Leica DM4500 P User manual
Leica DM4000 B
Leica DM4000 M
Leica DM4500 P
Leica DM5000 B
Operating Manual
Bedienungsanleitung
1

Published September 2007 by:
Herausgegeben September 2007 von:
Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH
Ernst-Leitz-Straße
D-35578 Wetzlar (Germany)
Responsible for contents:
Verantwortlich für den Inhalt:
Dr. Jasna Roeth, Stefan Motyka
(Marketing CM, Compound Microscopy, Product Management)
(Marketing CM, Compound Microscopy, Produktmanagement)
Holger Grasse
(Safety Officer according to MPG §30)
(Sicherheitsbeauftragter nach MPG §30)
In case of questions, please contact the hotline:
Bei Fragen wenden Sie sich bitte an die Hotline:
2
Phone +49(0)64 41-29 2286
Fax +49(0)64 41-2922 55
E-Mail: MQM-Hotline@leica-microsystems.com
Leica DM4000 B
Leica DM4000 M
Leica DM4500 P
Leica DM5000 B
Operating Manual
3

Copyrights
Copyrights
All rights to this documentation are held by
Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH. Reproduction
of text or illustrations (in whole or in part) by
print, photocopy, microfilm or other method
(including electronic systems) is not allowed
without express written permission from Leica
Microsystems CMS GmbH.
The term "Windows" may appear in the following
text without further identification. It is, however,
a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. The names of companies and products
used herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
The instructions contained in the following documentation reflect state-of-the-art technology
and knowledge standards. We have compiled
the texts and illustrations as accurately as possible. Nevertheless, no liability of any kind may
be assumed for the accuracy of this manual’s
contents. Still, we are always grateful for comments and suggestions regarding potential mistakes within this documentation.
The information in this manual is subject to modification at any time and without notification.
4

Contents
Contents
1. Important notes about this manual ....... 7
2. Intended purpose of the microscope .... 8
3. Safety notes................................................ 9
3.1 General safety notes................................. 9
3.2 Electrical safety ......................................... 10
3.3 Disposal....................................................... 11
4. Overview of the instrument .................... 12
5. Unpacking the microscope..................... 17
6. Assembling the microscope ................... 19
6.1 Specimen stage ......................................... 19
6.2 Condenser ................................................... 21
6.3 Tube and eyepieces .................................. 22
6.4 Objectives ................................................... 23
6.5 Light sources for the transmitted
light axis ...................................................... 23
6.6 Light sources for the incident
light axis ...................................................... 25
6.7 Equipping the incident light
turret disk .................................................... 30
6.8 Polarizer and analyzer .............................. 31
6.9 DIC prisms ................................................... 32
6.10 Optional accessories ................................ 33
6.11 Connection to the power supply ............ 34
6.12 Connecting to the CTR5000
electronics box .......................................... 34
7. Startup ......................................................... 35
7.1 Functional principle .................................. 35
7.2 Switching on the unit ................................ 38
7.3 The display
(DM4000 B/4500 B/4000 M/4500 P)......... 39
7.4 The function keys ...................................... 40
7.5 Köhler illumination .................................... 41
7.5.1 Transmitted light ............................. 41
7.5.2 Incident light.................................... 42
7.6. Checking the phase contrast rings ........ 44
7.7 Setting the motorized polarizer
(DM4500 P/DM5000 B) .............................. 45
7.8 Adjusting the light sources...................... 45
8. Operation .................................................... 51
8.1 Switching on the unit ................................ 51
8.2 Stages and object displacement............ 51
8.3 Focusing ...................................................... 53
8.4 Tubes....................................................... 53
8.5 Eyepieces .................................................... 55
8.6 Objectives ................................................... 55
8.7 Magnification changer ............................. 58
8.8 HC P 1x/1.6x tube optics........................... 58
8.9 Light sources .............................................. 59
8.10 Aperture diaphragm and
field diaphragm .......................................... 59
5

Contents
9. Contrast methods for
Leica DM4000 B/DM4500 B/
DM4500 P/DM5000 B ................................ 60
9.1 Transmitted light ........................................ 60
9.1.1 Bright field ......................................... 60
9.1.2 Phase contrast.................................. 60
9.1.3 Dark field............................................ 61
9.1.4 Polarization........................................ 61
9.1.4.1 Manual method............................. 61
9.1.4.2 DM4500 P - examinations
in polarized transmitted light...... 62
9.1.4.3 Motorized method ........................ 68
9.1.4.4 Combined methods....................... 68
9.1.5 Differential interference
contrast ............................................ 68
9.1.5.1 DM4500 B/DM4500 P .................... 68
9.1.5.2 DM5000 B........................................ 69
9.2 Fluorescence.............................................. 70
10. Contrast methods for
Leica DM4000 M ........................................ 71
10.1 Incident light .............................................. 71
10.1.1 Bright field ....................................... 71
10.1.2 Dark field.......................................... 71
10.1.3 Polarization...................................... 72
10.1.4 Interference contrast .................... 73
10.2 Transmitted light ........................................ 73
10.2.1 Bright field ....................................... 73
10.2.2 Polarization...................................... 73
11. Troubleshooting......................................... 74
12. Care of the microscope ........................... 77
12.1 Dust cover ................................................... 77
12.2 Cleaning ....................................................... 77
12.3 Handling acids and bases ....................... 78
13. Essential wear and spare parts ............. 79
14. Abbreviations and pictograms ............... 80
15. Index ............................................................ 81
16. EU Declaration of Conformity................. 82
6
1. Important notes about this manual
1. Important notes about this manual
Caution!
This operating manual is an essential component of the microscope, and must be read
carefully before the microscope is assembled and put into operation.
Text symbols, pictograms and their meanings:
(1.2)
→ p.20
!
This operating manual contains important instructions and information for the operational
safety and maintenance of the microscope and
accessories. It must therefore be kept safely for
future reference.
Numbers in parentheses, such as "(1.2)", correspond to illustrations (in the example, Figure 1,
Item 2).
Numbers with pointer arrows (for example →
p.20), point to a certain page of this manual.
Caution!
Special safety instructions within this manual are indicated with the triangle symbol
shown here, and have a gray background.
Caution! The microscope and accessories can
be damaged when operated incorrectly.
Explanatory note.
Instructions on disposing of the microscope,
accessory components and consumables.
Item not contained in all configurations.
*
7
2. Intended purpose of the microscope
2. Intended purpose of the microscope
The DM4000 – DM5000 microscopes to which
these operating instructions belong, and which
have the identifying letter B, are intended for
biological routine and research applications.
This includes examining specimens taken from
the human body for the purpose of gaining information about physiological or pathological conditions or inborn anomalies, or testing for safety
and compatibility for potential recipients, or for
monitoring therapeutic measures.
The microscopes that have the identifying letters M or P are intended for materials science,
geological or mineralogical examinations.
The manufacturer assumes no liability for
damage caused by, or any risks arising from
using the microscopes for other purposes
than those for which they are intended or
not using them within the specifications of
Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH.
In such cases the declaration of conformity
shall cease to be valid.
Caution!
Caution!
The above-named microscopes comply with the
Council Directive 98/79/EEC concerning in vitro
diagnostics. They also conform to the Council
Directives 73/23/EEC concerning electrical apparatus and 89/336/EEC concerning electromagnetic compatibility for use in an industrial environment.
8
These (IVD) instruments are not intended for
use in the patient environment defined by
DIN VDE 0100-710. Nor are they designed to
be combined with medical instruments in
accordance with EN 60601-1. If a
microscope is electrically connected to a
medical instrument in accordance with
EN 60601-1, the requirements defined in
EN 60601-1-1 shall apply.
3. Safety notes
3.1 General safety notes
This safety class 1 device was built and tested
in accordance with the safety regulations for
electrical measuring, control, regulating and
laboratory devices in accordance with
EN 61010-2-101:2002
EN 61010-1:2001
IEC 1010-1:2001
Caution!
3. Safety notes
Caution!
The devices and accessories described in
this operating manual have been tested for
safety and potential hazards.
The responsible Leica affiliate or the main
plant in Wetzlar, Germany, must be consulted whenever the device is altered, modified
or used in conjunction with non-Leica
components that are outside of the scope of
this manual.
In order to maintain this condition and to ensure safe operation, the user must follow the
instructions and warnings contained in this
operating manual.
Unauthorized alterations to the device or
noncompliant use shall void all rights to any
warranty claims and void product liability!
9
3. Safety notes
3.2 Electrical safety
General specifications
Leica CTR5000 electronics box (for DM5000 B)
For indoor use only.
Supply voltage:
Frequency:
Power input:
Fuses:
90-250 V~
50-60 Hz
max. 290VA
T6.3 A
(IEC 60127-2/3)
Ambient temperature:
Relative humidity:
Overvoltage category:
Pollution degree:
15-35°C
max. 80% to 30°C
II
2
Microscope
For indoor use only.
Supply voltage:
Frequency:
90-250 V~
50-60 Hz
Power input:
DM4000
DM4500
DM5000
max. 180 VA
max. 180 VA
max. 290VA
Fuses:
DM4000
DM4500
DM5000
Ambient temperature:
Relative humidity:
Overvoltage category:
Pollution degree:
T6.3 A (IEC 60127-2/3)
T6.3 A (IEC 60127-2/3)
See CTR5000
15-35°C
max. 80% to 30°C
II
2
ebq 100 supply unit*
For indoor use only.
Supply voltage:
Frequency:
Power input:
Fuses:
Ambient temperature:
Relative humidity:
Overvoltage category:
Pollution degree:
90-250 V~
50-60 Hz
max. 155VA
2xT2A (IEC 127)
10-36°C
max. 80% to 30°C
II
2
(see enclosed manual)
Caution!
The power plug may only be plugged into an
outlet equipped with a grounding contact.
Do not interfere with the grounding function by using an extension cord without a
ground wire. Any interruption of the ground
wire inside or outside of the device, or release of the ground wire connection, can
cause the device to become hazardous.
Intentional ground interruption is not permitted!
Caution!
Through connection to the grounding connection, ancillary equipment with its own
and/or extra power supply may be brought
to the same ground wire potential. For connections without a ground connector, Leica
Service must be consulted.
10
Caution!
Never use any fuses as replacements other
than those of the types and the current ratings listed here. Bypassing fuse holders is
not permitted.
Caution!
The microscope’s electrical accessory components are not protected against water.
Water can cause electric shock.
Caution!
Protect the microscope from excessive temperature fluctuations. Such fluctuations can
lead to the accumulation of condensation,
which can damage the electrical and optical components.
Operating temperature: 15-35°C
3. Safety notes
3.3 Disposal
Once the product has reached the end of its service life, please contact Leica Service or Sales
about disposal.
Please observe and comply with the national
and federal laws and regulations that are equivalent to EU guidelines such as WEEE.
Note!
Like all electronic devices, the microscope,
its accessory components and consumables
must never be disposed of with general
household waste.
Caution!
Before exchanging the fuses or lamps, be
absolutely certain to switch off the main
power switch and remove the power cable.
11
4. Overview of the instrument
4. Overview of the instrument
Specification
Contrast methods
Transmitted light axis
Incident light axis
Leica DM4000 B
Leica DM5000 B
• Transmitted light:
DM4000 B: BF, DF, PH, Pol
DM5000 B: and ICT (mot.)
• Incident light: Fluorescent
• Automatic illumination manager (mot. aperture diaphragm
and field diaphragm, mot. intensity control)
• Automatic constant-color intensity control
• Motorized shutter
• Integrated into the stand
• Motorized 5x filter turret disk
(DM5000 B 8x optional)
• With FIM (fluorescence intensity manager) for reducing the light intensity in 5 increments
• Mechanical booster lens for
increasing fluorescence intensity
• Motorized shutter
Leica DM4000 M
Leica DM4500 P
• Transmitted light:
DM4000 M: BF, DF, PH, ICT,
Pol
DM4500 P: BF, DF, PH, ICT,
Pol (conoscopy)
• Incident light:
BF, DF, ICR, Pol, Fluo
• Integrated into the stand
• Motorized 4x filter turret
disk
• Automatic
illumination manager
• DM4000 M: motorized
shutter
Z pinion
Objective turret
12
• Manual
• Manual, fully encoded
• DM4000 B: 6x/7x with
M25 thread
DM5000 B: 7x (M25)
DM5000 B: With object prism
disk (3 positions)
• Manual, fully encoded
• DM4000 M: 6x with
M32 thread
DM4500 P: 6x with
M25 thread, centerable,
encoded
• Receptacle for DIC prisms
and Pol compensators
(for DM4000 M: optional)
4. Overview of the instrument
Specification
X/Y stage
Tube
Condenser
Magnification changer
(optional)
Controls
Leica DM4000 B
Leica DM5000 B
• Manual
• Replaceable specimen stage
• Coaxial drive length: 155 mm
Leica DM4000 M
Leica DM4500 P
• Manual
• DM4000 M:
Replaceable specimen stage
•
•
Coaxial drive length: 140 mm
DM4500 P:
• Replaceable Pol stage
• Manual or motorized (DM4500P: manual)
• Optionally with one or two camera outputs
• DM4500 P: conoscopy module
(tube optics HC P1x/1.6x with Bertrand lens, encoded)
• Motorized condenser head
• Condenser disk for the light ring, DF-Stop, DIC prisms
• Automatic Köhler illumination
• Optional polarizer (integrated and motorized)
• Manual
• 3x fully encoded
• 1x; 1.25x; 1.6x
• Manual
• 3x fully encoded
• 1x; 1.5x; 2x
• Operating buttons on the stand for all motorized
microscope functions
• Additional variable multifunction keys
• Focus wheels
• LCD
• DM5000 B with Leica SmartTouch
Computer interface
Software tools
• USB2.0
• Leica Application Suite (LAS)
TM
for Windows
2000, XP, Vista
• With plug-ins for:
• Microscope and camera configuration
• Microscope and camera control
• Image acquisition
13
4. Overview of the instrument
Specification
Electronics box
Leica CTR5000
Leica DM4000 B
Leica DM5000 B
Only for the Leica DM5000 B:
Separate operating unit with a
power supply for 100 W halogen
lamps. See → p.10
(Electrical safety)
Leica DM4000 M
Leica DM4500 P
14

14
4. Overview of the instrument
1
2
3
4
5
6
13
12
Fig. 1 Left side of the stand with the advanced AET22 ErgoTube
1 Eyepiece
2 Eyepiece tube
3 Tube
4 Objective turret with objectives
5 Specimen stage with specimen holder
6 Condenser
7 LCD
8 Field diaphragm operating buttons
9 Transmitted light / incident light switch
10 Aperture diaphragm operating buttons
11 Brightness adjustment buttons
12 Focus wheel with coarse and fine adjustment
13 Variable function keys (preset at the factory)
14 Lamp adjustment window
7
891011
15

4. Overview of the instrument
22
15
16
21 20 19 18 17
Fig. 2 Right side of the stand with the advanced ErgoTube AET22
15 Lamp housing for incident light
16 Lamp housing for transmitted light
17 Transmitted light filter, optional
18 Transmitted light filter, optional
19 Variable function keys (preset at the factory)
20 x/y coaxial drive, adjustable height
21 Handwheel for fine focus
22 Motorized filter block exchanger
16
5. Unpacking the microscope
5. Unpacking the microscope
The microscope is delivered in two packages.
The stand package contains the following com-
ponents:
• Stand with integrated incident light axis and
objective turret
• Specimen stage with stage bracket
• Power cable and PC connecting cable
• CD with Leica Application Suite (LAS) software package
• Instructions and list of microscope default
settings
The system package contains the microscope’s
accessories:
• Tube
• Eyepieces
The external ebq 100 supply unit* is delivered in
a separate package.
For the Leica DM5000 B microscope:
The Leica CTR5000 electronics box is delivered
in a separate package.
First, carefully remove all components from the
transportation and packaging materials.
Note:
If at all possible, avoid touching the lens surfaces of the objectives. If fingerprints do appear on
the glass surfaces, remove them with a soft
leather or linen cloth. Even small traces of finger
perspiration can damage the surfaces of optical
devices in a short time. See the chapter on "Care
of the microscope" →
structions.
Caution!
p. 77 for additional in-
• Objectives
• Condenser
• Lamp housings with accessories
• Assembly tools
• Additional microscope accessories such as
filter cubes, etc. depending on product configuration
Do not connect the microscope or peripherals to an AC power source at this time
under any circumstances!
17
5. Unpacking the microscope
Installation location
Work with the microscope should be performed
in a dust-free room, which is free of oil vapors
and other chemical vapors, as well as extreme
humidity. At the workstation, large temperature fluctuations, direct sunlight and vibrations
should be avoided. These conditions can distort
measurements and micrographic images.
Allowable ambient conditions
Temperature 15-35°C
Relative humidity maximum 80% up to 30°C
Microscopes in warm and warm-damp climatic
zones require special care in order to prevent
the build up of fungus.
See the chapter on "Care of the microscope" →
p. 77 for additional instructions.
Caution!
Electrical components must be assembled at
least 10 cm away from the wall and from
flammable substances.
Transport
For shipping or transporting the microscope
and its accessory components, the original
packaging should be used.
As a precaution to prevent damage from vibrations, the following components should be disassembled and packaged separately:
• Unscrew the objectives.
• Remove the condenser.
• Remove the specimen stage.
• Remove the lamp housings.
• Disassemble the burner of 106 z lamp housing.
• Remove all moving or loose parts.
18

6. Assembling the microscope
6. Assembly
The microscope components are logically assembled in this order:
• Specimen stage
• Condenser with condenser head
• Tube
• Eyepieces
• Objectives
• Lamp housings with light sources
• Equipment for the incident light turret disk*
Only a few commonly used screwdrivers and
keys are necessary for assembly; these are included in the delivery package.
When using intermediate systems and optical
accessories, the sequence may vary.
In this case, read chapter,
"6.10 Optional accessories" →
p.33
6.1 Specimen stage
!
Caution:
Never install objectives before assembling the
stage.
• Place the specimen holder on the stage and
fasten it with the two screws (3.1).
• Using the condenser height adjuster (3.2), turn
the condenser holder completely upwards,
i.e. as close to the stage as possible.
• Loosen the stage clamp (3.3) slightly.
Fig. 3 Mechanical object stage
1 Locking screws for specimen holder
2 Condenser height adjuster
3 Stage clamp
1
23
19

6. Assembly
• From above, set the stage clamp onto the
dovetail guide (4.2) and push the stage downwards until the upper end of the dovetail
guide is tightly fastened to the upper end of
the stage clamp.
• Firmly tighten the stage clamp (4.1).
Note:
For thicker specimens (Leica DM4000 M) the
stage can be set to a correspondingly lower level.
Fig. 4 Assembling the stage
1 Stage clamp
2 Dovetail guide
• Only for DM4500 P:
Pol attachable mechanical stage*
Adjust the attachable mechanical stage so
that the fastening screw is visible below the
holes (4a.1). Set the attachable mechanical
stage in the guide holes on the rotating stage
and tighten the fastening screw using the
hexagonal key.
Attachable mechanical stage*
The attachable mechanical stage can be installed on the left, on the right or on the front
(not pictured). The two clamping screws fasten it into place.
Fig. 4a Pol rotating stage* and Pol 3 attachable mechanical stage*
1 Holes for the fastening screw.
2 Lever for the holder for glass slides of various formats,
which can be turned inward and outward
3 Storage for the centering key
4 Locking button pair
5 45° click stop
6 Clamping system for the stage rotation
20
4
3
1
1
2
5
2
6

6.2 Condenser
6. Assembly
• Screw the condenser head into the condenser.
• Using the condenser height adjuster (5.4), turn
the condenser holder (5.1) downward as far
as it will go.
• Unscrew the clamping screw for the condenser (5.3) far enough so that the condenser
can be inserted from the front.
• From the front, insert the condenser into the
condenser holder as far as it will go. On the
underside of the condenser, there is an orientation pin (6.1) that must be locked into place
in the guiding notch (7.1).
• Tighten the condenser’s clamping screw (5.3)
until the condenser locks into place.
• Connect the condenser over the connection
(8.1) with the stand.
Note:
The condenser must be centered before using
the microscope.
Köhler illumination p. 41.
→
Fig. 6
Underside of condenser
1 Orientation pin
Fig. 7 Condenser holder
1 Guiding groove
1
1
Fig. 5 Condenser holder
1 Condenser holder
2 Condenser centering
3 Clamping screw for the condenser
4 Condenser height adjuster
1
23 4
Fig. 8 Condenser connection
1 Condenser cable socket
1
21

6. Assembly
6.3 Tube and eyepieces
The tube is mounted on the stand either directly
or with the use of intermediate modules. The
side clamping screw fastens it into place (9b.1).
For the MBDT motorized tube only:
•
Remove the transport anchor (9a.1) on the underside of the tube.
• Partially unscrew the clamping screw (9b.1).
• Insert the tube into the circular receptacle
(dovetail ring).
• Retighten the clamping screw (9b.1).
For the MBDT motorized tube only:
•
Connect the tube to the stand with the connector bushing (10.1).
• The eyepieces are inserted into the eyepiece
tubes on the tube.
For the BDTP tube only:
•
The Pol eyepieces are inserted into the eyepiece tubes (using the locking groove).
Fig. 9b Fastening the tube
1 Clamping screw
1
Fig. 9a Underside of the tube
1 Transport anchor
1
22
Fig. 10 Motorized tube connection
1 Connector socket
1
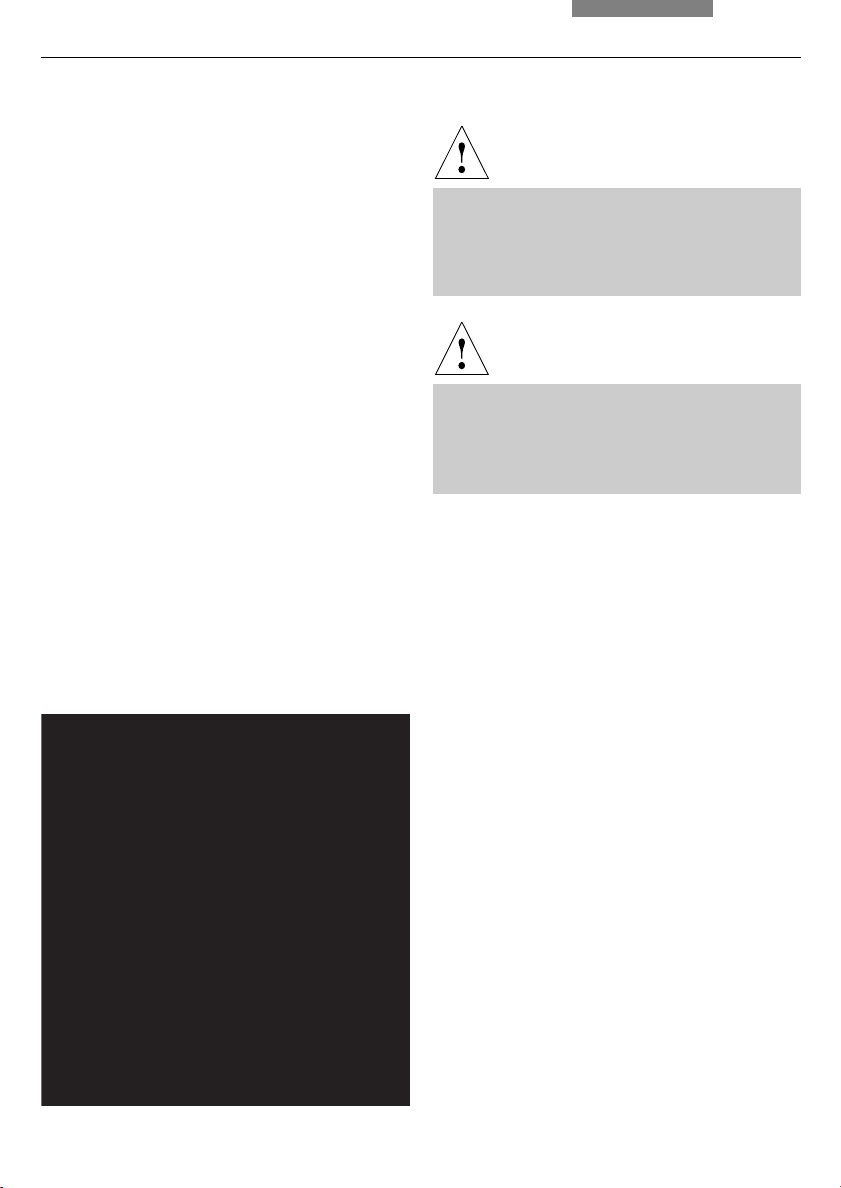
6. Assembly
6.4 Objectives
The receptacles on the objective turrets are
numbered (Fig. 11). Based on your equipment,
the individual objectives have already been assigned to specific positions at the factory.
For details on the exact positions of the objectives, please refer to the enclosed identification sheet.
!
Caution:
Close vacant threads in the turret with dust protection caps!
Fig. 11
Objective turret with engraved objective receptacles
6.5 Light sources for the transmitted light axis
Caution!
Ensure that the lamp housing has been disconnected from the power supply. Unplug
the power plug and the power supply during
assembly.
Caution!
Light sources pose a potential irradiation risk
(glare, UV-radiation, IR-radiation). Therefore,
lamps have to be operated in closed housings.
Lamp housing 107/2
This lamp housing is used with a 12 V 100 W
halogen lamp, which is already mounted.
In case the lamp has to be removed:
• Remove the fastener screw on the housing
(Fig. 12).
• Remove the housing by pulling it upwards.
• Remove the lamp.
23
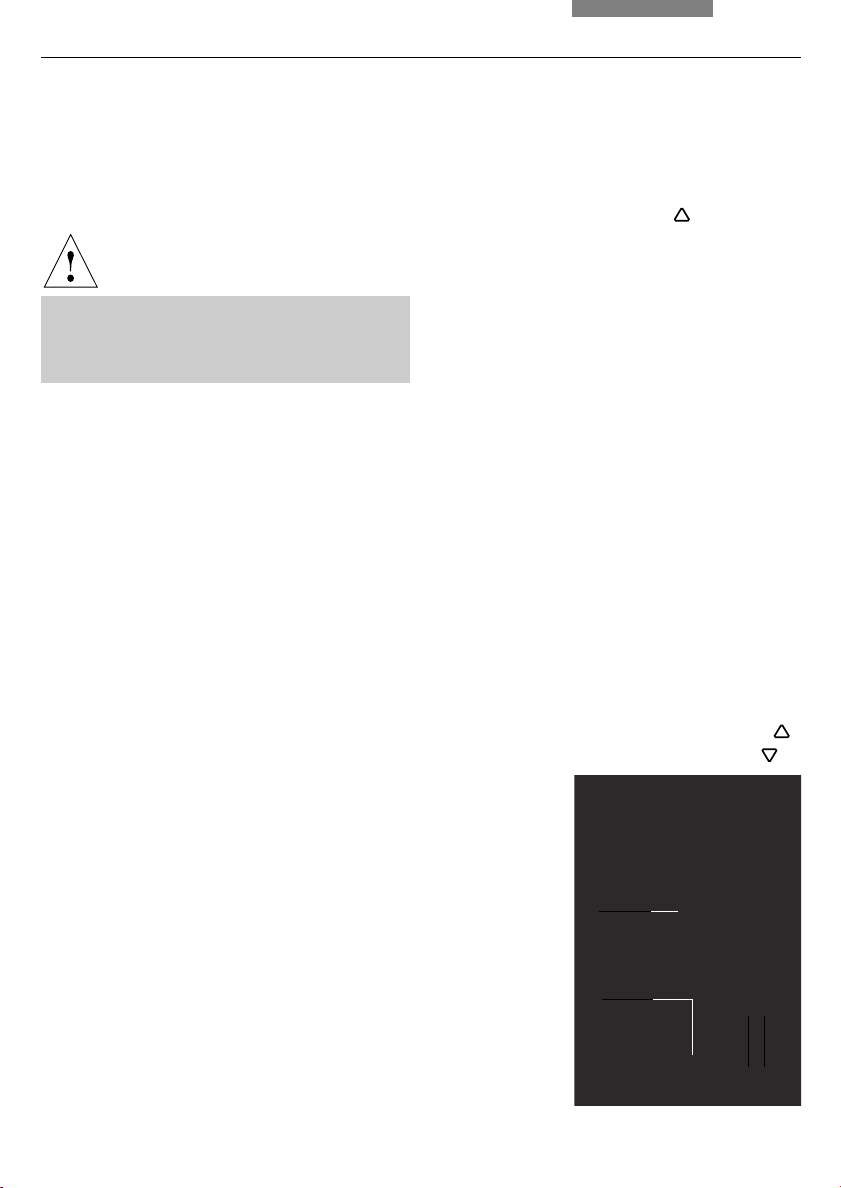
6. Assembly
• Insert the new 12 V 100 W lamp (13.1) with the
dust cover straight into the socket until it
stops. Be sure that the lamp is inserted
straight.
• Remove the lamp’s dust cover.
Caution!
Do not remove the lamp’s dust cover until after you have installed the lamp. Avoid fingerprints on the lamp.
• Replace the housing and fasten it in place using the fastening screw.
Fig. 12
Lamp housing 107/2
Releasing the
fastening screw
• Place the lamp housing in the transmitted
light lamp housing receptacle (14.2) and fasten it with the clamping screw on the side.
• Connect the lamp housing to the power supply
for transmitted light (symbol:
Fig. 14 Rear view of the stand
1 Incident light lamp housing receptacle
2 Transmitted light lamp housing receptacle
3 12 V 100 W connection for transmitted light (symbol: )
4 12 V 100 W connection for incident light (symbol: )
) (14.3).
Fig. 13
Lamp housing 107/2
opened
1 Mount with
halogen bulb
2 Collector
24
1
1
2
2
34
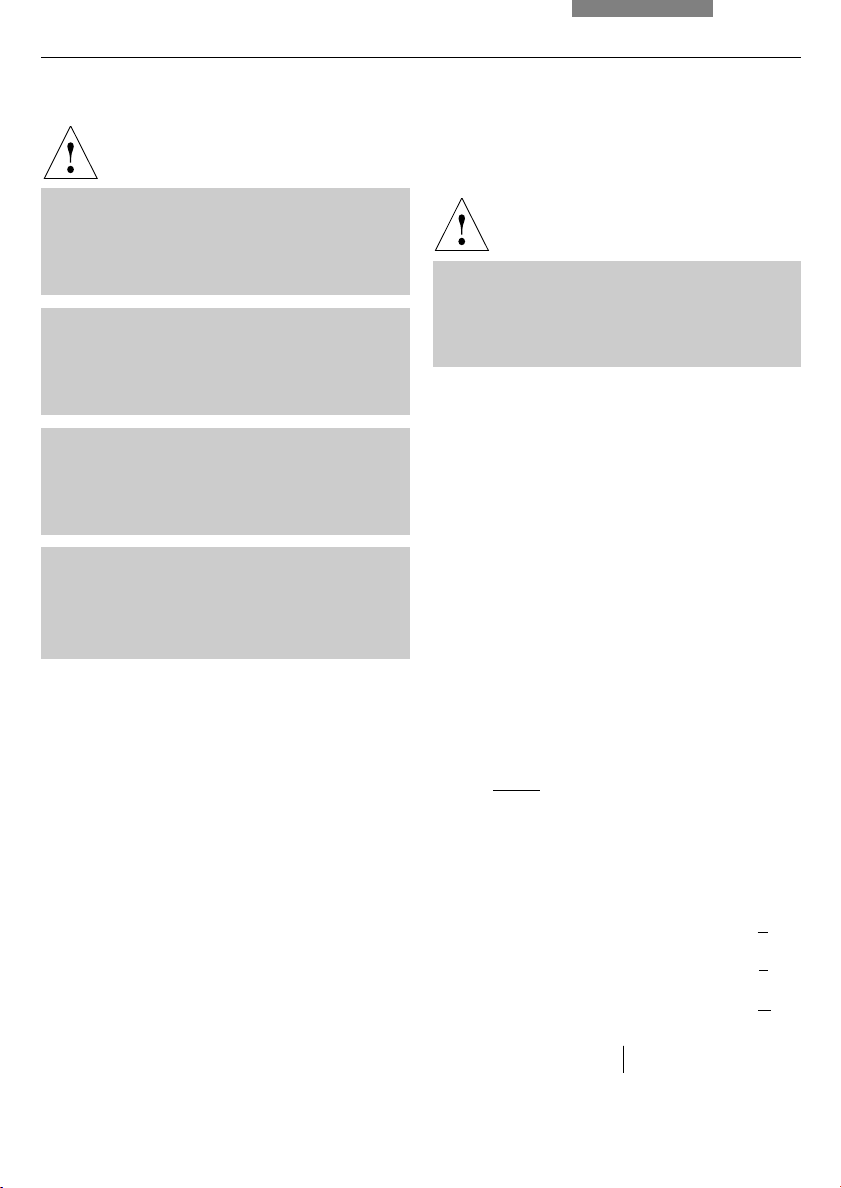
6. Assembly
6.6 Light sources for the incident light axis
Caution!
Light sources pose a potential irradiation
risk (glare, UV-radiation, IR-radiation).
Therefore, lamps have to be operated in
closed housings.
Ensure that the lamp housing has been disconnected from the power supply. Unplug
the power plug and the power supply during
assembly.
During assembly work on xenon burners,
always wear the protective gloves and face
protection supplied (Fig. 15) (risk of explosion).
Never touch the glass parts of the burner
with bare hands.
Never look directly into the beam path
(blinding hazard).
Lamp housing 106/106 z
This lamp housing is suitable for use with a 12 V
100 W halogen lamp or a variety of gas discharge
lamps.
Caution!
Make sure to follow the instructions and
safety notes of the lamp supplier.
Before changing lamps allow it to cool down
for at least 30 min.!
Fig. 16 106/106 z lamp housing (on the side, open)
1 Cover raised
2 Collector
3 12 V 100 W lamp or
gas discharge lamp in mount
4 Reflector (mirror)
5, 6, 7 Adjusting screw for x-y reflector
8 Fastening screw for the lamp mount
9 Socket for contact plug
Fig. 15
Protective gloves and mask
1
2
4
5
3
6
7
898
25
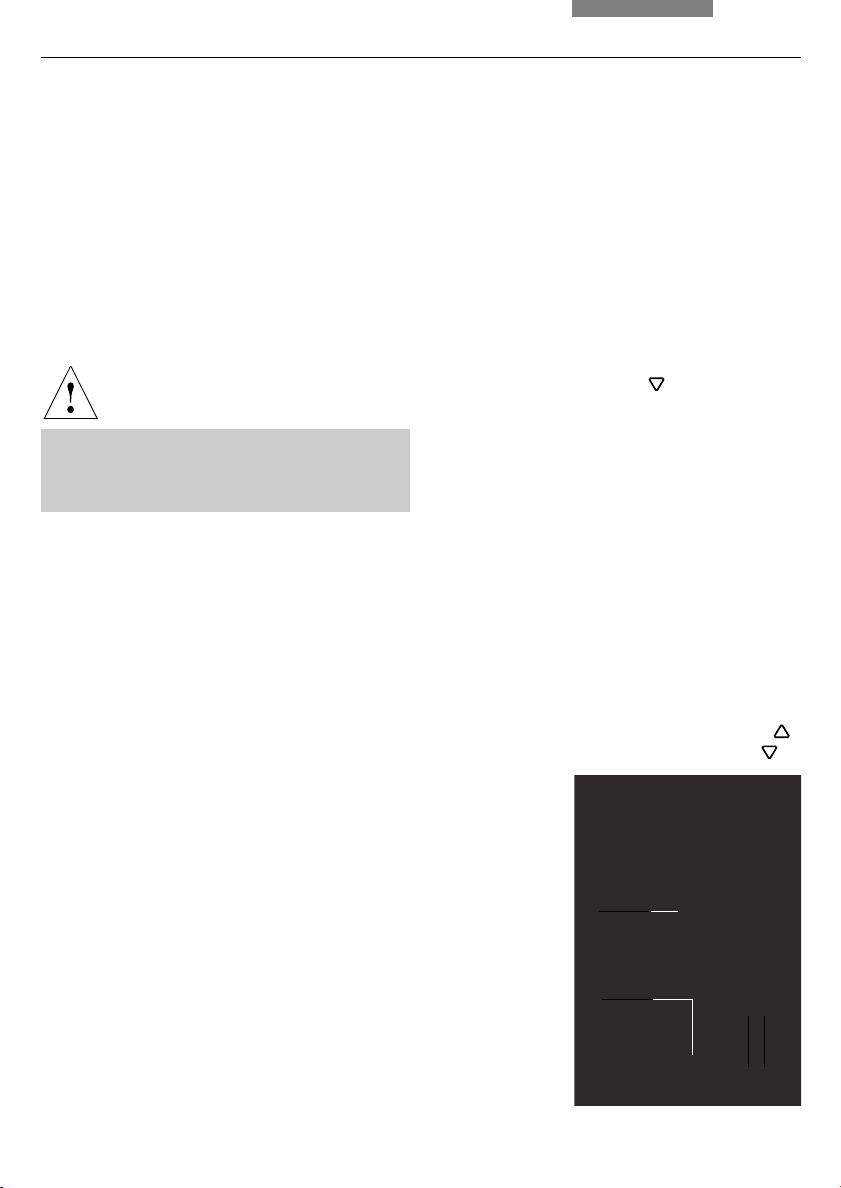
6. Assembly
Inserting the 12 V 100W halogen bulb into the
106/106 z lamp housing
• Unscrew the fastening screws of the cover
and flip the cover up (16.1).
• Unscrew the fastening screws of the lamp
mount (16.8) and pull out the mount (Fig. 17).
• Insert the lamp with the dust cover straight
into the socket until it stops.
Caution!
Do not remove the lamp’s dust cover until after you have installed the lamp. Avoid fingerprints on the lamp.
• Remove the dust cover.
Fig. 17 Lamp mount with 12 V 100 W halogen bulb
• Insert the lamp mount, with the burner installed, into the lamp housing and tighten it
with the screws (16.8).
• Close the lamp housing and retighten the fastening screws.
• Place the lamp housing in the incident light
lamp housing receptacle (18.1) and fasten it
with the clamping screw on the side.
• Connect the lamp housing to the power supply
for incident light (symbol:
Fig. 18 Rear view of stand
1 Incident light lamp housing receptacle
2 Transmitted light lamp housing receptacle
3 12 V 100 W connection for transmitted light (symbol: )
4 12 V 100 W connection for incident light (symbol: )
) (18.4).
26
1
2
34
6. Assembly
Inserting gas discharge lamps (Hg and Xe) into
the 106/106z lamp housing
Hg and Xe lamps are powered by separate supply units.
Please also read the separate instruction manual provided with these supply units.
The following gas discharge lamps may be used
and require different power supplies and lamp
mounts (Fig. 19):
Type Typical bulb life*
50 W high-pressure mercury burner (alternating current) 100 hrs.
100 W high-pressure mercury burner (direct current) 200 hrs.
100 W high-pressure mercury burner (direct current, type 103 W/2) 300 hrs.
75 W high-pressure xenon burner (direct current) 400 hrs.
* Please observe the data sheets of the lamp manufacturer.
27
6. Assembly
• To open the 106 z lamp housing, unscrew the
fastening screws on the cover.
Caution!
• Remove the transport anchor (red plastic rod
in place of the burner) in the lamp mount. To
do so, remove the lower clamp (19.1). Pull up
the cooling element (19.3) and turn it to the
side. Detach the lower clamp system (19.2)
and remove the transport anchor.
• Install the burner in reverse order.
Fig. 19 a-c Lamp mounts for gas discharge lamps
1 Upper clamping system, 2 Lower clamping system, 3 Cooling element
4 Melt nipple for the Hg 50 arc lamp, 5 Dust cover for the Xe 75 arc lamp
Hg 50
1
4
a
3
2
Hg 50 burner:
After installation, the labeling must be
right.
If a glass melt nipple is present (19a.4), position it by turning the burner so that the
nipple does not impede the beam path later,
but instead is positioned
Xe 75 burner:
Remove the burner’s dust cover (19b.5) after
you have installed the burner.
Xe 75
up-
sideways.
b
3
1
5
2
28
Hg 100
1
2
c
3

• Insert the lamp mount, with the burner installed, into the lamp housing and tighten it
with the screws (20.8).
6. Assembly
• Close the lamp housing and retighten the fastening screws.
• Place the lamp housing in the incident light
lamp housing receptacle (21.1) and fasten it
with the clamping screw on the side.
• Connect the lamp housing to the external
power supply (22.1).
Fig. 21 Rear view of the stand
1 Incident light lamp housing receptacle
2 Transmitted light lamp housing receptacle
3 12 V 100 W connection for transmitted light (symbol: )
4 12 V 100 W connection for incident light (symbol: )
Fig. 20 106/106 z lamp housing (on the side, open)
1 Cover raised
2 Collector
3 12 V 100 W lamp or
gas discharge lamp in mount
4 Reflector (mirror)
5, 6, 7 Adjusting screw for x-y reflector
8 Fastening screw for lamp mount
9 Socket for contact plug
1
2
3
898
4
5
6
7
Fig. 22 Rear panel of the ebq 100 supply unit
1 Lamp connection
1
1
2
34
29

6. Assembly
6.7 Equipping the incident light turret disk
The positions in the turret disk are numbered.
Depending on how they are equipped, the individual filter and/or reflector cubes are set in
pre-assigned positions at the factory. For
details, check the identification sheet included
with your order.
Insert the filter and reflector cubes in the following manner:
• Never fit the incident light turret disk while
the microscope is in operation.
• Remove the face plate from the upper part of
the microscope (Fig. 25). Press the locking pin
(25.2) to turn the turret disk. When the locking
pin is released, the turret disk locks into place
again.
• With the holder facing you squarely, insert the
filter cube or reflector cube into the holder as
described in the identification sheet provided.
To do so, place the filter or reflector cube on
the right side and press it toward the left into
the mounting (Fig. 26).
Fig. 23 Filter cube,
front side
Fig. 25 Removing the front panel
1 Filter receptacle
2 Locking pin
3 Front panel
Fig. 24 Filter cube,
back side
1
2
3
• Press the locking pin (25.2) and turn the filter
turret to the next click stop.
• Make sure that the turret engages (the locking pin springs forward) and insert the next filter and/or reflector cube as described above.
• When all filters and reflector cubes have been
inserted, close the front cover plate again.
30
Fig. 26 Inserting the filter or reflector cubes
1 Mounting
1
1
 Loading...
Loading...