HP PcAnywhere SW, SmartCache White Paper

Technology implementation in HP ProLiant G6
Intel-based servers
Technology brief
Table of contents
Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 2
Processor technologies ......................................................................................................................... 2
Intel QuickPath Technology ............................................................................................................... 2
Integrated memory controller ............................................................................................................. 3
Three-level cache hierarchy ............................................................................................................... 3
Intel Hyper-Threading Technology ...................................................................................................... 4
Intel Turbo Boost Technology ............................................................................................................. 4
DDR3 memory technology .................................................................................................................... 4
HP Smart Array technologies................................................................................................................. 5
SATA native command queuing ......................................................................................................... 5
Improved battery life......................................................................................................................... 5
Flash-backed write-cache .................................................................................................................. 5
HP Smart Array Advanced Pack......................................................................................................... 5
HP Thermal Logic technologies .............................................................................................................. 5
HP Dynamic Power Capping ............................................................................................................. 6
Sea of Sensors................................................................................................................................. 6
HP common-slot power supplies ......................................................................................................... 7
Infrastructure management technologies ................................................................................................. 7
HP Insight Control ............................................................................................................................ 7
HP Insight Control for Linux ............................................................................................................... 7
HP Remote Management................................................................................................................... 8
Virtualization technologies .................................................................................................................... 8
HP Insight Dynamics suite for ProLiant................................................................................................. 8
Virtual Connect Flex-10 technology .................................................................................................... 9
HP Insight Server Migration software for ProLiant ................................................................................. 9
For more information.......................................................................................................................... 10
Call to action .................................................................................................................................... 10

Introduction
HP engineers designed HP ProLiant G6 DL, ML, and BladeSystem servers with more processing,
memory, and I/O capacity to support more users, more transactions, or more virtual machines than
previous ProLiant servers. These technologies include Intel
the Intel
®
Microarchitecture Nehalem, Double Data Rate-3 (DDR3) memory, HP Smart Array
®
Xeon® 5500 series processors based on
controllers, and HP smart management tools. ProLiant G6 server technologies enable IT to produce
more using fewer physical machines; maximize energy efficiency; reclaim power capacity hidden by
conservative power management practices; and unite physical and virtual environments to maximize
productivity.
Compared to the previous generation of servers, ProLiant G6 servers deliver up to 2.5 times more
power efficiency using Thermal Logic technology. Originally offered only on the HP BladeSystem,
Thermal Logic technology is implemented across all ProLiant ML, DL, and BL G6 servers. It includes
Dynamic Power Capping, integrated thermal sensors, and common slot power supplies.
This technology brief summarizes the processor, memory, storage, power management, infrastructure
management, and virtualization technologies in ProLiant G6 servers. You will find links to additional
resources and information throughout this paper and in the “For more information” section.
Processor technologies
HP uses the enhanced technologies in Intel Xeon 5500 series quad-core processors as building blocks
to construct a range of performance and power options for dual-processor ProLiant G6 servers. These
technologies include Intel
cache hierarchy, Intel
Power Management. HP and Intel co-developed the advanced power capping feature that increases
the power cap dynamic range and improves its responsiveness in the processors and memory subsystem. Intel Xeon 5500 series processors are available in high-performance 95-watt, standard 80watt, and low-power 60-watt versions (Table 1).
®
QuickPath Technology, an integrated memory controller, a three-level
®
Hyper-Threading Technology, Intel® Turbo Boost Technology, and Dynamic
Table 1. 60-Watt, 80-Watt, and 95-Watt Intel Xeon 5500 series processor specifications
L5530 (2.40
GHz)
L5520 (2.26
GHz)
Turbo Boost
L5506 (2.13
GHz)
No Turbo Boost
60W 80W 95W
8MB L3,
5.86 GT/s QPI,
800/1066
MHz DDR3,
HyperThreading
4MB L3,
4.8 GT/s QPI,
800 MHz
DDR3,
No HyperThreading
E5540 (2.53
GHz)
E5530 (2.40
GHz)
E5520 (2.26
GHz)
E5506 (2.13
GHz)
E5504 (2.00
GHz)
E5502 (1.86
GHz)
8MB L3
5.86 GT/s
QPI
1066 MHz
DDR3
HyperThreading
4MB L3
4.8 GT/s
QPI
800 MHz
DDR3
No HyperThreading
E5570
(2.93 GHz)
E5560
(2.80 GHz)
E5550
(2.66 GHz)
8MB L3
6.40 GT/s QPI
800/1066/1333
MHz DDR3
Hyper-Threading
Intel QuickPath Technology
The Intel® QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) is a high-speed, point-to-point interconnect that directly links
the processors and I/O chipset to boost data transfer between the processors and other system
components (Figure 1). The QPI replaces the shared front-side bus and memory controller hub found
2
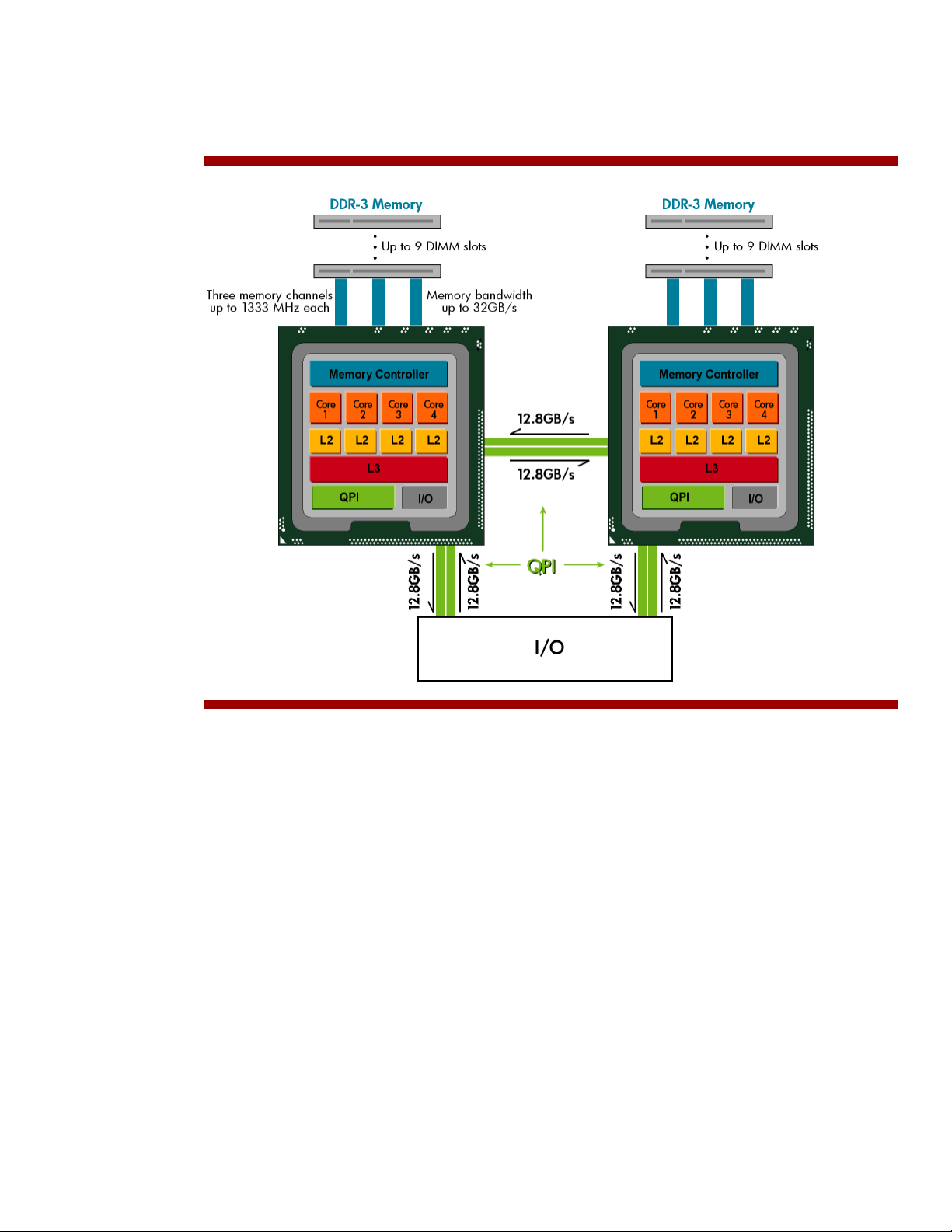
in previous-generation Intel architectures. Each QPI consists of two uni-directional links that operate
simultaneously in opposite directions with a total bandwidth up to 25.6GB/s. Each uni-directional link
consists of twenty 1-bit lanes that transmit up to16 data packets in multiple parallel transfers. Of the
remaining lanes, one is used as a clock lane and three are used for clock or data fail-over.
Figure 1. Intel Microarchitecture Nehalem
Integrated memory controller
One of the most notable improvements in Intel Xeon 5500 series processors is the integrated memory
controller. The memory controller uses three channels (up to 1333-MHz each) to access dedicated
DDR3 memory sockets. This design delivers a substantial performance improvement over previous Intel
architectures that provided only two memory channels and required processors to share a single pool
of system memory. HP optimized the design to support the maximum memory speed for topologies
with two DIMMs per channel. The three memory channels have a total bandwidth of 32GB/s.
Three-level cache hierarchy
HP has implemented the three-level cache hierarchy present in each Intel Xeon 5500 series processor.
This consists of an on-core 64-KB L1 cache, a separate 256-KB L2 cache for each core, and an
inclusive, shared L3 cache of up to 8MB. The L3 cache duplicates the data stored in each core’s L1
and L2 cache. This data duplication eliminates unnecessary searches, or snoops, to those caches and
minimizes latency. Additional data tracking technology in the L3 cache ensures inter-core cache
coherency. If one processor needs to access the cache or DDR3 memory of the other processor, it
uses the high-speed QPI between the two processors.
3
 Loading...
Loading...