Page 1

Field Guide
Leica Geosystems GS20
Version 1.1
English
Page 2

Leica Geosystems GS20
Symbols Used in This Manual
Congratulations on your purchase of a new Leica
Geosystems System GS20.
To use the equipment in the permitted
manner, please refer to the detailed safety
instructions in the User Manual.
© 2004 Leica Geosystems AG Heerbrugg, ® All rights
reserved.
Symbols used in this manual have the following meanings:
WARNING.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation or an
unintended use which, if not avoided, could result in
death or serious injury.
Important paragraphs which must be adhered to in
)
practice as they enable the product to be used in a
technically correct and efficient manner
Tip: Indicates useful information that may help you execute
a task.
Remember: These paragraphs contain summarized
information or important tips.
Leica Geosystems GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
2
Page 3

View of chapters
1. Basic Operation .................................................................11
2. Data Collection...................................................................21
3. Data Management ..............................................................35
4. Navigation...........................................................................43
5. Job Management................................................................47
6. Codelist Management........................................................53
7. Applications .......................................................................55
8. Utilities ................................................................................61
9. Setup ...................................................................................63
10. Status ..................................................................................93
11. Glossary..............................................................................95
12. Index....................................................................................99
Leica Geosystems GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
3
View of chapters
Page 4

Introduction
The Leica Geosystems GS20
The Leica Geosystems GS20 PDM was conceived to provide
the GIS community with a GPS data collection device that
combines the simplicity of a recreational GPS handheld with
the power and flexibility of a professional grade mapping
system. The Leica Geosystems GS20 represents a true
turnkey GPS/GIS mapping solution by integrating the GPS
receiver and antenna within the chassis of handheld data
collector. Add to this the built-in efficiency of Bluetooth
wireless technology and you only need add power and sky;
the rest is up to you.
Philosophy of Operation
• Data Collection is used for the initial recording and
attribution of points, lines, and areas.
• Data Management is used for the update of attribution
and geometry of an object; including relocation and
continuation of existing geometry
• Navigation is only used for the purpose of finding a known
location. Any update to the navigated object must be done
in Data Management.
• Utilities contains File Browser, Firmware Update and
Sensor Transfer
• Setup allows the user to configure software operation
settings such as GPS controls, Data Collection Quality
Control, external Interfaces, and Units and Formats, and
Languages.
• Status provide the user with information related to GPS,
external interfaces and the condition of hardware and
software.
Leica Geosystems GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
4
Introduction
Page 5

Registration
Congratulations on your purchase of the Leica Geosystems GS20 Professional Data Mapper.
To ensure premium support and service of your new GS20, please take the time to fill out and mail the attached Registration
Card.
Customer/Business Name
Primary Contact
Address
City, State (Province), Country
Email and Telephone No.
Leica Geosystems GS20 Serial Number
*Firmware Version
Accessories Purchased
Accessory Serial Numbers
Who was your Leica Dealer?
How was your out of the box experience?
* Firmware version can be located on the startup screen, or by accessing the Hardware Screen in Status.
Leica Geosystems GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
5
Registration
Page 6
Company stamp, additional notes/information:
Leica dealer:
Leica Geosystems GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
6
Registration
Page 7

Table of Contents
1. Basic Operation............................................ 11
1.1 Batteries and Charging ............................... 11
1.1.1 Calibrating the Battery ..............................11
1.2 Powering On the Unit .................................. 12
1.3 Icons ............................................................ 12
1.3.1 Accuracy Indicator ....................................12
1.3.2 Stop and Go Indicators .............................13
1.3.3 Satellite Indicator ......................................13
1.3.4 Differential Corrections .............................13
1.3.5 Memory Card Status .................................13
1.3.6 Battery and Time Indicators ......................13
1.4 Button Functions ......................................... 14
1.4.1 Alpha Numeric Keys .................................14
1.4.2 Power Key ................................................14
1.4.3 Enter and Escape .....................................15
1.4.4 Cursor Keys ..............................................15
1.4.5 Menu Button .............................................15
1.4.6 The Main Menu .........................................16
1.4.7 Paging .......................................................16
1.5 Software User Interface .............................. 17
1.5.1 Map Views ................................................17
1.5.2 GPS Symbol and Zoom Controls ..............18
1.5.3 Context Menus ..........................................18
1.5.4 Tables and Filtering ..................................19
1.5.5 Filtering .....................................................19
1.5.5.1 Map Filters ................................................19
1.5.5.2 Table Filters ..............................................20
2. Data Collection ............................................. 21
2.1 Job Management ........................................21
2.2 Background Files in the GS20 ....................22
2.2.1 Overview ...................................................22
2.2.2 Adding Background Files to a GS20 Job ..22
2.2.3 Creating a Background File in
GIS DataPRO ...........................................23
2.2.4 Transferring a background File .................23
2.2.5 Viewing the Map .......................................24
2.2.6 Turning off the background in the Map
Display ......................................................24
2.3 Code Management ...................................... 25
2.3.1 Creating Codelists ....................................25
2.3.2 Using the Codelist Manager .....................26
2.3.3 Steps for codelist creation ........................26
2.3.3.1 Step 1: Creating a new codelist in
GIS Data Pro ............................................27
2.3.3.2 Step 2: Creating Codes in GIS DataPRO .27
2.3.3.3 Step 3: Creating Attributes ........................28
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
7
Table of Contents
Page 8

2.3.3.4 Step 4: Display Attributes: Attaching Map
Symbology ............................................... 29
2.3.3.5 Step 5: Transferring Codelist to the
Sensor ...................................................... 29
2.4 The Codelist and Occupation ...................... 30
2.4.1 The Job Codelist .......................................30
2.4.2 Attribution ..................................................30
2.4.3 Point Collection .........................................30
2.4.3.1 Point Offsets ............................................. 31
2.4.4 Line and Area Collection ...........................32
2.4.5 Modes of Collection ..................................33
3. Data Management......................................... 35
3.1 Philosophy of Feature Selection ................. 35
3.1.1 Options with Nothing Selected ..................35
3.1.2 Options with a Feature Selected ...............35
3.1.3 Options with a Node Selected ..................36
3.2 Selecting a Feature ..................................... 36
3.2.1 Feature Management ...............................36
3.2.1.1 Table Filtering .......................................... 37
3.2.2 Selecting a Node or “Vertex” ....................37
3.2.2.1 Node Management ................................... 37
3.2.3 Feature Submenu .....................................37
3.2.4 Node Submenu .........................................38
3.2.4.1 Re-Occupying Nodes ............................... 38
3.2.4.2 Copying and Pasting Nodes ..................... 39
3.2.4.3 Inserting, Appending, and Prepending in
Existing Lines and Areas ..........................39
3.3 Using the Geographic Clipboard .................40
3.3.1 Purpose of the Geographic Clipboard ......40
3.3.2 Flow of use (Sharing a common node
between blocks) ........................................41
3.3.3 Creating Point Topology ...........................42
4. Navigation..................................................... 43
4.1 The Navigation Screen ................................ 44
4.2 Waypoint Selection and Management ........ 45
4.3 Creating a new Waypoint feature ................ 45
4.4 Updating a Navigated Feature ....................46
5. Job Management .......................................... 47
5.1 Coordinate Systems .................................... 48
5.1.1 Introduction ...............................................48
5.1.2 Overview ...................................................49
5.1.3 Attaching a Coordinate System ................49
5.1.4 Field File ...................................................50
6. Codelist Management.................................. 53
6.1 Creating a New Codelist .............................53
6.2 Creating a New Code .................................. 54
6.2.1 Creating a New Attribute ...........................54
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
8
Table of Contents
Page 9

7. Applications.................................................. 55
7.1 Cultivated Field Control ............................... 55
7.1.1 Introduction ...............................................55
7.1.2 Setup ........................................................55
7.1.3 Using the Program ....................................57
8. Utilities .......................................................... 61
8.1 File Browser ................................................ 61
8.1.1 Browser Controls ......................................61
8.1.2 Context Menu ...........................................61
8.1.3 Firmware Update ......................................62
8.1.4 Sensor Transfer ........................................62
8.1.5 Clear System Memory ..............................62
9. Setup ............................................................. 63
9.1 Selecting, Modifying and Creating
Configurations ............................................. 63
9.1.1 Selecting ...................................................63
9.1.2 Modifying ..................................................63
9.1.3 Creating ....................................................63
9.2 Tree Directory Navigation ...........................64
9.3 Hardware Management ............................... 64
9.3.1 Hardware ..................................................64
9.3.2 Contrast ....................................................65
9.3.3 Wireless (Bluetooth Connectivity) .............65
9.3.3.1 Selecting a Wireless Device .................... 65
9.3.4 Clearing a Selected Device ......................66
9.3.5 Real-Time Corrections with a Mobile
Phone .......................................................66
9.3.6 Linking with the Bluetooth .........................67
9.3.7 Configuring your Device ...........................67
9.3.8 Modifying your Configuration ....................68
9.3.8.1 Status Indication .......................................68
9.3.9 Connecting to the Station .........................68
9.4 ID Template Management ........................... 69
9.4.1 Creating an ID Template ...........................69
9.4.2 Modifying an Existing Template ................69
9.5 Device Manager ..........................................70
9.5.1 Creating a New Device .............................70
9.5.2 Modifying an Existing Device ....................70
9.6 GPS .............................................................70
9.6.1 Tracking ....................................................70
9.6.2 Minimum Satellites ....................................71
9.6.3 Antenna Type ...........................................71
9.6.4 Logging .....................................................71
9.6.5 Initialization ...............................................72
9.7 Data Collection ............................................ 72
9.7.1 Quality Monitor ..........................................72
9.8 Interfaces ....................................................73
9.8.1 Real-Time .................................................73
9.8.2 GS20 Phase Wizard .................................74
9.8.2.1 Overview ...................................................74
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
9
Table of Contents
Page 10

9.8.2.2 Static Phase ............................................. 75
9.8.2.3 Kinematic Phase ...................................... 75
9.8.2.4 The Interface ............................................ 75
9.8.2.5 Collecting Static points, including kinematic
points of initialization ................................ 76
9.8.3 WAAS and EGNOS ..................................77
9.8.3.1 Understanding the WAAS Corrections ..... 78
9.8.3.2 Changes to the Real-Time Screen ........... 79
9.8.4 Connecting to WoRCS Beacon ................79
9.8.4.1 Powering on the WoRCS ......................... 80
9.8.4.2 Checking the Bluetooth Link .................... 80
9.8.4.3 Checking the WoRCS Real-Time Link ..... 81
9.8.4.4 WoRCS Real-Time Beacon ..................... 81
9.8.5 Connecting to WoRCS Real-Time Satellite
(RTS) ........................................................82
9.8.5.1 Powering on the WoRCS ......................... 83
9.8.5.2 Checking the Bluetooth Link .................... 83
9.8.5.3 Checking the WoRCS Real-Time Link ..... 85
9.8.5.4 WoRCS RTS ............................................ 85
9.8.6 Offset Devices ..........................................86
9.8.6.1 Configuration of the GS20. ....................... 86
9.8.6.2 Overview of the basic methodologies of
point offset data collection. ....................... 88
9.8.6.3 Explanation of individual point offset data
collection methodologies. ......................... 89
9.8.7 ASCII Input ...............................................91
9.9 Units and Formats ....................................... 92
9.9.1 Units of Measure .......................................92
9.9.2 Language ..................................................92
9.9.3 Formats .....................................................92
10.Status............................................................ 93
10.1 GPS .............................................................93
10.1.1Position .....................................................93
10.1.2Satellite Information ..................................93
10.1.3Satellite View ............................................94
10.2 Interfaces ....................................................94
10.2.1Real-Time .................................................94
10.2.1.1 RTB Coast Guard Beacon ........................94
10.3 Hardware .....................................................94
11.Glossary ....................................................... 95
12.Index ............................................................. 99
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
10
Table of Contents
Page 11

1. Basic Operation
1.1 Batteries and Charging
Leica Geosystems GEB90, 7.2 volt, 2100 mAh Lithium-Ion
batteries must be used to power the Leica GS20 and WoRCS
equipment. Charge only with the Leica Geosystems battery
charger provided in the system.
WARNING:
The battery chargers are intended for indoor use only.
Use a battery charger in a dry room only, never
outdoors. Charge batteries only at an ambient
temperature between 10° C and 30° C (50° F to 86° F).
We recommend a temperature of 0° C to +20° C (32° F
to 68° F) for storing the batteries.
1.1.1 Calibrating the Battery
The Leica Geosystems GEB90 battery uses a microprocessor
to accurately monitor the battery status. To calibrate the
battery microprocessor, allow the Leica Geosystems GS20 to
rundown and automatically power off.
The Leica Geosystems GEB90 battery can be
)
referenced and ordered by Leica part number 724117.
The Leica Geosystems GKL24 Dual Bay Battery
Charger can be referenced and ordered by Leica part
number 731771.
Use only the Leica Geosystems batteries, chargers,
)
and accessories, or accessories recommended by
Leica Geosystems.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
11
Basic Operation
Page 12
1.2 Powering On the Unit
Press and release the Power Button located on lower left of
the keyboard. The unit will reply with an audible tone, then
proceed to a splash screen and then to the Main Menu.
Remember: Although the unit can power on without the flash
card, most functionality will not be available.
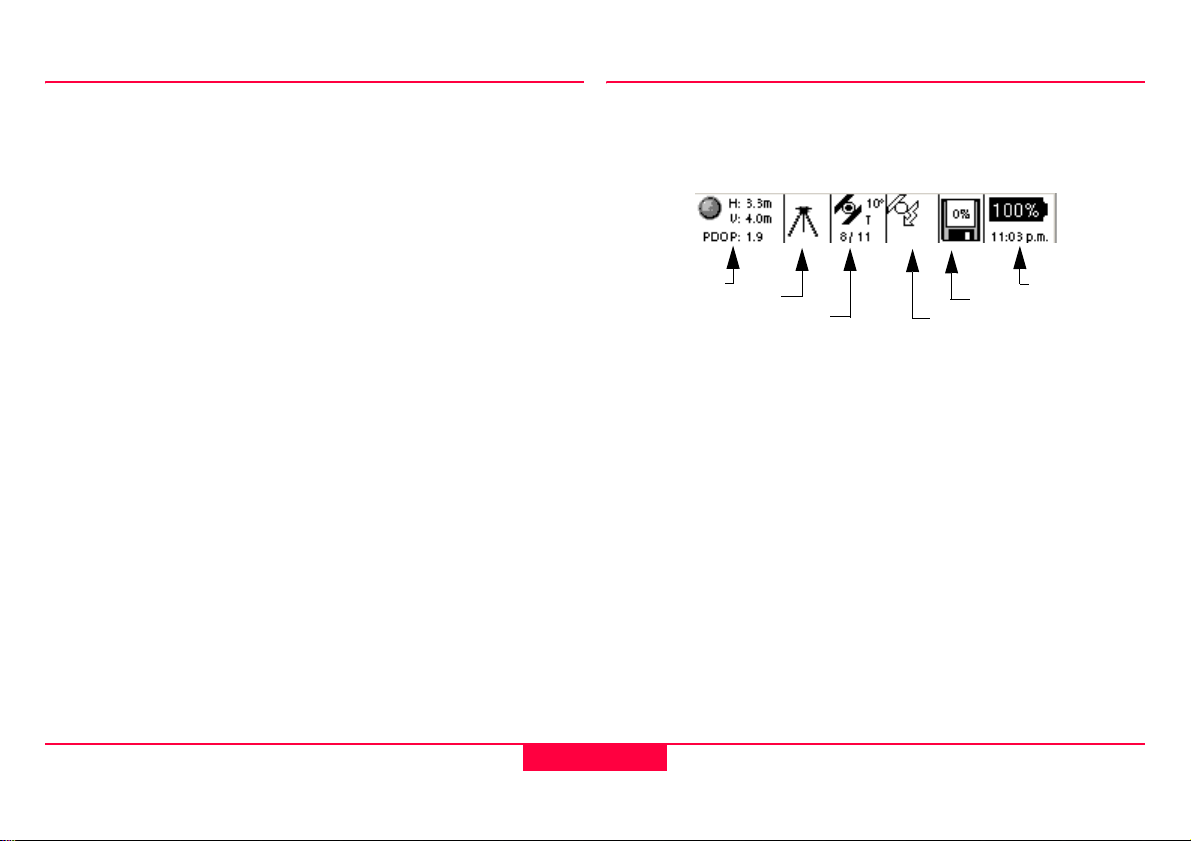
1.3 Icons
The Icon area is displayed to provide the user with current
information about the GPS and hardware.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
1.3.5
1.3.4
1.3.6
Figure 1-1: Accuracy Indicator
1.3.1 Accuracy Indicator
The accuracy indicator is displayed once a solution is
calculated. The open sphere indicates that an autonomous
position has been determined and the bullseye target
indicates a DGPS solution. Additionally information provided
in the text include horizontal and vertical qualities, as well as
PDOP.
12
Basic Operation
Page 13

1.3.2 Stop and Go Indicators
When a static position is located, such as a point or a node (in
a line or area), the stop and go indicator is displayed as a
tripod. Once the icon returns to the walkingman, the user can
proceed to the next collection point.
1.3.3 Satellite Indicator
The satellite indicator provides text based information
including the satellite tracking angle, the number of satellites
visible (according to the almanac) and the number of satellites
currently tracked.
(Satellites Tracked / Satellites Visible)
1.3.4 Differential Corrections
When differential corrections are received and interpreted, the
differential icon appears. If the correction is lost after 1/3 of the
selected age (see 9.8.1 "Real-Time"), an exclamation point
will appear in the lower left hand corner of the window. If it is
still absent after 2/3 of the selected age, an additional
exclamation mark will appear. If corrections are lost beyond
the selected age, a third exclamation will appear and the icon
will then disappear.
1.3.5 Memory Card Status
The memory card status icon provides a graphical
representation of the percentage of the compact flash used.
1.3.6 Battery and Time Indicators
The battery and time indicators provide information about the
current status of the onboard battery and the current time
obtained by satellites.
• Because the Battery indicator is based on a
microprocessor in the Lithium Ion battery, only the onboard
battery status can be provided in percentages.
• Because the Leica Geosystems GS20 does not rely on
internal batteries for clock function, time is only displayed
when 1 or more satellites is tracked.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
13
Basic Operation
Page 14

1.4 Button Functions
1.4.1 Alpha Numeric Keys
Keys 1-9 represent the alpha numeric entry keys of the GS20.
Similar to a cellular phone, buttons 2-9 contain alpha
characters; by pressing the key continuously, all characters
on that key will be scrolled. The selection of a character can
be made by either selecting a different key, or waiting for the
2 second time-out. Special characters can be found on the
decimal key on the lower right of the keyboard.
1.4.2 Power Key
To power the unit on, the power key needs only to be pressed
and released. The unit will then respond with an audible tone,
followed by the splash screen.
Time to splash screen may depend on compact flash
)
size and the amount of data on disk.
While in operation, the backlight can be turned on with a
button press of less than 3 seconds.
If the power key is depressed and held for three seconds, the
unit will power down and give a message confirming the
power down and saving of data.
Figure 1-2: Leica GS20 Keypad
Remember: Depressing and holding the key acts like
multiple key presses.
Multiple functions: Keys 3 and 9 have been provided with
additional functionality. In a map display, 3 and 9 function as
zoom keys; in a table, 3 and 9 function as page up and page
down.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
14
Basic Operation
Page 15

Table 1-1: Overloaded Button Functions
Map Table
3 Down Zoom In Page Down
9 Up Zoom Out Page Up
1.4.3 Enter and Escape
Similar to standard Windows’ controls, the Enter key is used
to either accept a choice or advance an action. The Escape
key functions both as a back key, to escape from a current
screen; as well as a backspace in edit fields.
1.4.4 Cursor Keys
Cursor keys are found on the face and the side of the unit; the
side cursors function exactly the same as the up and down
cursor on the face. If held down, the cursor key will
automatically speed up, such as in the map display, table, or
edit field. Because the cursor key is so integral to control and
entry, its functions vary in different controls.
1. Menus: Left and Right function as home and end.
2. Edit Fields: Up and Down function as home and end.
3. Check Boxes and Radio Buttons: Left/Right toggle makes
a field selection.
4. Combo Box and Spin Controls: Left and Right scroll
selections.
5. Map: Controls the cursor
1.4.5 Menu Button
The Menu key is the prime key in the Leica Geosystems GS20
user interface. Not only can Menu bring you quickly back to
the Main Menu to load the paging queue and select new
application, it also opens the context menu which contains all
of the high level controls for the unit.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
15
Basic Operation
Page 16

1.4.6 The Main Menu
The Main Menu is the base level of the Leica Geosystems
GS20 user interface. The Main Menu can be quickly accessed
from an application by double clicking the Menu button. By
returning to the Main Menu in an open application, it is
possible to run several application simultaneously; this is
referred to as the paging function.
1.4.7 Paging
Because it is often necessary to access several applications
at once (e.g. data collection, navigation, satellite view, etc.)
Leica Geosystems has created the Power Paging function.
Power Paging allows the user to quickly and easily flip through
running applications in the order they were opened. To place
an application in the paging queue, simply open the
application from the Main Menu. To add an additional
application to the queue, double click Menu to return to the
Main Menu, then open a new application. The paging button
will then page through the open applications. To remove an
application from the page, simply Escape from the application
to the Main Menu.
Figure 1-3: GS20 Main Menu
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
16
Basic Operation
Page 17
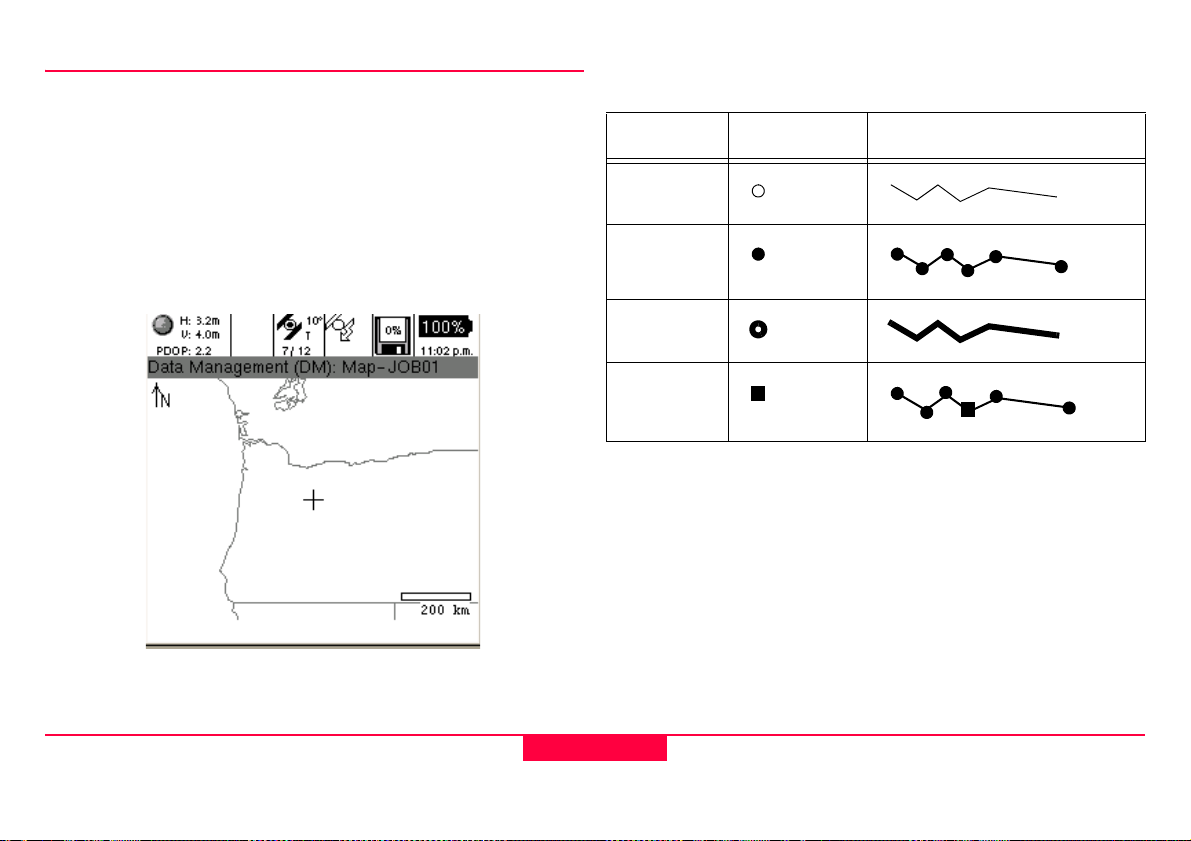
1.5 Software User Interface
Table 1-2: Mapview Legend
1.5.1 Map Views
The map view is the common interface on which all main
applications are built. Data Collection, Data Management and
Navigation all contain a map interface that has similar controls
and are continuously updated, but have independent settings.
Zooms, filtering, selection, and autopan GPS are all unique to
each applications mapview.
Figure 1-4: Mapview (Selected and Filtered)
Points Lines and Areas
Normal
Selected
Filtered
Selected
Node
Normal: Standard features in Mapview
Selected: The currently active feature selection
Filtered: Display of features in a current table
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
17
Basic Operation
Page 18

1.5.2 GPS Symbol and Zoom Controls
By default, an open mapping screen zooms to the full extent
of data in a job; however if no data exists, the map will be
centered on the GPS location (scaled to 1:20m) awaiting
collected data.
The map submenu contains zoom controls for
• Zoom In, Zoom Out, Zoom To Full Extents
• Center Cursor, Center GPS, Center Selected
• Autopan GPS
Remember: “3” and “9” function as zoom controls !
Remember: The mapview is only capable of displaying
12,000 nodes, being points or line/area
verticies. A warning will be issued at 9500
nodes, that the map will be discontinued. A final
warning will be issued before the map display is
turned off.
Tip: To minimize nodes in a job; consider streaming lines
and areas by distance or at a slower rate. An 8 hour
constant collection at a 5 second interval only produces
5760 nodes.
The map display can be turned off in the Job
)
Management Screen.
1.5.3 Context Menus
The context menu in the Leica
Geosystems GS20 functions
similarly to a Windows’ context
menu, however the right mouse
click is replaced with the Menu
button. When the Menu button is depressed, a list of choices
will be displayed based on the application and the actions
taken.
• Choices in the context menu can either be selected using
the cursor arrows (Left and Right being home and end) or
directly accessed via the number keys.
• To simplify submenus appear where common groupings
exist such as map control functions. The submenu is
denoted with a right arrow and is accessed via enter or the
number key. In some instances, sub-submenus exist.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
18
Basic Operation
Page 19
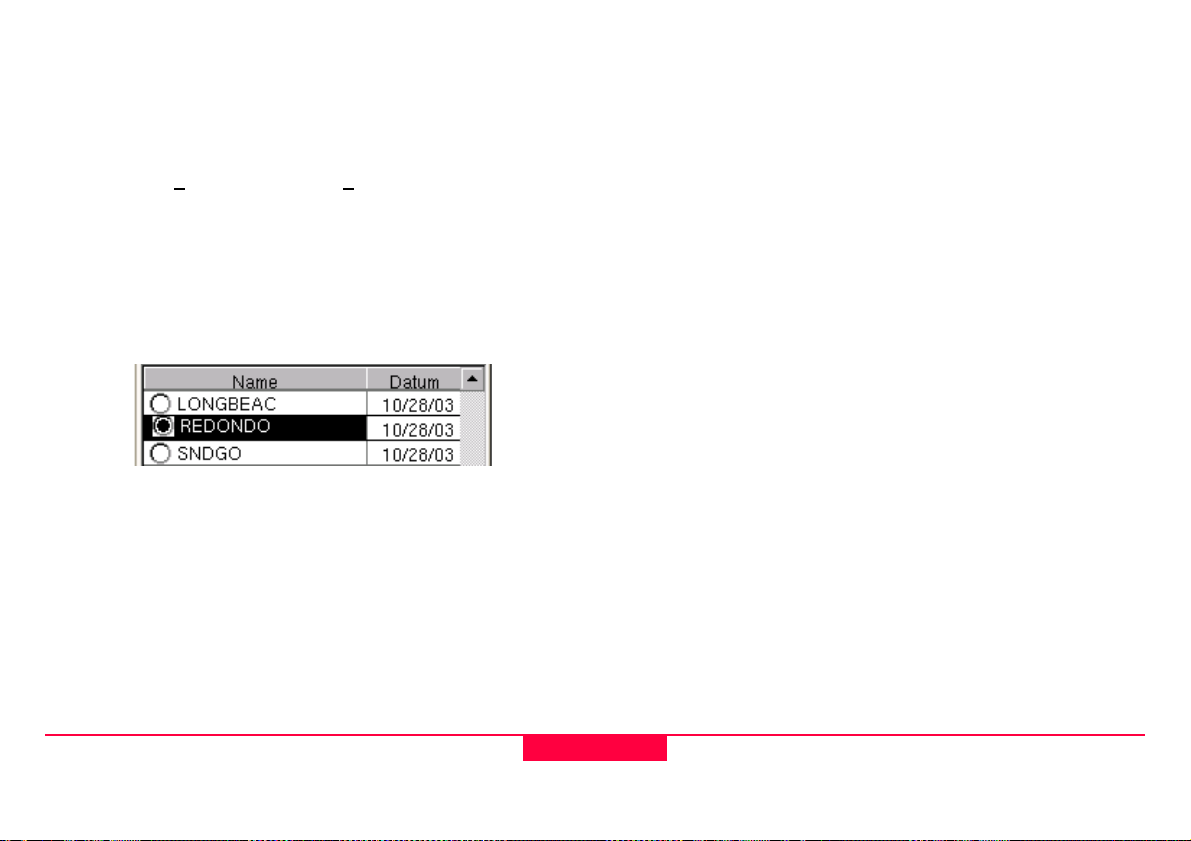
1.5.4 Tables and Filtering
Tables are used to display multiple attribute data that cannot
be directly edited. The table can be navigated by the cursor
keys (left and right being home and end) as well as the
overload keys 3
Two main types of tabular data found in the GS20 are
selectable and informative.
• Selectable fields allow the user to make a selection such
as choosing a Job or Codelist, and are usually identified by
a radio button (selectable circle). Additional options, such
as New, Delete, etc. usually exist in the context menu.
• Informative fields allow the user to view and manipulate
information about the tabled object.
Page Down and 9 Page Up.
Figure 1-5: Selectable Table
1.5.5 Filtering
In order to provide power and flexibility to the user, the Leica
Geosystems GS20 maintains separate filters for individual
tables and maps.
1.5.5.1 Map Filters
Map filters provide the user with the ability to hide or display
data in the map.
Map filters allow the user to discriminate data based on
• Feature Code (Layer name)
• Feature Name (Feature ID)
• Feature Type (Point, Line, or Area)
• Time of collection
• Waypoint Status (Flag as Waypoint (i.e. to be navigated to)
or Visited)
Similarly data can be filtered in a table for selection, edits,
clipboard function or changing the Waypoint status.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
19
Basic Operation
Page 20

1.5.5.2 Table Filters
Table filters allow the user to search for data based upon the
same criteria as listed above in map filters.
Once a table is filtered, the user can select from the filtered
table, or view the selected filters in the map view via the
context menu choice Table Features.
This differs from map filtering in that the data remains
)
displayed, but appears highlighted.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
20
Basic Operation
Page 21
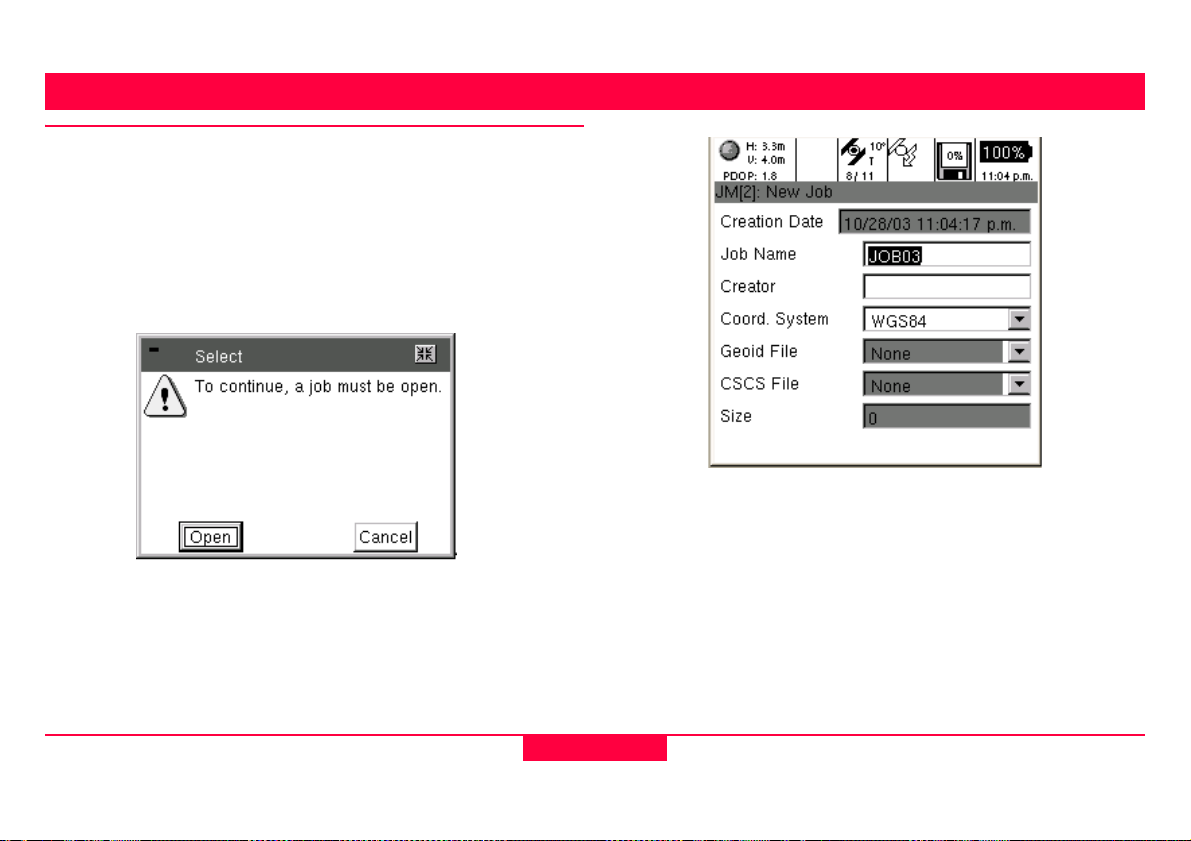
2. Data Collection
2.1 Job Management
When Data Collection is opened, if no job is currently
selected, the user will be prompted to either “Open” an
existing job or create a “New” job to continue. If a new or
empty job is selected, the unit will prompt the user to attach a
codelist; otherwise the program will proceed to the Data
Collection map.
Figure 2-1: Job Management Screenflow
Figure 2-2: Job Management Screenflow
Tip: When you create a new job, you have the option of
attaching a Coordinate System and Geoid file with
creation of the job.
Tip: See 5. "Job Management" for more info
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
21
Data Collection
Page 22
2.2 Background Files in the GS20
Often it is important for a user to see the location of they’re
current position and those Features they have collected within
a larger context. However, it is not always necessary or even
beneficial to have that data selectable. With the ability to
create vector background data, the GS20 can now:
• Attach larger vector reference files
• Use the same vector reference file for multiple jobs
• Reference multiple files to a job
• Reference previously collected jobs in an open job
• Only re-import collected or updated data
2.2.1 Overview
GS20 background files are graphic files that can be created in
GIS DataPRO, and are automatically created when job data
is collected in the GS20. The graphic file contains the file
extension qtr, which stands for quadtree; a method of spatially
indexing vector data. When a job is created in the GS20, a
graphic file of that same name is also created. From job
management, a background screen can be accessed,
allowing the user to reference other “background” graphical
data to the job. Background graphic files are for visual
reference only, and are not selectable.
2.2.2 Adding Background Files to a GS20 Job
To add a background Map, enter Job management, highlight
a selected job, and select “Background Maps” from the
context menu.
Figure 2-3: Background Maps
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
22
Data Collection
Page 23
A status of available memory will be available to provide
information on how much information can be attached to a job.
Memory used in background files will affect the amount of
map data that can be collected, so be conservative in your
estimates.
A successful attachment will be shown in the Status column
and Memory Available will be recalculated.
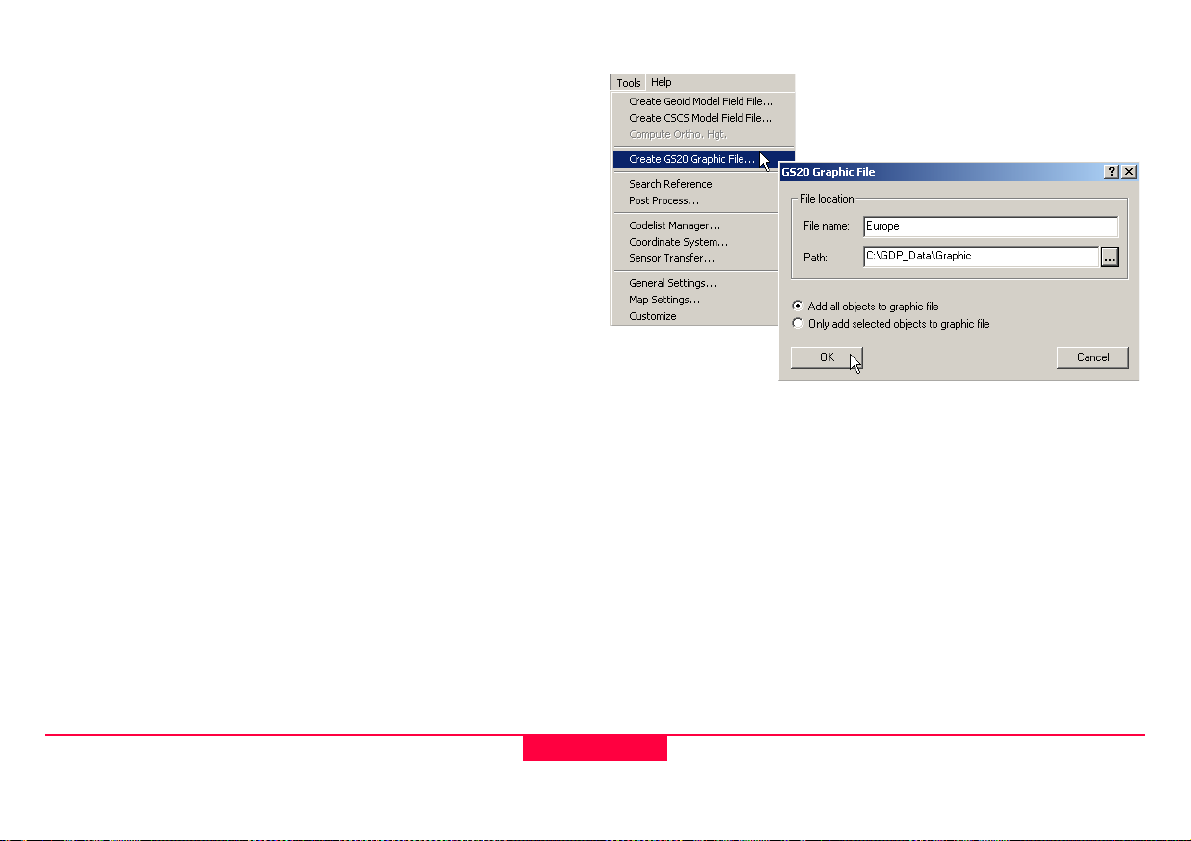
2.2.3 Creating a Background File in GIS DataPRO
In order to create a graphic file in GIS DataPRO, it will be
necessary to first import the data into the GIS DataPRO
database.
Data that is added to GIS DataPRO with the +, or add
shapes cannot be converted into a graphics file.
To create the Graphics file, select “Create GS20 Graphic File”
from the Tools pull-down menu.
A dialog will prompt for a filename and path, with the default
being active. The user can select to create a background from
all data, or only selected objects.
Figure 2-4: Creating a background
2.2.4 Transferring a background File
To transfer a graphic file, open Tools / Sensor Transfer. Right
click on Sensors, and Add a Sensor. Under My Computer,
browse to the location of the Graphics file.
Right Click on the Graphic File and send to your connected
Device.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
23
Data Collection
Page 24
2.2.5 Viewing the Map
If all has gone according to plan, the graphic file will be
attached to the current job, and will be displayed in Map View
applications. Because the memory used by the graphic files
are not recovered during use, it will be necessary to reboot to
reclaim lost space once a background is detached from a job.
Figure 2-5: Viewing the Map
2.2.6 Turning off the background in the Map Display
Similar to the Filtering ability of layers and data types in a Map
View, Background files can be turned on and off. To turn off a
Map view, select the Map Filter from the Map context menu,
and press enter on the layer with the new Background Icon.
Figure 2-6: Turning off the background
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
24
Data Collection
Page 25

2.3 Code Management
Because the Leica Geosystems GS20 is designed for GIS
data creation and update, existing feature layer will be used
as a code template for each particular job. Additional codelists
can be attached to a job via Codelist Manager.
In order to protect database integrity, a consistency check is
performed when codelists are attached to a job. If the same
code occurs in both the feature table and the codelist, the job
feature data will be used.
Codelists can be attached and detached as well as created
and modified from the Codelist Manager in the MAIN menu.
2.3.1 Creating Codelists
What is a Code? Codes are used to describe objects of the
same type. The code in GIS DataPRO is equivalent to the
Theme in ArcView 3.2. Each code has it’s own type, with only
one type per code: point, line or polygon For example: Tree
(Point), Roads(Line), Parcels(Polygon).
A code contains attribute information that may be assigned to
the Codes (points, lines or areas) during measurement in the
field.
For example: Fire Hydrant (Code): Serial Number and Color
(Attributes).
A Codelist contains codes to be collected in a job, and is
attached to a job.
A codelist can be created in three ways:
1. Create your own codelist/code.
2. Copy another codelist/code from another project.
3. Import codes from existing shapefile.
Codelists are created in the Codelist Manager in GIS
DataPRO.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
25
Data Collection
Page 26
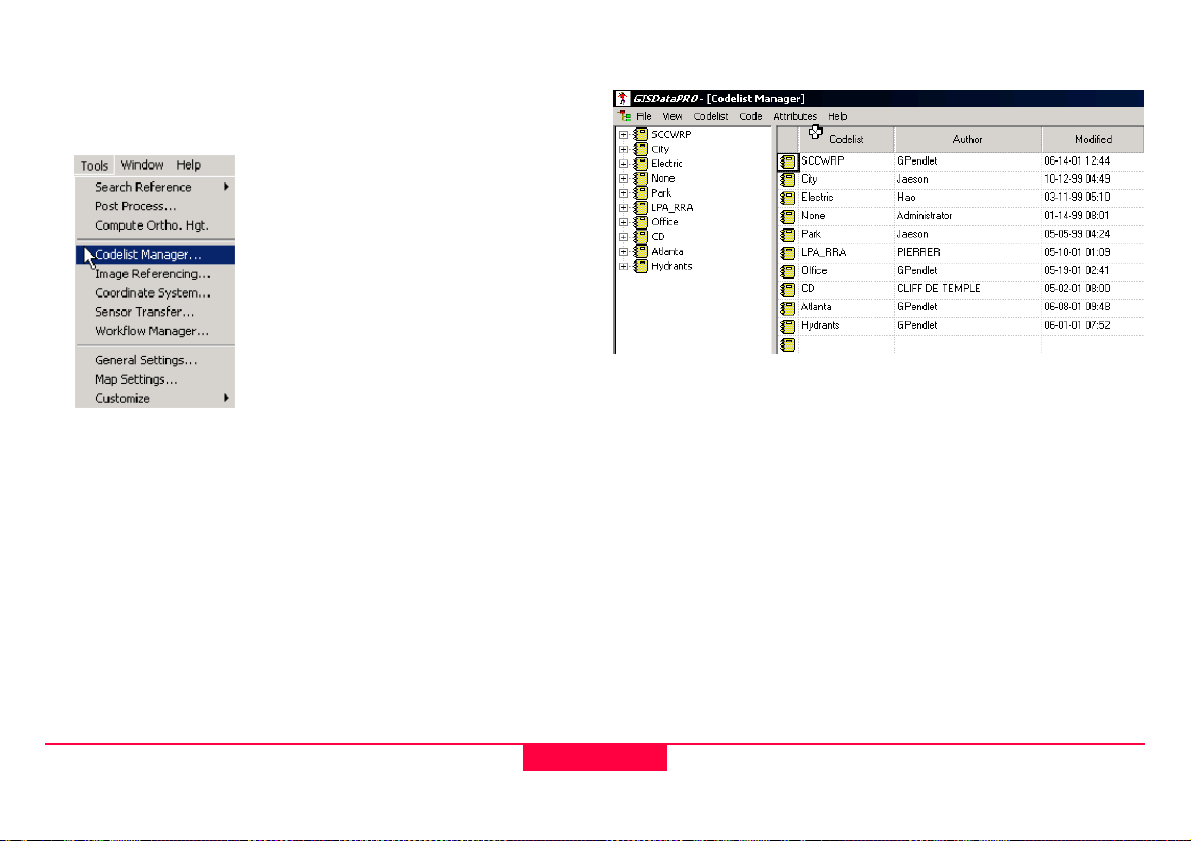
2.3.2 Using the Codelist Manager
1. Select Tools from the Main Menu.
2. Select Codelist Manager, this is the interface you will see.
Listed below are the steps for codelist creation. We will list
them here, and then look at each one in depth.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
2.3.3 Steps for codelist creation
1. Create a Codelist in GIS DataPRO
2. Create Codes Unlimited codes in a codelist
3. Create Attributes Maximum 60 Attributes per code
4. Attach Map Symbology to each code in a codelist
5. Save codelist
6. Transfer a Codelist to sensor.
26
Data Collection
Page 27
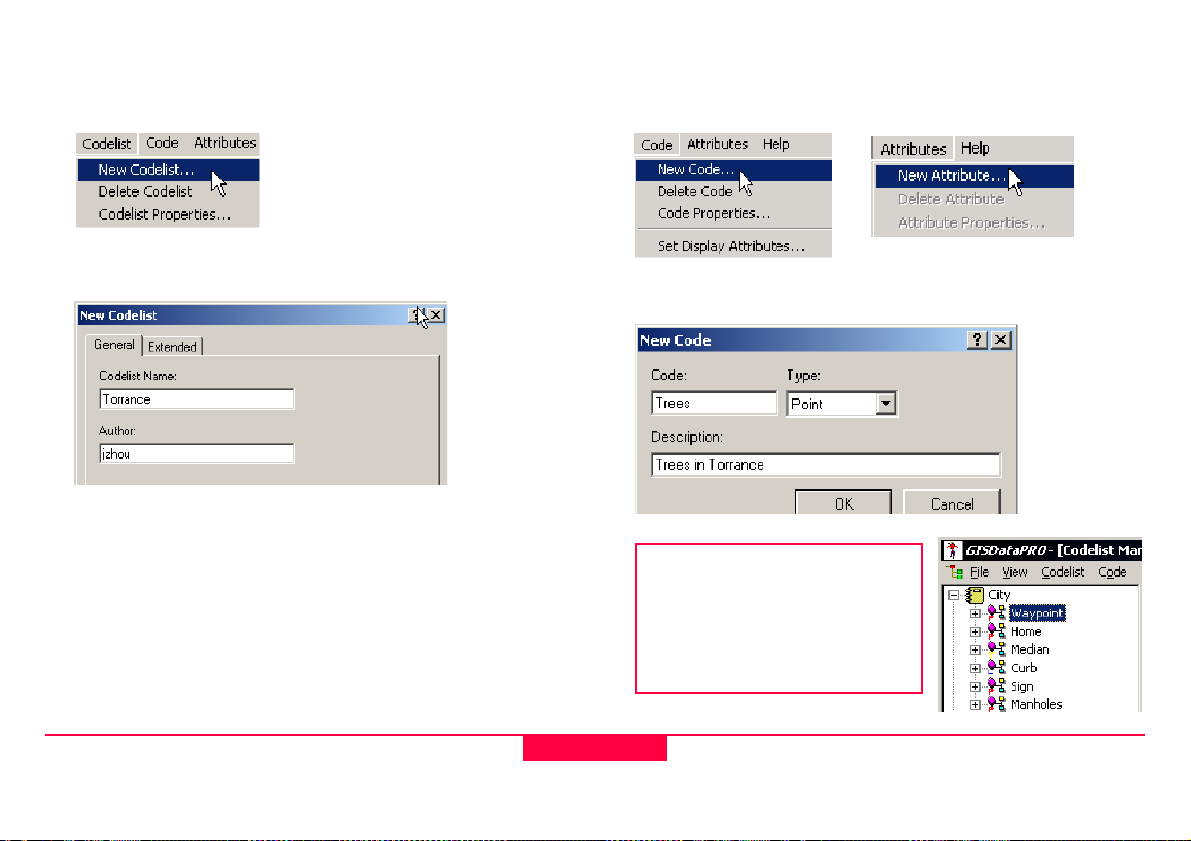
2.3.3.1 Step 1: Creating a new codelist in GIS Data Pro
1. Click on Codelist and select New Codelist
2. Type in name of the New Codelist.
3. Click OK.
Your new codelist is now created, highlighted and ready to be
populated.
2.3.3.2 Step 2: Creating Codes in GIS DataPRO
1. From the pull down menu choose new code
2. Create a new Code Name and Description
When a codelist is
)
created the first code is
always Waypoint and
cannot be changed!
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
27
Data Collection
Page 28
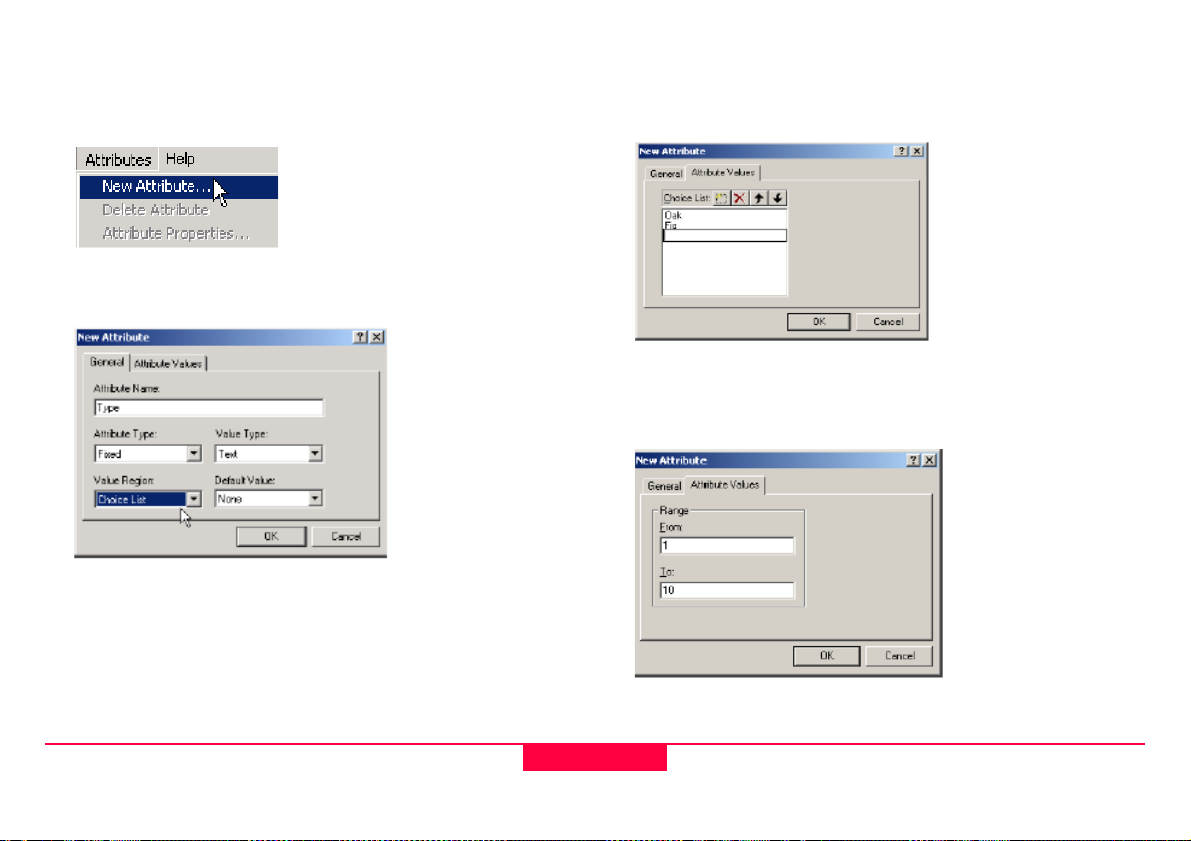
2.3.3.3 Step 3: Creating Attributes
1. From the Attribute pull down menu choose New Attribute
2. Fill in the attribute name and properties.
3. The attribute Type can be Normal, Mandatory or Fixed
4. The attribute Value can be Text, Real or Integer
5. The attribute Value Region Can be None, Choice List or
Range
6. The Default Value can be typed in if None or Range was
selected in the Value region. It can be selected if Choice
List was used.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
28
Data Collection
Page 29
Facts About Attributes:
1. The Z attribute is reserved and cannot be changed.
2. The Z attribute contains elevation data
3. Maximum 256 characters per Choice List
4. Attribute names must begin with a letter
5. Limit the attribute names to 10 characters
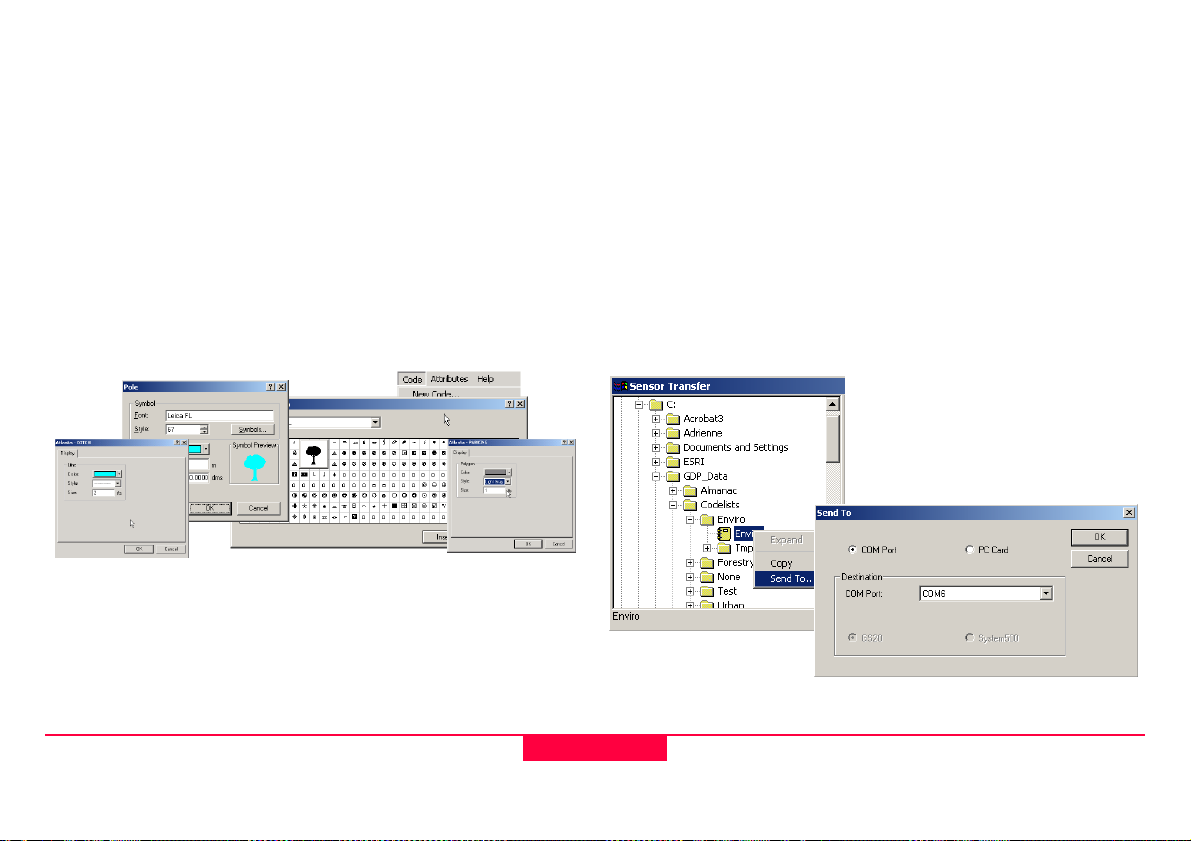
2.3.3.4 Step 4: Display Attributes: Attaching Map Symbology
The display properties are used to display each feature in the
GIS DataPRO after data collection.
From the Code pull down, choose “Set Display Attributes.
The Codelist may now be saved with map symbology intact.
Figure 2-7: Map Symbology
2.3.3.5 Step 5: Transferring Codelist to the Sensor
1. Open Sensor Transfer
2. Add Sensor
3. Browse to location where codelists are stored (default
location: C:\GDP_Data\Codelists)
4. Right click on codelist and select Send Files...
5. In the Send Files... dialog select the codes you would like
transferred
6. Select the appropriate COM port and select Codelist from
the File Type Choice
With your codelist now on the sensor, you are ready to attach
it to your job and collect GIS Data.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
29
Figure 2-8: Transferring Codelists
Data Collection
Page 30
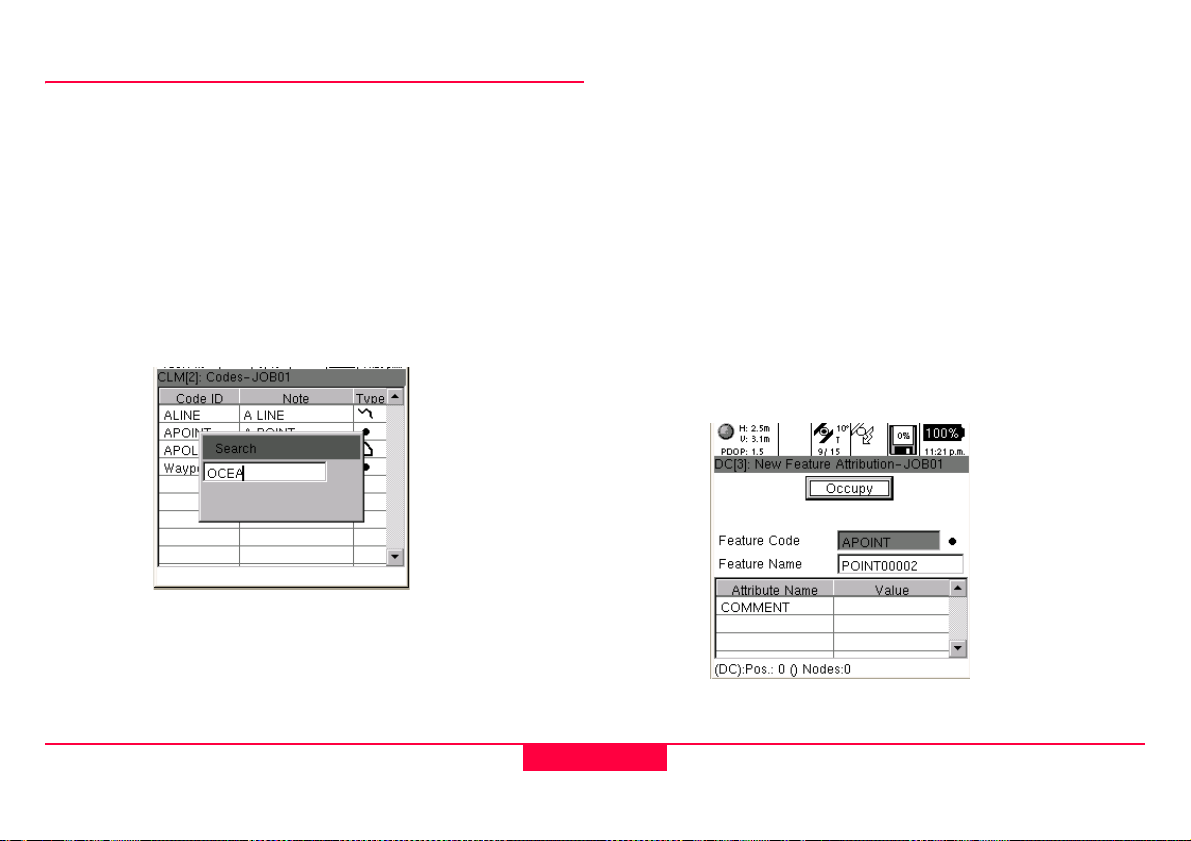
2.4 The Codelist and Occupation
2.4.1 The Job Codelist
If a job is new (i.e. does not contain any data), the user will be
taken to the code table; otherwise the user is defaulted into a
map view. From the mapview, you can enter features via the
context menu, or by just pressing Enter. From the code table
screen, the code template can be selected by using the cursor
or searching with the pop-up dialog (which opens with an
alpha numeric key.)
Figure 2-9: Data Collection / Job Codelist
2.4.2 Attribution
After a code is selected, press Enter to open the attribution
screen. By default the focus is on the Occupy button;
however, by using the cursor and Enter key, attribution values
can be entered. Additional occupation selections can be
accessed via the context menu.
2.4.3 Point Collection
Point collection is often as simple as entering attributes,
pressing Occupy and Save; however different user defined
quality settings can determine how the feature is collected
(see Setup/Data Collection.) In addition to direct locations, the
user can also choose from a list of point offsets.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
30
Figure 2-10: Attribution / Point Occupation
Data Collection
Page 31

2.4.3.1 Point Offsets
”
When a point cannot be collected directly, an offset can be
used to collect a point from a more accessible location. Offset
information can be entered either manually, or via an external
rangefinder. The choice of point offsets available are listed
below.
Aux “A”
Azimuth Distance
35
125
m
o
30’
0
0”
+
O/S Pt
Figure 2-11: Example of Dist.Dist O/S
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
Aux “A”
1
o
1
0
Azimuth - Azimuth
O/S Pt (Left Solution)
+
2
m
5
3
Aux “A”
Distance Distance
5
m
R
(Right Solution)
+
O/S Pt
o
0
2
2
Aux “B”
Aux “B
Figure 2-12: Offset Methods (Graphical)
31
Data Collection
Page 32

When collecting a point offset, it is important to input the offset
data before occupying the auxiliary point.
• Azimuth Distance: Enter Azimuth, Distance and Delta
Height before occupying the point.
• Azimuth Azimuth: Enter Azimuth and Delta Ht for 1st
position from Aux Pt. A; then repeat for PT B.
• Distance Distance: Enter Distance and Delta Ht for 1st
position from Aux Pt A; repeat for position B and choose
the solution method (i.e. Left or Right)
Remember: Because two solutions exist for a double
distance intersections, the user must tell the
software on what side of point A-B the offset
point lies.
• Backwards Azimuth and Distance: Useful when locating
a point by direct occupation when no GPS exists. The BAD
works by providing an azimuth and distance to a previously
located point. The calculation then reverses the course
and distance.
2.4.4 Line and Area Collection
Unlike point collection, lines and areas offer multiple methods
of collection; noding (i.e. collecting by vertex), streaming by
time or distance, locating nodes by point offsets, creating
linear offsets to either side of the collected line, pasting a node
from the clipboard, and nesting additional features. Because
the Start/Stop button is necessary to both stop in noding and
pause in streaming, features must be saved by the Done
button or the Save Feature in the context menu.
Figure 2-13: Line and Area
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
Tip: When escaping the feature collection, a dialog will
allow the user to save or discard the current feature.
32
Data Collection
Page 33

2.4.5 Modes of Collection
When a line or area feature is selected, the attribution screen
will display the current mode of collection (i.e. stream or
node.) The last selected mode becomes the default by being
stored in the user’s recent value file.
Figure 2-14: Attribution screen
2 Node Mode or noding is the manual collection of nodes or
“vertices.” Like points, nodes can be collected using the
autostop which can be found in Data Collection\Quality
Control settings in the Setup menu.
3
Streaming is the automatic collection of nodes (i.e. vertices)
based on time or distance (length between nodes.)
Additionally, streaming criteria can be based on the horizontal
quality defined in 8
configuration setting, select Data Collection and Quality
Control in the Setup configuration.
Streaming options can be selected from the attribution\
collection screen via the context menu.
4
Line Offsets allow the user to enter linear offsets, either left,
right or in both directions with different values.
mode
, the offset selection will become a submenu offering all
methods of point collection for individual nodes.
The 8
More selection allows the user to Paste from Clipboard,
as well as Append or Prepend an existing line.
Paste from Clipboard allows multiple features to share
common nodes. In order to paste a node, it must first be
3
Copied to Clipboard in Data Management. (See 3.2.4.2
"Copying and Pasting Nodes")
Setup, 1 Config Sets, select the proper
When in node
Remember: Point features cannot be created with pasted
node data in Data Collection. However, points
already collected can have their node replaced
with the 2
Paste from Clipboard function,
allowing multiple point features to share a
common node.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
33
Data Collection
Page 34

Tip: Another way to share a common node is by locating a
new position with the Backward Azimuth and Distance.
The trick is to leave all fields to zero and Paste Node for
location.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
34
Data Collection
Page 35

3. Data Management
3.1 Philosophy of Feature Selection
Data Management selection options and context menus
behave differently depending on what data has been
selected. Once a feature is selected, the user must
5
Deselect via the context menu in order to select another
feature. Three different levels of selection exist in Data
Management.
3.1.1 Options with Nothing Selected
With nothing selected, the user can select features either
graphically in the map or tabularly via the Feature
Management, view and select all nodes in the entire job via
2
Node Management table, or 4 Create New Waypoints to
be navigated.
3.1.2 Options with a Feature Selected
With a feature selected, the user can select from a list of
nodes common to the selected feature either graphically in the
map or tabularly via the Node Management table, view or
modify the feature’s 2
selected feature as a Waypoints via the 3
graphically depict filtered table data in 4
5
Deselect the currently selected feature.
Attribution, copy, delete or flag the
Feature submenu,
Table Features, or
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
35
Data Management
Page 36

3.1.3 Options with a Node Selected
When a node is selected on a feature, the user can select
another node common to the feature graphically in the map,
view the coordinates or re-occupy the node via 1
or use the 2
1. Progress to the First, Last, Previous or Next node.
2. Copy to, Select from, or Paste from a node via the
Clipboard.
3. Insert New nodes Before or After the current node
selected.
4. Delete the selected nodes.
Node submenu to:
Geography,
3.2 Selecting a Feature
In order to view or manipulate feature data, a feature must first
be selected. Selection can be performed from a table of
features via Feature Management, or graphically from a map.
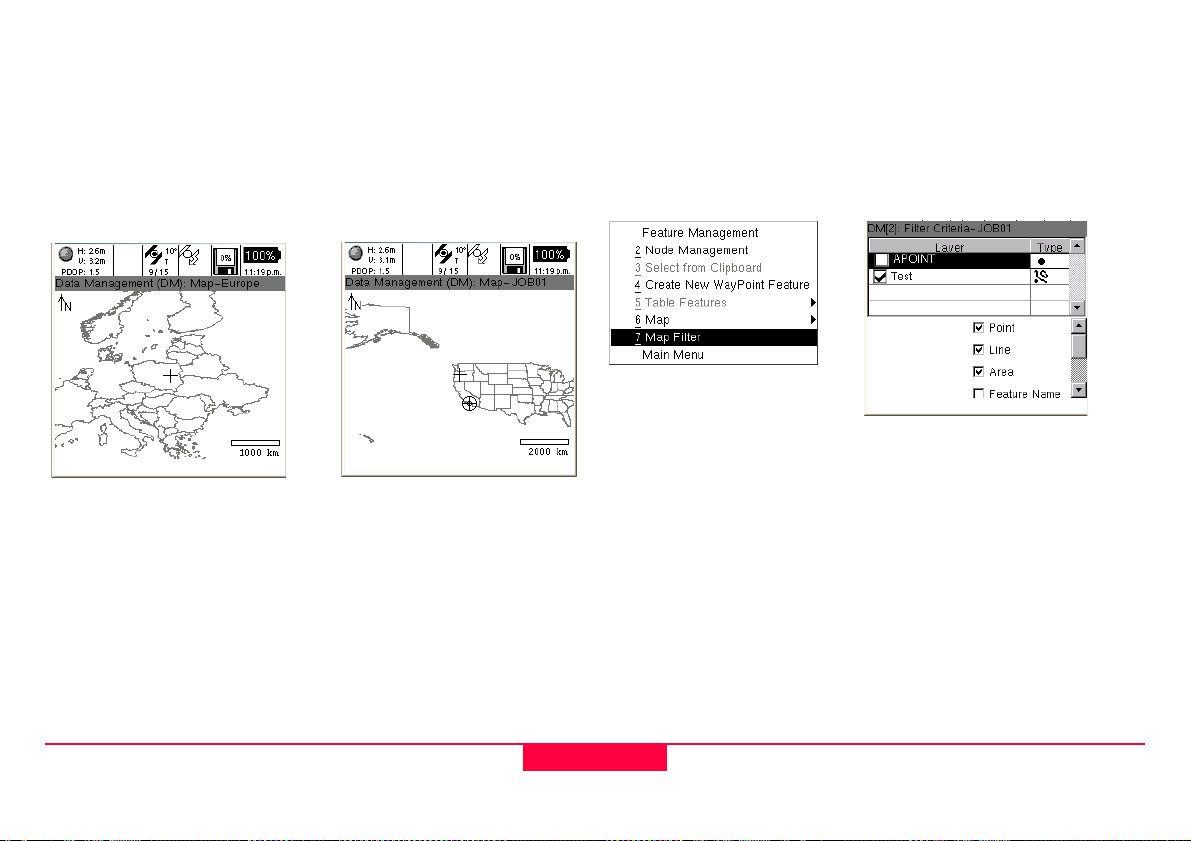
3.2.1 Feature Management
Tabular selection of a feature is done from the Feature
Management menu. Once in Feature Management, by default
features will be listed alphabetically; point, line and area
templates will group like features and present them in a
numerical order. However, by choosing Menu and Sort the
table can be sorted by Name, Code, Feature Type and by
Ascending or Descending order.
• To view the attributes of a table selection, press menu and
choose 3
• To select the feature, press Menu and choose 2
from the context menu.
Other options of a selected feature include feature
manipulation (e.g. delete and clipboard functions) and the
ability to flag a selected feature as a Waypoint.
Tip: Linear Perimeter and Polygon area can be calculated in
Attribution, or simply press Enter.
Select
the Attribution screen if a coordinate system has been
selected.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
36
Data Management
Page 37

3.2.1.1 Table Filtering
As previously discussed in chapter 1.5.4 "Tables and
Filtering", Table Filtering provides a way to search based on:
• Code (Feature Name)
• Feature Type (i.e. Point, Line or Area)
• Code/Feature Name (using wildcards)
• Range of Time
• Waypoint Status
Once data has been filtered, the user can either manipulate or
select based on the filtered table, or display the filter in the
map using the context menu choice Tabled Features and
Highlight. The Traverse submenu choice, allows the user to
graphically progress through each filtered table feature row by
row.
Remember: Filtered data is shown by a bold outline and can
be progressed through using the feature Next
and 2
Previous submenu choice.
3.2.2 Selecting a Node or “Vertex”
3.2.2.1 Node Management
Node Management can be selected from the context menu
when nothing is selected, providing a list of all nodes in a job.
3.2.3 Feature Submenu
When an object is selected at the feature level, the Feature
Submenu provides the user with the ability to
1. Move to the Next and 2
objects are selected.
2. 3 Copy a feature to Clipboard.
3. 4
Select from Clipboard when a feature has been
previously copied (such as in Navigation).
4. 5
Delete the selected feature.
Remember: Leica Geosystems GS20 does not have Undo!
5. Set a database flag indicating the feature is a Waypoint
and if it has been visited via the 6
Previous feature when multiple
Waypoint submenu.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
37
Data Management
Page 38

3.2.4 Node Submenu
When a node or “vertex” has been selected on a feature, a
node submenu provides additional node selection ability as
well as the ability to modify the feature on a node level.
1. Choose the 1
a feature.
Remember: Very handy for determining the direction of a
2. 5 Clipboard function to Copy to, Select from or Paste from
a previously selected node Before or After a node.
3. 6
Insert New functions provide the ability to insert single
nodes or stream to append an existing object.
4. 7
Delete the selected node.
First, 2 Previous, 3 Next, or 4 Last node on
feature.
3.2.4.1 Re-Occupying Nodes
Nodes can be moved or Re-Occupied by choosing
1
Geography from the menu. When the Re-Occupy soft key
is selected the attribution/collection screen is opened and the
focus will be on the Occupy button.
Remember: Node Re-Occupation works in the same way as
point collection.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
38
Data Management
Page 39

3.2.4.2 Copying and Pasting Nodes
In order to copy a node, a node must first be selected. This
can be done directly from a node table, or most commonly on
a feature level.
Copying
1. Select the desired feature either graphically or from
Feature Management.
2. Select a node either graphically or from the 2
Management table.
3. Select menu and choose the 2
4. Select the 5
5. Select Copy to.
Clipboard submenu.
Node submenu
Node
Tip: Before you can paste, you must deselect the copied
feature.
Pasting
1. Select the desired feature either graphically or from
Feature Management.
2. Select a node adjacent to the point you wish to insert either
graphically or from the 2
3. Select menu and choose the 2
4. Select the 5
5. Select 3
6. Select to paste Before, 2
Clipboard submenu.
Paste from.
Node Management table.
Node submenu.
After, or 3 Replace.
3.2.4.3 Inserting, Appending, and Prepending in Existing Lines and Areas
Previously collected lines and areas can be amended or
continued by Inserting, Appending, or Prepending with noded
or streamed data.
One of the complexities of adding new data is knowing the
order in which a feature was collected. This can be done by
using the Previous and Next commands in the Node submenu
to discern the direction of collection.
Inserting into a Feature (Node Mode)
1. Select the desired feature to be appended, either
graphically or from Feature Management.
2. Select a node adjacent to the point you wish to insert either
graphically or from the 2
3. Select Menu and choose the
4. Select 6
5. Select Before or 2
Insert New.
Node Management table.
2 Node submenu.
After.
Tip: Because the nature of collection is to continue in the
same direction as the collected feature, it is advised to
insert After an existing node for multiple nodes or
streaming!
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
39
Data Management
Page 40

Appending a Line or Area by Streaming
1. To append a line or area by streaming select the last node
of the line and insert 2
2. In the attribution/collection screen, change the collection
mode to stream and occupy as you would with a normal
collection.
Prepending a Line or Area by Streaming
Tip: If you are adding to the beginning of a line by
streaming, you will need to reverse the direction of your
collection
1. To prepend a line or area, select the first node and insert
Before.
2. In the attribution/collection screen, select 8
3. Select the insertion order 2
direction of collection.
Advance usage of Prepend and Append can be used to
)
approach the beginning or end of a line from the
opposite direction.
After.
More.
Prepend. This will reverse the
3.3 Using the Geographic Clipboard
3.3.1 Purpose of the Geographic Clipboard
New and Unique to the GS20 is the Geographic Clipboard
functionality.
The clipboard functionality is similar to the copy and paste
functionality found in many Windows styled applications.
This functionality allows the user to select and copy a feature
or node to the clipboard, and in turn, the user can paste to or
“Select from” the clipboard.
Nodes can be shared between features that can create
shared edges. For example: Street Intersections and Water
Lines can have a node topology that facilitates network
analysis. Parcel corners and edges can allow for shared
boundaries. Parent / Child Topology of point objects can allow
a transformer to be intrinsically tied to a power pole. Thus
moving or deleting the parent, would result in the child is also
being moved or deleted.
By creating this topology in the field, you remove the
guesswork from the office.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
40
Data Management
Page 41

3.3.2 Flow of use (Sharing a common node between blocks)
Select a Feature, and then select a node. If the feature is a
point object, you can copy the feature or the node.
1. Open Data Collection
2. Open Data Management, select a feature, and then select
a node.
3. Copy the node to the clipboard.
4. Page to Data Collection.
5. From Data Collection, select New Feature
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
41
Data Management
Page 42

6. Select More from the menu choices, and Paste the node
from the clipboard.
7. Repeat as necessary.
3.3.3 Creating Point Topology
Points features can be linked to other points or nodes by
taking advantage of the paste functionality in the Point offset
menu. Because the pasted point is the base reference of the
newly created feature, when the base is moved or deleted, the
connected feature is also modified.
Once a point or node is copied (as shown above), it can be
pasted as the Auxiliary or base point in a point offset. This can
be done from Azimuth Distance, using the paste function, or
is done automatically with Back. Azimuth Dist.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
42
Data Management
Page 43

4. Navigation
The navigation application is purely a means to guide the user
to a point with known coordinate values. The points to be
navigated are known in the GPS world as “Waypoints,” from
their origin as destinations along the way. The user also has
the option to navigate to points that have never been visited
before.
Rather than having a special feature code for “Waypoints,” the
Leica Geosystems GS20 uses a database flag in the feature
that can be toggled to define a Waypoint as:
Flagged: As a feature that should be navigated to
or
Visited: Providing closure to the workflow
Waypoints can be created in the Leica Geosystems GS20 by
several methods:
• Selecting points graphically from the mapview in both
Navigation and Data Management.
• Tabling a known feature and setting the database
Waypoint flag in Data Management.
• Setting the node on a linear feature as a temporary
Waypoint in both Navigation and Data Management.
• Creating a new Waypoint by entering known coordinates in
Data Management.
• Uploading GIS or CAD data set with a Waypoint flag from
Leica Geosystems GIS DataPro to the Leica GS20.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
43
Navigation
Page 44

4.1 The Navigation Screen
The navigation screen is framed to provide the map display
along with active navigational controls and text.
The framed control panel contains a directional guidance
arrow, and text fields providing:
1. Azimuth to the Waypoint.
2. Distance to the Waypoint.
3. The user’s course Azimuth
4. The user’s course Velocity.
Remember: Because the GPS bearing and velocity are
calculated using GPS positions, the user must
be moving for course data to be displayed.
• If the user is stopped, the arrow and course fields will
become inactive.
• If the user is moving, but no Waypoint is selected, the
arrow becomes a North Compass.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
44
Navigation
Page 45

4.2 Waypoint Selection and Management
Similar to Data Management, the Navigation context menu
changes depending on whether data is selected.
When features or nodes have not been selected, the context
menu provides the user with access to:
1. Waypoint Management which provides a list of features or
nodes flagged as Waypoints.
2. Select from Clipboard if a node was previously copied from
Data Management.
If a feature is selected, the context menu then provides
Waypoint with the options for the feature or node to be:
• Flagged as a Waypoint.
• Flag a point as 2
• Access back to the 3
• Select the 4
Visited once it has been navigated to.
Waypoint Management.
Previous or 5 Next Waypoint feature.
4.3 Creating a new Waypoint feature
Waypoint feature may be created by selecting MENU and
Create New Waypoint feature from the navigation screen.
This menu allows the user to add a waypoint using WGS84 or
Local Grid Coordinate Systems. To access the local
coordinate system options, hit MENU and select local grid.
This selection will stay toggled until changed by the user.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
45
Navigation
Page 46

4.4 Updating a Navigated Feature
Once a Waypoint has successfully been reached, a feature or
node can be updated by:
1. Select Menu and choose 2
2. If Data Management is currently open, Page to the Data
Management application. Otherwise, press the Menu key
twice to return to the Main Menu, then Select 2
Management.
3. In Data Management, select Menu and choose 3
from Clipboard.
4. The feature of the node can now be modified as previously
discussed in chapter 3. "Data Management".
Copy to Clipboard.
Data
Select
Tip: Keep both Navigation and Data Management in the
paging queue to easily update Waypoints.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
46
Navigation
Page 47

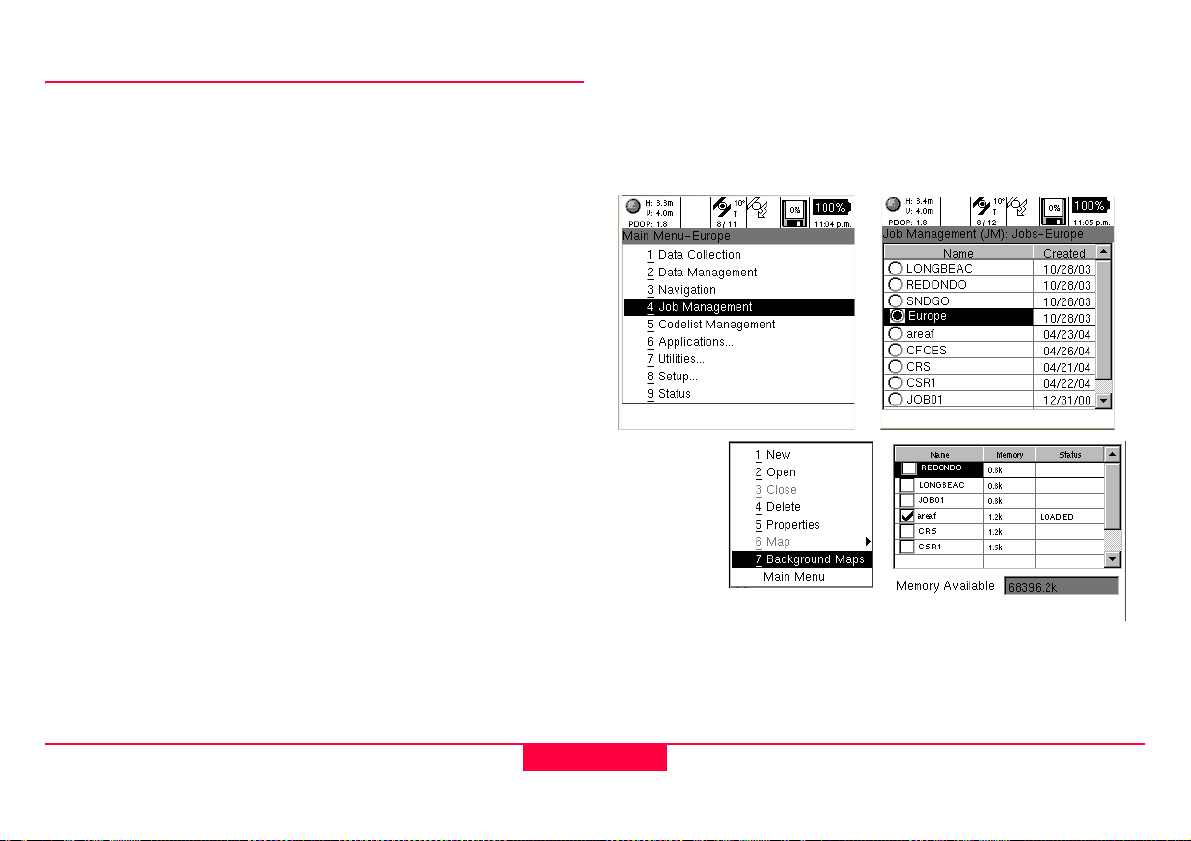
5. Job Management
The Job Management application is where jobs are created,
selected, deselected, deleted, and modified.
1. Creation of a job is performed by selecting Menu and
1
New.
2. Selection and deselection of existing jobs is toggled using
the Enter key or choosing 2
menu.
3. 4
Deleting is performed via the context menu
4. Viewing or modifying job 5
the context menu
5. Rebuilding, Repairing or Disabling the 6
in the context menu.
Coordinate systems can be attached to a job after the
)
job is opened.
Remember: A Coordinate System must be attached to a
project to calculate perimeter, area or local
coordinates.
Coordinate Systems and Codelists are linked to a job,
however only the coordinate system is a control in the job
properties. The last selected codelist of an open job will be
attached to the job.
Open or 3 Close in the context
Properties must be selected in
Map is perfomred
Figure 5-1: New Job Dialog
Remember: In order to save a new or modified job, it is
necessary to Save in the context menu or
escape dialog.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
47
Job Management
Page 48

5.1 Coordinate Systems
5.1.1 Introduction
Although the GS20 stores all GPS data in a WGS84
geographic coordinate format, it is possible to translate your
data into a local datum, projection, or coordinate system. A
pre-defined coordinate system is usually made up of
1. An ellipsoid: or a spheroid created to model the earths
surface
a. If different from WGS84, a translation is necessary for
orientation
2. A Projection: or a means to transform a spherical surface
to a 2 dimensional grid
a. Cones and Cylinders are the most common forms of
projection
3. A transformation: or a shifting of the system
a. 3 dimensional transformations involve both Cartesian
X,Y,Z shift, as well as a rotation and scaling factor
b. 2 dimensional transformation usually involve an
Euclidean X,Y shift, as well as a rotation, and scaling
factor. The Z value, perpendicular to the XY plane can
also be shifted.
4. Geoid: or an equipotential surface which coincides with
mean-sea level, and which may be imagined to extend
through the continents. This surface is everywhere
perpendicular to the direction of the force of gravity
a. The geoid is also an interpolation file, and is based on
a grid network of gravity reading. Usually this type of file
is local to a geographic region, such as a country or
continent.
5. CSCS: or Country Specific Coordinate System is an
interpolation file that estimates nonlinear error between
known points with both WGS and local coordinate values
a. These CSCS can be geographic. Cartesian or local grid
in nature. An example of this is the NADCON or North
American Datum Conversion.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
48
Job Management
Page 49

5.1.2 Overview
When creating a job, it is possible to attach a pre-defined
coordinate system, as well as interpolation files for non-linear
transformations, and calculations of elevation above mean
sea level. It is also possible to re-project a job into a
coordinate system of datum at any time in the Job
management application.
Coordinate Systems can be created in either GIS DataPRO or
SKI PRO office software, as well as pre-defined coordinate
systems which can be downloaded from local websites. The
coordinate systems can be transferred via bluetooth, serial
cable, or directly onto the compact flash, and is contained in a
GPSTRF.dat file.
Although the CSCS and Geoid files are attached to a
coordinate system in the office software, it is necessary to
make a smaller more localized “Field file” for use in the GPS
hardware. These files can then be used in conjunction to the
coordinate system on the GS20 to provide transformations,
and orthometric height values.
5.1.3 Attaching a Coordinate System
A coordinate system can be attached to a new job upon
creation, or to an existing job via the job properties in Job
Management. In order for a Geoid or CSCS field file to be
attached to a selected coordinate system, it is necessary that
the system be defined with a Global Geoid or CSCS file
attachment. This is done in either DataPRO or SKIPRO
coordinate system management.
Figure 5-2: Coordinate System
Definition Dialog in GDP
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
49
Job Management
Page 50

5.1.4 Field File
Geoid Field File
The field file is a subset of the global interpolation file in order
to reduce the overall memory taken on the hardware.
In this example, the GEOID99 was reduced to a field file
called LA to serve the Los Angeles Area. The CSCS was
named after the global Field File NADCON, for the North
America Data Conversion program it was created for. To
create a field file in DataPRO or SKI PRO, simply select the
field file generator from the tools pull-down.
or
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
50
Job Management
Page 51

1. To Create a Geoid Field file, choose the Global Geoid file,
and then select a center and radius, or South-West and
North-East limits can be selected.
• Geographic or Grid coordinate entry will be determined
based on the coordinate type defined in your global
geoid file.
• Pay special attention to the cardinal direction of
geographic coordinates
2. Select a spacing for the field file to be interpolated
extrapolate to.
• Geoid99 was created on a grid of 1 arc minute, or
roughly 1800 meters. It is probably not necessary to
expand or refine this spacing.
3. Select a Radius if using the Center and Radius method,
and Save
Save the Geoid file to the C:\GDP_Data\Geoid
)
directory for easy transfer using data exchange. CSCS
field files work under the same methodology, without
the need to choose spacing, and instead save to a path
C:\GDP_Data\CSCS.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
51
Job Management
Page 52

Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
52
Job Management
Page 53

6. Codelist Management
The Codelist Management application is also used to create,
select, deselect, delete, and modify codelists. New Codelists,
Codes, and Attributes can only be created in the Codelist
Manger (i.e. not in the Data Collection codelist).
6.1 Creating a New Codelist
1. Select 5 Codelist Management from the Main Menu.
2. Select Menu and 1
3. Edit the Codelist name, otherwise a default name will be
provided.
4. A Creator Name can also be entered (Optional).
New.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
53
Codelist Management
Page 54

6.2 Creating a New Code
1. Highlight an existing Codelist, select Menu, and choose
6
Code Management.
2. Select Menu and 1
3. Edit the Code Name, otherwise a default name will be
provided.
4. Select the Code Type (i.e. Point, Line, or Area).
5. A Code Description can also be entered (Optional).
New Code.
6.2.1 Creating a New Attribute
1. Highlight an existing Codelist, select Menu and choose
6
Code Management. (Assuming you are not already in
the Code Management screen)
2. Select Menu and choose 2
Name, otherwise a default will be provided.
Tip: Because of shapefile conventions, Attribute names
must start with a letter!
3. Select the Attribute type:
• Text: All alpha numeric character types
• Decimal: Real number values
• Integer: Whole number values
New Attribute Edit an Attribute
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
54
Codelist Management
Page 55

7. Applications
7.1 Cultivated Field Control
7.1.1 Introduction
CFC or Cultivated Field Control is a GS20 application aimed
at providing an accurate record of crop quantities and
tolerance in accordance with European Union CAP subsidies.
A user can collect and select a polygon, and calculate the
area with an error estimate corresponding to a user-defined
tolerance. Additional functionality also allows the user to
subtract areas within the external area, and save the
subsequent data to a text log file that can be exported to a
personal computer.
CFC is an additional application that will require a keycode
file. To purchase the application and receive a keycode,
please contact your local Leica representative.
7.1.2 Setup
With the possibility to use a mask file, the application is open
to a variety of output into different ASCII file interfaces. The
mask file *.MAS is a simple ASCII text file to be opened with
any text editor on a PC.
• The @LEICA CFC MASK@ is the identifier for any mask
file.
• The @@@ is the identifier for the end of the mask file.
• The lines between the both identifiers are restricted to an
amount of 15, each line with 80 Characters maximum.
• The @00@ until @99@ are placeholders for the numerical
values or code/ attribute info. This gives full and easy
flexibility to create different output masks for any ASCII type.
• A sample Leica.mas file (right) is provided and can be
edited to the needs of the user.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
55
Applications
Page 56

All identifiers are listed below:
Case 00: // new line
Case 01: // @
Case 05: // Active Job-name
Case 06: // Current Date
Case 07: // Current Time
Case 09: // Number of excluded areas
Case 10: // Area Size [m²]
Case 11: // Area Accuracy [m²]
Case 12: // Perimeter [m]
Case 13: // EC Tolerance [m²]
Case 14: // EC Tolerance [% ]
Case 15: // Area Id
Case 16: // lower Boundary [m²]/ upper boundary [m²]
Case 17: // lower Boundary [m²]
Case 18: // upper boundary [m²]
Case 20: // Area Code
Case 21: // Attribute
...
Case 40: // Area Attribute Value 1-20
Case 41: // Area Code Note
Case 60: // point id
Case 61: // north(*)
Case 62: // east(*)
Case 63: // height [m]
Case 64: // height type (Orthometric/Ellipsoidal)
Case 65: // geoid height [m]
Case 66: // Point Date
Case 67: // Point Time
Case 71: // CQ North [m]
Case 72: // CQ East [m]
Case 73: // CQ Hgt [m]
Case 74: // CQ Pos [m]
Case 75: // CQ 3D [m]
Case 80: // iterator, starts with 1 for first point of each area
point block.
Case 99: // end of point block, only necessary to divide point
block from footer lines.
(*) north and east are displayed with 3 digits in meter [m]. If no
coordinate system definition is available it is displayed as 360
degree decimal with 9 digits.
The *.MAS file should be placed in the Data/Apps/CFC
directory of the GS20 compact flash. A LOG file name defined
by the user will be output to this directory as well.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
56
Applications
Page 57

7.1.3 Using the Program
Cultivated Field Control can be found under the Application
selection in the main menu. If a job is not yet opened, the
workflow will request that you open or create a job. Once in
the CFC main screen, the user will be required to:
• Select the Area for calculation (Mandatory)
• Select any internal areas to be subtracted from the
calculation (Optional)
• Select a mask file (Mandatory to save a log file)
• Provide the name of the Log file to be saved.
• Select a tolerance or error limit for the calculation.
The main Cultivated Field Control menu provides the ability to:
• Select a feature to calculate
• Select interior features to exclude from the calculations
• Choose a mask file to properly format the output file
• Enter the name of the output or “LOG” file
• Enter the tolerance or error of calculation
To Select a feature, make the feature box the focus of the
cursor, and press the menu button. Areas can also be
calculated from this menu.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
57
Applications
Page 58

An area can be selected from the table by highlighting the
area and pressing enter.
An area may also be selected by copying it to the clipboard
from a map or table display in Data Management or
Navigation.
Areas internal to the main feature, or parent area, can be
excluded from the calculation. The selection process is
identical to selecting a main feature, but it is possible to select
multiple features to be excluded. The 09 command will not
only provide the number of features excluded, but will
provide detail about each feature.
The application does not verify that the area is within
)
the parent object. Be careful when calculating!
Available mask files will appear in the mask selection box.
A mask file is necessary to create an output file!
)
• Enter the name of the Logfile to be saved (In the LOG
directory)
• Select a Tolerance or limit of error.
To Calculate, press Menu and select Calculate. A brief
narrative of the calculation will appear on screen.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
58
Applications
Page 59

To save your data, and/or get a view of the generated log file,
press enter and select one of two choices.
The log file will now be available from the flash card, either
directly, or by using the Data Exchange.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
59
Applications
Page 60

Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
60
Applications
Page 61

8. Utilities
8.1 File Browser
The File Browser is the Leica Geosystems GS20 equivalent
of Windows’ File Explorer. The file browser provides the ability
to view the directory and file structure of the compact flash
and system memory. Other functions of the file browser
include the ability to:
1. Copy, Paste, Rename and Delete files.
2. Format the Flashcard.
3. Select and Deselect individual, multiple, and all files.
8.1.1 Browser Controls
The File Browser screen can be reduced to four main controls.
• The Device/Path control allows the user to choose
between the PCCARD and the SM “System Memory.”
• The File list allows the selection of files and directories. To
open a directory, press Enter once, to select a file, press
Enter twice. Multiple files can be selected and HOME/END
PGUP/PGDN are valid.
Tip: To move up one directory, press “..”; Escape will exit
the File Browser.
• The Group by name control allows the user to group all job
files into a single selection for easier viewing and
manipulation.
• The Filter allows for files to be viewed by extension.
8.1.2 Context Menu
Most of the File Browser tools are available via the context
menu, including:
• 2
Copy, 3 Paste, 4 Delete
• Compact Flash 5
• 6
Select All, 7 Deselect All
Format utility
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
61
Utilities
Page 62

8.1.3 Firmware Update
When new firmware (or software) is available for the Leica
Geosystems GS20, the update will normally be provided on
compact flash media. If however the file is delivered in another
format, (e.g. E-mail or ftp) it will need to be copied to compact
flash in order to perform the upgrade.
Tip: It is advisable to load firmware files directly onto a
compact flash via a card reader in order to avoid
possible sensor transfer checksum errors.
There are three types of firmware upgrades available for
the Leica Geosystems GS20 Sensor
1. Firmware: Application software
• FileDesc.doc
• Build_##.bin
• Ventura.znc
• logoshde.jpg
2. Sensor: GPS Engine software (Indigo.run)
3. Loader: System boot, diagnostics and upgrade utilities
(Loader.Bin)
All firmware upgrade files must be placed in the
)
GPS\Prog directory. Make sure to have a fully charged
battery and exit all applications before beginning the
update process. After start is selected, the program will
prompt a reboot to begin the update process. After the
update is finished the user will be prompted to reboot
the device to continue.
8.1.4 Sensor Transfer
Sensor Transfer is used to transfer files between Leica
Geosystems GIS DataPRO and the Leica Geosystems GS20
via serial cable or bluetooth. Sensor Transfer provides the
ability to choose the port (Port1 or Bluetooth), define the port
settings (i.e. baud, parity, bits, etc.) and accept any changes.
Tip: Device setting are available via the context menu.
Remember: Because of the exclusive nature of Sensor
Transfer, all other applications must be
shutdown before beginning a transfer.
8.1.5 Clear System Memory
Clear System Memory: will set all user defined configs, recent
settings, ID-templates, stations, ports e.t.c. back to factory
defaults. This application requires also a full shut-down
immidiately after proceeding.
Remember: Leica Geosystems GS20 does not have Undo!
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
62
Utilities
Page 63

9. Setup
The Setup application contains both default and user defined
configurations that determine how a unit operates. Three
default configurations are preloaded on the Leica
Geosystems GS20 to allow the user to begin data collection
immediately. New configurations can be created and default
configurations can be modified, but any modifications to a
default must be saved under a different name.
9.1 Selecting, Modifying and Creating
Configurations
The Setup screen opens to a setup menu that displays the
Config Sets, Hardware Management, ID Template
Management and Device Management.
9.1.1 Selecting
A configuration can be selected by selecting Config Sets and
highlighting the table row and pressing Enter. The selection is
shown by a filled circle or "radio button".
9.1.2 Modifying
If Enter is pressed again on a selected field, Setup will open
the configuration for editing. If a Default Configuration is
modified, the user will have to 1
menu, or exit dialog on Escaping.
Tip: Changes will not take place until the configuration is
saved.
Save As via the context
9.1.3 Creating
To create a new configuration from the table, select Menu and
choose 1
to be entered and saved. The configuration will then be
selected and editable.
)
New. A text entry dialog will open requiring a name
When creating a new configuration, values will be
copied from the previously highlighted configuration.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
63
Setup
Page 64

9.2 Tree Directory Navigation
The tree style directory menu of Setup groups similar screens
into expandable branches. Each branch of the tree can be
navigated using the up and down arrows. Sub-branches of a
tree are depicted by a “+” to the left of the branch; this can be
expanded by pressing Enter. Similarly an expanded branch is
depicted by a “-” to the left of the branch and can be
contracted by pressing Enter. If no sub-branch exists for a
branch, it is a application screen that can be opened by
pressing Enter.
The main branches of the Setup tree is broken into:
• GPS: Satellite tracking and logging controls.
• Data Collection: Quality assurance and autostop
functions.
• Interfaces: External devices connected via wireless or
hardware serial ports.
• Units and Formats: How data is entered and displayed on
the unit.
9.3 Hardware Management
Hardware Management is used to modify functions unique to
the Leica Geosystems GS20 unit. This is accessed by
selecting 8. from the Main Menu and 2. Hardware
Management.
9.3.1 Hardware
1. Allows the user to personalize the unit name, by default the
unit name is the serial number.
Remember: The Unit Name directly effects the prefix of the
datafile names.
2. Backlight time-out dictates how long the backlight is active
after the power key is depressed.
3. Enable or disable the speaker.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
64
Setup
Page 65

4. Character edit time-out changes the amount of time a
character is in edit mode. After the time-out the selected
becomes an entered value, and the cursor moves right to
the next edit field.
9.3.2 Contrast
Provides contrast controls using the left and right arrow.
Tip: Blind access to the contrast controls are always
available by pressing Menu in the Main Menu. (i.e.
pressing Menu on Startup or 3 Menus from any screen)
9.3.3 Wireless (Bluetooth Connectivity)
The Bluetooth connectivity controls provide the user with the
ability to select and connect to the Leica Geosystems WoRCS
accessory belt and the PC Sensor Transfer unit.
Either a Bluetooth Friendly name or the device address
)
will be displayed upon sucessful inquiry.
9.3.3.1 Selecting a Wireless Device
1. Expand the “Wireless” and “Bluetooth: Leica” tree
branches.
2. Highlight the wireless port to be connected (i.e. WoRCS,
Sensor Transfer, Virtual Serial 1, Virtual Serial 2) and
press Enter.
3. Select Inquire to search for bluetooth devices. "Please
wait..." will be displayed during the search, Cancel will stop
the inquiry.
4. When the soft button returns to Inquire, select from the list
of Available devices.
5. Select Menu and choose Save.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
65
Setup
Page 66

9.3.4 Clearing a Selected Device
1. Expand the “Wireless” and “Bluetooth: Leica” tree
branches.
2. Highlight the wireless port to be cleared and select Menu
and choose Clear.
9.3.5 Real-Time Corrections with a Mobile Phone
Just as real-time corrections can be broadcast over UHF/VHF
radio and satellite signals,correction packets can be sent via
mobile phone and modem alike. Version 1.15 builds on the
current real-time capabilities of the GS20 by adding GSM and
modem capabilities.
Version 1.15 also provides support for additional RTK data
correction formats such as RTCM 18-21, Leica, and Trimble
CMR. Finally by using the Bluetooth technology, your realtime correction system can be as small as your GS20 and
your phone.
Overview
In order to use the GSM or Modem abilities with the GS20,
you must either have a hardware device currently supported
(see list), or information concerning the AT commands for a
particular device. GSM or modem devices can be connected
to the GS20 in 3 ways:
1. Bluetooth connection directly to the GS20: Using a Virtual
BT Port.
2. Bluetooth connection via the WoRCS belt: Using Lemo or
DB9 connection.
3. Bluetooth connection directly to the GS20: Using a
modified cable with RTS/CTS leads.
This cable can also be created by modifying the existing
download cable 731354.
This will not affect the functionality of the cable for
)
sensor transfer or connection to external devices.
A reference station list must be defined either on the device,
or by text file which includes:
• Dial in number: Mandatory
• Reference Station name: Mandatory
• Reference Coordinates: Optional. However Reference
coordinates provides baseline data.
Finally, a configuration must be created that will reference the
device being used, the connection type listed above, and the
real-time correction format.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
66
Setup
Page 67

9.3.6 Linking with the Bluetooth
The cleanest way to link to a mobile phone is using a
Bluetooth Virtual Serial port. Both the Sony Ericson and
Siemens S56 have proven to work well with the GS20.
Although Bluetooth is a consortium standard, Bluetooth
devices don’t always work together. By all means, try a device
before you buy a device, or call your local Leica support
technician.
Making the connect
1. From the Main Menu, select 8
Management.
2. At the bottom of the Hardware Management screen, you
will find the:
• Wireless
Setup, and 2 Hardware
• Bluetooth
• Virtual Serial 1 and 2
3. Enter the Virtual Screen, and Inquire for a Bluetooth
Device.
Make sure to expand the list to ensure you have the
)
correct device.
4. Select Menu and Save.
9.3.7 Configuring your Device
1. From the Main Menu, select 8 Setup, and 4 Device
Management.
2. Choose your device from the list, and create a new device
based on that.
Once you enter the edit field up is home and down is
)
end.
3. Modify your Device Name to begin with Z! This makes it
easy to access from the bottom of the list.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
67
Setup
Page 68

4. One AT String you may wish to change is dial. By default
it is set to pulse dialing, but it can be set to tone with an
additional T.
Dial ATDT^#^M
5. The Device Also Requires that a station be selected.
However, it is necessary to create a station list or transfer
from an external source. To create a station file, select
Menu and 3
6. From the Station list, enter a dialing number and station
name. For the initial test, keep the station Analog, unless
experience dictates otherwise. You can also add
coordinate values if you have them.
7. Save the Station file, and select the newly created station
in the Device.
Station. Create a New Station
9.3.8 Modifying your Configuration
For this exercise, we will select the existing Beacon
configuration, and create a user defined configuration from it.
1. From the Main Menu, select 8
2. Highlight the Beacon Configuration, Select Menu and
Create New
3. Name the configuration GSM or Modem and Select and
Open the configuration
4. Enter the +Interface +Real-time Screen
5. From the Real-time, select
Setup, and 1 Config Sets
a. The format of the reference station corrections. (i.e.
RTCM, Leica, or CMR)
b. The Device Being used (Press the right arrow to go to
the end of the list “Z”)
c. The Port being used (Virtual 1)
6. Save the configuration
If you chose to use a Bluetooth Device
• After saving the Configuration, power off both the GS20
and the Mobile Phone
• Power On both units, and you should be prompted for a
Keycode for bonding.
9.3.8.1 Status Indication
If everything has been configured correctly, you should have
• A real-time icon Arrow (Hollow)
• A Bluetooth Icon: If Bluetooth is used: With a Chain “Link”
beneath it
• A Mobile Phone Icon: With a Link
9.3.9 Connecting to the Station
1. From the Main Menu, select 8 Setup, and 4 Device
Management.
2. Right arrow to get to your device at the bottom “Z”
3. Select Menu and Connect…………Your phone should be
dialing
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
68
Setup
Page 69

More Status
If your station connects, you will receive a link under the
Arrow: Still Hollow.
If your corrections are good you should receive a solid arrow,
and an indication in the status bar.
If your corrections are processed with the GPS, your
positional Icon should be bullseye, and your qualities will
reflect the corrections.
9.4 ID Template Management
The ID Template Management application allows for points,
auxiliary points (offset base points), lines, and area features
to be automatically and sequentially marked for easier
selection and query. Templates can be modified, created
New, and Deleted via the context menu.
By Default, each existing ID Template type comes with two
existing templates. Time and Date, and the Template type
followed by ##### (e.g. Point00001). Additionally, No
Template can be selected, allowing for manual entry by the
user.
9.4.1 Creating an ID Template
1. From the ID Template Manager, select Menu and choose
1
New.
2. Choose the Object Type from the drop down picklist.
3. Enter a template Prefix (i.e. USGS)
4. Select the start number, otherwise defaulted to 1.
5. Select an auto increment number.
9.4.2 Modifying an Existing Template
1. In the ID Template Manager, select the Object Type to be
modified.
2. Select the ID Template Name to be modified.
3. Edit the Prefix, Start # and Auto Increment fields.
4. Select Menu and enter on Save.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
69
Setup
Page 70

9.5 Device Manager
The Device Manager provides a library of all devices available
for Real-Time, Offset, and ASCII Input. The Device Manager
allows for existing devices to be modified as well as New
Devices to be created.
9.5.1 Creating a New Device
1. From the Device List, select Menu and choose 1 New.
Tip: The Properties of the previously highlighted device will
be copied, including the next sequential number of the
Device name.
2. Edit the Device name, and edit the hardware port settings
if necessary.
3. Select Menu and choose Save.
9.5.2 Modifying an Existing Device
1. From the Device List, select Menu and choose
2
Properties.
2. Modify the Device name, and edit the hardware port
settings if necessary.
3. Select Menu and choose Save.
9.6 GPS
The GPS subgroup allows the user to specify tracking and
logging parameters, define the antenna to be used and enter
initial coordinates for first time tracking to a new region.
9.6.1 Tracking
The tracking screen is comprised of three controls.
• Max Accuracy / Max Track / Hyper Track radio button: Is
a selection that is mostly dependant upon the GPS
environment. Max Track and Hyper Track are Leica
Geosystems innovations that allows for signals to be
tracked at a lower strength threshold, which provides
reception in dense foliage.
Tip: Max/Hyper Track does not allow for phase collection.
High precision points should be collected in Max
Accuracy.
• Mask Angle: Is the angle above the horizon which
determines the cutoff for tracking satellites.
Remember: Because a greater distance through the
atmosphere must be penetrated for low
elevation satellites, a default of 10 degrees is
preset and recommended as a minimum!
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
70
Setup
Page 71

•The DOP, or Dilution of Precision Filter is user definable
mask based on satellite geometry. This is a setting
normally used for autonomous (i.e. correctionless)
collection.
Tip: The Leica Geosystems GS20 automatically senses
when an antenna has been plugged in or unplugged.
The unit opens and resets the antenna configuration
accordingly.
9.6.2 Minimum Satellites
The Minimum Satellite control allows the user to define how
many satellites must be tracked to calculate a positions. The
default setting is 4 satellites, because a minimum of 4
satellites is necessary to calculate a 3 dimensional position.
Three satellites can calculate a position assuming
)
a fixed ellipsoidal elevation; however this is only
recommended for navigational purposes.
9.6.3 Antenna Type
By default, each configuration is set to the internal patch
antenna of the Leica Geosystems GS20. However, because
external antennas can be connected, it is necessary to define
the parameters unique to a given antenna.
A default library of 3 antenna types is available, the Leica
Geosystems GS20 Internal, the AT501 Pole (external), and
the AT501 Tripod (external). For normal use, the user will only
need to define the height of antenna above the point be
occupied.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
9.6.4 Logging
The Logging screen contains controls to store raw pseudorange data for post-processing, Static and Moving
Observations as well as set the positional update rate for the
receiver (default 1 second.)
Data collected without enabling the logging cannot
)
be post processed for corrections!
To Enable Post Processing, select the static or moving check
box and set the observable logging rate. This rate controls
both moving and static logging rates, so it is recommended
that 1 second be used when collecting lines and areas in a
job.
71
Setup
Page 72

9.6.5 Initialization
The time and initial position controls help the unit to obtain
satellites faster in a new geographic location or when there is
no almanac data present on the unit.
Time/Date and position controls can be edited by selecting
8. Setup, 2. Hardware Management, GPS, Initialization.
New almanac data is sent by a satellite every 12.5
)
minutes. This can mean that it may take a maximum of
25 minutes depending when the first satellite is
collected. After the first position is calculated, the Time
and Initial Position fields will update to reflect the last
position.
Remember: Valid limits are 0-90 degrees for Latitude and
0-180 degrees (East and West) for Longitude.
9.7 Data Collection
The Data Collection subgroup is where quality minimums are
defined for both automatic collection and notification alarms.
9.7.1 Quality Monitor
The Quality Monitor controls are subdivided into Point Quality
(which is also applicable for linear node collection) and Line/
Area streaming.
Point Quality
1. Defined By: Horizontal, Vertical, Horizontal & Vertical, or
None.
If only Horizontal or Vertical quality is chosen, the other
)
edit field will be disabled!
2. Point Autostop:
• None: Occupation is manually controlled (i.e. started
and stopped) by the user.
• Quality: The occupation will be stopped once the
Quality defined (e.g. Horizontal) is achieved.
• Positions: The occupation will be stopped once the
number of positions required are collected.
Positions must achieve the required quality to be
)
stored.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
72
Setup
Page 73

3. CQ Warning (Coordinate Quality): Even if Point Autostop
is set to none, a notification alarm can be set to alert the
user that the defined quality has been exceeded.
Line Quality
1. Defines the horizontal quality tolerance for linear
streaming.
Tip: The Line Quality can be used to filter or just notify the
user of positions that exceed quality. This setting can
be found in the Streaming Options in Data Collection.
9.8 Interfaces
The Interface subgroup controls how external devices interact
with the Leica Geosystems GS20. The Interfaces can be
further subdivided into Real-Time, Offset Devices, and NMEA
Output.
9.8.1 Real-Time
Real-Time or “Differential” correction allows a GPS to use a
known reference position to correct the less accurate
autonomous position. The Leica Geosystems GS20 supports
two combined message formats of the RTCM "Radio
Technical Commission for Maritime services" standard.
RTCM (9,2) (1,2) (18,19) and (20,21).
Several default devices are available for Real-Time Interface.
• RTB: CSI Real Time Coast Guard Beacon.
• RTS: Racal LandStar Satellite Subscription Service.
• RS232: An open standard for 3rd party devices.
•GSM
• Modem Devices
To view or edit the properties of the device being used, Select
Menu and choose 2
Tip: Additional properties unique to a device such as the
RTB (Frequency, Bit Rate) and RTS (Channel and
Station) can be defined by the user in Device
Properties.
Device Properties.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
73
Setup
Page 74

Port: Three ports are currently available for connection to a
Real-Time device.
• Port 1: Serial Lemo connection on the bottom of the GS20
• WoRCS 1: The 5 pin Lemo Port located on the bottom of
the WoRCS Bluetooth Hub.
• WoRCS 2: The 8 pin Lemo Port located on the switch side
of the WoRCS Bluetooth Hub.
Remember: The Bluetooth must be bonded WoRCS in the
Hardware Management.
Log without Corrections: If Real-Time corrections are lost,
Data can continue to be recorded for post-processing in the
GIS DataPRO office software.
Maximum Age of Correction: The user can define how long
to use corrections to calculate a Real-Time position after the
correction source is lost.
Although old corrections can be used for longer
)
time periods, the degradation of quality becomes
exponential with time.
RTCM: The user can choose from type (9,2) which is used
with RTB Coast Guard Beacon, or (1,2) which is used with
RTS and other Satellite correction sources.
(See above section ALMANAC for further explanation)
)
9.8.2 GS20 Phase Wizard
This document is intended to provide the user with insight into
how the Phase Wizard works, and step-by-step instructions
on its use. Because the GS20 can be used with both SKI PRO
and GIS DataPRO, both platforms will be discussed below.
For additional information about the use of SKI PRO or GIS
DataPRO, please refer to the documentation included with
those packages.
9.8.2.1 Overview
The phase wizard was created to provide the user with an
easy to use interface for collecting high-accuracy data with the
GS20. Additionally, the phase wizard collects data in a way
that can be processed more efficiently in SKI PRO or GIS
DataPRO, creating a simplified process for the user both in
the field, and in the office.
The GS20 Phase Wizard allows the user to select from Static
Phase Collection, Kinematic Phase collection, or No-Phase
(Code only) Collection. By choosing one of these methods,
the setup/configuration file is automatically modified without
additional input from the user.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
74
Setup
Page 75

9.8.2.2 Static Phase
Static Phase collection is optimized for high accuracy single
point occupations, which require that each ambiguity
resolution be a separate calculation. In order to optimize this
collection, moving or kinematic chain data is not logged and
streaming occupation is unavailable.
In this configuration, the user will enter antenna height and
baseline length from the reference station. A status indicator
will then provide user feedback on the length of time needed
to occupy a point to provide a high level of confidence that the
ambiguity of the point will be resolved.
9.8.2.3 Kinematic Phase
Kinematic Phase collection is designed to resolve ambiguities
on an initial static point, and apply those same corrections to
all collected data within an unbroken “kinematic chain”. The
user is initially prompted to occupy a static point, and the
method of collection will be similar to that of static phase
collection. Once the point has been occupied for a sufficient
amount of time based on the status indicator, point and linear
streaming data can be collected in a normal fashion. If,
however, at any time the GPS lock drops below 4 satellites,
the phase chain will be broken and the user will be required to
initialize another static point.
9.8.2.4 The Interface
In order to select a mode of phase collection,
the user simply needs to press the menu button in the Codes
screen. The user will then have the ability to select from three
modes of collection:
1. No Phase
2. Static Phase
3. Kinematic Phase
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
75
Setup
Page 76

When a phase mode has been switched, a message will pop
up to indicate that settings may have been changed to the
configuration. If you are currently in a default configuration,
the system will indicate that the changes must be saved into
a new configuration, and a prompt will appear to name that
configuration.
9.8.2.5 Collecting Static points, including kinematic points of initialization
In order to assist in the amount of time required to occupy a
point to resolve phase ambiguities, a status indicator has
been included in the phase wizard. The status screen
provides the user with an estimated time needed to occupy a
point based on the number of satellites, the satellite geometry,
and the baseline length to the reference GPS.
In order to provide the correct information, the user must enter
a baseline selection. Both the baseline length and antenna
height of an occupation can be entered from a menu dialog in
the codes screen.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
76
Setup
Page 77

9.8.3 WAAS and EGNOS
The Wide Area Augmentation System, or WAAS is a free realtime correction for GPS available in North America, and is
comparable to the European EGNOS correction, currently in
a testing phase. These corrections are broadcast on the same
frequency as GPS, it can be received without the need for
additional hardware and free of charge. To set WAAS as the
active correction, you can either use the default, create a new
configuration or edit a user defined configuration.
1. Select 8
WAAS is selectable from this MENU.
Setup from the Main Menu and 1 Config Sets.
2. The most simple way to receive a WAAS correction is to
select the default.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
77
Setup
Page 78

3. Most likely, you will want to select a User Defined
configuration or press Menu and create a New
configuration based on your highlighted default.
4. Enter the configuration, and expand the Interface branch.
Focus on the Tracking branch and press enter.
5. Set the source to WAAS. That’s it.
9.8.3.1 Understanding the WAAS Corrections
1. The immediate and most notable change will be the WAAS
Satellite Icon in the real-time window. This indicates the
unit is set for WAAS corrections.
2. When the icon and lightening bolt fill to black, this is an
indication that the WAAS signal is being received.
3. Once the corrections have been calculated, the WAAS
Satellite Icon will become Bold, the status bar will indicate
Reference Data is Available, and the positional Indicator
will become a bulls eye.
4. WAAS corrections are able to extrapolate, or coast for 60
seconds. If the correction is lost, a numeric indicator under
the WAAS Satellite Icon will display how many seconds
since the last correction.
5. WAAS Satellites will can be viewed in the Satellite Status
Screen 9. WAAS Signal Strength is also indicated in the
Status Real-time Screen.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
78
Setup
Page 79

9.8.3.2 Changes to the Real-Time Screen
A new Source selection allows the user to select none (no
correction), WAAS, RTCM (Including Real-time Beacon, and
Real-time Satellite), Leica and Trimble CMR.
If the RTCM, Leica or Trimble CMR source is selected, you
must then specify a device.
New devices can be created and configured in the
)
Setup \ DeviceManagement screen.
User defined quality settings can determine how the feature is
collected (see Setup\Data Collection.) In addition to direct
locations, the user can also choose from a list of point offsets.
9.8.4 Connecting to WoRCS Beacon
If you purchased the Leica Geosystems GS20 with the
Wireless real-time Correction System, the WoRCS, you are
only steps away from collecting real-time sub-meter data. The
WoRCS comes preconfigured with Bluetooth linked to your
GS20.
WoRCS Belt
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
79
Setup
Page 80

9.8.4.1 Powering on the WoRCS
1. The Bluetooth Module is the only belt item with
configurable controls. By Default, Power should be set to
On, and Line should be set to Bluetooth.
2. Follow the procedure listed previously for charging the
batteries. Once the batteries are fully charged, you can
place them in any of the three bays of the battery insert
shown below. The battery insert is both hot swappable and
self-switching. The batteries will be drawn down from bay
one to bay three without interruption in power.
9.8.4.2 Checking the Bluetooth Link
If your Bluetooth link is successfully connected, the bluetooth
icon with a chain below and a status message “Bluetooth Link
Restored” will appear at the bottom of the screen. You can
now proceed to Checking the real-time Link; if not follow the
steps listed below:
1. Power on the GS20 and select 8
Management and the Bluetooth_Wireless Selection.
2. Expand the Wireless tree, expand the Bluetooth, and view
WoRCS.
3. If the GS20 has been linked to the WoRCS Bluetooth
Module, an address that corresponds to the address on
the top of the Bluetooth Module will appear. If the address
does not correspond, press menu and select clear.
4. If the address area displays zeros, you will need to
establish a connection.
5. Highlight the WoRCS branch and press enter; this will take
you to the Bluetooth Setup screen.
6. Press Inquire and wait until the Cancel button becomes
Inquire again.
7. You will see the Available Devices in the choice list. By
highlighting the available devices and pressing Enter, you
will see the entire list of available bluetooth devices in the
choice list. If multiple devices have been found, select the
device that matches your WoRCS bluetooth address,
displayed on the top of the bluetooth module.
Setup, 2 Hardware
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
80
Setup
Page 81

8. Finally, press the Menu key and Save, then Escape back
to the main menu.
Tip: Ensure batteries are charged and correctly inserted.
Ensure bluetooth module is set to line and on. The
single flashing red light indicates that power is
available. When the light changes to green a
BLUETOOTH connection is established but no data is
exchanged. When both green lights are flashing data is
exchanged.
9.8.4.3 Checking the WoRCS Real-Time Link
Once the Bluetooth Link is established, you will need to make
sure that your real-time device is linked and active. If the
status message “Reference Data is Available” appears, setup
is complete, and there is no need to proceed any further.
Otherwise, follow the steps of the status check below.
9.8.4.4 WoRCS Real-Time Beacon
1. From the Main Menu select 9 Status. Expand the
Interfaces branch and select Real-Time. If you have
communication with the Real-time Beacon module (RTB),
you will see information about the frequency, signal
strength etc; otherwise, you will see all zero values.
The real-time screen does not refresh automatically; to
)
refresh the values, you will need to escape and re-enter.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
81
Setup
Page 82

2. If the Real-time values are all zero, there is no
communication to the real-time beacon module. So you
will need to verify the configuration.
3. Escape to the Main Menu and select 8
Verify the user-defined configuration named
)
“WRCSBEACON” is selected; if WRCSBEACON exists
and is not selected, highlight and press Enter,
otherwise select the default “Beacon”.
4. Press Enter again on the selected configuration to edit the
setup values.
5. Expand the Interfaces branch, highlight the Real-time
branch and press enter.
6. Make sure the Device is set to RTB, and the port is set
WoRCS 2.
Setup.
7. Escape and save the values, then escape and save the
configuration.
If you are editing a default configuration, you will be
)
prompted to provide a configuration name.
8. Escape to the main menu, and return to the status/
Interface/Real-time branch to check the status of the realtime device. You should now see values for the frequency,
bitrate, etc.
9.8.5 Connecting to WoRCS Real-Time Satellite (RTS)
If you purchased the Leica Geosystems GS20 with the
Wireless real-time Correction System, the WoRCS, you are
only steps away from collecting real-time sub-meter data. The
WoRCS comes preconfigured with the Bluetooth linked to
your GS20.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
82
Setup
Page 83

WoRCS Belt
1. WoRCS Power Supply Module
2. WoRCS RTB Module
3. WoRCS BLUETOOTH Module
4. WoRCS Belt with Belt keepers
5. WoRCS Power Supply Jacked
6. WoRCS RTB Module Jacked
7. WoRCS BLUETOOTH Module Jacked
8. Power Supply to BLUETOOTH Module Cable
9.8.5.1 Powering on the WoRCS
1. The Bluetooth Module is the only belt item with
configurable controls. By Default, Power should be set to
On, and Line should be set to Bluetooth.
2. Follow the procedure listed previously for charging the
batteries. Once the batteries are fully charged, you can
place them in any of the three bays of the battery insert
shown below. The battery insert is both hot swappable and
self-switching. The batteries will be drawn down from bay
one to bay three without interruption in power.
9.8.5.2 Checking the Bluetooth Link
If your Bluetooth link is successfully connected, you will see
the bluetooth icon appear with a chain below and a status
message “Bluetooth Link Restored” will appear at the bottom
of the screen. You can now proceed to Checking the real-time
Link; if not follow the steps listed below:
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
83
Setup
Page 84

1. Power on the GS20 and select 8 Setup, 2 Hardware
Management and the Bluetooth_Wireless Selection.
2. Expand the Wireless tree, expand the Bluetooth, and view
WoRCS.
3. If the GS20 has been linked to the WoRCS Bluetooth
Module, an address that corresponds to the address on
the top of the Bluetooth Module will appear. If the address
does not correspond, press menu and select clear.
4. If the address area displays zeros, you will need to
establish a connection.
5. Highlight the WoRCS branch and press enter; this will take
you to the Bluetooth Setup screen.
6. Press Inquire and wait until the Cancel button becomes
Inquire again.
7. You will see the Available Devices in the choice list. By
highlighting the available devices and pressing Enter, you
will see the entire list of available bluetooth devices in the
choice list. If multiple devices have been found, select the
device that matches your WoRCS bluetooth address,
displayed on the top of the bluetooth module.
8. Finally, press the Menu key and Save, then Escape back
to the main menu.
Tip: Ensure batteries are charged and correctly inserted.
Ensure bluetooth module is set to line and on. The
single flashing red light indicates that power is
available. When the light changes to green a
BLUETOOTH connection is established but no data is
exchanged. When both green lights are flashing data is
exchanged.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
84
Setup
Page 85

9.8.5.3 Checking the WoRCS Real-Time Link
Once the Bluetooth Link is established, you will need to make
sure that your real-time device is linked and active. If the
status message “Reference Data is Available” appears, setup
is complete, and there is no need to proceed any further.
Otherwise, follow the steps of the status check below.
9.8.5.4 WoRCS RTS
1. From the Main Menu select Status. Expand the Interfaces
branch and select Real-Time. If you have communication
with the RACAL module (RTS), you will see information
about the Station ID, frequency, signal strength etc.
The real-time screen does not refresh automatically; to
)
refresh the values, you will need to escape and reenter.
2. If the Station = -1, this means the Racal Unit does not have
a subscription. You will need to contact Racal-LandStar to
check the status of your subscription. To find the office
nearest you, go to www.landstar-dgps.com.
3. If the station id is present and all lights are on, on the
RACAL Module, escape to the Main Menu and select
8 Setup.
Verify the user-defined configuration named
)
“WRCSRTS” is selected; if WRCSRTS exists and is not
selected, highlight and press Enter, otherwise select
the default “RACAL”.
4. Press Enter again on the selected configuration to edit the
setup values.
5. Expand the Interfaces branch, highlight the Real-time
branch and press enter.
6. Make sure the Device is set to RTS, and the port is set to
WoRCS 1.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
85
Setup
Page 86

7. Escape and save the values, then escape and save the
configuration.
If you are editing a default configuration, you will be
)
prompted to provide a configuration name.
8. Escape to the main menu, and return to the status/
Interface/Real-time branch to check the status of the realtime device. You should now see values for the Station ID,
frequency, bitrate, etc.
9.8.6 Offset Devices
9.8.6.1 Configuration of the GS20.
When points cannot easily or accurately be accessed by
direct GPS location, you have the option of calculating using
an offset method.
The GS20 offers four point offset collection methods and
works with most laser range finders.
The WoRCS Belt supports the laser range finder and
transmits the data cablefree to the GS20. Again, we will be
using the Leica Laser Locator (see below).
Leica Geosystems Laser
Locator
• Laser Rangefinder
• Inclinometer
• Magnetic Compass
The Rangefinder can be interfaced with the GS20 directly in
serial port 1, or the WoRCS belt utilizing ports 1 or 2. Data can
then be transmitted to the GS20 cable free.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
86
Setup
Page 87

Not all Lemo connections are wired the same!
)
Consult your vendor and rangefinder manual to ensure
your cable is correct!
If using a DB9 cable interface, it may be necessary to
)
use a null modem.
A null modem switches the 2 and 3 pin of a serial
interface.
Once the Rangefinder is connected to the system via one of
the above methods, you will need to configure the port for the
specific device. This will depend upon the device you are
using and how you chose to connect it to the system.
1. From the GS20 Main Menu, select Setup and Enter your
selected configuration.
2. Expand the Interface branch and select Offset Devices.
3. Select the appropriate device and the corresponding port.
Selecting Port1 connects to the GS20 directly. Selecting
WoRCS1 utilizes the wireless connection.
When using the WoRCS belt, make sure the bluetooth
)
setting has been inquired and saved.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
87
Setup
Page 88

4. Escape and save changes. Once you have the device and
”
port settings set to match the offset device and port
connection you are using, you will be ready to collect data.
9.8.6.2 Overview of the basic methodologies of point offset data collection.
When collecting a point offset, it is important to input the offset
data before occupying the auxiliary point.
Azimuth Distance: Enter Azimuth, Distance and Delta
Height before occupying the point.
Azimuth Azimuth: Enter Azimuth and Delta Ht for 1st position from Aux Pt. A; then repeat for PT B.
Aux “A”
Azimuth Distance
Aux “A”
1
1
0
125
o
35m
30’00”
+
O/S Pt
Aux “B”
o
o
0
2
2
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
Azimuth - Azimuth
+
m
5
3
Aux “A”
Distance Distance
88
+
O/S Pt
O/S Pt (Left Solution)
2
5
m
Aux “B
R
(Right Solution)
Setup
Page 89

Distance Distance: Enter Distance and Delta Ht for 1st
position from Aux Pt A; repeat for position B and choose the
solution method (i.e. Left or Right)
Because two solutions exist for a double distance
)
intersections, the user must tell the software on what
side of point A-B the offset point lies.
Backwards Azimuth and Distance: Useful when locating a
point by direct occupation when no GPS exists. The BAD
works by providing an azimuth and distance to a previously
located point. The calculation then reverses the course and
distance.
9.8.6.3 Explanation of individual point offset data collection
methodologies.
To Collect a Point using offset methods, select the desired
code as you would for a standard point collection. When in the
collection screen, select Menu and choose 2 Offset. You will
then be presented with the following options for collection:
1. Once in the offset screen, select Azimuth Distance.
2. Collect the value with your rangefinder or enter them
manually.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
89
Setup
Page 90

3. If your rangefinder only calculates a distance, you must
manually enter the other parameters.
4. Select Occupy, similar to normal point collection. Both
manual and auto-stop work in offset occupation.
Although a default Auxiliary
)
or base point is created for
the offset, you can use the
geo-clipboard to select from a
stored base point for multiple occupations.
Double Azimuth or Double Distance.
Collecting an offset using double Azimuth or Double distance
methods requires collecting both range and occupation
information from two locations.
1. Populate the “A” fields manually or with a range finder,
then occupy the point.
2. After the “A” occupation has taken place, the “A” fields are
no longer editable.
3. Populate the “B” fields, then take the “B” occupation.
Escaping will allow for points to be re-occupied, however it
is not possible to keep the “B” collection and re-occupy “A”.
Reverse Azimuth and Distance.
The backward, or reverse Azimuth and Distance method
allows you to calculate your position, by sighting a reference
point of known origin.
A known node or point feature must be copied to the GeoClipboard.
The node or point can be copied to the Geo-Clipboard by map
or table in Data Management or Navigation.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
90
Setup
Page 91

The known feature is automatically selected from the GeoClipboard in the offset screen. No Occupation is necessary.
By Calculating the Back. Azimuth Dist. Offset without
)
populating the fields (i.e. zero), it is possible to create
new features with a shared topology to the parent
“pasted” node. This topology is maintained when the
parent node is post-processed or deleted.
9.8.7 ASCII Input
Data from external devices can be incorporated into node and
feature data for applications such as:
• Photos Hyper linking to Features
• Depth Finders to range water depth from a GPS position
• Bar Code Scanners
To link an external ASCII Device:
1. Set the RS232 Device Properties by Selecting Menu and
choose 2
2. Select the Port to be used.
3. Define if the ASCII device being defines the end of
message by CR “Character Return”, LF “Line Feed” or a
combination of the two.
4. Select User Defined if the ASCII information should be
written to an Attribute field. If selected, enter the name of
the Attribute field.
Device Properties.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
91
Setup
Page 92

9.9 Units and Formats
Units and Formats allow the Leica Geosystems GS20 to be
entered and display according to the users specifications.
9.9.1 Units of Measure
A list of choice controls defining
• Length
•Area
•Velocity
• Angle Units
• Angle Formats (And Point of Reference)
Tip: Magnetic Azimuth and Bearing Information can be
entered and displayed. However, the user must define
the local declination.
9.9.2 Language
Language selections for the software interface can be
selected if additional language files are available on the unit.
9.9.3 Formats
• Local Time Zones (Arranged by distance from Greenwich
Mean Time)
• Daylight Savings Time: Check box
• Date Format
• 12/24 Hour or Civilian/Military Time
• Coordinate Format: Radio Button
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
92
Setup
Page 93

10. Status
The Status application of the Leica Geosystems GS20
provides feedback concerning current position, satellite
location, signal strength, real-time differential corrections, and
system information.
Similar to Setup, the Status application is displayed in a tree
view, with like items grouped into branches. Setup can be
accessed as choice 9. from the Main Menu.
10.1 GPS
10.1.1 Position
The position screen provides coordinate information
containing:
• Coordinate system toggle
• Current time
• X,Y coordinates
• Ellipsoidal Elevation (EHeight)
• Position and Height Quality
10.1.2 Satellite Information
The satellite information screen displays a tabular listing of the
satellites that should be visible based on the current almanac
and setup mask angle. Data in the table includes:
• Tracking status of the satellite (Check box)
• Satellite Number (Sat)
• Elevation above the horizon and information if the satellite
is rising or falling. (^ = rising) (Elev)
• Azimuth (A)
• Signal to Noise Ratio, or strength of reception (SNR)
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
93
Status
Page 94

10.1.3 Satellite View
The satellite view provides a user friendly interface for viewing
visible vs. tracked satellites. Satellites are displayed by their
corresponding number. Tracked satellites appear highlighted
with the satellite number inverted.
10.2 Interfaces
10.2.1 Real-Time
The real-time interface provides information about the RTCM
corrections being received by the device. Interface data will be
specific to the device being used, for example:
10.2.1.1 RTB Coast Guard Beacon
• Station ID
• Frequency
• Channel
• Bit Rate
• Signal Strength
• Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
• Correction Age
• % Correction Received
Figure 10-1: Status/Satellite View
The exterior ring represents the mask angle, the next
)
interior ring is 45 degrees, and the most interior 60
degrees.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
10.3 Hardware
The hardware screen displays information pertaining to
• Serial Number
• Firmware Version
• Total Available RAM (in bytes)
• Battery Level
94
Status
Page 95

11. Glossary
Almanac
Library of coarse satellite orbital data used to calculate
satellite position, rise time, elevation, and azimuth.
ASCII
American Standard Code for Information Interchange,
developed through the American National Standards
Institute. ASCII is a scheme of binary notation for
machine- readable data.
Attribute
A data field of a database, often defined by the type of
string, integer, real-number or boolean.
Auxiliary points
A base or reference point used to collect an offset point or
feature.
Azimuth
A horizontal angle measured clockwise from a direction
(such as North)
Bluetooth
A non-proprietary wireless cable replacement.
Code
1. A template of a feature layer, containing information
about the object type and attribution.
2. C/A Code: The Coarse Acquisition GPS data message
modulated on the L1 signal.
Coordinate Systems
The combination of an Ellipsoidal with a referenced
angular or grid projection.
Course Azimuth
Azimuth of the GPS operators direction.
Course Velocity
Velocity of the GPS operator.
DGPS (Differential GPS)
A GPS system that utilizes differential code corrections to
achieve an enhanced positional accuracy; usually 0.5-5
meters.
Differential Corrections
The determination of relative coordinates between the
rover receiver from a reference receiver which are
simultaneously tracking the same GPS signals.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
95
Glossary
Page 96

Dilution of precision (DOP )
A description of the purely geometrical contribution of the
uncertainty in a position fix.
Ellipsoid
A mathematical figure formed by revolving an ellipse
about its minor axis, used in geodesy to best fit the shape
of the earth.
Ellipsoidal elevation
The vertical distance of a point above the ellipsoid.
Firmware
Embedded software that resides on a hardware device.
Geoid
An equipotential surface which coincides with mean sea
level and extends everywhere, perpendicular with the
force of gravity.
GIS (Geographic Information System)
Geographic Information System
GIS DataPRO
The office software used interact between the Leica
Geosystems GS20 and GIS and CAD packages.
GPS
Global Positioning System
GPS Time
A continous time system based on the Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC) from 6th January 1980.
Greenwich Mean Time
The mean solar time of the meridian of Greenwhich. Used
as the prime basis of standard time throughout the world.
HyperTrack
Leica’s Trademark tracking technology created for very
inhospitable environments, for ex. Urban Canyons.
Job
A Leica Geosystems GS20 Project consisting of multiple
filetypes.
Latitude
The angle between the ellipsoidal normal and the
equatorial plane. Latitude is zero on the equator and 90o
at the poles.
Loader
The software that loads the firmware into the hardwares
system memory on boot.
Local Time
Local time equals GPS time + time zone.
Logging rate
The rate in which raw GPS data are written
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
96
Glossary
Page 97

Longitude
Longitude is the angle between the meridian ellipse which
passes through Greenwich and the meridian ellipse
containing the point in question.
Mask Angle
The minimum elevation angle below which no more GPS
satellites are tracked by the receiver.
Max Accuracy (ClearTrack)
The tracking mode incorporating carrier phase smoothing
with the highest discriminating tracking algorithms.
Max Track
Leica’s Trademark tracking technology created for dense
foliage and other inhospitable environments.
Maximum Age of Correction
The amount of time a real-time correction will be used to
adjust a GPS position, once the correction link is lost.
Meridian
An imaginary line joining north to south pole and passing
through the equater at 90
Multipath Error
A positioning error resulting from interference between
split radio waves which have travelled to the receiver from
differing paths.
o
.
NMEA
National Marine Electronics Association. A standered
originally defined to enable marine electronics
instruments, communication, and navigation equipment to
communicate.
Orthometric Height
The distance of a point above the geoid (or mean sea
level). Ortho = Elipsoid - Geoid.
PDOP
Positional dilution of precision. See DOP
Post-processing
The process of computing positions in non-real-time,
using data previously collected by GPS receivers. See
differential corrections.
Pseudo-range
A measure of the apparent signal propagation time from
the satellite to the receiver antenna, scaled into distance
by the speed of light. Pseudorange differs from the actual
range by the inlfuence of satellite and user clock.
Quality
A measure of precision calculated by residuals calculated
using a 2D sigma (67% confidence)
Real-Time
A DGPS position calculated by correcting autonomous
GPS with a differential correction.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
97
Glossary
Page 98

RTCM
Radio Technicial Comission for Maritime services.
Commission set up to define differential data link to relay
GPS messages from a monitor station to a field user.
Selective Availability
Degradation of GPS point positioning accuracy for civilian
users by the U.S. Department of Defense. SA is produced
by clock dithering or orbit degradation.
Signal to Noise Ratio
A ratio of the radio frequency signal strength and the
noise floor.
Time and Initial Position
The time and position value a GPS receiver will use with
an almanac to more quickly locate satellites.
WAAS
The Wide Area Augmentation System, or WAAS is a free
real-time correction for GPS available in North America,
and is compatible with the European EGNOS correction,
currently in a testing phase. Because this correction is
broadcast on the same frequency as GPS, it can be
received without the need for additional hardware, and
free of charge.
Waypoints
A point, or node on a line or area flagged for navigation.
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
98
Glossary
Page 99

12. Index
A
Almanac
ASCII ............................................................... 70
Attribute ........................................................... 54
Auxiliary points ............................................... 69
Azimuth .................................................... 32, 93
B
Bluetooth
C
CFC
CFC Mask ....................................................... 55
Code ................................................................ 25
Coordinate systems ...................................... 47
Course Azimuth ............................................. 44
Course Velocity .............................................. 44
Cultivated Field Control ................................ 55
D
DGPS
Differential Corrections ................................. 13
DOP ................................................................. 71
E
Ellipsoidal Elevation
Ellipsoidal elevation ...................................... 71
................................................... 13, 72
......................................................... 65
.................................................................. 55
.............................................................. 12
...................................... 93
F
Firmware
G
Geoid Field File
GIS ...................................................................25
GIS DataPRO .................................................62
GPS ..................................................................18
Greenwich Mean Time ..................................92
J
Job
L
Latitude
Loader ..............................................................62
Logging rate ....................................................71
Longitude .........................................................72
M
Mask Angle
Max Accuracy .................................................70
Max Track ........................................................70
Maximum Age of Correction ........................74
Multiple functions
..........................................................62
..............................................50
....................................................................19
............................................................72
.....................................................70
3
................................................................14
9 ................................................................14
N
NMEA
.............................................................. 73
P
Paging
............................................................. 16
Post Processing ............................................. 71
Pseudo-range ................................................ 71
Q
Quality
............................................................. 72
R
Real-Time
RTCM .............................................................. 73
S
Sensor
Signal to Noise Ratio .................................... 93
T
Time and Initial Position
W
Waypoints
....................................................... 73
............................................................. 65
............................... 72
....................................................... 43
Leica GS20 Field Guide-1.1.0en
99
Page 100

Leica Geosystems AG, Heerbrugg,
Switzerland, has been certified as
being equipped with a quality system
which meets the International
Standards of Quality Management and
Quality Systems (ISO standard 9001)
and Environmental Management
Systems (ISO standard 14001).
733607-1.1.0en
Printed in Switzerland - Copyright Leica Geosystems AG,
Heerbrugg, Switzerland 2004
Original text
Total Quality ManagementOur commitment to total
customer satisfaction.
Ask your local Leica agent for
more information about our TQM
program.
Leica Geosystems AG
CH-9435 Heerbrugg
(Switzerland)
Phone +41 71 727 31 31
Fax +41 71 727 46 73
www.leica-geosystems.com
 Loading...
Loading...