Page 1

HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server
Software Configuration Guide
Part number: 458197-001
First edition: January 2008
Page 2

Legal notices
© Copyright 2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Windows Server 2003 is a
trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Intel, Pentium, and Itanium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or
its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Contents
System BIOS configuration
System BIOS overview............................................................................................................................ 5
AMIBIOS software ................................................................................................................................. 5
AMIBIOS Setup Utility............................................................................................................................. 5
Accessing the Setup Utility.................................................................................................................. 6
Navigating through the Setup Utility .................................................................................................... 6
Setup Utility menus ............................................................................................................................ 8
Main Menu................................................................................................................................. 8
Advanced menu ........................................................................................................................ 10
Boot Menu ................................................................................................................................ 18
Security menu............................................................................................................................ 18
Exit menu.................................................................................................................................. 21
Recording custom Setup values ......................................................................................................... 21
Loading system defaults ................................................................................................................... 21
Clearing CMOS ............................................................................................................................. 22
Power-On Self Test (POST)..................................................................................................................... 22
POST error indicators ...................................................................................................................... 22
Recoverable POST Errors ............................................................................................................ 23
POST-related troubleshooting............................................................................................................ 23
Reprogramming the BIOS with the crisis recovery jumper ..........................................................................24
NOS installation
Supported NOS................................................................................................................................... 25
NOS pre-installation procedure.............................................................................................................. 25
Hardware setup.............................................................................................................................. 25
BIOS update .................................................................................................................................. 26
Installing Microsoft Windows NOS ........................................................................................................ 26
Pre-installation instructions ................................................................................................................ 26
Installation flow............................................................................................................................... 26
Section 1. Creating the driver diskettes .............................................................................................. 26
Section 2. Installing Windows NOS .................................................................................................. 27
Section 3. Completing the installation ................................................................................................ 28
Phase 1 - Installing the chipset driver ............................................................................................ 28
Phase 2 - Installing the HP network driver......................................................................................28
Phase 3 - Installing the embedded video driver .............................................................................. 29
Section 4. Configuring the system ..................................................................................................... 29
Phase 1 - Performing a hardware status check ............................................................................... 29
Phase 2 - Initializing the hard drive .............................................................................................. 30
Phase 3 - Adding Windows Terminal Services ............................................................................... 30
Section 5. Configuring the network ................................................................................................... 31
Phase 1 - Configuring the server’s IP address................................................................................. 31
Phase 2 - Attaching clients to the network and testing the network link .............................................. 31
Phase 3 - Configuring the domain controller setup.......................................................................... 32
Section 6. Installing additional HP accessories.................................................................................... 33
Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux NOS.................................................................................................. 33
Installation flow............................................................................................................................... 33
Pre-installation instructions ................................................................................................................ 33
3
Page 4

Contents
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 installation ...................................................................................... 34
Section 1. Launching the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installer .............................................................. 34
Section 2. Customizing the installation.......................................................................................... 34
Section 3. Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 .................................................................... 35
Section 4. Configuring the initial setup settings .............................................................................. 35
Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server NOS............................................................................................ 36
Installation flow............................................................................................................................... 36
Pre-installation instructions ................................................................................................................ 36
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 installation ......................................................................................... 37
Section 1. Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9........................................................................ 37
Section 2. Customizing the installation.......................................................................................... 37
Section 3. Completing the installation........................................................................................... 37
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Installation ....................................................................................... 38
Section 1. Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10...................................................................... 38
Section 2. Customizing the Installation.......................................................................................... 38
Section 3. Completing the installation........................................................................................... 39
Installing Sun Solaris 10 ....................................................................................................................... 39
Pre-installation instructions ................................................................................................................ 39
Installation flow............................................................................................................................... 40
Sun Solaris 10 installation................................................................................................................ 40
Section 1. Launching the Sun Solaris10 installer............................................................................. 40
Section 2. Customizing the installation.......................................................................................... 40
Section 3. Completing the installation........................................................................................... 41
Server management
Pre- and post-installation procedures....................................................................................................... 43
Pre-installation procedures................................................................................................................ 43
Post-installation procedures............................................................................................................... 43
Configuring the BMC ........................................................................................................................... 43
Index
4
Page 5

System BIOS configuration
This chapter describes the basic functions of the AMIBIOS software.
System BIOS overview
A Basic Input/Output System, or BIOS, is a set of programs permanently stored in an EEPROM chipset
located on the system board. These programs serve as an interface between the server’s hardware
components and its operating system. This ProLiant server features the AMIBIOS software—a ROM BIOSbased diagnostic tool that monitors system activity and performs constant hardware testing to ensure
proper system operation.
AMIBIOS software
System BIOS configuration
The AMIBIOS software serves three functions:
• Configure the system settings via the AMIBIOS Setup Utility
Using the Setup Utility, you can install, configure, and optimize the hardware devices on your system
(such as clock, memory, and hard drives).
• Initialize hardware at boot via POST routines
At power-on or reset, the software performs Power-On Self Test (POST) routines to test system
resources and run the operating system.
• Perform run-time routines
Using the software, perform basic hardware routines that can be called from OS-based applications.
AMIBIOS Setup Utility
NOTE: For ease of reading, the AMIBIOS Setup Utility will be referred to as “Setup” or “Setup
Utility” in this guide. Also, the screenshots used in this guide display default system values. These
values may not be the same as those in your server.
The AMIBIOS Setup Utility is a hardware configuration program built into the server BIOS. Because most
systems are already properly configured and optimized, there is normally no need to run this utility.
You need to run this utility under the following conditions:
• When changing the system configuration, including:
○ Setting the system time and date
○ Configuring the hard drives
○ Specifying the boot device sequence
○ Configuring the power management modes
○ Setting up system passwords or making other changes to the security setup
5
Page 6
• When a configuration error is detected by the system and you are prompted by a "Run Setup"
message to make changes to the BIOS settings.
NOTE: If you repeatedly receive “Run Setup” messages, the battery located on the system board
may be defective. In this case, the system cannot retain configuration values in CMOS. Ask a
qualified technician for assistance.
The Setup Utility loads the configuration values in a battery-backed nonvolatile memory called CMOS
RAM. This memory area is not part of the system RAM, which allows configuration data to be retained
when power is turned off. The values take effect when the system is booted. POST uses these values to
configure the hardware. If the values and the actual hardware do not agree, POST generates an error
message. You must run the Setup Utility to change the BIOS settings from the default or current
configuration.
Accessing the Setup Utility
1. Turn on the monitor and the server.
If the server is already turned on, save your data and exit all open applications, then restart the
server.
System BIOS configuration
During POST, press F10. If you fail to press F10 before POST is completed, you need to restart the
server and repeat this step. The first page displayed is the Main menu. Use the left (←) and right (→)
arrow keys to move between selections on the menu bar.
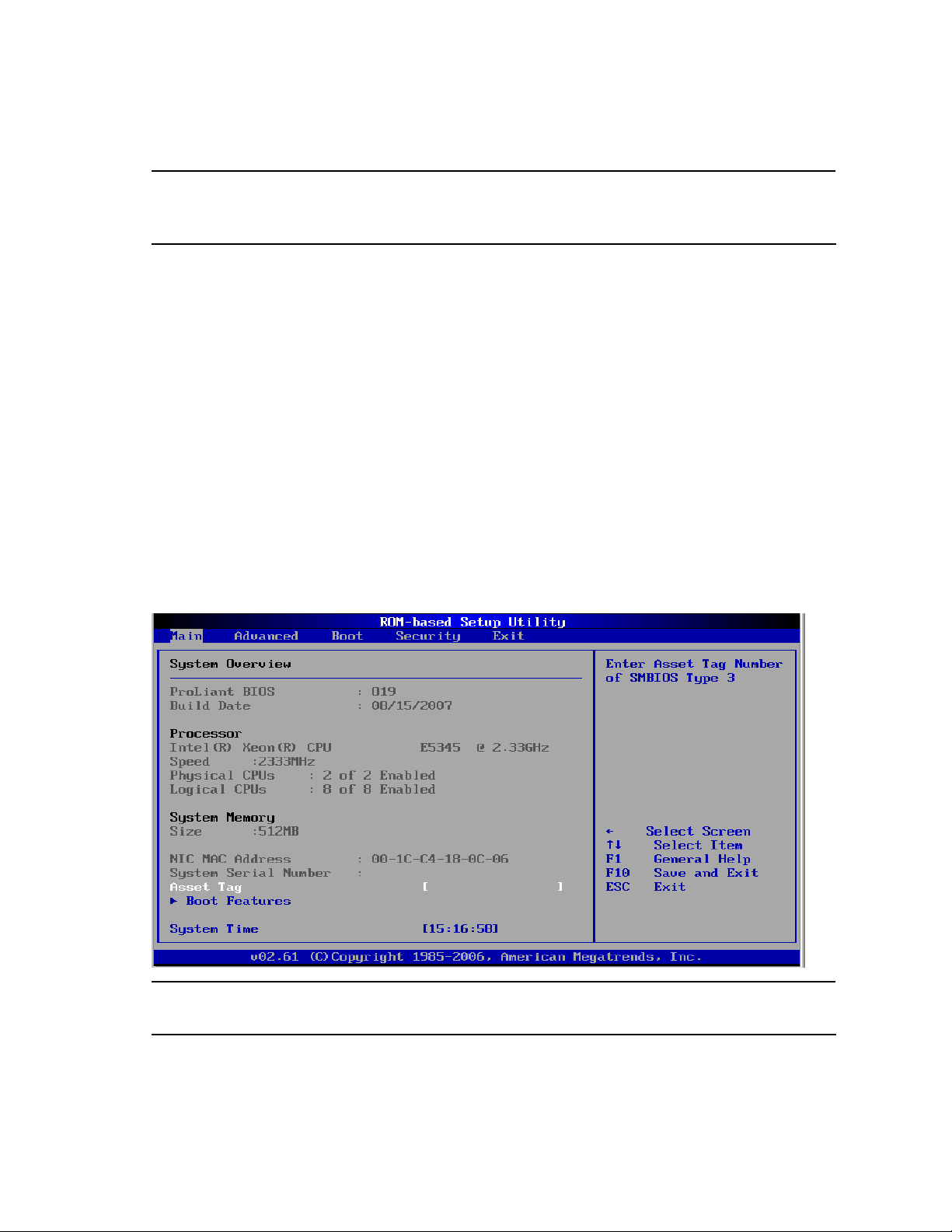
Figure 1 Main menu
NOTE: System Serial Number and Asset Tag are not updated even when CMOS defaults are
loaded or CMOS is cleared.
Navigating through the Setup Utility
Use the keys listed in the legend bar on the bottom of the Setup screen to access the various menu and
submenu screens of the Setup Utility. Figure 1 in the previous section shows the legend bar at the bottom
6
Page 7

System BIOS configuration
of the Main menu. Table 1 Setup Utility navigation keys lists these legend keys and their respective
functions.
Table 1 Setup Utility navigation keys
Key Function
← and → Move between selections on the menu bar.
↑ and ↓ Move the cursor to the field you want.
The currently selected field is highlighted. The right side of each menu screen displays the Item
Specific Help panel. This panel displays the help text for the selected field. It updates as you move
the cursor to each field.
<+>, <–> Select a value for the currently selected field if it is user-configurable.
Press the (+) or (-) keys repeatedly to scroll through each value one at a time, or press the Enter key to
choose from a pop-up menu that displays all possible values at once.
A parameter that is enclosed in square brackets [ ] is user-configurable.
Grayed-out parameters are not user-configurable for one of the following reasons:
• The field value is auto-configured or auto-detected.
• The field value is informational only.
• The field is password-protected.
Enter Select a field value or display a submenu screen.
►
Esc When you press this key:
Indicates a submenu field.
To view a submenu screen, use the ↑ and ↓ keys to move the cursor to the submenu you want, then
press Enter.
• On a primary menu screen, the Exit menu displays.
• On a submenu screen, the previous screen displays.
• On a pop-up menu, closes the pop-up without making a selection.
F1 Displays the General Help window. See Figure 2. The General Help window describes other Setup
navigation keys that are not displayed on the legend bar.
F9 Loads the default system values.
F10 Saves all changes to settings and closes the Setup Utility.
7
Page 8
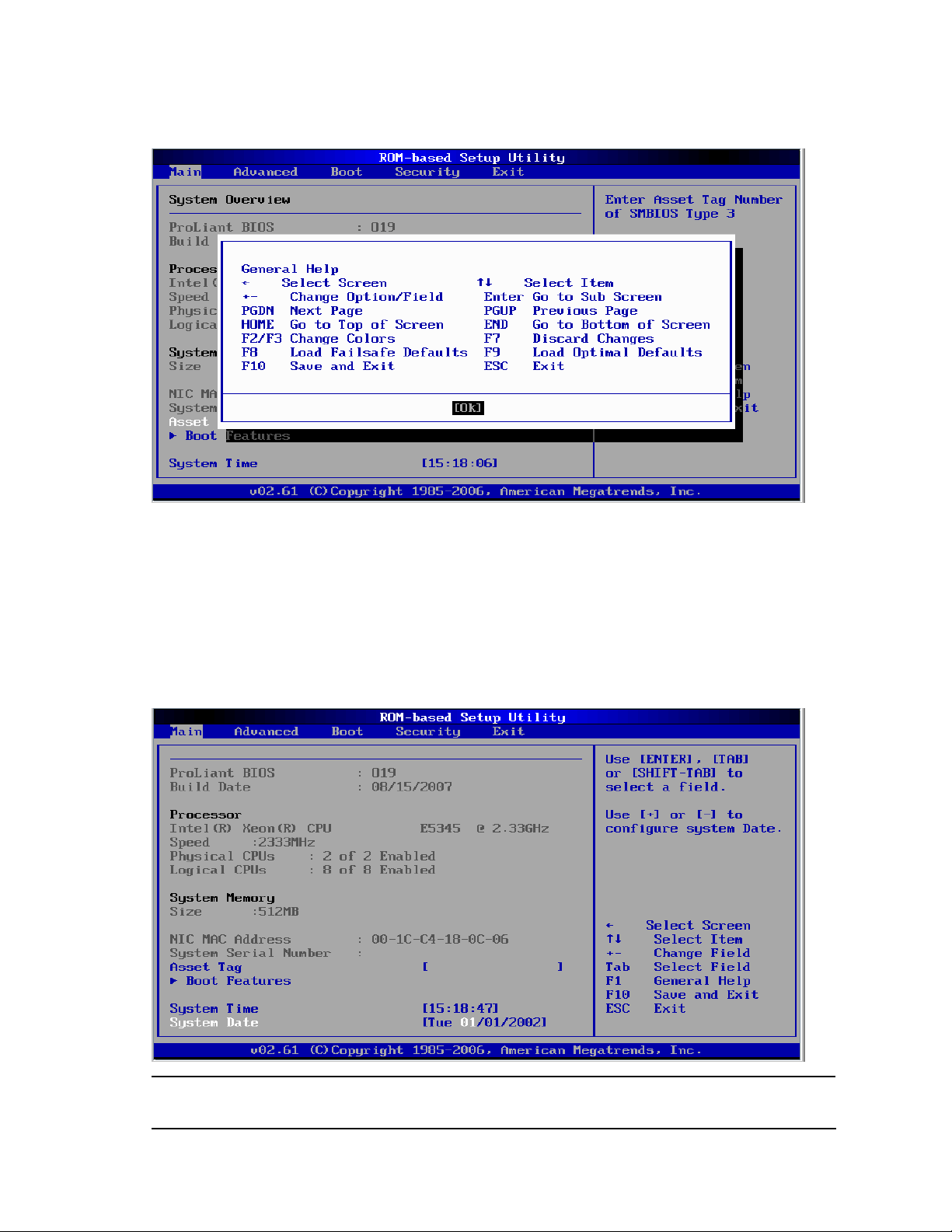
Figure 2 General Help Screen
System BIOS configuration
Setup Utility menus
The Setup Utility menu bar displays the five primary menu selections. For detailed information and
screenshots of these Setup menus and their related submenus, refer to the following sections.
Main Menu
Figure 3 Main Menu
NOTE: The time is in 24-hour format. For example, 5:30 A.M. appears as 05:30:00, and 5:30
P.M. as 17:30:00. If you clear CMOS, setup time and date values will be BIOS release date.
8
Page 9

System BIOS configuration
Table 2 Main menu fields
Field Description
System Overview Displays the system ROM version, the date when the Setup utility was created and
identification number.
Processor Displays the CPU type, speed and count.
System Memory Displays the amount of conventional memory detected.
Asset Tag Enter the server asset tag.
System Serial
Number
System Time Adjusts the system time.
System Date Adjusts the system date.
Boot Features
Enter the server serial number. The serial number is indicated on the serial number label pull
tab on the front panel.
Sets which options to run during system boot up. Press Enter to access the related submenu.
For details on the submenu options, see the “Boot Features submenu” section.
Boot Settings Configuration submenu
Figure 4 Boot Features submenu
Table 3 Boot Features fields
Field Description Options
Quick Boot Set this value to allow BIOS to skip certain tests while booting. This will decrease
the time needed to boot the system.
Enabled
9
Page 10

System BIOS configuration
Table 3 Boot Features fields
Field Description Options
Resume On LAN Set this value to allow system wake up on LAN from Hibernation. Enabled
Cannot wake up the system from Hibernation if set to Disabled Disabled
Bootup NumLock
This option does not enable the keyboard Num Lock automatically. To use the
Restore on AC
Power Loss
Set this value to let system always boot up automatically when AC power is
Set this value to allow Num Lock on the keyboard to be enabled automatically
when the computer system boots up. This allows the immediate use of the numeric
keypad located on the right side of the keyboard. To confirm this, the Num Lock
LED on the keyboard will be on. This is the default setting.
numeric keypad, need press the “Num Lock” key located on the upper left-hand
corner of the numeric keypad. The Num Lock LED on the keyboard will be on
when Num lock is engaged.
Set this value to restores previous power state before loss occurred. Last State
restored.
Enabled
Disabled
Power on
Set this value not to boot up the system until the power button is pressed. Stay Off
POST F1 Prompt Set this value to let system wait up to 15 seconds to continue in case POST errors
Set this value to wait indefinitely for an F1 press. Enabled
Advanced menu
Figure 5 Advanced menu
Delayed
detected, or press F1to skip it.
Set this value to boot without waiting for an F1 press. Disabled
10
Page 11

System BIOS configuration
NOTE: The CPU Configuration setup screen varies depending on the installed processor.
Table 4 Advanced menu fields
Field Description
CPU Configuration Use this screen to select options for the CPU Configuration Settings.
Harddisk
Configuration
I/O Device
Configuration
IPMI
Console
Redirection
Use this screen to select options for the Harddisk Configuration Settings.
Use this screen to select options for the I/O device configuration settings. Use the up and down
<Arrow> keys to select an item. Use the <Plus> and <Minus> keys to change the value of the
selected option. The settings are described on the following pages.
Select this option to view the contents of IPMI. A delay may be noticed when selecting IPMI,
due to the time required for retrieval of sensor data.
Configuration options for Console redirection.
USB Configuration Configuration options for the system USB controller.
CPU Configuration submenu
Figure 6 CPU Configuration submenu
11
Page 12

Table 5 CPU Configuration submenu fields
Field Description Options
Core Multi-processing Set this value to support multi-core processor. The optimal and setup
default setting is Enabled.
This setting configures single logical option processor mode; Only core 0,
logical processor 0 remains active.
Intel(R) SpeedStep (tm
Tech)
Disabling SpeedStep ensures that the CPU will run at maximum speed. Disabled
This setting is available if the processor supports SpeedStep. Enabling this
value will let CPU run at appropriate speed and voltage as determined
by the OS per system requirements.
Harddisk Configuration submenu
Figure 7 Harddisk Configuration submenu
System BIOS configuration
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Table 6 Harddisk Configuration submenu fields
Field Description Options
Configure SATA #1 as
Set this option to support RAID (Redundant Array of Independent
Disks) technology, the optimal and default setting is disabled.
Enhanced (non-AHCI and non-RAID) mode, SATA drives are auto-
detected and placed in Native IDE mode.
Hot Plug Set this value to allow the hard disk drive to be used normally. Read,
write, and erase functions can be performed to the hard disk drive. This
is the default setting.
RAID
IDE
Disabled
12
Page 13
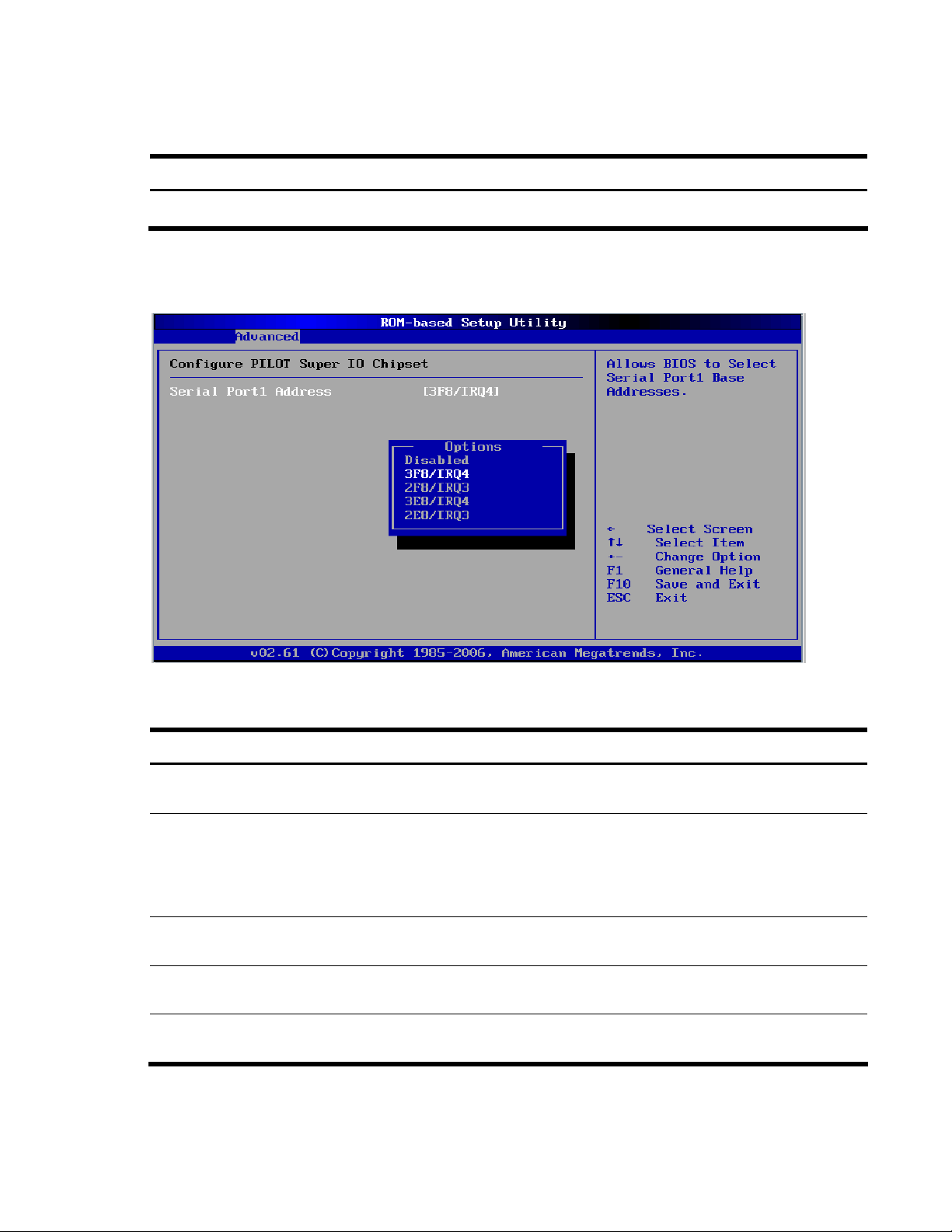
Table 6 Harddisk Configuration submenu fields
Field Description Options
Set this value to prevent the hard disk drive from being erased. Enabled
I/O Device Configuration submenu
Figure 8 I/O Device Configuration submenu
System BIOS configuration
Table 7 I/O Device Configuration submenu fields
Option Description
Disabled Set this value to prevent the serial port from accessing any system resources. When this option is
set to Disabled, the serial port physically becomes unavailable
3F8/IRQ4 Set this value to allow the serial port to use 3F8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 4 for the interrupt
address. This is the default setting. The majority of serial port 1 or COM1 ports on computer
systems use IRQ4 and I/O Port 3F8 as the standard setting. The most common serial device
connected to this port is a mouse. If the system will not use a serial device, it is best to set this port
to Disabled.
3E8/IRQ4 Set this value to allow the serial port to use 3E8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 4 for the interrupt
address. If the system will not use a serial device, it is best to set this port to Disabled.
2E8/IRQ3 Set this value to allow the serial port to use 2E8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 3 for the interrupt
address. If the system will not use a serial device, it is best to set this port to Disabled.
2F8/IRQ3 Set this value to allow the serial port to use 2F8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 3 for the interrupt
address. If the system will not use a serial device, it is best to set this port to Disabled
13
Page 14

IPMI Configuration submenu
Figure 9 IPMI Configuration submenu
System BIOS configuration
Table 8 IPMI Device Configuration submenu fields
Field Description
System Event Logging Select to enable/disable IPMI event logging. Disabling will still log events received via the
system interface.
Event Log Control Select to control event log configuration, from this configuration screen.
BIOS Post Watchdog Select to enable POST watchdog.
OS Boot Watchdog Select to enable OS boot watchdog.
14
Page 15

System BIOS configuration
Table 8 IPMI Device Configuration submenu fields
Field Description
Serial Port Assignment Select to assign the serial port connector to the system or to the BMC (Baseboard
Management Controller)
Serial Port Switching Enabling received escape sequences to switch serial port connector assignment.
DCD Snooping Select to enable/disable mux switch to BMC on DVD loss.
Serial Port Connection
Model
BMC Ping Response Enabling this selection will enable ICMP ping responses
BMC Telnet Service Enabling this selection will Telnet access.
BMC HTTP Service Select this section to enable HTTP access.
Select modem connect mode or direct connect mode.
Figure 10 SEL Configuration submenu
Table 9 SEL Configuration submenu fields
Field Description
View BMC System
Event Log
Clear BMC System
Event Log
Select to view the contents of the System Event log.
If the BMC Event log is full, you can choose this item to clear out the BMC Event log. If this
option is selected, a confirmation prompt will appear before the log is cleared.
Console Redirection submenu
Figure 11 Console Redirection submenu
15
Page 16

System BIOS configuration
Table 10 Console Redirection submenu fields
Field Description Options
Console Redirection Setting this value will enable console redirection. Enabled
Setting this value will disable console redirection and prevent
configuration of serial port.
USB Configuration submenu
Figure 12 USB Configuration submenus
Disabled
16
Page 17

System BIOS configuration
Table 11 USB Configuration submenu fields
Field Description Options
USB Controller This setting enables the onboard USB controller. This is the default setting. Enabled
This setting disables the onboard USB controller. Disabled
USB 2.0 Controller
Mode
This setting allows the use of USB ports at a data transfer rate of 12 Mbps.
This setting allows the use of USB ports at a data transfer rate of 480 Mbps. Full Speed
Hi Speed
This is the default setting.
17
Page 18

Boot Menu
Figure 13 Boot Menu
System BIOS configuration
Table 12 Boot Menu fields
Field Description
1st Boot Device Set the device as the first boot device. (e.g. system boot from CD-ROM)
2nd Boot Device
3rd Boot Device Set the device as the third boot device.
Removable Drives Enter this submenu is to view and configure removable drives in the system.
Embedded NIC Port
PXE
USB boot precedence USB as the first boot device at any time if set this value is Enabled.
Security menu
The Security menu allows users to set an administrator password. When entered, this password allows
the user to access and change all settings in the Setup Utility.
Set the device as the seconde boot device
Use this screen to configure the embedded NIC Port PXE boot option. The default value is
enabled.
Figure 14 Security menu
18
Page 19

System BIOS configuration
This panel indicates whether or not an Administrator Password has been configured.
To set an administrator password:
1. In the Security menu screen, in the Change Admin Password field, press Enter.
The Enter New Password window displays.
Figure 15 Enter New Password
2. Type a new password in the Enter New Password box. The password may consist of up to six
alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9), Next, press Enter, and the Confirm New Password window
displays.
19
Page 20

System BIOS configuration
Figure 16 Confirm New Password
3. Retype the new password in the Confirm New Password box to verify the first entry, and then press
Enter. The Password Installed OK windows display. Press OK to continue.
4. Press F10 to save the password and close the Setup Utility.
To change the Power-on password:
1. In the Security menu screen, in the Change Power-on Password field, press Enter. The Enter
New Password window displays. Type a new password in the Enter New Password box.
2. Type the same password in the Confirm New Password box to verify the first entry, and then
press Enter. The Password Installed OK window displays. Press Enter to finish.
Figure 17 Change the Power-on Password
20
Page 21

Exit menu
The Exit menu displays several options for how to quit the Setup Utility. Select any of the exit options and
press Enter.
Figure 18 Exit menu
System BIOS configuration
Table 13 Exit menu fields
Option Description
Save Changes and Exit Save the changes made and exit the Setup Utility
Discard Changes and Exit Discard the changes and exit the Setup utility
Discard Changes Discard any changes made thus far in the Setup utility.
Load Option Default Loads the default settings for all BIOS setup fields.
Recording custom Setup values
Write down the settings from the Setup Utility and keep them in a safe place. If the custom values ever
need restoring (after clearing CMOS, for example), you must run the Setup Utility and enter these custom
settings again. Having a record of these custom settings makes this much easier.
Loading system defaults
If the system fails after you make changes in the Setup menus, reboot the server, enter Setup, and load the
system default settings to correct the error. These default settings have been selected to optimize the
server’s performance. Setup default settings are quite demanding in terms of resource consumption. If you
are using low-speed memory chips or other types of low-performance components and you choose to load
these settings, the system might not function properly.
To load the system defaults:
21
Page 22

1. Reboot the server in a normal manner.
2. During POST, press F10 to access the Setup Utility.
3. Press F9 to load the default values.
4. Press F10 to save the changes and close the Setup Utility.
Clearing CMOS
You may need to clear the Setup configuration values (CMOS) if the configuration has been corrupted, or
if incorrect settings made in the Setup Utility have caused error messages to be unreadable. Clearing the
CMOS data removes the administrator password.
The clear CMOS setting is on clear CMOS button (SW5) on the system board. Refer to the HP ProLiant
DL180 Generation 5 Server Maintenance and Service Guide for the location of this jumper block and the
clear CMOS setting.
To clear CMOS:
1. Perform the pre-installation procedures.
2. If necessary, remove any expansion boards, assemblies, or cables that prevent access to the press
CMOS button (SW5).
System BIOS configuration
3. Locate the clear CMOS button (SW5) on the system board.
4. Press clear CMOS button (SW5) to clear the CMOS memory.
5. Perform the post-installation procedures.
6. During POST, press F10 to access the Setup Utility.
7. Press F9 to load the system default values.
8. Press F10 to save the changes you made and close the Setup Utility.
Power-On Self Test (POST)
When the server boots up, a series of tests are displayed on the screen. This is referred to as Power-On
Self-Test (POST). POST is a series of diagnostic tests that checks firmware and assemblies to ensure that
the server is properly functioning. This diagnostic function automatically runs each time the server is
powered on.
These diagnostics, which reside in the BIOS ROM, isolate server-related logic failures and indicate the
board or component that needs to be replaced, as indicated by the error messages. Most server
hardware failures are accurately isolated during POST. The number of tests displayed depends on the
configuration of the server.
POST error indicators
When POST detects a system failure, it either:
• Displays a POST error message
• Emits a series of beep codes (requires an optional expansion board)
22
Page 23

Recoverable POST Errors
Whenever a non-fatal error occurs during POST, an error message describing the problem appears
onscreen. These text messages are displayed in normal video (white text on black background). It shows
the details of the error. The following is an example of a POST error message:
Error message 1 of 1: Error code 0103
Keyboard not detected - Keyboard error
In some cases an error message may include recommendations for troubleshooting or require that you
press the Enter key to display recommendations. Follow the instructions on the screen.
It is recommended that you correct the error before proceeding, even if the server appears to boot
successfully. If your system displays one of the messages marked below with an asterisk (*), write down
the code and message and contact your HP Customer Support provider
POST-related troubleshooting
Perform the following procedures when POST fails to run, error messages are displayed, or beep codes
are emitted.
System BIOS configuration
If the POST failure is during a routine bootup, verify the following conditions:
• All external cables and power cables are firmly plugged in.
• The power outlet to which the server is connected is working.
• The server and monitor are both turned on. The bicolor power status LED indicator on the front panel
must be green.
• The monitor's contrast and brightness settings are correct.
• All internal cables are properly connected and all boards firmly seated.
• The processor is fully seated in its socket on the system board.
• The heat sink is properly installed on top of the processor.
• All memory modules are properly installed.
If the POST failure occurs after installing an accessory, perform the following steps:
1. Perform the pre-installation procedure.
2. If necessary, remove any expansion boards, assemblies, or cables that prevent access to the system
components.
3. Check the following conditions:
a. If you have installed an expansion board, verify that the board is firmly seated in its slot and any
switches or jumpers on the board are properly set. Refer to the documentation provided with the
expansion board.
b. All internal cabling and connections are in their proper order.
c. If you have changed any switches on the system board, verify that each one is properly set.
4. Perform the post-installation procedure.
5. Turn on the monitor.
6. If the server still does not work, repeat step 2.
7. Remove all accessories, except the primary boot hard disk drive.
23
Page 24

8. Repeat steps 4 and 5.
If the server now works, replace the boards and accessories one at a time to determine which one is
causing the problem.
System BIOS configuration
Reprogramming the BIOS with the crisis recovery jumper
If the BIOS become corrupted, use the crisis recovery jumper to reprogram the BIOS. You will also need a
USB floppy drive and the HP crisis recovery floppy disk. The crisis recovery jumper is on jumper block
P56 on the system board. Refer to the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Maintenance and Service
Guide for the location of this jumper block and the crisis recovery setting.
To reprogram the BIOS:
1. Perform the pre-installation procedures.
2. If necessary, remove any expansion boards, assemblies, or cables that prevent access to the crisis
recovery jumper block.
3. Connect a USB floppy drive to one of the USB ports on the server.
4. Insert the HP crisis recovery floppy disk into the floppy drive.
5. Locate the crisis recovery jumper (P56) on the system board.
By default, the jumper is installed in the park position on the left and middle pins (as viewed from the
front of the server).
6. Set the jumper over the middle and right pins to enable the boot block, which forces the server to
boot from the floppy drive.
7. If the DIMM1 and DIMM2 memory slots are empty, move the installed memory in slots DIMM3 and
DIMM4 to slots DIMM1 and DIMM2.
8. Perform all of the post-installation procedures except for step 4; do not reinstall the top cover of the
server.
9. When the server begins reading the floppy disk, reinstall the crisis recovery jumper over the left and
middle pins. The system reprograms the BIOS from the floppy disk and then reboots normally with
the reprogrammed BIOS.
10. If you did not move memory modules in step 7, perform step 4 of the post-installation procedures to
reinstall the top cover of the server. If you did move memory modules in step 7, move the memory
modules back to their original locations:
a. Perform the pre-installation procedures.
b. Move the memory modules installed in slots DIMM1 and DIMM2 to their original locations in
slots DIMM3 and DIMM4.
c. Perform the post-installation procedures.
24
Page 25

NOS installation
Supported NOS
Table 14 Supported network operating systems (NOS)
NOS Version On-line information site
NOS installation
Microsoft Windows Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2—Enterprise,
Standard, and Web Editions Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 R2 SP2—Enterprise, Standard, and Web
Editions Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2 for 32bit and 64-bit
Red Hat Enterprise
Linux
SUSE Linux Enterprise
Server
Sun Solaris Enterprise Sun Solaris 10 (64-bit) http:www.sun.com/solaris
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 (32- and 64-bit),
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (32- and 64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 (32- and 64-bit),
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 (32- and 64-bit)
NOS pre-installation procedure
Perform the two pre-NOS installation steps in this section before installing the NOS of your choice.
1. Configure the hardware aspect of the server.
2. Update the server BIOS.
Microsoft World Wide Web
access: http://www.microsoft.com
Microsoft Product Support Services:
http://support.microsoft.com/direct
ory
Microsoft Software BBS: 206-9366735
http://www.redhat.com
http:www.novell.com/linux
Hardware setup
Prepare the server following the instructions in the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Installation
Sheet.
It is recommended that you do not install any third party adapter until you verify that the HP equipment is
functioning properly and you complete the NOS installation.
Your ProLiant server comes with new hard disk drive(s) that do not need specific setup. However, if you
install additional used hard disk drives in your new server:
• Note that most NOS installations remove all data from the hard disk on which they are installed. If
you want to use additional hard disk drives to access existing data in the new server, HP
recommends that you install and configure any of these hard drives after completing the NOS
installation.
25
Page 26

NOS installation
• If you want to recycle used hard drives, use a utility such as fdisk to erase all data and partitions
from that particular hard drive.
BIOS update
HP recommends that you update the server BIOS with the latest system BIOS version to take advantage of
the most recent compatibility fixes. You can download the latest HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 server
BIOS at www.hp.com.
NOTE: For ease of reading, the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD will be simply
referred to as the “Support CD.”
Installing Microsoft Windows NOS
The procedures in this section apply to all Microsoft Windows NOS versions supported by your ProLiant
server. Refer to the page for a list of these NOS versions.
CAUTION: If you install the default ATA driver from the installation CD, you must change the SATA
mode setting in the Serial ATA submenu from SATA to PATA; otherwise, the operating system kernel
will hang.
Pre-installation instructions
1. Complete the NOS pre-installation procedures.
2. Have the following installation requirements on hand:
○ HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD
○ The applicable Microsoft Windows NOS CD-ROM(s)
○ Six blank, formatted 3.5-inch diskettes
○ A Windows PC that has a Floppy drive Optical media drive Browser that supports HTML
○ Two or more clients for testing purposes (optional)
Installation flow
1. Create the driver diskettes using the Support CD.
2. Install the Microsoft Windows NOS.
3. Complete the installation—install the drivers for the chipsets, network, and VGA.
4. Configure the system.
5. Configure the network.
6. Install additional HP accessories.
Section 1. Creating the driver diskettes
To create the appropriate Windows NOS driver diskette:
1. Insert one blank, formatted 3.5" diskette into the floppy drive.
26
Page 27

2. Insert the Support CD into the optical media drive. By default, the Support CD automatically runs and
displays the Welcome page. However, if this does not occur, double-click the Startup.htm file located
on the root directory of the Support CD.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to create the Windows NOS driver diskette.
4. Label, date, and save the driver diskette as HP disk [Windows NOS version].
Section 2. Installing Windows NOS
1. Boot the server from the Windows NOS CD-ROM.
The Setup is inspecting your hardware configuration message displays; then the Setup screen
displays.
Press F6 if you want to install a third party controller; otherwise, proceed to step 2.
NOTE: If you missed pressing F6 before the message is invalidated, you need to reboot the system
to display the message prompt again.
NOS installation
2. Follow the procedures corresponding to the type of hard disk that is installed in the server.
3. At the Welcome to Setup screen, press Enter to continue.
4. Press F8 to accept the licensing agreement.
5. At the drives partitioning screen, select the target drive.
If you want to use the entire drive to install the Windows NOS, press Enter. Otherwise, press C to
create a drive partition.
NOTE: Windows Server 2003 does not have the 2-GB limitation present in Windows NT 4.0.
In this example, we will create a 10-GB partition.
a. Press C to create a partition.
b. At the Create partition size prompt, type 10240, then press Enter.
c. Select unpartitioned space and press C again to create additional partitions. HP
recommends that you create all the partitions needed for each hard drive present on your system.
6. Select the target drive to be used to install the Windows NOS, then press Enter.
7. On the next screen, select Format the partition using the NTFS file system, then press Enter.
The installer formats and copies files to the hard drive, after which the system reboots and launches
the Windows NOS graphic interface. Be sure to remove the Windows NOS CD-ROM before
rebooting.
You can now customize your installation using the graphical interface.
NOTE: The network settings may need to be customized to your environment. Refer to the Windows
NOS manual should you need further details on the networking settings.
8. After completing the customization phase, click Next to proceed with the installation.
The installation status is indicated by the Install Network progress bar. This may take some time.
After the installation is completed, the system automatically reboots.
9. At the Welcome to Windows dialog box, press Ctrl-Alt-Del, and then log on as Administrator.
27
Page 28

If you have successfully installed the Windows NOS, the Configure Your Server wizard launches.
Close this window to postpone the customization of the server until all of the installation steps are
completed.
You can open the Configure Your Server wizard at any point by clicking Start | Programs
|Administrative Tools | Configure Your Server.
Section 3. Completing the installation
Phase 1 - Installing the chipset driver
1. Insert the Support CD in the server’s optical media drive.
By default, the Support CD automatically runs and displays the Welcome page. However, if this
does not occur, double-click the Startup.htm file located on the root directory of the Support CD.
2. Click the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 server drivers for chipset, Network, and
Video link.
NOS installation
3. Select the ServerEngines chipset driver option for Windows [NOS version] option.
The File Download dialog box displays.
4. Click Open to download the driver.
The Security Warning dialog box displays.
5. Click Yes.
The installation menu for the selected driver is displayed.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the ServerEngines chipset driver.
7. After completing the installation, reboot the server.
Phase 2 - Installing the HP network driver
During the Windows NOS installation, the OS may not detect the embedded HP network interface card.
The following procedure helps you install the LAN driver using the Support CD.
1. Insert the Support CD in the server’s optical media drive. By default, the Support CD automatically
runs and displays the Welcome page. Close this window.
2. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel | System | Hardware | Device Manager.
3. Open the Other Devices tree, labeled with a yellow question mark (?), and double-click on the
appropriate Ethernet Controller option to display its menu.
4. Follow the installation wizard for additional configuration.
5. Wait for the system to find the appropriate driver, and then click Next.
6. Click Finish after the LAN driver has loaded.
7. Close all open windows and restart the server to properly initialize the LAN adapter.
8. After restarting Windows, configure the network settings for the LAN card to connect to your
network. Verify connectivity.
28
Page 29

Phase 3 - Installing the embedded video driver
1. Insert the Support CD in the server’s optical media drive. By default, the Support CD automatically
runs and displays the Welcome page. However, if this does not occur, double-click the Startup.htm
file located on the root directory of the Support CD.
2. Click the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 server drivers for chipset, Network, and
Video link.
3. Select the embedded VGA driver for the Windows [NOS version] option. The File
Download dialog box displays.
4. Click Open to download the driver. The Security Warning dialog box displays.
5. Click Yes. The installation menu for the selected driver is displayed.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the embedded VGA driver.
7. After completing the installation, reboot the server.
Section 4. Configuring the system
NOS installation
Phase 1 - Performing a hardware status check
In this section, you will run the Windows NOS Device Manager tool to identify any issues with the
installed devices or resource conflicts.
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel | System | Hardware | Device Manager.
2. Verify that no devices have either a yellow exclamation mark (!) or question mark (?) symbol next to
it.
○ An exclamation mark (!) means that there is a resource issue with the device.
○ A question mark (?) means that the device is unknown.
If (!) or (?) symbols are reported, double-click each of the devices with (!) or (?). Refer to the
Device Status message for troubleshooting. If a printer is available, click View | Print to get a
report.
3. Verify that the installed drivers are digitally signed:
a. In the Device Manager window, select the device (such as HP AHA-29160) that you want to
verify.
b. Right-click Properties, then click the Driver tab.
c. Locate the Digital Signer.
If the driver of that device is digitally signed, the message MS Windows 2003 Publisher or
Microsoft Windows Hardware Compatibility Publisher displays.
If the driver of the device is not digitally signed, HP recommends that you check HP’s website at
www.hp.com to install the latest driver package.
4. Close the Device Manager, System Properties, and Control Panel windows.
5. Click Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Event Viewer to make sure that there are
no errors in the log.
NOTE: The Windows NOS Event Viewer may have recorded network errors because your network
is not yet configured. Please disregard these errors.
6. Close the Event Viewer window.
29
Page 30

Phase 2 - Initializing the hard drive
There are two types of hard drive configurations: Dynamic and Basic. You can select the appropriate type
by right-clicking on the disk drive icon.
• Dynamic drives are used to create volumes, which can contain more than one physical hard drive.
• Basic drives are used to create primary or local partitioned drives.
To manage different drives and partitions:
1. Click Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Computer Management.
2. Double-click Storage in the tree, and then click Disk Management. The Write Signature and
Upgrade wizard starts if you have new hard drives with no signatures on them.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to create the signature.
4. Select the available hard disk space on the graphic and use menus to create additional partitions.
5. Format all partitions that are not yet formatted.
6. Close the Computer Management window.
NOS installation
Phase 3 - Adding Windows Terminal Services
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel | Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Add/Remove Windows Components.
3. Locate then select the Terminal Services checkbox, then click Next.
4. Select the mode you want to use, and then click Next. There are two mode options: Remote
administration mode and Application server mode.
NOTE: The following instructions are based on the Application server mode. Please note the
licensing requirement listed on the screen for this mode. Consult with your Microsoft representative
for setting the licensing server.
5. Select the default permissions for application compatibility, then click Next.
6. Click Next to accept the support tools and administrator tools settings.
7. If prompted, insert the Windows NOS CD-ROM.
8. Click Finish to close the wizard.
9. Click Yes to reboot the system. Be sure to remove the Windows NOS CD-ROM from the drive.
10. After the system reboots, log on to the system.
11. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel | Administrative Tools.
12. Check that the following services are now available:
○ Terminal Services Client Creator
○ Terminal Services Configuration
○ Terminal Services Manager
To create the client installation diskettes:
1. Double-click Terminal Services Client Creator.
2. Select the appropriate client type for your environment.
3. Click Format disk if needed.
30
Page 31

4. Check the number of disks required and label them as Terminal Services for […] Disk [x/y].
5. Click OK to proceed.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to create the diskette copies.
7. Click OK at the [y] floppies were created… screen.
8. Click Cancel to close the Create Installation Disks utility.
Section 5. Configuring the network
Phase 1 - Configuring the server’s IP address
During the installation process, the system was configured to use DHCP. If no DHCP server is found on the
network, the system autoconfigures a random IP address to start functioning. It is important that you
configure the proper IP address to be able to communicate with the clients.
1. Right-click My Network Places | Properties, then double-click Local Area Connection on
your server.
NOS installation
NOTE: If your ProLiant server hosts several network adapters, the window shows one local area
connection (LAN) icon for each network adapter present in the system. Identify the proper adapter
by browsing each one.
2. Click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) | Properties | Use the following IP address.
3. Enter an appropriate IP address.
4. Click OK to continue, and then OK again to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
5. Click Yes to restart your server and apply these settings.
Phase 2 - Attaching clients to the network and testing the network link
1. Create a new folder in your server’s hard drive and set is as a shared folder (right-click the folder,
then select Sharing…).
2. Create users using the Windows [NOS version] Computer Management utility. To open the utility,
click Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Computer Management | System
Tools | Local Users and Groups | Users.
3. Connect the client PCs to the network your ProLiant server operates on.
4. Open a command prompt window to verify the TCP/IP configuration and enter the command:
ipconfig /all
5. To verify the server and clients can communicate properly:
○ From one of the clients, open a command prompt and type:
ping computername
where computername is the server name you entered during the Windows NOS installation.
You should get four replies from your new server. If there is a connection problem, you must fix it
before going any further.
○ You may test the link further by doing a ping between two clients. At the same command prompt
type:
ping other_client_IPaddress
You should get four replies from the second client.
31
Page 32

NOS installation
6. Copy files back and forth from the clients to the server.
To test the network link using Terminal Services:
1. Click Start | Programs | Terminal Services Client | Terminal Services Client on a client
you installed Terminal Services on.
2. Select the target server from the Available Servers list displayed on the screen.
3. Click Connect.
4. Complete the User ID and Password login form.
Phase 3 - Configuring the domain controller setup
The Windows NOS manual calls this process "Promoting the server to a domain controller.”
1. Click Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Configure Your Server.
2. Select Active Directory.
3. Scroll down and click Start the Active Directory wizard.
4. Click Next to continue.
NOTE: The following instructions correspond to the standard steps for new domain creation. You
may customize the options proposed by your Windows NOS to match your environment.
5. Click Next at Domain Controller Type to accept the default setting—Domain controller for a new
domain.
6. Click Next at Create Tree or Child Domain to accept the default setting—Create a new domain
tree.
7. Click Next at Create or Join Forest to accept the default setting—Create a new forest of domain
trees.
8. At the Full DNS name for new domain text box, type in the assigned DNS name for your server (for
example: mycompany.com).
9. Click Next. The system may take a few minutes before moving to the next screen. NOS installation
38
10. Click Next at the NetBIOS Domain Name dialog box to accept the default setting—Domain
NetBIOS name.
11. Click Next at Database and Log Locations to accept the default directories.
12. Click Next at Shared System Volume to accept the default settings. The system displays a dialog
box that reads: "The Wizard can not contact the DNS Server…"
13. Confirm your DNS configuration, or install and configure a DNS server on this computer.
14. Click OK.
15. Click Next to accept the installation of DNS on your new server.
16. Click Next to accept the default permission value—Permissions compatible with pre-Windows
Server [2003].
17. Enter and confirm an administrator password, then click Next.
18. Review the Summary display, and then click Next to continue. The system starts configuring the
active directory display. It will take a few minutes to complete.
32
Page 33

19. If prompted, insert the Windows NOS CD-ROM, and then click OK to continue. The Configuring
active directory display shows again.
20. Click Finish to close the Wizard utility. This completes the active directory installation.
21. Click Restart Now to reboot the system. Remove the Windows NOS CD-ROM if it is present.
22. At the login prompt:
a. Type in the administrator password you set.
b. Click Options and verify that the Log on to: HOST displays on the dialog box.
c. Click OK to start the login process. A dialog box, This Server is Now a Domain Controller,
displays after the login.
23. Click Finish.
NOS installation
Section 6. Installing additional HP accessories
The HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD includes the drivers for accessories compatible to
your server.
Refer to the product manual enclosed with the accessory for the detailed installation procedure and/or to
the attached readme.txt file associated with the driver. The readme.txt file can be found on the
appropriate driver diskette.
Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux NOS
Installation flow
1. Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux [version]. For the specific procedure for each RHEL NOS version,
refer to the following sections.
2. Install additional HP accessories.
The HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD includes the drivers for accessories
compatible to your server.
Refer to the product manual enclosed with the accessory for the detailed installation procedure
and/or to the attached readme.txt file associated with the driver. The readme.txt file can be
found on the appropriate driver diskette.
Pre-installation instructions
1. Complete the NOS pre-installation procedures.
2. Have the following installation requirements on hand:
○ HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD
○ Red Hat Enterprise Linux CD-ROMs
− Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 – 4 discs for the 32-bit version, 5 discs for the 64-bit version
− Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 – 4 discs for the 32-bit version, 5 discs for the 64-bit version
○ A Windows PC that has a:
− Floppy drive
− Optical media drive
33
Page 34

NOS installation
− Browser that supports HTML
○ Two or more clients for testing purposes (optional)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 installation
The procedures in this section apply to all versions of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 supported by
your ProLiant server. Refer to Table 14 on page 25 for a list of these NOS versions.
NOTE: If the system has more than 4 GB of memory, the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation
requires the pci=nommconf parameter.
Section 1. Launching the Red Hat Enterprise Linux installer
1. Turn on the server and insert the Red Hat Enterprise Linux CD 1. The system displays a text menu.
2. Press Enter to start the installation.
3. At the CD Found dialog box, click Skip. The Welcome to Red Hat Enterprise Linux page displays.
4. Click OK to proceed to the customization of your installation.
Section 2. Customizing the installation
Language Selection
Select the language you prefer for the installation, then click Next to continue.
Keyboard Configuration
Your HP server comes with a Generic 104-key PC keyboard. After selecting the appropriate option for the
keyboard layout, click Next to continue.
Disk Partitioning Setup
HP recommends selecting the automatic partitioning mode.
1. Click Automatically partition to continue.
2. Remove all system partitions, then select a hard drive.
3. Click Next to continue.
4. If a Warning dialog box appears, click Yes to continue.
5. At the Partitioning dialog box, click Next.
6. Review the Disk Setup settings and modify if necessary, then click Next.
Boot Loader Configuration
HP recommends keeping the default option, then click Next to continue.
Network Configuration
Review the Network Configuration settings and verify that they fit your environment, then click Next to
continue.
Firewall Configuration
Review the Firewall Configuration settings and modify if necessary, then click Next to continue.
Additional Language Support
34
Page 35

Review the Additional Language Support setting and modify if necessary, then click Next to continue.
Time Zone Selection
Review the Time Zone Selection setting and modify if necessary, then click Next to continue.
Set Root Password
Enter a root password consisting of at least six alphanumeric characters, then click Next to continue.
Package Defaults
Review the software selection and modify if necessary, then click Next to continue.
Package Group Selection
Review and modify the selection as necessary, then click Next to continue.
If you selected the Custom install option, pre-determined packages have already been selected. However,
depending upon your network environment additional packages may be necessary.
NOTE: Remember to select the appropriate package groups that match your network settings. For
example, the DNS Name Server package may be required if you have set up your new server to be
the DNS controller.
NOS installation
Section 3. Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5
About to Install
Once you complete the customization, the installation program asks for confirmation before proceeding
with the install.
1. Click Next to proceed with the installation.
2. On the Required install media dialog box, click Continue to start installation.
You may be prompted to insert the rest of the RHEL4/5 CD-ROMs, depending on the packages you have
chosen to install.
Complete Installation
After completing the installation, click Reboot to close the installation program and reboot the system.
Section 4. Configuring the initial setup settings
Once the system reboots, the new Red Hat environment is loaded. You need to configure the initial setup
settings.
Welcome
Click Next to start the initial setup configuration.
License Agreement
Read the license agreement. If the terms of the agreement are acceptable, click Next.
Date and Time
Modify the Date and Time settings, then click Next to continue.
Display
HP Confidential
35
Page 36

Retain the default display setting, then click Next to continue.
System User
1. Skip the option to create a new user, then click Next to continue.
2. On the Warning dialog box, click Next to continue.
Additional CDs
Ignore this page. Click Next to continue.
Finish Setup
The initial setup configuration is complete. Click Next to proceed to the login window.
Login
Type root and the password you set during the NOS installation, then press Enter.
NOS installation
Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server NOS
The procedures in this section apply to the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server NOS, version 9 and 10.
Installation flow
1. Install SUSE Linux Enterprise [version]. For the specific procedure for each SLE NOS version, refer to
the following sections.
2. Install additional HP accessories.
The HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD includes the drivers for accessories
compatible to your server.
Refer to the product manual enclosed with the accessory for the detailed installation procedure
and/or to the attached readme.txt file associated with the driver. The readme.txt file can be found
on the appropriate driver diskette.
Pre-installation instructions
1. Complete the NOS pre-installation procedures listed on page 62.
2. Have the following installation requirements on hand:
○ HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD
○ SUSE Linux Enterprise Server CD-ROMs
− SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 – 6 discs
− SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 – 4 discs
○ A Windows PC that has a:
− Floppy drive
− Optical media drive
− Browser that supports HTML
○ Two or more clients for testing purposes (optional)
36
Page 37

NOS installation
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 installation
Section 1. Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9
1. Turn on the server and insert the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9 SP3 (SLES9) CD 1.
2. Reboot the system to the SLES9 SP3 CD 1.
3. Select Installation, then press Enter to start the installation.
4. Remove the SLES9 SP3 CD1 and insert the SLES9 CD 2 once prompted.
5. Press Enter to proceed to the customization of your installation.
Section 2. Customizing the installation
Software License Agreement
Read the license agreement. If the terms of the agreement are acceptable, click I Agree.
Language
Select the language you prefer for the installation, then click Accept to continue.
Installation Setting
1. Click New Installation, then click OK.
The installer automatically enables the default settings.
2. Review the default installation settings and modify them to meet your network environment.
3. Click Accept to initialize the installation process.
4. Click Yes, install on the warning dialog box to start the file copying.
You may be prompted to insert the rest of the SLES9 CD-ROMs, depending on the installation settings you
have chosen.
After copying all the necessary files for installation, the system automatically reboots.
Section 3. Completing the installation
Root Password
Enter a root password consisting of at least six alphanumeric characters, then click Next to continue.
Network Configuration
Review the Network Configuration settings and verify that they fit your environment, then click Next to
continue.
Test Internet Connect
Skip this test. You can test the network connection after completing the NOS installation. Click Next to
proceed with the installation.
Service Configuration
Review the Services settings and select those items that are required by your environment, then click Next
to continue.
User Authentication Method
HP Confidential
37
Page 38

Select the authentication method appropriate for your environment, then click Next to continue.
Add a New Local User
Follow the prompt to add a new local user account, then click Next to continue.
Release Note
Review the release notes, then click Next to continue.
Hardware Configuration
Review the default hardware settings and modify them as necessary, then click Next to continue.
Installation Completed
Click Finish to proceed to the login window.
NOS installation
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 Installation
Section 1. Installing SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10
1. Turn on the server and insert the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP1 (SLES10) CD 1.
2. Reboot the system to the SLES10 SP1 CD 1.
3. Select Installation, then press Enter to proceed to the customization of your installation.
Section 2. Customizing the Installation
Language
Select the language you prefer for the installation, then click Accept to continue.
Media Check
Skip this stage of the installation. Click Next to continue.
License Agreement
Read the license agreement. If the terms of the agreement are acceptable, click Yes, I agree to the license
agreement, then click Next to continue.
Installation Mode
Click New Installation, then click Next to continue.
Clock and Time Zone
Modify the Clock and Time Zone settings, then click Next to continue.
Installation Setting
1. Review the default installation settings and modify them to meet your network environment.
2. Click Accept to initialize the installation process.
3. Click Install to start the file copying.
The system automatically reboots once the first part of the file copying is completed. You may be
prompted to insert the rest of the SLES10 CD-ROMs, depending on the packages you have chosen to
install.
38
Page 39

Section 3. Completing the installation
Hostname and Domain Name
Set host name and domain name, then click Next to continue.
Password for the System Administrator
Enter a root password consisting of at least six alphanumeric characters, then click Next to continue.
Network Configuration
Review the Network Configuration settings and verify that they fit your environment, then click Next to
continue.
Test Internet Connect
Review the Network Configuration settings and verify that they fit your environment, then click Next to
continue.
Installation Setting
NOS installation
Review the installation settings once again, then click Next to continue.
User Authentication Method
Select the authentication method appropriate for your environment, then click Next to continue.
Add a New Local User
Follow the prompt to add a new local user account, then click Next to continue.
Release Note
Review the release notes, then click Next to continue.
Hardware Configuration
Review the default hardware settings and modify them as necessary, then click Next to continue.
Installation Completed
Click Finish to reboot the system and proceed to the login window
Installing Sun Solaris 10
Perform the procedures in this section to install Sun Solaris 10 to your ProLiant server.
Pre-installation instructions
1. Complete the NOS pre-installation procedures listed on page 62.
2. Have the following installation requirements on hand:
○ HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD
○ Sun Solaris 10 Update 4 DVD
NOTE: You must first install a DVD-compatible optical media drive on your ProLiant server before
installing Sun Solaris 10.
○ A Windows PC that has a:
39
Page 40

− Floppy drive
− Optical media drive
− Browser that supports HTML
○ Two or more clients for testing purposes (optional)
Installation flow
1. Install Sun Solaris 10.
Refer to the next section for detailed instructions.
2. Install additional HP accessories.
The HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5 Server Support CD includes the drivers for accessories
compatible to your server.
Refer to the product manual enclosed with the accessory for the detailed installation procedure
and/or to the attached readme.txt file associated with the driver. The readme.txt file can be found
on the appropriate driver diskette.
NOS installation
Sun Solaris 10 installation
Section 1. Launching the Sun Solaris10 installer
1. Turn on the server and insert the Sun Solaris 10 DVD.
2. Reboot the system to the SS10U4 DVD.
3. Click Solaris, then press Enter.
4. Type 1 to select the Solaris Interactive Installation option.
After a few minutes, the Proposed Window System Configuration for Installation list appears. These
settings are incorrect and should be modified.
5. Press Esc to modify the settings and customize the installation.
Section 2. Customizing the installation
The Sun Solaris10 Installer shifts to a text-based screen for customizing the hardware selection and other
options.
Use the arrow keys to navigate through them and press F2 to enable a setting.
Kdmconfig – View and Edit Window System Configuration
1. Click Change Pointing Device, then press F2.
2. Select the pointing device used by your system, then press F2.
3. Select Change Video Device/Monitor, then press F2.
4. Verify that the Video Device setting shows XF86-VESA Matrox Graphics, Inc. Unknown Board, then
press F2.
5. Select the display device used by your system, then press F2. If you are using a 17-inch CRT monitor,
select MultiFrequency 38KHz (Up to 1024x768 interlaced).
6. Select your display device’s screen size, then press F2.
7. Set the preferred Resolution/Color/Refresh Rate settings, then press F2.
40
Page 41

HP recommends the 1024 x 768 – 65536 colors option.
8. Select Save and Test the Window System Configuration, then press F2.
9. Press F2 again to test the hardware configuration settings you selected.
If you are able to view the sample display, click Yes to return to the GUI installation mode. If the
hardware test fails, repeat steps 1-9 until the correct settings are made.
Select Language
Select the language you prefer for the installation, then press Enter to continue.
Welcome
The Welcome screen appears. Click Next to proceed with the customization.
Network Connectivity
Click Non-networked, then click Next to continue.
Hostname
NOS installation
Enter a hostname for the system, then click Next to continue.
Time Zone
Click Geographic Continent/Country/Region, then click Next to continue.
Continent and Country
Select the continent and country of your location, then click Next to continue.
Date and Time
Set the system date and time. If the default date and time settings displayed are correct, click Next.
Otherwise,
adjust the date and time settings, then click Next.
Click Geographic Continent/Country/Region, then click Next to continue.
Root Password
Enter a root password. Re-enter the password in the second box, then click Next to continue.
Confirm Information
A configuration information summary is displayed. Verify this information, then click Confirm to proceed
to the installation proper.
Section 3. Completing the installation
Welcome
The Welcome screen appears. Click Next to proceed with the installation.
Installation Options Retain the default installation option settings, then click Next to continue.
Specify Media Click CD/DVD, then click Next to initialize the installation process.
License Read the license agreement. If the terms of the agreement are acceptable, select the Accept check
box, then click Next to continue.
Select Type of Install
41
Page 42

NOS installation
Click Custom Install, then click Next to choose the Solaris options you intend to install.
Select Software Localizations
Click a > on the GUI to expand a geographic region option, then select the appropriate localization(s).
Click Next to continue.
Select System Locale
Select the appropriate locale once the installation is complete, then click Next to continue.
Select Products Select the Solaris software products you need, then click Next to continue.
Additional Products
For the initial installation, no additional Solaris software is required. Click Next to continue.
Select Solaris Software Group
Click Entire Group, then click Next to continue.
Disk Selection
Select a boot disk. If the system contains more than one hard disk, select a disk from the list, then click
Next to continue.
Select Disks for fdisk Partition Customization
Select a disk for custom partitioning, then click Next to continue.
Customize fdisk Partitions – Disk c0d0
Enter the preferred partition size, then click Next to continue.
Layout File System Review the default file system layout and modify if necessary, then click Next to
continue.
Ready to Install
An installation information summary is displayed. Verify this information, then click Install Now to start the
installation process.
Upon completing the installation, the system automatically reboots. You can now eject the SS10U4 DVD.
Once the system reboots, the new Sun Solaris environment is loaded. The following message appears:
Do you need to override the system’s default NFS version 4 domain name?
Keep the default setting (No), then press Enter to proceed to the login window
42
Page 43

Server management
Pre- and post-installation procedures
Pre-installation procedures
WARNING: Failure to properly turn off the server before you open the server or before you start
removing or installing hardware components may cause serious damage as well as bodily harm.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the chassis and any
installed hardware components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: Follow the ESD precautions listed in Chapter 2 of the HP ProLiant DL180 Generation 5
Server Maintenance and Service Guide when handling any hardware component.
1. Turn off the server and all the peripherals connected to it.
2. Disconnect the AC power cord from the power supply cable located on the server rear panel to turn
off the service processor and reduce the risk of electrical shock.
3. Remove the top cover from the chassis.
4. Place the top cover in a safe place for reinstallation later.
Post-installation procedures
1. Be sure all components are installed according to the described step-by-step instructions.
2. Check to make sure you have not left loose tools or parts inside the server.
3. Reinstall any expansion boards, riser board assemblies, peripherals, board covers, brackets, and
system cables that you have removed.
4. Reinstall the top cover:
a. Place the cover on the chassis approximately 1.25 cm (0.5 in) toward the rear of the unit, then
slide the cover forward into place.
b. Tighten the captive screw on the rear panel.
5. Connect all external cables and the AC power cord to the system.
Route the cables properly through the available cable management arrangement.
6. Press the power button on the front panel to turn on the server.
Configuring the BMC
The server includes a BMC for systems management, which you can access through a 10/100 Mbps LAN
port for IPMI management. To access the BMC through this LAN port, you must configure the IP address.
You can configure the settings for the BMC by using either the Setup Utility or another system (such as a
43
Page 44

Server management
laptop) that is connected to the serial port on the server. The serial port can be controlled by the server or
shared between the server and the BMC (the default setting).
To configure the BMC through the Setup Utility:
1. In the IPMI submenu, set the Serial port Assignment field to System or BMC.
2. In the LAN Settings field under the IPMI submenu, set the IP address, default gateway, and IP subnet
mask for the BMC. You can set the addresses manually or use DHCP to set the addresses
automatically.
3. Also in the LAN Settings field, set the LAN Controller field to select which connection the BMC uses
for the IPMI LAN interface.
To configure the BMC through the serial port:
1. Connect another system (such as a laptop) to the serial port on the server.
2. Configure your terminal session with the following settings:
○ Bits per second: 9600
○ Data bits: 8
○ Parity: None
○ Stop bits: 1
○ Flow control: None
3. Press Esc+( to switch serial connector from system to BMC; press Esc+Q to switch serial connector
from BMC to system.
4. Start your terminal session.
5. Press Enter to bring up a prompt.
6. If the first prompt is for a password, press Enter again.
7. At the Login prompt, type your user name and press Enter. The default user name is admin.
8. At the Password prompt, type your password and press Enter. The default password is admin.
The message CLP Session Initiated displays.
9. At the prompt, type cd map1/nic1 to navigate to the correct directory. The command line interface
is SMASH-compliant.
10. Type show to display the current settings.
11. Modify the settings you want to change.
NOTE: The set variables are case-sensitive.
For example, by default, the BMC is set to use DHCP to get the IP address. To manually set the IP
address, type
set oemhp_dhcp_enable=FALSE to disable DHCP, then type set
networkaddress=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx to set the IP address you want.
To revert to using DHCP to set the IP address, type set oemhp_dhcp_enable=TRUE to enable DHCP.
The system takes a few seconds to set the new IP address.
12. Open a browser and enter the IP address that you set manually or that was set automatically using
DHCP.
13. When prompted, enter the same user name and password you used in your terminal session.
44
Page 45

Server management
14. Browse the server settings using the user interface that displays.
To enable console redirection via the Setup Utility:
1. In the serial port assignment, set the Serial port Mode field to BMC.
2. In the Console Redirection submenu, set BIOS Serial console and EMS Support(SPCR) as Enable.
3. Press F10 to Save and Exit Console Redirection submenu fields.
45
Page 46

Index
A
administrator password, 18
administrator password changing,
20
AMIBIOS Setup Utility, 5
asset tag, 9
B
Basic Input/Output System, 5
BIOS overview, 5
Boot Device Priority, 18
Boot Settings Configuration, 9
Bootup Num-Lock, 10
C
Clear BMC System Event Log, 15
CMOS, 6, 22
console, 44
CPU version, 9
D
default gateway, 44
Discard Changes, 21
Discard Changes and Exit, 21
E
Embedded NIC PXE, 18
Exit menu, 21
G
General Help Screen, 8
I
IDE, 13
IP subnet mask, 44
IPMI LAN interface, 44
L
LAN Controller, 44
Load Option Default, 21
M
Main Manu, 8
Main menu, 6
memory, 9
N
New Password box, 19
P
POST, 5, 22
Power-On Self-Test, 22
Index
Pre-installation, 39
R
RAID, 13
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3, 35
Remote Access, 16
Restore on AC Power Loss, 10
ROM version, 9
S
Save Changes and Exit, 21
Setup, 5
software, 5
Sun Solaris 10, 40
system configuration changing, 5
System Date, 9
system defaults, 22
System Time, 9
system time and date setting, 5
U
USB 2.0 Controller, 17
USB Controller, 17
V
View BMC System Event Log, 15
46
 Loading...
Loading...