
AOM
User Guide
Issue 01
Date 2020-08-27
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2020. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i

AOM
User Guide Contents
Contents
1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................. 1
2 Subscribing to AOM................................................................................................................ 9
3 Permissions Management................................................................................................... 11
3.1 Creating a User and Granting Permissions.................................................................................................................. 11
3.2 Creating a Custom Policy................................................................................................................................................... 12
4 Connecting Resources to AOM...........................................................................................14
4.1 Installing the ICAgent (HUAWEI CLOUD Host)......................................................................................................... 14
4.2
Conguring Application Discovery Rules...................................................................................................................... 17
4.3 Conguring Log Collection Paths.................................................................................................................................... 21
4.3.1 Conguring Container Log Collection Paths............................................................................................................ 21
4.3.2 Conguring VM Log Collection Paths........................................................................................................................ 27
5 Overview................................................................................................................................. 31
5.1 O&M.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 31
5.2 Dashboard............................................................................................................................................................................... 38
6 Alarm Management..............................................................................................................44
6.1 Usage Description................................................................................................................................................................. 44
6.2 Static Threshold Rules......................................................................................................................................................... 44
6.2.1 Creating Static Threshold Rules....................................................................................................................................45
6.3 Creating
6.4 Viewing Alarms......................................................................................................................................................................51
6.5 Viewing Events....................................................................................................................................................................... 51
Notication Rules............................................................................................................................................... 48
7 Resource Monitoring............................................................................................................ 53
7.1 Usage Description................................................................................................................................................................. 53
7.2 Application Monitoring....................................................................................................................................................... 53
7.3 Component Monitoring...................................................................................................................................................... 54
7.4 Host Monitoring.................................................................................................................................................................... 56
7.5 Container Monitoring.......................................................................................................................................................... 58
7.6 Metric Monitoring.................................................................................................................................................................59
7.7 Cloud Service Monitoring...................................................................................................................................................62
8 Log Management.................................................................................................................. 65
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii

AOM
User Guide Contents
8.1 Usage Description................................................................................................................................................................. 65
8.2 Searching for Logs................................................................................................................................................................ 65
8.3 Viewing Log Files.................................................................................................................................................................. 67
8.4 Adding Log Buckets..............................................................................................................................................................69
8.5 Structuring Logs.................................................................................................................................................................... 70
8.6 Viewing Bucket Logs............................................................................................................................................................ 77
8.7 Adding Log Dumps............................................................................................................................................................... 79
8.8 Creating Statistical Rules....................................................................................................................................................83
Conguration Management............................................................................................... 86
9
9.1 Agent Management (HUAWEI CLOUD Host).............................................................................................................86
9.1.1 Installing the ICAgent...................................................................................................................................................... 86
9.1.2 Upgrading the ICAgent....................................................................................................................................................91
9.1.3 Uninstalling the ICAgent.................................................................................................................................................91
9.1.4 ICAgent Management (Non-HUAWEI CLOUD Host)........................................................................................... 94
9.1.4.1 Installing the ICAgent................................................................................................................................................... 94
9.1.4.2 Upgrading the ICAgent................................................................................................................................................ 97
9.1.4.3 Uninstalling the ICAgent............................................................................................................................................. 97
9.2 Log Conguration................................................................................................................................................................. 98
9.2.1 Setting the Log Quota..................................................................................................................................................... 98
9.2.2 Conguring Delimiters.....................................................................................................................................................98
9.2.3 Log Collection...................................................................................................................................................................102
9.3 Quota Conguration......................................................................................................................................................... 103
9.4 Metric Conguration......................................................................................................................................................... 103
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
1 Introduction
Application Operations Management (AOM) is a one-stop and multi-dimensional
O&M management platform for cloud applications. It monitors applications and
related cloud resources in real time, collects and associates resource metrics, logs,
and events to analyze application health status, and supports alarm reporting and
data visualization, helping you detect faults in a timely manner and monitor the
running status of applications, resources, and services in real time.
Specically, AOM monitors and uniformly manages servers, storage devices,
networks, web containers, and applications hosted in Docker and Kubernetes,
eectively preventing problems, facilitating fault locating, and reducing O&M
costs. Unlike traditional monitoring systems, AOM monitors services by
applications. It meets enterprises' requirements for high
iteration, provides eective IT support for their services, and protects and
optimizes their IT assets, enabling enterprises to achieve strategic goals.
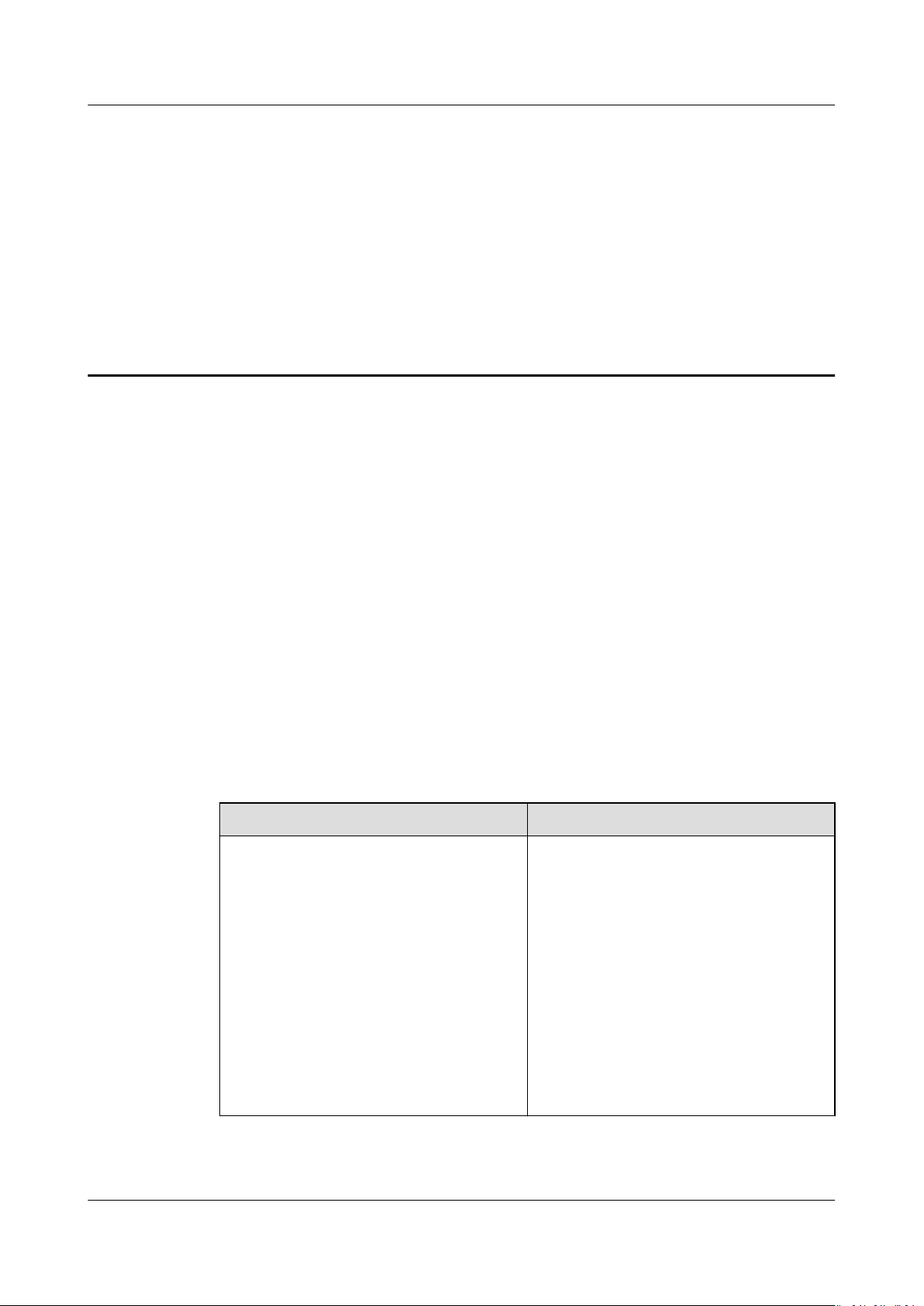
Console Description
Table 1-1 AOM console description
Item
Overview Both the O&M overview and
eciency and fast
Description
dashboard are provided.
● O&M overview
The O&M page supports full-link,
multi-layer, and one-stop O&M for
resources, applications, and user
experience.
● Dashboard
With a dashboard,
such as line graphs and digit graphs
are displayed on the same screen,
enabling you to understand
monitoring data comprehensively.
dierent graphs
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1

AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
Item Description
Alarm center Alarm center includes the alarm list,
event list, threshold rules, and
notication rules.
● Alarm list
Alarms are the information which is
reported when AOM or an external
service is abnormal or may cause
exceptions. You need to take
measures accordingly. Otherwise,
service exceptions may occur.
The alarm list displays the alarms
generated within a
specied time
range.
● Event list
Events generally carry some
important information, informing
you of the changes of AOM or an
external service. Such changes do
not necessarily cause exceptions.
The event list displays the events
generated within a
specied time
range.
● Threshold rules
You can set threshold conditions for
metrics by using threshold rules.
When metric values meet
conditions, AOM will generate
threshold alarms. When no metric
data is reported, AOM will report
insucient data events. In this way,
you can identify and handle
exceptions at the earliest time.
Notication rules
●
AOM supports alarm
notication.
You can use this function by
creating
notication rules. When
alarms are reported due to an
exception in AOM or an external
service, alarm information can be
sent to
specied personnel by email
or Short Message Service (SMS)
message. In this way, these
personnel can rectify faults in time
to avoid service loss.
● Intelligent thresholds
When a metric value meets the
preset threshold condition, the
system generates a threshold-
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
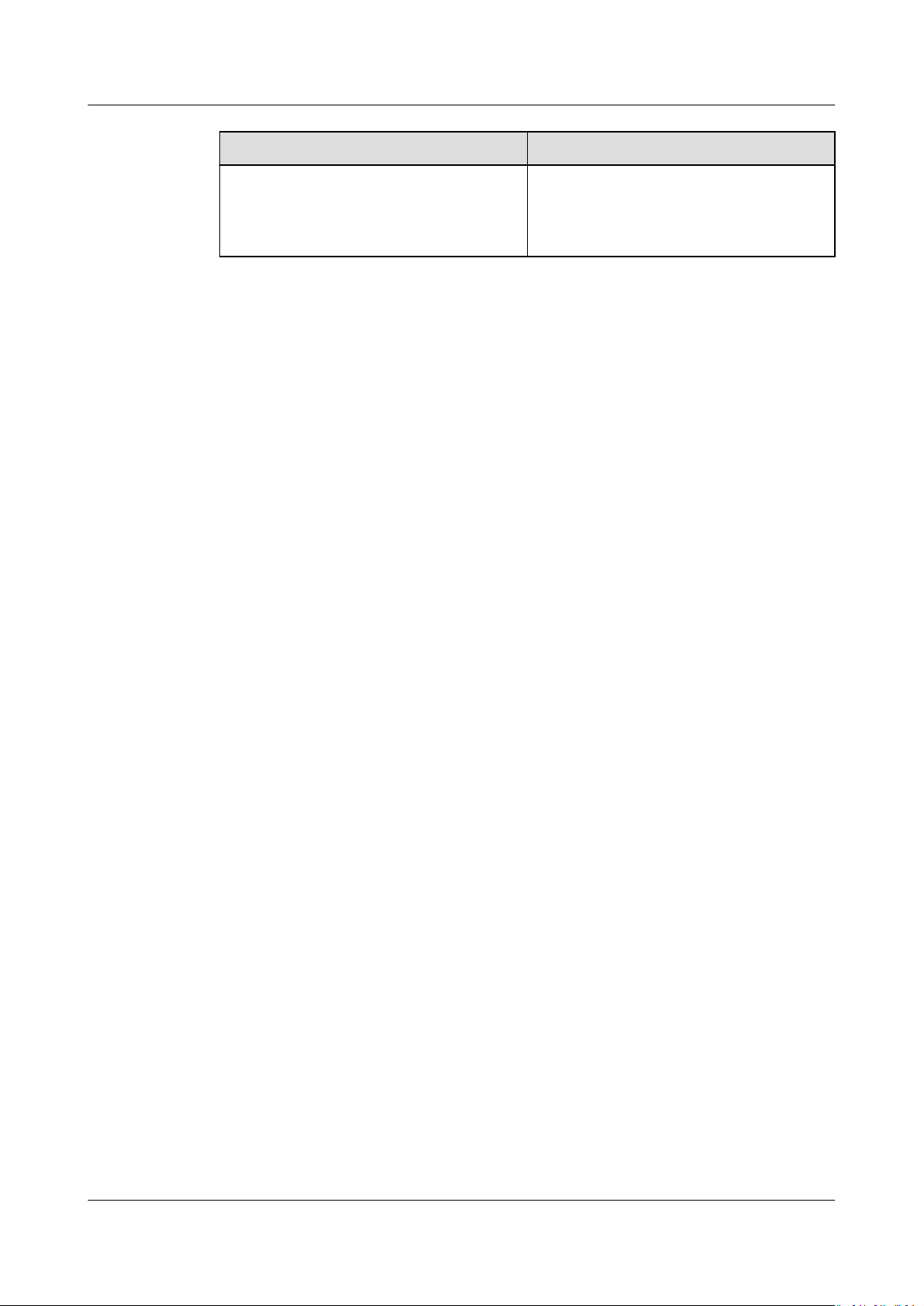
Item Description
crossing alarm. If the notication
function is enabled, alarm
information wil be sent to specied
users by SMS message or email.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3

AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
Item Description
Monitoring Functions such as application
monitoring, component monitoring,
host monitoring, container monitoring,
and metric monitoring are provided.
● Application monitoring
An application is a group of the
same or similar components divided
based on service requirements.
AOM supports monitoring by
application.
● Component monitoring
Components refer to the services
that you deploy, including
containers and common processes.
The Component Monitoring page
displays information such as type,
CPU usage, memory usage, and
status of each component. AOM
supports drill-down from
components to instances, and then
to containers, enabling multidimensional monitoring.
● Host monitoring
The Host Monitoring page enables
you to monitor common system
devices such as disks and
le
systems, and resource usage and
health status of hosts and service
processes or instances running on
them.
● Container monitoring
Only workloads deployed by using
Cloud Container Engine (CCE) and
applications created by using
ServiceStage are monitored.
● Metric monitoring
The Metric Monitoring page
displays metric data of each
resource. You can monitor metric
values and trends in real time, add
desired metrics to dashboards,
create threshold rules, and export
monitoring reports. In this way, you
can monitor services in real time
and perform data correlation
analysis.
● Cloud service monitoring
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
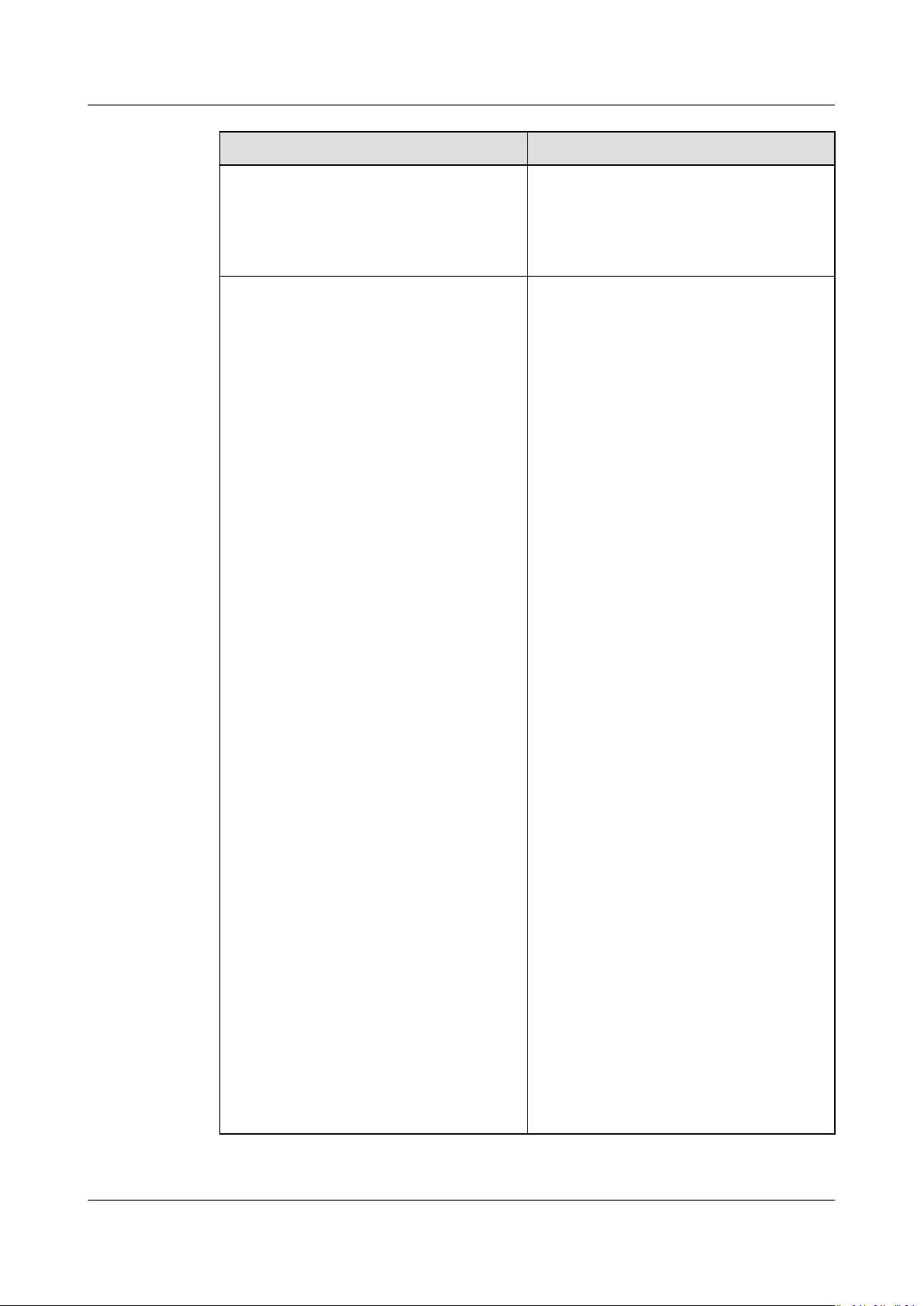
Item Description
The Cloud Service Monitoring
page displays historical
performance curves of each cloud
service instance. You can view cloud
service data in the last six months.
Log Functions such as log search, log le,
log dump, and path conguration are
provided.
● Log search
AOM enables you to quickly query
logs, and locate faults based on log
sources and contexts.
● Log
les
You can quickly view log les of
component instances to locate
faults.
● Log dumps
AOM enables you to dump logs to
Object Storage Service (OBS)
buckets for long-term storage.
● Path
conguration
AOM can collect and display VM
logs. VM refers to an Elastic Cloud
Server (ECS) or a Bare Metal Server
(BMS) running Linux. Before
collecting logs, ensure that you
congured a log collection
have
path.
● Log buckets
A log bucket is a logical group of
les. You dump log les, create
log
statistical rules, and view logs by
log bucket.
● Statistical rules
A statistical rule takes
eect by log
bucket. You can congure keywords
in statistical rules. Then, AOM
periodically counts the number of
such keywords in log buckets and
generates log metrics.
● Log structuring
In log structuring, original logs can
be separated by regular expressions
or special characters so that
structured logs can be queried and
analyzed based on the SQL syntax.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
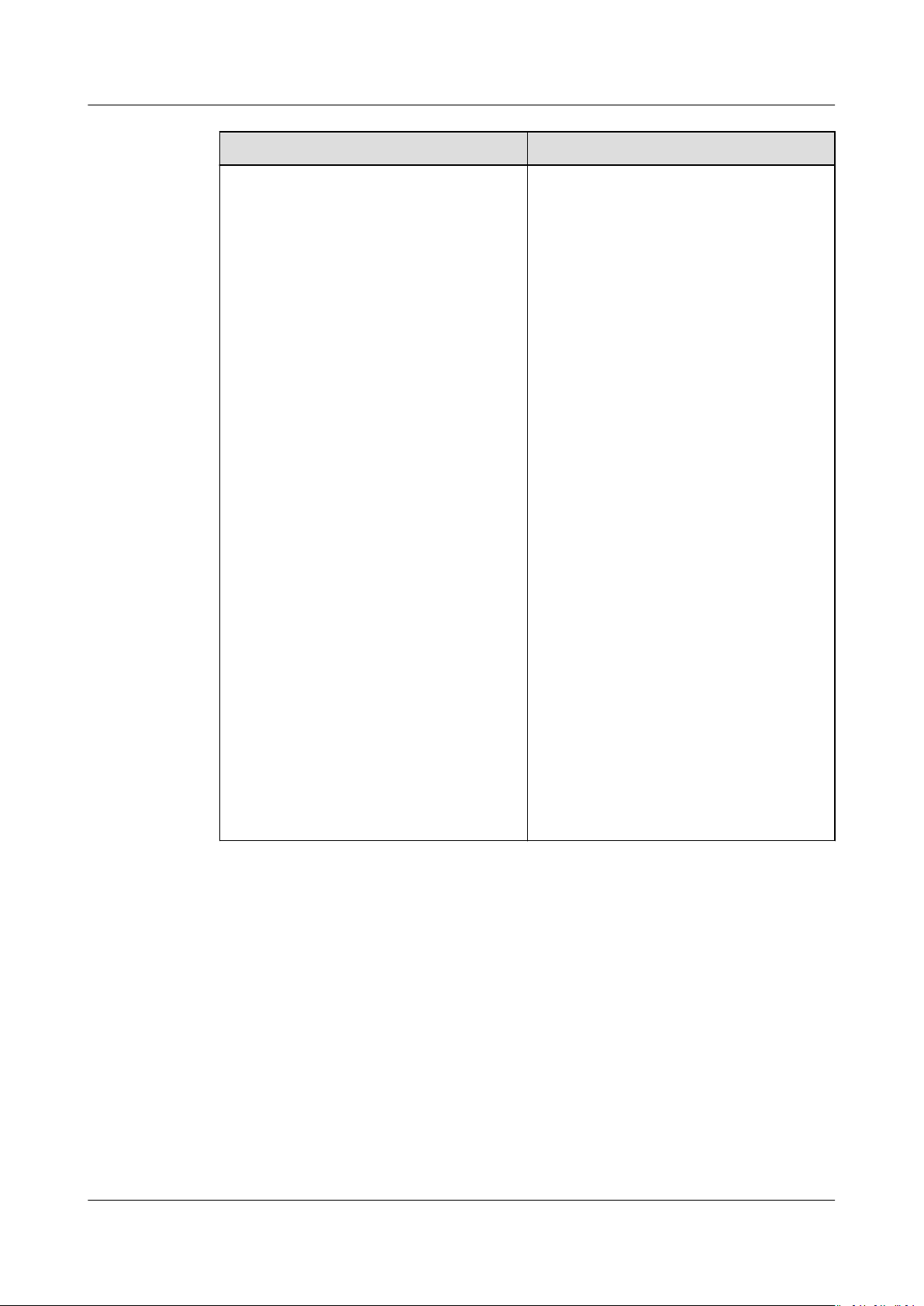
Item Description
Conguration management Functions such as agent management,
application discovery, and log
conguration are provided.
● Agent management
The ICAgent collects metrics, logs,
and application performance data
in real time. For hosts purchased
from the Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)
or Bare Metal Server (BMS)
console, you need to manually
install the ICAgent. For hosts
purchased from the Cloud
Container Engine (CCE) console, the
ICAgent is automatically installed.
● Application discovery
AOM can discover applications and
collect their metrics based on
congured rules.
● Log
● Quota conguration
● Metric
conguration
Log quotas and delimiters can be
congured.
Earlier metrics will be deleted when
the metric quota is exceeded.
You can change the metric quota by
switching between the basic edition
(free) and pay-per-use edition.
conguration
You can enable the metric
collection function to collect
metrics (excluding SLA and custom
metrics).
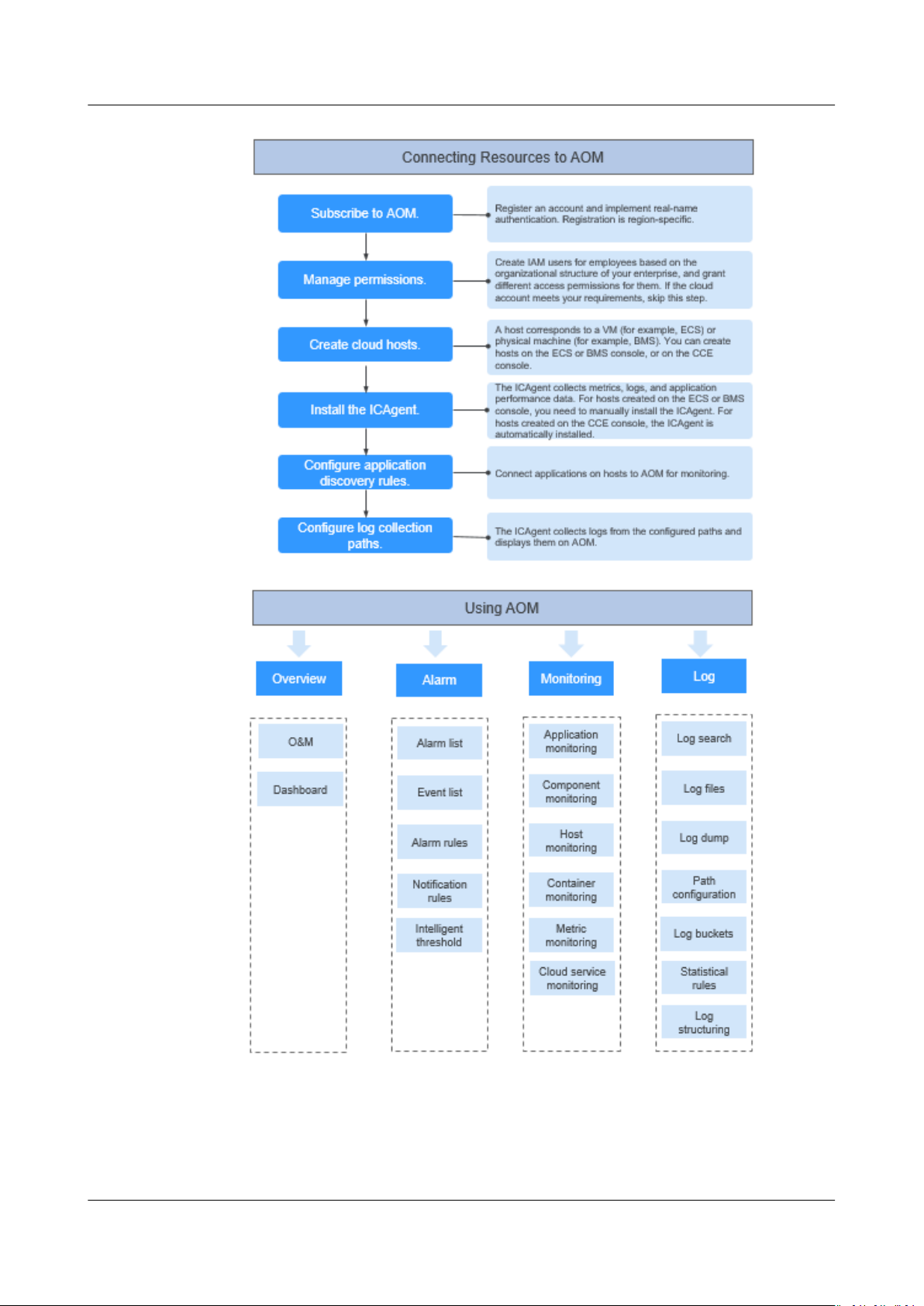
Process for Using AOM
The following gure shows the process of using AOM.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
1. (Mandatory) Subscribe to AOM.
2. (Optional) Create a sub-account and set permissions.
3. (Mandatory) Create a cloud host.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7

AOM
User Guide 1 Introduction
4. (Mandatory) Install the ICAgent.
The ICAgent is a collector used to collect metric, log, and application
performance data in real time.
If an ECS is purchased through CCE, the ICAgent is automatically installed on
the ECS.
5. (Optional)
Congure application discovery rules.
For the applications that meet built-in application discovery rules, they will
be automatically discovered after the ICAgent is installed. For the applications
that cannot be discovered using built-in application discovery rules, you need
congure custom application discovery rules.
to
6. (Optional)
Congure log collection paths.
To use AOM to monitor host logs, you need to congure log collection paths.
7. (Optional) Implement O&M.
You can use AOM functions such as Overview, Alarm Management,
Resource Monitoring, and Log Management to perform routine O&M.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
AOM
User Guide 2 Subscribing to AOM
2 Subscribing to AOM
Before subscription, ensure that you have registered an account and implemented
real-name authentication.
Registering an Account
Step 1 Log in to the cloud at https://www.huaweicloud.com/intl/en-us/.
Step 2 Click Register in the upper right corner of the page.
Complete the registration as prompted.
----End
Implementing Real-Name Authentication
You can use Application Operations Management (AOM) only after real-name
authentication is complete.
Step 1 After logging in to the cloud, click the username in the upper right corner on the
page and select My Account from the drop-down list.
Step 2 On the Basic Information page, click Authenticate to the right of
Authentication Status.
Complete real-name authentication as prompted.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9

NO TE
AOM
User Guide 2 Subscribing to AOM
Subscribing to AOM
AOM resources are region-specic and cannot be used across regions. When
dierent regions (such as AP-Hong Kong and AP-Bangkok) exist, select a region
before subscribing to AOM.
Click Console in the upper right corner and then click in the upper left corner
to select a region. Then, click Service List and choose Application > Application
Operations Management. In the dialog box that is displayed, click Subscribe for
Free to enable AOM for free.
AOM provides both basic and pay-per-use editions. The basic edition is used by default. You
can click Switch Edition as required.
Switching Edition
AOM provides both basic and pay-per-use editions. The basic edition is used by
default. You can click Switch Edition as required.
Step 1 Log in to the AOM console, choose Overview > O&M in the navigation pane, and
click Switch Edition in the upper right corner of the page.
Step 2 Select an edition, select the prompt information, and click Switch Now.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10

AOM
User Guide 3 Permissions Management
3 Permissions Management
3.1 Creating a User and Granting Permissions
This section describes the ne-grained permissions management provided by
Identity and Access Management (IAM) for your Application Operations
Management (AOM). With IAM, you can:
Prerequisites
● Create IAM users for employees based on the organizational structure of your
enterprise. Each IAM user has their own security credentials, providing access
to AOM resources.
● Grant only the permissions required for users to perform a task.
● Entrust a HUAWEI CLOUD account or cloud service to perform professional
ecient O&M on your AOM resources.
and
If your HUAWEI CLOUD account does not need individual IAM users, then you
may skip over this chapter.
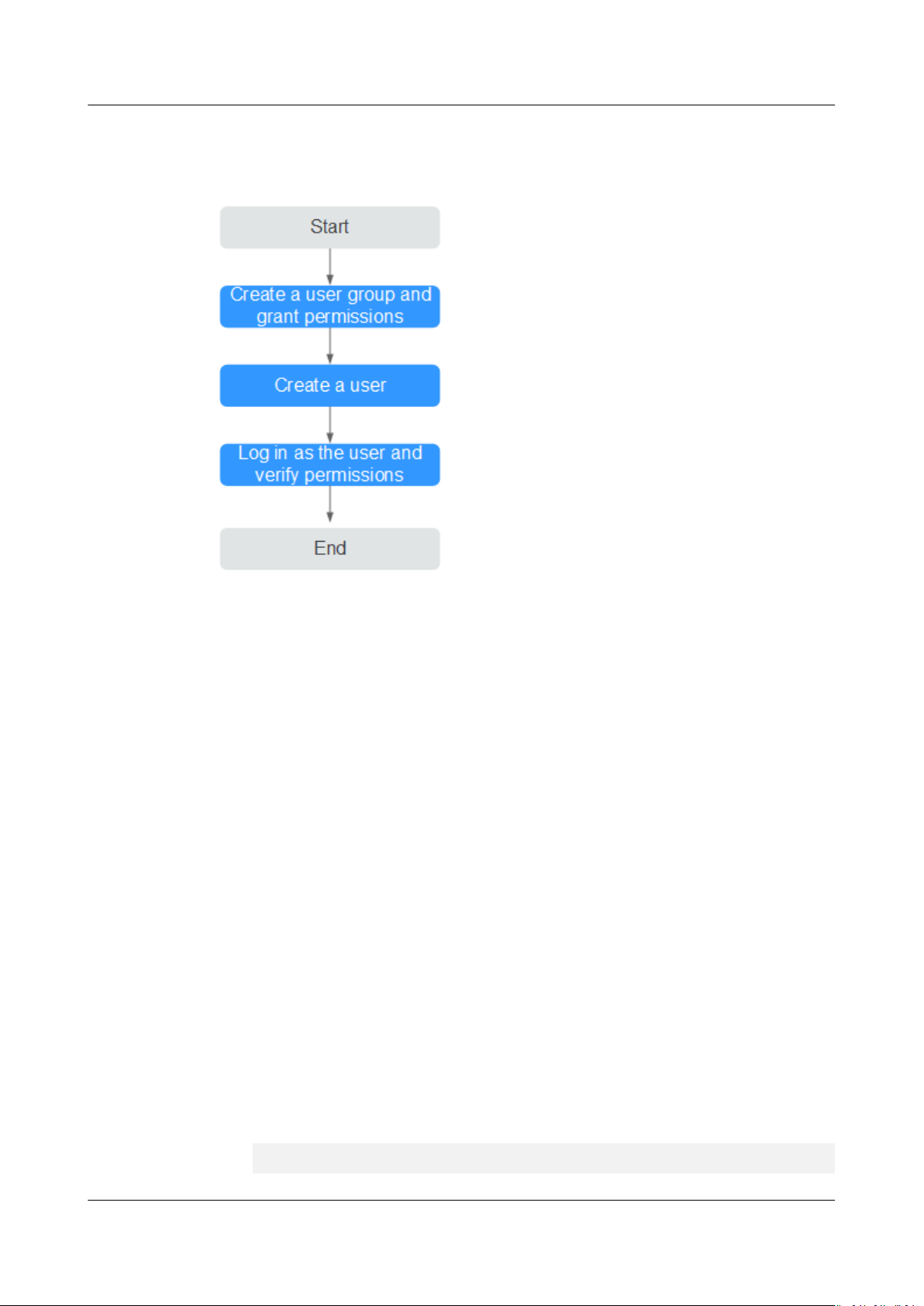
This section describes the procedure for granting permissions (see Figure 3-1).
Before assigning permissions to user groups, you should learn about the AOM
permissions listed in Permissions Management. For the system permissions of
other services, see System Permissions.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
AOM
User Guide 3 Permissions Management
Process
Figure 3-1 Process for granting AOM permissions
1. Creating a User Group and Assigning Permissions
Create a user group on the IAM console, and assign the AOM
ReadOnlyAccess policy to the group.
2. Creating an IAM User
Create a user on the IAM console and add the user to the group created in 1.
3. Logging In Using an IAM User and Verifying Permissions
Log in to the AOM console as the created user, and verify that it only has read
permissions for AOM.
3.2 Creating a Custom Policy
Custom policies can be created as a supplement to the system policies of
Application Operations Management (AOM). For the actions supported for custom
policies, see Permissions Policies and Supported Actions.
You can create custom policies in either of the following two ways:
● Visual editor: Select cloud services, actions, resources, and request conditions
without the need to know policy syntax.
● JSON: Edit JSON policies from scratch or based on an existing policy.
For details, see Creating a Custom Policy. The following section contains
examples of common AOM custom policies.
Example Custom Policies
● Example 1: Allowing a user to create threshold rules
{
"Version": "1.1",
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12

AOM
User Guide 3 Permissions Management
"Statement": [
{
"Eect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"aom:alarmRule:create"
]
}
]
}
● Example 2: Forbidding a user to delete application discovery rules
A deny policy must be used in conjunction with other policies to take
eect. If
the permissions assigned to a user contain both Allow and Deny actions, the
Deny actions take precedence over the Allow actions.
To grant a user the AOM FullAccess system policy but forbid the user to
delete application discovery rules, create a custom policy that denies the
deletion of application discovery rules, and grant both the AOM FullAccess
and deny policies to the user. Because the Deny action takes precedence, the
user can perform all operations except deleting application discovery rules.
The following is an example deny policy:
{
"Version": "1.1",
"Statement": [
{
"Eect": "Deny",
"Action": [
"aom:discoveryRule:delete"
]
}
]
}
● Example 3:
Dening permissions for multiple services in a policy
A custom policy can contain actions of multiple services that are all of the
project-level type. The following is an example policy containing actions of
multiple services:
{
"Version": "1.1",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"aom:*:list",
"aom:*:get",
"apm:*:list",
"apm:*:get"
]
},
{
"Action": [
"cce:cluster:get",
"cce:cluster:list",
"cce:node:get",
"cce:node:list"
]
}
]
}
"Eect": "Allow",
"Eect": "Allow",
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
4 Connecting Resources to AOM
4.1 Installing the ICAgent (HUAWEI CLOUD Host)
The ICAgent collects metrics, logs, and application performance data in real time.
For hosts purchased from the Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) or Bare Metal Server
(BMS) console, you need to manually install the ICAgent. For hosts purchased
from the Cloud Container Engine (CCE) console, the ICAgent is automatically
installed.
Prerequisites
● Before installing the ICAgent, ensure that the time and time zone of the local
browser are consistent with those of the server. If multiple servers are
deployed, ensure that the local browser and multiple servers use the same
time zone and time. Otherwise, metric data of applications and servers
displayed on the UI may be incorrect.
● The ICAgent process needs to be installed and run by the root user.
Installation Methods
There are two methods to install the ICAgent. Note that the two methods are not
applicable to container nodes (that is, nodes created using ServiceStage or CCE).
For container nodes, you do not need to manually install the ICAgent. Instead, you
only need to perform certain operations when creating clusters or deploying
applications.
For details, see Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 Installation methods
Method
Initial
installation
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Scenario
This method is used when the following conditions are met:
1. An Elastic IP Address (EIP) has been bound to the server.
2. The ICAgent has never been installed on the server.
NO TE
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Method Scenario
Inherited
installation
Initial Installation
After you apply for a server and install the ICAgent for the
following operations:
Step 1 Obtain an Access Key ID/Secret Access Key (AK/SK).
● If you have obtained the AK/SK, skip this step.
● If you have not obtained the AK/SK, obtain them
Step 2 In the navigation pane, choose Conguration Management > Agent
Management.
Step 3 Click Install ICAgent.
This method is used when the following conditions are met:
You have multiple servers with ICAgent installed. One server is
bound to an EIP, but others are not. The ICAgent has been
installed on the server bound to an EIP by using the initial
installation method. You can use the inherited method to
install the ICAgent on the remaining servers.
See Inherited Installation.
rst time, perform the
rst.
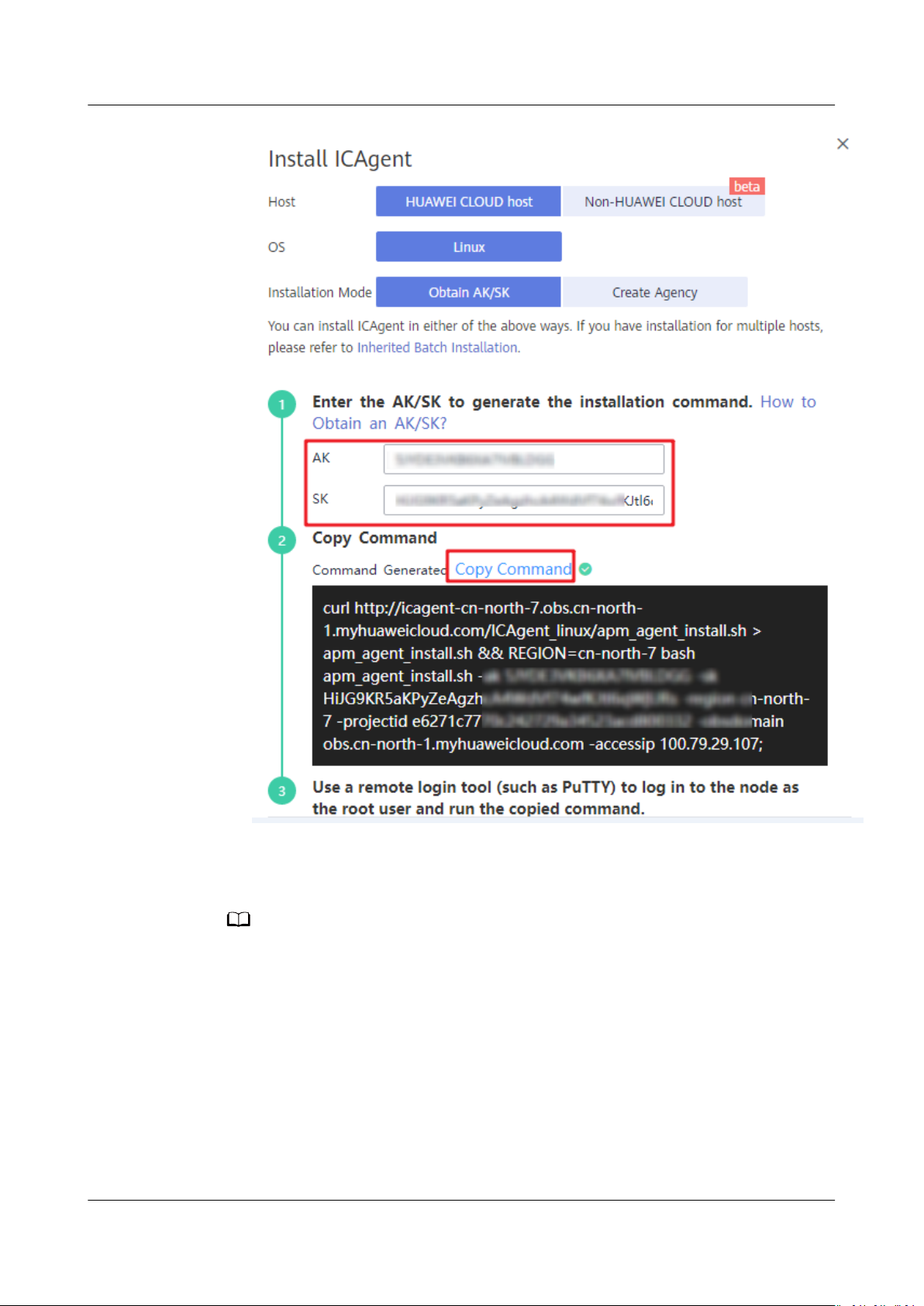
Step 4 Generate the ICAgent installation command and copy it.
1. Enter the obtained AK/SK in the text box to generate the ICAgent installation
command.
Ensure that the AK/SK are correct. Otherwise, the ICAgent cannot be installed.
2. Click Copy Command.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
NO TE
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Step 5 Use a remote login tool, such as PuTTY, to log in to the server where the ICAgent
is to be installed as the root user and run the command copied in Step 4.2 to
install the ICAgent.
● If the message ICAgent install success is displayed, the ICAgent is successfully installed
in the /opt/oss/servicemgr/ directory. After the ICAgent is successfully installed, choose
Conguration Management > Agent Management to view the ICAgent status.
● If the ICAgent fails to be installed, uninstall the ICAgent according to Uninstalling the
ICAgent Through Logging In to the Server and then install it again. If the problem
persists, contact technical support.
----End
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16

AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Follow-up Operations
For more information about how to install, upgrade, and uninstall the ICAgent,
see Agent Management (HUAWEI CLOUD Host).
4.2
Conguring Application Discovery Rules
Filtering Rules
Application Operations Management (AOM) can discover applications and collect
their metrics based on
congured rules. There are two modes to congure
application discovery: auto mode and manual mode. This section mainly describes
the manual mode.
● Automatic
conguration
After you install the ICAgent on a host according to Installing the ICAgent,
the ICAgent automatically discovers applications on the host based on Built-
in Service Discovery Rules and displays them on the Application
Monitoring page.
● Manual
conguration
After you add a custom service discovery rule on the application discovery
page and apply it to the host where the ICAgent is installed (for details, see
Installing the ICAgent), the ICAgent discovers applications on the host based
on the
congured service discovery rule and displays them on the application
monitoring page.
The ICAgent will periodically implement detection on the target host to nd out
all its processes. The
eect is similar to that of running the ps -e -o
pid,comm,lstart,cmd | grep -v defunct command on the target host. Then, the
ICAgent checks whether processes match the
ltering rules in Table 4-2. If a
process meets a ltering rule, the process is ltered out and is not discovered by
AOM. If a process does not meet any ltering rules, the process is not ltered out
and is discovered by AOM.
ICAgent detection results may as follows:
PID COMMAND STARTED CMD
1 systemd Tue Oct 2 21:12:06 2018 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system -deserialize 20
2 kthreadd Tue Oct 2 21:12:06 2018 [kthreadd]
3 ksoftirqd/0 Tue Oct 2 21:12:06 2018 (ksoftirqd/0)
1140 tuned Tue Oct 2 21:12:27 2018 /usr/bin/python -Es /usr/sbin/tuned -l -P
1144 sshd Tue Oct 2 21:12:27 2018 /usr/sbin/sshd -D
1148 agetty Tue Oct 2 21:12:27 2018 /sbin/agetty --keep-baud 115200 38400 9600 hvc0 vt220
1154 docker-containe Tue Oct 2 21:12:29 2018 docker-containerd -l unix:///var/run/docker/libcontainerd/
docker-containerd.sock --shim docker-containerd-shim --start-timeout 2m --state-dir /var/run/docker/
libcontainerd/containerd --runtime docker-runc --metrics-interval=0
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Table 4-2 Filtering rules
Filtering Rule Example
If the COMMAND value of a process is
docker-containe, vi, vim, pause, sshd,
ps, sleep, grep, tailf, tail, or systemdudevd, and the process is not running
in the container, the process is ltered
out and is not discovered by AOM.
If the CMD value of a process starts
with [ and ends with ], the process is
ltered out and is not discovered by
AOM.
If the CMD value of a process starts
with ( and ends with ), the process is
ltered out and is not discovered by
AOM.
If the CMD value of a process starts
with /sbin/, the process is ltered out
and is not discovered by AOM.
In the preceding information, the
process whose PID is 1154 is not
discovered by AOM because its
COMMAND value is docker-containe.
In the preceding information, the
process whose PID is 2 is not
discovered by AOM because its CMD
value is [kthreadd].
In the preceding information, the
process whose PID is 3 is not
discovered by AOM because its CMD
value is (ksoftirqd/0).
In the preceding information, the
process whose PID is 1148 is not
discovered by AOM because its CMD
value starts with /sbin/.
Built-in Service Discovery Rules
AOM provides two built-in discovery rules: Sys_Rule and Default_Rule. These
rules are executed on all hosts, including hosts added later. The priority of
Sys_Rule is higher than that of Default_Rule. That is, Sys_Rule is executed on the
rst. If Sys_Rule is met, Default_Rule is not executed. Otherwise,
host
Default_Rule is executed. Rule details are as follows:
Sys_Rule (cannot be disabled)
● For the component name, obtain the value of -Dapm_tier in the command,
the value of the environment variable PAAS_APP_NAME, and the value of -
Dapm_tier of the environment variable JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS based on the
priorities in descending order.
● For the application name, obtain the value of -Dapm_application in the
command, the value of environment variable PAAS_MONITORING_GROUP,
and the value of -Dapm_application in the environment variable
JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS based on the priorities in descending order.
In the following example, the component name is atps-demo and the application
name is atpd-test.
PAAS_MONITORING_GROUP=atpd-test
PAAS_APP_NAME=atps-demo
JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS=-javaagent:/opt/oss/servicemgr/ICAgent/pinpoint/pinpoint-bootstrap.jar Dapm_application=atpd-test -Dapm_tier=atps-demo
Default_Rule (can be disabled)
● If the COMMAND value of a process is java, obtain the name of the JAR
package in the command, the main class name in the command, and the
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
rst

NO TE
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
keyword that does not start with a hyphen (-) in the command based on the
priorities in descending order as the component name, and use the default
value unknownapplicationname as the application name.
● If the COMMAND value of a process is python, obtain the name of the
rst .py/.pyc script in the command as the component name, and use the
default value unknownapplicationname as the application name.
● If the COMMAND value of a process is node, obtain the name of the
script in the command as the component name, and use the default value
unknownapplicationname as the application name.
Custom Discovery Rules
Step 1 In the navigation pane, choose
Step 2 Click Add Custom Application Discovery Rule and congure an application
discovery rule.
Step 3 Select a host for pre-detection.
1. Customize a rule name, for example, ruletest.
2. Select a typical host, for example, hhhhhh-27465, to check whether the
application discovery rule is valid. The hosts that execute the rule will be
congured in Step 6. Then, click Next.
Step 4 Set an application discovery rule.
1. Click Add Check Items. AOM can discover processes that meet the conditions
of check items.
For example, AOM can detect the processes whose command parameters
contain ovs-vswitchd unix: and environment variables contain
SUDO_USER=paas.
rst .js
Conguration Management > Service Discovery.
– To precisely detect processes, you are advised to add check items about unique
features of the processes.
– You need to add one check item at least and can add ve check items at most. If
there are multiple check items, AOM only discovers the processes that meet the
conditions of all check items.
2. After adding check items, click Detect to search for the processes that meet
the conditions.
If no process is detected within 20s, modify the discovery rule and detect
processes again. Only when at least one process is detected, go to the next
step.
Step 5 Set a component name and log path.
1. Set a component name.
In the Component Name Settings area, click Add Naming Rule to set a
component name for the discovered process. For example, add the
xed text
app-test as a component name.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19

NO TE
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
– If you do not set a component name, the default name
unknownapplicationname is used.
– When you add multiple naming rules, all the naming rules are combined as the
component name of the process. Metrics with the same component name are
aggregated.
2. Set the function of collecting process logs.
Turn on Enable Automatic Log Association to obtain the .log, .trace,
and .out les opened by processes. In this way, you can collect the les for log
analysis when monitoring processes.
This function is enabled by default. If you do not need it, disable it. In this
case, no log list will be displayed in the Preview Component Name table.
3. Preview the component name.
If the name does not meet your requirements, click
in the Preview
Component Name table to rename it.
Congure a log path.
4.
If you have turned on Enable Automatic Log Association, click Congure
Log Path in the Operation column of the Preview Component Name table
to bind the application name, component name, and log path of the detected
process to its command parameters.
Step 6 Set a priority and detection range.
1. Set a priority: When there are multiple rules, set priorities. Enter 1 to 9999. A
smaller value indicates a higher priority. For example, 1 indicates the highest
priority and 9999 indicates the lowest priority.
2. Set a detection range: Select a host to be detected. That is, select the host to
which the
congured rule is applied. If no host is selected, this rule will be
executed on all hosts, including hosts added later.
Step 7 Click Add to complete the
conguration. AOM collects metrics of the process.
Step 8 Wait for about two minutes, choose Monitoring > Component Monitoring in the
navigation pane, select the hhhhhh-27465 host from the cluster drop-down list,
nd out the /openvswitch/ component that has been monitored.
and
----End
More Operations
After creating an application discovery rule, you can also perform the operations
described in Table 4-3.
Table 4-3 Related operations
Operation
Viewing rule
details
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
Description
In the Name column, click the name of an application
discovery rule.
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Operation Description
Enabling or
disabling a
rule
Deleting a
rule
Modifying a
rule
● Click Enable in the Operation column.
● Click Disable in the Operation column. After a rule is
disabled, AOM does not collect corresponding process
metrics.
● To delete an application discovery rule, click More in the
Operation column and select Delete.
● To delete one or more application discovery rules, select it or
them and click Delete above the rule list.
NOTE
Built-in application discovery rules cannot be deleted.
Click More in the Operation column and select Modify from
the drop-down list.
NOTE
Built-in application discovery rules cannot be modied.
4.3 Conguring Log Collection Paths
4.3.1 Conguring Container Log Collection Paths
Precautions
Procedure
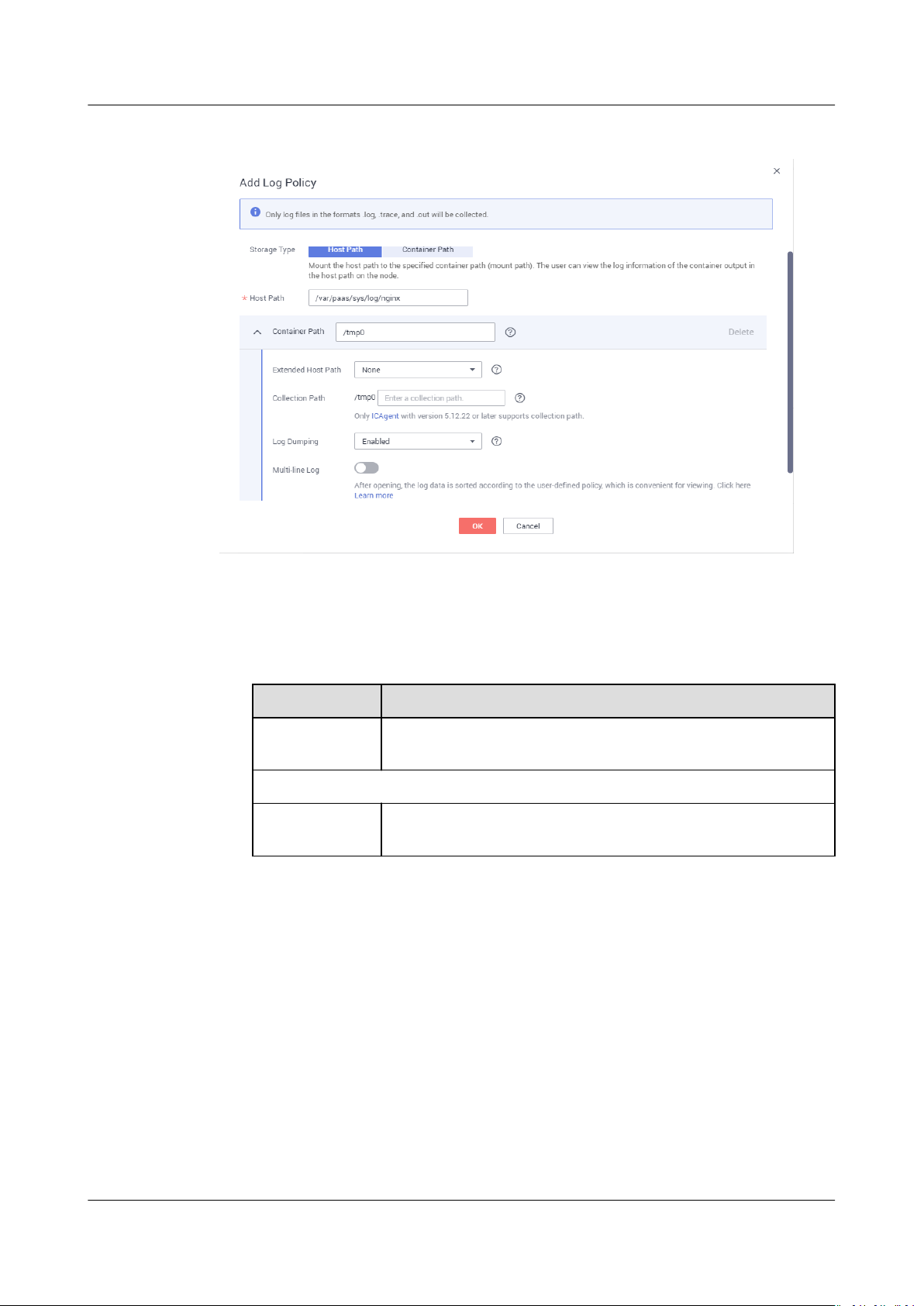
Step 1 When creating a workload on Cloud Container Engine (CCE), click Log Policies
Step 2 Click Add Log Policy. On the displayed page,
Application Operations Management (AOM) can collect and display container
logs. To do so, congure a log collection path according to the following
procedure.
● The ICAgent only collects *.log, *.trace, and *.out text log
● AOM collects standard container output log by default.
Adding a Log Policy on CCE
after adding a container.
congure parameters as required.
The following uses Nginx as an example.
les.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Figure 4-1 Adding a log policy
Step 3 Set Storage Type to Host Path or Container Path.
● Host Path: You can mount a host path to a
specied container path. Set
parameters according to the following table.
Table 4-4 Parameters for adding log policies (host path)
Parameter
Description
Storage Type Set this parameter to Host Path. You can mount a host
path to a specied container path.
Add Container Path
*Host Path Host path to which a container log le is mounted.
Example: /var/paas/sys/log/nginx
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Parameter Description
Container Path Container path to which a data volume is mounted.
Example: /tmp
NOTICE
– Do not mount a data volume to a system directory such as /
or /var/run. Otherwise, the container becomes abnormal. You
are advised to mount log les to an empty directory. If the
directory is not empty, ensure that there are no
aect container startup. Otherwise, les will be replaced,
causing container startup failures or workload creation
failures.
– If the volume is mounted to a high-risk directory, you are
advised to use an account with minimum permissions to start
the container; otherwise, high-risk les on the host may be
damaged.
– AOM collects only the rst 20 log les that have been
modied recently. It collects les from 2 levels of
subdirectories by default.
– AOM only collects .log, .trace, and .out text log les in
mounting paths.
les that
Extended Host
Path
Level-3 directory added to the original volume directory or
subdirectory. This path enables you to obtain output les
of a single pod more easily.
– None: No extended paths congured.
– PodUID: Pod ID.
– PodName: Pod name.
– PodUID/ContainerName: Pod ID/container name.
– PodName/ContainerName: Pod name/container name.
Collection Path Path for collecting logs precisely. Details are as follows:
– If no collection path is specied, log les in .log, .trace,
and .out formats will be collected from the current
path by default.
– If a collection path contains double asterisks (**), log
les in .log, .trace, and .out formats will be collected
from 5 levels of subdirectories.
– If a collection path contains an asterisk (*), a fuzzy
match is performed.
Example: If the collection path is /tmp/**/test*.log,
all .log
les prexed with test will be collected from /tmp
and its 5 levels of subdirectories.
CAUTION
To use the collection path function, ensure that the ICAgent
version is 5.12.22 or later.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
NO TE
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Parameter Description
Log Dumping Log dumping here refers to rolling local log les.
– Enabled: AOM scans log les every minute. When a log
le exceeds 50 MB, it is dumped immediately. A
new .zip le is generated in the directory where the log
le locates. For a log le, AOM stores only the latest
20 .zip
les. When the number of .zip les exceeds 20,
earlier .zip les will be deleted. After the dump is
complete, the log le in AOM will be cleared.
– Disabled: If you select Disabled, AOM does not dump
les.
log
NOTE
– AOM log le rolling is implemented in the copytruncate mode.
During conguration, ensure that log les are written in the
append mode. Otherwise, le holes may occur.
– Currently, mainstream log components such as Log4j and
Logback support log
support rolling, skip the conguration. Otherwise, conicts
may occur.
– You are advised to congure log le rolling for your own
services to
exibly control the size and number of rolled les.
le rolling. If your log les already
● Container Path: Logs will be stored in a container path. No host path needs
to be mounted into the container. Set parameters according to the following
table.
Ensure that the ICAgent version is 5.10.79 or later.
Table 4-5 Parameters for adding log policies (container path)
Parameter
Description
Storage Type Set this parameter to Container Path.
Logs will be stored in a container path. No host path
needs to be mounted into the container. Ensure that the
ICAgent version is 5.10.79 or later.
Add Container Path
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Parameter Description
Container Path Container path to which a data volume is mounted.
Example: /tmp
NOTICE
– Do not mount log les to a system directory such as / or /var/
run. Otherwise, the container becomes abnormal. You are
advised to mount the volume to an empty directory. If the
directory is not empty, ensure that there are no
aect container startup. Otherwise, les will be replaced,
causing container startup failures or workload creation
failures.
– If the volume is mounted to a high-risk directory, you are
advised to use an account with minimum permissions to start
the container; otherwise, high-risk les on the host may be
damaged.
– AOM collects only the rst 20 log les that have been
modied recently. It collects les from 2 levels of
subdirectories by default.
– AOM only collects .log, .trace, and .out text log les in
mounting paths.
les that
Collection
Path
Path for collecting logs precisely. Details are as follows:
– If no collection path is specied, log les in .log, .trace,
and .out formats will be collected from the current
path by default.
– If a collection path contains double asterisks (**), log
les in .log, .trace, and .out formats will be collected
from 5 levels of subdirectories.
– If a collection path contains an asterisk (*), a fuzzy
match is performed.
Example: If the collection path is /tmp/**/test*.log,
all .log
les prexed with test will be collected from /tmp
and its 5 levels of subdirectories.
CAUTION
To use the collection path function, ensure that the ICAgent
version is 5.12.22 or later.
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
AOM
User Guide 4 Connecting Resources to AOM
Parameter Description
Log Dumping Log dumping here refers to rolling local log les.
– Enabled: AOM scans log les every minute. When a log
le exceeds 50 MB, it is dumped immediately. A
new .zip le is generated in the directory where the log
le locates. For a log le, AOM stores only the latest
20 .zip
les. When the number of .zip les exceeds 20,
earlier .zip les will be deleted. After the dump is
complete, the log le in AOM will be cleared.
– Disabled: If you select Disabled, AOM does not dump
les.
log
NOTE
– AOM log le rolling is implemented in the copytruncate mode.
During conguration, ensure that log les are written in the
append mode. Otherwise, le holes may occur.
– Currently, mainstream log components such as Log4j and
Logback support log
support rolling, skip the conguration. Otherwise, conicts
may occur.
– You are advised to congure log le rolling for your own
services to
exibly control the size and number of rolled les.
le rolling. If your log les already
----End
Adding a Log Policy on ServiceStage
Step 1 When deploying a component on ServiceStage, add an image, click Advanced
Settings, and then click the Container Log tab.
Step 2 Add a log policy.
The procedure for adding log policies on ServiceStage is the same as that on CCE.
For details, see Step 3.
----End
Viewing Container Logs
After the log collection paths are
such paths. This operation takes about 1 minute to complete. After collecting logs,
you can perform the following operations:
● Viewing Container Log Files
In the navigation pane, choose Log > Log Files. On the Component tab,
select the corresponding cluster, namespace, and component to view log
as shown in the following gure. For details, see Viewing Log Files.
congured, the ICAgent collects log les from
les,
Issue 01 (2020-08-27) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
 Loading...
Loading...