HP INA-12063-TR1, INA-12063-BLK Datasheet
1.5 GHz Low Noise Self-Biased
Transistor Amplifier
Technical Data
INA-12063
Features
• Integrated, Active Bias
Circuit
• Single Positive Supply
Voltage (1.5 – 5V)
• Current Adjustable, 1 to
10mA
• 2 dB Noise Figure at
900␣ MHz
• 16 dB Gain at 900 MHz
25 dB Gain at 100 MHz
Applications
• Amplifier Applications for
Cellular, Cordless, Special
Mobile Radio, PCS, ISM,
and Wireless LAN
Applications
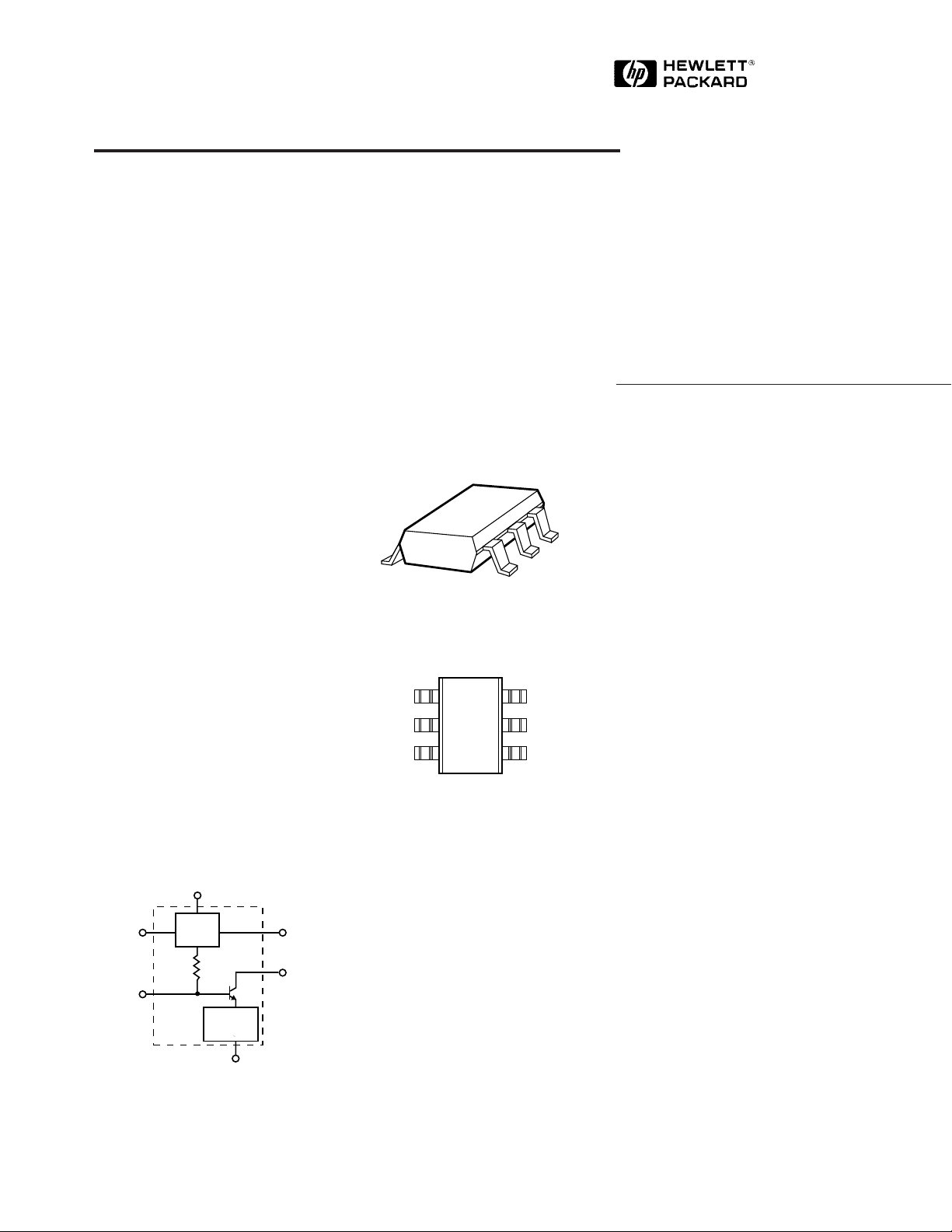
Equivalent Circuit
(Simplified)
V
d
ACTIVE
GND 2
INPUT
RF
BIAS
CIRCUIT
FEEDBACK
GND 1
RF
NETWORK
I
bias
RF
OUTPUT
and V
Surface Mount Package
SOT-363 (SC-70)
Pin Connections and Package Marking
I
1
bias
GND 2
2
RF INPUT
Note:
Package marking provides orientation
and identification.
c
3
12
RF OUTPUT
6
and V
GND 1
5
4V
d
Description
Hewlett-Packard’s INA-12063 is a
Silicon monolithic self-biased
transistor amplifier that offers
excellent gain and noise figure for
applications to 1.5 GHz. Packaged
in an ultra-miniature SOT-363
package, it requires half the board
space of a SOT-143 package.
The INA-12063 is a unique RFIC
that combines the performance
flexibility of a discrete transistor
C
with the simplicity of using an
integrated circuit. Using a patented bias circuit, the performance and operating current of
the INA-12063 can be adjusted
over the 1 to 10␣ mA range.
The INA-12063 is fabricated using
HP’s 30 GHz f
ISOSAT™
MAX
Silicon bipolar process which
uses nitride self-alignment
submicrometer lithography,
trench isolation, ion implantation,
gold metalization, and polyimide
intermetal dielectric and scratch
protection to achieve superior
performance, uniformity, and
reliability.
5965-5365E
6-116

INA-12063 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute
Symbol Parameter Units Maximum
V
d
V
c
I
c
P
in
T
j
T
STG
Supply Voltage, to Ground V 7
Collector Voltage V 7
Collector Current mA 15
CW RF Input Power dBm 13
Junction Temperature °C 150
Storage Temperature °C -65 to 150
[1]
Thermal Resistance
θ
= 170°C/ W
j-c
[2]
:
Notes:
1. Operation of this device above any
one of these limits may cause
permanent damage.
2. TC = 25°C (TC is defined to be the
temperature at the package pins
where contact is made to the
circuit board).
Electrical Specifications, T
Symbol Parameters and Test Conditions Units Min. Typ. Max. Std.Dev.
G
NF Noise Figure f = 900 MHz
P
IP
I
Power Gain (|S21|2) f = 900 MHz
P
Output Power at 1 dB Gain Compression f = 900 MHz
1dB
Third Order Intercept Point f = 900 MHz
3
Device Current
dd
[4]
= 25°C, Vd = 3 V, unless noted
C
f = 250 MHz
f = 250 MHz
f = 250 MHz
f = 250 MHz
900 MHz LNA
250 MHz IF Amp
[1]
d B 14.5 16 0.36
[2]
[1]
d B 2.0 2.6 0.2
[2]
[1]
dBm 0
[2]
[1]
dBm 15
[2]
[1]
m A 5 7 0.6
[2]
19
5.0
-7
2
1.5
[3]
Notes:
1. See Test Circuit in Figure 32.
2. See Test Circuit in Figure 33.
3. Standard deviation number is based on measurement of at least 500 parts from three non-consecutive wafer lots during
the initial characterization of this product, and is intended to be used as an estimate for distribution of the typical
specification.
4. Idd is the total current into Pins 1, 4, and 6 of the device, i.e. Idd = Ic + I
bias
+ Id.
6-117
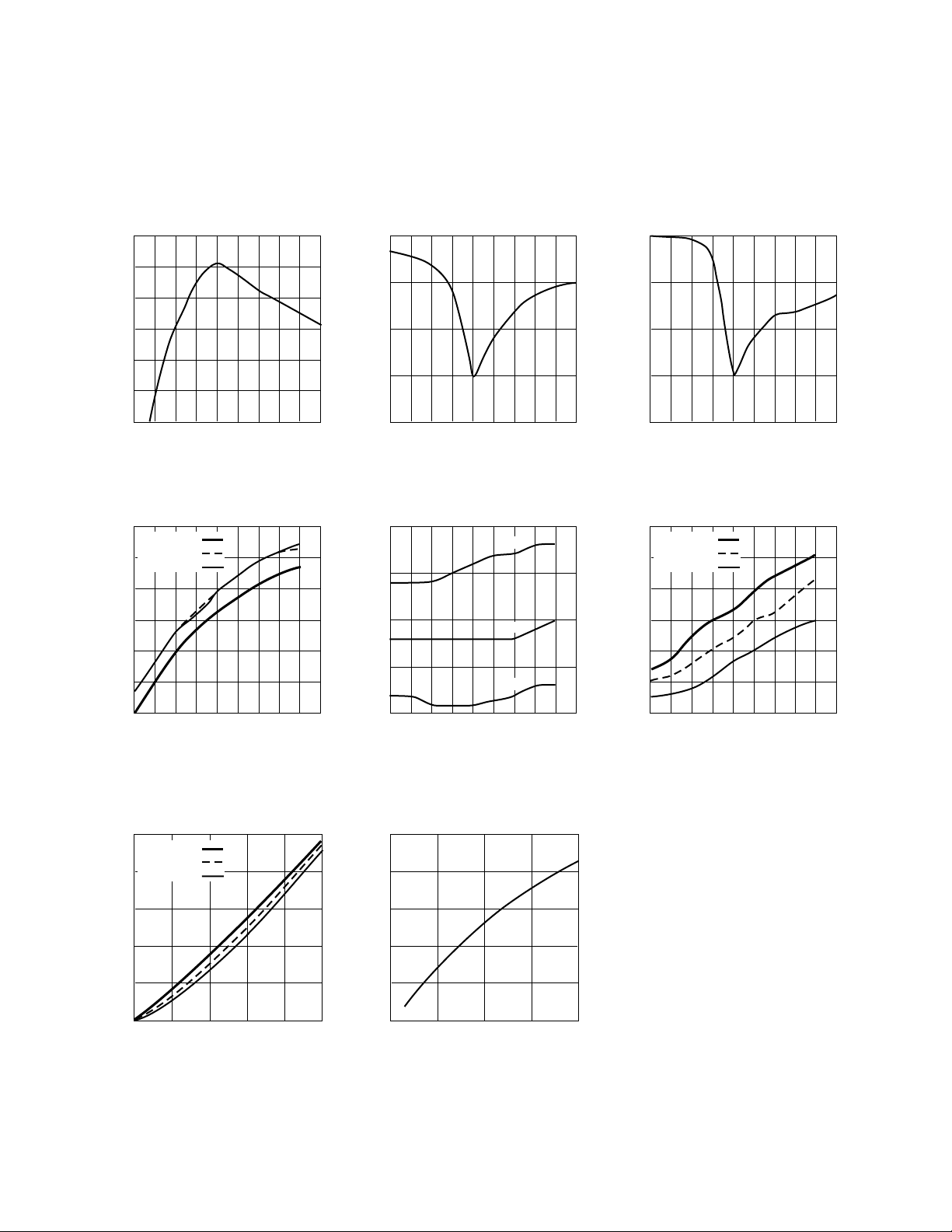
INA-12063 Typical Performance, 900 MHz LNA (900 MHz Test Circuit, see Figure 32)
TC = 25° C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vd = 3 V, IC = 5 mA, unless noted
20
15
10
5
GAIN (dB)
0
-5
-10
0.1 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.10.3 1.3 1.71.5 1.9
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 1. Gain vs. Frequency.
17.2
TA = +85°C
= +25°C
T
A
16.8
= –40°C
T
A
16.4
16.0
GAIN (dB)
15.6
15.2
0
-5
-10
RETURN LOSS (dB)
-15
-20
0.1 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.10.3 1.3 1.71.5 1.9
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 2. Input Return Loss vs.
Frequency.
2.7
2.45
2.2
NOISE FIGURE (dB)
1.95
+85°C
+25°C
–40°C
0
-5
-10
RETURN LOSS (dB)
-15
-20
0.1 0.5 0.7 0.9 1.10.3 1.3 1.71.5 1.9
FREQUENCY (GHz)
Figure 3. Output Return Loss vs.
Frequency.
4
TA = +85°C
= +25°C
T
A
3
= –40°C
T
A
2
(dBm)
1
1dB
P
0
-1
14.8
12345
(V)
V
d
Figure 4. Gain at 900 MHz vs. Voltage
and Temperature.
10
TA = +85°C
= +25°C
T
A
8
= –40°C
T
A
6
4
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
2
0
10 2345
Vd (V)
Figure 7. Supply Current vs. Voltage
and Temperature.
1.7
12345
(V)
V
d
Figure 5. Noise Figure at 900 MHz vs.
Voltage and Temperature.
9
6
3
(dBm)
1 dB
0
P
-3
-6
Figure 8. Output P
Device Current for V
426810
DEVICE CURRENT (mA)
at 900MHz vs.
1 dB
= 3 V.
d
-2
12345
(V)
V
d
Figure 6. Output P
at 900 MHz vs.
1dB
Voltage and Temperature.
6-118
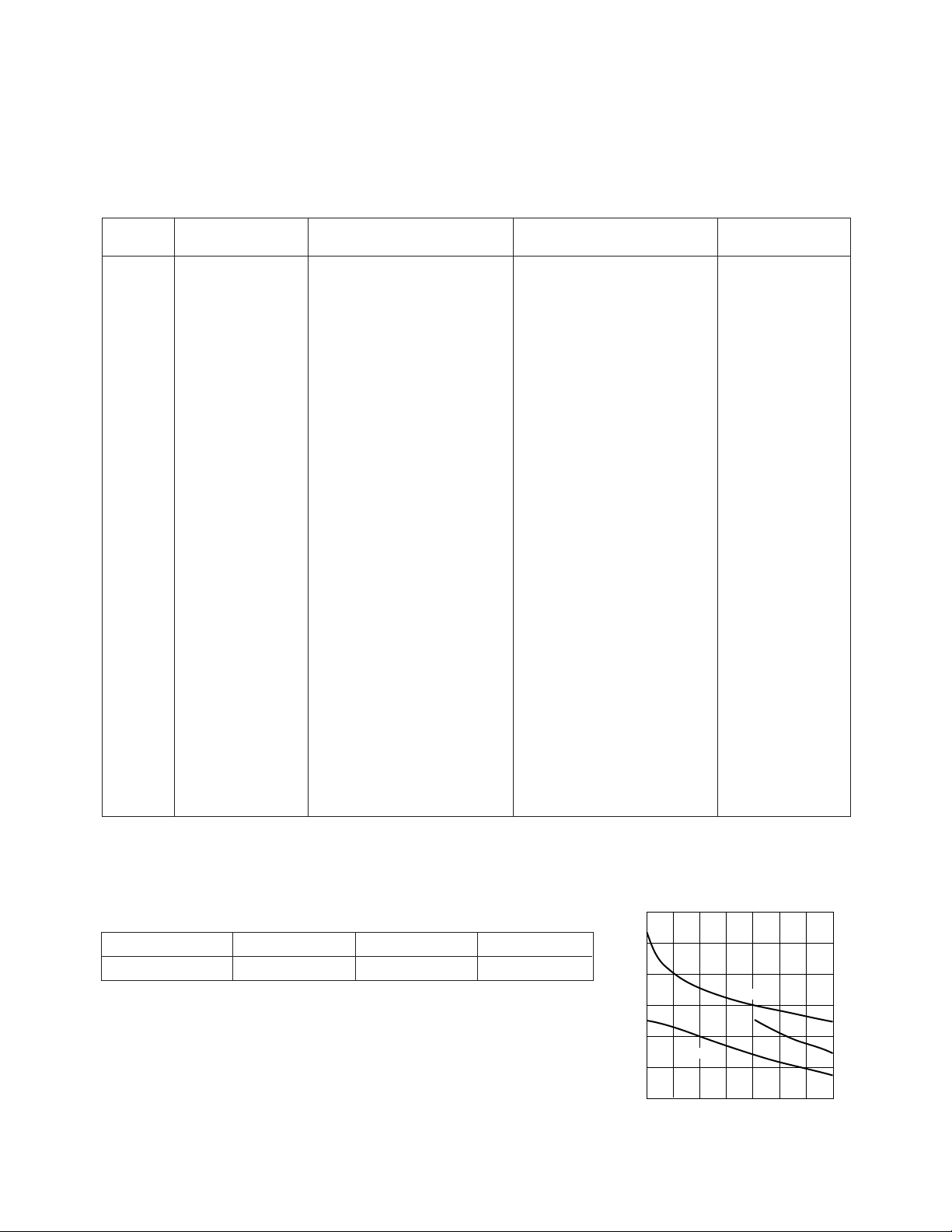
INA-12063 Typical Scattering Parameters
TC=25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vd= 3.0 V
[1]
, IC = 1.5 mA
Freq. S
11
S
21
S
12
S
GHz Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. Mag. Ang.
0.1 0.93 -8 12.6 4.26 172 -42.2 0.01 86 0.99 -3
0.2 0.92 -16 12.5 4.20 164 -36.2 0.02 79 0.99 -7
0.3 0.90 -24 12.3 4.11 157 -32.8 0.02 73 0.98 -10
0.4 0.89 -32 12.0 4.00 149 -30.5 0.03 69 0.96 -13
0.5 0.83 -38 11.7 3.83 141 -29.1 0.04 64 0.94 -16
0.6 0.79 -45 11.3 3.69 135 -27.9 0.04 60 0.93 -19
0.7 0.75 -52 10.9 3.49 128 -26.8 0.05 56 0.91 -21
0.8 0.72 -58 10.4 3.32 122 -26.1 0.05 53 0.89 -23
0.9 0.69 -64 10.1 3.18 116 -25.5 0.05 50 0.87 -26
1.0 0.65 -69 9.6 3.03 111 -24.9 0.06 47 0.86 -28
1.1 0.61 -74 9.2 2.89 106 -24.5 0.06 45 0.84 -30
1.2 0.59 -80 8.7 2.72 102 -24.2 0.06 43 0.83 -32
1.3 0.55 -84 8.4 2.64 97 -23.9 0.06 41 0.82 -34
1.4 0.52 -89 8.1 2.54 92 -23.6 0.07 40 0.81 -35
1.5 0.49 -94 7.7 2.43 88 -23.3 0.07 38 0.80 -37
1.6 0.47 -98 7.3 2.33 84 -23.2 0.07 36 0.79 -39
1.7 0.44 -103 7.0 2.23 80 -22.9 0.07 35 0.78 -40
1.8 0.42 -107 6.6 2.15 77 -22.9 0.07 35 0.77 -42
1.9 0.40 -112 6.4 2.08 73 -22.5 0.07 34 0.77 -44
2.0 0.38 -116 6.0 1.99 69 -22.3 0.08 33 0.76 -45
2.1 0.36 -120 5.7 1.93 66 -22.1 0.08 32 0.75 -47
2.2 0.34 -124 5.3 1.83 63 -22.0 0.08 29 0.74 -49
2.3 0.31 -129 5.2 1.82 59 -21.9 0.08 30 0.74 -51
2.4 0.31 -133 4.7 1.72 57 -22.0 0.08 29 0.73 -52
2.5 0.29 -137 4.6 1.70 54 -21.7 0.08 31 0.73 -54
2.6 0.28 -144 4.3 1.65 50 -21.4 0.08 30 0.73 -56
2.7 0.27 -149 4.1 1.60 47 -21.0 0.09 29 0.72 -58
2.8 0.25 -154 3.7 1.54 44 -20.7 0.09 27 0.71 -60
2.9 0.23 -156 3.5 1.50 41 -20.9 0.09 24 0.70 -61
3.0 0.24 -162 3.5 1.49 39 -21.0 0.09 28 0.71 -63
Note:
1. Reference plane per Figure 31 in Applications Information section.
22
Typical Noise Parameters @ 900 MHz, I
Fmin (dB) Γ
1.4 0.6 36 23
Mag. Γ
opt
opt
Ang.
= 1.5 mA
C
6-119
RN
(Ω)
30
25
20
15
GAIN (dB)
10
5
0
0.1 0.9 1.7 2.5
|S21|
FREQUENCY (GHz)
MSG
MAG
2

INA-12063 Typical Scattering Parameters
[1]
, IC = 2.5 mA
TC=25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vd= 3.0 V
Freq. S
11
S
21
S
12
S
GHz Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. Mag. Ang.
0.1 0.90 -10 16.0 6.33 171 -42.2 0.01 87 0.99 -4
0.2 0.88 -18 15.8 6.19 161 -36.2 0.02 79 0.98 -8
0.3 0.85 -27 15.5 5.98 153 -33.2 0.02 73 0.96 -11
0.4 0.82 -35 15.2 5.74 144 -31.1 0.03 68 0.94 -15
0.5 0.76 -42 14.6 5.37 135 -29.6 0.03 62 0.91 -18
0.6 0.71 -49 14.1 5.07 128 -28.4 0.04 59 0.90 -20
0.7 0.67 -56 13.5 4.73 122 -27.5 0.04 55 0.87 -23
0.8 0.62 -62 12.9 4.43 116 -26.6 0.05 53 0.85 -25
0.9 0.59 -67 12.4 4.18 110 -26.1 0.05 51 0.83 -27
1.0 0.54 -72 11.9 3.93 104 -25.6 0.05 49 0.82 -29
1.1 0.51 -76 11.4 3.71 100 -25.1 0.06 48 0.80 -30
1.2 0.49 -81 10.8 3.47 95 -24.8 0.06 46 0.79 -32
1.3 0.45 -84 10.4 3.31 91 -24.5 0.06 44 0.77 -34
1.4 0.42 -89 10.0 3.15 87 -24.1 0.06 44 0.76 -35
1.5 0.39 -93 9.5 2.98 83 -23.6 0.07 42 0.76 -37
1.6 0.37 -96 9.1 2.84 79 -23.5 0.07 41 0.74 -39
1.7 0.35 -100 8.7 2.72 76 -23.3 0.07 40 0.73 -40
1.8 0.33 -104 8.3 2.60 72 -23.0 0.07 41 0.73 -42
1.9 0.31 -108 8.0 2.51 69 -22.5 0.07 40 0.72 -43
2.0 0.29 -112 7.6 2.40 66 -22.2 0.08 40 0.72 -45
2.1 0.27 -115 7.3 2.31 62 -22.0 0.08 38 0.72 -47
2.2 0.25 -119 6.8 2.20 59 -21.8 0.08 36 0.71 -49
2.3 0.24 -122 6.6 2.15 56 -21.6 0.08 36 0.70 -50
2.4 0.23 -126 6.2 2.05 54 -21.7 0.08 36 0.69 -52
2.5 0.22 -131 6.1 2.01 51 -21.2 0.09 38 0.69 -53
2.6 0.20 -136 5.8 1.95 48 -20.7 0.09 36 0.69 -55
2.7 0.19 -142 5.5 1.89 45 -20.4 0.10 35 0.68 -57
2.8 0.18 -145 5.2 1.81 42 -20.0 0.10 32 0.68 -60
2.9 0.16 -146 4.9 1.75 39 -20.2 0.10 29 0.66 -60
3.0 0.17 -153 4.8 1.75 37 -20.1 0.10 32 0.68 -62
Note:
1. Reference plane per Figure 31 in Applications Information section.
22
Typical Noise Parameters @ 900 MHz, I
Fmin (dB) Γ
1.5 0.54 36 20
Mag. Γ
opt
opt
Ang.
= 2.5 mA
C
6-120
RN
(Ω)
30
25
20
15
GAIN (dB)
10
5
0
0.1 0.9 1.7 2.5
MSG
MAG
2
|S21|
FREQUENCY (GHz)
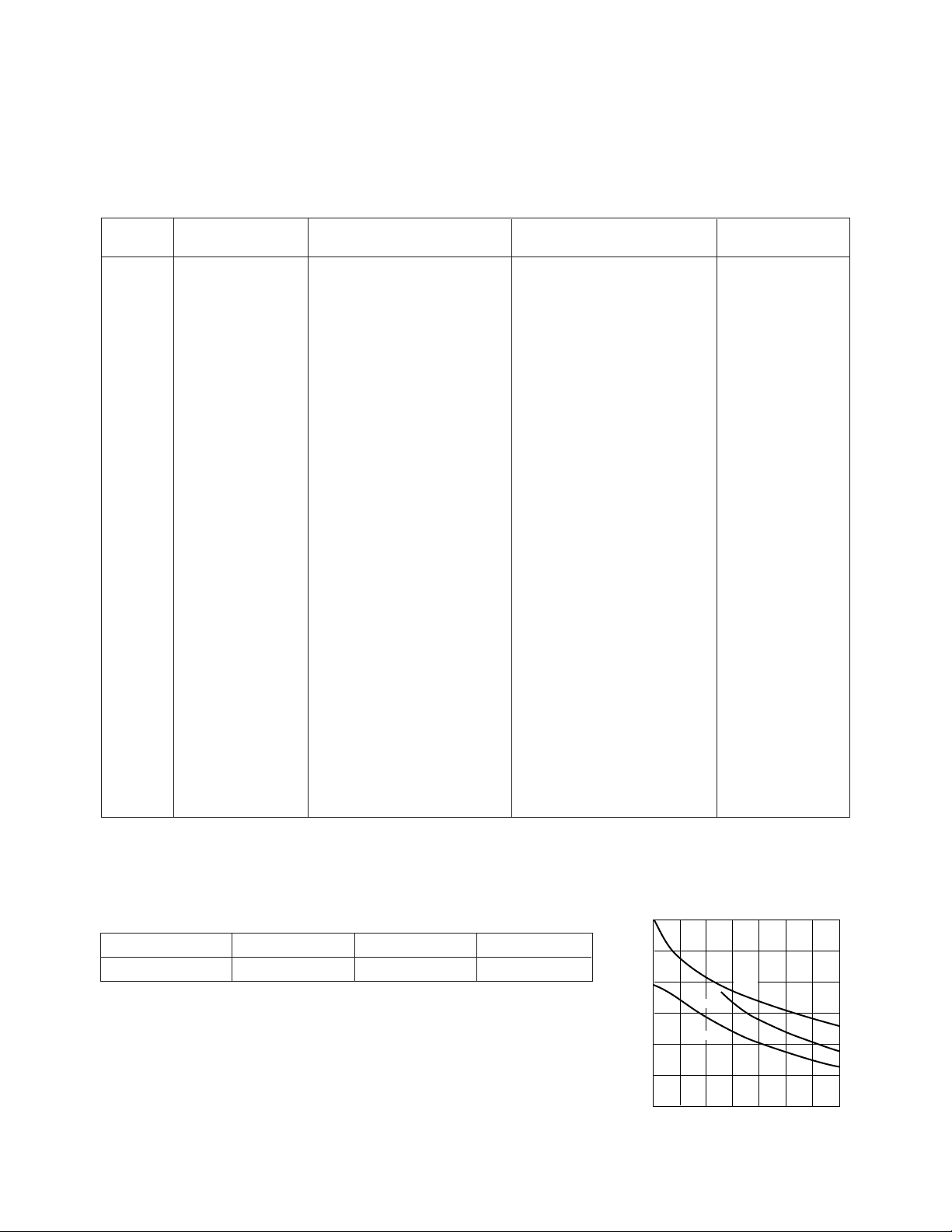
INA-12063 Typical Scattering Parameters
[1]
, IC = 5 mA
TC=25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vd= 3.0 V
Freq. S
11
S
21
S
12
S
GHz Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. Mag. Ang.
0.1 0.86 -11 19.6 9.56 168 -42.2 0.01 79 0.98 -5
0.2 0.82 -22 19.3 9.18 157 -36.8 0.01 73 0.96 -10
0.3 0.78 -31 18.7 8.65 146 -33.8 0.02 71 0.93 -13
0.4 0.73 -40 18.1 8.07 137 -31.7 0.03 68 0.90 -17
0.5 0.65 -46 17.3 7.34 128 -30.4 0.03 62 0.86 -20
0.6 0.59 -53 16.6 6.75 120 -28.7 0.04 61 0.85 -22
0.7 0.55 -59 15.8 6.18 114 -28.0 0.04 59 0.82 -24
0.8 0.50 -64 15.1 5.68 108 -27.2 0.04 56 0.80 -26
0.9 0.46 -68 14.4 5.26 103 -26.9 0.04 55 0.78 -27
1.0 0.43 -72 13.8 4.88 97 -26.3 0.05 52 0.77 -29
1.1 0.40 -76 13.2 4.55 93 -25.8 0.05 52 0.74 -30
1.2 0.37 -79 12.6 4.24 89 -25.3 0.05 52 0.74 -32
1.3 0.35 -81 12.0 3.99 85 -24.8 0.06 51 0.72 -34
1.4 0.33 -85 11.5 3.76 81 -24.3 0.06 50 0.72 -35
1.5 0.30 -87 11.0 3.55 78 -23.9 0.06 48 0.71 -36
1.6 0.28 -90 10.5 3.37 75 -23.5 0.07 48 0.70 -38
1.7 0.27 -94 10.1 3.21 71 -23.2 0.07 47 0.69 -39
1.8 0.25 -95 9.7 3.05 68 -22.9 0.07 48 0.69 -41
1.9 0.23 -99 9.3 2.93 64 -22.2 0.08 46 0.69 -42
2.0 0.22 -101 9.0 2.81 61 -22.0 0.08 45 0.68 -44
2.1 0.20 -104 8.5 2.67 58 -21.6 0.08 43 0.67 -45
2.2 0.18 -104 8.1 2.55 56 -21.3 0.09 41 0.67 -48
2.3 0.17 -107 7.8 2.47 53 -21.1 0.09 41 0.66 -50
2.4 0.17 -109 7.5 2.37 51 -20.8 0.09 41 0.66 -51
2.5 0.15 -114 7.3 2.31 48 -20.5 0.09 42 0.65 -53
2.6 0.14 -118 7.0 2.24 45 -20.0 0.10 40 0.66 -55
2.7 0.13 -123 6.7 2.17 42 -19.6 0.11 39 0.64 -56
2.8 0.12 -125 6.4 2.08 39 -19.3 0.11 36 0.63 -59
2.9 0.11 -126 6.1 2.02 37 -19.3 0.11 33 0.62 -59
3.0 0.11 -133 6.0 2.00 35 -19.3 0.11 35 0.64 -61
Note:
1. Reference plane per Figure 31 in Applications Information section.
22
Typical Noise Parameters @ 900 MHz, I
Fmin (dB) Γ
1.8 0.41 38 16
Mag. Γ
opt
opt
Ang.
= 5 mA
C
6-121
RN
(Ω)
30
25
20
15
GAIN (dB)
10
5
0
0.1 0.9 1.7 2.5
MSG
MAG
2
|S21|
FREQUENCY (GHz)

INA-12063 Typical Scattering Parameters
[1]
, IC = 8 mA
TC=25°C, ZO = 50 Ω, Vd= 3.0 V
Freq. S
11
S
21
S
12
S
GHz Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. dB Mag. Ang. Mag. Ang.
0.1 0.80 -13 22.3 12.97 166 -41.9 0.01 73 0.98 -5
0.2 0.76 -24 21.7 12.17 152 -37.4 0.01 72 0.94 -11
0.3 0.69 -35 20.9 11.10 141 -33.9 0.02 75 0.90 -15
0.4 0.63 -44 20.1 10.06 130 -32.2 0.02 69 0.86 -18
0.5 0.55 -49 19.0 8.89 121 -30.6 0.03 64 0.83 -21
0.6 0.50 -55 18.1 8.00 114 -29.6 0.03 64 0.80 -23
0.7 0.45 -59 17.1 7.20 107 -28.9 0.04 59 0.77 -24
0.8 0.41 -64 16.3 6.56 102 -28.0 0.04 59 0.76 -25
0.9 0.37 -67 15.6 6.02 97 -26.9 0.05 58 0.73 -26
1.0 0.34 -69 14.9 5.53 92 -26.5 0.05 58 0.71 -29
1.1 0.32 -72 14.1 5.08 88 -25.9 0.05 57 0.71 -30
1.2 0.30 -76 13.5 4.72 84 -25.4 0.05 56 0.70 -31
1.3 0.28 -76 12.9 4.40 81 -24.7 0.06 55 0.69 -33
1.4 0.26 -79 12.4 4.18 77 -24.1 0.06 53 0.68 -34
1.5 0.24 -82 11.7 3.86 74 -23.5 0.07 53 0.67 -36
1.6 0.23 -81 11.4 3.71 71 -23.4 0.07 52 0.65 -38
1.7 0.21 -84 10.8 3.48 68 -22.8 0.07 52 0.66 -39
1.8 0.20 -85 10.5 3.34 65 -22.7 0.07 51 0.66 -41
1.9 0.19 -89 9.9 3.14 62 -22.0 0.08 50 0.67 -42
2.0 0.17 -88 9.6 3.01 59 -21.5 0.08 48 0.66 -44
2.1 0.17 -91 9.2 2.89 56 -21.2 0.09 47 0.64 -45
2.2 0.15 -91 8.8 2.77 53 -21.0 0.09 44 0.63 -47
2.3 0.14 -93 8.6 2.68 51 -20.6 0.09 43 0.64 -49
2.4 0.14 -94 8.3 2.59 48 -20.4 0.09 43 0.64 -49
2.5 0.13 -98 8.0 2.51 47 -19.9 0.10 43 0.63 -51
2.6 0.12 -102 7.7 2.42 43 -19.5 0.11 42 0.61 -53
2.7 0.11 -103 7.3 2.32 40 -19.0 0.11 41 0.61 -56
2.8 0.10 -107 7.1 2.25 37 -18.6 0.12 38 0.61 -58
2.9 0.10 -101 6.7 2.17 36 -18.7 0.12 34 0.58 -60
3.0 0.09 -110 6.8 2.18 34 -18.7 0.12 35 0.61 -60
Note:
1. Reference plane per Figure 31 in Applications Information section.
22
Typical Noise Parameters @ 900 MHz, I
Fmin (dB) Γ
2.0 0.30 41 15
Mag. Γ
opt
opt
Ang.
= 8 mA
C
6-122
RN
(Ω)
30
25
20
15
GAIN (dB)
10
5
0
0.1 0.9 1.7 2.5
MAG
|S21|
FREQUENCY (GHz)
MSG
2
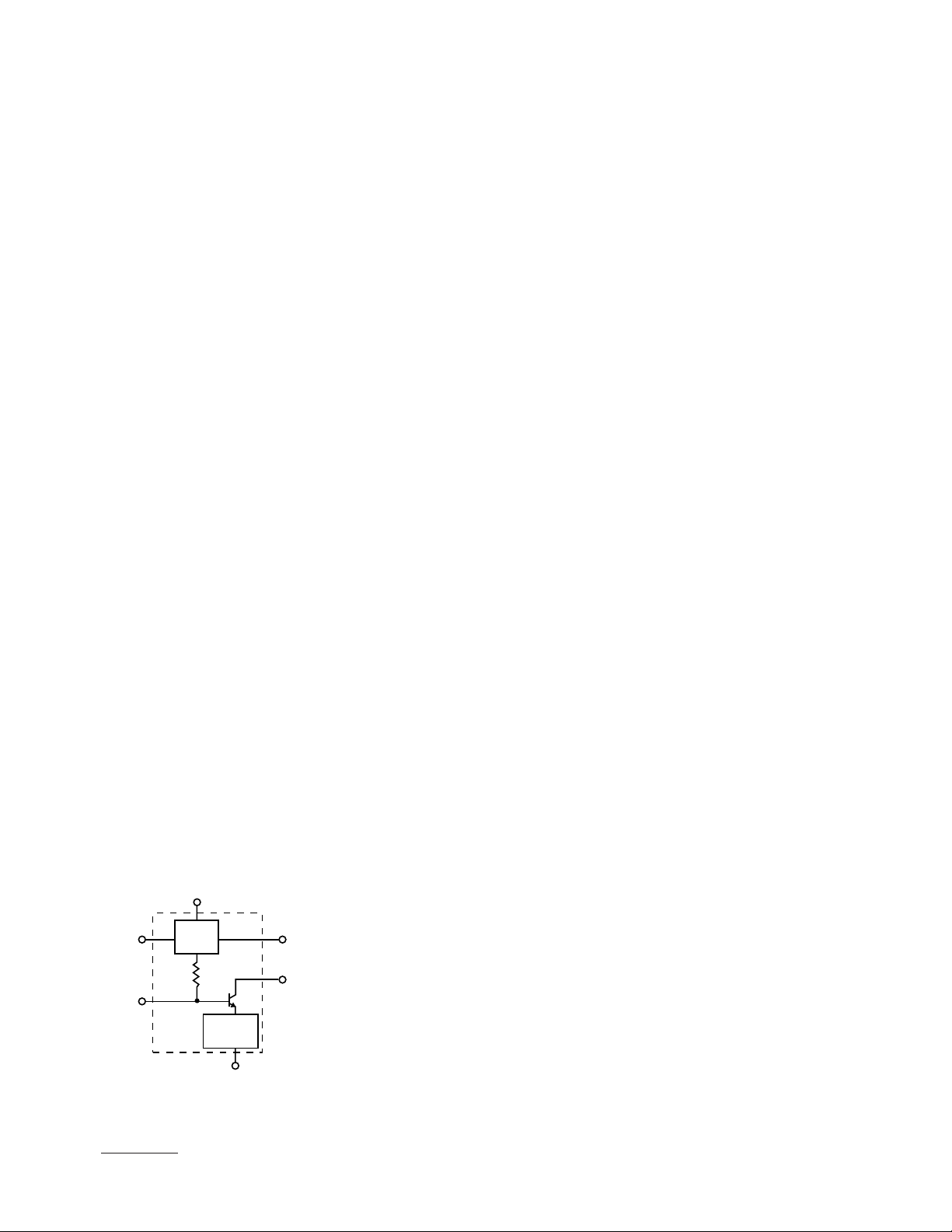
INA-12063 Applications Information
Introduction
The INA-12063 is a unique RFIC
configuration that combines the
performance flexibility of a
discrete transistor with the
simplicity of using an integrated
circuit.
The INA-12063 is an integrated
circuit that combines three
functions: (1) a silicon bipolar RF
transistor, (2) an RF feedback
network, and (3) a patented
bias regulation circuit. A simplified schematic diagram of the
INA-12063 is shown in Figure 9.
The result is a versatile gain stage
that can be operated from a single
+1.5 to +5 volt power supply with
the device current set by the user.
The INA-12063 is designed for use
in battery powered equipment
demanding high performance
with low supply voltages and
minimal current drain. Typical
applications for the INA-12063
include low noise RF amplifiers,
IF amplifiers, gain and buffer
stages through 2 GHz. The
INA-12063 is an excellent choice
for use in cellular and cordless
telephones, PCS, W/LAN’s, RF
modems and other commercial
wireless equipment.
V
d
ACTIVE
GND 2
RF
INPUT
Figure 9. INA-12063 Schematic.
BIAS
CIRCUIT
TRANSISTOR
FEEDBACK
GND 1
RF
RF
NETWORK
[1]
I
bias
RF
OUTPUT
and V
c
Description
The active bias circuit solves
three problems normally encountered with traditional approaches
for biasing discrete transistors.
First, as an active bias circuit, the
emitter of the RF transistor is DC
grounded. This permits the
collector current to be controlled
without the need for resistors
and/or bypass capacitors in the
emitter that may degrade RF
performance.
Second, the internal bias circuit
greatly simplifies the design tasks
commonly associated with biasing transistors, such as accurately
regulating the collector current,
allowing for variations in hFE,
making a non-intrusive DC
connection to the base of the
transistor, and stabilizing current
over temperature.
And, third, the integrated bias
circuit eliminates the cost, parts
count, and associated PCB space
required for as many as 8 additional DC components.
The integrated bias control circuit
is very easy to use. For most
applications, the collector current
for the RF transistor can be set
with a single resistor.
The geometry of the integrated
RF transistor is designed to
provide an excellent balance
between low noise figure, high
gain, and good dynamic range
while retaining practical impedance matching levels. The operating current is typically in the 1 to
10 mA range.
The integrated RF feedback
contains an inductive element in
the emitter circuit of the RF
transistor. This series feedback
configuration is of the type often
implemented in discrete transistor designs for the purpose of
improving stability and bringing
the optimum noise match at the
input of the transistor closer to
50␣ Ω. The result is that for many
applications, a simple, series
inductor is often all that is needed
to adequately match the input of
the INA-12063 to 50 Ω.
In contrast to amplifiers that use
resistive feedback to achieve
broadband 50 Ω input and output
matches, the INA-12063 leaves
the designer with the flexibility of
optimizing performance for a
particular frequency band. For
example, frequency selective
input and output impedance
matching circuits can be used to
tune for optimum NF, maximum
output power, low input VSWR,
or to tailor the passband response
to eliminate undesirable gain
responses.
Setting the Bias Current
The integrated, active bias circuit
is a 10:1 current mirror. The
current mirror forces the collector current in the RF transistor to
be approximately 10 times the
current supplied to the I
In normal use, a voltage between
+1.5 and +5 volts, is applied to
both the Vd and Vc terminals of
the INA-12063. Although normally
connected to the same supply
voltage, it is not necessary that
both Vd and Vc be at the same
voltage.
The collector current of the RF
transistor is then set by injecting
a small control current into the
I
pin that is approximately
bias
1/10 of the desired collector
current.
bias
pin.
1
U.S. Patent Number 5436595
6-123
 Loading...
Loading...