Page 1

EtherFast®Layer 3 Management
4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Use this guide to install:
EF1704
User Guide
Instant EtherFast®Series
Page 2

COPYRIGHT & TRADEMARKS
Copyright © 2002 Linksys, All Rights Reserved. EtherFast, Linksys, and the Linksys logo
are registered trademarks of Linksys. Microsoft, Windows, and the Windows logo are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other trademarks and brand names
are the property of their respective proprietors.
LIMITED WARRANTY
Linksys guarantees that every EtherFast®Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet
Switch is free from physical defects in material and workmanship under normal use for
FIVE years from the date of purchase, when used within the limits set forth in the
Specifications chapter of this User Guide. If the product proves defective during this warranty period, call Linksys Technical Support in order to obtain a Return Authorization
Number . BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF PURCHASE.
When returning a product, mark the Return Authorization Number clearly on the outside
of the package and include a copy of your original proof of purchase. All customers outside of the United States of America and Canada shall be held responsible for shipping
and handling charges.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’ LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT ISSUE REFUNDS. WARRANTY
DOES NOT COVER NATURAL DISASTERS OR ACTS OF NATURE.
Linksys makes no warranty or representation, expressed, implied, or statutory, with
respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for any particular purpose. Linksys reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity.
Please direct all inquiries to:
Linksys P.O. Box 18558, Irvine, CA 92623.
FCC STATEMENT
The EtherFast
®
Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch has been tested and
found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used according to the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, ther e is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which is found by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment or devices
• Connect the equipment to an outlet other than the receiver’s
• Consult a dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for assistance
UG-EF1704-110602NC KL
EC Declaration of Conformity (Europe)
In compliance with the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC, Low Voltage Dir ective 73/23/EEC, and
Amendment Directive 93/68/EEC, this product meets the requirements of the following
standards:
• EN55022 Emission
• EN55024 Immunity
Industry Canada (Canada)
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe (B) est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Page 3

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Appendix A: Troubleshooting 105
Common Problems and Solutions 105
Appendix B: Upgrading Firmware via the Serial Port106
Appendix C: Installing the Fiber Module 108
Appendix D: Glossary 109
Appendix E: Specifications 115
Environmental 116
Appendix F: Warranty Information 117
Appendix G: Contact Information 118
Instant EtherFast®Series
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
The EtherFast Layer 3 Management
4-Port 10/100 Gigabit Ethernet Switch 1
Features 1
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the Switch 2
LEDs 2
The RJ-45 Ports 3
The Gigabit Ports 3
The Console Port 3
Chapter 3: Installing the Switch 4
Pre-Installation Considerations 4
Rack-Mounting the Switch 5
Powering on the Switch 5
Uplinking the Switch 5
Chapter 4: Switch Management 6
Chapter 5: Connecting the Serial Cable
to the Switch and Computer 10
Chapter 6: Configuring the Switch
Using the Console Interface 11
Overview 12
Logging On to the Switch 12
Main Menu 12
System Information Menu 13
Management Setup Menu 16
Device Control Menu 28
Network Monitor Menu 74
System Restart Menu 103
Exit 104
Page 4

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
2
Instant EtherFast®Series
Chapter 1: Introduction
Migrate your network to Gigabit speed with the EtherFast Layer 3 Management
4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch. Perfect for today's large-scale network
demands, this switch from Linksys delivers Layer 3 switching and blazing
Gigabit transfer speeds for all your network applications.
Layer 3 switches route packets based on IP address, so unlike standard (Layer
2) switches, they can link different subnets without the need for a router, at
much higher speed, and much lower cost. Use the EtherFast 1704 Switch as
your network's backbone, and connect y our servers' dif ferent subnets at Gigabit
speeds. The four built-in auto MDI/MDI-X ports deliver 8Gbps of non-blocking switching performance. And as your needs grow, add Gigabit Ethernet or
Gigabit Fiber ports using the four available expansion slots.
The EtherFast 1704 Switch provides broadcast storm suppression, has hardware MAC and IP address learning, and supports packet filtering and port
security. Partition your network into up to 256 VLANs, using port-based
802.1q tagging. Configuration and monitoring network performance is a snap
using the Web management interface, console, telnet, or SNMP/RMON.
This expandable, managed switch is the perfect solution for y our Gigabit enterprise backbone.
• 4 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet ports
• 4 Expansion slots for optional Gigabit Ethernet or Gigabit Fiber Modules
(EFPC2SC, and EFPC2GE)
• Auto MDI/MDI-X on the 4 10/100/1000 Ethernet Ports
• Supports half duplex and full duplex modes for all 10/100/1000BaseTX
ports
• Provides 8Gbps non-blocking switching performance
• Full wire-speed Layer 3 IP Switching
• Provides broadcast storm suppression
• MAC address learning and aging
• Support for up to 256 Port-Based VLANs
• Support up to 9K jumbo frame packet
The EtherFast®Layer 3 Management
4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Features
Chapter 2: Getting to Know the
Switch
Information about the Switch’s activity is displa y ed through its LEDs, shown in
Figure 2-1.
Fan (Green) The LED will illuminate when a fan has failed.
TEMP (Green) The LED will illuminate w hen the s witch is o v erheating.
Power (Green) The LED will illuminate w hen the s witch is powered on.
1000/100/10 Each port (1-4) has three separate LEDs designating the speed at
which the port is transmitting data. When transmitting at 1000
Mbps or 100 Mbps, the corresponding green LED will illuminate. When transmitting at 10 Mbps, the corresponding yellow
LED with illuminate.
PER PORT
FDX (Yellow) The LED will illuminate when there are ports operating
in full-duplex mode.
Act (Green) The LED will illuminate when there are active ports.
LEDs
Figure 2-1
1
Page 5

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Chapter 3: Installing the Switch
Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Considerations
If you will be using the Switch for Fast Ethernet (100Mbps) or Gigabit
(1000Mbps) applications, you must observe this guideline:
The maximum UTP cabling length using Category 5 cable is 328 feet (100m).
Full-Duplex Considerations
As previously mentioned, the Switch provides full-duplex support for its RJ-45
ports. Full-duplex operation allows data to be sent and received simultaneously, doubling a port’s potential data throughput.
If you will be using the Switch in full-duplex mode, the maximum UTP cable
length using Category 5e (or better) cable is 328 feet (100 m).
Positioning the Switch
Before you choose a location for the Switch, observe the following guidelines:
• Keep cabling away from sources of electrical noise, power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures.
• Position the Switch away from water and moisture sources.
• To ensure adequate air flow around the Switch, be sure to provide a
minimum of one inch (25 mm) clearance.
• Do not stack free-standing Switches more than four units high.
4
Instant EtherFast®Series
3
Pre-Installation Considerations
The Switch is equipped with four 10/100/1000 RJ-45 ports, shown in Figure 2-
2. These RJ-45 ports support network speeds of 10/100 Mbps half-duplex and
20/200 Mbps full duplex Ethernet and Fast Ethernet speeds as well as up to
2000 Mbps Gigabit speed. Auto-sensing technology enables each port to automatically detect the speed of the device connected to it, and adjust its speed and
duplex accordingly.
T o connect a de vice to a
port, you will need to
use a network cable. If
you are using
100BaseTX devices
you will need to use
UTP Category 5 (or
better) cable. Gigabit
devices require UTP
Category 5e cable (or
better).
The Switch is equipped with four Gigabit-module ports. These ports allow you
to add four high-speed ports, transmitting at speeds of up to 1000Mbps
(Gigabit Ethernet).
The Switch is equipped with a RS-232 serial port (located on the rear of the
Switch, as shown in Figure 2-3) that allows you to connect to a computer (for
configuration pur poses) using the provided serial cable.
The RJ-45 Ports
The Gigabit-module Ports
The Console Port
Figure 2-2
Figure 2-3
Page 6
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
6
Instant EtherFast®Series
5
Chapter 4: Switch Management
The Switch offers an easy-to-use, menu-driven configuration program. This
program can be accessed by a console interface, a Web browser, a telnet connection, or SNMP/RMON. Using this configuration program, you can perform
various switch configuration and management activities, including:
• Enable/disable any port
• Set the communication mode for any port
• Configure SNMP parameters
• Add ports to network VLANs
• Create and manage VLAN Configurations
Local Console Management
You can manage the Switch locally using HyperTerminal; simply connect the
Switch to a PC or workstation through the serial port.
The serial port settings need to be configured before connecting to the Switch.
In order to change the settings of your port, run the HyperTerminal program.
This program comes packaged with Windows, but it may not be installed on
your computer. It should be located as is shown below (varies according to
operating system). If it is not, consult your Windows documentation for
instructions on installing HyperTerminal.
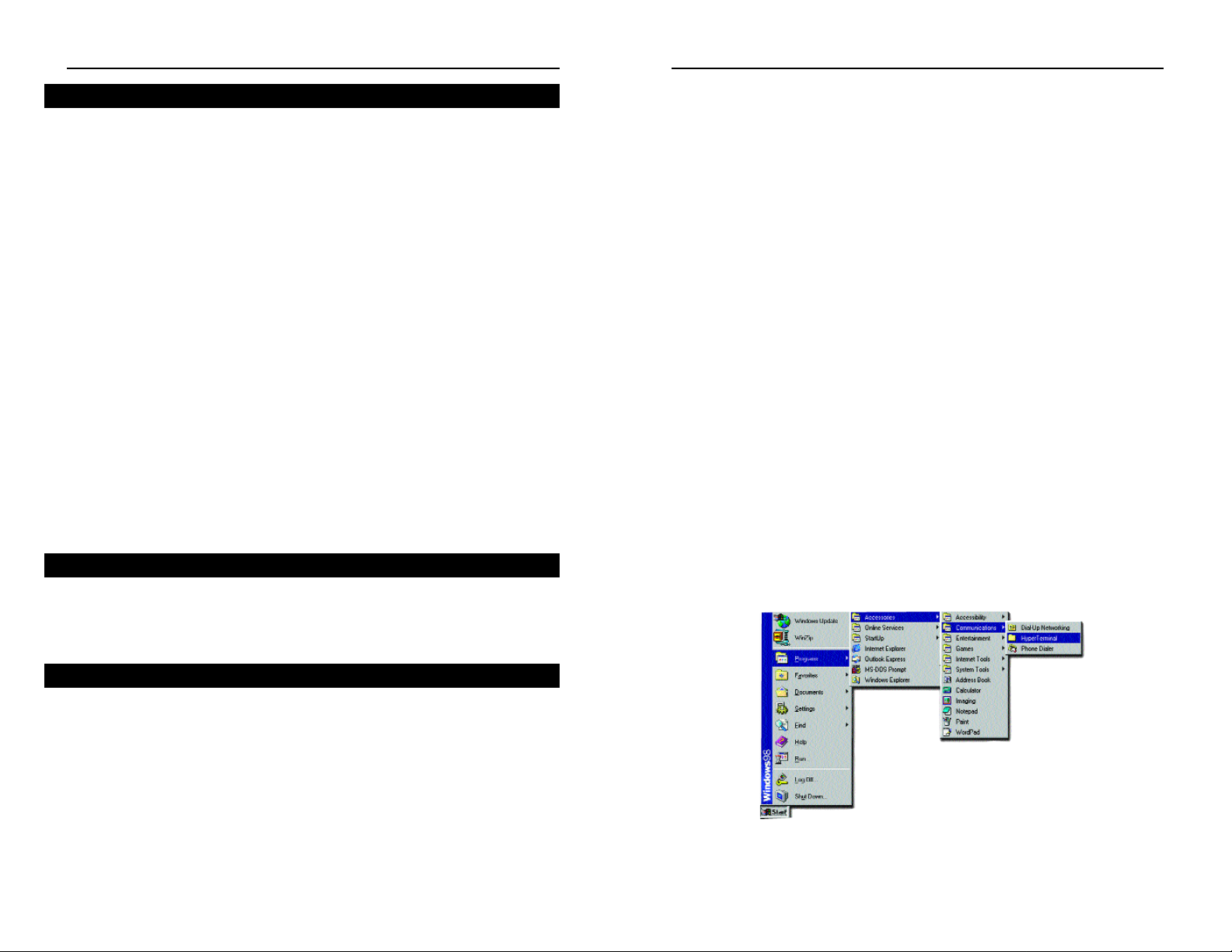
1. Click the Start button. Select Accessories and then Communications.
Hyperterminal should be one of the options listed in this menu. Select
HyperTerminal, as shown in Figure 4-1.
The Switch can be used as a free-standing unit, or installed in any standard 19inch rack.
Use the following instructions to rack-mount the Switch:
Before you begin, disconnect all cables from the Switch.
1. Place the Switch right side up, with the front panel facing you.
2. Position a mounting bracket over the screw holes on one side of the Switch.
3. Secure the mounting bracket by inserting three screws into the screw holes.
Use a screwdriver to tighten the screws, ensuring that they are fastened
fir mly in place.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 to install the other mounting bracket on the opposite
side of the Switch.
5. Insert the Switch into the 19-inch rack and secure it with suitable screws
(not provided). Ensure that the ventilation holes are not obstructed.
The rack-mount installation is complete.
You can now re-connect the cables to the Switch.
To power on the Switch, simply connect the AC power cord to the back of the
Switch, and then plug the power cord into an electrical outlet. The Switch will
boot up within approximately 30 seconds.
Any of the Switch’s ports can act as an uplink port, allowing you to uplink to
other switches or hubs using a standard Ethernet connection. UTP Category 5e
(or better) cable is recommended when using the Gigabit ports.
To uplink the switch, connect one end of a network cable into the Switch, and
then connect the other end of the cable into the desired network device’s uplink
port.
Rack-Mounting the Switch
Powering on the Switch
Uplinking the Switch
Figure 4-1
Page 7
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
8
Instant EtherFast®Series
2. The following screen will appear. Enter a Name for this connection. In the
example shown in F igure 4-2, the name of the connection is EF1704. Click
the OK button.
3. The screen shown in
Figure 4-3 will appear.
In the bottom drop down
box labeled Connect
using:, click the arrow
and choose the COM
port that the Switch will
be connected to. In the
example below, COM1
is the port selected.
Click the OK button.
7
4. When the screen shown in Figure 4-4 appears, make sure that the port settings are as follows:
BAUD RATE: 19200
DATA BITS: 8
PARITY: None
STOP BITS: 1
FLOW CONTROL: None
Click the OK button.
Web Management
The IP address is already conf igured on the Switch by default. Use a standard
Web browser (Internet Explorer 4.0 or above, or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or
above is suggested) from an y computer attached to the netw ork. The Switch has
a default IP address of 192.168.1.254 and a default subnet address of
255.255.255.0.
Figure 4-2
Figure 4-4
Figure 4-3
Page 8

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Chapter 5: Connecting the
Serial Cable to the Switch and
Computer
To enable communications with the Switch, the serial cable must be connected
between the Switch and the computer.
1. Make sure both the Switch and the computer are powered down.
2. Plug one end of the serial cable into the console port of the Switch.
3. Plug the other end of the serial cable into the COM1 port on the back panel
of your computer.
4. Tur n on the Switch and computer.
The serial cable connection is complete.
You can now configure the Switch.
10
Instant EtherFast®Series
9
Telnet Management
Use telnet from any computer attached to the network. You can telnet into the
Switch at any time.
SNMP/RMON Management
SNMP/RMON management is available; you can manage the Switch from any
network computer using network management software. You must have a
TCP/IP connection to the Switch in order to use it.
NNoottee::
The Switch’s configuration program only provides access
to basic configuration functions. To access the full range of
SNMP management functions, you must use SNMP-based network management software.
Page 9
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
12
Instant EtherFast®Series
Chapter 6: Configuring the Switch
Using the Console Interface
The Switch’s menu-driven configuration program may be configured using the
console port, a Web browser, telnet, or SNMP/RMON. The remote management methods can be used once the IP parameters have been set via the local
console.
When logging on to the Switch, you will receive the following screen prompt:
User Name:
Password:
Enter the default user name, admin, in the User Name field (as shown in Figure
6-1, and press Enter. Do not enter anything for the Password, and press Enter.
When you select User Configuration from the Management Setup Menu, you
will be allowed to def ine a new administrator password.
11
After you log on to the Switch, the Main Menu screen, shown in Figure 6-2,
will appear.
The Main Menu screen consists of a series of options. Each option leads you to
the screen for that management setting. Highlighting any option selects it;
pressing the Enter key takes you to that screen.
To navigate through the Console Interface, use the Tab or arrow keys to move,
the Enter key to select, and the Esc key to return to the previous selection.
Scroll through choices using the spacebar. Options for the currently selected
item are displayed in the highlighted area at the bottom of the interface screen.
The text string in the top right corner of the screen shows if the Switch is operating as a Layer 2 switch or as a multilayer routing switch. The default is multilayer.
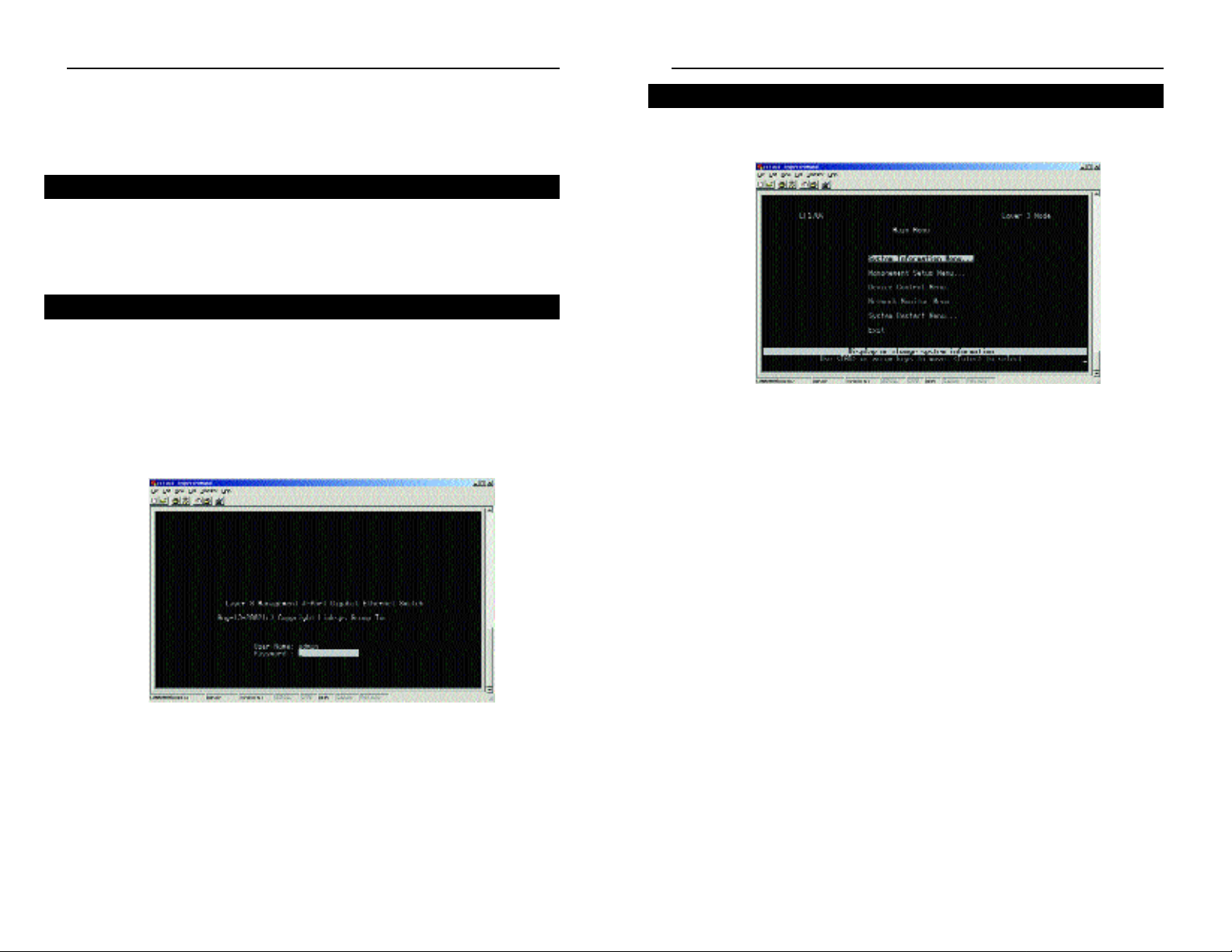
• System Information Menu - Displays a basic description of the switch,
including contact information, hardware and fir mware versions, uptime, and
location.
• Management Setup Menu - Configures the IP address for the Switch, seri-
al port settings for console management, SNMP parameters, and user privileges.
• Device Control Menu - Controls a broad range of functions, including port
mode, port mirroring, por t trunking, spanning tree, VLANs, IP subnets, multicast filtering, and routing protocols.
Main Menu
Overview
Logging On to the Switch
Figure 6-1
Figure 6-2
Page 10

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
14
Instant EtherFast®Series
• Network Monitor Menu - Provides access to por t statistics, RMON statis-
tics, address tables, VLAN registration and forwarding information, multicast
groups, and subnet addresses.
• System Restart Menu - Resets the management agent and allows you to
restore the Switch to its default conf iguration.
• Exit - Exits the program and terminates communications with the Switch for
the current session to restart your management session.
The System Information Menu, shown in Figure 6-3, displays a basic description of the Switch, including contact information and hardware and fir mware
versions.
• System Information - Provides basic system descriptions, including contact
information, uptime, system name, location, and system object ID.
• Switch Information - Shows hardware and firmware version numbers,
power status, Gigabit port usage of the Switch, number of ports, fan power
status, and serial number (this information cannot be changed).
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
13
System Information
The System Information screen, shown in Figure 6-4, displays descriptive
information about the Switch or system.
• System Description - System hardware description:
• System Object ID - MIB II object identif ier for the Switch’s network man-
agement subsystem.
• System Up T ime- Length of time the Switch has been running. Note that the
first value is in centiseconds.
• System Name* - Name assigned to the switch system. (By default, this field
is blank.)
• System Contact* - Contact person for the system. (This is usually the sys-
tem administrator.)
• System Location* - Specifies the area or location where the system resides.
* The maximum string length is 99, but the screen only displays 45 characters.
You can use the arrow keys to browse the entire string.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
System Information Menu
Figure 6-3
Figure 6-4
Page 11
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
16
Instant EtherFast®Series
15
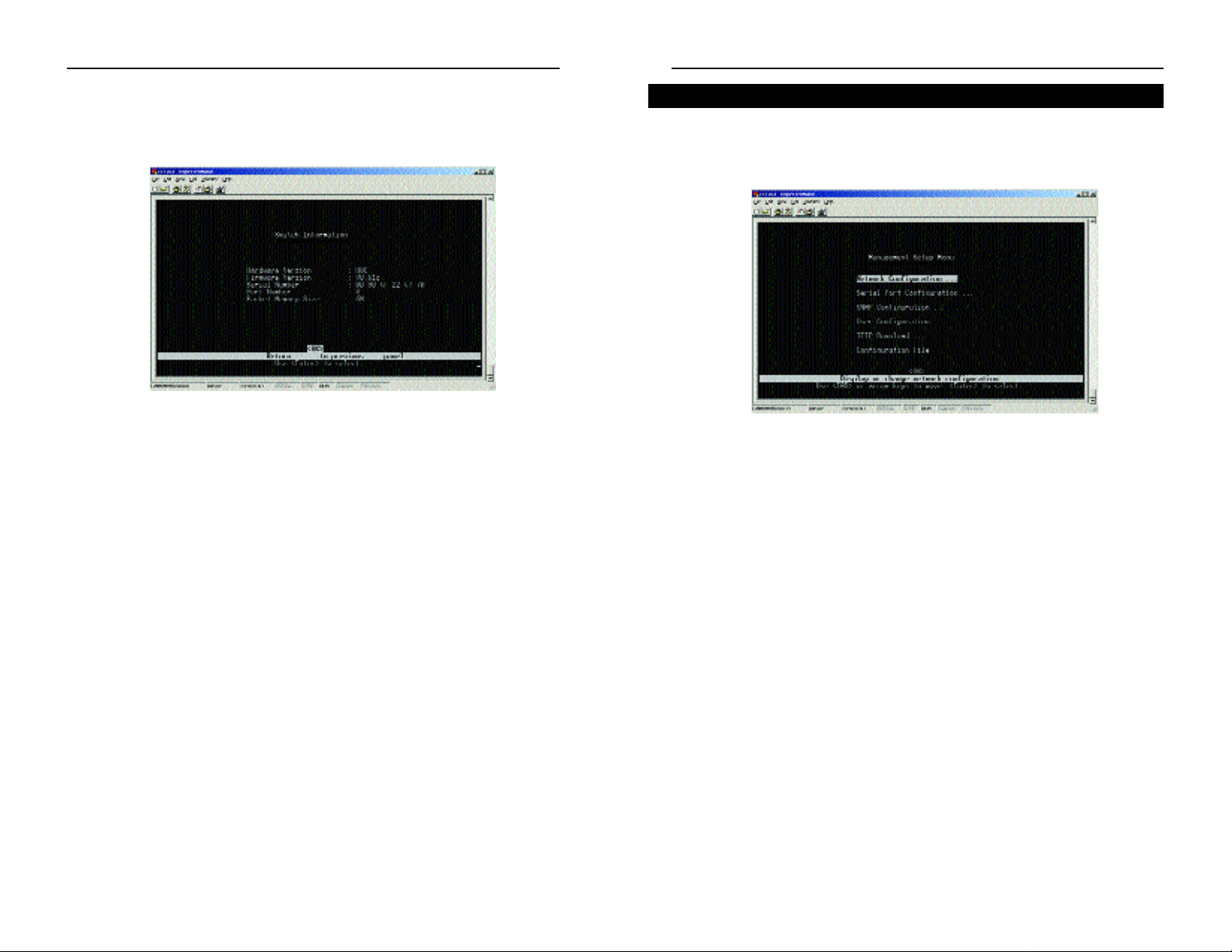
The Management Setup Menu screen, shown in Figure 6-6, allows you to configure the IP address for the Switch, serial port settings for console management, SNMP parameters, and user privileges.
• Network Configuration - Includes IP setup, ping facility, and HTTP setup
for the on-board Web agent.
• Serial Port Configuration - Sets communication parameters for the serial
port, including baud rate, console time-out, and screen data refresh interval.
• SNMP Configuration - Activates authentication failure traps and configures
communities and trap managers.
• User Configuration - Sets the user names and passwords for system access.
• TFTP Download - Downloads new version of firmware to update your sys-
tem.
• Configuration File - Allows downloading of a configuration file.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Management Setup Menu
Switch Information
The Switch Information screen, shown in Figure 6-5, displays hardware and
fir mware version numbers for the main board, as well as the power status.
• Hardw are Version - Hardware version of the main board.
• Firmware Version - System firmware version in ROM.
• Serial Number - Serial number of the main board (MAC address of the
Switch).
• Port Number - Number of ports available on this Switch.
• Packet Memory Size - Shows the amount of memory the Switch has for
packet buffering.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Figure 6-5
Figure 6-6
Page 12

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
18
Instant EtherFast®Series
17
IP Connectivity Test (Ping)
The IP Connectivity Test, shown in Figure 6-8, is used to see if another site
or node on the network can be reached.
•
IP
Address - IP address of the device you want to ping.
•Test Times - The number of ICMP echo requests to send to the specified
site. Range varies from 1 to 1000.
•Success/Failure - The number of times the specified site has responded—
or not—to a ping request.
Note: There is a 10-second interval between pings.
Select Start to begin the test. Select Cancel to cancel the test.
Network Configuration
The Network Configuration menu, shown in Figure 6-7, allows you to test IP
connectivity with other nodes on your network or enable the on-board Web
management.
• IP Connectivity T est (Ping) - Tests IP connectivity to a specified device. You
can plug in a workstation on the network to check for connectivity.
• HTTP Configuration - Allows the admin to enable or disable the Web
administration feature of the Switch.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Figure 6-7
Figure 6-8
Page 13

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
20
Instant EtherFast®Series
19
Serial Port Configuration
The Serial Port Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-10, allows you to
access the communication parameters for the Switch’s serial port. (Linksys recommends that you do not change the default settings.)
• Baud Rate - The rate at w hich data is sent betw een de vices. Default is 19200.
Options are 9600, 19200, and 38400 baud.
• Data Bits - Sets the data bits of the RS-232 port. Options are 7 and 8.
• Stop Bits - Sets the stop bits of the RS-232 port. Options are 1 and 2.
• Parity - Sets the parity of the RS-232 port. Default is None. Options are none,
odd, and even.
• Time-Out - If no input is received from the attached device after this inter-
val, the current session is automatically closed. Default is 10 minutes. The
range is 0 to 100 minutes, where 0 indicates disabled.
• Auto Refr esh- Sets the interval before a console session will auto refresh the
console information, such as Spanning Tree Information, Port Configuration,
Port Statistics, and RMON Statistics. Default is 1 second. The range is 0, or
5 to 255 seconds, where 0 indicates disabled.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
HTTP Configuration
The HTTP Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-9, allows you to enable
or disable Web management.
Note: Port 80 is used for HTTP service.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Figure 6-9
Figure 6-10
Page 14

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
22
Instant EtherFast®Series
21
SNMP Communities
The SNMP Communities screen, shown in Figure 6-12, allows you to configure the community strings authorized for management access. Up to five
community names may be entered.
•Community Name - A community entry authorized for management
access. Maximum string length is 19 characters.
•Access - Management access is restricted to Read Only or Read/Write.
•Status - Sets administrative status of entry to enabled or disabled.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
SNMP Configuration
The SNMP Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-11, displays parameters
for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
• Send Authentication Fail Traps - Issue a trap message to a specified IP trap
managers whenever authentication of an SNMP request fails. Default is
enabled.
• SNMP Communities - Assigns SNMP access based on specified strings.
• IP Trap Managers - Specifies management stations that will receive authen-
tication failure messages or other trap messages from the Switch.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Figure 6-11
Figure 6-12
Page 15
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
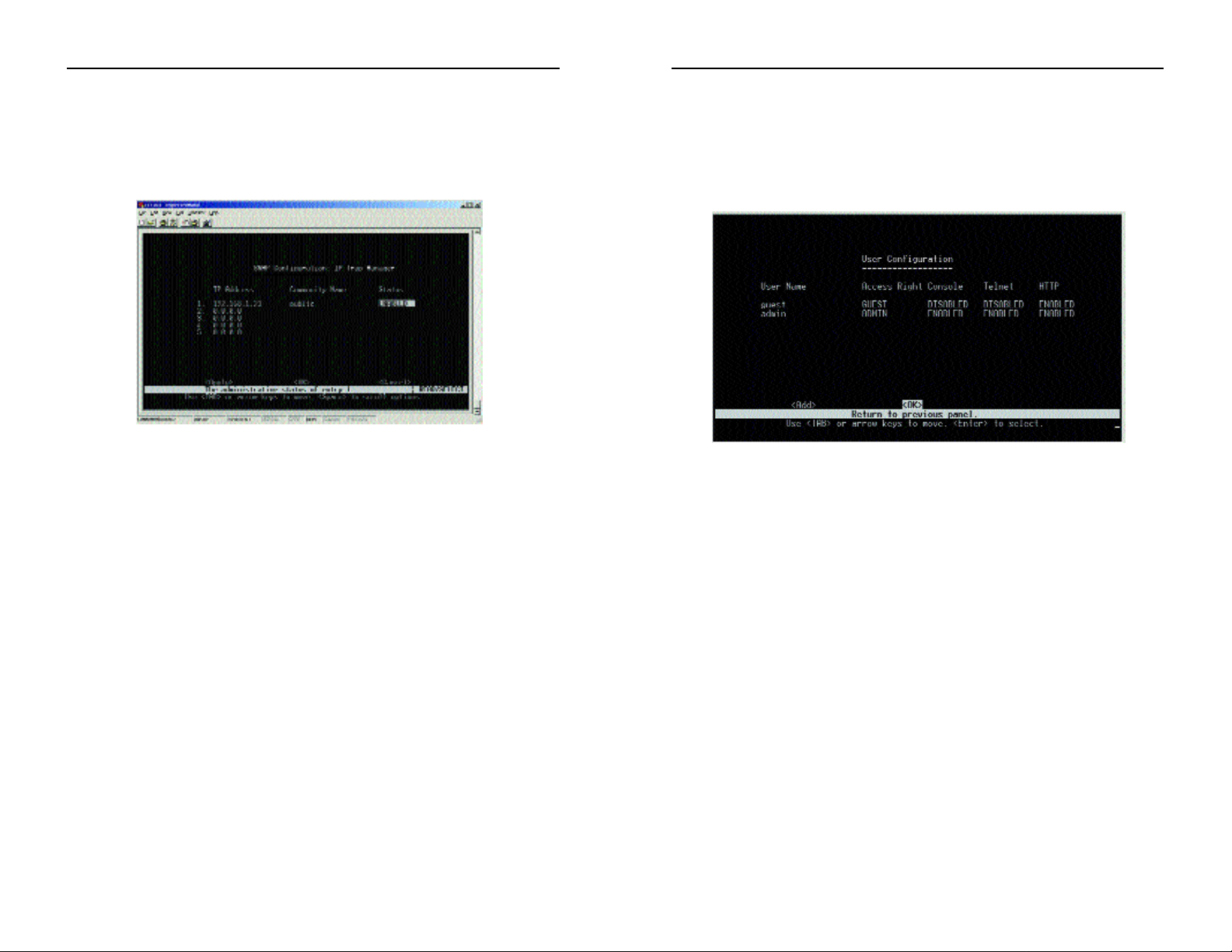
User Configuration
The User Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-14, can be used to restrict
management access based on specified user names and passwords. There are
two user types, Administrator and Guest. Only the Administrator has write
access for parameters governing the SNMP agent.
•User Name - Specifies user authorized management access to the
Switch via the console, telnet, or the Web.
•Access Right - ADMIN: Read/Write for all screens.
GUEST: Read Only for all screens.
•Console - Enables and Disables management via the console.
•Telnet - Enables and Disables management via a telnet connection.
•HTTP - Enables and Disables management via HTTP, e.g., a Web brows-
er.
Select Add to add a user. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
24
Instant EtherFast®Series
23
IP Trap Manager
The IP Trap Manager screen, shown in Figure 6-13, specif ies management
stations that will receive authentication failure messages or other trap messages from the Switch. Up to five trap managers may be entered.
•IP Address - IP address of the trap manager.
•Community Name - A community specified for trap management
access.
• Status - When Enabled, trap messages will be sent to the specified IP
Address.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Figure 6-13
Figure 6-14
Page 16

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
TFTP Download
The TFTP Download screen, shown in Figure 6-16, lets you load software
updates to permanent flash ROM in the Switch. After downloading the new
software, the agent will automatically restart itself. You must be running a
TFTP server on your network to use the TFTP Download feature.
•Download Server IP - IP address of the TFTP ser ver on your network.
•Download Filename - The binary file to download.
•Download Option - You may choose either Runtime Code or Post
Code.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
26
Instant EtherFast®Series
Add User
The Add User screen, shown in Figure 6-15, allows you to add a user.
•User Name - Specif ies user authorized management rights/access to the
Switch via the console, telnet, or the Web.
•Password - Sets up the password for the new user.
•Access Right - ADMIN: Read/Write for all screens.
GUEST: Read Only for all screens.
•Console Access - Authorizes management via the console.
•Telnet Access - Authorizes management via a telnet connection.
•HTTP Access - Authorizes management via HTTP, e.g., a Web browser.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
25
Figure 6-15
Figure 6-16
Page 17

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The Device Control Menu, shown in Figure 6-18, is used to control a broad
range of functions, including port mode, port mirroring, port trunking,
Spanning Tree, VLANs, IP subnets, multicast filtering, and routing protocols.
Note: This screen shots shows the Device Control Menu displayed by a multilayer switch.
• Layer 2 Menu - Configures port communication mode, mir ror ports, and
port trunking.
• Bridge Menu - Configures the Spanning Tree Protocol for the bridge or for
specific por ts, GMRP and GVRP for automatic registration of multicast and
VLAN groups, traffic class priority threshold, and address aging time.
• VLAN Menu - Configures VLAN settings for specific por ts and defines the
port membership for VLAN groups.
• IP Menu - Conf igures the subnets for each VLAN group, global conf igura-
tion for unicast and multicast routing protocols, and IGMP snooping. (Only
displayed for multilayer mode)
• Security Menu - Conf igures security settings.
• Jumbo Packet Menu - Allows the administrator to configure the default
packet size sent and received by the Switch.
28
Device Control Menu
Instant EtherFast®Series
Configuration File
The Configuration File screen, shown in Figure 6-17, allows you to load a configuration file on any Switch on the network.
•Station IP - IP address of the Switch you want the configuration f ile to
be sent to.
•Operation - Gives you the choice of downloading the configuration f ile
from your Switch.
Download from switch - Downloads the current switch configuration to a file on the client PC.
Upload to switch - Uploads a configuration f ile to the Switch from
the client PC.
Select Start to begin the download. Select Cancel to cancel the download.
27
Figure 6-17
Figure 6-18
Page 18

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
30
Instant EtherFast®Series
Layer 2 Menu
The Layer 2 Menu, shown in Figure 6-19, contains options for port configuration, port mirroring, and por t trunking.
•Port Configuration - Enables any port, enables/disables flow control,
and sets communication mode to auto-negotiation, full duplex, or half
duplex.
•Mirror Port Configuration - Sets the source and target ports for mir-
roring.
•Port Trunking Configuration - Specif ies ports to group into aggregate
trunks.
•Static Unicast Address Configuration - Used to manually configure
host MAC addresses in the unicast table.
•Static Multicast Address Configuration - Used to manually configure
host MAC addresses in the multicast table.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
29
Port Configuration
The Port Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-20, lets you displa y or set
communication parameters for any port on the Switch, including administrative status, auto-negotiation, default communication speed and duplex
mode, as well as flow control in use.
•Port (#) - Number of the port.
•Link Status - Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an
external device.
•Admin Status - Allows you to enable or disable administrative rights per
port.
•Auto Negotiate - Enables or disables auto-negotiation for port speed,
duplex mode, and flow control.
•Default Type - If auto-negotiation is disabled, the port will be set to the
indicated speed and duplex mode.
•Current T ype - Indicates the current speed and duplex mode of each port.
Port Configuration
•Flow Control - Used to enable or disable flow control under the “Config”
heading. Flow control can eliminate frame loss by “blocking” traffic from
end stations or segments connected directly to the Switch when its buffers
fill. When enabled, back pressure is used for half duplex and IEEE 802.3x
for full duplex.
Note: Flow control should not be used (set to OFF under “Status”) if a port
is connected to a hub.
Figure 6-19
Figure 6-20
Page 19
EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
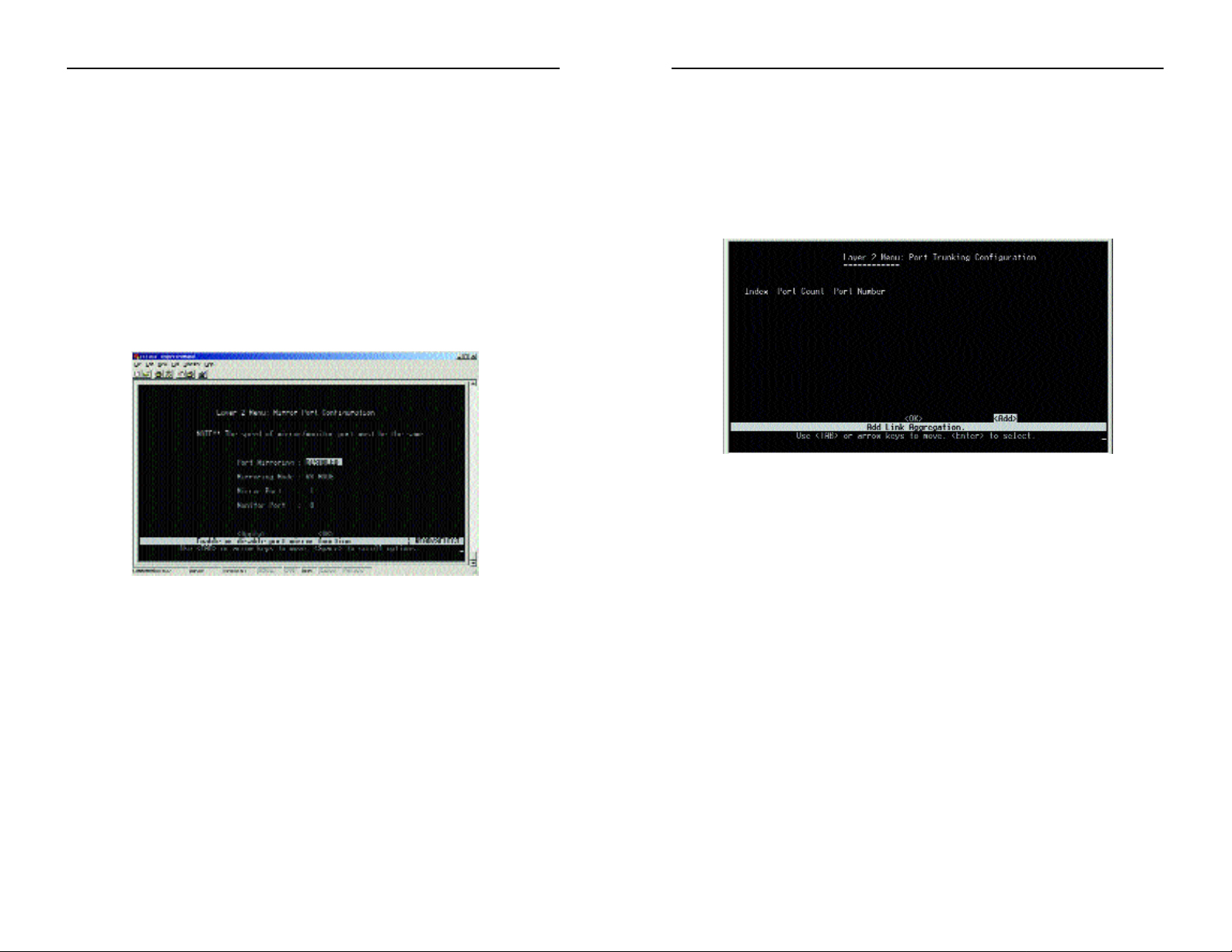
Port Trunking Configuration
From the screen shown in F igure 6-22, ports can be combined into an aggregate link to increase the bandwidth of a network connection or ensure fault
recovery. You can conf igure trunks between any two switches. The RJ-45
ports on this Switch can be grouped into a trunk consisting of two or four
creating an aggregate bandwidth up to 400 or 800Mbps when operating at
full duplex.
•Index - The trunk identif ier.
•Port Count - Trunks can contain two or four ports.
•Port Number - The ports assigned to each trunk.
Select OK to return to the previous panel. Select Add to add a trunk. To delete
a trunk group, highlight the trunk g roup and press the Enter key.
32
Instant EtherFast®Series
•Jack Type - Shows the jack type for each port. Ports 1-26 are RJ-45.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Pa ge to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page.
Mirror Port Configuration
The Mirror Port Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-21, allows you to
mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for real-time analysis.
You can then attach a logic analyzer or RMON probe to the target port and
study the traffic crossing the source port in a completely unobtrusive manner. When mirroring port traff ic, the target port must be included in the
same VLAN as the source port.
•Port Mirroring - Enables or disables the mirror function.
• Mirroring Mode - Allows you to set the port to RX_MODE for receive or
TX_Mode for transmit.
•Mirror Port (Tx/Rx) - The port whose transmitted or received traffic
will be mirrored.
•Monitor Port - The port that will duplicate the transmitted or received
traffic appearing on the mirrored por t.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Add to add a port.
31
Figure 6-21
Figure 6-22
Page 20

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add Static Address Entry
The Add Static Address Entr y screen, shown in Figure 6-24, allows you to
add static addresses for unicasting.
• Address - The MAC address of a host device attached to this Switch.
• Port - The switch port the host device is attached to.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
34
Instant EtherFast®Series
Static Unicast Address Configuration
The Static Unicast Address Table, shown in Figure 6-23, can be used to
assign the MAC address for a host device to a specific port on this Switch.
Static unicast addresses are never aged out, and cannot be learned on another port.
•Address - The MAC address of a host device attached to this Switch.
• VLAN - Shows when connected to a VLAN on this address.
•Port - The switch port the host device is attached to.
To assign a destination MAC address to one or more ports, use Add. To delete
or modify an address, highlight it with the cursor and press Enter. Select
Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel. Select Prev
Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To dis-
play a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then press
Apply.
33
Figure 6-23
Figure 6-24
Page 21

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add Multicast Address Entry
The Add Static Address Entr y screen, shown in Figure 6-26, allows you to
add static addresses for multicasting.
• VLAN - The VLAN corresponding to this multicast service.
• Address - The destination MAC address for a multicast ser vice.
• Port - The ports to which this multicast traff ic can be forwarded.
For each port number, there are two choices: “M” or nothing. Use the
spacebar to scroll through the choices.
Select the letter “M” to indicate that the VLAN has access to messages
transmitted by that particular port.
Select a blank space to indicate that there is no access to messages transmitted by that particular port.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
36
Instant EtherFast®Series
Static Multicast Address Configuration
The Static Multicast Address Table, shown in Figure 6-25, can be used to
assign a destination MAC address (and the corresponding ports) to the
VLAN group used for a specific multicast service. Static multicast addresses are never aged out, and traffic with these addresses can only be forwarded to ports specif ied in this table.
•VLAN - The VLAN corresponding to this multicast service.
•Address - The destination MAC address for a multicast service.
•Port - The ports to which this multicast traffic can be forwarded. Read
the numbers vertically; they range from 1-26. For each port number,
there are two choices:
If the letter “M” is present, it indicates that the VLAN has access to
messages transmitted by that particular port.
If there is no letter “M,” then there is no access to messages transmitted by that particular port.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
35
Figure 6-25
Figure 6-26
Page 22

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Bridge Configuration
The Bridge Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-28, allows you to configure global bridge settings.
•Spanning Tree - Enable this parameter to participate in a STA compliant
network.
•Bridge Priority - Bridge priority is used in selecting the root device,
root port, and designated port. The device with the lowest priority
becomes the STA root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest MAC address will then become the root
device. The lower the numeric value, the higher the priority.
•Hello Time - Time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a configuration message.
•Forward Delay - The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will
wait before changing states.
•Max Age - The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without
receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
•GVRP - GVRP defines a way for switches to exchange VLAN information in order to register VLAN members on ports across the network.
This function should be enabled to permit automatic VLAN registration,
and to support VLANs which extend beyond the local switch.
38
Instant EtherFast®Series
Bridge Menu
The Bridge Menu, shown in Figure 6-27, is used to configure settings for the
Spanning Tree Algorithm, as well as the global bridge settings for GMRP
(GARP Multicast Registration Protocol) and GVRP (GARP VLAN
Registration Protocol), traffic classes priority threshold, and address aging
time.
• Bridge Configuration - Contains global bridge settings for STA (including
bridge priority, hello time, forward delay, maximum message age), GMRP,
GVRP, traffic class priority threshold, and address aging time.
• Spanning Tree Port Conf iguration - Contains STA settings for individual
ports, including port priority, path cost, and fast forwarding.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
37
Figure 6-27
Figure 6-28
Page 23

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
•Fast Forwarding - This parameter is used to enable/disable the Fast
Spanning Tree mode for the selected port.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Pa ge to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page.
VLAN Menu
The VLAN Menu, shown in Figure 6-30, is used to assign any port on the
Switch to any of up to 256 VLAN groups. By using IEEE 802.1Q compliant
VLANs, you can organize any group of network nodes into separate broadcast
domains, confining broadcast traff ic to the originating group. This also provides a more secure and cleaner network environment.
•VLAN Port Configuration - Configures GARP, the default VLAN identi-
fier, default port priority, VLAN tagging on the attached link, GVRP and
GMRP status, and filtering of incoming frames for VLAN groups a specific port does not belong to.
•VLAN Table Conf iguration - Use this screen to create a new VLAN or
modify the settings for an existing VLAN.
• Reset Addr ess T able Mode - Opens the Reset Address Table Mode screen
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
40
Instant EtherFast®Series
•High/Medium/Low Priority - This Switch supports Quality of Service
(QoS) by using three priority queues, with Weighted Fair Queuing for each
port.
•Aging Time - Time-out period in seconds for aging out dynamically
learned forwarding information. Range varies from 10-415 seconds.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Spanning Tree Port Configuration
The Spanning Tree Port Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-29, allows
you to configure spanning tree port settings.
• Port - This shows the number of the port to be configured.
•Type - Shows port type as 100TX for 10Base-T/100Base-TX, or
1000T for 1000Base-T.
•Priority - Def ines the priority for the use of a port in the STA algorithm.
If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the
highest priority (that is, lowest value) will be configured as an active link in
the Spanning Tree. When more than one port is assigned the highest priority, the port with the lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. The range is
0-255.
•Cost - This parameter is used by the STA algorithm to determine the best
path between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to
ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with
slower media. (This takes precedence over port priority.)
39
Figure 6-29
Figure 6-30
Page 24

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
•Port Default Priority - Sets the default ingress priority to any value
beneath the priority threshold to specify the low priority queue, or to any
value equal to or above this threshold to specify the high priority queue.
•VLAN Tagging - Indicates whether or not VLAN tags will be included
on frames passing through this port.
•GVRP - Enables or disables GVRP for this port. When disabled, any
GVRP packets received on this port will be discarded and no GVRP registrations will be propagated from other ports. Note: GMVP must be
enabled for the Switch before this setting can take effect.
•Ingress Filtering - If enabled, incoming frames for VLANs that do not
include this ingress port in their member set will be discarded at the
ingress port.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Port to view the previous
port. Select Next Port to view the next port. To display a specific port, set the
port number in the Page field and then press Apply.
VLAN Table Configuration
The VLAN Table Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-32, is used to
create a new VLAN or modify the settings for an existing VLAN.
•VLAN - The ID for the VLAN currently displayed. The range is 1-2048.
42
Instant EtherFast®Series
41
VLAN Port Configuration
The VLAN Port Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-31, allows you to
configure GARP, the def ault VLAN identifier, default port priority, VLAN
tagging on the attached link, GVRP and GMRP status, and filtering of
incoming frames for VLAN groups a specific port does not belong to.
GARP
Group Address Registration Protocol is used by GVRP and GMRP to register or deregister client attributes for client services within a bridged LAN.
•Join Time - The interval (centiseconds) between transmitting
requests/queries to participate in a group.
•Leave Time - The interval (centiseconds) a port waits before leaving a
group. This time should be set to more than twice the Join Time. This
ensures that after a Leave or Leave All message has been issued, the
applicants can re-join before the port actually leaves the group.
•Leave All Time - The interval (centiseconds) between sending out a
Leave All quer y message for group participants and the port leaving the
group. This interval should be considerably larger than the Leave Time to
minimize the amount of traffic generated by nodes rejoining the group.
VLAN and Priority
These fields set the default values for VLANs, port priority, GVRP, and
GMRP.
•Port VID - The VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames received on this
port.
Figure 6-31
Figure 6-32
Page 25

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IP Menu
The IP Menu, shown in Figure 6-34, is used to configure the IP subnets for
each VLAN on your Switch, the unicast and multicast routing protocols, and
IGMP.
• Subnet Configuration - Specifies the IP interface for VLANs configured on
this Switch, including the subnet address and routing protocols.
• Protocol Configuration - Enables the unicast and multicast routing proto-
cols globally for this Switch.
• Static ARP Configuration - Specifies the static Address Resolution
Protocol.
• Static Route - Conf igures a static route.
• Default Route - Defines the router to which this Switch will forward all traf-
fic for unknown networks.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
44
Instant EtherFast®Series
• MEMBERS - Allows you to specify a port to a specific VLAN.
• UNTAG - Allows you to set traffic to be tagged or untagged per port.
Each port can be modif ied with the following character:
– (Normal) Uses GVRP to determine port membership.
S (Static) Adds por t as a static entry. GVRP protocol is dis-
abled.
R (Registration Fixed) Adds port as a static entry. GVRP
protocol messages are still forwarded through this port.
X (Forbidden) Disables GVRP for this VLAN on the
specified por t.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply. Select Add to add a VLAN.
Reset Address T able Mode
The Reset Address Table Mode screen, shown in Figure 6-33, is used to
assign VLAN tables to existing VLANs.
• SVL - Specifies that all VLANs share one VLAN table.
• IVL - Specifies that each VLAN utilizes its own VLAN table.
43
Figure 6-33
Figure 6-34
Page 26

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
46
Instant EtherFast®Series
45
•DVMRP - Distance-Vector Multicast Routing Protocol.
•Status - Status of the VLAN IP.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Page to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To display a specific page, set
the page number in the Page field and then press Apply. Select Add to add an
IP interface.
Modify Subnet
The Modify Subnet screen, shown in Figure 6-36, allows you to mod-
ify an IP interface.
• VLAN - The VLAN associated with this IP interface.
• Select - Use this option to create or modify a VLAN.
• IP Address - The IP address associated with the specified VLAN
interface.
• Subnet Mask - A template that identifies the address bits in the
host address used for routing to specific subnets.
• Proxy ARP - Enable or disable the Proxy Address Resolution
Protocol.
Subnet Configuration
The Subnet Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-35, allows you to specify an IP interface for any VLAN conf igured on this Switch that needs to
communicate with a device outside of its own group (that is, another network segment).
• Intf. - This identifies the IP Interface configured.
•IP Address - The IP address associated with the specified VLAN interface.
By convention, the last three digits should be set to “254” to readily distinguish this device as a router port. To modify this IP interface, select it and
press Enter. The default address is 192.168.1.254.
•Subnet Mask - A template that identifies the address bits in the host
address used for routing to specific subnets. Each bit that corresponds
to a “1” is part of the network/subnet number, and each bit that
corresponds to “0” is part of the host number.
•VLAN - The VLAN associated with this IP interface.
•RIP - Routing Infor mation Protocol for unicast routing.
•OSPF - Open Shor test Path First routing protocol.
Figure 6-35
Figure 6-36
Page 27

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
48
Instant EtherFast®Series
47
• Receive T ype - Select the kind of routing protocol messages accepted
on this port.
• Default Metric - This is used for the default route in RIP updates
originated on this interface. A value of zero indicates that no default
route should be originated.
• Poison Reverse - This propagates routes back to an interface port
from which they have been acquired, but it sets the distance vector
metrics to infinity.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Subnet Configuration: Modify OSPF Configuration
The Subnet Configuration: Modify OSPF Conf iguration screen,
shown in Figure 6-38, allows you to modify the OSPF parameters.
• Area ID - A 32-bit number assigned to each interface or subnet run-
ning the OSPF protocol.
• Router Priority - When two routers are attached to a network, both
attempt to become the designated router, and the one with the highest
priority takes precedence.
• Interface Cost - The cost of sending a packet on the interface.
• RIP - Enable or disable the Routing Information Protocol for
unicast routing. Select Advanced to make more changes.
• OSPF - Enable or disable the Open Shortest Path First protocol.
Select Advanced to make more changes.
• DVMRP - Enable or disable the Distance-Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol. Select Advanced to make more changes.
Select Delete to delete a subnet. Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to
return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Subnet Configuration: Modify RIP Conf iguration
The Subnet Configuration: Modify RIP Conf iguration screen, shown
in Figure 6-37, allows you to modify the RIP parameters.
• Authentication Type - Authentication can be used to ensure that
routing information comes from a valid source. Select either No
Authentication or Simple Password.
• Authentication Key- A simple password must be provided if authen-
tication is enabled. It is case-sensitive and can have up to 16 characters.
• Send T ype - Select the type of protocol used for traff ic sent from this
port.
Figure 6-37
Figure 6-38
Page 28

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• Metrics - This value is used to select the best reverse path to netw orks
that are connected directly to an interface on the Switch.
• Probe Interval - The interval between sending neighbor probe mes-
sages to the multicast group address for all DVMRP users.
• Neighbor Timeout - The interval to wait without hearing from a
DVMRP neighbor before declaring it dead.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Add Subnet
The Add Subnet screen, shown in Figure 6-40, allows you to add an
IP interface.
• VLAN - The VLAN associated with this IP interface.
• Select - Use this option to create or modify a VLAN.
• IP Address - The IP address associated with the specified VLAN
interface.
• Subnet Mask - A template that identifies the address bits in the
host address used for routing to specific subnets.
• Proxy ARP - Enable or disable the Proxy Address Resolution
Protocol.
50
Instant EtherFast®Series
49
• Transit Delay - The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit
a Link State Update Packet over this interface.
• Retransmit Interval - The number of seconds between LAS retrans-
missions, for adjacencies belonging to this interface.
• Hello Interval - The length of time, in seconds, between the Hello
Packets that the router sends on the interface.
• Dead Interval -After ceasing to hear a router’s Hello Packets, the
number of seconds before its neighbors declare the router to be down.
• Poll Interval - After beginning to hear a router’s Hello Packets, the
period of time after its neighbors declare the router to be up.
• Authentication Type - Identif ies the authentication procedure to be
used on the attached network.
• Authentication Key- The configured data allows the authentication
procedure to verify OSPF protocol packets received over the interface.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Subnet Configuration: Modify DVMRP Configuration
The Subnet Configuration: Modify DVMRP Configuration screen ,
shown in Figure 6-39, allows you to modify the DVMRP parameters.
Figure 6-39
Figure 6-40
Page 29

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
52
Instant EtherFast®Series
• RIP - Enable or disable the Routing Information Protocol for
unicast routing.
• OSPF - Enable or disable the Open Shortest Path First protocol.
• DVMRP - Enable or disable the Distance-Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Protocol Configuration
The Protocol Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-41, is used to globally enable or disable unicast or multicast routing protocols for the Switch.
•ARP - Address Resolution Protocol. Select Advanced for additional
configuration.
•Proxy ARP - Enable or disable the Proxy Address Resolution Protocol.
•RIP - Enable or disable the Routing Information Protocol for unicast
routing. Select Advanced for additional configuration.
•OSPF - Enable or disable the Open Shortest Path First protocol. Select
Advanced for additional configuration.
•DHCP Relay - Enable or disable the Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol relay. Select Advanced for additional conf iguration.
51
•IGMP Snooping - Enable or disable IGMP multicast filtering. Select
Advanced for additional configuration.
•DVMRP - Enable or disable the Distance-Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
ARP Configuration
The ARP Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-42, allows you to
specify the timeout duration.
• ARP Timeout - Duration of timeout (in minutes).
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Figure 6-41
Figure 6-42
Page 30

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
OSPF Configuration Menu
The OSPF Conf iguration Menu screen, shown in Figure 6-44, allows
you to configure the OSPF parameters.
• Router ID Selection - Allows you to assign an algorithm.
• Router ID - The OSPF identifier for the router at the other end of the
link.
• AS Border Status - Enable or disable the router that exchanges rout-
ing information with routers that belong to other Autonomous
Systems.
• RFC 1583 Compatibility - Controls the preference rules when
choosing among multiple AS-external-LSAs advertising the same
destination.
• Area ID Configuration - Defines an area within which all OSPF
routers actively exchange routing information to ensure that they all
have an identical link state database.
• OSPF Area Range Configuration - Defines a range of subnetwork
addresses. An area range is used to summarize route information
exchanges between Area Border Routers.
• OSPF Virtual Link Configuration - Def ines a virtual link that can
be used to connect an OSPF area not physically adjacent to the OSPF
backbone, or to create a backup link to any area.
54
Instant EtherFast®Series
RIP Configuration
The RIP Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-43 allows you to
specify how routers exchange routing table information.
• RIP Update Time - Duration of timeout (in seconds).
• Default Route Advertisement - Enable or disable the use of
default route messages.
• Static Route Advertisement - Enable or disable the use of
static route messages.
• Ignore Host Route - Enable or disable the use of host routes. If
you enable the Ignore Host Route feature, then host routes will not
be used.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
53
Figure 6-43
Figure 6-44
Page 31

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
OSPF Area Configuration:Add OSPF Area
The OSPF Area Conf iguration: Add OSPF Area screen, shown in
Figure 6-46, allows you to add an area.
• Area ID - The ID of the OSPF area.
• Stub - The type of the OSPF area.
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
56
Instant EtherFast®Series
• OSPF Host Router Configuration - Def ines a main route of OSPF
to connect to other areas.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
IP Menu: OSPF Area Configuration
The IP Menu: OSPF Area Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-45,
allows you to configure the Area ID parameters.
• Area ID - Allows you to assign an algorithm.
• Type - Select the Area Type. “Standard” means that AS-External-
LSAs are included in the area. “Stub” means that AS-External-LSAs
are excluded from the area.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Page to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To display a specific page, set
the page number in the Page field and then press Apply. Select Add to add an
area.
55
Figure 6-45
Figure 6-46
Page 32

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add OSPF Range
The Add OSPF Range screen, shown in Figure 6-48, allows y ou to add
an OSPF range.
• Area Identity - The OSPF Area to which the attached network
belongs.
• IP Address - The IP protocol address for this interf ace.
• Address Mask - This indicates the portion of the IP interface address
with the IP interface.
• Advertise - Select whether or not this OSPF range should be adver-
tised or not.
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
58
Instant EtherFast®Series
OSPF Area Range Configuration
The OSPF Area Range Conf iguration Menu screen, shown in Figure
6-47, allows you to configure the area range parameters.
• Area Identity - The OSPF Area to which the attached network
belongs.
• IP Address - The IP protocol address for this interf ace.
• Address Mask - This indicates the portion of the IP interface address
with the IP interface.
• Advertisement - Unit of data describing the local state of a router or
network.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Page to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To display a specific page, set
the page number in the Page field and then press Apply. Select Add to add an
area range.
57
Figure 6-47
Figure 6-48
Page 33

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add OSPF Virtual Link
The Add OSPF Virtual Link screen, shown in Figure 6-50, allo ws you
to add an OSPF virtual link.
• Area ID - This is a 32-bit number that identif ies the area.
• Neighbor Router ID - The ID of the routers that have interfaces to a
common network.
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
60
Instant EtherFast®Series
OSPF Virtual Link Configuration
The OSPF Virtual Link Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-49,
allows you to configure the OSPF parameters.
• Area ID - This is a 32-bit number that identif ies the area.
• Neighbor Router ID - The ID of the routers that have interfaces to a
common network.
• Status - Shows the interface is linked or down.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Page to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To display a specific page, set
the page number in the Page field and then press Apply. Select Add to add a
virtual link.
59
Figure 6-49
Figure 6-50
Page 34

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add OSPF Host Route
The Add OSPF Host Route screen, shown in Figure 6-52, allows you
to add an OSPF host route.
• IP Address - The IP address applied for this interface.
• Cost - The cost of sending a packet on the interface, expressed in the
link state metric.
• Area ID - The OSPF area to which the attached network belongs to.
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
62
Instant EtherFast®Series
OSPF Host Route Configuration
The OSPF Host Route Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-51,
allows you to configure the OSPF host route parameters.
• IP Address - The IP address applied for this interface.
• Cost - The cost of sending a packet on the interface, expressed in the
link state metric.
• Area ID - The OSPF area to which the attached network belongs to.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes. Select Prev Page to view the previous
page. Select Next Page to view the next page. To display a specific page, set
the page number in the Page field and then press Apply. Select Add to add a
host route.
61
Figure 6-51
Figure 6-52
Page 35

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IGMP Snooping Configuration
The IGMP Snooping Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure 6-55,
allows you to set up IGMP snooping. IGMP snooping is used to monitor for any attached hosts who want to receive a specif ic multicast
service. It looks up the IP Multicast Group used for this service and
adds any port that received a similar request to that group.
• IGMP Router Timeout - A switch port that stops receiving multicast
protocol packets for this interval will be removed from the IGMP
forwarding list. The range is 3-5 minutes.
• IGMP Group Timeout - The time between last spotting an IGMP
Report message for an IP multicast address on a specif ic port and the
Switch removing that entry from its list. The range is 3-5 minutes.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
64
Instant EtherFast®Series
63
BOOTP Relay Database Configuration
The BOOTP Relay Database Conf iguration screen, shown in Figure
6-53, allows you to specify the IP address for a BOOTP relay server.
• Index Server Address - Used to define any preferred DHCP
servers or the outbound subnetwork for relaying a DHCP request
broadcast. (Up to five entries are permitted.)
Select OK to return to the previous panel. Select Add to add another entry.
Add BOOTP Relay Server
The Add BOOTP Relay Server screen, shown in Figure 6-54, allows
you to add an entry.
• IP Address - IP address of ser ver.
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Figure 6-53
Figure 6-54
Figure 6-55
Page 36

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add Static ARP Entry
The Add Static ARP Entry screen, shown in Figure 6-57, is used to
add a static ARP entry.
• IP Address - IP address statically mapped to a physical MAC
address.
• MAC Address - MAC address statically mapped to the correspon-
ding IP address.
• Interface - The index number of the IP interface that will use
this static ARP entry. (Port “0” refers to the CPU.)
Select OKto return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
66
Instant EtherFast®Series
Static ARP T able
The Static ARP Table screen, shown in Figure 6-56, is used to specify the
static Address Resolution Protocol.
•IP Address - IP address statically mapped to a physical MAC address.
•MAC Address - MAC address statically mapped to the corresponding
IP address.
•Interface - The index number of the IP interface that will use this static
ARP entry. (Por t “0” refers to the CPU.)
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply. Select Add to add a static ARP entry.
65
Figure 6-56
Figure 6-57
Page 37

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add Routing Entry
The Add Routing Entr y screen, shown in Figure 6-59, is used to add
a routing entry.
• IP Address - IP address of static ARP entry.
• MAC Address - MAC address of static ARP entr y.
• Next Hop - The IP address of the router at the next hop.
• Routing Metric - Indicate the number of hops to the destination
network.
Select OK to return to the previous panel. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
68
Instant EtherFast®Series
67
Static Route Table
The Static Route Table screen, shown in Figure 6-58, is used to configure
a static route.
•Destination Network - A destination network, subnet, or host.
•Destination Mask - The subnet mask that specifies the bits to match.
A routing entry will be used for a packet if the bits in the address set by
the destination mask match the destination network.
•VLAN - The VLAN within which the gateway or destination address
resides.
•Next Hop - The IP address of the router at the next hop.
•Type - The IP route type for the destination network.
Direct - A directly connected subnetwork
Indirect - A remote IP subnetwork or host address
Myself - A switch IP address on a specific IP subnetwork
Bcast - A subnetwork broadcast address
Mcast - An IP multicast address
Invalid - An illegal IP address to be filtered
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply. Select Add to add a routing entry.
Figure 6-58
Figure 6-59
Page 38

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
MACFiltering Configuration
The MAC Filtering Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-62, allo ws you
to filter out specified MAC addresses. An y node that presents a security risk
or is malfunctioning can be filtered from this Switch. Security filtering can
be used to drop all the traffic from a host device based on a specif ied MAC
address.
T o add a MA C address, use Ad d. To delete an address, highlight it with the cursor and press Enter. Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the
previous panel. Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page
to view the next page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the
Page field and then press Apply.
70
Instant EtherFast®Series
Default Route Menu
The Default Route Menu screen, shown in Figure 6-60, is used to define the
router to which the Switch will forward all traff ic for unknown networks.
You can have primary and secondary default routes.
• VLAN - The VLAN route where traffic will be sent.
•Next Hop Address - IP address of the default router.
•Metric - Number of hops required to reach the def ault route.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Security Menu
The Security Menu is used to configure security options.
• MAC Filtering Configuration - Security filtering can be used to drop all the
traffic from a host device based on a specif ied MAC address. Traffic with
either a source or destination address listed in the MAC Filtering
Configuration table will be filtered.
• IP Filtering Configuration - Conf igures IP filtering settings. (Only avail-
able when the Switch is in multilayer mode)
69
Figure 6-60
Figure 6-61
Figure 6-62
Page 39

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
72
Add IP Address Filter
The Add IP Address Filter screen, shown in Figure 6-65, allows you
to add IP addresses.
• IP Address - The IP address to be filtered.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
Instant EtherFast®Series
Add MACAddress Filter
The Add MAC Address Filter screen, shown in Figure 6-63, allows
you to add MAC addresses.
• MAC Address - The MAC address of a host device attached to this
Switch.
Select OK to confirm the changes. Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
IP Security Filtering Configuration
Security filtering (from the Security Filtering Conf iguration screen, shown
in Figure 6-64) can be used to drop all the traffic from a specified IP
address.
To add an IP address, use Add. To delete an address, highlight it with the cursor and press Enter. Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the
previous panel. Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page
to view the next page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the
Page field and then press Apply.
71
Figure 6-63
Figure 6-64
Figure 6-65
Page 40

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The Network Monitor Menu, sho wn in F igure 6-67, provides access to port statistics, RMON statistics, address tables, VLAN registration and forwarding
information, multicast groups, and subnet addresses.
• Port Statistics/Statistics Menu - Displays statistics on network traffic pass-
ing through the selected port. You have a choice of viewing port or RMON
statistics.
• Layer 2 Address Table - Displays detailed statistical information for the
selected port, such as packet type and frame size counters.
• Bridge Menu - The Bridge menu displays settings for the Spanning Tree
Algorithm, as well as the global bridge settings for GMRP (GARP Multicast
Registration Protocol) and GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol), traffic classes priority threshold, and address aging time.
• VLAN Menu - Includes learned ports in the VLAN Dynamic Registration
Information table, and the ports that are currently forwarding VLAN traff ic
in the VLAN Forwarding Information table.
• IP Menu - Displays information regarding a variety of IP settings, including
subnets, ARP table, routing table, and multicast groups.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
74
Instant EtherFast®Series
Jumbo Packet Configuration
The Jumbo Packet Configuration screen, shown in Figure 6-66, allows you to
utilize jumbo packets. The IEEE 802.3 standard specifies the maximum size of
Ethernet frames at 1,518 bytes. A jumbo packet is simply one having up to
65,535 bytes. In a case where a server has to receiv e a massive amount of data,
the required overhead of processing the individual frames could have negative
effects on the server's CPU, and ultimately on overall server performance.
• Load Default Size - If enabled , the Switch will use the default size for jumbo
packets, which is 1536 bytes.
• Jumbo Packet Length - With Default Size disabled, you can set the jumbo
packet length between 1536 and 9216 bytes.
Select Apply to make changes. Select Return to retur n to the previous panel.
Select Cancel to cancel any changes.
73
Network Monitor Menu
Figure 6-66
Figure 6-67
Page 41

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
76
Instant EtherFast®Series
Port Statistics/Statistics Menu
The Port Statistics/Statistics Menu, shown in Figure 6-68, allows you to view
the port or RMON statistics.
• Port Statistics - Displays statistics on network traffic passing through the
selected port. You have a choice of viewing port or RMON statistics.
• RMON Statistics - Displays statistics for each port from RMON group 1
(RMON groups 2, 3, and 9 can only be accessed using SNMP management
software).
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Port Statistics
Port Statistics, on the screen shown in Figure 6-69, display key statistics
from the Interfaces Group and Ethernet-like MIBs for each port. Er ror statistics on the traffic passing through each port are displayed. This information can be used to identify potential problems with the Switch (such as a
faulty port or unusually heavy loading). The values displayed have been
accumulated since the last system reboot.
Select the required port.
75
Interfaces
•In Octets - The total number of octets received on the interface, includ-
ing framing characters.
•In Unicast Pkts - The number of unicast packets delivered to a higher-
layer protocol.
•In Non-Unicast Pkts - The number of non-unicast (that is, subnetwork-
broadcast or subnetwork-multicast) packets delivered to a higher-layer
protocol.
•In Discards - The number of inbound packets which were chosen to be
discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being
deliverable to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding
such a packet could be to free up buffer space.
•In Errors - The number of inbound packets that contained errors pre-
venting them from being deliverable to a higher-layer protocol.
•Alignment Errors - The number of alignment errors (mis-synchronized
data packets).
•Out Octets - The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface,
including framing characters.
•Out Unicast Pkts - The total number of packets that higher-level proto-
cols requested be transmitted to a subnetwork-unicast address, including
those that were discarded or not sent.
Figure 6-68
Figure 6-69
Page 42

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
•Fragments - The total number of frames received that were less than 64
octets in length (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and
had either an FCS or alignment error.
•Jabbers - The total number of frames received that were longer than
1518 octets (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets), and had
either an FCS or alignment error.
Select Apply to make changes. Select Refresh to refresh the statistics. Select
OK to retur n to the previous panel. Select Reset to reset a specif ic statistic.
Select Reset All to reset the all statistics. Select Prev Port to view the previous
port. Select Next Port to view the next port. To display a specific port, set the
port number in the Port field and then press Apply.
RMON Statistics
The RMON Statistics screen, shown in Figure 6-70, provides access to a
broad range of statistics, including a total count of different frame types and
sizes passing through each port. The values displayed have been accumulated since the last system reboot.
Select the required port.
•Drop Events - The total number of events in which packets were
dropped due to lack of resources.
•Bytes - Total number of bytes of data received on the network. This
statistic can be used as a reasonable indication of Ethernet utilization.
78
Instant EtherFast®Series
• Out Non-Unicast Pkts - The total number of packets that higher-level
protocols requested be transmitted to a non-unicast (that is, a subnetwork-broadcast or subnetwork-multicast) address, including those that
were discarded or not sent.
•Out Discards - The number of outbound packets which were chosen to
be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their
being transmitted. One possible reason for discarding such a packet
could be to free up buffer space.
•Out Errors - The number of outbound packets that could not be trans-
mitted because of errors.
•CRC Errors - Number of Ethernet Cyclic Redundancy Check errors
detected by this device.
Ethernet
•Single Collisions - The number of successfully transmitted frames for
which transmission is inhibited by exactly one collision.
•Deferred Transmissions - A count of frames for which the first trans-
mission attempt on a particular interface is delayed because the medium
was busy.
•Excessive Collisions - The number of frames for which transmission
failed due to excessive collisions.
•Drop Events - The total number of events in which packets were
dropped due to lack of resources.
•Octets - Number of octets passing through this por t.
•Multiple Collisions - A count of successfully transmitted frames for
which transmission is inhibited by more than one collision.
•Late Collisions - The number of times that a collision is detected later
than 512 bit-times into the transmission of a packet.
•Carrier Sense Errors - The number of times that the carrier sense con-
dition was lost or never asserted when attempting to transmit a frame.
77
Figure 6-70
Page 43

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
•256-511 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad pack-
ets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within the
specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
•512-1023 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad
packets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within
the specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
•1024-1518 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad
packets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within
the specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
•1519-1536 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad
packets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within
the specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
Select Apply to make changes. Select Refresh to refresh the statistics. Select
OK to retur n to the previous panel. Select Reset to reset a specif ic statistic.
Select Reset All to reset the all statistics. Select Prev Port to view the previous
port. Select Next Port to view the next port. To display a specific port, set the
port number in the Port field and then press Apply.
Layer 2 Address Table
When you select Layer 2 Address Table from the Network Monitor Menu, you
will see a screen that allows you to select the Unicast Ad dress T able, shown in
Figure 6-71. This contains the MAC addresses associated with each port (that
is, the source port associated with the address).
• Address - The MAC address of a node seen on this Switch.
• VLAN - The is the VLAN where the MAC address and port are assigned.
• Port - The port whose address table includes this MAC address.
80
Instant EtherFast®Series
79
•Frames - The total number of frames (bad, broadcast, and multicast)
received.
•Broadcast Frames - The total number of good frames received that were
directed to the broadcast address. This does not include multicast packets.
•Multicast Frames - The total number of multicast frames.
•CRC/Alignment Errors - The number of CRC/alignment errors (FCS or
alignment errors).
•Undersize Frames - The total number of frames received that were less
than 64 octets long (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets)
and were otherwise well formed.
•Oversize Frames - The total number of frames received that were longer
than 1518 octets long (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets)
and were otherwise well formed.
•Fragments - The number of outbound packets that could not be trans-
mitted because of errors.
•Jabbers - The total number of frames received that were longer than
1518 octets long (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets) and
had either an RCS or alignment error.
•Collisions- The best estimate of the total number of collisions on this
Ethernet segment.
•64 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad packets)
received and transmitted that were 64 octets in length (excluding framing
bits, but including FCS octets).
•65-127 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad pack-
ets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within the
specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
•128-255 Byte Frames - The total number of frames (including bad pac-
ets) received and transmitted where the number of octets fall within the
specified range (excluding framing bits, but including FCS octets).
Page 44

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• Spanning Tree Port Information - Displays a list of STA values used for
each port, including status, designated cost, designated bridge, and designated port.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Spanning Tree Bridge Information
The STA Bridge Information screen, shown in Figure 6-73, displays a summary of STA information for the overall bridge.
•Priority - Device priority is used in selecting the root device, root port,
and designated port. The device with the lowest priority becomes the
STA root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the
device with the lowest MAC address will then become the root device.
•Hello Time - The time interval (in seconds) at which the root device
transmits a configuration message.
•Max Age - The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait without
receiving a configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
•Forward Delay - The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will
wait before changing states (i.e., listening to learning to forwarding).
•Hold Time - The minimum interval between the transmission of consecutive Configuration BPDUs.
82
Instant EtherFast®Series
81
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
Bridge Menu
The Bridge Menu, shown in Figure 6-72, is used to display settings for the
Spanning Tree Algorithm, as well as the global bridge settings for GMRP
(GARP Multicast Registration Protocol) and GVRP (GARP VLAN
Registration Protocol), traffic classes priority threshold, and address aging
time.
• Spanning Tree Bridge Information - Displays a full list of STA values used
for the bridge.
Figure 6-71
Figure 6-72
Figure 6-73
Page 45

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
84
Instant EtherFast®Series
•Designated Root - The priority and MAC address of the device in the
Spanning Tree that this switch has accepted as the root device.
•Root Cost - The path cost from the root port on this Switch to the root
device.
•Root Port - The number of the port on this Switch that is closest to the
root. This Switch communicates with the root device through this port. If
there is no root port, then this Switch has been accepted as the root
device of the Spanning Tree network.
•Configuration Changes - The number of times the Spanning Tree has
been reconfigured.
•Topology Up Time - The time since the Spanning Tree was last recon-
figured.
Select OK to retur n to the previous panel.
Spanning Tree Port Information
The STA Port Information screen, shown in Figure 6-74, displays a summary of STA information for the various ports.
•Port (#) - Number of the port.
83
•Type - Shows port type as:
100TX 10BaseT/100Base-TX
1000T 1000Base-T
•Status - Displays current state of this por t within the Spanning Tree:
Disabled No link has been established on this port.
Otherwise, the port has been disabled by the user
or has failed diagnostics.
Blocking Port received STA conf iguration messages, but
does not forward packets.
Listening Port will leave blocking state due to a topology
change. It starts transmitting conf iguration messages, but does not yet forward packets.
Learning Port has transmitted configuration messages for an
interval set by the Forward Delay parameter with
out receiving contradictory information. Port
address is cleared, and the port begins learning
addresses.
Forwarding The port forwards packets, and continues learning
addresses.
•Designated Cost - The cost for a packet to travel from this port to the
root in the current Spanning Tree configuration. The slower the media,
the higher the cost.
•Designated Bridge (ID) - The priority and MAC address of the device
through which this port must communicate to reach the root of the
Spanning Tree.
•Designated Port (ID) - The priority and number of the port on the des-
ignated bridging device through which this Switch must communicate with
the root of the Spanning Tree.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Figure 6-74
Page 46

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
VLAN Dynamic Registration Information
The VLAN Dynamic Registration Information screen, shown in Figure 676, shows the ports that have been automatically learned via GVRP.
•VLAN - The ID for the VLAN.
•Po rt - The ports on the Switch. Read the numbers vertically; they range
from 1-8. For each port number, there are two choices:
If the letter “D” is present, it indicates that the port has been automatically learned via GVRP.
If there is no letter “D,” it indicates that the port has not been
automatically learned via GVRP.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
86
Instant EtherFast®Series
VLAN Information
The VLAN Information screen, shown in Figure 6-75, offers access to information on the ports that have been automatically learned via GVRP and all the
ports that have been configured by dynamic or static means to forward VLAN
traffic.
• VLAN Dynamic Registration Information - Shows the ports that ha ve been
automatically learned via GVRP.
• VLAN Forwarding Information - Shows all the ports that have been con-
figured by either dynamic or static means to forward VLAN traffic.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
85
Figure 6-75
Figure 6-76
Page 47

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IP Menu
The IP Menu, shown in Figure 6-78, displays information regarding a variety
of IP settings, including subnets, ARP table, routing table, and multicast
groups. (Only available in multilayer mode).
• Subnet Information - Displays settings for the IP interface of VLANs.
• ARP Table - Shows the IP-to-MAC addresses discovered by ARP.
• Routing T able - Shows the routes through which all reco gnized Ethernet net-
works (and the corresponding VLAN) can be reached.
• Multicast Table - Displays all the multicast groups active on this Switch,
including the multicast IP address and the corresponding VLANs.
• OSPF Table - Displays the OSPF routing information.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
88
Figure 6-78
Instant EtherFast®Series
VLAN Forwarding Information
The VLAN Forwarding Information screen, shown in Figure 6-77, shows all
the ports that have been configured by either dynamic or static means to forward VLAN traffic.
•VLAN - The ID for the VLAN.
•Po rt - The ports on the Switch. Read the numbers vertically; they range
from 1-26. For each port number, there are two choices:
If the letter “D” is present, it indicates that the port has been configured by dynamic means.
If the letter “S” is present, it indicates that the port has been configured by static means.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
87
Figure 6-77
Page 48

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ARP Table
The ARP Table, shown in Figure 6-80, shows the IP-to-MAC addresses discovered by ARP.
•IP Address - IP addresses for which ARP has resolved the physical
address through a broadcast message.
•MAC Address - MAC address that maps to the corresponding IP
address.
•VLAN - The VLAN group this host has been assigned to.
•Port - The port this host device is attached to.
Select OK to retur n to the previous panel. Select First Page to view the first
page. Select Next Page to view the next page.
Routing Table
The Routing Table, shown in Figure 6-81, lists the routes through which all
recognized Ethernet networks (and corresponding VLAN) can be reached.
•Destination Network - A destination network, subnet, or host.
•Destination Mask - The subnet mask that specifies the bits to match.
90
Instant EtherFast®Series
Subnet Information
The Subnet Information screen, shown in Figure 6-79, displays information
about the IP interface for VLANs configured on this Switch.
•IP Address - The IP address associated with the specified VLAN inter-
face.
•Subnet Mask - A template that identifies the address bits in the host
address used for routing to specific subnets.
•VLAN - The VLAN associated with this IP interface.
•(Ports) - The ports on the Switch.
Read the numbers vertically; they range from 1-8. For each port
number, there are two choices: “S” or “P.” Use the spacebar to
scroll through the choices.
The letter “S” indicates a static entry.
The letter “P” indicates the port is a static entry, and the port’s PVID
is set to this VLAN ID.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
89
Figure 6-80
Figure 6-79
Page 49

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Multicast Table Menu
The Multicast Table Menu, shown in Figure 6-82, offers a variety of multicasting settings.
•IP Multicast Registration Table - Displays all the multicast groups active
on the Switch, including the multicast IP address and the corresponding
VLANs.
•IGMP Cache - Cache for IGMP.
•Multicast Forwarding Cache Table - Cache for multicast forwarding.
•DVMRP Routing Table - Routing table for Distance-Vector Multicast
Routing Protocol.
•DVMRP Neighbor Table - Table of neighbors for Distance-Vector
Multicast Routing Protocol.
Select OK to return to the previous panel.
92
Instant EtherFast®Series
•VLAN - The VLAN within which the gateway or destination address
resides.
•Next Hop - The IP address of the router at the next hop.
•Type - The IP route type for the destination network.
Direct: A directly connected subnetwork
Indirect: A remote IP subnetwork or host address
Myself: A switch IP address on a specific IP subnetwork
Bcast: A subnetwork broadcast address
Mcast: An IP multicast address
Invalid: An illegal IP address to be f iltered
•Protocol - How the route was learned.
Local: Manually configured
Mgmt: Set via SNMP
ICMP: Obtained via ICMP redirect
RIP: Learned via RIP protocol
Other: Learned by some other method
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply. Select Flush RIP to flush the RIP protocol.
91
Figure 6-82
Figure 6-81
Page 50

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
IGMP Cache
The IGMP Cache screen, shown in Figure 6-84, shows the setting
for the IGMP cache.
• Group Address - An IP multicast group address with subscribers
directly attached or downstream from this Switch.
• Intf - The IP interface on this Switch that has received traffic
directed to the IP multicast group address.
• Reporter - IP address of the source of the last membership report
received for this multicast group on this interface. If no membership report has been received, this object has the value 0.0.0.0.
• Up Time - The time elapsed since this entry was created.
• Expire - The time remaining before this entry will be aged out.
(The default is 260 seconds.)
94
Instant EtherFast®Series
IP Multicast Registration Table
The IP Multicast Registration Table, shown in Figure 6-83, displa ys all the multicast groups active on the Switch, including the multicast IP address and the
corresponding VLANs.
• VLAN - A VLAN with host members that have asked to receive the indicat-
ed multicast service.
• Multicast IP - A source IP address that represents a specific multicast serv-
ice.
• (Multicast Group Port Lists) - The ports that belong to the indicated VLAN
group. Read the numbers vertically; they range from 1-8. For each port number, there are two choices:
If the letter “M” is present, it indicates that the VLAN has access to
messages transmitted by that particular port.
If there is no letter “M,” then there is no access to messages trans
mitted by that particular port.
• Learned by - Shows if this entry was learned dynamically or via IGMP
Snooping. An entry is learned dynamically if a multicast packet was seen
crossing the port, or via IGMP Snooping if an IGMP registration packet was
seen crossing the port.
93
Figure 6-84
Figure 6-83
Page 51

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• Protocol - The multicast routing protocol associated with this
entry.
• Up Time - The time elapsed since this entry was created.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
DVMRP Routing Table
The DVMRP Routing Table, shown in Figure 6-86, shows the routes
for the Distance-Vector Multicast Routing Protocol.
• Source Address - The IP subnetwork at the root of the multicast
delivery tree. This subnetwork contains a known multicast source.
• Mask - Subnet mask that is used for the source address. This mask
identifies the host address bits used for routing to specific subnets.
• Upstream Nbr - The IP address of the network device immediately
upstream for this multicast delivery tree.
• Interface - The IP interface on this Switch that connects to the
upstream neighbor.
• Metric - The metric for this interface used to calculate distance
vectors.
96
Instant EtherFast®Series
• V1 Timer - The time remaining until the Switch assumes that there
are no longer any IGMP Version 1 members on the IP subnet
attached to this interface. (The default is 400 seconds.) If the
Switch receives an IGMP Version 1 Membership Report, it sets a
timer to note that there are Version 1 hosts present which are members of the group for which it heard the report. If there are Version
1 hosts present for a particular group, the Switch will ignore any
Leave Group messages that it receives for that group.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
Multicast Forwarding Cache
The Multicast Forw arding Cache, on the screen shown in Figure 6-85,
displays the settings for the cache.
• Group Address - An IP multicast group address with subscribers
directly attached or downstream from this Switch.
• Source Address - The IP subnetwork at the root of the multicast
delivery tree. This subnetwork contains a known multicast source.
• Mask - Subnet mask that is used for the source address. This mask
identifies the host address bits used for routing to specific subnets.
• Upstream Nbr - The IP address of the network device immediately
upstream for this group.
95
Figure 6-86
Figure 6-85
Page 52

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• RcvRoute - The total number of routes received in valid DVMRP
packets from this neighbor. This can be used to diagnose problems
such as unicast route injection, as well as giving an indication of
the level of DVMRP route exchange activity.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
OSPF Table Menu
The OSPF Table Menu, shown in Figure 6-88, shows a variety of tables you
can have displayed regarding the OSPF information..
•Interface Tab le - Displays information about the OSPF interfaces.
•Link State Table - Displays information about the OSPF link states.
•Neighbor Tab le - Displays information about the OSPF neighbors.
•Virtual Neighbor Table - Displays information about the OSPF virtual
neighbors.
Select OK to retur n to the previous panel.
98
Instant EtherFast®Series
• Up Time - The time elapsed since this entry was created.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
DVMRP Neighbor Table
The D VMRP Neighbor T ab le, sho wn in F igure 6-87, sho ws information
about the neighbors used for the Distance-Vector Multicast Routing
Protocol.
• Interface - The IP interface on this Switch that connects to the
upstream neighbor.
• Neighbor Address - The IP address of the network device
immediately upstream for this multicast delivery tree.
• UpTime- The time since this device last became a DVMRP neigh-
bor to this Switch.
• ExpireTime - The time remaining before this entry will be aged
out.
• Ver - The neighboring router’s DVMRP version number.
97
Figure 6-88
Figure 6-87
Page 53

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
OSPF Link State Table
The OSPF Link State Table screen, shown in Figure 6-90, shows
information about the OSPF link states.
• Area Identity - A 32-bit number assigned to each interface or subnet.
• Type - Description of the link.
• Link State ID - The ID of the device that is connected via the link.
• Router ID - A 32-bit number assigned to the router.
• Sequence No - A 32-bit number that indicates the usage of a link state
advertisement.
• Age - Age of a link state advertisement.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
100
Instant EtherFast®Series
OSPF Interface Table
The OSPF Interface Table screen, shown in Figure 6-89, shows
information about the interfaces for the OSPF protocol.
• IP Address - The IP address of an interf ace.
• Rtr ID - The ID of the router.
• Designated Rtr - The IP address of the designated router.
• Backup DR - The IP address of the back-up designated router.
• Status - This shows whether the interface is down or not.
• Events - The number of events that have occurred.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
99
Figure 6-90
Figure 6-88
Page 54

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
OSPF Virtual Neighbor Table
The OSPF Virtual Neighbor Table screen, shown in Figure 6-92,
shows information about the OSPF virtual neighbors.
• Area ID - A 32-bit number assigned to each interface or subnet.
• Router ID - A 32-bit number assigned to the router.
• IP Address - The IP address of the OSPF vir tual neighbor.
• Option - The option selected for the OSPF virtual neighbor.
• State - The state of the conversation with the virtual neighbor.
• Events - The number of events that have occurred.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
102
Instant EtherFast®Series
OSPF Neighbor T ab le
The OSPF Neighbor Table screen, shown in Figure 6-91, displays
information about the OSPF neighbors.
• IP Address - The IP address of the OSPF neighbor.
• ID - The ID of the OSPF neighbor.
• Router ID - A 32-bit number assigned to the router.
• Option - The optional capabilities that are available.
• Priority State - The state of the neighbor’s priority.
• Events - The number of events that have occurred.
Select Apply to make changes. Select OK to return to the previous panel.
Select Prev Page to view the previous page. Select Next Page to view the next
page. To display a specific page, set the page number in the Page field and then
press Apply.
101
Figure 6-92
Figure 6-91
Page 55

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The Exit command under the Main Menu is used to exit the configuration program and terminate communications with the Switch for the cur rent session.
When using this command, y ou will see the screen sho wn in F igure 6-93. If y ou
need to return to the program, press Enter repeatedly.
104
Instant EtherFast®Series
The System Restart Menu, shown in Figure 6-93, resets the management agent.
• Reload Factory Defaults- Choose whether or not you want to reload the fac-
tory defaults.
• [Restart] - Restarts the Switch.
Note: When restarting the system, it will alw a ys run the Po wer-On Self-Test.
It will also retain all system information, unless you select to reload the factory defaults.
Select Restart to restart the Switch. Select Cancel to cancel the system restart.
103
Exit
Figure 6-93
System Restart Menu
Figure 6-93
Page 56

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Appendix B: Upgrading
Firmware via the Serial Port
You can upgrade system f irmware by connecting your computer to the serial
port on the Switch and using a console interface package that supports the
XModem protocol.
1. Restart the system by using the Restart System command, or b y pulling out
the power cord to reset the power, waiting f ive seconds, and plugging it
back in.
2. When the system initialization screen appears as shown below, press “D”
to download system firmware, and then indicate the code type (<r>
Runtime image or <d> Diagnostic image).
106
Instant EtherFast®Series
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This section provides possible solutions to problems regarding the installation
and operation of the Layer 3 Management 4-Por t Gigabit Ethernet Switch. If
your situation is described here, the problem should be solved by applying the
corresponding solution. If you can’t find an answer here, check the Linksys
website at www.linksys.com.
1. I can’t connect to the Switch using the telnet, Web browser, or SNMP software.
• Be sure you have conf igured the agent with a valid IP address, subnet mask,
and default gateway.
• Check that you have a valid network connection to the Switch and that the
port you are using has not been disabled.
• Check the network cabling between the management station and the Switch.
• If you cannot connect using telnet, there may already be four active sessions.
Try connecting again at a later time.
2. I forgot or lost the password.
• Reinstall the switch firmware as described in the Appendix. Otherwise, con-
tact Linksys Technical Support for help.
105
POST Version V2.55.A03 8/18/2000
------ Power-On SElf Test (POST) -----Int. Loopback Testing SCC2 UART Channel ...PASS
Testing the System SDRAM ...PASS
Int. Loopback Testing _____UART Channel ...PASS
Int. Loopback Testing _____UART Channel ...PASS
CPU Self Test ...PASS
FlashROM CheckSum Test ...PASS
!!! If you want to download image file, Please press <D>
to download:
!!! Download Runtime image, press <r>
!!! Download Diagnostic image, press <d>
!!! Clear the system parameter block, press <c>r
Please input the Baud Rate as following:
Press 1: Baud Rate = 9600
Press 2: Baud Rate = 19200
Press 3: Baud Rate = 38400
Press 4: Baud Rate = 57600
Press 5: Baud Rate = 115200
Select a number and then press <ENTER> !!! 5
Please change local console BaudRate to exact rate and
press <ENTER>!!!
Common Problems and Solutions
Page 57

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Appendix C: Installing the Fiber
Module
You can increase the number of ports on the Switch from four to eight by
installing Fiber Modules on the Switch’s four available slots.
To install the Fiber Modules do the following:
1. Power off the Switch.
2. Remove the Fiber Module’s slot with a phillips screwdriver.
3. Slide the Module into the slot.
(See Figure C-1 or C-2,
depending upon the type of
module you use.)
4. Tighten the Module’s thumb-
screws.
5. Connect a UTP Category 5e
(or better) cable.
6. Power on the Switch.
108
Instant EtherFast®Series
3. Change your baud rate to the selected value, and press Enter to enable
download. From the terminal emulation program, select the file you want
to download, set the protocol to XModem, and then initialize downloading.
Note: If you use Windows Hyperterminal, disconnect it. Set the baud rate,
and reconnect it.
Note: The download f ile should be a binary f ile or an image file; otherwise, the agent will not accept it.
4. After the file has been downloaded, the console screen will display infor-
mation similar to that shown below. Press Enter to download to permanent
memory, and change the baud rate back to 19200. Press Enter to start
decompressing the new firmware, and then press Enter to open the Logon
screen.
Your firmware has now been updated.
107
Figure C-1
Figure C-2
XModem Download to 0x00400020: ... SUCCESS !
(P)ermanent or (T)emporary Download: [P]
Update RunTime Image at 0x03040000 ... ... SUCCESS !
Change to original Baud Rate and Press <ENTER> to Run
Application !!!
Decompress now...... !!!
run-time code starting now. !!! Starting System ...
MAINBOARD OCTOPUS0 RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
MAINBOARD OCTOPUS1 RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
MAINBOARD OCTOPUS2 RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
MAINBOARD OCTOPUS3 RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
MAINBOARD DOLPHIN RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
MAINBOARD STARFISH RAMBIST TEST ...... PASS!
Press <Enter> to start UI
Page 58

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
110
Instant EtherFast®Series
109
Category 5e - The additional cabling performance parameters of return loss and
far-end crosstalk (FEXT) specified for 1000Base-T and not specified for
10Base-T and 100Base-TX are related to differences in the signaling implementation. 10Base-T and 100Base-TX signaling is unidirectional—signals are transmitted in one direction on a single wire pair. In contrast, Gigabit Ethernet is bidirectional—signals are transmitted simultaneously in both directions on the
same wire pair; that is, both the transmit and receive pair occupy the same wire
pair.
Data Packet - One frame in a packet-switched message. Most data communications is based on dividing the transmitted message into packets. F or e xample,
an Ethernet packet can be from 64 to 1518 bytes in length.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - A protocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate the assignment of Internet
Protocol (IP) addresses in an organization’s network. Using the Internet’s set of
protocol (TCP/IP), each machine that can connect to the Internet needs a
unique IP address. When an organization sets up its computer users with a connection to the Internet, an IP address must be assigned to each machine.
Without DHCP, the IP address must be entered manually at each computer, and,
if computers move to another location in another part of the network, a new IP
address must be entered. DHCP lets a network administrator supervise and distribute IP addresses from a central point and automatically sends a new IP
address when a computer is plugged into a different place in the network.
DHCP uses the concept of a “lease” or amount of time that a given IP address
will be valid for a computer. The lease time can vary depending on how long a
user is likely to require the Internet connection at a particular location. It’s
especially useful in education and other environments where users change frequently. Using very short leases, DHCP can dynamically reconfigure networks
in which there are more computers than there are available IP addresses.
DHCP supports static addresses for computers containing Web servers that
need a permanent IP address.
DVMRP (Distance-Vector Multicast Routing Protocol) - Used for routing multicast messages through the Internet.
Ethernet - IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data is placed on
and retrieved from a common transmission medium. Has a transfer rate of
10Mbps. Forms the underlying transport vehicle used by several upper-level protocols, including TCP/IP and XNS.
Fast Ethernet - A 100 Mbps technology based on the 10Base-T Ethernet
CSMA/CD network access method.
Appendix D: Glossary
10BaseT - An Ethernet standard that uses twisted wire pairs.
100BaseTX - IEEE physical layer specification for 100Mbps over two pairs of
Category 5 UTP wire.
1000BASE-T - Provides half-duplex (CSMA/CD) and full-duplex 1000Mbps
Ethernet service over Category 5e links as defined by ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-A.
Topology rules for 1000Base-T are the same as those used for 100Base-TX.
Category 5e link lengths are limited to 100 meters by the ANSI/TIA/EIA-568A cabling standard. Only one CSMA/CD repeater will be allowed in a collision
domain.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) - A TCP/IP protocol used to f igure out a
host’s Ethernet address from its Internet address.
Auto-negotiate - To automatically determine the correct settings. The term is
often used with communications and networking. For example, Ethernet
10/100 cards, hubs, and switches can determine the highest speed of the node
they are connected to and adjust their transmission rate accordingly.
Backbone - The part of a network that connects most of the systems and networks together and handles the most data.
Bandwidth - The transmission capacity of a given facility, in terms of how
much data the facility can transmit in a fixed amount of time; expressed in bits
per second (bps).
BOOTP (BOOTstrap Protocol) - A TCP/IP protocol that lets a device connected to the network be automatically configured and booted up. An IP address is
automatically assigned for a specific length of time.
Category 5 - ANSI/EIA (American National Standards Institute/Electronic
Industries Association) Standard 568 is one of several standards that specify
“categories” (the singular is commonly referred to as “CAT”) of twisted pair
cabling systems (wires, junctions, and connectors) in terms of the data rates
that they can sustain. CAT 5 cable has a maximum throughput of 100Mbps and
is usually utilized for 100BaseTX networks.
Page 59

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The IEEE fosters the development of standards that often become national and
international standards. The organization publishes a number of journals, has
many local chapters, and has several lar ge societies in special areas, such as the
IEEE Computer Society.
IGMP (Inter net Group Management Protocol) - A multicast host registration
protocol that allows any host to inform its local router that it wants to receive
transmissions addressed to a specific multicast g roup.
LAN - A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated
devices that share a common communications line and typically share the
resources of a single processor or server within a small geographic area (for
example, within an office building).
Layer 2 - Data Link layer in the ISO 7-Layer Data Communications Protocol.
This is directly related to the hardware interface for network devices and passes traffic based on MAC addresses.
Layer 3 - Network layer in the ISO 7-Layer Data Communications Protocol.
This layer handles the routing functions for data moving from one open system
to another.
MAC Addr ess - The MAC (Media Access Control) address is your computer’s
unique hardware number.
Mbps (MegaBits Per Second) - One million bits per second; unit of measurement for data transmission.
Multicast Routing Protocol - A routing protocol that supports multicast packets (one to many).
Multicasting - Sends data to a group of nodes instead of a single destination.
Network - A system that transmits any combination of voice, video, and/or
data between users.
Port - A pathway into and out of the computer or a network device such as a
switch or router. For example, the serial and parallel ports on a personal computer are external sockets for plugging in communications lines, modems, and
printers.
112
Instant EtherFast®Series
111
Full Duplex - The ability of a device or line to transmit data simultaneously in
both directions.
GARP (General Attributes Registration Protocol) - A standard for registering or
deregistering client attributes for client services within a bridged LAN.
GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol) - Allows network devices to
register endstations with multicast groups. GMRP requires that any participating network devices or endstations comply with the IEEE 802.1p standard.
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol) - Defines a way for switches to
exchange VLAN information in order to register VLAN members on ports
across the network.
Half Duplex - Data transmission that can occur in two directions over a single
line, but only one direction at a time.
Hardware - Hardware is the physical aspect of computers, telecommunications,
and other information technology devices. The term arose as a way to distinguish
the “box” and the electronic circuitry and components of a computer from the program you put in it to make it do things. The pro gram came to be known as the software.
Hub - The device that serves as the central location for attaching wires from
workstations. Can be passive, where there is no amplification of the signals; or
active, where the hubs are used like repeaters to provide an extension of the
cable that connects to a workstation.
HyperTerminal - A basic communications pro gram that is an accessory for all
Windows operating systems, starting with Windows 95. It enables your computer to communicate with other compatible devices, using either a standard
RS-232 cable, null modem cable, or modem. It can also be referred to as a
VT100 or ANSI terminal application.
IEEE - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. The IEEE
describes itself as “the world’s largest technical professional society—promoting the development and application of electrotechnology and allied sciences
for the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the wellbeing of our members.”
Page 60

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
UTP - Unshielded twisted pair is the most common kind of copper telephone
wiring. Twisted pair is the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many
business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated copper wires are
twisted around each other. Each signal on twisted pair requires both wires.
Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections,
twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single
cable.
VLAN (Virtual LAN) - A logical association that allows users to communicate
as if they were physically connected to a single LAN, independent of the actual physical configuration of the network.
114
Instant EtherFast®Series
113
Port Trunk - Def ines a network link aggregation and trunking method, which
specifies how to create a single high-speed logical link that combines several
lower-speed physical links.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) - A simple routing protocol that is part of
the TCP/IP protocol suite. It determines a route based on the smallest hop count
between source and destination. RIP is a distance vector protocol that routinely broadcasts routing information to its neighboring routers and is known to
waste bandwidth. AppleTalk, DECnet, TCP/IP, NetWare, and VINES all use
incompatible versions of RIP.
RJ-45 (Registered Jack-45) - A connector similar to a telephone connector that
holds up to eight wires, used for connecting Ethernet devices.
RMON (Remote MONitoring) - RMON provides comprehensive network
monitoring capabilities. It eliminates the polling required in standard SNMP,
and can set alarms on a variety of traffic conditions, including specif ic error
types.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)- A widely used netw ork monitoring and control protocol. Data is passed from SNMP agents, which are
hardware and/or software processes reporting activity in each network device
(hub, router, bridge, etc.) to the workstation console used to oversee the network. The agents return information contained in a MIB (Management
Information Base), which is a data structure that def ines what is obtainable
from the device and what can be controlled (turned off, on, etc.).
Static Routing - Forwarding data in a network via a fixed path. Static routing
cannot adjust to changing line conditions as can dynamic routing.
Subnet Mask - The method used for splitting IP networks into a series of subgroups, or subnets. The mask is a binary pattern that is matched up with the IP
address to turn part of the host ID address field into a f ield for subnets.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) - A version of the TCP/IP FTP protocol
that has no directory or password capability.
Throughput- The amount of data mov ed successfully from one place to another in a given time period.
Unicast Routing Protocol - A routing protocol that does not support multicast.
Page 61

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Dimensions 16.93" x 1.75" x 13.78"
(430 mm x 44.45 mm x 350 mm)
Unit Weight 8.82 lbs. (4 kg)
Power Input 110-120V AC,60Hz
Certifications FCC Part 15, Class A
Operating Temp. 0° C to 50° C (32° F to 122° F)
Storage Temp. -40° C to 70° C (-40° F to 158° F)
Operating Humidity 20 % to 95 %, Non-Condensing
Storage Humidity 20 % to 95%, Non-Condensing
116
Instant EtherFast®Series
115
Environmental
Appendix E: Specifications
Standards IEEE 802.1D,IEEE 802.1p, IEEE 802.1Q,
IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3ab,IEEE 802.3u,
IEEE 802.3x, IEEE 802.1ad
Ports 4 10/100/1000BaseTX
4 Expansion Slots for 1000BaseTX/SX Modules
Speed Per Port (Mbps)
10/100 Ports 10 or 100 (Half Duplex)
20 or 200 (Full Duplex)
1000 Ports 1000 (Half Duplex)
2000 (Full Duplex)
Address Table
MAC Address 16k
IP Address 16k
Max Frame Size 9 KB
Buffer Memory 6MB
Back-Plane Bandwidth 8Gbps
Switch Technology Store and Forward
IP Switching Wired Speed IP Forwarding
Routing Protocol RIP or RIP1, RIP2, OSPF v2
Multicast Protocol GMRP, IGMP, and DVMRP
Management Interface RS-232,Telnet,Web,SNMP Application
SNMP Protocol SNMP v1/v2, MIB II and Bridge MIB,
MAUs MIB,IGMP MIB, DVMRP MIB,
RIPII MIB,IP Forwarding Table MIB,
RMON MIB,private MIB, OSPF v2 MIB
Cabling Type UTP Category 5e or Better
LEDs Fan,TEMP, Power,1000/100/10 (1-4 each)
FDX and 100 per port
Page 62

EtherFast® Layer 3 Management 4-Port Gigabit Ethernet Switch
118
Instant EtherFast®Series
117
Appendix G: Contact
Information
For help with the installation or operation of this product, contact Linksys
Technical Suppor t at one of the phone numbers or Inter net addresses below.
Sales Information 800-546-5797 (LINKSYS)
Technical Support 800-326-7114
RMA Issues 949-271-5461
Fax 949-265-6655
Email support@linksys.com
Web http://www.linksys.com
FTP Site ftp.linksys.com
Appendix F: Warranty
Information
BE SURE TO HAVE YOUR PROOF OF PURCHASE AND A BARCODE
FROM THE PRODUCT’S PACKAGING ON HAND WHEN CALLING.
RETURN REQUESTS CANNOT BE PROCESSED WITHOUT PROOF OF
PURCHASE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL LINKSYS’LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID
FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE
OF THE PRODUCT, ITS ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION. LINKSYS DOES NOT OFFER REFUNDS FOR ANY PRODUCT.
LINKSYS OFFERS CROSS SHIPMENTS, A FASTER PROCESS FOR PROCESSING AND RECEIVING YOUR REPLACEMENT. LINKSYS PAYS
FOR UPS GROUND ONLY. ALL CUSTOMERS LOCATED OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AND CANADA SHALL BE HELD
RESPONSIBLE FOR SHIPPING AND HANDLING CHARGES. PLEASE
CALL LINKSYS FOR MORE DETAILS.
Page 63

© Copyright 2002 Linksys,All Rights Reserved.
http://www.linksys.com
 Loading...
Loading...