Page 1
hp40g+.book Page i Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
HP 40gs graphing calculator
user's guide
Edition1
Part Number F2225AA-90001
Page 2
title.fm Page ii Friday, February 17, 2006 9:48 AM
Notice
REGISTER YOUR PRODUCT AT: www.register.hp.com
THIS MANUAL AND ANY EXAMPLES CONTAINED HEREIN ARE
PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT
NOTICE. HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
HEWLETT-PACKARD CO. SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY
ERRORS OR FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
IN CONNECTION WITH THE FURNISHING, PERFORMANCE, OR
USE OF THIS MANUAL OR THE EXAMPLES CONTAINED HEREIN.
© Copyright 1994-1995, 1999-2000, 2003, 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of this manual is prohibited without
prior written permission of Hewlett-Packard Company, except as allowed
under the copyright laws.
Hewlett-Packard Company
4995 Murphy Canyon Rd,
Suite 301
San Diego, CA 92123
Printing History
Edition 1 April 2005
Page 3
hp40g+.book Page iii Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Contents
Preface
Manual conventions .............................................................. P-1
Notice ................................................................................. P-2
1 Getting started
On/off, cancel operations......................................................1-1
The display ..........................................................................1-2
The keyboard .......................................................................1-3
Menus .................................................................................1-8
Input forms ...........................................................................1-9
Mode settings.....................................................................1-10
Setting a mode...............................................................1-11
Aplets (E-lessons).................................................................1-12
Aplet library ..................................................................1-16
Aplet views....................................................................1-16
Aplet view configuration..................................................1-18
Mathematical calculations ....................................................1-19
Using fractions....................................................................1-25
Complex numbers ...............................................................1-29
Catalogs and editors ...........................................................1-30
2 Aplets and their views
Aplet views ..........................................................................2-1
About the Symbolic view ...................................................2-1
Defining an expression (Symbolic view) ..............................2-1
Evaluating expressions ......................................................2-3
About the Plot view...........................................................2-5
Setting up the plot (Plot view setup).....................................2-5
Exploring the graph..........................................................2-7
Other views for scaling and splitting the graph ..................2-13
About the numeric view...................................................2-16
Setting up the table (Numeric view setup) ..........................2-16
Exploring the table of numbers.........................................2-17
Building your own table of numbers..................................2-19
“Build Your Own” menu keys...........................................2-20
Example: plotting a circle ................................................2-20
3 Function aplet
About the Function aplet ........................................................3-1
Getting started with the Function aplet.................................3-1
iii
Page 4
hp40g+.book Page iv Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Function aplet interactive analysis........................................... 3-9
Plotting a piecewise-defined function ................................ 3-12
4 Parametric aplet
About the Parametric aplet .................................................... 4-1
Getting started with the Parametric aplet............................. 4-1
5 Polar aplet
Getting started with the Polar aplet ......................................... 5-1
6 Sequence aplet
About the Sequence aplet...................................................... 6-1
Getting started with the Sequence aplet .............................. 6-1
7 Solve aplet
About the Solve aplet............................................................ 7-1
Getting started with the Solve aplet .................................... 7-2
Use an initial guess............................................................... 7-5
Interpreting results ................................................................ 7-6
Plotting to find guesses .......................................................... 7-7
Using variables in equations ................................................ 7-10
8 Linear Solver aplet
About the Linear Solver aplet ................................................. 8-1
Getting started with the Linear Solver aplet.......................... 8-1
9 Triangle Solve aplet
About the Triangle Solver aplet .............................................. 9-1
Getting started with the Triangle Solver aplet....................... 9-1
10 Statistics aplet
About the Statistics aplet...................................................... 10-1
Getting started with the Statistics aplet.............................. 10-1
Entering and editing statistical data ...................................... 10-6
Defining a regression model.......................................... 10-12
Computed statistics ........................................................... 10-14
Plotting............................................................................ 10-15
Plot types .................................................................... 10-16
Fitting a curve to 2VAR data ......................................... 10-17
Setting up the plot (Plot setup view) ................................ 10-18
Trouble-shooting a plot ................................................. 10-19
Exploring the graph ..................................................... 10-19
Calculating predicted values ......................................... 10-20
11 Inference aplet
iv
Page 5
hp40g+.book Page v Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
About the Inference aplet .....................................................11-1
Getting started with the Inference aplet .............................11-1
Importing sample statistics from the Statistics aplet..............11-4
Hypothesis tests ..................................................................11-8
One-Sample Z-Test..........................................................11-8
Two-Sample Z-Test ..........................................................11-9
One-Proportion Z-Test....................................................11-10
Two-Proportion Z-Test ....................................................11-11
One-Sample T-Test ........................................................11-12
Two-Sample T-Test ........................................................11-14
Confidence intervals..........................................................11-15
One-Sample Z-Interval...................................................11-15
Two-Sample Z-Interval ...................................................11-16
One-Proportion Z-Interval...............................................11-17
Two-Proportion Z-Interval ...............................................11-17
One-Sample T-Interval ...................................................11-18
Two-Sample T-Interval....................................................11-19
12 Using the Finance Solver
Background........................................................................12-1
Performing TVM calculations ................................................12-4
Calculating Amortizations................................................12-7
13 Using mathematical functions
Math functions....................................................................13-1
The MATH menu ............................................................13-1
Math functions by category ..................................................13-2
Keyboard functions.........................................................13-3
Calculus functions...........................................................13-6
Complex number functions...............................................13-7
Constants ......................................................................13-8
Conversions...................................................................13-8
Hyperbolic trigonometry..................................................13-9
List functions ................................................................13-10
Loop functions..............................................................13-10
Matrix functions ...........................................................13-11
Polynomial functions .....................................................13-11
Probability functions......................................................13-12
Real-number functions ...................................................13-14
Two-variable statistics....................................................13-17
Symbolic functions........................................................13-17
Test functions ...............................................................13-19
Trigonometry functions ..................................................13-20
v
Page 6
hp40g+.book Page vi Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Symbolic calculations........................................................ 13-20
Finding derivatives....................................................... 13-21
Program constants and physical constants ........................... 13-24
Program constants........................................................ 13-25
Physical constants ........................................................ 13-25
14 Computer Algebra System (CAS)
What is a CAS? ................................................................. 14-1
Performing symbolic calculations .......................................... 14-1
An example .................................................................. 14-2
CAS variables.................................................................... 14-4
The current variable ....................................................... 14-4
CAS modes ....................................................................... 14-5
Using CAS functions in HOME ............................................. 14-7
Online Help....................................................................... 14-8
CAS functions in the Equation Writer .................................... 14-9
ALGB menu................................................................. 14-10
DIFF menu................................................................... 14-16
REWRI menu ............................................................... 14-28
SOLV menu................................................................. 14-33
TRIG menu .................................................................. 14-38
CAS Functions on the MATH menu ..................................... 14-45
Algebra menu ............................................................. 14-45
Complex menu ............................................................ 14-45
Constant menu ............................................................ 14-46
Diff & Int menu ............................................................ 14-46
Hyperb menu .............................................................. 14-46
Integer menu ............................................................... 14-46
Modular menu............................................................. 14-51
Polynomial menu ......................................................... 14-55
Real menu................................................................... 14-60
Rewrite menu .............................................................. 14-60
Solve menu ................................................................. 14-60
Tests menu .................................................................. 14-61
Trig menu ................................................................... 14-61
CAS Functions on the CMDS menu ..................................... 14-62
15 Equation Writer
Using CAS in the Equation Writer ....................................... 15-1
The Equation Writer menu bar......................................... 15-1
Configuration menus ...................................................... 15-3
Entering expressions and subexpressions............................... 15-5
How to modify an expression ....................................... 15-11
vi
Page 7
hp40g+.book Page vii Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Accessing CAS functions....................................................15-12
Equation Writer variables .................................................15-16
Predefined CAS variables .............................................15-16
The keyboard in the Equation Writer ..............................15-17
16 Step-by-Step Examples
Introduction .......................................................................16-1
17 Variables and memory management
Introduction ........................................................................17-1
Storing and recalling variables .............................................17-2
The VARS menu ..................................................................17-4
Memory Manager...............................................................17-9
18 Matrices
Introduction ........................................................................18-1
Creating and storing matrices...............................................18-2
Working with matrices.........................................................18-4
Matrix arithmetic.................................................................18-6
Solving systems of linear equations ...................................18-8
Matrix functions and commands..........................................18-10
Argument conventions...................................................18-10
Matrix functions ...........................................................18-10
Examples .........................................................................18-13
19 Lists
Displaying and editing lists...................................................19-4
Deleting lists ..................................................................19-6
Transmitting lists .............................................................19-6
List functions .......................................................................19-6
Finding statistical values for list elements ................................19-9
20 Notes and sketches
Introduction ........................................................................20-1
Aplet note view...................................................................20-1
Aplet sketch view ................................................................20-3
The notepad.......................................................................20-6
21 Programming
Introduction ........................................................................21-1
Program catalog ............................................................21-2
Creating and editing programs.............................................21-4
Using programs ..................................................................21-7
Customizing an aplet...........................................................21-9
vii
Page 8
hp40g+.book Page viii Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Aplet naming convention .............................................. 21-10
Example ..................................................................... 21-10
Programming commands ................................................... 21-13
Aplet commands.......................................................... 21-14
Branch commands ....................................................... 21-17
Drawing commands ..................................................... 21-19
Graphic commands...................................................... 21-21
Loop commands .......................................................... 21-23
Matrix commands ........................................................ 21-24
Print commands ........................................................... 21-25
Prompt commands........................................................ 21-26
Stat-One and Stat-Two commands.................................. 21-29
Stat-Two commands ..................................................... 21-30
Storing and retrieving variables in programs ................... 21-31
Plot-view variables ....................................................... 21-31
Symbolic-view variables................................................ 21-38
Numeric-view variables ................................................ 21-40
Note variables............................................................. 21-43
Sketch variables .......................................................... 21-43
22 Extending aplets
Creating new aplets based on existing aplets......................... 22-1
Using a customized aplet................................................ 22-3
Resetting an aplet ............................................................... 22-3
Annotating an aplet with notes............................................. 22-4
Annotating an aplet with sketches......................................... 22-4
Downloading e-lessons from the web .................................... 22-4
Sending and receiving aplets............................................... 22-4
Sorting items in the aplet library menu list.............................. 22-6
Reference information
Glossary.............................................................................. R-1
Resetting the HP 40gs ........................................................... R-3
To erase all memory and reset defaults ............................... R-3
If the calculator does not turn on ........................................ R-4
Operating details ................................................................. R-4
Batteries ......................................................................... R-4
Variables............................................................................. R-6
Home variables ............................................................... R-6
Function aplet variables.................................................... R-7
Parametric aplet variables................................................. R-8
Polar aplet variables ........................................................ R-9
Sequence aplet variables ................................................ R-10
viii
Page 9
hp40g+.book Page ix Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Solve aplet variables.......................................................R-11
Statistics aplet variables ..................................................R-12
MATH menu categories .......................................................R-13
Math functions ...............................................................R-13
Program constants ..........................................................R-15
Physical Constants ..........................................................R-16
CAS functions ................................................................R-17
Program commands........................................................R-19
Status messages..................................................................R-20
Limited Warranty
Service.......................................................................... W-3
Regulatory Notices ......................................................... W-5
Index
ix
Page 10
hp40g+.book Page x Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Page 11
hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Preface
The HP 40gs is a feature-rich graphing calculator. It is
also a powerful mathematics learning tool, with a built-in
computer algebra system (CAS). The HP 40gs is designed
so that you can use it to explore mathematical functions
and their properties.
You can get more information on the HP 40gs from
Hewlett-Packard’s Calculators web site. You can
download customized aplets from the web site and load
them onto your calculator. Customized aplets are special
applications developed to perform certain functions, and
to demonstrate mathematical concepts.
Hewlett Packard’s Calculators web site can be found at:
http://www.hp.com/calculators
Manual conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual to
represent the keys that you press and the menu options
that you choose to perform the described operations.
• Key presses are represented as follows:
, , , etc.
• Shift keys, that is the key functions that you access by
pressing the key first, are represented as
follows:
CLEAR, MODES, ACOS, etc.
• Numbers and letters are represented normally, as
follows:
5, 7, A, B, etc.
• Menu options, that is, the functions that you select
using the menu keys at the top of the keypad are
represented as follows:
, , .
• Input form fields and choose list items are represented
as follows:
Function, Polar, Parametric
• Your entries as they appear on the command line or
within input forms are represented as follows:
2
2*X
-3X+5
P-1
Page 12
Preface.fm Page 2 Friday, February 17, 2006 9:47 AM
Notice
This manual and any examples contained herein are
provided as-is and are subject to change without notice.
Except to the extent prohibited by law, Hewlett-Packard
Company makes no express or implied warranty of any
kind with regard to this manual and specifically disclaims
the implied warranties and conditions of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose and Hewlett-Packard
Company shall not be liable for any errors or for
incidental or consequential damage in connection with
the furnishing, performance or use of this manual and the
examples herein.
Copyright 1994-1995, 1999-2000, 2003, 2006
©
Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The programs that control your HP 40gs are copyrighted
and all rights are reserved. Reproduction, adaptation, or
translation of those programs without prior written
permission from Hewlett-Packard Company is also
prohibited.
P-2
Page 13
hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Getting started
On/off, cancel operations
To turn on Press to turn on the calculator.
To cancel When the calculator is on, the key cancels the
current operation.
To turn off Press OFF to turn the calculator off.
To save power, the calculator turns itself off after several
minutes of inactivity. All stored and displayed information
is saved.
If you see the ((•)) annunciator or the Low Bat message,
then the calculator needs fresh batteries.
1
HOME HOME is the calculator’s home view and is common to all
aplets. If you want to perform calculations, or you want to
quit the current activity (such as an aplet, a program, or
an editor), press . All mathematical functions are
available in the HOME. The name of the current aplet is
displayed in the title of the home view.
Protective cover The calculator is provided with a slide cover to protect the
display and keyboard. Remove the cover by grasping
both sides of it and pulling down.
You can reverse the slide cover and slide it onto the back
of the calculator. this will help prevent you losing the
cover while you are using the calculator.
To prolong the life of the calculator, always place the
cover over the display and keyboard when you are not
using the calculator.
Getting started 1-1
Page 14
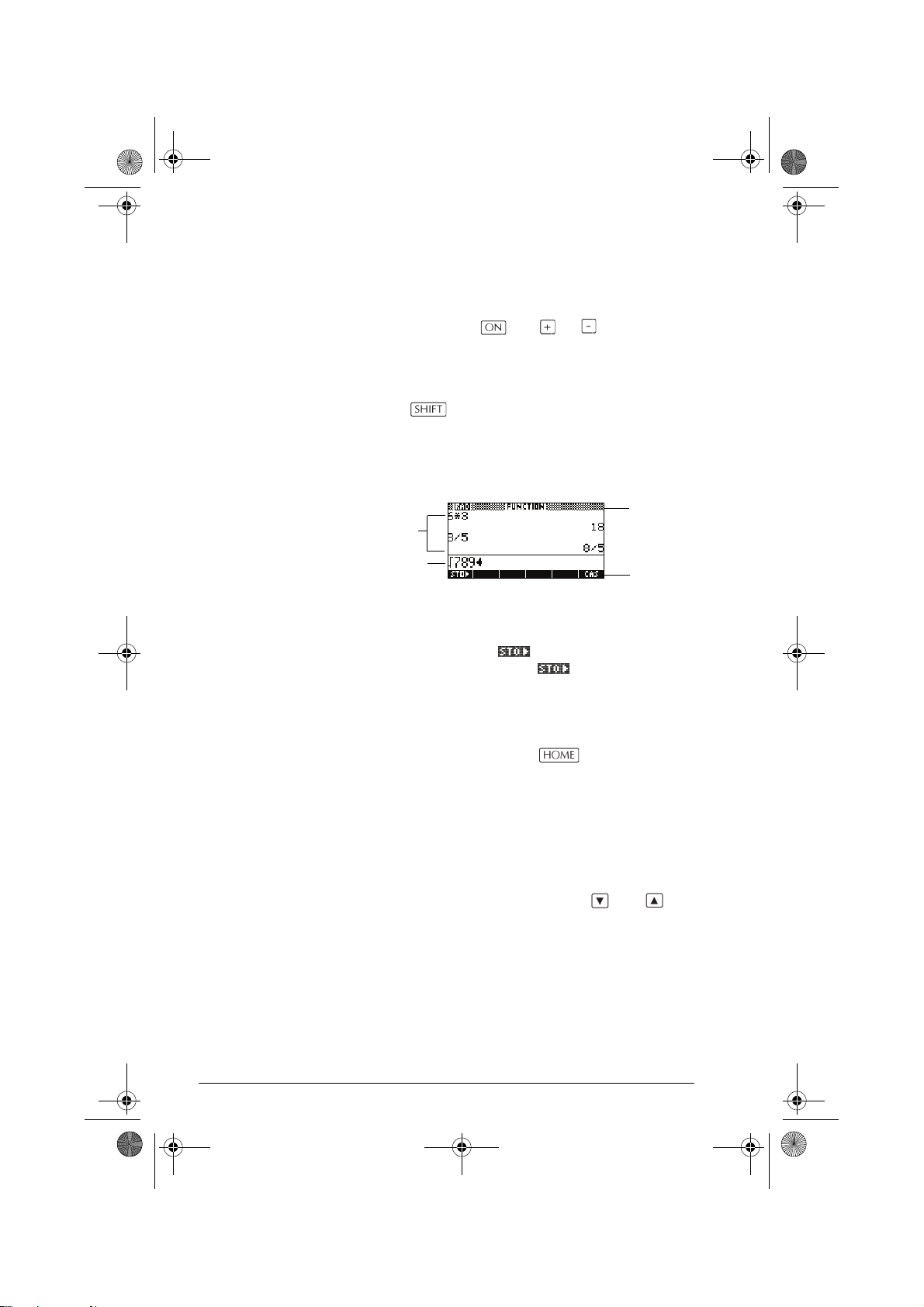
hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
The display
To adjust the
contrast
Simultaneously press and (or ) to increase (or
decrease) the contrast.
To clear the display • Press CANCEL to clear the edit line.
• Press
display history.
CLEAR to clear the edit line and the
Parts of the
display
History
Edit line
Menu key or soft key labels. The labels for the menu
keys’ current meanings. is the label for the first
menu key in this picture. “Press ” means to press the
first menu key, that is, the leftmost top-row key on the
calculator keyboard.
Edit line. The line of current entry.
History. The HOME display ( ) shows up to four
lines of history: the most recent input and output. Older
lines scroll off the top of the display but are retained in
memory.
Title. The name of the current aplet is displayed at the top
of the HOME view. RAD, GRD, DEG specify whether
Radians, Grads or Degrees angle mode is set for HOME.
T and S symbols indicate whether there is more
The
history in the HOME display. Press the and to
scroll in the HOME display.
Title
Menu key
labels
1-2 Getting started
Page 15
hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Annunciators. Annunciators are symbols that appear
above the title bar and give you important status
information.
Annunciator Description
α Alpha in effect for next keystroke.
((•)) Low battery power.
Data is being transferred.
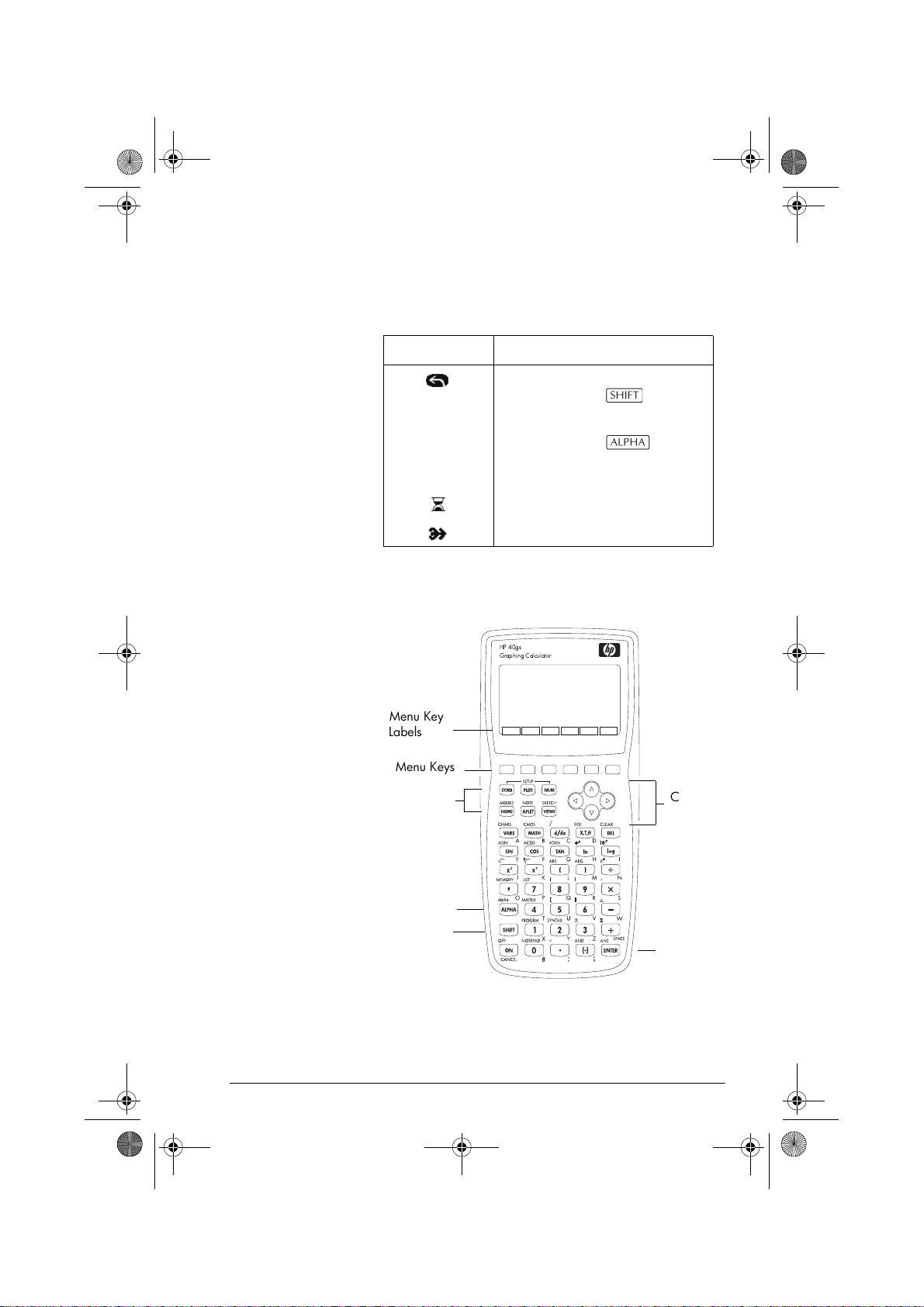
The keyboard
Shift in effect for next keystroke.
To cancel, press again.
To cancel, press again.
Busy.
HP 40gs
Graphing Calculator
Menu Key
Labels
Menu Keys
Aplet Control
Keys
Alpha Key
Shift Key
Getting started 1-3
Cursor
Keys
Enter
Key
Page 16
hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
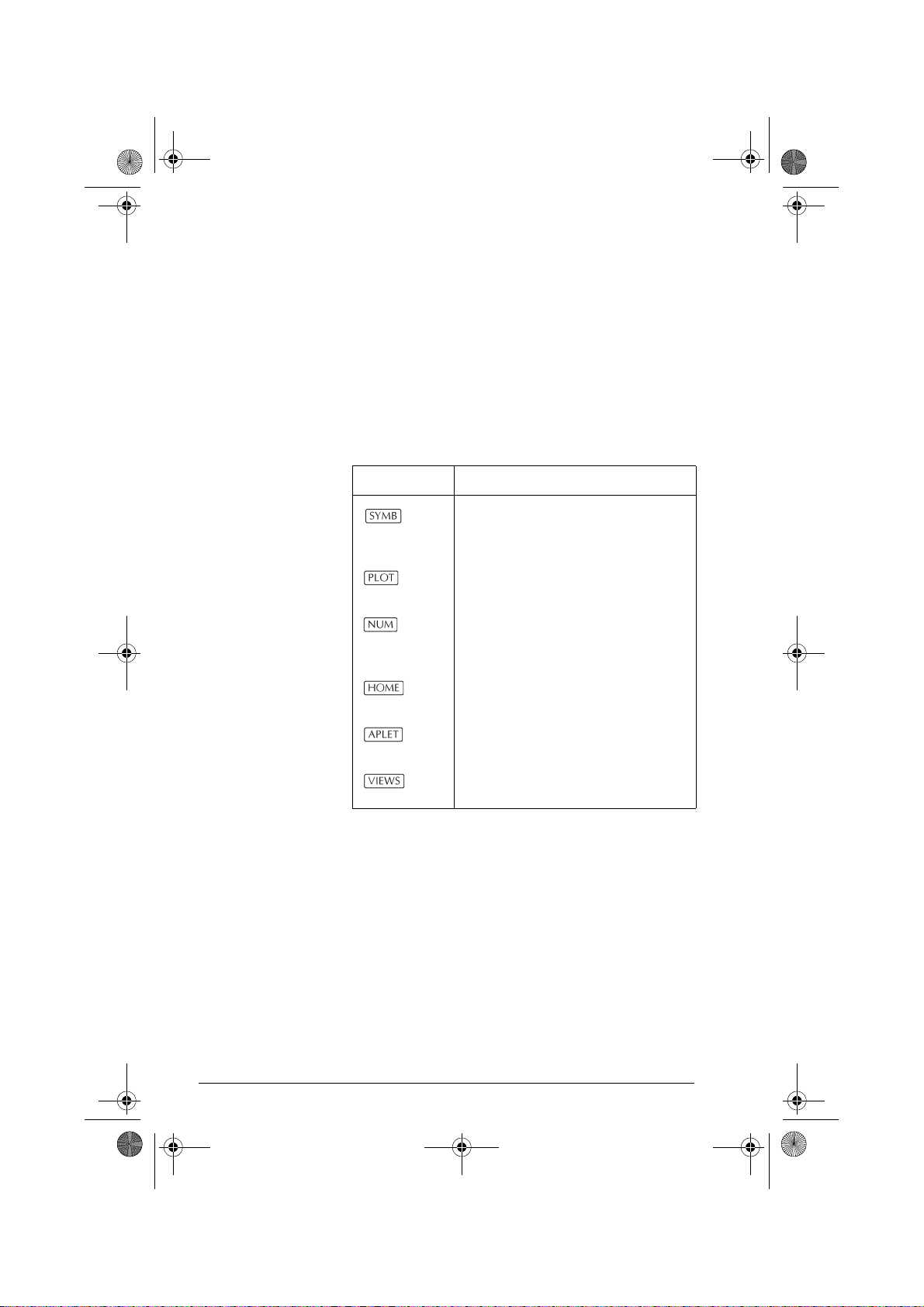
Menu keys
• On the calculator keyboard, the top row of keys are
called menu keys. Their meanings depend on the
context—that’s why they are blank. The menu keys
are sometimes called “soft keys”.
• The bottom line of the display shows the labels for the
menu keys’ current meanings.
Aplet control keys
The aplet control keys are:
Key Meaning
Displays the Symbolic view for the
current aplet. See “Symbolic view”
on page 1-16.
Displays the Plot view for the current
aplet. See “Plot view” on page 1-16.
Displays the Numeric view for the
current aplet. See “Numeric view” on
page 1-17.
Displays the HOME view. See
“HOME” on page 1-1.
Displays the Aplet Library menu. See
“Aplet library” on page 1-16.
Displays the VIEWS menu. See
“Aplet views” on page 1-16.
1-4 Getting started
Page 17
hp40g+.book Page 5 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Entry/Edit keys
The entry and edit keys are:
Key Meaning
(
CANCEL)
CLEAR
, , ,
Cancels the current operation if the
calculator is on by pressing .
Pressing , then
OFF turns the
calculator off.
Accesses the function printed in blue
above a key.
Returns to the HOME view, for
performing calculations.
Accesses the alphabetical
characters printed in orange below
a key. Hold down to enter a string
of characters.
Enters an input or executes an
operation. In calculations,
acts like “=”. When or
is present as a menu key,
acts the same as pressing or
.
Enters a negative number. To enter
–25, press 25. Note: this is not
the same operation that the subtract
button performs ().
Enters the independent variable by
inserting X, T, θ, or N into the edit
line, depending on the current
active aplet.
Deletes the character under the
cursor. Acts as a backspace key if
the cursor is at the end of the line.
Clears all data on the screen. On a
settings screen, for example Plot
Setup, CLEAR returns all
settings to their default values.
Moves the cursor around the
display. Press first to move to
the beginning, end, top or bottom.
Getting started 1-5
Page 18
hp40g+.book Page 6 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Key Meaning (Continued)
CHARS Displays a menu of all available
characters. To type one, use the
arrow keys to highlight it, and press
select each and press , then
press .
Shifted keystrokes
There are two shift keys that you use to access the
operations and characters printed above the keys:
and .
Key Description
Press the key to access the
operations printed in blue above the
keys. For instance, to access the
Modes screen, press , then
press . (MODES is labeled in
blue above the key). You do
not need to hold down when
you press HOME. This action is
depicted in this manual as “press
To cancel a shift, press again.
. To select multiple characters,
MODES.”
The alphabetic keys are also shifted
keystrokes. For instance, to type Z,
press Z. (The letters are
printed in orange to the lower right of
each key.)
To cancel Alpha, press
again.
For a lower case letter, press
.
For a string of letters, hold down
while typing.
1-6 Getting started
Page 19
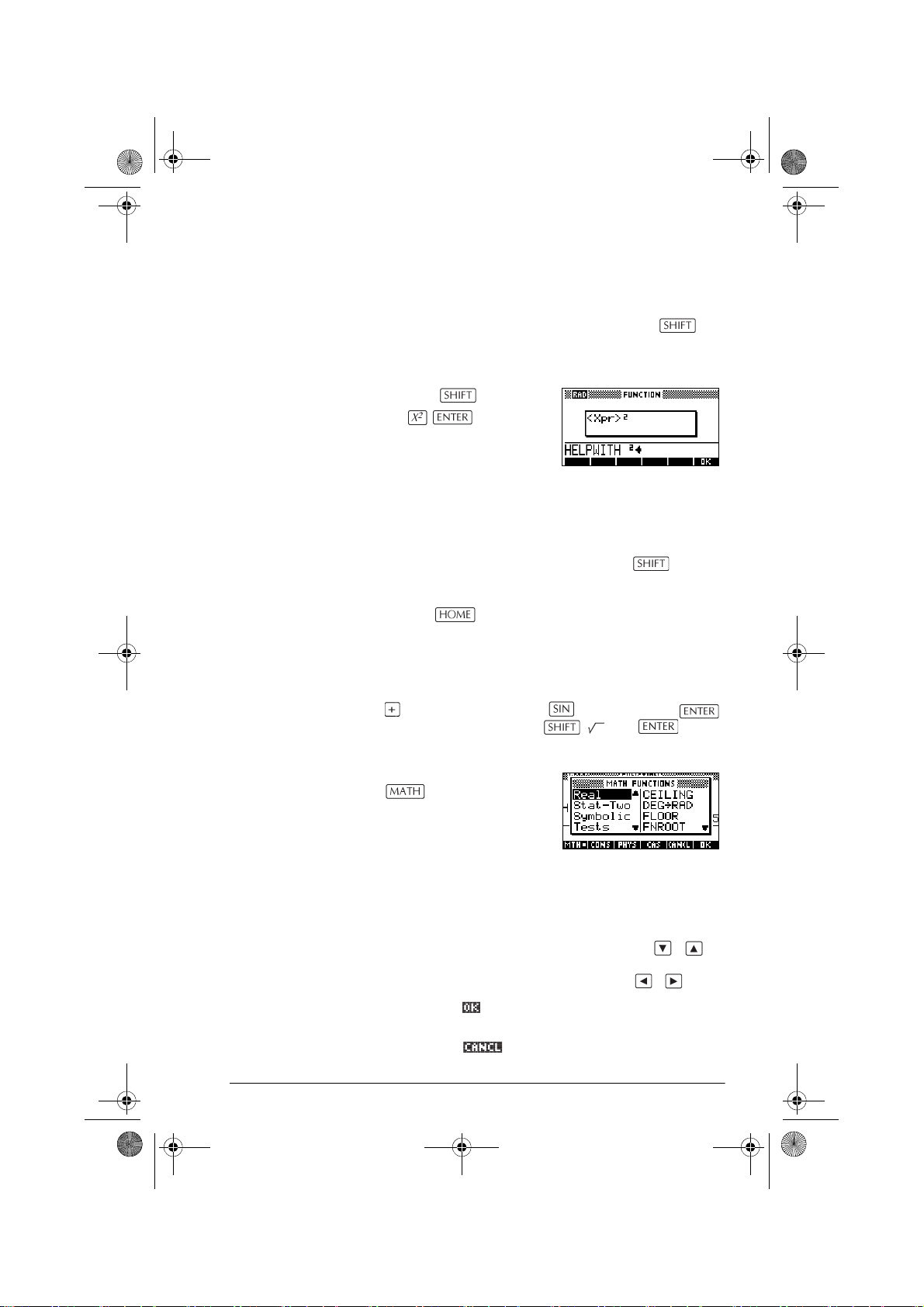
chapter-1.fm Page 7 Friday, December 16, 2005 2:20 PM
HELPWITH The HP 40gs built-in help is available in HOME only. It
provides syntax help for built-in math functions.
Access the HELPWITH command by pressing
SYNTAX and then the math key for which you require
syntax help.
Example Press SYNTAX
Note: Remove the left parenthesis from built-in
functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent before
invoking the HELPWITH command.
Note: In the CAS system, pressing the SYNTAX
will show the CAS help menu.
Math keys HOME ( ) is the place to do non-symbolic
calculations. (For symbolic calculations, use the computer
algebra system, referred throughout this manual as CAS).
Keyboard keys. The most common operations are
available from the keyboard, such as the arithmetic (like
) and trigonometric (like ) functions. Press
to complete the operation: 256
displays 16.
.
MATH menu. Press
to open the MATH
menu. The MATH menu is a
comprehensive list of math
functions that do not appear
on the keyboard. It also
includes categories for all other functions and constants.
The functions are grouped by category, ranging in
alphabetical order from Calculus to Trigonometry.
• The arrow keys scroll through the list ( , )
and move from the category list in the left column
to the item list in the right column ( , ).
• Press to insert the selected command onto the
edit line.
• Press to dismiss the MATH menu without
selecting a command.
Getting started 1-7
Page 20

hp40g+.book Page 8 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
• Pressing displays the list of Program
Constants. You can use these in programs that
you develop.
• Pressing displays a menu of physical
constants from the fields of chemistry, physics,
and quantum mechanics. You can use these
constants in calculations. (pSee “Physical
constants” on page 13-25 for more information.)
• Pressing takes you to the beginning of the
MATH menu.
See “Math functions by category” on page 13-2 for
details of the math functions.
HINT
When using the MATH menu, or any menu on the
HP 40gs, pressing an alpha key takes you straight to the
first menu option beginning with that alpha character.
With this method, you do not need to press first.
Just press the key that corresponds to the command’s
beginning alpha character.
Note that when the MATH menu is open, you can also
access CAS commands. You do this by pressing .
This enables you to use CAS commands on the HOME
screen, without opening CAS. See Chapter 14 for details
of CAS commands.
Program
commands
Pressing CMDS displays the list of Program
Commands. See “Programming commands” on
page 21-13.
Inactive keys If you press a key that does not operate in the current
context, a warning symbol like this appears. There is
no beep.
!
Menus
A menu offers you a choice
of items. Menus are
displayed in one or two
columns.
• The arrow in the
display means more
items below.
• The arrow in the
display means more items above.
1-8 Getting started
Page 21

hp40g+.book Page 9 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
To search a menu • Press or to scroll through the list. If you press
or , you’ll go all the way to
the end or the beginning of the list. Highlight the item
you want to select, then press (or ).
• If there are two columns, the left column shows
general categories and the right column shows
specific contents within a category. Highlight a
general category in the left column, then highlight an
item in the right column. The list in the right column
changes when a different category is highlighted.
Press or when you have highlighted your
selection.
• To speed-search a list, type the first letter of the word.
For example, to find the Matrix category in ,
press , the Alpha “M” key.
• To go up a page, you can press . To go
down a page, press .
To cancel a menu Press (for CANCEL) or . This cancels the
current operation.
Input forms
An input form shows several fields of information for you
to examine and specify. After highlighting the field to
edit, you can enter or edit a number (or expression). You
can also select options from a list ( ). Some input
forms include items to check ( ). See below for
examples input forms.
Reset input form
values
Getting started 1-9
To reset a field to its default values in an input form, move
the cursor to that field and press . To reset all default
field values in the input form, press CLEAR.
Page 22
hp40g+.book Page 10 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Mode settings
You use the Modes input form to set the modes for HOME.
HINT
Although the numeric setting in Modes affects only
HOME, the angle setting controls HOME and the current
aplet. The angle setting selected in Modes is the angle
setting used in both HOME and current aplet. To further
configure an aplet, you use the
and ).
SETUP keys (
Press
MODES to access the HOME MODES input
form.
Setting Options
Angle
Measure
Angle values are:
Degrees. 360 degrees in a circle.
Radians. 2π radians in a circle.
Grads. 400 grads in a circle.
The angle mode you set is the angle
setting used in both HOME and the
current aplet. This is done to ensure
that trigonometric calculations done in
the current aplet and HOME give the
same result.
Number
Format
The number format mode you set is the
number format used in both HOME
and the current aplet.
Standard. Full-precision display.
Fixed. Displays results rounded to a
number of decimal places. Example:
123.456789 becomes 123.46 in
Fixed 2 format.
Scientific. Displays results with an
exponent, one digit to the left of the
decimal point, and the specified
number of decimal places. Example:
123.456789 becomes 1.23E2 in
Scientific 2 format.
1-10 Getting started
Page 23
hp40g+.book Page 11 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Setting Options (Continued)
Engineering. Displays result with an
exponent that is a multiple of 3, and
the specified number of significant
digits beyond the first one. Example:
123.456E7 becomes 1.23E9 in
Engineering 2 format.
Fraction. Displays results as fractions
based on the specified number of
decimal places. Examples:
123.456789 becomes 123 in
Fraction 2 format, and .333 becomes
1/3 and 0.142857 becomes 1/7.
See “Using fractions” on page 1-25.
Mixed Fraction. Displays results as
mixed fractions based on the specified
number of decimal places. A mixed
fraction has an integer part and a
fractional part. Examples:
123.456789 becomes 123+16/35
in Fraction 2 format, and 7÷ 3 returns
2+1/3. See “Using fractions” on
page 1-25.
Decimal
Mark
Dot or Comma. Displays a number
as 12456.98 (Dot mode) or as
12456,98 (Comma mode). Dot mode
uses commas to separate elements in
lists and matrices, and to separate
function arguments. Comma mode
uses periods (dot) as separators in
these contexts.
Setting a mode
This example demonstrates how to change the angle
measure from the default mode, radians, to degrees for
the current aplet. The procedure is the same for changing
number format and decimal mark modes.
1. Press
form.
Getting started 1-11
MODES to open the HOME MODES input
Page 24

chapter-1.fm Page 12 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:26 AM
The cursor (highlight) is
in the first field, Angle
Measure.
2. Press to display a
list of choices.
3. Press to select
Degrees,
and press
. The angle measure
changes to degrees.
4. Press to return to
HOME.
HINT
Whenever an input form has a list of choices for a field,
you can press to cycle through them instead of using
.
Aplets (E-lessons)
Aplets are the application environments where you
explore different classes of mathematical operations. You
select the aplet that you want to work with.
Aplets come from a variety of sources:
• Built-in the HP 40gs (initial purchase).
• Aplets created by saving existing aplets, which have
been modified, with specific configurations. See
“Creating new aplets based on existing aplets” on
page 22-1.
• Downloaded from HP’s Calculators web site.
• Copied from another calculator.
Aplets are stored in the
Aplet library. See “Aplet
library” on page 1-16 for
further information.
You can modify
configuration settings for
the graphical, tabular, and
1-12 Getting started
Page 25
hp40g+.book Page 13 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
symbolic views of the aplets in the following table. See
“Aplet view configuration” on page 1-18 for further
information.
Aplet
Use this aplet to explore:
name
Function Real-valued, rectangular functions y in
terms of x. Example: .
y 2x23x 5++=
Inference Confidence intervals and Hypothesis
tests based on the Normal and
Students-t distributions.
Parametric Parametric relations x and y in terms of
t. Example: x = cos(t) and y = sin(t).
Polar Polar functions r in terms of an angle θ.
Example: .
r 24θ()cos=
Sequence Sequence functions U in terms of n, or
in terms of previous terms in the same or
another sequence, such as and
U
. Example: , and
n 2–
U
n
n 2–
U10= U21=
U
+=
n1–
.
Solve Equations in one or more real-valued
variables. Example: .
U
x 1+ x
n 1–
2
x–2–=
Finance Time Value of Money (TVM)
calculations.
Linear
Solver
Solutions to sets of two or three linear
equations.
Triangle
Solver
Unknown values for the lengths and
angles of triangles.
Statistics One-variable (x) or two-variable (x and
y) statistical data.
In addition to these aplets, which can be used in a variety
of applications, the HP 40gs is supplied with two
teaching aplets: Quad Explorer and Trig Explorer. You
cannot modify configuration settings for these aplets.
A great many more teaching aplets can be found at HP’s
web site and other web sites created by educators,
together with accompanying documentation, often with
student work sheets. These can be downloaded free of
Getting started 1-13
Page 26
hp40g+.book Page 14 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
charge and transferred to the HP 40gs using the provided
Connectivity Kit.
Quad Explorer
aplet
HINT
The Quad Explorer aplet is used to investigate the
behaviour of as the values of a, h and
yaxh+()
2
v+=
v change, both by manipulating the equation and seeing
the change in the graph, and by manipulating the graph
and seeing the change in the equation.
More detailed documentation, and an accompanying
student work sheet can be found at HP’s web site.
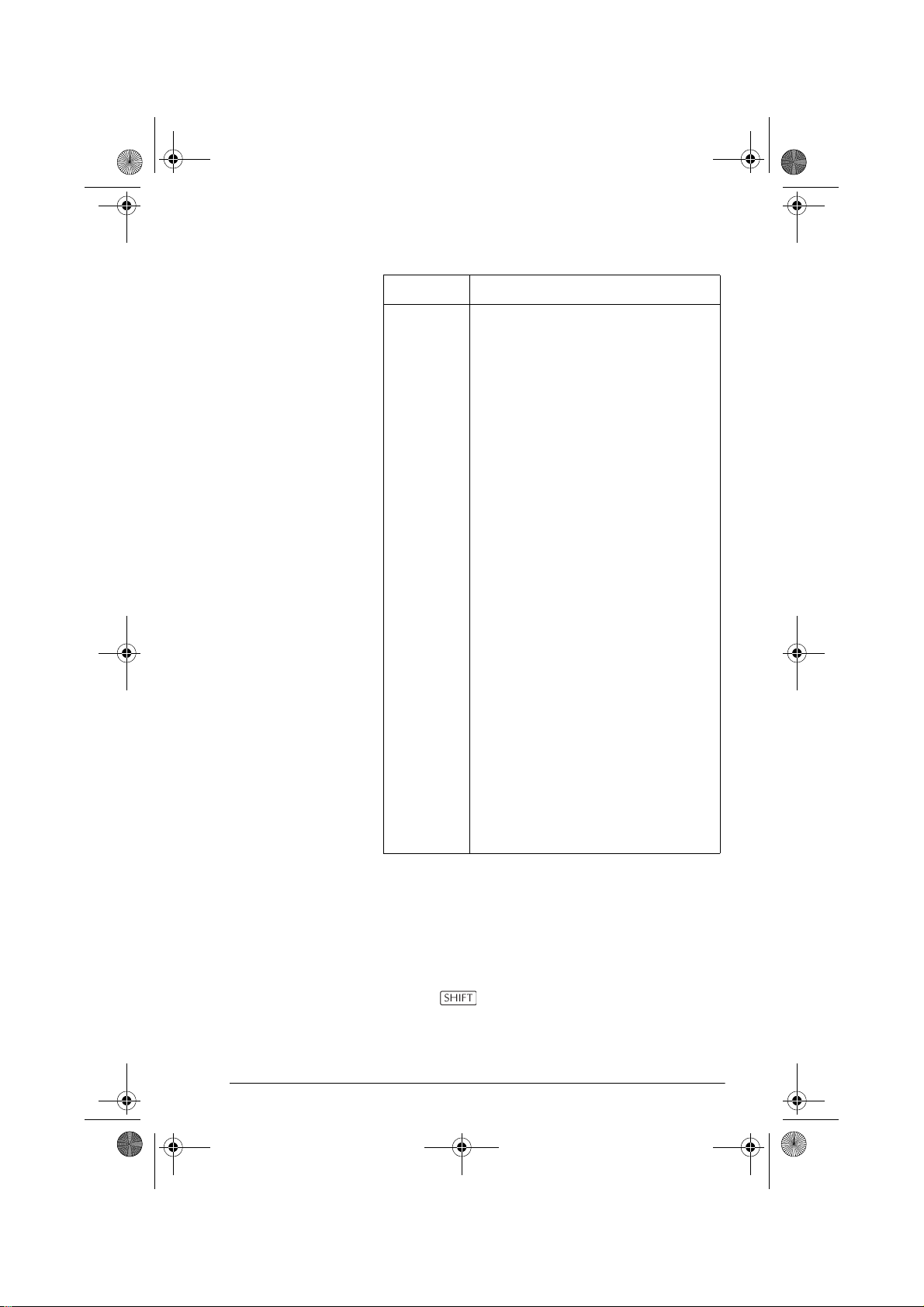
Press , select Quad
Explorer, and then press
. The Quad Explorer
aplet opens in
mode, in which the arrow
keys, the and keys,
and the key are used to change the shape of the
graph. This changing shape is reflected in the equation
displayed at the top right corner of the screen, while the
original graph is retained for comparison. In this mode
the graph controls the equation.
It is also possible to have the
equation control the graph.
Pressing displays a
sub-expression of your
equation.
Pressing the and key moves between subexpressions, while pressing the and key changes
their values.
Pressing allows the user to select whether all three
sub-expressions will be explored at once or only one at a
time.
A button is provided to
evaluate the student’s
knowledge. Pressing
displays a target quadratic
graph. The student must
manipulate the equation’s parameters to make the
equation match the target graph. When a student feels
that they have correctly chosen the parameters a
button evaluates the answer and provide feedback. An
button is provided for those who give up!
1-14 Getting started
Page 27
hp40g+.book Page 15 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
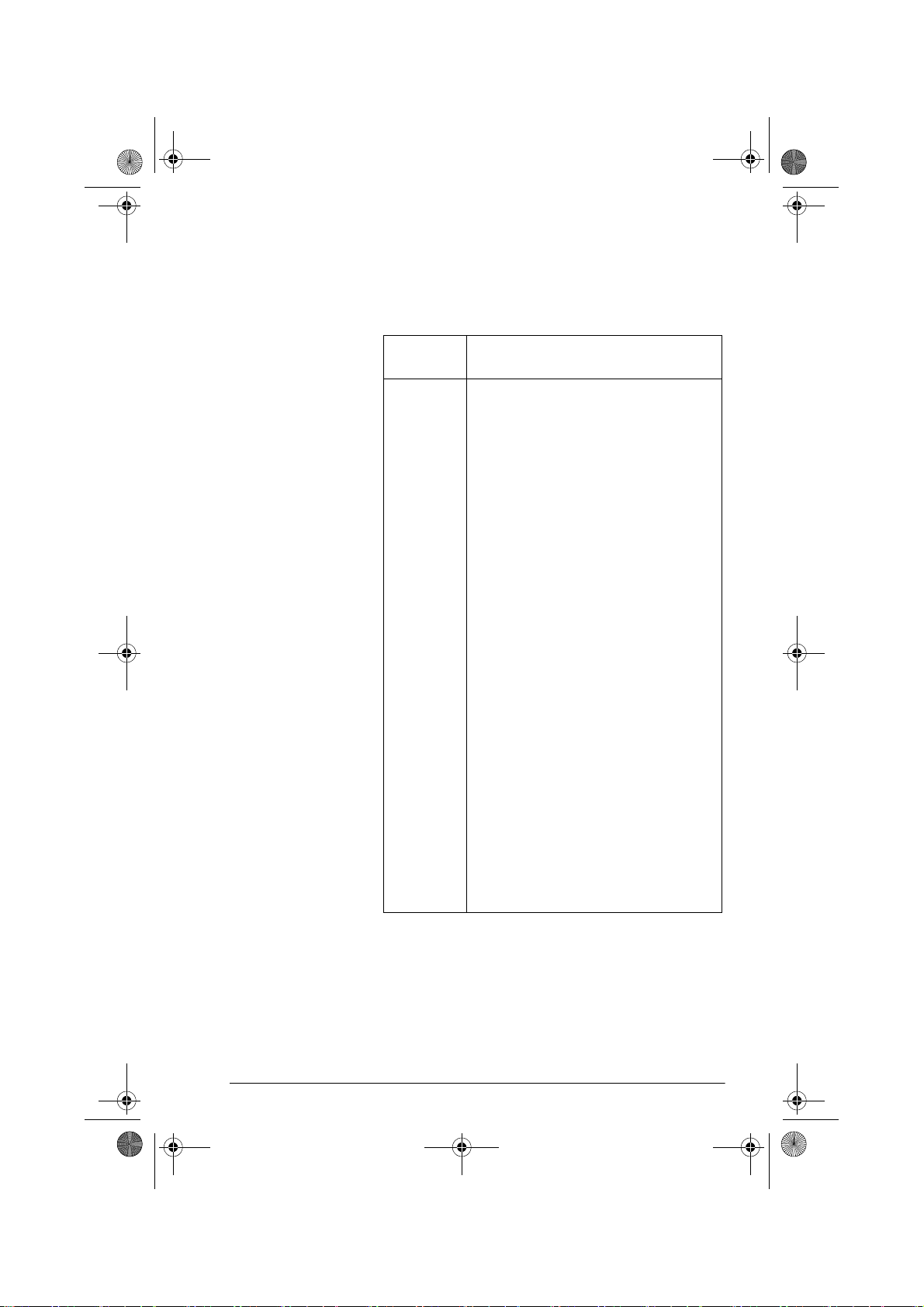
Trig Explorer aplet The Trig Explorer aplet is used to investigate the
behaviour of the graph of as the
values of a, b, c and d change, both by manipulating the
equation and seeing the change in the graph, or by
manipulating the graph and seeing the change in the
equation.
Press , select Trig
Explorer, and then press
to display the screen
shown right.
In this mode, the graph
controls the equation.
Pressing the and
keys transforms the
graph, with these
transformations reflected in the equation.
The button labelled is
a toggle between
and . When
is chosen, the ‘point of
control’ is at the origin (0,0)
and the and
keys control vertical and
horizontal transformations. When is chosen the
‘point of control’ is on the first extremum of the graph (i.e.
for the sine graph at .
ya bxc+()d+sin=
Origin
π 21,⁄()
The arrow keys change the
amplitude and frequency of
Extremum
the graph. This is most easily
seen by experimenting.
Pressing displays the
equation at the top of the
screen. The equation is
controlled by the graph.
Pressing the and
keys moves from parameter
to parameter. Pressing the or key changes the
parameter’s values.
The default angle setting for this aplet is radians. The
angle setting can be changed to degrees by pressing
.
Getting started 1-15
Page 28
hp40g+.book Page 16 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Aplet library
Aplets are stored in the Aplet library.
To open an aplet Press to display the Aplet library menu. Select the
aplet and press or .
From within an aplet, you can return to HOME any time
by pressing .
Aplet views
When you have configured an aplet to define the relation
or data that you want to explore, you can display it in
different views. Here are illustrations of the three major
aplet views (Symbolic, Plot, and Numeric), the six
supporting aplet views (from the VIEWS menu), and the
two user-defined views (Note and Sketch).
Note: some aplets—such as the Linear Solver aplet and
the Triangle Solver aplet—only have a single view, the
Numeric view.
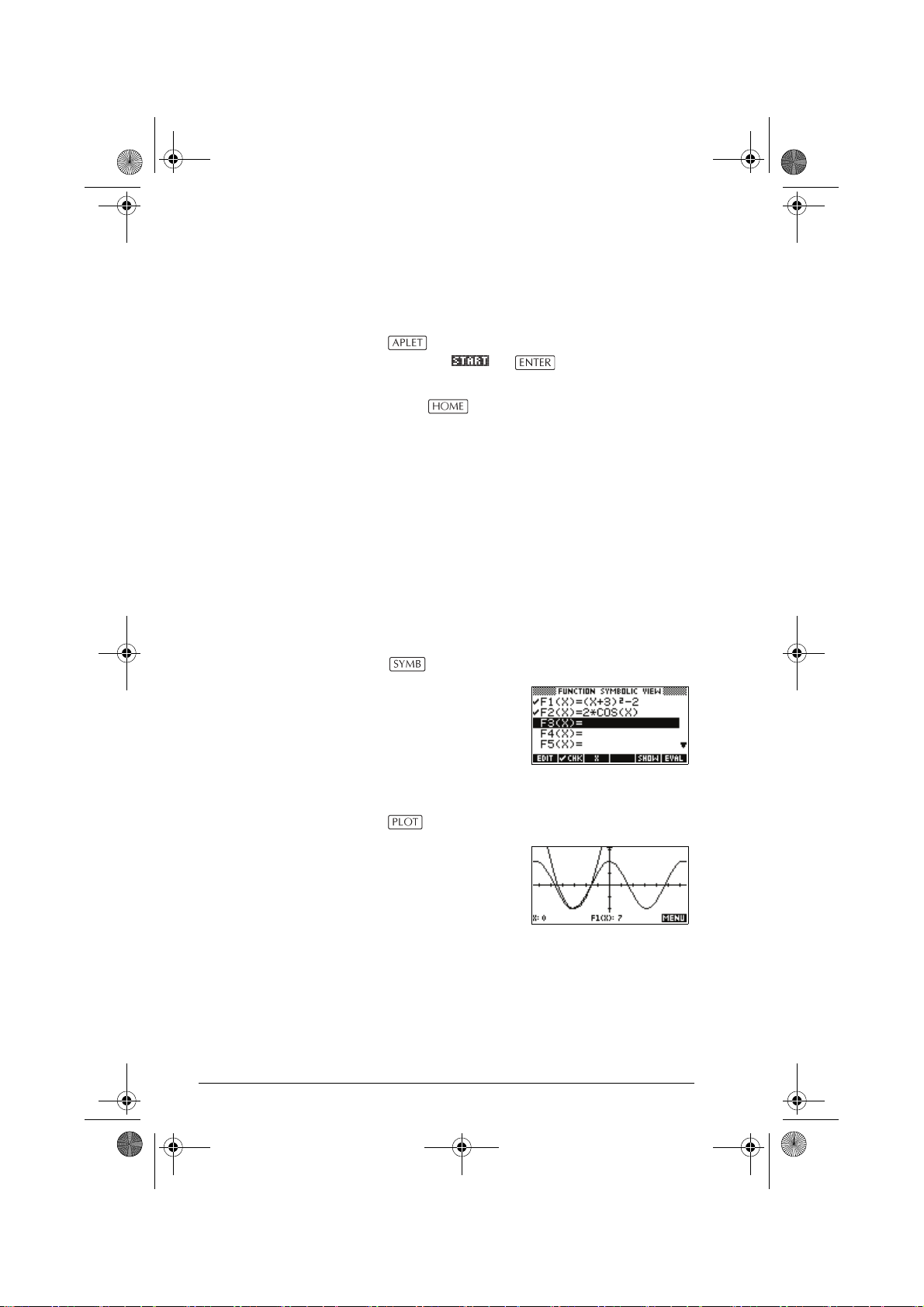
Symbolic view Press to display the aplet’s Symbolic view.
You use this view to define
the function(s) or equation(s)
that you want to explore.
See “About the Symbolic
view” on page 2-1 for
further information.
Plot view Press to display the aplet’s Plot view.
In this view, the functions that
you have defined are
displayed graphically.
See “About the Plot view” on
page 2-5 for further
information.
1-16 Getting started
Page 29
hp40g+.book Page 17 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
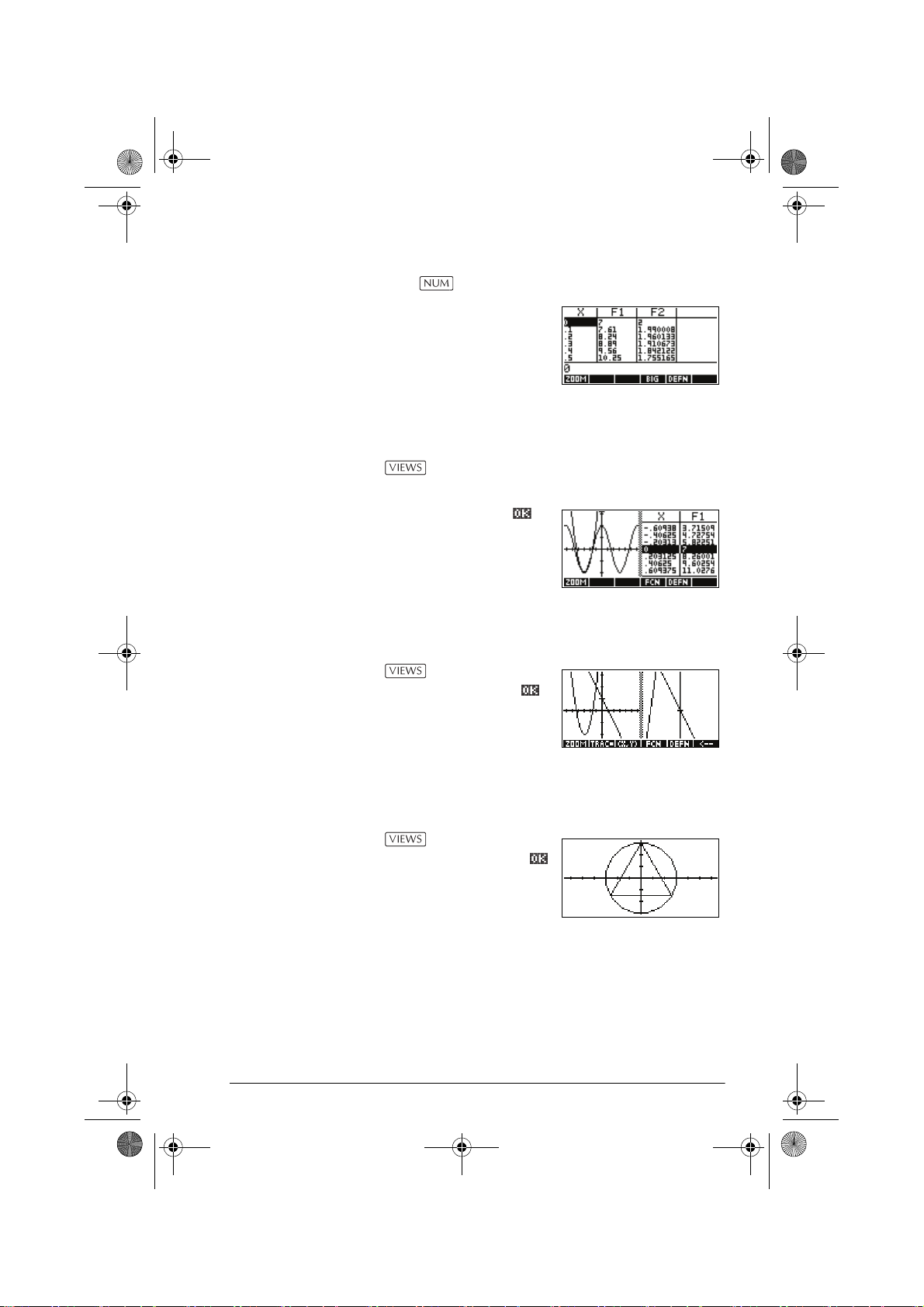
Numeric view Press to display the aplet’s Numeric view.
In this view, the functions that
you have defined are
displayed in tabular format.
See “About the numeric
view” on page 2-16 for
further information.
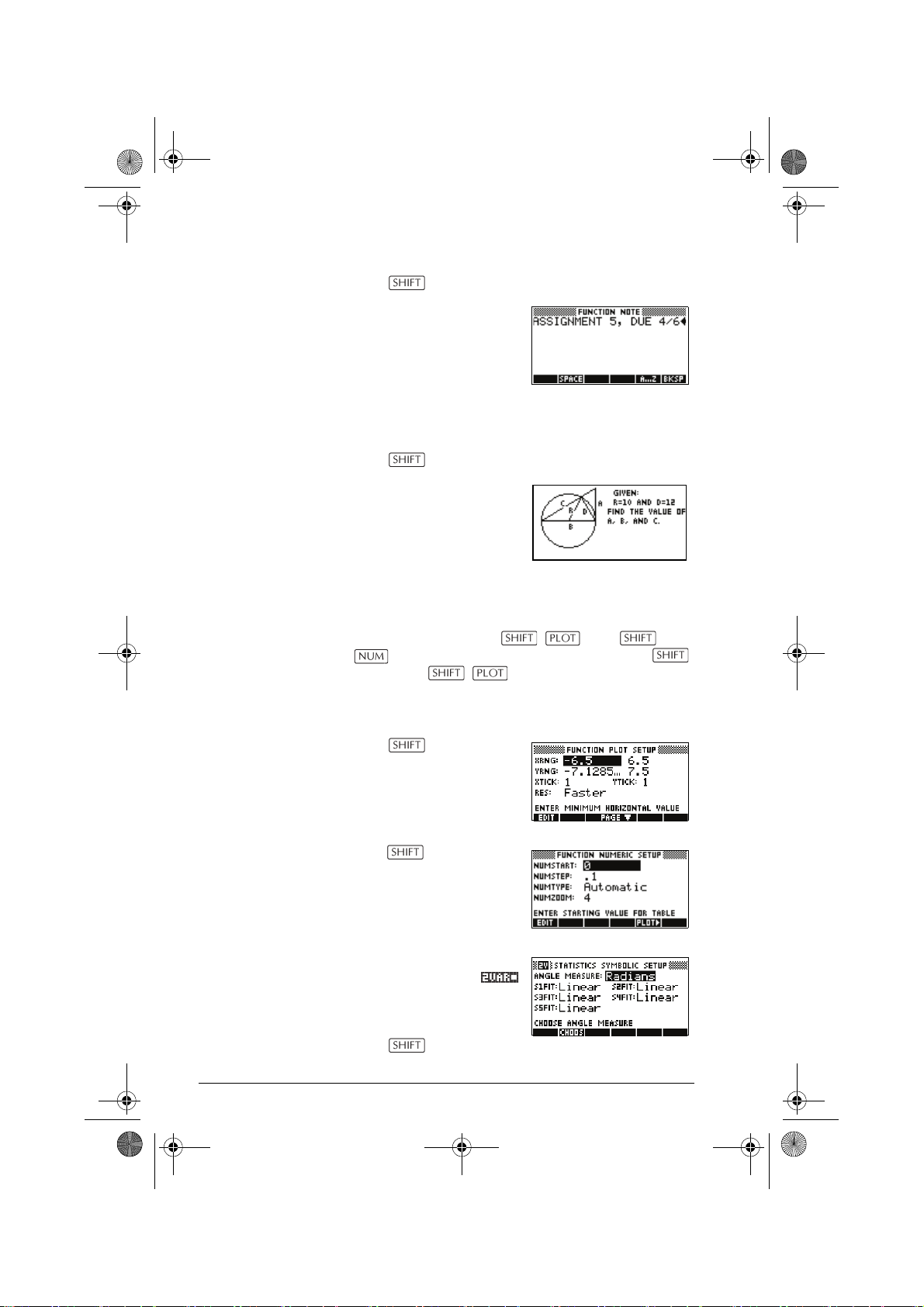
Plot-Table view The VIEWS menu contains the Plot-Table view.
Select Plot-Table
Splits the screen into the plot
and the data table. See
“Other views for scaling and
splitting the graph” on
page 2-13 for futher information.
Plot-Detail view The VIEWS menu contains the Plot-Detail view.
Select Plot-Detail
Splits the screen into the plot
and a close-up.
See “Other views for scaling and splitting the graph” on
page 2-13 for further information.
Overlay Plot
view
Getting started 1-17
The VIEWS menu contains the Overlay Plot view.
Select Overlay Plot
Plots the current
expression(s) without erasing
any pre-existing plot(s).
See “Other views for scaling and splitting the graph” on
page 2-13 for further information.
Page 30
hp40g+.book Page 18 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Note view Press NOTE to display the aplet’s note view.
This note is transferred with
the aplet if it is sent to
another calculator or to a
PC. A note view contains text
to supplement an aplet.
See “Notes and sketches” on page 20-1 for further
information.
Sketch view Press SKETCH to display the aplet’s sketch view.
Displays pictures to
supplement an aplet.
See “Notes and sketches” on
page 20-1 for further
information.
Aplet view configuration
You use the SETUP keys ( , and
) to configure the aplet. For example, press
SETUP-PLOT ( ) to display the input form for
setting the aplet’s plot settings. Angle measure is
controlled using the
Plot Setup Press SETUP-PLOT.
Sets parameters to plot a
graph.
Numeric Setup Press SETUP-NUM. Sets
parameters for building a
table of numeric values.
Symbolic Setup This view is only available in
the Statistics aplet in
mode, where it plays an
important role in choosing
data models.
Press
MODES view.
SETUP-SYMB.
1-18 Getting started
Page 31

hp40g+.book Page 19 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
To change views Each view is a separate environment. To change a view,
select a different view by pressing , ,
keys or select a view from the VIEWS menu. To change
to HOME, press . You do not explicitly close the
current view, you just enter another one—like passing
from one room into another in a house. Data that you
enter is automatically saved as you enter it.
To save aplet
configuration
You can save an aplet configuration that you have used,
and transfer the aplet to other HP 40gs calculators. See
“Creating new aplets based on existing aplets” on
page 22-1.
Mathematical calculations
The most commonly used math operations are available
from the keyboard. Access to other math functions is via
the MATH menu ( ). You can also CAS for symbolic
calculations. See “Computer Algebra System (CAS)” on
page 14-1 for further information.
To access programming commands, press
See “Programming commands” on page 21-13 for
further information.
Where to start The home base for the calculator is the HOME view
( ). You can do all non-symbolic calculations here,
and you can access all operations. (Symbolic
calculations are done using CAS.)
Entering
expressions
• In the HOME view, you enter an expression in the
same left-to-right order that you would write the
expression. This is called algebraic entry. (In CAS
you enter expressions using the Equation Writer,
explained in detail in Chapter 15, “Equation
Writer”.)
CMDS.
• To enter functions, select the key or MATH menu item
for that function. You can also enter a function by
using the Alpha keys to spell out its name.
• Press to evaluate the expression you have in
the edit line (where the blinking cursor is). An
expression can contain numbers, functions, and
variables.
Getting started 1-19
Page 32

hp40g+.book Page 20 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Example Calculate :
23214 8–
---------------------------3–
23
14
8
3
45
45()ln
Long results If the result is too long to fit on the display line, or if you
want to see an expression in textbook format, press
to highlight it and then press .
Negative
numbers
Scientific
notation
(powers of 10)
Example Calculate
Type to start a negative number or to insert a
negative sign.
To raise a negative number to a power, enclose it in
parentheses. For example, (–5)
–25.
A number like or is written in
scientific notation, that is, in terms of powers of ten. This
is simpler to work with than 50000 or 0.000000321. To
enter numbers like these, use
using 10 .)
410
×()610
----------------------------------------------------
4
510
× 3.21 107–×
13–
×
310
2
= 25, whereas –52 =
EEX. (This is easier than
23
×()
5–
4
13
6
23 3 EEX
5
Explicit and
implicit
multiplication
1-20 Getting started
Implied multiplication takes place when two operands
appear with no operator in between. If you enter AB, for
example, the result is A*B.
EEX
EEX
Page 33

hp40g+.book Page 21 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
However, for clarity, it is better to include the
multiplication sign where you expect multiplication in an
expression. It is clearest to enter AB as A*B.
HINT
Implied multiplication will not always work as expected.
For example, entering A(B+4) will not give A*(B+4).
Instead an error message is displayed: “Invalid User
Function”. This is because the calculator interprets
A(B+4) as meaning ‘evaluate function A at the value
B+4’, and function A does not exist. When in doubt, insert
the * sign manually.
Parentheses You need to use parentheses to enclose arguments for
functions, such as SIN(45). You can omit the final
parenthesis at the end of an edit line. The calculator
inserts it automatically.
Parentheses are also important in specifying the order of
operation. Without parentheses, the HP 40gs calculates
according to the order of algebraic precedence (the next
topic). Following are some examples using parentheses.
Entering... Calculates...
45 π sin (45 + π)
45 π sin (45) + π
85 9
85 9
Getting started 1-21
85 9×
85 9×
Page 34

hp40g+.book Page 22 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Algebraic
precedence
order of
evaluation
Largest and
smallest
numbers
Clearing
numbers
Functions within an expression are evaluated in the
following order of precedence. Functions with the same
precedence are evaluated in order from left to right.
1. Expressions within parentheses. Nested parentheses
are evaluated from inner to outer.
2. Prefix functions, such as SIN and LOG.
3. Postfix functions, such as !
4. Power function, ^, NTHROOT.
5. Negation, multiplication, and division.
6. Addition and subtraction.
7. AN D a nd NOT.
8. OR and XOR.
9. Left argument of | (where).
10.Equals, =.
The smallest number the HP 40gs can represent is
–499
1×10
zero. The largest number is 9.99999999999 × 10
(1E499). A greater result is displayed as this number.
• clears the character under the cursor. When the
cursor is positioned after the last character,
deletes the character to the left of the cursor, that is, it
performs the same as a backspace key.
(1E–499). A smaller result is displayed as
499
CANCEL ( ) clears the edit line.
•
•
Using previous
results
1-22 Getting started
The HOME display ( ) shows you four lines of
input/output history. An unlimited (except by memory)
number of previous lines can be displayed by scrolling.
You can retrieve and reuse any of these values or
expressions.
CLEAR clears all input and output in the
display, including the display history.
Input
Last input
Edit line
Output
Last output
Page 35

hp40g+.book Page 23 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
When you highlight a previous input or result (by pressing
), the and menu labels appear.
To copy a previous
line
To reuse the last
result
Highlight the line (press ) and press . The
number (or expression) is copied into the edit line.
Press ANS (last answer) to put the last result from the
HOME display into an expression.
is updated each time you press .
To repeat a
previous line
To repeat the very last line, just press . Otherwise,
highlight the line (press ) first, and then press .
The highlighted expression or number is re-entered. If the
previous line is an expression containing the
calculation is repeated iteratively.
Example See how
(50), and updates
50 25
You can use the last result as the first expression in the edit
line without pressing
, (or other operators that require a preceding
argument) automatically enters
You can reuse any other expression or value in the HOME
display by highlighting the expression (using the arrow
keys), then pressing . See “Using previous results”
on page 1-22 for more details.
The variable
ANS is different from the numbers in HOME’s
display history. A value in
full precision of the calculated result, whereas the
displayed numbers match the display mode.
ANS is a variable that
ANS, the
ANS retrieves and reuses the last result
ANS (from 50 to 75 to 100).
ANS. Pressing , , , or
ANS before the operator.
ANS is stored internally with the
Getting started 1-23
Page 36

hp40g+.book Page 24 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
HINT
Storing a value
in a variable
When you retrieve a number from ANS, you obtain the
result to its full precision. When you retrieve a number
from the HOME’s display history, you obtain exactly what
was displayed.
Pressing evaluates (or re-evaluates) the last input,
whereas pressing
into the edit line.
You can save an answer in a variable and use the
variable in later calculations. There are 27 variables
available for storing real values. These are A to Z and θ.
See Chapter 17, “Variables and memory management”
for more information on variables. For example:
1. Perform a calculation.
45 8 3
2. Store the result in the A variable.
A
ANS copies the last result (as ANS)
3. Perform another calculation using the A variable.
95 2 A
1-24 Getting started
Page 37

hp40g+.book Page 25 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Accessing the
display history
Clearing the
display history
Pressing enables the highlight bar in the display
history. While the highlight bar is active, the following
menu and keyboard keys are very useful:
Key Function
, Scrolls through the display history.
Copies the highlighted expression to
the position of the cursor in the edit line.
Displays the current expression in
standard mathematical form.
Deletes the highlighted expression from
the display history, unless there is a
cursor in the edit line.
CLEAR
It’s a good habit to clear the display history (
CLEAR) whenever you have finished working in HOME. It
saves calculator memory to clear the display history.
Remember that all your previous inputs and results are
saved until you clear them.
Clears all lines of display history and
the edit line.
Using fractions
To work with fractions in HOME, you set the number
format to Fraction or Mixed Fraction, as follows:
Setting Fraction
mode
Getting started 1-25
1. In HOME, open the HOME MODES input form.
MODES
Page 38

hp40g+.book Page 26 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
2. Select Number Format, press to display the
options, and highlight Fraction or Mixed
Fraction.
3. Press to select the Number Format option, then
move to the precision value field.
4. Enter the precision value that you want to use, and
press to set the precision. Press to return
to HOME.
See “Setting fraction precision” below for more
information.
Setting fraction
precision
1-26 Getting started
The fraction precision setting determines the precision in
which the HP 40gs converts a decimal value to a fraction.
The greater the precision value that is set, the closer the
fraction is to the decimal value.
By choosing a precision of 1 you are saying that the
fraction only has to match 0.234 to at least 1 decimal
place (3/13 is 0.23076...).
The fractions used are found using the technique of
continued fractions.
When converting recurring decimals this can be
important. For example, at precision 6 the decimal
0.6666 becomes 3333/5000 (6666/10000) whereas
at precision 3, 0.6666 becomes 2/3, which is probably
what you would want.
For example, when converting .234 to a fraction, the
precision value has the following effect:
Page 39

hp40g+.book Page 27 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
• Precision set to 1:
• Precision set to 2:
• Precision set to 3:
• Precision set to 4
Fraction
calculations
When entering fractions:
• You use the key to separate the numerator part
and the denominator part of the fraction.
• To enter a mixed fraction, for example, 11/2, you
enter it in the format (1+
1
/2).
For example, to perform the following calculation:
3(23/4 + 57/8)
1. Set the Number format mode to Fraction or
Mixed Fraction and specify a precision value of
4.
In this example, we’ll select Fraction as our
format.)
MODES
Select
Fraction
4
Getting started 1-27
Page 40

hp40g+.book Page 28 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
2. Enter the calculation.
323
457
8
Note: Ensure you are in
the HOME view.
3. Evaluate the calculation.
Note that if you had
selected Mixed
Fraction instead of
Fraction as the
Number format, the answer would have been
expressed as 25+7/8.
Converting
decimals to
fractions
To convert a decimal value to a fraction:
1. Set the number format mode to Fraction or Mixed
Fraction.
2. Either retrieve the value from the History, or enter the
value on the command line.
3. Press to convert the number to a fraction.
When converting a decimal to a fraction, keep the
following points in mind:
• When converting a recurring decimal to a fraction,
set the fraction precision to about 6, and ensure that
you include more than six decimal places in the
recurring decimal that you enter.
In this example, the
fraction precision is set
to 6. The top
calculation returns the
correct result. The
bottom one does not.
• To convert an exact decimal to a fraction, set the
fraction precision to at least two more than the
number of decimal places in the decimal.
1-28 Getting started
Page 41

hp40g+.book Page 29 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
In this example, the
fraction precision is set
to 6.
Complex numbers
Complex results The HP 40gs can return a complex number as a result for
some math functions. A complex number appears as an
ordered pair (x, y), where x is the real part and y is the
imaginary part. For example, entering returns (0,1).
1–
To enter complex
numbers
Storing complex
numbers
Enter the number in either of these forms, where x is the
real part, y is the imaginary part, and i is the imaginary
constant, :
• (x, y) or
• x + iy.
To enter i:
• press
or
• press , or keys to select Constant,
select i, and .
There are 10 variables available for storing complex
numbers: Z0 to Z9. To store a complex number in a
variable:
• Enter the complex number, press , enter the
variable to store the number in, and press .
1–
to move to the right column of the menu, to
45
Z 0
Getting started 1-29
Page 42

hp40g+.book Page 30 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Catalogs and editors
The HP 40gs has several catalogs and editors. You use
them to create and manipulate objects. They access
features and stored values (numbers or text or other items)
that are independent of aplets.
• A catalog lists items, which you can delete or
transmit, for example an aplet.
• An editor lets you create or modify items and
numbers, for example a note or a matrix.
Catalog/Editor Contents
Aplet library
()
Sketch editor
( SKETCH)
List (
LIST)
Matrix (
MATRIX)
Notepad (
NOTEPAD)
Program (
PROGRM)
Equation Writer
()
Aplets.
Sketches and diagrams, See
Chapter 20, “Notes and
sketches”.
Lists. In HOME, lists are
enclosed in {}. See Chapter 19,
“Lists”.
One- and two-dimensional
arrays. In HOME, arrays are
enclosed in []. See Chapter 18,
“Matrices”.
Notes (short text entries). See
Chapter 20, “Notes and
sketches”.
Programs that you create, or
associated with user-defined
aplets. See Chapter 21,
“Programming”.
The editor used for creating
expressions and equations in
CAS. See Chapter 15,
“Equation Writer”.
1-30 Getting started
Page 43

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Aplets and their views
Aplet views
This section examines the options and functionality of the
three main views for the Function, Polar, Parametric, and
Sequence aplets: Symbolic, Plot, and Numeric views.
About the Symbolic view
The Symbolic view is the defining view for the Function,
Parametric, Polar, and Sequence aplets. The other views
are derived from the symbolic expression.
You can create up to 10 different definitions for each
Function, Parametric, Polar, and Sequence aplet. You
can graph any of the relations (in the same aplet)
simultaneously by selecting them.
2
Defining an expression (Symbolic view)
Choose the aplet from the Aplet Library.
Press or to
select an aplet.
The Function,
Parametric, Polar, and Sequence aplets start in the
Symbolic view.
If the highlight is on an existing expression, scroll to
an empty line—unless you don’t mind writing over the
expression—or, clear one line ( ) or all lines
(
CLEAR).
Expressions are selected (check marked) on entry. To
deselect an expression, press . All
expressions are plotted.
Aplets and their views 2-1
selected
Page 44

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
– For a Function
definition, enter
an expression to
define F(X). The
only independent
variable in the
expression is X.
– For a
Parametric
definition, enter
a pair of
expressions to
define X(T) and
Y(T). The only
independent variable in the expressions is T.
– For a Polar
definition, enter
an expression to
define R(θ). The
only independent
variable in the
expression is θ.
– For a Sequence
definition, either
enter the first term,
or the first and
second terms, for U
(U1, or...U9, or
U0). Then define
the nth term of the sequence in terms of N or of
the prior terms, U(N–1) and/or U(N–2). The
expressions should produce real-valued
sequences with integer domains. Or define the
nth term as a non-recursive expression in terms of
n only. In this case, the calculator inserts the first
two terms based on the expression that you
define.
– Note: You will have to enter the second term if the
hp40gs is unable to calculate it automatically.
Typically if Ux(N) depends on Ux(N–2) then you
must enter Ux(2).
2-2 Aplets and their views
Page 45

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Evaluating expressions
In aplets In the Symbolic view, a variable is a symbol only, and
does not represent one specific value. To evaluate a
function in Symbolic view, press . If a function calls
another function, then resolves all references to
other functions in terms of their independent variable.
1. Choose the Function
aplet.
Select Function
2. Enter the expressions in the Function aplet’s Symbolic
view.
A
B
F1
F2
3. Highlight F3(X).
4. Press
Note how the values
for F1(X) and F2(X) are
substituted into F3(X).
Aplets and their views 2-3
Page 46

hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
In HOME You can also evaluate any expression in HOME by
entering it into the edit line and pressing .
For example, define F4 as below. In HOME, type
F4(9)and press . This evaluates the expression,
substituting 9 in place of X into F4.
SYMB view keys The following table details the menu keys that you use to
work with the Symbolic view.
Key Meaning
Copies the highlighted expression to
the edit line for editing. Press
when done.
Checks/unchecks the current
expression (or set of expressions).
Only checked expression(s) are
evaluated in the Plot and Numeric
views.
Enters the independent variable in the
Function aplet. Or, you can use the
key on the keyboard.
Enters the independent variable in the
Parametric aplet. Or, you can use the
key on the keyboard.
Enters the independent variable in the
Polar aplet. Or, you can use the
key on the keyboard.
Enters the independent variable in the
Sequence aplet. Or, you can use the
key on the keyboard.
Displays the current expression in text
book form.
Resolves all references to other
definitions in terms of variables and
evaluates all arithmetic expressions.
Displays a menu for entering variable
names or contents of variables.
2-4 Aplets and their views
Page 47

hp40g+.book Page 5 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Key Meaning (Continued)
CHARS Displays special characters. To enter
CLEAR Deletes all expressions in the list or
About the Plot view
After entering and selecting (check marking) the
expression in the Symbolic view, press . To adjust
the appearance of the graph or the interval that is
displayed, you can change the Plot view settings.
You can plot up to ten expressions at the same time.
Select the expressions you want to be plotted together.
Displays the menu for entering math
operations.
one, place the cursor on it and press
. To remain in the CHARS menu
and enter another special character,
press .
Deletes the highlighted expression or
the current character in the edit line.
clears the edit line.
Setting up the plot (Plot view setup)
Press SETUP-PLOT to define any of the settings
shown in the next two tables.
1. Highlight the field to edit.
– If there is a number to enter, type it in and press
or .
– If there is an option to choose, press ,
highlight your choice, and press or .
As a shortcut to , just highlight the field to
change and press to cycle through the
options.
– If there is an option to select or deselect, press
to check or uncheck it.
2. Press to view more settings.
3. When done, press to view the new plot.
Aplets and their views 2-5
Page 48

hp40g+.book Page 6 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Plot view
settings
The plot view settings are:
Field Meaning
XRNG, YRNG Specifies the minimum and
maximum horizontal (X) and
vertical (Y) values for the plotting
window.
RES For function plots: Resolution;
“Faster” plots in alternate pixel
columns; “Detail” plots in every
pixel column.
TRNG Parametric aplet: Specifies the t-
values (T) for the graph.
θRNG Polar aplet: Specifies the angle (θ)
value range for the graph.
NRNG Sequence aplet: Specifies the
index (N) values for the graph.
TSTEP For Parametric plots: the increment
for the independent variable.
θSTEP For Polar plots: the increment
value for the independent
variable.
SEQPLOT For Sequence aplet: Stairstep or
Cobweb types.
XTICK Horizontal spacing for tickmarks.
YTICK Vertical spacing for tickmarks.
Those items with space for a checkmark are settings you
can turn on or off. Press to display the second
page.
Field Meaning
SIMULT If more than one relation is being
plotted, plots them simultaneously
(otherwise sequentially).
INV. CROSS Cursor crosshairs invert the status
of the pixels they cover.
2-6 Aplets and their views
Page 49

hp40g+.book Page 7 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Field Meaning (Continued)
CONNECT Connect the plotted points. (The
LABELS Label the axes with XRNG and
AXES Draw the axes.
GRID Draw grid points using XTICK
Sequence aplet always connects
them.)
YRNG values.
and YTICK spacing.
Reset plot
settings
To reset the default values for all plot settings, press
CLEAR in the Plot Setup view. To reset the default
value for a field, highlight the field, and press .
Exploring the graph
Plot view gives you a selection of keys and menu keys to
explore a graph further. The options vary from aplet to
aplet.
PLOT view keys The following table details the keys that you use to work
with the graph.
Key Meaning
CLEAR Erases the plot and axes.
Offers additional pre-defined views
for splitting the screen and for scaling
(“zooming”) the axes.
Moves cursor to far left or far right.
Moves cursor between relations.
or Interrupts plotting.
Continues plotting if interrupted.
Aplets and their views 2-7
Page 50

hp40g+.book Page 8 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Key Meaning (Continued)
Turns menu-key labels on and off.
When the labels are off, pressing
• Pressing once displays the
• Pressing a second time
• Pressing a third time
Displays the ZOOM menu list.
Turns trace mode on/off. A white box
appears over the on .
Opens an input form for you to enter
an X (or T or N or θ) value. Enter the
value and press . The cursor jumps
to the point on the graph that you
entered.
Function aplet only: turns on menu list
for root-finding functions (see
“Analyse graph with FCN functions”
on page 3-4).
Displays the current, defining
expression. Press to restore the
menu.
turns them back on.
full row of labels.
removes the row of labels to
display only the graph.
displays the coordinate mode.
Trace a graph You can trace along a function using the or key
which moves the cursor along the graph. The display also
shows the current coordinate position (x, y) of the cursor.
Trace mode and the coordinate display are automatically
set when a plot is drawn.
Note: Tracing might not appear to exactly follow your
plot if the resolution (in Plot Setup view) is set to Faster.
This is because RES: FASTER plots in only every other
column, whereas tracing always uses every column.
In Function and Sequence Aplets: You can also
scroll (move the cursor) left or right beyond the edge of
the display window in trace mode, giving you a view of
more of the plot.
To move between
relations
2-8 Aplets and their views
If there is more than one relation displayed, press or
to move between relations.
Page 51

hp40g+.book Page 9 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
To jump directly to
a value
To jump straight to a value rather than using the Trace
function, use the menu key. Press , then enter
a value. Press to jump to the value.
To turn trace on/off If the menu labels are not displayed, press first.
• Turn off trace mode by pressing .
• Turn on trace mode by pressing .
• To turn the coordinate display off, press .
Zoom within a
graph
One of the menu key options is . Zooming redraws
the plot on a larger or smaller scale. It is a shortcut for
changing the Plot Setup.
The Set Factors... option enables you to set the
factors by which you zoom in or zoom out, and whether
the zoom is centered about the cursor.
ZOOM options Press , select an option, and press . (If
is not displayed, press .) Not all options are
available in all aplets.
Option Meaning
Center Re-centers the plot around the
current position of the cursor without
changing the scale.
Box... Lets you draw a box to zoom in on.
See “Other views for scaling and
splitting the graph” on page 2-13.
In Divides horizontal and vertical
scales by the X-factor and Y-factor.
For instance, if zoom factors are 4,
then zooming in results in 1/4 as
many units depicted per pixel. (see
Set Factors...)
Out Multiplies horizontal and vertical
scales by the X-factor and Y-factor
(see Set Factors...).
X-Zoom In Divides horizontal scale only, using
X-factor.
X-Zoom Out Multiplies horizontal scale, using
X-factor.
Aplets and their views 2-9
Page 52

hp40g+.book Page 10 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Option Meaning (Continued)
Y-Zoom In Divides vertical scale only, using
Y-factor.
Y-Zoom Out Multiplies vertical scale only, using
Y-factor.
Square Changes the vertical scale to match
the horizontal scale. (Use this after
doing a Box Zoom, X-Zoom, or
Y-Zoom.)
Set
Factors...
Sets the X-Zoom and Y-Zoom factors
for zooming in or zooming out.
Includes option to recenter the plot
before zooming.
Auto Scale Rescales the vertical axis so that the
display shows a representative
piece of the plot, for the supplied x
axis settings. (For Sequence and
Statistics aplets, autoscaling
rescales both axes.)
The autoscale process uses the first
selected function only to determine
the best scale to use.
Decimal Rescales both axes so each pixel =
0.1 units. Resets default values for
XRNG
(–6.5 to 6.5) and YRNG (–3.1 to
3.2). (Not in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
Integer Rescales horizontal axis only,
making each pixel =1 unit. (Not
available in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
Trig Rescales horizontal axis so
1 pixel = π/24 radians, 7.58, or
1
/3grads; rescales vertical axis
8
so
1 pixel = 0.1 unit.
(Not in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
2-10 Aplets and their views
Page 53

hp40g+.book Page 11 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Option Meaning (Continued)
Un-zoom Returns the display to the previous
zoom, or if there has been only one
zoom, un-zoom displays the graph
with the original plot settings.
ZOOM examples The following screens show the effects of zooming options
on a plot of .
Plot of
Zoom In:
3 xsin
3 xsin
In
Un-zoom:
Un-zoom
Note: Press to move to
the bottom of the Zoom list.
Zoom Out:
Out
Now un-zoom.
X-Zoom In:
X-Zoom In
Now un-zoom.
X-Zoom Out:
X-Zoom Out
Now un-zoom.
Aplets and their views 2-11
Page 54

hp40g+.book Page 12 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Y-Zoom In:
Y-Zoom In
Now un-zoom.
Y-Zoom Out:
Y-Zoom Out
Zoom Square:
Square
To box zoom The Box Zoom option lets you draw a box around the
area you want to zoom in on by selecting the endpoints
of one diagonal of the zoom rectangle.
1. If necessary, press to turn on the menu-key
labels.
2. Press and select Box...
3. Position the cursor on one corner of the rectangle.
Press .
4. Use the cursor keys
( , etc.) to drag to
the opposite corner.
5. Press to zoom in
on the boxed area.
2-12 Aplets and their views
Page 55

hp40g+.book Page 13 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
To set zoom factors 1. In the Plot view, press .
2. Press .
3. Select Set Factors... and press .
4. Enter the zoom factors. There is one zoom factor for
the horizontal scale (XZOOM) and one for the vertical
scale (YZOOM).
Zooming out multiplies the scale by the factor, so that
a greater scale distance appears on the screen.
Zooming in divides the scale by the factor, so that a
shorter scale distance appears on the screen.
Other views for scaling and splitting the graph
The preset viewing options menu ( ) contains
options for drawing the plot using certain pre-defined
configurations. This is a shortcut for changing Plot view
settings. For instance, if you have defined a trigonometric
function, then you could select Trig to plot your function
on a trigonometric scale. It also contains split-screen
options.
In certain aplets, for example those that you download
from the world wide web, the preset viewing options
menu can also contain options that relate to the aplet.
VIEWS menu
Press , select an option, and press .
options
Option Meaning
PlotDetail
Plot-Table Splits the screen into the plot and
Overlay
Plot
Aplets and their views 2-13
Splits the screen into the plot and a
close-up.
the data table.
Plots the current expression(s)
without erasing any pre-existing
plot(s).
Page 56

hp40g+.book Page 14 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Option Meaning (Continued)
Auto Scale Rescales the vertical axis so that the
display shows a representative
piece of the plot, for the supplied x
axis settings. (For Sequence and
Statistics aplets, autoscaling
rescales both axes.)
The autoscale process uses the first
selected function only to determine
the best scale to use.
Decimal Rescales both axes so each pixel =
0.1 unit. Resets default values for
XRNG
(–6.5 to 6.5) and YRNG (–3.1 to
3.2). (Not in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
Integer Rescales horizontal axis only,
making each pixel=1 unit. (Not
available in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
Trig Rescales horizontal axis so
1 pixel=π/24 radian, 7.58, or
1
8
1 pixel = 0.1 unit.
(Not in Sequence or Statistics
aplets.)
/3 grads; rescales vertical axis so
Split the screen The Plot-Detail view can give you two simultaneous views
of the plot.
1. Press . Select Plot-Detail and press .
The graph is plotted twice. You can now zoom in on
the right side.
2. Press
select the zoom method
and press or
right side. Here is an
example of split screen with Zoom In.
– The Plot menu keys are available as for the full
plot (for tracing, coordinate display, equation
display, and so on).
2-14 Aplets and their views
,
. This zooms the
Page 57

hp40g+.book Page 15 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
– moves the leftmost cursor to the
screen’s left edge and moves the
rightmost cursor to the screen’s right edge.
– The menu key copies the right plot to the left
plot.
3. To un-split the screen, press . The left side takes
over the whole screen.
The Plot-Table view gives you two simultaneous views of
the plot.
1. Press . Select
Plot-Table and
press . The screen
displays the plot on the
left side and a table of
numbers on the right side.
2. To move up and down the table, use the and
cursor keys. These keys move the tra.ce point left or
right along the plot, and in the table, the
corresponding values are highlighted.
3. To move between functions, use the and
cursor keys to move the cursor from one graph to
another.
4. To return to a full Numeric (or Plot) view, press
(or ).
Overlay plots If you want to plot over an existing plot without erasing
that plot, then use Overlay Plot instead of
. Note that tracing follows only the current
functions from the current aplet.
Decimal scaling Decimal scaling is the default scaling. If you have
changed the scaling to Trig or Integer, you can change it
back with Decimal.
Integer scaling Integer scaling compresses the axes so that each pixel is
and the origin is near the screen center.
11×
Trigonometric
scaling
Aplets and their views 2-15
Use trigonometric scaling whenever you are plotting an
expression that includes trigonometric functions.
Trigonometric plots are more likely to intersect the axis at
points factored by π.
Page 58

hp40g+.book Page 16 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
About the numeric view
After entering and selecting
(check marking) the
expression or expressions
that you want to explore in
the Symbolic view, press
to view a table of
data values for the independent variable (X, T, θ, or N)
and dependent variables.
Setting up the table (Numeric view setup)
Press NUM to define
any of the table settings.
Use the Numeric Setup
input form to configure the
table.
1. Highlight the field to edit. Use the arrow keys to move
from field to field.
– If there is a number to enter, type it in and press
or . To modify an existing number,
press .
– If there is an option to choose, press ,
highlight your choice, and press or .
– Shortcut: Press the key to copy values
from the Plot Setup into NUMSTART and
NUMSTEP. Effectively, the menu key allows
you to make the table match the pixel columns in
the graph view.
2. When done, press to view the table of
numbers.
Numeric view
settings
2-16 Aplets and their views
The following table details the fields on the Numeric
Setup input form.
Field Meaning
NUMSTART The independent variable’s
starting value.
NUMSTEP The size of the increment from
one independent variable value
to the next.
Page 59
hp40g+.book Page 17 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Field Meaning (Continued)
NUMTYPE Type of numeric table: Automatic
NUMZOOM Allows you to zoom in or out on a
or Build Your Own. To build your
own table, you must type each
independent value into the table
yourself.
selected value of the independent
variable.
Reset numeric
settings
To reset the default values for all table settings, press
CLEAR.
Exploring the table of numbers
NUM view
menu keys
The following table details the menu keys that you use to
work with the table of numbers.
Key Meaning
Displays ZOOM menu list.
Toggles between two character
sizes.
Displays the defining function
expression for the highlighted
column. To cancel this display, press
.
Aplets and their views 2-17
Page 60

hp40g+.book Page 18 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Zoom within a
table
Zooming redraws the table of numbers in greater or
lesser detail.
ZOOM options The following table lists the zoom options:
Option Meaning
In Decreases the intervals for the
independent variable so a narrower
range is shown. Uses the NUMZOOM
factor in Numeric Setup.
Out Increases the intervals for the
independent variable so that a
wider range is shown. Uses the
NUMZOOM factor in Numeric Setup.
Decimal Changes intervals for the
independent variable to 0.1 units.
Starts at zero. (Shortcut to changing
NUMSTART and NUMSTEP.)
Integer Changes intervals for the
independent variable to 1 unit.
Starts at zero. (Shortcut to changing
NUMSTEP.)
Trig Changes intervals for independent
variable to π/24 radian or 7.5
degrees or 8
zero.
Un-zoom Returns the display to the previous
zoom.
1
/3 grads. Starts at
The display on the right is a Zoom In of the display on the
left. The ZOOM factor is 4.
HINT
2-18 Aplets and their views
To jump to an independent variable value in the table,
use the arrow keys to place the cursor in the independent
variable column, then enter the value to jump to.
Page 61

hp40g+.book Page 19 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Automatic
recalculation
You can enter any new value in the X column. When you
press , the values for the dependent variables are
recalculated, and the entire table is regenerated with the
same interval between X values.
Building your own table of numbers
The default NUMTYPE is “Automatic”, which fills the table
with data for regular intervals of the independent (X, T, θ,
or N) variable. With the NUMTYPE option set to “Build
Your Own”, you fill the table yourself by typing in the
independent-variable values you want. The dependent
values are then calculated and displayed.
Build a table 1. Start with an expression defined (in Symbolic view) in
the aplet of your choice. Note: Function, Polar,
Parametric, and Sequence aplets only.
2. In the Numeric Setup ( NUM), choose
NUMTYPE: Build Your Own.
3. Open the Numeric view ( ).
4. Clear existing data in the table (
5. Enter the independent values in the left-hand column.
Type in a number and press . You do not have
to enter them in order, because the function
can rearrange them. To insert a number between two
others, use .
CLEAR).
F1 and F2
You enter
numbers into
the X column
entries are
generated
automatically
Clear data Press CLEAR, to erase the data from a table.
Aplets and their views 2-19
Page 62

hp40g+.book Page 20 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
“Build Your Own” menu keys
Key Meaning
Puts the highlighted independent
value (X, T, θ, or N) into the edit
line. Pressing replaces
this variable with its current value.
Inserts a zero value at the position
of the highlight. Replace a zero
by typing the number you want
and pressing .
Sorts the independent variable
values into ascending or
descending order. Press
and select the ascending or
descending option from the
menu, and press .
CLEAR
Example: plotting a circle
Plot the circle, x
y 9 x2–±=
To plot both the positive and negative y values, you need
to define two equations as follows:
y 9 x2–= y 9 x2––=
1. In the Function aplet, specify the functions.
2
.
and
Toggles between two character
sizes.
Displays the defining function
expression for the highlighted
column.
Deletes the highlighted row.
Clears all data from the table.
2
+ y
= 9. First rearrange it to read
2-20 Aplets and their views
Page 63

hp40g+.book Page 21 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Select
Function
9
9
2. Reset the graph setup to the default settings.
SETUP-PLOT
CLEAR
3. Plot the two functions
and hide the menu so
that you can see all the
circle.
4. Reset the numeric setup to the default settings.
SETUP-NUM
CLEAR
5. Display the functions in numeric form.
Aplets and their views 2-21
Page 64
hp40g+.book Page 22 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Page 65

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Function aplet
About the Function aplet
The Function aplet enables you to explore up to 10
real-valued, rectangular functions y in terms of x. For
example .
Once you have defined a function you can:
• create graphs to find roots, intercepts, slope, signed
• create tables to evaluate functions at particular
This chapter demonstrates the basic tools of the Function
aplet by stepping you through an example. See “Aplet
views” on page 2-1 for further information about the
functionality of the Symbolic, Numeric, and Plot views.
y 2x 3+=
area, and extrema
values.
3
Getting started with the Function aplet
The following example involves two functions: a linear
function and a quadratic equation
yx3+()
Open the
1. Open the Function aplet.
Function aplet
Function aplet 3-1
y 1 x–=
2
2–=
.
Select Function
The Function aplet starts
in the Symbolic view.
The Symbolic view is the defining view for Function,
Parametric, Polar, and Sequence aplets. The other
views are derived from the symbolic expression.
Page 66

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Define the
expressions
2. There are 10 function definition fields on the Function
aplet’s Symbolic view screen. They are labeled F1(X)
to F0(X). Highlight the function definition field you
want to use, and enter an expression. (You can press
to delete an existing line, or CLEAR to
clear all lines.)
1
3
2
Set up the plot You can change the scales of the x and y axes, graph
resolution, and the spacing of the axis ticks.
3. Display plot settings.
SETUP-PLOT
Note: For our example, you can leave the plot
settings at their default values since we will be using
the Auto Scale feature to choose an appropriate y
axis for our x axis settings. If your settings do not
match this example, press
default values.
CLEAR to restore the
4. Specify a grid for the graph.
Plot the
5. Plot the functions.
functions
3-2 Function aplet
Page 67

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Change the
scale
6. You can change the scale to see more or less of your
graphs. In this example, choose Auto Scale. (See
“VIEWS menu options” on page 2-13 for a
description of Auto Scale).
Select Auto
Scale
Trace a graph 7. Trace the linear function.
6 times
Note: By default, the
tracer is active.
8. Jump from the linear function to the quadratic
function.
Function aplet 3-3
Page 68

hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Analyse graph
with FCN
functions
To find a root of the
quadratic function
9. Display the Plot view menu.
From the Plot view menu, you can use the functions
on the FCN menu to find roots, intersections, slopes,
and areas for a function defined in the Function aplet
(and any Function-based aplets). The FCN functions
act on the currently selected graph. See “FCN
functions” on page 3-10 for further information.
10.Move the cursor to the graph of the quadratic
equation by pressing the or key. Then move
the cursor so that it is near by pressing the
or key.
Select
Root
x 1–=
The root value is
displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
Note: If there is more
than one root (as in our
example), the
coordinates of the root closest to the current cursor
position are displayed.
To find the
intersection of the
two functions
3-4 Function aplet
11.Find the intersection of the two functions.
Page 69

hp40g+.book Page 5 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
12.Choose the linear function whose intersection with the
quadratic function you wish to find.
The coordinates of the
intersection point are
displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
Note: If there is more
than one intersection
(as in our example), the coordinates of the
intersection point closest to the current cursor position
are displayed.
To find the slope of
the quadratic
function
To find the signed
area of the two
functions
13.Find the slope of the quadratic function at the
intersection point.
Select Slope
The slope value is
displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
14.To find the area between the two functions in the
range –2 ≤ x ≤ –1, first move the cursor to
F1 x() 1 x–=
Select Signed area
15.Move the cursor to x = –2 by pressing the or
key.
and select the signed area option.
Function aplet 3-5
Page 70

hp40g+.book Page 6 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
16.Press to accept using F2(x) = (x + 3)
other boundary for the integral.
17.Choose the end value
for x.
1
The cursor jumps to
x = –1 on the linear
function.
2
– 2 as the
18.Display the numerical
value of the integral.
Note: See “Shading
area” on page 3-11
for another method of
calculating area.
To find the
extremum of the
quadratic
19.Move the cursor to the quadratic equation and find
the extremum of the quadratic.
Select Extremum
The coordinates of the
extremum are
displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
3-6 Function aplet
Page 71

hp40g+.book Page 7 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
HINT
Display the
The Root and Extremum functions return one value only
even if the function has more than one root or extremum.
The function finds the value closest to the position of the
cursor. You need to re-locate the cursor to find other roots
or extrema that may exist.
20.Display the numeric view.
numeric view
Set up the table 21.Display the numeric setup.
SETUP-NUM
See “Setting up the table (Numeric view setup)” on
page 2-16 for more information.
22.Match the table settings to the pixel columns in the
graph view.
Explore the
23.Display the table of values.
table
Function aplet 3-7
Page 72

hp40g+.book Page 8 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
To navigate around
a table
To go directly to a
value
To access the zoom
options
24.Move to X = –5.9.
6 times
25.Move directly to X = 10.
1 0
26.Zoom in on X = 10 by a factor of 4. Note: NUMZOOM
has a setting of 4.
In
To change font size 27. Display table numbers in large font.
To display the
symbolic definition
of a column
3-8 Function aplet
28.Display the symbolic definition for the F1 column.
The symbolic definition of
F1 is displayed at the
bottom of the screen.
Page 73

hp40g+.book Page 9 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Function aplet interactive analysis
From the Plot view ( ), you can use the functions on
the FCN menu to find roots, intersections, slopes, and
areas for a function defined in the Function aplet (and any
Function-based aplets). See “FCN functions” on page 3-
10. The FCN operations act on the currently selected
graph.
The results of the FCN functions are saved in the following
variables:
• Area
• Extremum
• Isect
• Root
• Slope
For example, if you use the Root function to find the root
of a plot, you can use the result in calculations in HOME.
Access FCN
variables
Function aplet 3-9
The FCN variables are contained on the VARS menu.
To access FCN variables in HOME:
Select Plot FCN
or to choose a
variable
To access FCN variable in the Function aplet’s Symbolic
view:
Select Plot FCN
or to choose a variable
Page 74

hp40g+.book Page 10 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
FCN functions The FCN functions are:
Function Description
Root Select Root to find the root of the
Extremum Select Extremum to find the
current function nearest the
cursor. If no root is found, but only
an extremum, then the result is
labeled EXTR: instead of ROOT:.
(The root-finder is also used in the
Solve aplet. See also “Interpreting
results” on page 7-6.) The cursor
is moved to the root value on the
x-axis and the resulting x-value is
saved in a variable named
ROOT.
maximum or minimum of the
current function nearest the
cursor. This displays the
coordinate values and moves the
cursor to the extremum. The
resulting value is saved in a
variable named EXTREMUM.
Slope Select Slope to find the numeric
derivative at the current position
of the cursor. The result is saved in
a variable named SLOPE.
Signed area Select Signed area to find the
numeric integral. (If there are two
or more expressions
checkmarked, then you will be
asked to choose the second
expression from a list that
includes the x-axis.) Select a
starting point, then move the
cursor to selection ending point.
The result is saved in a variable
named AREA.
3-10 Function aplet
Page 75
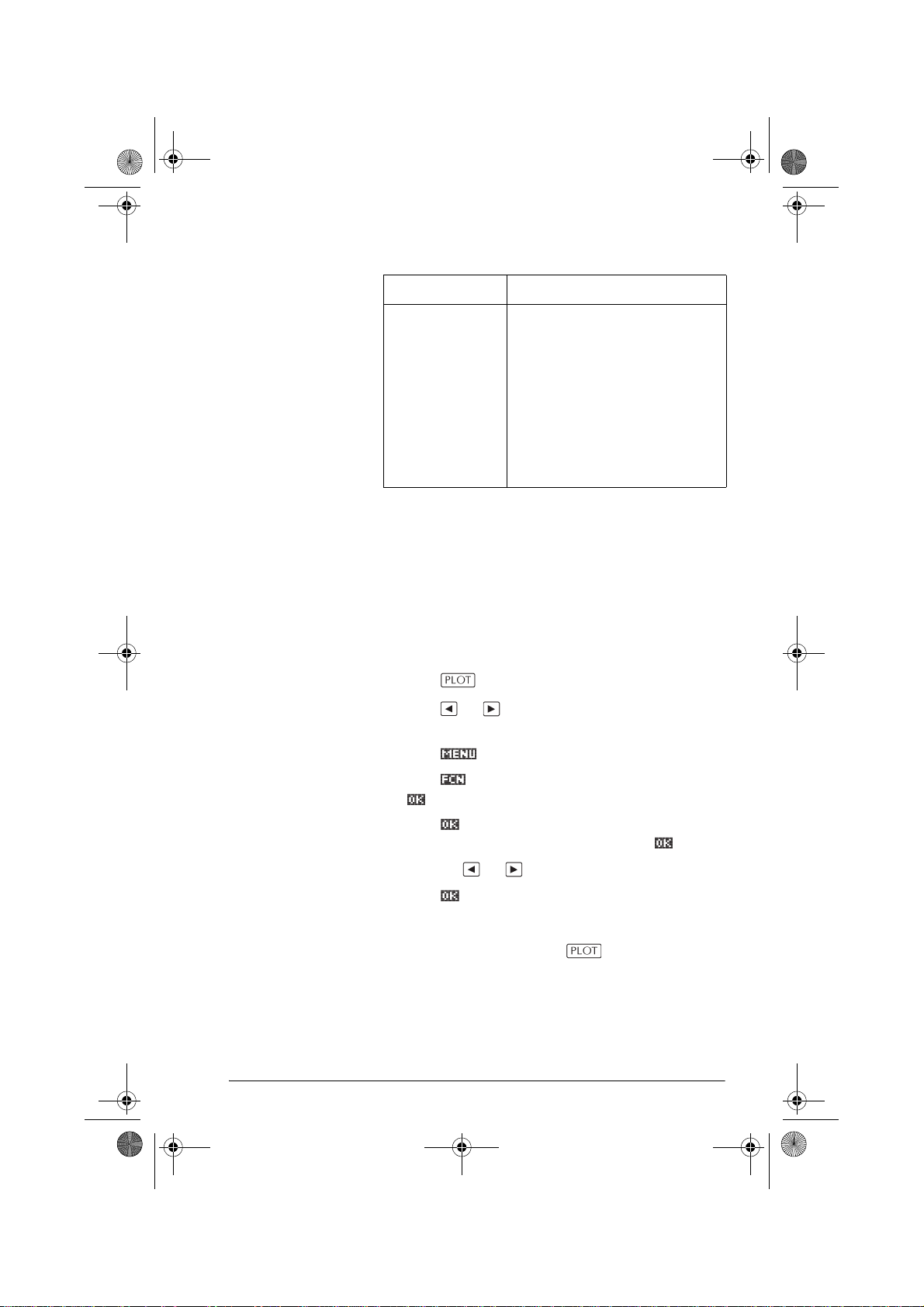
hp40g+.book Page 11 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Function Description (Continued)
Intersection Select Intersection to find the
intersection of two graphs nearest
the cursor. (You need to have at
least two selected expressions in
Symbolic view.) Displays the
coordinate values and moves the
cursor to the intersection. (Uses
Solve function.) The resulting x-
value is saved in a variable
named ISECT.
Shading area You can shade a selected area between functions. This
process also gives you an approximate measurement of
the area shaded.
1. Open the Function aplet. The Function aplet opens in
the Symbolic view.
2. Select the expressions whose curves you want to
study.
3. Press to plot the functions.
4. Press or to position the cursor at the starting
point of the area you want to shade.
5. Press .
6. Press , then select Signed area and press
.
7. Press , choose the function that will act as the
boundary of the shaded area, and press .
8. Press the or key to shade in the area.
9. Press to calculate the area. The area
measurement is displayed near the bottom of the
screen.
To remove the shading, press to re-draw the plot.
Function aplet 3-11
Page 76

hp40g+.book Page 12 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Plotting a piecewise-defined function
Suppose you wanted to plot the following piecewisedefined function.
⎧
x 2 x 1–≤;+
⎪
fx()
1. Open the Function
2. Highlight the line you want to use, and enter the
2
=
⎨
x
⎪
4 xx1≥;–
⎩
1– x 1≤<;
aplet.
Select
Function
expression. (You can press to delete an existing
line, or
CLEAR to clear all lines.)
2
CHARS ≤
1
CHARS > 1
AND CHARS ≤ 1
4
CHARS > 1
Note: You can use the menu key to assist in the
entry of equations. It has the same effect as pressing
.
3-12 Function aplet
Page 77

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Parametric aplet
About the Parametric aplet
The Parametric aplet allows you to explore parametric
equations. These are equations in which both x and y are
defined as functions of t. They take the forms
and .
ygt()=
Getting started with the Parametric aplet
The following example uses the parametric equations
xt() 3 t
yt() 3 tcos=
sin=
4
xft()=
Note: This example will produce a circle. For this
example to work, the angle measure must be set to
degrees.
Open the
Parametric aplet
Define the
expressions
Parametric aplet 4-1
1. Open the Parametric aplet.
Select
Parametric
2. Define the expressions.
3
3
Page 78

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Set angle
measure
3. Set the angle measure to degrees.
MODES
Select Degrees
Set up the plot 4. Display the graphing options.
PLOT
The Plot Setup input form has two fields not included
in the Function aplet, TRNG and TSTEP. TRNG
specifies the range of t values. TSTEP specifies the
step value between t values.
5. Set the TRNG and TSTEP so that t steps from 0° to
360° in 5° steps.
360
5
Plot the
expression
4-2 Parametric aplet
6. Plot the expression.
7. To see all the circle, press twice.
Page 79

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Overlay plot 8. Plot a triangle graph over the existing circle graph.
PLOT
120
Select Overlay Plot
A triangle is displayed
rather than a circle (without changing the equation)
because the changed value of TSTEP ensures that
points being plotted are 120° apart instead of nearly
continuous.
You are able to explore the graph using trace, zoom,
split screen, and scaling functionality available in the
Function aplet. See “Exploring the graph” on page 27 for further information.
Display the
9. Display the table of values.
numbers
You can highlight a
t-value, type in a
replacement value,
and see the table jump
to that value. You can also zoom in or zoom out on
any t-value in the table.
You are able to explore the table using ,
, build your own table, and split screen
functionality available in the Function aplet. See
“Exploring the table of numbers” on page 2-17 for
further information.
Parametric aplet 4-3
Page 80

hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Page 81
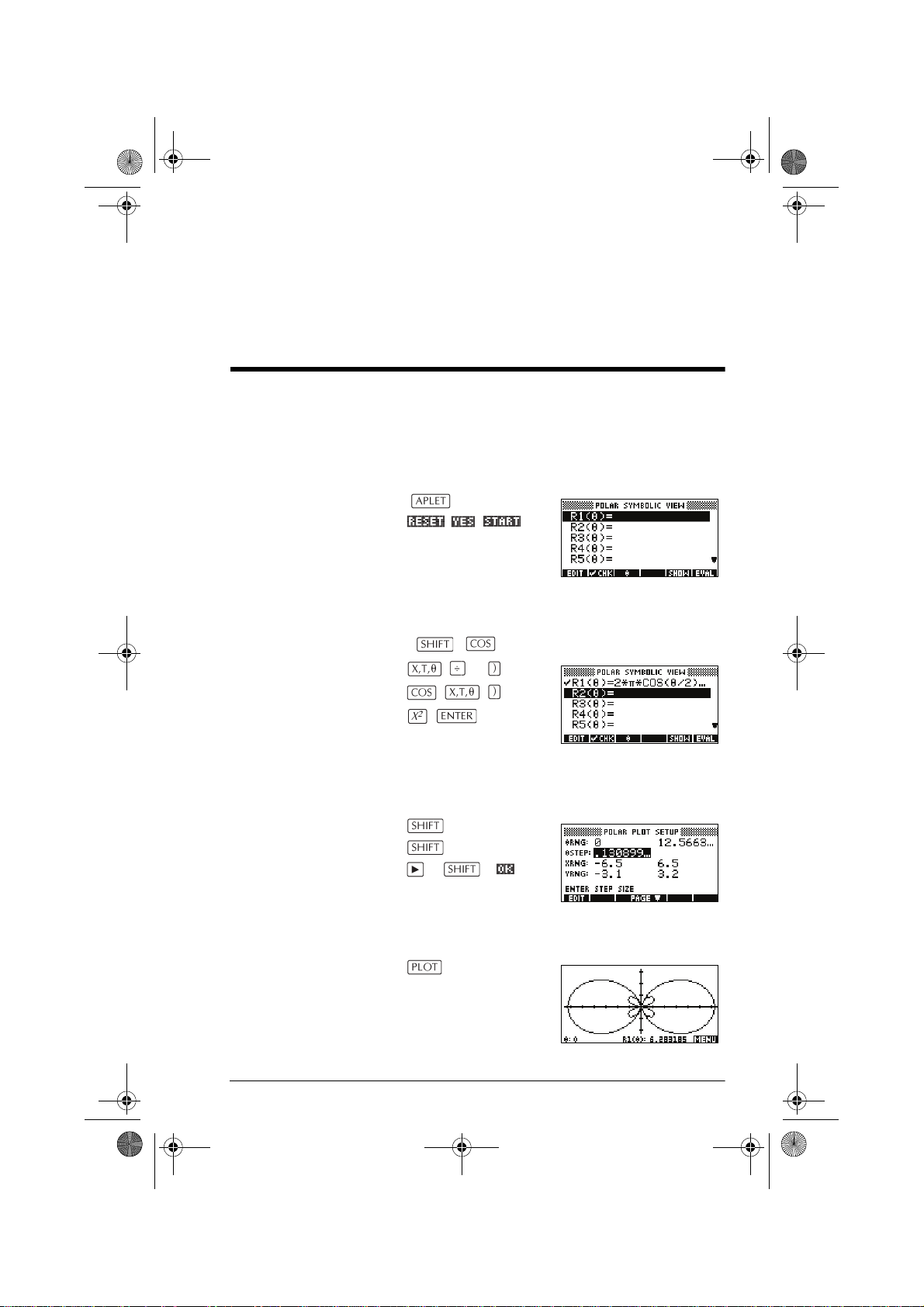
hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Polar aplet
Getting started with the Polar aplet
5
Open the Polar
aplet
Define the
expression
Specify plot
settings
1. Open the Polar aplet.
Select Polar
Like the Function aplet,
the Polar aplet opens
in the Symbolic view.
2. Define the polar equation .
2 π
2
3. Specify the plot settings. In this example, we will use
the default settings, except for the θRNG fields.
SETUP-PLOT
CLEAR
4 π
r 2πθ2⁄()θ()
2
coscos=
Plot the
4. Plot the expression.
expression
Polar aplet 5-1
Page 82

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Explore the
graph
Display the
numbers
5. Display the Plot view menu key labels.
The Plot view options
available are the same
as those found in the
Function aplet. See
“Exploring the graph”
on page 2-7 for further information.
6. Display the table of values for θ and R1.
The Numeric view
options available are
the same as those
found in the Function
aplet. See “Exploring the table of numbers” on
page 2-17 for further information.
5-2 Polar aplet
Page 83

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Sequence aplet
About the Sequence aplet
The Sequence aplet allows you to explore sequences.
You can define a sequence named, for example, U1:
• in terms of n
• in terms of U1(n–1)
•in terms of U1(n–2)
• in terms of another sequence, for example, U2(n)
• in any combination of the above.
The Sequence aplet allows you to create two types of
graphs:
6
– A Stairsteps graph plots n on the horizontal
axis and U
– A Cobweb graph plots U
axis and Un on the vertical axis.
on the vertical axis.
n
n–1
on the horizontal
Getting started with the Sequence aplet
The following example defines and then plots an
expression in the Sequence aplet. The sequence
illustrated is the well-known Fibonacci sequence where
each term, from the third term on, is the sum of the
preceding two terms. In this example, we specify three
sequence fields: the first term, the second term and a rule
for generating all subsequent terms.
However, you can also define a sequence by specifying
just the first term and the rule for generating all
subsequent terms. You will, though,have to enter the
second term if the hp40gs is unable to calculate it
automatically. Typically if the nth term in the sequence
depends on n–2, then you must enter the second term.
Sequence aplet 6-1
Page 84

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Open the
Sequence aplet
Define the
expression
1. Open the Sequence aplet.
Select
Sequence
The Sequence aplet
starts in the Symbolic
view.
2. Define the Fibonacci sequence, in which each term
(after the first two) is the sum of the preceding two
terms:
U11= U21=
In the Symbolic view of the Sequence aplet, highlight
the U
1 1
Note: You can use the
equations.
, , for .
U
n
U
+= n 3>
n 1–
n2–
1(1) field and begin defining your sequence.
, , ,
, and menu keys to assist in the entry of
Specify plot
settings
6-2 Sequence aplet
3. In Plot Setup, first set the SEQPLOT option to
Stairstep. Reset the default plot settings by
clearing the Plot Setup view.
SETUP-PLOT
CLEAR
8
8
Page 85

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Plot the
sequence
4. Plot the Fibonacci
sequence.
5. In Plot Setup, set the SEQPLOT option to Cobweb.
SETUP-PLOT
Select Cobweb
Display the table 6. Display the table of values for this example.
Sequence aplet 6-3
Page 86

hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Page 87

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Solve aplet
About the Solve aplet
The Solve aplet solves an equation or an expression for
its unknown variable. You define an equation or
expression in the symbolic view, then supply values for all
the variables except one in the numeric view. Solve works
only with real numbers.
Note the differences between an equation and an
expression:
• An equation contains an equals sign. Its solution is a
value for the unknown variable that makes both sides
have the same value.
• An expression does not contain an equals sign. Its
solution is a root, a value for the unknown variable
that makes the expression have a value of zero.
You can use the Solve aplet to solve an equation for any
one of its variables.
7
When the Solve aplet is started, it opens in the Solve
Symbolic view.
• In Symbolic view, you specify the expression or
equation to solve. You can define up to ten equations
(or expressions), named E0 to E9. Each equation can
contain up to 27 real variables, named A to Z and θ.
• In Numeric view, you specify the values of the known
variables, highlight the variable that you want to
solve for, and press .
You can solve the equation as many times as you want,
using new values for the knowns and highlighting a
different unknown.
Note: It is not possible to solve for more than one variable
at once. Simultaneous linear equations, for example,
should be solved using the Linear Solver aplet,matrices or
graphs in the Function aplet.
Solve aplet 7-1
Page 88

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Getting started with the Solve aplet
Suppose you want to find the acceleration needed to
increase the speed of a car from 16.67 m/sec (60 kph)
to 27.78 m/sec (100 kph) in a distance of 100 m.
The equation to solve is:
2
U22AD+=
Open the Solve
aplet
Define the
equation
Enter known
variables
1. Open the Solve aplet.
Select Solve
The Solve aplet starts in
the symbolic view.
2. Define the equation.
V
U
2
A
D
Note: You can use the menu key to assist in the
entry of equations.
3. Display the Solve numeric view screen.
7-2 Solve aplet
Page 89

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
4. Enter the values for the known variables.
2 7 7 8
1 6 6 7
1 0 0
HINT
If the Decimal Mark setting in the Modes input form
( MODES) is set to Comma, use instead of .
Solve the
unknown
variable
Plot the
equation
5. Solve for the unknown variable (A).
Therefore, the acceleration needed to increase the
speed of a car from 16.67 m/sec (60 kph) to 27.78
m/sec
(100 kph) in a distance of 100 m is approximately
2.47 m/s
Because the variable A in the equation is linear we
know that we need not look for any other solutions.
The Plot view shows one graph for each side of the
selected equation. You can choose any of the
variables to be the independent variable.
The current equation is .
One of these is , with , that is,
Y 771.7284=
The other graph will be , with
U 16.67= D 100=
Y 200A 277.8889+=
desired solution is the value of A where these two
lines intersect.
2
.
2
U22AD+=
2
YV
= V 27.78=
. This graph will be a horizontal line.
U22AD+=
and , that is,
. This graph is also a line. The
Solve aplet 7-3
Page 90
hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
6. Plot the equation for variable A.
Select Auto
Scale
7. Trace along the graph
representing the left
side of the equation
until the cursor nears
the intersection.
20 times
Note the value of A displayed near the bottom left
corner of the screen.
The Plot view provides a convenient way to find an
approximation to a solution instead of using the
Numeric view Solve option. See “Plotting to find
guesses” on page 7-7 for more information.
Solve aplet’s NUM view keys
The Solve aplet’s NUM view keys are:
Key Meaning
Copies the highlighted value to the
edit line for editing. Press when
done.
Displays a message about the
solution (see “Interpreting results” on
page 7-6).
Displays other pages of variables, if
any.
Displays the symbolic definition of the
current expression. Press when
done.
Finds a solution for the highlighted
variable, based on the values of the
other variables.
7-4 Solve aplet
Page 91
hp40g+.book Page 5 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Key Meaning (Continued)
CLEAR Resets all variable values to zero or
Use an initial guess
You can usually obtain a faster and more accurate
solution if you supply an estimated value for the unknown
variable before pressing . Solve starts looking for
a solution at the initial guess.
Before plotting, make sure the unknown variable is
highlighted in the numeric view. Plot the equation to help
you select an initial guess when you don’t know the range
in which to look for the solution. See “Plotting to find
guesses” on page 7-7 for further information.
Clears highlighted variable to zero or
deletes current character in edit line,
if edit line is active.
clears the edit line, if cursor is in edit
line.
HINT
An initial guess is especially important in the case of a
curve that could have more than one solution. In this case,
only the solution closest to the initial guess is returned.
Number format You can change the number format for the Solve aplet in
the Numeric Setup view. The options are the same as in
HOME MODES: Standard, Fixed, Scientific,
Engineering, Fraction and Mixed Fraction. For all except
Standard, you also specify how many digits of accuracy
you want. See “Mode settings” on page 1-10 for more
information.
You might find it handy to set a different number format
for the Solve aplet if, for example, you define equations
to solve for the value of money. A number format of
Fixed 2 would be appropriate in this case.
Solve aplet 7-5
Page 92

hp40g+.book Page 6 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Interpreting results
After Solve has returned a solution, press in the
Numeric view for more information. You will see one of
the following three messages. Press to clear the
message.
Message Condition
Zero The Solve aplet found a point where
both sides of the equation were
equal, or where the expression was
zero (a root), within the calculator's
12-digit accuracy.
Sign Reversal Solve found two points where the
difference between the two sides of
the equation has opposite signs, but
it cannot find a point in between
where the value is zero. Similarly,
for an expression, where the value
of the expression has different signs
but is not precisely zero. This might
be because either the two points are
neighbours (they differ by one in the
twelfth digit), or the equation is not
real-valued between the two points.
Solve returns the point where the
value or difference is closer to zero.
If the equation or expression is
continuously real, this point is
Solve’s best approximation of an
actual solution.
Extremum Solve found a point where the value
of the expression approximates a
local minimum (for positive values)
or maximum (for negative values).
This point may or may not be a
solution.
Or: Solve stopped searching at
9.99999999999E499, the largest
number the calculator can
represent.
Note that the value returned is
probably not valid.
7-6 Solve aplet
Page 93
hp40g+.book Page 7 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
If Solve could not find a solution, you will see one of the
following two messages.
Message Condition
HINT
The Root-Finder
at work
Bad Guess(es) The initial guess lies outside the
domain of the equation.
Therefore, the solution was not a
real number or it caused an error.
Constant? The value of the equation is the
same at every point sampled.
It is important to check the information relating to the
solve process. For example, the solution that the Solve
aplet finds is not a solution, but the closest that the
function gets to zero. Only by checking the information
will you know that this is the case.
You can watch the process of the root-finder calculating
and searching for a root. Immediately after pressing
to start the root-finder, press any key except .
You will see two intermediate guesses and, to the left, the
sign of the expression evaluated at each guess. For
example:
+ 2 2.219330555745
– 1 21.31111111149
You can watch as the root-finder either finds a sign
reversal or converges on a local extrema or does not
converge at all. If there is no convergence in process, you
might want to cancel the operation (press ) and start
over with a different initial guess.
Plotting to find guesses
The main reason for plotting in the Solve aplet is to help
you find initial guesses and solutions for those equations
that have difficult-to-find or multiple solutions.
Consider the equation of motion for an accelerating
body:
2
AT
TVX +=
0
Solve aplet 7-7
2
Page 94

hp40g+.book Page 8 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
where X is distance, V0 is initial velocity, T is time, and A
is acceleration. This is actually two equations, Y = X and
T + (AT 2) / 2.
Y = V
0
Since this equation is quadratic for T, there can be both
a positive and a negative solution. However, we are
concerned only with positive solutions, since only positive
distance makes sense.
1. Select the Solve aplet and enter the equation.
Select Solve
X
V
T
A
T 2
2. Find the solution for T (time) when X =30, V=2, and
A=4. Enter the values for X, V, and A; then highlight
the independent variable, T.
30
2
4
to highlight T
3. Use the Plot view to find an initial guess for T. First set
appropriate X and Y ranges in the Plot Setup. With
equation X = V x T + A x T
two graphs: one for and one for
X = V x T + A x T
2
/2. Since we have set in
this example, one of the graphs will be .
2
/2, the plot will produce
YX=
X 30=
Y 30=
Therefore, make the YRNG –5 to 35. Keep the XRNG
default of – 6.5 to 6.5.
SETUP-PLOT
5 35
4. Plot the graph.
7-8 Solve aplet
Page 95

hp40g+.book Page 9 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
5. Move the cursor near the positive (right-side)
intersection. This cursor value will be an initial guess
for T.
Press until the
cursor is at the
intersection.
The two points of
intersection show that
there are two solutions for this equation. However,
only positive values for X make sense, so we want to
find the solution for the intersection on the right side
of the y-axis.
6. Return to the Numeric
view.
Note: the T-value is filled in with the position of the
cursor from the Plot view.
7. Ensure that the T value is highlighted, and solve the
equation.
Use this equation to solve for another variable, such as
velocity. How fast must a body’s initial velocity be in
order for it to travel 50 m within 3 seconds? Assume the
same acceleration, 4 m/s
2
. Leave the last value of V as
the initial guess.
3
50
Solve aplet 7-9
Page 96

hp40g+.book Page 10 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Using variables in equations
You can use any of the real variable names, A to Z and
θ. Do not use variable names defined for other types,
such as M1 (a matrix variable).
Home variables All home variables (other than those for aplet settings, like
Xmin and Ytick) are global, which means they are
shared throughout the different aplets of the calculator. A
value that is assigned to a home variable anywhere
remains with that variable wherever its name is used.
Therefore, if you have defined a value for T (as in the
above example) in another aplet or even another Solve
equation, that value shows up in the Numeric view for this
Solve equation. When you then redefine the value for T
in this Solve equation, that value is applied to T in all
other contexts (until it is changed again).
This sharing allows you to work on the same problem in
different places (such as HOME and the Solve aplet)
without having to update the value whenever it is
recalculated.
HINT
As the Solve aplet uses existing variable values, be sure
to check for existing variable values that may affect the
solve process. (You can use
values to zero in the Solve aplet’s Numeric view if you
wish.)
CLEAR to reset all
Aplet variables Functions defined in other aplets can also be referenced
in the Solve aplet. For example, if, in the Function aplet,
you define F1(X)=X
the Solve aplet to solve the equation X
7-10 Solve aplet
2
+10, you can enter F1(X)=50 in
2
+10=50.
Page 97

hp40g+.book Page 1 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
Linear Solver aplet
About the Linear Solver aplet
The Linear Solver aplet allows you to solve a set of linear
equations. The set can contain two or three linear
equations.
In a two-equation set, each equation must be in the form
ax by+ k=
be in the form .
You provide values for a, b, and k (and c in three-
equation sets) for each equation, and the Linear Solver
aplet will attempt to solve for x and y (and z in threeequation sets).
The hp40gs will alert you if no solution can be found, or
if there is an infinite number of solutions.
. In a three-equation set, each equation must
ax by cz++ k=
8
Note that the Linear Solver aplet only has a numeric view.
Getting started with the Linear Solver aplet
The following example defines a set of three equations
and then solves for the unknown variables.
Open the
Linear Solver
aplet
Choose the
equation set
Linear Solver aplet 8-1
1. Open the Linear Sequence aplet.
Select Linear
Solver
The Linear Equation
Solver opens.
2. If the last time you used
the Linear Solver aplet
you solved for two
equations, the twoequation input form is
displayed (as in the
Page 98

hp40g+.book Page 2 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
example in the previous step). To solve a threeequation set, press . Now the input form
displays three equations.
If the three-equation input form is displayed and you want
to solve a two-equation set, press .
In this example, we are going to solve the following
equation set:
6x 9y 6z++ 5=
7x 10y 8z++ 10=
6x 4y+6=
Hence we need the three-equation input form.
Define and
solve the
equations
3. You define the equations you want to solve by
entering the co-efficients of each variable in each
equation and the constant term. Notice that the cursor
is immediately positioned at the co-efficient of x in the
first equation. Enter that co-efficient and press or
.
4. The cursor moves to the next co-efficient. Enter that coefficient, press or , and continue doing
likewise until you have defined all the equations.
Note: you can enter the name of a variable for any
co-efficient or constant. Press and begin
entering the name. The menu key appears.
Press that key to lock alphabetic entry mode. Press it
again to cancel the lock.
Once you have entered
enough values for the
solver to be able to
generate solutions,
those solutions appear
on the display. In the
example at the right,
the solver was able to find solutions for x, y, and z as
soon as the first co-efficient of the last equation was
entered.
8-2 Linear Solver aplet
Page 99

hp40g+.book Page 3 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
As you enter each of
the remaining known
values, the solution
changes. The example
at the right shows the
final solution once all
the co-efficients and
constants are entered for the set of equations we set
out to solve.
Linear Solver aplet 8-3
Page 100
hp40g+.book Page 4 Friday, December 9, 2005 1:03 AM
 Loading...
Loading...