HP PROLIANT DL320 G2 User Manual

technical
white paper
industry
standard
November 2002
servers
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server highdensity deployment
table of
contents
abstract .................................................................................................... 2
executive summary ................................................................................. 2
general guidelines................................................................................... 2
power and thermal budgeting .................................................................3
power distribution units..........................................................................8
planning rack configurations ............................................................... 13
weight considerations ..........................................................................14
rack builder online............................................................................... 15
special considerations for Compaq branded racks.................................16
rack management systems...................................................................16
suggested rack configurations ............................................................ 18
configuration A: maximum performance density (42 derated servers, 24 A
high voltage) ....................................................................................... 18
configuration B: maximum flexibility (35 derated servers, low voltage) ...22
configuration C: traditionalist (28 servers, 24 A low voltage)..................26
installation procedures......................................................................... 30
symbols on equipment, server warnings, and rack warnings ..................30
server preparation ............................................................................... 32
rack preparation .................................................................................. 32
installing PDUs.................................................................................... 33
installing the rack rails.........................................................................34
installing the server in a rack ...............................................................34
connecting cables................................................................................ 35
completing the installation ...................................................................36
reference information and glossary .................................................... 37
references...........................................................................................37
glossary ..............................................................................................37

hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 2
abstract
This white paper is intended for use as a planning guide to expedite the concentrated deployment
of several HP ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 servers. Use this white paper in conjunction with
other documents for the ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server and Compaq branded rack
deployment products. This paper is intended for Field Systems Engineers (FSEs) and customers
(IT managers, system managers, account managers, and installers).
executive summary
Many business enterprises and service providers use network infrastructure and web applications
that work best on dedicated servers. This creates the need to fit a large number of smaller servers
into existing server rooms and data centers. HP meets this need with the density-optimized line of
ProLiant servers, such as the ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server. At a height of 1U each, up to
42 servers can fit in a single Compaq branded 42U rack. While this server has clear space saving
benefits, its compressed size presents new challenges for rapid server deployment, as well as
cable management and environmental considerations.
HP engineers have developed innovations in rapid high-volume deployment and improved cable
management for large installations of ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 servers. This white paper
introduces planning, power and thermal considerations, server and rack requirements, and
installation configurations. It also outlines the products associated with high-volume deployment
in Compaq branded rack configurations, such as keyboard, video, and mouse infrastructure.
IMPORTANT: This document principally discusses the ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server,
the Compaq branded 7000-, 9000-, and 10000-series racks and related Compaq branded rack
options. This document does not discuss other servers, products, or racks not manufactured by
HP.
general guidelines
Power, thermal, and weight are the most important considerations for optimizing a hardware
installation in high-volume server environments.
HP designed the dense ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server to meet the challenges associated
with deploying a high concentration of servers in a single rack. HP suggests that customers
evaluate their environments, power distribution, console, cable, and thermal management choices
well in advance to ensure efficient deployments.
All discussions of power requirements for this server are based on the input power of the server.
This document uses the maximum rated power supply input of 180 W for calculation purposes.
However, derating the input power might be effective to help:
• Minimize the number of PDUs required for each rack.
• Match the rack current requirements with the existing circuit breaker capacity.
• Match the rack cooling requirements with the existing facility cooling capability.

hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 3
IMPORTANT: In this document, derating the input power budget means using less than the
maximum rated input power values for the power supply. HP strongly recommends using the
installation planner to ensure that the derated power budget will satisfy all the installation
requirements, including future upgrade plans.
Refer to the HP ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 Server QuickSpecs for detailed specifications and
options for this server.
power and thermal budgeting
accounting for server input power
Note: In this document, derating the input power budget means not using the maximum rated
input power values for the power supply. HP strongly recommends using the installation
planner to ensure that the derated power budget will satisfy all the installation
requirements, including future upgrade plans.
All power requirement discussions in this document are based on the input power of the server,
since this number has direct impact in planning for the PDU selection and the facility power
source. One of the following methods can be used to account for input power in the facility power
distribution planning:
• Use the maximum rated input power of 277 W.
• Use the derated input power, which can be calculated by subtracting the power budgets of
uninstalled optional components from the rated input power.
• Use the allocated input power, which can be calculated by dividing the maximum power of a
PDU by the number of servers. This calculated power should be at least 250 W to support all
the optional components initially released with the server.
The power budgets of optional components, referred to in the following sections, were derived
from the system input power of a set of selectively measured server configurations. These
configurations measured range from a basic low-end configuration to a fully populated high-end
configuration. Since the input power values used in an installation might vary depending on the
software applications, the information provided in this section should be used as a guideline only.
The server power supply is designed to support future upgrades of processors, DIMMs, and hard
drives. As such, the power supply output power is rated at 180 W. Assuming the power supply
efficiency of 65 percent (including the Power Factor Correction), the power supply input power
is rated at 277 W. This input power value may be used in planning for the power source
implementation and facility cooling requirements. In some cases the input power requirement for
each server might be desired to be lower than 277 W.
The input power requirement might be lowered in the following instances:
• To minimize the number of PDUs, that is, the number of facility power feed lines, required
for each rack.
• To match the rack current requirements with the existing facility branch circuit breakers.
• To match the rack cooling requirements with the existing facility environment.
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 4
Table 1 demonstrates how significant reduction in input current and thermal dissipation can be
realized, if a deployment plan can limit each server configuration over the useful lifetime of a
rack configuration.
Table 1. Derated Current and Thermal Dissipation for Reduced Input Power Assumptions
Input Power Derated Fully Rated
120 W 250 W 277 W
Input Current at 110 VAC 1.09 A 2.27 A 2.52 A
Input Current at 208 VAC 0.57 A 1.20 A 1.33A
Thermal Dissipation 409 BTUs/hour 852 BTUs/hour 944 BTUs/hour
The derated input power values of 120 W and 250 W can be correlated with the measured input
power values for the minimum and maximum configurations of the server. However, the derated
input power value must be high enough to account for any future upgrades for a deployment plan.
As stated earlier, the power supply is designed to support future processor and hard drive
upgrades. When installing 42 servers, the number of PDUs to be installed will depend on the
support for the input current requirement. Carefully derating the input power may very well
satisfy deployment needs and also reduce the number of PDUs per rack. Reducing the number of
PDUs has a direct impact on the deployment time and maintenance of an installation.
DL320 generation 2 server power, thermal, and weight parameters
Table 2 provides server parameters necessary to calculate the power, thermal, and weight
requirements for any number of servers.
Table 2. ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 Server Parameters
Item @ Specification
Dimensions HxWxD
4.24x48.3x55.6 cm (1.67x19.0x21.9 in) – including bezel
Server Weights
Minimum Configuration: 1x processor, 1x128-MB DIMM, 1x CD/Diskette Blank, 0x HDD 19.8 lb (8.98 kg)
Standard Configuration: 1x processor, 1x128-MB DIMM, 1x HDD, 1x CD/Diskette Assembly 22.1 lb 10.02 kg)
Maximum Configuration: 1x processor, 4x DIMMs, 2x HDDs, 1x SA431, 1x CD/Diskette
Assembly
Component Weights
CD/Diskette Drive Assembly 1.4 lb (0.63 kg)
DIMM 0.1 lb (0.05 kg)
HDD 1.3 lb (0.59 kg)
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition 0.5 lb (0.23 kg)
SA5302 1.0 lb (0.45 kg)
Power Ratings
Maximum Power Supply Rated Input AC Power
24.6 lb 11.16 kg)
240 V 277 W
Maximum System Measured Input AC Power
110 V 231 W
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 5
Item @ Specification
Maximum Power Supply Rated Input Current
100 VAC 2.77A
200 VAC 1.38A
Maximum System Measured Input Current
Maximum System Thermal Dissipation (per hour)
944BTUs
Relative Humidity (noncondensing)
Operating 10 to 90%
Nonoperating 10 to 95%
Note: The SA5302 option is a PCI card available from HP. Any third-party PCI cards used in the
server must comply with the industry-standard PCI specifications for dimension, weight, power,
and thermal requirements.
input current and thermal dissipation calculations
Input power is the key in deriving input current and thermal dissipation. For a given input power,
the input current will vary depending on the input voltage level.
The relationship among the current, the voltage, and the power for the power supply input is as
follows:
Input Current = Input Power/Input Voltage
For example,
Input Current = 100 W/110 V = 0.91 A
Input Current = 100 W/208 V = 0.48 A
The input power of a server depends on the operational state of the system. For example, during
the initial power up, a server consumes more power due to the hard drives’ spin-ups. It should be
noted that in the ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server, the two hard drives spin-up one after the
other. Therefore, the peak input power requirement changes significantly when the first drive is
added, but not as much when the second drive is added. After the initial power up, the input
power varies depending on the operating system and the application software running on the
server. During standby, only the auxiliary portion of the power supply is consuming power to
support operations of a very limited part of the system, for example, the Remote Insight
Lights-Out Edition (RILOE) option, NICs, and so on.
Thermal dissipation can be calculated from the input power as follows:
Thermal Dissipation = Input Power * 3.41
For example,
Thermal Dissipation = 100 W * 3.41 = 341 BTUs/hour
Thermal Dissipation = 292 W * 3.41 = 996 BTUs/hour
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 6
The easiest way to calculate the thermal dissipation for the entire rack is to add the input power
requirements for all the servers and other units populated in a rack, and then multiply the total
input power by 3.41.
The “measured input power” section explains more on how adding or removing of an optional
subsystem component affects the input power and thermal calculations.
measured input power
Table 3 lists the measured input power of the server with varying subsystem components, to
illustrate the effects of adding or removing optional components.
Table 3. Measured Input Power for Selected Server Configurations
Configuration
Number
1 1x2.26 GHz, 1x128 MB, 1xATA (base-line) 143 W/158 W
2 1x2.26 GHz, 1x128 MB, + 2x18.2 GB SCSI 148 W/168 W
3 1x2.26 GHz, 1x128 MB, 4 GB + 2xATA 165 W/191 W
4 1x2.26 GHz, 1x128 MB, 4 GB + 2x36 GB SCSI 188 W/212 W
5 1x2.26 GHz, 1x128 MB, 4 GB + 2x36 GB SCSI + 5304 209 W/231 W
ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 Server Configuration
Power Input
Typical/Peak
Note: The peak power listed in Table 3 is of a fully configured ProLiant DL320 Generation 2
server (Configuration 4 was measured to be only about 83 percent of its rated peak input power).
Note: DIMM and HDD input power can vary depending on the component and drive
manufacturer.
input power budget derating
If a deployment plan limits the future expansion beyond certain configuration options, which may
be added in the future, then adjustments can be made to the expected input current and thermal
requirements of the servers.
To derate the input power, start with the minimum configuration 1 from Table 2. Add the typical
power of the components included in the desired system configuration to calculate the derated
power budget. Typical input powers for various components are listed in Table 3.
Example
Assuming the desired server configuration is as follows; use to calculate the derated power
budget using the typical power from Table 3.
Processor: 2.26 GHz
Memory: 4x128 MB
Storage: 2x18.2 GB
Smart Array Controller 5304: 1x SA5304
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 7
Table 4. Example Derating Worksheet
Maximum Rated Input Power for the Base Configuration Typical Power 143 W
1. Add the typical power for the additional memory. 2 W per DIMM
2. Add the typical power for the second HDD. 5 W
3. Add the typical power for the PCI card
Typical power for the desired configuration
4. Calculate the thermal dissipation.
Thermal dissipation for the desired configuration (in BTUs)
Therefore, the new power budget for this configuration is 169 W (compared to the rated 277 W),
and the thermal dissipation is approximately 576 BTUs/hour (compared to the rated 945
BTUs/hour).
The rated input power for the server power supply is 277 W. Therefore, the power budget for a
maximum configuration is 231 W, and the thermal dissipation will be approximately
231 * 3.41 = 788 BTUs/hour.
This derated input power budget significantly reduces the power and thermal requirements for
highly populated racks, which reduces the number of PDUs for certain configurations. Fewer
PDUs decreases deployment time and lowers costs. Costs for the facility electrical plumbing, data
center floor ventilation, and facility air conditioning installation can also be reduced.
15W
169 W
×3.41
576 BTUs/hour
IMPORTANT: HP strongly recommends verifying that the derated power budget satisfies all
the installation requirements, including future upgrade plans.
input power budget allocation
This section explains how to allocate the input power budget for each server. This method can be
used when a PDU supports a known number of servers. It is important to verify that the
calculated power budget allocation will be sufficient to support the worst-case server
configurations that are to be deployed.
The allocated input power for each server is calculated by multiplying the allocated input current
for each server by the line voltage.
Allocated Input Power = Allocated Input Current * Input Line Voltage
Example
Assume a high-voltage PDU rated at 24 A is to support 21 servers. Each server can be allocated
1.143 A. If the line voltage is assumed to be at 208 V, then the allocated input power budget for
each server will be (1.143*208) = 238 W.
Since the input power budget of 238 W satisfies the fully configured system measured input
power of 185 W (as shown in Table 3), 21 servers may be supported by a 24 A high-voltage
PDU. That means only two of these PDUs are needed to support 42 servers in a 42U rack.
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 8
power distribution units
HP offers a wide range of 1U/0U PDUs, supporting both low voltage and high voltage
applications. Designed especially for high volume rack deployments, HP PDUs help with cable
management and power distribution within the rack. These PDUs are equipped with circuit
breakers to provide short circuit and over current protection.
The Modular PDUs (mPDUs), range from 16 A to 40 A, and provide up to 32 outlets*, easy
accessibility, and improved cable management. These mPDUs have a unique modular
architecture that allows increased flexibility and customization. And all mounting hardware,
including both the 0U and 1U mounting brackets are included in the Modular PDU kit (no
additional mounting brackets need to be purchased).
In addition, HP also offers the Dual Input PDU, a fault-tolerant solution that automatically
switches over to a secondary input source when the first source fails. Equipped with two input
ends and a built-in AC transfer switch, this device is designed for mission critical environments
where customers depend on the reliability of redundant power systems housed in their facility.
The Dual Input PDUs ship with both 0U and 1U mounting brackets (no additional mounting
brackets need to be purchased).
*The number of outlets vary by model, please refer to the Table 5 for more specific information.
Additional information is also available at www.hp.com/products/ups
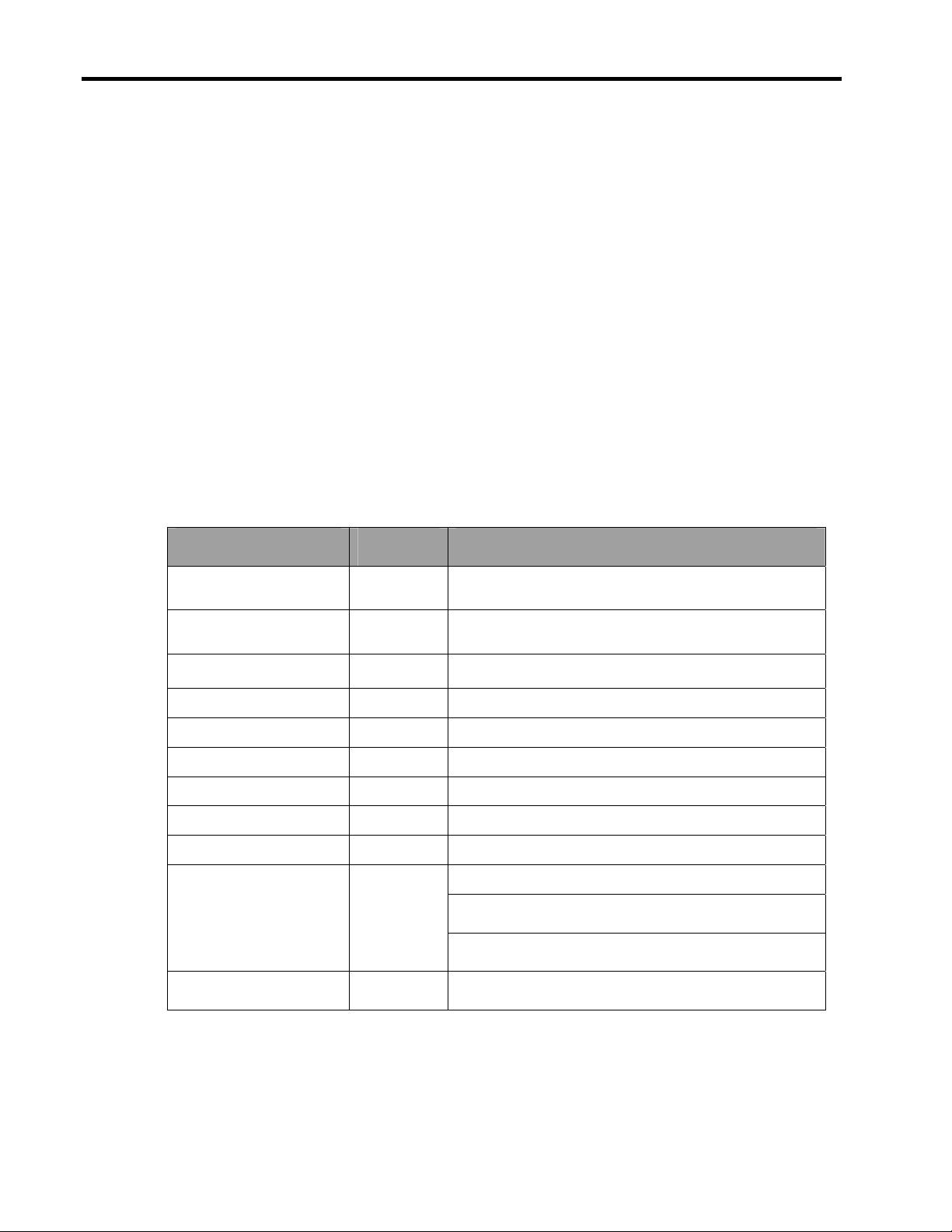
Table 5. HP PDUs
Part Number
252663-B243
252663-D71
252663-D72
252663-B313
252663-B21
207590-B214 Worldwide High 16A 10 Detachable input
continued
Availability
Input
Voltage
Current
Rating
Maximum
Servers per
PDU
Input
Connectors
and Cord
Modular PDUs (Up to 32 outlets, 0U/1U mounting)
Worldwide High 16A 10 Detachable input
3
North
America,
Japan
3
North
America,
Japan
International High 32 A 21 NEMA L6-30P
2,3
Worldwide High 40 A 27 Hardwired
Low 24 A 8 NEMA L5-30P
High 24 A 16 NEMA L6-30P
cord;
IEC 320 C-20
12-ft cord
12-ft cord
12-ft cord
Single Input PDUs (Up to 12 outlets, 0U/1U mounting)
cord;
IEC 320 C-20
Output
Connectors
16 X IEC320-C13 2 X 10 A 17.5 x 1.62 x 5.6 in
32 × NEMA 5-15R 4 × 15 A
32 × IEC 320-C13 4 × 15 A
32 × IEC 320-C13 4 × 15 A
24 × IEC 320-C13
4 × IEC 320-C19
12 X IEC320-C13 2 X 10 A 17.0 x 1.65 x 8.0 in
Output
Breakers
4 × 15 A
Dimensions
(444.5 x 41.2 x 142.2mm)
17.5 x 1.62 x 5.6 in
(444.5 x 41.2 x 142.2mm)
17.5 x 1.62 x 5.6 in
(444.5 x 41.2 x 142.2mm)
17.5 x 1.62 x 5.6 in
(444.5 x 41.2 x 142.2mm)
17.5 x 1.62 x 5.6 in
(444.5 x 41.2 x 142.2mm)
(431.8 x 41.9 x 203.2mm)
Weight
18 lb
(8.16 kg)
18 lb
(8.16 kg)
18 lb
(8.16 kg)
18 lb
(8.16 kg)
18 lb
(8.16 kg)
7 lbs
(3.2 kgs)

hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 9
Table 5. HP PDUs (continued)
Part Number
191186-001
191186-B31
Note 1: This PDU supports power from two different sources. If one power source fails, the PDU uses the alternate source.
Note 2: This PDU must be hardwired to the power source by a certified electrician.
Note 3: This PDU is using the maximum rated power supply input and not the derated values.
Note 3: This PDU to discontinue 1H2003.
Availability
1
North America High 24 A 16 x2 NEMA L6-
1
International High 30 A 20 x2 IEC 309-32A
Input
Voltage
Current
Rating
Maximum
Servers per
PDU
Input
Connectors
Dual Input PDU (12 Outlets, built-In Transfer switch, 0U/1U mounting)
30P
12-ft cord
12-ft cord
and Cord
Output
Connectors
12 × IEC 320-C13 4 × 10 A
12 × IEC 320-C13 4 × 10 A
Output
Breakers
Dimensions
1.72 x 17 x 15.25 in (4.37
x 43.18 x 38.74cm)
1.72 x 17 x 15.25 in (4.37
x 43.18 x 38.74cm)
Figuring Type and Number of PDUs
Comment – make sure all examples use the new Modular PDUs, 252663-xxx
The type and number of PDUs required to power a full rack of servers depends on each server’s
power requirement, the number of servers deployed in the rack, and the available power for the
servers.
HP PDUs support both high-voltage and low-voltage applications. The input current rating for a
ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server is either 1.38 A at 200 to 240 V or 2.77 A at 100 to 120 V.
To determine the number of servers supported by a PDU, divide the PDU’s current rating by the
server’s total input current rating.
Weight
20 lb
(9.1 kg)
20 lb
(9.1 kg)
IMPORTANT: The examples shown in the following sections use the maximum rating of the
power supply. They are for reference only.
Example
PDU number 295363-003 is a high-voltage PDU with a current rating of 24 A. The server has
a total input current rating of 1.38 A at 200 V.
24 A (PDU current rating)/1.38 A (server total input current rating) = 17.4
PDU number 295363-003 can support a maximum of 17 servers at full server input current
ratings.
For more information, refer to the “Power Distribution Unit High Voltage Models for North
America and International Use, (NA CPQ # 295363-002; INT'L CPQ # 295363-B31)” website:
www.hp.com/servers/proliant/manage
Example
PDU number 295363-001/291 is a low-voltage PDU with a current rating of 24 A. The server
has a total input current rating of 2.77A at 100 V.
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 10
24 A (PDU current rating)/2.77 A (server total input current rating) = 8.7
PDU number 295363-001/291 can support a maximum of 8 servers at full server input
current ratings.
For more information on high-voltage PDUs, refer to the “Power Distribution Unit High-Voltage
Models for North America and International Use, (NA CPQ # 295363-002; INT'L CPQ #
295363-B31)” website:
www.hp.com/servers/proliant/manage
For more information on low-voltage PDUs, refer to the “Power Distribution Unit Low-Voltage
Models for North America and International Use” website:
www.hp.com/servers/proliant/manage
The HP ProLiant DL320 Generation 2 server does not support either a DC input power supply or
a redundant power supply. However, the power supply for this server automatically senses input
voltage level.
selecting server power cords
The appropriate server power cord to use depends on the cable management system installed in
the rack. Generally, the sliding rail cable management system requires a power cord that is
1.83 m (6 ft) in length. This length provides enough slack for the power cord to route through the
cable management solution.
high-voltage Y-cables
The Vertical-Mount PDU Bracket with High-Voltage Cables kit includes 11 Y-cables, each of
which is 3.0 m (10 ft) long. The single-cord PDU section is 1.8 m (6 ft) long, and the dual-cord
server section is 1.3 m (4 ft) long. Refer to Table 6 for part numbers.
Y-cables have a single-cord section with an IEC connector that connects to the PDU, a dividing
joint in the center, and a dual-cord section with IEC connectors that connect to the servers. One
Y-cable supplies power from the PDU to two servers in the standard configuration.
CAUTION: When installing server power cords into the PDUs, ensure that the load is
balanced among the output circuit breakers. Do not exceed the ratings of the circuit
breakers.
Table 6. HP High-Voltage Power Cables
Description HP Part # Description
10A IEC-to-IEC Cables Kit
142257-001 (6 ft)
142257-002 (8 ft)
142257-003 (10 ft)
The IEC-to-IEC cables can be used either as individual
power cords for the server or to extend the length of the
high-voltage Y-cables. The cables are available in six-,
eight-, and ten-foot lengths. The ProLiant DL320
Generation 2 Server ships with one 10-ft IEC to IEC
cable, part number 142257-003.
power cords
The server ships with an IEC-IEC power cord (PN 142257-002) used for rack mounting with
high-voltage Power Distribution Units (PDUs). For low-voltage, stand-alone deployments or
installation without a rack, country-specific power cord options are available.
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 11
U.S. and Japanese models ship with two power cords - IEC-IEC and a country-specific cord:
• Power cord, US, IEC320-C13 to IEC320-C14, 10 A 250 V, Straight (10 ft/2.5 m)
(PN 142257-002)
• Power cord, US, IEC320-C13 to NEMA 5–15P, 15 A 125 V, Straight (10 ft/3 m)
(PN 103541-001)
Console Management Systems
A KVM (keyboard, video, and mouse) console management Table 7 system enables a single
keyboard and video console to control multiple servers. An in-rack console management system
may be used to manage a single rack of servers or groups of racks. The HP IP console switch
products have 16 ports that can access up to 128 servers. The HP IP Consoling Solution combines
analog and digital technology to provide flexible, centralized KVM control of data center servers.
This solution provides enterprise customers with a significant reduction in cable volume, secure
remote access, and high-performance server KVM access. Using the IP console viewer, users can
access local KVM functions from any Windows or Linux workstation by means of a 10/100
network connection. Alternatively, an off-rack console management system may also be used in
the local vicinity of the servers it manages.
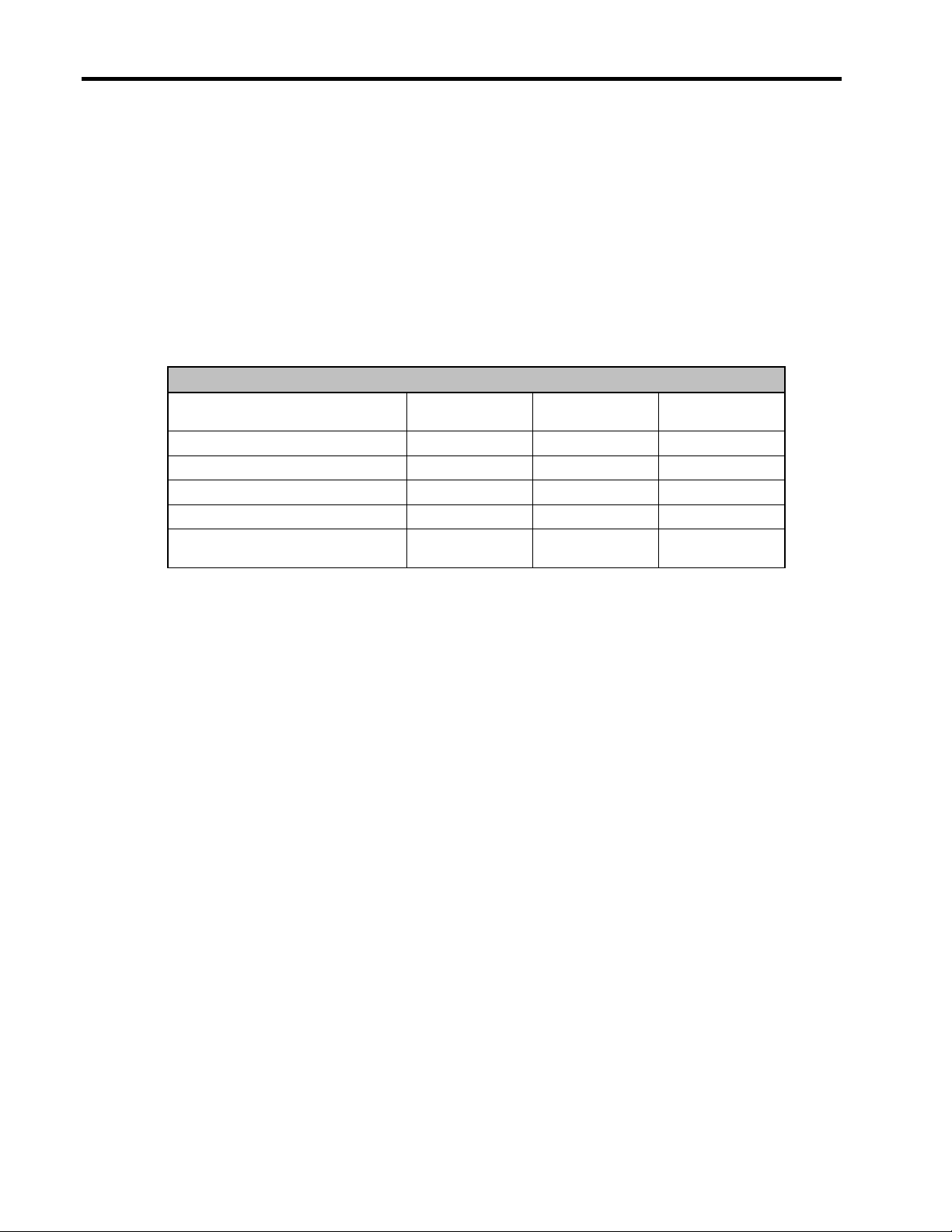
Table 7. Local/IP Console Management Options
Product Name HP
1x1x16 IP Console Switch 262585-B21
3x1x16 IP Console Switch 262586-B21
Interface Adapters (8 per
Pack)
Interface Adapters (Single
Pack)
Expansion Module 262589-B21
CAT5 Cables 3FT (4 per
Pack)
CAT5 Cables 6FT (8 per
Pack)
CAT5 Cables 12FT (8 per
Pack)
CAT5 Cables 20FT (4 per
Pack)
CAT5 Cables 40FT (1 per
Pack)
TFT5600 Rack-Mount
Keyboard and Monitor
TFT5110R Flat Panel
Monitor
1U Integrated Keyboard
with Hot Keys
Part No.
262587-B21
262588-B21
263474-B21 4-pack of 3ft UTP CAT5 cables with RJ-45 connectors
263474-B22 8-pack of 6ft UTP CAT5 cables with RJ-45 connectors
263474-B23 8-pack of 12ft UTP CAT5 cables with RJ-45 connectors
263474-B24 4-pack of 20ft UTP CAT5 cables with RJ-45 connectors
263474-B25 Single 40ft UTP CAT5 cable with RJ-45 connectors
221546-001 1U integrated keyboard and monitor.
281683-B21 1U rack-optimized monitor (keyboard not included).
257054-001 1U Form Factor
Description
16-port Keyboard Video Mouse switch - provides access for 2
simultaneous user sessions (1 network session and 1 local
session at a rackmounted console)
16-port Keyboard Video Mouse switch - provides access for up to
4 simultaneous user sessions (3 network sessions and 1 local
session at a rackmounted console)
Transitions traditional keyboard/video/mouse cabling to CAT5 one needed for each server (convenient 8-pack)
Transitions traditional keyboard/video/mouse cabling to CAT5 one for each server
Enables tiering of up to 8 servers per port on the IP console
switch
In-Rack Local IP Consoles
With an in-rack local console, all equipment, servers, switchboxes, keyboards, keyboard drawers,
and video displays are installed together in the same rack. The HP switchboxes mount behind the
keyboard drawer and do not consume extra U-space in the rack. Using the TFT5600RKM and an
hp ProLiant DL320 generation 2 server high-density deployment technical white paper 12
IP console switch will consume a total of 1U to accommodate up to 128 servers. One console
switchbox can support up to 16 directly attached servers with no user blocking. Up to eight
servers may be tiered or cascaded on each switch port using either a legacy Compaq KVM switch
or an Expansion Module; however, only one user can access tiered switches or servers connected
by Expansion Modules at any one time. Critical devices requiring frequent access should be
attached directly to a switch port. Server accessibility should be assessed by the IT manager prior
to deployment to determine the appropriate server density per console switch.
Table 8 outlines the number of devices that fully populate a 47U, 42U or 36U rack with an inrack local console (Figure 1).
Table 8. Device Configuration for an In-Rack Local IP Console
Device or Cable 47U Rack 42U Rack 36U Rack
ProLiant DL360/320 Generation 3
Servers
KVM IP Console Switches 1 1 1
Interface adapters 46 41 35
UTP CAT5 cables for KVM access 46 41 35
Expansion modules 4-16 3-16 3-16
TFT5600 RKM (integrated
monitor/keyboard)
46
1
41 35
1 1
Each server deployed in a fully populated rack with an in-rack IP console management system
requires the following accessories for successful deployment and operation:
• Interface adapter
• UTP CAT5 cable [1.8 m (6-ft) cables for sliding rail solutions].
• Universal Rack Rail (the quick deploy rail kit that ships standard with the server and comes
with a cable management solution), or the option Sliding Rail Kit (with cable management
solution), or optional telco rack solution, or third party rail kit.
 Loading...
Loading...