Page 1

A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
®
Model No.
Broadband Router
WIRED
RT042
with QoS
User Guide
Page 2

Broadband Router
Copyright and Trademarks
Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain
other countries. Copyright © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
WARNING: This product contains chemicals, including lead, known to the State of California to
cause cancer, and birth defects or other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
How to Use this Guide
This User Guide has been designed to make understanding networking with the Router easier than ever. Look for
the following items when reading this Guide:
This checkmark means there is a Note of interest about something
you should pay special attention to while using the Router.
This exclamation point means there is a Caution or Warning about
something that could damage your property or the Router.
This question mark provides you with a reminder about something
you might need to do while using the Router.
In addition to these symbols, there are definitions for technical terms that are presented like this:
word: definition.
Also, each figure (diagram, screenshot, or other image) is provided with a figure number and description, like
this:
Figure numbers and descriptions can also be found in the “List of Figures” section in the “Table of Contents”.
RT042-UG-50323A BW
Figure 0-1: Sample Figure Description
Page 3

Broadband Router
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Welcome 1
What’s in this Guide? 2
Chapter 2: Networking Basics 4
An Introduction to LANs 4
The Use of IP Addresses 4
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Broadband Router 6
The Front Panel 6
The Back and Side Panels 7
Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router 8
Overview 8
Connection Instructions 9
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router 10
Overview 10
How to Access the Web-based Utility 12
System Summary Tab 12
Basic Setup Tab - Network 13
Basic Setup Tab - Password 15
Basic Setup Tab - Time 16
Basic Setup Tab - MAC Clone 16
Parental Control Tab - On-Line Scheduler 17
Parental Control Tab - Website Hit Rate 17
Parental Control Tab - Application Usage 18
Parental Control Tab - Performance Optimization 18
Parental Control Tab - Block List 19
Advanced Setup Tab - DMZ Host 20
Advanced Setup Tab - Forwarding 20
Advanced Setup Tab - UPnP 21
Advanced Setup Tab - DDNS 22
Advanced Setup Tab - Advanced Routing 22
Advanced Setup Tab - VPN Pass Through 24
Advanced Setup Tab - Remote Management 24
Page 4

Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - System Management 25
Log Tab - System Log 27
Log Tab - System Statistics 28
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 29
Common Problems and Solutions 29
Frequently Asked Questions 39
Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware 43
Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for
Your Ethernet Adapter 44
Windows 98 or Me Instructions 44
Windows 2000 or XP Instructions 44
For the Router’s Web-based Utility 45
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility 46
Starting the Utility 46
Router Information 47
Usage Configuration Screens 47
Appendix E: The Setup Wizard 51
Appendix F: Windows Help 54
Appendix G: Glossary 55
Appendix H: Specifications 59
Appendix I: Warranty Information 60
Appendix J: Regulatory Information 61
Appendix K: Contact Information 62
Page 5

Broadband Router
List of Figures
Figure 3-1: Front Panel 6
Figure 3-2: Back Panel 7
Figure 4-1: Example of a Typical Network 8
Figure 4-2: Connect a PC 9
Figure 4-3: Connect the Internet 9
Figure 4-4: Connect the Power 9
Figure 5-1: Entering the Router’s IP Address 12
Figure 5-2: Accessing the Web-Based Utility 12
Figure 5-3: The Site Map Button 12
Figure 5-4: Site Map 12
Figure 5-5: System Summary Tab 13
Figure 5-6: Basic Setup Tab - Network 13
Figure 5-7: Obtain an IP Automatically 14
Figure 5-8: Static IP 14
Figure 5-9: PPPoE 14
Figure 5-10: PPTP 15
Figure 5-11: Basic Setup Tab - Password 15
Figure 5-12: Basic Setup Tab - Time 16
Figure 5-13: Basic Setup Tab - MAC Clone 16
Figure 5-14: Parental Control Tab - On-Line Scheduler 17
Figure 5-15: Parental Control Tab - Website Hit Rate 17
Figure 5-16: Parental Control Tab - Application Usage 18
Figure 5-17: Parental Control Tab - Performance Optimization 18
Figure 5-18: Parental Control Tab - Performance Optimization:
Add/Edit New Applications 19
Figure 5-19: Parental Control Tab - Block List 19
Figure 5-20: Advanced Setup Tab - DMZ Host 20
Figure 5-21: Advanced Setup Tab - Forwarding 20
Page 6

Broadband Router
Figure 5-22: Service Management 21
Figure 5-23: Advanced Setup Tab - UPnP 21
Figure 5-24: Advanced Setup Tab - DDNS 22
Figure 5-25: Advanced Setup Tab - Advanced Routing 22
Figure 5-26: Advanced Setup Tab - VPN Pass Through 24
Figure 5-27: Advanced Setup Tab - Remote Management 24
Figure 5-28: Advanced Setup Tab - System Management 25
Figure 5-29: Log Tab - System Log 27
Figure 5-30: Log Tab - System Statistics 28
Figure B-1: Advanced Setup Tab - System Management 43
Figure C-1: IP Configuration Screen 44
Figure C-2: MAC Address/Adapter Address 44
Figure C-3: MAC Address/Physical Address 45
Figure C-4: MAC Address Clone 45
Figure D-1: The Utility’s Main Screen 46
Figure D-2: The Router Information Screen 47
Figure D-3: The On-Line Scheduler 48
Figure D-4: The Hit Rate Screen 48
Figure D-5: The Real Time Usage Screen 49
Figure D-6: The Hit Rate Screen 49
Figure D-7: The Performance Optimization Screen 50
Figure E-1: Basic Setup Tab - Network 51
Figure E-2: Enter Host and Domain Names 51
Figure E-3: Select WAN connection Type 52
Figure E-4: Obtain an IP automatically 52
Figure E-5: Static IP 53
Figure E-6: PPPoE 53
Figure E-7: Basic Setup Tab - Network 53
Page 7

Broadband Router
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
Thank you for choosing the Broadband Router. The Linksys Broadband Router with QoS is a kind of "splitter" for
your Internet connection. Just connect your DSL or Cable Modem to the Router, and all the computers in your
home or office can share the Internet at the same time. Use the built-in 4-port switch to attach four local PCs
directly, or daisy-chain out to more hubs and switches as your network grows. It has Auto MDI/MDI-X cross-over
detection so you don't have to worry about the cable type.
The Router's QoS (Quality of Service) feature lets you define the amount of the available bandwidth for each of
the devices on your network. This means that you can prioritize time-sensitive data like Voice Over IP phone calls
or streaming media ahead of less sensitive email and web surfing. The dual Internet ports let you optionally
connect a second Internet line for additional bandwidth.
Of course, once your computers are connected to the Internet through the Router, they can communicate with
each other too, sharing resources and files. All your computers can print on a shared printer connected
anywhere in the home. And you can share all kinds of files between computers, like music, digital pictures, and
other documents.
In addition to this, you can control access to the Internet through the Router’s Parental Control features. This
allows you to set a schedule, see what websites and programs are being used, optimize performance, and block
those sites you don’t wish to be accessed.
This user guide will give you all the information you need to connect, set up, and configure your Router.
broadband: an always-on,
fast Internet connection.
network: a series of computers or devices
connected for the purpose of data sharing,
storage, and/or transmission between users.
bandwidth: the transmission capacity
of a given device or network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) : a networking
protocol that allows administrators to assign temporary IP
addresses to network computers by "leasing" an IP
address to a user for a limited amount of time.
browser: an application program that provides a way to
look at and interact with all the information on the Internet.
Ethernet: a network protocol that specifies
how data is placed on and retrieved from a
common transmission medium.
firewall: a set of related programs located at a
network gateway server that protects the resources
of a network from users from other networks.
router: a networking device that
connects multiple networks together.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Welcome
1
Page 8

Broadband Router
What’s in this Guide?
This user guide covers the steps for setting up and using the Broadband Router.
• Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter describes the Router’s applications and this User Guide.
• Chapter 2: Networking Basics
This chapter describes the basics of networking.
• Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Broadband Router
This chapter describes the physical features of the Router.
• Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router
This chapter instructs you on how to connect the Router to your network.
• Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Router
This chapter explains how to use the Web-Based Utility to set up the Router and configure its settings.
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix describes some problems and solutions, as well as frequently asked questions, regarding the
Router’s installation and usage.
• Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware
This appendix instructs you on how to upgrade the Router’s firmware if you should need to do so.
• Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for your Ethernet Adapter.
This appendix describes how to find the MAC address for your computer’s Ethernet adapter so you can use
the Router’s MAC address cloning feature.
• Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
This appendix describes the Router Utility that comes on the Router’s CD.
• Appendix E: The Setup Wizard
This appendix describes the Setup Wizard included with the Web-based utility, for easy Internet set up.
• Appendix F: Windows Help
This appendix describes how you can use Windows Help for instructions about networking, such as installing
the TCP/IP protocol.
• Appendix G: Glossary
This appendix gives a brief glossary of terms frequently used in networking.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
firmware: the programming code that
runs a networking device.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address
that a manufacturer assigns to each networking device.
adapter: a device that adds network
functionality to your PC.
IP (Internet Protocol): a protocol used
to send data over a network.
ip address: the address used to identify a
computer or device on a network.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): a network
protocol for transmitting data that requires
acknowledgement from the recipient of data sent.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol): a set of instructions PCs use to
communicate over a network.
2
Page 9

Broadband Router
• Appendix H: Specifications
This appendix provides the Router’s technical specifications.
• Appendix I: Warranty Information
This appendix contains the Router’s warranty information.
• Appendix J: Regulatory Information
This appendix supplies the regulatory information regarding the Router.
• Appendix K: Contact Information
This appendix provides contact information for a variety of Linksys resources, including Technical Support.
Chapter 1: Introduction
What’s in this Guide?
3
Page 10

Broadband Router
Chapter 2: Networking Basics
An Introduction to LANs
A Router is a network device that connects two networks together.
The Router connects your local area network (LAN), or the group of PCs in your home or office, to the Internet. The
Router processes and regulates the data that travels between these two networks.
LAN: the computers and networking products that
make up your local network
The Router’s Network Address Translation (NAT) technology protects your network of PCs so users on the Internet
cannot “see” your PCs. This is how your LAN remains private. The Router protects your network by inspecting the
first packet coming in through the Internet port before delivery to the final destination on one of the Ethernet
ports. The Router inspects Internet port services like the web server, ftp server, or other Internet applications,
and, if allowed, it will forward the packet to the appropriate PC on the LAN side.
The Use of IP Addresses
IP stands for Internet Protocol. Every device in an IP-based network, including PCs, print servers, and routers,
requires an IP address to identify its location, or address, on the network. This applies to both the Internet and
LAN connections.
There are two ways of assigning IP addresses to your network devices.
A static IP address is a fixed IP address that you assign manually to a PC or other device on the network. Since a
static IP address remains valid until you disable it, static IP addressing ensures that the device assigned it will
always have that same IP address until you change it. Static IP addresses are commonly used with network
devices such as server PCs or print servers.
If you use the Router to share your cable or DSL Internet connection, contact your ISP to find out if they have
assigned a static IP address to your account. If so, you will need that static IP address when configuring the
Router. You can get the information from your ISP.
A dynamic IP address is automatically assigned to a device on the network. These IP addresses are called
dynamic because they are only temporarily assigned to the PC or other device. After a certain time period, they
expire and may change. If a PC logs onto the network (or the Internet) and its dynamic IP address has expired, the
DHCP server will assign it a new dynamic IP address.
NAT (Network Address Translation):
NAT technology translates IP
addresses of a local area network to a
different IP address for the Internet.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): a protocol used
to transfer files over a TCP/IP network.
Packet: a unit of data sent over a network.
server: any computer whose function in a
network is to provide user access to files,
printing, communications, and other services.
Static IP address: a fixed address
assigned to a computer or device that
is connected to a network.
Dynamic IP address: a temporary IP
address assigned by a DHCP server.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): an always-on
broadband connection over traditional phone lines.
ISP (Internet Service Provider): a company that
provides access to the Internet.
Chapter 2: Networking Basics
An Introduction to LANs
4
Page 11

Broadband Router
A DHCP server can either be a designated PC on the network or another network device, such as the Router. By
default, the Router’s Internet Connection Type is Obtain an IP automatically (DHCP).
The PC or network device obtaining an IP address is called the DHCP client. DHCP frees you from having to assign
IP addresses manually every time a new user is added to your network.
For DSL users, many ISPs may require you to log on with a user name and password to gain access to the
Internet. This is a dedicated, high-speed connection type called Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE).
PPPoE is similar to a dial-up connection, but PPPoE does not dial a phone number when establishing a
connection. It also will provide the Router with a dynamic IP address to establish a connection to the Internet.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet): a type of
broadband connection that provides authentication
(username and password) in addition to data transport.
Chapter 2: Networking Basics
The Use of IP Addresses
5
Page 12

Broadband Router
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Broadband Router
The Front Panel
The Router’s LEDs are located on the front panel.
Figure 3-1: Front Panel
LEDs
Ethernet 1-4 Green. The Ethernet LEDs serves two purposes. If an LED is continuously lit, the Router
is connected to a device through the corresponding port (1, 2, 3, or 4). If an LED is
flashing, the Router is actively sending or receiving data over that port.
Internet1 Green. The Internet1 LED lights up when the Router is connected to your cable or DSL
modem through the corresponding Internet port.
Internet2 Green. The Internet2 LED lights up when the Router is connected to your cable or DSL
modem through the second Internet port.
Diag Orange. The Diag LED lights up when the system is not ready. The LED goes off when
the system is ready.
System Green. The System LED lights up when the Router is powered on. If the LED is flashing,
the Router is running a diagnostic test.
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Broadband Router
The Front Panel
port: the connection point on a computer or networking
device used for plugging in cables or adapters.
6
Page 13

Broadband Router
The Back and Side Panels
The Router’s ports and Reset button are located on the back panel of the Router.
Ethernet
Internet1
Figure 3-2: Back Panel
Internet2
Reset Button
Reset Button The Reset button can be used in one of two ways:
If the Router is having problems connecting to the Internet, press the Reset button for just a
second with a paper clip or a pencil tip. This is similar to pressing the Reset button on your PC to
reboot it.
If you are experiencing extreme problems with the Router and have tried all other
troubleshooting measures, press and hold in the Reset button for 30 seconds. This will restore
the factory defaults and clear all of the Router’s settings, such as port forwarding or a new
password.
Ports
Ethernet 1-4 These four Ethernet ports connect to network devices, such as PCs, print servers, or additional
switches.
Internet1 The Internet1 port connects to a cable or DSL modem.
Internet2 The Internet2 port acts as an additional Internet port and connects to a cable or DSL modem.
boot: to start a device and cause it to
start executing instructions.
Power The Power port is where you will connect the included AC power cable.
Proceed to “Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router.”
Chapter 3: Getting to Know the Broadband Router
The Back and Side Panels
7
Page 14
Broadband Router
Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router
Overview
To set up your network, you will need to do the following:
• Connect the Router to one of your PCs according to the instructions in this chapter.
• Set up and configure the Router with the setting(s) provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) according
to “Chapter 5: Setting up and Configuring the Broadband Router.”
The installation technician from your ISP should have left the setup information with you after installing your
broadband connection. If not, you can call your ISP to request the information. Once you have the setup
information for your specific type of Internet connection, then you can begin installation and setup of the Router.
Notebook with
Ethernet Adapter
Cable or DSL
Modem
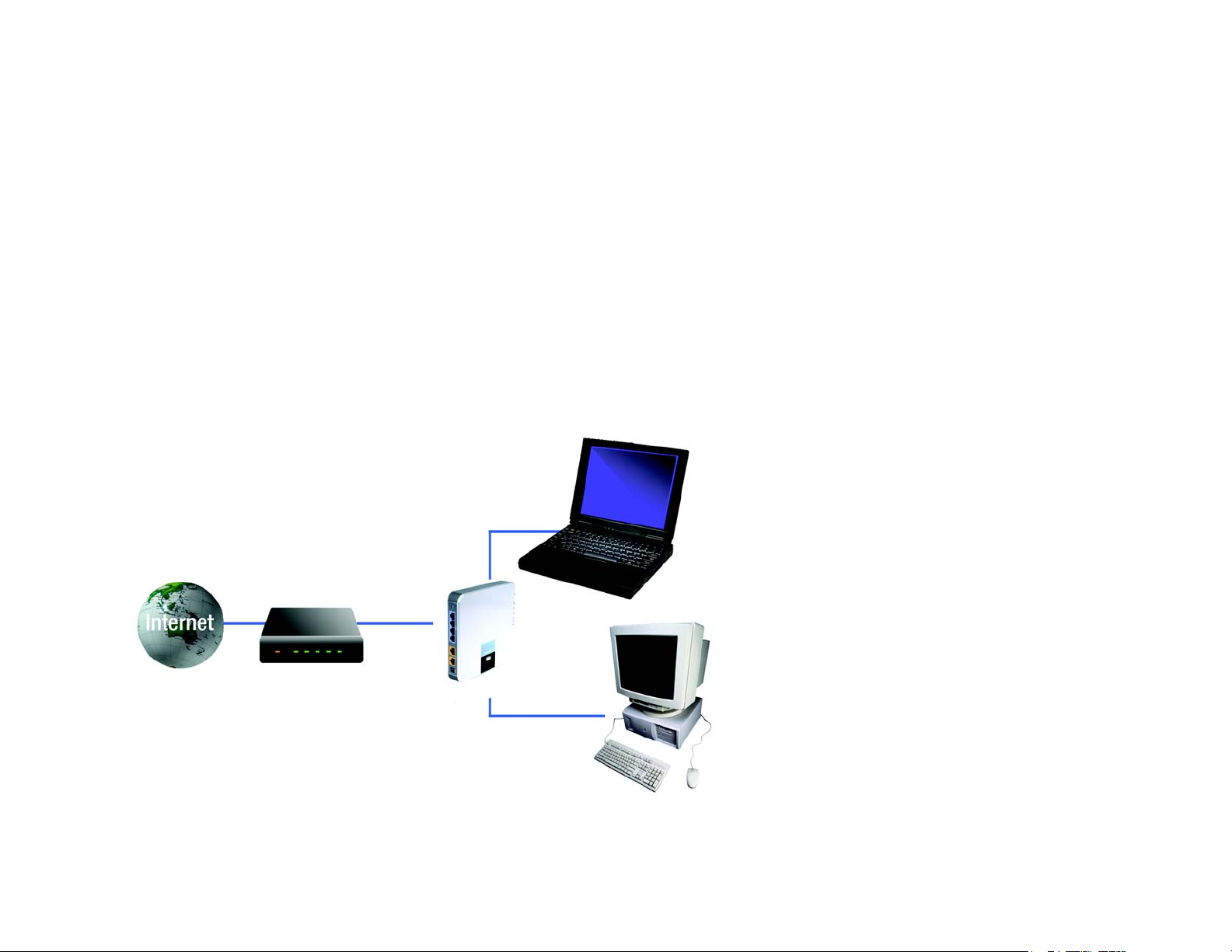
Figure 4-1: Example of a Typical Network
Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router
Overview
Broadband
Router
PC with Ethernet
Adapter
8
Page 15
Broadband Router
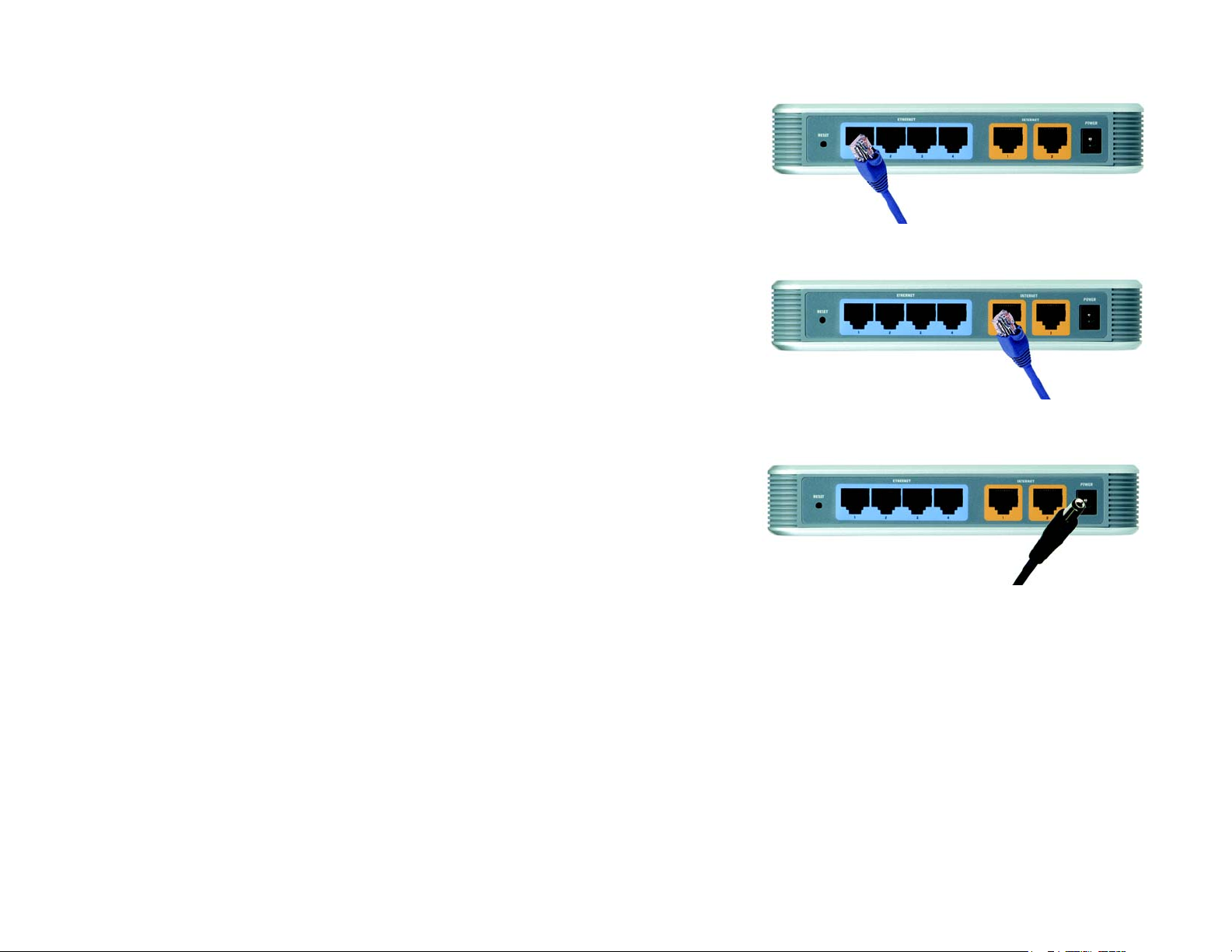
Connection Instructions
1. Before you begin, make sure that all of your hardware is powered off, including the Router, PCs, hubs,
switches, and cable or DSL modem.
2. Connect one end of an Ethernet network cable to one of the Ethernet ports on the back of the Router. Connect
the other end to an Ethernet port on a network device, e.g., a PC, print server, hub, or switch.
Repeat this step to connect more PCs or other network devices to the Router.
3. Connect your cable or DSL modem’s Ethernet cable to one of the Router’s Internet ports. If using the Internet2
port, connect a second cable to it, and the other end to the network device, e.g., modem or public server.
4. Power on the cable or DSL modem and the other network device if using one.
5. Connect the included AC power cable to the Router’s Power port, and then plug the power adapter into an
electrical outlet.
The System LED on the front panel will light up as soon as the power adapter is connected properly.
Proceed to “Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router.”
Figure 4-2: Connect a PC
Figure 4-3: Connect the Internet
Figure 4-4: Connect the Power
Chapter 4: Connecting the Broadband Router
Connection Instructions
9
Page 16

Broadband Router
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Overview
For your convenience, use the Router’s Web-based Utility to set it up and configure it. This chapter will explain all
of the functions in this Utility.
There are five main tabs in the Utility: System Summary, Basic Setup, Parental Control, Advanced Setup, and Log.
Additional tabs will be available after you click one of the main tabs. The tabs, and each of its screens, are
described below:
System Summary Tab
The System Summary Tab displays the router’s current status and settings. You can also configure the user and
IP bandwidth. Clicking any underlined text will take you to any related pages in the utility.
Basic Setup Tab
• Network. Use this screen to enter your Internet connection information and network settings.
• Password. You can change the Router’s password on this screen. For better network security, you should
change the password from the Router’s default.
• Time. Change the time on this screen. Make sure you change it from the default setting, if necessary, to show
the accurate time.
• MAC Clone. Some ISPs require that you register a MAC address. This feature “clones” your network adapter's
MAC address onto the Router, and prevents you from having to call your ISP to change the registered MAC
address to the Router's MAC address.
Parental Control Tab
• On-Line Scheduler. This feature allows you to allow or deny Internet access, according to the schedule, to
any of the users on your network.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Overview
10
Page 17

Broadband Router
• Website Hit Rate. This feature allows you to view the frequency at which each of your network’s users are
viewing their ten most favorite websites. You can also block these sites, if you wish.
• Application Usage. This feature allows you to view which applications, according to user, are taking up the
most bandwidth on your network and block those sites if you wish.
• Performance Optimization. This feature allows you to list the network applications most often used on your
network, according to user, and set the priority at which it is run.
• Block List. This feature allows you to find out which websites or applications are blocked for each of your
users, and unblock them if you wish.
Advanced Setup Tab
• DMZ Host. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet, not
protected by the Router’s firewall, to use a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or video
conferencing.
• Forwarding. Port forwarding can be used to set up public services on your network. You may use this
function to establish a Web server or FTP server via an IP Gateway.
• UPnP. UPnP forwarding can be used to set up public services on your network.
DMZ: removes the Router's firewall protection from
one PC, allowing it to be "seen" from the Internet.
gateway: device that interconnects networks with
different, incompatible communications protocols.
DDNS: allows the hosting of a website, FTP server,
or e-mail server with a fixed domain name (e.g.,
www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP address.
• DDNS. DDNS (Dynamic DNS) service allows you to assign a fixed domain name to a dynamic Internet IP
address. This allows you to host your own Web, FTP or other type of TCP/IP server in your LAN.
• Advanced Routing. The Router's dynamic routing feature can be used to automatically adjust to physical
changes in the network's layout. The static routing feature allows multiple routers to operate on one network.
• VPN Pass Through. This tab allows you to enable or disable IPSec Pass Through, PPTP Pass Through, and
L2TP Pass Through.
• Remote Management. This allows you to manage the Router through a remote location over the Internet.
• System Management. This screen includes tools to help troubleshoot network problems, reset the Router to
factory default settings, upgrade the Router’s firmware, and store and retrieve configuration files.
Log Tab
• System Log. The System Log displays Syslog, E-mail and Log Settings.
• System Statistics. This tab displays the system statistics.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Overview
domain: a specific name for a
network of computers.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security): a VPN protocol used
to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): a VPN
protocol that allows the Point to Point Protocol (PPP) to
be tunneled through an IP network. This protocol is
also used as a type of broadband connection in Europe.
upgrade: to replace existing software
or firmware with a newer version.
11
Page 18
Broadband Router
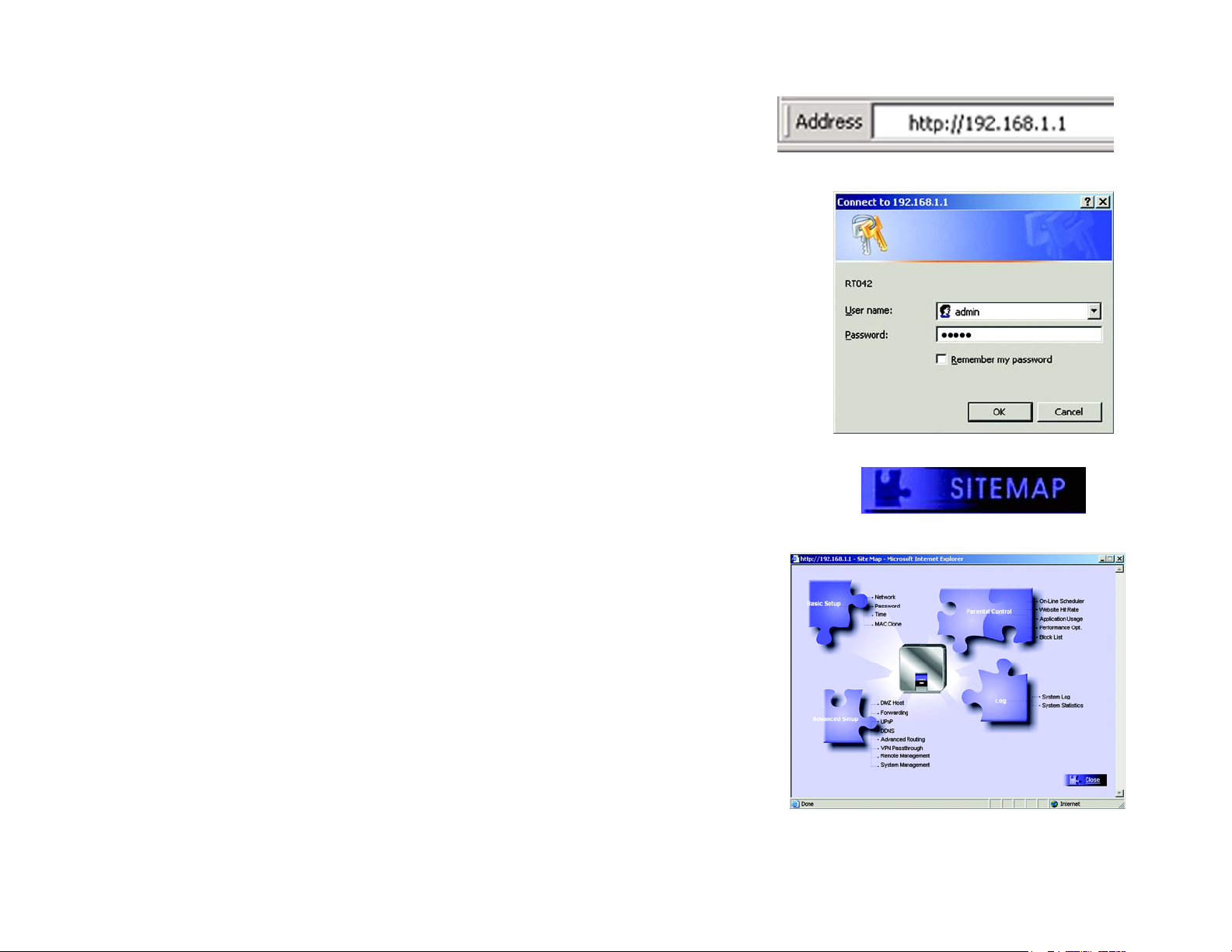
How to Access the Web-based Utility
To access the Router’s Web-based Utility, launch Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, and enter the Router’s
default IP address, 192.168.1.1, in the Address field. Then, press the Enter key.
A screen will appear asking you for your User name and Password. Enter admin in the User name field and the
Password field. Then, click the OK button.
System Summary Tab
The first screen that appears is System Summary Tab. This screen displays the router’s current status and
settings. This information is read only. Clicking underlined text will take you to related setup pages. On the right
side of the screen and all other screens in the Utility will be a link to the Site Map, which has links to all of the
Utility’s tabs. Click the Site Map button to view the Site Map. Then, click on desired tab subject.
Figure 5-1: Entering the Router’s IP Address
System Information
System Up Time: The length of time in Days, Hours, and Minutes that the Router is active and the current time
are displayed.
Internet IP Addresses: This shows the current IP Address for each Internet port. You can release and renew
each of these addresses, depending upon your settings. Clicking the underlined text will take you to the Network
screen on the Basic Settings tab.
User Usage
This is a graphic display of the users on your network, showing which Internet connection they are accessing and
how much bandwidth they are consuming.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
How to Access the Web-based Utility
Figure 5-2: Accessing the Web-Based Utility
Figure 5-3: The Site Map Button
Figure 5-4: Site Map
12
Page 19

Broadband Router
User Bandwidth
This is a list of all users on your network, displaying how they’re connected and allowing you to set the amount of
bandwidth they are allowed and to delete them as users on your network. The headings for this list are:
User Name: Shows the name of this user on your network.
IP: Shows the IP Address of this user’s PC.
Interface: Shows the Internet port the user is accessing. You can also configure the user to go through the
other Internet port by selecting the interface from the drop-down menu when dual Internet ports are used.
Min.Rate (Kbit/Sec): Enter the minimum allowable bandwidth for this user. The default setting is 0.
Max.Rate (Kbit/Sec): Enter the maximum allowable bandwidth for this user. The default setting is 512.
Delete: Click the trashcan icon if you wish to delete this user from the user bandwidth or from Internet
access.
ISP Bandwidth
This section allows you to set the maximum upstream or downstream bandwidth per Internet port, maximizing
your network’s performance. This information can be obtained from your ISP.
Figure 5-5: System Summary Tab
Click the Save Settings button to save the network settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Basic Setup Tab - Network
The Basic Setup tab contains all of the router’s basic setup functions.The first screen that appears, the Network
screen, includes basic settings for your network. The router can be used in most network settings without
changing any of the default values. Some users may need to enter additional information in order to connect to
the Internet through an ISP (Internet Service Provider) or broadband (DSL, cable modem) carrier.
If you need help to configuring the router, click the Setup Wizard button. A walk-through of the Wizard is
provided in “Appendix E: The Setup Wizard”.
Host Name & Domain Name: Enter a host and domain name for the Router. Some ISPs may require these names
as identification, and these settings can be obtained from your ISP. In most cases, leaving these fields blank will
work.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Basic Setup Tab - Network
Figure 5-6: Basic Setup Tab - Network
13
Page 20

Broadband Router
LAN Setting
This shows the Router’s MAC Address, which is a 12-digit code assigned to each piece of hardware for
identification. Also listed here are the Router’s IP Address and Subnet Mask. The default value is 192.168.1.1 for
IP address and 255.255.255.0 for the Subnet Mask.
Internet Connection Type
Obtain an IP Automatically
If your ISP automatically assigns an IP Address, select Obtain an IP automatically. Your ISP will assign these
values. If you check the box for Use the Following DNS Server Addresses, enter a specific DNS Server IP.
Multiple DNS IP Settings are common. In most cases, the first available DNS entry is used.
Static IP
If you have to specify the Internet IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway Address, and DNS Server, select
Static IP. You must obtain this information from your ISP.
hardware: the physical aspect of
computers, telecommunications, and
other information technology devices.
subnet mask: an address code that
determines the size of the network.
Figure 5-7: Obtain an IP Automatically
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) (most DSL users)
You have to check with your ISP to make sure whether PPPoE should be enabled or not. If they do use PPPoE:
1. Enter your User Name and Password.
2. If you select Connect on Demand option, the PPPoE connection will be disconnected if it has been idle for a
period longer than the Max Idle Time setting.
3. If you select Keep Alive option, the Router will keep the connection alive by sending out a few data packets
at the Redial Period, so your Internet service thinks that the connection is still active.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Basic Setup Tab - Network
Figure 5-8: Static IP
Figure 5-9: PPPoE
14
Page 21
Broadband Router
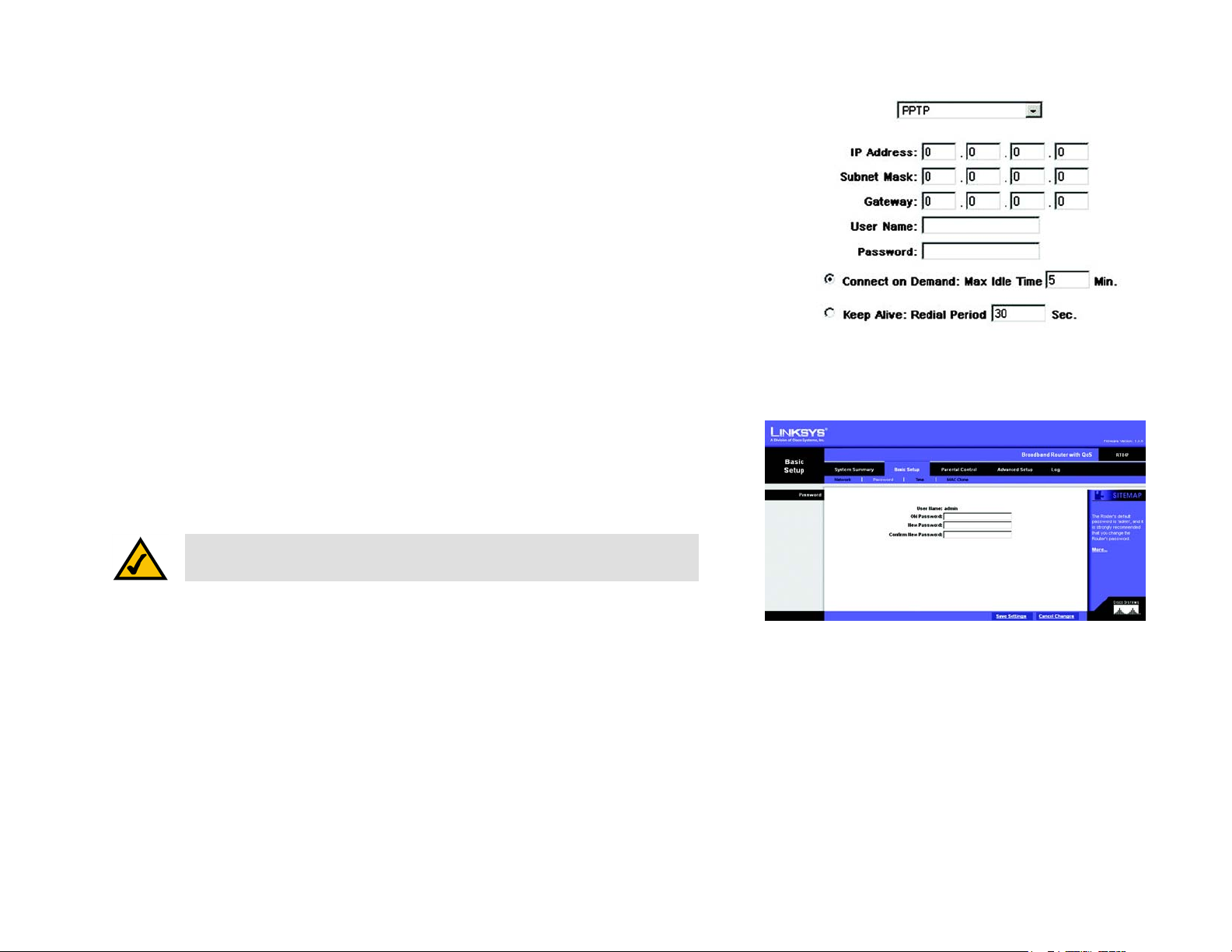
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
1. Enter the Specify IP Address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway Address that is provided by your ISP.
2. Enter your User Name and Password.
3. If you select Connect on Demand option, the connection will be disconnected if it has been idle for a period
longer than the Max Idle Time setting.
4. If you select Keep Alive option, the Router will keep the connection alive by sending out a few data packets
at the Redial Period, so your Internet service thinks that the connection is still active.
Click the Save Settings button to save the network settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Basic Setup Tab - Password
The Router's default User Name and password is admin. For greater network security, you should change the
Router's password from this default to one of your own. If you leave the password field blank, all users on your
network will be able to access the Router simply by entering admin into the password field.
Old Password: Enter the old password. The default Password is admin when you first power up the Router.
NOTE: The password cannot be recovered if it is lost or forgotten. If the password is
lost or forgotten, you have to reset the Router to its factory default settings.
New Password: Enter a new password for the Router. Your password must be less than 15 characters long and
it can’t contain any spaces.
Confirm New Password: Re-enter the password for confirmation.
Click the Save Settings button to save the Password settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo the
changes.
Figure 5-10: PPTP
Figure 5-11: Basic Setup Tab - Password
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Basic Setup Tab - Password
15
Page 22

Broadband Router
Basic Setup Tab - Time
Time
The Router uses the time settings to time stamp log events, to automatically update the Content Filter List, and
for other internal purposes.
Set the local time using Network Time Protocol (NTP) automatically or manually.
Automatic: Select the Time Zone and enter the Daylight Saving and NTP Server. The default Time Zone is Pacific
Time.
Manual: Enter the Hours, Minutes, Seconds, Month, Day and Year.
Click the Save Settings button to save the Time settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo the
changes.
Basic Setup Tab - MAC Clone
Some ISPs require that you register a MAC address. This feature “clones” your network adapter's MAC address
onto the Router, and prevents you from having to call your ISP to change the registered MAC address to the
Router's MAC address. The Router's MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a unique piece of hardware for
identification.
Enter the MAC Address in the User Defined MAC Address field for Internet ports 1 or 2, or click the Clone button
to add the MAC Address from the PC viewing the Web-based Utility.
Click Save Settings to save the MAC Cloning settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Figure 5-12: Basic Setup Tab - Time
Figure 5-13: Basic Setup Tab - MAC Clone
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Basic Setup Tab - Time
16
Page 23

Broadband Router
Parental Control Tab - On-Line Scheduler
The Parental Control tab allows you to control and optimize your user’s access to the Internet from your network.
This control can also be exercised through the Utility provided on the CD included with the Router.
The first screen to appear, On-Line Scheduler, allows you to allow or deny Internet access, according to the
schedule, to any of the users on your network.
Select User: From this drop-down menu, select the user whose access you wish to schedule.
From the schedule below, you can restrict or allow access to the Internet. Each day in the schedule is broken into
eight blocks of time. Each block is divided into three hours. Click on any of the boxed hours to make the box red
or green. A red box means that access is restricted. A green box means the user is allowed access.
You can also restrict or allow entire days, or daytime or evening periods, in the lower portion of the screen.
Click Save Settings to save the Scheduler settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Parental Control Tab - Website Hit Rate
From this screen, you can view the frequency at which each of your network’s users are viewing their ten most
favorite websites. You can also block these sites, if you wish.
Figure 5-14: Parental Control Tab - On-Line Scheduler
Select User: From this drop-down menu, select the user whose top websites you wish to view.
Select Date: From this drop-down menu, select the date when the websites were viewed.
Refresh Data: Clicking this button will update the information displayed on the screen.
Website information is displayed in ranking order, from most viewed to least viewed, with the amount of “hits”
displayed. Each website is displayed as a link, so you can click the name to bring up the site. Clicking the Block
box will restrict that user from viewing that website.
Click Save Settings to save the settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Parental Control Tab - On-Line Scheduler
Figure 5-15: Parental Control Tab - Website Hit Rate
17
Page 24

Broadband Router
Parental Control Tab - Application Usage
From this screen, you can view which applications are taking up the most bandwidth on your network, according
to user, and block those sites if you wish.
Select User: From this drop-down menu, select the user whose application usage you wish to view.
Select Date: From this drop-down menu, select the date when the applications were used.
Refresh Data: Clicking this button will update the information displayed on the screen.
Application information is displayed in ranking order, from most viewed to least viewed, with the amount of
usage displayed for each application. For each application, there is also a column showing the protocol and port
number used. Clicking the Block box will restrict that user from utilizing that application.
Click Save Settings to save the settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Parental Control Tab - Performance Optimization
From this screen, you can list the network applications most often used on your network, according to user, and
set the priority at which it is run. If an application is not listed, you can add it or you can edit those listed by
clicking the Add/Edit New Applications button.
Select User: From this drop-down menu, select the user whose application performance you wish to optimize.
All applications are set at a Good level of optimization by default. To change this setting, click the Enable box
next to the application. Otherwise, the performance optimization settings will be “greyed-out”. Then, click the
radio button for Normal, Good, or Better optimization. Selecting Normal will decrease performance. Selecting
Better will increase performance.
Click Save Settings to save the performance settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Adding/Editing New Applications
To add or edit applications, click the Add/Edit New Applications button from the Performance Optimization
screen on the Parental Control tab. Enter the Application Name when adding new applications or select the
application you wish to edit from the list displayed.
Then, you can edit the protocol from the Protocol drop-down menu and edit the port range from the Port Range
boxes. You can also change the application speed in the Kbit/Sec box.
Figure 5-16: Parental Control Tab - Application Usage
Figure 5-17: Parental Control Tab -
Performance Optimization
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Parental Control Tab - Application Usage
18
Page 25

Broadband Router
Click the Add to List button to add the new or newly edited selection to your list of applications. To delete an
application, select from the list and click the Delete Selected Application button.
Click Save Settings to save the settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes. If you wish to
leave this screen without saving your changes, click the Exit button.
Parental Control Tab - Block List
From this screen, you can find out which websites or applications are blocked for each of your users, and unblock
them if you wish.
Select User: From this drop-down menu, select the user whose web or application usage you wish to view.
Refresh Data: Clicking this button will update the information displayed on the screen.
Change the information displayed on this screen by clicking the Web Site Block List for viewing blocked web
sites or the Application Block List for viewing blocked applications. The web sites and/or applications are then
listed. An option for Un-Blocking is provided and is used by clicking the Un-Block button.
Figure 5-18: Parental Control Tab - Performance
Optimization: Add/Edit New Applications
Click Save Settings to save the settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Parental Control Tab - Block List
Figure 5-19: Parental Control Tab - Block List
19
Page 26

Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - DMZ Host
The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host feature allows one local user to be exposed to the Internet, not protected by
the Router’s firewall, to use a special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or video conferencing.
Check the Enable DMZ Host box to use this feature. Then, enter the DMZ Private IP Address, which is the IP
Address of the PC using this feature. The Default value zero (0) will deactivate the DMZ Host.
Click the Save Settings button to save the DMZ Host setting or click the Cancel Changes button to undo the
changes.
Advanced Setup Tab - Forwarding
Port forwarding can be used to set up public services on your network. When users from the Internet make
certain requests of your network, the Router can forward those requests to computers equipped to handle them.
If, for example, you set port number 80 (HTTP) to be forwarded to IP Address 192.168.1.2, then all HTTP requests
from outside users will be forwarded to 192.168.1.2.
You may use this function to establish a Web server or FTP server via an IP Gateway. Be sure that you enter a valid
IP Address. (You may need to establish a static IP address in order to properly run an Internet server.) For added
security, Internet users will be able to communicate with the server, but they will not actually be connected. The
packets will simply be forwarded through the Router.
Port Range Forwarding
1. Select the Service from the pull-down menu.
2. If the Service you need is not listed in the menu, please click the Service Management button to add the
new Service Name. On the screen that opens, enter the Service Name, Protocol and Port Range. Click the
Add to List button. Then, click the Save Setting button. Click the Exit button. The screen will close and you
will be returned to the Forwarding screen.
3. Enter the IP Address of the server that you want the Internet users to access. Then enable the entry by
clicking the box below Enable.
4. Click the Add to List button, and configure as many entries as you would like. Click the Save Settings button
to activate the settings you’ve changed. You can also click Delete selected application, to delete those
settings you don’t wish to use.
Figure 5-20: Advanced Setup Tab - DMZ Host
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol): the communications
protocol used to connect to servers on the Internet.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - DMZ Host
Figure 5-21: Advanced Setup Tab - Forwarding
20
Page 27

Broadband Router
Port Triggering
Some Internet applications or games use alternate ports to communicate between server and LAN host. When
you want to use those applications, enter the triggering (outgoing) port and alternate incoming port in this table.
The Router will forward the incoming packets to the LAN host.
1. Enter the Application Name, Range of trigger port numbers, and the Incoming Port Range.
2. Click the Add to List button to add Port Triggering or Delete selected application to delete applications.
Click the Show Tables button to display the services you have assigned for Port Forwarding or Port Triggering.
Click the Save Settings button to save the settings, click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes, click
the Show Tables to see the details.
Advanced Setup Tab - UPnP
UPnP forwarding can be used to set up public services on your network. Windows XP can modify those entries
via UPnP when UPnP function is enabled by selecting Yes.
Figure 5-22: Service Management
1. Select the Service from the pull-down menu.
2. Enter the Name or IP Address of the server that you want the Internet users to access. Then enable the entry
by clicking the box below Enable.
3. If the Service you need is not listed in menu, please click the Service Management button. A new screen
will open and, from there, add the new Service Name, and Protocol as well as External and Internal Ports.
Click the Add to List button. Then, click the Save Setting button. Click the Exit button and you will be
returned to the UPnP screen.
4. Click the Add to List button, and configure as many entries as you would like. Click the Save Settings button
to activate the settings you’ve changed. You can also click Delete selected application, to delete those
settings you don’t wish to use.
Click the Show Tables button to display the services you have assigned for Port Forwarding or Port Triggering.
Click the Save Settings button to save the settings, click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes, click
the Show Tables to see the details.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - UPnP
Figure 5-23: Advanced Setup Tab - UPnP
21
Page 28

Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - DDNS
DDNS (Dynamic DNS) service allows you to assign a fixed domain name to a dynamic Internet IP address. This
allows you to host your own Web, FTP or other type of TCP/IP server in your LAN over either of the Internet ports.
Before configuring DDNS, you need to visit www.dyndns.org and register a domain name. (The DDNS service is
provided by DynDNS.org).
DDNS Service: The DDNS feature is disabled by default. To enable this feature, select DynDNS.org from the
pull-down menu, and enter the User name, Password, and Host Name of the account you set up with
DynDNS.org.
Internet IP Address: The current Internet IP Address of the Internet port being utilized is displayed here.
Because it is dynamic, this will occasionally change.
Status: The status of the DDNS function and Internet connection is displayed.
Click the Save Settings button to save the DDNS settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes.
Advanced Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
Dynamic Routing
The Router's dynamic routing feature can be used to automatically adjust to physical changes in the network's
layout. The Router uses the dynamic RIP protocol. It determines the route that the network packets take based on
the fewest number of hops between the source and the destination. The RIP protocol regularly broadcasts
routing information to other routers on the network.
Working Mode: Select NAT mode if this Router is hosting your network’s connection to the Internet. Select
Router mode if this Router exists on a network with other routers, including a separate network gateway that
handles the Internet connection. In Router Mode, any computer connected to the Router will not be able to
connect to the Internet unless you have another router function as the gateway.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol): The Router, using the RIP protocol, calculates the most efficient route for the
network’s data packets to travel between the source and the destination, based upon the shortest paths.
Receive RIP versions: Choose a protocol for receiving data from the network. (None, RIPv1, RIPv2, Both RIPv1
and v2).
Figure 5-24: Advanced Setup Tab - DDNS
Figure 5-25: Advanced Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - DDNS
22
Page 29

Broadband Router
Transmit RIP versions: Choose a protocol for transmitting data on the network. (None, RIPv1, RIPv2-Broadcast,
RIPv2-Multicast)
Static Routing
You will need to configure Static Routing if there are multiple routers installed on your network. The static routing
function determines the path that data follows over your network before and after it passes through this Router.
You can use static routing to allow different IP domain users to access the Internet.
In many cases, it is better to use dynamic routing (see above), as that allows the Router to automatically adjust to
physical changes in the network's layout. In order to use static routing, the Router's DHCP settings must be
disabled.
To set up static routing, add routing entries in the Router's table that tell the device where to send all incoming
packets. All of your network routers should direct the default route entry to this Router.
Enter the following data to create a static route entry:
1. Destination IP: Enter the network address of the remote LAN segment. For a standard Class C IP domain, the
network address is the first three fields of the Destination LAN IP, while the last field should be zero.
2. Subnet Mask: Enter the Subnet Mask used on the destination LAN IP domain. For Class C IP domains, the
Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0.
3. Default Gateway: If this Router is used to connect your network to the Internet, then your gateway IP is the
Router's IP Address. If you have another router handling your network's Internet connection, enter the IP
Address of that router instead.
4. Hop Count (max. 15): This value gives the number of nodes that a data packet passes through before
reaching its destination. A node is any device on the network, such as switches, PCs, etc.
static routing: forwarding data
in a network via a fixed path.
NOTE: Static Routing is an advanced feature.
Please proceed with caution.
default gateway: a device that forwards
Internet traffic from your local area network.
node: a network junction or connection
point, typically a computer or work station.
5. Interface (LAN, Internet1, Internet2): Select whether your network is on the LAN or one of the Internet ports.
If you’re connecting to a sub-network, select LAN. If you’re connecting to another network through one of the
Internet ports, select Internet1 or Internet2.
Click Add to list to add a static route entry or click Delete Selected IP to delete the static route entry.
Click the Save Settings button to save the Routing settings, click the Cancel Changes button to undo your
changes or click the Show Routing Table button to view the current routing table.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - Advanced Routing
23
Page 30

Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - VPN Pass Through
The VPN Pass Through screen allows you to enable or disable IPSec Pass Through, PPTP Pass Through, and L2TP
Pass Through.
IPSec Pass Through: Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a suite of protocols used to implement secure
exchange of packets at the IP layer. IPSec Pass Through is enabled by default to allow IPSec tunnels to pass
through the Router.
PPTP Pass Through: Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) Pass Through is the method used to enable VPN
sessions. PPTP Pass Through is enabled by default.
L2TP Pass Through: Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Pass Through is the method used to enable VPN sessions.
PPTP Pass Through is enabled by default.
Click the Save Settings button when you finish the VPN Pass Through settings, or click the Cancel Changes
button to undo the changes.
Advanced Setup Tab - Remote Management
If you want to manage this Router from a remote location over the Internet, click the Enable button. You can
enter any port number from 0 to 65, 535 for remote management. You can also set up remote management for a
different number.
Click the Save Settings button to save your settings, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo the changes.
Figure 5-26: Advanced Setup Tab - VPN Pass Through
VPN (Virtual Private Network): a security
measure to protect data as it leaves one
network and goes to another over the Internet.
Figure 5-27: Advanced Setup Tab - Remote Management
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - VPN Pass Through
24
Page 31

Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - System Management
The System Management screen includes several tools to help troubleshoot network problems, such as looking
up DNS names, ping tests, resetting the Router to factory default settings, upgrading the Router’s firmware, and
storing and retrieving configuration files.
Diagnostics
DNS Name Lookup
The Internet has a service called the Domain Name Service (DNS), which allows users to enter an easily
remembered host name, such as www.RT042.com, instead of numerical TCP/IP addresses to access Internet
resources. The Router has a DNS lookup tool that will return the numerical TCP/IP address of a host name.
Enter the host name to look up in the Look up the name field and click the Go button. Do not add the prefix http://,
otherwise the result will be Address Resolving Failed. The Router will then query the DNS server and display the
result in the Diagnostics section of the screen.
NOTE: The IP address of the DNS server must be entered in the Network
Settings page for the DNS Name Lookup feature to function.
Ping
The Ping test bounces a packet off an IP Address across the Internet, which returns to the sender. This test shows
if the Router is able to contact a remote host. If users on the LAN are having problems accessing services on the
Internet, try pinging the DNS server, or another IP Address at the ISP’s location. If this test is successful, try
pinging addresses outside the ISP. This will show if the problem lies with the ISP’s connection.
Enter the IP address you wish to pinged and click the Go button. The test will take a few seconds to complete.
Once completed, a message showing the results will be displayed in the Diagnostics section of the screen. The
results include Packets transmitted / received / loss and Round Trip Time (Minimum, Maximum, and Average).
Figure 5-28: Advanced Setup Tab - System Management
DNS (Domain Name Server): the IP address of your ISP's server,
which translates the names of websites into IP addresses.
ping: an Internet utility used to determine
whether a particular IP address is online.
NOTE: Ping tests require an IP address. The Router’s DNS Name
Lookup tool may be used to find the IP address of a host.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - System Management
25
Page 32

Broadband Router
Factory Default
The Factory Default feature can be used to clear all of your configuration information and restore the Router to its
factory default settings. Only use this feature if you wish to discard all other configuration preferences.
Click the Return to Factory Default Setting button if you want to restore the Router to the factory default
settings. After clicking the button, another screen will appear, confirming that you’d like to restore the factory
default settings. Click OK to reboot the Router.
Firmware Upgrade
Users can use the following function to upgrade the Router’s firmware to the newest version. If you have already
downloaded the firmware into your computer, then click the Browse button to look for the file. Then, click the
Firmware Upgrade Right Now button.
Firmware Download
Users can click the Firmware Download from Linksys Web Site button to link to the downloads on the Support
page of the Linksys website. Select the Router from the pull-down menu and choose the firmware from the
options. After downloading the firmware, follow the Firmware Upgrade instructions above.
Import Configuration File
Before importing a configuration file, you will need to specify where it is located. Click the Browse button, and
select a file that you have previously saved using the Export button in the window that opens. After you select the
file, click the Import button. This process may take up to a minute. You will then need to restart the Router in
order for the changes to take effect.
Export Configuration File
To export a configuration file, click the Export button. You will be asked where you would like to store the file.
This file will be called “RV042.exp” by default, but you may rename it if you wish. This process may take up to a
minute.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Advanced Setup Tab - System Management
download: to receive a file
transmitted over a network.
26
Page 33

Broadband Router
Log Tab - System Log
The System Log screen contains three functions: Syslog, E-mail and Log Setting.
Syslog
The System Log (of Syslog) function logs network activity with the use of a separate Syslog server. You need a
Syslog server for this feature to work.
Enable Syslog: Check this box to enable logging.
Syslog Server: In addition to the standard event log, the Router can send a detailed log to an external Syslog
server. Syslog is an industry-standard protocol used to capture information about network activity. The Router’s
Syslog captures all log activity and includes every connection source and destination IP address, IP service, and
number of bytes transferred. Enter the Syslog server name or IP address in the Syslog Server field. Restart the
Router for logging to take effect.
E-mail
Enable E-Mail Alert: Check this box to enable E-Mail Alert, informing you of network activity.
Mail Server: To have a log or alert information e-mailed to you, enter the name or IP address of your SMTP server
here. Your Internet Service Provider can provide you with this information.
Send E-mail To: This is the E-mail address where your log files will be sent. Leave this field blank if you do not
want to receive copies of your log information.
Figure 5-29: Log Tab - System Log
byte: aunit of data that is
usually eight bits long
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): the
standard e-mail protocol on the Internet.
Log Queue Length: The default length is 50 entries. The Router will e-mail the log when the number of log
entries exceeds the queue.
Log Time Threshold: The default time is 10 minutes. In this case, the Router will e-mail the log every 10
minutes.
The Router will e-mail the log when it meets either the Log Queue Length or Log Time Threshold settings.
E-mail Log Now: Click the E-mail Log Now button to immediately send the log to the address in the Send E-mail
to field.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Log Tab - System Log
27
Page 34

Broadband Router
Log Setting
Alert Log
Check the appropriate box when you want receive alert logs for any of the following events: Syn Flooding, IP
Spoofing, Win Nuke, Ping of Death and Unauthorized Login Attempt.
General Log
Check the appropriate box when you want to receive alert logs for any of the following events: System Error
Messages, Deny Policies, Allow Policies, Configuration Changes and Authorized Login.
View System Log: Click this button to view ALL logs, System Log, Access Log, Firewall Log, or VPN Log.
Outgoing Log Table: Click this button to view the outgoing packet information.
Incoming Log Table: Click this button to view the incoming packet information.
Clear Log Now: This button will clear out your log without e-mailing it. Only use this button if you don't mind
losing your log information.
Click the Save Settings button to save your Log settings, or click the Cancel Changes button to undo the
changes.
Log Tab - System Statistics
This tab displays the system statistics including the Device Name, Status, IP Address, MAC Address, Subnet
Mask, Default Gateway, DNS, Received Packets, Sent Packets, Total Packets, Received Bytes, Sent Bytes, Total
Bytes, Error Packets Received and Dropped Packets Received for the Ethernet ports as well as both of the
Internet ports.
Click the Refresh button to update these statistics.
Chapter 5: Setting Up and Configuring the Broadband Router
Log Tab - System Statistics
Figure 5-30: Log Tab - System Statistics
28
Page 35

Broadband Router
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This appendix provides solutions to problems that may occur during the installation and operation of the Router.
Read the descriptions below to help solve your problems. If you can't find an answer here, check the Linksys
website at www.linksys.com.
Common Problems and Solutions
1. I need to set a static IP address on a PC.
The Router, by default, assigns an IP address range of 192.168.1.100 to 192.168.1.149 using the DHCP server
on the Router. To set a static IP address, you can only use the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and
192.168.1.150 to 192.168.1.254. Each PC or network device that uses TCP/IP must have a unique address to
identify itself in a network. If the IP address is not unique to a network, Windows will generate an IP conflict
error message. You can assign a static IP address to a PC by performing the following steps:
For Windows 98 and Millennium:
A. Click Start, Setting, and Control Panel. Double-click Network.
B. In The following network components are installed box, select the TCP/IP-> associated with your
Ethernet adapter. If you only have one Ethernet adapter installed, you will only see one TCP/IP line with no
association to an Ethernet adapter. Highlight it and click the Properties button.
C. In the TCP/IP properties window, select the IP address tab, and select Specify an IP address. Enter a
unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the network connected to the Router. You can
only use an IP address in the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to 192.168.1.254.
Make sure that each IP address is unique for each PC or network device.
D. Click the Gateway tab, and in the New Gateway prompt, enter 192.168.1.1, which is the default IP
address of the Router. Click the Add button to accept the entry.
E. Click the DNS tab, and make sure the DNS Enabled option is selected. Enter the Host and Domain names
(e.g., John for Host and home for Domain). Enter the DNS entry provided by your ISP. If your ISP has not
provided the DNS IP address, contact your ISP to get that information or go to its website for the
information.
F. Click the OK button in the TCP/IP properties window, and click Close or the OK button for the Network
window.
G. Restart the computer when asked.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
29
Page 36

Broadband Router
For Windows 2000:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Network and Dial-Up Connections.
B. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet adapter you are using, and
select the Properties option.
C. In the Components checked are used by this connection box, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and
click the Properties button. Select Use the following IP address option.
D. Enter a unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the network connected to the Router.
You can only use an IP address in the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to
192.168.1.254.
E. Enter the Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0.
F. Enter the Default Gateway, 192.168.1.1 (Router’s default IP address).
G. Toward the bottom of the window, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the
Preferred DNS server and Alternative DNS server (provided by your ISP). Contact your ISP or go on its
website to find the information.
H. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, and click the OK button in the
Local Area Connection Properties window.
I. Restart the computer if asked.
For Windows XP:
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the default interface. If you are using the
Classic interface (where the icons and menus look like previous Windows versions), please follow the
instructions for Windows 2000.
A. Click Start and Control Panel.
B. Click the Network and Internet Connections icon and then the Network Connections icon.
C. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet adapter you are using, and
select the Properties option.
D. In the This connection uses the following items box, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). Click the
Properties button.
E. Enter a unique IP address that is not used by any other computer on the network connected to the Router.
You can only use an IP address in the ranges 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.99 and 192.168.1.151 to
192.168.1.254.
F. Enter the Subnet Mask, 255.255.255.0.
G. Enter the Default Gateway, 192.168.1.1 (Router’s default IP address).
H. Toward the bottom of the window, select Use the following DNS server addresses, and enter the
Preferred DNS server and Alternative DNS server (provided by your ISP). Contact your ISP or go on its
website to find the information.
I. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window. Click the OK button in the Local
Area Connection Properties window.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
30
Page 37

Broadband Router
2. I want to test my Internet connection.
A. Check your TCP/IP settings.
For Windows 98 and Millennium:
Refer to “Appendix F: Windows Help” for details. Make sure Obtain IP address automatically is selected in
the settings.
For Windows 2000:
1. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Network and Dial-Up Connections.
2. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet adapter you are using,
and select the Properties option.
3. In the Components checked are used by this connection box, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP),
and click the Properties button. Make sure that Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain
DNS server address automatically are selected.
4. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, and click the OK button in the
Local Area Connection Properties window.
5. Restart the computer if asked.
6. Click the OK button in the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, and click the OK button in the
Local Area Connection Properties window.
7. Restart the computer if asked.
For Windows XP:
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the default interface. If you are using the
Classic interface (where the icons and menus look like previous Windows versions), please follow the
instructions for Windows 2000.
1. Click Start and Control Panel.
2. Click the Network and Internet Connections icon and then the Network Connections icon.
3. Right-click the Local Area Connection that is associated with the Ethernet adapter you are using,
and select the Properties option.
4. In the This connection uses the following items box, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click
the Properties button. Make sure that Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server
address automatically are selected.
B. Open a command prompt.
• For Windows 98 and Millennium, click Start and Run. In the Open field, type command. Press the
Enter key or click the OK button.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
31
Page 38

Broadband Router
• For Windows 2000 and XP, click Start and Run. In the Open field, type cmd. Press the Enter key or
click the OK button.
C. In the command prompt, type ping 192.168.1.1 and press the Enter key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is communicating with the Router.
• If you do NOT get a reply, check the cable, and make sure Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected in the TCP/IP settings for your Ethernet adapter.
D. In the command prompt, type ping followed by your Internet IP address and press the Enter key. The
Internet IP Address can be found in the web interface of the Router. For example, if your Internet IP
address is 1.2.3.4, you would enter ping 1.2.3.4 and press the Enter key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is connected to the Router.
• If you do NOT get a reply, try the ping command from a different computer to verify that your original
computer is not the cause of the problem.
E. In the command prompt, type ping www.linksys.com and press the Enter key.
• If you get a reply, the computer is connected to the Internet. If you cannot open a webpage, try the
ping command from a different computer to verify that your original computer is not the cause of the
problem.
• If you do NOT get a reply, there may be a problem with the connection. Try the ping command from a
different computer to verify that your original computer is not the cause of the problem.
3. I am not getting an IP address on the Internet with my Internet connection.
A. Refer to “Problem #2, I want to test my Internet connection” to verify that you have connectivity.
B. If you need to register the MAC address of your Ethernet adapter with your ISP, please see “Appendix C:
Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter.” If you need to clone the MAC address
of your Ethernet adapter onto the Router, see the MAC Address Clone section of “Chapter 5: Setting up
and Configuring the Broadband Router” for details.
C. Make sure you are using the right Internet settings. Contact your ISP to see if your Internet connection
type is DHCP, Static IP Address, or PPPoE (commonly used by DSL consumers). Please refer to the Basic
Setup section of “Chapter 5: Setting up and Configuring the Broadband Router” for details on Internet
Connection Type settings.
D. Make sure you use the right cable. Check to see if the Internet LED is solidly lit.
E. Make sure the cable connecting from your cable or DSL modem is connected to the Router’s Internet port.
Verify that the Status page of the Router’s Web-based Utility shows a valid IP address from your ISP.
F. Turn off the computer, Router, and cable/DSL modem. Wait 30 seconds, and then turn on the Router,
cable/DSL modem, and computer. Check the Status tab of the Router’s Web-based Utility to see if you get
an IP address.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
32
Page 39

Broadband Router
4. I am not able to access the Router’s Web-based Utility Setup page.
A. Refer to “Problem #2, I want to test my Internet connection” to verify that your computer is properly
connected to the Router.
B. Refer to “Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter” to verify that
your computer has an IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS.
C. Set a static IP address on your system; refer to “Problem #1: I need to set a static IP address.”
D. Refer to “Problem #10: I need to remove the proxy settings or the dial-up pop-up window (for PPPoE
users).”
5. I can’t get my Virtual Private Network (VPN) to work through the Router.
Access the Router’s web interface by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router, and go to
the VPN => VPN Pass Through tab. Make sure you have IPsec passthrough and/or PPTP passthrough
enabled.
VPNs that use IPSec with the ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload known as protocol 50) authentication will
work fine. At least one IPSec session will work through the Router; however, simultaneous IPSec sessions
may be possible, depending on the specifics of your VPNs.
VPNs that use IPSec and AH (Authentication Header known as protocol 51) are incompatible with the Router.
AH has limitations due to occasional incompatibility with the NAT standard.
Change the IP address for the Router to another subnet to avoid a conflict between the VPN IP address and
your local IP address. For example, if your VPN server assigns an IP address 192.168.1.X (X is a number from
1 to 254) and your local LAN IP address is 192.168.1.X (X is the same number used in the VPN IP address), the
Router will have difficulties routing information to the right location. If you change the Router’s IP address to
192.168.2.1, that should solve the problem. Change the Router’s IP address through the Basic Setup tab of
the Web-based Utility. If you assigned a static IP address to any computer or network device on the network,
you need to change its IP address accordingly to 192.168.2.Y (Y being any number from 1 to 254). Note that
each IP address must be unique within the network.
Your VPN may require port 500/UDP packets to be passed to the computer that is connecting to the IPSec
server. Refer to “Problem #7, I need to set up online game hosting or use other Internet applications” for
details.
Check the Linksys website at www.linksys.com for more information.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
33
Page 40

Broadband Router
6. I need to set up a server behind my Router.
To use a server like a web, ftp, or mail server, you need to know the respective port numbers they are using.
For example, port 80 (HTTP) is used for web; port 21 (FTP) is used for FTP, and port 25 (SMTP outgoing) and
port 110 (POP3 incoming) are used for the mail server. You can get more information by viewing the
documentation provided with the server you installed. Follow these steps to set up port forwarding through
the Router’s Web-based Utility. We will be setting up web, ftp, and mail servers.
A. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router. Go
to the Advanced Setup => Forwarding tab.
B. Select the Service from the pull-down menu. If the Service you need is not listed in the menu, click the
Service Management button to add the new Service Name, and enter the Protocol and Port Range. Click
the Add to List button. Then click the Save Setting button. Click the Exit button.
C. Enter the IP Address of the server that you want the Internet users to access. For example, if the web
server’s Ethernet adapter IP address is 192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided. Check
“Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter” for details on getting an
IP address. Then check the Enable checkbox for the entry. Consider the examples below:
Application Start and End Protocol IP Address Enable
Web server 80 to 80 Both 192.168.1.100 X
FTP server 21 to 21 TCP 192.168.1.101 X
SMTP (outgoing) 25 to 25 Both 192.168.1.102 X
POP3 (incoming) 110 to 110 Both 192.168.1.102 X
D. Click the Add to List button, and configure as many entries as you like.
When you have completed the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
34
Page 41

Broadband Router
7. I need to set up online game hosting or use other Internet applications.
If you want to play online games or use Internet applications, most will work without doing any port
forwarding or DMZ hosting. There may be cases when you want to host an online game or Internet
application. This would require you to set up the Router to deliver incoming packets or data to a specific
computer. This also applies to the Internet applications you are using. The best way to get the information on
what port services to use is to go to the website of the online game or application you want to use. Follow
these steps to set up online game hosting or use a certain Internet application:
A. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router. Go
to the Advanced Setup => Forwarding tab.
B. Select the Service from the pull-down menu. If the Service you need is not listed in the menu, click the
Service Management button to add the new Service Name, and enter the Protocol and Port Range. For
example, if you have a web server, you would enter the range 80 to 80. Click the Add to List button. Then
click the Save Setting button. Click the Exit button.
C. Enter the IP Address of the server that you want the Internet users to access. For example, if the web
server’s Ethernet adapter IP address is 192.168.1.100, you would enter 100 in the field provided. Check
“Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter” for details on getting an
IP address. Then check the Enable checkbox for the entry. Consider the examples below:
Application Start and End Protocol IP Address Enabled
UT 7777 to 27900 Both 192.168.1.100 X
Halflife 27015 to 27015 Both 192.168.1.105 X
PC Anywhere 5631 to 5631 UDP 192.168.1.102 X
VPN IPSEC 500 to 500 UDP 192.168.1.100 X
D. Click the Add to List button, and configure as many entries as you like.
When you have completed the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
35
Page 42

Broadband Router
8. I can’t get the Internet game, server, or application to work.
If you are having difficulties getting any Internet game, server, or application to function properly, consider
exposing one PC to the Internet using DeMilitarized Zone (DMZ) hosting. This option is available when an
application requires too many ports or when you are not sure which port services to use. Make sure you
disable all the forwarding entries if you want to successfully use DMZ hosting, since forwarding has priority
over DMZ hosting. (In other words, data that enters the Router will be checked first by the forwarding settings.
If the port number that the data enters from does not have port forwarding, then the Router will send the data
to whichever PC or network device you set for DMZ hosting.) Follow these steps to set DMZ hosting:
A. Access the Router’s Web-based Utility by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router. Go
to the Setup => Forwarding tab.
B. Disable or remove the entries you have entered for forwarding. To delete an entry, select it and then click
the Delete selected application button. Keep this information in case you want to use it at a later time.
C. Click the DMZ Host tab.
D. Enter the Ethernet adapter’s IP address of the computer you want exposed to the Internet. This will
bypass the NAT security for that computer. Please refer to “Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP
Address for Your Ethernet Adapter” for details on getting an IP address.
Once completed with the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
9. I forgot my password, or the password prompt always appears when saving settings to the Router.
Reset the Router to factory defaults by pressing the Reset button for ten seconds and then releasing it. If you
are still getting prompted for a password when saving settings, then perform the following steps:
A. Access the Router’s web interface by going to http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the Router. Enter
the default password admin, and click the Setup => Password tab.
B. Enter the old password in the Old Password field.
C. Enter a different password in the New Password field, and enter the new password in the Confirm New
Password field to confirm the password.
D. Click the Save Settings button.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
36
Page 43

Broadband Router
10. I am a PPPoE user, and I need to remove the proxy settings or the dial-up pop-up window.
If you have proxy settings, you need to disable these on your computer. Because the Router is the gateway for
the Internet connection, the computer does not need any proxy settings to gain access. Please follow these
directions to verify that you do not have any proxy settings and that the browser you use is set to connect
directly to the LAN.
For Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher:
A. Click Start, Settings, and Control Panel. Double-click Internet Options.
B. Click the Connections tab.
C. Click the LAN settings button and remove anything that is checked.
D. Click the OK button to go back to the previous screen.
E. Click the option Never dial a connection. This will remove any dial-up pop-ups for PPPoE users.
For Netscape 4.7 or higher:
A. Start Netscape Navigator, and click Edit, Preferences, Advanced, and Proxies.
B. Make sure you have Direct connection to the Internet selected on this screen.
C. Close all the windows to finish.
11. To start over, I need to set the Router to factory default.
Hold the Reset button for up to 30 seconds and then release it. This will return the password, forwarding, and
other settings on the Router to the factory default settings. In other words, the Router will revert to its original
factory configuration.
12. I need to upgrade the firmware.
In order to upgrade the firmware with the latest features, you need to go to the Linksys website and download
the latest firmware at www.linksys.com. Follow these steps:
A. Go to the Linksys website at http://www.linksys.com and download the latest firmware, or use the
Web-based Utility to be automatically redirected to the download webpage. Go to System Management -
Firmware Upgrade, and click the Firmware Download from Linksys Web Site button. Select the Router
from the pull-down menu and choose the firmware from the options.
B. Extract the firmware file on your computer.
C. To upgrade the firmware, follow the steps in the Upgrade section found in “Chapter 5: Setting up and
Configuring the Broadband Router” or “Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware.”
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
37
Page 44

Broadband Router
13. My DSL service’s PPPoE is always disconnecting.
PPPoE is not actually a dedicated or always-on connection. The DSL ISP can disconnect the service after a
period of inactivity, just like a normal phone dial-up connection to the Internet. There is a setup option to
“keep alive” the connection. This may not always work, so you may need to re-establish connection
periodically.
A. To connect to the Router, go to the web browser, and enter http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the
Router.
B. Enter the password, if asked. (The default password is admin.)
C. On the Basic Setup tab, select the option Keep Alive, and set the Redial Period option at 20 (seconds).
D. Click the Save Settings button.
E. Click the Status tab, and click the Connect button.
F. You may see the login status display as Connecting. Press the F5 key to refresh the screen, until you see
the login status display as Connected.
If the connection is lost again, follow steps E and F to re-establish connection.
14. I need to use port triggering.
Port triggering looks at the outgoing port services used and will trigger the Router to open a specific port,
depending on which port an Internet application uses. Follow these steps:
A. To connect to the Router, go to the web browser, and enter http://192.168.1.1 or the IP address of the
Router.
B. Enter the password, if asked. (The default password is admin.)
C. Click the Advanced Setup => Forwarding tab.
D. Enter any name you want to use for the Application Name.
E. Enter the Start and End Ports of the Triggered Port Range. Check with your Internet application provider
for more information on which outgoing port services it is using.
F. Enter the Start and End Ports of the Forwarded Port Range. Check with your Internet application provider
for more information on which incoming port services are required by the Internet application.
Once completed with the configuration, click the Save Settings button.
15. When I enter a URL or IP address, I get a time-out error or am prompted to retry.
• Check if other PCs work. If they do, ensure that your workstation’s IP settings are correct (IP Address,
Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS). Restart the computer that is having a problem.
• If the PCs are configured correctly, but still not working, check the Router. Ensure that it is connected and
powered on. Connect to it and check its settings. (If you cannot connect to it, check the LAN and power
connections.)
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Common Problems and Solutions
38
Page 45

Broadband Router
• If the Router is configured correctly, check your Internet connection (DSL/cable modem, etc.) to see if it is
working correctly. You can remove the Router to verify a direct connection.
• Manually configure the TCP/IP with a DNS address provided by your ISP.
• Make sure that your browser is set to connect directly and that any dial-up is disabled. For Internet
Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options, and then the Connection tab. Make sure that Internet Explorer is
set to Never dial a connection. For Netscape Navigator, click Edit, Preferences, Advanced, and Proxy.
Make sure that Netscape Navigator is set to Direct connection to the Internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is IPSec Passthrough supported by the Router?
Yes, enable or disable IPSec Passthrough on the VPN => VPN Pass Through tab.
Where is the Router installed on the network?
In a typical environment, the Router is installed between the cable/DSL modem and the LAN. Plug the Router into
the cable/DSL modem’s Ethernet port.
Does the Router support IPX or AppleTalk?
No. TCP/IP is the only protocol standard for the Internet and has become the global standard for communications.
IPX, a NetWare communications protocol used only to route messages from one node to another, and AppleTalk, a
communications protocol used on Apple and Macintosh networks, can be used for LAN to LAN connections, but
those protocols cannot connect from the Internet to the LAN.
What is Network Address Translation and what is it used for?
Network Address Translation (NAT) translates multiple IP addresses on the private LAN to one public address that
is sent out to the Internet. This adds a level of security since the address of a PC connected to the private LAN is
never transmitted on the Internet. Furthermore, NAT allows the Router to be used with low cost Internet accounts,
such as DSL or cable modems, when only one TCP/IP address is provided by the ISP. The user may have many
private addresses behind this single address provided by the ISP.
Does the Router support any operating system other than Windows 98, Millennium, 2000, or XP?
Yes, but Linksys does not, at this time, provide technical support for setup, configuration or troubleshooting of
any non-Windows operating systems.
Does the Router support ICQ send file?
Yes, with the following fix: click ICQ menu => preference => connections tab=>, and check I am behind a
firewall or proxy. Then set the firewall time-out to 80 seconds in the firewall setting. The Internet user can then
send a file to a user behind the Router.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
39
Page 46

Broadband Router
I set up an Unreal Tournament Server, but others on the LAN cannot join. What do I need to do?
If you have a dedicated Unreal Tournament server running, you need to create a static IP for each of the LAN
computers and forward ports 7777, 7778, 7779, 7780, 7781, and 27900 to the IP address of the server. You can
also use a port forwarding range of 7777 to 27900. If you want to use the UT Server Admin, forward another port
(8080 usually works well but is used for remote admin. You may have to disable this.), and then in the
[UWeb.WebServer] section of the server.ini file, set the ListenPort to 8080 (to match the mapped port above) and
ServerName to the IP assigned to the Router from your ISP.
Can multiple gamers on the LAN get on one game server and play simultaneously with just one public IP
address?
It depends on which network game or what kind of game server you are using. For example, Unreal Tournament
supports multi-login with one public IP.
How do I get Half-Life: Team Fortress to work with the Router?
The default client port for Half-Life is 27005. The computers on your LAN need to have “+clientport 2700x”
added to the HL shortcut command line; the x would be 6, 7, 8, and on up. This lets multiple computers connect
to the same server. One problem: Version 1.0.1.6 won’t let multiple computers with the same CD key connect at
the same time, even if on the same LAN (not a problem with 1.0.1.3). As far as hosting games, the HL server does
not need to be in the DMZ. Just forward port 27015 to the local IP address of the server computer.
How can I block corrupted FTP downloads?
If you are experiencing corrupted files when you download a file with your FTP client, try using another FTP
program.
The web page hangs; downloads are corrupt, or nothing but junk characters are being displayed on the
screen. What do I need to do?
Force your Ethernet adapter to 10Mbps or half duplex mode, and turn off the “Auto-negotiate” feature of your
Ethernet adapter as a temporary measure. (Please look at the Network Control Panel in your Ethernet adapter’s
Advanced Properties tab.) Make sure that your proxy setting is disabled in the browser. Check our website at
www.linksys.com for more information.
If all else fails in the installation, what can I do?
Reset the Router by holding down the Reset button for ten seconds. Reset your cable or DSL modem by powering
the unit off and then on. Obtain and flash the latest firmware release that is readily available on the Linksys
website, www.linksys.com.
How can I be notified of new Router firmware upgrades?
All Linksys firmware upgrades are posted on the Linksys website at www.linksys.com, where they can be
downloaded for free. The Router’s firmware can be upgraded using the Web-based Utility. If the Router’s Internet
connection is working well, there is no need to download a newer firmware version, unless that version contains
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
40
Page 47

Broadband Router
new features that you would like to use. Downloading a more current version of Router firmware will not
enhance the quality or speed of your Internet connection, and may disrupt your current connection stability.
Will the Router function in a Macintosh environment?
Yes, but the Router’s setup pages are accessible only through Internet Explorer 5.0 or Netscape Navigator 5.0 or
higher for Macintosh.
I am not able to get the web configuration screen for the Router. What can I do?
You may have to remove the proxy settings on your Internet browser, e.g., Netscape Navigator or Internet
Explorer. Or remove the dial-up settings on your browser. Check with your browser documentation, and make
sure that your browser is set to connect directly and that any dial-up is disabled. Make sure that your browser is
set to connect directly and that any dial-up is disabled. For Internet Explorer, click Tools, Internet Options, and
then the Connection tab. Make sure that Internet Explorer is set to Never dial a connection. For Netscape
Navigator, click Edit, Preferences, Advanced, and Proxy. Make sure that Netscape Navigator is set to Direct
connection to the Internet.
What is DMZ Hosting?
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) allows one IP address (computer) to be exposed to the Internet. Some applications
require multiple TCP/IP ports to be open. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP if you
want to use DMZ Hosting. To get the LAN IP address, see “Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address
for Your Ethernet Adapter.”
If DMZ Hosting is used, does the exposed user share the public IP with the Router?
No.
Does the Router pass PPTP packets or actively route PPTP sessions?
The Router allows PPTP packets to pass through.
Is the Router cross-platform compatible?
Any platform that supports Ethernet and TCP/IP is compatible with the Router.
How many ports can be simultaneously forwarded?
Theoretically, the Router can establish 4,000 sessions at the same time, but you can only forward 30 ranges of
ports.
Does the Router replace a modem? Is there a cable or DSL modem in the Router?
No, this version of the Router must work in conjunction with a cable or DSL modem.
Which modems are compatible with the Router?
The Router is compatible with virtually any cable or DSL modem that supports Ethernet.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
41
Page 48

Broadband Router
How can I check whether I have static or DHCP IP addresses?
Ask your ISP to find out.
How do I get mIRC to work with the Router?
Under the Setup => Forwarding tab, set port forwarding to 113 for the PC on which you are using mIRC.
If your questions are not addressed here, refer to the Linksys website, www.linksys.com.
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
Frequently Asked Questions
42
Page 49

Broadband Router
Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware
You can use the Router’s Web-based Utility to upgrade the firmware; however, if you do so, you may lose the
settings you have configured on the Router.
To upgrade the Router’s firmware, follow these instructions:
1. Download the Router’s firmware upgrade file from the Linksys website, www.linksys.com or click the
Firmware Download from Linksys Web Site button that appears on the System Management screen under
the Advanced Setup tab. Select the Router from the pull-down menu and choose the firmware from the
options.
2. After downloading the file, extract it on your computer.
3. Under Firmware Upgrade, on the same screen, click the Browse button to select the firmware file.
4. Click the Firmware Upgrade Right Now button, and follow the on-screen instructions.
Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware
Figure B-1: Advanced Setup Tab - System Management
43
Page 50

10/100 4-Port VPN Router
Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter
This section describes how to find the MAC address for your computer’s Ethernet adapter so you can use the MAC
address cloning feature of the Router. You can also find the IP address of your computer’s Ethernet adapter. This
IP address is used for the Router’s filtering, forwarding, and/or DMZ features. Follow the steps in this appendix to
find the adapter’s MAC or IP address in Windows 98, Me, 2000, or XP.
Windows 98 or Me Instructions
1. Click Start and Run. In the Open field, enter winipcfg. Then press the Enter key or the OK button.
2. When the IP Configuration screen appears, select the Ethernet adapter you have connected to the Router via a
CAT 5 Ethernet network cable.
3. Write down the Adapter Address as shown on your computer screen. This is the MAC address for your
Ethernet adapter and is shown as a series of numbers and letters.
The MAC address/Adapter Address is what you will use for MAC address cloning or MAC filtering.
The example shows the Ethernet adapter’s IP address as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something
different.
Note: The MAC address is also called the Adapter Address.
Windows 2000 or XP Instructions
1. Click Start and Run. In the Open field, enter cmd. Press the Enter key or click the OK button.
2. At the command prompt, enter ipconfig /all. Then press the Enter key.
Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter
Windows 98 or Me Instructions
Figure C-1: IP Configuration Screen
Figure C-2: MAC Address/Adapter Address
44
Page 51

10/100 4-Port VPN Router
3. Write down the Physical Address as shown on your computer screen; it is the MAC address for your Ethernet
adapter. This appears as a series of numbers and letters.
The MAC address/Physical Address is what you will use for MAC address cloning or MAC filtering.
Note: The MAC address is also called the Physical Address.
The example shows the Ethernet adapter’s IP address as 192.168.1.100. Your computer may show something
different.
For the Router’s Web-based Utility
Some ISPs require that you register a MAC address. This feature “clones” your network adapter's MAC address
onto the Router, and prevents you from having to call your ISP to change the registered MAC address to the
Router's MAC address. The Router's MAC address is a 12-digit code assigned to a unique piece of hardware for
identification.
Enter the MAC Address in the User Defined MAC Address field for Internet ports 1 or 2, or click the Clone button
to add the MAC Address from the PC viewing the Web-based Utility.
Click Save Settings to save the MAC Cloning settings or click the Cancel Changes button to undo your changes.
Figure C-3: MAC Address/Physical Address
Figure C-4: MAC Address Clone
Appendix C: Finding the MAC Address and IP Address for Your Ethernet Adapter
For the Router’s Web-based Utility
45
Page 52

Broadband Router
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
While many of the Router’s functions can be utilized through the Web-based Utility, a separate utility also comes
on the Router’s CD. This RT042 Utility is more graphically oriented and can do many, though not all, of the things
the Web-based Utility can do.
Starting the Utility
To start the utility, put the Router’s CD in your PC’s CD-Rom drive and open it. Then, double-click the Utility icon
on the CD. You will then need to enter a password, this is the same as the Web-based Utility’s password, which is
by default, admin.
After entering the password and clicking the OK button, the Utility will automatically detect the PC connected to
the Router on your network and its settings. The main Utility screen will then open.
This screen gives a graphical representation of the Router’s connection to the Internet, displaying which Internet
ports are active. From this screen, you can also control the amount of bandwidth used.
NOTE: You can change the Router’s password by clicking the PassPort Configuration icon at the
bottom of the screen. You will be enter the old password. Then, enter the new password once in the
New Password field and again in the Confirm New Password field for confirmation. Then, click the
Save button, to save the new password.
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
Starting the Utility
Figure D-1: The Utility’s Main Screen
46
Page 53
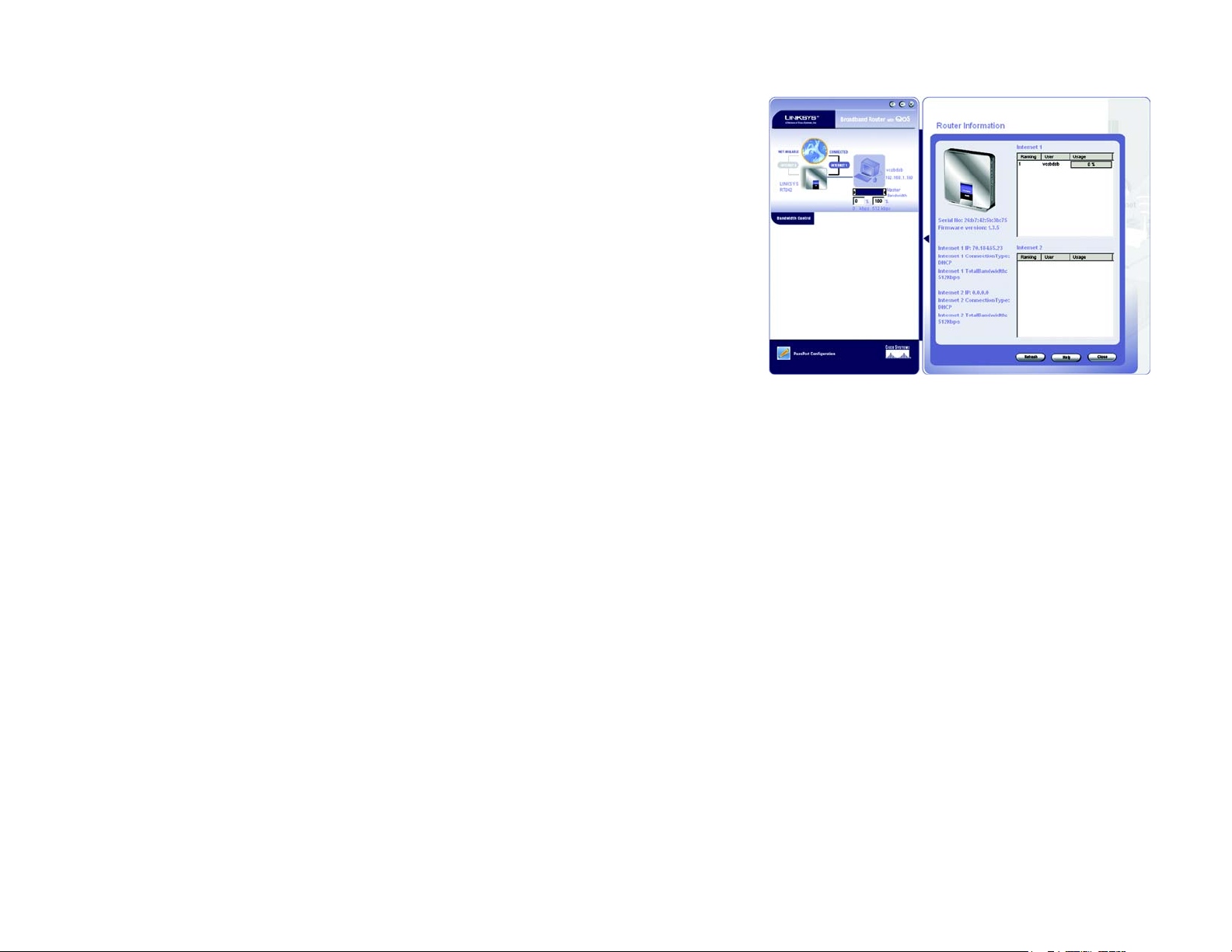
Broadband Router
Router Information
Clicking on the image of the Router will open up the Router Information screen.
The left side of this screen gives general statistics about the Router: Serial Number, Firmware Version, and
Internet Connection types as well as bandwidth for each Internet port.
The right side of the screen provides user information for your network users, depending upon which Internet
port they are accessing. You can also view which user is taking up the most bandwidth on your network from the
usage percentage information.
From this screen, you can select PCs on your network whose usage you want to configure, either by restricting or
optimizing their performance. By double-clicking the user listed, that user will appear as the PC icon on the
Utility’s main screen.
Usage Configuration Screens
Connection Status
Figure D-2: The Router Information Screen
The icons in the upper left corner also provide the following information on your connection status.
Router Status (earth) Icon: The earth icon shows the network connection status. The earth will spin when the
router is connectin to the Internet.
Internet 1/Internet 2 Icons: Click the Internet2 button to switch to the other Internet port. Click the Internet 1
button to view and edit the Internet configuration. As you change the Internet port, the screen will change
acccordingly. If dual Internet is used , you can see who is going through Internet1 and Internet2. If only Internet 1
is used the status of Internet 2 will be shown as NOT AVAILABLE.
PC Status Icon: All PCs that are connected to the Router will be recorded and displayed. The off-line PCs will be
shown as Intenet Disconnected, and on-line PCs will be shown as Internet Connected. PCs with a blue dot can be
connected to the Internet, and the PCs with an orange dot can’t connect to the Internet. When PCs are connecting
to the Internet, the dot will flicker. You can prevent the selected PC from connecting to the Internet by clicking the
blue dot, which will turn it orange. You can then click the orange dot again to allow it to connect to the Internet.
The Host Name and IP Address of all PCs will display, and you can click the right mouse button to rename the host
name for the PC.
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
Router Information
47
Page 54

Broadband Router
Right Mouse click options: Select the PC, click the right mouse button, and the following tools will be available.
• View button: Click View Scheduler / View Hit Rate / View Usage / View Performance Optimization button to
view the page of the user’s passport.
• Connect to Internet 1/2: You can click the button to connect to the other internet port if both wan ports are
used.
• Remove: You can click the Remove button to remove the selected PC from the topology. Because the PC
was once connected to your home network by an occasional user, it will be recorded, and you can use this
tool to remove the PC if you don’t need to manage it from the topology.
Bandwidth Control
The left arrow controls the guaranteed bandwidth, and right arrow limits the bandwidth for each user. The
percentage and bandwidth (kbps) from the minimum to maximum will display accordingly. The default is no
guarantee and limit bandwidth, so the default min rate is 0% and max rate is 100%. You can allocate the
guaranteed bandwidth for each user, with the total minimum bandwidth being 100% of the max bandwidth
provided by the ISP. For example, if the max upstream bandwidth provided by ISP is 512Kbit/sec, and you allocate
50% for user A, he will get 256Kbit/sec guaranteed bandwidth. The max bandwidth user A can use will be
512Kbit/sec, but you also can lower the max bandwidth to limit the bandwidth for this user. For example, if you
limit the max as 70%, the maximum bandwidth user A can use will be around 358Kbit/sec.
Once you change the bandwidth settings or rename the host name of PC, the Save bar will appear. After finishing
the changes click the Save button to apply the changes, or click the Cancel button to undo the changes.
Figure D-3: The On-Line Scheduler
As noted above, you can configure each user’s access to the Router, either by restricting or optimizing
performance, by clicking the right arrow bar or the PC icon on the Utility’s main screen, after selecting the user.
This will open up the configuration screens. These are:
On-Line Scheduler: This allows you to allow or deny Internet access, according to the schedule, to any of the
users on your network.
Hit Rate: From this screen, you can view the frequency at which each of your network’s users are viewing their
ten most favorite websites. You can also block these sites, if you wish.
Real Time Usage: From this screen, you can view which applications are taking up the most bandwidth on your
network, according to user, and block those sites if you wish.
Performance Optimization: From this screen, you can list the network applications most often used on your
network, according to user, and set the priority at which it is run.
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
Usage Configuration Screens
Figure D-4: The Hit Rate Screen
48
Page 55

Broadband Router
On-Line Scheduler
From the schedule, you can restrict or allow access to the Internet. Select any day in the schedule or hours of
time.
To refresh the information on the screen, click the Refresh button. If you need help on-line, click the Help button.
Click Save to save the schedule or click the Cancel button to undo your changes.
Figure D-5: The Real Time Usage Screen
Hit Rate
From the Hit Rate screen, you can view the frequency at which each of your network’s users are viewing their ten
most favorite websites. You can also block these sites, if you wish.
Website information is displayed in ranking order, from most viewed to least viewed, with the amount of “hits”
displayed. Each website is displayed as a link, so you can click the name to bring up the site. Clicking the Block
box will restrict that user from viewing that website.
View URL Block List: Clicking this button will show which sites have been blocked for this user.
View One Week History: Click this button will display which websites this user viewed in the past week. You can
also select individual days for further information.
To refresh the information on the screen, click the Refresh button. If you need help on-line, click the Help button.
Click Save to save the blocked list or click the Cancel button to undo your changes.
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
Usage Configuration Screens
Figure D-6: The Hit Rate Screen
49
Page 56

Broadband Router
Real Time Usage
From this screen, you can view which applications are taking up the most bandwidth on your network, according
to user, and block those sites if you wish.
Application information is displayed in ranking order, from most viewed to least viewed, with the amount of usage
displayed for each application. For each application, there is also a column showing port number used. Clicking
the Block box will restrict that user from utilizing that application.
View Application Block List: Clicking this button will show which applications have been blocked for this user.
View One Week History: Click this button will display which applications used in the past week. You can also
select individual days for further information.
To refresh the information on the screen, click the Refresh button. If you need help on-line, click the Help button.
Click Save to save the blocked list or click the Cancel button to undo your changes.
Performance Optimization
From the Performance Optimization screen, you can list the network applications most often used on your
network, according to user, and set the priority at which it is run.
All applications are set at a Good level of optimization, shown in green, by default. To change this setting, click
the Enable box next to the application. Then, you can move the slider to Normal optimization, shown in yellow, or
Better optimization, shown in blue. Moving the slider towards yellow will decrease performance, while moving
the slider towards blue will increase performance.
To refresh the information on the screen, click the Refresh button. If you need help on-line, click the Help button.
Click Save to save the blocked list or click the Cancel button to undo your changes.
Appendix D: Using the RT042 Utility
Usage Configuration Screens
Figure D-7: The Performance Optimization Screen
50
Page 57

Broadband Router
Appendix E: The Setup Wizard
While the Broadband Router can be set up using the Web-based Utility, Internet connection can also be set up
using the Setup Wizard, located on the Network screen of the Basic Setup tab. This wizard will walk you through
the steps necessary to set up your Internet connection.
1. Click the Setup Wizard button on the Network screen to run the Setup Wizard to quickly set up the Router’s
Internet access.
Figure E-1: Basic Setup Tab - Network
2. The first screen to appear will ask for a Host and Domain name. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) may
require this information. If your ISP requires them, enter the Host Name and Domain Name in the fields
provided. Click Next to continue. Click Previous if you want to return to the previous screen. Click Exit if you
want to exit the wizard.
Appendix E: The Setup Wizard
Figure E-2: Enter Host and Domain Names
51
Page 58

Broadband Router
3. From the next screen, choose your WAN (or Internet) connection type. Obtain an IP automatically is chosen
by default. Click Next to continue. Click Previous if you want to return to the previous screen. Click Exit if you
want to exit the wizard.
Figure E-3: Select WAN connection Type
4. The next screen that appears depends on your Internet Connection Type.
If you chose Obtain an IP automatically, the Obtain an IP automatically screen appears. Select Use DNS
Server provided by ISP (default) or Use the Following DNS Server Addresses, if you want to enter a
specific IP. Click Next to continue. Click Previous if you want to return to the previous screen. Click Exit if you
want to exit the wizard.
Appendix E: The Setup Wizard
Figure E-4: Obtain an IP automatically
52
Page 59

Broadband Router
If you chose Static IP, the Static IP screen appears. Enter the Static IP, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway
provided by your ISP. Click Next to continue. Click Previous if you want to return to the previous screen. Click
Exit if you want to exit the wizard.
If you chose PPPoE, the PPPoE screen appears. Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Click Next to continue. Click Previous if you want to return to the previous screen. Click Exit if you want to
exit the wizard.
Figure E-5: Static IP
5. On the final screen, you can save your settings, if you don’t need to make any changes. Click Previous if you
want to return to the previous screen. Click Exit if you want to exit the wizard.
Appendix E: The Setup Wizard
Figure E-6: PPPoE
Figure E-7: Basic Setup Tab - Network
53
Page 60

Broadband Router
Appendix F: Windows Help
All Linksys networking products require Microsoft Windows. Windows is the most used operating system in the
world and comes with many features that help make networking easier. These features can be accessed through
Windows Help and are described in this appendix.
TCP/IP
Before a computer can communicate with the Router, TCP/IP must be enabled. TCP/IP is a set of instructions, or
protocol, all PCs follow to communicate over a wired or wireless network. Your PCs will not be able to utilize
networking without having TCP/IP enabled. Windows Help provides complete instructions on enabling TCP/IP.
Shared Resources
If you wish to share printers, folders, or files over your network, Windows Help provides complete instructions on
utilizing shared resources.
Network Neighborhood/My Network Places
Other PCs on your network will appear under Network Neighborhood or My Network Places (depending upon the
version of Windows you're running). Windows Help provides complete instructions on adding PCs to your
network.
Appendix F: Windows Help
54
Page 61

Broadband Router
Appendix G: Glossary
Adapter - A device that adds network functionality to your PC.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given device or network.
Bit - A binary digit.
Boot - To start a device and cause it to start executing instructions.
Broadband - An always-on, fast Internet connection.
Browser - An application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the information on the
Internet.
Byte - A unit of data that is usually eight bits long
Cable Modem - A device that connects a computer to the cable television network, which in turn connects to the
Internet.
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) - Allows the hosting of a website, FTP server, or e-mail server with a
fixed domain name (e.g., www.xyz.com) and a dynamic IP address.
Default Gateway - A device that forwards Internet traffic from your local area network.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A networking protocol that allows administrators to assign
temporary IP addresses to network computers by "leasing" an IP address to a user for a limited amount of time,
instead of assigning permanent IP addresses.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) - Removes the Router's firewall protection from one PC, allowing it to be "seen" from
the Internet.
DNS (Domain Name Server) - The IP address of your ISP's server, which translates the names of websites into IP
addresses.
Domain - A specific name for a network of computers.
Download - To receive a file transmitted over a network.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - An always-on broadband connection over traditional phone lines.
Appendix G: Glossary
55
Page 62

Broadband Router
Dynamic IP Address - A temporary IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
Ethernet - A network protocol that specifies how data is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission
medium.
Firewall - A set of related programs located at a network gateway server that protects the resources of a
network from users from other networks.
Firmware - The programming code that runs a networking device.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - A protocol used to transfer files over a TCP/IP network.
Full Duplex - The ability of a networking device to receive and transmit data simultaneously.
Gateway - A device that interconnects networks with different, incompatible communications protocols.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single line, but only one direction at a
time.
Hardware - The physical aspect of computers, telecommunications, and other information technology devices.
HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol) - The communications protocol used to connect to servers on the Internet.
IP (Internet Protocol) - A protocol used to send data over a network.
IP Address - The address used to identify a computer or device on a network.
IPCONFIG - A Windows 2000 and XP utility that displays the IP address for a particular networking device.
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) - A VPN protocol used to implement secure exchange of packets at the IP layer.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet.
LAN - The computers and networking products that make up your local network.
MAC (Media Access Control) Address - The unique address that a manufacturer assigns to each networking
device.
mIRC - An Internet Relay Chat program that runs under Windows.
NAT (Network Address Translation) - NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a different
IP address for the Internet.
Appendix G: Glossary
56
Page 63

Broadband Router
Network - A series of computers or devices connected for the purpose of data sharing, storage, and/or
transmission between users.
Node - A network junction or connection point, typically a computer or work station.
Packet - A unit of data sent over a network.
Ping (Packet INternet Groper) - An Internet utility used to determine whether a particular IP address is online.
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) - A standard mail server commonly used on the Internet.
Port - The connection point on a computer or networking device used for plugging in cables or adapters.
PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - A type of broadband connection that provides authentication
(username and password) in addition to data transport.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) - A VPN protocol that allows the Point to Point Protocol (PPP) to be
tunneled through an IP network. This protocol is also used as a type of broadband connection in Europe.
Router - A networking device that connects multiple networks together.
Server - Any computer whose function in a network is to provide user access to files, printing, communications,
and other services.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - The standard e-mail protocol on the Internet.
SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection) Firewall - A technology that inspects incoming packets of information before
allowing them to enter the network.
Static IP Address - A fixed address assigned to a computer or device that is connected to a network.
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path.
Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network.
Switch - 1. A data switch that connects computing devices to host computers, allowing a large number of
devices to share a limited number of ports. 2. A device for making, breaking, or changing the connections in an
electrical circuit.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that requires acknowledgement
from the recipient of data sent.
Appendix G: Glossary
57
Page 64

Broadband Router
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) - A set of instructions PCs use to communicate over a
network.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol that has no directory or password
capability.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) - A network protocol for transmitting data that does not require acknowledgement
from the recipient of the data that is sent.
Upgrade - To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) - The address of a file located on the Internet.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) - A security measure to protect data as it leaves one network and goes to another
over the Internet.
WAN (Wide Area Network)- The Internet.
WINIPCFG - A Windows 98 and Me utility that displays the IP address for a particular networking device.
Appendix G: Glossary
58
Page 65

Broadband Router
Appendix H: Specifications
Standards IEEE 802.3, 802.3u
Ports Power, Internet, and Ethernet
Button Reset
Cabling Type Cat-5
LEDs Ethernet, Internet1, Internet2, Diag, and System
UPnP able/cert able
Security Features SPI, port, MAC, IP filter
Dimensions 6.69" x 6.69" x 1.26"
(W x H x D) (170 mm x 170 mm x 32 mm)
Unit Weight 11.29 oz. (3.32 kg)
Power 3.3V 2.5A
Certifications FCC
Operating Temp. 0ºC to 40ºC (32ºF to 104ºF)
Storage Temp. 0ºC to 70ºC (32ºF to 158ºF)
Operating Humidity 10% to 85% Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 5% to 90% Non-Condensing
Appendix H: Specifications
59
Page 66

Broadband Router
Appendix I: Warranty Information
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys warrants to You that, for a period of one year (the “Warranty Period”), your Linksys Product will be substantially
free of defects in materials and workmanship under normal use. Your exclusive remedy and Linksys' entire liability under
this warranty will be for Linksys at its option to repair or replace the Product or refund Your purchase price less any
rebates. This limited warranty extends only to the original purchaser.
If the Product proves defective during the Warranty Period call Linksys Technical Support in order to obtain a Return
Authorization Number, if applicable. BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING. If You are
requested to return the Product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside of the package and include a
copy of your original proof of purchase. RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE. You
are responsible for shipping defective Products to Linksys. Linksys pays for UPS Ground shipping from Linksys back to You
only. Customers located outside of the United States of America and Canada are responsible for all shipping and handling
charges.
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE LIMITED
TO THE DURATION OF THE WARRANTY PERIOD. ALL OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED. Some jurisdictions do not
allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts, so the above limitation may not apply to You. This warranty gives
You specific legal rights, and You may also have other rights which vary by jurisdiction.
This warranty does not apply if the Product (a) has been altered, except by Linksys, (b) has not been installed, operated,
repaired, or maintained in accordance with instructions supplied by Linksys, or (c) has been subjected to abnormal
physical or electrical stress, misuse, negligence, or accident. In addition, due to the continual development of new
techniques for intruding upon and attacking networks, Linksys does not warrant that the Product will be free of
vulnerability to intrusion or attack.
TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL LINKSYS BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST DATA, REVENUE OR PROFIT,
OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES, REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF
LIABILITY (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE PRODUCT
(INCLUDING ANY SOFTWARE), EVEN IF LINKSYS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
WILL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE AMOUNT PAID BY YOU FOR THE PRODUCT. The foregoing limitations will apply even
if any warranty or remedy provided under this Agreement fails of its essential purpose. Some jurisdictions do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to You.
Please direct all inquiries to: Linksys, P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
Appendix I: Warranty Information
60
Page 67

Broadband Router
Appendix J: Regulatory Information
FCC Statement
This product has been tested and complies with the specifications for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used according to the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the equipment off and on,
the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver's
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator and your body.
Industry Canada (Canada)
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
The use of this device in a system operating either partially or completely outdoors may require the user to obtain
a license for the system according to the Canadian regulations.
Appendix J: Regulatory Information
61
Page 68

Broadband Router
Appendix K: Contact Information
Need to contact Linksys?
Visit us online for information on the latest products and updates
to your existing products at: http://www.linksys.com or
ftp.linksys.com
Can't find information about a product you want to buy
on the web? Do you want to know more about networking
with Linksys products? Give our advice line a call at: 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Or fax your request in to: 949-823-3002
If you experience problems with any Linksys product,
you can call us at: 800-326-7114
Don't wish to call? You can e-mail us at: support@linksys.com
If any Linksys product proves defective during its warranty period,
you can call the Linksys Return Merchandise Authorization
department for obtaining a Return Authorization Number at: 949-823-3000
(Details on Warranty and RMA issues can be found in the Warranty
Information section in this Guide.)
Appendix K: Contact Information
62
 Loading...
Loading...