Knight Equipment A PLUS Installation Manual
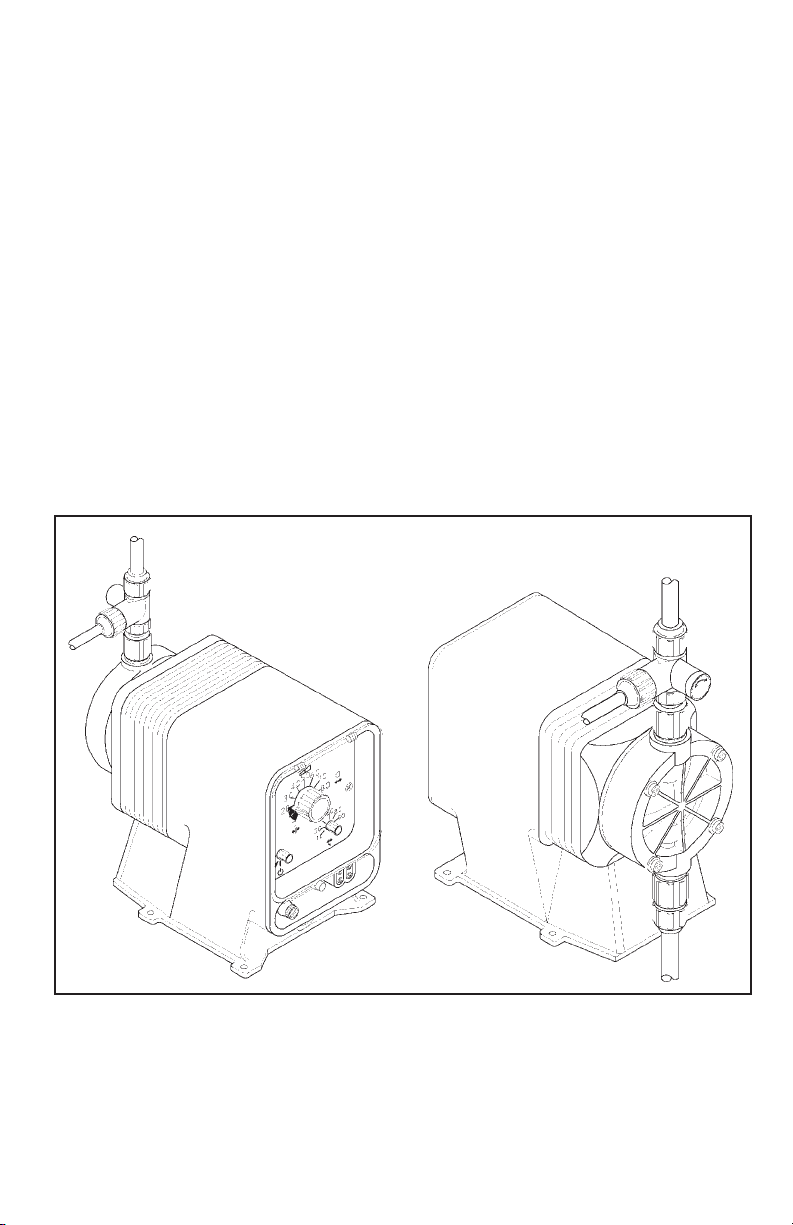
Electronic Metering Pumps
Series C, C PLUS, A PLUS, E, E-DC, E PLUS and HV
Installation
Operation
Maintenance
Instruction
READ ALL WARNINGS CAREFULLY
BEFORE INSTALLING

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
1.0 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ..... ............................................................................. 3
1.1 General Safety Considerations .................................................................. 3
1.2 Safety Operating Procedures ..................................................................... 3
2.0 UNPACKING THE PUMP ................................................................................... 6
3.0 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................ 6
3.1 Principle of Operation ................................................................................ 6
3.2 Materials of Construction.......................................................................... 6
4.0. INSTALLATION ................................................................................................. 7
4.1 Mounting ................................................................................................... 7
4.2 Piping ....................................................................................................... 9
4.3 Wiring ...................................................................................................... 10
4.4 Well Pump System Installation ................................................................. 10
5.0 START UP AND OPERATION ........................................................................... 11
5.1 Power ...................................................................................................... 11
5.2 Priming ...................................................................................................... 11
5.3 Capacity Control .......................................................................................13
5.3.1 Stroke Frequency Adjustment ...................................................... 13
5.3.2 Stroke Length Adjustment ............................................................ 13
5.3.3 Controlling Procedure ................................................................... 13
5.4 Control Panel Symbols ............................................................................. 14
5.5 Operation By External Input Signals......................................................... 15
5.5.1 Stop Functions .............................................................................15
5.5.2 External Pacing Function .............................................................. 15
5.5.3 4-20mA DC Input Function ........................................................... 16
6.0. MAINTENANCE ............................................................................................... 17
6.1 Routine Maintenance ...............................................................................17
6.2 Disassembly and Assembly Diaphragm Removal .................................... 18
6.3 Diaphragm Replacement ........................................................................... 18
6.4 Valve Replacement .................................................................................... 19
7.0 TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................................................................... 20
8.0. POLICIES AND PROCEDURES ......................................................................... 23
8.1 Manufacturer's Product Warranty ............................................................ 23
8.2 European Technical File Location .............................................................23
8.3 Returns ..................................................................................................... 24
8.4 Credits ...................................................................................................... 24
2
1.0 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
When using chemical feed pumps, basic safety precautions should always be followed to reduce risk of
fire, electric shock, and personal injury. Failure to
follow these instructions could result in death or
serious injury.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS
1.1 GENERAL SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
• Always wear protective clothing including gloves and safety goggles when
working on or near chemical metering pumps.
• Inspect tubing regularly when replenishing chemical solution for cracking or
deterioration and replace as necessary. (Always wear protective clothing and
safety glasses when inspecting tubing.)
• When pump is exposed to direct sunlight use U.V. resistant tubing.
• Follow directions and warnings provided with the chemicals from the chemical
manufacturer. User is responsible for determining chemical compatibility with
chemical feed pump.
• Secure chemicals and metering pumps, making them inaccessible to children and
pets.
• Make sure the voltage on the chemical metering pump matches the voltage at the
installation site.
• Do not cut plug or the ground lug off of the electrical cord – consult a licensed
electrician for proper installation.
• Pump is NOT to be used to handle flammable liquids.
1.2 SAFETY OPERATING PROCEDURES
Each Electronic Metering Pump has been tested to meet prescribed specifications and
safety standards.
Proper care in handling, installation and operation will help in ensuring a trouble free
installation.
3

Please read all these cautionary notes prior to installation and start-up of your
metering pump.
Important: P ump must be installed and used with supplied back pressure/injection
valve. Failure to do so could result in excessive pump output.
• Handle the pump with care. Dropping or heavy impact causes not only external
damage to the pump, but also to electrical parts inside.
• Install the pump in a place where the ambient temperature does not exceed 104°F
(40°C). The pump is water resistant and dust proof by construction and can be
use outdoors, however do not operate the pump submerged. To avoid high
internal pump temperatures, do not operate in direct sunlight.
Solenoid housing, head and pump housing may be hot to touch
160oF (70oC).
• Install the pump in a place convenient for its future maintenance and inspection,
and then secure it to prevent vibration.
• Protective caps must be removed prior to installing tubing onto valve assemblies.
Use tubing of specified size. Connect the tubing to the suction side securely to
prevent the entrance of outside air. Make sure that there is no liquid leakage on
the discharge side.
• Be careful to check that the voltage of the installation matches voltage indicated
on the pump data label. Most pump models are equipped with a three-prong plug.
Always be sure the pump is grounded. To disconnect, do not pull wire but grip
the plug with fingers and pull out. Do not use the receptacle in common with heavy
electrical equipment, which generates surge voltage. It can cause failure of the
electronic circuit inside the pump.
• Tampering with electrical devices can be potentially hazardous. Always place
chemicals and pump installation well out of the reach of children.
• Never repair or move the metering pump while operating. Always disconnect
electrical power. For safety, always wear protective clothing (protective gloves
and safety glasses) when working on or near chemical metering pumps.
• An air bleed valve is available for most models with tubing connections. Air
purges should be performed when the pump-chamber contains no fluid at the time
of start-up. As a safety measure, connect the return tubing to the air bleed valve
and bypass fluid back to storage tank or a suitable drain.
• For accurate volume output, the pump must be calibrated under typical operating
conditions.
4

• Chemicals used may be dangerous and should be used carefully and according
to warnings on the label. Follow the directions given with each type of chemical.
Do not assume chemicals are the same because they look alike. Always store
chemicals in a safe location away from children and others. We cannot be
responsible for the misuse of chemicals being fed by the pump. Always have the
material safety data sheet (MSDS) available for any fluid being pumped.
• All pumps are pretested with water before shipment. Remove head and dry
thoroughly if you are pumping a material that will react with water, (i.e. sulfuric
acid, polymers). Valve seats, ball checks, gaskets, and diaphragm should also be
dried. Before placing pump into service, extreme care should be taken to follow
this procedure.
• Valve cartridges are stamped to indicate fluid flow direction. Always install so
that markings read from top to bottom, with the arrow pointing in the direction of
flow.
• When metering hazardous material DO NOT use plastic tubing, strictly use proper
rigid pipe. Consult supplier for special adapters or valve assemblies.
• Pump is NOT to be used to handle or meter flammable liquids or materials.
• Standard white discharge tubing is not recommended for installations exposed
to direct sunlight. Consult supplier for special black tubing.
• Factory will not be held responsible for improper installation of pump, or
plumbing. All cautions are to be read thoroughly prior to hookup and plumbing.
For all installations a professional plumber should be consulted. Always adhere
to local plumbing codes and requirements.
• When using pump with pressurized systems, make sure the pressure of the system
does not exceed the maximum pressure rating on the pump data label. Be sure to
depressurize system prior to hook up or disconnecting a metering pump.
• Electronic power modules are equipped with automatic reset thermal overload
devices and may reset unexpectedly.
5
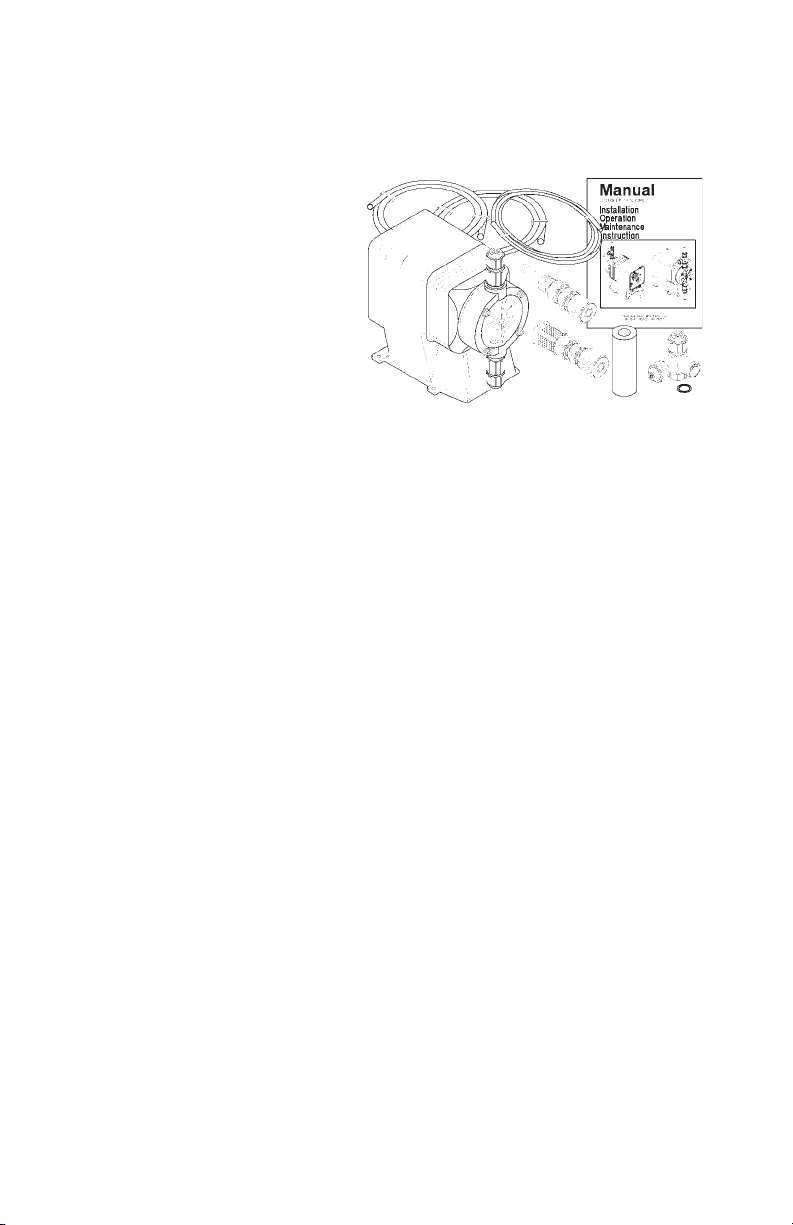
2.0 UNPACKING THE PUMP
Check all equipment for completeness against the order and for any evidence of shipping
damage. Shortages or damages should be reported immediately to the carrier and to the
seller of the equipment.
The carton should Contain:
-Metering Pump
-Clear Flexible Suction Tubing*
-Stiff White Discharge Tubing*
-Foot valve/Strainer Assembly
-Backpressure Injection
Valve Assembly
-Manual
-Bleed Valve Assembly*
-Strainer Weight*
*Items may or may not be included depending on model.
Make sure that all items have been removed from the shipping carton before it is discarded.
FIGURE 1
3.0 INTRODUCTION
These installation, operation and maintenance instructions cover your electronic metering
pump. Refer to the pump data label to determine the actual model.
3.1 PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
Diaphragm metering pumps are used to dispense chemicals or fluids. This is
achieved by an electromagnetic drive mechanism (solenoid), which is connected to
a diaphragm. When the solenoid is pulsed by the control circuit it displaces the
diaphragm, which, through the use of check valves, moves the fluid out the
discharge under pressure. When the solenoid is de-energized it returns the
diaphragm and pulls more fluid into the pump head and the cycle repeats.
The pump stroke rate is controlled by an internal circuit and is changed by turning
the rate knob. The mechanical stroke length is controlled by the stroke length
knob. Some models do not allow stroke rate control and do not have the stroke
rate knob.
3.2 MATERIALS OF CONSTRUCTION
The wetted materials (those parts that contact the solution being pumped)
available for construction are FPP (glass filled polypropylene), PVC, SAN,
Hypalon, Viton, PTFE, 316 Stainless Steel, PVDF, Ceramic and Alloy C. These
materials are very resistant to most chemicals. However, there are some chemicals,
such as strong acids or organic solvents, which cause deterioration of some
elastomer and plastic parts, such as the diaphragm, valve seats, or head.
6

3.2 MATERIALS OF CONSTRUCTION cont'd.
Consult a Chemical Resistance Guide or Supplier for information on chemical
compatibility.
Various manufacturers of plastics, elastomers and pumping equipment publish
guidelines that aid in the selection of wetted materials for pumping commercially
available chemicals and chemical compounds. Two factors must always be
considered when using an elastomer or plastic part to pump chemicals. They are:
• The temperature of service: Higher temperatures increase the effect of chemi-
cals on wetted materials. The increase varies with the material and the chemical
being used. A material quite stable at room temperature might be affected at
higher temperatures.
• Material choice: Materials with similar properties may differ greatly from one
another in performance when exposed to certain chemicals.
4.0 INSTALLATION
The metering pump should be located in an area that allows convenient connections
to both the chemical storage tank and the point of injection. The pump is water
resistant and dust proof by construction and can be used outdoors, however, do not
operate submerged. Avoid continuous temperatures in excess of 104°F (40°C). To
do otherwise could result in damage to the pump.
4.1 MOUNTING
Typical mounting arrangements are shown in Figures 3, 4, and 5.
Important: Injection point must be higher than the top of the solution supply
tank to prohibit gravity feeding, unless suitable backpressure is
always present at the injection point. Installation of an antisiphon
valve will prohibit gravity feeding.
• ALL HIGH VISCOSITY PUMPS (SERIES HV) REQUIRE FLOODED
SUCTION.
• For wall or shelf mounting refer to Figure 3. Connect suction tubing to suction
valve of chemical pump. Suction valve is the lower valve. Tubing should be
long enough so that the foot valve/strainer assembly hangs about 1-2 inches
(2-5 cm) above the bottom of chemical tank. To keep chemical from being
contaminated, the tank should have a cover.
7
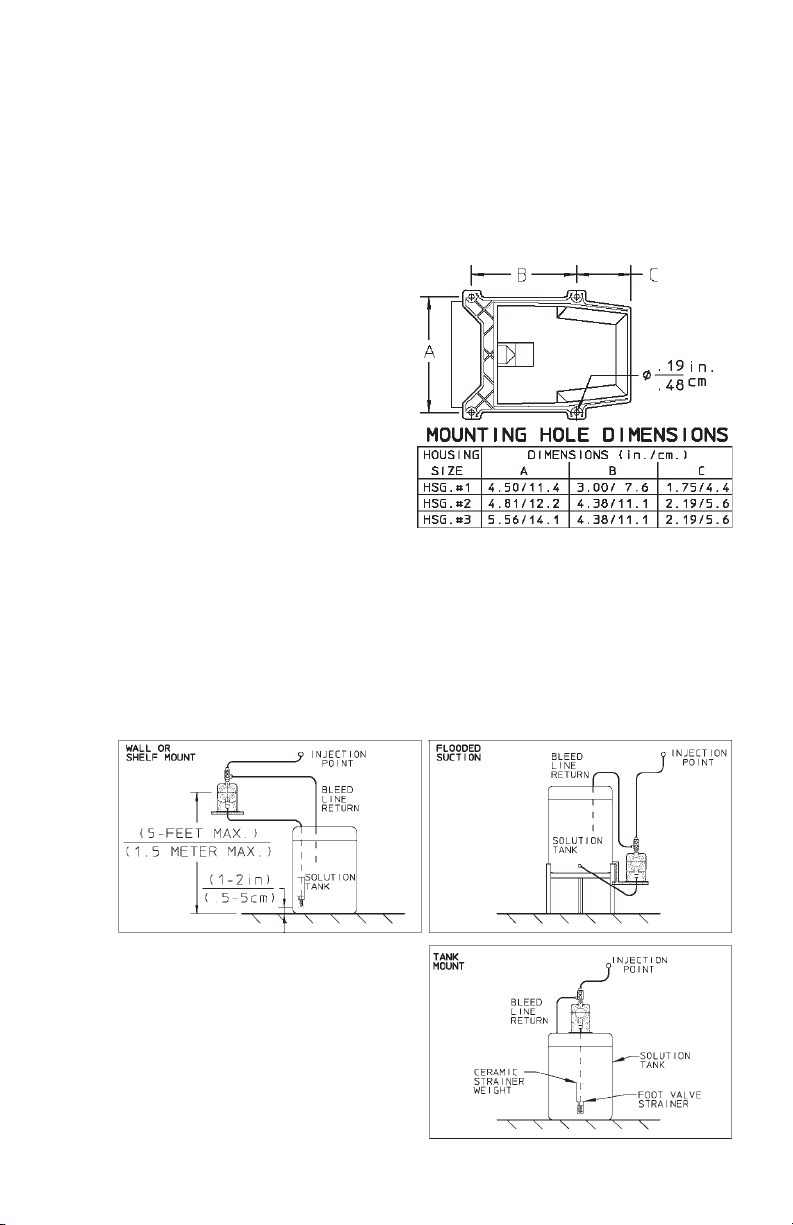
• Flooded suction mounting (installing the pump at the base of the chemical
storage tank, Figure 4) is the most trouble free type of installation and is
recommended for very low output requirements. Since the suction tubing is
filled with chemical, priming is accomplished quickly and the chance of losing
prime is reduced.
To mount pump, drill four holes of .25” (6 mm) diameter in the shelf as shown in
the dimension drawing (Figure 2). Attach pump securely using four #10 (M5) bolts
and nuts.
• The pump can be mounted on
top of a solution tank as shown
in Figure 5. Install chemical pump
on the cover. Insert suction tubing through the center hole and
cut tubing so foot valve/strainer
hangs about 1 or 2 inches (2-5
cm) above the bottom of the tank.
Mount the chemical pump rigidly by drilling four .25” (6 mm)
holes and using four #10 (M5)
screws and nuts.
FIGURE 2
• USE AN ANTI-SIPHON VALVE IN THE DISCHARGE LINE whenever the
fluid pressure in the discharge line is below atmospheric pressure. This can
occur if the injection point is on the suction side of a water pump or against
a "negative" head such as when feeding down into a well.
FIG. 4FIG. 3
FIG. 5
8
 Loading...
Loading...