Page 1

24-Port or 48-Port 10/100 +
4-Port 10/100/1000 Gigabit
Resilient Clustering Smart
Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
USER GUIDE
BUSINESS SERIES
Model: SLM224G4S (G5), SLM248G4S (G5)
Page 2
About This Guide
Icon Descriptions
While reading through the User Guide you may see
various icons that call attention to specific items. Below is
a description of these icons:
NOTE: This check mark indicates that there is
a note of interest and is something that you
should pay special attention to while using the
product.
WARNING: This exclamation point indicates
that there is a caution or warning and it is
something that could damage your property or
product.
About This Guide
WEB: This globe icon indicates a noteworthy
website address or e-mail address.
Online Resources
Website addresses in this document are listed without
http:// in front of the address because most current web
browsers do not require it. If you use an older web browser,
you may have to add http:// in front of the web address.
Resource Website
Linksys Europe www.linksys.eu
Linksys International www.linksys.com/international
Linksys www.linksys.com
Glossary www.linksys.com/glossary
Network Security www.linksys.com/security
Copyright and Trademarks
Linksys is a registered trademark or
trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/
or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain
other countries. Copyright © 2008
Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Other brands and product names are
trademarks or registered trademarks
of their respective holders.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
i
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Chapter 2: Product Overview
SLM224G4S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
SLM248G4S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Front Panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Chapter 3: Installation 4
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Pre-Installation Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Fast Ethernet Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Full-Duplex Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1000BASE-T Cable Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Positioning the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Placement Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Desktop Placement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Rack-Mount Placement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Hardware Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Uplinking the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Conguring Stacking Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Reassigning a Slave Unit as the Master Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Replacing a Stacked Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2
Chapter 4: Conguration Using the Console Interface 8
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Using the HyperTerminal Application. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Using telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How to Use the Console Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Switch Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
System Conguration Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Port Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Port Conguration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
System Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Chapter 5: Conguration Using the Web-based Utility 15
Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Setup > Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Setup > Zoom. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
i
Page 4

Table of Contents
Setup > Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Setup > Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Setup > Stack Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Port Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Port Management > Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Port Management > Link Aggregation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Port Management > LACP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
VLAN Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
VLAN Management > Create VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
VLAN Management > Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
VLAN Management > Port to VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
VLAN Management > VLAN to Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Statistics > RMON Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Statistics > RMON History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Statistics > RMON Alarms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Statistics > RMON Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Statistics > Port Utilization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Statistics > Interface Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Security > 802.1x Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Security > Port Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Security > Storm Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Security > RADIUS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
QoS > CoS Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
QoS > Queue Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
QoS > DSCP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
QoS > Bandwidth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
QoS > Basic Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Spanning Tree. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Spanning Tree > STP Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Spanning Tree > Global STP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Multicast > IGMP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Multicast > Bridge Multicast . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Multicast > Bridge Multicast Forward All . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
SNMP > Global Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
SNMP > Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
SNMP > Group Prole . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
SNMP > Group Membership. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
ii
Page 5

Table of Contents
SNMP > Communities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
SNMP > Notication Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
SNMP > Notication Recipient . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Admin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Admin > User Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Admin > Static Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Admin > Dynamic Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Admin > Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Admin > Cable Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Admin > Save Conguration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Admin > Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Admin > Reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Admin > Factory Default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Admin > Logging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Admin > Server Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Admin > Memory Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Admin > Flash Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Appendix A: About Gigabit Ethernet and Fiber Optic Cabling 49
Gigabit Ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Fiber Optic Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Appendix B: About Switch Stacking 50
Standalone Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Stack Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Stack Building Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Normal (Self-Ordering) Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Manually Ordered Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Stack Resiliency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Advanced Stacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Unit IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Stack Units Startup Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
User Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Stacking Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Replacing a Failed Stack Member in a Running Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Stack Master Failure and Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Splitting a Stack. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Merging Two Stacks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Stacking Cable Failure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Inserting Too Many Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Standalone Unit Inserted into a Running Stack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Appendix C: Glossary 58
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
iii
Page 6

Table of Contents
Appendix D: Specications 62
SLM224G4S/SLM248G4S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Appendix E: Warranty Information 64
Limited Warranty. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Exclusions and Limitations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Obtaining Warranty Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Appendix F: Regulatory Information 66
FCC Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Safety Notices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Industry Canada Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Avis d’ Industrie Canada . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
EC Declaration of Conformity (Europe) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
User Information for Consumer Products Covered by EU Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste
Electric and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Appendix G: Contact Information 71
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
iv
Page 7

Chapter 1
Chapter 1:
Introduction
Thank you for choosing the Linksys 24/48-Port 10/100
+ 4-Port Gigabit Smart Switch with Resilient Clustering
Technology and 2 Combo SFPs.
These switches allow you to expand your network securely.
Configuration of the switch is secured using SSL for Web
access. User control is secured using 802.1x security using
a RADIUS authentication mechanism and can also be
controlled using MAC filtering.
Extensive QoS features makes the solution ideal for realtime applications like Voice and Video. The four priority
queues together with the Weighted Round Robin and
Strict Priority scheduling techniques facilitate efficient
co-existence of real-time traffic with data traffic allowing
them each to meet their QoS needs. Individual users or
applications can be prioritized above others using various
Class of Service options—by port, Layer 2 priority (802.1p),
and Layer 3 priority (TOS or DSCP). Intelligent Broadcast
and Multicast storm control minimize and contain the
effects of these types of traffic on regular traffic. IGMP
Snooping limits bandwidth-intensive video traffic to only
the requestors without flooding to all users. Incoming
traffic can be policed and outgoing traffic can be shaped
allowing you to control network access and traffic flow.
Introduction
There are features that allow you to expand and grow your
network of switches. Link aggregation allows multiple
high-bandwidth trunks between switches to be set up.
This also provides a level of reliability in that the system
continues to operate if one of the links breaks. Spanning
Tree (STP) and Fast Link allow you to build a mesh of
switches increasing the availibility of the system.
The rich management functionality of the Smart Switches
with Resilient Clustering Technology includes SNMP,
RMON, Telnet, and HTTP Management options, allowing
you to flexibly integrate and manage these devices in your
network.
NOTE: Throughout this User Guide, the term
reset refers to cycling the power to the Switch;
that is, powering the Switch off, then on again.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
1
Page 8
Chapter 2
Product Overview
Chapter 2:
Product Overview
SLM224G4S
Front Panel
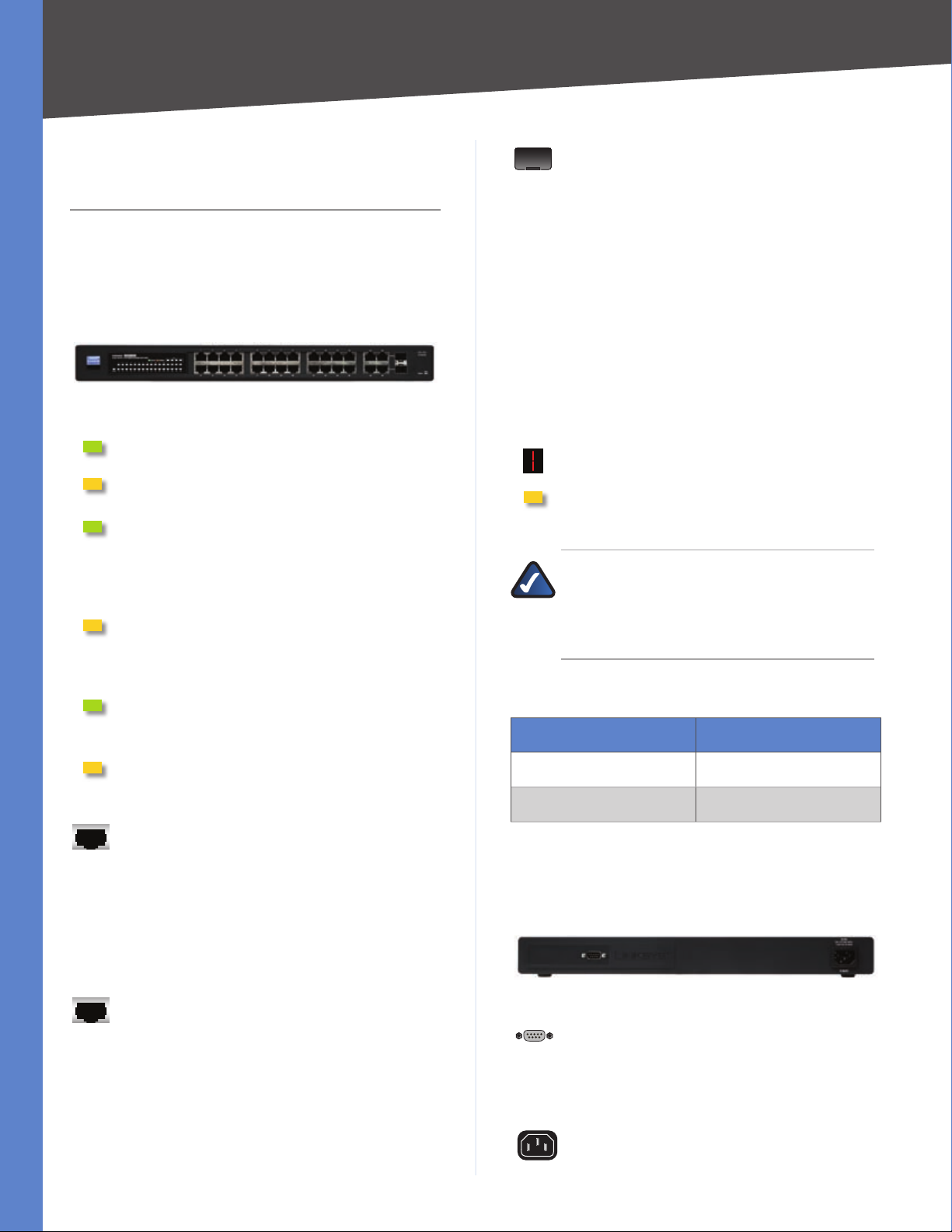
The Switch’s LEDs and ports are located on the front panel.
Front Panel of the SLM224G4S
System (Green/Amber) Lights up green to
indicate that the Switch is powered on.
Lights up amber while the Switch is performing a
system self-test. Blinks amber if the self-test fails.
LINK/ACT (1-24) (Green) Lights up to indicate
a functional 10/100 Mbps network link through
the corresponding port (1 through 24) with
an attached device. Blinks while the Switch is
actively sending or receiving data over that port.
Stack (G1-G4) (Amber) Lights up to indicate
that the corresponding port (G1 through G4) is
linked to another switch. (Two of these LEDs will
be lit if switch stacking is properly configured.)
LINK/ACT (G1-G4) (Green) Blinks when the
Switch is actively sending or receiving data over
the corresponding port (G1 through G4).
1000M (G1-G4) (Yellow)
functional 1 Gbps connection on the corresponding
port (G1 through G4) with an attached device.
Ethernet 1-24 The Switch is equipped with 24
auto-sensing, Ethernet network ports, which
use RJ-45 connectors. The Fast Ethernet ports
support network speeds of 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
They can operate in half- and full-duplex modes.
Auto-sensing technology enables each port to
automatically detect the speed of the device
connected to it (10 Mbps or 100 Mbps), and
adjust its speed and duplex accordingly.
G1-G4
sensing Gigabit Ethernet network ports, which
use RJ-45 connectors. The Gigabit Ethernet ports
support network speeds of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or
1000 Mbps. They can operate in half- and full-duplex
modes. Auto-sensing technology enables each port
to automatically detect the speed of the device
connected to it (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps),
and adjust its speed and duplex accordingly.
The Switch is equipped with 4 auto-
Lights up to indicate a
miniGBIC (1-2) The miniGBIC (gigabit interface
converter) port is a connection point for a
miniGBIC expansion module, so the Switch can
be uplinked via fiber to another switch. The
MiniGBIC port provides a link to a high-speed
network segment or individual workstation at
speeds of up to 1000 Mbps.
To establish a Gigabit Ethernet connection using
a miniGBIC port, you will need to install a MGBT1,
MGBSX1, or MGBLH1 Gigabit expansion module
and use Category 5e cabling or fiber optic cabling.
To establish a Fast Ethernet connection using a
miniGBIC port, you will need to install a MFEFX1
(100BASE-FX) or MFELX1 (100BASE-LX) 100SFP
Transceiver and use fiber optic cabling.
Stack ID Displays the S
the Switch is in stack mode.
Stack Master (Amber)
the stack Master during stack mode.
NOTE: On the SLM224G4S, MiniGBIC ports are
shared with standard ports. If a miniGBIC port is
used, then the shared standard port on the Switch
cannot be used. The following table defines the
shared port mapping of the SLM224G4S Switch.
SLM224G4S Shared Port Mapping
miniGBIC Port Standard Port
miniGBIC 1 G3
miniGBIC 2 G4
witch’s unit ID number if
Lights up if the switch is
Back Panel
The Console port and power port are located on the back
panel of the Switch.
Back Panel of the SLM224G4S
CONSOLE The Console port is a serial port that
allows you to connect to a computer’s serial port
(for configuration purposes) using the provided
serial cable. You can use HyperTerminal to
manage the Switch using the console port.
POWER The Power port is where you connect
the AC power.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
2
Page 9

Chapter 2
Product Overview
SLM248G4S
Front Panel
The Switch’s LEDs and ports are located on the front
panel.
Front Panel of the SLM248G4S
System (Green/Amber) Lights up green to
indicate that the Switch is powered on.
Lights up amber while the Switch is performing a
system self-test. Blinks amber if the self-test fails.
LINK/ACT (1-48) (Green) Lights up to indicate
a functional 10/100 Mbps network link through
the corresponding port (1 through 24) with
an attached device. Blinks while the Switch is
actively sending or receiving data over that port.
Stack (G1-G4) (Amber) Lights up to indicate
that the corresponding port (G1 through G4) is
linked to another switch. (Two of these LEDs will
be lit if switch stacking is properly configured.)
G1-G4 (Green/Amber) Blinks green
when the Switch is actively sending or
receiving data at 10/100 Mbps over the
corresponding port (G1 through G4).
Blinks yellow when the Switch is actively
sending or receiving data at 1000 Gbps over the
corresponding port (G1 through G4).
Ethernet 1-48 The Switch is equipped with 48
auto-sensing, Ethernet network ports, which
use RJ-45 connectors. The Fast Ethernet ports
support network speeds of 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
They can operate in half- and full-duplex modes.
Auto-sensing technology enables each port to
automatically detect the speed of the device
connected to it (10 Mbps or 100 Mbps), and
adjust its speed and duplex accordingly.
G1-G4
sensing Gigabit Ethernet network ports, which
use RJ-45 connectors. The Gigabit Ethernet ports
support network speeds of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or
1000 Mbps. They can operate in half- and full-duplex
modes. Auto-sensing technology enables each port
to automatically detect the speed of the device
connected to it (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps),
and adjust its speed and duplex accordingly.
The Switch is equipped with 4 auto-
miniGBIC (1-2) The miniGBIC (gigabit interface
converter) port is a connection point for a
miniGBIC expansion module, so the Switch can
be uplinked via fiber to another switch. The
MiniGBIC port provides a link to a high-speed
network segment or individual workstation at
speeds of up to 1000 Mbps.
To establish a Gigabit Ethernet connection using
a miniGBIC port, you will need to install a MGBT1,
MGBSX1, or MGBLH1 Gigabit expansion module
and use Category 5e cabling or fiber optic cabling.
To establish a Fast Ethernet connection using a
miniGBIC port, you will need to install a MFEFX1
(100BASE-FX) or MFELX1 (100BASE-LX) 100SFP
Transceiver and use fiber optic cabling.
Stack ID Displays the S
the Switch is in stack mode.
Stack Master (Amber)
the stack Master during stack mode.
NOTE: On the SLM248G4S, MiniGBIC ports are
shared with Gigabit Ethernet ports. If a miniGBIC
port is used, then the shared Gigabit Ethernet
port on the Switch cannot be used. The following
table defines the shared port mapping of the
SLM248G4S Switch.
SLM248G4S Shared Port Mapping
miniGBIC Port Gigabit Port
miniGBIC 1 Port G3
miniGBIC 2 Port G4
witch’s unit ID number if
Lights up if the switch is
Back Panel
The Console port and power port are located on the back
panel of the Switch
CONSOLE The Console port is a serial port that
allows you to connect to a computer’s serial port
(for configuration purposes) using the provided
serial cable. You can use HyperTerminal to
manage the Switch using the console port.
POWER The Power port is where you connect
the AC power.
.
Back Panel of the SLM248G4S
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
3
Page 10

Chapter 3
Installation
Chapter 3:
Installation
Overview
This chapter will explain how to connect network devices
to the Switch. The following diagram shows a typical
network configuration.
Cable/DSL
Internet
When you connect your network devices, make sure you
do not exceed the maximum cabling distances, which are
listed in the following table:
Modem Router Wireless Access Point Server
10/100/1000
Desktop
Typical Network Configuration for the SLM248G4S
Maximum Cabling Distances
From To Maximum Distance
Switch Switch or Hub 100 meters
10/100
Notebook
Uplink via Fiber to
Switch
Pre-Installation Considerations
Fast Ethernet Considerations
If you are using the Switch for Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps)
applications, you must observe the following guidelines:
Full-Duplex Considerations
The Switch provides full-duplex support for its RJ-45
ports. Full-duplex operation allows data to be sent and
received simultaneously, doubling a port’s potential data
throughput. If you will be using the Switch in full-duplex
mode, the maximum cable length using Category 5 cable
is 100 meters.
1000BASE-T Cable Requirements
All Category 5 UTP cables that are used for 100BASE-TX
connections should also work for 1000BASE-T, providing
that all four wire pairs are connected. However, it is
recommended that for all critical connections, or any
new cable installations, Category 5e (enhanced Category
5) or Category 6 cable should be used. The Category
5e specification includes test parameters that are only
recommendations for Category 5. Therefore, the first
step in preparing existing Category 5 cabling for running
1000BASE-T is a simple test of the cable installation to be
sure that it complies with the IEEE 802.3ab standards.
Positioning the Switch
Before you choose a location for the Switch, observe the
following guidelines:
Make sure that the Switch is accessible and that the
Hub† Hub 5 meters
Switch or Hub† Computer 100 meters
A hub refers to any type of 100 Mbps hub. A 10 Mbps hub connected
†
to another 10 Mbps hub can span up to 100 meters.
•
cables can be connected easily.
Keep cabling away from sources of electrical noise,
•
power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures.
Position the Switch away from water and moisture
•
sources.
To ensure adequate air flow around the Switch, be
•
sure to provide a minimum clearance of two inches
(50 mm).
Do not stack free-standing Switches more than four
•
units high.
Placement Options
There are two ways to physically install the Switch, either
set the Switch on its four rubber feet for desktop placement
or mount the switch in a standard-sized, 486,2-mm wide,
1U-high rack for rack-mount placement.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
4
Page 11

Chapter 3
Installation
Desktop Placement
Attach the rubber feet to the recessed areas on the
•
bottom of the Switch.
Place the Switch on a desktop near an AC power source.
•
Keep enough ventilation space for the switch and
•
check the environmental restrictions mentioned in the
Specifications Appendix as you are placing the Switch.
Connect the Switch to network devices according to
•
the Hardware Installation instructions below.
Attaching the Switch’s Rubber Feet
Rack-Mount Placement
To rack-mount the Switch in any standard 486,2-mm wide,
1U-high rack, follow the instructions described below.
Place the Switch on a hard flat surface with the front
1.
panel facing you.
Attach a rack–mount bracket to one side of the Switch
2.
with the supplied screws and secure the bracket
tightly.
Attaching the Brackets
Follow the same steps to attach the other bracket to
3.
the opposite side.
After the brackets are attached to the Switch, use
4.
suitable screws to securely attach the brackets to any
standard 486,2-mm rack.
When rack-mounting the Switch, please observe the
following guidelines
Elevated Operating Ambient If installed in a closed
•
or multi-unit rack assembly, the operating ambient
temperature of the rack environment may be greater
than room ambient. Therefore, consideration should
be given to installing the equipment in an environment
compatible with the maximum ambient temperature
(Tma) specified by the manufacturer.
Reduced Air Flow Installation of the equipment
•
in a rack should be such that the amount of air flow
required for safe operation of the equipment is not
compromised.
Mechanical Loading Mounting of the equipment in
•
the rack should be such that a hazardous condition is
not achieved due to uneven mechanical loading.
Circuit Overloading Consideration should be given
•
to the connection of the equipment to the supply
circuit and the effect that overloading of the circuits
might have on overcurrent protection and supply
wiring. Appropriate consideration of equipment
nameplate ratings should be used when addressing
this concern.
Reliable Earthing Reliable earthing of rack-mounted
•
equipment should be maintained. Particular attention
should be given to supply connections other than
direct connections to the branch circuit (e.g. use of
power strips).
Mounting in Rack
Connect the Switch to network devices according to
5.
the Hardware Installation instructions below.
Hardware Installation
To connect network devices to the Switch, follow these
instructions:
Make sure all the devices you will connect to the Switch
1.
are powered off.
For a 10/100 Mbps device:
2.
Connect a Category 5 Ethernet network cable to
•
one of the numbered ports on the Switch.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
5
Page 12

Chapter 3
Installation
For a 1000 Mbps device:
Connect a Category 5e Ethernet network cable to
•
port G1, G2, G3, or G4 on the Switch.
Connect the other end of the network cable to a PC or
3.
other network device.
Repeat steps 2 and 3 to connect additional devices.
4.
If you are using a miniGBIC port, then connect a
5.
miniGBIC module to a miniGBIC port. For more detailed
instructions, refer to “Uplinking the Switch“.
Connect the supplied power cord to the Switch’s
6.
power port, and plug the other end into an electrical
outlet. When connecting power, always use a surge
protector.
IMPORTANT: Make sure you use the power
cord that is supplied with the Switch. Use of a
different power cord could damage the Switch.
Power on the devices connected to the Switch. Each
7.
active port’s corresponding LED will light up on the
Switch.
Uplinking the Switch
The hardware installation is complete. Proceed to
“Chapter 5: Configuration Using the Web-based Utility”,
for directions on how to set up the Switch.
Configuring Stacking Mode
The SLM224G4S and SLM248G4S Switches can operate in
either standalone mode or stacking mode. In standalone
mode, the switch operates independently of other
switches. In stacking mode, multiple Resilient Clustering
Smart Switches are connected together to effectively form
a single switch. The default operating mode is stacking
mode.
A Switch stack can contain any combination of SLM224G4S
and SLM248G4S units, with the following limits:
SLM224G4S only: Maximum of 6 units
•
SLM248G4S only: Maximum of 4 units
•
SLM224G4S and SLM248G4S: Maximum of 192 10/100
•
ports (total among all switches)
Each switch in a stack is assigned a unique unit number.
These numbers indicate the switch’s status in the stack:
Unit 1: The switch is the Master unit. The master handles
•
the management functions for the entire stack.
Unit 2: The switch is the Backup Master unit. The backup
To uplink the Switch using a 1000 Mbps Ethernet port,
connect one end of a Cat 5e (or better) Ethernet network
cable to a Gigabit port, then connect the other end of the
cable into the peripheral device’s uplink port. MDI/MDIX
will automatically detect the speed and cable type.
To uplink the Switch using the miniGBIC port, connect
a miniGBIC module to a miniGBIC port whose shared
Ethernet port is not being used (a miniGBIC port and its
shared Ethernet port cannot be used at the same time).
The following table shows which Ethernet ports are shared
with the miniGBIC ports.
Ethernet Ports Shared with miniGBIC Ports
Switch
SLM248G4S G3 G4
SLM224G4S G3 G4
To establish a Gigabit Ethernet connection using a miniGBIC
port, you will need to install a MGBT1, MGBSX1, or MGBLH1
Gigabit expansion module and use Category 5e cabling or
fiber optic cabling.
To establish a Fast Ethernet connection using a miniGBIC
port, you will need to install a MFEFX1 (100BASE-FX) or
MFELX1 (100BASE-LX) 100SFP Transceiver and use fiber
optic cabling.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Port Shared with
miniGBIC1
Port Shared with
miniGBIC2
•
master automatically becomes the new master if the
master fails.
Unit 3, 4, 5, 6: The switch is a Slave unit. (Depending on
•
the switch models used, 5 and 6 may not be valid.)
The Switches are connected together using a pair of Gigabit
ports on each Switch: G1 and G2, G3 and G4, or miniGBIC1
and miniGBIC2. Linksys recommends using Gigabit ports
G1 and G2 (the default stacking ports). Connections are
made using Category 5e Ethernet network cables.
To set up a stack with six switches, follow these steps:
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
1.
cable to port G1 on Unit 1.
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit 2.
2.
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
3.
cable to port G1 on Unit 2.
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit 3.
4.
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
5.
cable to port G1 on Unit 3.
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit 4.
6.
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
7.
cable to port G1 on Unit 4.
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit
8.
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
9.
cable to port G1 on Unit 5.
5.
6
Page 13

Chapter 3
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit 6.
10.
Connect one end of a Category 5e Ethernet network
11.
cable to port G1 on Unit 6.
Connect the cable’s other end to port G2 on Unit 1.
12.
For a stack with less than 6 switches, the steps are similar
except that port G1 of the last switch in the stack must be
connected back to port G2 of the first switch in the stack.
The following is an example of setting up a stacked
configuration using three SLM248G4S switches.
Connect port G1 on Unit 1 to port G2 on Unit 2.
1.
Installation
For detailed information on switch stacking, refer to
“Appendix B: About Switch Stacking.”
For more information on stack configuration using the
Console Interface, refer to “Stack Configuration” and
“System Mode” in “Chapter 4: Configuration Using the
Console Interface” .
For more information on stack configuration using the
Web-based Utility, refer to “Setup > Stack Management”
in “Chapter 5: Configuration Using the Web-based Utility”.
Reassigning a Slave Unit as the Master Unit
You can reassign a slave unit so that it becomes the master
unit. To do this, you swap their unit numbers. For example,
to make slave unit 5 be the master, you change the master’s
unit number from 1 to 5 and the slave’s unit number from
5 to 1. To change the unit numbers, you can use either the
Web-based utility or the console interface.
Connect Unit 1 to Unit 2
Connect port G1 on Unit 2 to port G2 on Unit 3.
2.
Connect Unit 2 to Unit 3
Connect port G1 on Unit 3 to port G2 on Unit 1.
3.
The following describes the procedure for changing a
slave unit into the master unit. In this example, unit 5 is
made the master unit.
Swap the unit numbers. That is, change the unit
1.
number of the current master from 1 to 5, and change
the unit number of slave unit 5 from 5 to 1. (The order
in which these are performed is not significant.)
Power off the new unit 5 (the former master unit).
2.
Power off the new master unit 1 (the former slave unit
3.
5) briefly, then power it on again.
Power up the new unit 5.
4.
NOTE: If unit 2 (the backup master) is made the
master unit, steps 2 through 4 can be skipped.
Replacing a Stacked Switch
To replace one switch in a stack with another switch
without having to reboot or power down the stack:
Run the Web-based utility.
1.
Go to the Setup > Stack Configuration screen.
2.
Make sure that the Stacking Ports After Reset setting
3.
matches the type of stacking ports (Copper Ports or
Combo Ports) that are used to connect the switches.
Verify that the Unit No. After Reset settings specify the
4.
correct unit number for the switch being replaced.
Click Save Settings to save the stack settings.
5.
Disconnect the switch being replaced, then connect
6.
the new switch using the same stacking ports (copper
or combo) as before.
Connect Unit 3 to Unit 1
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
The stack should continue to operate as before.
7
Page 14
Chapter 4
Chapter 4:
Configuration Using the
Installation
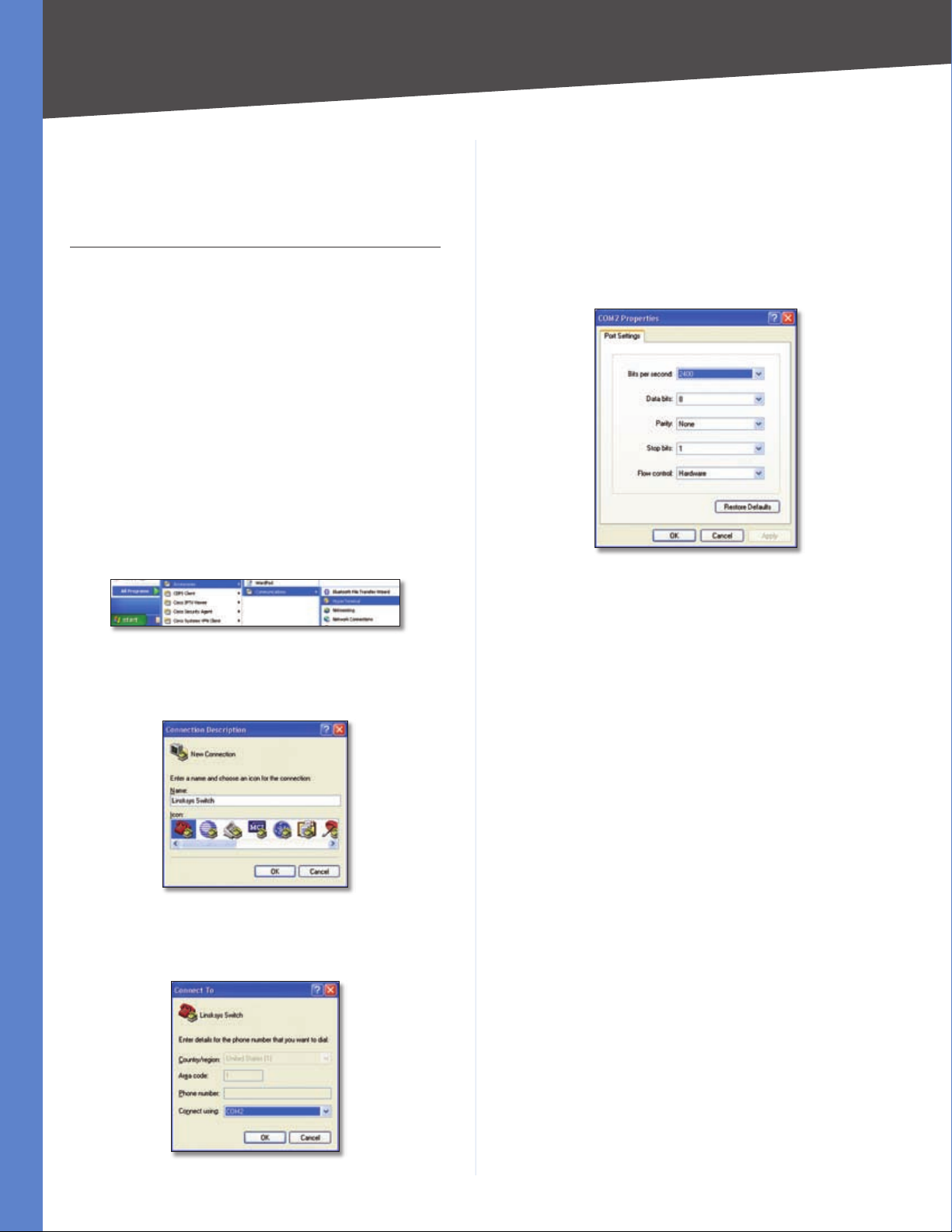
Set the serial port settings as follows, then click OK.
5.
Bits per Second: 38400
Databits: 8
Console Interface
Overview
The Switch features a menu-driven console interface that
lets you perform basic switch configuration and easily
manage your network. To use the console interface, you
either run the HyperTerminal application to configure a
serial connection through the Switch’s console port, or
run a telnet session over an Ethernet connection.
Using the HyperTerminal Application
To access the console interface using HyperTerminal:
Click the Start button.
1.
Select All Programs > Accessories > Communications
2.
> HyperTerminal.
Start > All Programs > Accessories > Communications > HyperTerminal
Enter a name for this connection. Select an icon for the
3.
application, then click OK.
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
HyperTerminal Properties Screen
The Login screen appears. Proceed to the “Login”
6.
section below.
Using telnet
In addition to using HyperTerminal to operate the console
interface through the Switch’s console port, you can also
use a telnet session to operate the console interface
through an Ethernet connection.
Click Start, then select All Programs > Accessories >
1.
Command Prompt to open a command prompt.
At the prompt, enter telnet 192.168.1.254, then press
2.
Enter.
The Login screen appears. Proceed to the “Login”
3.
section below.
HyperTerminal Connection Description Screen
Select a port to communicate with the switch. Select
4.
COM1 or COM2.
HyperTerminal Connect To Screen
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
8
Page 15

Chapter 4
Installation
How to Use the Console Interface
The Console Interface consists of a hierarchical series of
menu screens and settings screens. Each menu displays
a list of options. Selecting an option brings up a settings
screen where you can configure the relevant settings.
To select a menu option, either press the number of the
option in the list (for example, press 5 to select Help from
the Main Menu), or use the arrow keys to move up or down
the list until the option is highlighted, then press Enter.
The lower portion of each settings screen lists the actions
and navigation keys. The actions (Edit, Save, Quit) allow
you to make changes to the settings. The navigation keys
(Arrow Keys, Tab, Backspace, Space, Esc) allow you to
highlight and select different items within the screen.
To change a setting, highlight Edit, then press Enter. Use
the arrow keys to highlight the setting to be changed,
then enter its new value (or press Space to toggle through
the list of values). To save your changes and remain in the
settings screen, highlight Save, then press Enter. To return
to the previous screen, highlight Quit, then press Enter.
To cancel all changes and return to the previous screen,
press Esc, then select Quit.
Switch Main Menu
After successful login, the Main Menu screen appears. This
screen displays six menu choices: System Configuration
Menu, Port Status, Port Configuration, System Mode, Help,
and Log Out.
Main Menu
System Configuration Menu
Login
The console interface starts by displaying the Login screen.
The first time you open the console interface, use the
default username admin and leave the password blank,
then press the Enter key. You can set a password later
from the User and Password Settings screen.
Console Login Screen
If you are using HyperTerminal, enter the username and
password at the prompts. Then press Enter to log in.
If you are using telnet, use the arrow keys to select Edit
and press Enter. Enter the username and password in the
respective fields. Then press Esc to return to the Login
screen. Use the arrow keys to select Execute and press
Enter to complete the login process.
System Configuration Menu
The System Configuration Menu provides the following
options:
System Information
1.
Management Settings
2.
User and Password Settings
3.
Security Settings
4.
IP Configuration
5.
File Management
6.
Restore System Default Settings
7.
Reboot System
8.
Stack Configuration
9.
0. Back to Main Menu
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
9
Page 16

Chapter 4
Installation
System Information
From the System Information screen you can check current
firmware versions and other general switch information.
System Information
Versions
The Versions screen displays version-related information
for each switch in the system.
Management Settings
The Management Settings screen displays the Serial Port
Configuration option.
Management Settings
Serial Port Configuration
The Serial Port Configuration screen displays the current
baud rate setting. To change the baud rate, select Edit,
then use the spacebar to toggle through the different
baud rates. Use the Save action to set the new baud rate.
Versions
Unit The unit number of the switch, from 1 to 6.
Status The status of the switch, either master or slave.
Software Version The version number of the software .
Boot Version The version number of the boot file.
Hardware Version The Switch’s current hardware setup.
User & Password Settings
The User & Password Settings screen displays all the user
accounts defined on the system.
General System Information
The General System Information screen displays the System
Description, System Up Time, System MAC Address, System
Contact, System Name and System Location.
The default account is admin. You cannot edit this account
(its user name and password cannot be changed). For
security purposes, Linksys recommends creating at least
one user account with a unique user name and password.
General System Information
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
You can create up to five user accounts total.
Serial Port Configuration
User & Password Settings
10
Page 17

Chapter 4
Installation
(When you create your first user account, it will appear as
though you are editing the admin account; however, you
are only
The admin account is not overwritten or deleted.)
Once you have created a user account, you can edit it
(change the user name and/or password) or delete it. If the
system contains only one user account and you delete that
account, the original admin account will reappear in its
place. This is because the system must always have at least
one account.
To add a new user, use the arrow keys to select Edit,
press Enter, then enter the new account’s user name and
password in the Username and Password columns, and
re-enter the password in the Password Again column to
confirm the password.
To delete an existing user account, use the arrow keys to
select Edit, press Enter, then delete the user name in the
Username column.
To save your changes, press Esc, use the arrow keys to
select Save, then press Enter.
replacing the admin account with the new account.
Security Settings
IP Configuration
The IP Configuration screen displays three menu choices:
IP Address Settings, HTTP Configuration, and Network
Configuration.
IP Configuration
IP Address Settings
The IP Address Settings screen allows you to set the IP
information for the Switch.
The IP Configuration screen displays one option: Disable
Active Management Access Profile.
Security Settings
Selecting this option will prompt you to confirm that you
want to disable the active management access profile.
NOTE: This setting has no effect when
Management Access Rules are not defined.
IP Address Configuration
IP Address This sets the Switch’s IP Address. The default
setting is 192.168.1.254. If you change the IP address,
verify that the address you enter is correct and does not
conflict with another device on the network.
Subnet Mask This combined with the IP Address defines
the Switch’s network address.
Default Gateway This defines the IP Address for the
default gateway of the network.
Management VLAN This is the ID number of the
Management VLAN.
DHCP Client The status of the DHCP client is displayed.
If you want the Switch to be a DHCP client, then select
ENABLE. If you want to assign an static IP address to the
Switch, then enter the IP settings and select DISABLE.
HTTP
The HTTP screen allows you to set the Hyper Text Transfer
Protocol server (web server) information for the Switch.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
11
Page 18

Chapter 4
Installation
HTTP
HTTP Server Enable or disable the Switch’s HTTP server
function.
HTTP Server port Set the TCP port that HTTP packets are
sent and received from.
Network Configuration
The Network Configuration screen offers a choice of two
tests, Ping and TraceRoute.
Network Configuration
Ping The Ping screen displays the IP address of the
location you want to contact.
TraceRoute
Select Edit to change the IP address, and select Execute
to begin the traceroute test.
After the traceroute test is complete, the TraceRoute
screen displays the IP address, status, and statistics of the
traceroute test.
File Management
The File Management screen allows you to upload or
download files, such as the startup configuration, boot, or
image file, using a TFTP server.
File Management
Source File Specify the location of the file to transfer.
Select one of the following:
TFTP If the file is located on a TFTP server.
•
Image If the file is a software code file.
•
Startup-config If the file is a configuration file.
•
Destination File Specify where the file is to be transferred.
Select one of the following:
TFTP If the file is to be uploaded to a TFTP server.
•
Ping
Select Edit to change the IP address, and select Execute
to begin the ping test.
After the ping test is complete, the Ping screen displays
the IP address, status, and statistics of the ping test.
TraceRoute The TraceRoute screen displays the IP address
of the address whose route you want to trace.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Image If the file is to be downloaded as a software
•
code file.
Startup-config If the file is a configuration file
•
Boot If the file is a boot file.
•
File Name Enter the name of the file to be uploaded or
downloaded.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the TFTP server that
will transfer the file.
12
Page 19

Chapter 4
Installation
Select Edit to change the settings. When your changes
are complete, press Esc to return to the Action menu, and
select Execute to upload or download the designated file.
If you are downloading a new boot image, please follow
these steps:
Download the new boot code. DO NOT RESET THE
1.
DEVICE!
Download the new software image.
2.
Reset the device now.
3.
Restore System Default Settings
To restore the Switch back to the factory default settings,
select Restore System Default Setting and press Enter.
A prompt appears in the lower part of the screen asking
you to confirm the requested action. Press Y to continue
or N to cancel the action.
Restore Default
Reboot System
If you want to restart the Switch, select Reboot System
and press Enter. When you are prompted to confirm the
action, press Y to continue or N to cancel the action.
Stack Configuration
The Stack Configuration screen displays information about
the switch stack and allows you to change those settings.
Unit The unit number of the switch, from 1 to 6.
MAC Address The MAC address of the switch.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Reboot System
Stack Configuration
13
Page 20

Chapter 4
Installation
Software The version number of the software that runs
the switch.
Uplink The ID number of the switch that has an uplink
connection to this switch.
Downlink The ID number of the switch that has a
downlink connection from this switch.
Status The status of the switch, either master or slave.
ID After Reset The ID number that the Switch will have
after the next system reset. Values are Auto or 1 to 6.
Back to Main Menu
Select Back to Main Menu to exit the System Configuration
Menu and return to the Main Menu screen.
Port Status
The Port Status screen displays status information for each
of the switch’s ports, consisting of the port number, the
port’s status, the link status, the port’s speed and duplex
mode, and flow control status.
The settings on the Port Status screen cannot be edited.
If you want to change a port’s settings, use the Port
Configuration screen.
System Mode
The System Mode screen displays information about the
system mode:
System Mode
Current System Mode This is always set to Layer 2.
System Mode The system mode, either Stack or
Standalone. This cannot be changed.
Stacking Mode after Reset This indicates the mode,
Stack or Standalone, that the system will be in following
the next system reset. The default mode is Stack.
Help
The Help screen explains how to navigate the various
screens of the console interface.
Port Status
Port Configuration
The Port Configuration screen allows you to change a
port’s settings. You can enable or disable a port, or set
its auto-negotiation status, speed and duplex mode, and
flow control status.
Port Configuration
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Logout
Select Logout to log out of the console interface.
Help
14
Page 21
Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Chapter 5:
Configuration Using the
Web-based Utility
This chapter describes the features included in the
Web-based Utility. All features shown in this chapter,
unless specifically identified, are included in all Resilient
Clustering Smart Switches. Unique features for specific
Switches are noted.
NOTE: The web-based utility is optimized for
a screen resolution of 1024 x 768. Internet
Explorer version 5.5 or above is required.
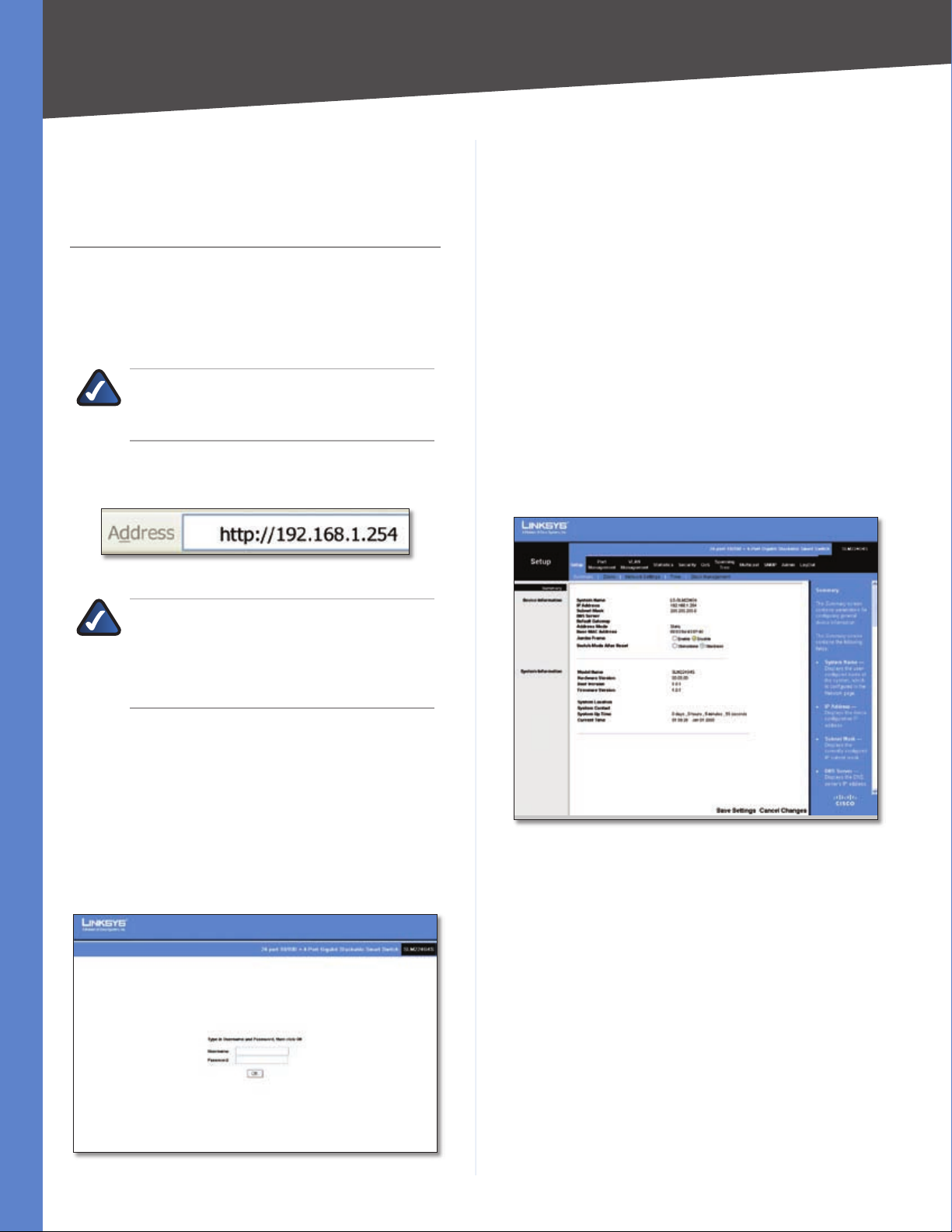
To use the utility, open your web browser, enter
http://192.168.1.254 in the Address field, then press Enter.
Address Bar
Each time you log in, the web-based utility first displays
the Setup tab’s Summary screen. To access another screen,
you first select the appropriate category from among
the 11 tabs that appear at the top of the screen: Setup,
Port Management, VLAN Management, Statistics,
Security, QoS, Spanning Tree, Multicast, SNMP, Admin,
and Logout. Then, select the desired screen from the list
directly below the tab names.
Setup
The Setup tab contains the Summary, Zoom, Network
Settings, Time, and Stack Management screens.
Setup > Summary
The Summary screen displays a summary of Switch
information. The settings shown cannot be modified
from the Summary screen; however, many of them can be
modified from the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
NOTE: The default IP address is 192.168.1.254.
If you have changed the IP address or are using
DHCP to assign it, enter the new IP address
instead. The computer you use for configuration
should be on the same subnet as the Switch.
The Login screen appears. Enter admin in the Username
field and enter the password in the Password field. If this is
the first time you are using the utility, leave the Password
blank. Then press OK to log in. The Setup tab’s Summary
screen appears.
(After you have completed your first login, f
purposes it is recommended that you set a password at
a later time. For detailed information on changing the
password, refer to section “Admin > User Authentication.”
or security
Setup > Summary
The Summary screen has two sections: Device Information
)
and System Information. These are described below.
Device Information
System Name Displays the name of the Switch, if one has
been entered on the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
IP Address The IP address assigned to the Switch. The
Switch’s default IP address is 192.168.1.254. This setting
can be configured from the Setup tab’s Network Settings
screen.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask assigned to the Switch.
The default is 255.255.255.0. This setting can be
configured from the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
Login Screen
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
15
Page 22

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
DNS Server The IP address of your ISP’s server that
translates the names of websites into IP addresses. This
setting can be configured from the Setup tab’s Network
Settings screen.
Default Gateway The IP address (default 0.0.0.0) of the
gateway router between the Switch and management
stations on other network segments. This setting can be
configured from the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
NOTE: The Default Gateway cannot be
configured if the system IP address is set to
192.168.1.254. (The system IP Address is set
using Setup > Network Settings.)
Address Mode Specifies whether the Switch’s IP address
is Static or dynamically assigned using DHCP (Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol). This setting can be
configured from the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
The default setting is Static.
Base MAC Address Displays the Switch’s MAC address.
Jumbo Frame This setting enables or disables Jumbo
frames on the Switch. A maximum packet size of 9 KB is
supported. Jumbo frames allow data to be transmitted
using fewer frames, providing lower overhead, quicker
processing time, and fewer interruptions. Select either
Enable or Disable (default).
NOTE: The Jumbo Frame feature functions only
on the Gigabit ports (G1-G4).
Switch Mode After Reset This setting specifies the
system mode following a system reset. Select either
Standalone or Stackable (default).
Click Save Settings to save your changes. Click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Setup > Zoom
The Zoom screen depicts the status of all the ports in the
system. This screen displays a front-panel view of each
Switch. The color of each switch port indicates its status:
Green This port has a connection.
Gray This port has no connection.
Orange The administrator has closed down this port.
Setup > Zoom
Clicking on a port displays the Port Configuration screen.
NOTE: The port colors in the Zoom screen are
not related to the colors of the port LEDs. The
port LEDs display different status information,
as described in “Chapter 2: Overview.”
System Information
Model Name Displays the model name of the Switch.
Hardware Version
Boot Version Displays the current boot version.
Firmware Version Displays the current software version
System Location Displays the location of the system if it
has been defined. This setting can be configured from the
Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
System Contact The name of the administrator appears
here, if one has been defined. This setting can be configured
from the Setup tab’s Network Settings screen.
System Up Time Displays the length of time that has
elapsed since the Switch was last reset.
Current Time Displays the current time. This setting can
be configured from the Setup tab’s Time screen.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Displays the current hardware version.
Setup > Network Settings
Setup > Network Settings
16
Page 23
Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
The Network Settings screen allows you to edit the
following information.
Identification
System Name Specifies the name of the Switch. Enter the
name into the text field provided. By default, the system
name is LS-SLM224G4 or LS-SLM248G4.
System Location This is used to enter a description of
where the Switch is physically located, such as 3rd Floor.
System Contact Enter the name of the administrator
responsible for the system.
System Object ID This is used for SNMP purposes and is
set to 1.3.6.1.4.1.3955.6.5.224(248).2.
Base MAC Address
Displays the Switch’s physical address
IP Configuration
Management VLAN This drop-down menu allows you to
select the Management VLAN. The default value is 1.
WARNING: If the system IP address (IP Address
field) is set to 192.168.1.254, then keep the
default values for the Management VLAN field
(default value: 1), and the Default Gateway
field (default value: 0.0.0.0). These fields must
remain set to the default values. Otherwise, you
may not be able to access the system.
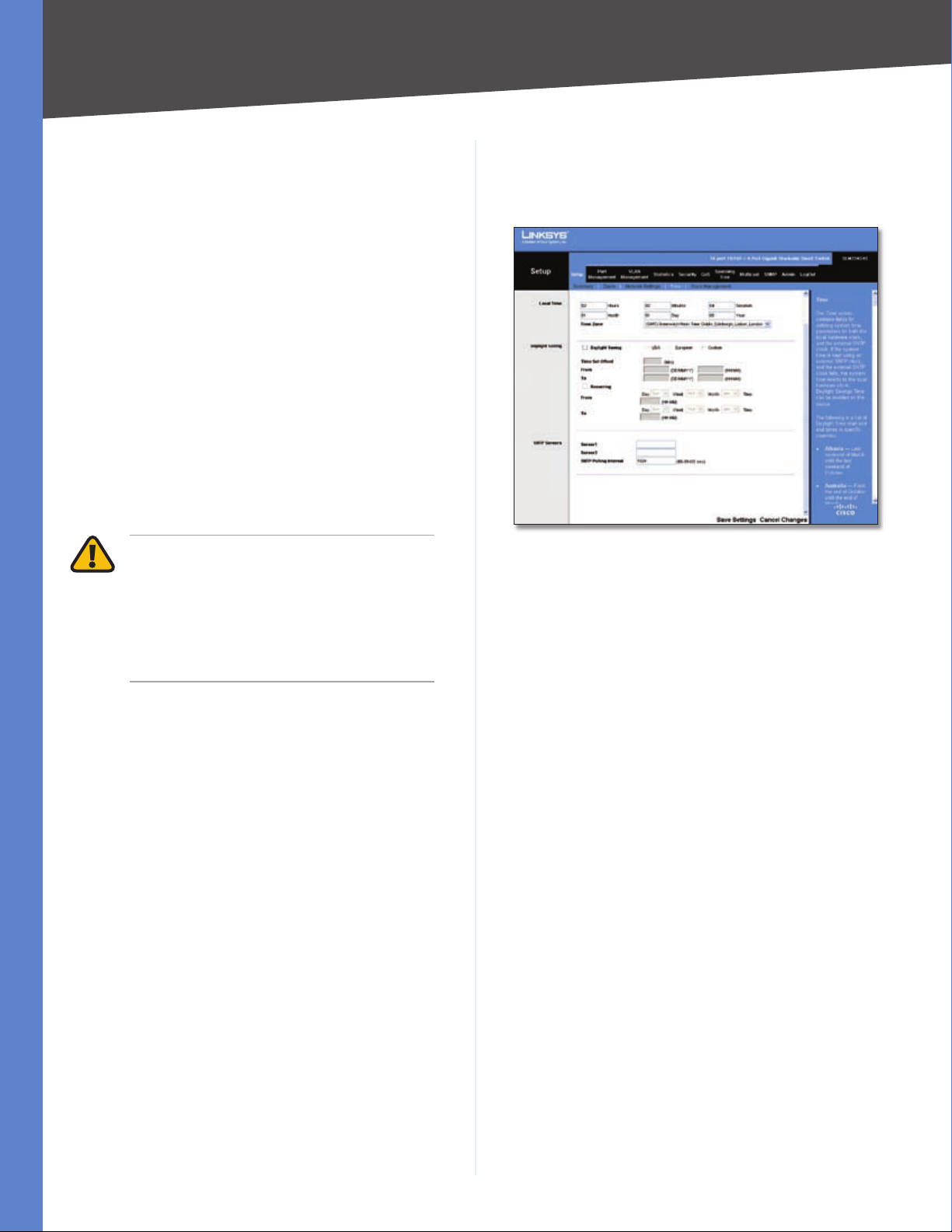
Setup > Time
The Time screen allows you to configure the time settings
for the Switch.
.
Setup > Time
Local Time
Here you set the system date and time for the Switch. All
settings noted as “two-digit” must contain a leading zero if
the value is less than 10 (for example, 01 instead of 1).
Hours Enter the two-digit hour here.
IP Address Mode Specifies whether the Switch’s IP
address is Static or dynamically assigned using DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Selecting Static
allows you to enter a static IP address, subnet mask and
default gateway using the text field provided. The default
setting is Static.
IP Address If you are using a static IP address, enter
the IP address here. The Switch’s default IP address is
192.168.1.254.
Subnet Mask If you are using a static IP address, enter
the subnet mask for the currently configured IP address.
The default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway If you are using a static IP address,
enter the IP address of the default gateway. The default
value is 0.0.0.0.
DNS Server If you are using a static IP address, enter the
IP address of the DNS server. A second DNS address can be
specified in the additional text field provided.
Click Save Settings to save your changes. Click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
Minutes Enter the two-digit minutes here.
Seconds Enter the two-digit seconds here.
Month Enter the two-digit month here.
Day Enter the two-digit day here.
Year Enter the last two digits of the year here (for example,
07 instead of 2007).
Time Zone Select your time zone from the drop-down
menu. Time zones are identified by the difference between
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and local time.
Daylight Saving
This is where you configure Daylight Saving Time.
Daylight Saving To enable daylight saving time, check
the box, then select either USA or European to use US
or European daylight saving time, respectively. To use a
different type of daylight saving time, select Custom, then
customize the following settings:
Time Set Offset Enter the time difference in minutes
•
for daylight saving time. The default is 60 minutes.
From Enter the starting date for daylight saving time
•
using the format DD/MM/YY.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
17
Page 24

Chapter 5
To Enter the ending date for daylight saving time
•
using the format DD/MM/YY.
Recurring If daylight saving time has fixed start and
•
end dates, check this box and fill in these fields:
From Specify the day, week, month, and time
•
when daylight saving time will be enabled.
To Specify the day, week, month, and time when
•
dalight saving time will be disabled.
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
NOTE: If unit 1 is the master unit and unit 1
becomes unavailable, unit 2 will immediately
become the master unit. If unit 1 becomes
available again within 10 minutes, unit 1 will be
restored as the master unit. If unit 1 becomes
available after 10 minutes, unit 2 will remain the
master unit. In this case, to restore unit 1 as the
master unit, set Master Election to specify unit 1
as the master unit, then reboot the stack.
SNTP Servers
This is where you configure a Simple Network Time
Protocol (SNTP) server. SNTP servers are used to set the
system time and date automatically at set intervals.
Server1 The IP address of the primary SNTP server.
Server2 The IP address of a secondary SNTP server to be
accessed if the primary SNTP server is unavailable.
SNTP Polling Interval Enter the polling interval in
seconds. The valid range of values is 60 to 86400. The
default value is 1024 seconds (approx. 17 minutes).
Setup > Stack Management
The Stack Management screen allows you to configure the
settings for the Switch stack.
Stacking Ports After Reset This indicates which Gigabit
ports will be used for stacking when the system is reset.
Select either Copper Ports (default) or Combo Ports.
Unit No. After Reset This is used to change the unit
numbers of the switches in the stack when the system is
reset. To change a switch’s unit number, locate the unit in
the Unit No. column, then select the new unit number in
the Unit No. After Reset column.
Port Management
The Port Management tab contains the Port Settings, Link
Aggregation, and LACP screens.
Port Management > Port Settings
The Port Settings screen displays the settings for the ports
on each switch in the system. The information on the Port
Settings screen is read-only. Click Detail to the right of a
port’s information to edit that port’s settings using the
Port Configuration screen. For detailed information on the
Port Configuration screen, refer to the “Port Configuration“
section.
Setup > Stack Management
Master Election If you want the system to assign the
master unit, keep the default setting, Automatically. If
you want to specify the master unit yourself, select Force
Master, then select unit 1 or 2 from the drop-down
menu.
The Port Settings screen displays the following information.
For more information on these settings, refer to the “Port
Configuration“ section.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Port Management > Port Settings
18
Page 25

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Unit No. The unit (switch) that you are managing. The
default is the Master unit’s number. To manage a different
unit, select its number from the drop-down menu.
Port The port number (preceded by the unit number).
For example, 2/e1 indicates Unit 2, Ethernet Port 1.
Description The user-defined port description.
Administrative Status Select Down to take the port
offline. When Up is selected, the port can be accessed
normally.
Link Status The port’s operational status. The value is
either Up (the port has an active connection) or Down
(the port has no active connection, or has been taken
offline by an administrator).
Speed The port’s configured rate in Mbps.
Duplex The port’s current duplex mode, Half or Full.
MDI/MDIX The port’s MDI/MDIX type. The MDI setting is
used if the port is connected to an end station. The MDIX
setting is used if the port is connected to a hub or another
switch.
Flow Control This is the flow control status of the port. It
is active when the port uses Full Duplex Mode.
Port The port number. To edit the information for
another port, select the port from the drop-down menu.
(Port numbers consist of either “e” for Ethernet, or “g” for
Gigabit, followed by the appropriate number.)
Description The user-defined port description of up to
64 characters. This field is blank by default.
Port Type (Read-only) The port’s connection type and
speed. The types are:
copper The port has a copper connection.
•
ComboC The Gigabit port has a copper connection.
•
ComboF The Gigabit port has a fiber optic
•
connection.
The port speed is prexed onto the type, for example
10M-copper indicates a 10 Mbps copper connection.
Admin Status The port’s administrative status. Select
either Up or Down to enable or disable traffic forwarding
through the port.
Current Port Status (Read-only) The port’s connection
status, either Up or Down.
Reactivate Suspended Port If the port has been
suspended, select this checkbox to reactivate the port.
Type Displays the port type.
LAG This indicates if the port belongs to a LAG.
Port Configuration
The Port Configuration screen lets you configure a port’s
settings. To use this screen, click Detail in the Detail
column on the Port Settings screen.
Port Management > Port Settings> Port Configuration
The Port Configuration screen contains the following fields
(“Read-only” indicates that a field cannot be edited).
Operational Status (Read-only) Displays whether the
port is operational or non-operational.
Admin Speed Use this to manually set the port’s
configured transmission rate in Mbps. You can select 10M,
100M, or 1000M (Gigabit ports only). Before you change
this setting, make sure that Auto Negotiation is disabled.
Current Port Speed (Read-only) The port’s current rate
in Mbps.
Admin Duplex The port’s duplex mode, either Full or
Half.
Current Duplex Mode (Read-only) The port’s current
duplex mode.
Auto Negotiation Select Enable (default) or Disable
to enable or disable Auto-Negotiation on the port. AutoNegotiation allows a port to advertise its transmission rate,
duplex mode, and flow control settings to other ports. If
you are using an SFP module on a port, Auto Negotiation
for that port should be set to Disable.
Current Auto Negotiation (Read-only) The port’s current
Auto-Negotiation status.
Admin Advertisement Select the speed(s) and duplex
mode(s) that the port will advertise. The available speeds
are determined by the port type. The following capabilities
are supported.
Max Capability The port advertises all speeds and
•
duplex mode settings.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
19
Page 26

Chapter 5
10 Half The port advertises 10 Mbps half-duplex
•
operation.
10 Full The port advertises 10 Mbps full-duplex
•
operation.
100 Half The port advertises 100 Mbps half-duplex
•
operation.
100 Full The port advertises 100 Mbps full-duplex
•
operation.
1000 Full (Gigabit ports only) The port advertises
•
1000 Mbps full-duplex operation.
Current Advertisement (Read-only) The speed
and duplex mode settings that the port is currently
advertising.
Neighbor Advertisement (Read-only) The speed and
duplex mode settings that the neighbor port (the port to
which the selected port is connected) is advertising. If the
port has no neighbor port, this field displays “Unknown.”
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Port Management > Link Aggregation
Port Management > Link Aggregation
Back Pressure Select Enable or Disable (default) to
enable or disable Back Pressure mode on the port.
Current Back Pressure (Read-only) The current Back
Pressure mode on the port.
Flow Control Select Enable or Disable to manually
enable or disable flow control, or select Auto-Negotiation
for automatic selection of flow control on the port.
Current Flow Control (Read-only) The current flow
control setting.
MDI/MDIX Select the port’s MDI/MDIX type, either MDI,
or MDIX. The MDI setting is used if the port is connected
to an end station. The MDIX setting is used if the port is
connected to a hub or another switch.
Current MDI/MDIX (Read-only) The port’s current MDI/
MDIX type.
LAG (Read-only) The LAG to which this port belongs, if
the port is a LAG member.
Click Save to save the settings and leave the screen open.
Click Save & Close to save the settings and close the
screen. Click Close to close the screen without saving the
settings.
You can create multiple links between devices that work
as one virtual, aggregate link. This is known as a Link
Aggregrated Group (LAG). LAGs offers a dramatic increase
in bandwidth for network segments where bottlenecks
exist, as well as providing a fault-tolerant link between two
devices. You can create up to eight LAGs on the Switch.
Each LAG can contain up to eight ports.
LAG The LAG number (1-8).
Description The user-defined description for the LAG.
Admin Status The administrative status of the interface.
To change the status, select Up to enable the interface, or
select Down to disable it.
Type Indicates if a LAG has been manually configured
(static) or dynamically set through LACP.
Link Status Displays the status of the link.
Speed Displays the port speed.
Duplex Displays the duplex mode.
Flow Control Displays the flow control.
LAG Mode Displays the LAG mode.
Detail To create a new LAG, click Detail in the Detail
column to display the Link Aggregation detail screen.
LAG Configuration
The Link Aggregation detail screen lets you configure a
LAG. You can create a LAG, select its ports, enable/disable
the LAG, and set the capability advertisements, speed,
duplex mode, and flow control. To use this screen, click
Detail on the Port Settings screen.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
20
Page 27

Chapter 5
Port Management > Link Aggregation > Detail
LAG The LAG number (1-8). To display or edit another
LAG, select the number from the drop-down menu.
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Current Flow Control (Read-only) The current flow
control setting.
Select Ports To add a port to the LAG, select its checkbox
in this section. You can select up to 8 ports per LAG.
Click Save to save the settings and leave the screen open.
Click Save & Close to save the settings and close the
screen. Click Close to close the screen without saving the
settings.
Port Management > LACP
In addition to LAGs that you create by manually grouping
ports together, you can also use the Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP) to automatically negotiate a LAG
link between the Switch and another network device.
The LACP screen contains fields for configuring LACP
LAGs.
Description The user-defined LAG description of up to
64 characters. This field is blank by default.
LACP Select the checkbox to enable Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP).
LAG Type (Read-only) The LAG type. The values are:
eth100m The LAG contains 100 Mbps Ethernet ports.
•
eth1000m The LAG contains 1000 Mbps Ethernet
•
ports.
Administrative Status The LAG’s administrative status.
Select either Up or Down to enable or disable the LAG.
Current Status (Read-only) The LAG’s status, either Up or
Down.
Admin Auto Negotiation Select Enable (default) or
Disable to enable or disable Auto-Negotiation on the
LAG. Auto-Negotiation allows a LAG to advertise its
transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control settings
to other LAGs.
Current Auto Negotiation (Read-only) The LAG’s current
Auto-Negotiation status.
Admin Speed Use this to manually set the LAG’s
configured transmission rate in Mbps. You can select 10M,
100M, or 1000M (Gigabit ports only). Before you change
this setting, make sure that Admin Auto Negotiation is
disabled.
Current LAG Speed (Read-only) The LAG’s current rate in
Mbps.
Admin Flow Control Select Enable or Disable to
manually enable or disable flow control, or select AutoNegotiation for automatic selection of flow control.
Port Management > LACP
Global Parameter
LACP System Priority The global LACP priority value,
from 1 to 65535. The default value is 1.
Port Priority
Unit No The number of the unit that you are managing.
Port The port to which the timeout and priority values
will be assigned. To configure a different port, select it
from the drop-down menu. If the port is not listed, click
Next in the LACP Port Table.
LACP Port Priority Defines the LACP priority value for
the port, from 1 to 65535. The default value is 1.
LACP Timeout The administrative LACP timeout value.
Select either Short or Long (default).
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
21
Page 28

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Admin Key (Read-only) A channel will only be formed
between ports with the same admin key. This only applies
to ports located on the same switch.
When you are finished entering the settings above, click
Update to apply the settings.
LACP Port Table
This section provides a read-only display of the current
LACP settings. For each port on the currently selected
unit, this table displays the Port Priority, LACP Timeout,
and Admin Key,
After you are finished setting the LACP parameters,
click Save Settings to save the settings, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel your changes.
VLAN Management
A VLAN is a group of ports that can be located anywhere
in the network, but communicate as though they belong
to the same physical segment.
VLANs help to simplify network management by allowing
you to move devices to a new VLAN without having
to change any physical connections. VLANs can be
easily organized to reflect departmental groups (such
as Marketing or R&D), usage groups (such as e-mail), or
multicast groups (used for multimedia applications such
as videoconferencing). You can create up to 128 VLANs on
the Switch.
Single VLAN
To create a single VLAN, enter the VLAN ID and VLAN
Name, up to 32 characters long, and click Add.
VLAN ID ID of the VLAN being configured (2-4093, no
leading zeroes).
VLAN Name Name of the VLAN (1 to 32 characters).
VLAN Range
To create a range of VLANs, enter the range of their IDs in
the VLAN Range fields and then click Add Range.
VLAN Table
This lists the ID, name, and status of each configured VLAN,
and the total number of VLANs. The VLAN status is either
Static (user-defined VLAN) or Default (default VLAN).
To remove a VLAN or a range of VLANs, select the VLANs in
the VLAN Table, then click Delete.
VLAN Management > Port Settings
The Port Settings screen allows you to manage the ports in
a VLAN. The port default VLAN ID (PVID) is configured from
the Port Settings screen. All untagged packets arriving at a
VLAN port are tagged with the port’s PVID.
VLAN Management > Create VLAN
The Create VLAN screen lets you create and configure
global parameters for VLANs.
VLAN Management > Create VLAN
VLAN Management > Port Settings
You can configure VLAN behavior for specific ports,
including the accepted frame type, VLAN identifier (PVID),
and ingress filtering.
Unit No. The number of the unit that you are managing.
Port The number of the port.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
22
Page 29

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Acceptable Frame Type This specifies the type of frames
that the port will accept. If All (default) is selected, the port
will accept all frame types, including tagged or untagged
frames. If Tagged is selected, the port accepts only tagged
frames. When set to All, each untagged frame received is
assigned to the specific VLAN that matches the PVID.
PVID Use this field to select the VLAN ID that will be
assigned to untagged frames received on the port.
Valid IDs are 1 (default) to 4093. VLAN 4094 is reserved
for internal use. VLAN 4095 is defined per standard and
industry practice as the Discard VLAN. Frames tagged for
the Discard VLAN are dropped.
Ingress Filtering Enables or disables Ingress filtering
on the port. Ingress filtering discards packets that do not
match port ingress rules. The default is Enabled.
LAG Displays the LAG, if any, to which the port belongs. A
port’s LAG settings override the VLAN port settings.
Click Save Changes to save your changes, or click Cancel
Changes to cancel.
VLAN Management > Port to VLAN
You use the Port to VLAN screen to add ports to a VLAN and
delete ports from a VLAN. When you add a port to a VLAN,
you also specify whether the port is tagged or untagged.
The Port to VLAN screen contains a Port Table with VLAN
parameters for each port. To add a port to or delete a
port from the VLAN, you select the port’s appropriate
configuration options from this table.
For each port in the VLAN, select the appropriate
configuration option:
Tagged The interface is a member of the VLAN. All
•
packets transmitted by the port will be tagged and will
carry VLAN information.
Untagged The interface is a member of the VLAN. All
•
packets transmitted by the port will be untagged and
will not carry VLAN information.
Excluded The interface is excluded from the VLAN.
•
This is the default option.
VLAN Management > VLAN to Port
The VLAN to Port screen displays each port’s VLAN
membership information. It is also used to add a port to or
delete a port from a VLAN.
Unit No. The unit number that contains the ports whose
VLAN information you wish to configure.
Port The number of the port being configured.
Join VLAN To configure the port’s VLAN membership,
press Join VLAN to bring up the Join VLAN to Port screen.
VLANs
belongs. Each VLAN ID ends with “T” if the port is tagged or
with “U” if the port is untagged in that VLAN.
LAG Displays the LAG to which the port belongs, if any.
If a port belongs to a LAG, it cannot belong to a VLAN.
However, the LAG to which the port belongs can be
configured to belong to a VLAN.
Displays the IDs of the VLANs to which the port
VLAN Management > Port to VLAN
Select VLAN Select the ID of the VLAN whose port
membership you are configuring.
Unit No. Select the unit that contains the ports for the
VLAN you are configuring.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Join VLAN to Port
The Join VLAN to Port screen appears when you click Join
VLAN in the VLAN to Port screen. You use this screen to
configure the port’s VLAN membership.
VLAN Management > VLAN to Port
23
Page 30

Chapter 5
VLAN Management > VLAN to Port > Join VLAN to Port
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
This screen allows you to display RMON statistics for the
Ethernet port or LAG that you specify. You can also specify
the rate at which the display will be refreshed.
Interface To display statistics for an Ethernet port, select
Unit No., then select the desired unit number and port
from the drop-down menus. To display statistics for a LAG,
select LAG and then select the desired LAG from the dropdown menu.
Refresh Rate Select the rate at which to refresh the
statistics display. The values are 15 sec, 30 sec, 60 sec, and
No Refresh (default).
Select VLAN This contains two fields. The field on the left
lists the IDs of all available VLANs to which the port can
belong; the field on the right lists the IDs of the VLANs to
which the port already belongs.
Add To add the port to an available VLAN, select the VLAN
from the list on the left, then select the desired Tagging
option and click Add. The VLAN ID now ending with “T” or
“U” will appear in the list on the right.
Remove To remove the port from a VLAN, select the VLAN
from the list on the right and click Remove. The VLAN ID
will appear in the list on the left without the “T” or “U”.
Tagging When you are adding a port to a VLAN, specify
whether the port is Tagged (default) or Untagged.
Click Save to save your changes and leave the screen open,
Save & Close to save your changes and close the screen, or
click Close to close the screen without saving your changes.
Statistics
The Statistics tab contains the Interface Statistics screen,
which lets you display statistics for a specified interface.
Statistics > RMON Statistics
Drop Events Displays the number of dropped events
that have occurred on the interface since the device was
last refreshed.
Received Bytes (Octets) Displays the number of octets
received on the interface since the device was last
refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS
octets, but excludes framing bits.
Received Packets Displays the number of packets
received on the interface, including bad packets,
Multicast and broadcast packets, since the device was last
refreshed.
Broadcast Packets Received Displays the number of
good broadcast packets received on the interface since
the device was last refreshed. This number does not
include Multicast packets.
Multicast Packets Received Displays the number of
good Multicast packets received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
CRC & Align Errors Displays the number of CRC and
Align errors that have occurred on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
Undersize Packets Displays the number of undersized
packets (less than 64 octets) received on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
Oversize Packets Displays the number of oversized
packets (over 1518 octets) received on the interface since
the device was last refreshed.
Fragments Displays the number of fragments (packets
with less than 64 octets, excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
Jabbers Displays the total number of received packets
that were longer than 1518 octets. This number excludes
frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of
octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral octet
(Alignment Error) number. The field range to detect
jabbers is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Statistics > RMON Statistics
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
24
Page 31

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Collisions Displays the number of collisions received on
the interface since the device was last refreshed.
Frames of xx Bytes Number of xx-byte frames received
on the interface since the device was last refreshed.
Clear Counters Click Clear Counters to reset all the
counters on this screen to zero.
Refresh Now Click Refresh Now to refresh the display
immediately with the latest information.
Statistics > RMON History
The RMON History screen contains information about
samples of data taken from ports. For example, the samples
may include interface definitions or polling periods.
Log Table
Source Interface Displays the interface from which the
history samples were taken.
Sampling Interval Indicates the time in seconds that
samplings are taken from the port.
Sampling Requested Displays the number of samples to
be saved. The range is 1-65535. The default value is 50.
Current Number of Samples Displays the current
number of samples taken.
Owner Displays the RMON station or user that requested
the information.
Click View History Table to open the RMON History Table
screen.
To delete an entry from the Log Table, select the entry,
then click Delete.
RMON History Table
Statistics > RMON History
RMON History
Source Interface Indicates the interface from which the
history samples were taken. To specify the interface, select
Unit No. (default) and specify the unit number and port
from the drop-down menus, or select LAG and select the
LAG number from the drop-down menu.
Sampling Interval Indicates (in seconds) how often
samples are taken from the ports. The range is 1 to 3600.
The default is 1800 seconds (30 minutes).
Current Number of Samples to Keep Indicates the
number of samples to save.
Owner Displays the RMON station or user that requested
the RMON information. Maximum length is 20 characters.
Click Add to List to add the configured RMON sampling
to the Log Table at the bottom of the screen.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
The RMON History Table screen contains interface specific
statistical network samplings. Each table entry represents
all counter values compiled during a single sample.
History Entry No. Displays the history table entry
number.
Owner Displays the RMON station or user that requested
the RMON information. The maximum length is 20
characters.
Sample No. Indicates the sample number from which
the statistics were taken.
Received Bytes (Octets) Displays the number of octets
received on the interface since the device was last
refreshed. This number includes bad packets and FCS
octets, but excludes framing bits.
Received Packets Displays the number of packets
received on the interface since the device was last
refreshed, including bad packets, Multicast and Broadcast
packets.
Statistics > RMON History > RMON HIstory Table
25
Page 32

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Broadcast Packets Displays the number of good
Broadcast packets received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed. This number does not include
Multicast packets.
Multicast Packets Displays the number of good Multicast
packets received on the interface since the device was last
refreshed.
CRC Align Errors Displays the number of CRC and Align
errors that have occurred on the interface since the device
was last refreshed.
Undersize Packets Displays the number of undersized
packets (less than 64 octets) received on the interface
since the device was last refreshed.
Oversize Packets Displays the number of oversized
packets (over 1518 octets) received on the interface since
the device was last refreshed.
Fragments Displays the number of fragments (packets
with less than 64 octets, excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) received on the interface since the
device was last refreshed.
Jabbers Displays the total number of received packets
that were longer than 1518 octets. This number excludes
frame bits, but includes FCS octets that had either a bad
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) with an integral number of
octets (FCS Error) or a bad FCS with a non-integral octet
(Alignment Error) number. The field range to detect
jabbers is between 20 ms and 150 ms.
Collisions Displays the number of collisions received on
the interface since the device was last refreshed.
Utilization Displays the percentage of the interface utilized.
Statistics > RMON Alarms
The RMON Alarm screen is used to set network alarms.
Network alarms occur when a network problem, or event,
is detected. Rising and falling thresholds generate events.
Add Alarm
Alarm Entry Indicates a specific alarm.
Interface Indicates the interface for which RMON
statistics are displayed. To specify the interface, select
Unit No. (default) and specify the unit number and port
from the drop-down menus, or select LAG and select the
LAG number from the drop-down menu.
Counter Name Displays the selected MIB variable.
Sample Type Defines the sampling method for the
selected variable and comparing the value against the
thresholds. The possible field values are:
Absolute Compares the values directly with the
•
thresholds at the end of the sampling interval.
Delta Subtracts the last sampled value from the
•
current value. The difference in the values is compared
to the threshold.
Rising Threshold Displays the rising counter value that
triggers the rising threshold alarm. The rising threshold
is presented on top of the graph bars. Each monitored
variable is designated a color.
Rising Event Displays the mechanism in which the alarms
are reported. The possible field values are:
LOG Indicates there is not a saving mechanism for
•
either the device or in the management system. If the
device is not reset, the entry remains in the Log Table.
TRAP Indicates that an SNMP trap is generated, and
•
sent via the Trap mechanism. The Trap can also be
saved using the Trap mechanism.
Both Indicates that both the Log and Trap mechanism
•
are used to report alarms.
Falling Threshold Displays the falling counter value that
triggers the falling threshold alarm. The falling threshold
is graphically presented on top of the graph bars. Each
monitored variable is designated a color.
Falling Event Displays the mechanism in which the
alarms are reported. The possible field values are:
LOG Indicates there is not a saving mechanism for
•
either the device or in the management system. If the
device is not reset, the entry remains in the Log Table.
TRAP Indicates that a SNMP trap is generated, and
•
sent via the Trap mechanism. The Trap can also be
saved using the Trap mechanism.
Both Indicates that both the Log and Trap mechanism
•
are used to report alarms.
Statistics > RMON Alarm
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Startup Alarm Displays the trigger that activates alarm
generation. Rising is defined by crossing the threshold
from a low-value threshold to a higher-value threshold.
26
Page 33

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Interval Defines the alarm interval time in seconds.
Owner Displays the device or user that defined the alarm.
Click Add to List to add an entry to the Alarm Table.
Alarm Table
The Alarm Table lists the alarms that have been defined
using the Add Alarm section. The Alarm Table contains a
colunn for each field in the Add Alarm section, plus the
following column:
Counter Value Displays the current counter value for the
particular alarm.
Statistics > RMON Events
The RMON Events screen is used to define RMON events.
Event Table
The Event Table lists all events defined using the Add Event
fields. The Event Table contains columns for all the Add
Event fields, plus the following additional column:
Time Displays the time that the event occurred.
Statistics > Port Utilization
Statistics > RMON Events
Add Event
Event Entry Displays the event.
Community Displays the community to which the event
belongs.
Description Displays the user-defined event description.
Type Describes the event type. Possible values are:
None Indicates that no event occurred.
•
Log Indicates that the event is a log entry.•Trap.
•
Indicates that the event is a trap.
Log and Trap Indicates that the event is both a log
•
entry and a trap.
Statistics > Port Utilization
The Port Utilization screen displays the amount of resources
each interface is currently consuming. Ports in green are
functioning normally, while ports in red are currently
transmitting an excessive amount of network traffic.
Refresh Rate Select the rate at which to refresh the
statistics display: No Refresh (default), 15 sec, 30 sec, or
60 sec.
Statistics > Interface Statistics
Owner Displays the device or user that defined the
event.
Click Add to List to add the configured RMON event to
the Event Table at the bottom of the screen.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Statistics > Interface Statistics
27
Page 34

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
The Interface Statistics screen is used to display statistics
for the Ethernet port or LAG that you specify. You can also
specify the rate at which the display will be refreshed.
Interface
Unit No., then select the desired unit and port from the
drop-down menus. To display statistics for a LAG, select LAG,
then select the desired LAG from the drop-down menu.
Refresh Rate Select the rate at which to refresh the
display: 15 sec, 30 sec, 60 sec, or No Refresh (default).
To display statistics for an Ethernet port, select
Interface
This section displays statistics for the packets transmitted
and received on the selected interface.
Receive Statistics Statistics on received packets
Total Bytes (Octets) Displays the number of octets
•
received on the selected interface.
Unicast Packets Displays the number of Unicast
•
packets received on the selected interface.
Multicast Packets Displays the number of Multicast
•
packets received on the selected interface.
Broadcast Packets Displays the number of Broadcast
•
packets received on the selected interface.
Received Pause Frames Displays the number of received
paused frames on the selected interface.
Transmitted Pause Frames Displays the number of
paused frames transmitted from the selected interface.
Clear Counters Click the Clear Counters button to reset
all the counters on this screen to zero.
Security
Security > 802.1x Settings
The 802.1x Settings screen is used to configure a port’s
802.1x authentication settings.
Packets with Errors Displays the number of error
•
packets received from the selected interface.
Transmit Statistics Statistics on transmitted packets
Total Bytes (Octets) Displays the number of octets
•
transmitted from the selected interface.
Unicast Packets Displays the number of Unicast
•
packets transmitted from the selected interface.
Multicast Packets Displays the number of Multicast
•
packets transmitted from the selected interface.
Broadcast Packets Displays the number of Broadcast
•
packets transmitted from the selected interface.
Ethernet-like
This section displays the following statistics for the
selected interface.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) Errors Displays the
number of FCS errors received on the selected interface.
Single Collision Frames Displays the number of single
collision frames received on the selected interface.
Late Collisions Displays the number of late collision
frames received on the selected interface.
Oversize Packets Displays the number of oversize packet
errors on the selected interface.
Internal MAC Receive Errors Displays the number of
internal MAC received errors on the selected interface.
Security > 802.1x Settings
Port-based authentication enables authenticating system
users on a per-port basis via an external server. Only
authenticated and approved system users can transmit
and receive data. Ports are authenticated via a RADIUS
server using the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)
.
Parameters
Enable 802.1x Select the checkbox to enable 802.1x
authentication. The default is not enabled.
Interface The interface on which to configure 802.1x.
Unit No. Select the unit number from the drop-down
•
menu.
Port Select the port from the drop-down menu.
•
Status Port Control Sets the port authentication mode
to one of the following options:
ForceAuthorized (Default) Forces the port to grant
•
access to all clients, either dot1x-aware or otherwise.
ForceUnauthorized Forces the port to deny access
•
to all clients, either dot1x-aware or otherwise.
Auto Causes the port authentication mode to be
•
selected automatically.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
28
Page 35

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Enable Periodic Reauthentication Select the checkbox
to permit periodic port reauthentication.
Setting Timer Click this button to open the Setting Timer
screen to configure ports for 802.1x functionality.
Update If you click this button, your changes are saved
and appear immediately in the screen’s Table section.
Table
This part of the 802.1x Settings screen displays a summary
of the settings that appear in the Parameters section of the
screen. If you click More Details, the settings described in
the “Setting Timer” section are added to the table.
Click Save Settings to apply the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Setting Timer
The Setting Timer screen appears when you click Setting
Timer on the 802.1x Settings screen. You use the Setting
Timer screen to configure a port’s 802.1x functionality.
Server Timeout The number of seconds that lapses
before the switch resends a request to the authentication
server The range is 1 to 65535. The default is 30 seconds.
Click Save to save your changes and leave the screen
open. Click Save & Close to save your changes and close
the screen. Click Close to close the screen without saving
your changes.
Security > Port Security
The Port Security screen is used to configure a port’s
security settings.
Security > 802.1x Settings > Setting Timer
Port Displays the port name.
Reauthentication Period Specifies the number
of seconds after which a connected client must be
reauthenticated. The range is 300 to 4294967295
seconds. The default value is 3600 seconds.
Quiet Period Specifies the time that a switch port waits
after Max EAP Requests is exceeded before attempting
to acquire a new client. The range is 1 to 65535 seconds.
The default is 60 seconds.
Resending EAP Specifies the time that the switch waits
for a response to an EAP request/identity frame from the
client before retransmitting an EAP packet. The range is 1
to 65535 seconds. The default is 30 seconds.
Max EAP Requests Specifies the maximum number
of times the switch port will retransmit an EAP request
packet to the client before it times out the authentication
session. The range is 1 to 10 times. The default is 2 retries.
Supplicant Timeout Displays the number of seconds that
lapses before EAP requests are resent to the supplicant. The
range is 1 to 65535 seconds. The default is 30 seconds.
Security > Port Security
Network security can be increased by limiting access on
a specific port only to users with specific MAC addresses.
MAC addresses can be dynamically learned or statically
configured.
Locked port security monitors both received and learned
packets that are received on specific ports. Access to the
locked port is limited to users with specific MAC addresses.
These addresses are either manually defined on the port,
or learned on that port up to the point when it is locked.
When a packet is received on a locked port, and the
packet’s source MAC address is not tied to that port (either
it was learned on a different port, or it is unknown to the
system), the protection mechanism is invoked, and can
provide various options. Unauthorized packets arriving at
a locked port are either:
Forwarded
•
Discarded
•
Cause the port to be shut down
•
Locked port security also enables storing a list of MAC
addresses in the configuration file. The MAC address list
can be restored after the device has been reset.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
29
Page 36

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Disabled ports can be reactivated from the Port Settings
screen of the Port Management tab.
Interface Select Unit No. or LAG, then select the desired
interface from the appropriate drop-down menu.
Lock Interface Select this option to lock the interface.
The default is not selected (interface not locked).
Learning Mode Defines the locked port type. This field
is enabled only if Lock Interface is not selected. The
possible values are:
Classic Lock Locks the port using the classic lock
•
mechanism. The port is immediately locked, regardless
of how many addresses have already been learned.
Limited Dynamic Lock Locks the port by deleting
•
the current dynamic MAC addresses associated with
the port. The port learns up to the maximum number
of addresses allowed on the port. Both relearning and
aging MAC addresses are enabled.
In order to change the Learning Mode, the Lock Interface
must be unselected. Once the Learning Mode is changed,
the Lock Interface can be reinstated.
Max Entries Specifies the number of MAC addresses
that can be learned on the port. This field is enabled only
if Learning Mode is set to Limited Dynamic Lock. The
default value is 1.
Security > Management Access List
Use the Management Access List screen to specify IP
addresses that are to be allowed to manage the device,
using an IP address and wildcard mask.
Security > IP Access List
Web IP Filtering
Action on Violation Indicates the action to be applied to
packets arriving on a locked port. The possible values are:
Discard Discards packets from any unlearned source.
•
This is the default value.
Forward Forwards packets from an unknown source
•
without learning the MAC address.
Discard Disable Discards packets from any unlearned
•
source and shuts down the port. The port remains shut
down until reactivated, or until the device is reset.
Enable Trap Enables traps when a packet is received on
a locked port.
Trap Frequency The amount of time (in seconds)
between traps. The default value is 10 seconds.
Update If you click this button, your changes are saved
and appear immediately in the table at the bottom of the
Port Security screen.
The lower portion of the Port Security screen displays
a summary of the settings in the upper portion of the
screen. The settings are displayed for each of the ports
on the Switch.
Click Save Settings to apply the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
The Management Access List screen contains two sections,
Web IP Filtering and SNMP IP Filtering. These sections are
identical except for the types of IP addresses that they
relate to.
IP Address Enter the web IP address or SNMP IP address
to be allowed.
Wildcard Mask Enter the wildcard mask for the web IP
address or SNMP IP address. Wildcard masks specify which
bits are used and which bits are ignored. A wild card mask
of 255.255.255.255 indicates that no bit is important. A
wildcard of 0.0.0.0 indicates that all the bits are important.
For example, if the source IP address is 149.36.184.198
and the wildcard mask is 255.36.184.00, the first eight bits
of the IP address are ignored, while the last eight bits are
used.
Add to List Click this button to save the IP address and
Wildcard Mask. The information will appear in the list at
the bottom of the screen.
The bottom portions of both the Web IP Filtering and SNMP
IP Filtering sections displays the current IP access list, where
each entry consists of an IP Address and Wildcard Mask. To
delete an entry from the list, select it and click Delete.
Click Save Settings to apply the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
30
Page 37

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Security > Storm Control
The Storm Control screen is used to configure broadcast
and multicast storm control.
Security > Storm Control
Storm Control enables limiting the amount of Multicast and
Broadcast frames accepted and forwarded by the Switch.
A Broadcast Storm results when an excessive amount of
broadcast messages is simultaneously transmitted across
a network by a single port. Forwarded message responses
are heaped onto the network, straining network resources
or causing the network to time out.
To enable Storm Control on a port, you specify the packet
type (broadcast/multicast) and maximum transmission
rate. The system measures the incoming Broadcast and
Multicast frame rates separately on each port and discards
frames when the rate exceeds the specified maximum.
Interface Select the unit number and port from which
storm control is enabled.
Broadcast Control Select the checkbox to apply
Broadcast control on the selected interface. Broadcast
control limits the amount of Broadcast packet types to be
forwarded. The default is not selected (disabled).
Mode Specifies the Broadcast mode currently enabled
on the device. The possible values are:
Multicast & Broadcast Counts Broadcast and
•
Multicast traffic together.
Broadcast Only Counts only Broadcast traffic.
•
Rate Threshold The maximum rate (packets per second)
at which unknown packets are forwarded. The ranges are
70 kbps to 100 Mbps for FE ports, and 3.5 to 100 Mbps
for GE ports. The default value is 3500 kbps.
The Update button adds the Storm Control settings to the
Storm Control table at the bottom of the screen.
Security > RADIUS
The RADIUS screen is used to configure a Remote
Authorization Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server for user
authentication.
Security > RADIUS
RADIUS servers provide additional security for networks
by providing a centralized authentication method for web
access. Up to eight RADIUS servers can be configured. The
Switch attempts authentication using the listed sequence
of servers. The process ends when a server either approves
or denies access to a user.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the authentication
server.
Priority The server priority. The possible values are 0
to 65535, where 0 is the highest priority. This priority
determines the order in which RADIUS servers are queried
when more than one RADIUS server is configured. The
default priority is 0.
Authentication Port Enter the authentication port. The
authentication port is used to verify the RADIUS server
authentication. The default value is 1812.
Number of Retries Defines the number of transmitted
requests sent to RADIUS server before a failure occurs. The
possible values are 1 to 10. The default is 3.
Timeout for Reply Defines the amount of the time in
seconds the device waits for an answer from the RADIUS
server before retrying the query, or switching to the next
server. The possible values are 1 to 30. The default is 3.
Dead Time Defines the amount of time (minutes) that a
RADIUS server is bypassed for service requests. The range
is 0 to 2000. The default is 0 minutes.
Key String Defines the default key string used to
authenticate and encrypt all RADIUS communications
between the device and the RADIUS server. This key must
match the RADIUS encryption.
Source IP Address Defines the source IP address that is
used for communication with RADIUS servers.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
31
Page 38

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Usage Type This is the RADIUS server authentication
type. The possible values are:
Login (Default value) Indicates that the RADIUS server
•
is used for authenticating user name and passwords.
802.1X Indicates that the RADIUS server is used for
•
802.1X authentication.
All Indicates that the RADIUS server is used for
•
authenticating user name and passwords, and 802.1X
port authentication.
Click Add to List to add the RADIUS configuration to the
RADIUS table at the bottom of the screen.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
QoS
Network traffic is usually unpredictable, and the only
basic assurance that can be offered is best effort traffic
delivery. To overcome this challenge, Quality of Service
(QoS) is applied throughout the network. This ensures that
network traffic is prioritized according to specified criteria,
and that specific traffic receives preferential treatment.
QoS in the network optimizes network performance and
entails two basic facilities:
Classifying incoming traffic into handling classes, based
on an attribute, including:
The ingress interface
•
Packet content
•
A combination of these attributes
•
Providing various mechanisms for determining the
allocation of network resources to different handling
classes, including:
The assignment of network traffic to a particular
•
hardware queue
The assignment of internal resources
•
Traffic shaping
•
The terms Class of Service (CoS) and QoS are used in the
following context:
QoS > CoS Settings
The CoS Settings screen is used to enable or disable CoS.
QoS > CoS Settings
CoS Settings
QoS Mode Indicates if QoS is enabled. The possible
values are:
Disable Disables QoS.
•
Basic Enables QoS. This is the default value.
•
Class of Service Specifies the CoS priority tag values,
where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest.
Queue Defines the traffic forwarding queue to which the
CoS priority is mapped. Four traffic priority queues are
supported.
Click Restore Defaults to restore the device factory
defaults for mapping CoS values to a forwarding queue.
CoS Default
Unit No.
The unit to which the CoS configuration applies
.
CoS provides varying Layer 2 traffic services. CoS
•
refers to classifying traffic into traffic classes, where
each class is handled as an aggregate whole, with no
per-flow settings. CoS is usually related to the 802.1p
service that classifies flows according to their Layer 2
priority, as set in the VLAN header.
QoS refers to Layer 2 traffic and above. QoS handles
•
per-flow settings, even within a single traffic class.
The QoS configuration options are CoS Settings, Queue
Settings, DSCP Settings, and Basic Mode.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Default CoS Determines the default CoS value for
incoming packets for which a VLAN tag is not defined. The
possible field values are 0-7. The default CoS is 0.
LAG The LAG to which the port belongs, if relevant. If the
port is a member of a LAG, the LAG settings override the
port settings.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
32
Page 39

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
QoS > Queue Settings
The Queue Settings screen is used to define the QoS queue
forwarding types.
QoS > Queue Settings
Strict Priority Indicates that traffic scheduling for the
selected queue is based strictly on the queue priority.
WRR Indicates that traffic scheduling for the selected
queue is based strictly on the WRR.
The DSCP Settings screen allows you to map Differentiated
Services Code Point (DSCP) values to specific queues.
DSCP Indicates the DSCP value in the incoming packet.
Select a DSCP value from the drop-down menu to map
that value to the associated queue. You can select the
DSCP value for the High, Medium, and Normal priority
queues. The DSCP values for the Low priority queue are
selected automatically based on the other DSCP values.
Queue The queue (1-4) to which the DSCP value is being
mapped.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
QoS > Bandwidth
Queue Displays the queue (1-4) for which the queue
settings are displayed.
WRR Weight Displays the WRR weights to queues.
% of WRR Bandwidth Displays the percentage of
bandwidth assigned to the queue. These values are fixed
and cannot be modified.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
QoS > DSCP Settings
QoS > Bandwidth
The Bandwidth screen allows network managers to define
the bandwidth settings for a specified egress or ingress
interface. Modifying queue scheduling affects the queue
settings globally. The Bandwidth screen is not used with
the Service mode, as bandwidth settings are based on
services.
Queue shaping can be based per queue and/or per
interface. Shaping is determined by the lower specified
value. The queue shaping type is selected in the Bandwidth
screen.
Interface The interface for which the queue shaping
information is displayed. Either select Unit No and select
the unit number and port from the drop-down menus,
or select LAG and select the LAG number from the dropdown menu.
Enable Ingress Rate Limit Status Indicates if rate limiting
is defined on the interface.
QoS > DSCP Settings
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Enable Egress Shaping Rate Indicates if rate limiting is
enabled on the interface.
33
Page 40

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Committed Information Rate (CIR) Defines CIR as
the queue shaping type. The allowed values are 64 to
62500 Kbps for the 10/100 ports and 64 to 1000000 Kbps
for the Gigabit ports.
Committed Burst Size (CBS) Defines CBS as the queue
shaping type. The possible field value is 4096 to 15769020
bits. Commited Burst Size cannot be configured on FE
ports.
Click Add to List to add the Bandwidth configuration to
the Bandwidth Table at the bottom of the screen.:
QoS > Basic Mode
The Switch supports the Classic STP version of STP, which
provides a single path between end stations, avoiding
and eliminating loops.
Spanning Tree > STP Status
The STP Status screen displays the STP status on the Switch.
This information is read-only and cannot be modified.
QoS > Basic Mode
The Basic Mode screen contains the following fields:
Trust Mode Displays the trust mode. If a packet’s CoS
tag and DSCP tag are mapped to different queues, the
Trust Mode determines the queue to which the packet is
assigned. Possible values are:
CoS Sets trust mode to CoS on the device. The CoS
•
mapping determines the packet queue
DSCP Sets trust mode to DSCP on the device. The
•
DSCP mapping determines the packet queue.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Spanning Tree
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree topography for
any arrangement of bridges. STP also provides one path
between end stations on a network, eliminating loops.
Loops occur when alternate routes exist between hosts.
Loops in an extended network can cause bridges to
forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in increased traffic
and reducing network efficiency.
Spanning Tree > STP Status
Spanning Tree State Indicates whether STP is enabled
on the device.
Spanning Tree Mode The STP mode by which STP is
enabled on the device.
Bridge ID The Bridge priority and MAC address.
Designated Root Identifies the bridge priority and MAC
address of the root bridge.
Root Port The port number that offers the lowest cost
path from this bridge to the Root Bridge. It is significant
when the Bridge is not the Root. The default is 0.
Root Path Cost The cost of the path from this bridge to
the root.
Root Maximum Age (sec) The device Maximum Age
Time, which indicates the amount of time in seconds a
bridge waits before sending configuration messages. The
default is 20 seconds. The range is 6 to 40 seconds.
Root Hello Time (sec) The device Hello Time. The Hello
Time indicates the amount of time in seconds a root bridge
waits between configuration messages. The default is 2
seconds. The range is 1 to 10 seconds.
Root Forward delay (sec) The device forward delay time.
The Forward Delay Time indicates the amount of time in
seconds a bridge remains in a listening and learning state
before forwarding packets. The default is 15 seconds. The
range is 4 to 30 seconds.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
34
Page 41

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Topology Changes Counts The total amount of STP
state changes that have occurred.
Last Topology Change The elapsed time since the bridge
was initialized or reset, and the last topographic change
occurred. The time is displayed in a day hour minute
second format, for example, 2 days 5 hours 10 minutes
and 4 seconds.
Spanning Tree > Global STP
The Global STP screen contains global parameters for STP
on the Switch.
Bridge Settings
Priority Specifies the bridge priority value. When
switches or bridges are running STP, each is assigned a
priority. After exchanging BPDUs, the device with the
lowest priority value becomes the Root Bridge. The default
value is 32768. The value must be a multiple of 4096. For
example, 4096, 8192, 12288, etc. The range is 0 to 65535.
Hello Time Specifies the device Hello Time (the amount of
time in seconds a root bridge waits between configuration
messages). The default is 2 seconds. The range is 1 to 10
seconds.
Max Age Specifies the device Maximum Age Time (the
amount of time in seconds that a bridge waits before
sending configuration messages). The default is 20
seconds. The range is 6 to 40 seconds.
Forward Delay Specifies the device forward delay time
(the amount of time in seconds a bridge remains in a
listening and learning state before forwarding packets).
The default is 15 seconds. The range is 4 to 30 seconds.
Choose settings for the Hello Time, Max Age, and Forward
Delay parameters so that both of the following are true:
Max Age ≥ 2 × (Hello Time + 1)
2 × (Forward Delay – 1) ≥ Max Age
Spanning Tree > Global STP
Global Setting
Spanning Tree State Select Enable or Disable from the
drop-down menu to enable or disable STP on the Switch.
The default is Enable.
BPDU Handling Determines how BPDU packets are
managed when STP is disabled on the port or Switch.
BPDUs are used to transmit spanning tree information.
The possible values are:
Filtering Filters BPDU packets when spanning tree is
•
disabled on an interface.
Flooding Floods BPDU packets when spanning tree is
•
disabled on an interface. This is the default value.
Path Cost Default Values The method used to assign
default path costs to STP ports. The possible values are:
Short Specifies a range of 1-65.535 for port path
•
costs.
Long Specifies a range of 1-200.000.000 for port path
•
costs. The default path costs assigned to an interface
varies according to the selected method. This is the
default value.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
The STP Port Settings screen allows network administrators
to assign STP settings to specific interfaces.
Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings
Interface Indicates the port or LAG on which STP is
enabled. Select either Port (default) or LAG, then select
the interface from the drop-down menu.
Enable STP Select this to enable STP on the port. The
default is Enabled.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
35
Page 42

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Port Fast Indicates if Fast Link is enabled on the port.
If Fast Link mode is enabled for a port, the Port State
is automatically placed in the Forwarding state when
the port link is up. Fast Link optimizes the STP protocol
convergence. STP convergence can take 30-60 seconds in
large networks. The possible values are Enable, Auto, and
Disable. The default is Disable.
Port State Displays the current STP state of a port. If
enabled, the port state determines what forwarding
action is taken on traffic. Possible port states are:
Disabled STP is currently disabled on the port. The
•
port forwards traffic while learning MAC addresses.
Blocking The port is currently blocked and cannot
•
forward traffic or learn MAC addresses.
Listening The port is in Listening mode. The port
•
cannot forward traffic nor can it learn MAC addresses.
Learning The port is in Learning mode. The port
•
cannot forward traffic, but can learn new MAC
addresses.
Forwarding The port is in Forwarding mode. The port
•
can forward traffic and learn new MAC addresses.
Speed Displays the speed at which the port is operating.
Path Cost Indicates the port contribution to the root path
cost. The path cost is adjusted to a higher or lower value,
and is used to forward traffic when a path being rerouted.
The default value is 2000000 for a 10M port, 200000 for a
100M port, and 20000 for a 1G port or a LAG.
Default Path Cost When selected the default path cost is
implemented. The default is unselected.
Priority Priority value of the port. This value influences
the port choice when a bridge has two ports connected in
a loop. The range of values is 0 -240. The default is 128.
Designated Bridge ID Displays the bridge priority and
the MAC Address of the designated bridge.
Multicast
Multicast configuration options include IGMP Snooping,
Bridge Multicast, and Bridge Multicast Forward All.
Multicast > IGMP Snooping
Multicast > IGMP Snooping
When IGMP Snooping is enabled globally, all IGMP packets
are forwarded to the CPU. The CPU analyzes the incoming
packets and determines:
Which ports want to join which Multicast groups
•
Which ports have Multicast routers generating IGMP
•
queries
Which routing protocols are forwarding packets and
•
Multicast traffic
Ports requesting to join a specific Multicast group issue an
IGMP report, specifying that Multicast group is accepting
members. This results in the creation of the Multicast
filtering database.
Designated Port ID Displays the selected port’s priority
and interface.
Designated Cost Displays the cost of the port
participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost
are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops.
Forward Transitions Displays the number of times the
port has changed from the Blocking state to Forwarding
state.
Click Update to update the screen with your changes.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
The Bridge Multicast Forward All screen contains two
sections, IGMP Global and VLAN IGMP Settings. These
sections and the fields they contain are described below.
IGMP Global
Enable IGMP Snooping Select this option to enable
IGMP Snooping on the device. IGMP Snooping can be
enabled only if Bridge Multicast Filtering is enabled. The
default is disabled (option not selected).
VLAN IGMP Settings
VLAN ID Select the VLAN ID from the drop-down menu.
IGMP Status Select this option to enable IGMP snooping
on the VLAN. Default is disabled (option not selected).
36
Page 43

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Auto Learn Select this option to enable Auto Learn on the
device. If Auto Learn is enabled, the device automatically
learns where other Multicast groups are located. The
default is enabled (option is selected).
Host Timeout Indicates the amount of time host waits to
receive a message before timing out. The default time is
260 seconds.
MRouter Timeout Indicates the amount of the time the
Multicast router waits to receive a message before it times
out. The default value is 300 seconds.
Leave Timeout Indicates the amount of time the host
waits, after requesting to leave the IGMP group and not
receiving a Join message from another station, before
timing out. If a Leave Timeout occurs, the switch notifies
the Multicast device to stop sending traffic The Leave
Timeout value is either user-defined, or an immediate
leave value. The default timeout is 10 seconds.
Click Update to update the screen with your changes.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Multicast > Bridge Multicast
The Bridge Multicast screen displays the ports and LAGs
attached to the Multicast service group in the Ports and
LAGs tables. The Port and LAG tables also reflect the
manner in which the port or LAGs joined the Multicast
group.
The Bridge Multicast screen contains the following fields:
VLAN ID Identifies a VLAN to be configured to a Multicast
service.
Bridge Multicast Address Identifies the Multicast group
MAC address/IP address.
Bridge IP Multicast Displays the port that can be added
to a Multicast service.
Interface, Gigabit, LAG Lists switch interfaces and LAGs
that can be added to a Multicast service. The configuration
options are as follows:
Static Indicates the port is user-defined.
•
Dynamic Indicates the port is configured
•
dynamically.
Forbidden Forbidden ports are not included the
•
Multicast group, even if IGMP snooping designated
the port to join a Multicast group.
None The port is not configured for Multicast service.
•
Click Add to List to add the configured static multicast
address to the table at the bottom of the screen.
Click Show All to display all multicast addresses on all
VLANs in the table at the bottom of the screen.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Multicast > Bridge Multicast Forward All
Multicast > Bridge Multicast
Ports can be added either to existing groups or to new
Multicast service groups. The Bridge Multicast screen
permits new Multicast service groups to be created. The
Bridge Multicast screen also assigns ports to a specific
Multicast service address group.
The Bridge Multicast Forward All screen contains fields for
attaching ports or LAGs to a device that is attached to a
neighboring Multicast router or switch.
Multicast > Bridge Multicast Forward All
Once IGMP Snooping is enabled, Multicast packets are
forwarded to the appropriate port or VLAN.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
37
Page 44

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
The Bridge Multicast Forward All screen contains the
following fields:
VLAN ID Displays the VLAN for which Multicast
parameters are displayed.
Interface Interfaces with the following configuration
options:
Static The port is user-defined.
•
Dynamic The port is configured dynamically.
•
None The port is not configured for Multicast service.
•
Gigabit Gigabit ports with the following configuration
options:
Static The Gigabit port is user-defined.
•
Dynamic The Gigabit port is configured dynamically.
•
None The Gigabit port is not configured for Multicast
•
service.
LAG LAGs with the following configuration options:
Static The LAG is user-defined.
•
Dynamic The LAG is configured dynamically.
•
None The LAG is not configured for Multicast service.
•
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
SNMP
The Global Parameters screen contains parameters for
defining SNMP notification parameters.
Local Engine ID Indicates the local device engine ID. The
field value is a hexadecimal string. Each byte in hexadecimal
character strings consists of two hexadecimal digits. Each
byte can be separated by a period or a colon. The Engine
ID must be defined before SNMPv3 is enabled. For standalone devices, select a default Engine ID that is comprised
of Enterprise number and the default MAC address. For a
stacked system configure the Engine ID, and verify that
the Engine ID is unique for the administrative domain.
This prevents two devices in a network from having the
same Engine ID.
Use Default Uses the device generated Engine ID. The
default Engine ID is based on the device MAC address and
is defined per standard as:
First 4 octets First bit = 1, the rest is IANA Enterprise
•
number.
Fifth octet Set to 3 to indicate the MAC address that
•
follows.
Last 6 octets MAC address of the device.
•
SNMP Notifications Indicates if the device can send
SNMP notifications.
Authentication Notifications Indicates if SNMP
Authentication failure notification is enabled on the
device.
The SNMP tab includes the following screens: Global
Parameters, Views, Group Profile, Group Membership,
Communities, Notification Filter, and Notification Recipient.
SNMP > Global Parameters
SNMP > Global Parameters
SNMP > Views
The SNMP Views screen provides access or block access to
device features or feature aspects. For example, a view can
be defined that states that SNMP Group A has Read Only
(R/O) access to Multicast groups, while SNMP Group B
has Read-Write (R/W) access to Multicast groups. Feature
access is granted via the MIB name, or MIB Object ID.
SNMP > Views
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
38
Page 45

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
View Name Displays the user-defined views. The options
are as follows:
Default Displays the default SNMP view for read and
•
read/write views.
DefaultSuper Displays the default SNMP view for
•
administrator views.
Subtree ID Tree Indicates the device feature OID included
or excluded in the selected SNMP view. The options to
select the Subtree are as follows:
Select from List Select the Subtree from the list
•
provided.
Insert Enables a Subtree not included in the Select
•
from List field to be entered.
View Type Indicates if the defined OID branch will be
included or excluded in the selected SNMP view.
Click Add to List to add the Views configuration to the
Views Table at the bottom of the screen.
SNMP > Group Profile
The Group Profile screen allows you to create SNMP groups
and assign SNMP access control privileges to SNMP groups.
Groups allow network managers to assign access rights to
specific device features, or features aspects.
No Authentication Indicates that neither the
•
Authentication nor the Privacy security levels are
assigned to the group.
Authentication Authenticates SNMP messages, and
•
ensures the SNMP messages origin is authenticated.
Privacy Encrypts SNMP messages.
•
Operation Defines the group access rights. The possible
field values are:
Read The management access is restricted to read-
•
only, and changes cannot be made to the assigned
SNMP view.
Write The management access is read-write and
•
changes can be made to the assigned SNMP view.
Notify Sends traps for the assigned SNMP view.
•
SNMP > Group Membership
The Group Membership screen provides information
for assigning SNMP access control privileges to SNMP
groups.
SNMP > Group Profile
User Name Provides a user-defined local user list.
Group Name Displays the user-defined group to which
access control rules are applied. The field range is up to
30 characters.
Security Model Defines the SNMP version attached to
the group. The possible field values are:
SNMPv1 SNMPv1 is defined for the group.
•
SNMPv2 SNMPv2 is defined for the group.
•
SNMPv3 SNMPv3 is defined for the group.
•
Security Level Defines the security level attached to the
group. Security levels apply to SNMPv3 only. The possible
field values are:
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Engine ID Indicates either the local or remote SNMP entity
to which the user is connected. Changing or removing the
local SNMP Engine ID deletes the SNMPv3 User Database.
Local Indicates that the user is connected to a local
•
SNMP entity.
Remote Indicates that the user is connected to a
•
remote SNMP entity. If the Engine ID is defined, remote
devices receive inform messages.
Group Name Contains a list of user-defined SNMP
groups. SNMP groups are defined in the SNMP Group
Profile page.
SNMP > Group Membership
39
Page 46

Chapter 5
Authentication Method Use this to enable or disable
Authentication between the SNMP Agent on the Switch
and the SNMP Manager.
None Disables authentication between the SNMP
•
Agent on the Switch and the SNMP Manager.
MD5 Password Enables authentication using HMAC-
•
MD5-96 password authentication.
SHA Password Enables authentication using HMAC-
•
SHA-96 password authentication.
MD5 Key Enables authentication using the HMAC-
•
MD5 algorithm.
SHA Key Enables authentication using HMAC-SHA-96
•
authentication.
Password Defines the local user password. Local user
passwords can contain up to 159 characters.
Authentication Key Defines the HMAC-MD5-96 or
HMAC-SHA-96 authentication level. The authentication
and privacy keys are entered to define the authentication
key. If only authentication is required, 16 bytes are defined.
If both privacy and authentication are required, 32 bytes
are defined. Each byte in hexadecimal character strings is
two hexadecimal digits. Each byte can be separated by a
period or a colon.
Privacy Key Defines the Privacy Key (LSB). If only
authentication is required, 20 bytes are defined. If both
privacy and authentication are required, 36 bytes are
defined. Each byte in hexadecimal character strings is
two hexadecimal digits. Each byte can be separated by a
period or colon.
Click Add to List to add the Group Membership
configuration to the respective table at the bottom of the
screen.
SNMP > Communities
The Communities screen is used to define SNMP
communities. The Communities screen contains the
following three areas: Communities, Basic Table and
Advanced Table.
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
SNMP > Communities
SNMP Management Station Defines the management
station IP address for which the advanced SNMP community
is defined. There are two definition options: either select
the first radio button and enter the management station
IP address in the field (default), or select All to include all
management station IP addresses.
Community String Defines the password used to
authenticate the management station to the device.
Basic Enables SNMP Basic mode for a selected community
and contains the following fields:
Access Mode Defines the access rights of the community.
The possible field values are:
Read Only Management access is restricted to read-
•
only, and changes cannot be made to the community.
Read Write Management access is read-write and
•
changes can be made to the device configuration, but
not to the community.
SNMP Admin User can access all device configuration
•
options, and can modify the community.
View Name Contains a list of user-defined SNMP views.
Advanced Enables SNMP Advanced mode for a selected
community and contains the following fields:
Group Name Defines advanced SNMP communities
group names.
Click Add to List to add the Communities configuration to
the respective Table at the bottom of the screen.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
40
Page 47

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Base Table
Management Station
IP address for which the basic SNMP community is defined
Community String Displays the password used to
authenticate the management station to the device.
Access Mode Displays the access rights of the
community.
View Name Displays the user-defined SNMP view.
Displays the management station
Advanced Table
Management Station Displays the management station
IP address for which the basic SNMP community is
defined.
Community String Displays the password used to
authenticate the management station to the device.
Group Name Displays advanced SNMP communities
group name.
SNMP > Notification Filter
The Notification Filter screen permits filtering traps based
on OIDs. Each OID is linked to a device feature or a feature
aspect. The Notification Filter screen also allows network
managers to filter notifications.
Filter Type Indicates whether informs or traps are sent
regarding the OID to the trap recipients.
Excluded Restricts sending OID traps or informs.
.
•
Included Sends OID traps or informs.
•
Click Add to List to add the Notification Filter configuration
to the Notification Filter Table at the bottom of the screen.
SNMP > Notification Recipient
The Notification Recipient screen contains information for
defining filters that determine whether traps are sent to
specific users, and the trap type sent. SNMP notification
filters provide the following services:
Identifying Management Trap Targets
•
Trap Filtering
•
Selecting Trap Generation Parameters
•
Providing Access Control Checks
•
Recipient IP Indicates the IP address to whom the traps
are sent.
Notification Type Defines the notification sent. The
possible field values are:
Traps Indicates traps are sent.
SNMP > Notification Filter
Filter Name Contains a list of user-defined notification
filters.
New Object Identifier Subtree Displays the OID for
which notifications are sent or blocked. If a filter is
attached to an OID, traps or informs are generated and
sent to the trap recipients. Object IDs are selected from
either the Select from List or the Object ID List. There are
two configuration options:
Select from List Select the OID from the list provided.
•
Object ID Enter an OID not offered in the Select from
•
List option.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
•
Informs Indicates informs are sent.
•
SNMPv1,2 Enables SNMPv1,2 as the Notification
Recipient. Either SNMPv1,2 or SNMPv3 can be enabled at
any one time, but not both at the same time. If SNMPv1,2
is enabled, the Community String and Notification Version
fields are enabled for configuration:
Community String Identifies the community string of
the trap manager.
Notification Version Determines the trap type. The
possible field values are:
SNMP V1 Indicates SNMP Version 1 traps are sent.
•
SNMP V2 Indicates SNMP Version 2 traps are sent.
•
SNMP > Notification Recipient
41
Page 48

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
SNMPv3 Enables SNMPv3 as the Notification Recipient.
Either SNMPv1,2 or SNMPv3 can be enabled at any one
time, but not both at the same time. If SNMPv3is enabled,
the User Name and Security Level fields are enabled for
configuration:
User Name Defines the user to whom SNMP notifications
are sent.
Security Level Defines the means by which the packet is
authenticated. The possible field values are:
No Authentication Indicates the packet is neither
•
authenticated nor encrypted.
Authentication Indicates the packet is
•
authenticated.
Privacy Indicates the packet is both authenticated
•
and encrypted.
UDP Port Displays the UDP port used to send notifications.
The default is 162.
Filter Name Indicates if the SNMP filter for which the
SNMP Notification filter is defined.
Timeout
waits before resending informs. The default is 15 seconds.
Indicates the amount of time (seconds) the device
The User Authentication screen is used to modify user
account information. You can modify the password or
user name for an existing account, or create additional
accounts.
User Authentication
Authentication Type Defines the user authentication
methods. Combinations of all the authentication methods
can be selected. The possible field values are:
Local Authenticates the user at the device level.
•
The device checks the user name and password for
authentication.
RADIUS Authenticates the user at the RADIUS server.
•
None Assigns no authentication method to the
•
authentication profile.
Local User Edit
User Name Displays the user name.
Password The password for the specified User Name. For
security purposes, the password is not displayed; instead,
a“*” is displayed for each character. The password must be
between 1 and 159 characters in length.
Retries Indicates the amount of times the device resends
an inform request. The default is 3 seconds.
Click Add to List to add the Notification Recipient configuration
to the relevant table at the bottom of the screen.
Admin
The Admin tab provides access to system administration
settings and tools. It includes the following screens:
Admin > User Authentication
Confirm Password Confirms the password when you
change an existing password or create a new one (for
a new User Name). The password entered into this field
must be exactly the same as the password entered in the
Password field.
Add to List/Update The name of this button depends on
the function being performed. When you create a new user
name, it is Add to List; when you edit an existing password
or user name, it is Update. For detailed information on its
use, refer to the “Local Users Table” section below.
Local Users Table
The Local Users Table at the bottom of the screen lists all
existing user names (for security purposes, passwords are
not displayed). You use this table to edit or delete existing
user names and/or passwords, as described below.
Create a new user name
Make sure no entry is selected in the Local Users Table. If
one is selected, click Cancel. Enter the new user name in
the User Name field, and the password in the Password and
Confirm Password fields. Then click Add to List to add a
new entry to the Local Users Table.
Change a password
Highlight the associated user name in the Local Users
Table. The User Name, Password, and Confirm Password
Admin > User Authentication
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
fields will then be populated for editing. Enter the new
password in the Password field, then enter it again in the
42
Page 49

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Confirm Password Field. Then click Update to save the
changes to the Local Users Table.
Change a user name
Highlight the user name in the Local Users Table. The User
Name, Password, and Confirm Password fields will then be
populated for editing. Modify the user name in the User
Name field, then click Update to update the entry in the
Local Users Table.
Delete a user name
Select the user name from the table, then click Delete.
If you accidentally select the wrong entry in the table, click
Cancel to unselect the highlighted user name.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel
Changes to cancel the changes.
Admin > Static Address
VLAN ID The VLAN ID number (1-4094) of the configured
VLAN that is associated with the specified interface. If you
use this field the VLAN Name field is disabled.
VLAN Name The name of the VLAN associated with the
specified interface. If you use this field, the VLAN ID field
is disabled.
Status The static address type. The possible values are::
Permanent (Default) Keep the entry permanently.
•
Delete on Reset Delete the entry when the Switch is
•
reset.
Delete on Timeout Delete the entry when a timeout
•
occurs. The default timeout period is 300 seconds.
Secure The entry is defined for locked ports.
•
After you have entered the information listed above, click
Add to List. The static address will then appear in the list
of static addresses. To delete a static MAC address from
the list, select the entry in the list, then click Delete.
Admin > Dynamic Address
Admin > Static Address
The Static Address screen lets you assign a static address to
a specific Switch interface. A static address is bound to its
assigned interface and cannot be moved. If a static address
is seen on an interface to which it is not assigned, the
address is ignored and is not written to the address table.
A list of all static addresses on the Switch appears at the
bottom of the screen. The top part of the screen contains
the following fields for creating static address entries:
Interface The interface that is associated with the static
address. Select Port or LAG, then select the desired
interface from the accompanying drop-down menu.
MAC Address This is the physical address that is being
mapped to the specified interface.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
The Dynamic Address screen lets you query the Dynamic
Address Table to find specific dynamic MAC addresses, or
display MAC addresses associated with a specific interface
or VLAN. Query criteria include interface type, MAC
address, VLAN, and table sort key. You can also set the
Dynamic MAC Address Table’s address aging parameter or
clear the table.
Address Aging Specifies the amount of time (in seconds)
that a MAC address remains in the Dynamic MAC Address
table before it times out, if no traffic from the source is
detected. The default value is 300 seconds.
Clear Table If selected, this clears the MAC Address
table.
Admin > Dynamic Address
43
Page 50

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Query
Interface Use this to query the table for a specific port or
LAG. Select Port or LAG and select the interface from the
drop-down menu.
MAC Address Use this to query the table for a specific
MAC address. Enter the MAC address in the field.
VLAN ID Use this to query the table for a specific VLAN ID.
Enter the VLAN ID in the field.
Address Table Sort Key Specifies how the search results
will be sorted—by Address, VLAN, or Interface.
Specify the search criteria (Interface, MAC Address, or
VLAN) and the sort method for the search results, then
click Query to display the dynamic addresses matching
the search criteria.
Admin > Port Mirroring
Port mirroring monitors and mirrors network traffic by
forwarding copies of incoming and outgoing packets
from one port to a monitoring port. Port mirroring can be
used as diagnostic tool and/or a debugging feature. Port
mirroring also enables switch performance monitoring.
Type Allows you to select which traffic to mirror to the
target port; receive, transmit, or both.
RxOnly (Default) Mirror only received traffic.
•
TxOnly Mirror only transmitted traffic.
•
Both Mirror both received and transmitted traffic.
•
Specify the source port, the traffic type to be mirrored, and
the target port, then click Add to List. The mirror session
is displayed in the text box.
Admin > Cable Test
The Cable Test screen uses Time Domain Reflectometry
(TDR) technology to test the quality and characteristics of
a copper cable attached to a port. The cable being tested
can be up to 120 m in length. Before you can perfom the
test, the port to which the cable is connected must be in
the down state.
Network administrators configure port mirroring by
selecting a target port to which the packets are copied,
and the source port(s) from which the packets are copied.
Port mirroring supports a maximum of one target port
and four source ports.
Admin > Port Mirroring
Set the following attributes for port mirroring using the
Port Mirroring screen.
Target Port The port that will mirror the traffic on the
source port.
Source Port The port whose traffic will be monitored.
Admin > Cable Test
The Cable Test screen contains the following fields.
Unit No. The unit to which the test cable is connected.
Port The port to which the test cable is connected.
Test Result The results of the test. Possible values are:
OK The cable passed the test.
•
No Cable No cable is connected to the port.
•
Open Cable The cable is connected on only one side.
•
Short Cable A short has occurred in the cable.
•
Undefined
•
Last Update Displays when the last cable test was
performed on the port.
Test Click this to start testing the cable attached to the
port. The test results will appear in the Test Result column.
The test could not be properly performed.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
44
Page 51

Chapter 5
Admin > Cable Test - Gigabit Ports
Advanced (Gigabit ports only) Click the Advanced
button to open the Copper Cable Extended Feature screen.
The Copper Cable Extended Feature screen contains the
following fields.
Cable Status Displays the cable status.
•
Speed Indicates the speed at which the cable is
•
transmitting packets.
Link Status Displays the current link status.
•
Pair The pair of cables under test.
•
Distance to Fault Indicates the distance between the
•
port and where the cable error occurred.
Status Displays the cable status.
•
Cable length Displays the cable length.
•
Channel Displays the cable’s channel.
•
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Admin > Save Configuration
Admin > Save Configuration
The Save Configuration screen allows you to upload Switch
configuration files to a TFTP server, or to download saved
Switch configuration files from a TFTP server or from your
computer via the HTTP interface.
Via TFTP Select this to upload to or download from a
TFTP server. When you select this option, the following
fields are displayed.
UPGRADE Select this option to restore the Switch
•
configuration from the file located on a TFTP server.
Polarity Automatic polarity detection and correction
•
allows for automatic adjustment of wiring errors on all
RJ-45 ports.
Pair Skew Reaction or transmission time in
•
nanoseconds for the selected cable pair and given
cable length.
Test Now Press this button to begin the cable test.
•
Admin > Cable Test - Gigabit Ports > Copper Cable Extended Feature
TFTP Server Enter the TFTP Server IP Address that
•
contains the source file to download.
File Name Enter the name of the configuration file
•
on the TFTP Server.
BACKUP To back up the Switch configuration to a
•
TFTP server, enter the TFTP server address.
TFTP Server Enter the TFTP Server IP Address to
•
which the configuration file will be saved.
File Name Enter the name of the configuration
•
file. The default is none (blank).
Via HTTP Select this to download a configuration file to
the Switch from your computer using the HTTP interface.
(HTTP only supports the upgrade operation. You cannot
back up the configuration file using HTTP.) When you
select this option, the following field is displayed.
Source File Enter the name and path of the file or
•
click Browse to locate the configuration file.
Click Save Settings to begin the download or upload.
After you have downloaded the configuration file to the
Switch during an upgrade, the configuration file’s settings
will not take effect until the system is rebooted.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
45
Page 52

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Admin > Firmware Upgrade
Admin > Firmware Upgrade
The Firmware Upgrade screen allows you to download
firmware upgrade files from a TFTP server, or from your
computer via the HTTP interface.
Via TFTP Select this to download from or upload to a
TFTP server. When you select this option, the following
fields are displayed.
UPGRADE Select this option to upgrade the switch
•
from a file located on a TFTP server.
File Type Select the type of file to download,
•
either Software Image or Boot Code.
TFTP Server Enter the TFTP Server IP Address that
•
contains the source file to upgrade from.
File Name Enter the name of the upgrade file on
•
the TFTP Server.
Admin > Reboot
The Reboot screen is used to reset one Switch or the entire
stack. From the drop-down menu, select the unit number
or Stack, then click Reboot, then click OK to confirm. The
configuration settings are automatically saved before the
system reboots.
Admin > Reboot
Admin > Factory Default
The Factory Default screen allows network managers to
reset the Switch to the factory defaults shipped with the
switch. This results in erasing the configuration file.
NOTE: Restoring factory defaults erases all
current configuration settings. You can save a
copy of your configuration settings beforehand
using the Admin > Save Configuration screen.
BACKUP To back up the firmware to a TFTP server,
•
enter the TFTP server address.
TFTP Server Enter the TFTP Server IP Address to
•
which the firmware file will be saved.
File Name Displays the name of the firmware file.
•
This field cannot be edited.
Via HTTP Select this to download an upgrade file using
the HTTP interface. When you select this option, the
following field is displayed:
Source File Enter the name and path of the file or
•
click Browse to locate the upgrade file.
Click Save Settings to begin the download or upload.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Admin > Factory Default
46
Page 53

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
To restore the factory defaults, click Reset Default, then
click OK to confirm. Then restart the Switch by going to
the Admin > Reboot screen; once there, select the master
unit number (if applicable), click Reboot, then click OK.
Admin > Logging
Admin > Logging
If you enable Logging, use the checkboxes to set the level
of event messages to be logged to RAM (Memory Logs)
and flash memory (Flash Logs), then click Save Settings.
Admin > Server Logs
The Server Logs screen contains information for viewing
and configuring the Remote Log Servers. New log servers
can be defined, and the log severity sent to each server.
The System Logs allow you to view device events in real
time, and recording the events for later usage. System
Logs record and manage events and report errors or
informational messages.
Event messages have a unique format, as per the
SYSLOG protocols recommended message format for
all error reporting. For example, Syslog and local device
reporting messages are assigned a severity code, and
include a message mnemonic, which identifies the source
application generating the message. It allows messages
to be filtered based on their urgency or relevancy. Each
message severity determines the set of event logging
devices that are sent per each event logging.
Enable Logging If this option is selected, device global
logs for Cache, File, and Server Logs are enabled. The
default is enabled.
Emergency The system is not functioning.
•
Alert The system needs immediate attention.
•
Critical The system is in a critical state.
•
Error A system error has occurred.
•
Warning A system warning has occurred.
•
Notice The system is functioning properly, but system
•
notice has occurred.
Informational Provides device information.
•
Debug
•
a Debug error occurs, contact Customer Tech Support.
Provides detailed information about the log. If
Admin > Server Logs
Server Specifies the server to which logs can be sent.
UDP Port (1-65535) Defines the UDP port to which the
server logs are sent. The possible range is 1 to 65535. The
default value is 514.
Facility Defines a user-defined application from which
system logs are sent to the remote server. Only one facility
can be assigned to a single server. If a second facility level
is assigned, the first facility is overridden. All applications
defined for a device utilize the same facility on a server.
The default value is Local 7. The range of values is Local
0 to Local 7.
Description Provides a user-defined server description.
Minimum Severity Indicates the minimum severity from
which logs are sent to the server. For example, if Notice
is selected, all logs from a Notice severity and higher are
sent to the remote server.
Click Add to List to add the Server Log configuration to
the Server Log Table at the bottom of the screen.
Admin > Memory Logs
The Memory Log screen displays all system logs in the
chronological order that they are saved in RAM (Cache).
Log Index Displays the log number.
Log Time Displays the date and time of log generation.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
47
Page 54

Chapter 5
Configuration Using the Web-based Utility
Severity Displays the log severity.
Description Displays the log message text.
Admin > Memory Logs
Admin > Flash Logs
The Flash Log screen contains information about log
entries saved to the Log File in flash memory, including
the time the log was generated, the log severity, and
a description of the log message. The Message Log is
available after reboot.
Logout
The Logout tab is used to terminate the login session.
When you select the Logout tab, the following dialog box
asks you to verify if you want to log out.
Logout Verification
Select Yes to log out of the web-based configuration
utility.
Admin > Flash Logs
Log Index Displays the log number.
Log Time Displays the date and time at which the log
was generated.
Severity Displays the log severity.
Description Displays the log message text.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
48
Page 55

Appendix A
Appendix A:
About Gigabit Ethernet
and Fiber Optic Cabling
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet runs at speeds of 1Gbps (Gigabit per
second), ten times faster than 100Mbps Fast Ethernet, but
it still integrates seamlessly with 100Mbps Fast Ethernet
hardware. Users can connect Gigabit Ethernet hardware
with either fiber optic cabling or copper Category
5e cabling, with fiber optics more suited for network
backbones. As the Gigabit standard gradually integrates
into existing networks, current computer applications will
enjoy faster access time for network data, hardware, and
Internet connections.
About Gigabit Ethernet and Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber optic cabling is made from flexible, optically efficient
strands of glass and coated with a layer of rubber tubing,
fiber optics use photons of light instead of electrons to
send and receive data. Although fiber is physically capable
of carrying terabits of data per second, the signaling
hardware currently on the market can handle no more
than a few gigabits of data per second.
Fiber cables come with two main connector types. The
most commonly used fiber optic cable is multi-mode
fiber cable (MMF), with a 62,5 micron fiber optic core.
Single-mode fiber cabling is somewhat more efficient
than multi-mode but far more expensive, due to its smaller
optic core that helps retain the intensity of traveling light
signals. A fiber connection always require two fiber cables:
one transmits data, and the other receives it.
Each fiber optic cable is tipped with a connector that fits
into a fiber port on a network adapter, hub, or switch.
In the USA, most cables use a square SC connector that
slides and locks into place when plugged into a port or
connected to another cable. In Europe, the round ST
connector is more prevalent.
For Gigabit Ethernet, you must use the Linksys MGBT1,
MGBSX1, or MGBLH1 miniGBIC modules with the Linksys
Gigabit Switches. The MGBSX1 and the MGBLH1 require
fiber cabling with LC connectors, and the MGBT1 requires
a Category 5e Ethernet cable with an RJ-45 connector.
For Fast Ethernet, you must use the MFEFX1 (100BASE-FX)
or MFELX1 (100BASE-LX) SFP transceivers.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
49
Page 56

Appendix B
About Switch Stacking
Appendix B:
About Switch Stacking
A switch may operate in one of two modes: Stack or
Standalone. You can select either mode during software
boot or using the web-based utility’s Setup > Summary
screen, with the new mode taking effect after the unit is
reset. The factory default is Stack mode.
Standalone Mode
A switch operating in Standalone mode runs as an
independent, single unit. All ports of a standalone switch
operate as normal Ethernet links. A Standalone switch
does not participate in a Stack even if physically connected
to a Stack.
Stack Mode
A switch operating in Stack mode is not an independent
unit, but a member of an organized group of switches
known as a Stack. A Stack consists of one Master control
switch, a Master Backup switch, and up to four Stack
Member SLM224G4S switches, or up to two Stack Member
SLM248G4S switches.
Building a New Stack
To build a new self-ordering stack, use a group of switches,
each of which is set to the factory defaults.
All that is necessary to do is to connect the units physically
(through the stacking ports, using standard Ethernet
cables) and turn the units on. After a short interval the stack
will become operational with one of the units selected as
the Master of the stack. The unit selected as Master will
be indicated by the Stack Master LED on its front panel lit
amber. If a serial console connection is desired, the serial
cable should be connected to the console port of the unit
serving as stack Master.
If the units to be used in building the new stack were used
before then it is highly recommended to reset them back
to factory default (by holding the reset button for at least
10 seconds) and proceeding as described above.
Adding Units to a Running Stack
Restore the factory defaults to each of the units to be
added to the stack. Then connect the units physically to
the stack and turn the units on. After a short while the new
units will become stack members.
Manually Ordered Stack
As a special case, a unit in Stack mode not connected
•
to any other units may operate as a “stack–of-one”.
NOTE: When a unit is in Stack mode, two of
its ports are reserved for use with stacking
links, and cannot be used for regular network
connections.
Two ports of each unit in Stack mode (ports G1 and G2)
are reserved for stacking links, and cannot be used for
regular network connections.
Stack Building Quick Start
Stacking allows you to build a switch with many more
ports than would be available in a single unit. The stack is
managed by one of the units called the Master and all the
other units serve as ports only.
When building a stack there are two distinct cases:
Building a stack from scratch
•
Adding units to a running (operational) stack to make
•
it bigger
The system administrator can manually decide which unit
will be the Master. To do that the system administrator
has to assign a unique Unit ID from 1 to 6 (1 to 4 for
SLM248G4S-only stacks) to each stack member.
NOTE: It is highly recommended that if any
unit is assigned its Unit ID manually, then all
the units be assigned their Unit IDs manually.
It is NOT recommended to have a mixed case
with some Unit IDs assigned manually, and
others automatically allocated at runtime by
the stack Master (even though such a mixed
stack may well function flawlessly).
Building a New Stack
Reset all of the units to the factory defaults and build the
stack as described above in “Normal (Self-Ordering) Stack”.
Then, when the stack is operational, assign each unit with
its desired number, making sure no duplicates exist, and
reset the stack.
Adding Units to a Running Stack
Normal (Self-Ordering) Stack
The easiest way to build a stack is to have the switches’
automatically determine their order in the stack.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
Restore the factory defaults to each of the units to be
added to the stack. Then, connect the units physically to
the stack and turn the units on. After a short while they
will become stack members, but will have auto-assigned
Unit IDs. Assign each such unit its desired Unit ID (using
50
Page 57

Appendix B
About Switch Stacking
the Console port, Telnet or Web-based Utility) and reset
the units to make this assignment permanent.
The unit that is assigned number 1 will act as the Master;
this is indicated by the Stack Master LED on its front panel
being lit amber. The unit that is assigned number 2 will act
as the Backup Master.
Stack Resiliency
A stack’s topology may be either Ring or Chain. The best
practice is to configure the stack in Ring topology, due to
its higher resiliency in case of unit failure or stacking link
failure.
Additionally, if a redundant power supply is used, it is
recommended to make sure that the Master and Backup
Master units are connected to the redundant power
supply.
Advanced Stacking
In order to understand the operation of the stack it is
necessary to understand two key concepts:
Unit IDs, and how they are allocated
•
Stack unit start up process
•
Units that are assigned Unit IDs 3-6 (SLM224G4S) or
•
Unit IDs 3-4 (SLM248G4S) are called Stack Members.
A stack member will only operate as a member of
the stack under the direction of an operational stack
Master (or a Backup Master that has taken over the
role).
Stack members are not directly manageable and
configurable, and must be managed through the
stack Master, and do not contain any meaningful
configuration information (not even their own
configuration). If an operational master is not present
and reachable, these units will not be functional.
Master Enabled units
•
Units that are assigned a unit ID number of 1 or 2 are
called master enabled units. Only master enabled units
participate in master election (see below) whenever
they are initiated, inserted into a new stack or lose
connectivity with the existing master. Only master
enabled units can become the stack master or backup
master. Units with assigned IDs of 3-6 (SLM224G4S)
or 3-4 (SLM248G4S) can become neither a master nor
a backup master unless this is done manually by the
system administrator or they are reset to the factory
default first.
Unit IDs
Each unit in a stack has an assigned unique Unit ID number.
Unit ID numbers are meaningful as follows:
The unit that is assigned Unit ID=1 will serve as the
•
Stack Master. All other units will be stack members.
The stack Master provides a single point of control,
configuration and management for the entire stack,
and stores the configuration for all stack members
(which themselves do not store any configuration
information at all).
The unit that is assigned Unit ID=2 is a special stack
•
member, which serves as the Stack Backup Master.
A stack Backup Master, in addition to being a stack
member, serves as a Backup in case the stack Master
fails or is disconnected for any reason. If that should
happen, the Backup Master takes over the role of stack
Master for the remaining stack members.
To make this possible, the stack Master will store a copy
of the active configuration on the Backup Master, but
this copy will only be used if and when it takes over the
role of stack Master. Note that only the configuration
file is copied. Any dynamically filled tables, e.g.
addresses learned, are not copied from the Master to
the Backup Master. If the Backup Master takes over
the role of stack Master, it will start building its own
dynamic tables from scratch.
Unit ID Allocation
Units are shipped from the factory with no Unit ID, and
must be assigned a unique Unit ID before they can operate
as part of a stack. Unit ID numbers are assigned to units in
one of two ways:
Assigned by the system administrator, in which case
•
they can only be changed manually by the system
administrator
Allocated to a stack member unit by the stack Master
•
during system initialization
In general, a unit that was assigned a Unit ID will tend
to keep this number even after it is rebooted. The stack
Master may reallocate Unit IDs during system initialization
to resolve duplicate Unit ID conflicts (see below). Manually
assigned Unit IDs cannot be changed by the stack Master,
even if they are in conflict.
Unit ID assignment/change takes effect only during
system initialization and does not take place during runtime of the system.
Units of a stack do not have to be numbered in sequence
or in order, and may be interconnected as desired, as long
as each unit has a unique ID and at least one unit of the
stack serves as stack Master.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
51
Page 58

Appendix B
About Switch Stacking
Stack Units Startup Process
Whenever a unit in stack mode is initialized (powered
up or rebooted) it goes through the same exact process,
consisting of the following three steps:
Master Discovery/Election.
1.
Unit ID allocation by the Master (including duplicate
2.
Unit ID conflict resolution)
Unit/port configuration by the Master
3.
Master Discovery
Whenever a unit in stack mode initializes, its behavior will
depend on its Unit ID (if any).
If the unit does not have a current Unit ID (that is, the
•
unit is in factory default mode).
If there is a master, the unit performs Unit ID Allocation
(refer to section “Unit ID Allocation and Duplicate Unit
ID Conflict Resolution”), where it will get a number from
the master. If there is no master, then it will participate
in Master-election, and may even end up as the new
master or backup master.
If the unit’s current Unit ID is 1 or 2 (previously allocated,
•
perhaps even in a different stack), then the unit will
participate in the Master election.
If the unit has a current Unit ID (previously allocated,
•
perhaps even in a different stack), it will try to use this
number in the new stack. If the unit’s current Unit ID is
3-6 (3-4 for SLM248G4S), then it will try and connect
to the running stack Master, and will not proceed to
the next stage until contact with the Master is made. In
particular, such units will NOT participate in the Master
election process, and if no Master is present, the units
will be effectively shut down.
Both the master and all other stack units carry out a
continuous process of master discovery by frequently
exchanging stack control messages. This allows them to
discover whenever a unit fails or becomes unreachable.
Master Election
Whenever a unit (or more than one) in stack mode comes
up, one of the units is elected to be the stack Master. The
unit selected as Stack Master is chosen as follows:
If a unit in the stack was set to “Force Master” by the
1.
system administrator, that unit will be the stack Master.
Only master enabled stack units, i.e. unit ID=1 or unit
ID=2 can be selected as “Force Master”.
Otherwise, if the stack contains units whose unique
2.
Unit ID is either 1 or 2, then one of these two units
will be the stack Master. It does not matter if the Unit
ID was originally assigned automatically or manually.
(Such units are called Master-enabled units).
If there is only one such unit, it will be selected as
•
the stack Master (even if its Unit ID=2).
If there are two such units, the two units will
•
decide which of them is the Master by checking:
Which one has been running for a longer time
•
(in increments of 10 minutes). The unit running
for a longer time will be the stack Master.
If they have been running for the same amount
•
of time, Unit ID=1 will be the stack Master.
If both units have been running for the same
•
amount of time and both units have the same
Unit ID, the unit with a lower MAC address will
be selected as stack Master.
Otherwise, if the stack contains one or more units
3.
without a current Unit ID (that is to say in factory
default state), then the stack Master will be one of
these units. The unit selected to be the Master will be
the one running for the longest time (in increments
of 10 minutes) or, if all units are running for the
same amount of time, the one with the lowest MAC
address.
The end result of Master Election is that the stack has a
stack Master. The Stack master has unit ID=1 and the
Backup Master, if it exists, unit ID=2. Alternatively, the
Stack master has unit ID=2 and the Backup Master, if it
exists, unit ID=1.
If a Master-enabled (Unit ID=1 or 2) unit is added to a
stack and turned on, then when it comes up, it will invoke
master-election, even though the rest of the stack already
has an elected master. Because it is new, it will lose the
election and join as a member or backup master.
Unit ID Allocation and Duplicate Unit ID Conflict Resolution
Once a stack Master is elected, it will allocate Unit IDs to
units that do not have a currently assigned Unit ID (that is,
units in factory default mode).
In addition, the stack Master will try to resolve all cases of
units with duplicate Unit IDs. This is done by changing the
Unit IDs of offending units that have a duplicate current
Unit ID, provided that there are available, unused Unit
IDs.
In the case of a merged stack scenario, units that were
initially in the sub-group of the Master that remained as
Master will have the same unit IDs as they had before.
Members of the other sub-group will be renumbered.
If the conflict occurs after the units reboot then the
following will take place:
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
52
Page 59

Appendix B
If both duplicate units are in auto (self ordering) mode,
•
then the unit ID will be decided by the Mac address.
The unit with the lower Mac will keep its unit ID. The
other will be reassigned a new unit ID.
If one of the duplicates is in auto (self ordering)
•
mode and the other unit is in manual mode then the
manual mode unit will keep its ID and the other will be
reassigned a new unit ID.
If both duplicate units are in manual mode then both
•
of them will be shut down.
If the stack Master is able to allocate a unique Unit ID to
each unit, then all units can operate as a stack. If the stack
Master is unable to allocate a Unit ID to any unit, that unit
is effectively shut down and will not participate in the
stack.
In particular, units with a conflicting manually set Unit ID
number will be shut down because the Master cannot
override the system administrator’s assignment to resolve
the conflict.
If there are more units than the maximum number allowed
in a stack and the incoming units are already in factory
default state (which means they do not have unit ID
assigned) then a Master will be elected following Master
Discovery and Master Election processes. All other units
will remain shut down. Please note that in some extreme
cases, due to a race condition during the boot process,
some of the units might be connected and join the stack..
If the incoming units already have a unit ID then none of
them will join the stack and all will be left in shutdown
mode (since there is no way to know which of them are
preferable).
NOTE: If a unit is shut down, its stacking
links will be inactive. Moreover, if the stacking
units are connected in a chain topology, the
shutdown of one unit breaks the chain and may
cause other units to be shut down if they have
no active link to the Master unit.
About Switch Stacking
the stack Master and will be copied to the Backup Master
(if it exists).
User Controls
Using either the CLI or the graphical user interface (GUI),
the user can configure the following settings:
Set the operational mode of the unit (which will take
•
effect after next reboot) – Standalone or Stack.
Force a unit to be the stack Master after the next reset
•
Assign a static Unit ID, or, allow the unit to be
•
renumbered.
Stacking Examples
Replacing a Failed Stack Member in a Running
Stack
In this example, a non-master unit fails in a running stack.
When notified of the failure, a system administrator
removes the failed unit and replaces it with another one.
When the unit fails, the stack Master detects (via the
ongoing Master Discovery process) that the unit no longer
responds, and directs all other stack members to route
unit-to-unit traffic around the failed unit using the ring
topology of the stacking connections. At the same time
the stack Master notifies the system administrator (using
SYSLOG messages and SNMP traps) of the failure.
When the failed unit is disconnected from the stack, all
traffic will already be routed around it, and as long as all
other stacking connections are left intact, the stack should
continue to run.
When a new unit is inserted in the stack and powered up,
the following will happen:
The incoming unit, being in stack mode, will perform
1.
Master discovery, and perhaps participate in a Master
Election, as described above for any stacking-mode
unit powering up.
Unit and Port Configuration
At this point, each unit in the stack has a unique Unit-ID;
one of the units is the stack Master, and, possibly, one of
the units serves as Backup Master. The stack Master will
now configure each of the member units and its ports
according to the configuration file present on the Master.
If the stack has a Backup Master the configuration file will
also be copied to the Backup Master.
Once all the units and ports are configured, the stack will
go into normal operational mode. If any change is made
to the system configuration, the change will be stored by
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
•
•
The stack Master at this stage will carry out a Unit ID
2.
allocation and conflict resolution process.
If the incoming unit has a Unit ID of 1 or 2, i.e. it
is a master enabled unit, it will initiate a Master
Election. However, since the running stack Master
has a longer run time, it will remain elected as
the stack Master and the incoming unit will not
become a new stack Master.
If the incoming unit has a Unit ID of 3 to 6 (3 to 4
for SLM248G4S), it will try to become a member
unit of the stack subject to the already running
stack Master, and Master Election will not take
place.
53
Page 60

Appendix B
If the incoming unit did not have an assigned Unit
•
ID (that is, it was in factory default mode), it will
be assigned the lowest available Unit ID by the
Master. It is strongly recommended that automatic
assigned unit ID mode be used since it provides
better resiliency to the stack.
If the incoming unit already has an assigned Unit
•
ID, and that Unit ID is unused in the current stack,
the incoming unit will keep its assigned Unit ID
and the Master will apply to it any configuration
relevant to that Unit ID.
If the incoming unit already has an assigned Unit
•
ID, and that Unit ID conflicts with a unit ID in the
current stack, the Master will reallocate a new
Unit ID to the incoming unit, giving it the lowest
available Unit ID (assuming, of course, that the
incoming unit does not have a manually assigned
Unit ID, which the Master cannot change).
If the incoming unit cannot be assigned an
•
available Unit ID for any reason (in the case of unit
replacement that can only happen if the incoming
unit has a manually assigned Unit ID), then it will
be effectively shut down—that is, it will not be
joined to the stack.
The stack Master will now carry out Unit and port
3.
configuration for the incoming unit.
Any configuration information the Master has
•
that is relevant to the number assigned to the
incoming unit will be applied. In particular, if the
incoming unit was assigned the same Unit ID of
the unit it replaces, then it will receive the same
configuration as the failed unit, to the extent
possible.
If the incoming unit is identical in makeup to the
replaced unit, the entire configuration of the replaced
unit will be applied to the incoming one and the stack
will go back to the state it was in before unit failure.
However, sometimes the incoming unit is not identical
to the unit that failed in these cases. The stack Master
will apply the configuration in the following manner:
If a 24-port unit replaces a failed 48-port unit,
•
then the ports of the incoming unit will be
configured according to the way the first 24
ports of the failed unit were configured.
(Note that the configuration of all 48 ports of the
failed unit is remembered, even though only the
first 24 are currently applied. If, in the future, a 48
port unit is inserted and assigned the same Unit
ID, it will be configured as the original failed 48port unit was configured).
About Switch Stacking
If a 48-port unit replaces a 24-port unit, then
•
the first 24 ports of the incoming unit will be
configured according to the way the ports of the
failed unit were configured, and the rest of the
ports of the incoming unit will be configured at
default settings.
If the units (the failed one and its replacement)
•
had/have uplink ports, then the first uplink of
the incoming unit will be configured as was the
first uplink of the failed unit, and so on.
Stack Master Failure and Replacement
In this example, the master unit fails in a running stack.
When notified of the failure, a system administrator
removes the failed unit and replaces it with another one.
When the unit fails, the stack Backup Master detects (via
the ongoing monitoring Master Discovery process) that
the master unit no longer responds and takes over as the
stack master. The backup master directs all other stack
members to route unit-to-unit traffic around the failed
unit using the ring topology of the stacking connections.
At the same time the stack Backup Master notifies the
system administrator (using SYSLOG messages and SNMP
traps) of the failure.
When the failed unit is disconnected from the stack, all
traffic will already be routed around it, and as long as all
other stacking connections are left intact, the stack should
continue to run.
When a new unit is inserted in the stack and powered up,
the following will happen:
The incoming unit will perform Master discovery, and
1.
perhaps participate in a Master Election, as described
above.
If the incoming unit has a Unit ID of 1 or 2 (that
•
is, the unit is a master-enabled unit), then Master
Election will be initiated. However, since the
running stack Backup Master has a longer run
time, assuming that it has been running for more
then 10 minutes, it will remain elected as the stack
Master and the incoming unit will not become a
new stack Master. This may result in an incoming
unit using Unit ID=1, and serving as the stack
backup master, while the already running unit
with Unit ID=2 remains the active stack master.
The stack Master at this stage will carry out a Unit ID
2.
allocation and conflict resolution process.
If the incoming unit did not have an assigned Unit
•
ID (that is, it was in factory default mode), it will
be assigned the lowest available Unit ID by the
Master. It is strongly recommended that automatic
assigned unit ID mode be used since it provides
better resiliency to the stack.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
54
Page 61

Appendix B
If the incoming unit already has an assigned Unit
•
ID, and that Unit ID is unused in the current stack,
the incoming unit will keep its assigned Unit ID
and the Master will apply to it any configuration
relevant to that Unit ID.
If the incoming unit already has an assigned Unit
•
ID, and that Unit ID conflicts with a unit ID in the
current stack, the Master will reallocate a new
Unit ID to the incoming unit, giving it the lowest
available Unit ID (assuming, of course, that the
incoming unit does not have a manually assigned
Unit ID, which the Master cannot change).
If the incoming unit cannot be assigned an
•
available Unit ID for any reason (in the case of unit
replacement that can only happen if the incoming
unit has a manually assigned Unit ID), then it will
be effectively shut down—that is, it will not be
joined to the stack.
The stack Master will now carry out Unit and port
3.
configuration for the incoming unit.
Any configuration information the Master has
•
that is relevant to the number assigned to the
incoming unit will be applied. In particular, if the
incoming unit was assigned the same Unit ID of
the unit it replaces, then it will receive the same
configuration as the failed unit, to the extent
possible, as described in section “Replacing a
Failed Stack Member in a Running Stack“ above.
Splitting a Stack
In this example, let us assume that a working stack is
split into two groups, either by failure of a stacking link
connecting two units in the stack or by a failed unit in a
chain topology which causes disconnection between two
units in the stack. In this case we should consider each
subgroup as an independent running stack configuration.
For each subgroup three suboptions will be considered:
Both the Master unit and the Backup master unit are
•
part of the subgroup.
Either the Master unit or the Backup master unit are
•
part of the subgroup.
Neither the Master unit nor the Backup Master unit are
•
part of the subgroup.
The following describes what happens within each
subgroup for each of these three suboptions.
Subgroup Contains Both Master Unit and Backup Master Unit
Nothing changes, except the master sees the missing
•
units as having been removed, and routes traffic
around them, as described in section “Replacing a
Failed Stack Member in a Running Stack” above.
About Switch Stacking
Since this subgroup contains both master and backup,
•
the subgroup works, and the other subgroup will not
work. Refer to step 3 below for detailed information.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
•
The Master Discovery, Master Election and Unit ID
a.
Allocation & Duplicate Unit ID Conflict Resolution
processes will be executed.
Any configuration information that the Master
b.
has that is relevant to the units remaining in the
subgroup will remain unchanged.
Topology information (the information for each
c.
unit on how to send traffic to any other unit in the
stack) managed by the master will include only
units that are reachable (connected) following the
split.
The subgroup continues to work as before, except
d.
that the number of the unit is lower than prior to
the split.
No unit ID changes are made in either subgroup.
e.
The Master notifies the system administrator (using
f.
SYSLOG messages and SNMP traps) of the removed
units and ports which belong to the unreachable
units and will be reported as ‘not present’.
Subgroup Contains Either Master Unit or Backup Master Unit
If the Master unit remains in this subgroup,
•
this is the same as described in section
“Replacing a Failed Stack Member in a Running
Stack” above. If the Backup Master unit remains in
this subgroup, then this is the same as section “Stack
Master Failure and Replacement” above.
It should be emphasized that if the stack is split into
•
two parts, one with the master and one with the
backup, both parts will work.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
•
The Master Discovery, Master Election and Unit ID
a.
Allocation & Duplicate Unit ID Conflict Resolution
processes will be executed.
If the subgroup contains the Master unit, the
b.
stack Master notices (using the master detection
process) that some units no longer respond. At
the same time the stack Master notifies the system
administrator (using SYSLOG messages and SNMP
traps) of the removed units and ports which belong
to the unreachable units and will be reported as
‘not present’.
If the subgroup contains the Backup Master unit,
c.
the Backup Master will see as a case of Master
failure and take over and manage the remaining
units as a stack, while keeping its number as it was
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
55
Page 62

Appendix B
About Switch Stacking
before the split. Since the Backup Master was not
acting as a master prior to the split, it will initiate
a topology database and port-learning process.
Traffic might be halted for a short period of time
until synchronization (unit and port configuration)
is completed. New units learned by the Backup
Master will notify the system administrator (using
SYSLOG messages and SNMP traps).
In either case (steps b and c above), the subgroup
d.
will continue to work as it did before the split,
except that the number of units is lower than prior
to the split.
No unit ID changes are made in either subgroup.
e.
Each new stack will have a Master (one has the
f.
original Master, the other has the Backup). They
thus operate as two separate stacks, both having
the same configuration and hence the same IP
address.
WARNING: Both resulting stacks will have the
same IP Address. This may lead to problems on
the network, since there would be no way for
users to connect to one of the stacks through
its IP address.
Subgroup Contains Neither Master Unit nor Backup Master
Unit
Please note that this is exactly the same as the case of a
failed master, where no backup is available.
In this case the units with ID 3-6 (3-4 for SLM248G4S) in
•
this subgroup will not renumber themselves, and will
remain shut down until a stack Master enabled unit is
connected, and starts to operate as stack master. It is
the responsibility of the Master-discovery process to
see that the master is gone.
In this subgroup, the units lose connection with the
•
Master. Since they started as a running stack and none
of them are in factory default mode, renumbering will
not take place, and even a Reset of the units will not
affect unit ID assignment (As noted above, units can
be renumbered only by a stack Master).
No unit ID changes are made in either subgroup.
•
Again it should be emphasized that none of the units in
either half of the stack will renumber themselves.
Merging Two Stacks
In this example, the user would like to merge two working
stacks and create one stack out of those two stacks. In this
example one should distinguish between two scenarios:
The incoming units are turned off before insertion and
•
then powered back up afterward
The two stacks are kept running during the insertion
•
(for example, the stacking cables of the two stacks are
connected)
Incoming Units Turned Off Before Insertion, then Turned On
After Insertion
This is exactly the same as inserting units into a running
stack (refer to “Replacing a Failed Stack Member in a
Running Stack”). The only difference is that more than
one unit will be inserted into the stack and therefore for
each unit inserted to the stack the same process will be
executed.
Both Stacks Kept Running During Insertion
If each of the joined stacks has a Master unit, both Master
units will perform Master discovery and participate in a
Master Election, as described above. One of the Master
units will be selected as the Master unit—for the merged
stack. The criteria for choosing the master are:
Force Master
•
System Up Time
•
Lowest Unit ID
•
Lowest MAC
•
The process of master selection between the two master
units is as follows:
If force master is enabled then the unit which is forced
•
is chosen.
Up time is measured by quantities of periods of 10
•
minutes. If the number of 10 minute periods is higher
for one of the units then this unit is chosen.
If both units have the same up time (measured in
•
periods of 10 minutes) the unit with the lowest unit
ID is elected.
If both Master unit IDs are equal the unit with the
•
Lower MAC is chosen.
The Master unit that loses its “mastership” in the Master
•
election process will be renumbered if the unit ID was
dynamically allocated. renumbering will now allocate
it a new number by the new Master, as a stack member,
or possibly Backup Master. It should be emphasized
that in no case will there be two units with the same
Unit ID at the end of this process.
The Master unit that loses its mastership in the Master
•
election process will be shut down if the unit ID was
manually allocated. It is recommended that the
administrator configure it to auto-assigned Unit ID
before reconnecting it to the stack.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
56
Page 63

Appendix B
About Switch Stacking
It should be emphasized that when two stacks are
combined, all of the configuration information for one of
the stacks will be lost. Only the surviving master (after the
discovery/election process completes) will maintain its
configuration information.
The best practice to combine two stacks is to reset the
switches in one stack to the factory defaults and then
add the switches as described in the “Adding Units to
a Running Stack” subsection of section “Normal (SelfOrdering) Stack).”
If one of the merged stacks had neither a Master unit
•
nor a Backup Master unit, then units belonging to
this group will be inserted into the stack in the exact
way as described in section “Replacing a Failed Stack
Member in a Running Stack” above. The Master will
either connect the running units to the stack using the
current numbers or will renumber them as necessary.
The process described in section ““Replacing a Failed
Stack Member in a Running Stack” applies to this case
as well.
It should be emphasized that any time two stacks are
combined into one stack, there is no way to maintain
the configuration for both sets of switches. All dynamic
information of the units that belong to the portion of
the stack that was not reelected to be the master will be
relearned.
Stacking Cable Failure
In this example, let us assume that stacking connection
cables failed and caused a stack split, as described in
section “Splitting a Stack.” When the stacking cable
connection is fixed and units are reconnected, it results in
merging two stacks as described in section “Merging Two
Stacks.”
A running group of units is added to an existing stack,
2.
assuming each one of the stack groups has an elected
Master. The total of existing units and inserted units
would exceed the maximum allowed number of units
in a stack, which is 6 units for SLM224G4S, or 4 units
for SLM248G4S:
Master Detection and Master Election processes
•
would determine the master out of one of two
combined stacking groups.
When switches are added to a running stack,
•
the Unit ID Allocation and Duplicate ID Conflict
Resolution process will detect an error if too many
switches are present in the stack, and no changes
will be made to units that originally belonged
to the group managed by the newly elected
master. The original switches will retain their ID
assignments and configurations. The units that
originally belonged to the group managed by
the master that lost its master status will be shut
down.
Standalone Unit Inserted into a Running Stack
Since the unit is in standalone mode it will not participate
in a master discovery process (it will not look for a master
and will not respond to master queries). As a result it will
not join the stack but will continue to run as a standalone
manageable unit.
The ports that are connected to the other units’ stacking
links will not pass any traffic, and the master will consider
them as failed stacking links and route all traffic around
them.
This scenario is feasible only if the topology of the stack
is Chain topology. Single stacking cable failure will not
cause a stack split if a Ring topology is used.
Inserting Too Many Units
In this example, a user tries to insert too many units into
a stack.
All units (existing and newly inserted) are powered on
1.
at the same time:
A Master is elected following the Master Discovery
•
and Master Election processes.
All other units will shut down.
•
NOTE: In some extreme cases, due to a race
condition during the boot process, some of the
units might be connected and join the stack.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
57
Page 64

Appendix C
Glossary
Appendix C:
Glossary
This glossary contains some basic networking terms you
may come across when using this product.
WEB: For additional terms, please visit the
glossary at www.linksys.com/glossary
Access Mode
is granted to the system.
Access Point A device that allows wireless-equipped
computers and other devices to communicate with a
wired network. Also used to expand the range of a wireless
network.
Access Profiles Allows network managers to define
profiles and rules for accessing the device. Access to
management functions can be limited to user groups,
which are defined by the following criteria:
Ingress interfaces
•
Source IP address and/or Source IP subnets.
•
ACE Filters in Access Control Lists (ACL) that determine
which network traffic is forwarded. An ACE is based on the
following criteria:
Protocol
•
Protocol ID
•
Source Port
•
Destination Port
•
Wildcard Mask
•
Source IP Address
•
Destination IP Address
•
ACL (Access Control List) Access Control Lists are
used to grant, deny, or limit access devices, features, or
applications.
Auto-negotiation Allows 10/100 Mbps or 10/100/1000
Mbps Ethernet ports to automatically establish the
optimal duplex mode, flow control, and speed.
Back Pressure A mechanism used with Half Duplex mode
that enables a port not to receive a message.
Bandwidth The transmission capacity of a given device
or network.
Bandwidth Assignments Indicates the amount of
bandwidth assigned to a specific application, user, and/or
interface.
Specifies the method by which user access
Baud Indicates the number of signaling elements
transmitted each second.
Best Effort Indicates that traffic is assigned to the lowest
priority queue, and packet delivery is not guaranteed.
Bit A binary digit.
Boot To start a device and cause it to start executing
instructions.
Browser An application program that provides a way to
look at and interact with all the information on the World
Wide Web.
Bridge A device that connect two networks. Bridges are
hardware specific, however they are protocol independent.
Bridges operate at Layer 1 and Layer 2 levels.
Broadcast Domain Devices sets that receive broadcast
frames originating from any device within a designated
set. Routers bind Broadcast domains, because routers do
not forward broadcast frames.
Broadcast Storm An excessive amount of broadcast
messages simultaneously transmitted across a network
by a single port. Forwarded message responses are
heaped onto the network, overloading network resources
or causing the network to time out.
Burst A packet transmission at faster than normal rates.
Bursts are limited in time and only occur under specific
conditions.
Burst Size Indicates the burst size transmitted at a faster
than normal rate.
Byte A unit of data that is usually eight bits long
Cable Modem A device that connects a computer to the
cable television network, which in turn connects to the
Internet.
CBS (Committed Burst Size) Indicates the maximum
number of data bits transmitted within a specific time
interval.
CIR (Committed Information Rate) The data rate is
averaged over a minimum time increment.
Class Maps An aspect of Quality of Service system that is
comprised of an IP ACL and/or a MAC ACL. Class maps are
configured to match packet criteria, and are matched to
packets in a first-fit fashion.
Combo Ports A single logical port with two physical
connections, including an RJ-45 connection and a SFP
connection.
Communities Specifies a group of users which retain the
same system access rights.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
58
Page 65

Appendix C
Glossary
CoS (Class of Service) The 802.1p priority scheme. CoS
provides a method for tagging packets with priority
information. A CoS value between 0-7 is added to the
Layer II header of packets, where zero is the lowest priority
and seven is the highest.
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) Allows the
hosting of a website, FTP server, or e-mail server with a
fixed domain name (e.g., www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP
address.
Default Gateway A device that forwards Internet traffic
from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) A
networking protocol that allows administrators to assign
temporary IP addresses to network computers by “leasing”
an IP address to a user for a limited amount of time, instead
of assigning permanent IP addresses.
DHCP Clients An Internet host using DHCP to obtain
configuration parameters, such as a network address.
DHCP Server An Internet host that returns configuration
parameters to DHCP clients.
DNS (Domain Name Server) The IP address of your ISP’s
server, which translates the names of websites into IP
addresses.
Domain A specific name for a network of computers.
Download To receive a file transmitted over a network.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) An always-on broadband
connection over traditional phone lines.
DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) Provides a method of
tagging IP packets with QoS priority information.
Dynamic IP Address A temporary IP address assigned by
a DHCP server.
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol) Provides fast convergence, support for variable-
length subnet mask, and supports multiple network layer
protocols.
Encryption Encoding data transmitted in a network.
Ethernet IEEE standard network protocol that specifies
how data is placed on and retrieved from a common
transmission medium.
Firmware The programming code that runs a networking
device.
Flow Control Enables lower speed devices to
communicate with higher speed devices. This is
implemented by the higher speed device refraining from
sending packets.
Full Duplex The ability of a networking device to receive
and transmit data simultaneously.
GARP (General Attributes Registration
Protocol) Registers client stations into a multicast
domain.
Gateway A device that interconnects networks with
different, incompatible communications protocols.
GBIC (GigaBit Interface Converter) A hardware module
used to attach network devices to fiber-based transmission
systems. GBIC converts the serial electrical signals to serial
optical signals and vice versa.
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) Registers
client stations into a VLANs.
Half Duplex Data transmission that can occur in two
directions over a single line, but only one direction at a
time.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) The
communications protocol used to connect to servers on
the World Wide Web.
HTTPS (HyperText Transport Protocol Secure) An
extension to the standard HTTP protocol that provides
confidentiality by encrypting the traffic from the website.
By default this protocol uses TCP port 443.
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Allows the
gateway or destination host to communicate with the
source host. For example, to report a processing error.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) Allows
hosts to notify their local switch or router that they want
to receive transmissions assigned to a specific multicast
group.
IP (Internet Protocol) A protocol used to send data over
a network.
IP Address The address used to identify a computer or
device on a network.
IPCONFIG A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays
the IP address for a particular networking device.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) A VPN protocol used
to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) A company that provides
access to the Internet.
Jumbo Frames Enable transporting identical data in
fewer frames. Jumbo Frames reduce overhead, lower
processing time, and ensure fewer interrupts.
LAG (Link Aggregated Group) Aggregates ports or
VLANs into a single virtual port or VLAN.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) A protocol used to transfer
files over a TCP/IP network.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
LAN The computers and networking products that make
up your local network.
59
Page 66

Appendix C
Glossary
MAC (Media Access Control) Address The unique
address that a manufacturer assigns to each networking
device.
Mask A filter that includes or excludes certain values, for
example parts of an IP address.
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) One million bits per
second; a unit of measurement for data transmission.
MD5 (Message Digest 5) An algorithm that produces a
128-bit hash. MD5 is a variation of MD4, and increases MD4
security. MD5 verifies the integrity of the communication
and authenticates the origin of the communication.
MDI (Media Dependent Interface) A cable used for end
stations.
MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover) A
cable used for hubs and switches.
MIB (Management Information Base) MIBs contain
information describing specific aspects of network
components.
Multicast Transmits copies of a single packet to multiple
ports.
Network A series of computers or devices connected for
the purpose of data sharing, storage, and/or transmission
between users.
NMS (Network Management System) An interface that
provides a method of managing a system.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User
Service) A protocol that uses an authentication server to
control network access.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) An Ethernet connector that
holds up to eight wires.
RMON (Remote Monitoring) Provides network
information to be collected from a single workstation.
Router A networking device that connects multiple
networks together.
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) Detects and uses
network topologies that allow a faster convergence of the
spanning tree, without creating forwarding loops.
Server Any computer whose function in a network is to
provide user access to files, printing, communications,
and other services.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) The standard email protocol on the Internet.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) A
widely used network monitoring and control protocol.
SSH Secure Shell. A utility that uses strong authentication
and secure communications to log in to another computer
over a network.
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) Encryption technology for
the Internet used to provide secure transactions, such as
the transmission of credit card numbers for e-commerce.
OID (Object Identifier) Used by SNMP to identify
managed objects. In the SNMP Manager/Agent network
management paradigm, each managed object must have
an OID to identify it.
Packet A unit of data sent over a network.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) An Internet utility used
to determine whether a particular IP address is online.
Policing Determines if traffic levels are within a specified
profile. Policing manages the maximum traffic rate used
to send or receive packets on an interface.
Port The connection point on a computer or networking
device used for plugging in cables or adapters.
Port Mirroring Monitors and mirrors network traffic by
forwarding copies of incoming and outgoing packets
from one port to a monitoring port.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) A technology enabling an
Ethernet network cable to deliver both data and power.
QoS (Quality of Service) Provides policies that contain
sets of filters (rules). QoS allows network managers
to decide how and what network traffic is forwarded
according to priorities, application types, and source and
destination addresses.
Static IP Address A fixed address assigned to a computer
or device that is connected to a network.
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) Prevents loops in network
traffic. The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides tree
topography for any arrangement of bridges. STP provides
one path between end stations on a network, eliminating
loops.
Subnet (Sub-network) Subnets are portions of a
network that share a common address component. In
TCP/IP networks, devices that share a prefix are part of
the same subnet. For example, all devices with a prefix of
157.100.100.100 are part of the same subnet.
Subnet Mask An address code that determines the size
of the network.
Switch Filters and forwards packets between LAN
segments. Switches support any packet protocol type.
TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access Control
System Plus) Proprietary Cisco enhancement to Terminal
Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS). Provides
additional support for authentication, authorization, and
accounting.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
60
Page 67

Appendix C
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) A network protocol
for transmitting data that requires acknowledgement
from the recipient of data sent.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol) A set of instructions PCs use to communicate
over a network.
Telnet A user command and TCP/IP protocol used for
accessing remote PCs.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) A version of the
TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no directory or password
capability.
Throughput The amount of data moved successfully
from one node to another in a given time period.
Trunking Link Aggregation. Optimizes port usage by
linking a group of ports together to form a single trunk
(aggregated groups).
TX Rate Transmission Rate.
Glossary
UDP (User Data Protocol) Communication protocol that
transmits packets but does not guarantee their delivery.
Upgrade To replace existing software or firmware with a
newer version.
Upload To transmit a file over a network.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) The address of a file
located on the Internet.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Networks) Logical subgroups
that constitute a Local Area Network (LAN). This is done in
software rather than defining a hardware solution.
WAN (Wide Area Network) Networks that cover a large
geographical area.
Wildcard Mask Specifies which IP address bits are
used, and which bits are ignored. A wild card mask
of 255.255.255.255 indicates that no bit is important.
A wildcard of 0.0.0.0 indicates that all the bits are
important.
For example, if the destination IP address is 149.36.184.198
and the wildcard mask is 255.36.184.00, the first two bits
of the IP address are used, while the last two bits are
ignored.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
61
Page 68

Appendix D
Appendix D:
Specifications
Specifications
SLM224G4S/SLM248G4S
Specications
Ports
10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, and
1000BASE-T with 2 shared SFP slots
and 2 Gigabit ports
Buttons None
Cabling Type
10BASE-T/100BASE-T,
UTP CAT 5e or better for 1000BASE-T
LEDs Power, Link/Act, Speed
Performance
Switching Capacity SLM224G4S:
12,8 Gbps non-blocking
SLM248G4S:
17,6 Gbps non-blocking
MAC Table Size 8K
Number of VLANs 128
Stacking
Stack Operation SLM224G4S: Up to 6 in stack
(max. 192 ports with SLM248G4S)
SLM248G4S: Up to 4 in stack
(max. 192 ports with SLM224G4S)
Hot Insertion and removal
Ring and Chain stacking options
Master and Backup master for
resilient stack control
Auto-numbering or manual
conguration of units in stack
Management
Web User Interface Built-in Web UI for easy browser based conguration (HTTP)
SNMP SNMP versions 1, 2c, 3
Support for traps
SNMP MIBs RFC1213 MIB-2, RFC2863 Interface
MIB, RFC2665 Ether-like MIB,
RFC1493 Bridge MIB, RFC2674
Extended Bridge MIB (P-bridge,
Q-bridge), RFC2819 RMON MIB
(groups 1,2,3,9 only), RFC2737
Entity MIB, RFC 2618 RADIUS Client
MIB
24 or 48 RJ-45 connectors for
UTP CAT 5 or better for
RMON Embedded Remote Monitoring
(RMON) software agent supports
four RMON groups (history,
statistics, alarms, and events) for
enhanced trac management,
monitoring, and analysis
Firmware Upgrade Web Browser upgrade (HTTP)
and TFTP upgrade
Port Mirroring Trac on a port can be mirrored
to another port for analysis
with a network analyzer or RMON
probe
Other Management Switch Audit Log
DHCP Client
BootP
SNTP
Xmodem upgrade
Cable Diagnostics
Port Mirroring
PING
Security Features
IEEE 802.1x 802.1X - RADIUS Authentication.
MD5 Encryption
Access Control ToS/DSCP
Availability
Link Aggregation Link Aggregation using
IEEE 802.3ad LACP
Storm Control Broadcast and Multicast
Spanning Tree IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree,
Fast Linkover
IGMP Snooping
for fast client joins and leaves of
multicast streams and limits
bandwidth-intensive video trac
to only the requestors.
Up to 8 ports in up to 8 trunks
IGMP (v1/v2) Snooping provides
QoS
Priority levels 4 Hardware queues
Scheduling Priority Queueing and
Weighted Round Robin (WRR)
Class of Service Port-based
802.1p VLAN priority-based
IPv4 IP precedence/ToS/DSCP
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
62
Page 69

Appendix D
Layer 2
VLAN
HOL Blocking Head of line blocking prevention
Jumbo frame Supports up to 9K byte frames
Standards
802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet,
802.3z Gigabit Ethernet,
802.3x Flow Control
Environmental
Dimensions SLM224G4S:
(W x H x D) 430 x 44,45 x 203,3 mm
SLM248G4S:
440 x 44,45 x 350,8 mm
Unit Weight SLM224G4S: 1,927 kg
SLM248G4S: 3,98 kg
Power 100-240V 0,5A
Certication FCC Part15 Class A, CE Class A,
UL CSA (CSA22.2), CE mark, CB
Operating Temp. 0 to 40ºC
Storage Temp. -20 to 70ºC
Operating Humidity 20 to 95% Noncondensing
Storage Humidity 5 to 90% Noncondensing
Port-based and 802.1q-based VLANs
802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet,
802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet
Specifications
,
Specications are subject to change without notice.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
63
Page 70

Appendix E
Warranty Information
Appendix E:
Warranty Information
Limited Warranty
Linksys warrants this Linksys hardware product against
defects in materials and workmanship under normal
use for the Warranty Period, which begins on the
date of purchase by the original end-user purchaser
and lasts for the period specified for this product at
www.linksys.com/warranty. The internet URL address
and the web pages referred to herein may be updated by
Linksys from time to time; the version in effect at the date
of purchase shall apply.
This limited warranty is non-transferable and extends only
to the original end-user purchaser. Your exclusive remedy
and Linksys’ entire liability under this limited warranty
will be for Linksys, at its option, to (a) repair the product
with new or refurbished parts, (b) replace the product
with a reasonably available equivalent new or refurbished
Linksys product, or (c) refund the purchase price of the
product less any rebates. Any repaired or replacement
products will be warranted for the remainder of the
original Warranty Period or thirty (30) days, whichever is
longer. All products and parts that are replaced become
the property of Linksys.
Exclusions and Limitations
This limited warranty does not apply if: (a) the product
assembly seal has been removed or damaged, (b) the
product has been altered or modified, except by Linksys, (c)
the product damage was caused by use with non-Linksys
products, (d) the product has not been installed, operated,
repaired, or maintained in accordance with instructions
supplied by Linksys, (e) the product has been subjected to
abnormal physical or electrical stress, misuse, negligence,
or accident, (f) the serial number on the Product has been
altered, defaced, or removed, or (g) the product is supplied
or licensed for beta, evaluation, testing or demonstration
purposes for which Linksys does not charge a purchase
price or license fee.
ALL SOFTWARE PROVIDED BY LINKSYS WITH THE
PRODUCT, WHETHER FACTORY LOADED ON THE
PRODUCT OR CONTAINED ON MEDIA ACCOMPANYING
THE PRODUCT, IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND. Without limiting the foregoing, Linksys does
not warrant that the operation of the product or software
will be uninterrupted or error free. Also, due to the
continual development of new techniques for intruding
upon and attacking networks, Linksys does not warrant
that the product, software or any equipment, system or
network on which the product or software is used will be
free of vulnerability to intrusion or attack. The product
may include or be bundled with third party software or
service offerings. This limited warranty shall not apply to
such third party software or service offerings. This limited
warranty does not guarantee any continued availability
of a third party’s service for which this product’s use or
operation may require.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, ALL IMPLIED
WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY,
SATISFACTORY QUALITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE ARE LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE
WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED.
Some jurisdictions do not allow limitations on how long
an implied warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not
apply to you. This limited warranty gives you specific legal
rights, and you may also have other rights which vary by
jurisdiction.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT
WILL LINKSYS BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE
OR PROFIT, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS OF THE
THEORY OF LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), ARISING
OUT OF OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO
USE THE PRODUCT (INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN
IF LINKSYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY
EXCEED THE AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT.
The foregoing limitations will apply even if any warranty
or remedy provided under this limited warranty fails of
its essential purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow
the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not
apply to you.
Obtaining Warranty Service
If you have a question about your product or experience a
problem with it, please go to www.linksys.com/support
where you will find a variety of online support tools and
information to assist you with your product. If the product
proves defective during the Warranty Period, contact the
Value Added Reseller (VAR) from whom you purchased
the product or Linksys Technical Support for instructions
on how to obtain warranty service. The telephone number
for Linksys Technical Support in your area can be found
in the product User Guide and at www.linksys.com.
Have your product serial number and proof of purchase
on hand when calling. A DATED PROOF OF ORIGINAL
PURCHASE IS REQUIRED TO PROCESS WARRANTY CLAIMS.
If you are requested to return your product, you will be
given a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) number. You
are responsible for properly packaging and shipping your
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
64
Page 71

Appendix E
product to Linksys at your cost and risk. You must include
the RMA number and a copy of your dated proof of
original purchase when returning your product. Products
received without a RMA number and dated proof of
original purchase will be rejected. Do not include any
other items with the product you are returning to Linksys.
Defective product covered by this limited warranty will be
repaired or replaced and returned to you without charge.
Customers outside of the United States of America and
Canada are responsible for all shipping and handling
charges, custom duties, VAT and other associated taxes
and charges. Repairs or replacements not covered under
this limited warranty will be subject to charge at Linksys’
then-current rates.
Technical Support
This limited warranty is neither a service nor a support
contract. Information about Linksys’ current technical
support offerings and policies (including any fees for
support services) can be found at:
www.linksys.com/support.
Warranty Information
This limited warranty is governed by the laws of the
jurisdiction in which the Product was purchased by you.
Please direct all inquiries to: Linksys, P.O. Box 18558, Irvine,
CA 92623.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
65
Page 72

Appendix F
Regulatory Information
Appendix F:
Regulatory Information
FCC Statement
This equipment has been tested and complies with
the specifications for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own expense.
WARNING: You are cautioned that changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void
your authority to operate the equipment.
Industry Canada Statement
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian
ICES-003.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
This device may not cause interference and
1.
This device must accept any interference, including
2.
interference that may cause undesired operation of
the device.
Avis d’ Industrie Canada
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la
norme NMB-003 d’ Industrie Canada.
Le fonctionnement est soumis aux conditions suivantes :
Ce périphérique ne doit pas causer d’interférences;
1.
Ce périphérique doit accepter toutes les interférences
2.
reçues, y compris celles qui risquent d’entraîner un
fonctionnement indésirable.
EC Declaration of Conformity (Europe)
In compliance with the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, Low
Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC, and Amendment Directive
93/68/EEC, this product meets the requirements of the
following standards:
EN55022 Emission
•
Safety Notices
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire, use only No.26 AWG
•
or larger telecommunication line cord.
Do not use this product near water, for example, in a
•
wet basement or near a swimming pool.
Avoid using this product during an electrical storm.
•
There may be a remote risk of electric shock from
lightning.
EN55024 Immunity
•
EN60950 Safety
•
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
66
Page 73

Appendix F
Regulatory Information
User Information for Consumer Products
Covered by EU Directive 2002/96/EC on
Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment
(WEEE)
This document contains important information for users
with regards to the proper disposal and recycling of
Linksys products. Consumers are required to comply with
this notice for all electronic products bearing the following
symbol:
English - Environmental Information for Customers in
the European Union
European Directive 2002/96/EC requires that the equipment
bearing this symbol on the product and/or its packaging must
not be disposed of with unsorted municipal waste. The symbol
indicates that this product should be disposed of separately
from regular household waste streams. It is your responsibility to
dispose of this and other electric and electronic equipment via
designated collection facilities appointed by the government or
local authorities. Correct disposal and recycling will help prevent
potential negative consequences to the environment and
human health. For more detailed information about the disposal
of your old equipment, please contact your local authorities,
waste disposal service, or the shop where you purchased the
product.
Български (Bulgarian) - Информация относно
опазването на околната среда за потребители в
Европейския съюз
Европейска директива 2002/96/EC изисква уредите, носещи
този символ върху изделието и/или опаковката му, да не
се изхвърля т с несортирани битови отпадъци. Символът
обозначава, че изделието трябва да се изхвърля отделно от
сметосъбирането на обикновените битови отпадъци. Ваша
е отговорността този и другите електрически и електронни
уреди да се изхвърлят в предварително определени от
държавните или общински органи специализирани пунктове
за събиране. Правилното изхвърляне и рециклиране
ще спомогнат да се предотвратят евентуални вредни за
околната среда и здравето на населението последствия. За
по-подробна информация относно изхвърлянето на вашите
стари уреди се обърнете към местните власти, службите за
сметосъбиране или магазина, от който сте закупили уреда.
Ceština (Czech) - Informace o ochraně životního
prostředí pro zákazníky v zemích Evropské unie
Evropská směrnice 2002/96/ES zakazuje, aby zařízení označené
tímto symbolem na produktu anebo na obalu bylo likvidováno
s netříděným komunálním odpadem. Tento symbol udává,
že daný produkt musí být likvidován odděleně od běžného
komunálního odpadu. Odpovídáte za likvidaci tohoto produktu
a dalších elektrických a elektronických zařízení prostřednictvím
určených sběrných míst stanovených vládou nebo místními
úřady. Správná likvidace a recyklace pomáhá předcházet
potenciálním negativním dopadům na životní prostředí a lidské
zdraví. Podrobnější informace o likvidaci starého vybavení si
laskavě vyžádejte od místních úřadů, podniku zabývajícího se
likvidací komunálních odpadů nebo obchodu, kde jste produkt
zakoupili.
Dansk (Danish) - Miljøinformation for kunder i EU
EU-direktiv 2002/96/EF kræver, at udstyr der bærer dette symbol
på produktet og/eller emballagen ikke må bortskaffes som
usorteret kommunalt affald. Symbolet betyder, at dette produkt
skal bortskaffes adskilt fra det almindelige husholdningsaffald.
Det er dit ansvar at bortskaffe dette og andet elektrisk og
elektronisk udstyr via bestemte indsamlingssteder udpeget
af staten eller de lokale myndigheder. Korrekt bortskaffelse
og genvinding vil hjælpe med til at undgå mulige skader for
miljøet og menneskers sundhed. Kontakt venligst de lokale
myndigheder, renovationstjenesten eller den butik, hvor du
har købt produktet, angående mere detaljeret information om
bortskaffelse af dit gamle udstyr.
Deutsch (German) - Umweltinformation für Kunden
innerhalb der Europäischen Union
Die Europäische Richtlinie 2002/96/EC verlangt, dass technische
Ausrüstung, die direkt am Gerät und/oder an der Verpackung mit
diesem Symbol versehen ist , nicht zusammen mit unsortiertem
Gemeindeabfall entsorgt werden darf. Das Symbol weist darauf
hin, dass das Produkt von regulärem Haushaltmüll getrennt
entsorgt werden sollte. Es liegt in Ihrer Verantwortung, dieses
Gerät und andere elektrische und elektronische Geräte über
die dafür zuständigen und von der Regierung oder örtlichen
Behörden dazu bestimmten Sammelstellen zu entsorgen.
Ordnungsgemäßes Entsorgen und Recyceln trägt dazu bei,
potentielle negative Folgen für Umwelt und die menschliche
Gesundheit zu vermeiden. Wenn Sie weitere Informationen zur
Entsorgung Ihrer Altgeräte benötigen, wenden Sie sich bitte an
die örtlichen Behörden oder städtischen Entsorgungsdienste
oder an den Händler, bei dem Sie das Produkt erworben haben.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
67
Page 74

Appendix F
Regulatory Information
Eesti (Estonian) - Keskkonnaalane informatsioon
Euroopa Liidus asuvatele klientidele
Euroopa Liidu direktiivi 2002/96/EÜ nõuete kohaselt on
seadmeid, millel on tootel või pakendil käesolev sümbol ,
keelatud kõrvaldada koos sorteerimata olmejäätmetega. See
sümbol näitab, et toode tuleks kõrvaldada eraldi tavalistest
olmejäätmevoogudest. Olete kohustatud kõrvaldama käesoleva
ja ka muud elektri- ja elektroonikaseadmed riigi või kohalike
ametiasutuste poolt ette nähtud kogumispunktide kaudu.
Seadmete korrektne kõrvaldamine ja ringlussevõtt aitab vältida
võimalikke negatiivseid tagajärgi keskkonnale ning inimeste
tervisele. Vanade seadmete kõrvaldamise kohta täpsema
informatsiooni saamiseks võtke palun ühendust kohalike
ametiasutustega, jäätmekäitlusfirmaga või kauplusega, kust te
toote ostsite.
Español (Spanish) - Información medioambiental para
clientes de la Unión Europea
La Directiva 2002/96/CE de la UE exige que los equipos que
lleven este símbolo en el propio aparato y/o en su embalaje
no deben eliminarse junto con otros residuos urbanos no
seleccionados. El símbolo indica que el producto en cuestión
debe separarse de los residuos domésticos convencionales con
vistas a su eliminación. Es responsabilidad suya desechar este y
cualesquiera otros aparatos eléctricos y electrónicos a través de
los puntos de recogida que ponen a su disposición el gobierno y
las autoridades locales. Al desechar y reciclar correctamente estos
aparatos estará contribuyendo a evitar posibles consecuencias
negativas para el medio ambiente y la salud de las personas. Si
desea obtener información más detallada sobre la eliminación
segura de su aparato usado, consulte a las autoridades locales,
al servicio de recogida y eliminación de residuos de su zona o
pregunte en la tienda donde adquirió el producto.
ξλληνικά (Greek) - Στοιχεία περιβαλλοντικής
προστασίας για πελάτες εντός της Ευρωπαϊκής
Ένωσης
Η Κοινοτική Οδηγία 2002/96/EC απαιτεί ότι ο εξοπλισμός ο οποίος
φέρει αυτό το σύμβολο στο προϊόν και/ή στη συσκευασία
του δεν πρέπει να απορρίπτεται μαζί με τα μικτά κοινοτικά
απορρίμματα. Το σύμβολο υποδεικνύει ότι αυτό το προϊόν θα
πρέπει να απορρίπτεται ξεχωριστά από τα συνήθη οικιακά
απορρίμματα. Είστε υπεύθυνος για την απόρριψη του παρόντος
και άλλου ηλεκτρικού και ηλεκτρονικού εξοπλισμού μέσω των
καθορισμένων εγκαταστάσεων συγκέντρωσης απορριμμάτων οι
οποίες παρέχονται από το κράτος ή τις αρμόδιες τοπικές αρχές.
Η σωστή απόρριψη και ανακύκλωση συμβάλλει στην πρόληψη
πιθανών αρνητικών συνεπειών για το περιβάλλον και την υγεία.
Για περισσότερες πληροφορίες σχετικά με την απόρριψη του
παλιού σας εξοπλισμού, παρακαλώ επικοινωνήστε με τις τοπικές
αρχές, τις υπηρεσίες απόρριψης ή το κατάστημα από το οποίο
αγοράσατε το προϊόν.
Français (French) - Informations environnementales
pour les clients de l’Union européenne
La directive européenne 2002/96/CE exige que l’équipement
sur lequel est apposé ce symbole sur le produit et/ou son
emballage ne soit pas jeté avec les autres ordures ménagères. Ce
symbole indique que le produit doit être éliminé dans un circuit
distinct de celui pour les déchets des ménages. Il est de votre
responsabilité de jeter ce matériel ainsi que tout autre matériel
électrique ou électronique par les moyens de collecte indiqués
par le gouvernement et les pouvoirs publics des collectivités
territoriales. L’élimination et le recyclage en bonne et due forme
ont pour but de lutter contre l’impact néfaste potentiel de ce
type de produits sur l’environnement et la santé publique. Pour
plus d’informations sur le mode d’élimination de votre ancien
équipement, veuillez prendre contact avec les pouvoirs publics
locaux, le service de traitement des déchets, ou l’endroit où vous
avez acheté le produit.
Italiano (Italian) - Informazioni relative all’ambiente
per i clienti residenti nell’Unione Europea
La direttiva europea 2002/96/EC richiede che le apparecchiature
contrassegnate con questo simbolo sul prodotto e/o
sull’imballaggio non siano smaltite insieme ai rifiuti urbani
non differenziati. Il simbolo indica che questo prodotto non
deve essere smaltito insieme ai normali rifiuti domestici. È
responsabilità del proprietario smaltire sia questi prodotti sia
le altre apparecchiature elettriche ed elettroniche mediante
le specifiche strutture di raccolta indicate dal governo o dagli
enti pubblici locali. Il corretto smaltimento ed il riciclaggio
aiuteranno a prevenire conseguenze potenzialmente negative
per l’ambiente e per la salute dell’essere umano. Per ricevere
informazioni più dettagliate circa lo smaltimento delle vecchie
apparecchiature in Vostro possesso, Vi invitiamo a contattare gli
enti pubblici di competenza, il servizio di smaltimento rifiuti o il
negozio nel quale avete acquistato il prodotto.
Latviešu valoda (Latvian) - Ekoloģiska informācija
klientiem Eiropas Savienības jurisdikcijā
Direktīvā 2002/96/EK ir prasība, ka aprīkojumu, kam pievienota
zīme uz paša izstrādājuma vai uz tā iesaiņojuma, nedrīkst
izmest nešķirotā veidā kopā ar komunālajiem atkritumiem
(tiem, ko rada vietēji iedzīvotāji un uzņēmumi). Šī zīme nozīmē
to, ka šī ierīce ir jāizmet atkritumos tā, lai tā nenonāktu kopā ar
parastiem mājsaimniecības atkritumiem. Jūsu pienākums ir šo
un citas elektriskas un elektroniskas ierīces izmest atkritumos,
izmantojot īpašus atkritumu savākšanas veidus un līdzekļus, ko
nodrošina valsts un pašvaldību iestādes. Ja izmešana atkritumos
un pārstrāde tiek veikta pareizi, tad mazinās iespējamais
kaitējums dabai un cilvēku veselībai. Sīkākas ziņas par
novecojuša aprīkojuma izmešanu atkritumos jūs varat saņemt
vietējā pašvaldībā, atkritumu savākšanas dienestā, kā arī veikalā,
kur iegādājāties šo izstrādājumu.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
68
Page 75

Appendix F
Regulatory Information
Lietuvškai (Lithuanian) - Aplinkosaugos informacija,
skirta Europos Sąjungos vartotojams
Europos direktyva 2002/96/EC numato, kad įrangos, kuri ir
kurios pakuotė yra pažymėta šiuo simboliu (įveskite simbolį),
negalima šalinti kartu su nerūšiuotomis komunalinėmis
atliekomis. Šis simbolis rodo, kad gaminį reikia šalinti atskirai
nuo bendro buitinių atliekų srauto. Jūs privalote užtikrinti, kad
ši ir kita elektros ar elektroninė įranga būtų šalinama per tam
tikras nacionalinės ar vietinės valdžios nustatytas atliekų rinkimo
sistemas. Tinkamai šalinant ir perdirbant atliekas, bus išvengta
galimos žalos aplinkai ir žmonių sveikatai. Daugiau informacijos
apie jūsų senos įrangos šalinimą gali pateikti vietinės valdžios
institucijos, atliekų šalinimo tarnybos arba parduotuvės, kuriose
įsigijote tą gaminį.
Malti (Maltese) - Informazzjoni Ambjentali għal Klijenti
fl-Unjoni Ewropea
Id-Direttiva Ewropea 2002/96/KE titlob li t-tagħmir li jkun fih issimbolu fuq il-prodott u/jew fuq l-ippakkjar ma jistax jintrema
ma’ skart muniċipali li ma ġiex isseparat. Is-simbolu jindika
li dan il-prodott għandu jintrema separatament minn ma’ liskart domestiku regolari. Hija responsabbiltà tiegħek li tarmi
dan it-tagħmir u kull tagħmir ieħor ta’ l-elettriku u elettroniku
permezz ta’ faċilitajiet ta’ ġbir appuntati apposta mill-gvern jew
mill-awtoritajiet lokali. Ir-rimi b’mod korrett u r-riċiklaġġ jgħin
jipprevjeni konsegwenzi negattivi potenzjali għall-ambjent u
għas-saħħa tal-bniedem. Għal aktar informazzjoni dettaljata
dwar ir-rimi tat-tagħmir antik tiegħek, jekk jogħġbok ikkuntattja
lill-awtoritajiet lokali tiegħek, is-servizzi għar-rimi ta’ l-iskart, jew
il-ħanut minn fejn xtrajt il-prodott.
Nederlands (Dutch) - Milieu-informatie voor klanten
in de Europese Unie
De Europese Richtlijn 2002/96/EC schrijft voor dat apparatuur die
is voorzien van dit symbool op het product of de verpakking,
niet mag worden ingezameld met niet-gescheiden huishoudelijk
afval. Dit symbool geeft aan dat het product apart moet worden
ingezameld. U bent zelf verantwoordelijk voor de vernietiging
van deze en andere elektrische en elektronische apparatuur via de
daarvoor door de landelijke of plaatselijke overheid aangewezen
inzamelingskanalen. De juiste vernietiging en recycling van
deze apparatuur voorkomt mogelijke negatieve gevolgen voor
het milieu en de gezondheid. Voor meer informatie over het
vernietigen van uw oude apparatuur neemt u contact op met
de plaatselijke autoriteiten of afvalverwerkingsdienst, of met de
winkel waar u het product hebt aangeschaft.
Norsk (Norwegian) - Miljøinformasjon for kunder i EU
EU-direktiv 2002/96/EF krever at utstyr med følgende symbol
avbildet på produktet og/eller pakningen, ikke må kastes
sammen med usortert avfall. Symbolet indikerer at dette
produktet skal håndteres atskilt fra ordinær avfallsinnsamling
for husholdningsavfall. Det er ditt ansvar å kvitte deg med
dette produktet og annet elektrisk og elektronisk avfall via egne
innsamlingsordninger slik myndighetene eller kommunene
bestemmer. Korrekt avfallshåndtering og gjenvinning vil
være med på å forhindre mulige negative konsekvenser for
miljø og helse. For nærmere informasjon om håndtering av
det kasserte utstyret ditt, kan du ta kontakt med kommunen,
en innsamlingsstasjon for avfall eller butikken der du kjøpte
produktet.
Magyar (Hungarian) - Környezetvédelmi információ az
európai uniós vásárlók számára
A 2002/96/EC számú európai uniós irányelv megkívánja, hogy
azokat a termékeket, amelyeken, és/vagy amelyek csomagolásán
az alábbi címke megjelenik, tilos a többi szelektálatlan lakossági
hulladékkal együtt kidobni. A címke azt jelöli, hogy az adott
termék kidobásakor a szokványos háztartási hulladékelszállítási
rendszerektõl elkülönített eljárást kell alkalmazni. Az Ön
felelõssége, hogy ezt, és más elektromos és elektronikus
berendezéseit a kormányzati vagy a helyi hatóságok által
kijelölt gyűjtõredszereken keresztül számolja fel. A megfelelõ
hulladékfeldolgozás segít a környezetre és az emberi egészségre
potenciálisan ártalmas negatív hatások megelõzésében. Ha
elavult berendezéseinek felszámolásához további részletes
információra van szüksége, kérjük, lépjen kapcsolatba a helyi
hatóságokkal, a hulladékfeldolgozási szolgálattal, vagy azzal
üzlettel, ahol a terméket vásárolta.
Polski (Polish) - Informacja dla klientów w Unii
Europejskiej o przepisach dotyczących ochrony
środowiska
Dyrektywa Europejska 2002/96/EC wymaga, aby sprzęt
oznaczony symbolem znajdującym się na produkcie i/lub jego
opakowaniu nie był wyrzucany razem z innymi niesortowanymi
odpadami komunalnymi. Symbol ten wskazuje, że produkt
nie powinien być usuwany razem ze zwykłymi odpadami z
gospodarstw domowych. Na Państwu spoczywa obowiązek
wyrzucania tego i innych urządzeń elektrycznych oraz
elektronicznych w punktach odbioru wyznaczonych przez władze
krajowe lub lokalne. Pozbywanie się sprzętu we właściwy sposób
i jego recykling pomogą zapobiec potencjalnie negatywnym
konsekwencjom dla środowiska i zdrowia ludzkiego. W celu
uzyskania szczegółowych informacji o usuwaniu starego sprzętu,
prosimy zwrócić się do lokalnych władz, służb oczyszczania
miasta lub sklepu, w którym produkt został nabyty.
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
69
Page 76

Appendix F
Regulatory Information
Português (Portuguese) - Informação ambiental para
clientes da União Europeia
A Directiva Europeia 2002/96/CE exige que o equipamento
que exibe este símbolo no produto e/ou na sua embalagem
não seja eliminado junto com os resíduos municipais não
separados. O símbolo indica que este produto deve ser
eliminado separadamente dos resíduos domésticos regulares.
É da sua responsabilidade eliminar este e qualquer outro
equipamento eléctrico e electrónico através das instalações
de recolha designadas pelas autoridades governamentais ou
locais. A eliminação e reciclagem correctas ajudarão a prevenir
as consequências negativas para o ambiente e para a saúde
humana. Para obter informações mais detalhadas sobre a
forma de eliminar o seu equipamento antigo, contacte as
autoridades locais, os serviços de eliminação de resíduos ou o
estabelecimento comercial onde adquiriu o produto.
Română (Romanian) - Informaţii de mediu pentru
clienţii din Uniunea Europeană
Directiva europeană 2002/96/CE impune ca echipamentele care
prezintă acest simbol pe produs şi/sau pe ambalajul acestuia să
nu fie casate împreună cu gunoiul menajer municipal. Simbolul
indică faptul că acest produs trebuie să fie casat separat de
gunoiul menajer obişnuit. Este responsabilitatea dvs. să casaţi
acest produs şi alte echipamente electrice şi electronice prin
intermediul unităţilor de colectare special desemnate de guvern
sau de autorităţile locale. Casarea şi reciclarea corecte vor ajuta
la prevenirea potenţialelor consecinţe negative asupra sănătăţii
mediului şi a oamenilor. Pentru mai multe informaţii detaliate
cu privire la casarea acestui echipament vechi, contactaţi
autorităţile locale, serviciul de salubrizare sau magazinul de la
care aţi achiziţionat produsul.
Slovenčina (Slovak) - Informácie o ochrane životného
prostredia pre zákazníkov v Európskej únii
Podľa európskej smernice 2002/96/ES zariadenie s týmto
symbolom na produkte a/alebo jeho balení nesmie byť
likvidované spolu s netriedeným komunálnym odpadom.
Symbol znamená, že produkt by sa mal likvidovať oddelene
od bežného odpadu z domácností. Je vašou povinnosťou
likvidovať toto i ostatné elektrické a elektronické zariadenia
prostredníctvom špecializovaných zberných zariadení určených
vládou alebo miestnymi orgánmi. Správna likvidácia a recyklácia
pomôže zabrániť prípadným negatívnym dopadom na životné
prostredie a zdravie ľudí. Ak máte záujem o podrobnejšie
informácie o likvidácii starého zariadenia, obráťte sa, prosím, na
miestne orgány, organizácie zaoberajúce sa likvidáciou odpadov
alebo obchod, v ktorom ste si produkt zakúpili.
Slovenčina (Slovene) - Okoljske informacije za stranke
v Evropski uniji
Evropska direktiva 2002/96/EC prepoveduje odlaganje opreme,
označene s tem simbolom – na izdelku in/ali na embalaži – med
običajne, nerazvrščene odpadke. Ta simbol opozarja, da je treba
izdelek odvreči ločeno od preostalih gospodinjskih odpadkov.
Vaša odgovornost je, da to in preostalo električno in elektronsko
opremo odnesete na posebna zbirališča, ki jih določijo
državne ustanove ali lokalna uprava. S pravilnim odlaganjem
in recikliranjem boste preprečili morebitne škodljive vplive na
okolje in zdravje ljudi. Če želite izvedeti več o odlaganju stare
opreme, se obrnite na lokalno upravo, odpad ali trgovino, kjer
ste izdelek kupili.
Suomi (Finnish) - Ympäristöä koskevia tietoja EUalueen asiakkaille
EU-direktiivi 2002/96/EY edellyttää, että jos laitteistossa on tämä
symboli itse tuotteessa ja/tai sen pakkauksessa, laitteistoa
ei saa hävittää lajittelemattoman yhdyskuntajätteen mukana.
Symboli merkitsee sitä, että tämä tuote on hävitettävä erillään
tavallisesta kotitalousjätteestä. Sinun vastuullasi on hävittää
tämä elektroniikkatuote ja muut vastaavat elektroniikkatuotteet
viemällä tuote tai tuotteet viranomaisten määräämään
keräyspisteeseen. Laitteiston oikea hävittäminen estää
mahdolliset kielteiset vaikutukset ympäristöön ja ihmisten
terveyteen. Lisätietoja vanhan laitteiston oikeasta hävitystavasta
saa paikallisilta viranomaisilta, jätteenhävityspalvelusta tai siitä
myymälästä, josta ostit tuotteen.
Svenska (Swedish) - Miljöinformation för kunder i
Europeiska unionen
Det europeiska direktivet 2002/96/EC kräver att utrustning med
denna symbol på produkten och/eller förpackningen inte får
kastas med osorterat kommunalt avfall. Symbolen visar att denna
produkt bör kastas efter att den avskiljts från vanligt hushållsavfall.
Det faller på ditt ansvar att kasta denna och annan elektrisk och
elektronisk utrustning på fastställda insamlingsplatser utsedda
av regeringen eller lokala myndigheter. Korrekt kassering och
återvinning skyddar mot eventuella negativa konsekvenser
för miljön och personhälsa. För mer detaljerad information om
kassering av din gamla utrustning kontaktar du dina lokala
myndigheter, avfallshanteringen eller butiken där du köpte
produkten.
WEB: For additional information, please visit
www.linksys.com/international
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
70
Page 77

Appendix G
Contact Information
Appendix G:
Contact Information
If you experience problems with any Linksys product, you
can contact support by visiting the appropriate website:
Region Web Address
Algeria (Arabic) www.linksys.com/DZar/support
Algeria (English) www.linksys.com/DZen/support
Argentina www.linksys.com/AR/support
Australia www.linksys.com/AU/support
Austria www.linksys.com/AT/support
Bahrain (Arabic) www.linksys.com/BHar/support
Bahrain (English) www.linksys.com/BHen/support
Belgium www.linksys.com/BE/support
Bolivia www.linksys.com/BO/support
Brazil www.linksys.com/BR/support
Cameroon www.linksys.com/CM/support
Canada (English) www.linksys.com/CAen/support
Canada (Français) www.linksys.com/CAfr/support
China www.linksys.com/CN/support
Colombia www.linksys.com/CO/support
Costa Rica www.linksys.com/CR/support
Czech Republic www.linksys.com/CZ/support
Denmark www.linksys.com/DK/support
Dominican Republic www.linksys.com/DO/support
Ecuador www.linksys.com/EC/support
Egypt (Arabic) www.linksys.com/EGar/support
Region Web Address
Egypt (English) www.linksys.com/EGen/support
Estonia www.linksys.com/EE/support
Ethiopia www.linksys.com/ET/support
Finland www.linksys.com/FI/support
France www.linksys.com/FR/support
Germany www.linksys.com/DE/support
Ghana www.linksys.com/GH/support
Honduras www.linksys.com/HN/support
Hong Kong www.linksys.com/HK/support
Iceland www.linksys.com/IS/support
India www.linksys.com/IN/support
Indonesia www.linksys.com/ID/support
Ireland www.linksys.com/IE/support
Italy www.linksys.com/IT/support
Jordan (Arabic) www.linksys.com/JOar/support
Jordan (English) www.linksys.com/JOen/support
Kenya www.linksys.com/KE/support
Korea www.linksys.com/KR/support
Kuwait (Arabic) www.linksys.com/KWar/support
Kuwait (English) www.linksys.com/KWen/support
Latvia www.linksys.com/LV/support
Lebanon (Arabic) www.linksys.com/LBar/support
Lebanon (English) www.linksys.com/LBen/support
Lithuania www.linksys.com/LT/support
Macedonia www.linksys.com/MK/support
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
71
Page 78

Appendix G
Contact Information
Region Web Address
Malaysia www.linksys.com/MY/support
Mauritius www.linksys.com/MU/support
Mexico www.linksys.com/MX/support
Morocco (Arabic) www.linksys.com/MAar/support
Morocco (English) www.linksys.com/MAen/support
Namibia www.linksys.com/NA/support
Netherlands www.linksys.com/NL/support
New Zealand www.linksys.com/NZ/support
Nigeria www.linksys.com/NG/support
Norway www.linksys.com/NO/support
Oman (Arabic) www.linksys.com/OMar/support
Oman (English) www.linksys.com/OMen/support
Pakistan www.linksys.com/PK/support
Panamá www.linksys.com/PA/support
Paraguay www.linksys.com/PY/support
Perú www.linksys.com/PE/support
Philippines www.linksys.com/PH/support
Poland www.linksys.com/PL/support
Portugal www.linksys.com/PT/support
Qatar (Arabic) www.linksys.com/QAar/support
Qatar (English) www.linksys.com/QAen/support
România www.linksys.com/RO/support
Region Web Address
Saudi Arabia
(English)
Serbia &
Montenegro
Seychelles www.linksys.com/SC/support
Singapore www.linksys.com/SG/support
Slovakia www.linksys.com/SK/support
Slovenia www.linksys.com/SI/support
South Africa www.linksys.com/ZA/support
Spain www.linksys.com/ES/support
Sweden www.linksys.com/SE/support
Switzerland www.linksys.com/CH/support
Tanzania www.linksys.com/TZ/support
Thailand www.linksys.com/TH/support
Tunisia (Arabic) www.linksys.com/TNar/support
Tunisia (English) www.linksys.com/TNen/support
Turkey www.linksys.com/TR/support
UAE (Arabic) www.linksys.com/AEar/support
UAE (English) www.linksys.com/AEen/support
UK www.linksys.com/UK/support
Uruguay www.linksys.com/UY/support
Venezuela www.linksys.com/VE/support
Vietnam www.linksys.com/VN/support
www.linksys.com/SAen/support
www.linksys.com/CS/support
Russia www.linksys.com/RU/support
Saudi Arabia
(Arabic)
24/48-Port 10/100 + 4-Port Gigabit Resilient Clustering Smart Switch with 2 Combo SFPs
www.linksys.com/SAar/support
8012510A-AI
72
 Loading...
Loading...