Page 1

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-0
2
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
GENERAL INFORMATION
__________________________________________________________________________________
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER/IDENTIFICATION ........................ 2- 1
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS ........................................................ 2- 2
SERVICE INFORMATION........................................................ 2-10
TORQUE VALUES................................................................... 2-12
SPECIAL TOOLS ..................................................................... 2-13
LUBRICATION POINTS........................................................... 2-15
WIRING DIAGRAM.................................................................. 2-16
CABLE & HARNESS ROUTING ............................................... 2-18
TROUBLESHOOTING.............................................................. 2-22
2
Page 2
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-1
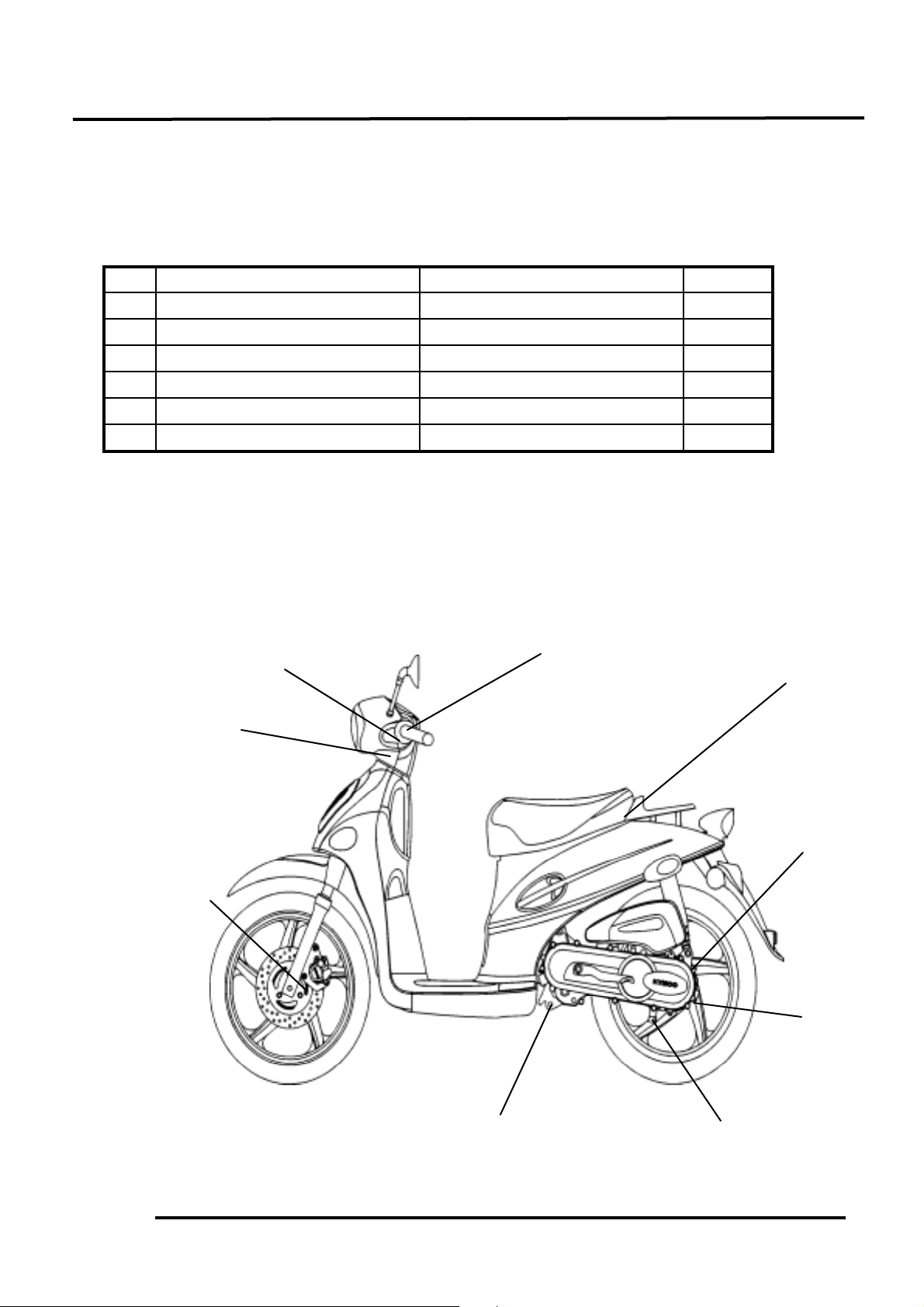
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBER/IDENTIFICATION
Location of Engine Serial Number
Page 3
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-2
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
n Make sure to install new gaskets, O-rings,
circlips, cotter pins, etc. when reassembling.
n When tightening bolts or nuts, begin with
larger-diameter to smaller ones at several
times, and tighten to the specified torque
diagonally.
n Use genuine parts and lubricants.
n When servicing the motorcycle, be sure to
use special tools for removal and
installation.
n After disassembly, clean removed parts.
Lubricate sliding surfaces with engine oil
before reassembly.
Page 4
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-3
n Apply or add designated greases and
lubricants to the specified lubrication
points.
n After reassembly, check all parts for
proper tightening and operation.
n When two persons work together, pay
attention to the mutual working safety.
n Disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal
before operation.
n When using a spanner or other tools, make
sure not to damage the motorcycle surface.
n After operation, check all connecting
points, fasteners, and lines for proper
connection and installation.
n When connecting the battery, the positive
(+) terminal must be connected first.
n After connection, apply grease to the
battery terminals.
n Terminal caps shall be installed securely.
Page 5
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-4
n If the fuse is burned out, find the cause and
repair it. Replace it with a new one
according to the specified capacity.
n After operation, terminal caps shall be
installed securely.
n When taking out the connector, the lock on
the connector shall be released before
operation.
n Hold the connector body when connecting
or disconnecting it.
n Do not pull the connector wire.
n Check if any connector terminal is bending,
protruding or loose.
Confirm
Capacity
Page 6
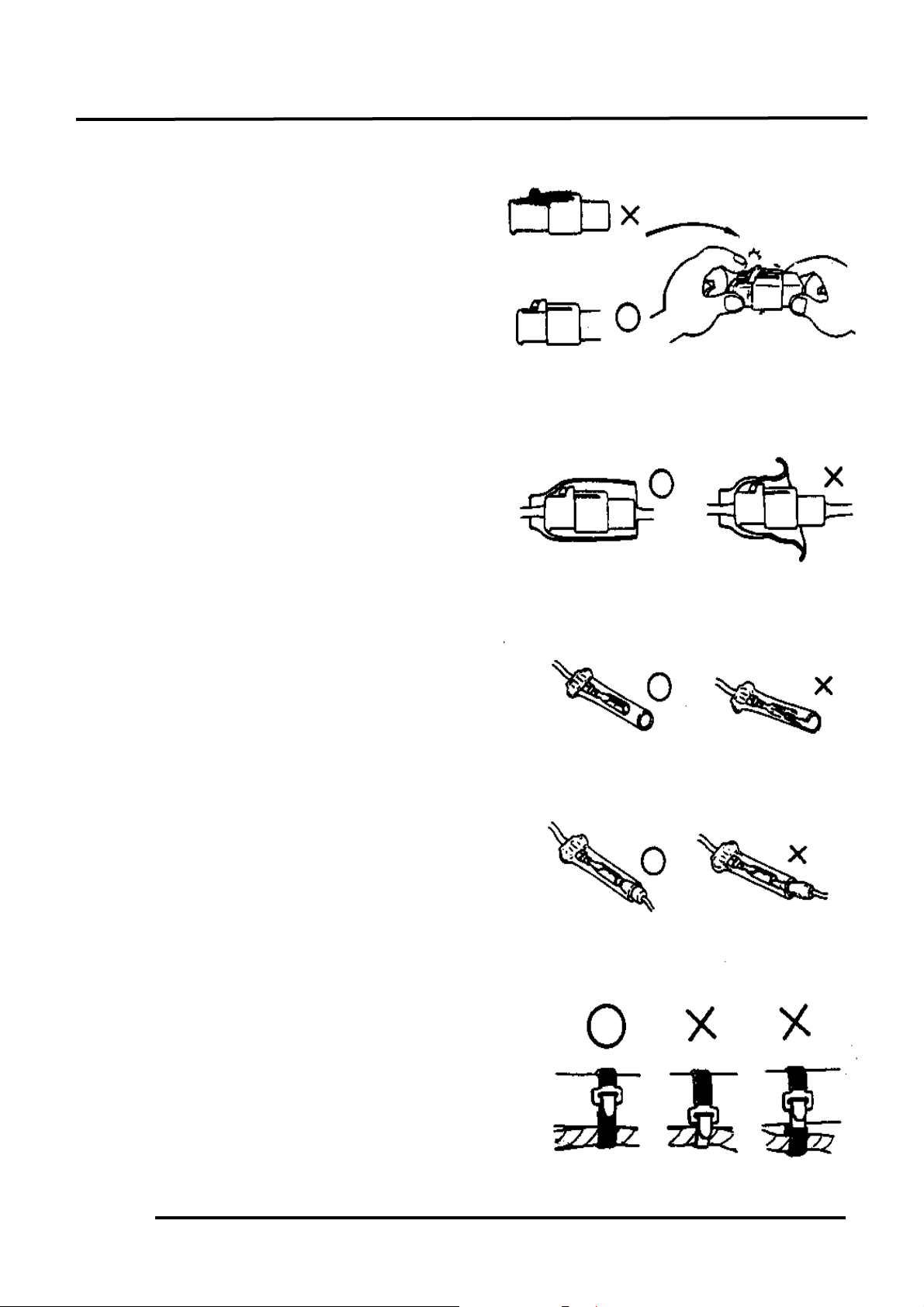
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-5
n The connector shall be inserted
completely.
n If the double connector has a lock, lock
it at the correct position.
n Check if there is any loose wire.
n Before connecting a terminal, check for
damaged terminal cover or loose negative
terminal.
n Check the double connector cover for
proper coverage and installation.
n Insert the terminal completely.
n Check the terminal cover for proper
coverage.
n Do not make the terminal cover opening
face up.
n Secure wire harnesses to the frame with
their respective wire bands at the
designated locations.
Tighten the bands so that only the
insulated surfaces contact the wire
harnesses.
Snapping!
Page 7
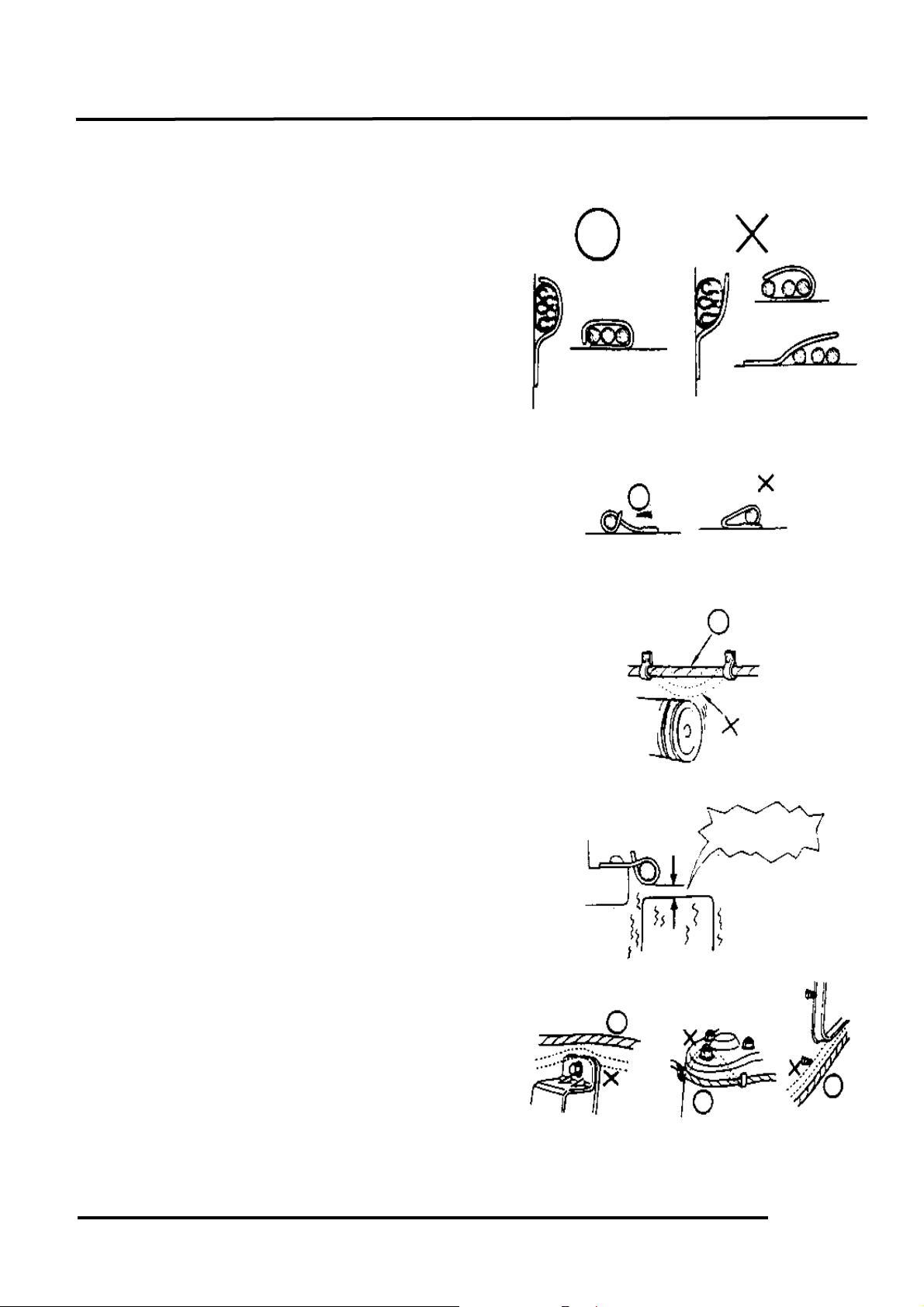
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-6
n After clamping, check each wire to make
sure it is secure.
n Do not squeeze wires against the weld or
its clamp.
n After clamping, check each harness to make
sure that it is not interfering with any
moving or sliding parts.
n When fixing the wire harnesses, do not
make it contact the parts which will
generate high heat.
n Route wire harnesses to avoid sharp edges
or corners. Avoid the projected ends of
bolts and screws.
n Route wire harnesses passing through the
side of bolts and screws. Avoid the
projected ends of bolts and screws.
No Contact !
Page 8

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-7
n Route harnesses so they are neither
pulled tight nor have excessive slack.
n Protect wires and harnesses with electrical
tape or tube if they contact a sharp edge or
corner.
n When rubber protecting cover is used to
protect the wire harnesses, it shall be
installed securely.
n Do not break the sheath of wire.
n If a wire or harness is with a broken sheath,
repair by wrapping it with protective tape
or replace it.
n When installing other parts, do not press or
squeeze the wires.
Do not pull
too tight!
Do not press or
squeeze the wire.
Page 9
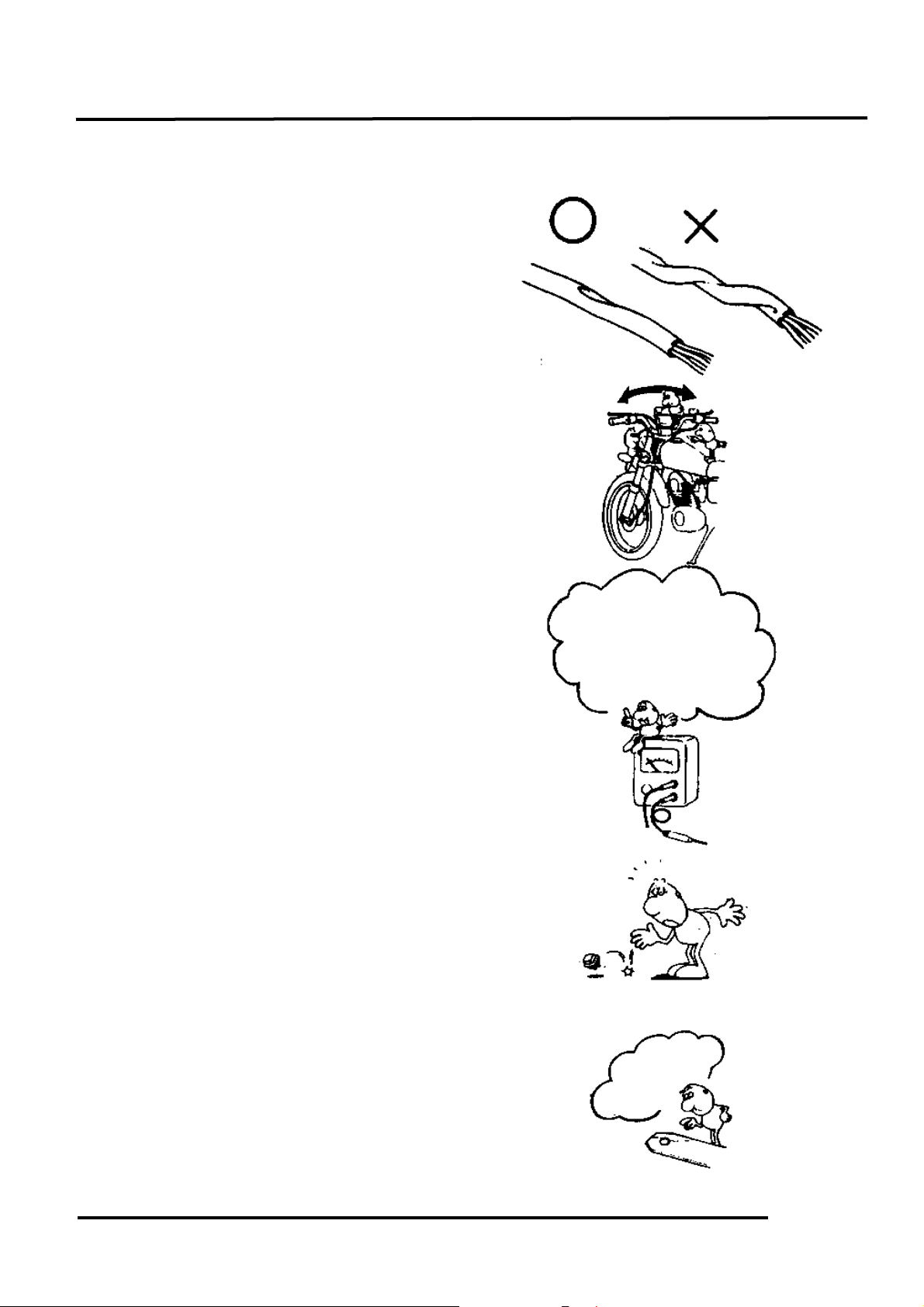
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-8
n After routing, check that the wire harnesses
are not twisted or kinked.
n Wire harnesses routed along with handlebar
should not be pulled tight, have excessive
slack or interfere with adjacent or
surrounding parts in all steering positions.
n When a testing device is used, make sure to
understand the operating methods
thoroughly and operate according to the
operating instructions.
n Be careful not to drop any parts.
n When rust is found on a terminal, remove
the rust with sand paper or equivalent
before connecting.
Do you understand
the instrument? Is
the instrument set
correctly?
Remove Rust !
Page 10
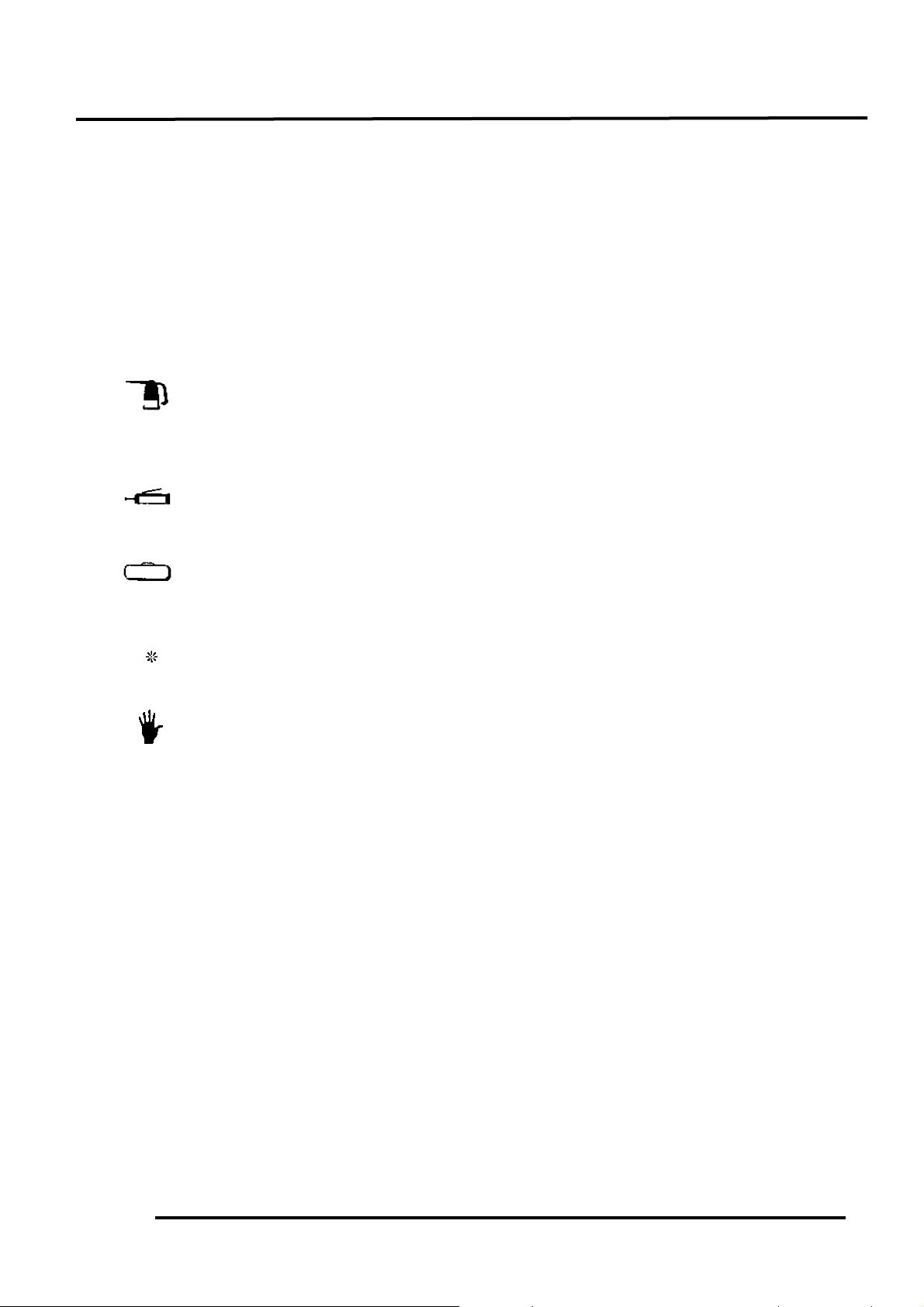
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-9
n Symbols:
The following symbols represent the
servicing methods and cautions included in
this service manual.
: Apply engine oil to the
specified points. (Use
designated engine oil for
lubrication.)
: Apply grease for lubrication.
: Use special tool.
: Caution
: Warning
Engine Oil
Grease
Special
*
Page 11

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-10
SERVICE INFORMATION
ENGINE
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Item
BA10AB.AC.
BA10AB.AC.
Cylinder head warpage
æ
0.10
Piston O.D.(5mm from bottom of piston
38.970_ 38.955
38.90
Cylinder-to- piston clearance
0.10
Piston pin hole I.D.
12.002_ 12.008
12.03
Piston pin O.D.
11.994_ 12.0
11.98
Piston-to-piston pin clearance
¨
¨
Piston ring end gap (top/second)
0.10_ 0.25
0.40
Connecting rod small end I.D.
17.005_ 17.017
17.03
Cylinder bore
39.0_ 39.025
39.05
Drive belt width
18
17
Drive pulley collar O.D.
20.01_ 20.025
¨
Movable drive face ID.
20.035_ 20.085
19.97
Weight roller O.D.
13.0
12.4
Clutch outer I.D.
107_ 107.2
107.5
Driven face spring free length
87.9
82.6
Driven face O.D.
¨
¨
Movable driven face I.D.
¨
¨
Connecting rod big end side clearance
¨
¨
Connecting rod big end radial clearance
¨
¨
Crankshaft runout A/B
æ
¨
CARBURETOR
BA10AB.AC
Venturi dia.
14mm
Identification number
PB058
Float level
8.6mm
Main jet
#85
Slow jet
#35
Air screw opening
1_ ± _
Idle speed
2000±100rpm
Throttle grip free play
2_ 6mm
Jet needle clip notch
1st notch
A
Page 12

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-11
FRAME
Standard (mm)
Service Limit (mm)
Item
BA10AB.AC.
BA10AB.AC.
Axle shaft runout
æ
0.2
Radial
Front wheel rim runout
Axial
Front shock absorber spring free length
200.0
182.8
Rear wheel rim runout
2.0
Brake drum I.D.
Front/rear
110
111
Brake lining thickness
Front/rear
4.0/4.0
2.0/2.0
Brake disk runout
Front/rearæ0.30
Rear shock absorber spring free length
235.7
218.7
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
BA10AB.AC
Capacity
12V4AH
Voltage
13.0_ 13.2V
Charging
Standard
0.4A/5H
Battery
current
Quick
4A/0.5H
Spark plug
(NGK)
BR8HSA
Spark plug gap
0.6_ 0.7mm
Primary coil
0.153_ 0.187W
Secondary coil
(with plug cap)
6.99_ 10.21KW
Ignition coil resistance
Secondary coil
(without plug cap)
3.24_ 3.96KW
Pulser coil resistance (20℃ )
80_ 160W
Ignition timing
8°~14°±1.5°BTDC/2000rpm
Page 13

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-12
TORQUE VALUES
ENGINE
Item
Thread dia. (mm)
Torque (kg-m)
Remarks
Cylinder head bolt
Clutch drive plate nut
Clutch outer nut
Drive face nut
Oil check bolt
Engine mounting bolt
Engine hanger bracket bolt
Exhaust muffler joint lock nut
Exhaust muffler lock bolt
Spark plug
BF7x115
10
NH10
NH12
10
BF10x95
BF10x50
NC6mm
BF8x35
1.5_ 1.7
3.5_ 4.0
3.5_ 4.5
5.0_ 6.0
1.0_ 1.5
4.5_ 5.5
3.5_ 4.5
1.0_ 1.4
3.0_ 3.6
1.1_ 1.7
(cold)
(cold)
FRAME
Item
Thread dia. (mm)
Torque (kg-m)
Remarks
Handlebar lock nut
Steering stem lock nut
Steering top cone race
Front axle nut
Rear axle nut
Rear brake arm bolt
Front shock absorber:
upper mount bolt
lower mount bolt
hex bolt
Front damper nut
Front pivot arm bolt
Rear shock absorber:
upper mount bolt
lower mount bolt
lower joint nut
10
25.4
25.4
12
16
8
8
10
8
8
4.5_ 5.0
8.0_ 12.0
0.5_ 1.3
5.0_ 7.0
11.0_ 13.0
3.3
3.3
1.5_ 3.0
1.5_ 3.0
3.5_ 4.5
2.4_ 3.0
1.5_ 2.5
Flange bolt/U-nut
Flange U-nut
Flange U-nut
Flange nut
Flange bolt/U-nut
Cross head
Apply locking agent
Flange screw/U-nut
Flange nut
Torque specifications listed above are for important fasteners. Others should be tightened to
standard torque values below.
STANDARD TORQUE VALUES SH bolt: 8mm Flange 6mm bolt
Item
Torque (kg-m)
Item
Torque (kg-m)
5mm bolt, nut
6mm bolt, nut
8mm bolt, nut
10mm bolt, nut
12mm bolt, nut
0.45_ 0.6
0.8_ 1.2
1.8_ 2.5
3.0_ 4.0
5.0_ 6.0
5mm screw
6mm screw, SH bolt
6mm flange bolt, nut
8mm flange bolt, nut
10mm flange bolt, nut
0.35_ 0.5
0.7_ 1.1
1.0_ 1.4
2.4_ 3.0
3.5_ 4.5
Page 14

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-13
SPECIAL TOOLS
Tool Name
Tool No.
Remarks
Universal bearing puller
Crankshaft bearing removal
Lock nut wrench, 39mm
Drive pulley disassembly/assembly
Lock nut socket wrench
Top cone race holding
Lock nut wrench,
Stem lock nut tightening
Crankcase puller
Crankcase disassembly
Bearing remover set, 12mm
(Spindle assy, 15mm)
(Remover weight)
Drive shaft bearing removal/installation
Bearing remover set, 15mm
(Spindle assy, 15mm)
(Remover head, 15mm)
(Remover shaft, 15mm)
Drive shaft bearing removal/installation
Bearing outer driver, 28x30mm
Bearing installation
Bearing remover
Driven pulley outer bearing installation
Clutch spring compressor
Driven pulley disassembly/assembly
Crankcase assembly collar
Driven shaft, crankshaft & crankcase
assembly
Crankcase assembly tool
Crankshaft & crankcase assembly
Rear shock absorber remover
Front shock absorber disassembly/
assembly
Ball race remover
Steering stem bearing races
Rear shock absorber compressor
Rear shock absorber disassembly/assembly
Float level gauge
Carburetor fuel level check
Lock nut socket wrench, 32mm
One-way clutch lock nut removal/
installation
Universal holder
Flywheel holding
Flywheel puller
Flywheel removal
Pilot, 12mm
Drive shaft bearing installation
Bearing outer driver, 32x35mm
Drive shaft bearing installation
Final shaft bearing installation
Page 15

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-14
Tool Name
Tool No.
Remarks
Bearing outer driver, 37x40mm
Drive shaft bearing installation Final shaft
bearing installation Crankshaft bearing
installation
Outer driver, 24x26mm
Driven pulley bearing installation
Pilot, 10mm
Front wheel bearing installation
Bearing driver pilot, 17mm
Drive shaft bearing installation
Snap ring pliers (close)
Circlip removal/installation
Bearing outer driver, 42x47mm
Crankshaft bearing installation
Pilot, 20mm
Crankshaft bearing installation
Bearing outer driver handle A
Bearing installation
Drive in ball race
Bearing puller head, 10mm
Front wheel bearing removal
Universal bearing puller
Crankshaft bearing removal
Bearing puller
Front wheel bearing removal
Pressure tester set
Cylinder compression gauge
Page 16
1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-15
LUBRICATION POINTS
ENGINE
NO.
Lubrication Points
Lubricant
Remarks
1
Crankcase sliding & movable parts
JASO-FC or API-TC
2
Cylinder movable parts
3
Transmission gear (final gear)
SAE-90#
4
Kick starter spindle bushing
Grease
5
Drive pulley movable parts
Grease
6
Starter pinion movable parts
Grease
FRAME
Apply clean engine oil or grease to cables and movable parts not specified. This will avoid
abnormal noise and rise the durability of the motorcycle.
Front/Rear Brake Lever
Seat Lock
Rear Wheel
Bearing
Throttle Cable
Speedometer Cable
Main Stand Pivot
Grease
Engine Oil
Grease
Engine Oil
Speedometer Gear/
Brake Cam/Front
Shock Absorber
Lower Mount
Bushings/Pivot
Grease
Grease
Grease
Grease
Engine Oil
Rear Brake Cable
Brake Cam/
Anchor Pin
Page 17

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-16
BA10AB.AC. WIRING DIAGRAM
B
Black
Br
Brown
Y
Yellow
O
Orange
L
Blue
Sb
Light blue
G
Green
Lg
Light green
R
RedPPink
W
WhiteGrGray
Page 18

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-17
CABLE & HARNESS ROUTING
Front Brake Reservoir
Rear Brake Cable
Throttle Cable
Ignition Switch
Regulator/Rectifier
Front Brake Fluid
Tube
Ground
Speedometer Cable
Horn
Starter Relay
Page 19

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-18
Wire Harness
Starter Relay
Rear Brake Cable
Throttle Cable
Front Brake Fluid Tube
Speedometer Cable
Page 20

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-19
Ignition Coil
Fuel Unit
Fuel Filter
Left Crankcase Breather
Oil Tube
Spark Plug
Fuel Vapor Recovery Tube
Ignition Coil
Page 21

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-20
Ignition Coil
Vacuum Tee
Throttle Cable
Oil Meter
Spark Plug Cap
Oil Filter
Oil Pump
Control Cable
Auto Bystarter
Oil Tube
Fuel Unit
Fuel Tank Cap
Fuel Tube
Fuel Filter
Oil Tank Cap
Page 22
1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-21
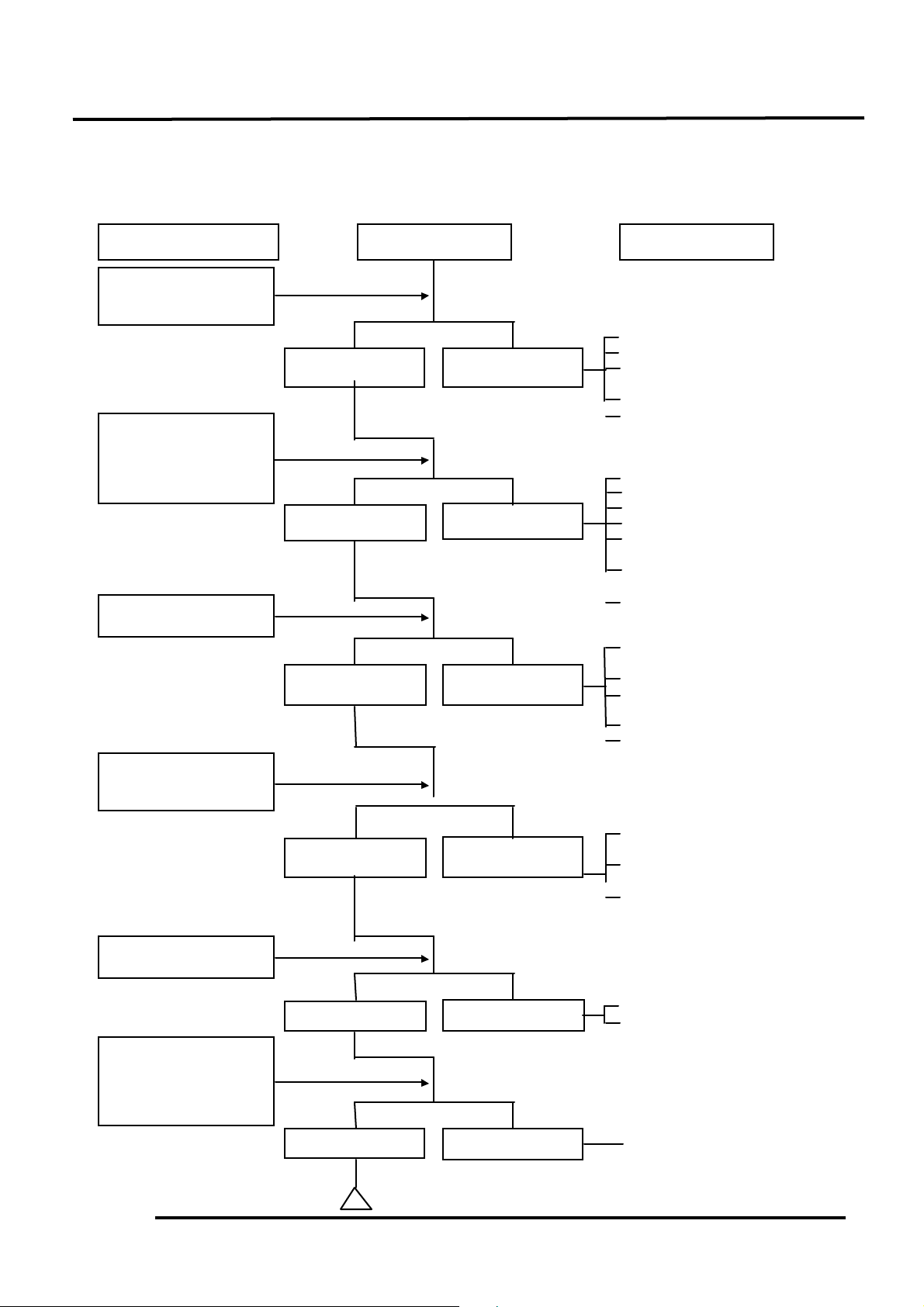
TROUBLESHOOTING
ENGINE WILL NOT START OR IS HARD TO START
Å Empty fuel tank
Ç Clogged float valve
É Clogged charcoal
canister
Ñ Clogged fuel filter
Ö Faulty auto fuel valve
Å Faulty spark plug
Ç Fouled spark plug
É Faulty CDI unit
Ñ Faulty A.C. generator
Ö Broken or shorted
ignit ion coil
Ü Broken or shorted
exciter coil
áFaulty ignition switch
Å Burned or worn
cylinder piston
Ç Faulty reed valve
É Blown cylinder head
gasket
Ñ Leaking crankcase
Ö Faulty crankcase oil
seal
Å Incorrectly adjusted idle
speed
Ç Air leaking through
intake pipe
É Incorrect ignition
timing
Å Flooded carburetor
Ç Throttle valve
excessively open
Å Faulty auto bystarter
Check if fuel reaches
carburetor by
loosening drain screw.
Remove spark plug
and install it into
spark plug cap to test
spark by connecting it
to engine ground.
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Fuel reaches
carburetor
Spark jumps
Dry spark plug
Not clogged
Normal
compression
Engine does not
fire
Fuel does not
reach carburetor
Weak or no spark
Wet spark plug
Clogged
Low or no
compression
Engine fires but
does not start
Test cylinder
compression.
Remove spark plug and
inspect again.
Wait for 30 minutes
and then remove the
carbu-retor auto choke
circuit hose and blow
the hose with mouth.
Start engine by following normal starting
procedure.
Page 23
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-22
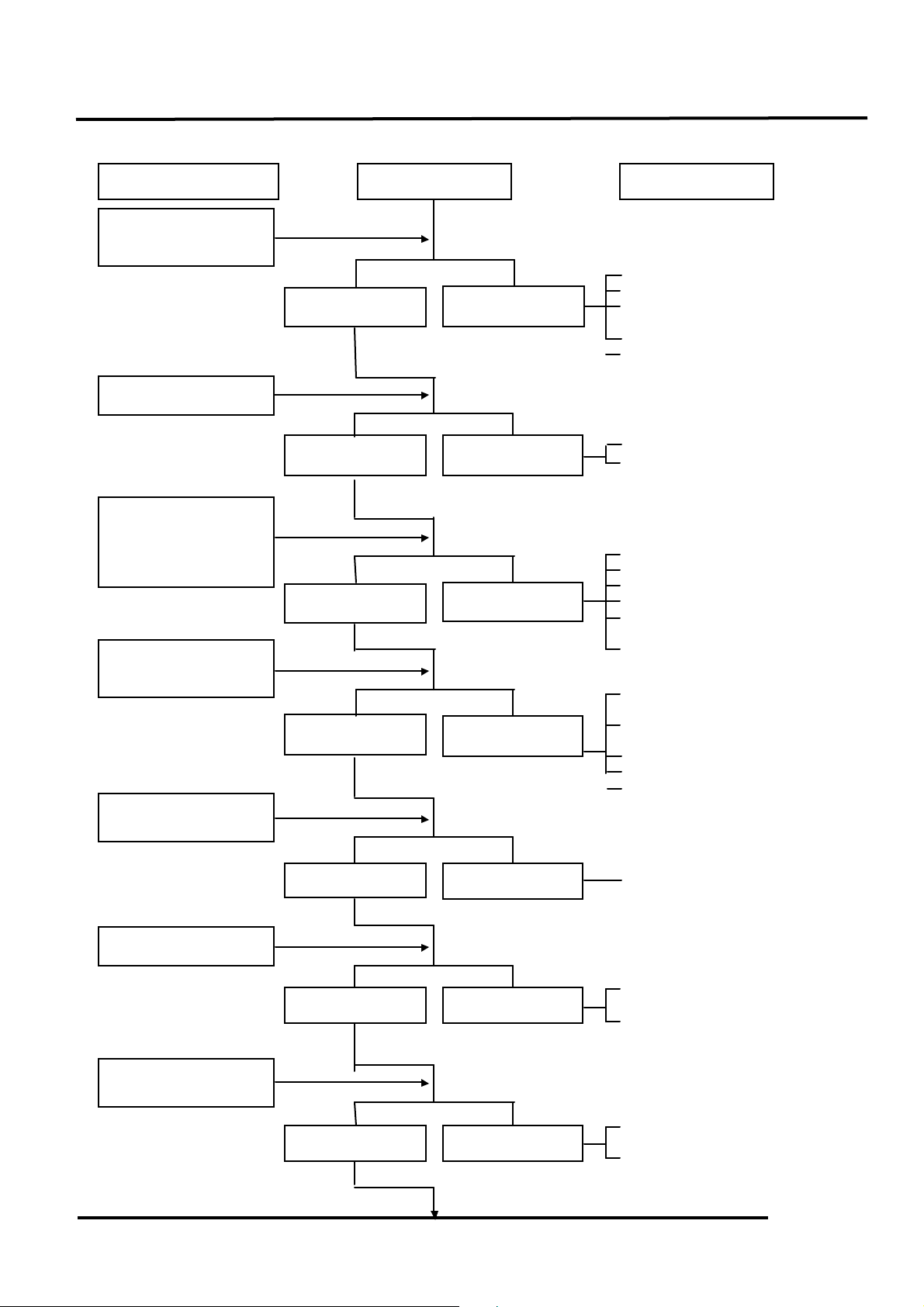
ENGINE STOPS IMMEDIATELY AFTER IT STARTS
Å Empty fuel tank
Ç Clogged float valve
É Clogged charcoal
canister
Ñ Clogged fuel filter
Ö Faulty auto fuel valve
Å Fouled spark plug
Ç Incorrect heat range
plug
Å Fouled spark plug
Ç Faulty CDI unit
É Faulty A.C. generator
Ñ Faulty ignition coil
Ö Broken or shorted high
tension wire
Ü Faulty ignition switch
Å Worn cylinder and
piston rings
Ç Blown cylinder head
gasket
É Flaws in cylinder head
Ñ Faulty reed valve
Ö Seized piston
Å Clogged carburetor jets
Å Faulty CDI unit or A.C.
generator
Ç A.C.G. flywheel not
aligned
Å Mixture too rich (turn
screw out)
Ç Mixture too lean (turn
screw in)
Check if fuel reaches
carburetor by
loosening drain screw.
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Fuel reaches
carburetor
Good spark
Correct timing
Correctly adjusted
Plug not fouled or
discolored
Normal
compression
Not Clogged
Fuel does not
reach carburetor
Weak or inter mittent spark
Incorrect timing
Incorrectly adjusted
Plug fouled or
discolored
Abnormal
compression
Clogged
Remove spark plug.
Test cylinder
compression (using a
compression gauge).
Check carburetor for
clogging.
Check ignition timing.
Check carburetor air
screw adjustment.
Remove spark plug
and install it into
spark plug cap to test
spark by connecting it
to engine ground.
Page 24
1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-23
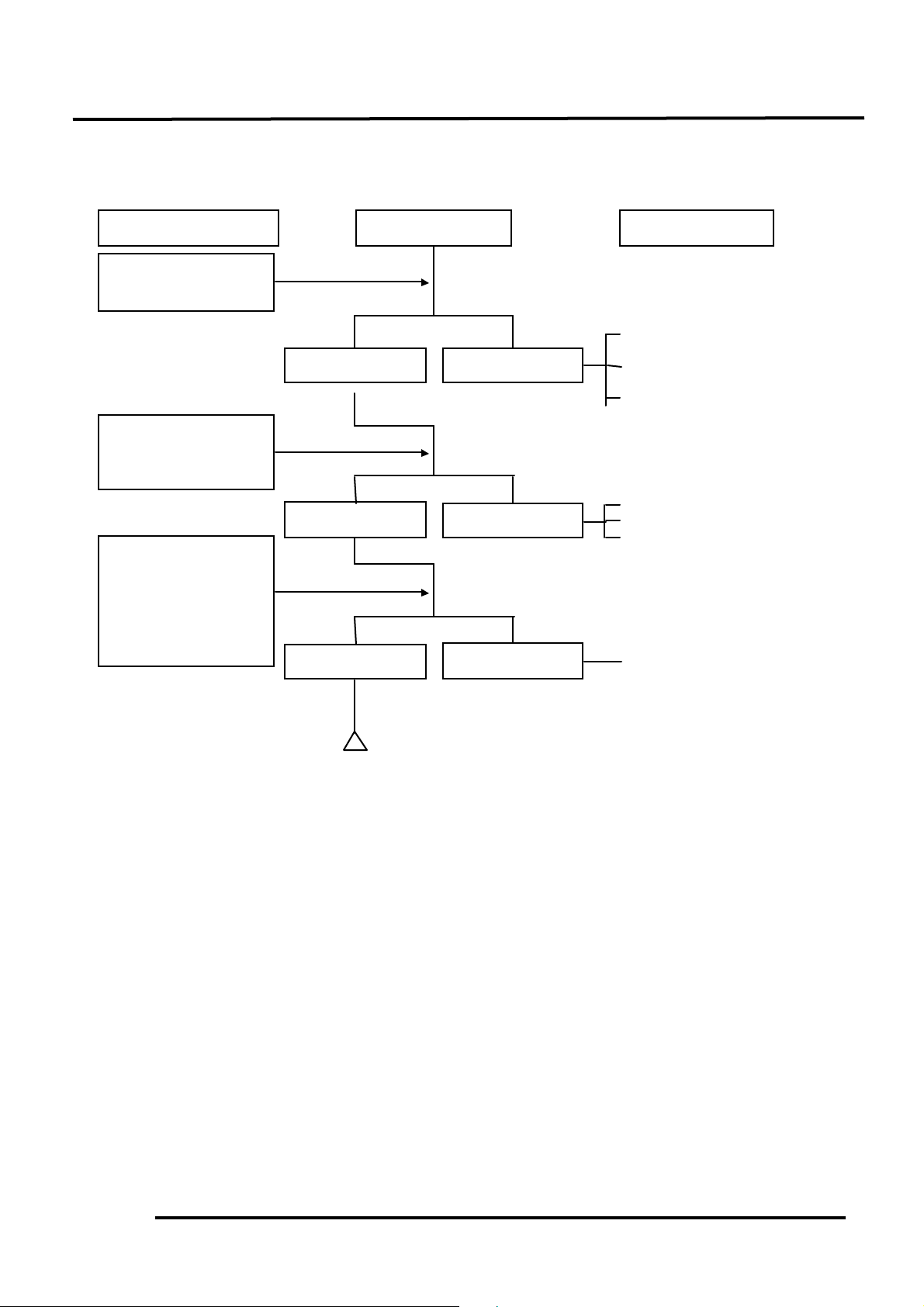
Å Carburetor not securely
tightened
Ç Faulty intake manifold
gasket
É Deformed or broken
carburetor O-ring
Å Broken cable
Ç Dirty auto bystarter
É Faulty auto bystarter
Å Faulty auto bystarter
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
No air leak
Not clogged
Clogged
Air leaks
Clogged
Not Clogged
Check carburetor
gasket for air leaks.
Connect auto bystarter
wire to battery. Wait
for 5 minutes, then
connect a hose to fuel
enriching circuit and
then blow the hose
with mouth.
Remove auto bystarter
connecting wire and
check if bypass fuel
line is clogged.
Page 25
2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-24
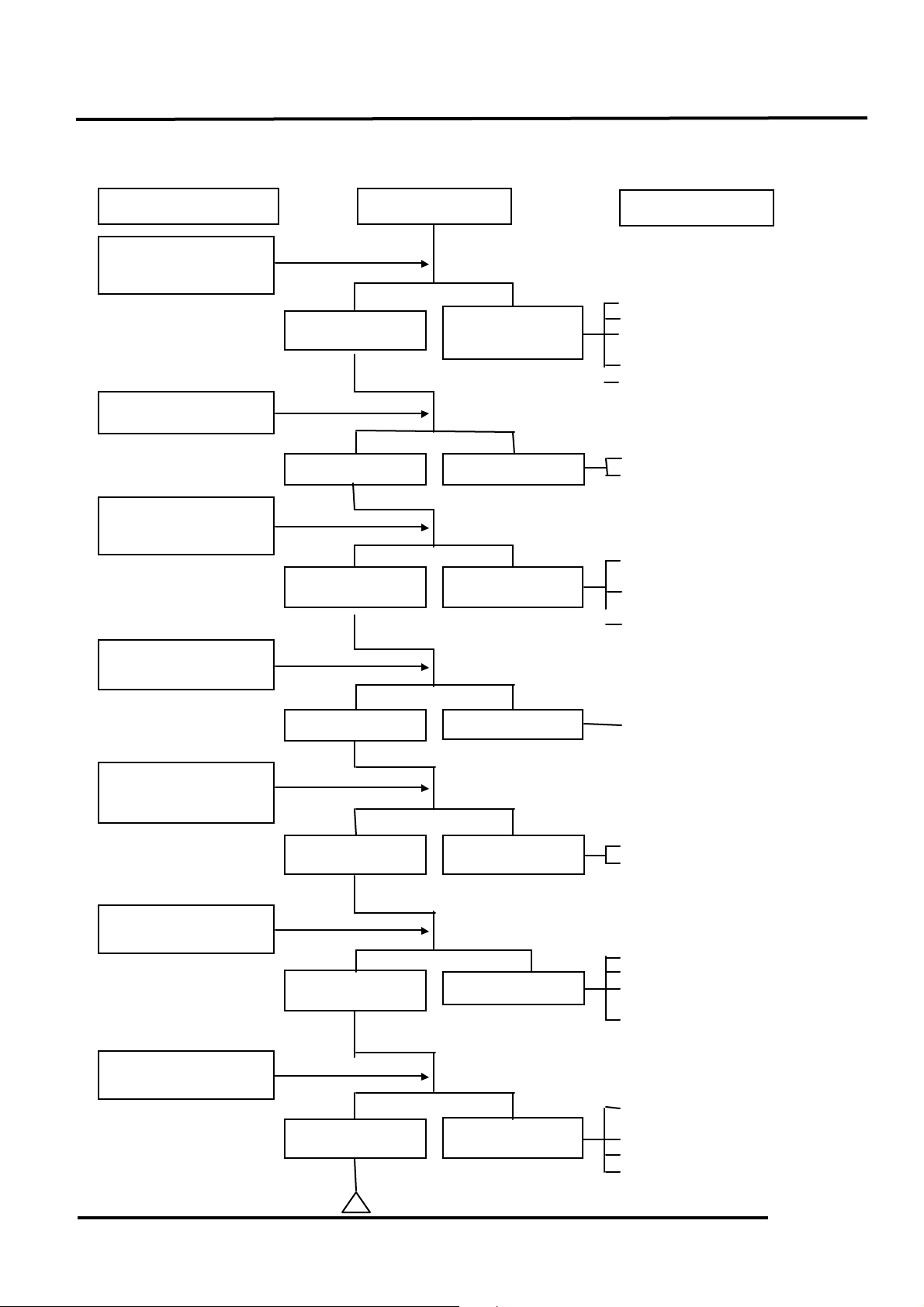
ENGINE LACKS POWER
Å Clogged air cleaner
Ç Clogged fuel filter
É Clogged exhaust
muffler
Ñ Faulty auto bystarter
Ö Faulty charcoal canister
Å Faulty CDI unit
Ç Faulty A.C. generator
Å Worn cylinder and
piston rings
Ç Blown cylinder head
gasket
É Faulty reed valve
Å Clogged carburetor jets
Å Fouled spark plug
Ç Incorrect heat range
plug
Å Mixture too lean
Ç Poor quality fuel
É Excessive carbon build-
up in combustion chamber
Ñ Ignition timing too
early
Å Excessive carbon build-
up in combustion chamber
Ç Poor quality fuel
É Clutch slipping
Ñ Mixture too lean
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Engine speed
increases
Engine overheats
Correct timing
Engine does not
knock
Plug not fouled or
discolored
Normal
compression
Not Clogged
Engine speed does
not increase
sufficiently
Engine does not
overheats
Incorrect timing
Engine knocks
Plug fouled or
discolored
Abnormal
compression
Clogged
Start engine and
accelerate lightly for
observation.
Check ignition timing
(using a timing light).
Rapidly accelerate or
run at high speed
Test cylinder
compression (using a
compression gauge)
Check carburetor for
clogging
Remove spark plug
and
inspect
Check if engine
overheats
Page 26

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-25
POOR PERFORMANCE (ESPECIALLY AT IDLE AND LOW SPEEDS)
Å Faulty CDI unit
Ç Faulty A.C. generator
Å Mixture too rich (turn
screw out)
Ç Mixture too lean (turn
screw in)
Å Carburetor not securely
tightened
Ç Faulty int ake manifold
gasket
É Deformed carburetor
O-ring
Å Faulty or fouled spark
plug
Ç Faulty CDI unit
É Faulty A.C. generator
Ñ Faulty ignition coil
Ö Broken or shorted high
tension wire
Ü Faulty ignition switch
Å Broken auto bystarter
wire
Ç Faulty auto bystarter
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Clogged
Not clogged
Remove spark plug
and install it into
spark plug cap to test
spark by connecting it
to engine ground.
Check ignition timing.
Connect auto bystarter
wire to battery. Wait
for 5 minutes, then
connect a hose to fuel
enriching circuit and
then blow the hose
with mouth.
Remove auto bystarter
connecting wire and
check if bypass fuel
line is clogged.
Check carburetor
gasket for air leaks.
Check carburetor air
screw adjustment.
Correct timing
Incorrect timing
Correctly adjusted
Incorrectly adjusted
No air leak
Air leaks
Good spark
Weak or inter mittent spark
Not clogged
Clogged
Page 27

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-26
POOR PERFORMANCE (AT HIGH SPEED)
Å Faulty CDI unit
Ç Loose A.C.G. stator
É Faulty A.C. generator
Å Empty fuel tank
Ç Clogged fuel tube or
filter
É Clogged charcoal
canister
Å Clean and unclog
Å Broken auto bystarter
wire
Ç Faulty auto bystarter
Å Faulty auto bystarter
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Probable Cause
Clogged
Not clogged
Check ignition timing.
Connect auto bystarter
wire to battery. Wait
for 5 minutes, then
connect a hose to fuel
enriching circuit and
then blow the hose
with mouth.
Remove auto bystarter
connecting wire and
check if bypass fuel
line is clogged.
Check carburetor jets
for clogging.
Check auto fuel valve
for fuel supply.
Correct timing
Incorrect timing
Fuel flows freely
Fuel flow
Not clogged
Clogged
Not clogged
Clogged
Page 28

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-27
CLUTCH, DRIVE AND DRIVEN PULLEYS
Å Worn or slipping drive belt
Ç Broken ramp plate
É Broken driven face spring
Ñ Separated clutch lining
Ö Damaged driven pulley shaft
splines
Ü Damaged final gear
á Seized final gear
Å Broken shoe spring
Ç Clutch outer and clutch weight
stuck
ÉSeized pivot
Å Worn or slipping drive belt
Ç Worn weight rollers
É Seized drive pulley bearings
Ñ Weak driven face spring
Ö Worn or seized driven pulley
bearings
Å Worn or slipping drive belt
Ç Worn weight rollers
É Worn or seized driven pulley
bearings
Å Oil or grease fouled drive belt
Ç Worn drive belt
É Weak driven face spring
Ñ Worn or seized driven pulley
bearings
STEERING HANDLEBAR DOES NOT TRACK STRAIGHT
(Front and rear tire pressures are normal)
Å Steering stem nut too tight
Ç Broken steering steel balls
Å Excessive wheel bearing play
Ç Bent rim
É Loose axle nut
Å Misaligned front and rear wheels
Ç Bent front fork
Engine starts but
motor-cycle does not
move
Engine lacks power at
start of a grade (poor
slope performance)
Steering is heavy
Front or rear wheel is
wobbling
Symptom
Symptom
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Engine lacks power at
high speed
There is abnormal
noise
or smell while running
Motorcycle creeps or
engine starts but soon
stops or seems to rush
out (Rear wheel
rotates when engine
idles)
Steering handlebar pulls
to one side
Page 29

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-28
POOR SUSPENSION PERFORMANCE
(Front and rear tire pressures are normal)
Å Weak shock spring
Ç Excessive load
É Shock damper oil leaking
Å Bent fork tube or shock rod
Ç Fork slider and tube binding
Å Fork tube and spring binding
Ç Fork slider and tube binding
POOR BRAKE PERFORMANCE
(Adjust brake according to standards)
Å Worn brake linings
Ç Worn brake cam contacting area
on
brake shoes
É Worn brake cam
Ñ Worn brake drum
Å Worn brake linings
Ç Foreign matter on brake linings
É Rough brake drum contacting area
Å Sluggish or elongated brake cables
Ç Brake shoes improperly contact
brake drum
É Water and mud in brake system
Ñ Oil or grease on brake linings
Å Faulty brake master cylinder
Ç Faulty brake caliper
É Oil or grease on brake disk
Ñ Deformed brake disk
Ö Leaking brake fluid tube
Suspension is too soft
Brake squeaks
Symptom
Symptom
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Suspension is too hard
Suspension is noisy
Brake performance is
poor
Index mark on brake
panel aligns with wear
indicator arrow
Expanding
Brake
Hydraulic
Brake
Page 30

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-29
Faulty
OIL METER
1. Motor oil indicator light does not come on when there is no motor oil (Ignition switch ON)
Å Burned out fuse
Ç Weak or dead battery
É Faulty ignition switch
Ñ Loose or disconnected
connector
Ö Broken wire harness
ÅBurned out bulb
Å Loose wire connector
Ç Broken wire harness
É Incorrectly connected
wire
Å Faulty float
Ç Broken or shorted wire
in
meter
2. Motor oil is sufficient but the indicator light remains on (Ignition switch ON)
Å Loose or disconnected
connector
Ç Broken wire harness
É Incorrectly connected
wire
Å Faulty float
Ç Broken or shorted wire
in meter
Å Damaged oil tank
Ç Foreign matters in oil
tank
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Inspection/Adjustment
Probable Cause
Symptom
Probable Cause
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
Bulb lights
Bulb does not light
Good
Faulty
Remove oil meter and
check operation of
indicator light by
moving float
Check connectors for
proper connection.
Good
Good
Faulty
Remove oil meter and
check operation of
indicator light by
moving float
Check connectors for
proper operation.
Connect indicator
light bulb to battery
for bulb inspection.
Check battery circuit
by operating turn
signals.
Good
Faulty
Float up = Light off
Float down = Light on
Float up = Light off
Float down = Light on
Page 31

2. GENERAL INFORMATION
2-30
FUEL GAUGE
1. Pointer does not register correctly (Ignition switch ON)
Å Burned out fuse
Ç Weak or dead battery
É Faulty ignition switch
Ñ Loose or disconnected
connector
Ö Broken wire harness
Å Faulty float
Å Broken or shorted fuel
unit wire
Å Loose or disconnected
connector
Ç Incorrectly connected
connector
Å Broken or shorted wire
in fuel gauge
2. Pointer fluctuates or swings (Ignition switch ON)
Å Burned out fuse
Ç Weak or dead battery
É Faulty ignition switch
Ñ Loose or disconnected
connector
Ö Broken wire harness
Å Poor contact in fuel
unit
Å Insufficient damping oil
in fuel gauge
Å Loose or disconnected
connector
Å Broken or shorted wire
in fuel gauge
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Symptom
Signals operate
properly
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
Pointer does not
move
Pointer does not
move
Good
Good
Pointer moves
Pointer moves
Pointer moves
Pointer does not
move in accordance with float
Faulty
Faulty
Pointer does not
move
Pointer moves in
accordance with
float
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Remove fuel unit and
check operation of
pointer by moving
float up and down.
Check battery circuit
by operating turn
signals.
Check operation of
pointer by opening
and shorting fuel unit
terminal on wire
harness side.
Check connectors for
proper connection.
Remove fuel unit and
check operation of
pointer by moving
float up and down.
Check battery circuit
by operating turn
signals and horn.
Move float up and
down rapidly (1 round
/sec.) to check the
operation of pointer.
Check connectors for
proper connection.
Page 32

1. SPECIFICATIONS
2-31
STARTER MOTOR
1. Starter motor won‘t turn
Å Burned out fuse
Ç Weak or dead battery
É Faulty stop switch
Ñ Loose or disconnected
connector
Ö Broken or shorted
ignition switch wire
Å Faulty or weak battery
Å Poor starter button
connection
Ç Faulty starter relay
É Loose or disconnected
connector
Å Faulty starter motor
Å Faulty wire harness
2. Starter motor turns slowly or idles
Å Weak or dead battery
Å Loose or disconnected
connector
Ç Faulty starter relay
Å Seized cylinder
Å Broken or shorted
starter motor cable
Ç Faulty starter pinion
3. Starter motor does not stop turning
Å Faulty starter pinion
Å Starter relay shorted or
stuck
closed
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Inspection/Adjustment
Symptom
Symptom
Symptom
Signals operate
properly
Signals operate
properly
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
Signals dim, remain
on or don‘t
Stoplight does not
come on
Starter motor
Turns easily
Not stopped
Stoplight comes
St arter does not
Hard to turn
Stopped
Relay operates
properly
Starter motor
turns slowly
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Probable Cause
Relay does not
operate
Starter motor
turns normally
Check operation of
stop switch by
applying brake.
Check battery
circuit by operating
turn signals.
Check battery
circuit by operating
turn signals.
Turn ignition switch
OFF.
Check operation of
starter relay by
depressing starter
button.
Connect starter
motor directly to
battery.
Connect starter
motor directly to
battery.
Rotate crankshaft.
 Loading...
Loading...