Page 1

LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide
September 2013
Order No.: 328999-002
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR
OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND
CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
A "Mission Critical Application" is any application in which failure of the Intel Product could result, directly or indirectly, in personal injury or death.
SHOULD YOU PURCHASE OR USE INTEL'S PRODUCTS FOR ANY SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, YOU SHALL INDEMNIFY AND HOLD INTEL AND
ITS SUBSIDIARIES, SUBCONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES, AND THE DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, AND EMPLOYEES OF EACH, HARMLESS AGAINST ALL
CLAIMS COSTS, DAMAGES, AND EXPENSES AND REASONABLE ATTORNEYS' FEES ARISING OUT OF, DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ANY CLAIM OF
PRODUCT LIABILITY, PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, WHETHER OR NOT INTEL
OR ITS SUBCONTRACTOR WAS NEGLIGENT IN THE DESIGN, MANUFACTURE, OR WARNING OF THE INTEL PRODUCT OR ANY OF ITS PARTS.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the absence or
characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined". Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The information here is subject to change without
notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published
specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling
1-800-548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm
This document contains information on products in the design phase of development.
Code Names are only for use by Intel to identify products, platforms, programs, services, etc. ("products") in development by Intel that have not been
made commercially available to the public, i.e., announced, launched or shipped. They are never to be used as "commercial" names for products. Also,
they are not intended to function as trademarks.
Intel, Intel Core, Pentium, Xeon, and the Intel logo, are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2013, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
2 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 3

Contents—LGA1150 Socket
Contents
Revision History..................................................................................................................6
1.0 Introduction................................................................................................................. 7
1.1 Related Documents.................................................................................................7
1.2 Definition of Terms................................................................................................. 7
2.0 LGA1150 Socket...........................................................................................................9
2.1 Board Layout......................................................................................................... 9
2.2 Attachment to Motherboard....................................................................................10
2.3 Socket Components.............................................................................................. 11
2.4 Package Installation / Removal............................................................................... 13
2.5 Durability.............................................................................................................14
2.6 Markings............................................................................................................. 14
2.7 Component Insertion Forces...................................................................................15
2.8 Socket Size..........................................................................................................15
3.0 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)......................................................................16
3.1 Design Concept.................................................................................................... 16
3.2 Assembly of Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) to a Motherboard......................... 19
3.3 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Interchangeability..........................................21
3.4 Markings............................................................................................................. 21
3.5 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Cover...........................................................21
4.0 LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications......................................................................24
4.1 Mechanical Specifications....................................................................................... 24
4.2 Electrical Requirements......................................................................................... 25
4.3 Environmental Requirements..................................................................................26
Appendix A Component Suppliers..................................................................................... 28
Appendix B Mechanical Drawings......................................................................................29
Appendix C Heatsink Back Plate Drawings........................................................................ 34
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 3
LGA1150 Socket
Page 4

LGA1150 Socket—Figures
Figures
1 LGA1150 Pick and Place Cover.................................................................................... 9
2 LGA1150 Socket Land Pattern................................................................................... 10
3 Attachment to Motherboard...................................................................................... 11
4 Pick and Place Cover................................................................................................ 13
5 Package Installation / Removal Features.....................................................................14
6 ILM Assembly with Installed Processor........................................................................17
7 Back Plate.............................................................................................................. 18
8 Shoulder Screw....................................................................................................... 19
9 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Assembly.........................................................20
10 Pin1 and Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Lever................................................. 20
11 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Cover..............................................................22
12 ILM Cover and PnP Cover Interference........................................................................23
13 Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology................................ 27
14 Socket/Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top)............................................. 30
15 Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)...................................31
16 Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top).......................................... 32
17 Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)................................. 33
18 Heatsink Back Plate Keep-in Zone.............................................................................. 35
19 Heatsink Back Plate................................................................................................. 36
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
4 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 5

Tables—LGA1150 Socket
Tables
1 Related Documents ...................................................................................................7
2 Terms and Descriptions..............................................................................................7
3 Socket Component Mass...........................................................................................24
4 1150-land Package and LGA1150 Socket Stackup Height.............................................. 24
5 Socket and ILM Mechanical Specifications .................................................................. 25
6 Electrical Requirements for LGA1150 Socket ...............................................................26
7 LGA1150 Socket and ILM Components........................................................................28
8 Supplier Contact Information ....................................................................................28
9 Mechanical Drawing List........................................................................................... 29
10 Mechanical Drawing List........................................................................................... 34
11 Supplier Contact Information.....................................................................................34
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 5
LGA1150 Socket
Page 6
Revision History
Revision Number Description Revision Date
001 • Initial release June 2013
002 • Added Desktop Intel® Pentium processor family September 2013
LGA1150 Socket—Revision History
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
6 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 7
Introduction—LGA1150 Socket
1.0 Introduction
This document covers the LGA1150 socket for Desktop systems using the Desktop 4th
Generation Intel® Core™ processor family, Desktop Intel® Pentium® processor family,
and for UP Server / Workstation systems using the Intel® Xeon® processor E3-1200
v3 product family.
The information in this document include:
• The thermal and mechanical specifications for the socket
• The mechanical interface requirements to properly integrate the socket into a
board design
1.1
Related Documents
Material and concepts available in the following documents may be beneficial when
reading this document.
Table 1. Related Documents
Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family and Desktop Intel
Pentium® Processor Family Datasheet - Volume 1 of 2
Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family and Desktop Intel
Pentium® Processor Family Datasheet - Volume 2 of 2
Intel® Xeon® Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family Datasheet - Volume 1 of 2 328907
Intel® Xeon® Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family Datasheet - Volume 2 of 2 329000
Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family and Intel® Xeon
Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family Thermal Mechanical Design Guidelines
Intel® 8 Series / C220 Series Chipset Family Platform Controller Hub (PCH)
Thermal Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines
1.2
Definition of Terms
Table 2. Terms and Descriptions
Term Description
Bypass Bypass is the area between a passive heatsink and any object that can act to form a duct.
CTE Coefficient of Thermal Expansion. The relative rate a material expands during a thermal
DTS Digital Thermal Sensor reports a relative die temperature as an offset from TCC activation
For this example, it can be expressed as a dimension away from the outside dimension of
the fins to the nearest surface.
event.
temperature.
Title Document Number /
®
®
®
Location
328897
328898
328900
328906
continued...
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 7
LGA1150 Socket
Page 8

LGA1150 Socket—Introduction
Term Description
FSC Fan Speed Control
IHS Integrated Heat Spreader: a component of the processor package used to enhance the
thermal performance of the package. Component thermal solutions interface with the
processor at the IHS surface.
ILM Independent Loading Mechanism provides the force needed to seat the LGA1150 land
package onto the socket contacts.
MD Metal Defined pad is one where a pad is individually etched into the PCB with a minimum
width trace exiting it.
PCH Platform Controller Hub. The PCH is connected to the processor using the Direct Media
Interface (DMI) and Intel® Flexible Display Interface (Intel® FDI).
LGA1150 socket The processor mates with the system board through this surface mount, 1150-land
socket.
PECI The Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) is a one-wire interface that provides a
communication channel between Intel processor and chipset components to external
monitoring devices.
Ψ
ca
Ψ
CS
Ψ
sa
Case-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter (psi). A measure of thermal solution
performance using total package power. Defined as (T
The heat source should always be specified for Y measurements.
– TLA ) / Total Package Power.
CASE
Case-to-sink thermal characterization parameter. A measure of thermal interface material
performance using total package power. Defined as (T
– TS ) / Total Package Power.
CASE
Sink-to-ambient thermal characterization parameter. A measure of heatsink thermal
performance using total package power. Defined as (TS – TLA ) / Total Package Power.
SMD The Solder Mask Defined pad is typically a pad in a flood plane where the solder mask
opening defines the pad size for soldering to the component to the printed circuit board.
T
T
CASE
CASE
or T
_
C
MAX
The case temperature of the processor, measured at the geometric center of the topside
of the TTV IHS.
The maximum case temperature as specified in a component specification.
TCC Thermal Control Circuit: Thermal monitor uses the TCC to reduce the die temperature by
using clock modulation and/or operating frequency and input voltage adjustment when
the die temperature is very near its operating limits.
T
CONTROL
T
is a static value that is below the TCC activation temperature and used as a
CONTROL
trigger point for fan speed control. When DTS > T
the TTV thermal profile.
, the processor must comply to
CONTROL
TDP Thermal Design Power: Thermal solution should be designed to dissipate this target
power level. TDP is not the maximum power that the processor can dissipate.
Thermal Monitor A power reduction feature designed to decrease temperature after the processor has
reached its maximum operating temperature.
Thermal Profile Line that defines case temperature specification of the TTV at a given power level.
TIM Thermal Interface Material: The thermally conductive compound between the heatsink
and the processor case. This material fills the air gaps and voids, and enhances the
transfer of the heat from the processor case to the heatsink.
TTV Thermal Test Vehicle. A mechanically equivalent package that contains a resistive heater
in the die to evaluate thermal solutions.
T
LA
The measured ambient temperature locally surrounding the processor. The ambient
temperature should be measured just upstream of a passive heatsink or at the fan inlet
for an active heatsink.
T
SA
The system ambient air temperature external to a system chassis. This temperature is
usually measured at the chassis air inlets.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
8 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 9
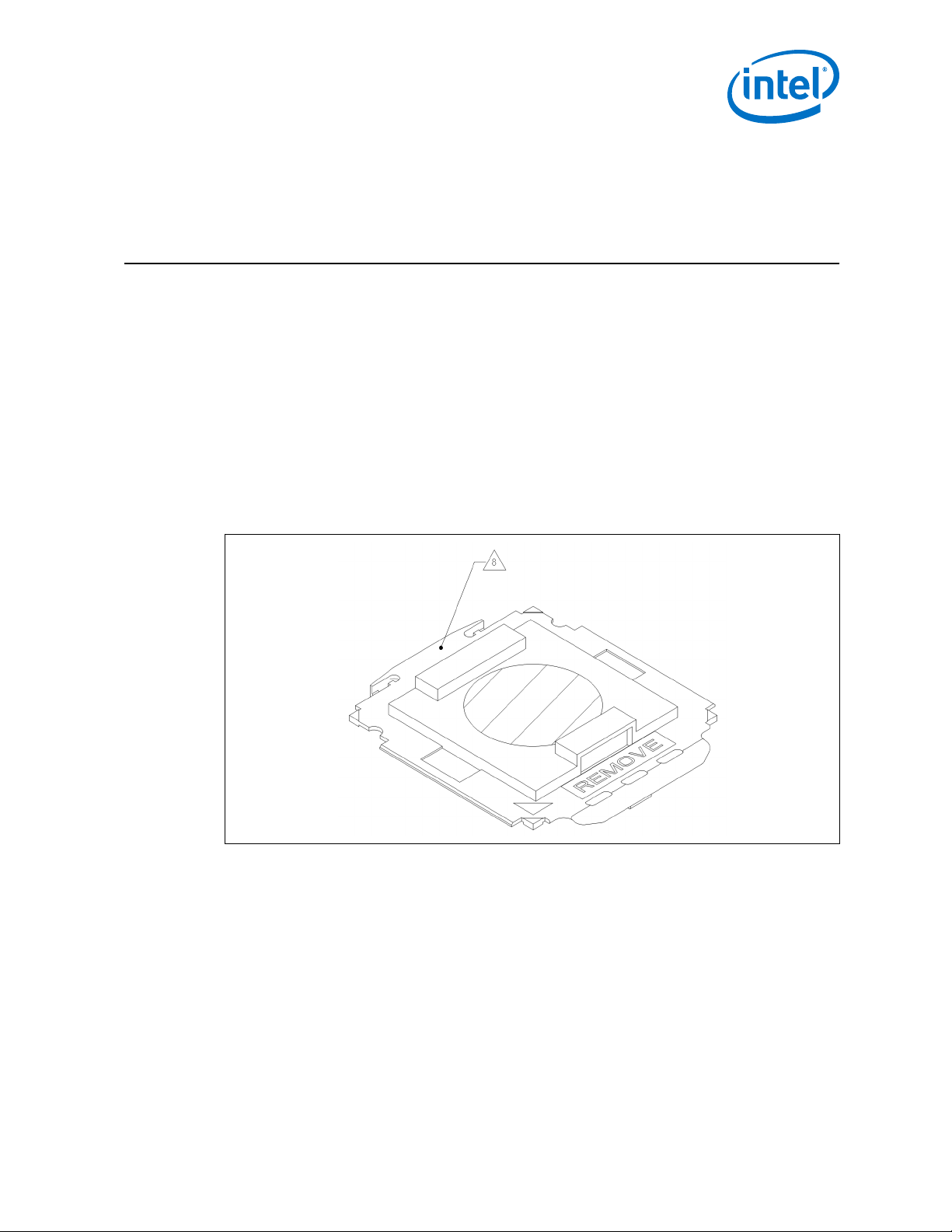
LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
2.0 LGA1150 Socket
This chapter describes a surface mount, LGA (Land Grid Array) socket intended for the
processors. The socket provides I/O, power and ground contacts. The socket contains
1150 contacts arrayed about a cavity in the center of the socket with lead-free solder
balls for surface mounting on the motherboard.
The contacts are arranged in two opposing L-shaped patterns within the grid array.
The grid array is 40 x 40 with 24 x 16 grid depopulation in the center of the array and
selective depopulation elsewhere.
The socket must be compatible with the package (processor) and the Independent
Loading Mechanism (ILM). The ILM design includes a back plate which is integral to
having a uniform load on the socket solder joints. Socket loading specifications are
listed in LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications on page 24.
Figure 1. LGA1150 Pick and Place Cover
2.1
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 9
Board Layout
The land pattern for the LGA1150 socket is 36 mils X 36 mils (X by Y) within each of
the two L-shaped sections. There is no round-off (conversion) error between socket
pitch (0.9144 mm) and board pitch (36 mil) as these values are equivalent. The two
L-sections are offset by 0.9144 mm (36 mil) in the x direction and 3.114 mm
(122.6 mil) in the y direction see Figure 2 on page 10. This was to achieve a
common package land to PCB land offset that ensures a single PCB layout for socket
designs from the multiple vendors.
LGA1150 Socket
Page 10
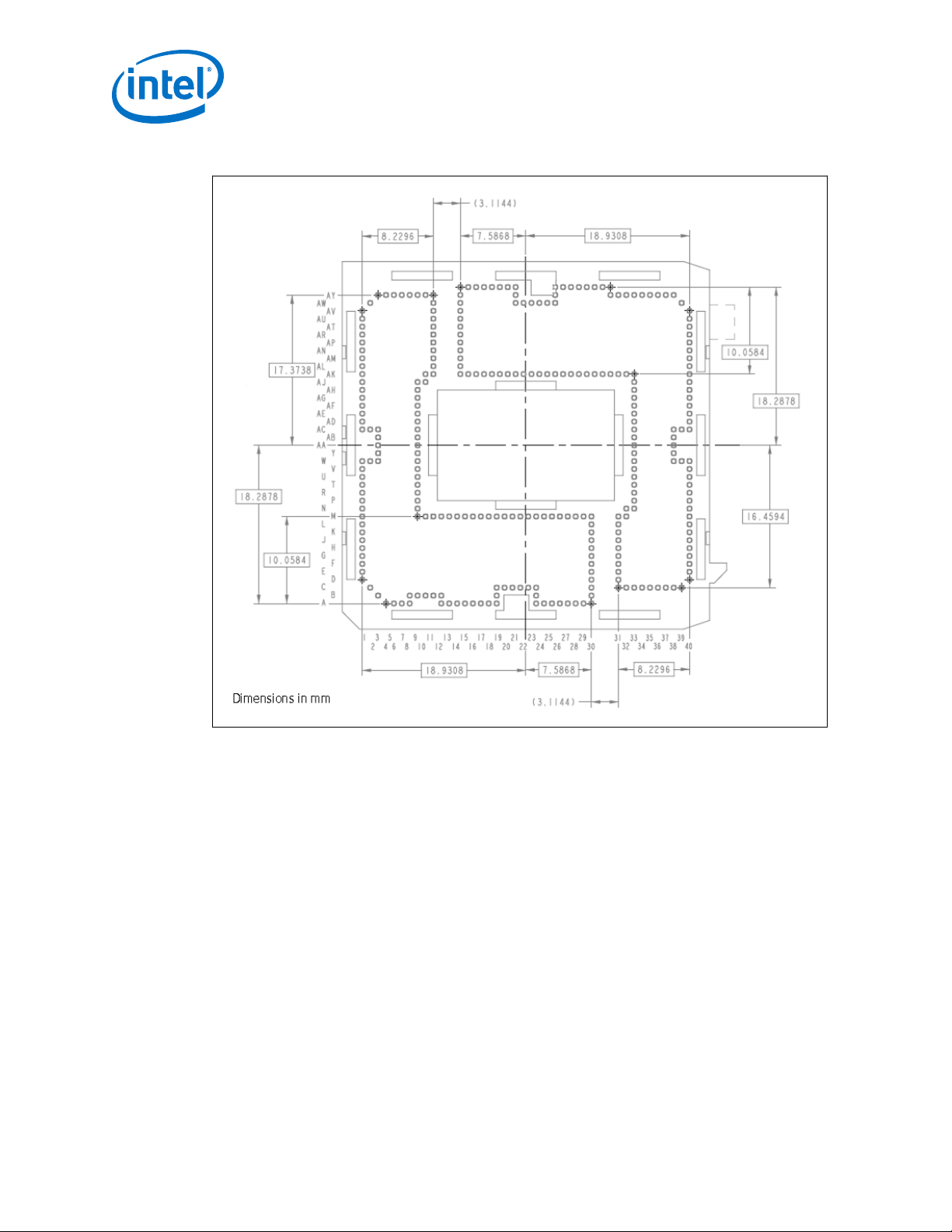
Figure 2. LGA1150 Socket Land Pattern
LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
2.2
Attachment to Motherboard
The socket is attached to the motherboard by 1150 solder balls. There are no
additional external methods (that is, screw, extra solder, adhesive, and so on) to
attach the socket.
As indicated in Figure 1 on page 9, the Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) is not
present during the attach (reflow) process.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
10 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 11
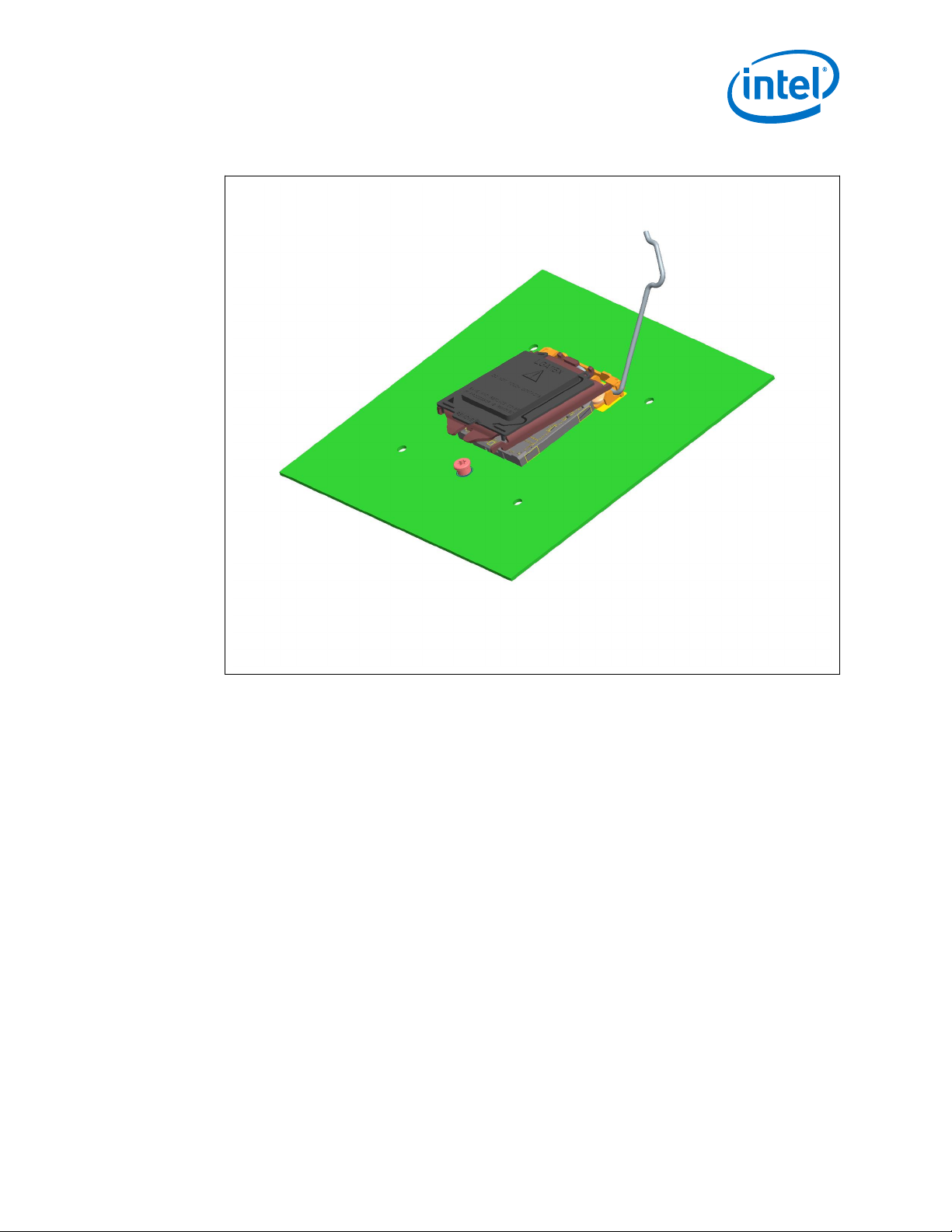
LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 3. Attachment to Motherboard
2.3
Socket Components
The socket has two main components, the socket body and Pick and Place (PnP)
cover, and is delivered as a single integral assembly. Refer to Socket Mechanical
Drawings for detailed drawings.
Socket Body Housing
The housing material is thermoplastic or equivalent with UL 94 V-0 flame rating
capable of withstanding 260 °C for 40 seconds, which is compatible with typical
reflow/rework profiles. The socket coefficient of thermal expansion (in the XY plane)
and creep properties must be such that the integrity of the socket is maintained for
the conditions listed in LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications on page 24.
The color of the housing will be dark as compared to the solder balls to provide the
contrast needed for pick and place vision systems.
Solder Balls
A total of 1150 solder balls corresponding to the contacts are on the bottom of the
socket for surface mounting with the motherboard. The socket solder ball has the
following characteristics:
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 11
LGA1150 Socket
Page 12

LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
• Lead free SAC (SnAgCu) 305 solder alloy with a silver (Ag) content between 3%
and 4% and a melting temperature of approximately 217 °C. The alloy is
compatible with immersion silver (ImAg) and Organic Solderability Protectant
(OSP) motherboard surface finishes and a SAC alloy solder paste.
• Solder ball diameter 0.6 mm ± 0.02 mm, before attaching to the socket lead.
The co-planarity (profile) and true position requirements are defined in Socket
Mechanical Drawings.
Contacts
Base material for the contacts is high strength copper alloy.
For the area on socket contacts where processor lands will mate, there is a 0.381 µm
[15 µinches] minimum gold plating over 1.27 µm [50 minches] minimum nickel
underplate.
No contamination by solder in the contact area is allowed during solder reflow.
Pick and Place Cover
The cover provides a planar surface for vacuum pick up used to place components in
the Surface Mount Technology (SMT) manufacturing line. The cover remains on the
socket during reflow to help prevent contamination during reflow. The cover can
withstand 260 °C for 40 seconds (typical reflow/rework profile) and the conditions
listed in LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications on page 24 without degrading.
As indicated in Figure 4 on page 13, the cover remains on the socket during ILM
installation, and should remain on whenever possible to help prevent damage to the
socket contacts.
Cover retention must be sufficient to support the socket weight during lifting,
translation, and placement (board manufacturing), and during board and system
shipping and handling. PnP Cover should only be removed with tools, to prevent the
cover from falling into the contacts.
The socket vendors have a common interface on the socket body where the PnP cover
attaches to the socket body. This should allow the PnP covers to be compatible
between socket suppliers.
As indicated in Figure 4 on page 13, a Pin 1 indicator on the cover provides a visual
reference for proper orientation with the socket.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
12 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 13
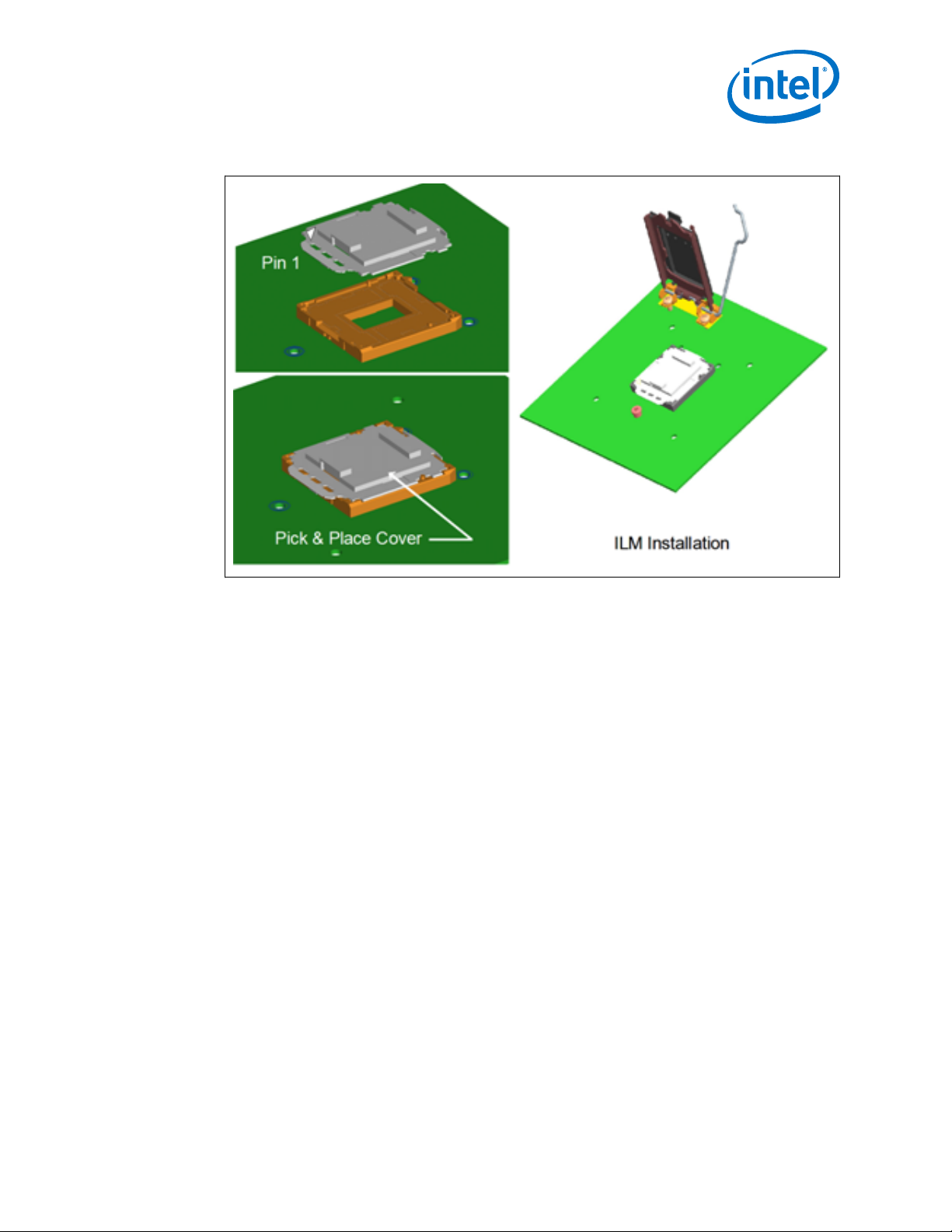
LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 4. Pick and Place Cover
2.4
Package Installation / Removal
As indicated in Figure 5 on page 14, access is provided to facilitate manual
installation and removal of the package.
To assist in package orientation and alignment with the socket:
• The package Pin 1 triangle and the socket Pin 1 chamfer provide visual reference
for proper orientation.
• The package substrate has orientation notches along two opposing edges of the
package, offset from the centerline. The socket has two corresponding orientation
posts to physically prevent mis-orientation of the package. These orientation
features also provide initial rough alignment of package to socket.
• The socket has alignment walls at the four corners to provide final alignment of
the package.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 13
LGA1150 Socket
Page 14

Figure 5. Package Installation / Removal Features
LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
2.5
2.6
Socket Standoffs and Package Seating Plane
Standoffs on the bottom of the socket base establish the minimum socket height after
solder reflow and are specified in Socket Mechanical Drawings.
Similarly, a seating plane on the topside of the socket establishes the minimum
package height. See Package / Socket Stackup Height on page 24 for the calculated
IHS height above the motherboard.
Durability
The socket must withstand 20 cycles of processor insertion and removal. The
maximum chain contact resistance from Table 6 on page 26 must be met when
mated in the 1st and 20th cycles.
The socket Pick and Place cover must withstand 15 cycles of insertion and removal.
Markings
There are three markings on the socket:
• LGA1150: Font type is Helvetica Bold - minimum 6 point (2.125 mm). This mark
will also appear on the pick and place cap.
• Manufacturer's insignia (font size at supplier discretion).
• Lot identification code (allows traceability of manufacturing date and location).
All markings must withstand 260 °C for 40 seconds (typical reflow/rework profile)
without degrading, and must be visible after the socket is mounted on the
motherboard.
LGA1150 and the manufacturer's insignia are molded or laser marked on the side wall.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
14 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 15

LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket
2.7
2.8
Component Insertion Forces
Any actuation must meet or exceed SEMI S8-95 Safety Guidelines for Ergonomics/
Human Factors Engineering of Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment, example
Table R2-7 (Maximum Grip Forces). The socket must be designed so that it requires
no force to insert the package into the socket.
Socket Size
Socket information needed for motherboard design is given in Appendix C.
This information should be used in conjunction with the reference motherboard keepout drawings provided in Appendix B to ensure compatibility with the reference
thermal mechanical components.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 15
LGA1150 Socket
Page 16

LGA1150 Socket—Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
3.0 Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
The ILM has two critical functions – deliver the force to seat the processor onto the
socket contacts and distribute the resulting compressive load evenly through the
socket solder joints.
The mechanical design of the ILM is integral to the overall functionality of the
LGA1150 socket. Intel performs detailed studies on integration of processor package,
socket and ILM as a system. These studies directly impact the design of the ILM. The
Intel reference ILM will be “build to print” from Intel controlled drawings. Intel
recommends using the Intel Reference ILM. Custom non-Intel ILM designs do not
benefit from Intel's detailed studies and may not incorporate critical design
parameters.
Note: There is a single ILM design for the LGA1150 socket, LGA1156 socket, and LGA1155
socket.
3.1
Design Concept
The ILM consists of two assemblies that will be procured as a set from the enabled
vendors. These two components are ILM assembly and back plate. To secure the two
assemblies, two types of fasteners are required – a pair (2) of standard 6-32 thread
screws and a custom 6-32 thread shoulder screw. The reference design incorporates a
T-20 Torx* head fastener. The Torx* head fastener was chosen to ensure end users
do not inadvertently remove the ILM assembly and for consistency with the LGA1366
socket ILM. The Torx* head fastener is also less susceptible to driver slippage. Once
assembled the ILM is not required to be removed to install / remove the motherboard
from a chassis.
ILM Assembly Design Overview
The ILM assembly consists of 4 major pieces – ILM cover, load lever, load plate, and
the hinge frame assembly.
All of the pieces in the ILM assembly except the hinge frame and the screws used to
attach the back plate are fabricated from stainless steel. The hinge frame is plated.
The frame provides the hinge locations for the load lever and load plate. An insulator
is pre-applied to the bottom surface of the hinge frame.
Figure 14 on page 30 through Figure 17 on page 33 list the applicable keep-out
zones of the socket and ILM. Figure 14 on page 30 describes recommended
maximum heights of neighboring components on the primary side of the board to
avoid interference with the Intel® reference thermal solution. The keep-out zone in
Figure 14 on page 30 does not prevent incidental contact with the ILM load plate
and ILM cover while it is open for insertion/removal of the processor. In designs
requiring no cosmetic marks to be made on capacitors along the hinge side of the ILM,
the recommendation is for the location of the capacitors to be against the keep-out
zone boundary closest to the hinge of the ILM. This location does not prevent contact
between the ILM and the capacitors; however it minimizes the load applied by the ILM
to the capacitors.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
16 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 17
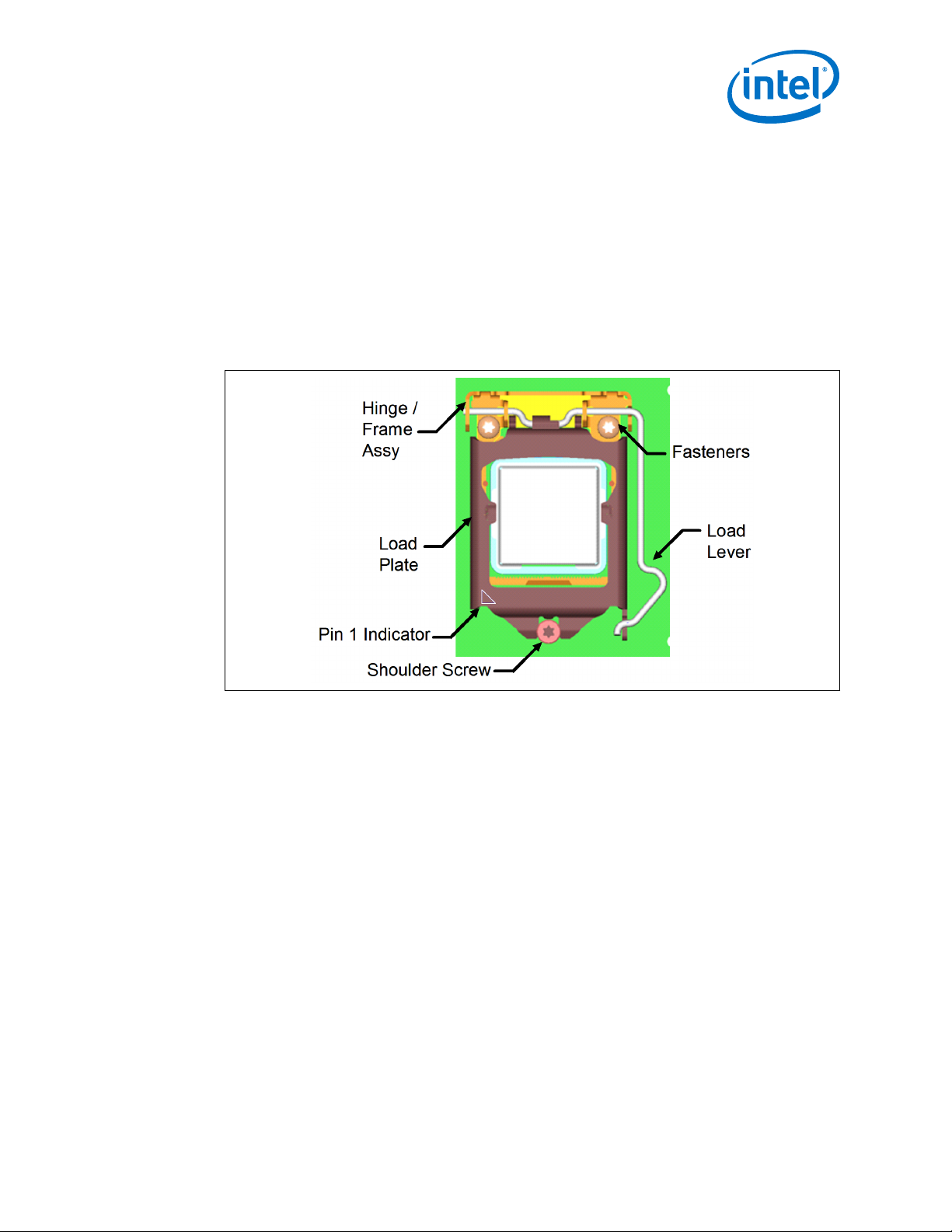
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)—LGA1150 Socket
The ILM assembly design ensures that, once assembled to the back plate, the only
features touching the board are the shoulder screw and the insulated hinge frame
assembly. The nominal gap of the load plate to the board is ~1 mm.
When closed, the load plate applies two point loads onto the IHS at the “dimpled”
features shown in Figure 6 on page 17. The reaction force from closing the load
plate is transmitted to the hinge frame assembly and through the fasteners to the
back plate. Some of the load is passed through the socket body to the board, inducing
a slight compression on the solder joints.
A pin 1 indicator will be marked on the ILM assembly.
Figure 6. ILM Assembly with Installed Processor
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Back Plate Design Overview
The back plate is a flat steel back plate with pierced and extruded features for ILM
attach. A clearance hole is located at the center of the plate to allow access to test
points and backside capacitors if required. An insulator is pre-applied. A notch is
placed in one corner to assist in orienting the back plate during assembly.
Note: The Server ILM back plate is different from the Desktop design. Since Server
secondary-side clearance of 3.0 mm [0.118 inch] is generally available for leads and
backside components, so Server ILM back plate is designed with 1.8 mm thickness
and 2.2 mm entire height including punch protrusion length.
Caution: Intel does NOT recommend using the server back plate for high-volume desktop
applications at this time as the server back plate test conditions cover a limited
envelope. Back plates and screws are similar in appearance. To prevent mixing,
different levels of differentiation between server and desktop back plate and screws
have been implemented.
For ILM back plate, three levels of differentiation have been implemented:
• Unique part numbers, please refer to part numbers listed in Table 7 on page 28.
• Desktop ILM back plate to use black lettering for marking versus server ILM back
plate to use yellow lettering for marking.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 17
LGA1150 Socket
Page 18

LGA1150 Socket—Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
• Desktop ILM back plate using marking “115XDBP” versus server ILM back plate
using marking “115XSBP”.
Note: When reworking a BGA component or the socket that the heatsink, battery, ILM and
ILM back plate are removed prior to rework. The ILM back plate should also be
removed when reworking through hole mounted components in a mini-wave or solder
pot). The maximum temperature for the pre-applied insulator on the ILM is
approximately 106 °C.
Figure 7. Back Plate
Shoulder Screw and Fasteners Design Overview
The shoulder screw is fabricated from carbonized steel rod. The shoulder height and
diameter are integral to the mechanical performance of the ILM. The diameter
provides alignment of the load plate. The height of the shoulder ensures the proper
loading of the IHS to seat the processor on the socket contacts. The design assumes
the shoulder screw has a minimum yield strength of 235 MPa.
The screws for Server ILM are different from Desktop design. The length of Server ILM
screws are shorter than the Desktop screw length to satisfy Server secondary-side
clearance limitation. Server ILM back plate to use black nickel plated screws, whereas
desktop ILM back plate to use clear plated screws. Unique part numbers, please refer
to Table 7 on page 28.
Note: The reference design incorporates a T-20 Torx* head fastener. The Torx* head
fastener was chosen to ensure end users do not inadvertently remove the ILM
assembly and for consistency with the LGA1366 socket ILM.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
18 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 19

Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 8. Shoulder Screw
3.2
Assembly of Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) to a Motherboard
The ILM design allows a bottoms up assembly of the components to the board. See
Figure 9 on page 20 for step by step assembly sequence.
1. Place the back plate in a fixture. The motherboard is aligned with the fixture.
2. Install the shoulder screw in the single hole near Pin 1 of the socket. Torque to a
minimum and recommended 8 inch-pounds, but not to exceed 10 inch-pounds.
3. Install two (2) 6–32 fasteners. Torque to a minimum and recommended 8 inchpounds, but not to exceed 10 inch-pounds.
4. Remove pick and place cover and close ILM leaving the ILM cover in place.
The thread length of the shoulder screw accommodates a nominal board thicknesses
of 0.062”.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 19
LGA1150 Socket
Page 20
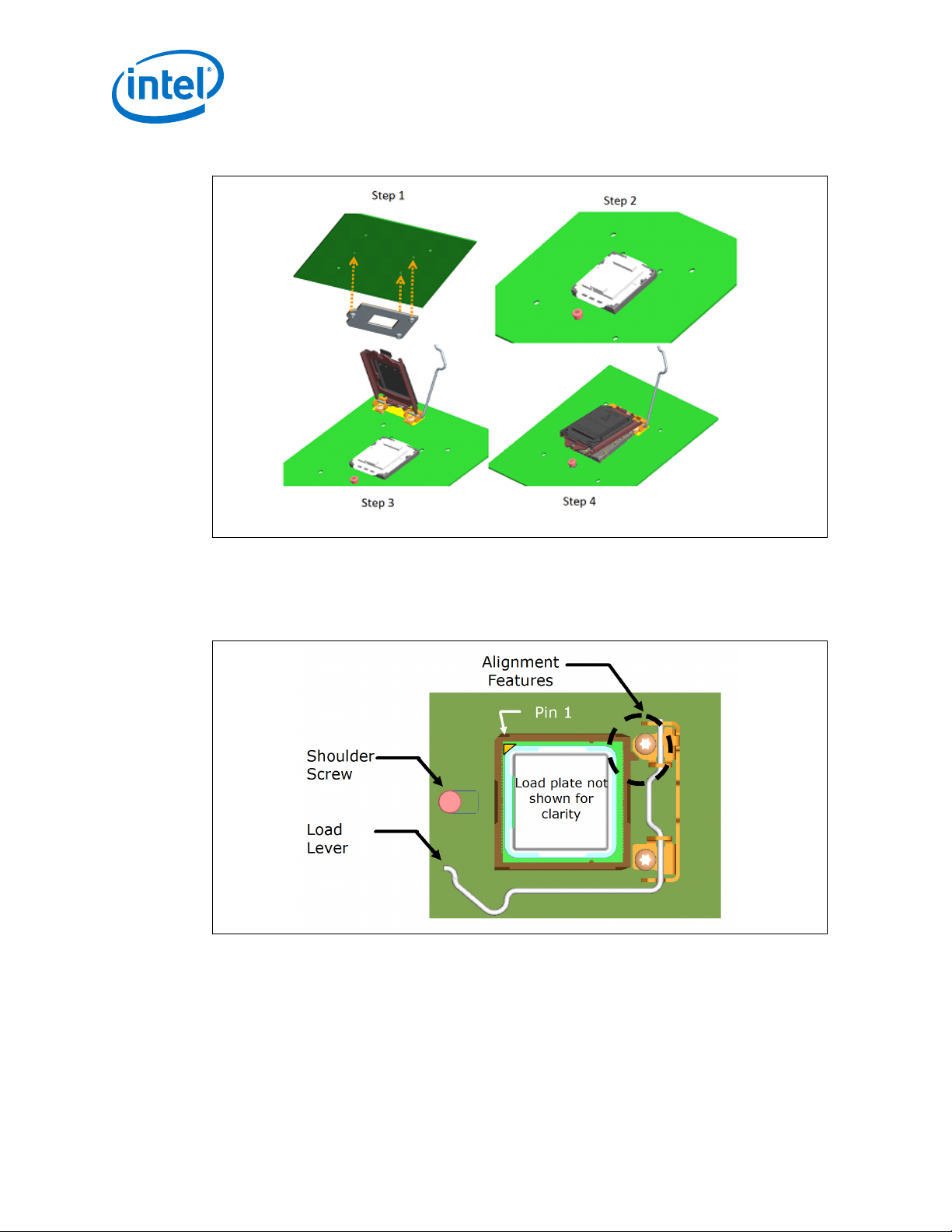
LGA1150 Socket—Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
Figure 9. Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Assembly
As indicated in Figure 10 on page 20, the shoulder screw, socket protrusion and ILM
key features prevent 180 degree rotation of ILM cover assembly with respect to
socket. The result is a specific Pin 1 orientation with respect to ILM lever.
Figure 10. Pin1 and Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Lever
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
20 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 21

Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)—LGA1150 Socket
3.3
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Interchangeability
ILM assembly and ILM back plate built from the Intel controlled drawings are intended
to be interchangeable. Interchangeability is defined as an ILM from Vendor A will
demonstrate acceptable manufacturability and reliability with a socket body from
Vendor A, B or C. ILM assembly and ILM back plate from all vendors are also
interchangeable.
The ILM are an integral part of the socket validation testing. ILMs from each vendor
will be matrix tested with the socket bodies from each of the current vendors. The
tests would include: manufacturability, bake and thermal cycling.
See Component Suppliers on page 28 for vendor part numbers that were tested.
Note: ILMs that are not compliant to the Intel controlled ILM drawings can not be assured to
be interchangeable.
3.4
Markings
There are four markings on the ILM:
• 115XLM: Font type is Helvetica Bold - minimum 6 point (2.125 mm).
• Manufacturer's insignia (font size at supplier's discretion).
• Lot identification code (allows traceability of manufacturing date and location).
• Pin 1 indicator on the load plate.
3.5
All markings must be visible after the ILM is assembled on the motherboard.
115XLM and the manufacturer's insignia can be ink stamped or laser marked on the
side wall.
Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Cover
Intel has developed an ILM Cover that will snap onto the ILM for the LGA115x socket
family. The ILM cover is intended to reduce the potential for socket contact damage
from operator and customer fingers being close to the socket contacts to remove or
install the pick and place cap. The ILM Cover concept is shown in Figure 11 on page
22.
The ILM Cover is intended to be used in place of the pick and place cover once the ILM
is assembled to the motherboard. The ILM will be offered with the ILM Cover preassembled as well as offered as a discrete component.
ILM Cover features:
• Pre-assembled by the ILM vendors to the ILM load plate. It will also be offered as
a discrete component.
• The ILM cover will pop off if a processor is installed in the socket, and the ILM
Cover and ILM are from the same manufacturer.
• ILM Cover can be installed while the ILM is open.
• Maintain inter-changeability between validated ILM vendors for LGA115x socket,
with the exception noted below.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 21
LGA1150 Socket
Page 22
LGA1150 Socket—Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)
• The ILM cover for the LGA115x socket will have a flammability rating of V-2 per
UL 60950-1.
Note: The ILM Cover pop off feature is not supported if the ILM Covers are interchanged on
different vendor’s ILMs.
Figure 11. Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) Cover
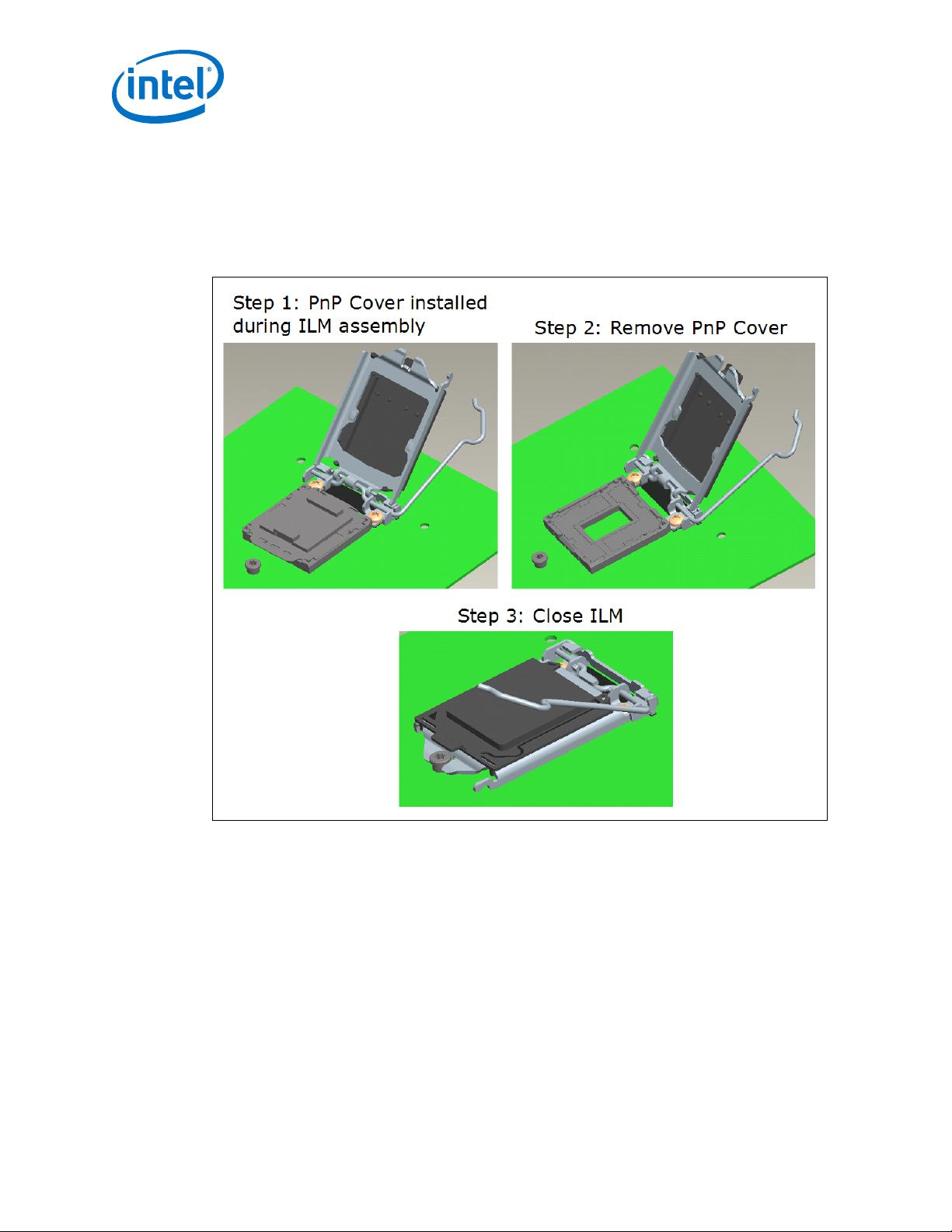
As indicated in Figure 11 on page 22, the pick and place cover should remain installed
during ILM assembly to the motherboard. After assembly the pick and place cover is
removed, the ILM Cover installed and the ILM mechanism closed. The ILM Cover is
designed to pop off if the pick and place cover is accidentally left in place and the ILM
closed with the ILM Cover installed. This is shown in Figure 12 on page 23.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
22 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 23

Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM)—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 12. ILM Cover and PnP Cover Interference
As indicated in Figure 12 on page 23, the pick and place cover cannot remain in place
and used in conjunction with the ILM Cover. The ILM Cover is designed to interfere
and pop off if the pick and place cover is unintentionally left in place. The ILM cover
will also interfere and pop off if the ILM is closed with a processor in place in the
socket.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 23
LGA1150 Socket
Page 24

LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications
4.0 LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications
This chapter describes the following specifications and requirements:
• Mechanical Specifications on page 24
• Electrical Requirements on page 25
• Environmental Requirements on page 26
4.1
Mechanical Specifications
Component Mass
Table 3. Socket Component Mass
Component Mass
Socket Body, Contacts and PnP Cover 10 g
ILM Cover 29 g
ILM Back Plate 38 g
Package / Socket Stackup Height
The following table provides the stackup height of a processor in the 1150-land LGA
package and LGA1150 socket with the ILM closed and the processor fully seated in the
socket.
Table 4. 1150-land Package and LGA1150 Socket Stackup Height
Component Stackup Height Note
Integrated Stackup Height (mm) From Top of Board to Top of IHS 7.781 ± 0.335 mm 2
Socket Nominal Seating Plane Height 3.4 ± 0.2 mm 1
Package Nominal Thickness (lands to top of IHS) 4.381 ± 0.269 mm 1
Note:
1. This data is provided for information only, and should be derived from: (a) the height of the socket
seating plane above the motherboard after reflow, given in Socket Mechanical Drawings, (b) the height of
the package, from the package seating plane to the top of the IHS, and accounting for its nominal
variation and tolerances that are given in the corresponding processor datasheet.
2. The integrated stackup height value is a RSS calculation based on current and planned processors that
will use the ILM design.
Loading Specifications
The socket will be tested against the conditions listed in Thermal Solution Quality and
Reliability Requirements Chapter of the Processor Thermal Mechanical Design
Guidelines (see Related Documents section) with heatsink and the ILM attached,
under the loading conditions outlined in this section.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
24 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 25

LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications—LGA1150 Socket
Table 5 on page 25 provides load specifications for the LGA1150 socket with the ILM
installed. The maximum limits should not be exceeded during heatsink assembly,
shipping conditions, or standard use condition. Exceeding these limits during test may
result in component failure. The socket body should not be used as a mechanical
reference or load-bearing surface for thermal solutions.
Table 5. Socket and ILM Mechanical Specifications
Parameter Minimum Maximum Notes
ILM static compressive load on processor
IHS
Heatsink static compressive load 0 N [0 lbf] 222 N [50 lbf] 1, 2, 3
Total static compressive Load (ILM plus
Heatsink)
Dynamic Compressive Load (with heatsink
installed)
Pick & Place cover insertion force N/A 10.2 N [2.3 lbf] –
Pick & Place cover removal force 2.2N [0.5 lbf] 7.56 N [1.7 lbf] 9
Load lever actuation force
Maximum heatsink mass N/A 500g 10
Notes:
1. These specifications apply to uniform compressive loading in a direction perpendicular to the IHS top
surface.
2. This is the minimum and maximum static force that can be applied by the heatsink and its retention
solution to maintain the heatsink to IHS interface. This does not imply the Intel reference TIM is validated
to these limits.
3. Loading limits are for the LGA1150 socket.
4. This minimum limit defines the static compressive force required to electrically seat the processor onto
the socket contacts. The minimum load is a beginning of life load.
5. Dynamic loading is defined as a load a 4.3 m/s [170 in/s] minimum velocity change average load
superimposed on the static load requirement.
6. Test condition used a heatsink mass of 500 gm [1.102 lb.] with 50 g acceleration (table input) and an
assumed 2X Dynamic Acceleration Factor (DAF). The dynamic portion of this specification in the product
application can have flexibility in specific values. The ultimate product of mass times acceleration plus
static heatsink load should not exceed this limit.
7. The maximum BOL value and must not be exceeded at any point in the product life.
8. The minimum value is a beginning of life loading requirement based on load degradation over time.
9. The maximum removal force is the flick up removal upwards thumb force (measured at 45°), not
applicable to SMT operation for system assembly. Only the minimum removal force is applicable to
vertical removal in SMT operation for system assembly.
10.The maximum heatsink mass includes the core, extrusion, fan and fasteners. This mass limit is evaluated
using the POR heatsink attach to the PCB.
311 N [70 lbf] 600 N [135 lbf] 3, 4, 7, 8
311 N [70 lbf] 822 N [185 lbf] 3, 4, 7, 8
N/A 712 N [160 lbf] 1, 3, 5, 6
N/A
20.9N [4.7lbf] in the vertical
direction 10.2 N [2.3 lbf] in
the lateral direction.
–
4.2
Electrical Requirements
LGA1150 socket electrical requirements are measured from the socket-seating plane
of the processor to the component side of the socket PCB to which it is attached. All
specifications are maximum values (unless otherwise stated) for a single socket
contact, but includes effects of adjacent contacts where indicated.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 25
LGA1150 Socket
Page 26

LGA1150 Socket—LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications
Table 6. Electrical Requirements for LGA1150 Socket
Parameter Value Comment
Mated loop inductance, Loop
<3.6nH
Socket Average Contact Resistance
(EOL)
19 mOhm
Max Individual Contact Resistance
(EOL)
Bulk Resistance Increase
Dielectric Withstand Voltage 360 Volts RMS
Insulation Resistance 800 MΩ
100 mOhm
≤3 mΩ
The inductance calculated for two contacts,
considering one forward conductor and one return
conductor. These values must be satisfied at the
worst-case height of the socket.
The socket average contact resistance target is
calculated from the following equation: sum (Ni X
LLCRi) / sum (Ni)
• LLCRi is the chain resistance defined as the
• Ni is the number of contacts within a chain.
• I is the number of daisy chain, ranging from 1
The specification listed is at room temperature
and has to be satisfied at all time.
The specification listed is at room temperature
and has to be satisfied at all time.
Resistance: The resistance of the socket contact,
solderball, and interface resistance to the
interposer land; gaps included.
The bulk resistance increase per contact from
25 °C to 100 °C.
resistance of each chain minus resistance of
shorting bars divided by number of lands in the
daisy chain.
to 119 (total number of daisy chains).
Socket Contact
4.3
Environmental Requirements
Design, including materials, shall be consistent with the manufacture of units that
meet the following environmental reference points.
The reliability targets in this section are based on the expected field use environment
for these products. The test sequence for new sockets will be developed using the
knowledge-based reliability evaluation methodology, which is acceleration factor
dependent. A simplified process flow of this methodology can be seen in Figure 13 on
page 27.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
26 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 27

LGA1150 Socket and ILM Specifications—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 13. Flow Chart of Knowledge-Based Reliability Evaluation Methodology
A detailed description of this methodology can be found at:
ftp://download.intel.com/technology/itj/q32000/pdf/reliability.pdf.
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 27
LGA1150 Socket
Page 28
LGA1150 Socket—Component Suppliers
Appendix A Component Suppliers
Note: The part numbers listed below identifies the reference components. End-users are
responsible for the verification of the Intel enabled component offerings with the
supplier. These vendors and devices are listed by Intel as a convenience to Intel's
general customer base, but Intel does not make any representations or warranties
whatsoever regarding quality, reliability, functionality, or compatibility of these
devices. Customers are responsible for thermal, mechanical, and environmental
validation of these solutions. This list and/or these devices may be subject to change
without notice.
Table 7. LGA1150 Socket and ILM Components
Item Intel PN Foxconn Molex Tyco Lotes ITW
LGA1150 Socket G27433-
LGA115X ILM with
cover
LGA115X ILM without
cover
LGA115X ILM cover
only
Desktop Backplate
with screws
1U Backplate (with
screws)
Notes:
1. The 1U Back Plate is a point solution for uP servers. This has not been validated for desktop design. This
should be used only were the clearance between the back of the motherboard and chassis is limited such
as 1U rack servers.
2. Individual ILM covers are made available for post-sales support
002
G11449002
E36142002
G12451001
E36143002
E66807001
PE115027-4
041-01F
PT44L61-6411N/A 2013882-8ACA-ZIF-078-
PT44L61-64014759688552013882-3ACA-ZIF-078-
012-1000-5377N/A 1-213450
PT44P19-64014759699302069838-2DCA-HSK-144-
PT44P18-6401N/A N/A DCA-HSK-157-
4759630322134930-1ACA-ZIF-138-
3-1
P01
Y28
Y19
ACA-ZIF-127P01
Y09
Y03
NA
FT1002-A-F
FT1002-A
FT1002-F
FT1002-B-CD
NA
Table 8. Supplier Contact Information
Supplier Contact Phone Email
Foxconn Eric Ling +1 503 693 3509 x225 eric.ling@foxconn.com
ITW Fastex Chak Chakir +1 512 989 7771 Chak.chakir@itweba.com
Lotes Co., Ltd. Windy Wang +1 604 721 1259 windy@lotestech.com
Molex Carol Liang +86 21 504 80889 x3301 carol.liang@molex.com
Tyco Alex Yeh (primary
contact)
Stanley Yen
(secondary contact)
+886 2 21715280 alex.yeh@te.com
+886 2 21715291 stanley.yen@te.com
The enabled components may not be currently available from all suppliers. Contact
the supplier directly to verify time of component availability.
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
28 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 29

Mechanical Drawings—LGA1150 Socket
Appendix B Mechanical Drawings
The following table lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix.
Table 9. Mechanical Drawing List
Drawing Description Figure Number / Location
Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top) Figure 14 on page 30
Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side (Bottom) Figure 15 on page 31
Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top) Figure 16 on page 32
Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side
(Bottom)
Figure 17 on page 33
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 29
LGA1150 Socket
Page 30

LGA1150 Socket—Mechanical Drawings
Figure 14. Socket/Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top)
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
30 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 31

Mechanical Drawings—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 15. Socket / Heatsink / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 31
LGA1150 Socket
Page 32

LGA1150 Socket—Mechanical Drawings
Figure 16. Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Primary Side (Top)
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
32 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 33

Mechanical Drawings—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 17. Socket / Processor / ILM Keep-out Zone Secondary Side (Bottom)
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 33
LGA1150 Socket
Page 34
LGA1150 Socket—Heatsink Back Plate Drawings
Appendix C Heatsink Back Plate Drawings
This heatsink back plate design is intended to adapt as a reference for OEMs that use
threaded fasteners on customized thermal solution, to comply with the mechanical
and structural requirements for the LGA115x socket. The heatsink back plate does not
have to provide additional load for socket solder joint protect. Structural design
strategy for the heatsink is to provide sufficient load for the Thermal Interface Material
(TIM) and to minimize stiffness impact on the motherboard.
Note: Design modifications for specific application and manufacturing are the responsibility
of OEM and the listed vendors for customized system implementation and validation.
These vendors and devices are listed by Intel as a convenience to Intel's general
customer base, but Intel does not make any representations or warranties whatsoever
regarding quality, reliability, functionality, or compatibility of these devices. Customers
are responsible for thermal, mechanical, and environmental validation of these
solutions. This list and/or these devices may be subject to change without notice.
Please refer to the motherboard keep-out zone listed in the LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide to ensure compliant with the heatsink back plate implementation.
Figure 18 on page 35 is the heatsink back plate keep-in zone for the design
implementation.
Table 10 on page 34 lists the mechanical drawings included in this appendix. Table
11 on page 34 lists the mechanical drawings
Table 10. Mechanical Drawing List
Drawing Description Figure Number/Location
Heatsink Back Plate Keep-in Zone Figure 18 on page 35
Heatsink Back Plate Figure 19 on page 36
Table 11. Supplier Contact Information
Supplier Contact Phone Email
CCI (Chaun Choung Technology
Corp.)
Monica Chih +886-2-29952666
The enabled components may not be currently available from supplier. Contact the
supplier directly to verify time of component availability.
x1131
monica_chih@ccic.com.tw
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
34 Order No.: 328999-002
Page 35

Heatsink Back Plate Drawings—LGA1150 Socket
Figure 18. Heatsink Back Plate Keep-in Zone
September 2013 Application Guide
Order No.: 328999-002 35
LGA1150 Socket
Page 36

Figure 19. Heatsink Back Plate
LGA1150 Socket—Heatsink Back Plate Drawings
LGA1150 Socket
Application Guide September 2013
36 Order No.: 328999-002
 Loading...
Loading...