Mitsubishi 4DQ5 Repair Manual

SERVICE
MANUAL
MITSUBISHI
DIESEL
4
ENGINE
5


GENERAL
INDEX
MAJOR DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION AND
REASSEMBLY
LUBRICATING SYSTEM
COOLING SYSTEM
FUEL
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
BENCH TEST
MAINTENANCE STANDARDS
SYSTEM
REPAIR
..........................................
..............................................
5
8
16
37
49
52
56
71
87
89
SEALANT APPLICATION DATA
TIGHTENING TORQUE
SPECIAL SERVICE TOOLS 105
TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
.............................................
102
103
110

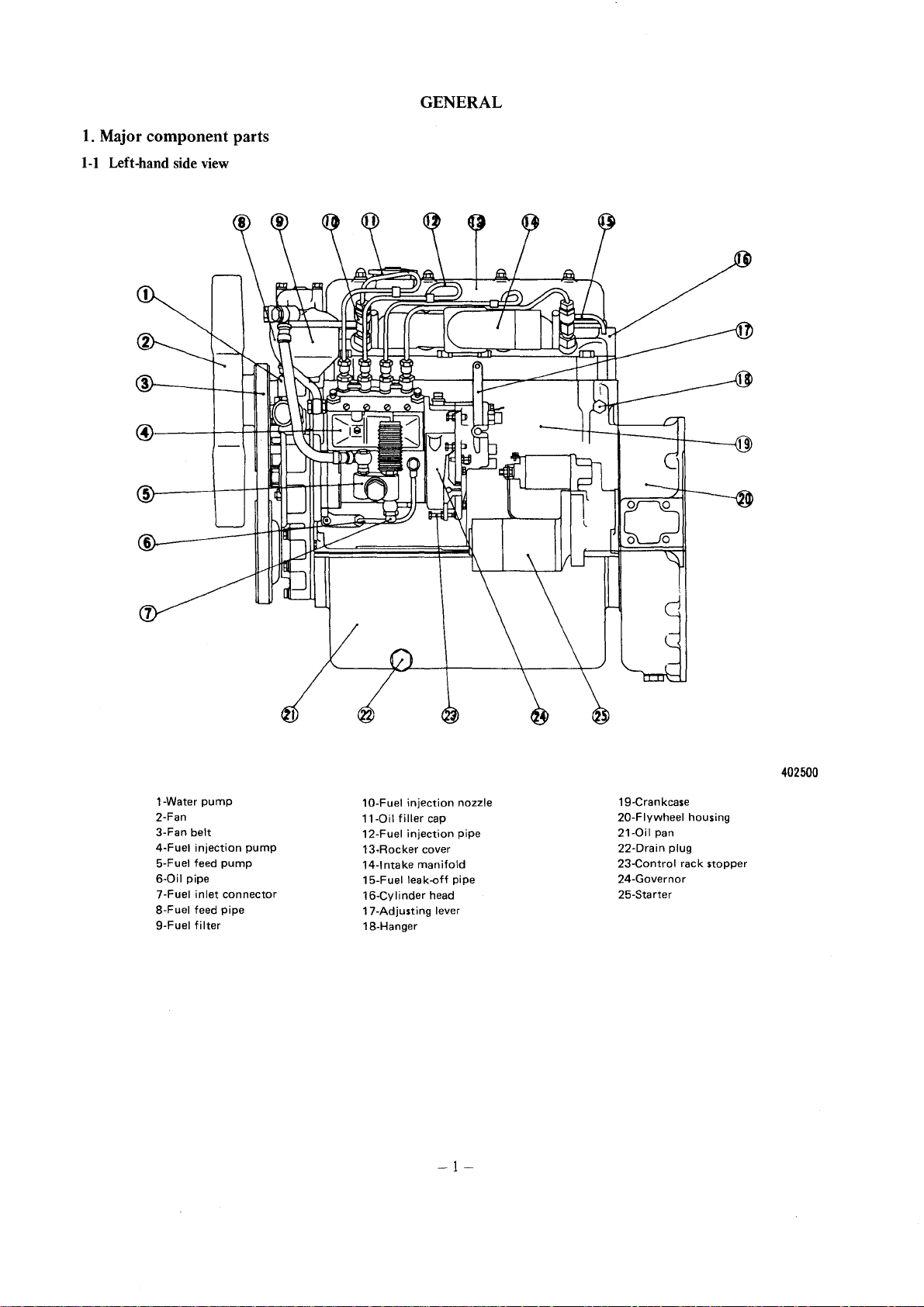
GENERAL
1. Major
1-1
component
Left-hand side view
parts
1-Water
pump
2-Fan
3-Fan
belt
4-Fuel
injection
5-Fuel feed
6-0il
pipe
7-Fuel
inlet
8-Fuel feed
9-Fuel
filter
pump
pump
connector
pipe
10-Fuel
injection
11-0il
filler
injection
12-Fuel
13.Rocker
14-lntake
15-Fuel
16-Cylinder
17-Adjusting
18-Hanger
manifold
leak-off
cap
cover
head
lever
-1-
nozzle
pipe
pipe
19-Cran kcase
20-Flywheel
21-0il
pan
22-Drain
23-Control
24-Governor
25-Starter
plug
housing
rack
402500
stopper
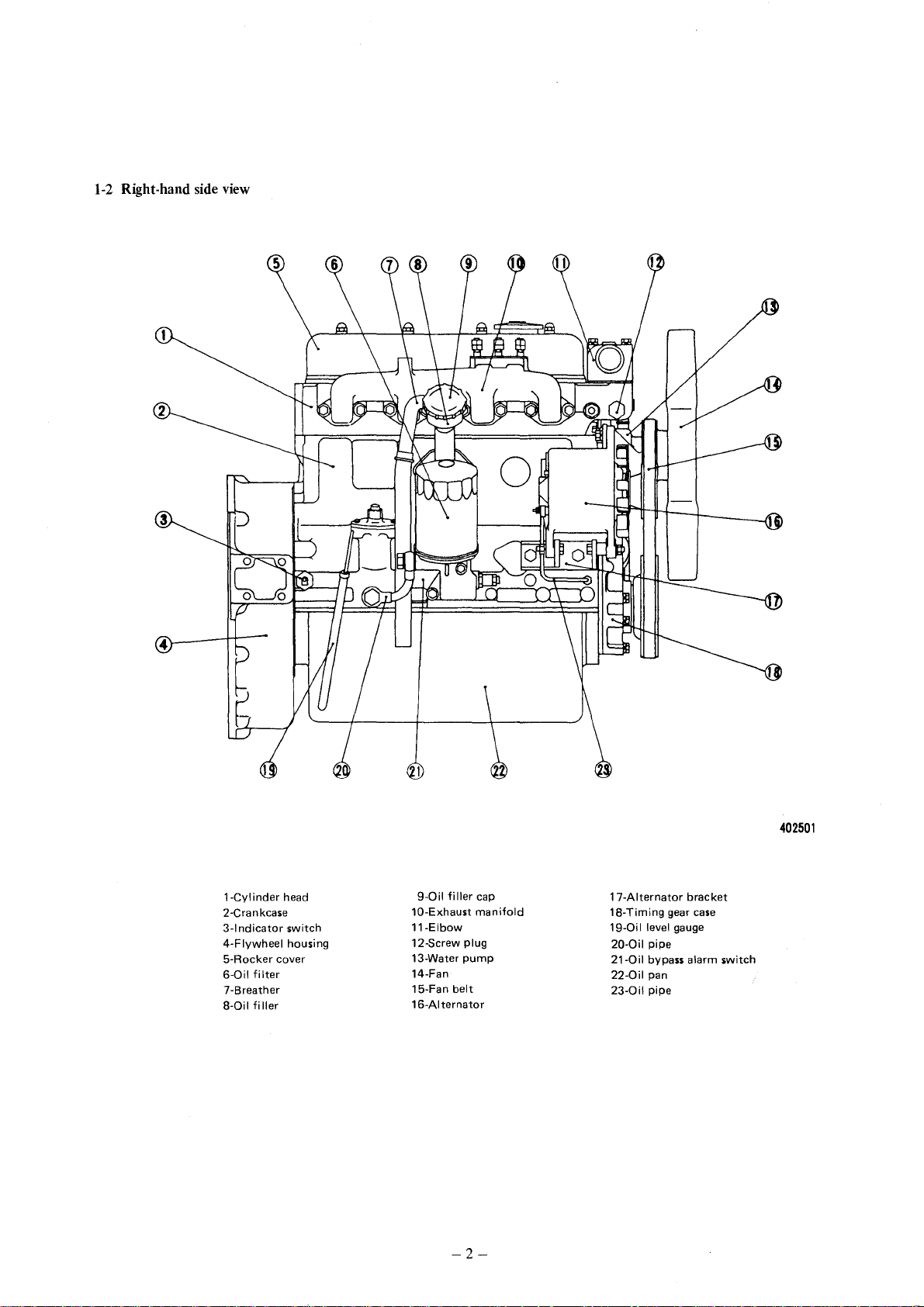
1-2 Right-hand side view
l-Cylinder
2-Crankcase
3-1
ndicator
4-Flywheel
5-Rocker
6-0il
7-Breather
8-0il
cover
filter
filler
head
switch
housing
9-0il
filler
10-Exhaust
ll-Elbow
l2-Screw
13-Water
14-Fan
l5-Fan
16-Alternator
plug
pump
belt
-2-
cap
manifold
l7-Alternator
18-Timing
19-0il
level gauge
20-0il
pipe
21-0il
bypass alarm
22-0il
pan
23-0il
pipe
gear
402501
bracket
case
switch
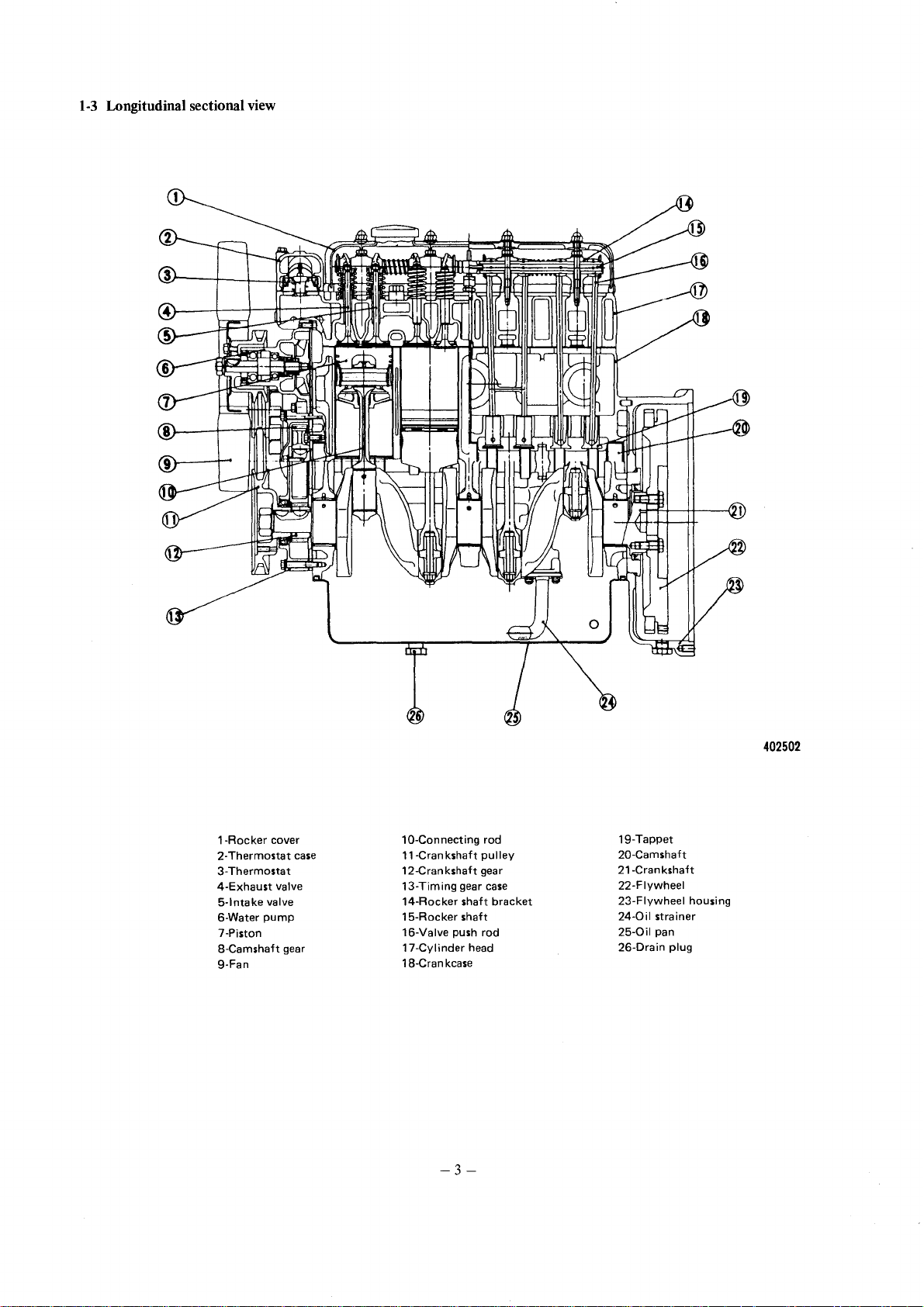
1-3
Longitudinal sectional view
1-Rocker
23-Thermostat
4-Exhaust
5-lntake
6-Water
7-Piston
8-Camshaft gear
9-Fan
cover
Thermostat
valve
valve
pump
case
10-Connecting rod
11-Cran
kshaft
gear
shaft
kcase
shaft
head
pu
case
bracket
12-Crankshaft gear
13-Timing
14-Rocker
15-Rocker
16-Valve push rod
17-Cylinder
18-Cran
-3-
lIey
19-Tappet
20-Camshaft
21-Crankshaft
22-Flywheel
23-Flywheel
24-0il
strainer
25-0il
pan
26-Drain plug
402502
housing
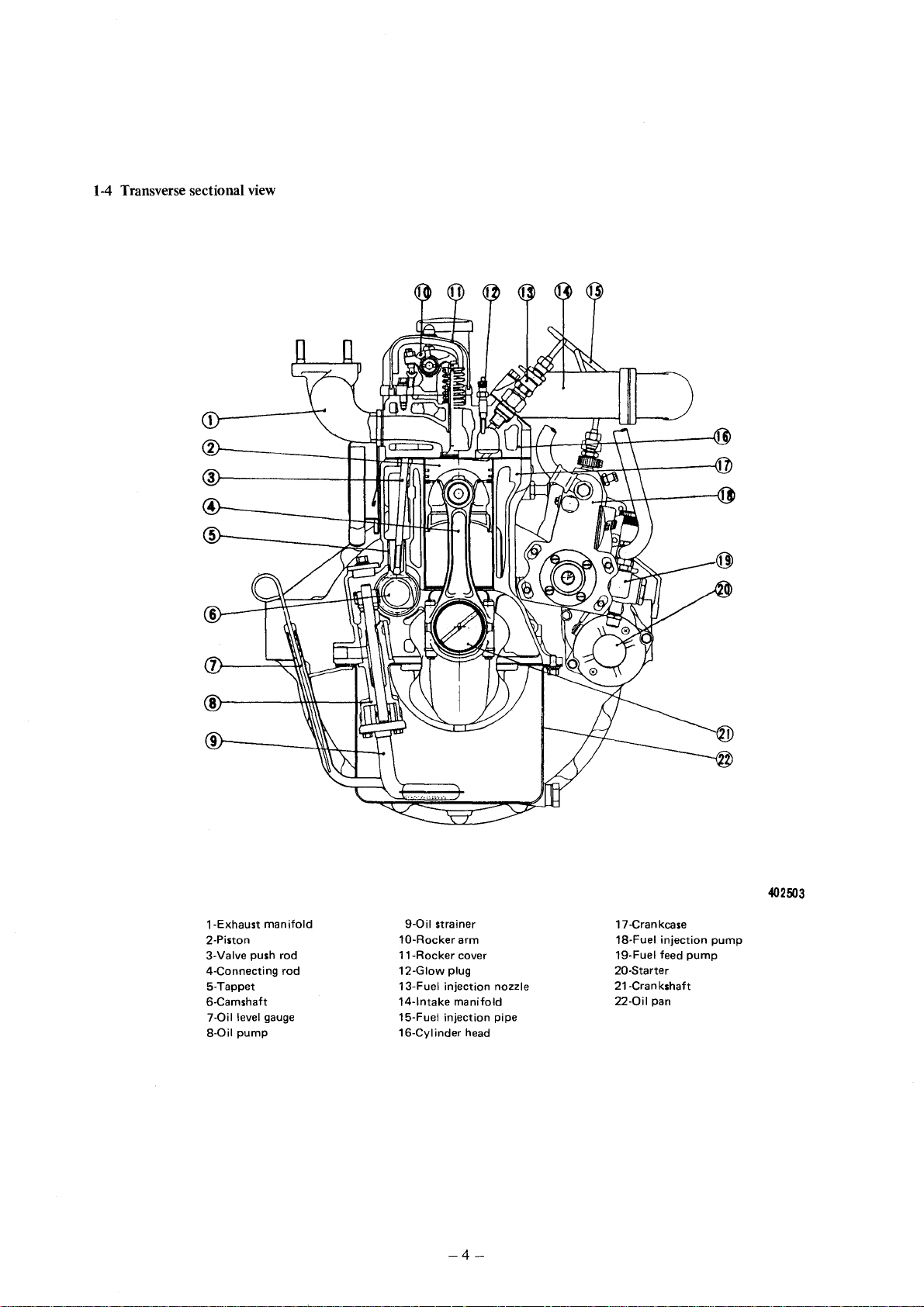
1-4
Transverse sectional view
1-Exhaust
2-Piston
3-Valve push rod
4-Connecting
5-Tappet
6-Camshaft
7-0il
8-0il
manifold
rod
level gauge
pump
9-0il
strainer
10-Rocker
11-Rocker
12-Glow
13-Fuel
14-lntake
15-Fuel
16-Cylinder
plug
injection
injection
-4-
arm
cover
manifold
head
nozzle
pipe
17 -Cran kcase
18-Fuel
injection
19-Fuel feed
20-Starter
21-Cra n kshaft
22-0il
pan
402503
pump
pump
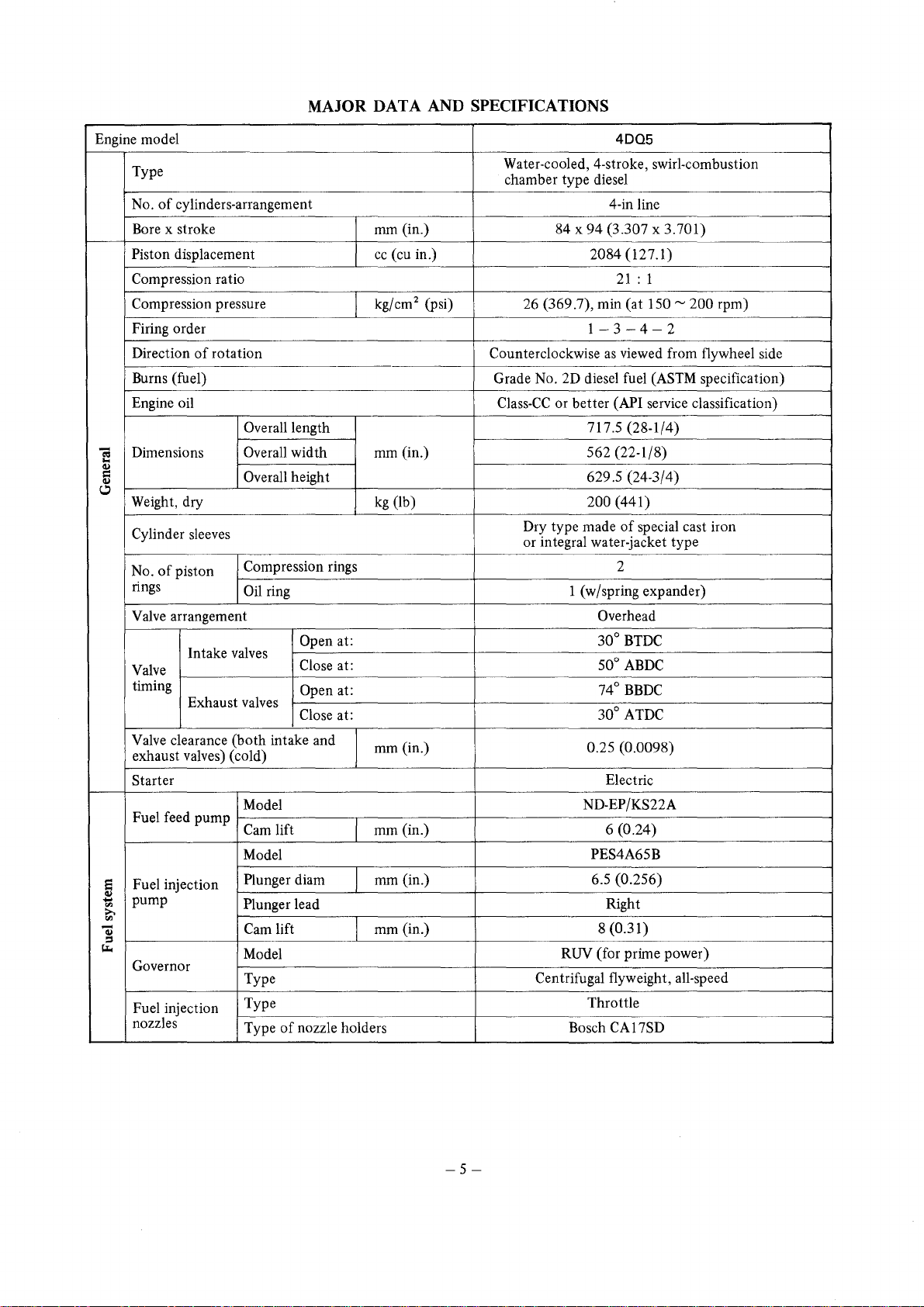
MAJOR DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
Engine model
Type
of
cylinders-arrangement 4-in line
No.
Bore x stroke mm (in.) 84 x
displacement
Piston
Compression ratio
Compression pressure
Firing order
Direction
Burns (fuel) Grade No. 2D diesel fuel (ASTM specification)
Engine oil
Dimensions Overall width mm (in.) 562 (22-1/8)
ca
..
a.I
=
a.I
(.!)
Weight, dry
Cylinder sleeves
No.
rings
Valve arrangement
Valve
timing
Valve clearance (both intake and
exhaust valves) (cold)
Starter
Fuel feed pump
Fuel injection
5
pump
"til
~
a:i
::I
r-
Governor
Fuel injection
nozzles
of
of
piston
Intake valves
Exhaust valves
rotation Counterclockwise
Overall length 717.5 (28-1/4)
Overall height
Compression rings 2
Oil ring
Open at:
Close at:
Open at:
Close
Model
Cam
lift mm (in.)
Model
Plunger diam mm (in.)
Plunger lead
Cam lift
Model
Type
Type
Type
of
nozzle holders
at:
cc(cuin.)
cm
2 (p si)
kg/
kg
(lb)
mm (in.)
mm (in.)
Water-cooled, 4-stroke, swirl-combustion
chamber type diesel
26 (369.7), min (at
Class-CC
or better (API service classification)
Dry type made
or integral water-jacket type
RUV (for prime power)
Centrifugal flyweight, all-speed
40Q5
94
(3.307 x 3.701)
2084
(127.l)
21
: 1
150 ~ 200 rpm)
1-3-4-2
as
viewed from flywheel side
629.5 (24-3/4)
200 (441)
of
special cast iron
1 (w/spring expander)
Overhead
30°
BTDC
50°
ABDC
74°
BBDC
30° ATDC
0.25 (0.0098)
Electric
ND-EP/KS22A
(0.24)
6
PES4A65B
(0.256)
6.5
Right
(0.31)
8
Throttle
CA
Bosch
1 7SD
-5-
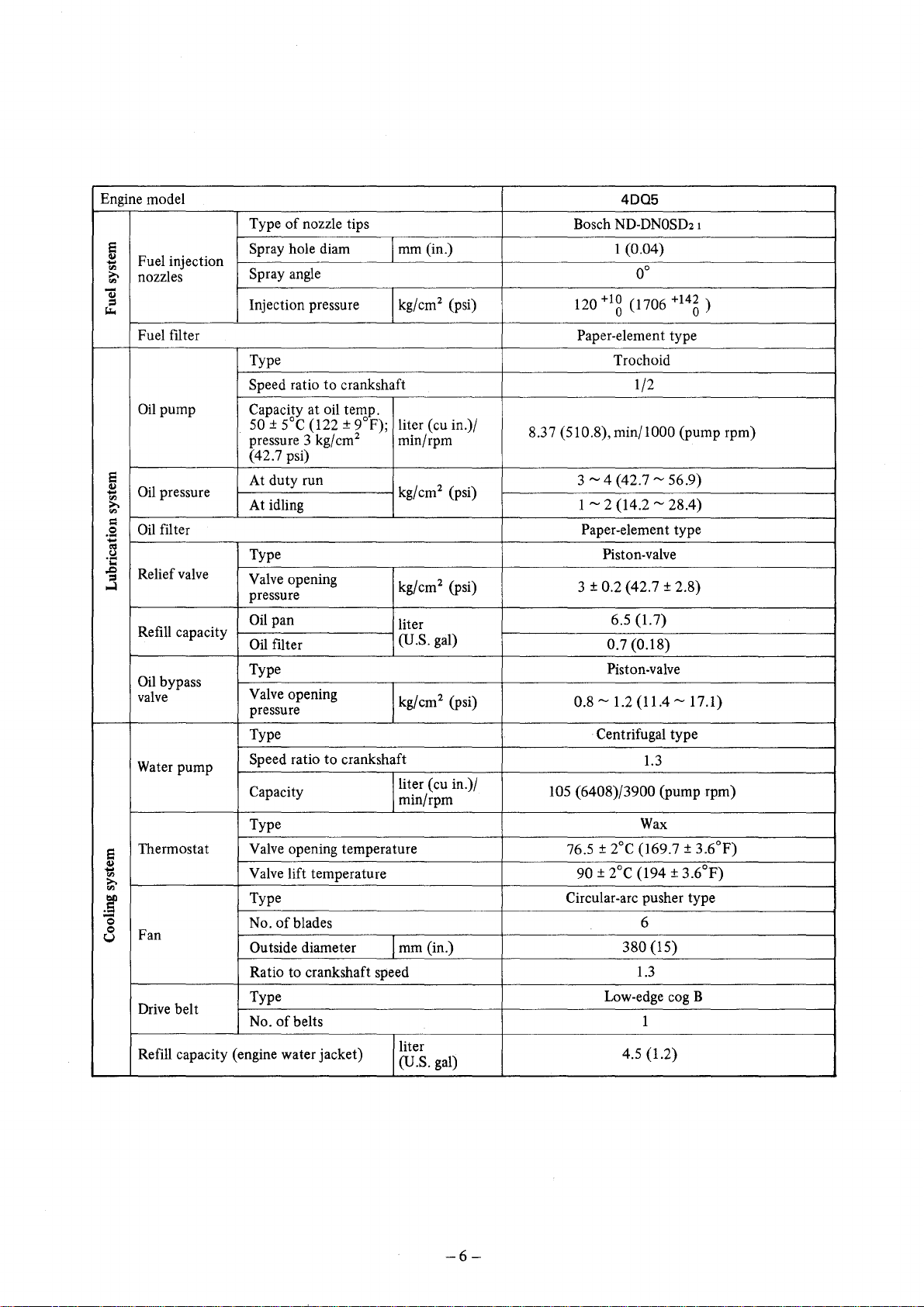
Engine model 4DQ5
Type
of
nozzle tips
~
Fuel injection
~
nozzles
~
'1:l
=
""-
Fuel filter Paper-element type
Oil
pump Capacity at oil temp.
e
III
~
Oil
>.
'"
'"
=
.sa
~
.~
'"
..
3
e
III
~
>.
'"
pressure
Oil
filter Paper-element type
Relief valve
Refill capacity
Oil
bypass
valve
Water pump
Thermostat
'"
.Sf
'0
0
Fan
U
Drive belt
Refill capacity (engine water jacket)
Spray hole diam mm (in.)
Spray angle
Injection pressure
Type
Speed ratio
50 ± 5°C (122 ± 9°F);
pressure 3 kg/cm
(42.7 psi)
At duty run
At idling 1 - 2 (14.2 - 28.4)
Type Piston-valve
Valve opening
pressure
Oil pan
Oil
filter
Type Piston-valve
Valve opening
pressure
Type
Speed ratio
Capacity
Type
Valve opening temperature 76.5 ± 2°C (169.7 ± 3.6°F)
Valve lift temperature
Type
No.
of
Outside diameter
Ratio to crankshaft speed 1.3
Type Low-edge cog B
No.
of
to
crankshaft
to
crankshaft
blades 6
belts 1
kg/cm2 (psi)
liter (cu in.)/
2
min/rpm
2
kg/cm
kg/ cm 2 (psi)
liter
(U.s. gal)
kg/ cm 2 (psi) 0.8 - 1.2 (11.4 - 17.1)
liter (cu in.)/
min/rpm
mm (in.)
liter
(U.S. gal)
(psi)
Bosch
ND-DNOSD21
1 (0.04)
0°
120 +18 (1706 +
Trochoid
1/2
8.37 (510.8), min/lOOO (pump rpm)
3
- 4 (42.7 - 56.9)
± 0.2 (42.7 ± 2.8)
3
6.5 (1. 7)
0.7 (0.18)
Centrifugal type
1.3
(6408)/3900 (pump rpm)
105
Wax
90 ± 2°C (194 ±
Circular-arc pusher type
380 (15)
4.5 (1.2)
14
6 )
3.6°p)
-6-
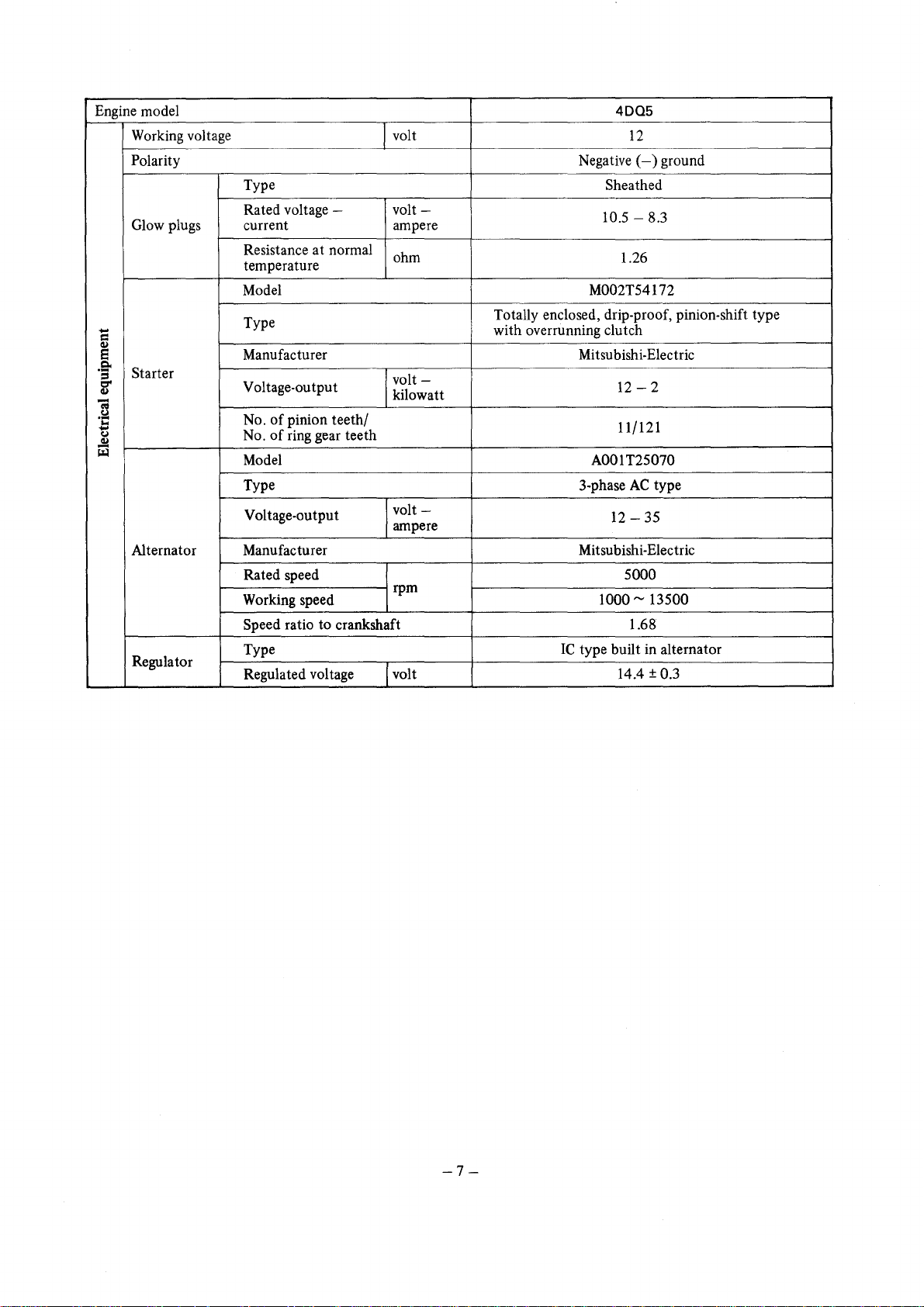
Engine model
Working voltage volt
Polarity
Type
Glow plugs current ampere
....
=
cv
S
.9-
Starter
i
co
.l:t
...
....
<:J
~
Alternator Manufacturer Mitsubishi-Electric
Regulator
Rated voltage -
Resistance at normal
temperature
Model
Type
Manufacturer
Voltage-output
No.
of
pinion teeth/
No.
of
ring gear teeth
Model A001T25070
Type 3-phase
V oltage-ou
Rated speed
Working speed
Speed ratio to crankshaft 1.68
Type
Regulated voltage volt
tpu
t
volt -
ohm
Totally enclosed, drip-proof, pinion-shift type
with overrunning clutch
volt kilowatt
volt ampere
rpm
Negative
Sheathed
10.5 - 8.3
M002T54172
Mi
tsu b
12
1000 ~ 13500
IC
type built in alternator
4DQ5
12
(-
1.26
ishi-
12
- 2
11/121
AC
- 35
5000
14.4
) ground
Electric
type
± 0.3
-7-
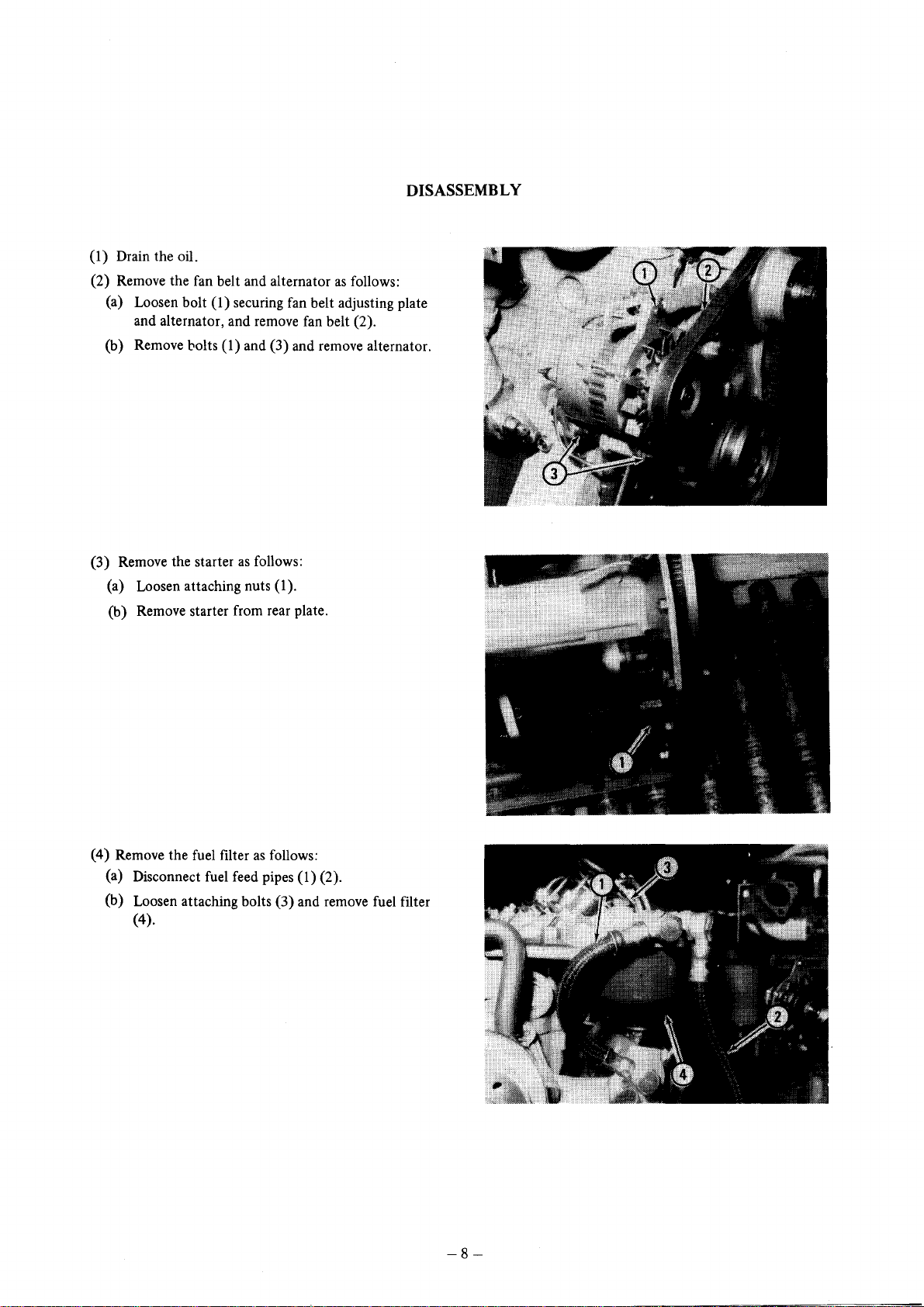
(1) Drain the oil.
(2) Remove the fan belt and alternator
(a) Loosen bolt
and alternator, and remove
(b) Remove
(1) securing fan belt adjusting plate
fan
bolts (1) and (3) and remove alternator.
as
follows:
belt (2).
DISASSEMBLY
(3) Remove the starter
(a) Loosen attaching nuts (1).
(b) Remove starter from rear plate.
(4) Remove the fuel filter
(a) Disconnect fuel feed pipes (1) (2).
(b) Loosen attaching bolts (3) and remove fuel filter
(4).
as
follows:
as
follows:
-8-

(5) Remove the injection pipes and injection nozzles
follows:
(a) Loosen connectors
pipes
(2).
(b) Remove fuel return pipe (3) by loosening union
nut.
(c) Loosen nuts (4) and remove fuel leak-off pipe (5).
(d) Remove nozzle assemblies.
(6) Remove the lube oil pipe from injection pump.
(1) and disconnect injection
as
(7) Remove the water pump pulley and crankshaft pulley
as
follows:
(a) Loosen water pump shaft nut
water pump pulley (2).
(b) Loosen crankshaft nut (3) and remove crankshaft
pulley (4).
(8) Remove the timing gear case.
(9) Remove the rocker cover.
(1) and remove
-9-
(10) Disconnect the water pump bypass hose and oil
pipe. To disconnect bypass hose, displace thermostat elbow and water pump clamp.
(I
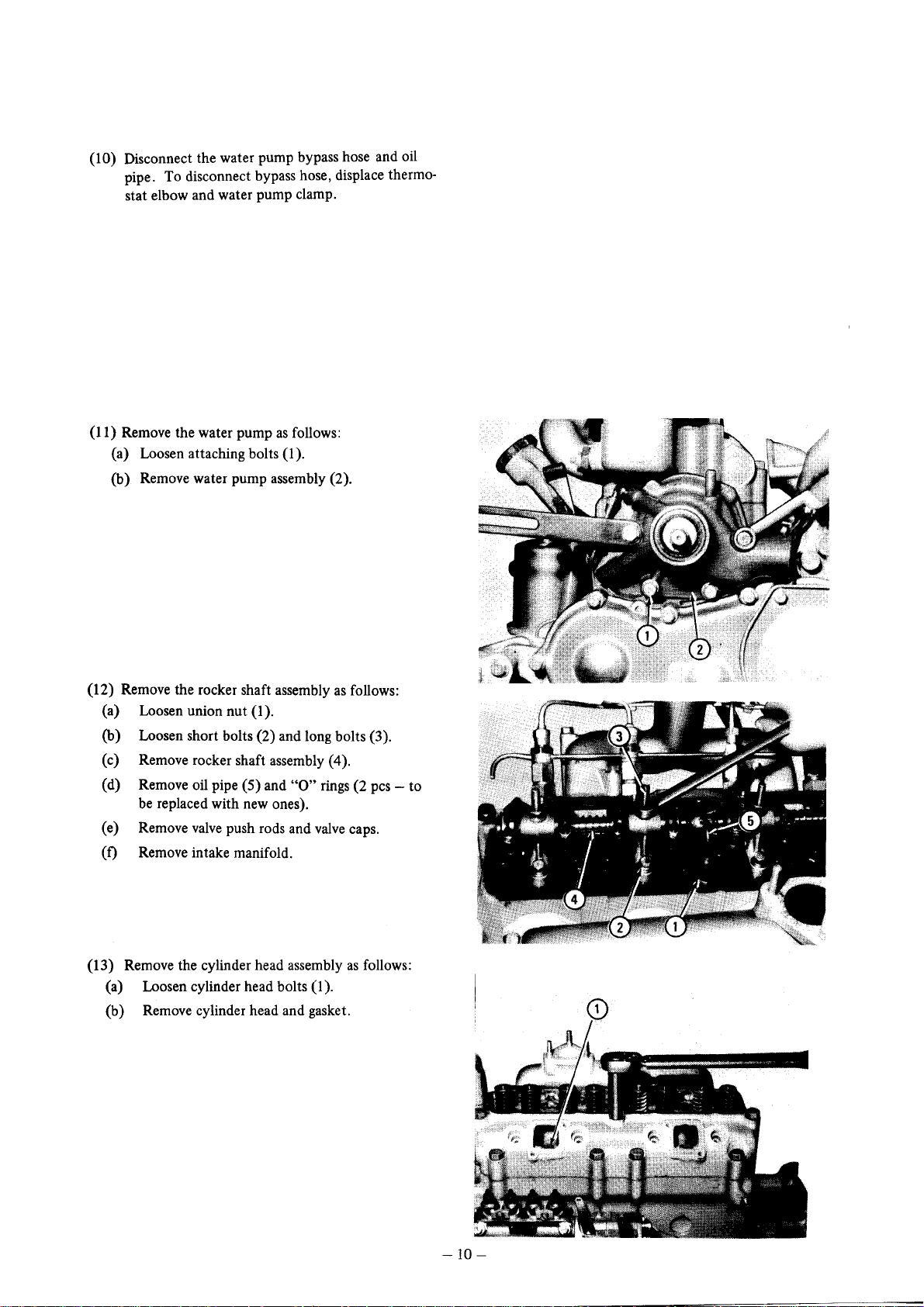
1) Remove the water pump
(a) Loosen attaching bolts (1).
(b) Remove water pump assembly (2).
as
follows:
as
(12) Remove the rocker shaft assembly
(a) Loosen union nut (1).
follows:
(b) Loosen short bolts (2) and long bolts (3).
(c) Remove rocker shaft assembly (4).
"0"
rings
valve
(2 pcs - to
caps.
as
(d) Remove oil pipe (5) and
be
replaced with new ones).
valve
(e) Remove
(f) Remove intake manifold.
(13) Remove the cylinder head assembly
(a) Loosen cylinder head bolts (1).
(b) Remove cylinder head and gasket.
push rods and
follows:
-10-
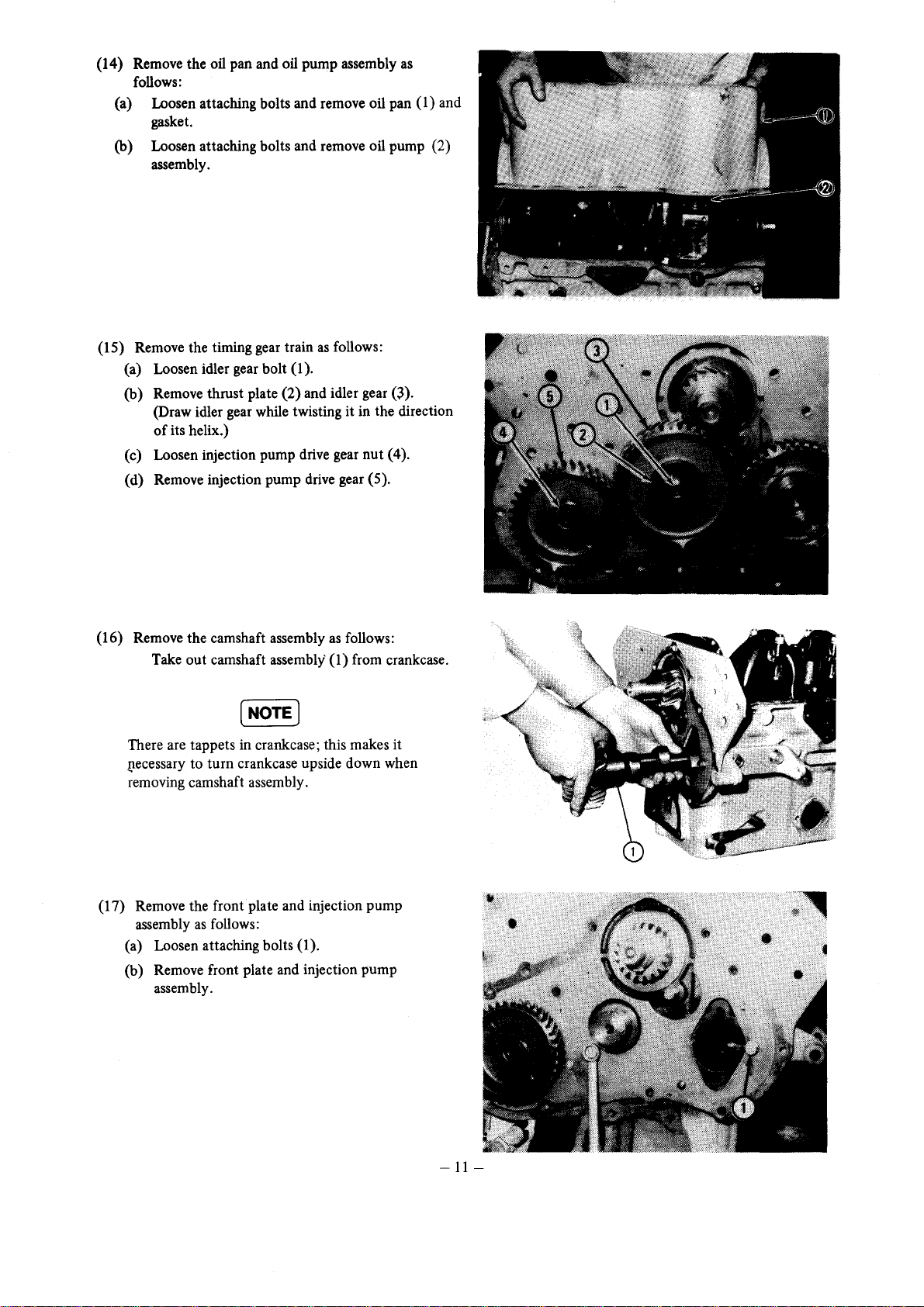
(14) Remove the oil pan and oil pump assembly
follows:
(a) Loosen attaching bolts and remove oil pan (1) and
gasket.
(b) Loosen attaching bolts and remove oil pump (2)
assembly.
as
(15) Remove the timing gear train
(a) Loosen idler gear bolt (1).
(b) Remove thrust plate (2) and idler gear
(Draw idler gear while twisting it in the direction
of
its helix.)
(c) Loosen injection pump drive gear nut (4).
(d) Remove injection pump drive gear (5).
(16) Remove the camshaft assembly
Take out camshaft assembly (1) from crankcase.
as
follows:
as
follows:
[NOTE]
There are tappets in crankcase; this makes it
!}ecessary to turn crankcase upside down when
removing camshaft assembly.
(3).
(17) Remove the front plate and injection pump
assembly
(a) Loosen attaching bolts (1).
(b) Remove front plate and injection pump
as
assembly.
follows:
-11-
•
..
.
..
~
......
@l
.
.,
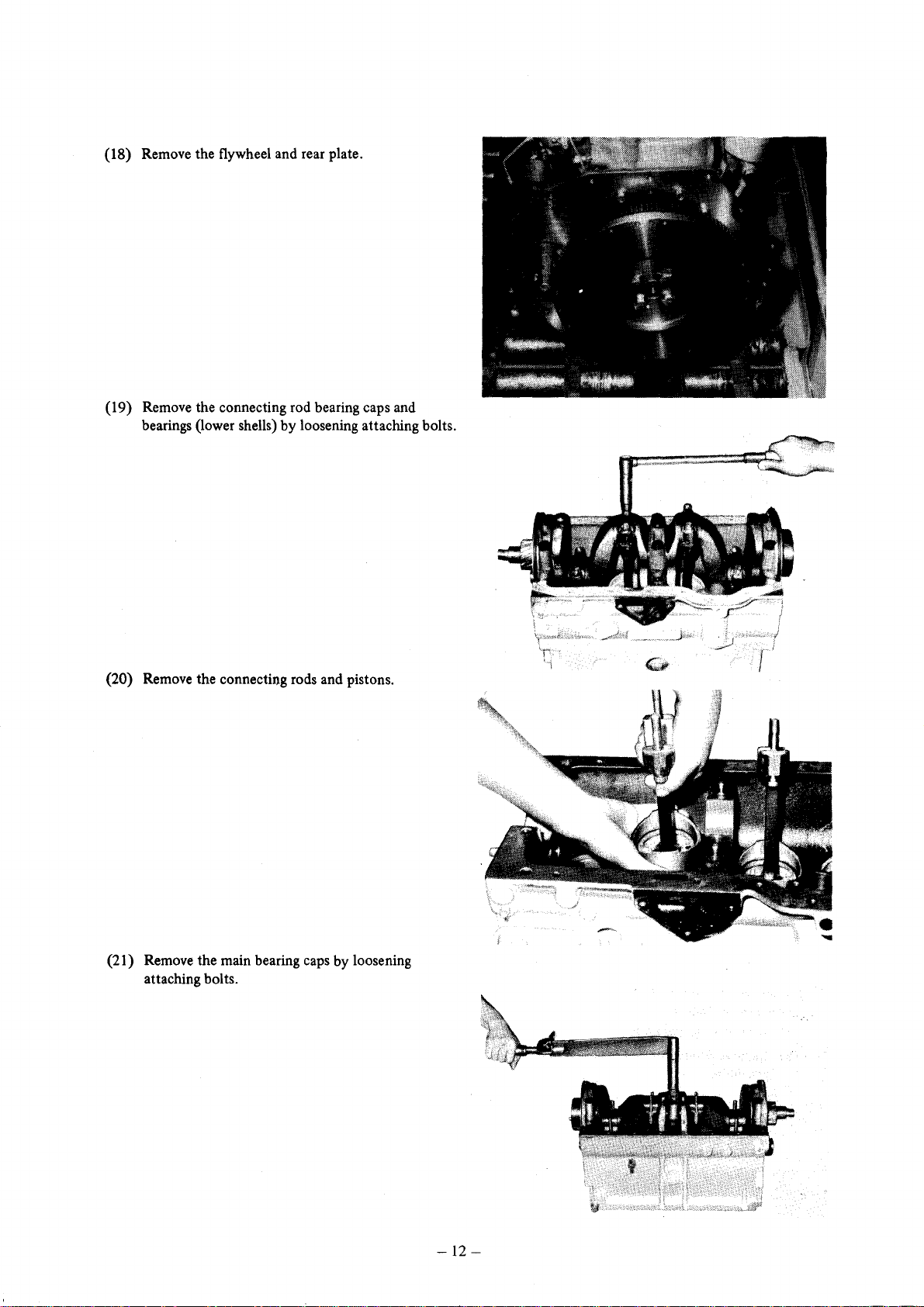
(18) Remove the flywheel and rear plate.
(19) Remove the connecting rod bearing caps and
bearings (lower shells) by loosening attaching bolts.
(20) Remove the connecting rods and pistons.
(21) Remove the main bearing caps by loosening
attaching bolts.
-12
-
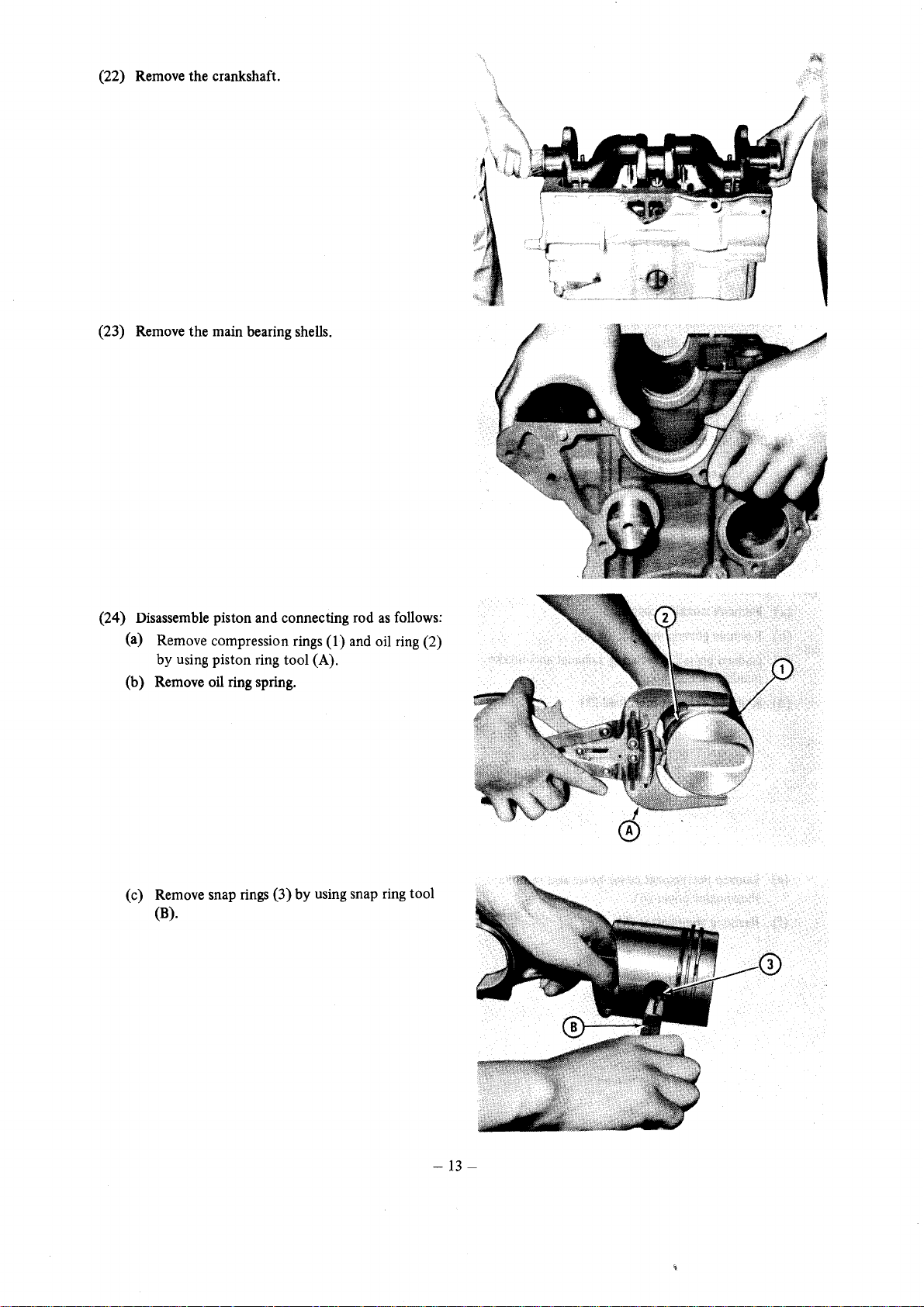
(22) Remove the crankshaft.
(23) Remove the main bearing shells.
(24) Disassemble piston and connecting rod
(a) Remove compression rings
by using piston ring tool (A).
(b) Remove oil ring spring.
(c) Remove snap
(B).
rings
(3) by using snap
(1) and oil ring (2)
as
follows:
ring
tool
-13-
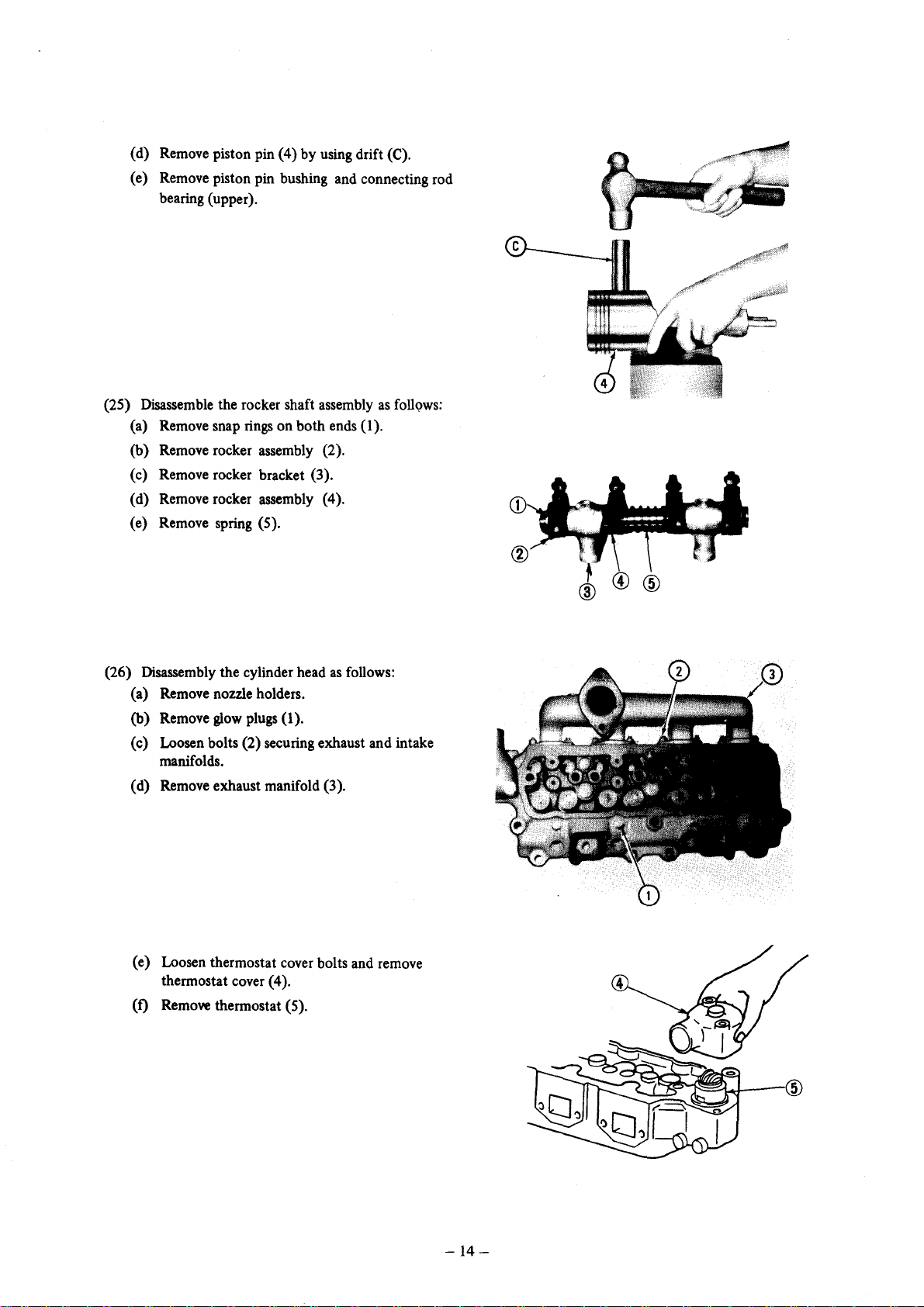
(d) Remove piston pin (4) by using drift (C).
(e) Remove piston pin bushing and connecting rod
bearing (upper).
(25) Disassemble the rocker shaft assembly
(a) Remove snap
(b) Remove rocker assembly (2).
(c) Remove rocker bracket (3).
(d) Remove rocker assembly (4).
(e) Remove spring (5).
rings
on both ends (1).
as
follQws:
(26) Disassembly the cylinder head
(a) Remove nozzle holders.
(b) Remove
(c) Loosen bolts (2) securing exhaust and intake
manifolds.
(d) Remove exhaust manifold (3).
(e) Loosen thermostat cover bolts and remove
thermostat cover (4).
glow
plugs
(l).
as
follows:
(f) Remove thermostat (5).
-14-
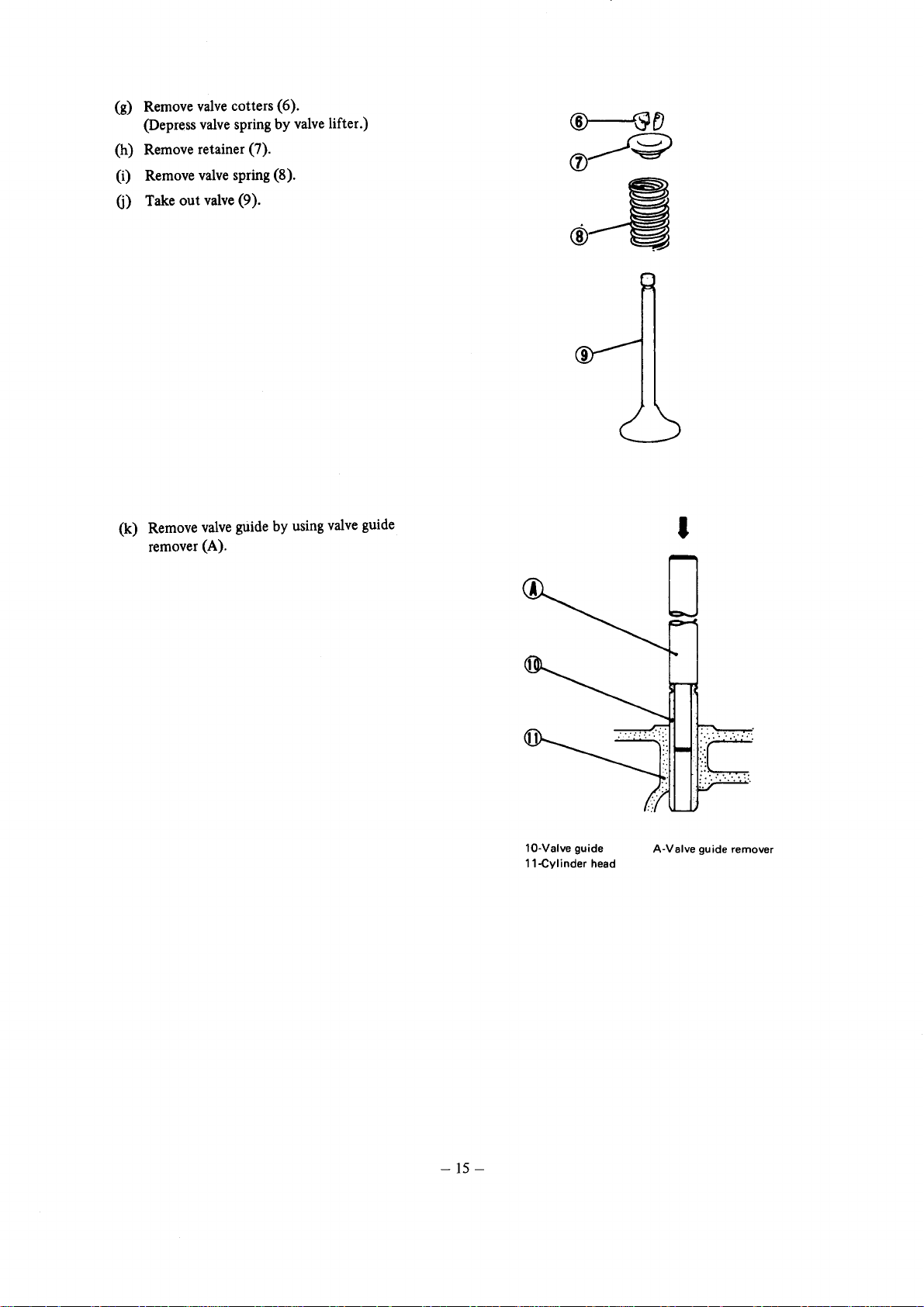
(g) Remove
(Depress valve spring
valve
cotters (6).
by
(h) Remove retainer (7).
(i) Remove valve spring (8).
G)
Take
out
valve (9).
(k)
Remove
valve
guide by using valve guide
remover (A).
valve lifter.)
-15
lO-Valve guide
ll-Cy
Ii nder head
A-Valve guide remover
-
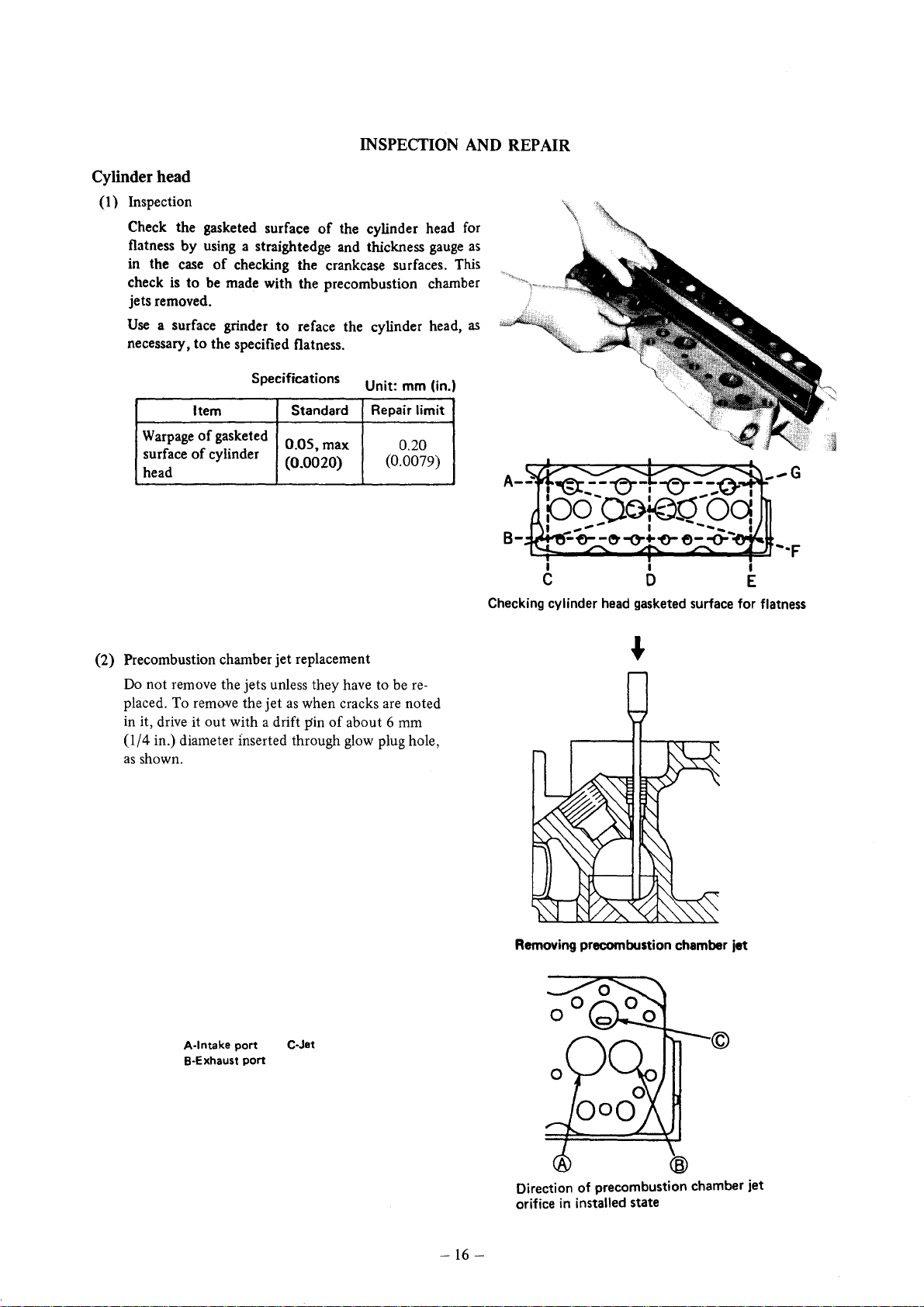
Cylinder head
(1) Inspection
INSPECTION AND REPAIR
Check the gasketed surface
flatness
in the case
check is
jets removed.
Use
necessary,
(2) Precombustion chamber
Do
placed. To remove the
in
by
using a straightedge and thickness
of
checking the crankcase surfaces. This
to
be made with the precombustion chamber
a surface grinder
to
the specified flatness.
Specifications Unit: mm (in.)
Item
Warpage
surface
head
not remove the jets unless they have to be
it, drive it
of
gasketed
of
cylinder
out
with a drift pin
jet
of
the cylinder head for
to
reface the cylinder head,
Standard
O.OS,max
(0.0020)
jet
replacement
as
when cracks are noted
of
about 6 mm
0/4 in.) diameter inserted through glow plug hole,
as
shown.
gauge
Repair limit
0.20
(0.0079)
re-
as
as
B-
L...::t=---
.....
--_
I
....
~
o
Checking cylinder head gasketed surface for flatness
...
·F
A·lntake
B-Exhaust
port
port
C·Jet
-16
Removing precombustion chamber jet
Direction of precombustion chamber jet
orifice
in
installed state
-
©
Valve guides
(1) Check each valve for carboning, burning, wear
other
for cracks. Replace the valve
(2) Check each valve guide for wear. Remember, the
guide wears down more rapidly
than
meter
part
meter
exceeds the repair limit in Table below, replace
the valve guide.
and
valve seats
defect
on
at
any
other
of
the guide
in
two
directions. Measure the outside dia-
of
each valve stem.
head; also check cap
if
parts. Measure the inside dia-
at
its ends and a t its middle
If
end
damaged.
at
its
both
the measurement
and stem
ends
or
,
,
)
~:
Wear
on
valve guide
(
,
,
.
:~
(3) Valve face and valve seat
Check
contact.
reface
valve, proceed
valve face and valve seat for wear and
If
valve face is found excessively worn,
it
by
using a valve refacer.
as
follows:
Item
Angle
To
reface the
Clearance
of
valve
stem in
valve guide
Valve guide
length outside hole
Valve stem
diameter
Specifications
Nominal
value limit
30°
Standard
Repair
Item
Specifications
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
Exhaust
Unit: mm (in.)
Standard
0.055 -0.OS5
(0.00217
(0.00276-0.00413)
(0315
(0315
-0.00335)
0.070-0.105
18
± 0.3
(0.709 ± 0.012)
S
-0.045
-0.060
-0.00177)
.
-0.00236
8
-0.060
-0.080
-0.00236)
. -0.00315
Service limit
Repair
limit
0.15
(0.0059)
0.20
(0.0079)
-0.10
(-0.0039)
-0.15
(-0.0059)
Unit: mm (in.)
Valve
seat
Valve margin
Sinkage
Width
O.S
1.4
1.7
(0.031)
(0.055)
(0.067)
±0.2
(±O.OOS)
±0.14
(±0.005S) (0.063)
-17
1.3
(0.051)
1.6
Reface up
1.2
(0.047)
-
Valve seat
to
angle l
~
~~~
C:J~
~I~am
~
~
t Valve sinkage 1
Counterbore
n
Face i
Valve
margin

Valve refacer
Set a valve refacer
(a)
(b) Grind the valve stock
is
margin
the valve.
Valve seat cutter
Repair
valve
(c)
When
as
prevent uneven cutting. After cutting, reface
the seat by rotating the cutter with No.
sandpaper put between the cutter and seat.
(d)
If
30-degree cutter.
1.6
seat. Also replace the seat when
exceeds
Valve
seat
less than
an
excessively worn
seat grinder
using a valve seat cutter, exercise
to apply a uniform pressure to
valve
seat width is overcut,
mm
(0.063 in.) due to wear,
1.3
installation
mm
(0.051 in.).
to
an
angle
of
45 degrees.
to
a minimum and,
1.2
mm (0.047 in.), replace
valve
seat by using a
or
valve
seat cutter.
repair
If
valve
seat width exceeds
valve
it using a
rep.lace
valve
if
the
care
so
seat to
400
the
sinkage
Chill the valve seat inserts in ether or alcohol containing
of
in
80°C
the
dry ice. Heat the cylinder head to a temperature
to 100°C (176°p to 212°p). Press the inserts
cylinder head by using the insert calking tools (3069102700 for intake valve, 30691-02800 for exhaust valve).
Leave the cylinder head and the inserts in the air until
shrinkage-expansion fit
is
obtained between the two.
Calk around the inserts with the insert calking tool to
machine the seat width.
(NOTE]
The insert calking tool may be used
pressing and calking the
reversing the calking ring.
valve
seat inserts
both
for
by
-18
-
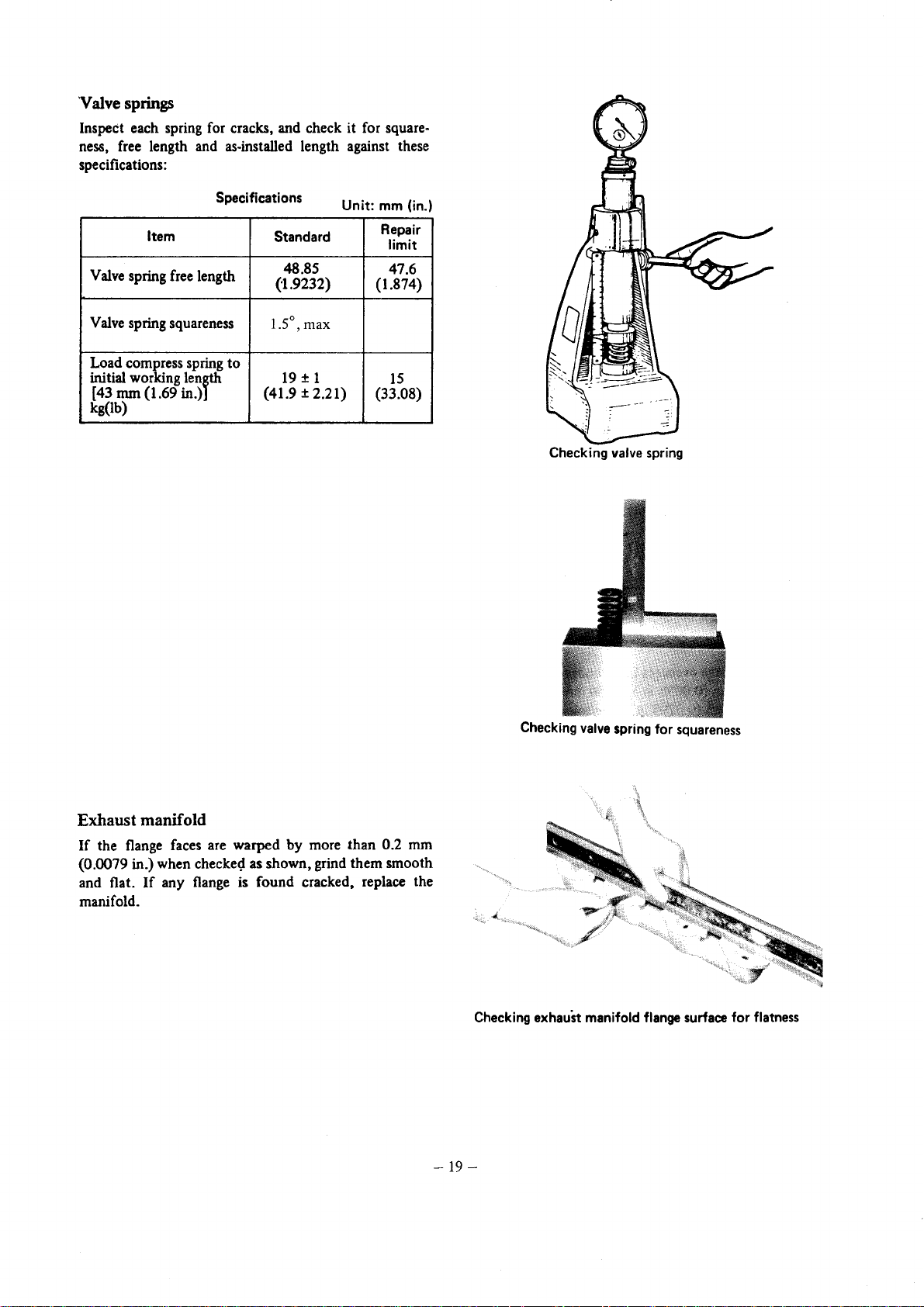
'Valve springs
Inspect each spring for cracks, and check it for squareness, free length and as-installed length against these
specifications:
Specifications
Item
Valve spring free length
Valve spring squareness
Load compress spring
initial working lenfth
[43 mm (1.69 in.)
kg(lb)
to
Standard
48.85
(·1.9232)
1.5°, max
19 ± 1
(41.9 ± 2.21)
Unit: mm (in.)
Repair
limit
47.6
(1.874)
15
(33.08)
Checking valve spring
Exhaust manifold
If
the flange faces are
(0.0079 in.) when
and flat.
manifold_
If
checke<;l
any flange is
warped
by
as shown, grind
found
cracked, replace the
more
than
them
0.2 mm
smooth
Checking exhaust
-19
-
Checking
valve
spring for squareness
manifold flange surface for flatness
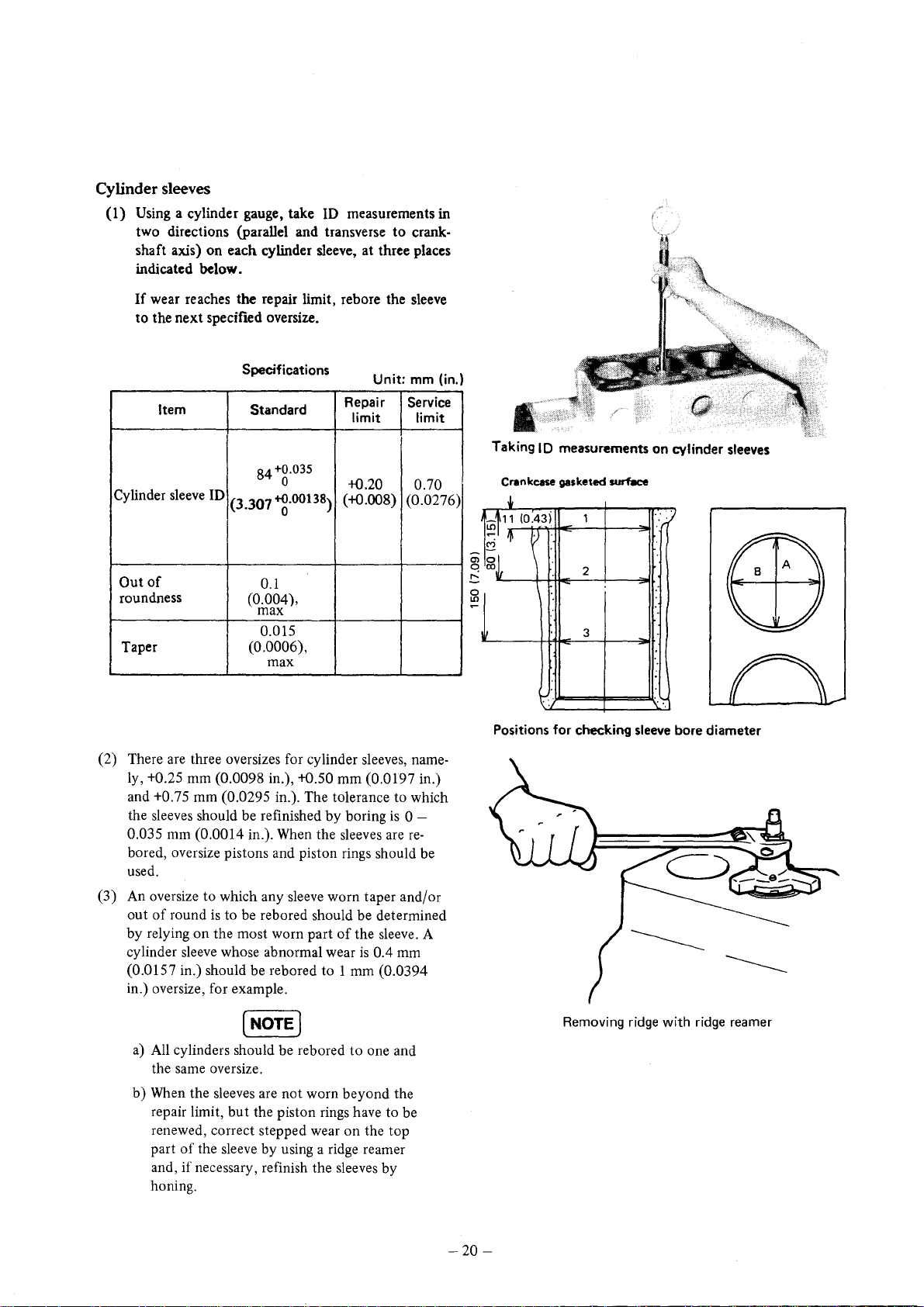
Cylinder sleeves
(1) Using a cylinder gauge, take ID measurements in
to
two directions (parallel and transverse
shaft axis)
indicated
If
wear reaches the repair limit, reb ore the sleeve
to the
on
each cylinder sleeve, at three places
below.
next
specifted oversize.
crank-
Specifications
Item Standard
84
+0.035
Cylinder
Out
roundness
Taper
(2) There are three oversizes for cylinder sleeves,
(3) An oversize to which any sleeve worn taper and/or
sleeve ID
of
ly, +0.25 mm (0.0098 in.), +0.50 mm (0.0197 in.)
and
+0.75 mm (0.0295 in.). The tolerance to which
the sleeves should be refinished by boring
0.035 mm (0.0014 in.). When the sleeves are
bored, oversize pistons and piston rings should be
used.
out
of
round
by relying
cylinder sleeve whose abnormal wear
(0.0157 in.) should be rebored to 1 mm (0.0394
in.) oversize, for example.
(3.307 +g.00138)
is
to be rebored should be determined
on
the most worn part
0
0.1
(0.004),
max
0.015
(0.0006),
max
Unit: mm (in.)
Repair
limit limit
+0.20
(+0.008)
is
0 -
of
the sleeve. A
is
0.4 mm
Service
0.70
(0.0276)
name-
re-
I
Taking
0111
~~'
ID
Crlnkcase
oJ,
(0.43i
r
measurements
gaske,ed
1
2
3
surfKe
on
cylinder sleeves
.:)
'.
Positions for checking sleeve bore diameter
(NOTE]
a)
All cylinders should be rebored
the same oversize.
b) When the sleeves are not worn beyond the
but
repair limit,
renewed, correct stepped wear on the top
part
of
the sleeve by using a ridge reamer
and, if necessary, refinish the sleeves by
honing.
the piston rings have to be
to
one and
-20
Removing ridge
-
with
ridge reamer
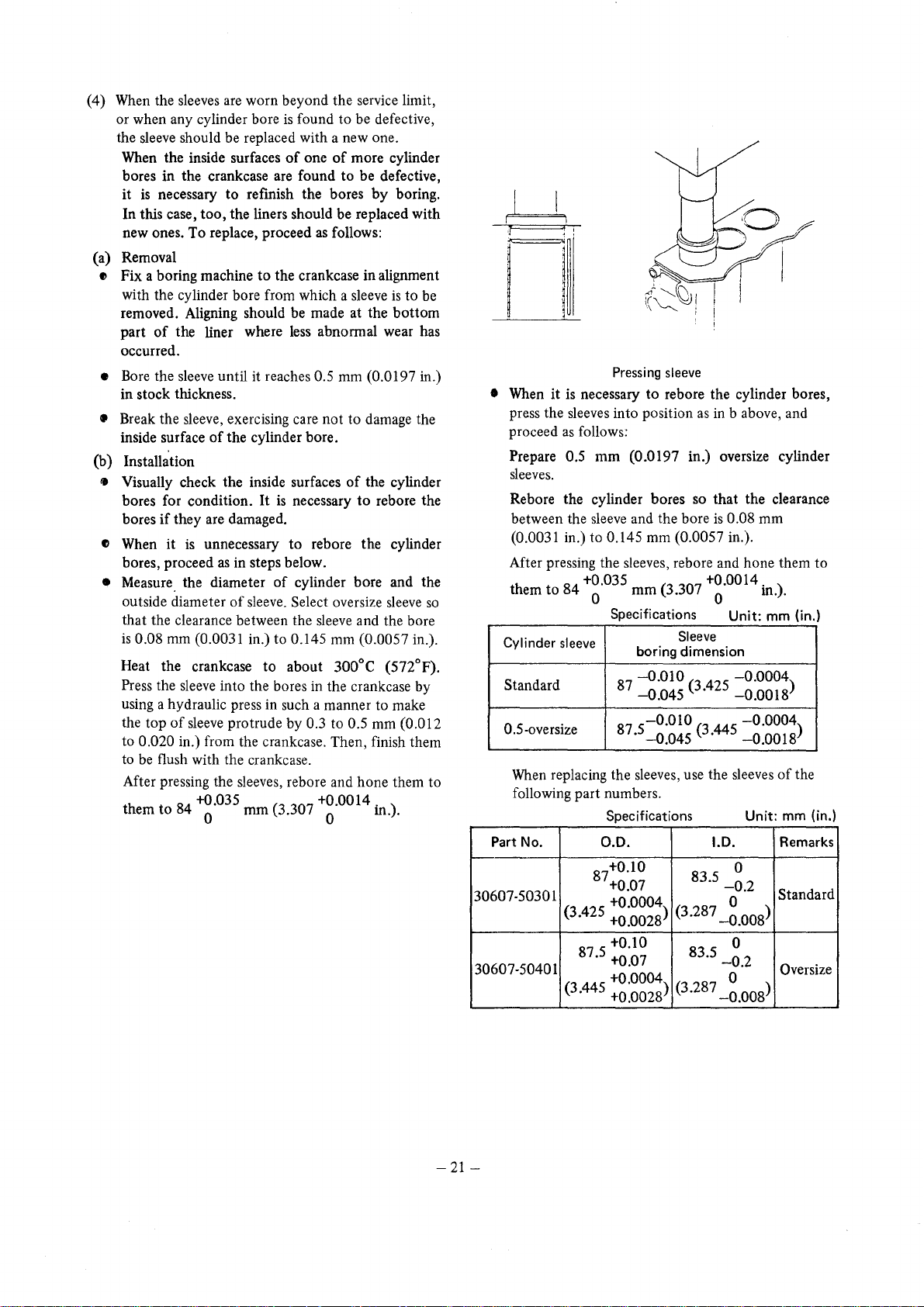
(4) When the sleeves are worn beyond the service limit,
or when any cylinder bore
the sleeve should be replaced with a new one.
When the inside surfaces
bores in the crankcase are found
it
is
necessary
In this case,
new ones. To replace, proceed
(a) Removal
to
too,
the liners should be replaced with
e Fix a boring machine
with the cylinder bore from which a sleeve
removed. Aligning should be made at the
part
of
the liner where
occurred.
• Bore the sleeve until it reaches 0.5 mm (0.0197 in.)
in stock thickness.
• Break the sleeve, exercising care not to damage the
inside surface
(b) Installation
It
Visually check the inside surfaces
bores for condition.
bores
if
e When
bores, proceed
• Measure. the diameter
outside diameter
that the clearance between the sleeve and the bore
is
0.08 mm (0.0031 in.) to 0.145 mm (0.0057 in.).
Heat the crankcase
Press the sleeve into the bores
using a hydraulic press in such a manner to make
the top
to 0.020 in.) from the crankcase. Then, finish them
to
be
flush with the crankcase.
After pressing the sleeves, rebore and hone them to
th
t
em a 0
of
the cylinder bore.
they are damaged.
it
is
unnecessary
as
in steps below.
of
of
sleeve protrude by 0.3 to 0.5 mm (0.012
84
+0.035
is
found to be defective,
of
one
of
more cylinder
to
be defective,
refinish the bores
as
to
the crankcase in alignment
less
abnormal wear has
It
is
necessary
to
reb ore the cylinder
of
cylinder bore and the
sleeve. Select oversize sleeve
to
about 300°C (572°F).
in
(3307
mm.
+0.0014. )
by
boring.
follows:
is
bottom
of
the cylinder
to
rebore the
the crankcase by
0
tn
..
to be
so
Pressing sleeve
• When
Cylinder sleeve
Standard
0.5 -oversize
Part
30607-50301
30607-50401
it
is necessary
press the sleeves into position
proceed
Prepare 0.5
sleeves.
Rebore the cylinder bores so
between the sleeve and the bore
(0.0031 in.)
After pressing the sleeves, rebore and hone them to
th
When replacing the sleeves, use the sleeves
following part numbers.
as
follows:
t 84 +0.035
em a 0
No.
mm
to
87+0.10
(3 425 +0.0004)
. +0.0028
875+
. +0.07
(3445
. +0.0028
to
rebore the cylinder bores,
as
in
b above, and
(0.0197 in.) oversize cylinder
that
the clearance
is
0.08 mm
0.145 mm (0.0057 in.).
(3307
mm.
Specifications
boring dimension
87
-0.010
-0.045
0
875-
.
-0.045
Specifications
0.0.
+0.07
10
0
.
+0.0004)
+0.0014. )
0 m
Unit·
Sleeve
(3 425
.
010
.
(3
445
.
1.0. Remarks
83.5
-0.2
83.5
0
0
-0.2
(3.287_
0
(3.287
-0.008)
-0.0004)
-0.0018
-0.0004)
-0.0018
Unit:
0
.
008
0
..
mm
(in )
of
the
mm (in.)
Standard
)
Oversize
-21-
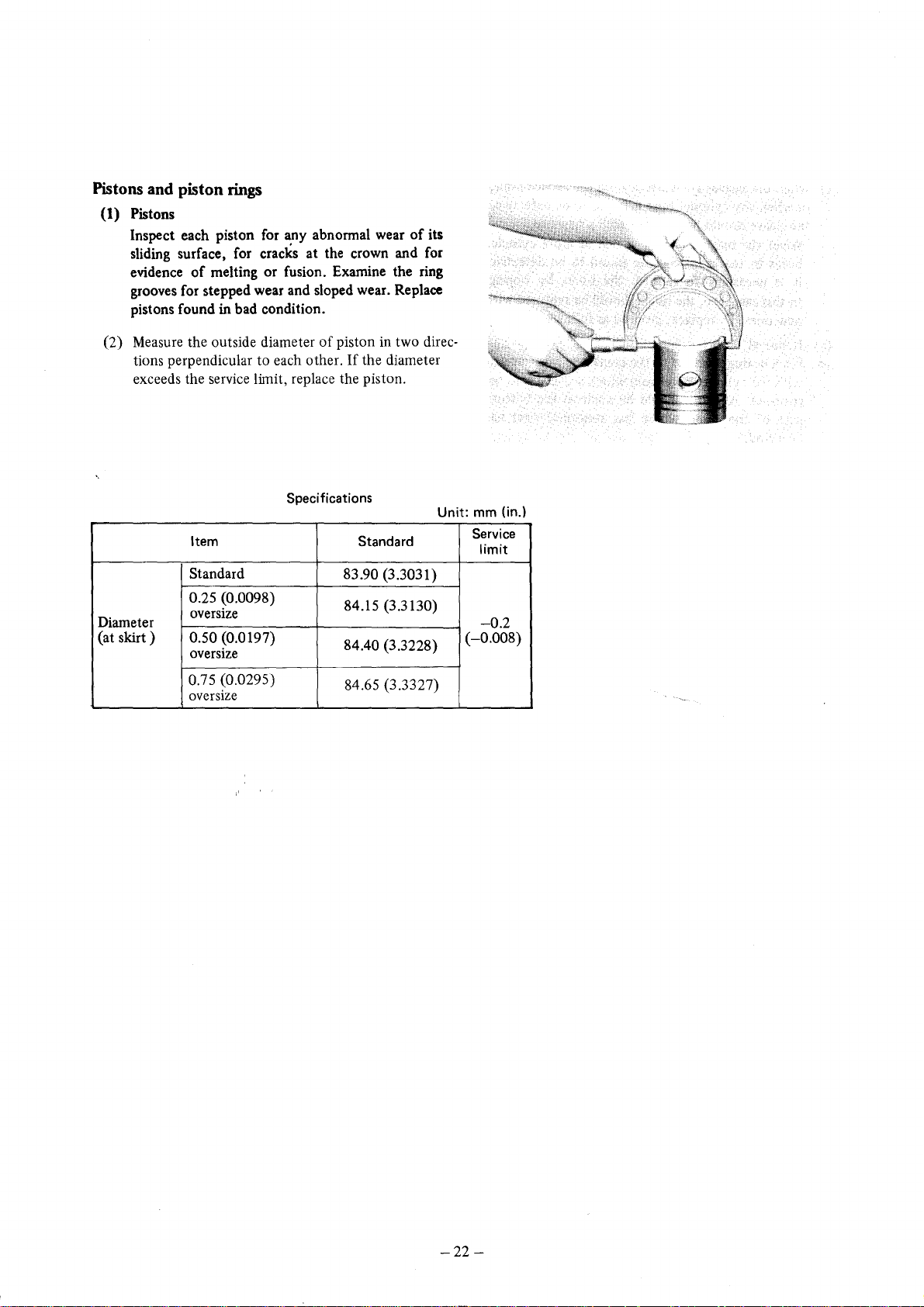
Pistons and piston rings
(1) Pistons
Inspect each piston for any abnormal wear
sliding surface, for cracks at the crown and for
evidence
grooves for stepped wear and sloped wear. Replace
pistons found in bad condition.
of
melting or fusion. Examine the ring
of
its
(2) Measure the outside diameter
tions perpendicular to each other.
exceeds the service limit, replace the piston.
Item
Standard
of
Specifications
0.25 (0.0098)
Diameter
(at
skirt)
oversize
0.50 (0.0197)
oversize
0.75 (0.0295)
oversize
piston in two direc-
If
the diameter
Unit:
Standard
83.90 (3.3031)
84.15 (3.3130)
84.40
(3.3228)
84.65 (3.3327)
mm
(in.)
Service
limit
-0.2
(-0.008)
-22-
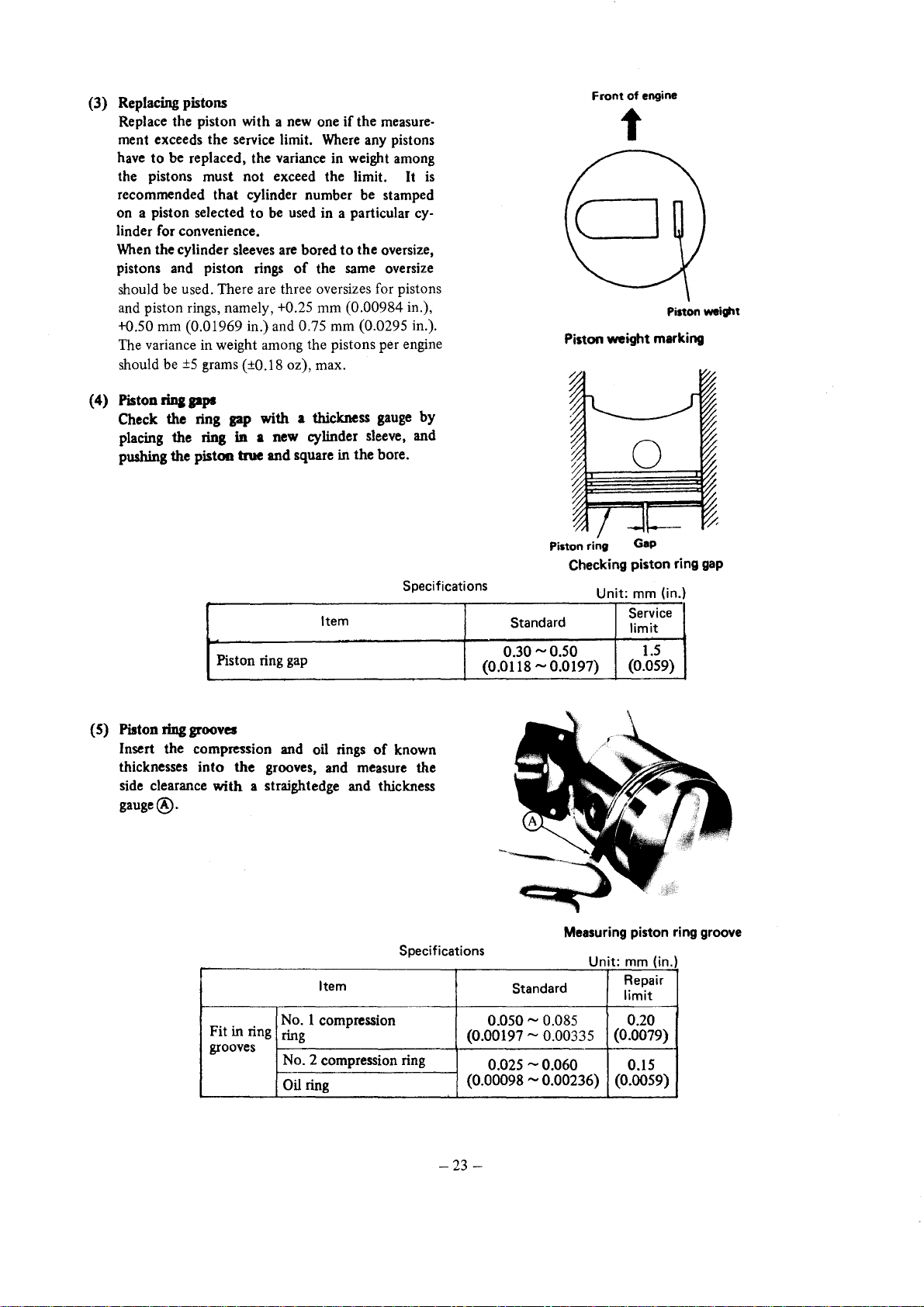
(3)
Replacing pistons
Replace the piston with a new one
ment exceeds
to
have
the pistons
recommended
on
a piston selected
linder for convenience.
When the cylinder sleeves are bored
pistons and piston rings
should be used. There are three oversizes for pistons
and piston rings, namely,
+0.50
mm
The variance in weight among the pistons per engine
should be
the
service limit. Where any pistons
be replaced, the variance in weight among
must
not
exceed the limit.
that
cylinder number be stamped
to
be used in a particular cy-
of
+0.25
(0.01969 in.) and 0.75
±5
grams (±0.18 oz), max.
if
the measure-
to
the
the same oversize
mm
(0.00984
mm
(0.0295 in.).
It
oversize,
in.),
Front
of
engine
t
is
Pilton
_ight
Piston weight marking
(4) Piston
(5) Piston ring
riD&
Check
placing
pushing
Insert the
thicknesses
side clearance
gauge@.
the
the
the
gaps
ring gap
ring
in
pistOll true
Piston ring gap
grooves
compreuion
into
the
with
a straightedge and thickness
with
a thickness gauge
by
a new cylinder sleeve, and
and
square
in
the
bore.
Specifications
Item
and oil rings
grooves, and measure the
of
known
Piston
ring
Checking piston ring gap
Standard
0.30
(0.0118 ~ 0.0197)
~0.50
Gap
Unit: mm (in.)
Service
limit
1.5
(0.059)
Fit
in ring
grooves
Item
No.1
compression
ring
No.2
compression ring
Oil
ring
Specifications
(0.00197 ~ 0.00335
(0.00098 ~ 0.00236)
-23
-
Measuring piston ring groove
Standard
0.050
~ 0.085
0.025 ~ 0.060
Unit·
mm
(in
Repair
limit
0.20
(0.0079)
0.15
(0.0059)
)
(6)
Replacing piston riDp
If
the rings are replaced, the gap width will exceed
the standard value,
concern, provided that the service limit
exceeded.
but
this
is
not
a matter
(7) Piston pin bosses
the piston pin bosses
Check
topic, Piston pins, piston pin bosses and piston
pin bushings, which follows.
by
referring
is
to
of
not
the
Piston pins, piston pin bosses
and
piston pin
bushings
(1) Check the pin clearance
piston by computing the difference between the
two
diameter readings, one taken
the other in the boss.
(clearance) exceeds the repair limit, replace
piston pin with a new one.
Specifications
Item
Piston pin
diameter
(2)
('heck the clearance
fitted to the small end
computing the difference between the two
meter readings. If the computed difference
(clearance) exceeds the repair limit, replace the pin
or the bushing whichever
in
the pin boss
on
If
the computed difference
Standard
0
25
-0.006
(0.984_8.00024 )
of
the pin
of
is
in
the connecting rod by
badly worn.
of
the pin and
Unit: mm
Repair
limit
the bushing
dia·
the
the
(in)
Miking piston pin bushing and piston pin
Item
Piston pin boss
ID
Piston pin clearance in piston
pin boss
Piston pin
bushingID
Piston pin clearance
in piston pin bushing
Specifications
Standard
25
(0.984 -8.00024)
0-0.016
(0
- 0.00063)
25
·+0.045
(0.984
0.020 - 0.051
(0.00079 -
-8.006
+0.020
+0.00079
+0.00177
0.00201)
Unit· mm
Repair
limit
0.05
(0.0020)
)
0.08
(0.0031)
(in
)
-24-
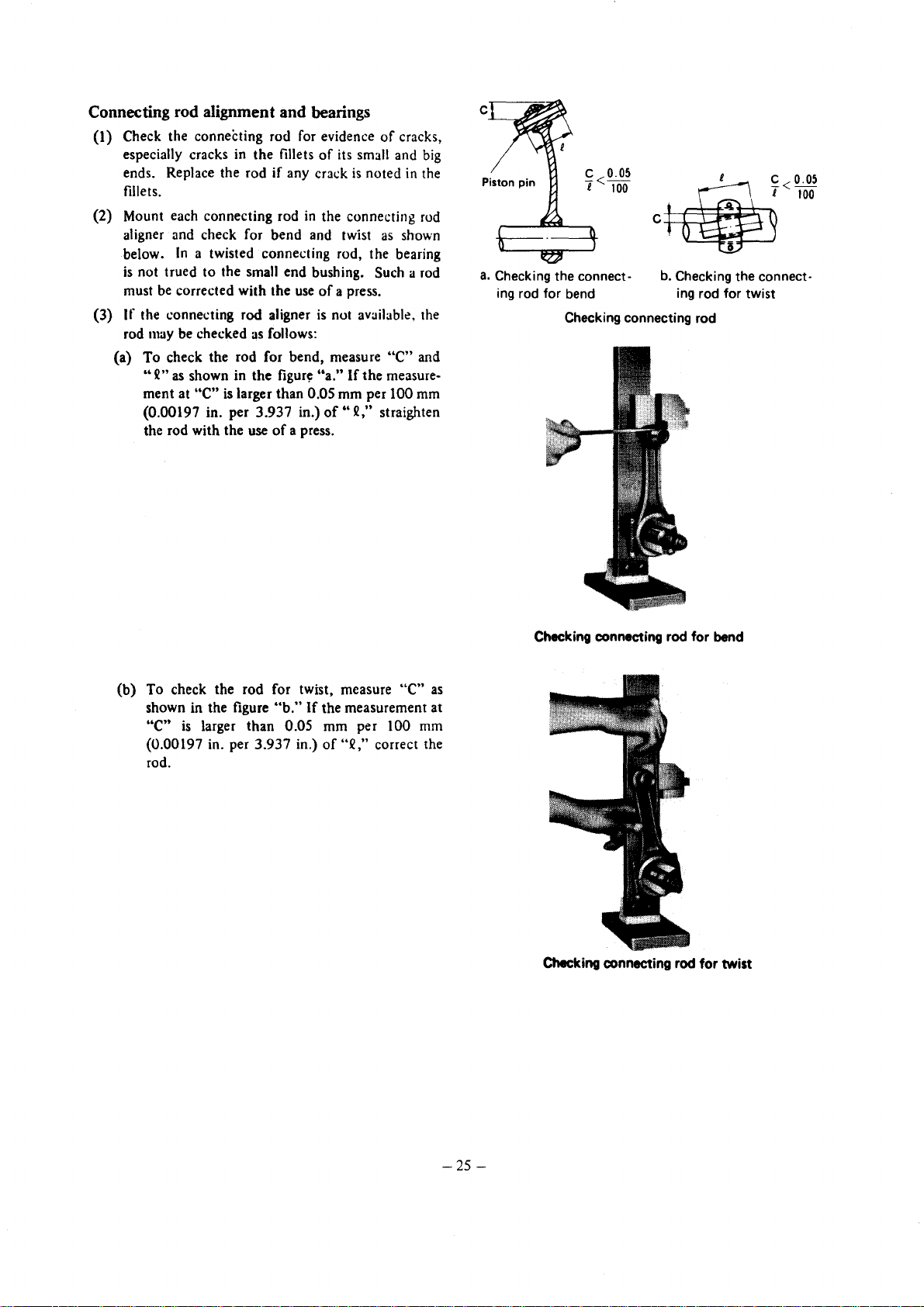
Connecting rod alignment and bearings
(l)
Check the connecting rod for evidence
of
especially cracks in the fillets
ends. Replace the rod if any cral:k
fillets.
(2) Mount each connecting rod
aligner and check for bend and twist
below.
is
must
(3)
If
rod
(a) To check the rod for bend, measure
In
a twisted connecting rod, the bearing
not trued
the connecting rod aligner
may
"2"
ment at "c"
(0.00197 in. per 3.937 in.)
the rod with the use
to
the small end bushing. Such a rod
be
corrected with the
be checked
as
shown in the
is
larger than 0.05 mm per 100 mm
as
follows:
figur~
of
a press.
its small and
is
in
the connecting rod
use
of
a press.
is
not available, the
"a."
If
of"
2," straighten
of
cracks,
big
noted
in
the
as
shown
"c" and
the measure-
f
t
a.
Checking the connect·
ing
rod for bend
Checking connecting rod
<0.05
100
b.
Checking the connect·
ing
rod for twist
(b) To check the rod for twist, measure
shown in the figure
"C"
is
larger than 0.05 mm per 100 mm
(0.00197 in. per 3.937 in.)
rod.
"b."
If
the measurement at
of
"2,"
correct the
"c"
Checking connecting rod for bend
as
Checking connecting rod for twist
-25
-
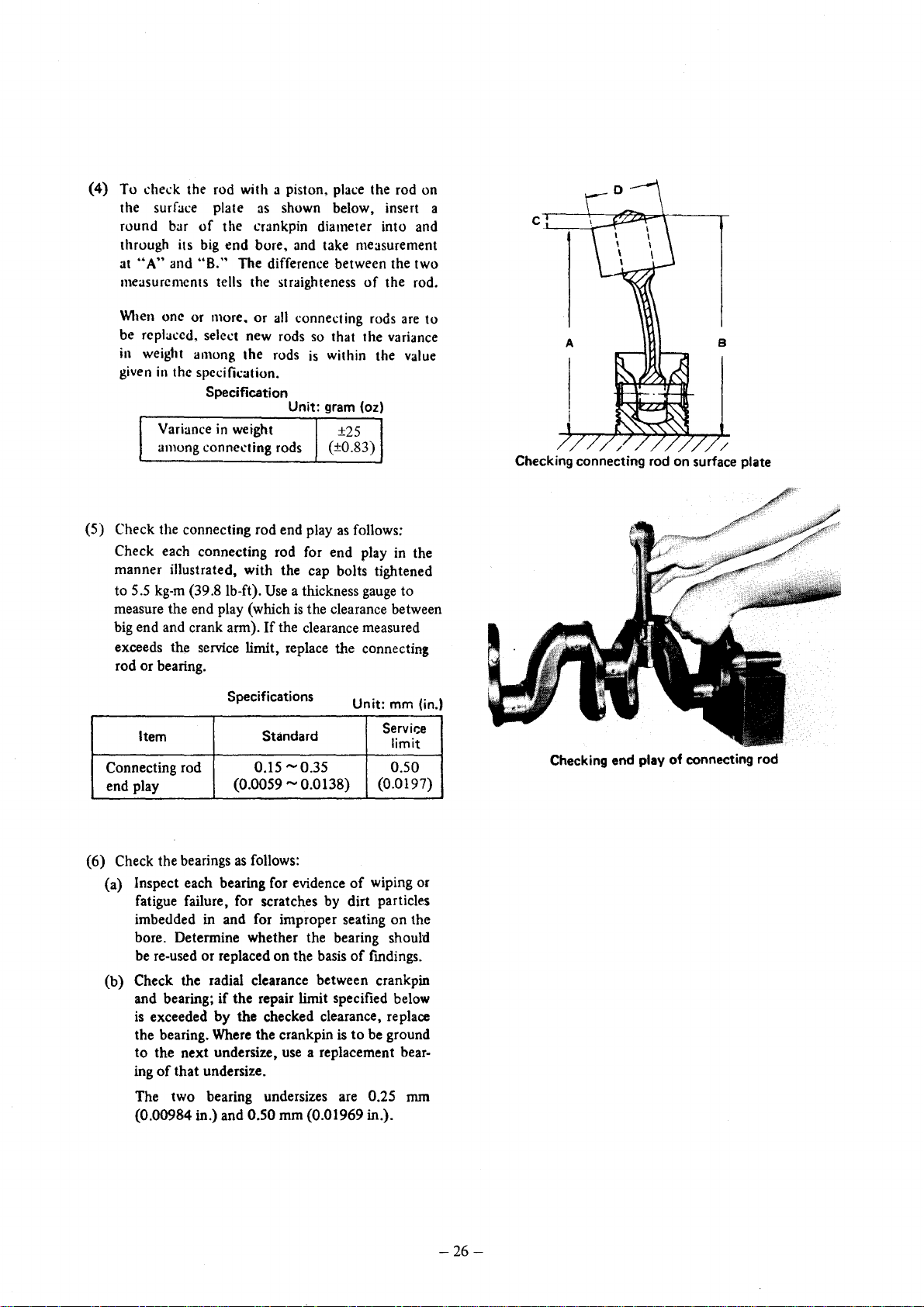
(4)
To
~he.:k
the
surfa~e
round bar
the rod with a piston,
plate
as
shown below, insert a
of
the
~rankpin
pla~e
diameter into and
through its big end bore, and take measurement
at
"A"
and
"B."
The differen.:e between the two
measurements
When
one or more, or
be
repla~ed,
in
weight among the rods
given
in
tel1s
the straighteness
sele~t
new rods
the spedfication.
all
connecting rods are to
so
that the variance
is
within the value
Specification
Unit: gram (oz)
Variance
in
weight
among connecting rods
the rod on
of
the rod.
A
//
B
/
Checking connecting rod on surface plate
(5) Check the connecting rod end
playas
follows:
Check each connecting rod for end play in the
manner illustrated, with the cap bolts tightened
to 5.5
kg-m
(39.8 lb-ft).
measure the end play (which
big end and crank arm).
Use
a thickness
is
the clearance between
If
the clearance measured
gauge
exceeds the service limit, replace the connecting
rod or bearing.
Specifications
Item
Connecting rod
end play
(6) Check the bearings
Standard
0.15 --0.35
(0.0059"" 0.0138)
as
follows:
(a) Inspect each bearing for evidence
Unit:
(0.0197)
of
wiping or
Service
fatigue failure, for scratches by dirt particles
imbedded in and for improper seating
bore. Determine whether the bearing should
be re-used
or
replaced on the basis
of
fmdings.
(b) Check the radial clearance between crankpin
and bearing;
is
exceeded
the bearing. Where the crankpin
to
the next undersize,
ing
of
that
if
the repair limit speCified below
by
the checked clearance, replace
is
to
use
a replacement bear-
undersize.
be ground
The two bearing undersizes are 0.25 mm
(0.00984 in.) and 0.50 mm (0.01969 in.).
to
mm
limit
0.50
on
(in.)
the
Checking end
play of connecting rod
-26-
 Loading...
Loading...