Page 1

Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor
9000 and 9100 Series
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9050
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9040
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 8 MB L3 Cache 9030
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.42 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9020
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.4 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9015
Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 6 MB L3 Cache 9010
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66/1.6 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9152
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9150M
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9150N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9140M
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9140N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.42 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9120N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 8 MB L3 Cache 9130M
Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9110N
Datasheet
October 2007
Document Number: 314054-002
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving,
life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future
changes to them
The Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® 9000 and 9100 series processor may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may
cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained
by calling1-800-548-4725, or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel, Itanium, and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United
States and other countries.
Copyright © 2002-2007, Intel Corporation
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
I2C is a two-wire communication bus /protocol developed by Phillips. SMBus is a subset of the I2C bus/protocol developed by Intel.
Implementation of the I2C bus/protocol or the SMBus bus/protocol may require licenses from various entities, including Phillips
Electronics, N.V. and North American Phillips Corporation.
2 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction............................................................................................................... 11
1.1 Overview ......................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Processor Abstraction Layer................................................................................ 11
1.3 Mixing Processors of Different Frequencies and Cache Sizes .................................... 12
1.4 Terminology ..................................................................................................... 12
1.5 State of Data.................................................................................................... 12
1.6 Reference Documents ........................................................................................ 13
2 Electrical Specifications ............................................................................................... 15
2.1 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series System Bus.................. 15
2.1.1 System Bus Power Pins ........................................................................ 15
2.1.2 System Bus No Connect ....................................................................... 15
2.2 System Bus Signals ........................................................................................... 15
2.2.1 Signal Groups ..................................................................................... 15
2.2.2 Signal Descriptions .............................................................................. 17
2.3 Package Specifications ....................................................................................... 18
2.4 Signal Specifications.......................................................................................... 18
2.4.1 Maximum Ratings................................................................................ 22
2.5 System Bus Signal Quality Specifications and Measurement Guidelines ..................... 23
2.5.1 Overshoot/Undershoot Magnitude.......................................................... 23
2.5.2 Overshoot/Undershoot Pulse Duration .................................................... 24
2.5.3 Activity Factor..................................................................................... 24
2.5.4 Reading Overshoot/Undershoot Specification Tables................................. 24
2.5.5 Determining if a System Meets the Overshoot/Undershoot
Specifications...................................................................................... 25
2.5.6 Wired-OR Signals ................................................................................ 25
2.6 Voltage Regulator Connector Signals.................................................................... 27
2.7 System Bus Clock and Processor Clocking............................................................. 31
2.8 Recommended Connections for Unused Pins.......................................................... 33
3 Pinout Specifications................................................................................................... 35
4 Mechanical Specifications............................................................................................. 65
4.1 Processor Package Dimensions............................................................................ 65
4.1.1 Voltage Regulator (MVR) to Processor Package Interface........................... 71
4.2 Package Marking ............................................................................................... 72
4.2.1 Processor Top-Side Marking ..................................................................72
4.2.2 Processor Bottom-Side Marking ............................................................. 73
5 Thermal Specifications ................................................................................................ 75
5.1 Thermal Features ..............................................................................................75
5.1.1 Thermal Alert...................................................................................... 75
5.1.2 Enhanced Thermal Management ............................................................ 76
5.1.3 Power Trip.......................................................................................... 76
5.1.4 Thermal Trip....................................................................................... 76
5.2 Case Temperature ............................................................................................. 76
6 System Management Feature Specifications ................................................................... 79
6.1 System Management Bus ................................................................................... 79
6.1.1 System Management Bus Interface........................................................ 79
6.1.2 System Management Interface Signals ................................................... 79
6.1.3 SMBus Device Addressing ..................................................................... 81
6.2 Processor Information ROM ................................................................................ 82
6.3 Scratch EEPROM ............................................................................................... 85
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 3
Page 4

6.4 Processor Information ROM and Scratch EEPROM Supported SMBus
Transactions .....................................................................................................85
6.5 Thermal Sensing Device .....................................................................................86
6.6 Thermal Sensing Device Supported SMBus Transactions..........................................87
6.7 Thermal Sensing Device Registers........................................................................88
6.7.1 Thermal Reference Registers .................................................................88
6.7.2 Thermal Limit Registers ........................................................................89
6.7.3 Status Register....................................................................................89
6.7.4 Configuration Register ..........................................................................89
6.7.5 Conversion Rate Register ......................................................................90
A Signals Reference .......................................................................................................91
A.1 Alphabetical Signals Reference ............................................................................91
A.1.1 A[49:3]# (I/O).......................................................................................91
A.1.2 A20M# (I) .............................................................................................91
A.1.3 ADS# (I/O)............................................................................................91
A.1.4 AP[1:0]# (I/O).......................................................................................91
A.1.5 ASZ[1:0]# (I/O).....................................................................................91
A.1.6 ATTR[3:0]# (I/O) ...................................................................................92
A.1.7 BCLKp/BCLKn (I) ....................................................................................92
A.1.8 BE[7:0]# (I/O).......................................................................................92
A.1.9 BERR# (I/O) ..........................................................................................93
A.1.10 BINIT# (I/O)..........................................................................................94
A.1.11 BNR# (I/O)............................................................................................94
A.1.12 BPM[5:0]# (I/O) ....................................................................................94
A.1.13 BPRI# (I) ..............................................................................................94
A.1.14 BR[0]# (I/O) and BR[3:1]# (I).................................................................94
A.1.15 BREQ[3:0]# (I/O)...................................................................................95
A.1.16 CCL# (I/O) ............................................................................................96
A.1.17 CPUPRES# (O) .......................................................................................96
A.1.18 D[127:0]# (I/O).....................................................................................96
A.1.19 D/C# (I/O) ............................................................................................96
A.1.20 DBSY# (I/O)..........................................................................................96
A.1.21 DBSY_C1# (O).......................................................................................96
A.1.22 DBSY_C2# (O).......................................................................................96
A.1.23 DEFER# (I)............................................................................................96
A.1.24 DEN# (I/O)............................................................................................97
A.1.25 DEP[15:0]# (I/O) ...................................................................................97
A.1.26 DHIT# (I)..............................................................................................97
A.1.27 DPS# (I/O)............................................................................................98
A.1.28 DRDY# (I/O)..........................................................................................98
A.1.29 DRDY_C1# (O).......................................................................................98
A.1.30 DRDY_C2# (O).......................................................................................98
A.1.31 DSZ[1:0]# (I/O) ....................................................................................98
A.1.32 EXF[4:0]# (I/O) .....................................................................................98
A.1.33 FCL# (I/O) ............................................................................................99
A.1.34 FERR# (O).............................................................................................99
A.1.35 GSEQ# (I).............................................................................................99
A.1.36 HIT# (I/O) and HITM# (I/O)....................................................................99
A.1.37 ID[9:0]# (I) ..........................................................................................99
A.1.38 IDS# (I)................................................................................................99
A.1.39 IGNNE# (I)............................................................................................99
A.1.40 INIT# (I)...............................................................................................99
A.1.41 INT (I) ................................................................................................100
A.1.42 IP[1:0]# (I).........................................................................................100
A.1.43 LEN[2:0]# (I/O) ...................................................................................100
A.1.44 LINT[1:0] (I) .......................................................................................100
4 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 5

A.1.45 LOCK# (I/O)........................................................................................ 100
A.1.46 NMI (I) ............................................................................................... 101
A.1.47 OWN# (I/O) ........................................................................................ 101
A.1.48 PMI# (I) ............................................................................................. 101
A.1.49 PWRGOOD (I)...................................................................................... 101
A.1.50 REQ[5:0]# (I/O) .................................................................................. 101
A.1.51 RESET# (I) ......................................................................................... 102
A.1.52 RP# (I/O) ........................................................................................... 102
A.1.53 RS[2:0]# (I) ....................................................................................... 103
A.1.54 RSP# (I) ............................................................................................. 103
A.1.55 SBSY# (I/O)........................................................................................ 103
A.1.56 SBSY_C1# (O)..................................................................................... 103
A.1.57 SBSY_C2# (O)..................................................................................... 103
A.1.58 SPLCK# (I/O) ...................................................................................... 103
A.1.59 STBn[7:0]# and STBp[7:0]# (I/O)......................................................... 103
A.1.60 TCK (I) ............................................................................................... 104
A.1.61 TDI (I)................................................................................................ 104
A.1.62 TDO (O).............................................................................................. 104
A.1.63 THRMTRIP# (O) ................................................................................... 104
A.1.64 THRMALERT# (O)................................................................................. 104
A.1.65 TMS (I)............................................................................................... 104
A.1.66 TND# (I/O) ......................................................................................... 104
A.1.67 TRDY# (I) ........................................................................................... 105
A.1.68 TRST# (I) ........................................................................................... 105
A.1.69 WSNP# (I/O)....................................................................................... 105
A.2 Signal Summaries ........................................................................................... 105
Figures
2-1 Generic Clock Waveform .................................................................................... 21
2-2 SMSC Clock Waveform....................................................................................... 22
2-3 System Bus Signal Waveform Exhibiting Overshoot/Undershoot............................... 23
2-4 Processors Power Tab Physical Layout .................................................................. 28
2-5 System Bus Reset and Configuration Timings for Cold Reset.................................... 31
2-6 System Bus Reset and Configuration Timings for Warm Reset ................................. 32
3-1 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Pinout.......................... 35
4-1 Processor Package............................................................................................. 66
4-2 Package Height and Pin Dimensions..................................................................... 67
4-3 Processor Package Mechanical Interface Dimensions .............................................. 69
4-4 Processor Package Top-Side Components Height Dimensions .................................. 70
4-5 Processor Package Bottom-Side Components Height Dimensions ............................. 70
4-6 Processor to MVR Interface Loads........................................................................ 71
4-7 Processor Top-Side Marking on IHS ..................................................................... 73
4-8 Processor Bottom-Side Marking Placement on Interposer........................................ 74
5-1 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Thermal
Features .......................................................................................................... 75
5-2 Itanium® Processor Package Thermocouple Location.............................................. 77
6-1 Logical Schematic of SMBus Circuitry ................................................................... 80
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 5
Page 6

Tables
2-1 Itanium® Processor System Bus Signal Groups ......................................................16
2-2 Nominal Resistance Values for Tuner1, Tuner2, and Tuner3.....................................17
2-3 Processor Package Specifications .........................................................................18
2-4 AGTL+ Signals DC Specifications..........................................................................19
2-5 Power Good Signal DC Specifications....................................................................19
2-6 System Bus Clock Differential HSTL DC Specifications.............................................19
2-7 TAP Connection DC Specifications ........................................................................19
2-8 SMBus DC Specifications.....................................................................................20
2-9 LVTTL Signal DC Specifications ............................................................................20
2-10 System Bus Clock Differential HSTL AC Specifications .............................................20
2-11 SMBus AC Specifications.....................................................................................21
2-12 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings.............................22
2-13 Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group and Wired-OR Signal Group
Absolute Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance ............................................................25
2-14 Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group Time-Dependent Overshoot/
Undershoot Tolerance for 400-MHz System Bus .....................................................26
2-15 Wired-OR Signal Group (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#)
Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance for 400-MHz System Bus......................................26
2-16 Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group Time-Dependent Overshoot/
Undershoot Tolerance for 533-MHz System Bus .....................................................26
2-17 Wired-OR Signal Group (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#)
Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance for 533-MHz System Bus......................................27
2-18 VR Connector Signals .........................................................................................27
2-19 Power Connector Pinouts ....................................................................................28
2-20 Processors Core Voltage Identification Code (VCORE and VCACHE)...........................30
2-21 Connection for Unused Pins.................................................................................33
2-22 TUNER1/TUNER3 Translation Table.......................................................................34
3-1 Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name ...........................................................36
3-2 Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location........................................................50
4-1 Processor Package Dimensions ............................................................................67
4-2 Processor Package Mechanical Interface Dimensions...............................................68
4-3 Processor Package Load Limits at Power Tab .........................................................71
5-1 Case Temperature Specification...........................................................................77
6-1 System Management Interface Signal Descriptions.................................................79
6-2 Thermal Sensing Device SMBus Addressing on the Dual-Core Intel
Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 series.............................................................81
6-3 EEPROM SMBus Addressing on the Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor
9000 and 9100 Series ........................................................................................82
6-4 Processor Information ROM Format ......................................................................82
6-5 Current Address Read SMBus Packet ....................................................................85
6-6 Random Address Read SMBus Packet ...................................................................86
6-7 Byte Write SMBus Packet....................................................................................86
6-8 Write Byte SMBus Packet....................................................................................87
6-9 Read Byte SMBus Packet ....................................................................................87
6-10 Send Byte SMBus Packet ....................................................................................87
6-11 Receive Byte SMBus Packet.................................................................................87
6-12 ARA SMBus Packet.............................................................................................87
6-13 Command Byte Bit Assignment............................................................................88
6-14 Thermal Sensing Device Status Register ...............................................................89
6-15 Thermal Sensing Device Configuration Register......................................................89
6-16 Thermal Sensing Device Conversion Rate Register..................................................90
®
6 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 7

A-1 Address Space Size ........................................................................................... 92
A-2 Effective Memory Type Signal Encoding................................................................ 92
A-3 Special Transaction Encoding on Byte Enables ....................................................... 93
A-5 BR0# (I/O), BR1#, BR2#, BR3# Signals for 2P Rotating Interconnect ...................... 95
A-4 BR0# (I/O), BR1#, BR2#, BR3# Signals for 4P Rotating Interconnect ...................... 95
A-6 BR[3:0]# Signals and Agent IDs ......................................................................... 95
A-7 DID[9:0]# Encoding .......................................................................................... 97
A-8 Extended Function Signals .................................................................................. 98
A-9 Length of Data Transfers .................................................................................. 100
A-10 Transaction Types Defined by REQa#/REQb# Signals........................................... 102
A-11 STBp[7:0]# and STBn[7:0]# Associations .......................................................... 104
A-12 Output Signals ................................................................................................ 105
A-13 Input Signals .................................................................................................. 105
A-14 Input/Output Signals (Single Driver) .................................................................. 106
A-15 Input/Output Signals (Multiple Driver)................................................................ 107
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 7
Page 8

Revision History
Document
Number
314054 -002
314054 -001 • Initial release of the document. July 2006
Revision
Number
Description Date
• Updated with 9100 series product information; updated brand name from
“Itanium 2” to “Itanium”.
October 2007
8 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 9

Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and
9100 Series
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9050
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9040
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 8 MB L3 Cache 9030
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.42 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9020
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.4 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9015
Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 6 MB L3 Cache 9010
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9150M
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 24 MB L3 Cache 9150N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9140M
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 18 MB L3 Cache 9140N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.42 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9120N
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.66 GHz with 8 MB L3 Cache 9130M
Intel® Itanium® Processor 1.6 GHz with 12 MB L3 Cache 9110N
Product Features
Dual Core
— Two complete 64-bit processing cores on one
processor.
EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing)
Technology for current and future requirements of
high-end enterprise and technical workloads
— Provide a variety of advanced
implementations of parallelism, predication,
and speculation, resulting in superior
Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP).
Hyper-Threading Technology
— Two times the number of OS threads per core
provided by earlier single-thread
implementations.
Wide, parallel hardware based on Intel® Itanium
architecture for high performance:
— Integrated on-die L3 cache of up to 24MB;
cache hints for L1, L2, and L3 caches for
reduced memory latency.
— 128 general and 128 floating-point registers
supporting register rotation.
— Register stack engine for effective
management of processor resources.
— Support for predication and speculation.
Extensive RAS features for business-critical
applications:
— Full SMBus compatibility.
— Enhanced machine check architecture with
extensive ECC and parity protection.
— Enhanced thermal management.
— Built-in processor information ROM (PIROM).
— Built-in programmable EEPROM.
— Socket Level Lockstep
— Core Level Lockstep
a. This feature is applicable to only the 9100 series processors
®
Intel® Virtualization Technology for virtualization for
data-intensive applications.
— Reduces virtualization complexity.
— Improves virtualization performance.
— Increases operating system compatibility.
Intel® Cache Safe Technology ensures mainframecaliber availability.
— Minimize L3 cache errors.
Outstanding Energy Efficiency.
— 20 percent less power than previous Intel
Itanium processor.
— 2.5 times higher performance per watt.
High-bandwidth system bus for multiprocessor
scalability:
— Up to 8.53GB/s bandwidth.
— 128-bit wide data bus.
— 50-bits of physical memory addressing and
64-bits of virtual addressing.
— Up to four physical processors on the same
system bus at 400-MHz or 533-MHz data bus
frequency.
— Expandable to systems with multiple system
buses.
Features to support flexible platform environments:
— IA-32 Execution Layer supports IA-32
application binaries.
— Bi-endian support.
— Processor abstraction layer eliminates
processor dependencies.
667-MHz, 1.66-GHz, 3-load bus
— This feature enables increased bandwidth for
Enterprise and HPC.
Demand Based Switching (DBS)
— Provides additional power management
capability.
a
a
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 9
Page 10

The Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® processor 9000 and 9100 series delivers new levels of flexibility,
reliability, performance, and cost-effective scalability for your most data-intensive business and
technical applications. With double the performance of previous Intel Itanium processors, the DualCore Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series provides more reasons than ever to migrate your
business-critical applications off RISC and mainframe systems and onto cost-effective Intel
architecture servers. The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series provides close to
triple the amount of L3 cache (24 megabytes), Hyper-Threading Technology for increased
performance, Intel® Virtualization Technology for improved virtualization, Intel® Cache Safe
Technology for increased availability, and 20 percent lower power consumption.
Dual-Core Itanium®-based systems are available from leading OEMs worldwide and run popular 64bit operating systems such as Microsoft* Windows Server* 2003; Linux* from SuSE, Red Hat, Red
Flag, and other distributions; HP NonStop*; OpenVMS*; and HP-UX*. More than 7,000 applications
are available for Itanium-based systems, from vendors such as Microsoft, BEA, IBM, Ansys, Gaussian,
Symantec/VERITAS, Oracle, SAP, and SAS. And with industry support growing and future Intel
Itanium processor family advances already in development, your Itanium-based server investment
will continue to deliver performance advances and savings for your most demanding applications.
§
10 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 11

Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series employs Explicitly Parallel
Instruction Computing (EPIC) design concepts for a tighter coupling between hardware
and software. In this design style, the interface between hardware and software is
engineered to enable the software to exploit all available compile-time information and
efficiently deliver this information to the hardware. It addresses several fundamental
performance bottlenecks in modern computers, such as memory latency, memory
address disambiguation, and control flow dependencies. The EPIC constructs provide
powerful architectural semantics and enable the software to make global optimizations
across a large scheduling scope, thereby exposing available Instruction Level
Parallelism (ILP) to the hardware. The hardware takes advantage of this enhanced ILP,
and provides abundant execution resources. Additionally, it focuses on dynamic runtime optimizations to enable the compiled code schedule to flow at high throughput.
This strategy increases the synergy between hardware and software, and leads to
greater overall performance.
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series provides a 6-wide and 8stage deep pipeline, running at up to 1.6 GHz. This provides a combination of abundant
resources to exploit ILP as well as increased frequency for minimizing the latency of
each instruction. The resources consist of six integer units, six multimedia units, two
load and two store units, three branch units, two extended-precision floating-point
units, and one additional single-precision floating-point unit per core. The hardware
employs dynamic prefetch, branch prediction, a register scoreboard, and non-blocking
caches to optimize for compile-time non-determinism. Three levels of on-die cache
minimize overall memory latency. This includes up to a 24 MB L3 cache, accessed at
core speed, providing up to 8.53 GB/sec. of data bandwidth. The system bus is
designed to support up to four physical processors (on a single system bus), and can
be used as an effective building block for very large systems. The balanced core and
memory subsystem provide high performance for a wide range of applications ranging
from commercial workloads to high-performance technical computing.
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series supports a range of
computing needs and configurations from a two-way to large SMP servers. This
document provides the electrical, mechanical and thermal specifications for the DualCore Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series for use while employing systems
with the processors.
1.2 Processor Abstraction Layer
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series requires implementationspecific Processor Abstraction Layer (PAL) firmware. PAL firmware supports processor
initialization, error recovery, and other functionality. It provides a consistent interface
to system firmware and operating systems across processor hardware
implementations. The Intel® Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 2: System Architecture, describes PAL. Platforms must provide access to the
firmware address space and PAL at reset to allow the processors to initialize.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 11
Page 12

Introduction
The System Abstraction Layer (SAL) firmware contains platform-specific firmware to
initialize the platform, boot to an operating system, and provide runtime functionality.
Further information about SAL is available in the Intel®Itanium®Processor Family
System Abstraction Layer Specification.
1.3 Mixing Processors of Different Frequencies and
Cache Sizes
All Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series on the same system bus
are required to have the same cache size (24 MB, 18 MB, 12 MB, 8 MB or 6 MB) and
identical core frequency. Mixing components of different core frequencies and cache
sizes is not supported and has not been validated by Intel. Operating system support
for multiprocessing with mixed components should also be considered.
While Intel has done nothing to specifically prevent processors within a multiprocessor
environment from operating at differing frequencies and differing cache sizes, there
may be uncharacterized errata that exist in such configurations. Customers would be
fully responsible for validation of system configurations with mixed components other
than the supported configurations described above.
1.4 Terminology
In this document, “the processor” refers to the “Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor
9000 and 9100 series” processor, unless otherwise indicated.
A ‘#’ symbol after a signal name refers to an active low signal. This means that a signal
is in the active state (based on the name of the signal) when driven to a low level. For
example, when RESET# is low, a processor reset has been requested. When NMI is
high, a non-maskable interrupt has occurred. In the case of lines where the name does
not imply an active state but describes part of a binary sequence (such as address or
data), the ‘#’ symbol implies that the signal is inverted. For example, D[3:0] = ‘HLHL’
refers to a hex ‘A’, and D [3:0] # = ‘LHLH’ also refers to a hex ‘A’ (H = High logic level,
L = Low logic level).
The term “system bus” refers to the interface between the processor, system core logic,
and other bus agents. The system bus is a multiprocessing interface to processors,
memory, and I/O.
A signal name has all capitalized letters, for example, VCTERM.
A symbol referring to a voltage level, current level, or a time value carries a plain
subscript, for example, V
1.5 State of Data
The data contained in this document is subject to change. It is the best information
that Intel is able to provide at the publication date of this document.
, or a capitalized, abbreviated subscript, for example, TCO.
core
12 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 13

Introduction
1.6 Reference Documents
The reader of this specification should also be familiar with material and concepts
presented in the following documents:
Intel®Itanium®2 Processor Specification Update
Intel® Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1:
Application Architecture
Intel® Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2: System
Architecture
Intel® Itanium® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 3: Instruction Set Reference
®
Itanium®2 Processor Reference Manual for Software Development and
Intel
Optimization
Intel®Itanium®Processor Family System Abstraction Layer Specification
ITP700 Debug Port Design Guide
System Management Bus Specification
Note: Contact your Intel representative or check http://developer.intel.com for the latest
revision of the reference documents.
§
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 13
Page 14

Introduction
14 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 15

Electrical Specifications
2 Electrical Specifications
This chapter describes the electrical specifications of the Dual-Core Intel Itanium
Processor 9000 and 9100 series.
2.1 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and
9100 Series System Bus
Most Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series signals use the Itanium
processor’s assisted gunning transceiver logic (AGTL+) signaling technology. The
termination voltage, V
reference voltage. The buffers that drive most of the system bus signals on the
processor are actively driven to V
times and reduce noise. These signals should still be considered open-drain and require
termination to V
terminated to V
termination, in which case, the termination is provided by external resistors connected
to V
CTERM
.
CTERM
CTERM
, is generated on the baseboard and is the system bus high
CTERM
during a low-to-high transition to improve rise
CTERM
which provides the high level. The processor system bus is
at each end of the bus. There is also support of off-die
AGTL+ inputs use differential receivers which require a reference signal (V
used by the receivers to determine if a signal is a logical 0 or a logical 1. The processor
generates V
source.
on-die, thereby eliminating the need for an off-chip reference voltage
REF
2.1.1 System Bus Power Pins
VCTERM (1.2 V) input pins on the processor provide power to the driver buffers and ondie termination. The GND pins, in addition to the GND input at the power tab connector,
provide ground to the processor. Power for the processor core is supplied through the
power tab connector by V
to provide power to the system management bus (SMBus). The V
pins must remain electrically separated from each other.
Core
, V
Cache, Vfixed.
2.1.2 System Bus No Connect
All pins designated as “N/C” or “No Connect” must remain unconnected.
2.2 System Bus Signals
2.2.1 Signal Groups
Table 2-1 shows processor system bus signals that have been combined into groups by
buffer type and whether they are inputs, outputs, or bidirectional, with respect to the
processor.
). V
REF
The 3.3 V pin is included on the processor
, 3.3 V, and GND
CTERM
REF
is
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 15
Page 16

..
Table 2-1. Itanium® Processor System Bus Signal Groups
Group Name Signals
AGTL+ Input Signals BPRI#, BR[3:1]#, DEFER#, GSEQ#, ID[9:0]#, IDS#, RESET#1, RS[2:0]#,
AGTL+ I/O Signals A[49:3]#, ADS#, AP[1:0]#, BERR#, BINIT#, BNR#, BPM[5:0]#1, BR0#,
AGTL+ Output Signals FERR#, THRMTRIP#, DBSY[1:0]#, DRDY[1:0]#, SBSY[1:0]#
Special AGTL+ Asynchronous
Interrupt Input Signals
Power Good Signal
HSTL Clock Signals BCLKn, BCLKp
TAP Input Signals
TAP Output Signals
System Management Signals13.3 V, SMA[2:0], SMSC, SMSD, SMWP, THRMALERT#
Power Signals GND, VCTERM
LVTTL Power Pod Signals
Other TERMA, TERMB, TUNER1, TUNER2, TUNER3, VCCMON, VSSMON
Notes:
1. Signals will not be terminated on-die even when on-die termination (ODT) is enabled. See the Intel®Itanium
2 Processor Hardware Developer’s Manual for further details.
1
1
1
1
RSP#, TRDY#
D[127:0]#, DBSY#, DEP[15:0]#, DRDY#, HIT#, HITM#, LOCK#,
REQ[5:0]#, RP#, SBSY#, STBN[7:0]#, STBP[7:0]#, TND#
A20M#, IGNNE#, INIT#, LINT[1,0], PMI#
PWRGOOD
TCK, TDI, TMS, TRST#
TDO
CPUPRES#, OUTEN, PPODGD#
Electrical Specifications
®
All system bus outputs should be treated as open drain signals and require a high-level
source provided by the V
AGTL+ inputs have differential input buffers which use V
output signals require termination to V
CTERM
supply.
as a reference level. AGTL+
. In this document, “AGTL+ Input Signals”
CTERM
REF
refers to the AGTL+ input group as well as the AGTL+ I/O group when receiving.
Similarly, “AGTL+ Output Signals” refers to the AGTL+ output group as well as the
AGTL+ I/O group when driving.
The Test Access Port (TAP) connection input signals use a non-differential receiver with
levels that are similar to AGTL+. No reference voltage is required for these signals. The
TAP Connection Output signals are AGTL+ output signals.
The processor system bus requires termination on both ends of the bus. The processor
system bus supports both on-die and off-die termination controlled by two pins, TERMA
and TERMB. Please see the TERMA and TERMB pin description in Section 2.2.2.
The HSTL clock signals are the differential clock inputs for the processor. The SMBus
signals and LVTTL power pod signals are driven using the 3.3 V CMOS logic levels listed
in Table 2-8 and Table 2-9, respectively.
16 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 17

Electrical Specifications
2.2.2 Signal Descriptions
Appendix A, “Signals Reference”, contains functional descriptions of all system bus
signals and LVTTL power pod signals. Further descriptions of the system management
signals are contained in Chapter 6. The signals listed under the “Power” and “Other”
group are described here:
V
CTERM
GND System ground.
N/C No connection can be made to these pins.
TERMA, TERMB The processor uses two pins to control the on-die termination
TUNER1, TUNER2,
TUNER3 The TUNER1 Pin can either be left as a no-connect or left
VCCMON, VSSMON These pins allows remote measurement of on-die Vcore voltage.
System bus termination voltage.
function: TERMA and TERMB. Both of these termination pins
must be pulled to VCTERM in order to terminate the system bus
using the on-die termination resistors. Both of these termination
pins must be pulled to GND in order to use off-die termination.
connected to VCTERM via resistor for the majority of platforms
supporting the Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and
9100 series. The TUNER2 resistor is used to control the
termination resistance for the system bus I/O buffers. A lower
resistance will cause a lower on-die termination resistance. Ondie termination mode will only be selected if the TERMA and
TERMB pins are terminated as indicated above. The TUNER3 pin
will not be required for the majority of platforms supporting the
Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series. The
TUNER3 pin is used only in the case where A[21:17]# are driven
to all zeros or all ones during the configuration cycles at reset.
When all zeros or all ones are observed by the processor the
presence of the TUNER3 and TUNER1 pins is used to determine
system bus frequency. See Table 2-22 for the various TUNER pin
combinations and resulting system bus frequency and slew rate
combination.
No connections that constitute a current load can be made to
these pins.
Table 2-2. Nominal Resistance Values for Tuner1, Tuner2, and Tuner3
5-Load Platform (Ohms)
Tuner1: NC
Tuner2: 150
Tuner3: NC
Notes:
1. Depending on system configuration, the processor may or may not require a resistor on the
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 17
400 MHz
1
1
TUNER pin. OEMs may leave the pin unconnected or connect it to VCTERM through a 150
or 100 ohm resistor. If A[21:17]:# are driven to all 0’s or all 1’s at reset, see Table 2-22
for proper use of the TUNER Pins.
3-Load Platform (Ohms)
Tuner1: NC
Tuner2: 150
Tuner3: NC
400 MHz
1
1
3-Load Platform (Ohms)
Tuner1: NC
Tuner2: 150
Tuner3: NC
533 MHz
1
1
Page 18
2.3 Package Specifications
Table 2-3 through Table 2-9 list the DC voltage, current, and power specifications for
the processor. The voltage and current specifications are defined at the processor pins.
Operational specifications listed in Table 2-3 through Table 2-9 are only valid while
meeting specifications for case temperature, clock frequency, and input voltages.
Table 2-3. Processor Package Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Symbol Parameter
V
core, PSVCC
V
cache, PSVcache
V
fixed, PSVfixed
V
CTERM
R
TERM
V
TAP
I
core,PS
I
cache,PS
I
fixed,PS
I
CTERM
PS
TT
PWR
max
PWR
TPE
PWR
TDP
Notes:
1. The range for Vcore is 1.0875 V to 1.25 V.
2. Vcache typical is 1.025 V.
3. The processor system bus is terminated at each end of the system bus. The processor supports both on-die
and off-die termination which is selected by the TERMA and TERMB pins. Termination tolerance is ±15% for
on-die termination measured at VOL and ±1% for off-die termination.
4. This is measured for On-Die Termination with a 45-ohm pull up resistor.
5. Max power is peak electrical power that must be provided for brief periods by the VR.
6. Represents the TDP level that should be used for system thermal design. Sustained power for all real-world
applications will remain at or below this power level.
from the Voltage
Regulator
from the Voltage
Regulator
from the Voltage
Regulator
Termination Voltage All 1.2-1.5% 1.2 1.2+1.5% V
Recommended Termination
Resistance
Test Access Port Voltage
)
(VCC
TAP
Core Current Required from
Power Supply
Cache Current Required from
Power Supply
Fixed Current Required from
Power Supply
Termination Voltage Current All 7.2 A
Power Supply Slew Rate for
the Termination Voltage at the
Processor Pins
Max Power All 177 W
Thermal Power Envelope All 130 W
Thermal Design Power – dual
core
Thermal Design Power –
single core
Core
Frequency
All VID-17 mV VID VID+17 mV V
All VID-17 mV VID VID+17 mV V
All 1.25-20 mV 1.25 1.25+20 mV V
All 45-15% 45 45+15% Ohm
All 1.2-1.5% 1.2 1.5 V
All 2.8 89 121 A
All 2.0 17 18 A
All 0.7 9.2 11 A
All 0.05 A/ns
All 104 W
1.6 GHz 75 W
Minimum Typ Maximum Unit Notes
1
2
3
4
5
6
2.4 Signal Specifications
This section describes the DC specifications of the system bus signals. The processor
signal’s DC specifications are defined at the processor pins. Table 2-4 through Table 2-9
describe the DC specifications for the AGTL+, PWRGOOD, HSTL clock, TAP port, system
management, and LVTTL signals. Please refer to the ITP700 Debug Port Design Guide
for the TAP connection signals’ DC specifications at the debug port.
18 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 19
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-4. AGTL+ Signals DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
I
OL
I
OL
I
L
C
AGTL+
Notes:
1. The typical transition point between VIL and VIH assuming 125 mV V
V
REF_low
and V
2. Parameter measured into a 22.5 ohm resistor to 1.2 V. Minimum VOL and IOL are guaranteed by design/
characterization.
3. Calculated using off-die termination through two 45 ohm ±1% resistors in parallel.
4. Calculated using on-die termination to a 45 ±15% resistor measured at VOL.
5. At 1.2 V ±1.5%. V
6. Total of I/O buffer with ESD structure and processor parasitics if applicable. Capacitance values guaranteed
by design for all AGTL+ buffers.
Input Low Voltage All 0.625 V
Input High Voltage All 0.875 V
Output Low Voltage All 0.3 0.4 V
Output High Voltage All V
Output Low Current @ 0.3 V All 34 mA
Output Low Current @ 0.3 V All 17 mA
Leakage Current All ±100 µA
AGTL+ Pad Capacitance All 2 pF
levels are V
levels are V
REF_low
±100 mV, respectively, for a system bus agent using on-board termination. V
REF
±125 mV, respectively, for a system bus agent using on-die termination.
REF
, minimum Vpin V
CTERM
Core
Frequency
, maximum.
CTERM
Minimum Typ Maximum Unit Notes
1
1
2
,
CTERM
minimum
V
CTERM
REF
V
,
CTERM
maximum
uncertainty for ODT. V
V
REF_high
3
4
5
6
and
REF_high
Table 2-5. Power Good Signal DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
Input Low Voltage 0.440 V
Input High Voltage 0.875 V
Table 2-6. System Bus Clock Differential HSTL DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
IH
V
IL
V
X
C
CLK
Input High Voltage 0.78 1.3 V
Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.5 V
Input Crossover Voltage 0.55 0.85 V
Input (Pad) Capacitance 1.75 pF
Table 2-7. TAP Connection DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
I
OL
I
IC
Notes:
1. There is a 100 mV hysteresis on TCK.
2. VIH, MAX = 1.5 V + 5%, VOH, MAX = 1.2 V +5%.
3. There is no internal pull-up. An external pull-up is always assumed. Max voltage tolerated at TDO is 1.5 V.
4. Per input pin.
Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.5 V
Input High Voltage 1.1 1.57 V
Output Low Voltage 0.3 V
Output High Voltage 1.2 V
Output Low Current 20 mA
Input Current 690 uA
1
1, 2
2, 3
4
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 19
Page 20
Table 2-8. SMBus DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Typ Maximum Unit Notes
3.3V VCC for the System Management
Components
V
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
IL
IH
OL
3.3V
OL
OL2
LI
LO
Input Low Voltage –0.3 0.3*3.3 V V
Input High Voltage 2.31 3.47 V Max =
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V
3.3V Supply Current 5.0 30.0 mA
Output Low Current 3 mA
Output Low Current 6 mA
Input Leakage Current 10 µA
Output Leakage Current 10 µA
Notes:
1. The value specified for IOLapplies to all signals except for THRMALERT#.
2. The value specified for I
applies only to THRMALERT#, which is an open drain signal.
OL2
Table 2-9. LVTTL Signal DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
Input Low Voltage 0.8 V
Input High Voltage 2.0 3.63 V
Output Low Voltage 0.4 V
Output High Voltage 2.4 V
Electrical Specifications
3.14 3.3 3.47 V 3.3 V ±5
3.3 +5%
Min +
0.7*3.3V
1
2
Table 2-10 through Table 2-11 list the AC specifications for the processor’s clock and
SMBus (timing diagrams begin with Figure 2-1). The processor uses a differential HSTL
clocking scheme with a frequency of 200, 266, or 333 MHz. The SMBus is a subset of
the I2C* interface which supports operation of up to 100 kHz.
Table 2-10.System Bus Clock Differential HSTL AC Specifications (Sheet 1 of 2)
System
Symbol Parameter
T
BCLKp Period 200 5.0 ns Figure 2-1
period
T
skew
f
BCLK
T
jitter
T
high
T
low
T
period
T
skew
f
BCLK
T
jitter
T
high
T
low
System Clock Skew 200 100 ps
BCLKp Frequency 200 200 200 MHz Figure 2-1
BCLKp Input Jitter 200 100 ps Figure 2-1
BCLKp High Time 200 2.25 2.5 2.75 ns Figure 2-1
BCLKp Low Time 200 2.25 2.5 2.75 ns Figure 2-1
BCLKp Period 266 3.75 ns Figure 2-1
System Clock Skew 266 60 ps
BCLKp Frequency 266 266 266 MHz Figure 2-1
BCLKp Input Jitter 266 50 ps Figure 2-1
BCLKp High Time 266 1.69 1.88 2.06 ns Figure 2-1
BCLKp Low Time 266 1.69 1.88 2.06 ns Figure 2-1
Bus
Clock
(MHz)
Minimum Typ Maximum Unit Figure Notes
1
2
3
4
4
5
2
3
4
4
20 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 21
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-10.System Bus Clock Differential HSTL AC Specifications (Sheet 2 of 2)
System
Symbol Parameter
T
rise
T
fall
V
PP
Notes:
1. The system clock skew is ±100 ps.
2. Measured on cross-point of rising edge of BCLKp and falling edge of BCLKn. Long-term jitter is defined as peak-to-peak variation
measured by accumulating a large number of clock cycles and recording peak-to-peak jitter.
3. Cycle-to-cycle jitter is defined as peak-to-peak variation measured over 10,000 cycles peak-to-peak jitter.
4. Measured on cross point of rising edge of BCLKp and falling edge of BCLKn.
5. The system clock skew is ±60 ps.
6. V
PPmin
7. The measurement is taken at 40-60% of the signal and extrapolated to 20-80%.
BCLKp Rise Time
BCLKp Fall Time
Minimum Input Swing All 600 mV Figure 2-1
is defined as the minimum input differential voltage which will cause no increase in the clock receiver timing.
7
7
Bus
Clock
(MHz)
All 333 500 667 ps Figure 2-1 20–80%
All 333 500 667 ps Figure 2-1 20–80%
Minimum Typ Maximum Unit Figure Notes
6
Table 2-11. SMBus AC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
f
SMSC
T
SMSC
t
high
t
low
t
rise
t
fall
t
VALID
t
SU
t
HLD
t
FREE
Notes:
1. Please refer to Figure 2-2 for the Standard Microsystems Corporation (SMSC)* clock waveform.
2. Bus Free Time is the minimum time allowed between request cycles.
SMSC Clock Frequency 100 kHz
SMSC Clock Period 10 µs
SMSC Clock High Time 4.0 µs
SMSC Clock Low Time 4.7 µs
SMSC Clock Rise Time 1.0 µs
SMSC Clock Fall Time 0.3 µs
SMBus Output Valid Delay 1.0 µs
SMBus Input Setup Time 250 ns
SMBus Input Hold Time 0 ns
Bus Free Time 4.7 µs
1
1
1
1
2
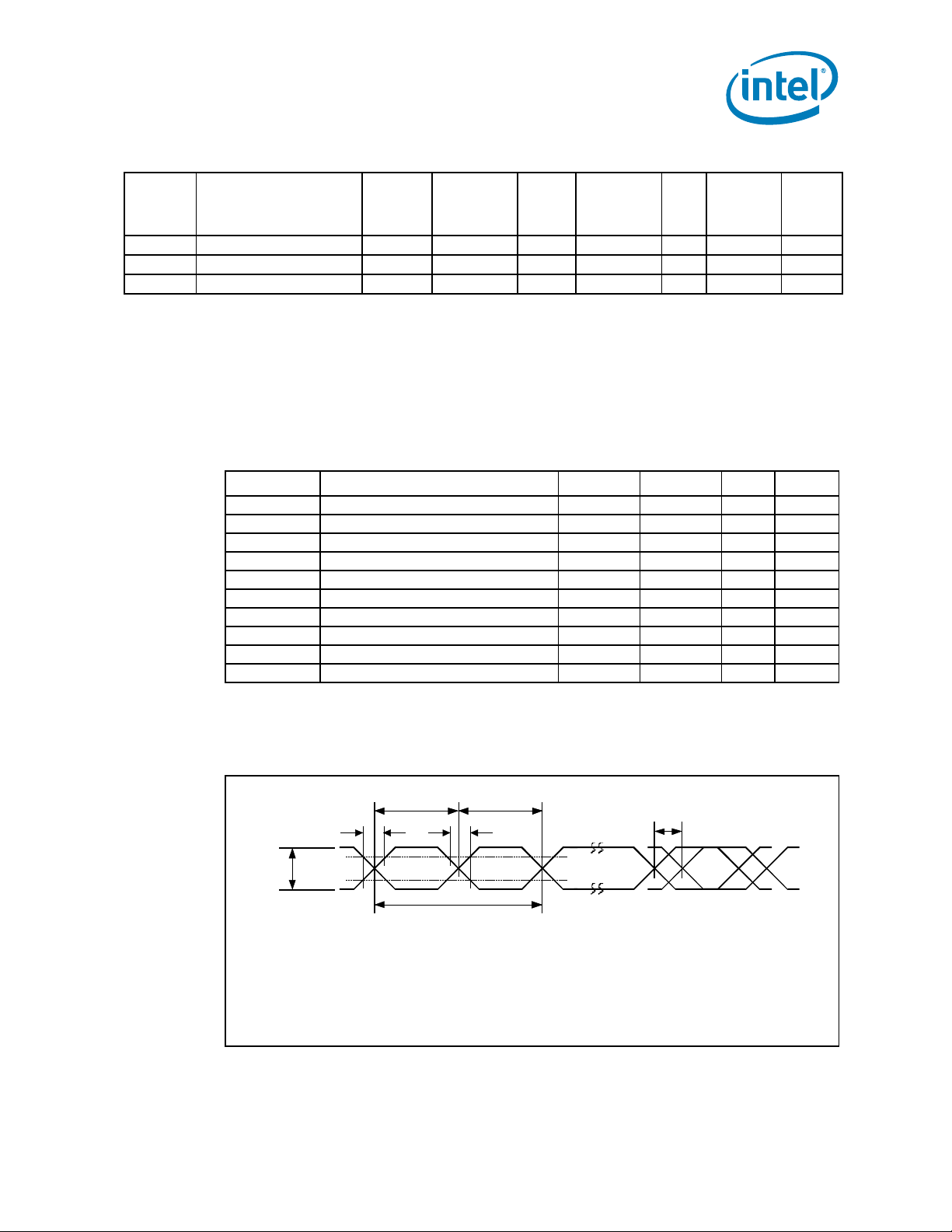
Figure 2-1. Generic Clock Waveform
T
high
T
rise
V
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 21
80%
pp
20%
T
Rise Time
=
rise
T
Fall Time
=
fall
T
High Time
=
high
T
Low Time
=
low
T
period
period
T
jitter
V
pp
T
low
T
fall
BCLKN
BCLKP
=T
Period
=
Long Term Peak-to-Peak Jitter
=
Peak-to-Peak Swing
=
T
jitter
000615
Page 22
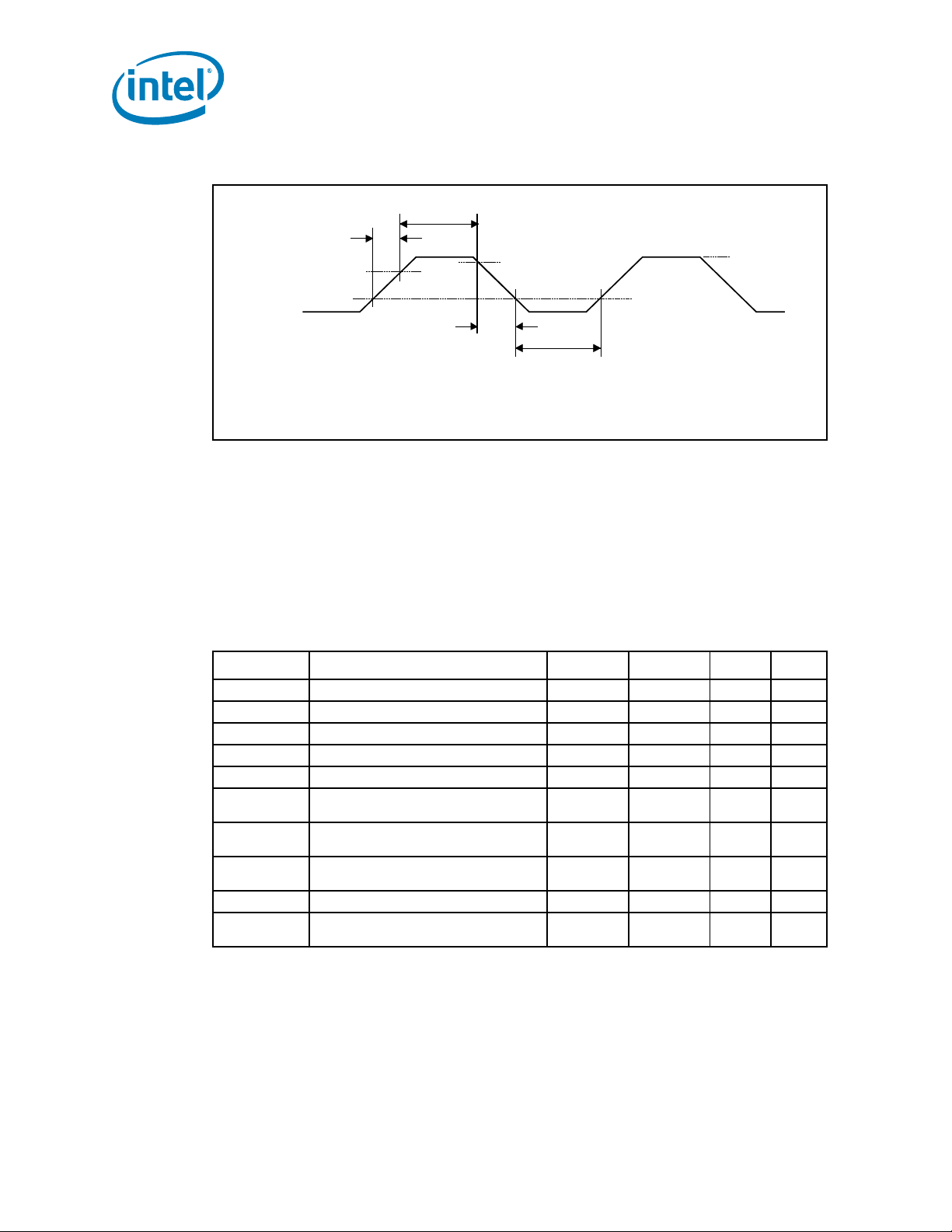
Figure 2-2. SMSC Clock Waveform
T
rise
75% V
T
T
rise
fall
cc
cc
Rise Time
=
Fall Time
=
SMSC
25% V
2.4.1 Maximum Ratings
Table 2-12 contains the processor stress ratings. Functional operation at the absolute
maximum and minimum is neither implied nor guaranteed. The processor should not
receive a clock while subjected to these conditions. Functional operating conditions are
given in the DC tables. Extended exposure to the maximum ratings may affect device
reliability. Furthermore, although the processor contains protective circuitry to resist
damage from static electric discharge, one should always take precautions to avoid
static voltages or electric fields.
T
T
T
high
T
fall
high
low
High Time
=
Low Time
=
90% V
Electrical Specifications
V (3.3V)
cc
T
low
cc
000618
Table 2-12. Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
T
storage
T
shipping
V
core
V
cache
V
fixed
3.3V Any 3.3 V Supply Voltage with Respect to
V
in, SMBus
V
in, AGTL+
V
CTERM
V
in,TAP
Notes:
1. Storage temperature is temperature in which the processor can be stored for up to one year.
2. Shipping temperature is temperature in which the processor can be shipped for up to 24 hours.
3. Parameters are from third-party vendor specifications.
4. Maximum instantaneous voltage at receiver buffer input.
5. Specification includes V
respect to GND.
Processor Storage Temperature –10 45 °C
Processor Shipping Temperature –45 75 °C
Any V
Any V
Any V
GND
SMBus Buffer DC Input Voltage with
Respect to GND
AGTL+ Buffer DC Input Voltage with
Respect to GND
Any V
TAP Buffer DC Input Voltage with Respect
to GND.
Voltage with Respect to GND -0.3 1.55 V
core
Voltage with Respect to GND -0.3 1.55 V
cache
Voltage with Respect to GND -0.3 1.55 V
fixed
–0.3 5.5 V
–0.1 6.0 V
–0.45 1.65 V
Voltage with Respect to GND -0.45 1.65 V
CTERM
-0.45 1.65 V
in,AGTL+
and V
in,AGTL+ ASYNCHRONOUS
(AGTL+ asynchronous buffer DC input voltage with
1
2
3
3
4, 5
4
22 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 23

Electrical Specifications
2.5 System Bus Signal Quality Specifications and
Measurement Guidelines
Overshoot (or undershoot) is the absolute value of the maximum voltage above the
nominal V
undershoot specifications limit transitions beyond V
edge rates. The processor can be permanently damaged by repeated overshoot or
undershoot events on any input, output, or I/O buffer if the charge is large enough
(that is, if the overshoot/undershoot is great enough). Determining the impact of an
overshoot/undershoot condition requires knowledge of the magnitude, the pulse
duration, and the activity factor (AF).
2.5.1 Overshoot/Undershoot Magnitude
Magnitude describes the maximum potential difference between a signal and its voltage
reference level. For the processor, both are referenced to GND, as shown in Figure 2-3.
It is important to note that overshoot and undershoot conditions are separate and their
impact must be determined independently. Overshoot/undershoot magnitude levels
must observe the absolute maximum specifications listed in Table 2-13 through
Table 2-17. These specifications must not be violated at any time, regardless of bus
activity or system state. Within these specifications are threshold levels that define
different allowed pulse duration. Provided that the magnitude of the overshoot/
undershoot is within the absolute maximum specifications, the pulse magnitude,
duration, and activity factors must all be used to determine if the overshoot/
undershoot pulse is within specifications.
voltage (or below GND), as shown in Table 2-3. The overshoot/
CTERM
or GND due to the fast signal
CTERM
Figure 2-3. System Bus Signal Waveform Exhibiting Overshoot/Undershoot
000588
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 23
Page 24

Electrical Specifications
2.5.2 Overshoot/Undershoot Pulse Duration
Pulse duration describes the total time that an overshoot/undershoot event exceeds the
overshoot/undershoot reference voltage (V
encompass several oscillations above the reference voltage. Multiple overshoot/
undershoot pulses within a single overshoot/undershoot event may need to be
measured to determine the total pulse duration.
Note: Oscillations below the reference voltage cannot be subtracted from the total overshoot/
undershoot pulse duration.
/GND). The total time could
CTERM
2.5.3 Activity Factor
Activity factor (AF) describes the frequency of overshoot (or undershoot) occurrence
relative to a clock. Since the highest frequency of assertion of any common clock signal
is every other clock, an AF = 1 indicates that the specific overshoot (or undershoot)
waveform occurs every other clock cycle. Thus, an AF = 0.01 indicates that the specific
overshoot (or undershoot) waveform occurs one time in every 200 clock cycles. For
source synchronous signals (data, and associated strobes), the activity factor is in
reference to the strobe edge. The highest frequency of assertion of any source
synchronous signal is every active edge of its associated strobe. So, an AF = 1
indicates that the specific overshoot (or undershoot) waveform occurs every other
strobe cycle. The specifications provided in Table 2-14 through Table 2-17 show the
maximum pulse duration allowed for a given overshoot/undershoot magnitude at a
specific activity factor. Each table entry is independent of all others, meaning that the
pulse duration reflects the existence of overshoot/undershoot events of that magnitude
ONLY. A platform with an overshoot/undershoot that just meets the pulse duration for a
specific magnitude where the AF <1, means that there can be no other overshoot/
undershoot events, even of lesser magnitude (if AF = 1, then the event occurs at all
times and no other events can occur).
Note: AF for the common clock AGTL+ signals is referenced to BCLKn, and BCLKp frequency.
The wired-OR Signals (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#) are common
clock AGTL+ signals.
Note: AF for source synchronous (2x) signals is referenced to STBP#[7:0], and STBN#[7:0].
2.5.4 Reading Overshoot/Undershoot Specification Tables
The overshoot/undershoot specification for the processor is not a simple single value.
Instead, many factors are needed in order to correctly interpret the overshoot/
undershoot specification. In addition to the magnitude of the overshoot, the following
parameters must also be known: the width of the overshoot and the AF. To determine
the allowed overshoot for a particular overshoot event, the following must be done:
1. Determine the signal group that the particular signal falls into. For AGTL+ signals
operating in the 2x source synchronous domain, use Table 2-14 through
Table 2-16. If the signal is a wired-OR AGTL+ signal operating in the common clock
domain, use Table 2-15 through Table 2-17.
2. Determine the magnitude of the overshoot, or the undershoot (relative to GND).
3. Determine the activity factor (how often does this overshoot occur?).
4. Next, from the appropriate specification table, determine the maximum pulse
duration (in nanoseconds) allowed. The pulse duration shown in the table refers to
the period where either the maximum overshoot (for high phase) and undershoot
(for low phase) occurred.
24 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 25

Electrical Specifications
5. Compare the specified maximum pulse duration to the signal being measured. If
the pulse duration measured is less than the pulse duration shown in the table,
then the signal meets the specifications.
6. Undershoot events must be analyzed separately from overshoot events, as they are
mutually exclusive.
2.5.5 Determining if a System Meets the Overshoot/Undershoot
Specifications
The overshoot/undershoot specifications listed in Table 2-13 through Table 2-17 specify
the allowable overshoot/undershoot for a single overshoot/undershoot event. However,
most systems will have multiple overshoot and/or undershoot events that each has
their own set of parameters (duration, AF and magnitude). While each overshoot on its
own may meet the overshoot specification, the total impact of all overshoot events may
cause the system to fail. A guideline to ensure a system passes the overshoot and
undershoot specifications is shown below:
1. Ensure that no signal ever exceeds V
2. If only one overshoot/undershoot event magnitude occurs, ensure that it meets the
specifications listed in Table 2-13 through Table 2-17.
3. If multiple overshoots and/or multiple undershoots occur, measure the worst-case
pulse duration for each magnitude and compare the results against the AF = 1
specifications. If all of these worst-case overshoot or undershoot events meet the
specifications (measured time < specifications) in the table (where AF = 1), then
the system passes.
CTERM
or GND.
2.5.6 Wired-OR Signals
To ensure platform compatibility between the processors, system bus signals must
meet certain overshoot and undershoot requirements. The system bus wired-OR
signals (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#) have the same absolute
overshoot and undershoot specification as the Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signals, but
they have different time-dependent overshoot/undershoot requirements.
Table 2-13. Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group and Wired-OR Signal Group Absolute
Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance
Parameter Description Specification Units
V
CTERM
V
MAX
V
MIN
Overshoot Time dependent overshoot amount above V
Undershoot Time dependent undershoot amount below GND.
Notes:
1. These parameters cannot be specified in absolute terms.
Notes: The following notes apply to Table 2-14 through Table 2-17:
1. Absolute Maximum Overshoot magnitude of 1.65 V must never be exceeded.
2. Absolute Maximum Overshoot is measured referenced to GND. Pulse duration of overshoot is measured
relative to V
3. Absolute Maximum Undershoot and Pulse Duration of undershoot is measured relative to GND.
4. Ringback below V
5. Lesser undershoot does not allocate overshoot with longer duration or greater magnitude.
6. All values specified by design characterization.
I/O power supply voltage (nominal). 1.20 V
Maximum absolute voltage for system bus signals at the input
of the receiver buffers.
Minimum absolute voltage for system bus signals at the input
of the receiver buffers.
CTERM .
.
CTERM
cannot be subtracted from overshoots/undershoots.
CTERM
1.65 V
–0.45 V
1
1
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 25
Page 26

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-14. Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group Time-Dependent Overshoot/
Undershoot Tolerance for 400-MHz System Bus
Absolute
Maximum (V)
Overshoot
1.65 –0.45 0.0035 0.0036 0.0037 0.0040 0.0121 0.0241 0.1207
1.55 –0.35 0.0124 0.0168 0.0255 0.0520 0.1309 0.2626 1.3107
1.45 –0.25 0.1304 0.1755 0.2671 0.5438 1.3629 2.5 2.5
1.35 –0.15 1.3163 1.7815 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5
1.25 –0.05 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5
Notes:
1. Activity Factor = 1 means signal toggles every 5 ns.
Under-
shoot
1.6 –0.4 0.0039 0.0040 0.0045 0.0157 0.0396 0.0799 0.3996
1.5 –0.3 0.0405 0.0546 0.0833 0.1682 0.4279 0.8546 2.5
1.4 –0.2 0.4136 0.5581 0.8524 1.7215 2.5 2.5 2.5
1.3 –0.1 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5 2.5
AF = 1
1
AF = 0.75 AF = 0.5 AF = 0.25 AF = 0.1 AF = 0.05 AF = 0.01
Pulse Duration (ns)
Table 2-15. Wired-OR Signal Group (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#)
Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance for 400-MHz System Bus
Absolute
Maximum (V)
Overshoot
1.65 –0.45 0.0166 0.0192 0.0306 0.0614 0.1539 0.3067 1.5374
1.55 –0.35 0.1659 0.2216 0.3342 0.6676 1.6734 3.3413 5
1.45 –0.25 1.7343 2.3194 3.4995 5 5 5 5
1.35 –0.15 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
Notes:
1. Activity Factor = 1 means signal toggles every 10 ns.
Under-
shoot
1.6 –0.4 0.0506 0.0674 0.1017 0.2032 0.5090 1.0213 5
1.5 –0.3 0.5413 0.7218 1.0840 2.1814 5 5 5
1.4 –0.2 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
AF = 1
1
AF = 0.75 AF = 0.5 AF = 0.25 AF = 0.1 AF = 0.05 AF = 0.01
Pulse Duration (ns)
Table 2-16. Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group Time-Dependent Overshoot/
Undershoot Tolerance for 533-MHz System Bus (Sheet 1 of 2)
Absolute
Maximum (V)
Overshoot
1.65 –0.45 0.0026 0.0027 0.0028 0.0030 0.0091 0.0181 0.0902
1.55 –0.35 0.0093 0.0126 0.0191 0.0387 0.0980 0.1963 0.9822
1.45 –0.25 0.3095 0.4191 0.6366 1.2965 1.875 1.875 1.875
26 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Under-
shoot
1.6 –0.4 0.0029 0.0030 0.0034 0.0118 0.0297 0.0600 0.2989
1.5 –0.3 0.0303 0.0409 0.0625 0.1268 0.3178 0.6406 1.875
AF = 11AF = 0.75 AF = 0.5 AF = 0.25 AF = 0.1 AF = 0.05 AF = 0.01
Pulse Duration (ns)
Page 27
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-16. Source Synchronous AGTL+ Signal Group Time-Dependent Overshoot/
Undershoot Tolerance for 533-MHz System Bus (Sheet 2 of 2)
Absolute
Maximum (V)
1.4 –0.2 0.9925 1.3358 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875
1.35 –0.15 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875
1.3 –0.10 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875 1.875
Notes:
1. Activity Factor = 1 means signal toggles every 3.75 ns.
Pulse Duration (ns)
Table 2-17. Wired-OR Signal Group (BINIT#, HIT#, HITM#, BNR#, TND#, BERR#)
Overshoot/Undershoot Tolerance for 533-MHz System Bus
Absolute
Maximum (V)
Overshoot
1.65 –0.45 0.01248 0.0144 0.0230 0.0461 0.1155 0.2301 1.1530
1.55 -0.35 0.1250 0.1668 0.2507 0.5004 1.2537 2.5059 3.75
1.45 –0.25 1.3013 1.7396 2.6246 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
1.35 –0.15 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
Notes:
1. Activity Factor = 1 means signal toggles every 7.5 ns.
Under-
shoot
1.6 –0.4 0.0380 0.0507 0.0763 0.1522 0.3814 0.7627 3.75
1.5 –0.3 0.4054 0.5424 0.8163 1.6302 3.75 3.75 3.75
1.4 -0.2 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75 3.75
AF = 1
1
AF = 0.75 AF = 0.5 AF = 0.25 AF = 0.1 AF = 0.05 AF = 0.01
Pulse Duration (ns)
2.6 Voltage Regulator Connector Signals
The VR module consists of three DC-DC converters, V
Table 2-18 lists all of the signals which are part of the processor package VR output
connector.
Table 2-18. VR Connector Signals
Group Name Signals
Voltage Regulator
Connector
PPODGD#, CPUPRES#, GND, Vid_valid, Vid_Core[5:0],
Vid_cache [5:0], Vcache_sense, Gnd_sense, Vcore_sense,
Vfixed_sense, OUTEN.
Warning: If the VR cannot supply the voltages requested by the components in the processor
package, then it must disable itself.
Figure 2-4 shows the top view of the processor package power tab. See Table 2-19 for
power tab connector signals.
core
, V
cache
, and V
fixed
.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 27
Page 28
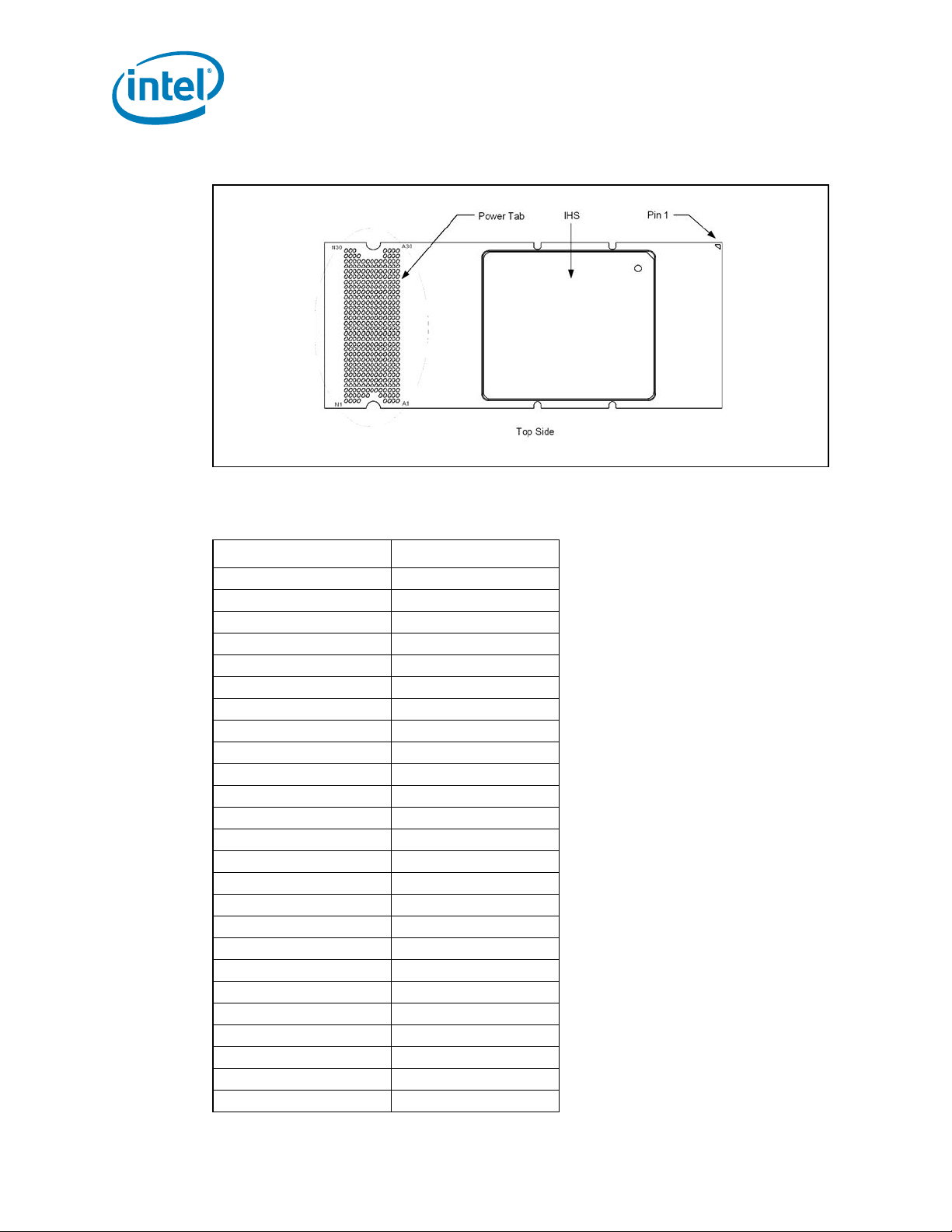
Figure 2-4. Processors Power Tab Physical Layout
Table 2-19. Power Connector Pinouts (Sheet 1 of 2)
Electrical Specifications
001356
Power Tab VR Pads Description
A1 - C1 GND
L1 - N1 GND
A2 PPODGD#
B2 CPUPRES#
D1, K1, C2, D2, E2 Vfixed
H2 - N2 Vfixed
A3 Vid_valid
B3 Vid_core [0]
C3 Vid_core [1]
D3 Vid_core [2]
E3 Vid_core [3]
F3 Vid_core [4]
G3 Vid_core [5]
H3 Vid_cache [0]
J3 Vid_cache [1]
K3 Vid_cache [2]
L3 Vid_cache [3]
M3 Vid_cache [4]
N3 Vid_cache [5]
A4 - N4 GND
A5 - N5 Vcache
A6 - N6 GND
A7 - N7 Vcore
A8 - N8 GND
A9 - N9 Vcore
28 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 29
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-19. Power Connector Pinouts (Sheet 2 of 2)
Power Tab VR Pads Description
A10 - N10 GND
A11 - N11 Vcore
A12 - N12 GND
A13 - N13 Vcore
A14 - N14 GND
A15 - N15 Vcore
A16 - N16 GND
A17 - N17 Vcore
A18 - N18 GND
A19 - N19 Vcore
A20 - N20 GND
A21 - N21 Vcore
A22 - N22 GND
A23 - N23 Vcore
A24 - N24 GND
A25 - N25 Vcore
A26 - N26 GND
A27 - N27 Vcache
A28 - N28 GND
A29 Vcache_sense
B29 Gnd_sense
C29 Vcore_sense
D29 Vfixed_sense
K29 GND
L29 Reserved
M29 Reserved
N29 OUTEN
A30 - D30 GND
L30 - N30 GND
The VR shall provide a selectable output voltage controlled via multiple binary weighted
Voltage Identification (VID) inputs. The VID value (high = 1; low = 0) is defined in
Table 2-20. VID pins will be controlled by the processor.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 29
Page 30
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-20. Processors Core Voltage Identification Code (V
Processor Pins (0 = low, 1 = high)
400 200 100 50 25 12.5 (mV) 400 200 100 50 25 12.5 (mV)
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0Vout
1 1 1 1 1 1 OFF 0 1 1 1 1 1 0.9125
1 1 1 1 1 0 1.3 0 1 1 1 1 0 0.9
1 1 1 1 0 1 1.2875 0 1 1 1 0 1 0.8875
1 1 1 1 0 0 1.275 0 1 1 1 0 0 0.875
1 1 1 0 1 1 1.2625 0 1 1 0 1 1 0.8625
1 1 1 0 1 0 1.25 0 1 1 0 1 0 0.85
1 1 1 0 0 1 1.2375 0 1 1 0 0 1 0.8375
1 1 1 0 0 0 1.225 0 1 1 0 0 0 0.825
1 1 0 1 1 1 1.2125 0 1 0 1 1 1 0.8125
1 1 0 1 1 0 1.2 0 1 0 1 1 0 0.8
1 1 0 1 0 1 1.1875 0 1 0 1 0 1 0.7875
1 1 0 1 0 0 1.175 0 1 0 1 0 0 0.775
1 1 0 0 1 1 1.1625 0 1 0 0 1 1 0.7625
1 1 0 0 1 0 1.15 0 1 0 0 1 0 0.75
1 1 0 0 0 1 1.1375 0 1 0 0 0 1 0.7375
1 1 0 0 0 0 1.125 0 1 0 0 0 0 0.725
1 0 1 1 1 1 1.1125 0 0 1 1 1 1 0.7125
1 0 1 1 1 0 1.1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0.7
1 0 1 1 0 1 1.0875 0 0 1 1 0 1 0.6875
1 0 1 1 0 0 1.075 0 0 1 1 0 0 0.675
1 0 1 0 1 1 1.0625 0 0 1 0 1 1 0.6625
1 0 1 0 1 0 1.05 0 0 1 0 1 0 0.65
1 0 1 0 0 1 1.0375 0 0 1 0 0 1 0.6375
1 0 1 0 0 0 1.025 0 0 1 0 0 0 0.625
1 0 0 1 1 1 1.0125 0 0 0 1 1 1 0.6125
1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0.6
1 0 0 1 0 1 0.9875 0 0 0 1 0 1 0.5875
1 0 0 1 0 0 0.975 0 0 0 1 0 0 0.575
1 0 0 0 1 1 0.9625 0 0 0 0 1 1 0.5625
1 0 0 0 1 0 0.95 0 0 0 0 1 0 0.55
1 0 0 0 0 1 0.9375 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.5375
1 0 0 0 0 0 0.925 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.525
VID5VID4VID3VID2VID1VID0Vout
(V)
CORE
and V
CACHE)
(V)
30 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 31

Electrical Specifications
2.7 System Bus Clock and Processor Clocking
The BCLKn and BCLKp inputs control the operating frequency of the processor system
bus interface. All processor system bus timing parameters are specified with respect to
the falling edge of BCLKn and rising edge of BCLKp. The address pins A[21:17]# will be
used to specify the system bus frequency during reset. The processor will ensure that
the correct bus/core ratio is elected based on the bus frequency that is specified during
reset.
Cold Reset Sequence:
• The configuration pins (A[21:17]#) must be asserted the entire time RESET# is
asserted.
• RESET# must be asserted before PWRGOOD is asserted.
• The duration from the assertion of PWRGOOD to the deassertion of RESET# must
be 1 millisecond minimum.
• After RESET# is deasserted, all the configuration, including pins A[21:17]#, must
remain valid for 2 BCLKs (minimum) to 3 BCLKs (maximum).
• BCLK is shown as a time reference to the BCLK period. It is not a requirement that
this is BCLKn or BCLKp signal.
• Configuration signals other than A[21:17]# must be asserted 4 BCLKs prior to the
deasserted edge of RESET# and must remain valid for 2 BCLKs (minimum) to 3
BCLKs (maximum) after the deasserted edge of RESET#.
Figure 2-5 outlines the timing relationship between the configuration pins, RESET# and
PWRGOOD for cold reset.
Figure 2-5. System Bus Reset and Configuration Timings for Cold Reset
t
T
A
BCLK
PWRGOOD
RESET#
Bus Ratio
(A[21:17]#)
Additional
Configuration
Signals
t
-4t-3
T
C
TA= 1.15 ns minimum; (set up time to BCLK for deassertion edge of RESET#)
TB= 1 ms minimum for cold reset
TC= Bus ratio signals must be asserted no later than RESET#
TD= 2 BCLKs minimum, 3 BCLKs maximum
TE= 4 BCLKs minimum
TF= 2 BCLKs minimum, 3 BCLKs maximum
T
B
t
-2t-1t0
T
E
t2t
1
T
D
T
F
3
000859b
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 31
Page 32

Warm Reset Sequence:
• PWRGOOD remains high throughout the entire sequence, as power is already
available and stable to the processor.
• The configuration pins (A[21:17]#) must be asserted the entire time RESET# is
asserted.
• The duration from the assertion of RESET# to the deassertion of RESET# must be 1
millisecond minimum.
• After RESET# is deasserted, the configuration pins must remain valid for two
BCLKs (minimum) to three BCLKs (maximum).
• BCLK is shown as a time reference to the BCLK period. It is not a requirement that
this is BCLKn or BCLKp signal.
• Configuration signals other than A[21:17]# must be asserted four BCLKs prior to
the deasserted edge of RESET# and must remain valid for two BCLKs (minimum) to
three BCLKs (maximum) after the deasserted edge of RESET#.
Figure 2-6 outlines the timing relationship between the configuration pins, RESET# and
PWRGOOD for warm reset.
Figure 2-6. System Bus Reset and Configuration Timings for Warm Reset
Electrical Specifications
BCLK
PWRGOOD
RESET#
Bus Ratio
(A[21:17]#)
Additional
Configuration
Signals
t
-4t-3
T
C
T
B
t
-2t-1t0
T
E
t1t2t
T
A
T
D
T
F
TA= 1.15 ns minimum; (set up time to BCLK for deassertion edge of RESET#)
TB= 1 ms minimum for warm reset
TC= Bus ratio signals must be asserted no later than RESET#
TD= 2 BCLKs minimum, 3 BCLKs maximum
TE= 4 BCLKs minimum
TF= 2 BCLKs minimum, 3 BCLKs maximum
3
000777b
32 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 33

Electrical Specifications
2.8 Recommended Connections for Unused Pins
Pins that are unused in an application environment (as opposed to testing
environment) should be connected to the states listed in Table 2-21. Pins that must be
used in an application are stated as such and do not have a recommended state for
unused connection.
Table 2-21. Connection for Unused Pins
Pins/Pin Groups
AGTL+ pins H
Recommended
Connections
Notes
1, 2
HSTL Clock Signals Must be used
All Power Signals Must be used
PWRGOOD Must be used
TAP Signals
TCK L
TRST# L
TDI H
TDO H
TMS H
1, 3
1, 3
1, 3
1, 3
1, 3
System Management Signals
3.3V GND
SMA[2:0] N/C
SMSC N/C
SMSD N/C
SMWP N/C
THRMALERT# H
1, 4
LVTTL Power Pod Signals
OUTEN Must be used
PPODGD# Must be used
PROCPRES# Must be used
Other Pins
N/C N/C
A20M# N/C
IGNNE# N/C
LOCK# N/C
FERR# N/C
TUNER1 N/C or H
TUNER2 H
TUNER3 N/C or H
3,5
1
3,5
Notes:
1. L = GND, H = V
2. AGTL+ output signals SBSY[0:1]#, DBSY[0:1]#, and DRDY[0,1]# may be left as N/C
if not used on platform.
3. Can be No-Connect or connected to V
4. THRMALERT# should be pulled up to 3.3 V through a resistor.
5. With A[21;17] settings to all 0’ or all 1’s, please refer to Table 2-22 for proper
connection.
CTERM
.
via a 100ohm or 150 ohm resistor.
CTERM
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 33
Page 34

Table 2-22. TUNER1/TUNER3 Translation Table
Electrical Specifications
A[21:17}#
Notes:
1. 0 = V
2. 0 = Resistor not present, 1 = Resistor present
1
TUNER1
0 0 0 667 1.7
0 0 1 533 1.4
0 1 N/A 400 0.8
1 0 0 667 1.92
1 0 1 533 1.7
1 1 N/A 400 0.82
, 1 = GND
CTERM
2
TUNER3
2
System
Bus (MHz)
§
Slew Rate
(V/ns)
34 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 35

Pinout Specifications
0
21314151617181920
2232425
3 Pinout Specifications
This chapter describes the Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series
signals and pinout.
Note: The pins labeled “N/C” must remain unconnected. The processor uses a JEDEC
standard pin naming convention.
In this chapter, pin names are the actual names given to each physical pin of the
processor. System bus signal names are the names associated with the functions of
those pins. For those pins associated with multiple functions, their pin names and
system bus signal names are not necessarily identical.
Figure 3-1 shows the processor pin location diagram from the top view.
Figure 3-1. Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Pinout
AH AG AF AE AD AC AB AA Y W V U T R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A
1
GND
2
GND
TERMA
3
TUNER[2] GND GND GND GND A05# D25# GND D23# GND D17# GND D13# GND D14# GND D01# GND NC GND GND
TUNER[1]
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
BCLKN
14
15
GOOD
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
A20M#
24
25
FERR#
OUTEN
GND
NC
NC
GND
TDO
TDI
INIT# RS1#
GND
TMS
TCK
REQ1# REQ2#
GND
NC
NC
REQ4#
GND
BCLKP
TRDY#
GND
PWR
PROC
PRES#
BREQ0# BREQ1#NCNC A36# A38# DEP11# VC
GND
NC
NC
BREQ3#NCNC BREQ2# A35# A29# VC
GND
NC
NC
GND
NC
NC
GND
IGNNE#
GND
TH_TRIP#
AH AG AF AE AD AC AB AA Y W V U T R P N M L K J H G F E D C B A
GND GND GND
GND
GND ID0# GND ID1# GND A07#
ID3#
TERMB
GND
RSP# ID8# ID9# A08# A03# VC
GND
REQ0#
GND
REQ3# GND DRDY# GND A23# GND GND NC GND D60# GNDSTBN3# GND D56# GND DEP5# GND D41# GND STBP2#GND D33# GNDVCCMON
GND
GND
SBSY#
LOCK#
GND
GND
BPRI# GNDSBSY1#GND GND GND GND D85# GND D82# GND DEP8# GND D79# GND D74# GND D70# GND GND
GND
PPOD
GD#
TRST#
GND
LINT0
BPM2# GND BPM3#GND AP1# GND GND A42# GND D126# GNDSTBN7#GND D116# GNDDEP13# GND D108# GNDSTBP6# GND D97# GND GND
LINT1 GND BPM4# GND BPM5# GND A43# A40# GND D123# VC
ID2#
ID4# ID5# A13#
ID7# A11# GND GND GND GND D19# GNDDEP1# GND D08# GNDSTBP0#GND D02# GND GND
GND
GND
ID6#
IDS# GNDDRDY0# GND GND A09# GND D31# GND D22# GND GND DEP0# GND GND D10# GND D00# GND THRM
RS0#
GND
RS2# A17# A15# DEP6# VC
GND GND
DBSY#
DSBY0#
HIT# A24# A20# VC
REQ5#
HITM# A25# A19# D62# VC
RP#
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND D52# D47# D43# D39# GND NC GND GND
GSEQ# DEFER# A34# A31# VC
GND TND# GND BINIT# GND GND A28# GND D92# GND D91# GND D81# GND D78# GND D71# GND D67# GND NC GND SMA2
GND GND GND GND GND GND GND D88# DEP9# D72# STBP4#GND D73# GND SMA1
RESET#NCADS# GND A39# A45# GNDDEP14# VC
GND GND GND GND GND D112# DEP12# D101# D96# GND D99# GNDSMWP
BPM0# BERR# A49# A47# VC
PMI# BPM1# AP0# GND VC
GND
SBSY0#
A33#
DRDY1#
GND
GND
GND
A04# VC
A06#
A10#
A12#
GND
A14#
GND GND
A21#
A26#
A22#
A37#
A32#
A30#
GND
A44#
A46#
A41#
GND
VC
GND GND VC
GND
TERM
D30# GND D27# VC
TERM
GND
GND DEP3# VC
TERM
D29#
NC
DEP2# D26# VC
TERM
TERM
GND GND GND D53# DEP4# D38#
D63#
A18#
DEP7#
TERM
TERM
D59#
A16#
D94#
TERM
TERM
D89#
BNR#
DEP10#
TERM
A27# GND D90#DBSY1#
D122# GND D118# VC
TERM
D124#
A48#
TERM
TERM
DEP15#
D125# VC
D120# GND D115# VC
TERM
D121# D119# GND D113# GND D110# GND D107# GND D100# GND NC GND VC
GND
D20# GND NC VC
TERM
D24# GNDSTBP1# VC
STBN1#
D28#
TERM
D54# D48# VC
D58#
D61# VC
STBP3# D50# VC
TERM
D57# D51# VC
D55#
D87# VC
D84# NC VC
TERM
D93# STBP5# VC
STBN5#
D95# VC
D86# D80# VC
TERM
GND
D127#
STBP7# D114# VC
TERM
GND
GND VC
TERM
TERM
D16# GND D12# VC
TERM
D18# VC
TERM
D21#
D49# GND D42# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
NC GND D46# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
D83# GND D76# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
D117# GND D111# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
NC GND D109# VC
TERM
GND GND VC
TERM
D11# GND D07# VC
D09#
GND
D32# STBN2# VC
GND
D75# D68# VC
GND
D77# D69# VC
GND
D105# STBN6# VC
TERM
STBN0# GND D03# VC
TERM
D06# VC
TERM
D15#
D45# GND D37# VC
TERM
D40# GND D35# GNDVSSMON
GND
TERM
D44# GND D36# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
STBN4# GND D66# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
D106# GND D102# VC
TERM
GND
TERM
D103# GND D104# VC
TERM
D04# GND 3.3V VC
D05# GND NC VC
D34# GND GNDVCTERM
D65# GND NC VC
D64# GND SMA0 VC
D98# GND SMSD
Power Pod
TERM
TERM
TERM
TERM
TERM
TERM
TERM
GND
TERM
NC NC
TERM
ALERT#
NC GND
TERM
NC GND
TERM
NC GND
TERM
SMSC GND
TERM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
11
1
21
2
VC
000638b
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 35
Page 36

Table 3-1 provides the Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series pin list
in alphabetical order.
Table 3-2 provides the Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series pin list
by pin location.
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 1 of 15)
Pin Name
3.3V B02 IN SMBus supply voltage
A003# AA03#/EXF0# V06 IN/OUT
A004# AA04#/EXF1# V02 IN/OUT
A005# AA05#/EXF2# U03 IN/OUT
A006# AA06#/EXF3# W03 IN/OUT
A007# AA07#/EXF4# Y02 IN/OUT
A008# AA08#/BE0# Y06 IN/OUT
A009# AA09#/BE1# U07 IN/OUT
A010# AA10#/BE2# V04 IN/OUT
A011# AA11#/BE3# AA05 IN/OUT
A012# AA12#/BE4# W05 IN/OUT
A013# AA13#/BE5# Y04 IN/OUT
A014# AA14#/BE6# W07 IN/OUT
A015# AA15#/BE7# V08 IN/OUT
A016# AA16#/DID0# U13 IN/OUT
A017# AA17#/DID1# Y08 IN/OUT
A018# AA18#/DID2# U09 IN/OUT
A019# AA19#/DID3# V12 IN/OUT
A020# AA20#/DID4# V10 IN/OUT
A021# AA21#/DID5# W09 IN/OUT
A022# AA22#/DID6# W13 IN/OUT
A023# AA23#/DID7# AA11 IN/OUT
A024# AA24#/DID8# Y10 IN/OUT
A025# AA25#/DID9# Y12 IN/OUT
A026# AA26#/AB26# W11 IN/OUT
A027# AA27#/xTPRValue0# U19 IN/OUT
A028# AA28#/xTPRValue1# U15 IN/OUT
A029# AA29#/xTPRValue2# V18 IN/OUT
A030# AA30#/xTPRValue3# W19 IN/OUT
A031# AA31#/xTPRDisable# V14 IN/OUT
A032# AA32#/ATTR0# W17 IN/OUT
A033# AA33#/ATTR1# AA17 IN/OUT
A034# AA34#/ATTR2# Y14 IN/OUT
A035# AA35#/ATTR3# Y18 IN/OUT
A036# AA36#/AB36# Y16 IN/OUT
A037# AA37#/AB37# W15 IN/OUT
A038# AA38#/AB38# V16 IN/OUT
A039# AA39#/AB39# Y20 IN/OUT
A040# AA40#/AB40# V24 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
36 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 37

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 2 of 15)
Pin Name
A041# AA41#/AB41# W25 IN/OUT
A042# AA42#/AB42# U23 IN/OUT
A043# AA43#/AB43# Y24 IN/OUT
A044# AA44#/AB44# W21 IN/OUT
A045# AA45#/AB45# V20 IN/OUT
A046# AA46#/AB46# W23 IN/OUT
A047# AA47#/AB47# V22 IN/OUT
A048# AA48#/AB48# U21 IN/OUT
A049# AA49#/AB49# Y22 IN/OUT
A20M# A20M# AH23 N/C
ADS# ADS# AB20 IN/OUT
AP0# AP0# AA25 IN/OUT
AP1# AP1# AA23 IN/OUT
BCLKn BCLKN AH13 IN
BCLKp BCLK AG13 IN
BERR# BERR# AB22 IN/OUT
BINIT# BINIT# AA15 IN/OUT
BNR# BNR# U17 IN/OUT
BPM0# BPM0# AD22 IN/OUT
BPM1# BPM1# AC25 IN/OUT
BPM2# BPM2# AE23 IN/OUT
BPM3# BPM3# AC23 IN/OUT
BPM4# BPM4# AD24 IN/OUT
BPM5# BPM5# AB24 IN/OUT
BPRI# BPRI# AE19 IN
BR0# BREQ0# AF16 IN/OUT
BR1# BREQ1# AD16 IN
BR2# BREQ2# AB18 IN
BR3# BREQ3# AF18 IN
CPUPRES# CPUPRES# AG15 OUT Power pod signal
D000# D00# C07 IN/OUT
D001# D01# E03 IN/OUT
D002# D02# C05 IN/OUT
D003# D03# D04 IN/OUT
D004# D04# D02 IN/OUT
D005# D05# D06 IN/OUT
D006# D06# F06 IN/OUT
D007# D07# F02 IN/OUT
D008# D08# G05 IN/OUT
D009# D09# H06 IN/OUT
D010# D10# E07 IN/OUT
D011# D11# H02 IN/OUT
D012# D12# H04 IN/OUT
D013# D13# J03 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 37
Page 38

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 3 of 15)
Pin Name
D014# D14# G03 IN/OUT
D015# D15# G07 IN/OUT
D016# D16# K04 IN/OUT
D017# D17# L03 IN/OUT
D018# D18# K06 IN/OUT
D019# D19# L05 IN/OUT
D020# D20# M02 IN/OUT
D021# D21# L07 IN/OUT
D022# D22# N07 IN/OUT
D023# D23# N03 IN/OUT
D024# D24# P04 IN/OUT
D025# D25# R03 IN/OUT
D026# D26# P06 IN/OUT
D027# D27# P02 IN/OUT
D028# D28# M06 IN/OUT
D029# D29# R05 IN/OUT
D030# D30# T02 IN/OUT
D031# D31# R07 IN/OUT
D032# D32# H10 IN/OUT
D033# D33# C11 IN/OUT
D034# D34# D10 IN/OUT
D035# D35# C09 IN/OUT
D036# D36# D12 IN/OUT
D037# D37# D08 IN/OUT
D038# D38# G09 IN/OUT
D039# D39# E13 IN/OUT
D040# D40# E09 IN/OUT
D041# D41# G11 IN/OUT
D042# D42# H08 IN/OUT
D043# D43# G13 IN/OUT
D044# D44# F12 IN/OUT
D045# D45# F08 IN/OUT
D046# D46# H12 IN/OUT
D047# D47# J13 IN/OUT
D048# D48# M08 IN/OUT
D049# D49# K08 IN/OUT
D050# D50# K10 IN/OUT
D051# D51# M12 IN/OUT
D052# D52# L13 IN/OUT
D053# D53# L09 IN/OUT
D054# D54# P08 IN/OUT
D055# D55# N13 IN/OUT
D056# D56# L11 IN/OUT
D057# D57# P12 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
38 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 39

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 4 of 15)
Pin Name
D058# D58# N09 IN/OUT
D059# D59# R13 IN/OUT
D060# D60# R11 IN/OUT
D061# D61# P10 IN/OUT
D062# D62# T12 IN/OUT
D063# D63# R09 IN/OUT
D064# D64# D18 IN/OUT
D065# D65# D14 IN/OUT
D066# D66# D16 IN/OUT
D067# D67# E15 IN/OUT
D068# D68# F14 IN/OUT
D069# D69# F18 IN/OUT
D070# D70# C19 IN/OUT
D071# D71# G15 IN/OUT
D072# D72# G17 IN/OUT
D073# D73# C17 IN/OUT
D074# D74# E19 IN/OUT
D075# D75# H14 IN/OUT
D076# D76# H16 IN/OUT
D077# D77# H18 IN/OUT
D078# D78# J15 IN/OUT
D079# D79# G19 IN/OUT
D080# D80# K18 IN/OUT
D081# D81# L15 IN/OUT
D082# D82# L19 IN/OUT
D083# D83# K16 IN/OUT
D084# D84# M14 IN/OUT
D085# D85# N19 IN/OUT
D086# D86# M18 IN/OUT
D087# D87# P14 IN/OUT
D088# D88# L17 IN/OUT
D089# D89# R17 IN/OUT
D090# D90# R19 IN/OUT
D091# D91# N15 IN/OUT
D092# D92# R15 IN/OUT
D093# D93# P16 IN/OUT
D094# D94# T14 IN/OUT
D095# D95# P18 IN/OUT
D096# D96# E21 IN/OUT
D097# D97# C23 IN/OUT
D098# D98# D22 IN/OUT
D099# D99# C21 IN/OUT
D100# D100# E25 IN/OUT
D101# D101# G21 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 39
Page 40

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 5 of 15)
Pin Name
D102# D102# D20 IN/OUT
D103# D103# F24 IN/OUT
D104# D104# D24 IN/OUT
D105# D105# H22 IN/OUT
D106# D106# F20 IN/OUT
D107# D107# G25 IN/OUT
D108# D108# G23 IN/OUT
D109# D109# H24 IN/OUT
D110# D110# J25 IN/OUT
D111# D111# H20 IN/OUT
D112# D112# L21 IN/OUT
D113# D113# L25 IN/OUT
D114# D114# K22 IN/OUT
D115# D115# M24 IN/OUT
D116# D116# L23 IN/OUT
D117# D117# K20 IN/OUT
D118# D118# M20 IN/OUT
D119# D119# N25 IN/OUT
D120# D120# P24 IN/OUT
D121# D121# R25 IN/OUT
D122# D122# P20 IN/OUT
D123# D123# T24 IN/OUT
D124# D124# R21 IN/OUT
D125# D125# P22 IN/OUT
D126# D126# R23 IN/OUT
D127# D127# N21 IN/OUT
DBSY# DBSY# AC09 IN/OUT
DBSY0# DBSY_C1# AA09 OUT
DBSY1# DBSY_C2# AA19 OUT
DEFER# DEFER# AB14 IN
DEP00# DEP0# J07 IN/OUT
DEP01# DEP1# J05 IN/OUT
DEP02# DEP2# T06 IN/OUT
DEP03# DEP3# T04 IN/OUT
DEP04# DEP4# J09 IN/OUT
DEP05# DEP5# J11 IN/OUT
DEP06# DEP6# T08 IN/OUT
DEP07# DEP7# T10 IN/OUT
DEP08# DEP8# J19 IN/OUT
DEP09# DEP9# J17 IN/OUT
DEP10# DEP10# T18 IN/OUT
DEP11# DEP11# T16 IN/OUT
DEP12# DEP12# J21 IN/OUT
DEP13# DEP13# J23 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
40 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 41

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 6 of 15)
Pin Name
DEP14# DEP14# T20 IN/OUT
DEP15# DEP15# T22 IN/OUT
DRDY# DRDY# AC11 IN/OUT
DRDY0# DRDY_C1# AA07 OUT
DRDY1# DRDY_C2# AA21 OUT
FERR# FERR# AH25 OUT
GND GND A01 IN
GND GND A03 IN
GND GND A05 IN
GND GND A08 IN
GND GND A13 IN
GND GND A16 IN
GND GND A19 IN
GND GND A20 IN
GND GND A23 IN
GND GND A24 IN
GND GND AA02 IN
GND GND AA20 IN
GND GND AA24 IN
GND GND AB01 IN
GND GND AB03 IN
GND GND AB05 IN
GND GND AB07 IN
GND GND AB09 IN
GND GND AB11 IN
GND GND AB13 IN
GND GND AB15 IN
GND GND AB17 IN
GND GND AB19 IN
GND GND AB21 IN
GND GND AB23 IN
GND GND AB25 IN
GND GND AC02 IN
GND GND AC24 IN
GND GND AD01 IN
GND GND AD03 IN
GND GND AD05 IN
GND GND AD07 IN
GND GND AD09 IN
GND GND AD11 IN
GND GND AD13 IN
GND GND AD15 IN
GND GND AD17 IN
GND GND AD19 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 41
Page 42

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 7 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND AD21 IN
GND GND AD23 IN
GND GND AD25 IN
GND GND AE02 IN
GND GND AE24 IN
GND GND AF01 IN
GND GND AF05 IN
GND GND AF07 IN
GND GND AF09 IN
GND GND AF11 IN
GND GND AF13 IN
GND GND AF15 IN
GND GND AF17 IN
GND GND AF19 IN
GND GND AF21 IN
GND GND AG02 IN
GND GND AG04 IN
GND GND AG06 IN
GND GND AG08 IN
GND GND AG10 IN
GND GND AG12 IN
GND GND AG14 IN
GND GND AG16 IN
GND GND AG18 IN
GND GND AG20 IN
GND GND AG22 IN
GND GND AG24 IN
GND GND AH01 IN
GND GND B03 IN
GND GND B05 IN
GND GND B07 IN
GND GND B09 IN
GND GND B10 IN
GND GND B11 IN
GND GND B13 IN
GND GND B15 IN
GND GND B17 IN
GND GND B19 IN
GND GND B21 IN
GND GND B23 IN
GND GND B25 IN
GND GND C02 IN
GND GND C06 IN
GND GND C10 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
42 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 43

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 8 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND C14 IN
GND GND C18 IN
GND GND C22 IN
GND GND D01 IN
GND GND D03 IN
GND GND D05 IN
GND GND D07 IN
GND GND D09 IN
GND GND D11 IN
GND GND D13 IN
GND GND D15 IN
GND GND D17 IN
GND GND D19 IN
GND GND D21 IN
GND GND D23 IN
GND GND D25 IN
GND GND E04 IN
GND GND E08 IN
GND GND E12 IN
GND GND E16 IN
GND GND E20 IN
GND GND E24 IN
GND GND F01 IN
GND GND F03 IN
GND GND F05 IN
GND GND F07 IN
GND GND F09 IN
GND GND F11 IN
GND GND F13 IN
GND GND F15 IN
GND GND F17 IN
GND GND F19 IN
GND GND F21 IN
GND GND F23 IN
GND GND F25 IN
GND GND G02 IN
GND GND H03 IN
GND GND H05 IN
GND GND H07 IN
GND GND H09 IN
GND GND H11 IN
GND GND H13 IN
GND GND H15 IN
GND GND H17 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 43
Page 44

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 9 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND H19 IN
GND GND H21 IN
GND GND H23 IN
GND GND H25 IN
GND GND J01 IN
GND GND J04 IN
GND GND J08 IN
GND GND J12 IN
GND GND J16 IN
GND GND J20 IN
GND GND J24 IN
GND GND K03 IN
GND GND K05 IN
GND GND K07 IN
GND GND K09 IN
GND GND K11 IN
GND GND K13 IN
GND GND K15 IN
GND GND K17 IN
GND GND K19 IN
GND GND K21 IN
GND GND K23 IN
GND GND K25 IN
GND GND L02 IN
GND GND M01 IN
GND GND M03 IN
GND GND M05 IN
GND GND M07 IN
GND GND M09 IN
GND GND M11 IN
GND GND M13 IN
GND GND M15 IN
GND GND M17 IN
GND GND M19 IN
GND GND M21 IN
GND GND M23 IN
GND GND M25 IN
GND GND N04 IN
GND GND N20 IN
GND GND N24 IN
GND GND P01 IN
GND GND P03 IN
GND GND P05 IN
GND GND P07 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
44 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 45

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 10 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND P09 IN
GND GND P11 IN
GND GND P13 IN
GND GND P15 IN
GND GND P17 IN
GND GND P19 IN
GND GND P21 IN
GND GND P23 IN
GND GND P25 IN
GND GND R02 IN
GND GND T01 IN
GND GND T03 IN
GND GND T05 IN
GND GND T07 IN
GND GND T09 IN
GND GND T11 IN
GND GND T13 IN
GND GND T15 IN
GND GND T17 IN
GND GND T19 IN
GND GND T21 IN
GND GND T23 IN
GND GND T25 IN
GND GND U04 IN
GND GND U20 IN
GND GND U24 IN
GND GND V01 IN
GND GND V03 IN
GND GND V05 IN
GND GND V07 IN
GND GND V09 IN
GND GND V11 IN
GND GND V13 IN
GND GND V15 IN
GND GND V17 IN
GND GND V19 IN
GND GND V21 IN
GND GND V23 IN
GND GND V25 IN
GND GND W02 IN
GND GND Y01 IN
GND GND Y03 IN
GND GND Y05 IN
GND GND Y07 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 45
Page 46

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 11 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND Y09 IN
GND GND Y11 IN
GND GND Y13 IN
GND GND Y15 IN
GND GND Y17 IN
GND GND Y19 IN
GND GND Y21 IN
GND GND Y23 IN
GND GND Y25 IN
GSEQ# GSEQ# AD14 IN
HIT# HIT# AB10 IN/OUT
HITM# HITM# AB12 IN/OUT
ID0# IDA0#/IP0# AD02 IN
ID1# IDA1#/IP1# AB02 IN
ID2# IDA2#/DHIT# AC03 IN
ID3# IDA3#/IDB3# AA03 IN
ID4# IDA4#/IDB4# AD04 IN
ID5# IDA5#/IDB5# AB04 IN
ID6# IDA6#/IDB6# AE05 IN
ID7# IDA7#/IDB7# AC05 IN
ID8# IDA8#/IDB8# AD06 IN
ID9# IDA9#/IDB9# AB06 IN
IDS# IDS# AC07 IN
IGNNE# IGNNE# AG23 N/C
INIT# INIT# AF08 IN
LINT0 INT AF22 IN
LINT1 NMI AF24 IN
LOCK# LOCK# AE15 N/C
N/C A04
N/C AB16
N/C AC17
N/C AC21
N/C AD18
N/C AE17
N/C AG05
N/C AG11
N/C AG17
N/C AG19
N/C AG21
N/C AH05
N/C AH11
N/C AH17
N/C AH19
N/C AH21
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
46 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 47

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 12 of 15)
Pin Name
N/C B04
N/C B06
N/C B08
N/C B14
N/C B16
N/C B20
N/C C03
N/C C13
N/C C15
N/C C25
N/C K02
N/C K12
N/C K14
N/C K24
N/C U05
N/C U11
OUTEN OUTEN AF04 IN Power pod signal
PMI# PMI# AE25 IN
PPODGD# PPODGD# AF20 OUT Power pod signal
PWRGOOD PWRGOOD AH15 IN
REQ0# REQA0#/LEN0# AE09 IN/OUT
REQ1# WSNP#, D/C#/LEN1# AF10 IN/OUT
REQ2# REQA2#/ REQB2# AD10 IN/OUT
REQ3# ASZ0#/DSZ0# AE11 IN/OUT
REQ4# ASZ1#/DSZ1# AF12 IN/OUT
REQ5# REQ5# AD12 IN/OUT
RESET# RESET# AD20 IN
RP# RP# AC13 IN/OUT
RS0# RS0# AE07 IN
RS1# RS1# AD08 IN
RS2# RS2# AB08 IN
RSP# RSP# AF06 IN
SBSY# SBSY# AE13 IN/OUT
SBSY0# SBSY_C1# AA13 OUT
SBSY1# SBSY_C2# AC19 OUT
SMA0 SMA0 B18 IN SMBus signal
SMA1 SMA1 A17 IN SMBus signal
SMA2 SMA2 A15 IN SMBus signal
SMSC SMSC B24 IN SMBus signal
SMSD SMSD B22 IN/OUT SMBus signal
SMWP SMWP A21 IN SMBus signal
STBN0# STBN0# F04 IN/OUT
STBN1# STBN1# N05 IN/OUT
STBN2# STBN2# F10 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 47
Page 48

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 13 of 15)
Pin Name
STBN3# STBN3# N11 IN/OUT
STBN4# STBN4# F16 IN/OUT
STBN5# STBN5# N17 IN/OUT
STBN6# STBN6# F22 IN/OUT
STBN7# STBN7# N23 IN/OuT
STBP0# STBP0# E05 IN/OUT
STBP1# STBP1# M04 IN/OUT
STBP2# STBP2# E11 IN/OUT
STBP3# STBP3# M10 IN/OUT
STBP4# STBP4# E17 IN/OUT
STBP5# STBP5# M16 IN/OUT
STBP6# STBP6# E23 IN/OUT
STBP7# STBP7# M22 IN/OUT
TCK TCK AG09 IN JTAG
TDI TDI AG07 IN JTAG
TDO TDO AH07 OUT JTAG
TERMA FSBT1 AF02 IN
TERMB FSBT2 AE03 IN
THRMTRIP# THRMTRIP# AG25 OUT
THRMALERT# THRMALERT# A07 OUT
TMS TMS AH09 IN JTAG
TND# TND# AC15 IN/OUT
TRDY# TRDY# AF14 IN
TRST# TRST# AE21 IN JTAG
TUNER[1] TUNER[1] AH03 IN
TUNER[2] TUNER[2] AG03 IN
TUNER[3] TUNER[3] B08 IN
VCCMON VCCMON A11 N/C
VCTERM VCTERM A02 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A06 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A10 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A14 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A18 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A22 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C04 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C08 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C12 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C16 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C20 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E02 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E06 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
48 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 49

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 14 of 15)
Pin Name
VCTERM VCTERM E10 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E14 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E18 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E22 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G04 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G08 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G12 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G16 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G20 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J02 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J06 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J10 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J14 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J18 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J22 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L04 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L08 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L12 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L16 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L20 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N02 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N06 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N10 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N14 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N18 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N22 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R04 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R08 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R12 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R16 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R20 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U02 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U06 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U10 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U14 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U18 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U22 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 49
Page 50

Table 3-1. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Name (Sheet 15 of 15)
Pin Name
VCTERM VCTERM U25 IN
VSSMON VSSMON A09 N/C
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 1 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND A01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A02 IN
GND GND A03 IN
N/C A04
GND GND A05 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A06 IN
THRMALERT# THRMALERT# A07 OUT
GND GND A08 IN
VSSMON VSSMON A09 N/C
VCTERM VCTERM A10 IN
VCCMON VCCMON A11 N/C
GND GND A13 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A14 IN
SMA2 SMA2 A15 IN SMBus signal
GND GND A16 IN
SMA1 SMA1 A17 IN SMBus signal
VCTERM VCTERM A18 IN
GND GND A19 IN
GND GND A20 IN
SMWP SMWP A21 IN SMBus signal
VCTERM VCTERM A22 IN
GND GND A23 IN
GND GND A24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM A25 IN
3.3V B02 IN SMBus supply voltage
GND GND B03 IN
N/C B04
GND GND B05 IN
N/C B06
GND GND B07 IN
Tuner[3] Tuner[3] B08 IN
GND GND B09 IN
GND GND B10 IN
GND GND B11 IN
GND GND B13 IN
N/C B14
GND GND B15 IN
N/C B16
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
50 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 51

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 2 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND B17 IN
SMA0 SMA0 B18 IN SMBus signal
GND GND B19 IN
N/C B20
GND GND B21 IN
SMSD SMSD B22 IN/OUT SMBus signal
GND GND B23 IN
SMSC SMSC B24 IN SMBus signal
GND GND B25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM C01 IN
GND GND C02 IN
N/C C03
VCTERM VCTERM C04 IN
D002# D02# C05 IN/OUT
GND GND C06 IN
D000# D00# C07 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM C08 IN
D035# D35# C09 IN/OUT
GND GND C10 IN
D033# D33# C11 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM C12 IN
N/C C13
GND GND C14 IN
N/C C15
VCTERM VCTERM C16 IN
D073# D73# C17 IN/OUT
GND GND C18 IN
D070# D70# C19 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM C20 IN
D099# D99# C21 IN/OUT
GND GND C22 IN
D097# D97# C23 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM C24 IN
N/C C25
GND GND D01 IN
D004# D04# D02 IN/OUT
GND GND D03 IN
D003# D03# D04 IN/OUT
GND GND D05 IN
D005# D05# D06 IN/OUT
GND GND D07 IN
D037# D37# D08 IN/OUT
GND GND D09 IN
D034# D34# D10 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 51
Page 52

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 3 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND D11 IN
D036# D36# D12 IN/OUT
GND GND D13 IN
D065# D65# D14 IN/OUT
GND GND D15 IN
D066# D66# D16 IN/OUT
GND GND D17 IN
D064# D64# D18 IN/OUT
GND GND D19 IN
D102# D102# D20 IN/OUT
GND GND D21 IN
D098# D98# D22 IN/OUT
GND GND D23 IN
D104# D104# D24 IN/OUT
GND GND D25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM E02 IN
D001# D01# E03 IN/OUT
GND GND E04 IN
STBP0# STBP0# E05 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM E06 IN
D010# D10# E07 IN/OUT
GND GND E08 IN
D040# D40# E09 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM E10 IN
STBP2# STBP2# E11 IN/OUT
GND GND E12 IN
D039# D39# E13 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM E14 IN
D067# D67# E15 IN/OUT
GND GND E16 IN
STBP4# STBP4# E17 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM E18 IN
D074# D74# E19 IN/OUT
GND GND E20 IN
D096# D96# E21 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM E22 IN
STBP6# STBP6# E23 IN/OUT
GND GND E24 IN
D100# D100# E25 IN/OUT
GND GND F01 IN
D007# D07# F02 IN/OUT
GND GND F03 IN
STBN0# STBN0# F04 IN/OUT
GND GND F05 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
52 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 53

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 4 of 15)
Pin Name
D006# D06# F06 IN/OUT
GND GND F07 IN
D045# D45# F08 IN/OUT
GND GND F09 IN
STBN2# STBN2# F10 IN/OUT
GND GND F11 IN
D044# D44# F12 IN/OUT
GND GND F13 IN
D068# D68# F14 IN/OUT
GND GND F15 IN
STBN4# STBN4# F16 IN/OUT
GND GND F17 IN
D069# D69# F18 IN/OUT
GND GND F19 IN
D106# D106# F20 IN/OUT
GND GND F21 IN
STBN6# STBN6# F22 IN/OUT
GND GND F23 IN
D103# D103# F24 IN/OUT
GND GND F25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM G01 IN
GND GND G02 IN
D014# D14# G03 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G04 IN
D008# D08# G05 IN/OUT
D015# D15# G07 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G08 IN
D038# D38# G09 IN/OUT
D041# D41# G11 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G12 IN
D043# D43# G13 IN/OUT
D071# D71# G15 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G16 IN
D072# D72# G17 IN/OUT
D079# D79# G19 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G20 IN
D101# D101# G21 IN/OUT
D108# D108# G23 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM G24 IN
D107# D107# G25 IN/OUT
D011# D11# H02 IN/OUT
GND GND H03 IN
D012# D12# H04 IN/OUT
GND GND H05 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 53
Page 54

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 5 of 15)
Pin Name
D009# D09# H06 IN/OUT
GND GND H07 IN
D042# D42# H08 IN/OUT
GND GND H09 IN
D032# D32# H10 IN/OUT
GND GND H11 IN
D046# D46# H12 IN/OUT
GND GND H13 IN
D075# D75# H14 IN/OUT
GND GND H15 IN
D076# D76# H16 IN/OUT
GND GND H17 IN
D077# D77# H18 IN/OUT
GND GND H19 IN
D111# D111# H20 IN/OUT
GND GND H21 IN
D105# D105# H22 IN/OUT
GND GND H23 IN
D109# D109# H24 IN/OUT
GND GND H25 IN
GND GND J01 IN
VCTERM VCTERM J02 IN
D013# D13# J03 IN/OUT
GND GND J04 IN
DEP01# DEP1# J05 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM J06 IN
DEP00# DEP0# J07 IN/OUT
GND GND J08 IN
DEP04# DEP4# J09 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM J10 IN
DEP05# DEP5# J11 IN/OUT
GND GND J12 IN
D047# D47# J13 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM J14 IN
D078# D78# J15 IN/OUT
GND GND J16 IN
DEP09# DEP9# J17 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM J18 IN
DEP08# DEP8# J19 IN/OUT
GND GND J20 IN
DEP12# DEP12# J21 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM J22 IN
DEP13# DEP13# J23 IN/OUT
GND GND J24 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
54 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 55

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 6 of 15)
Pin Name
D110# D110# J25 IN/OUT
N/C K02
GND GND K03 IN
D016# D16# K04 IN/OUT
GND GND K05 IN
D018# D18# K06 IN/OUT
GND GND K07 IN
D049# D49# K08 IN/OUT
GND GND K09 IN
D050# D50# K10 IN/OUT
GND GND K11 IN
N/C K12
GND GND K13 IN
N/C K14
GND GND K15 IN
D083# D83# K16 IN/OUT
GND GND K17 IN
D080# D80# K18 IN/OUT
GND GND K19 IN
D117# D117# K20 IN/OUT
GND GND K21 IN
D114# D114# K22 IN/OUT
GND GND K23 IN
N/C K24
GND GND K25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM L01 IN
GND GND L02 IN
D017# D17# L03 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L04 IN
D019# D19# L05 IN/OUT
D021# D21# L07 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L08 IN
D053# D53# L09 IN/OUT
D056# D56# L11 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L12 IN
D052# D52# L13 IN/OUT
D081# D81# L15 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L16 IN
D088# D88# L17 IN/OUT
D082# D82# L19 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L20 IN
D112# D112# L21 IN/OUT
D116# D116# L23 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM L24 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 55
Page 56

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 7 of 15)
Pin Name
D113# D113# L25 IN/OUT
GND GND M01 IN
D020# D20# M02 IN/OUT
GND GND M03 IN
STBP1# STBP1# M04 IN/OUT
GND GND M05 IN
D028# D28# M06 IN/OUT
GND GND M07 IN
D048# D48# M08 IN/OUT
GND GND M09 IN
STBP3# STBP3# M10 IN/OUT
GND GND M11 IN
D051# D51# M12 IN/OUT
GND GND M13 IN
D084# D84# M14 IN/OUT
GND GND M15 IN
STBP5# STBP5# M16 IN/OUT
GND GND M17 IN
D086# D86# M18 IN/OUT
GND GND M19 IN
D118# D118# M20 IN/OUT
GND GND M21 IN
STBP7# STBP7# M22 IN/OUT
GND GND M23 IN
D115# D115# M24 IN/OUT
GND GND M25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM N02 IN
D023# D23# N03 IN/OUT
GND GND N04 IN
STBN1# STBN1# N05 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM N06 IN
D022# D22# N07 IN/OUT
D058# D58# N09 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM N10 IN
STBN3# STBN3# N11 IN/OUT
D055# D55# N13 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM N14 IN
D091# D91# N15 IN/OUT
STBN5# STBN5# N17 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM N18 IN
D085# D85# N19 IN/OUT
GND GND N20 IN
D127# D127# N21 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM N22 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
56 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 57

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 8 of 15)
Pin Name
STBN7# STBN7# N23 IN/OuT
GND GND N24 IN
D119# D119# N25 IN/OUT
GND GND P01 IN
D027# D27# P02 IN/OUT
GND GND P03 IN
D024# D24# P04 IN/OUT
GND GND P05 IN
D026# D26# P06 IN/OUT
GND GND P07 IN
D054# D54# P08 IN/OUT
GND GND P09 IN
D061# D61# P10 IN/OUT
GND GND P11 IN
D057# D57# P12 IN/OUT
GND GND P13 IN
D087# D87# P14 IN/OUT
GND GND P15 IN
D093# D93# P16 IN/OUT
GND GND P17 IN
D095# D95# P18 IN/OUT
GND GND P19 IN
D122# D122# P20 IN/OUT
GND GND P21 IN
D125# D125# P22 IN/OUT
GND GND P23 IN
D120# D120# P24 IN/OUT
GND GND P25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM R01 IN
GND GND R02 IN
D025# D25# R03 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R04 IN
D029# D29# R05 IN/OUT
D031# D31# R07 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R08 IN
D063# D63# R09 IN/OUT
D060# D60# R11 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R12 IN
D059# D59# R13 IN/OUT
D092# D92# R15 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R16 IN
D089# D89# R17 IN/OUT
D090# D90# R19 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R20 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 57
Page 58

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 9 of 15)
Pin Name
D124# D124# R21 IN/OUT
D126# D126# R23 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM R24 IN
D121# D121# R25 IN/OUT
GND GND T01 IN
D030# D30# T02 IN/OUT
GND GND T03 IN
DEP03# DEP3# T04 IN/OUT
GND GND T05 IN
DEP02# DEP2# T06 IN/OUT
GND GND T07 IN
DEP06# DEP6# T08 IN/OUT
GND GND T09 IN
DEP07# DEP7# T10 IN/OUT
GND GND T11 IN
D062# D62# T12 IN/OUT
GND GND T13 IN
D094# D94# T14 IN/OUT
GND GND T15 IN
DEP11# DEP11# T16 IN/OUT
GND GND T17 IN
DEP10# DEP10# T18 IN/OUT
GND GND T19 IN
DEP14# DEP14# T20 IN/OUT
GND GND T21 IN
DEP15# DEP15# T22 IN/OUT
GND GND T23 IN
D123# D123# T24 IN/OUT
GND GND T25 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U02 IN
A005# AA05#/EXF2# U03 IN/OUT
GND GND U04 IN
N/C U05
VCTERM VCTERM U06 IN
A009# AA09#/BE1# U07 IN/OUT
A018# AA18#/DID2# U09 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM U10 IN
N/C U11
A016# AA16#/DID0# U13 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM U14 IN
A028# AA28#/xTPRValue1# U15 IN/OUT
BNR# BNR# U17 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM U18 IN
A027# AA27#/xTPRValue0# U19 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
58 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 59

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 10 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND U20 IN
A048# AA48#/AB48# U21 IN/OUT
VCTERM VCTERM U22 IN
A042# AA42#/AB42# U23 IN/OUT
GND GND U24 IN
VCTERM VCTERM U25 IN
GND GND V01 IN
A004# AA04#/EXF1# V02 IN/OUT
GND GND V03 IN
A010# AA10#/BE2# V04 IN/OUT
GND GND V05 IN
A003# AA03#/EXF0# V06 IN/OUT
GND GND V07 IN
A015# AA15#/BE7# V08 IN/OUT
GND GND V09 IN
A020# AA20#/DID4# V10 IN/OUT
GND GND V11 IN
A019# AA19#/DID3# V12 IN/OUT
GND GND V13 IN
A031# AA31#/xTPRDisable# V14 IN/OUT
GND GND V15 IN
A038# AA38#/AB38# V16 IN/OUT
GND GND V17 IN
A029# AA29#/xTPRValue2# V18 IN/OUT
GND GND V19 IN
A045# AA45#/AB45# V20 IN/OUT
GND GND V21 IN
A047# AA47#/AB47# V22 IN/OUT
GND GND V23 IN
A040# AA40#/AB40# V24 IN/OUT
GND GND V25 IN
GND GND W02 IN
A006# AA06#/EXF3# W03 IN/OUT
A012# AA12#/BE4# W05 IN/OUT
A014# AA14#/BE6# W07 IN/OUT
A021# AA21#/DID5# W09 IN/OUT
A026# AA26#/AB26# W11 IN/OUT
A022# AA22#/DID6# W13 IN/OUT
A037# AA37#/AB37# W15 IN/OUT
A032# AA32#/ATTR0# W17 IN/OUT
A030# AA30#/xTPRValue3# W19 IN/OUT
A044# AA44#/AB44# W21 IN/OUT
A046# AA46#/AB46# W23 IN/OUT
A041# AA41#/AB41# W25 IN/OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 59
Page 60

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 11 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND Y01 IN
A007# AA07#/EXF4# Y02 IN/OUT
GND GND Y03 IN
A013# AA13#/BE5# Y04 IN/OUT
GND GND Y05 IN
A008# AA08#/BE0# Y06 IN/OUT
GND GND Y07 IN
A017# AA17#/DID1# Y08 IN/OUT
GND GND Y09 IN
A024# AA24#/DID8# Y10 IN/OUT
GND GND Y11 IN
A025# AA25#/DID9# Y12 IN/OUT
GND GND Y13 IN
A034# AA34#/ATTR2# Y14 IN/OUT
GND GND Y15 IN
A036# AA36#/AB36# Y16 IN/OUT
GND GND Y17 IN
A035# AA35#/ATTR3# Y18 IN/OUT
GND GND Y19 IN
A039# AA39#/AB39# Y20 IN/OUT
GND GND Y21 IN
A049# AA49#/AB49# Y22 IN/OUT
GND GND Y23 IN
A043# AA43#/AB43# Y24 IN/OUT
GND GND Y25 IN
GND GND AA02 IN
ID3# IDA3#/IDB3# AA03 IN
A011# AA11#/BE3# AA05 IN/OUT
DRDY0# DRDY_C1# AA07 OUT
DBSY0# DBSY_C1# AA09 OUT
A023# AA23#/DID7# AA11 IN/OUT
SBSY0# SBSY_C1# AA13 OUT
BINIT# BINIT# AA15 IN/OUT
A033# AA33#/ATTR1# AA17 IN/OUT
DBSY1# DBSY_C2# AA19 OUT
GND GND AA20 IN
DRDY1# DRDY_C2# AA21 OUT
AP1# AP1# AA23 IN/OUT
GND GND AA24 IN
AP0# AP0# AA25 IN/OUT
GND GND AB01 IN
ID1# IDA1#/IP1# AB02 IN
GND GND AB03 IN
ID5# IDA5#/IDB5# AB04 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
60 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 61

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 12 of 15)
Pin Name
GND GND AB05 IN
ID9# IDA9#/IDB9# AB06 IN
GND GND AB07 IN
RS2# RS2# AB08 IN
GND GND AB09 IN
HIT# HIT# AB10 IN/OUT
GND GND AB11 IN
HITM# HITM# AB12 IN/OUT
GND GND AB13 IN
DEFER# DEFER# AB14 IN
GND GND AB15 IN
N/C AB16
GND GND AB17 IN
BR2# BREQ2# AB18 IN
GND GND AB19 IN
ADS# ADS# AB20 IN/OUT
GND GND AB21 IN
BERR# BERR# AB22 IN/OUT
GND GND AB23 IN
BPM5# BPM5# AB24 IN/OUT
GND GND AB25 IN
GND GND AC02 IN
ID2# IDA2#/DHIT# AC03 IN
ID7# IDA7#/IDB7# AC05 IN
IDS# IDS# AC07 IN
DBSY# DBSY# AC09 IN/OUT
DRDY# DRDY# AC11 IN/OUT
RP# RP# AC13 IN/OUT
TND# TND# AC15 IN/OUT
N/C AC17
SBSY1# SBSY_C2# AC19 OUT
N/C# AC21
BPM3# BPM3# AC23 IN/OUT
GND GND AC24 IN
BPM1# BPM1# AC25 IN/OUT
GND GND AD01 IN
ID0# IDA0#/IP0# AD02 IN
GND GND AD03 IN
ID4# IDA4#/IDB4# AD04 IN
GND GND AD05 IN
ID8# IDA8#/IDB8# AD06 IN
GND GND AD07 IN
RS1# RS1# AD08 IN
GND GND AD09 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 61
Page 62

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 13 of 15)
Pin Name
REQ2# REQA2#/ REQB2# AD10 IN/OUT
GND GND AD11 IN
REQ5# REQ5# AD12 IN/OUT
GND GND AD13 IN
GSEQ# GSEQ# AD14 IN
GND GND AD15 IN
BR1# BREQ1# AD16 IN
GND GND AD17 IN
N/C AD18
GND GND AD19 IN
RESET# RESET# AD20 IN
GND GND AD21 IN
BPM0# BPM0# AD22 IN/OUT
GND GND AD23 IN
BPM4# BPM4# AD24 IN/OUT
GND GND AD25 IN
GND GND AE02 IN
TERMB FSBT2 AE03
ID6# IDA6#/IDB6# AE05 IN
RS0# RS0# AE07 IN
REQ0# REQA0#/LEN0# AE09 IN/OUT
REQ3# ASZ0#/DSZ0# AE11 IN/OUT
SBSY# SBSY# AE13 IN/OUT
LOCK# LOCK# AE15 N/C
N/C AE17
BPRI# BPRI# AE19 IN
TRST# TRST# AE21 IN
BPM2# BPM2# AE23 IN/OUT
GND GND AE24 IN
PMI# PMI# AE25 IN
GND GND AF01 IN
TERM FSBT AF02 IN
OUTEN OUTEN AF04 IN Power pod signal
GND GND AF05 IN
RSP# RSP# AF06 IN
GND GND AF07 IN
INIT# INIT# AF08 IN
GND GND AF09 IN
REQ1# WSNP#, D/C#/LEN1# AF10 IN/OUT
GND GND AF11 IN
REQ4# ASZ1#/DSZ1# AF12 IN/OUT
GND GND AF13 IN
TRDY# TRDY# AF14 IN
GND GND AF15 IN
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Pinout Specifications
62 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 63

Pinout Specifications
Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 14 of 15)
Pin Name
BR0# BREQ0# AF16 IN/OUT
GND GND AF17 IN
BR3# BREQ3# AF18 IN
GND GND AF19 IN
PPODGD# PPODGD# AF20 OUT Power pod signal
GND GND AF21 IN
LINT0 INT AF22 IN
LINT1 NMI AF24 IN
GND GND AG02 IN
TUNER[2] AG03 IN
GND GND AG04 IN
N/C AG05
GND GND AG06 IN
TDI TDI AG07 IN JTAG
GND GND AG08 IN
TCK TCK AG09 IN JTAG
GND GND AG10 IN
N/C AG11
GND GND AG12 IN
BCLKp CLK AG13 IN
GND GND AG14 IN
CPUPRES# CPUPRES# AG15 OUT Power pod signal
GND GND AG16 IN
N/C AG17
GND GND AG18 IN
N/C AG19
GND GND AG20 IN
N/C AG21
GND GND AG22 IN
IGNNE# IGNNE# AG23 N/C
GND GND AG24 IN
THRMTRIP# THRMTRIP# AG25 OUT Thermal trip
GND GND AH01 IN
TUNER[1] AH03 IN
N/C AH05
TDO TDO AH07 OUT JTAG
TMS TMS AH09 IN JTAG
N/C AH11
BCLKn BCLKN AH13 IN
PWRGOOD PWRGOOD AH15 IN
N/C AH17
N/C AH19
N/C AH21
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 63
Page 64

Table 3-2. Pin/Signal Information Sorted by Pin Location (Sheet 15 of 15)
Pin Name
A20M# A20M# AH23 N/C
FERR# FERR# AH25 OUT
System Bus
Signal Name
Pin
Location
Input/Output Notes
§
Pinout Specifications
64 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 65

Mechanical Specifications
4 Mechanical Specifications
This chapter provides the mechanical specifications of the Dual-Core Intel Itanium
processor 9000 and 9100 series.
4.1 Processor Package Dimensions
Figure 4-1 through Figure 4-5 provide package mechanical drawings and dimensions of
the processor. Table 4-1 and Table 4-2 provide additional details on the package
dimensions. The main components of processor package are identified in Figure 4-2. All
specified package dimensions are in millimeters.
Figure 4-1 illustrates key package mechanical features. These features enable package
integration with socket, power pod, and cooling solution.
• Vcore, Vcache, Vfixed, GND, and VID Pads: Contact pads for delivering power
and I/O signals from the voltage regulator to the processor through its substrate.
• Socket Alignment Keyways: They define package position in X and Y direction
with respect to socket for proper alignment of package pins to socket contact holes.
• Pin Shroud Alignment Keyways: They define pin shroud position in X and Y
direction with respect to processor.
• Pin 1 Indicators: Identifies package orientation with respect to socket and
motherboard.
• Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS): Enhances dissipation of heat generated by the
processor. Provides interface surface between processor and cooling solution.
• Substrate: Processor mechanical and electrical integration vehicle with the
motherboard and processor enabling components.
• Pin Field (Grid): 28 x 25 partially-filled pin field for transmitting signals to and
from processor to motherboard.
• Voltage Regulator Connector Back Plate Keyway: It defines the VR connector
back plate position in X and Y direction with respect to the processor.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 65
Page 66

Figure 4-1. Processor Package
Mechanical Specifications
G
1
H
1
A1
J
2
A25 AH25
J
1
B
1
AH1
Bottom View
C
1
H
2
G
2
Side View
B
C
2
B
2
A1
Package
C
L
D
IHS
C
L
1
A
Top View
A
Front View
001349
66 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 67

Mechanical Specifications
Table 4-1. Processor Package Dimensions
Figure 4-2. Package Height and Pin Dimensions
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 67
Page 68

Table 4-2. Processor Package Mechanical Interface Dimensions
Mechanical Specifications
68 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 69

Mechanical Specifications
Figure 4-3. Processor Package Mechanical Interface Dimensions
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 69
Page 70

Mechanical Specifications
Figure 4-4. Processor Package Top-Side Components Height Dimensions
Note: Keepout zones indicate no components will be on the processor package.
Figure 4-5. Processor Package Bottom-Side Components Height Dimensions
Note: Keepout zones indicate no components will be on the processor package.
70 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 71

Mechanical Specifications
4.1.1 Voltage Regulator (MVR) to Processor Package Interface
Critical package mechanical requirements at its interface with the MVR are identified in
Figure 4-6 and Table 4-3. The processor interface boundary conditions with which MVR
must comply during and after installation are outlined in Table 4-3. These requirements
are intended to minimize potential damage to the processor that may result from
installation of the MVR.
Figure 4-6. Processor to MVR Interface Loads
Y
T
X
X
Z
Z
90
P
-z
T
A
90
y
P
+z
Processor Heatsink
Processor Heatsink
IHS
Socket
Table 4-3. Processor Package Load Limits at Power Tab (Sheet 1 of 2)
Parameter Description Value
A Final position of the package at the
power tab (unloaded) with respect to
system board
P Allowable load on the package in +z
and -z direction
d Allowable displacement at the
processor power tab in z direction
under load P
Tz Allowable torque on the package tip in
z axis
3.8+/-
0.1mm
22.25N max
+/- 0.3 mm
max
0 Package loading in Y direction is not
1
Position of the processor power tab is
based on the height of the mPGA700
ZIF socket height from the mother
post SMT
allowed. Hence, zero torque in Z-axis
Substrate
Mother Board
Comments
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 71
Page 72

Table 4-3. Processor Package Load Limits at Power Tab (Sheet 2 of 2)
Parameter Description Value
Tx Allowable torque at the package power
T+y Allowable torque at the package power
tab in X axis
tab in +y direction
Allowable torque at the package power
tab in -y direction
0.57Nm max
1.24 Nm max Torque on the package edge in +Y
T-y
Notes:
1. Load determination done with 100-lb. load on the processor heatsink.
1
0.93Nm
max
direction is determined by the load
applied in -Z and the distance from the
edge the package to the socket.
Torque on the package edge in -Y
direction is determined by the load
applied in +Z and the distance from
the edge the package to the heatsink
base.
To determine T+y, distance from the
edge the package to the socket of
55.7mm is applied
To determine T-y, distance from the
edge the package to the heatsink
pedestal of 42mm is applied
4.2 Package Marking
Mechanical Specifications
Comments
The following section details the processor top-side and bottom-side markings for
engineering samples and production units. This is provided to aid in identification.
Specific details regarding individual fields in the product markings will be furnished in a
future release of this document.
4.2.1 Processor Top-Side Marking
The top-side mark is a laser marking on the IHS. Figure 4-7 shows the general location
of the processor top-side mark that provides the following information:
• Intel
• Itanium® Processor Family Legal Mark
• Assembly Process Order (APO) Number
• Unit Serial Number
• 2D Matrix Mark
®
72 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 73

Mechanical Specifications
Figure 4-7. Processor Top-Side Marking on IHS
4.2.2 Processor Bottom-Side Marking
The processor bottom-side mark for the product is a laser marking on the pin side of
the interposer. Figure 4-8 shows the placement of the laser marking on the pin side of
interposer. The processor bottom-side mark provides the following information:
• Product ID
• S-Spec
• Finish Process Order (FPO)
• 2D Matrix Mark
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 73
Page 74

Figure 4-8. Processor Bottom-Side Marking Placement on Interposer
Laser Marking
2D Matrix Mark (see notes)
2D Matrix Mark (see notes)
Laser Marking
Mechanical Specifications
§
74 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 75

Thermal Specifications
5 Thermal Specifications
This chapter provides a description of the thermal features relating to the Dual-Core
Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series.
5.1 Thermal Features
The processor has an internal thermal circuit which senses when a certain temperature
is reached on the processor core. This circuit is used for controlling various thermal
states. In addition, an on-chip thermal diode is available for use by the thermal sensing
device on the processor. Figure 5-1 shows the relationship between temperature, time,
and the thermal alert, enhanced thermal management (ETM), and thermal trip points.
Note: Figure 5-1 is not intended to show a linear relationship in time or temperature as a
processor's thermal state advances from one state to the next state when the cooling
solution fails to control the processor temperature, as this is affected by many factors
such as cooling solution performance degradation and processor workload variations.
Figure 5-1. Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Thermal Features
5.1.1 Thermal Alert
THRMALERT# is a programmable thermal alert signal which is part of the processor
system management feature. THRMALERT# is asserted when the measured
temperature from the processor thermal diode equals or exceeds the temperature
threshold data programmed in the high temp (THIGH) or low temp (TLOW) registers on
the sensor. Intel recommends using the upper temperature reference byte listed in the
Processor Information ROM when programming the THIGH register (see Chapter 6 for
more details). This signal can be used by the platform to implement thermal regulation
features such as generating an external interrupt to tell the operating system that the
processor core die temperature is increasing.
Thermal Alert
Time
ETM
Thermal Trip
000653b
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 75
Page 76

5.1.2 Enhanced Thermal Management
ETM is a power and thermal protection feature. On the Dual-Core Intel Itanium
processor 9000 and 9100 series, ETM uses power and thermal sensing devices on the
die to monitor entry points, indicating dangerous operation exceeding the thermal or
power specification. Once the sensing devices observe the temperature rising above
the power or thermal entry point, the processor will enter a low power mode of
execution and notify the system by sending a Correctable Machine Check Interrupt
(CMCI). The processor will remain in this low power mode until the power and
temperature decrease below the entry points and remain there for approximately one
second, at which point it will send another CMCI and resume normal operation. If the
power and temperature cannot be reduced, and continue to rise to critical levels, the
processor will assert Power Trip or Thermal Trip. The ETM feature may be disabled
through the PAL.
5.1.3 Power Trip
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series protects itself and the
MVR from catastrophic over power by use of an internal power sensor. The sensor trip
point is set above the normal operating power to ensure that there are no false trips.
The processor will signal a continuable MCA when the power draw exceeds a safe
operating level.
Thermal Specifications
Warning: Data will be lost if the MVR overheats and shuts down as a result of an extended over
power condition.
Once power trip is activated, the processor can continue operation, but may continue to
signal continuable MCAs as long as the over power condition exists.
5.1.4 Thermal Trip
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series protects itself from
catastrophic overheating by use of an internal thermal sensor. The sensor trip point is
set well above the normal operating temperature to ensure that there are no false trips.
The processor will stop all execution when the junction temperature exceeds a safe
operating level.
Warning: Data will be lost if the processor goes into thermal trip (signaled to the system by the
THRMTRIP# pin).
Once thermal trip is activated, the processor remains stopped until RESET# is asserted.
The processor case temperature must drop below the specified maximum before
issuing a reset to the processor. Please see Section 5.2 for details on case temperature.
5.2 Case Temperature
See Table 5-1 for the case temperature specifications for the Dual-Core Intel Itanium
processor 9000 and 9100 series. The case temperature is defined as the temperature
measured at the center of the top surface of the IHS.
Warning: Data may be lost if the case temperature exceeds the specified maximum.
76 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 77

Thermal Specifications
2
Table 5-1. Case Temperature Specification
Symbol Parameter
Tcase Case Temperature 1.6GHz/24MB 5 76 °C
Core
Frequency
1.6GHz/18MB 5 76 °C
1.6GHz/9MB 5 76 °C
1.42GHz/12MB 5 76 °C
1.4GHz/12MB 5 76 °C
1.6GHz/6MB 5 74 °C
Minimum Maximum Unit Notes
Figure 5-2 contains dimensions for the thermocouple location on the processor
package. This is the recommended location for placement of a thermocouple for case
temperature measurement.
Figure 5-2. Itanium® Processor Package Thermocouple Location
4.13
45.00
All dimensions are measured in mm. Not to scale.
Thermocouple Location
001103a
§
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 77
Page 78

Thermal Specifications
78 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 79

System Management Feature Specifications
6 System Management Feature
Specifications
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series includes a system
management bus (SMBus) interface. This chapter describes the features of the SMBus
and SMBus components.
6.1 System Management Bus
6.1.1 System Management Bus Interface
The processor includes an Itanium processor family SMBus interface which allows
access to several processor features. The system management components on the
processor include two memory components (EEPROMs) and a thermal sensing device
(digital thermometer). The processor information EEPROM (PIROM) is programmed by
Intel with manufacturing and feature information specific to the Dual-Core Intel
Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series. This information is permanently writeprotected. Section 6.2 provides details on the PIROM. The other EEPROM is a scratch
EEPROM that is available for other data at the system vendor’s discretion. The thermal
sensor can be used in conjunction with the information in the PIROM and/or the Scratch
EEPROM for system thermal monitoring and management. The thermal sensing device
on the processor provides an accurate means of acquiring an indicator of the junction
temperature of the processor core die. The thermal sensing device is connected to the
anode and cathode of the processor on-die thermal diode. SMBus implementation on
the processor uses the clock and data signals as defined by SMBus specifications.
6.1.2 System Management Interface Signals
Table 6-1 lists the system management interface signals and their descriptions. These
signals are used by the system to access the system management components via the
SMBus.
Table 6-1. System Management Interface Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Pin Count Description
3.3V 1 Voltage supply for EEPROMs and thermal sensor.
SMA[2:0] 3 Address select passed through from socket.
SMSC 1 System management bus clock.
SMSD 1 System management serial address/data bus.
SMWP 1 Scratch EEPROM write protect.
THRMALERT# 1 Temperature alert from the thermal sensor.
Figure 6-1 shows the logical schematics of SMBus circuitry on the processor and shows
how the various system management components are connected to the SMBus. The
reference to the System Board at the lower left corner of Figure 6-1 shows how SMBus
address configuration for multiple processors can be realized with resistor stuffing
options.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 79
Page 80

Figure 6-1. Logical Schematic of SMBus Circuitry
System Management Feature Specifications
10K
10K
SMA0
SMA1
3.3V
10K
V
A0
A1
A2
A0
A1
A2
SMA23.3V
CC
Processor
Information
ROM
V
CC
Scratch
EEPROM
SC
SD
SC
SD
WP
10K 10K
10K
SMWP
SMSD
SMSC THRMALERT#
Intel® Itanium® 2 Processor
VCC
A0
Thermal
Sensing
A1
Device
ALERT
Core
THERMDA
THERMDC
STBY
SC
SD
System Board
3.3V
Stuffing
Options
System Board
3.3V
10K
NOTE:
1. Actual implementation may vary.
2. For use in general understanding of the architecture.
000668b
80 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 81

System Management Feature Specifications
6.1.3 SMBus Device Addressing
Of the addresses broadcast across the SMBus, the memory components claim those of
the form “1010XXYZb”. The “XX” and “Y” bits are used to enable the devices on the
processor at adjacent addresses. The Y bit is hard-wired on the processor to GND (‘0’)
for the Scratch EEPROM and pulled to 3.3 V (‘1’) for the processor information ROM.
The “XX” bits are defined by the processor socket via the SMA0 and SMA1 pins on the
processor connector. These address pins have a weak pull-down (10 k ) to ensure that
the memory components are in a known state in systems which do not support the
SMBus, or only support a partial implementation. The “Z” bit is the read/write bit for
the serial bus transaction.
The thermal sensing device internally decodes one of three upper address patterns
from the bus of the form “0011XXXZb”, “1001XXXZb” or “0101XXXZb”. The device’s
addressing, as implemented, uses SMA2 and SMA1 and includes a Hi-Z state for the
SMA2 address pin. Therefore, the thermal sensing device supports six unique resulting
addresses. To set the Hi-Z state for SMA2, the pin must be left floating. The system
should drive SMA1 and SMA0, and will be pulled low (if not driven) by the 10 k pulldown resistor on the processor substrate. Attempting to drive either of these signals to
a Hi-Z state would cause ambiguity in the memory device address decode, possibly
resulting in the devices not responding, thus timing out or hanging the SMBus. As
before, the “Z” bit is the read/write bit for the serial bus transaction.
Figure 6-1 shows a logical diagram of the pin connections. Table 6-2 and Table 6-3
describe the address pin connections and how they affect the addressing of the
devices.
Note: Addresses of the form “0000XXXXb” are Reserved and should not be generated by an
SMBus master. Also, system management software must be aware of the processor
select in the address for the thermal sensing device.
Table 6-2. Thermal Sensing Device SMBus Addressing on the Dual-Core Intel® Itanium
Processor 9000 and 9100 series
Address (Hex) Upper Address
3Xh 0011 0 0 0011000Xb
0011 0 1 0011010Xb
5Xh 0101 Z
0101 Z
9Xh 1001 1 0 1001100Xb
1001 1 1 1001110Xb
Notes:
1. Upper address bits are decoded in conjunction with the select pins.
2. A tri-state or “Z” state on this pin is achieved by leaving this pin unconnected.
1
Processor Select 8-Bit Address Word on Serial Bus
SMA2 SMA1 b[7:0]
2
b
0 0101001Xb
1 0101011Xb
®
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 81
Page 82

System Management Feature Specifications
Table 6-3. EEPROM SMBus Addressing on the Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000
and 9100 Series
Upper
Address
(Hex)
A0h/A1h 1010 0 0 0 X Scratch EEPROM 1
A2h/A3h 1010 0 0 1 X Processor Information ROM 1
A4h/A5h 1010 0 1 0 X Scratch EEPROM 2
A6h/A7h 1010 0 1 1 X Processor Information ROM 2
A8h/A9h 1010 1 0 0 X Scratch EEPROM 3
AAh/ABh 1010 1 0 1 X Processor Information ROM 3
ACh/ADh 1010 1 1 0 X Scratch EEPROM 4
AEh/AFh 1010 1 1 1 X Processor Information ROM 4
Notes:
1. Although this addressing scheme is targeted for up to four-way MP systems, more processors can be supported
by using a multiplexed (or separate) SMBus implementation.
Address
Bits 7–4
Processor Select
1
(SMA1)
Bit 3
(SMA0)
Bit 2
Memory
Device
Select
Bit 1 Bit 0
6.2 Processor Information ROM
An electrically programmed read-only memory (ROM) provides information about the
processor. The checksum bits for each category provide error correction and serve as a
mechanism to check whether data is corrupted or not. This information is permanently
write-protected. Table 6-4 shows the data fields and formats provided in the memory.
Read/
Write
Device Addressed
Note: The data, in byte format, is written and read serially, with the most significant bit first.
Table 6-4. Processor Information ROM Format (Sheet 1 of 3)
Offset/
Section
Header
00h 8 Data Format Revision Two 4-bit hex digits Start with 00h
01h 16 EEPROM Size Size in bytes (MSB first) Use a decimal to hex
03h 8 Processor Data Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 0Eh
04h 8 Processor Core Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 17h
05h 8 Processor Cache Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 28h
06h 8 Processor Data Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 37h
07h 8 Part Number Data Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 3Eh
08h 8 Thermal Reference Data
09h 8 Feature Data Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 67h
0Ah 8 Other Data Address Byte pointer, 00h if not present 7Ah
# of
Bits
Address
Function Notes Examples
transfer; 128 bytes =
0080h:
• 02h[7:4] = 0000
• 02h[3:0] = 0000
• 01h[7:4] = 1000
• 01h[3:0] = 0000
Byte pointer, 00h if not present 63h
82 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 83

System Management Feature Specifications
Table 6-4. Processor Information ROM Format (Sheet 2 of 3)
Offset/
Section
0Bh 16 Reserved Reserved for future use 0000h
0Dh 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Processor
0Eh 48 S-spec Number Six 8-bit ASCII characters S-spec number of S123
14h 2 Sample/Production 00b = Sample only (MSB First) 00000001b = Production
15h 8 Reserved Reserved for future use 00h
16h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Core
17h 8 Architecture Revision From CPUID
18h 8 Processor Core Family From CPUID Taken from
19h 8 Processor Core Model From CPUID Taken from
1Ah 8 Processor Core Stepping From CPUID Taken from
1Bh 24 Reserved Reserved for future use 000000h
1Eh 16 Maximum Core Frequency Four 4-bit hex digits (in MHz) 1 GHz = 1000h
20h 12 Maximum System Bus
22h 16 Core Voltage ID Voltage in four 4-bit hex digits
24h 8 Core Voltage Tolerance, High Edge finger tolerance in mV, +
25h 8 Core Voltage Tolerance, Low Edge finger tolerance in mV, –
26h 8 Reserved Reserved for future use 00h
27h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Cache
28h 32 Reserved Reserved for future use 00000000h
2Ch 16 Cache Size Four 4-bit hex digits (in Kbytes) 3072 Kbytes = 3072h
2Eh 64 Reserved Reserved for future use x0h
36h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum
Package
37h 32 Package Revision Four 8-bit ASCII characters NE:
3Bh 2 Substrate Revision Software ID2-bit revision number 00
# of
Bits
Function Notes Examples
1
Three 4-bit hex digits (in MHz) 200 MHz = 200h
Frequency
(in mV)
two 4-bit hex digits
two 4-bit hex digits
2’s complement.
would be:
• 13h = 00h
• 12h = 00h
• 11h = “3”
• 10h = “2”
• 0Fh = “1”
• 0Eh = “S”
2’s complement.
Taken from
CPUID[3].archrev.
CPUID[3].family.
CPUID[3].model.
CPUID[3].revision.
2
1
1500 mV = 1500h
1
1.5% = 22 mV = 22h
1.5% = 22 mV = 22h
2’s complement.
• 37h = N
• 38h = E
• 39h = 0
• 3Ah = 0
1
1
1,3
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 83
Page 84

System Management Feature Specifications
Table 6-4. Processor Information ROM Format (Sheet 3 of 3)
Offset/
Section
3Ch 8 Reserved Reserved for future use 00h
3Dh 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Part Numbers
3Eh 56 Processor Part Number Seven 8-bit ASCII characters 80549KC
45h 64 Processor Electronic
4Dh 168 Reserved Reserved for future use x0h
62h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Thermal Reference
63h 8 Upper Temp Reference Byte Hex value of thermal upper temp
64h 8 Thermal Calibration Offset
65h 8 Reserved Reserved for future use 00h
66h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Features
67h 32 IA-32 Processor Core
6Bh 64 Reserved Reserved (Processor core feature
73h 32 Processor Feature Flags All others are reserved:
77h 4 Number of Devices in TAP
78h 4 Reserved Reserved for future use 0h
79h 8 Checksum 1 byte checksum Add up by byte and take
Other
7Ah 16 Reserved Reserved for future use 0000h
# of
Bits
Function Notes Examples
Signature
Byte Present
Feature Flags
Chain
64-bit identification number May have padded zeros
limit
Number of degrees in error (±) will be set per
From 32 bit CPUID 4387FBFFh
flags implemented in the
Itanium® processor family)
[9] = Demand Based Switching
Enabled
[8] = Core Level Lockstep
Enabled
[7] = Socket Level Lockstep
Enabled
[6] = Dual Core Enabled
[5] = Hyper-Threading Enabled
[4] = Upper temp reference byte
[3] = Thermal calibration offset
byte present
[2] = Scratch EERPOM present
[1] = Core VID Present
One 4-bit hex digit 2h for dual-core
2’s complement
• 3Eh = “8”
• 3Fh = “0”
• 40h = “5”
• 41h = “4”
• 42h = “2”
• 43h = “K”
• 44h = “C”
2’s complement
Default = 92 = 5Ch
part and expected to be
~ +12C
2’s complement.
0000 0000 6380 811Bh
1 indicates EEPROM data
for specified field is valid.
processor
2’s complement.
84 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 85

System Management Feature Specifications
Notes:
1. Refer to the Intel® Itanium™ Architecture Software Developer’s Manual for details on CPUID registers.
2. The translation is using BCD.
3. Itanium 9000 and 9100 series use a hex-to-decimal conversion
6.3 Scratch EEPROM
Also available on the SMBus interface on the processor is an EEPROM which may be
used for other data at the system vendor’s discretion (Intel will not be using the scratch
EEPROM). The data in this EEPROM, once programmed, can be write-protected by
asserting the active-high SMWP signal. This signal has a weak pull-down (10 k ) to
allow the EEPROM to be programmed in systems with no implementation of this signal.
6.4 Processor Information ROM and Scratch EEPROM
Supported SMBus Transactions
The processor information ROM and scratch EEPROM responds to three of the SMBus
packet types: current address read, random address read, and sequential read.
Table 6-5 shows the format of the current address read SMBus packet. The internal
address counter keeps track of the address accessed during the last read or write
operation, incremented by one. Address “roll over” during reads is from the last byte of
the last eight byte page to the first byte of the first page. “Roll over” during writes is
from the last byte of the current eight byte page to the first byte of the same page.
Table 6-6 shows the format of the random read SMBus packet. The write with no data
loads the address desired to be read. Sequential reads may begin with a current
address read or a random address read. After the SMBus host controller receives the
data word, it responds with an acknowledge. This will continue until the SMBus host
controller responds with a negative acknowledge and a stop.
Table 6-7 shows the format of the byte write SMBus packet. The page write operates
the same way as the byte write, except that the SMBus host controller does not send a
stop after the first data byte and acknowledge. The Scratch EEPROM internally
increments its address. The SMBus host controller continues to transmit data bytes
until it terminates the sequence with a stop. All data bytes will result in an acknowledge
from the Scratch EEPROM. If more than eight bytes are written, the internal address
will “roll over” and the previous data will be overwritten.
In Table 6-5 through Table 6-7, ‘S’ represents the SMBus start bit, ‘P’ represents a stop
bit, ‘R’ represents a read, ‘W’ represents a write bit, ‘A’ represents an acknowledge, and
‘///’ represents a negative acknowledge. The shaded bits are transmitted by the
processor information ROM or Scratch EEPROM and the bits that are not shaded are
transmitted by the SMBus host controller. In the tables, the data addresses indicate
eight bits. The SMBus host controller should transmit eight bits, but as there are only
128 addresses, the most significant bit is a don’t care.
Table 6-5. Current Address Read SMBus Packet
Device
S
Address
1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 1
R A Data /// P
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 85
Page 86

Table 6-6. Random Address Read SMBus Packet
System Management Feature Specifications
Device
S
Address
1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 1
W A
Data
Address
A S
Table 6-7. Byte Write SMBus Packet
Device
S
Address
1 7 bits 0 1 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 1
W A
Data
Address
A Data A P
6.5 Thermal Sensing Device
The Dual-Core Intel Itanium processor 9000 and 9100 series thermal sensing device
provides a means of acquiring thermal data from the processor. The accuracy of the
thermal reading is expected to be better than ±5 °C. The thermal sensing device is
composed of control logic, SMBus interface logic, a precision analog to digital converter,
and a precision current source. The thermal sensing device drives a small current
through a thermal diode located on the processor core and measures the voltage
generated across the thermal diode by the current. With this information, the thermal
sensing device computes a byte of temperature data. Software running on the
processor or on a micro-controller can use the temperature data from the thermal
sensing device to thermally manage the system.
The thermal sensing device provides a register with a data byte (seven bits plus sign)
which contains a value corresponding to the sampled output of the thermal diode in the
processor core. The value of the byte read from the thermal sensor is always higher
than the actual processor core temperature; therefore, the offset from the reading
needs to be subtracted to obtain an accurate reading of the processor core
temperature. This data can be used in conjunction with the upper temperature
reference byte (provided in the Processor Information ROM) for thermal management
purposes. The temperature data from the thermal sensor can be read out digitally
using an SMBus read command (see Section 6.6). The thermal sensor detects when
SMBus power is applied to the processor, and resets itself at power-up.
Device
Address
R A Data /// P
The thermal sensing device also contains alarm registers to store thermal reference
threshold data. These values can be individually programmed on the thermal sensor. If
the measured temperature equals or exceeds the alarm threshold value, the
appropriate bit is set in the thermal sensing device status register, which is also
brought out to the processor system bus via the THRMALERT# signal (see
Section 6.1.1 for more details). At power-up, the appropriate alarm register values
need to be programmed into the thermal sensing device via the SMBus. It is
recommended that the upper thermal reference threshold byte (provided in the
processor information ROM) be used for setting the upper threshold value in the alarm
register. To account for the offset inherent in the thermal sensing device reading, the
actual programmed value of the upper threshold value in the alarm register should be
the sum of the upper thermal reference threshold byte and the thermal calibration
offset byte (both provided in the PIROM).
When polling the thermal sensing device on the processor to read the processor
temperatures, it is recommended that the polling frequency be every 0.5 to 1 second.
86 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 87

System Management Feature Specifications
6.6 Thermal Sensing Device Supported SMBus
Transactions
The thermal sensing device responds to five of the SMBus packet types: write byte,
read byte, send byte, receive byte, and alert response address (ARA). The send byte
packet is used for sending one-shot commands only. The receive byte packet accesses
the register commanded by the last read byte packet. If a receive byte packet was
preceded by a write byte or send byte packet more recently than a read byte packet,
then the behavior is undefined. Table 6-8 through Table 6-12 diagram the five packet
types. In these tables, ‘S’ represents the SMBus start bit, ‘P’ represents a stop bit, ‘Ack’
represents an acknowledge, and ‘///’ represents a negative acknowledge. The shaded
bits are transmitted by the thermal sensor and the unshaded bits are transmitted by
the SMBus host controller. Table 6-13 shows the encoding of the command byte.
Table 6-8. Write Byte SMBus Packet
S Address Write Ack Command Ack Data Ack P
1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 1
Table 6-9. Read Byte SMBus Packet
S Address Write Ack Command Ack S Address Read Ack Data
1 7 bits 0 1 8 bits 1 1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 1
Table 6-10. Send Byte SMBus Packet
S Address Write Ack Command Ack P
1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1
Table 6-11. Receive Byte SMBus Packet
S Address Read Ack Data /// P
1 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1 1
Table 6-12. ARA SMBus Packet
S ARA Read Ack Address /// P
1 0001 100 1 1 1001 1011 1 1
//
P
/
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 87
Page 88

Table 6-13. Command Byte Bit Assignment
Register Command Reset State Function
RESERVED 00h N/A Reserved for future use.
RRT 01h N/A Read processor core thermal data.
RS 02h N/A Read status byte (flags, busy signal).
RC 03h 0000 0000 Read configuration byte.
RCR 04h 0000 0010 Read conversion rate byte.
RESERVED 05h 0111 1111 Reserved for future use.
RESERVED 06h 1100 1001 Reserved for future use.
RRHL 07h 0111 1111 Read processor core thermal diode T
RRLL 08h 1100 1001 Read processor core thermal diode T
WC 09h N/A Write configuration byte.
WCR 0Ah N/A Write conversion rate byte.
RESERVED 0Bh N/A Reserved for future use.
RESERVED 0Ch N/A Reserved for future use.
WRHL 0Dh N/A Write processor core thermal diode T
WRLL 0Eh N/A Write processor core thermal diode T
OSHT 0Fh N/A One shot command (use send byte packet).
RESERVED 10h – FFh N/A Reserved for future use.
All of the commands are for reading or writing registers in the thermal sensor except
the one-shot command (OSHT). The one-shot command forces the immediate start of
a new voltage-to-temperature conversion cycle. If a conversion is in progress when the
one-shot command is received, then the command is ignored. If the thermal sensing
device is in standby mode when the one-shot command is received, a conversion is
performed and the sensor returns to standby mode. If the thermal sensor is in autoconvert mode and is between conversions, then the conversion rate timer resets, and
the next automatic conversion takes place after a full delay elapses. Please refer to
Section 6.7.4 for further detail on standby and auto-convert modes.
System Management Feature Specifications
limit.
HIGH
limit.
LOW
limit.
HIGH
limit.
LOW
The default command after reset is the reserved value (00h). After reset, receive byte
packets will return invalid data until another command is sent to the thermal sensing
device.
6.7 Thermal Sensing Device Registers
The system management software can configure and control the thermal sensor by
writing to and interacting with different registers in the thermal sensor. These registers
include a thermal reference register, two thermal limit registers, a status register, a
configuration register, a conversion rate register, and other reserved registers. The
following subsections describe the registers in detail.
6.7.1 Thermal Reference Registers
The processor core and thermal sensing device internal thermal reference registers
contain the thermal reference value of the thermal sensing device and the processor
core thermal diodes. This value ranges from +127 to –128 decimal and is expressed as
a two’s complement, eight-bit number. These registers are saturating, that is, values
above 127 are represented at 127 decimal, and values below –128 are represented as
–128 decimal.
88 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 89

System Management Feature Specifications
6.7.2 Thermal Limit Registers
The thermal sensing device has two thermal limit registers; they define high and low
limits for the processor core thermal diode. The encoding for these registers is the
same as for the thermal reference registers. If the diode thermal value equals or
exceeds one of its limits, then its alarm bit in the status register is triggered. This
indication is also brought out to the processor system bus via the THRMALERT# signal.
6.7.3 Status Register
The status register shown in Table 6-14 indicates which (if any) of the thermal value
thresholds have been exceeded. It also indicates if a conversion is in progress or if an
open circuit has been detected in the processor core thermal diode connection. Once
set, alarm bits stay set until they are cleared by a status register read. A successful
read to the status register will clear any alarm bits that may have been set, unless the
alarm condition persists. Note that the THRMALERT# interrupt signal is latched and is
not automatically cleared when the status flag bit is cleared. The latch is cleared by
sending the Alert Response Address (0001100) on the SMBus.
Table 6-14. Thermal Sensing Device Status Register
Bit Name Function
7 (MSB) BUSY A one indicates that the device’s analog to digital converter is busy converting.
6 RESERVED Reserved for future use.
5 RESERVED Reserved for future use.
4 RHIGH A one indicates that the processor core thermal diode high temperature alarm has
3 RLOW A one indicates that the processor core thermal diode low temperature alarm has
2 OPEN A one indicates an open fault in the connection to the processor core diode.
1 RESERVED Reserved for future use.
0 (LSB) RESERVED Reserved for future use.
been activated.
been activated.
6.7.4 Configuration Register
The configuration register controls the operating mode (standby vs. auto-convert) of
the thermal sensing device. Table 6-15 shows the format of the configuration register.
If the RUN/STOP bit is set (high) then the thermal sensing device immediately stops
converting and enters standby mode. The thermal sensing device will still perform
analog-to-digital conversions in standby mode when it receives a one-shot command.
If the RUN/STOP bit is clear (low) then the thermal sensor enters auto-conversion
mode. The thermal sensing device starts operating in free running mode, autoconverting at 0.25 Hz after power-up.
Table 6-15. Thermal Sensing Device Configuration Register
Bit Name
7 (MSB) RESERVED 0 Reserved for future use.
6 RUN/STOP 0 Standby mode control bit. If high, the device immediately stops
5–0 RESERVED 0 Reserved for future use.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 89
Reset
State
Function
converting, and enters standby mode. If low, the device converts in
either one-shot or timer mode.
Page 90

System Management Feature Specifications
6.7.5 Conversion Rate Register
The contents of the conversion rate register determine the nominal rate at which
analog-to-digital conversions happen when the thermal sensing device is in autoconvert mode. Table 6-16 shows the mapping between conversion rate register values
and the conversion rate. As indicated in Table 6-16, the conversion rate register is set
to its default state of 02h (0.25 Hz nominally) when the thermal sensing device is
powered-up. There is a ±25% error tolerance between the conversion rate indicated in
the conversion rate register and the actual conversion rate.
Table 6-16. Thermal Sensing Device Conversion Rate Register
Register Contents Conversion Rate (Hz)
00h 0.0625
01h 0.125
02h 0.25
03h 0.5
04h 1
05h 2
06h 4
07h 8
08h to FFh Reserved for future use
§
90 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 91

Signals Reference
A Signals Reference
This appendix provides an alphabetical listing of all Dual-Core Intel Itanium 9000 and
9100 series processor system bus signals. The tables at the end of this appendix
summarize the signals by direction: output, input, and I/O.
For a complete pinout listing including processor specific pins, please refer to
Chapter 3, “Pinout Specifications.”
A.1 Alphabetical Signals Reference
A.1.1 A[49:3]# (I/O)
The Address (A[49:3]#) signals, with byte enables, define a 250Byte physical memory
address space. When ADS# is active, these pins transmit the address of a transaction.
These pins are also used to transmit other transaction related information such as
transaction identifiers and external functions in the cycle following ADS# assertion.
These signals must connect the appropriate pins of all agents on the processor system
bus. The A[49:27]# signals are parity-protected by the AP1# parity signal, and the
A[26:3]# signals are parity-protected by the AP0# parity signal.
On the active-to-inactive transition of RESET#, the processors sample the A[49:3]#
pins to determine their power-on configuration.
A.1.2 A20M# (I)
A20M# is no connect and is ignored in the processor system environment.
A.1.3 ADS# (I/O)
The Address Strobe (ADS#) signal is asserted to indicate the validity of the transaction
address on the A[49:3]#, REQ[5:0]#, AP[1:0]# and RP#pins. All bus agents observe
the ADS# activation to begin parity checking, protocol checking, address decode,
internal snoop, or deferred reply ID match operations associated with the new
transaction.
A.1.4 AP[1:0]# (I/O)
The Address Parity (AP[1:0]#) signals can be driven by the request initiator along with
ADS# and A[49:3]#. AP[1]# covers A[49:27]#, and AP[0]# covers A[26:3]#. A
correct parity signal is high if an even number of covered signals are low and low if an
odd number of covered signals are low. This allows parity to be high when all the
covered signals are high.
A.1.5 ASZ[1:0]# (I/O)
The ASZ[1:0]# signals are the memory address-space size signals. They are driven by
the request initiator during the first Request Phase clock on the REQa[4:3]# pins. The
ASZ[1:0]# signals are valid only when REQa[2:1]# signals equal 01B, 10B, or 11B,
indicating a memory access transaction. The ASZ[1:0]# decode is defined in Table A-1.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 91
Page 92

Table A-1. Address Space Size
Signals Reference
ASZ[1:0]#
0 0 Reserved Reserved
0 1 36-bit 0 to (64 GByte - 1)
1 0 50-bit 64 GByte to
1 1 Reserved Reserved
Memory Address
Space
Any memory access transaction addressing a memory region that is less than 64 GB
(that is, Aa[49:36]# are all zeroes) must set ASZ[1:0]# to 01. Any memory access
transaction addressing a memory region that is equal to or greater than 64 GB (that is,
Aa[49:36]# are not all zeroes) must set ASZ[1:0]# to 10. All observing bus agents
that support the 64 GByte (36-bit) address space must respond to the transaction
when ASZ[1:0]# equals 01. All observing bus agents that support larger than the 64
GByte (36-bit) address space must respond to the transaction when ASZ[1:0]# equals
01 or 10.
A.1.6 ATTR[3:0]# (I/O)
The ATTR[3:0]# signals are the attribute signals. They are driven by the request
initiator during the second clock of the Request Phase on the Ab[35:32]# pins. The
ATTR[3:0]# signals are valid for all transactions. The ATTR[3]# signal is reserved. The
ATTR[2:0]# are driven based on the memory type. Please refer to Table A-2.
Table A-2. Effective Memory Type Signal Encoding
Memory Access
Range
(1 Pbyte –1)
ATTR[2:0]# Description
000 Uncacheable
100 Write Coalescing
101 Write-Through
110 Write-Protect
111 Writeback
A.1.7 BCLKp/BCLKn (I)
The BCLKp and BCLKn differential clock signals determine the bus frequency. All agents
drive their outputs and latch their inputs on the differential crossing of BCLKp and
BCLKn on the signals that are using the common clock latched protocol.
BCLKp and BCLKn indirectly determine the internal clock frequency of the processor.
Each processor derives its internal clock by multiplying the BCLKp and BCLKn
frequency by a ratio that is defined and allowed by the power-on configuration.
A.1.8 BE[7:0]# (I/O)
The BE[7:0]# signals are the byte-enable signals for partial transactions. They are
driven by the request initiator during the second Request Phase clock on the Ab[15:8]#
pins.
92 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 93

Signals Reference
For memory or I/O transactions, the byte-enable signals indicate that valid data is
requested or being transferred on the corresponding byte on the 128-bit data bus.
BE[0]# indicates that the least significant byte is valid, and BE[7]# indicates that the
most significant byte is valid. Since BE[7:0]# specifies the validity of only 8 bytes on
the 16 byte wide bus, A[3]# is used to determine which half of the data bus is validated
by BE[7:0]#.
For special transactions ((REQa[5:0]# = 001000B) and (REQb[1:0]# = 01B)), the
BE[7:0]# signals carry special cycle encodings as defined in Table A-3. All other
encodings are reserved.
Table A-3. Special Transaction Encoding on Byte Enables
Special Transaction Byte Enables[7:0]#
NOP 0000 0000
Shutdown 0000 0001
Flush (INVD) 0000 0010
Halt 0000 0011
Sync (WBINVD) 0000 0100
Reserved 0000 0101
StopGrant Acknowledge 0000 0110
Reserved 0000 0111
xTPR Update 0000 1000
For Deferred Reply transactions, BE[7:0]# signals are reserved. The Defer Phase
transfer length is always the same length as that specified in the Request Phase except
the Bus Invalidate Line (BIL) transaction.
A BIL transaction may return one cache line (128 bytes).
A.1.9 BERR# (I/O)
The Bus Error (BERR#) signal can be asserted to indicate a recoverable error with
global MCA. BERR# assertion conditions are configurable at the system level.
Configuration options enable BERR# to be driven as follows:
• Asserted by the requesting agent of a bus transaction after it observes an internal
error.
• Asserted by any bus agent when it observes an error in a bus transaction.
When the bus agent samples an asserted BERR# signal and BERR# sampling is
enabled, the processor enters a Machine Check Handler.
BERR# is a wired-OR signal to allow multiple bus agents to drive it at the same time.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 93
Page 94

A.1.10 BINIT# (I/O)
If enabled by configuration, the Bus Initialization (BINIT#) signal is asserted to signal
any bus condition that prevents reliable future operation.
If BINIT# observation is enabled during power-on configuration, and BINIT# is
sampled asserted, all bus state machines are reset. All agents reset their rotating IDs
for bus arbitration to the same state as that after reset, and internal count information
is lost. The L2 and L3 caches are not affected.
If BINIT# observation is disabled during power-on configuration, BINIT# is ignored by
all bus agents with the exception of the priority agent. The priority agent must handle
the error in a manner that is appropriate to the system architecture.
BINIT# is a wired-OR signal.
A.1.11 BNR# (I/O)
The Block Next Request (BNR#) signal is used to assert a bus stall by any bus agent
that is unable to accept new bus transactions to avoid an internal transaction queue
overflow. During a bus stall, the current bus owner cannot issue any new transactions.
Since multiple agents might need to request a bus stall at the same time, BNR# is a
wired-OR signal. In order to avoid wired-OR glitches associated with simultaneous edge
transitions driven by multiple drivers, BNR# is asserted and sampled on specific clock
edges.
Signals Reference
A.1.12 BPM[5:0]# (I/O)
The BPM[5:0]# signals are system support signals used for inserting breakpoints and
for performance monitoring. They can be configured as outputs from the processor that
indicate programmable counters used for monitoring performance, or inputs from the
processor to indicate the status of breakpoints.
A.1.13 BPRI# (I)
The Bus Priority-agent Request (BPRI#) signal is used by the priority agent to arbitrate
for ownership of the system bus. Observing BPRI# asserted causes all other agents to
stop issuing new requests, unless such requests are part of an ongoing locked
operation.The priority agent keeps BPRI# asserted until all of its requests are
completed, then releases the bus by deasserting BPRI#.
A.1.14 BR[0]# (I/O) and BR[3:1]# (I)
BR[3:0]# are the physical bus request pins that drive the BREQ[3:0]# signals in the
system. The BREQ[3:0]# signals are interconnected in a rotating manner to individual
processor pins. Table A-4 and Table A-4 give the rotating interconnection between the
processor and bus signals for both the 4P and 2P system bus topologies.
94 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 95

Signals Reference
Table A-4. BR0# (I/O), BR1#, BR2#, BR3# Signals for 4P Rotating Interconnect
Bus Signal Agent 0 Pins Agent 1 Pins Agent 2 Pins Agent 3 Pins
BREQ[0]# BR[0]# BR[3]# BR[2]# BR[1]#
BREQ[1]# BR[1]# BR[0]# BR[3]# BR[2]#
BREQ[2]# BR[2]# BR[1]# BR[0]# BR[3]#
BREQ[3]# BR[3]# BR[2]# BR[1]# BR[0]#
Table A-5. BR0# (I/O), BR1#, BR2#, BR3# Signals for 2P Rotating Interconnect
Bus Signal Agent 0 Pins Agent 3 Pins
BREQ[0]# BR[0]# BR[1]#
BREQ[1]# BR[1]# BR[0]#
BREQ[2]# Not Used Not Used
BREQ[3]# Not Used Not Used
During power-on configuration, the priority agent must assert the BR[0]# bus signal.
All symmetric agents sample their BR[3:0]# pins on asserted-to-deasserted transition
of RESET#. The pin on which the agent samples an asserted level determines its agent
ID. All agents then configure their pins to match the appropriate bus signal protocol as
shown in Table A-6.
Table A-6. BR[3:0]# Signals and Agent IDs
Pin Sampled
Asserted on
RESET#
BR[0]# 0 0
BR[3]# 1 2
BR[2]# 2 4
BR[1]# 3 6
Arbitration ID
A.1.15 BREQ[3:0]# (I/O)
The BREQ[3:0]# signals are the symmetric agent arbitration bus signals (called bus
request). A symmetric agent n arbitrates for the bus by asserting its BREQn# signal.
Agent n drives BREQn# as an output and receives the remaining BREQ[3:0]# signals
as inputs.
The symmetric agents support distributed arbitration based on a round-robin
mechanism. The rotating ID is an internal state used by all symmetric agents to track
the agent with the lowest priority at the next arbitration event. At power-on, the
rotating ID is initialized to three, allowing agent 0 to be the highest priority symmetric
agent. After a new arbitration event, the rotating ID of all symmetric agents is updated
to the agent ID of the symmetric owner. This update gives the new symmetric owner
lowest priority in the next arbitration event.
A new arbitration event occurs either when a symmetric agent asserts its BREQn# on
an Idle bus (all BREQ[3:0]# previously deasserted), or the current symmetric owner
deasserts BREQn# to release the bus ownership to a new bus owner n. On a new
arbitration event, all symmetric agents simultaneously determine the new symmetric
owner using BREQ[3:0]# and the rotating ID. The symmetric owner can park on the
bus (hold the bus) provided that no other symmetric agent is requesting its use. The
symmetric owner parks by keeping its BREQn# signal asserted. On sampling BREQn#
asserted by another symmetric agent, the symmetric owner deasserts BREQn# as soon
as possible to release the bus. A symmetric owner stops issuing new requests that are
not part of an existing locked operation on observing BPRI# asserted.
Agent ID
Reported
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 95
Page 96

A symmetric agent can deassert BREQn# before it becomes a symmetric owner. A
symmetric agent can reassert BREQn# after keeping it deasserted for one clock.
A.1.16 CCL# (I/O)
CCL# is the Cache Cleanse signal. It is driven on the second clock of the Request Phase
on the EXF[2]#/Ab[5]# pin. CCL# is asserted for Memory Write transaction to indicate
that a modified line in a processor may be written to memory without being invalidated
in its caches.
A.1.17 CPUPRES# (O)
CPUPRES# can be used to detect the presence of a processor in a socket. A ground
indicates that a processor is installed, while an open indicates that a processor is not
installed.
A.1.18 D[127:0]# (I/O)
The Data (D[127:0]#) signals provide a 128-bit data path between various system bus
agents. Partial transfers require one data transfer clock with valid data on the byte(s)
indicated by asserted byte enables BE[7:0]# and A[3]#. Data signals that are not valid
for a particular transfer must still have correct ECC (if data bus error checking is
enabled). The data driver asserts DRDY# to indicate a valid data transfer.
Signals Reference
A.1.19 D/C# (I/O)
The Data/Code (D/C#) signal is used to indicate data (1) or code (0) on REQa[1]#,
only during Memory Read transactions.
A.1.20 DBSY# (I/O)
The Data Bus Busy (DBSY#) signal is asserted by the agent that is responsible for
driving data on the system bus to indicate that the data bus is in use. The data bus is
released after DBSY# is deasserted.
DBSY# is replicated three times to enable partitioning of the data paths in the system
agents. This copy of the Data Bus Busy signal (DBSY#) is an input as well as an output.
A.1.21 DBSY_C1# (O)
DBSY# is a copy of the Data Bus Busy signal. This copy of the Data Bus Busy signal
(DBSY_C1#) is an output only.
A.1.22 DBSY_C2# (O)
DBSY# is a copy of the Data Bus Busy signal. This copy of the Data Bus Busy signal
(DBSY_C2#) is an output only.
A.1.23 DEFER# (I)
The DEFER# signal is asserted by an agent to indicate that the transaction cannot be
guaranteed in-order completion. Assertion of DEFER# is normally the responsibility of
the priority agent.
96 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 97

Signals Reference
A.1.24 DEN# (I/O)
The Defer Enable (DEN#) signal is driven on the bus on the second clock of the Request
Phase on the Ab[4]# pin. DEN# is asserted to indicate that the transaction can be
deferred by the responding agent.
A.1.25 DEP[15:0]# (I/O)
The Data Bus ECC Protection (DEP[15:0]#) signals provide optional ECC protection for
Data Bus (D[127:0]#). They are driven by the agent responsible for driving
D[127:0]#. During power-on configuration, bus agents can be enabled for either ECC
checking or no checking.
The ECC error correcting code can detect and correct single-bit errors and detect
double-bit or nibble errors.
A.1.26 DHIT# (I)
The Deferred Hit (DHIT#) signal is driven during the Deferred Phase by the deferring
agent. For read transactions on the bus DHIT# returns the final cache status that would
have been indicated on HIT# for a transaction which was not deferred. DID[9:0]# (I/
O)
DID[9:0]# are Deferred Identifier signals. The requesting agent transfers these signals
by using A[25:16]#. They are transferred on Ab[25:16]# during the second clock of
the Request Phase on all transactions, but Ab[20:16]# is only defined for deferrable
transactions (DEN# asserted). DID[9:0]# is also transferred on Aa[25:16]# during the
first clock of the Request Phase for Deferred Reply transactions.
The Deferred Identifier defines the token supplied by the requesting agent. DID[9]#
and DID[8:5]# carry the agent identifiers of the requesting agents (always valid) and
DID[4:0]# carry a transaction identifier associated with the request (valid only with
DEN# asserted). This configuration limits the bus specification to 32 logical bus agents
with each one of the bus agents capable of making up to 32 requests. Table A-7 shows
the DID encodings.
Table A-7. DID[9:0]# Encoding
DID[9]# DID[8:5]# DID[4:0]#
Agent Type Agent ID[3:0] Transaction ID[4:0]
DID[9]# indicates the agent type. Symmetric agents use 0. Priority agents use 1.
DID[8:5]# indicates the agent ID. Symmetric agents use their arbitration ID.
DID[4:0]# indicates the transaction ID for an agent. The transaction ID must be
unique for all deferrable transactions issued by an agent which have not reported their
snoop results.
The Deferred Reply agent transmits the DID[9:0]# (Ab[25:16]#) signals received
during the original transaction on the Aa[25:16]# signals during the Deferred Reply
transaction. This process enables the original requesting agent to make an identifier
match with the original request that is awaiting completion.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 97
Page 98

A.1.27 DPS# (I/O)
The Deferred Phase Enable (DPS#) signal is driven to the bus on the second clock of
the Request Phase on the Ab[3]# pin. DPS# is asserted if a requesting agent supports
transaction completion using the Deferred Phase. A requesting agent that supports the
Deferred Phase will always assert DPS#. A requesting agent that does not support the
Deferred Phase will always deassert DPS#.
A.1.28 DRDY# (I/O)
The Data Ready (DRDY#) signal is asserted by the data driver on each data transfer,
indicating valid data on the data bus. In a multi-cycle data transfer, DRDY# can be
deasserted to insert idle clocks.
DRDY# is replicated three times to enable partitioning of data paths in the system
agents. This copy of the Data Ready signal (DRDY#) is an input as well as an output.
A.1.29 DRDY_C1# (O)
DRDY# is a copy of the Data Ready signal. This copy of the Data Phase data-ready
signal (DRDY_C1#) is an output only.
Signals Reference
A.1.30 DRDY_C2# (O)
DRDY# is a copy of the Data Ready signal. This copy of the Data Phase data-ready
signal (DRDY_C2#) is an output only.
A.1.31 DSZ[1:0]# (I/O)
The Data Size (DSZ[1:0]#) signals are transferred on REQb[4:3]# signals in the
second clock of the Request Phase by the requesting agent. The DSZ[1:0]# signals
define the data transfer capability of the requesting agent. For the processor, DSZ# =
01, always.
A.1.32 EXF[4:0]# (I/O)
The Extended Function (EXF[4:0]#) signals are transferred on the A[7:3]# pins by the
requesting agent during the second clock of the Request Phase. The signals specify any
special functional requirement associated with the transaction based on the requestor
mode or capability. The signals are defined in Table A-8.
Table A-8. Extended Function Signals
Extended Function
Signal
EXF[4]# Reserved Reserved
EXF[3]# SPLCK#/FCL# Split Lock / Flush Cache Line
EXF[2]# OWN#/CCL# Memory Update Not Needed / Cache Cleanse
EXF[1]# DEN# Defer Enable
EXF[0]# DPS# Deferred Phase Supported
Signal Name Alias Function
98 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
Page 99

Signals Reference
A.1.33 FCL# (I/O)
The Flush Cache Line (FCL#) signal is driven to the bus on the second clock of the
Request Phase on the A[6]# pin. FCL# is asserted to indicate that the memory
transaction is initiated by the global Flush Cache () instruction.
A.1.34 FERR# (O)
The FERR# signal may be asserted to indicate a processor detected error when IERR
mode is enabled. If IERR mode is disabled, the FERR# signal will not be asserted in the
processor system environment.
A.1.35 GSEQ# (I)
Assertion of the Guaranteed Sequentiality (GSEQ#) signal indicates that the platform
guarantees completion of the transaction without a retry while maintaining
sequentiality.
A.1.36 HIT# (I/O) and HITM# (I/O)
The Snoop Hit (HIT#) and Hit Modified (HITM#) signals convey transaction snoop
operation results. Any bus agent can assert both HIT# and HITM# together to indicate
that it requires a snoop stall. The stall can be continued by reasserting HIT# and
HITM# together.
A.1.37 ID[9:0]# (I)
The Transaction ID (ID[9:0]#) signals are driven by the deferring agent. The signals in
the two clocks are referenced IDa[9:0]# and IDb[9:0]#. During both clocks, ID[9:0]#
signals are protected by the IP0# parity signal for the first clock, and by the IP[1]#
parity signal on the second clock.
IDa[9:0]# returns the ID of the deferred transaction which was sent on Ab[25:16]#
(DID[9:0]#).
A.1.38 IDS# (I)
The ID Strobe (IDS#) signal is asserted to indicate the validity of ID[9:0]# in that clock
and the validity of DHIT# and IP[1:0]# in the next clock.
A.1.39 IGNNE# (I)
IGNNE# is no connect and is ignored in the processor system environment.
A.1.40 INIT# (I)
The Initialization (INIT#) signal triggers an unmasked interrupt to the processor. INIT#
is usually used to break into hanging or idle processor states. Semantics required for
platform compatibility are supplied in the PAL firmware interrupt service routine.
Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet 99
Page 100

A.1.41 INT (I)
INT is the 8259-compatible Interrupt Request signal which indicates that an external
interrupt has been generated. The interrupt is maskable. The processor vectors to the
interrupt handler after the current instruction execution has been completed. An
interrupt acknowledge transaction is generated by the processor to obtain the interrupt
vector from the interrupt controller.
The LINT[0] pin can be software configured to be used either as the INT signal or
another local interrupt.
A.1.42 IP[1:0]# (I)
The ID Parity (IP[1:0]#) signals are driven on the second clock of the Deferred Phase
by the deferring agent. IP0# protects the IDa[9:0]# and IDS# signals for the first
clock, and IP[1]# protects the IDb[9:2, 0]# and IDS# signals on the second clock.
A.1.43 LEN[2:0]# (I/O)
The Data Length (LEN[2:0]#) signals are transmitted using REQb[2:0]# signals by the
requesting agent in the second clock of Request Phase. LEN[2:0]# defines the length of
the data transfer requested by the requesting agent as shown in Table A-9. The
LEN[2:0]#, HITM#, and RS[2:0]# signals together define the length of the actual data
transfer.
Signals Reference
Table A-9. Length of Data Transfers
LEN[2:0]# Length
000 0 – 8 bytes
001 16 bytes
010 32 bytes
011 64 bytes
100 128 bytes
101 Reserved
110 Reserved
111 Reserved
A.1.44 LINT[1:0] (I)
LINT[1:0] are local interrupt signals. These pins are disabled after RESET#. LINT[0] is
typically software configured as INT, an 8259-compatible maskable interrupt request
signal. LINT[1] is typically software configured as NMI, a non-maskable interrupt.Both
signals are asynchronous inputs.
A.1.45 LOCK# (I/O)
LOCK# is no connect and is ignored in the processor system environment.
100 Dual-Core Intel® Itanium® Processor 9000 and 9100 Series Datasheet
 Loading...
Loading...