Page 1

Desktop 10Base-T
Internet ISDN Gateway
User’s Manual
529930
I-ISS-020
Page 2

Introduction
The NexIP Internet Sharing Station is the most cost-effective Internet access solution available today for
users. With only a single Internet account and a low cost dial-up line, it lets a small network of more
than 2 desktop computers to share the vast resource available on the Internet simultaneously. Compare
to traditional leased-line router configuration, the Internet Sharing Station is not only easier to use, it
reduces ownership and maintenance cost dramatically with its innovative architecture. In dial-up
configuration, it connects to remote Internet Service Provider (ISP) network automatically only when local
users tried to access remote hosts on the Internet. To further improve performance when multiple users
access the Internet at the same time, the Internet Sharing Station provides additional asynchronous ports
with dial-on-demand functions. The Internet Sharing Station will dial up additional connections if the
primary line is congested, so the Internet access performance can be improved instantly.
Internet
Features
z Easy to Install. An auto-sensing LAN connection eliminates the need for configuration during
installation in a 10BASE2 or 10BASE-T Ethernet LAN.
z Simple Setup and Manage. Provides both Web browser and terminal interface for configuration.
z Dial-on-Demand. Establishes connections to the Internet as requi red.
z Bandwidth-on-Demand. Dial-up the second modem or ISDN TA only when needed.
z Idles Time Out. Hangs up the modem if no activity detected.
z High Speed Modem Supported. Supports 56K modem and 128K ISDN TA.
z PPP Authentication. Automatically validates the log-on to Internet Service Provider.
z DHCP Server Supported. Acts as a DHCP server and automatically allocates an IP address to
each computer on the LAN.
z Firewall Protection. Provides natural firewall and secure gateway for LAN users.
z RAS Function. Allow remote users on outside or at home to dial-in and share the network
resources.
z E-mail Sharing. Lets one E-mail account on ISP’s mail server to be shared with multiple LAN users.
z Status Monitoring. On-line che c ks the dial-up condition and the flow on each port.
z Configuration Security. Provides password protection to prevent unauthorized users from
modifying the configuration.
z Remote Management. Can be managed from a station running Web browser anywhere on the LAN
or Internet.
z Virtual Servers Supported. Puts your compa ny’s Web / FTP / TELNET servers on the Internet.
z Phone Number Hunting. Provides two accounts for each dial-up line.
z Flash Firmware Upgrade. Allows easy firmware upgrade via FTP utility.
1
Page 3
Package Contents
This package has:
1. One Internet Sharing Station
2. One power adapter
3. Wall Mounting kit
4. This user’s guide
Hardware Introduction
The components of the unit are shown as the following figure:
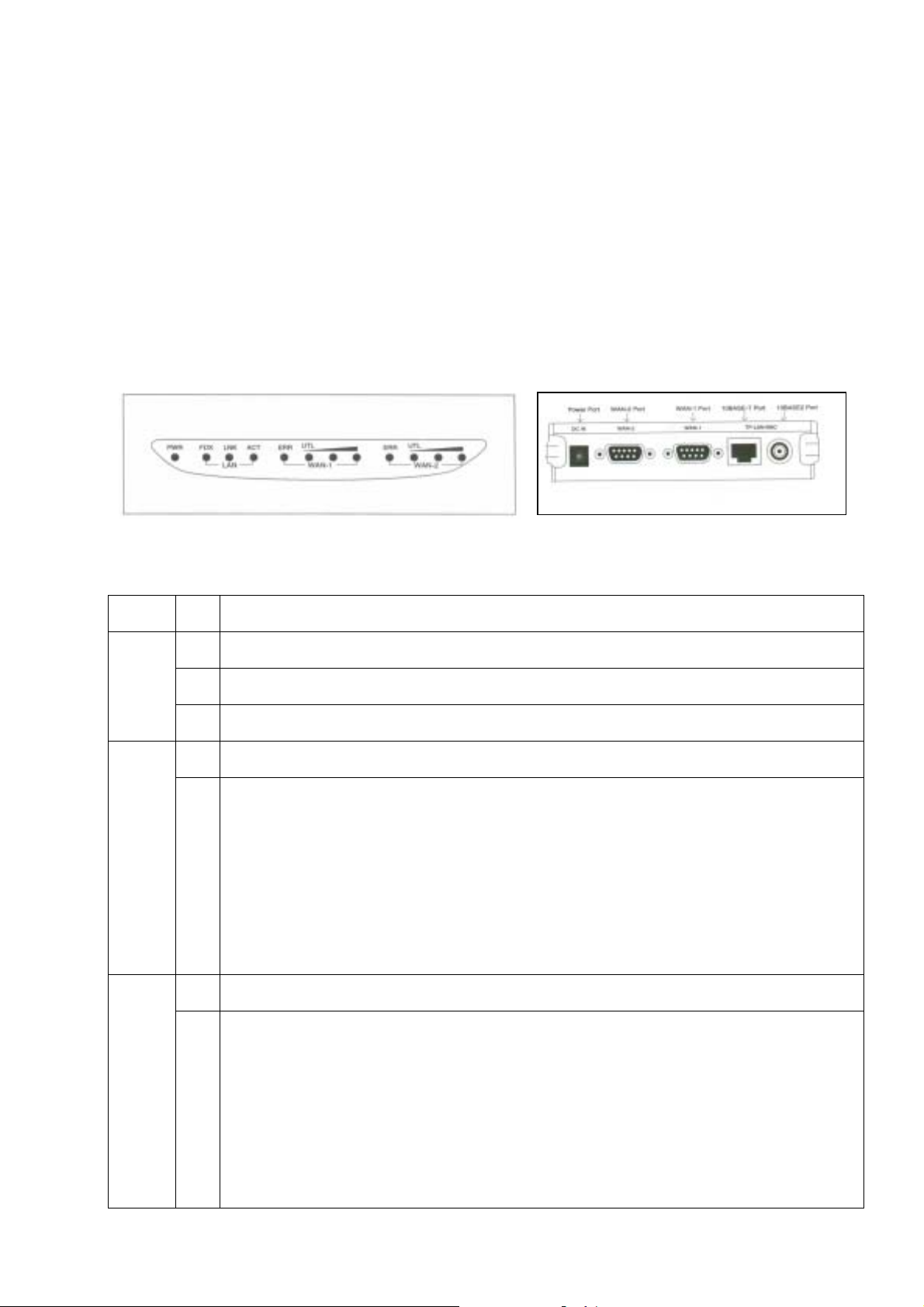
Front Panel
LED Status Table
PWR
LAN
WAN-1
WAN-2
ON: DC power is on
OFF: No DC power
FDX ON: Indicates communication on your LAN is operating at full-duplex mode.
OFF: Indicates transmission mode is half-duplex.
LNK ON: Ethernet interface is being connected.
OFF: Ethernet interface not connected
ACT Blinking: Indicates traffic passing through the Ethernet port.
OFF: No traffic
ERR ON: Error condition
OFF: Normal condition
UTL (ON=1; OFF=0) Enumerate from left to right.
When the WAN-1 port is connected to modem, and it is on idle state, the LEDs are used to
indicate baudrate. When connection is established, the LEDs are used to indicate utilization.
“000”- Port disconnected
“100”- Baudrate=9.6K; or Utilization=20%
“010”- Baudrate=19.2K
“110”- Baudrate=38.4K; or Utilization=60%
“001”- Baudrate=57.6K
“101”- Baudrate=115.2K
“011”- Baudrate=230.4K
“111”- Baudrate= reserved; or Utilization=100%
ERR ON: Error condition
OFF: Normal condition
UTL (ON=1; OFF=0) Enumerate from left to right.
When the WAN-2 port is connected to modem, and it is on idle state, the LEDs are used to
indicate baudrate. When connection is established, the LEDs are used to indicate utilization.
“000”- Port disconnected
“100”- Baudrate=9.6K; or Utilization=20%
“010”- Baudrate=19.2K
“110”- Baudrate=38.4K; or Utilization=60%
“001”- Baudrate=57.6K
“101”- Baudrate=115.2K
“011”- Baudrate=230.4K
“111”- Baudrate= reserved; or Utilization=100%
2
Page 4
Install the unit
This unit can be placed on a flat surface or mounted on a metallic surface or partition. Please comply with
the following steps for proper installation.
Desktop Installation
y Carefully take out the unit from its packaging
y You will find four self-adhesive rubber feet attached on the bottom of the unit, which provide space
for ventilation and cushion the unit needed against vibrations. Place the unit directly on your desk.
Magnetic Mounting Installation
y Inside each of the four rubber feet, you will find a magnetic ring. Adhere this unit to steel flat surface
using the magnets on the bottom of the unit.
Wall Mounting Installation
y There is a trough on the bottom of the unit, which is used for wall mounting.
y Use two screws to mount the mounting track plate onto the wall.
y Put the unit over the mounting track plate, and slide it to the suitable position.
Screw
Mounting
Track Plate
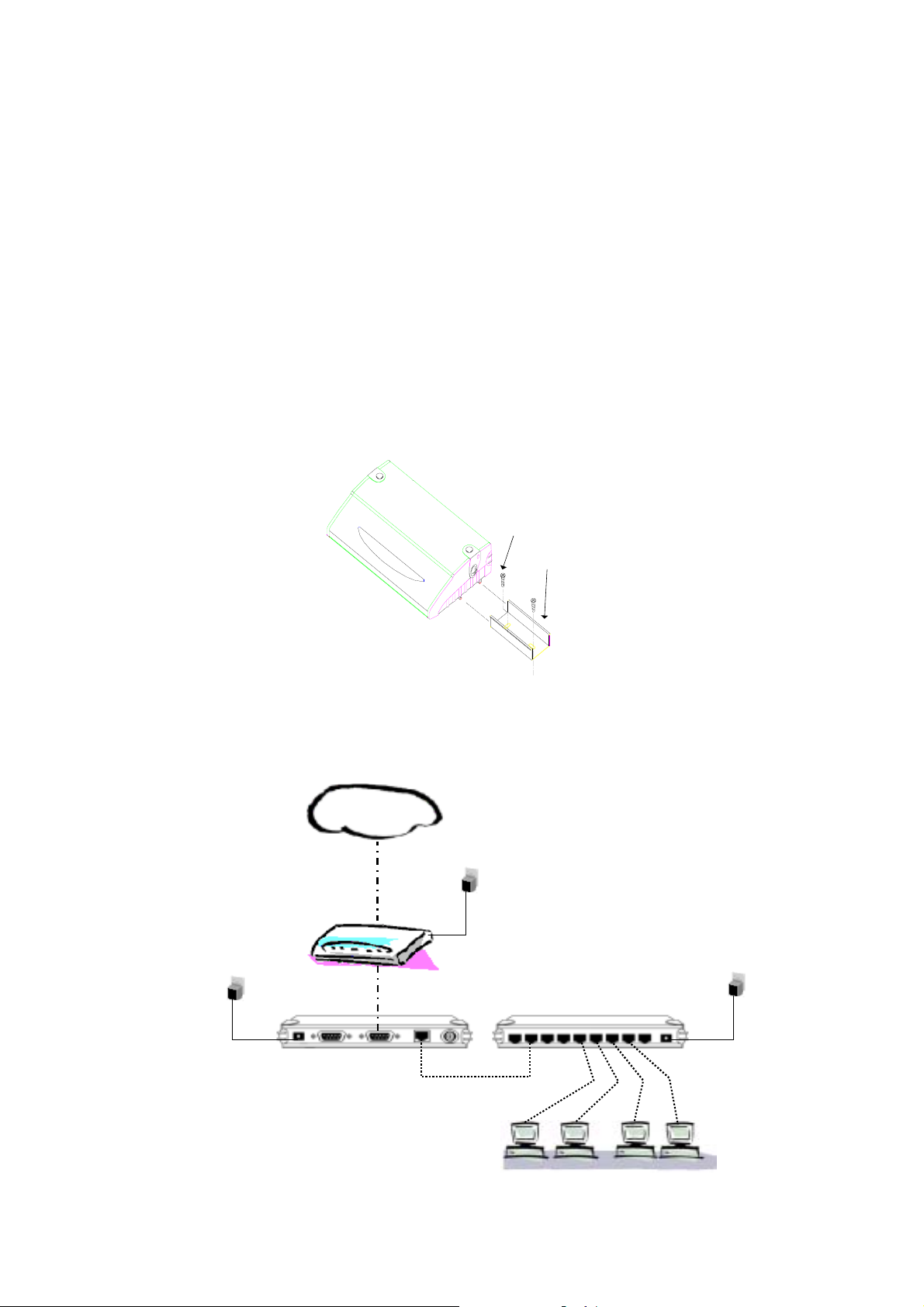
Connecting your equipment
Modem or
ISDN-TA
e
Internet Sharing Station
Internet
d
c
e
f
f
HUB
e
3
Page 5

1. Connecting the Ethernet cable.
Connect a network cable to the Internet Sharing Station’s RJ-45 or BNC port. This unit supports
two types of Ethernet cables: Thin Ethernet (10BASE2, BNC connector) and Twisted Pair
Ethernet (10BASE-T, RJ-45 connector). During power up, the unit automatically detects the type
of network cable and adjusts to that environment.
Note: Please do NOT use both of BNC and RJ-45 connections sim ultaneously.
2. Connect your modem.
Connect an external modem or ISDN TA, using a standard serial cable, to the WAN port on the
back of the unit and to a phone line
Notes:
z Turn off the power before conne cting or disconnecting modems.
z You can connect up to two modems to the Internet Sharing Station
3. Connect the power adapter.
Connect the power adapter to the units. The Power LED should lig ht.
4. Connect the Internet Sharing Station and all of your PCs to hub
Before proceeding this step, make sure each of your PCs has a network interface card installed.
Configuring the Internet Sharing Station
The easiest way to configure the Internet Sharing S tation is to use your existing Web browser. Once you
have set up your PC and installed web browser, you can launch your browser and view web p ages from
the Internet Sharing Station.
Setting up PC to configure the web
Before using browser to find the web pages from Internet Sharing Station, you have to manually configure
your PC for TCP/IP networking. The DHCP server function of Internet Sharing Station is enabled defaultly,
your PCs should be set to obtain an IP address automatically. This procedure is described in the following
section.
To configure a Windows NT 3.51 system
1. Open the Main group in Program Manager.
2. Open the Control Panel and open the Network icon.
3. Select TCP/IP Protocol within the Inst alled Network Software Window or inst all it if necessary . See
your Windows documentation.
4. Click the Configure button and select the Adapter Type.
5. Check the Enable Automatic DHCP Configuration checkbox.
6. Type your co mputer name in the Host name box. Click OK to close the TCP/IP configuration window.
7. Click OK to close and restart your computer.
To configure a Windows NT 4.0 system
1. Right-click Network Neighborhood and click Properties.
2. Click the Protocols tab and select the TCP/IP Protocol in the list. If TCP/IP does not appear, install it.
See your Windows documentation.
3. Click the Properties button and select the adapter type.
4. Make sure “Obtain an IP Address from A DHCP Server” is selected.
5. Type your co mputer name in the Host name box.
6. Click OK on the bottom of the TCP/IP window.
7. Click OK to close and restart your computer.
4
Page 6
To configure a Windows 95/98 system
1. Right-click Network Neighborhood.
2. Click Properties on the pop-up menu.
3. Click the Configuration tab and select the TCP/IP networking component and click Properties.
4. Make sure “Obtain an IP Address Automatically” is selected.
5. Select the DNS Configuration tab, and select Disable DNS.
6. Select the Gateway tab and remove any addresses. Click OK.
7. Click OK to close the Network Control window.
8. Click OK to close and restart your computer.
To configure other systems
See the documentation for your operating system and set the system up for TCP/IP. Configure the system
to be a DHCP client. If the system doesn’t support DHCP, set an IP address that is not conflicted to that
system and in the range from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.252.
Configuring the Internet Sharing Station
After you finish setting up and restart your computer, you can open web browser, type the following in the
Location (or Addres s) window, and press Ente r.
http://192.168.0.254
You should then see the first screen, which will prompt you for a password. Defaul t password is “admin”,
just type admin, then click OK to continue to the configure screen.
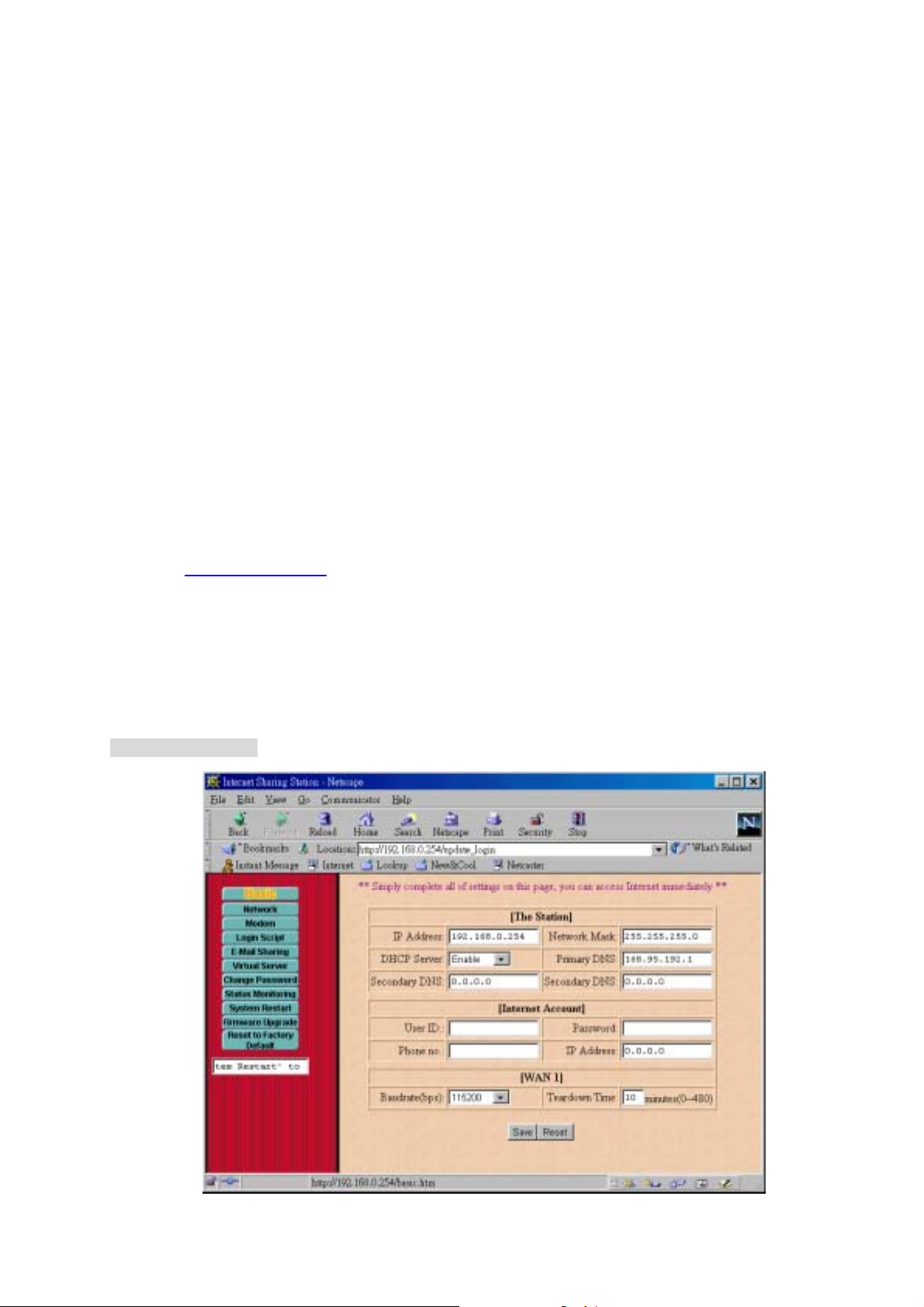
Quick Configuration
Simply connect modem to the WAN 1 port of the Internet Sharing Station, and complete all settings on
this first page, then restart the Internet Sharing Station, and then restart all of the PCs, you are ready to
access Internet.
Basic Configuration
5
Page 7
IP
Address:
Network
Mask:
[The
Station]
[Internet Account]
[WAN 1]
DHCP
Server:
Primary
DNS:
Secondar
y DNS:
Baudrate
(bps)
Teardown
Time
IP address for the Internet Sharing Station. Use the default value (192.168.0.254)
unless the address is already in use.
The default value 255.255.255.0 is OK for small networks.
Select “Enable” to enable the function of DHCP service for local LAN. Select
“Disable” to disable the function of DHCP service
Enter the DNS IP address (default value is 168.95.192.1) provided by your ISP.
Enter the other DNS IP address provided by your ISP, if possible.
Define the Internet account for the WAN 1 port.
User ID.: Enter the account name provided by your ISP.
Password: Enter the password for the corresponding account name.
Phone No.: Enter your ISP’s telephone number. Use the format described in your
modem’s user manual.
IP Address: Enter the IP address assigned to you by your ISP. For dynamic IP
address assignment, the IP address is 0.0.0.0.
Assign the data transmission speed on the serial line of WAN 1. Available speeds are
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 230400 bps
The period of idle time allowed when a connection is established. When timer
expired, the connection will be disconnected.
Advanced Configurations
Network Configuration
Network Settings:
6
Page 8
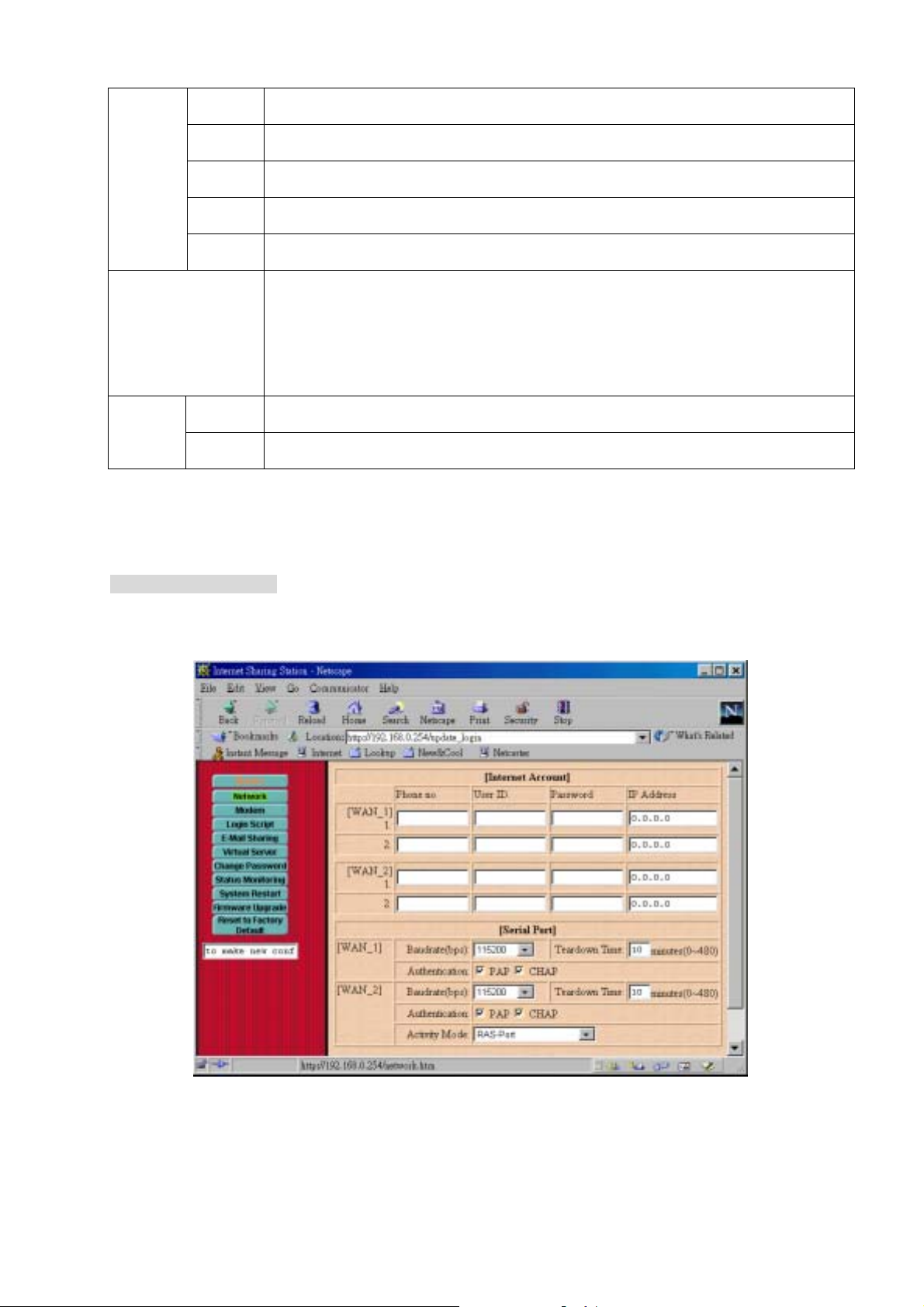
[Internet Account]
Baudrate
(bps)
Serial Port
[WAN 1]
Teardown
Time
Authentica
tion
Baudrate
(bps)
Teardown
Time
Serial Port
[WAN 2]
Authentica
tion
Activity
Mode
Modem Configuration
Define Internet accounts for each WAN 1 and WAN 2 ports.
Phone No.: Enter your ISP’s telephone number. Use the format described in your
modem’s user manual.
User ID.: Enter the account name provided by your ISP.
Password: Enter the password for the corresponding account name.
IP Address: Enter the IP address assigned to you by your ISP. For dynamic IP
address assignment, the IP address is 0.0.0.0.
Assign the data transmission speed on the serial line of WAN 1. Available speeds are
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 230400 bps
The period of idle time allowed when a connection is established. When timer
expired, the connection will be disconnected.
The allowed password checking protocols in PPP authentication phase.
(defaults to select both)
Assign the data transmission speed on the serial line of WAN 2. Available speeds are
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 230400 bps
The period of idle time allowed when a connection is established. When timer
expired, the connection will be disconnected.
The allowed password checking protocols in PPP authentication phase.
(defaults to select both)
Disable: WAN 2 will always be disabled
Bandwidth-on-Demand (BoD): WAN 2 will be activated only when WAN 1’s
bandwidth is full-load.
Always: WAN 2 will always be activated when the first client accesses the Internet.
RAS-Port: WAN 2 acts as a RAS port that allows user remote dial-in.
7
Page 9

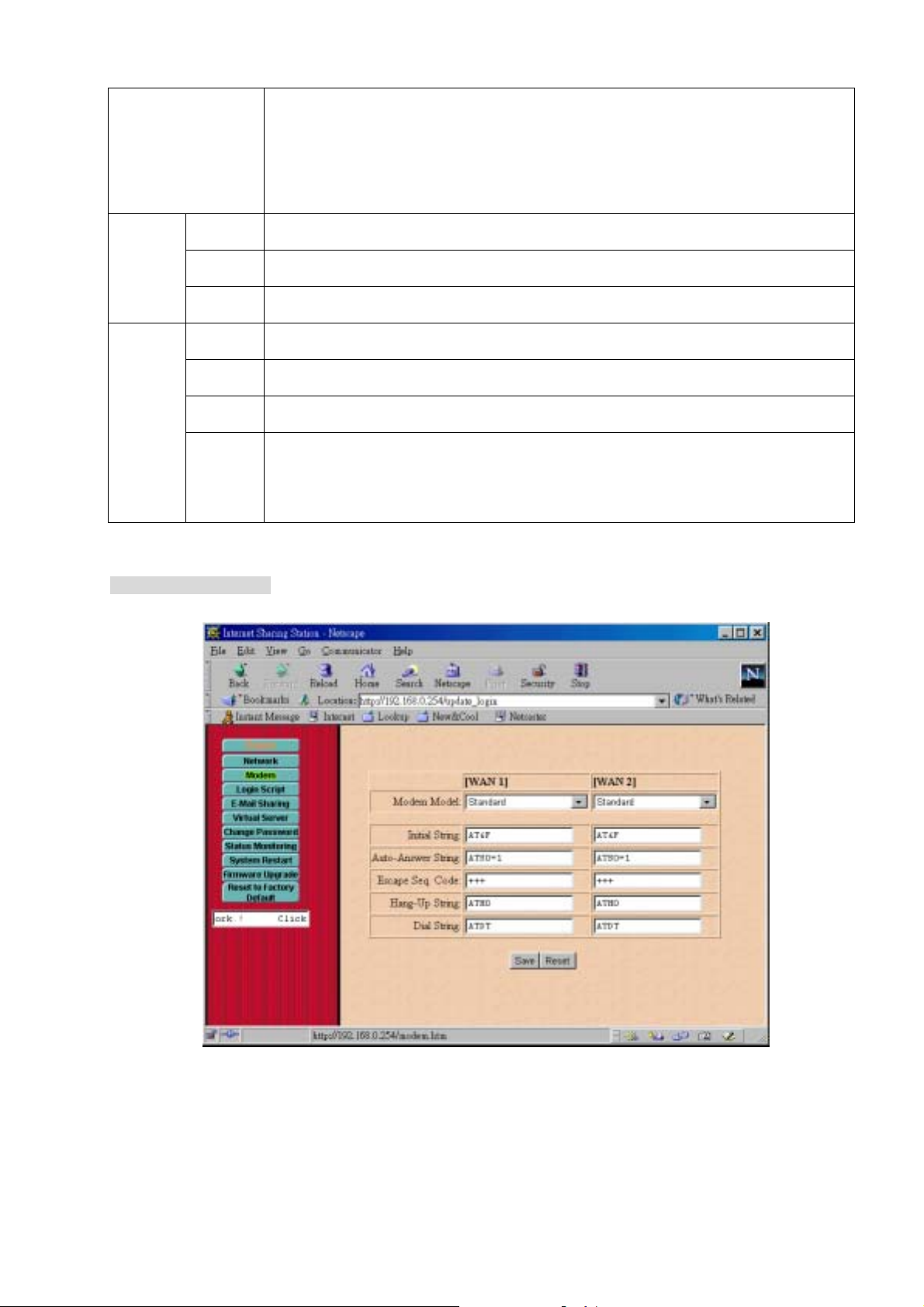
Modem AT Command Settings
If your model is listed, simply select it , then the modem initial string will be configured
automatically.
Model:
If your model is not listed, try “Standard” or “S tandard 56K” modem
If it still not work, select “Other”. You will have to enter the modem initial strings, as described
below. (You have to refer to modem’s user manual to set these strings)
Initial String: Specifies the command to configure your modem or ISDN TA correctly
Auto-Answe
Specifies the comm and to set the modem or ISDN TA’s auto-answer mode
r String:
Escape
Specifies the cod e to change modem from data transmission to AT command mode
Seq. Code:
Hang-Up
Specifies the command to hang-up phone call for modem
String:
Dial String:
Specifies the command (sometimes calle d “Dial Prefix String”) to dial a phone call for modem
or ISDN TA
Login Script Configuration
If your ISP uses a scripting process for logging onto the network before startin g a PPP connection, you
can do this with the login script. The login script lets you write a script that automatically logs in and starts
your PPP session as if you had typed the commands. Each line in the script waits for a prompt from the
host computer or sends a response to the host computer.
Login Script Settings
Enable Set “YES” to run script file before PPP takes over; set “NO” to run PPP directly
Line## The login script commands and some examples are described on Appendix A
8
Page 10

Email Sharing Configuration
The usage of Email sharing allows one Email account shared with multiple users. The [Mail Server
Account] specifies the shared Email account, and the [Local User Account] specify the sharing users. The
detail configurations to some popular Email clients such as “Outlook”, “Eudo ra”, and “Netscape
Messenger” are described on Appendix B.
Remote Access Service Configuration
Configures WAN 2 as RAS-Port
Internet
Internet
pc1 pc2
192.168.0.254
RAS-Port
192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2
Support Network Neighborhood
Internet Sharing Station
192.168.0.253
All allowed dial-in users are defined as E-mail Sharing users as described previous page. In this case, the
allowed users are supervisor, pc1, pc2, pc3, pc4, pc5, pc6, and pc7.
Note that the auto-answer mode should be enabled on the modem that connects to WAN 2, i.e., in the
modem configuration on WAN 2 port, the Auto-Answer-String should be set to “ATS0=x”, where x is a
number which large than or equal to 1.
9
Page 11

Virtual Server Configuration
Internet Sharing Station
Internet
Internet
CHAT Server
(192.168.0.10)
WWW Server
(192.168.0.1)
FTP Server
(192.168.0.2)
Telnet Server
(192.168.0.3)
External port on IS020
Any incoming IP packets send to the
external port will redirect to this
internal server on this port
This shows the internal servers that allowed to be accessed through the Internet Sharing Station from
Internet. Type 0.0.0.0 will prevent the Internet users from accessing the internal servers.
Virtual Server settings
FTP Server: Specifies the IP address of the computer that will act as FTP server on your local LAN
Telnet Server: Specifies the IP address of the computer that will act as Telnet server on your local LAN
WWW
Specifies the IP address of the computer that will act as WWW server on your local LAN
Server:
Console Password Configuration
The current password can be changed, the new password will be required for the next time that you want
to configure the unit.
10
Page 12

Firmware Upgrade Procedure
You may follow the procedure specified in this page to update your firmwa re.
Reset to Factory Default
This feature let all configurations return to the initial factory value.
System Restart
If complete all configurations, the new values may effect after you restart the Internet Sha ring Station.
Setting up the other PCs
Once the Internet Sharing Station has been configured on your LAN, it is ready for use. However, all of
the PCs must have a network interface card installed, and they must be co nfigured for TCP/IP
networking.
You have to set up all of the PCs on your LAN to be DHCP client s that will obtain an IP address from
Internet Sharing Station automatically. The following describes how to configure your Win95 station to be
a DHCP client. For other operating systems, see Setting up PC to configure web.
1. Right-click Network Neighborhood.
2. Click Properties on the pop-up menu.
3. Click the Configuration tab and select the TCP/IP networking component and click Properties.
4. Make sure “Obtain an IP address automat ically” is selected, like the following.
5. Select the DNS Configuration tab, and select Disable, but the fields can be lef t blank.
6. Select the Gateway tab and remove any addresses. Click OK.
7. Click OK to close the Network Control window.
8. Click OK to close and restart your computer, and you can access Internet.
11
Page 13

Note:
1 Once the Internet Sharing Station has been configured, all of the PCs should be restarted to get the
new TCP/IP settings from the Internet Sharing Station.
2 After restarting your computer, please make sure your computer has obtained an IP address, DNS
and Gateway IP address(192.168.0.254).
Customizing TCP/IP settings
The Internet Sharing Station is preconfigured for installation on a network that is not set up for TCP/IP. It
uses a range of private IP addresses in a range from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.254, with the address of
the Internet Sharing Station preset to 192.168.0.254.
If you have already set up the TCP/IP protocol on your network, you can customize the Internet Sharing
Station to fit your existing IP policy.
To customize TCP/IP settings for your existing network
1. Configure one of your PCs to be a DHCP client, and restart it, then your PC will obtain an IP address
automatically from Internet Sharing Station.
2. From the selected computer, launch web browser and connect to the Internet Sharing Station web
page (http://192.168.0.254), if the system on your network already have public IP addresses, set
‘DHCP Server:’ to “Disabl e”, then click “Save” button.
3. Change the Internet Sharing Station’s IP Address to the address that is valid for your network, then
click “Save” button, and then click ‘System Restart’ to restart the Internet Sharing Station.
4. Change the IP address of the selected computer b ack to its original setting.
5. Make sure the Gateway IP address of all PCs must be same as the Internet Sharing Station’s IP
address, DNS must be enabled, and DNS IP address(es) must be assigned.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting gives you solutions to problems that may occur during installation and operation of the
Internet Sharing Station.
1. Problem: No power to the Internet Sharing Station
Possible Cause: The power adapter is a defective one.
Solution: Check the power cord and power outlet to verify its connection. If it still remains unlit,
please replaced another power adapter.
2. Problem: Can’t connect to the Internet Sharing Station
Solution: 1. Check the TCP/IP setup on your PC.
On Windows 95/98: Run winipcfg from Run on the Start menu. The PC should have an
IP address of 192.168.0.n, where n is from 1 to 252. The Gateway IP address of the PC
must be 192.168.0.254. If the IP address is not in the range, click Release then click
12
Page 14

Renew.
On Windows NT: Ty p e ipconfig from the command prompt. The PC should have an IP
address of 192.168.0.n, where n is from 1 to 252. The Gateway IP address of the PC
must be 192.168.0.254. If the IP address is not in the range, type the following
commands:
ipconfig / release
ipconfig / renew
2. If you have used proxy on the browser, make sure it has 192.168.0.254 as an
exception
In Internet Explorer: Add 192.168.0.254 as an exception
In Netscape Navigator: Add 192.168.0.254 as an exception, mentioned as follow.
3. Problem: Can’t connect to the Internet
Solution: 1. Check the phone link
y Check the phone line. If it’s a regular analog line, connect a telephone and see if you
get a dial tone. Dial your ISP number to see if you get a modem tone.
y Is a 9 required for an outside line ?
2. Check the TCP/IP setup on your PC.
On Windows 95/98: Run winipcfg from Run on the Start menu. The PC should have an
IP address of 192.168.0.n, where n is from 1 to 252. The Gateway IP address of the PC
must be 192.168.0.254, and the DNS Server address(es) must not be empty. If the IP
address is not in the range, click Release then click Rene w.
On Windows NT: Ty p e ipconfig from the command prompt. The PC should have an IP
address of 192.168.0.n, where n is from 1 to 252. If the IP address is not in the range,
type the following commands:
ipconfig / release
ipconfig / renew
4. Problem: Can not communicate with the ISP.
Solution: 1. This is mostly likely a problem due to the fact that your baudrate setting is too high for
your modem or ISDN TA. Sometimes the maximum baudrate that your modem or ISDN
TA claims it can achieve is not really attainable because of phone line quality
2. Talk to your ISP to see if the login script is required.
13
Page 15

5. Problem: My Modem/ISDN TA is working fine with my PC running Windows 95. How do I find its
initial string ?
Solution:
1. Select My Computer, then Dial-Up Networking.
2. Select the icon for your connection, then properties.
3. Click the Configure button, then Connection tab.
4. Select Advanced , then check the option Record a log file, click OK and exit.
5. Use Dial-up Networking to make your on-line connection normally. A log file
MODEMLOG.TXT will be created in your Windows directory.
6. Examine the file to determine the Initial String,
14
Page 16

Specifications
Standards and Protocols
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T and 10BASE2
TCP/IP, PPP, CHAP/PAP/MS-CHAP, DHCP
Operational Characteristics
LAN port: 10BASE2/10BASE-T auto sensing
WAN speed: 230.4Kbps max. DTE speed
Power Characteristics
External Power Adapter:
Input Voltage: 100VAC, 60Hz / 120VAC, 60Hz / 230VAC, 50Hz / 240VAC, 50Hz
Output Volt age: 9 VDC, 1 A
Physical Characteristics
Number of ports: 1 x 10BASE-T/10BASE2, 2 x RS-232
Panel indicators: PWR, Link, Activity , Full Duplex, Error, Utilization/Baudrate
Weight: 0.28 kg
Dimensions: 135 x 104 x 35 mm (L x W x H)
Temperature:
Operating: 0℃ to 40℃;
Storage: – 20℃ to 70℃
Humidity: 5% to 95% (non-condensing)
Approvals:
EMI: FCC Class B,VCCI Class B, CISPR 22 Class B
Safety: TÜV/GS, UL, cUL
Regulatory Standards Compliance
EMI Information
FCC Class B (For USA Only)
FCC ID: NUKISCCM020
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Warning! This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from the one
which the receiver is connected to
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
You may use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) for RJ-45 connections.
VCCI Class B (For Japan Only)
15
Page 17

CE Mark Declaration of Conformity for EMC and Safety(EEC)
EMC:
EN55022 (1994)/CISPR 22 (1993) class B
IEC 1000-4-2 (1995) 4kV CD, 8kV AD
IEC 1000-4-3 (1995) 3V V/m
IEC 1000-4-4 (1995) 1kV - (power line) , 0.5kV - (signal line)
This product complies with the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and the EMC
Directive 89/336/EEC
Safety Compliance
EN60950, UL 1950
Sicherheitshinweise
1. Die Steckdose muß sich in der Nähe des Gerätes befinden und leicht zugänglich sein.
2. Zum Reinigen den Stecker aus der Steckdose ziehen. Beim Reinigen keine Flüssigreiniger oder
Sprays verwenden, sondern ein angefeuchtetes Tuch.
3. Das gerät nicht in Naßräume oder in der Nähe von Wasser benutzen, wie z.B. Badezimmer,
Schwimmbad, Spülbecken usw. . Das Eindringen von Wasser kann zur Zerstörung des Gerätes
führen.
4. Das gerät nicht auf einer unstabilen Unterlage, wie z.B. Rollwagen, Gestell usw., aufstellen. Es
könnte herunterfallen und Verletzungen oder Beschädigungen von Mensch und Gerät verursache n.
5. Die Belüftungsöffnungen nicht blockieren oder auf falscher Ober-fläche, wie Bett, Sofa usw., stellen.
Durch die Blockierung kann es zur Zerstörung des Gerätes durch Überhitzu ng kommen.
6. Versuchen Sie niemals dieses Gerät selbst zu warten, da beim Öffnen oder Abnehmen des
Gehäuses die Gefahr eines elektrischen Schlages besteht.
7. Keine Gegenstände auf das Anschlußkabel stellen, damit es nicht durch scharfe Kanten zerstört
werden kann.
8. Keinerlei Gegenstände durch die Öffungen in das Gerät stecken, da es dadurch sonst zu
Kurzschlüssen kommen kann.
9. Bei Störungen des G erätes den Wartungsdienst verständigen.
10. Bei Reperaturen dürfen nur Orginalersatzteile oder Bauteile mit gleichen Eigenschaften verwendet
werden. Andere Bauteile können Feuer , elektrischen Schlag oder andere Gefahren verursachen.
11. Nach Beendigung von Wartungsarbeiten oder Reperaturen durch den Kundendienst sollte die
Sicherheitsprüfung durchgeführt werden.
12. Bei längerem Stillstand des Gerätes, ist diese von der Versorgungs- spannung zu trennen. Dies
verhindert eine Beschädigung des Gerätes durch eine Überspannung in der Zuleitung.
13. Der arbeitsplatzbezogene Lärmschutzpegel nach DIN 45 635 ist kleiner 70dB (A).
16
Page 18

Appendix A: Login Script Files
This section describes the script file commands and syntax to be used when e diting script files.
Script file is only required if your ISP does not use a standard PPP negotiation.
Learn the script syntax
Five commands can be used to automate a proprietary negotiation process. The commands are as
follows:
send “<string>”
wait “<string>”
send_id
send_passwd
hangup
run or run_ppp
Send a data string and then go to next line
Wait to receive a data string, and then go to next line
Send user name
Send password corresponding to the user
Hang Up Modem
Start to run PPP and ignore rest of script
Example of the Login Script File
1. Scenario
Your ISP instructs you to log in and issue a PPP command. The system prompts for a login and
password. After the ISP’s host sends a welcome message, you enter the “ppp” command. If you
logged in manually with a username of “juns” and a password of “1234”, it would look like this:
Enter username: juns
Enter password: 1234
Welcome to Hinet!
ppp
Script for this scenario
Your script should look like this:
Wait “:”
Send “juns”
Wait “:”
Send “1234”
Wait “!”
Send “ppp”
Run_ppp
Note: You only need to include the last specific character in the text, in this case “!” in “Welcome to
Hinet!”
2. Script file used for CompuServe
The following is the login script used to log on to CompuServe.
Send
Send “CIS”
Wait “:”
Send_id
Wait “:”
Send_passwd
Wait “!”
Send “GO PPPCONNECT”
Run_ppp
17
Page 19

Appendix B: Configure Your E-mail Clients For E-mail Sharing Function
Email Sharing Operation Model
Internet
pc1
pc2
192.168.0.254
Internet
Email Server:
Host name: ms25.hinet.net
User name: unextest
Password : xxxxxxxx
E-mail setting on pc1 (or pc2) :
User name: pc1 (or pc2)
Password: xxxx
Incoming POP3 server: 192.168.0.254
Outgoing SMTP server: ms25.hinet.net
Send mail to pc1 :
1. pc1<unextest@ms25.hinet.net>, or
2.”pc1”<unextest@ms25.hinet.net>
In this case, E-mail sharing function allows your ISP E-mail address called unextest@ms25.hinet.net be
shared by PC1 and PC2, so that they can have their own e-mail address, mentioned as follow:
“pc1”<unextest@ms25.hinet.net> For PC1’s e-mail address
“pc2”<unextest@ms25.hinet.net> For PC2’s e-mail address
Outlook Express
Step 1: Select Tools->Accounts->Mail
1. Select one account
2. Press “Properties” button
18
Page 20

Netscape Messenger
Step 3: Fill in the incoming and outgoing mail server
The real mail server
The IP address of Intern e t Sharing Station
The user name defined in Internet Sharing
Station
The password for this user on Inte rn et Sharing
Station
Step 2: Fill in aliases name and real email address
Select the user name defined in IS020
The shared E-mail account
19
Page 21

Step 1: Select Edit->Preferences->Mail & Newsgroup->Identity
Select the user na me defined in
Internet Sharing Station
The shared E-mail account
Step 2: Fill in the incoming and outgoing mail server
The IP address of
Internet Sharing
Station
The real mail server
The user name de fined
in Internet Shari n g
Station
20
Page 22

Step 3: ->Select 192.168.0.254->Edit
Select “POP3 Server” as the
mail receiving pr o t oc ol
The user name defined in
Internet Sharing Station
Eudora 1.5.4 ~ 3.x.x
Step 1: Select Tools->Options->Getting Started
Select the email account on
Internet Sharing Station
Select the user n ame defined in
Internet Sharing Station
21
Page 23

Step 2: Tools->Options->Sending Mail
The shared E-mail account
The real mail server
Eudora 4.x.x and above
Step 1: Select Tools->Options->General
Select the user name defined in
Internet Sharing Station
The shared E-mail account
The IP address of Internet
Sharing Station
Select the user name defined in
Internet Sharing Station
The real mail server
22
Page 24

23
 Loading...
Loading...