Page 1
iRobot® Create
OPEN INTERFACE
www.irobot.com
Page 2

Table of Contents
iRobot Create® Open Interface Overview .................................................3
Physical Connections ..............................................................................4
Mini-DIN Connector ...............................................................................4
Cargo Bay Connector ............................................................................4
Serial Port Settings ................................................................................5
iRobot Create Open Interface Modes .......................................................6
Open Interface Command Reference........................................................7
Getting Started Commands ...................................................................7
Mode Commands .................................................................................7
Demo Commands .................................................................................8
Actuator Commands .............................................................................9
Input Commands ..................................................................................13
Script Commands .................................................................................15
Wait Commands ...................................................................................15
iRobot Create Open Interface Sensor Packets .........................................17
iRobot Create Open Interface Commands Quick Reference .......................22
iRobot Create Open Interface Sensor Packets Quick Reference ................24
2iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 3
iRobot Create
®
Open Interface
Overview
The Create Open Inter face (OI) consists of an electronic
interface and a software interface for controlling Create’s
behavior and reading its sensors. The electronic inter face
includes a 7 pin Mini-DIN connector and a DB-25 connector
in the Cargo Bay for connecting hardware and electronics
for sensors and actuators such as a robotic arm or light
sensor to Create. The software interface lets you manipulate
Create’s behavior and read its sensors through a series of
commands including mode commands, actuator commands,
song commands, demo commands, and sensor commands
that you send to Create’s serial por t by way of a PC or
microcontroller that is connected to the Mini-DIN connector
or Cargo Bay Connector.
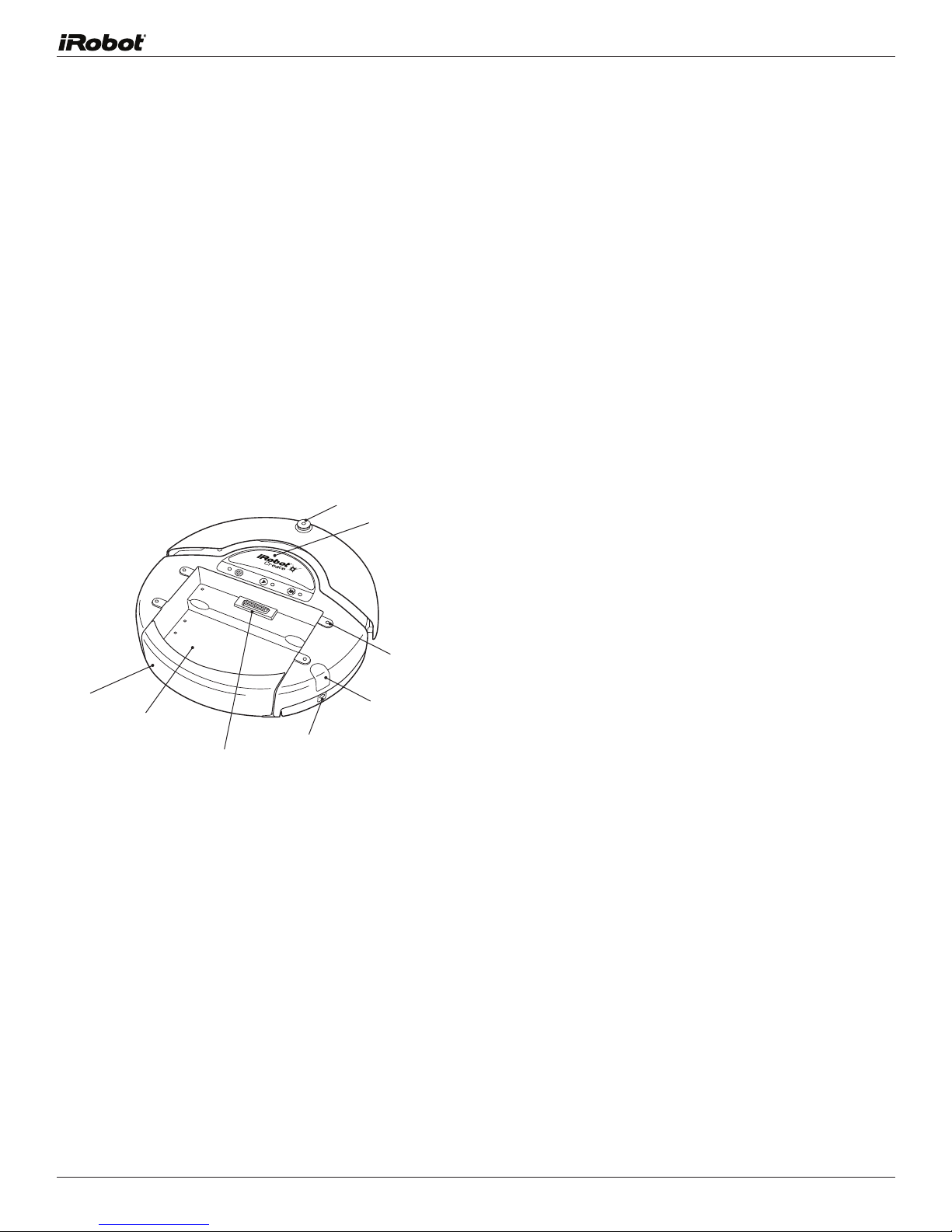
Anatomy
Tailgate
Cargo Bay
DB-25
Omnidirectional
IR Receiver
Handle
6-32 Mounting
Cavities
Mini-Din
Charging Socket
3iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 4
7
4
2
5
6
3
1
123456789101112
141516171717202122232425
13
Physical Connections
To use the OI, a processor capable of generating serial
commands such as a PC or a microcontroller must be
connected to the external Mini-DIN connector or the
Cargo Bay Connector on Create. These connectors provide
two-way, serial communication at TTL (0 – 5V) levels. The
connectors also provide an unregulated direct connection
to iRobot Create’s batter y, which you can use to power
the OI applications. The Cargo Bay Connector also provides
a regulated 5V power supply and several input and output
pins (see details below). The Mini-DIN connector is located
in the rear right side of Create, beneath a snap-fit plastic
guard, while the Cargo Bay Connector is located in the front
middle of the cargo bay.
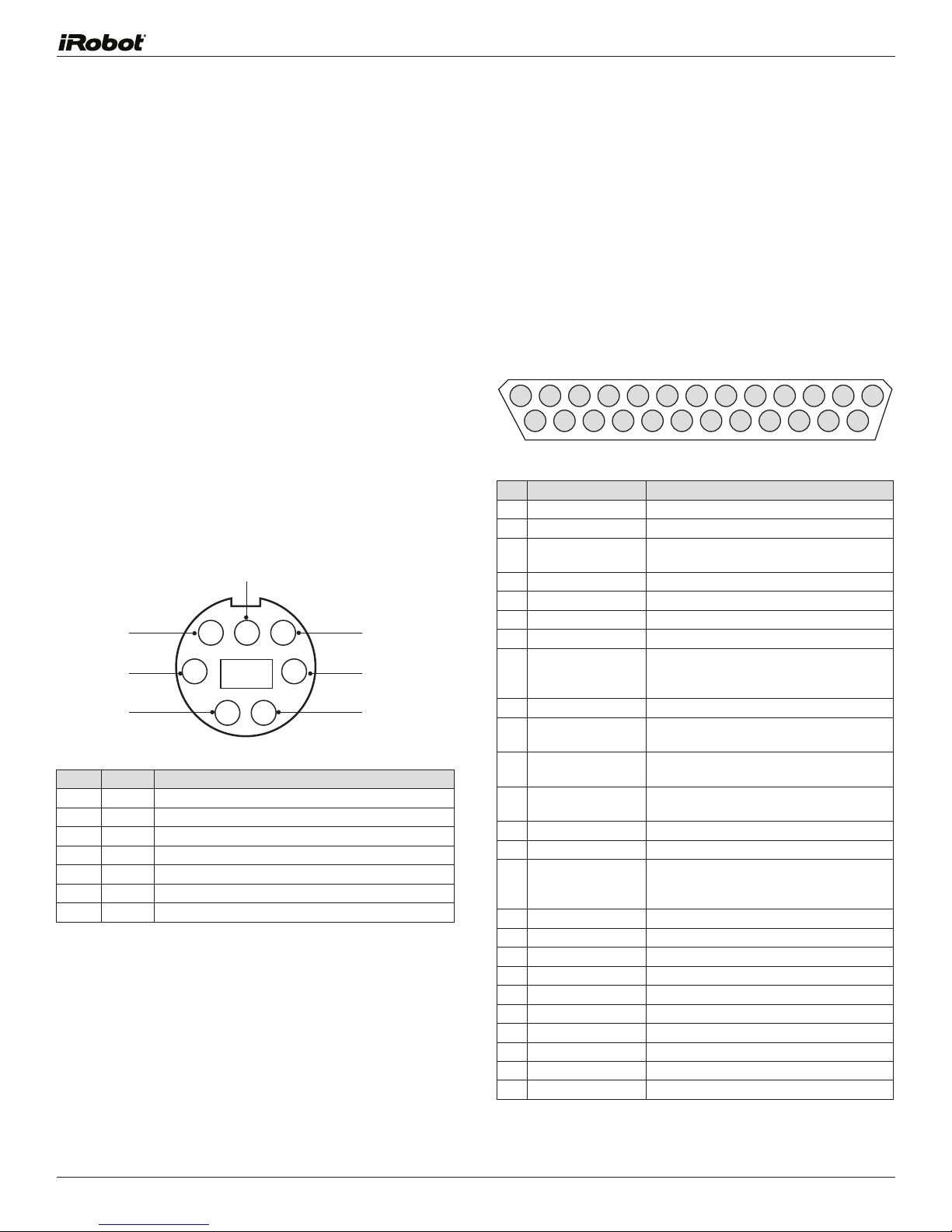
Mini-DIN Connector
This diagram shows the pinout of the top view of the female
connector in Create. Note that pins 5,6 and 7 are towards
the outside circumference of Create.
Pin Name Description
1 Vpwr Create battery + (unregulated)
2 Vpwr Create battery + (unregulated)
3 RXD 0 – 5V Serial input to Create
4 TXD 0 – 5V Serial output from Create
5 BRC Baud Rate Change
6 GND Create battery ground
7 GND Create battery ground
Since the RXD and TXD pins use 0 – 5V logic voltage and the
PC serial por ts use dif ferent voltages (rs232 levels), it is
necessary to shift voltage levels. To do this, use an iRobot
Create serial cable rather than a normal serial cable, as
the iRobot Create serial cable contains all of the necessary
hardware to shift the voltage levels, whereas the normal
serial cable does not.
Cargo Bay Connector
The Cargo Bay Connector, located in the front middle of
the cargo bay, contains 25 pins that you can use to attach
electronics for peripheral devices such as additional
sensors. The Cargo Bay Connector provides four digital
inputs, an analog input, three digital output s, three
high-current low side driver outputs (useful for driving
motors), a charging indicator, a power toggle input, serial Tx and
Rx, a 5V reference, batter y ground and batter y voltage.
Pin Name Description
1
RXD 0 – 5V Serial input to Create
2
TXD 0 – 5V Serial output from Create
3 Power control toggle Turns Create on or off on a low-to-high
transition
4 Analog input
5 Digital input 1 0 - 5V digital input to Create
6 Digital input 3 0 - 5V digital input to Create
7 Digital output 1 0 - 5V, 20 mA digital output from Create
8
Switched 5V Provides a regulated 5V 100 mA supply
9 Vpwr Create battery voltage (unregulated), 0.5A
10 Switched Vpwr Provides battery power @ 1.5 A when
11 Switched Vpwr Provides battery power @ 1.5 A when
12 Switched Vpwr Provides battery power @ 1.5 A when
13 Robot charging When Create is charging, this pin is high (5V)
14 GND Create batter y ground
15 Device Detect/Baud
Rate Change Pin
16 GND
17 Digital input 0 0 - 5V digital input to Create
18 Digital input 2 0 - 5V digital input to Create
19 Digital output 0
20 Digital output 2
21 GND Create batter y ground
22 Low side driver 0
23 Low side driver 1
24 Low side driver 2
25 GND
0 - 5V analog input to Create
and analog reference voltage when Create
is switched on
Create is powered on.
Create is powered on.
Create is powered on.
0-5V digital input to Create which can also
be used to change the baud rate to 19200
(see below)
Create battery ground
0 - 5V, 20 mA digital output from Create
0 - 5V, 20 mA digital output from Create
0.5A low side driver from Create
0.5A low side driver from Create
1.5A low side driver from Create
Create battery ground
4iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 5

Serial Port Settings
Baud: 57600 or 19200 (see below)
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
By default, iRobot Create communicates at 57600 baud.
If you are using a microcontroller that does not support
57600 baud, there are two ways to force Create to switch
to 19200:
Method 1:
When powering on Create, hold down the Play button.
After about 4 seconds, Create plays a tune of descending
pitches. Create will communicate at 19200 baud until the
power is turned off, the battery is removed and reinserted,
the batter y voltage falls below the minimum required for
processor operation, or the baud rate is explicitly changed
by way of the OI.
Method 2:
Use the Baud Rate Change pin (pin 15 on the Cargo Bay
Connector/pin 5 on the Mini-DIN connector) to change
Create’s baud rate. After turning on Create, wait 2 seconds
and then pulse the Baud Rate Change low three times.
Each pulse should last between 50 and 500 milliseconds.
Create will communicate at 19200 baud until the processor
loses battery power or the baud rate is explicitly changed
by way of the OI.
5iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 6

iRobot Create Open Interface Modes
The Create OI has four operating modes: Of f, Passive,
Safe, and Full. After a battery change or when is first
supplied, the OI is in “off” mode. When it is off, the OI listens
at the default baud rate (57600 or 19200 - see Serial Port
Settings above) for an OI Star t command. Once it receives
the Start command, you can enter into any one of the four
operating modes by sending a mode command to the OI.
You can also switch between operating modes at any time
by sending a command to the OI for the operating mode
that you want to use.
Passive Mode
Upon sending the Start command or any one of the demo
commands (which also starts the specific demo, e.g., Spot
Cover, Cover, Cover and Dock, or Demo), the OI enters
into Passive mode. When the OI is in Passive mode, you
can request and receive sensor data using any of the
sensors commands, but you cannot change the current
command parameters for the actuators (motors, speaker,
lights, low side drivers, digital outputs) to something else.
To change how one of the actuators operates, you must
switch from Passive mode to Full mode or Safe mode.
While in Passive mode, you can read Create’s sensors,
watch Create per form any one of its ten built-in demos,
and charge the batter y.
Full Mode
When you send a Full command to the OI, Create enters
into Full mode. Full mode gives you complete control over
Create, all of its actuators, and all of the safety-related
conditions that are restricted when the OI is in Safe mode,
as Full mode shuts of f the cliff, wheel-drop and internal
charger safety features. To put the OI back into Safe mode,
you must send the Safe command.
If no commands are sent to the OI when in Full mode, Create
waits with all motors and LEDs off and does not respond to
Play or Advance button presses or other sensor input.
Note that charging terminates when you enter Full Mode.
Safe Mode
When you send a Safe command to the OI, Create enters into
Safe mode. Safe mode gives you full control of Create, with
the exception of the following safety-related conditions:
• Detection of a cliff while moving forward (or moving
backward with a small turning radius, less than one robot
radius).
• Detection of a wheel drop (on any wheel).
• Charger plugged in and powered.
Should one of the above safety-related conditions occur
while the OI is in Safe mode, Create stops all motors and
reverts to the Passive mode.
If no commands are sent to the OI when in Safe mode, Create
waits with all motors and LEDs off and does not respond to
Play or Advance button presses or other sensor input.
Note that charging terminates when you enter Safe Mode.
6iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 7
Open Interface Command Reference
The following is a list of all of iRobot Create’s Open Inter face
commands. Each command starts with a one-byte opcode.
Some of the commands must be followed by data bytes.
All of Create’s OI commands including their required data
bytes are described below.
NOTE: Always send the required number of data bytes for
the command, otherwise, the processor will enter and
remain in a “waiting” state until all of the required data
bytes are received.
Getting Started Commands
The following commands star t the Open Inter face and get
it ready for use.
Start Opcode:128 Data Bytes: 0
This command starts the OI. You must always send the Start
command before sending any other commands to the OI.
• Serial sequence: [128].
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Passive. Create beeps once to
acknowledge it is starting from “off” mode.
Baud Opcode: 129 Data Bytes: 1
This command sets the baud rate in bits per second (bps)
at which OI commands and data are sent according to the
baud code sent in the data byte. The default baud rate at
power up is 57600 bps, but the star ting baud rate can
be changed to 19200 by holding down the Play button
while powering on Create until you hear a sequence
of descending tones. Once the baud rate is changed, it
persists until Create is power cycled by pressing the power
button or removing the battery, or when the battery voltage
falls below the minimum required for processor operation.
You must wait 100ms after sending this command before
sending additional commands at the new baud rate.
Note: at a baud rate of 115200, there must be at least
200μs between the onset of each character, or some
characters may not be received.
• Serial sequence: [129][Baud Code]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Baud data byte 1: Baud Code (0 - 11)
Baud Code Baud Rate in BPS
0
1
2 1200
3 2400
4 4800
5 9600
6
7 19200
8 28800
9
10 57600
11 115200
300
600
14400
38400
Mode Commands
Create has four operating modes: Off, Passive, Safe, and
Full. Create powers on in the Passive mode. The following
commands change Create’s OI mode.
Safe Opcode: 131 Data Bytes: 0
This command puts the OI into Safe mode, enabling user
control of Create. It turns off all LEDs. The OI can be in
Passive, Safe, or Full mode to accept this command.
• Serial sequence: [131]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Safe
Note: The effect and usage of the Control command (130)
is identical to the Safe command. The Control command is
deprecated but is present for backward compatibility with
the Roomba Open Interface. Use Safe command instead.
Full Opcode: 132 Data Bytes: 0
This command gives you complete control over Create
by putting the OI into Full mode, and turning of f the cliff,
wheel-drop and internal charger safety features. That is, in
Full mode, Create executes any command that you send
it, even if the internal charger is plugged in, or the robot
senses a cliff or wheel drop.
• Serial sequence: [132]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Full
Note: Use the Start command (128) to change the mode
to Passive.
7iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 8
Demo Commands
The following are commands to star t iRobot Create’s
built-in demos.
Demo Opcode: 136 Data Bytes: 1
This command starts the requested built-in demo.
• Serial sequence: [136][Which-demo]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Passive
• Demo data byte 1: Demo number (-1 - 9)
Demo Names, Descriptions and Numbers
Number Demo
-1 (255) Abort current demo
0 Cover
1 Cover and Dock Identical to the Cover demo, with one
2 Spot Cover Create covers an area around its
3 Mouse Create drives in search of a wall. Once
4 Drive Figure Eight Create continuously drives in a figure 8
5 Wimp Create drives forward when pushed from
6 Home
Description
Stops the demo that Create is currently
performing.
Create attempts to cover an entire
room using a combination of behaviors,
such as random bounce, wall following,
and spiraling.
exception. If Create sees an infrared
signal from an iRobot Home Base, it
uses that signal to dock with the Home
Base and recharge itself.
starting position by spiraling outward,
then inward.
a wall is found, Create drives along the
wall, traveling around circumference of
the room.
pattern.
behind. If Create hits an obstacle while
driving, it drives away from the obstacle.
Create drives toward an iRobot Vir tual
Wall as long as the back and sides of
the virtual wall receiver are blinded by
black electrical tape.
A Virtual Wall emits infrared signals
that Create sees with its Omnidirectional
Infrared Receiver, located on top of the
bumper.
Number
7
8
9 Banjo
Demo Description
Tag Identical to the Home demo, except
Create drives into multiple virtual walls
by bumping into one, turning around,
driving to the next virtual wall, bumping
into it and turning around to bump into
the next virtual wall.
Pachelbel Create plays the notes of Pachelbel’s
Canon in sequence when cliff sensors
are activated.
Create plays a note of a chord for each
of its four cliff sensors. Select the
chord using the bumper, as follows:
• No bumper: G major.
• Right/left bumper: D major 7
• Both bumpers (center): C major
You can also call the Cover, Cover and Seek Dock and Spot
Demos using the Opcodes specified below. This is present
for ensuring backward compatibility with the Roomba OI.
Cover Opcode: 135 Data Bytes: 0
This command starts the Cover demo.
• Serial sequence: [135]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Passive
Cover and Dock Opcode: 143 Data Bytes: 0
This command starts the Cover and Dock demo.
• Serial sequence: [143]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Passive
Spot Opcode: 134 Data Bytes: 0
This command starts the Spot Cover demo.
• Serial sequence: [134]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: Passive
If you want Create to home in on a
Virtual Wall, cover all but a small
opening in the front of the infrared
receiver with black electrical tape.
Create spins to locate a virtual wall,
then drives toward it. Once Create hits
the wall or another obstacle, it stops.
8iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 9

Actuator Commands
Drive Direct Opcode: 145 Data Bytes: 4
The following commands control iRobot Create’s actuators:
wheels, speaker, LEDS, dig ital outputs and low side
driver outputs.
Drive Opcode: 137 Data Bytes: 4
This command controls Create’s drive wheels. It takes four
data bytes, interpreted as two 16-bit signed values using
two’s complement. The first two bytes specify the average
velocity of the drive wheels in millimeters per second
(mm/s), with the high byte being sent first. The next two
bytes specify the radius in millimeters at which Create will
turn. The longer radii make Create drive straighter, while
the shorter radii make Create turn more. The radius is
measured from the center of the turning circle to the center
of Create. A Drive command with a positive velocity and a
positive radius makes Create drive forward while turning
toward the left. A negative radius makes Create turn toward
the right. Special cases for the radius make Create turn
in place or drive straight, as specified below. A negative
velocity makes Create drive backward.
NOTE: Internal and environmental restrictions may prevent
Create from accurately carrying out some drive commands.
For example, it may not be possible for Create to drive at
full speed in an arc with a large radius of curvature.
• Serial sequence: [137] [Velocity high byte] [Velocity low byte]
[Radius high byte] [Radius low byte]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Drive data byte 1: Velocity (-500 – 500 mm/s)
• Drive data byte 2: Radius (-2000 – 2000 mm)
Special cases:
Straight = 32768 or 32767 = hex 8000 or 7FFF
Turn in place clockwise = hex FFFF
Turn in place counter-clockwise = hex 0001
Example:
To drive in reverse at a velocity of -200 mm/s while
turning at a radius of 500mm, send the following serial
byte sequence:
[137] [255] [56] [1] [244]
Velocity = -200 = hex FF38 = [hex FF] [hex 38] = [255] [56]
Radius = 500 = hex 01F4 = [hex 01] [hex F4] = [1] [244]
This command lets you control the forward and backward
motion of Create’s drive wheels independently. It takes
four data bytes, which are interpreted as two 16-bit signed
values using two’s complement. The first two bytes specify
the velocity of the right wheel in millimeters per second
(mm/s), with the high byte sent first. The next two bytes
specify the velocity of the left wheel, in the same format.
A positive velocity makes that wheel drive forward, while a
negative velocity makes it drive backward.
• Serial sequence: [145] [Right velocity high byte]
[Right velocity low byte] [Left velocity high byte]
[Left velocity low byte]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Drive Direct data byte 1: Right wheel velocity
(-500 – 500 mm/s)
• Drive Direct data byte 1: Left wheel velocity
(-500 – 500 mm/s)
LEDs Opcode: 139 Data Bytes: 3
This command controls the LEDs on Create. The state of
the Play and Advance LEDs is specified by two bits in the
first data byte. The power LED is specified by two data
bytes: one for the color and the other for the intensity.
• Serial sequence: [139] [LED Bits] [Power Color]
[Power Intensity]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• LEDs data byte 1: LED Bits (0 – 10)
Advance and Play use green LEDs. 0 = off, 1 = on
Bit
LED n/a n/a
7 6 5
n/a n/a Advance
4 3 2
n/a Play n/a
1 0
Power uses a bicolor (red/green) LED. The intensity and
color of this LED can be controlled with 8-bit resolution.
• LEDs data byte 2: Power LED Color (0 – 255)
0 = green, 255 = red. Intermediate values are
intermediate colors (orange, yellow, etc).
• LEDs data byte 3: Power LED Intensity (0 – 255)
0 = off, 255 = full intensity. Intermediate values are
intermediate intensities.
Example:
To turn on the Advance LED and light the Power LED green
at half intensity, send the serial byte sequence [139] [8]
[0] [128].
9iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 10

Digital Outputs Opcode: 147 Data Bytes: 1
Visible LED
470 Ohms
DIGITAL_OUTPUT
+5V
DC MOTOR1N4001
1K Ohms
S8050
ANALOG_OUTPUT
SWITCHED_VPWR
DC MOTOR
LD1
SWITCHED_VPWR
This command controls the state of the 3 digital output
pins on the 25 pin Cargo Bay Connector. The digital outputs
can provide up to 20 mA of current.
• Serial sequence: [147] [Output Bits]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Digital Outputs data byte 1: Output Bits (0 –7);
0 = low (0V); 1 = high (5V).
Example schematics
Warning: When the Robot is switched ON, the Digital
Outputs are High for the first 3 seconds during the
initialization of the bootloader
Example:
To turn on low side driver 2 at 25% and low side driver 0 at
100%, send the serial byte sequence [144][32][0][128]
Low Side Drivers Opcode: 138 Data Bytes: 1
This command lets you control the three low side drivers. The
state of each driver is specified by one bit in the data byte.
Low side drivers 0 and 1 can provide up to 0.5A of current.
Low side driver 2 can provide up to 1.5 A of current. If too
much current is requested, the current is limited and the
overcurrent flag is set (sensor packet 14).
• Serial sequence: [138] [Driver Bits]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Low Side Drivers data byte 1: Driver bits (0 – 7)
Example schematic
Output
PWM Low Side Drivers Opcode: 144 Data Bytes: 3
This command lets you control the three low side drivers
with variable power. With each data byte, you specify the
PWM duty cycle for the low side driver (max 128). For
example, if you want to control a driver with 25% of battery
voltage, choose a duty cycle of 128 * 25% = 32.
• Serial sequence: [144] [Low Side Driver 2 Duty Cycle]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Low Side Drivers data byte 1: Duty cycle for low side
• Low Side Drivers data byte 2: Duty cycle for low side
• Low Side Drivers data byte 3: Duty cycle for low side
Bit
7 6
5
4 3
2 1
digital-out-2
(pin 20)
digital-out-1
(pin 7)
0
digital-out-0
(pin 19)
[Low Side Driver 1 Duty Cycle] [Low Side Driver 0 Duty Cycle]
driver 2 (0 - 128)
driver 1 (0 - 128)
driver 0 (0 - 128)
0 = off, 1 = on at 100% PWM duty cycle
Bit
7 6
5 4
3
Output
2 1
Side Driver
2 (pin 24)
Low Side
Driver 1
(pin 22)
0
Low Side
Driver 0
(pin 23)
Example:
To turn on only low side driver 1, send the serial byte
sequence [138] [2].
Note: Speed control of motors uses the PWM Low Side
Drivers Command. This command exists for Backward
compatibility with the Roomba OI.
10iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 11

Send IR Opcode: 151 Data Bytes: 1
180 Ohms
100 Ohms
IR LED
+5V
LD1
This command sends the requested byte out of low side
driver 1 (pin 23 on the Cargo Bay Connector), using the
format expected by iRobot Create’s IR receiver. You must
use a preload resistor (suggested value: 100 ohms) in
parallel with the IR LED and its resistor in order turn it on.
• Serial sequence: [151][Byte Value]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Send IR data byte 1: Byte value to send (0 - 255)
Example Schematic
Song Opcode: 140 Data Bytes: 2N+2,
where N is the number
of notes in the song
This command lets you specify up to sixteen songs to the OI
that you can play at a later time. Each song is associated
with a song number. The Play command uses the song
number to identify your song selection. Each song can
contain up to sixteen notes. Each note is associated with a
note number that uses MIDI note definitions and a duration
that is specified in fractions of a second. The number of data
bytes varies, depending on the length of the song specified.
A one note song is specified by four data bytes. For each
additional note within a song, add two data bytes.
• Serial sequence: [140] [Song Number] [Song Length]
[Note Number 1] [Note Duration 1] [Note Number 2]
[Note Duration 2], etc.
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Song data byte 1: Song Number (0 – 15)
The song number associated with the specific song. If
you send a second Song command, using the same song
number, the old song is overwritten.
• Song data byte 2: Song Length (1 – 16)
The lengt h of the song, accor ding to the number o f
musical notes within the song.
• Song data bytes 3, 5, 7, etc.: Note Number (31 – 127)
The pitch of the musical note Create will play, according
to the MIDI note numbering scheme. The lowest musical
note that Create will play is Note #31. Create considers
all musical notes outside the range of 31 – 127 as rest
notes, and will make no sound during the duration of
those notes.
• Song data bytes 4, 6, 8, etc.: Note Duration (0 – 255)
The duration of a musical note, in increments of 1/64th
of a second. Example: a half-second long musical note
has a duration value of 32
11iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 12

Note Durations
Number
31
32 G#
33
34
35 B
36
37 C#
38
39 D#
40
41 F 87.3 77 F 698.5 113 F 5587.7
42 F# 92.5 78 F# 740.0 114 F# 5919.9
43 G 98.0 79 G 784.0 115 G 6271.9
44 G# 103.8 80 G# 830.6 116 G# 6644.9
45 A 110.0 81 A 880.0 117 A 7040.0
46 A# 116.5 82 A# 932.3 118 A# 7458.6
47 B 123.5 83 B 987.8 119 B 7902.1
48 C 130.8 84 C 1046.5 120 C 8372.0
49 C# 138.6 85 C# 1108.7 121 C# 8869.8
50 D 146.8 86 D 1174.7 122 D 9397.3
51 D# 155.6 87 D# 1244.5 123 D# 9956.1
52 E 164.8 88 E 1318.5 124 E 10548.1
53 F 174.6 89 F 1396.9 125 F 11175.3
54 F# 185.0 90 F# 1480.0 126 F# 11839.8
55 G 196.0 91 G 1568.0 127 G 12543.9
56 G# 207.7 92 G# 1661.2
57 A 220.0 93 A 1760.0
58 A# 233.1 94 A# 1864.7
59 B 246.9 95 B 1975.5
Note
G
A
A# 58.3
C 65.4
D 73.4
E 82.4
Frequency
49.0
51.0 68
55.0
61.7
69.3 73
77.8
Number
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
69
70
71 B
72
74 D
75 D#
76
Note
C
C#
D
D#
E
F
F#
G
G#
A
A# 466.2
C 523.3
C#
E 659.3
Frequency
261.6
277.2
293.7
311.1
329.6
349.2
370.0
392.0
415.3 104
440.0
493.9 107
554.4 109
587.3
622.3 111
Number
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
105
106
108 C
110 D
112 E
Note
C
C#
D
D#
E
F
F#
G
G# 3322.4
A
A# 3729.3
B
C# 4434.9
D#
Frequency
2093.0
2217.5
2349.3
2489.0
2637.0
2793.8
2960.0
3136.0
3520.0
3951.1
4186.0
4698.6
4978.0
5274.0
12iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 13

Play Song Opcode: 141 Data Bytes: 1
This command lets you select a song to play from the songs
added to iRobot Create using the Song command. You must
add one or more songs to Create using the Song command
in order for the Play command to work. Also, this command
does not work if a song is already playing. Wait until a
currently playing song is done before sending this command.
Note that the “song playing” sensor packet can be used to
check whether Create is ready to accept this command.
• Serial sequence: [141] [Song Number]
• Available in modes: Safe or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Play Song data byte 1: Song Number (0 – 15)
The number of the song Create is to play.
Input Commands
The following commands let you read the state of Create’s
built-in sensors, digital and analog inputs, and some internal
state variables. Create updates these values internally
every 15 ms. Do not send these commands more frequently
than that.
Query List Opcode: 149 Data Bytes: N + 1,
where N is the number
of packets requested.
This command lets you ask for a list of sensor packets.
The result is returned once, as in the Sensors command.
The robot returns the packets in the order you specify.
• Serial sequence: [149][Number of Packets]
[Packet ID 1][Packet ID 2]...[Packet ID N]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Query List data byte 1: Number of packets requested
(0 - 255)
• Query List data bytes 2 - N: IDs of packets requested
(0 - 42)
Example:
To get the state of the left cliff sensor (packet 9) and
the Vir tual Wall detector (packet 13), send the following
sequence:
[149] [2] [9] [13]
Sensors Opcode: 142 Data Bytes: 1
This command requests the OI to send a packet of sensor
data bytes. There are 43 different sensor data packets. Each
provides a value of a specific sensor or group of sensors.
For more information on sensor packets, refer to the next
section, “Create Open Interface Sensor Packets.”
• Serial sequence: [142] [Packet ID]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Sensors data byte 1: Packet ID (0 - 42)
Identifies which of the 43 sensor data packets should be
sent back by the OI. A value of 6 indicates a packet with
all of the sensor data. Values of 0 through 5 indicate
specific subgroups of the sensor data (see Sensors
Quick Reference below).
13iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 14

Stream Opcode: 148 Data Bytes: N + 1,
where N is the number
of packets requested.
This command star ts a continuous stream of data packets.
The list of packets requested is sent every 15 ms, which is
the rate iRobot Create uses to update data.
This is the best method of requesting sensor data if you
are controlling Create over a wireless network (which has
poor real-time characteristics) with software running on a
desktop computer.
• Serial sequence: [148] [Number of packets]
[Packet ID 1] [Packet ID 2] [Packet ID 3] etc.
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Stream data byte 1: Number of packets requested
(0 - 43)
• Stream data bytes 2 - N: IDs of packets requested
(0 - 42)
The format of the data returned is:
[19][N-bytes][Packet ID 1][Packet 1 data…]
[Packet ID 2][Packet 2 data…][Checksum]
N-bytes is the number of bytes between the n-bytes byte and
the checksum.
The checksum is a 1-byte value. It is the 8-bit complement
of all of the bytes between the header and the checksum.
That is, if you add all of the bytes after the checksum, and
the checksum, the low byte of the result will be 0.
In the above stream segment, Create’s left cliff signal value
was 549 (0x0225) and there was no virtual wall signal.
It is up to you not to request more data than can be sent at
the current baud rate in the 15 ms time slot. For example,
at 57600 baud, a maximum of 86 bytes can be sent in 15 ms:
15 ms / 10 bits (8 data + start + stop) * 57600 = 86.4
If more data is requested, the data stream will eventually
become corrupted. This can be confirmed by checking the
checksum.
The header byte and checksum can be used to align your
receiving program with the data. All data chunks star t with
19 and end with the 1-byte checksum
Pause/Resume Stream Opcode: 150 Data Bytes: 1
This command lets you stop and restart the steam without
clearing the list of requested packets.
• Serial sequence: [150][Stream State]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Pause/Resume Stream data byte 1: Requested
stream state (0 - 1)
An argument of 0 stops the stream without clearing the list
of requested packets. An argument of 1 star ts the stream
using the list of packets last requested.
Example:
To get data from Create’s left cliff signal (packet 29)
and Virtual Wall detector (packet 13), send the following
command string to Create:
[148] [2] [29] [13]
NOTE: The left cliff signal is a 2-byte packet and the IR
Sensor is a 1-byte packet.
Create starts streaming data that looks like this:
19 5 29
header n-bytes packet
ID 1
NOTE: Checksum computation: (5 + 29 + 2 + 25 + 13 + 0
+ 182) = 256 and (256 & 0xFF) = 0.
2 25 13 0 182
Packet data
1 (2 bytes)
packet
ID 2
packet
data 2
(1 byte)
Checksum
14iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 15

Script Commands
Play Script Opcode: 153 Data Bytes: 0
The following commands let you specify a script for iRobot Create
to play at a later time.
Script Opcode: 152 Data Bytes: N + 1
where N is the number
of bytes in the script.
This command specifies a script to be played later. A script
consists of OI commands and can be up to 100 bytes long.
There is no flow control, but “wait” commands (see below)
cause Create to hold its current state until the specified
event is detected.
• Serial sequence: [152] [Script Length] [Opcode 1]
[Opcode 2] [Opcode 3] etc.
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Script data byte 1: Script Length (0 – 100)
Specifies the length of the script in terms of the
number of commands. Specify a length of 0 to clear
the current script.
• Script data bytes 2 and above: Open Interface commands
and data bytes
Tip: To make a script loop forever, use Play Script (153) as
the last command.
Example Scripts:
This command loads a previously defined OI script into the
serial input queue for playback.
• Serial sequence: [153]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
Show Script Opcode: 154 Data Bytes: 0
This command returns the values of a previously stored
script, starting with the number of bytes in the script and
followed by the script’s commands and data bytes. It first
halts the sensor stream, if one has been started with a
Stream or Pause/Resume Stream command. To restart the
stream, send Pause/Resume Stream (opcode 150).
• Serial sequence: [154]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
Wait Commands
The following commands cause Create to wait for a specific
time, distance, angle of rotation, or event to occur. While
it is waiting, Create does not change its state, nor does it
react to any inputs, serial or other wise. These commands
are intended for use in scripting only.
Drive 40 cm and stop:
152 13 137 1 44 128 0 156 1 144 137 0 0 0 0
Toggle led on bump:
152 17 158 5 158 251 139 2 0 0 158 5 158 251 139 0
0 0 153
Drive in a square:
152 17 137 1 44 128 0 156 1 144 137 1 44 0 1 157
0 90 153
Wait Time Opcode: 155 Data Bytes: 1
This command causes Create to wait for the specified time.
During this time, Create’s state does not change, nor does
it react to any inputs, serial or otherwise.
• Serial sequence: [155] [time]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Wait Time data byte 1: Time (0 - 255)
Specifies time to wait in tenths of a second with a resolution
of 15 ms.
15iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 16

Wait Distance Opcode: 156 Data Bytes: 2
This command causes iRobot Create to wait until it has
traveled the specified distance in mm. When Create travels
forward, the distance is incremented. When Create travels
backward, the distance is decremented. If the wheels
are passively rotated in either direction, the distance is
incremented. Until Create travels the specified distance,
its state does not change, nor does it react to any inputs,
serial or otherwise.
NOTE: This command resets the distance variable that is
returned in Sensors packets 19, 2 and 6.
• Serial sequence: [156] [Distance high byte]
[Distance low byte]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Wait Distance data bytes 1-2: 16-bit signed distance
in mm, high byte first (-32767 -32768)
Wait Angle Opcode: 157 Data Bytes: 2
This command causes Create to wait until it has rotated
through specified angle in degrees. When Create turns
counterclockwise, the angle is incremented. When Create
turns clockwise, the angle is decremented. Until Create
turns through the specified angle, its state does not change,
nor does it react to any inputs, serial or otherwise.
NOTE: This command resets the angle variable that is
returned in Sensors packets 20, 2 and 6.
• Serial sequence: [157] [Angle high byte] [Angle low byte]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Wait Angle data bytes 1-2: 16-bit signed angle in degrees,
high byte first (-32767 -32768)
To wait for the inverse of an event, send the negative of
its number using two’s complement notation. For example,
to wait for no bumps, send the serial byte sequence [158]
[-5], which is equivalent to [158] [251].
Wait Event: Unsigned Equivalent of Inverse
Event
Wheel Drop 1
Front Wheel Drop 2
Left Wheel Drop 3
Right Wheel Drop
Bump 5 251
Left Bump 6 250
Right Bump 7
Virtual Wall
Wall 9 247
Cliff 10
Left Cliff 11 245
Front Left Cliff 12 244
Front Right Cliff 13 243
Right Cliff 14 242
Home Base 15 241
Advance Button 16 240
Play Button 17 239
Digital Input 0 18 238
Digital Input 1 19 237
Digital Input 2 20 236
Digital Input 3 21 235
OI Mode = Passive 22 234
Number Unsigned Equivalent of Inverse
255
254
253
4
8
252
249
248
246
Wait Event Opcode: 158 Data Bytes: 1
This command causes Create to wait until it detects the
specified event. Until the specified event is detected,
Create’s state does not change, nor does it react to any
inputs, serial or otherwise.
• Serial sequence: [158] [Event number]
• Available in modes: Passive, Safe, or Full
• Changes mode to: No Change
• Wait Event data byte 1: Signed event number
(1 to 20 and -1 to -20)
signed
16iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 17

iRobot Create Open Interface
Sensor Packets
Create sends back one of 43 different sensor data packets,
depending on the value of the packet data byte, when
responding to a Sensors command, Query List command,
or Stream command’s request for a packet of sensor data
bytes. Some packets contain groups of other packets.
Some of the sensor data values are 16 bit values.
Most of the packets (numbers 7 – 42) contain the value of
a single sensor or variable, which can be either 1 byte or 2
bytes. Two-byte packets correspond to 16-bit values, sent
high byte first.
Some of the packets (0-6) contain groups of the singlevalue packets.
Wait Event: Unsigned Equivalent of Inverse
Group Packet ID Packet Size Contains packets
0
1
2 6 bytes 17 - 20
3 10 bytes
4 14 bytes 27 - 34
5 12 bytes 35 - 42
6 52 bytes 7 - 42
Bumps and Wheel Drops Packet ID: 7 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the bumper (0 = no bump, 1 = bump) and wheel
drop sensors (0 = wheel raised, 1 = wheel dropped) are sent
as individual bits.
Range: 0 - 31
26 bytes 7 - 26
10 bytes 7 - 16
21 - 26
unsigned
Cliff Front Left Packet ID: 10 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the cliff sensor on the front left of Create is
sent as a 1 bit value (0 = no cliff, 1 = cliff).
Range: 0 – 1
Cliff Front Right Packet ID: 11 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the cliff sensor on the front right of Create is
sent as a 1 bit value (0 = no cliff, 1 = cliff)
Range: 0 – 1
Cliff Right Packet ID: 12 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the cliff sensor on the right side of Create is
sent as a 1 bit value (0 = no cliff, 1 = cliff)
Range: 0 – 1
Virtual Wall Packet ID: 13 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the virtual wall detector is sent as a 1 bit value
(0 = no vir tual wall detected, 1 = vir tual wall detected).
Note that the force field on top of the Home Base also trips
this sensor.
Range: 0 – 1
unsigned
unsigned
unsigned
unsigned
Bit 7
Sensor n/a n/a
Wall Packet ID: 8 Data Bytes: 1
6
5 4
n/a
Wheeldrop
Caster
3
Wheeldrop
Left
The st ate of the wall sensor is sent as a 1 bit value
(0 = no wall, 1 = wall seen).
Range: 0 – 1
Cliff Left Packet ID: 9 Data Bytes: 1
The state of the clif f sensor on the left side of Create is
sent as a 1 bit value (0 = no cliff, 1 = cliff).
Range: 0 – 1
2 1
Wheeldrop
Right
Bump
Left
unsigned
unsigned
0
Bump
Right
Low Side Driver and Packet ID: 14 Data Bytes: 1
Wheel Overcurrents unsigned
The state of the three Low Side driver and two wheel
overcurrent sensors are sent as individual bits (0 = no
overcurrent, 1 = overcurrent).
Driver Current Limit
LD0 0.5A
LD1 0.5A
LD2 1.6A
Wheels 1.0A
Range: 0 - 31
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Motor n/a n/a n/a Left Wheel Right Wheel LD-2 LD-0 LD-1
17iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 18

Unused Bytes Packet IDs: 15 - 16 Data Bytes: 1
Force Field
Green
Buoy
Red
Buoy
Unused bytes: Two unused bytes are sent after the overcurrent
byte when the requested packet is 0, 1, or 6. The value of the
two unused bytes is always 0.
Range: 0
Infrared Byte Packet ID: 17 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
This value identifies the IR byte currently being received
by iRobot Create. A value of 255 indicates that no IR byte
is being received. These bytes include those sent by the
Roomba Remote, the Home Base, Create robots using the
Send IR command, and user-created devices.
Range: 0 – 255
Dock beam configuration
Sent by iRobot Device
Scheduling Remote
Home Base
Character Value
142 Send All
143
240 Reserved
248
244 Green Buoy
242 Force Field
252 Red Buoy and Green Buoy
250 Red Buoy and Force Field
246
254
Character Name
Seek Dock
Red Buoy
Green Buoy and Force
Field
Red Buoy, Green Buoy and
Force Field
Buttons Packet ID: 18 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
The state of Create’s Play and Advance buttons are sent as
individual bits (0 = button not pressed, 1 = button pressed).
Range: 0 - 5
Sent by iRobot Device
Remote Control 129 Left
Character Value Character Name
130
131 Right
132 Spot
133 Max
134 Small
135 Medium
136 Large / Clean
137 PAUSE
138 Power
139 arc-forward-left
140 arc-forward-right
141 drive-stop
Forward
Bit 7
Button
6 5
n/a n/a n/a
4
3 2
n/a n/a Advance n/a
1 0
Play
Distance Packet ID: 19 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The distance that Create has traveled in millimeters since the
distance it was last requested is sent as a signed 16-bit value,
high byte first. This is the same as the sum of the distance
traveled by both wheels divided by two. Positive values indicate
travel in the forward direction; negative values indicate travel
in the reverse direction. If the value is not polled frequently
enough, it is capped at its minimum or maximum.
Range: -32768 – 32767
18iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 19

Angle Packet ID: 20 Data Bytes: 2
signed
Battery Temperature Packet ID: 24 Data Bytes: 1
signed
The angle in degrees that iRobot Create has turned since the
angle was last requested is sent as a signed 16-bit value, high
byte first. Counter-clockwise angles are positive and clockwise
angles are negative. If the value is not polled frequently
enough, it is capped at its minimum or maximum.
Range: -32768 – 32767
NOTE: Create uses wheel encoders to measure distance
and angle. If the wheels slip, the actual distance or angle
traveled may differ from Create’s measurements.
Charging State Packet ID: 21 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
This code indicates Create’s current charging state.
Range: 0 - 5
Code
0 Not charging
1
2 Full Charging
3 Trickle Charging
4
5 Charging Fault Condition
Charging State
Reconditioning Charging
Waiting
The temperature of Create’s batter y in degrees Celsius.
Range: -128 – 127
Battery Charge Packet ID: 25 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The current charge of Create’s batter y in milliamp-hours (mAh).
The charge value decreases as the batter y is depleted
during running and increases when the batter y is charged.
Note that this value will not be accurate if you are using the
alkaline battery pack.
Range: 0 – 65535
Battery Capacity Packet ID: 26 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The estimated charge capacity of Create’s battery in milliamphours (mAh). Note that this value is inaccurate if you are using
the alkaline batter y pack.
Range: 0 – 65535
Wall Signal Packet ID: 27 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
Voltage Packet ID: 22 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
This code indicates the voltage of Create’s batter y in
millivolts (mV).
Range: 0 – 65535
Current Packet ID: 23 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The current in milliamps (mA) flowing into or out of Create’s
battery. Negative currents indicate that the current is flowing
out of the battery, as during normal running. Positive currents
indicate that the current is flowing into the battery, as during
charging.
Range: -32768 – 32767
The strength of the wall sensor’s signal is returned as an
unsigned 16-bit value, high byte first.
Range: 0-4095
Cliff Left Signal Packet ID: 28 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The strength of the left cliff sensor’s signal is returned as an
unsigned 16-bit value, high byte first.
Range: 0-4095
Cliff Front Left Signal Packet ID: 29 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The strength of the front left cliff sensor’s signal is returned as
an unsigned 16-bit value, high byte first.
Range: 0-4095
19iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 20

Cliff Front Right Signal Packet ID: 30 Data Bytes: 2
10K Ohms
+5V
DIGITAL_INPUT
1 2
10K Ohms
Light Dependent Resistor
(LDR)
+5V
ANALOG_INPUT
unsigned
Cargo Bay Analog Signal Packet ID: 33 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The strength of the front right cliff sensor’s signal is returned as
an unsigned 16-bit value, high byte first.
Range: 0-4095
Cliff Right Signal Packet ID: 31 Data Bytes: 2
unsigned
The strength of the right cliff sensor’s signal is returned as an
unsigned 16-bit value, high byte first.
Range: 0-4095
Cargo Bay Digital Inputs Packet ID: 32 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
The state of the digital inputs on the 25-pin Cargo Bay Connector
are sent as individual bits (0 = low, 1 = high (5V)). Note that the
Baud Rate Change pin is active low; it is high by default.
Example Schematic
The 10-bit value of the analog input on the 25-pin Cargo Bay
Connector is returned, high byte first. 0 = 0 volts; 1023 = 5
volts. The analog input is on pin 4.
Range: 0 - 1023
Example Schematic
Charging Sources Available Packet ID: 34 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
iRobot Create’s connection to the Home Base and Internal
Charger are returned as individual bits, as below.
Range: 0 - 31
Bit
Button n/a
Device Detect pin can be used to change Baud Rate. When
device detect/baud rate change Bit is low, the Baud Rate
is 19200. Otherwise it it 57600
7 6 5
n/a n/a Device
4 3 2
Detect
/Baud
Rate
Change
(pin 15)
Digital
Input 3
(pin 6)
Digital
Input 2
(pin 18)
1 0
Digital
Input 1
(pin 5)
Digital
Input 0
(pin 17)
Range: 0 - 3
1 = charging source present and powered; 0 = charging source
not present or not powered.
Bit
Charging
Source
7 6 5
n/a
n/a n/a n/a
4 3 2
n/a n/a Home
1 0
Base
Internal
Charger
OI Mode Packet ID: 35 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
Create’s connection to the Home Base and Internal Charger
are returned as individual bits, as below.
Range: 0 - 3
Number Mode
0 Off
1 Passive
2 Safe
3 Full
20iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 21

Song Number Packet ID: 36 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
The currently selected OI song is returned.
Range: 0-15
Song Playing Packet ID: 37 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
The state of the OI song player is returned. 1 = OI song
currently playing; 0 = OI song not playing.
Range: 0-1
Number of Stream Packets Packet ID: 38 Data Bytes: 1
unsigned
The number of data stream packets is returned.
Range: 0-43
Requested Velocity Packet ID: 39 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The velocity most recently requested with a Drive command
is returned as a signed 16-bit number, high byte first.
Range: -500 - 500 mm/s
Requested Radius Packet ID: 40 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The radius most recently requested with a Drive command
is returned as a signed 16-bit number, high byte first.
Range: -32768 - 32767 mm
Requested Right Velocity Packet ID: 41 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The right wheel velocity most recently requested with a Drive
Direct command is returned as a signed 16-bit number,
high byte first.
Range: -500 - 500 mm/s
Requested Left Velocity Packet ID: 42 Data Bytes: 2
signed
The left wheel velocity most recently requested with a Drive
Direct command is returned as a signed 16-bit number,
high byte first.
Range: -500 - 500 mm/s
21iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 22

iRobot Create Open Interface
Commands Quick Reference
Create OI Commands Quick Reference Table
Command
Start 128
Opcode
Data Bytes: 1 Data Bytes: 2
Data Bytes: 3 Data Bytes: 4
Etc.
Baud
Control
Safe 131
Full 132
Spot 134
Cover 135
Demo 136 Demos (-1 - 9)
Drive 137 Velocity (-500 – 500 mm/s) Radius (-2000 – 2000 mm)
Low Side Drivers 138 Output Bits (0 – 7)
LEDs 139 LED Bits (0 – 10) Power LED Color
Song 140 Song Number
Play 141 Song Number:
Sensors 142 Packet ID: (0 – 42)
Cover and Dock 143
PWM Low Side
Drivers
Drive Direct 145 Right wheel velocity (-500 – 500 mm/s) Left wheel velocity (-500 – 500 mm/s)
129 Baud Code: (0 – 11)
130
(0 - 15)
(0 – 15)
144 Low Side Driver 2
Duty Cycle (0 - 128)
(0 – 255)
Song Length
(1 - 16)
Low Side Driver 1
Duty Cycle (0 - 128)
Power LED Intensity
(0 – 255)
Note Number 1
(31 – 27)
Low Side Driver 0
Duty Cycle (0 - 128)
Note Duration 1
(0 - 255)
Note Number 2, etc.
Digital Outputs 147 Output Bits (0 –7)
Stream 148 Number of Packets Packet ID 1 (0 – 42) Packet ID 2, etc.
Query List 149 Packet ID 1 (0 – 42) Packet ID 2, etc.
Pause/Resume
Stream
Send IR 151 Byte (0 - 255)
Script 152 Script Length:
Play Script 153
Show Script 154
Wait Time 155 Time (0 – 255
Wait Distance 156
Wait Angle
Wait Event
150 Range: 0-1
(1 – 100)
seconds/10)
Distance (-32767 - 32768 mm)
157
158 Event ID
Angle (-32767 - 32768 degrees)
(1 to 20 and
-1 to -20)
Command Opcode 1 Command Data
Byte 1, etc.
Command Opcode 2 Etc.
22iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 23

Baud Code (0 – 11)
Baud Code
0
1
2 1200
3 2400
4
5
6
7 19200
8 28800
9 38400
10 57600
11 115200
Baud Rate in BPS
300
600
4800
9600
14400
LEDs Data Byte 1: LED Bits (0 – 10)
Advance and Play use green LEDs: 0 = off, 1 = on
Digital Outputs Data Byte 1: Output Bits (0 –7)
0 = low (0V); 1 = high (5V).
The digital outputs can provide up to 20 mA of current.
Bit
Output
Low Side Drivers Data Byte 1: Output bits (0 – 7)
7
6
5
4
3
2
digital output
2 (pin 20)
1
digital output
1 (pin 7)
0
digital output
0 (pin 19)
0 = off, 1 = on at 100% pwm duty cycle
Bit
Output
7
6
5
4
3
2
Low Side
Driver 2
1
Low Side
Driver 1
0
Low Side
Driver 0
Bit 7
LED n/a n/a
6
5 4
n/a n/a Advance n/a
3 2
1
Play n/a
0
LEDs Data Bytes 2 and 3: Power LED Color and Intensity (0 - 255)
Power uses a bicolor (red/green) LED. The intensity and
color of this LED can be controlled with 8-bit resolution.
LEDs data byte 2: Power LED Color (0 – 255)
0 = green, 255 = red. Intermediate values are intermediate
colors (orange, yellow, etc).
LEDs data byte 3: Power LED Intensity (0 – 255)
0 = off, 255 = full intensity. Intermediate values are
intermediate intensities.
23iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 24

iRobot Create Open Interface
Sensor Packets Quick Reference
Create sends back one of 43 different sensor data packets
in response to a Sensors command, depending on the value
of the packet ID data byte. Some packets contain groups
of other packets. Group packetsr send their component
values in sequential order. Some of the sensor data values
are 16 bit values. These values are sent as two bytes, high
byte first.
Group Packet Sizes and Contents
Group Packet ID Packet Size
0
1
2
26 bytes
10 bytes
6 bytes 17 - 20
3 10 bytes
4 14 bytes 27 - 34
5 12 bytes 35 - 42
6
52 bytes 7 - 42
Group Packet Sizes and Contents
Contains Packets
7 - 26
7 - 16
21 - 26
Packet Membership
4
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
5
35
36
37
38
39 Velocity
40
41 Right Velocity
42
Charging State Codes
Name
Wall Signal
Cliff Left Signal
Cliff Front Left Signal 2
Cliff Front Right Signal
Cliff Right Signal
User Digital Inputs
User Analog Input
Charging Sources
Available
OI Mode
Song Number 1
Song Playing 1
Number of Stream
Packets
Radius
Left Velocity
Bytes Value Range
2
0 - 4095
2
0 - 4095
0 - 4095
2
0 - 4095
2
0 - 4095
1
0 - 31
2
0 - 1023
1 0 - 3
1
0 - 3
0 - 15
0 - 1
1
0 - 42
2 -500 - 500
2 -32768 -
32767
2 -500 - 500
2 -500 - 500
Units
mm/s
mm
mm/s
mm/s
Packet Membership Name
0 1
2 17 IR Byte 1 0 - 255
3 21 Char ging State 1 0 - 5
6
7
Bumps and Wheel
Drops
8
Wall 1
9 Cliff Left
10
Cliff Front Left 1 0 - 1
11 Cliff Front Right 1
12 Cliff Right
13
Virtual Wall
14
Overcurrents 1 0 - 31
15 Unused 1
16 Unused 1 0
18 Buttons 1 0 - 15
19 Distance 2 -32768 -
20 Angle 2 -32768 -
22 Voltage 2 0 - 65535 mV
23 Current 2 -32768 -
24 Batter y Temperature
25 Batter y Charge 2
Battery Capacity 2 0 - 65535 mAh
26
Bytes Value Range Units
1
0 - 31
0 - 1
1 0 - 1
0 - 1
1 0 - 1
1 0 - 1
0
mm
32767
mm
32767
mA
32767
1 -128 - 127 degrees
Celsius
0 - 65535 mAh
Code Charging State
0 Not charging
1 Reconditioning Charging
2 Full Charging
3
Trickle Charging
4 Waiting
5 Charging Fault Condition
Bumps and Wheel Drops
Bit 7 6
Sensor n/a n/a n/a Wheel-
5 4 3 2 1 0
drop
Caster
Low Side Driver and Wheel Overcurrents
Bit
Motor n/a n/a n/a Left
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Wheel
Wheeldrop
Left
Right
Wheel
Wheeldrop
Right
Low
Side
Driver 2
Bump
Left
Low
Side
Driver 0
Bump
Right
0
Low
Side
Driver 1
24iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
Page 25

Buttons
Bit
Button n/a
7 6
n/a
5
n/a n/a
Cargo Bay Digital Inputs
Bit
Button
7
6 5
n/a n/a
n/a
4 3
Baud
Rate
Change
(pin 15)
Charging Sources Available
Bit 7 6 5
Charging
Source
n/a n/a n/a n/a
OI Mode
4 3
n/a Advance
Digital
Input 3
(pin 6)
4 3 2
n/a n/a Home
2 1
2
Digital
Input 2
(pin 18)
n/a
1 0
Digital
Input 1
(pin 5)
1 0
Base
0
Play
Digital
Input 0
(pin 17)
Internal
Charger
Number
0 Off
1
2 Safe
3
©2006 iRobot Corporation. All rights reserved.
iRobot, Roomba and Virtual Wall are registered trademarks of iRobot Corporation.
Home Base and Create are trademarks of iRobot Corporation.
U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,594,844 6,690,134, and 6,809,490. Other patents pending.
Mode
Passive
Full
25iRobot Create Open Interface (OI) Specification
 Loading...
Loading...