner Override....................................................................................223
12.2.2 Deceleration Check................................................................................................224
12.2.2.1 Exact Stop Check Mode............................................................................225
vi

12.2.2.2 Exact Stop Check......................................................................................225
12.2.2.3 Error Detection..........................................................................................225
12.2.2.4 Programmable In-position Check..............................................................226
12.3 High-speed and High-accuracy Functions.....................................................................227
12.3.1 High-speed Machining Mode I (G05P1)................................................................227
12.3.2 High-speed Machining Mode II (G05 P2)..............................................................228
12.3.3 High-speed High-accuracy Control 1 (G05.1Q1) ..................................................229
12.3.4 High-speed High-accuracy Control 2 (G5P10000)................................................230
12.3.5 High-accuracy Control 1 (G61.1/G08)...................................................................232
12.3.6 High-accuracy spline interpolation1 (G61.2) .........................................................236
12.3.8 SSS Control ...........................................................................................................237
12.4 Programming Support Functions....................................................................................238
12.4.1 Playback.................................................................................................................238
12.4.3 Simple Programming .............................................................................................238
12.4.4 G code Guidance...................................................................................................239
13 Machine Accuracy Compensation.......................................................................................240
13.1 Static Accuracy Compensation.......................................................................................240
13.1.1 Backlash Compensation........................................................................................240
13.1.2 Memory-type Pitch Error Compensation ...............................................................241
13.1.3 Memory-type Relative Position Error Compensation ............................................242
13.1.4 External Machine Coordinate System Compensation...........................................243
13.1.5 Circular Error Radius Compensation.....................................................................243
13.1.6 Ball Screw Thermal Expansion Compensation.....................................................244
13.1.7 Machine Rotation Center Error Compensation .....................................................245
13.1.8 Position-dependent Gradually Increasing-type Backlash Compensation.............246
13.2 Dynamic Accuracy Compensation .................................................................................247
13.2.1 Smooth High-gain (SHG) Control..........................................................................247
13.2.2 Dual Feedback.......................................................................................................248
13.2.3 Lost Motion Compensation....................................................................................248
13.2.4 OMR II (Backlash with Filter).................................................................................249
13.2.6 OMR-FF.................................................................................................................250
13.2.7 Distance-coded Reference Position Detection......................................................251
14. Automation Support Functions ..........................................................................................252
14.1 Measurement..................................................................................................................252
14.1.1 Skip ........................................................................................................................252
14.1.1.1 Skip............................................................................................................252
14.1.1.2 Multiple-step Skip......................................................................................253
14.1.1.4 PLC Skip....................................................................................................254
14.1.1.5 Speed Change Skip..................................................................................254
14.1.2 Automatic Tool Length Measurement....................................................................256
14.1.3 Manual Tool Length Measurement 1.....................................................................258
14.1.4 Manual Tool Length Measurement 2.....................................................................260
14.1.5 Workpiece Coordinate Offset Measurement.........................................................261
14.1.6 Workpiece Position Measurement.........................................................................262
14.1.7 Rotation Measurement...........................................................................................264
14.2 Tool Life Management....................................................................................................265
14.2.1 Tool Life Management...........................................................................................265
14.2.1.1 Tool Life Management I ............................................................................265
14.2.1.2 Tool Life Management II ...........................................................................265
14.2.2 Number of Tool Life Management Sets.................................................................266
14.3 Others .............................................................................................................................267
14.3.1 Programmable Current Limitation..........................................................................267
14.3.2 Auto Power OFF....................................................................................................267
15. Safety and Maintenance.......................................................................................................268
15.1 Safety Switches ..............................................................................................................268
vii

15.1.1 Emergency Stop ....................................................................................................268
15.1.2 Data Protection Key...............................................................................................268
15.2 Display for Ensuring Safety ............................................................................................269
15.2.1 NC Warning............................................................................................................269
15.2.2 NC Alarm................................................................................................................269
15.2.3 Operation Stop Cause ...........................................................................................270
15.2.4 Emergency Stop Cause.........................................................................................270
15.2.5 Thermal Detection..................................................................................................270
15.2.6 Battery Alarm/Warning...........................................................................................271
15.3 Protection........................................................................................................................272
15.3.1 Stroke End (Over Travel).......................................................................................272
15.3.2 Stored Stroke Limit.................................................................................................272
15.3.2.1 Stored Stroke Limit I/II...............................................................................273
15.3.2.2 Stored Stroke Limit IB ...............................................................................275
15.3.2.3 Stored Stroke Limit IIB ..............................................................................275
15.3.2.4 Stored Stroke Limit IC...............................................................................276
15.3.3 Stroke Check before Travel...................................................................................276
15.3.4 Chuck/Tailstock Barrier Check ..............................................................................277
15.3.5 Interlock..................................................................................................................278
15.3.6 External Deceleration.............................................................................................278
15.3.8 Door Interlock.........................................................................................................279
15.3.8.1 Door Interlock I..........................................................................................279
15.3.8.2 Door Interlock II.........................................................................................280
15.3.9 Parameter Lock......................................................................................................281
15.3.10 Program Protection (Edit Lock B, C) ...................................................................281
15.3.11 Program Display Lock..........................................................................................281
15.3.12 Safety Observation ..............................................................................................282
15.4 Maintenance and Troubleshooting.................................................................................283
15.4.1 Operation History...................................................................................................283
15.4.2 Data Sampling........................................................................................................283
15.4.3 NC Data Backup....................................................................................................284
15.4.4 MELDASNET.........................................................................................................284
15.4.4.1 Machine Tool Builder Network System.....................................................284
15.4.4.2 Anshin-net Service....................................................................................284
15.4.5 Servo Automatic Tuning.........................................................................................286
15.4.6 Automatic Backup..................................................................................................288
15.4.7 System Setup.........................................................................................................288
15.4.8 Servo/Spindle Waveform Display..........................................................................289
16. Drive System.........................................................................................................................290
16.1 Servo/Spindle..................................................................................................................290
16.1.1 Feed Axis...............................................................................................................290
16.1.1.1 MDS-D-V1/D-V2 (200V)............................................................................290
16.1.1.2 MDS-DH-V1/DH-V2 (400V) ......................................................................290
16.1.1.3 MDS-D-SVJ3 (200V).................................................................................291
16.1.2 Spindle ...................................................................................................................291
16.1.2.1 MDS-D-SP (200V).....................................................................................291
16.1.2.2 MDS-DH-SP (400V)..................................................................................291
16.1.2.3 MDS-D-SPJ3 (200V).................................................................................291
16.1.3 Auxiliary Axis..........................................................................................................291
16.1.3.1 Index/Positioning Servo : MR-J2-CT.........................................................291
16.1.4 Power Supply.........................................................................................................292
16.1.4.1 Power Supply : MDS-D-CV (200V)...........................................................292
16.1.4.2 Power Supply : MDS-DH-CV (400V) ........................................................292
16.1.4.3 AC Reactor for Power Supply...................................................................292
16.1.4.4 Ground Plate.............................................................................................292
viii

17. Machine Support Functions................................................................................................293
17.1 PLC.................................................................................................................................293
17.1.1 Built-in PLC Processing Mode...............................................................................293
17.1.2 PLC Functions........................................................................................................293
17.1.2.1 Built-in PLC Basic Function.......................................................................293
17.1.2.2 PLC Exclusive Instruction .........................................................................294
17.1.3 PLC Support Functions..........................................................................................297
17.1.3.1 Alarm Message Display ............................................................................297
17.1.3.2 Operator Message Display........................................................................297
17.1.3.3 Memory Switch (PLC Switch)....................................................................298
17.1.3.4 Load Meter Display ...................................................................................298
17.1.3.5 User PLC Version Display.........................................................................298
17.1.3.6 Multi-ladder Program Register and Execution..........................................298
17.1.4 Built-in PLC Capacity.............................................................................................299
17.1.5 Machine Contact Input/Output I/F..........................................................................299
17.1.6 Ladder Monitor.......................................................................................................304
17.1.7 PLC Development..................................................................................................304
17.1.7.1 On-board Development.............................................................................304
17.1.7.2 MELSEC Development Tool (GX Developer)...........................................304
17.1.8 PLC Parameter ......................................................................................................305
17.1.8.1 PLC Constant (150 Points) .......................................................................305
17.1.8.2 PLC Constant Extension (Up to 755 Points).............................................305
17.1.10 Pallet Program Registration.................................................................................306
17.1.11 Aditional PLC engine ...........................................................................................306
17.2 Machine Construction.....................................................................................................307
17.2.1 Servo OFF..............................................................................................................307
17.2.2 Axis Detachment....................................................................................................308
17.2.3 Synchronous Control .............................................................................................309
17.2.4 Inclined Axis Control..............................................................................................312
17.2.5 Position Switch.......................................................................................................313
17.2.7 Index Table Indexing..............................................................................................314
17.2.8 Auxiliary Axis Control (J2-CT)................................................................................315
17.2.9 Tool Length Compensation along the Tool Axis....................................................316
17.2.10 Tool Handle Feed & Interruption..........................................................................317
17.2.11 Tool Center Coordinate Display...........................................................................317
17.2.12 Tool Center Point Control ....................................................................................318
17.3 PLC Operation................................................................................................................320
17.3.1 Arbitrary Feed in Manual Mode .............................................................................320
17.3.2 Circular Feed in Manual Mode...............................................................................321
17.3.3 PLC Axis Control....................................................................................................323
17.4 PLC Interface..................................................................................................................324
17.4.1 CNC Control Signal................................................................................................324
17.4.2 CNC Status Signal.................................................................................................325
17.4.3 PLC Window ..........................................................................................................327
17.4.4 External Search......................................................................................................327
17.5 Machine Contact I/O.......................................................................................................328
17.6 External PLC Link...........................................................................................................329
17.6.3 CC-Link (Master/Slave)..........................................................................................329
17.6.4 PROFIBUS-DP (Master)........................................................................................335
17.7 Installing S/W for Machine Tools....................................................................................336
17.7.1 Customization (NC Designer)................................................................................336
17.7.2 User-defined Key...................................................................................................337
17.7.3 EZSocket I/F ..........................................................................................................337
17.7.4 APLC Release........................................................................................................338
17.7.5 Custom API Library................................................................................................338
ix

17.8 Others .............................................................................................................................339
17.8.1 Credit System.........................................................................................................339
17.8.2 NC Monitoring Tool................................................................................................339
Appendix 1. List of Specifications............................................................................................340
Appendix 2. 700 Series Installation Condition........................................................................341
2.1 Cabinet and Installation....................................................................................................341
2.1.1 Cabinet Construction ...............................................................................................341
2.1.2 General Specifications (Environment Conditions)...................................................347
2.2 Outline Drawing ................................................................................................................350
2.2.1 Control Unit ..............................................................................................................350
2.2.2 Display Unit..............................................................................................................353
2.2.2.1 FCU7-DA201 (8.4-type)..............................................................................353
2.2.2.2 FCU7-DA211 / FCU7-DA315 / FCU7-DA415 / FCU7-DA445 (10.4-type).353
2.2.2.3 FCU7-DA335 / FCU7-DA435 (15-type)......................................................355
2.2.2.4 FCU7-DA201 (8.4-type) / FCU7-DA211 (10.4-type) Rear View.................356
2.2.2.5 FCU7-DA315 / FCU7-DA415 / FCU7-DA445 / FCU7-DA335
/ FCU7-DA435 Rear View...........................................................................357
2.2.2.6 FCU7-EP102 (Front IC Card I/F Unit).........................................................358
2.2.3 Operation Panel I/O Unit..........................................................................................359
2.2.3.1 FCU7-DX670 / FCU7-DX671 / FCU7-DX770 / FCU7-DX771
Outline Drawing...........................................................................................359
2.2.4 Keyboard Unit ..........................................................................................................360
2.2.4.1 FCU7-KB021 / FCU7-KB022 (ONG Layout) ..............................................360
2.2.4.2 FCU7-KB041 (ABC Layout)........................................................................360
2.2.5 Hard Disk Unit..........................................................................................................361
2.2.5.1 FCU7-HD001-1 ...........................................................................................361
2.2.6 Floppy Disk Unit.......................................................................................................362
2.2.6.1 FCU7-FD221-1............................................................................................362
2.2.7 Card-sized I/O Card.................................................................................................363
2.2.7.1 HR361 / HR371 / HR381 / HR383..............................................................363
2.2.8 Remote I/O Unit Outline...........................................................................................365
2.2.8.1 FCUA-DX100 / FCUA-DX110 / FCUA-DX120 / FCUA-DX140
/ FCUA-DX101 / FCUA-DX111 / FCUA-DX121 / FCUA-DX141................365
2.3 Panel Cut Dimension Drawing / Installation Dimension Drawing ....................................366
2.3.1 Control Unit ..............................................................................................................366
2.3.2 Display Unit..............................................................................................................367
2.3.2.1 FCU7-DA201 (8.4-type)..............................................................................367
2.3.2.2 FCU7-DA211 / FCU7-DA315 / FCU7-DA415 / FCU7-DA445 (10.4-type).368
2.3.2.3 FCU7-DA335 / FCU7-DA435 (15-type)......................................................369
2.3.3 Operation Panel I/O Unit..........................................................................................370
2.3.3.1 FCU7-DX670 / FCU7-DX671 / FCU7-DX770 / FCU7-DX771....................370
2.3.4 Keyboard Unit ..........................................................................................................371
2.3.4.1 FCU7-KB021 / FCU7-KB022 (ONG Layout) ..............................................371
2.3.4.2 FCU7-KB041 (ABC Layout)........................................................................372
2.3.5 Hard Disk Unit..........................................................................................................373
2.3.5.1 FCU7-HD001...............................................................................................373
2.3.6 External Power Supply Unit.....................................................................................374
2.3.6.1 PD25............................................................................................................374
2.3.6.2 PD27............................................................................................................375
2.3.6.3 Mounting Direction and Clearance..............................................................375
2.3.7 Remote I/O Unit .......................................................................................................376
2.3.7.1 FCUA-DX100 / FCUA-DX110 / FCUA-DX120 / FCUA-DX140
/ FCUA-DX101 / FCUA-DX111 / FCUA-DX121 / FCUA-DX141................376
2.3.8 Manual Pulse Generator..........................................................................................377
2.3.8.1 UFO-01-2Z9 ................................................................................................377
x

2.3.8.2 HD60 ...........................................................................................................378
2.3.9 Synchronous Feed Encoder....................................................................................379
2.3.9.1 OSE-1024-3-15-68......................................................................................379
2.3.10 F Installation Plate..................................................................................................380
Appendix 3. 70 Series Installation Condition..........................................................................381
3.1 Cabinet and Installation....................................................................................................381
3.1.1 Cabinet Construction ...............................................................................................381
3.1.2 General Specifications (Environment Conditions)...................................................384
3.2 Outline Drawing ................................................................................................................386
3.2.1 Control Unit ..............................................................................................................386
3.2.1.1 FCU7-MU521/FCU7-MU522.......................................................................386
3.2.2 Display Unit..............................................................................................................388
3.2.2.1 FCU7-DU120-12 (8.4-type).........................................................................388
3.2.2.2 FCU7-DU140-12 (10.4-type).......................................................................388
3.2.3 Operation Panel I/O Unit..........................................................................................389
3.2.3.1 FCU7-DX710 / FCU7-DX711......................................................................389
3.2.3.2 FCU7-DX720 / FCU7-DX721 / FCU7-DX730 / FCU7-DX731....................390
3.2.4 Keyboard Unit ..........................................................................................................391
3.2.4.1 FCU7-KB024 (8.4-type) ..............................................................................391
3.2.4.2 FCU7-KB044 (10.4-type) ............................................................................391
3.2.5 Remote I/O Unit .......................................................................................................392
3.2.5.1 FCUA-DX100 / FCUA-DX110 / FCUA-DX120 / FCUA-DX140
/ FCUA-DX101 / FCUA-DX111 / FCUA-DX121 / FCUA-DX141................392
3.2.6 Card-sized I/O Card.................................................................................................393
3.2.6.1 HR361 / HR371 / HR381 / HR383..............................................................393
3.3 Panel Cut Dimension Drawing / Installation Dimension Drawing ....................................395
3.3.1 Display Unit..............................................................................................................395
3.3.1.1 FCU7-DU120-12 (8.4-type).........................................................................395
3.3.1.2 FCU7-DU140-12 (10.4-type).......................................................................396
3.3.2 Operation Panel I/O Unit..........................................................................................397
3.3.2.1 FCU7-DX710 / FCU7-DX711 / FCU7-DX720 / FCU7-DX721
/ FCU7-730 / FCU7-731..............................................................................397
3.3.3 Keyboard Unit ..........................................................................................................398
3.3.3.1 FCU7-KB024 (for 8.4-type).........................................................................398
3.3.3.2 FCU7-KB044 (for 10.4-type).......................................................................399
3.3.4 External Power Supply Unit.....................................................................................400
3.3.4.1 PD25............................................................................................................400
3.3.4.2 PD27............................................................................................................401
3.3.4.3 Mounting Direction and Clearance..............................................................401
3.3.5 Remote I/O Unit .......................................................................................................402
3.3.5.1 FCUA-DX100 / FCUA-DX110 / FCUA-DX120 / FCUA-DX140
/ FCUA-DX101 / FCUA-DX111 / FCUA-DX121 / FCUA-DX141...............402
3.3.6 Manual Pulse Generator..........................................................................................403
3.3.6.1 UFO-01-2Z9 ................................................................................................403
3.3.6.2 HD60 ...........................................................................................................404
3.3.7 Synchronous Feed Encoder....................................................................................405
3.3.7.1 OSE-1024-3-15-68......................................................................................405
MITSUBISHI CNC 700/70 Series Specifications List
xi
1. Control Axes
1.1 Control Axes
1. Control Axes
The NC axis, spindle, PLC axis and auxiliary axis are generically called the control axis.
The NC axis is an axis that can be manually operated, or automatically operated with the machining program.
The PLC axis is an axis that can be controlled from the PLC ladder.
1.1 Control Axes
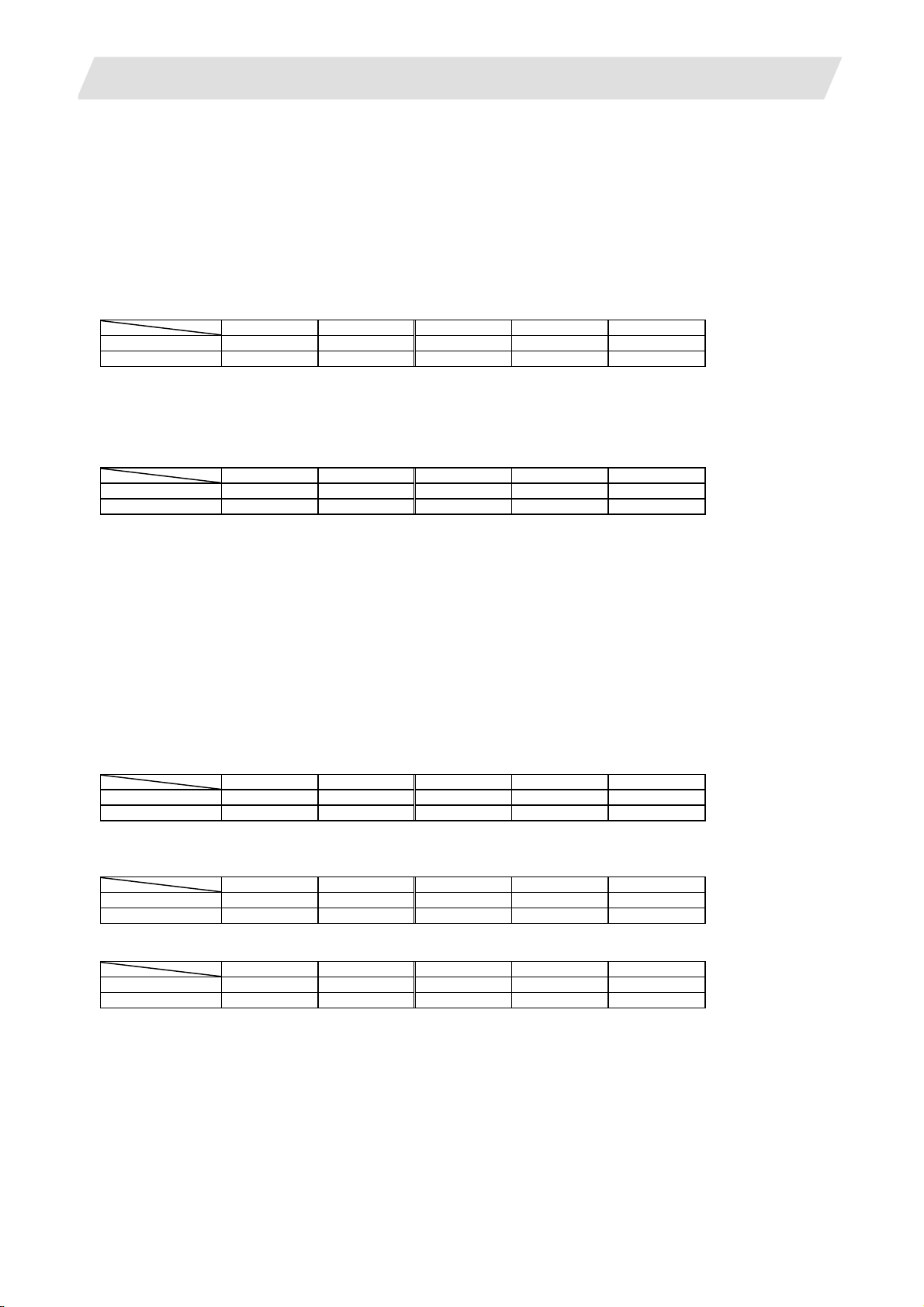
1.1.1 Number of Basic Control Axes (NC Axes)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system {3 {3 {3 {3 {3
L system {2 {2 {2 {2 {2
1.1.2 Max. Number of Axes (NC Axes + Spindles + PLC Axes)
Max. number of axes (NC axes + spindles + PLC axes)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 9 11 12 16 16
L system 9 11 12 16 16
A number of axes that are within the maximum number of axes, and that does not exceed the maximum
number given for the NC axis, spindle and PLC axis can be used.
Connection specifications of NC axis, PLC axis and spindle
There are two channels with which the servo and spindle are connected.
Maximum 8 axes can be connected with each channel.
NC axis, PLC axis, spindle : These can be connected with the optical servo communication channel (OPT).
The connection number of first axis to eighth axis is assigned to each channel.
Connect them from the first axis in order.
More than one axis must be connected with the channel 1.
Max. number of NC axes (in total for all the part systems)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 4 6 6 16 16
L system 4 7 12 16 16
Max. number of spindles
Includes analog spindles.
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 2 2 4 4 4
L system 2 3 4 4 4
Max. number of PLC axes
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 4 4 2 2 2
L system 4 4 2 2 2
1

1. Control Axes
1.1.3 Max. Number of Auxiliary Axes (MR-J2-CT)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 0 0 4 6 6
L system 0 0 4 6 6
Auxiliary axis: This can be connected to the channel (SV2) for J2-CT.
1.1.4 Number of Simultaneous Contouring Control Axes
Simultaneous control of all axes is possible as a principle in the same part system.
However, for actual use, the machine tool builder specification will apply.
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 4 4 4 4 8
L system 4 4 4 4 8
1.1.5 Max. Number of NC Axes in a Part System
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 4 6 6 8 8
L system 4 6 6 8 8
1.2 Control Part System
1.2.1 Standard Number of Part Systems
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system 1 1 1 1 1
L system 1 1 1 1 1
1.2.2 Max. Number of Part Systems
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system {1 {1 {1 {2 {2
L system {1 {2 U2 U4 U4
For actual use, the machine tool builder specification will apply.
1.2 Control Part System
2
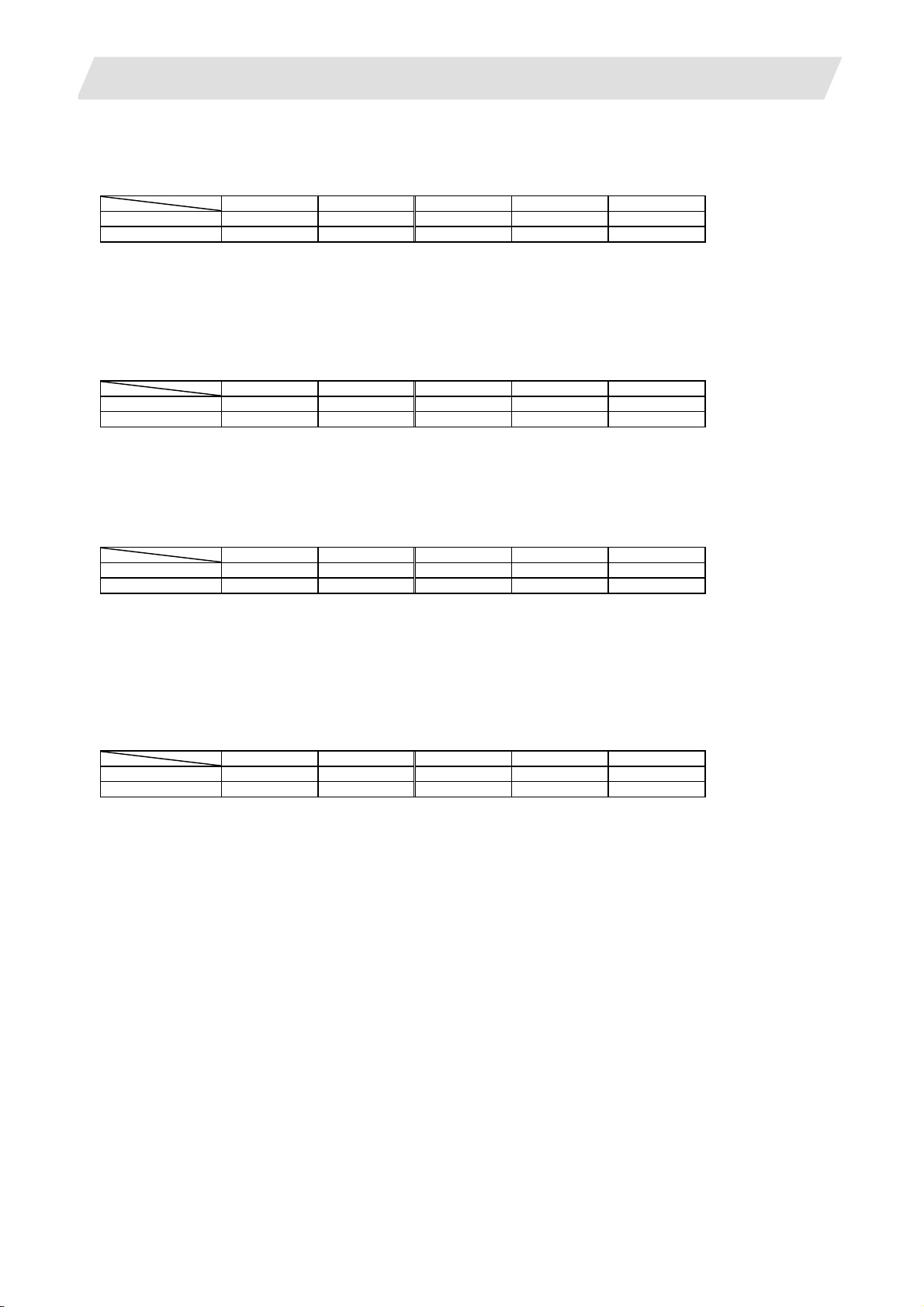
1. Control Axes
1.3 Control Axes and Operation Modes
1.3 Control Axes and Operation Modes
1.3.1 Tape (RS-232C Input) Mode
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
In this mode, operation is performed using the machining program data from the RS-232C interface built in
the NC unit. A paper tape reader must be provided if machining programs on paper tape are to be run.
1.3.2 Memory Mode
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
The machining programs stored in the memory of the NC unit are run.
1.3.3 MDI Mode
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
The MDI data stored in the memory of the NC unit is executed. Once executed, the MDI data is set to the
"setting incomplete" status, and the data will not be executed unless the "setting completed" status is
established by screen operations.
1.3.4 High-Speed Program Server Mode (CF Card in Control Unit)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - U U U
L system - - U U U
The machining program stored in CF card can be operated by installing a CF card in the control unit CF
(compact flash) card interface.
Machining programs can be copied to CF card with the front IC card or Ethernet on the input/output screen.
When a machining program stored in CF card is searched while "DS" is selected for device during operation
search, the machining program in CF card can be operated as a main program. (The operation mode is
"memory mode".) Also, when "M198 Pp;" is commanded in the main program, the machining program in CF
card can be called and operated as a sub program.
Macros such as WHILE, IF and GOTO can be used during high-speed prog ram server mode, as well.
Also, calling the sub program and macro program stored in memory or CF card is po ssible du ring hi gh-sp e ed
program server mode operation.
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
3
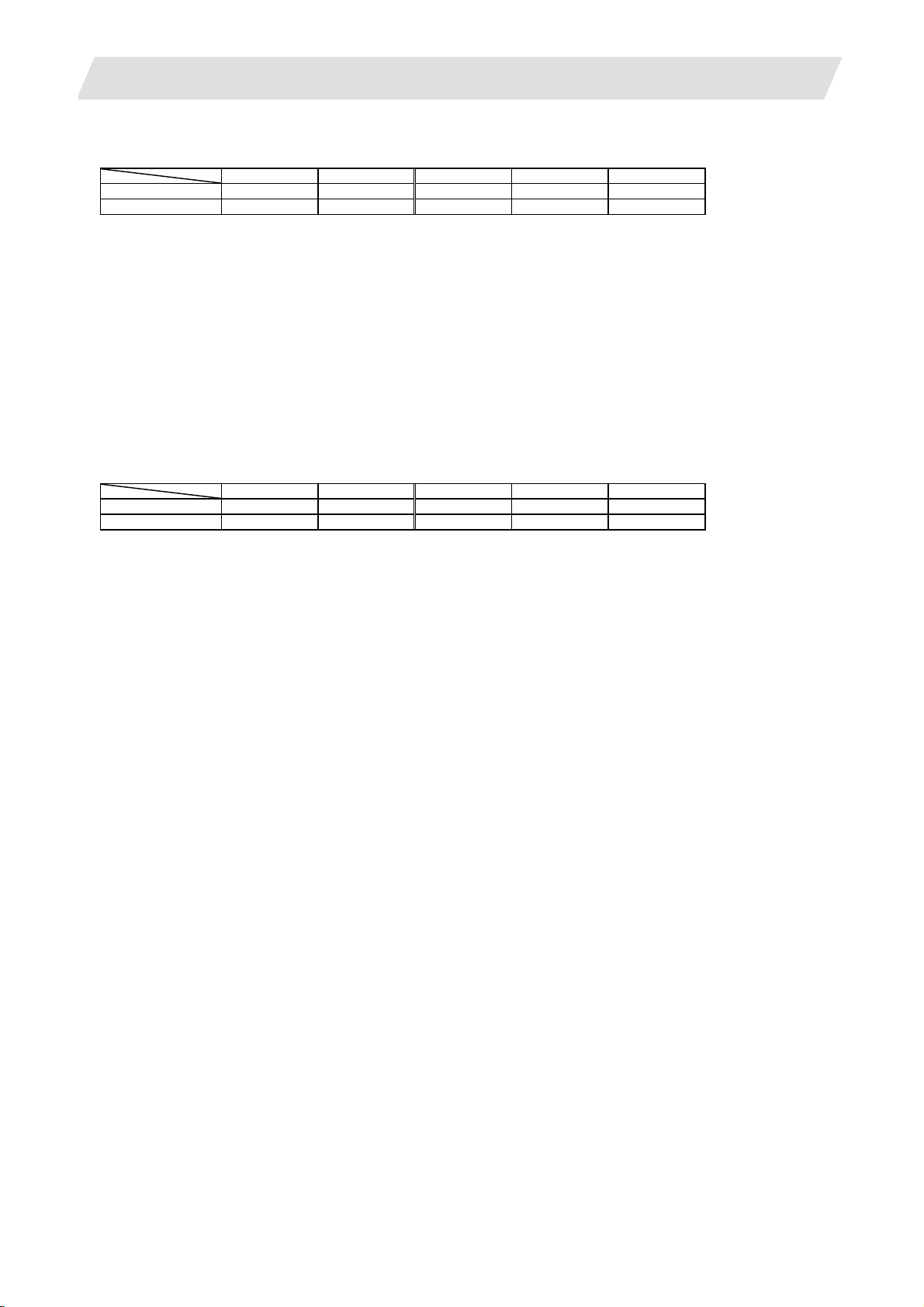
1. Control Axes
1.3 Control Axes and Operation Modes
1.3.5 Front IC Card Mode
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
{ {
{ {
U U U
-
The machining program stored in PCMCIA card can be operated by installing a PCMCIA card on the front of
control unit.
When a machining program stored in PCMCIA card is searched while "IC" is selected for device during
operation search, the machining program in PCMCIA card can be operated as a main program. (The
operation mode is "memory mode".) Also, when "M98 Pp ,Dd;" ("d" for designating a unit) is commanded in
the main program, the machining program in PCMCIA card can be called and operated as a sub program.
Macros such as WHILE, IF and GOTO can be used during IC card operation, as well.
Also, calling the sub program and macro program stored in memory or PCMCIA card is possible during IC
card operation.
1.3.6 Hard Disk Mode
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - U U U
L system - - -
The machining program stored in the hard disk can be operated when using a high-resolution type display (a
display with a hard disk mounted).
When a machining program stored in hard disk is searched while "HD" is select ed for device durin g operati on
search, the machining program in the hard disk can be operated as a main program. (The operation mode is
"memory mode".) Also, when "M98 Pp ,Dd;" ("d" for designating a unit) is commanded in the main program,
the machining program in the hard disk can be called and operated as a sub program.
Macros such as WHILE, IF and GOTO can be used during hard disk operation, as well.
Also, calling the sub program and macro program stored in memory or the hard disk is possible during hard
disk operation.
4
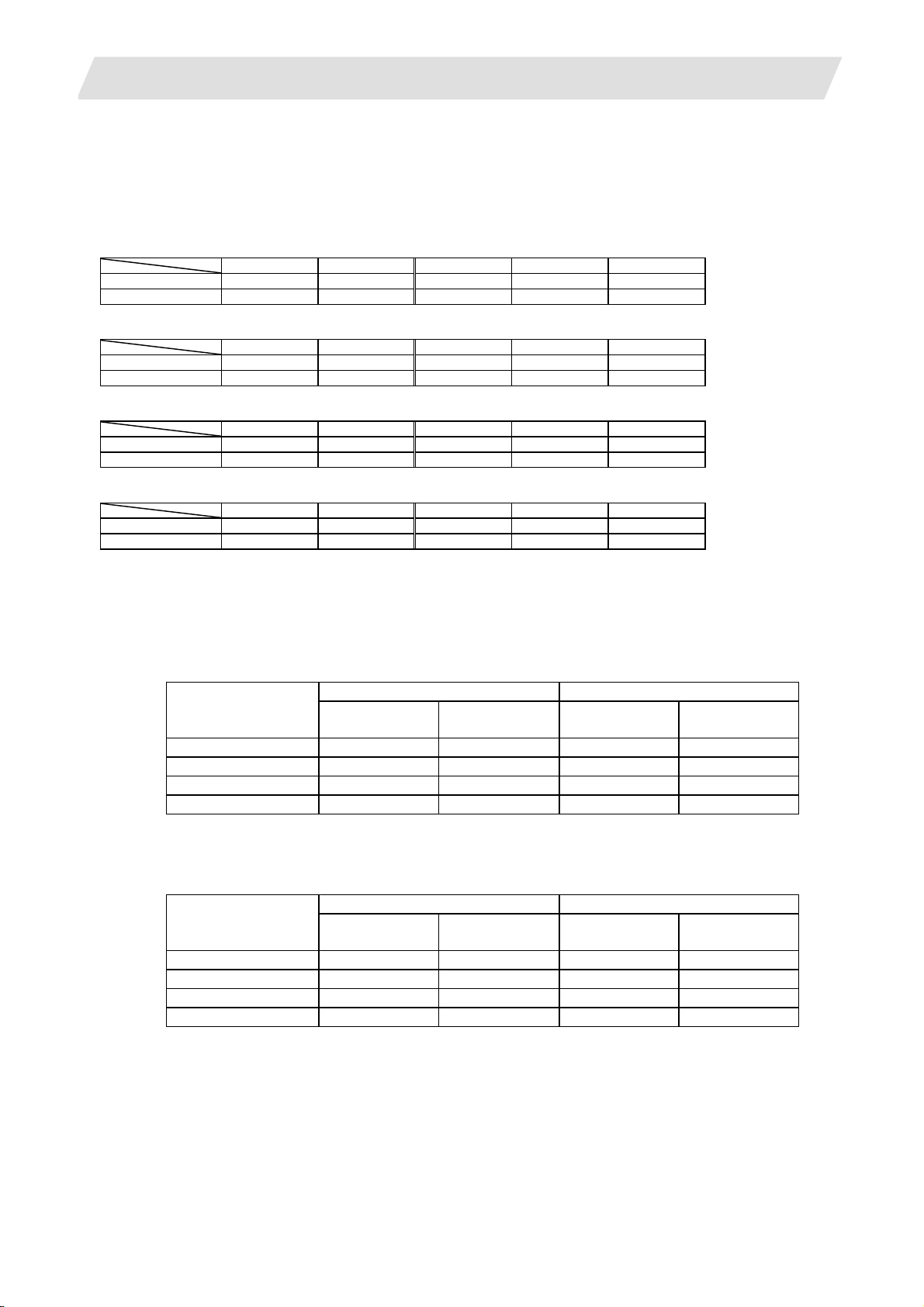
2. Input Command
2.1 Data Increment
2. Input Command
2.1 Data Increment
2.1.1 Least Command Increment
Least command increment: 1 µm (Input setting increment 1µm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
Least command increment: 0.1 µm (Input setting increment 0.1µm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
Least command increment: 0.01 µm (10nm) (Input setting increment 10nm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - U U
L system - - - U U
Least command increment: 0.001 µm (1nm) (Input setting increment 1nm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - U U
L system - - - U U
The data increment handled in the controller includes the input setting increment and command increment.
Each type is set with parameters.
(1) The input setting increment indicates the increment handled in the internal processing of the
controller.
The counter and tool compensation data, etc., input from the screen is handled with this increment.
This increment is applied per part system (1st to 4th part system, PLC axis).
Input setting
increment
(parameter)
1µm (B) 0.001 0.001 0.0001 0.001
0.1µm (C) 0.0001 0.0001 0.00001 0.0001
10nm (D) 0.00001 0.00001 0.000001 0.00001
1nm (E) 0.000001 0.000001 0.0000001 0.000001
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ {
{ {
U U U
U U U
Metric unit system Inch unit system
Linear axis
(Unit = mm)
Rotary axis
(Unit =
°)
Linear axis
(Unit = inch)
Rotary axis
(Unit = °)
(Note) The inch and metric systems cannot be used together.
(2) The command increment indicates the command increment of the movement command in the machining
program. This can be set per axis.
Command
increment
(parameter)
Metric unit system Inch unit system
Linear axis
(Unit = mm)
Rotary axis
(Unit =
°)
Linear axis
(Unit = inch)
Rotary axis
(Unit = °)
10 0.001 0.001 0.0001 0.001
100 0.01 0.01 0.001 0.01
1000 0.1 0.1 0.01 0.1
10000 1.0 1.0 0.1 1.0
(Note) The inch and metric systems cannot be used together.
5
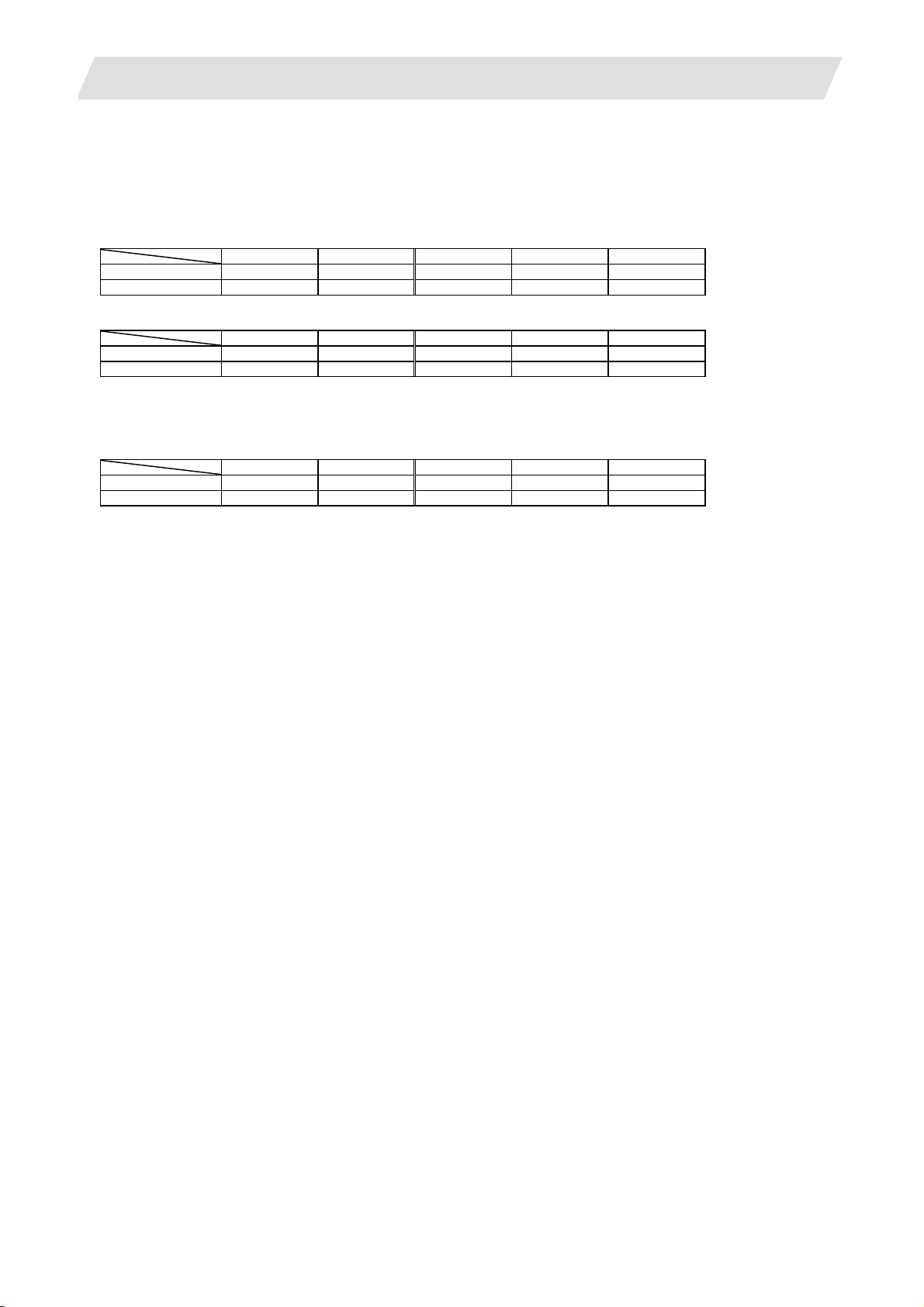
2. Input Command
2.1 Data Increment
2.1.2 Least Control Increment
The least control increment includes 0.01µm and 0.001µm.
These are increments which determine the NC's internal operation accuracy.
Least Control Increment 0.01µm (10nm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
Least Control Increment 0.001µm (1nm)
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - U U
L system - - - U U
2.1.3 Indexing Increment
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - -
L system - -
This function limits the command value for the rotary axis.
This can be used for indexing the rotary table, etc. It is possible to cause a program error with a program
command other than an indexing increment (parameter setting value).
(Example) When the indexing increment setting value is 2 degrees, only command with the 2-degree
increment are possible.
G90 G01 C102. 000 ; … Moves to the 102 degree angle.
G90 G01 C101. 000 : … Program error
G90 G01 C102 ; … Moves to the 102 degree angle. (Decimal point type II)
{ { {
{ { {
6
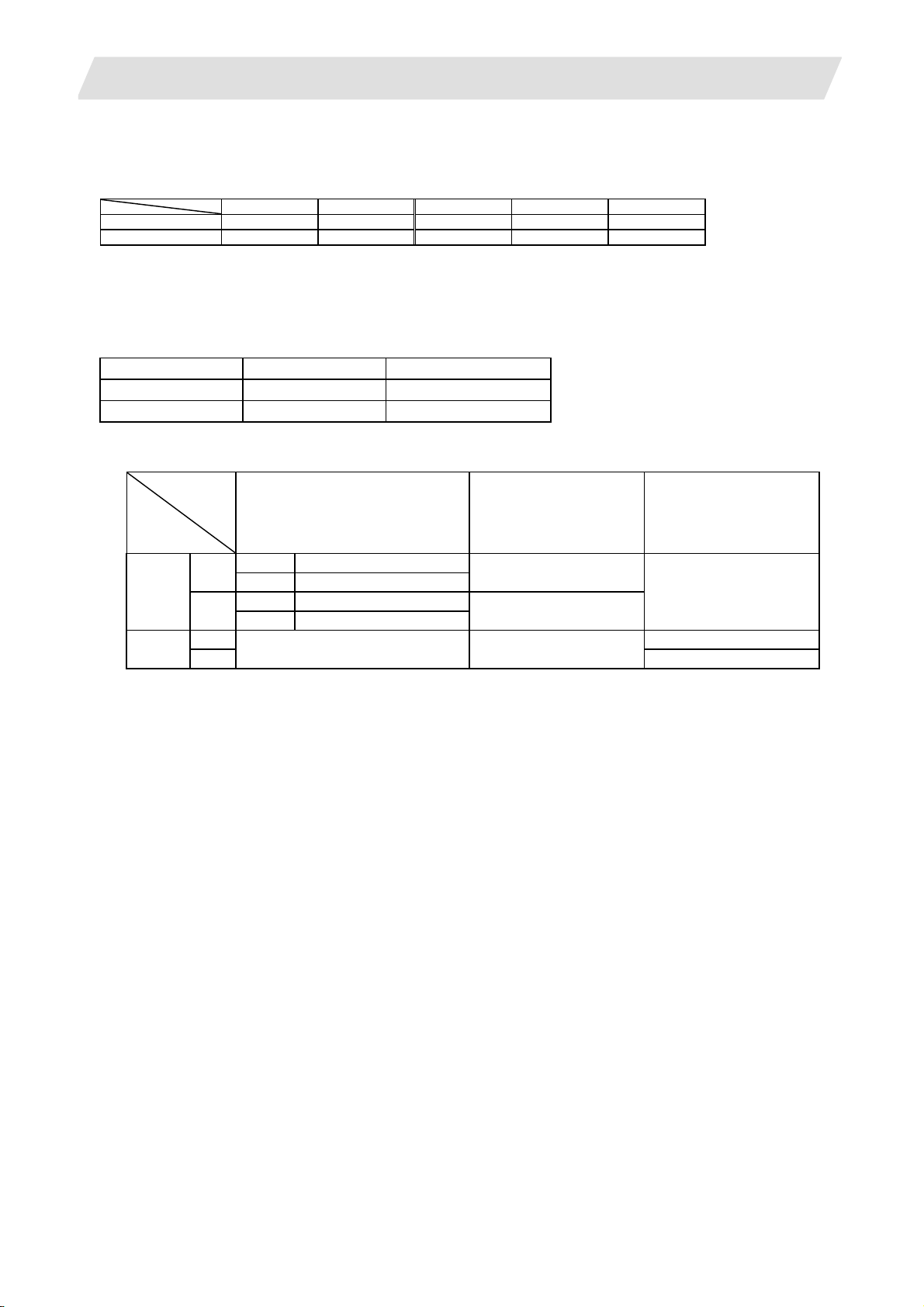
2. Input Command
2.2 Unit System
2.2 Unit System
2.2.1 Inch/Metric Changeover
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
The unit systems of the data handled in the controller include the metric unit system and inch unit system.
The unit (inch/mm) for the setting and display, as well as for the handle/incremental feed can be switched with
either the parameters or machining program (G20/G21 command).
An option is required when the unit is switched with the machining program command.
Unit system Length data Meaning
Metric unit system 1.0 1.0 mm
Inch unit system 1.0 1.0 inch
(Note) For the angle data, 1.0 means 1 degree (°) regardless of the unit system.
Data
Parameter
0
A
1
B
0 Metric unit system
1
(Note 1) The parameter changeover is valid after the power is turned ON again.
(Note 2) The unit system for the PLC axis can be switched wit h a parameter differe nt from the one u sed
with the NC axis.
The PLC axis unit system cannot be switched with the machining program (G20/G21
command).
{ {
{ {
Machining program
G20 Inch unit system
G21 Metric unit system
G20 Inch unit system
G21 Metric unit system
U U U
U U U
Screen data
(Compensation amount,
user parameter,
counter, etc.)
/ Feedrate of handle, etc.
Metric unit system
Inch unit system
Not affected Not affected
Machine parameter
/ PLC I/F machine
position, etc.
Not affected
Inch unit system
(Note 3) When the power is turned ON or resetting is performed, the command increment depends on
the parameter setting.
7
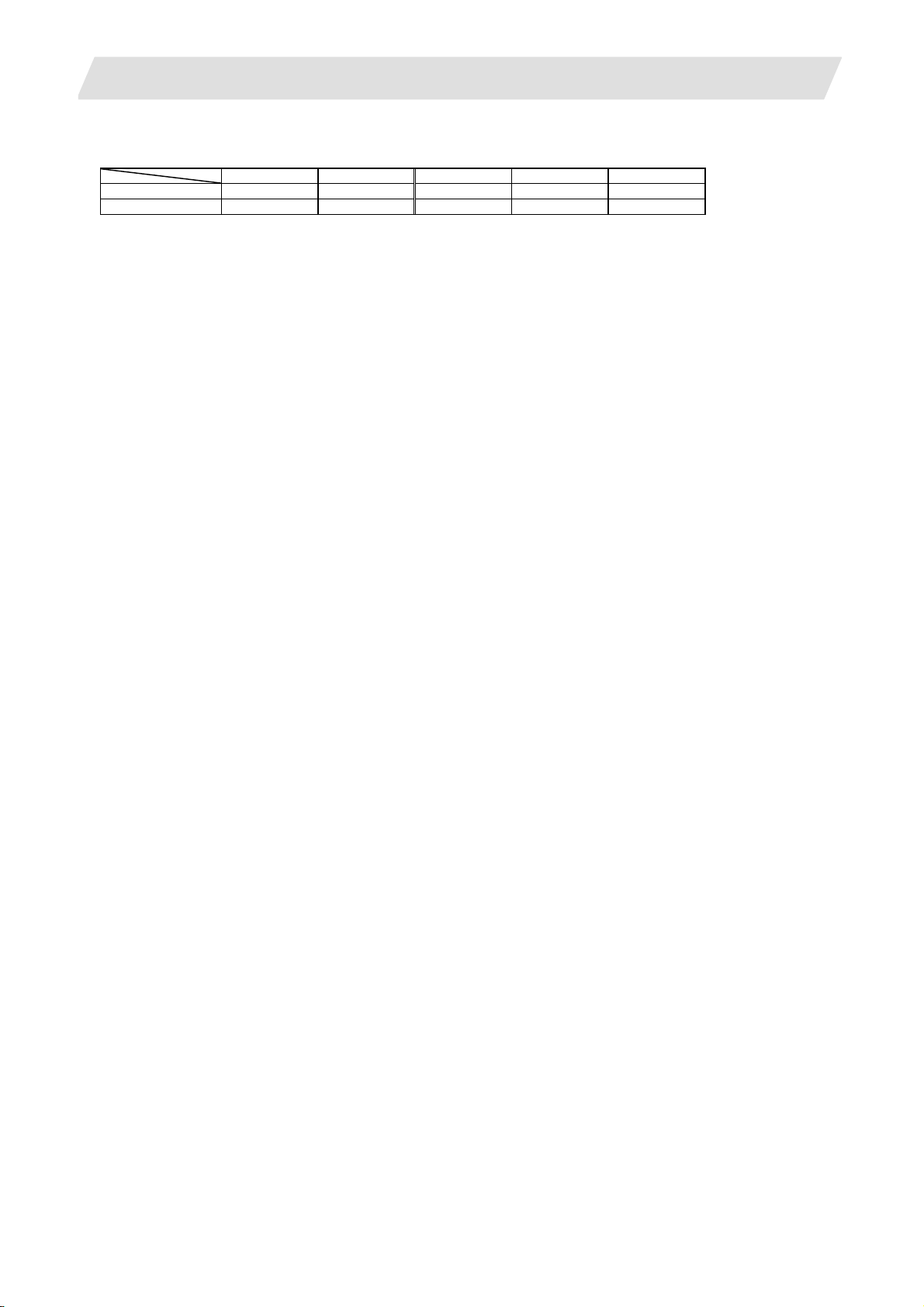
2. Input Command
2.2 Unit System
2.2.2 Input Command Increment Tenfold
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system - - - - -
{ { { { {
The program's command increment can be multiplied by an arbitrary scale with the parameter designation.
This function is valid when a decimal point is not used for the command increment.
For example, when running a machining program already created with a 10µm input command increment
with a CNC unit for which the command increment is set to 1µm and this function's parameter value is set to
"10", machining similar to before this function is possible. The scale is set with the parameters.
(Note 1) This function cannot be used for the dwell function G04_X_(P_);.
(Note 2) This function cannot be used for the compensation amount of the tool offset input.
(Note 3) This function can be used when decimal point type I is valid, but cannot be used when decimal
point type II is valid.
8
2. Input Command
2.3 Program Format
2.3 Program Format
2.3.1 Program Format
The G-code of L system is selected by parameter.
This specification manual explains the G function with G-code list 3 as standard.
2.3.1.1 Format 1 for Lathe (G-code List 2, 3)
2.3.1.2 Format 2 for Lathe (G-code List 4, 5)
2.3.1.3 Special Format for Lathe (G-code List 6, 7)
2.3.1.4 Format 1 for Machining Center (G-code List 1)
2.3.1.5 Format 2 for Machining Center (M2 Format)
2.3.1.6 MITSUBISHI CNC Special Format
The formats of the turning fixed cycles (G77 to G79), multiple repetitive turning fixed cycles (G71 to G76) and
drilling fixed cycles (G80 to G89) can be switched to the MITSUBISHI CNC special formats.
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - - -
L system
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - - -
L system
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - - -
L system
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system - - - - -
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system - - - - -
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - - -
L system
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
{ {
{ {
U U U
U U U
9
2. Input Command
2.4 Command Value
2.4 Command Value
2.4.1 Decimal Point Input I, II
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
There are two types of the decimal point input commands and they can be selected by parameter.
(1) Decimal point input type I
When axis coordinates and other data are issued in machining program commands, the assignment of
the program data can be simplified by using the decimal point input. The minimum digit of a command
not using a decimal point is the same as the least command increment.
Usable addresses can be applied not only to axis coordinate position but also to speed commands and
dwell commands.
The decimal point position serves as the millimetre unit in the metric mode, as the inch unit in the inch
mode and as the second unit in a time designation of dwell command.
(2) Decimal point input type II
As opposed to type I, when there is no decimal point, the final digit serves as the millimetre unit in the
metric mode, as the inch unit in the inch mode and as the second unit in the time designation.
The "." (point) must be added when commands below the decimal point are required.
G00 X100. Y-200.5 X100mm, Y-200.5mm
G1 X100 F20. X100µm, F20mm/min X100mm, F20mm/min
G2 Y200 F100 (*1) Y200µm, F100mm/min Y200mm, F100mm/min
G4 X1.5 Dwell 1.5 s
G4 X2 2ms 2s
(*1) The F unit is mm/min for either type (inch system : inch/min).
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
Unit interpretation (for metric system)
Type I Type II
←
←
10
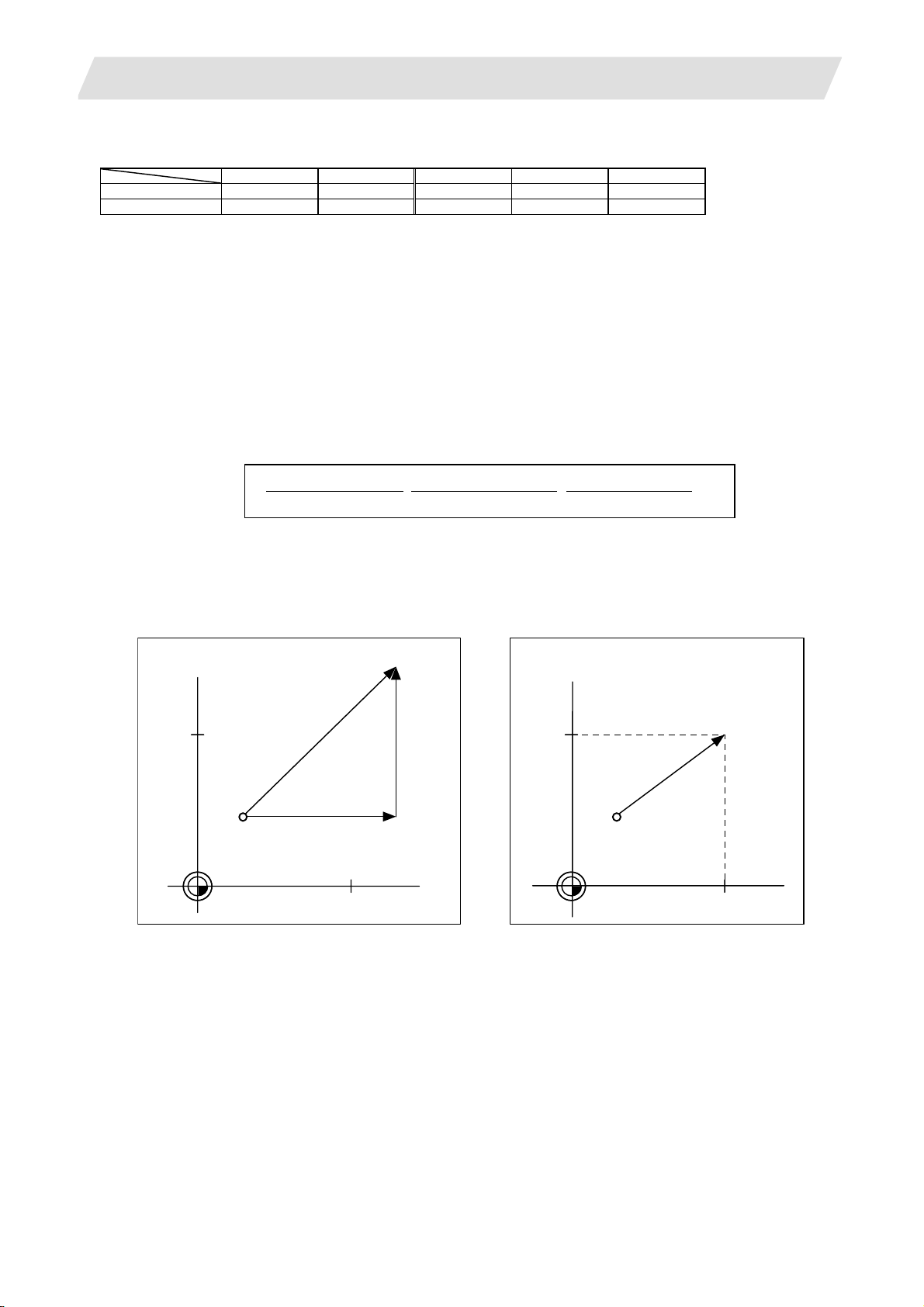
2. Input Command
2.4 Command Value
2.4.2 Absolute/Incremental Command
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
(1) M system
When axis coordinate data is issued in a machining p rogram co mmand, eithe r the increment al comma nd
method (G91) that commands a relative distance from the current position or the absolute command
method (G90) that moves to a designated position in a predetermined coordinate system can be
selected.
The absolute and incremental commands can be both used in one block, and are switched with G90 or
G91. However, the arc radius desig nation (R) and a rc center design ation (I, J, K) always use in crement al
designations.
G90 ... Absolute command (absolute command)
G91 ... Incremental command (incremental command)
These G codes can be commanded multiple times in one block.
Example
(Note 1) As with the memory command, if there is no G90/G91 designation in the MDI command, the
previously executed modal will be followed.
(Incremental command) (Absolute command)
G 91 X 100. Y100. ;
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
G90 X100. G91 Y200. G90 Z300.
Absolute position Incremental position Absolute position
G 90 X 100. Y100. ;
End
point
;
Y100.
Current position
(0, 0)
X 100.
X 100.
Y100.
Y100.
Current position
Program coordinate
(0, 0)
End point
X100.
11
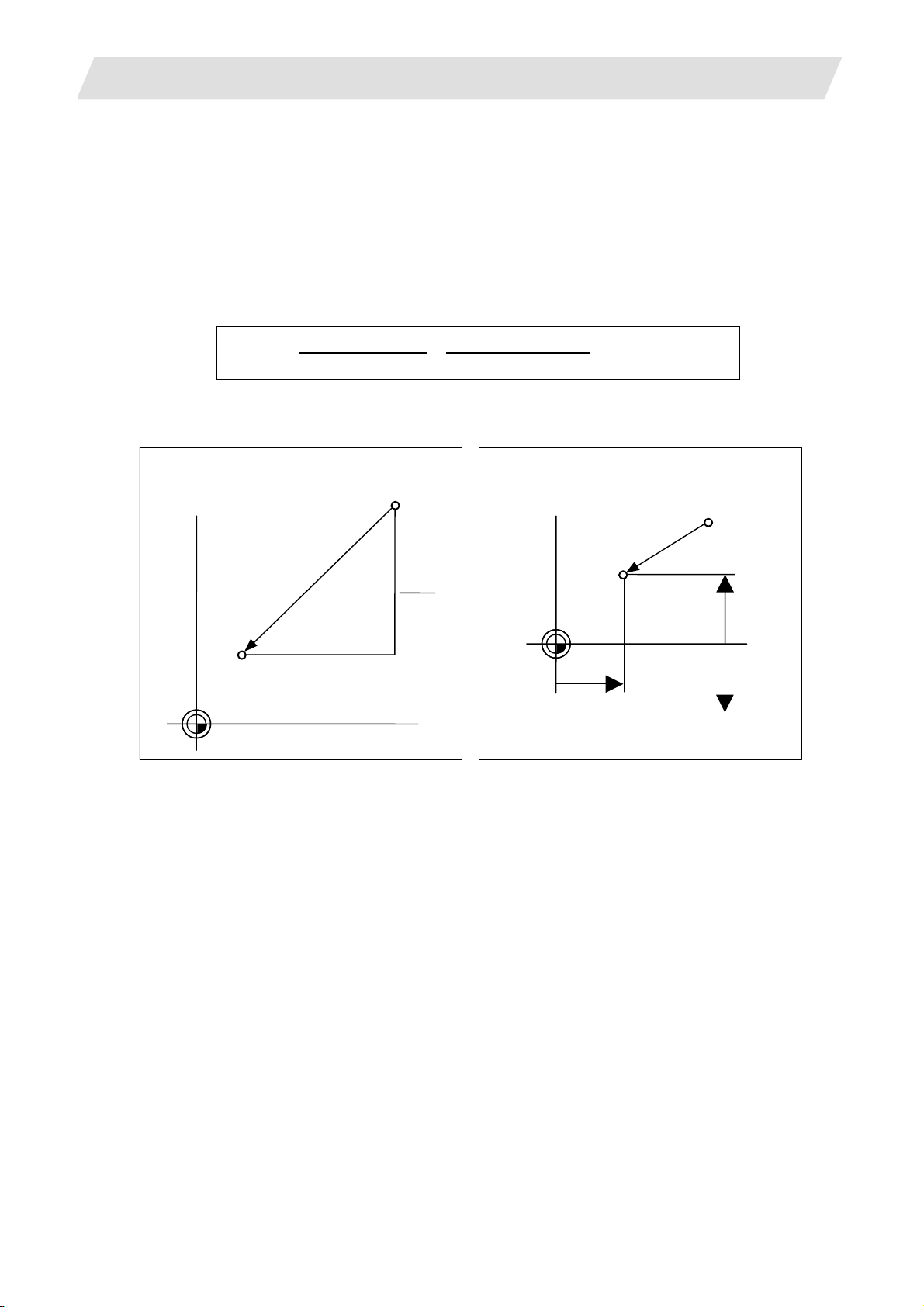
2. Input Command
2.4 Command Value
(2) L system
When axis coordinate data is issued in a machining p rogram co mmand, eithe r the increment al comma nd
method that commands a relative distance from the current position or the absolute command method
that moves to a designated position in a predetermined coordinate system can be selected.
When issuing an incremental command, register the axis address to be commanded as the incremental
axis name in the parameter. However, the arc radius designation (R) and arc center designation (I, J, K)
always use incremental designations.
Absolute command (absolute command) ... X, Z
Incremental command (incremental command) ... U, W
G00 X100. W200. ;
Absolute position Incremental position
(Incremental command)
(Absolute command)
G 00 X x1 Z z1 ;
Current position
X X
Current position
Example
G 00 U – u1 W – w1 ;
End point
u1
2
x1
Z
End point
w1
z1
Z
(0,0)
The above drawing shows the case
for the diameter command.
(Note) Absolute command and incremental command can be switched by the parameter. In addition to
the command method using the axis addresses as indicated above, a command method using G
code (G90/G91) may be selected.
The above drawing shows the case
for the diameter command.
12
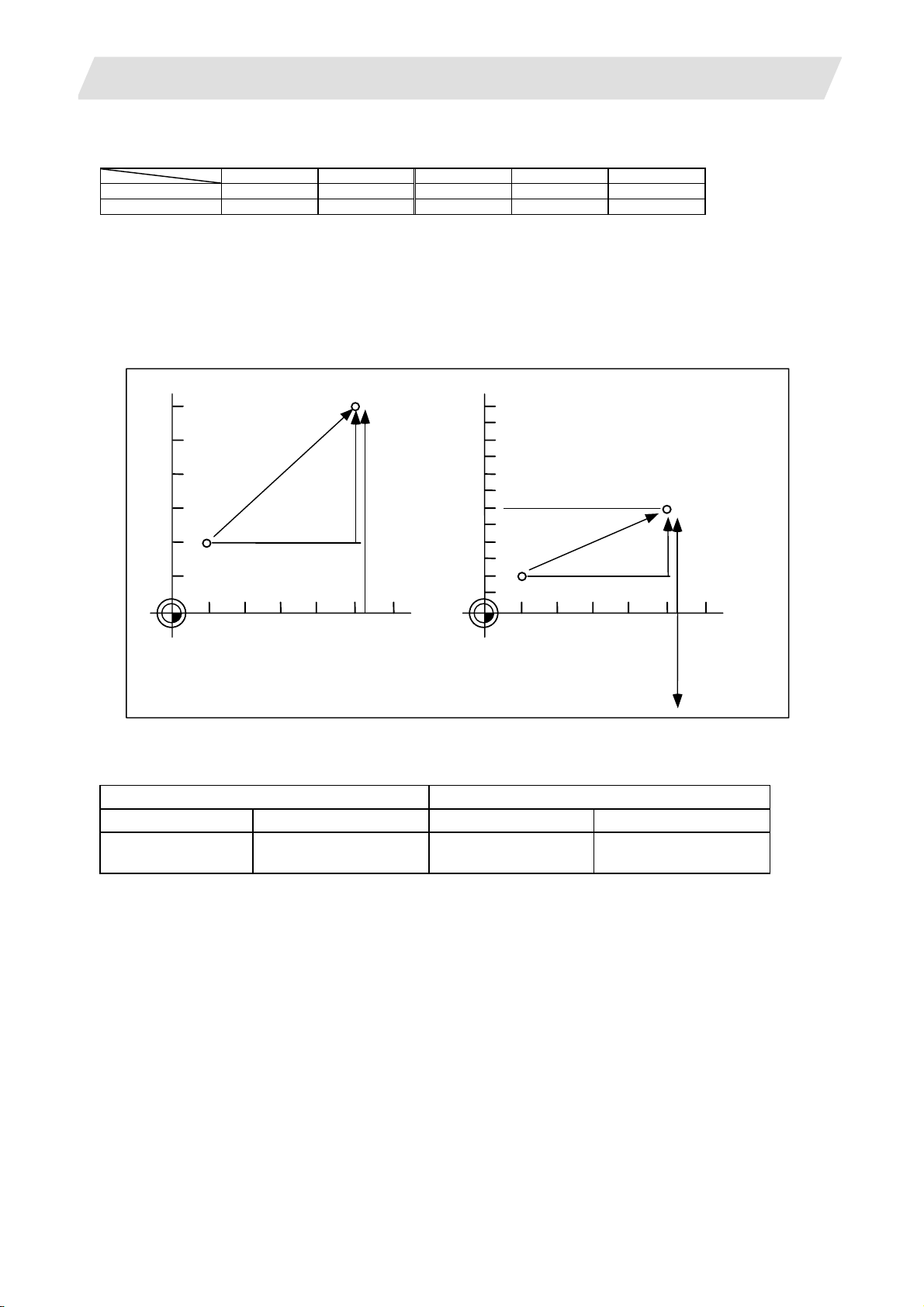
2. Input Command
2.4 Command Value
2.4.3 Diameter/Radius Designation
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system - - - - -
L system
For axis command value, the radius designation or diameter designation can be changed over with
parameters.
When the diameter designation is selected, the scale of the length of the selected axis is doubled. (For
instance, an actual length of 1 mm will be treated as 2 mm.)
This function is used when programming the workpiece dimensions on a lathe as diameters. Changing over
from the diameter designation to the radius designation or vice versa can be set separately for each axis.
X-axis radius designation
{ { { { {
X-axis diameter designation
X
X
u4
x6
u4
x6
Z
Coordinate zero point
Coordinate zero point
The difference in the diameter designation and radius designation is shown below.
Absolute command Incremental command
Radius designation Diameter designation Radius designation Diameter designation
Actual movement
amount = x1
Actual movement
amount = 2 x1
Actual movement
amount = u1
Actual movement
amount = 2 u1
Z
13
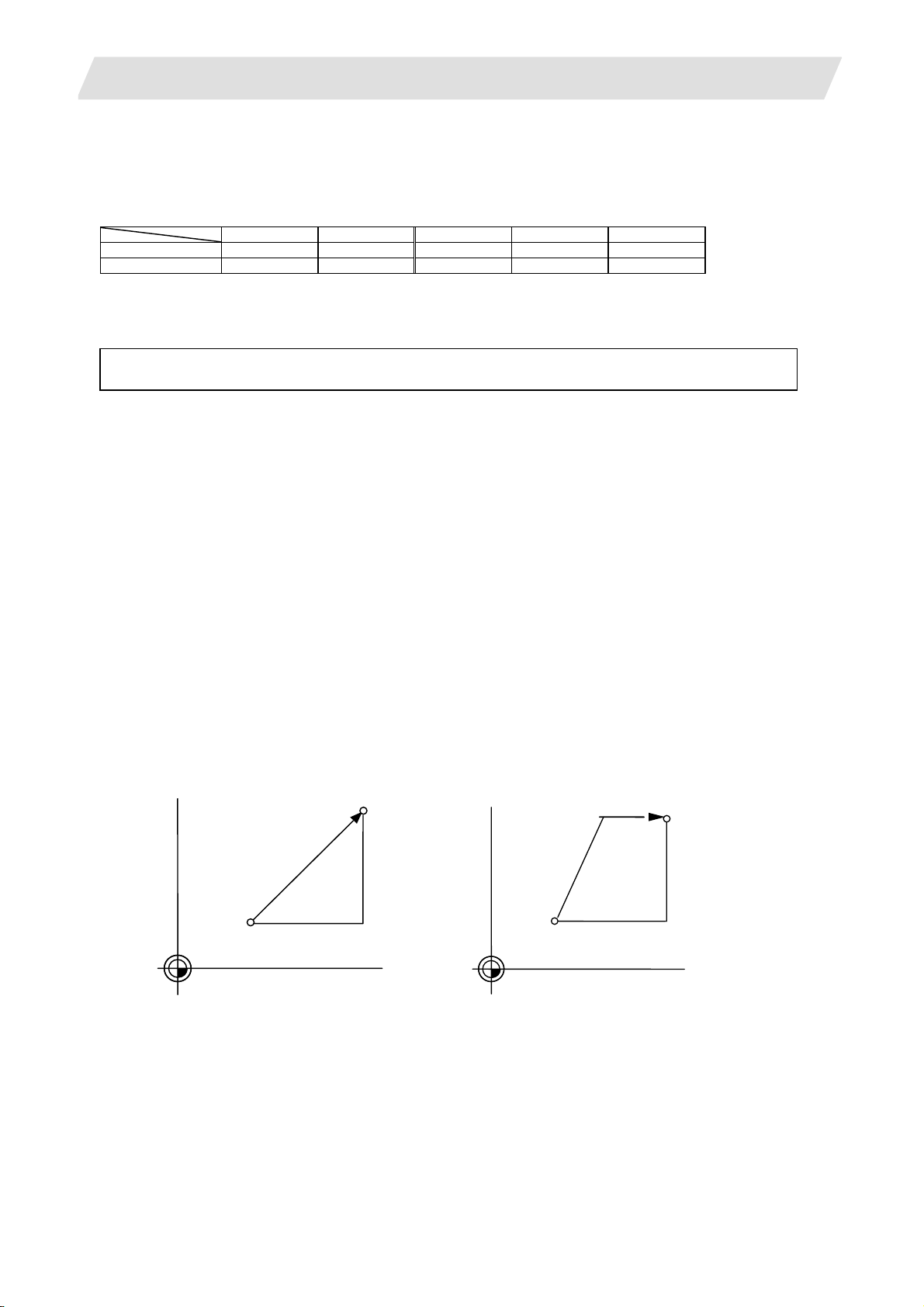
3. Positioning/Interpolat ion
3.1 Positioning
3. Positioning/Interpolation
3.1 Positioning
3.1.1 Positioning
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system
This function carries out high-speed positioning with rapid traverse rate, following the movement command
given in a program.
G00 Xx1 Yy1 Zz1 ; (Also possible for additional axes A, B, C, U, V, W simultaneously)
Xx1, Yy1, Zz1: Position data
The above command positions the tool by rapid traverse. The tool path takes the shortest distance to the end
point in the form of a straight line.
For details on the rapid traverse feed rate of the NC, re fer to the section entitled " Rapid Traverse Rate". Since
the actual rapid traverse feed rate depends on the machine, refer to the specifications of the machine
concerned.
(1) The rapid traverse feed rate for each axis can be set independently with parameters.
(2) The number of axes which can be driven simultaneously depends on the specifications (number of
simultaneously controlled axes). The axes can be used in any combination within this range.
(3) The feed rate is controlled within the range that it does not exceed the rapid traverse rate of each axis
and so that the shortest time is taken. (Linear type)
Parameter setting enables movement at the rapid traverse rates of the respective axes independently for
each axis. In this case, the tool path does not take the form of a straight line to th e end point. (Non-Li near
type)
(Example)
Linear type
(Moves lineary to the end point.)
G 00 G 91 X 100. Y 100. ;
{ { { { {
{ { { { {
(
Example)
Non-linear type
(Each axis moves at each parameter speed.)
G 00 G 91 X 100. Y 100. ;
Y
Current position
100.
End point
100.
Y
End point
100.
Current position
X
100.
X
(4) The tool is always accelerated at the start of the program command block and decelerated at the end
of the block.
14
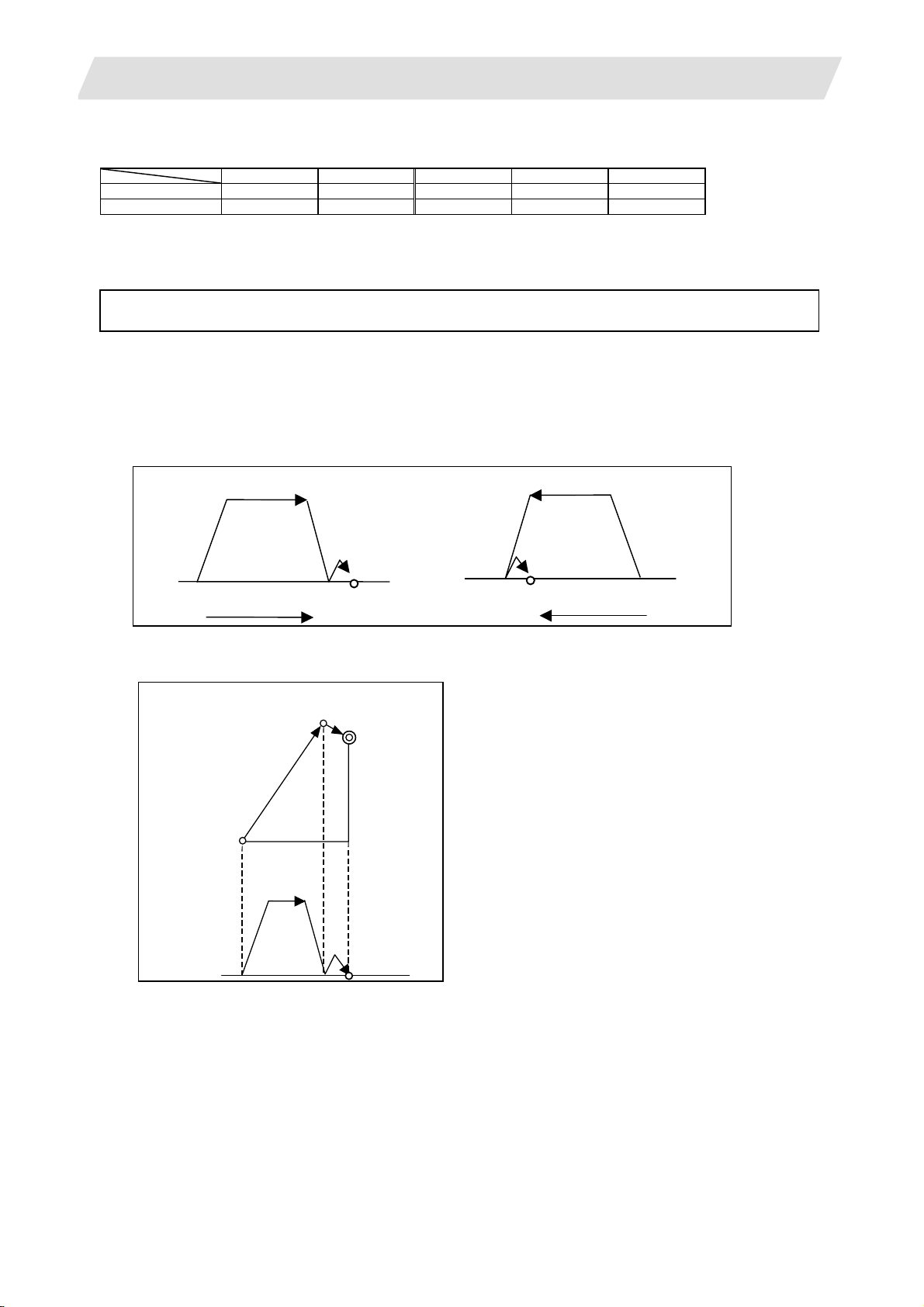
3. Positioning/Interpolat ion
3.1 Positioning
3.1.2 Unidirectional Positioning
M70 Type B M70 Type A M720 M730 M750
M system
L system - - - - -
The G60 command always moves the tool to the final position in a direction determined with parameters.
The tool can be positioned without backlash.
G60 Xx1 Yy1 Zz1 ; (Also possible for additional axes A, B, C, U, V, W simultaneously)
Xx1, Yy1, Zz1: Position data
With the above command, the tool is first moved to a position distanced from the end point by an amount
equivalent to the creep distance (parameter setting) with rapid traverse and then moved to its final positio n.
For details on the rapid traverse feed rate of the NC, refer to the section entitled "Rapid Traverse Rate". Since
the actual rapid traverse feed rate depends on the machine, refer to the specifications of the machine
concerned.
Positioning to the final point is shown below (when this positioning is in the "+" direction.)
{ {
U U U
– +
(Example)
G60 G91 X100. Y100. ;
Interim point
End point
1. The rapid traverse rate for each axis is the value
set with parameters as the G00 speed.
2. The vector speed to the interim point is the value
produced by combining the distance and
respective speeds.
Y100.
3. The creep distance between the interim and end
points can be set independently for each axis by
parameters.
Current position
X100.
(Note 1) The processing of the above pattern will be followed even for the machine lock and Z-axis
command cancel.
(Note 2) On the creep distance, the tool is moved with rapid traverse.
(Note 3) G60 is valid even for positioning in drilling in the fixed cycle.
(Note 4) When the mirror image function is on, the tool will be moved in the reverse direction by mirror
image as far as the interim position, but operation over the creep distance with the final advan ce
will not be affected by the mirror image.
15
 Loading...
Loading...