Page 1

Maintenance and Service Guide
HP 406 Microtower Business PC
Page 2

© Copyright 2016 HP Development Company,
L.P. The information contained herein is subject
to change without notice.
Intel, Core, Pentium, and Celeron are
trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and
other countries. Bluetooth is a trademark
owned by its proprietor and used by HP under
license. Windows is a U.S. registered
trademarks of the Microsoft group of
companies. SD Logo is a trademark of its
proprietor.
The following applies to HP systems with Intel
Skylake or next-generation silicon chip-based
system shipping with Windows 7 or Windows
10 Pro systems downgraded to Windows 7
Professional, Windows 8 Pro, or Windows 8.1:
This version of Windows running with the
processor or chipsets used in this system has
limited support from Microsoft. For more
information about Microsoft’s support, please
see Microsoft’s Support Lifecycle FAQ at
https://support.microsoft.com/lifecycle
The information contained herein is subject to
change without notice. The only warranties for
HP products and services are set forth in the
express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein
should be construed as constituting an
additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Product notice
This user guide describes features that are
common to most models. Some features may
not be available on your computer.
Not all features are available in all editions of
Windows. This computer may require upgraded
and/or separately purchased hardware, drivers
and/or software to take full advantage of
Windows functionality. Go to
http://www.microsoft.com for details.
Software terms
By installing, copying, downloading, or
otherwise using any software product
preinstalled on this computer, you agree to be
bound by the terms of the HP End User License
Agreement (EULA). If you do not accept these
license terms, your sole remedy is to return the
entire unused product (hardware and software)
within 14 days for a full refund subject to the
refund policy of your seller.
For any further information or to request a full
refund of the price of the computer, please
contact your seller.
First Edition: September 2016
Document Part Number: 900989-001
Page 3

Safety warning notice
WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the device, do not place
the device directly on your lap or obstruct the device air vents. Use the device only on a hard, at surface. Do
not allow another hard surface, such as an adjoining optional printer, or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs
or clothing, to block airow. Also, do not allow the AC adapter to contact the skin or a soft surface, such as
pillows or rugs or clothing, during operation. The device and the AC adapter comply with the user-accessible
surface temperature limits dened by the International Standard for Safety of Information Technology
Equipment (IEC 60950-1).
iii
Page 4

iv Safety warning notice
Page 5

Table of contents
1 Product features ........................................................................................................................................... 1
Front panel components ........................................................................................................................................ 1
Rear panel components ......................................................................................................................................... 2
Serial number location .......................................................................................................................................... 3
2 Illustrated parts catalog ................................................................................................................................ 4
Microtower (MT) chassis spare parts ..................................................................................................................... 4
Computer major components ............................................................................................................. 4
Drives ................................................................................................................................................... 5
Misc parts ............................................................................................................................................. 6
3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation .................................................................... 7
Electrostatic discharge information ...................................................................................................................... 7
Generating static ................................................................................................................................. 7
Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment ................................................................................. 8
Personal grounding methods and equipment .................................................................................... 8
Grounding the work area ..................................................................................................................... 8
Recommended materials and equipment ........................................................................................... 9
Operating guidelines .............................................................................................................................................. 9
Routine care ......................................................................................................................................................... 10
General cleaning safety precautions ................................................................................................ 10
Cleaning the computer case .............................................................................................................. 10
Cleaning the keyboard ....................................................................................................................... 10
Cleaning the monitor ......................................................................................................................... 11
Cleaning the mouse ........................................................................................................................... 11
Service considerations ......................................................................................................................................... 11
Tools and software requirements ..................................................................................................... 11
Screws ............................................................................................................................................... 11
Cables and connectors ...................................................................................................................... 12
Hard Drives ........................................................................................................................................ 12
Lithium coin cell battery .................................................................................................................... 12
SATA hard drives .................................................................................................................................................. 13
SMART ATA drives ................................................................................................................................................ 13
4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis .................................................................... 14
Preparation for disassembly ............................................................................................................................... 14
v
Page 6

Access panel ......................................................................................................................................................... 15
Front bezel ........................................................................................................................................................... 16
Front bezel security ............................................................................................................................................. 17
Slim optical drive bezel blank .............................................................................................................................. 18
Memory ................................................................................................................................................................ 19
DIMMs ................................................................................................................................................ 19
DDR4-SDRAM DIMMs ......................................................................................................................... 19
Populating DIMM sockets .................................................................................................................. 19
Installing DIMMs ................................................................................................................................ 20
Expansion cards ................................................................................................................................................... 22
Drives ................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Drive positions ................................................................................................................................... 26
Removing a 9.5 mm slim optical drive .............................................................................................. 27
Installing a 9.5 mm slim optical drive ............................................................................................... 28
Removing a hard drive ...................................................................................................................... 30
Installing a hard drive ........................................................................................................................ 31
Front I/O and power switch assembly ................................................................................................................. 34
Fan sink ................................................................................................................................................................ 35
Processor ............................................................................................................................................................. 37
Speaker ................................................................................................................................................................ 38
Rear chassis fan ................................................................................................................................................... 39
Power supply ....................................................................................................................................................... 40
System board ....................................................................................................................................................... 42
System board callouts ....................................................................................................................... 43
5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility ........................................................................................................................ 44
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities ............................................................................................................................ 44
Using Computer Setup (F10) Utilities ................................................................................................ 44
Computer Setup–Main ....................................................................................................................... 46
Computer Setup—Security ............................................................................................................... 48
Computer Setup—Advanced ............................................................................................................. 50
Recovering the Conguration Settings ............................................................................................................... 55
6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics ............................................................................................................ 56
Safety and comfort .............................................................................................................................................. 56
Before you call for technical support .................................................................................................................. 56
Helpful hints ........................................................................................................................................................ 57
Solving general problems .................................................................................................................................... 58
Solving power problems ...................................................................................................................................... 62
Solving hard drive problems ................................................................................................................................ 63
Solving media card reader problems ................................................................................................................... 65
vi
Page 7

Solving display problems .................................................................................................................................... 66
Solving audio problems ....................................................................................................................................... 70
Solving printer problems ..................................................................................................................................... 72
Solving keyboard and mouse problems .............................................................................................................. 73
Solving Hardware Installation Problems ............................................................................................................. 74
Solving Network Problems .................................................................................................................................. 76
Solving memory problems .................................................................................................................................. 79
Solving CD-ROM and DVD problems .................................................................................................................... 80
Solving USB ash drive problems ........................................................................................................................ 82
Solving front panel component problems .......................................................................................................... 83
Solving Internet access problems ....................................................................................................................... 83
Solving software problems .................................................................................................................................. 85
7 POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes ......................................................... 86
POST numeric codes and text messages ............................................................................................................. 86
Interpreting system validation diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes ................................................ 91
8 Password security and resetting CMOS .......................................................................................................... 93
Resetting CMOS and/or the password jumper .................................................................................................... 94
Changing a Setup or Power-On password ........................................................................................................... 95
Deleting a Setup or Power-On password ............................................................................................................ 95
9 HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ......................................................................................................................... 96
Why run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics ................................................................................................................. 96
How to access and run HP PC Hardware Diagnostics .......................................................................................... 96
Downloading HP PC Hardware Diagnostics (UEFI) to a USB device .................................................................... 96
10 System backup and recovery ...................................................................................................................... 98
Backing up, restoring, and recovering in Windows 10 ........................................................................................ 98
Creating recovery media and backups .............................................................................................. 98
Creating HP Recovery media (select products only) ...................................................... 98
Using Windows tools ......................................................................................................................... 99
Restore and recovery ........................................................................................................................ 99
Recovering using HP Recovery Manager ...................................................................... 100
What you need to know before you get started ........................................ 100
Using the HP Recovery partition (select products only) ............................ 101
Using HP Recovery media to recover ......................................................... 101
Changing the computer boot order ............................................................ 101
Removing the HP Recovery partition (select products only) ..................... 101
Backing up, restoring, and recovering in Windows 7 ........................................................................................ 102
vii
Page 8

Creating recovery media ................................................................................................................. 102
Creating recovery media using HP Recovery Manager (select models only) ............... 103
Creating recovery discs with HP Recovery Disc Creator (select models only) ............. 104
Creating recovery discs .............................................................................. 104
Backing up your information ........................................................................................ 104
System Restore ............................................................................................................................... 105
System Recovery ............................................................................................................................. 105
System Recovery when Windows is responding .......................................................... 106
System Recovery when Windows is not responding .................................................... 106
System Recovery using recovery media (select models only) ..................................... 107
Using HP Recovery Disc operating system discs (select models only) ........................ 107
Appendix A Battery replacement ................................................................................................................... 109
Appendix B Power Cord Set Requirements ...................................................................................................... 112
General Requirements ....................................................................................................................................... 112
Japanese Power Cord Requirements ................................................................................................................. 112
Country-Specic Requirements ........................................................................................................................ 113
Appendix C Statement of Volatility ................................................................................................................ 114
Appendix D Specications ............................................................................................................................. 115
Index ........................................................................................................................................................... 116
viii
Page 9
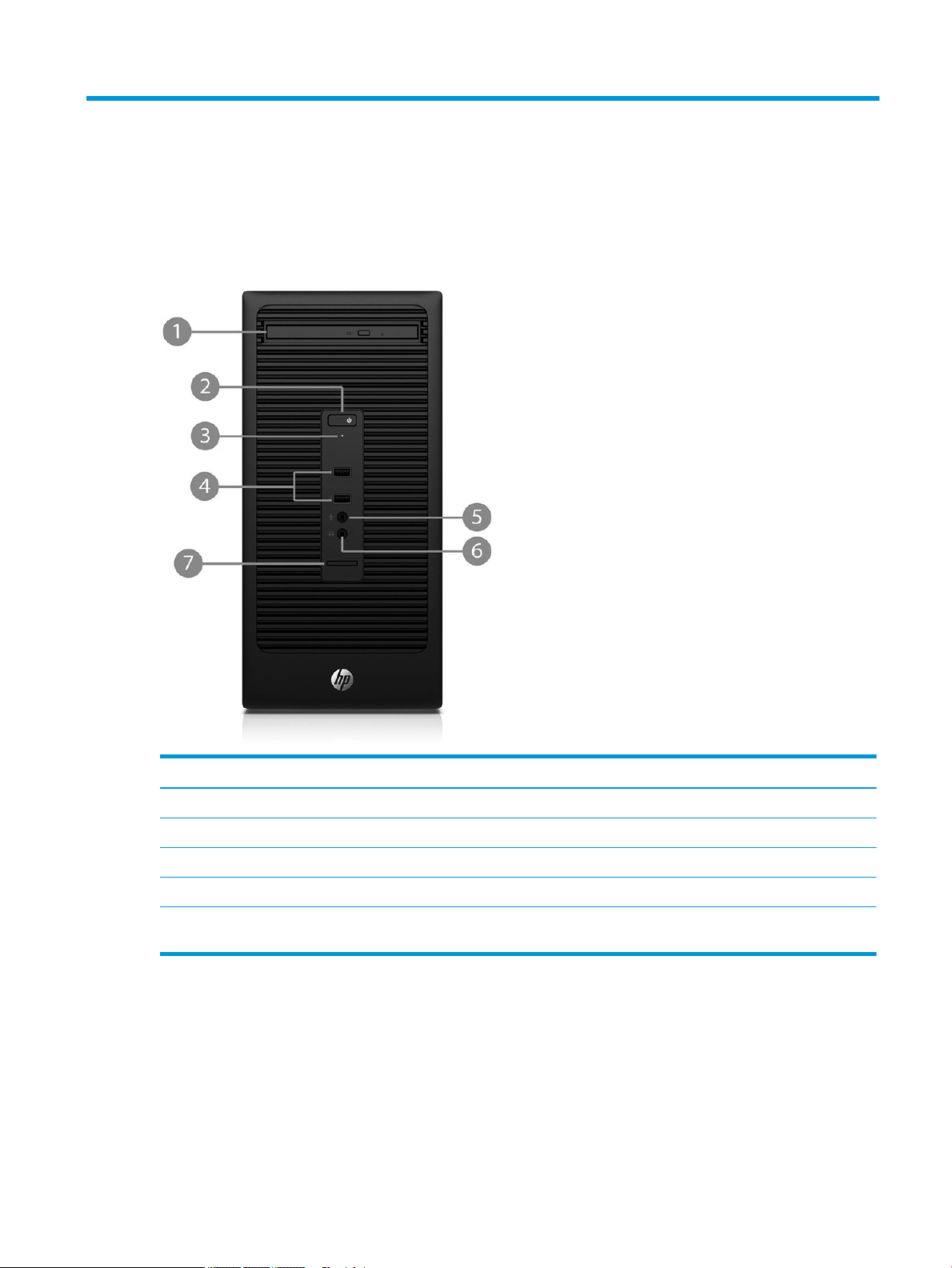
1 Product features
Front panel components
Drive conguration may vary by model. Some models have a bezel blank covering the optical drive bay.
Item Component Item Component
1 Slim optical drive (optional) 5 Microphone connector
2 Dual-state power button 6 Headphone connector
3 Hard drive activity light 7 SD card reader (optional)
4 USB 2.0 ports (2)
NOTE: The Power On Light is normally white when the power is on. If it is ashing red, there is a problem with the computer and it is
displaying a diagnostic code.
Front panel components 1
Page 10
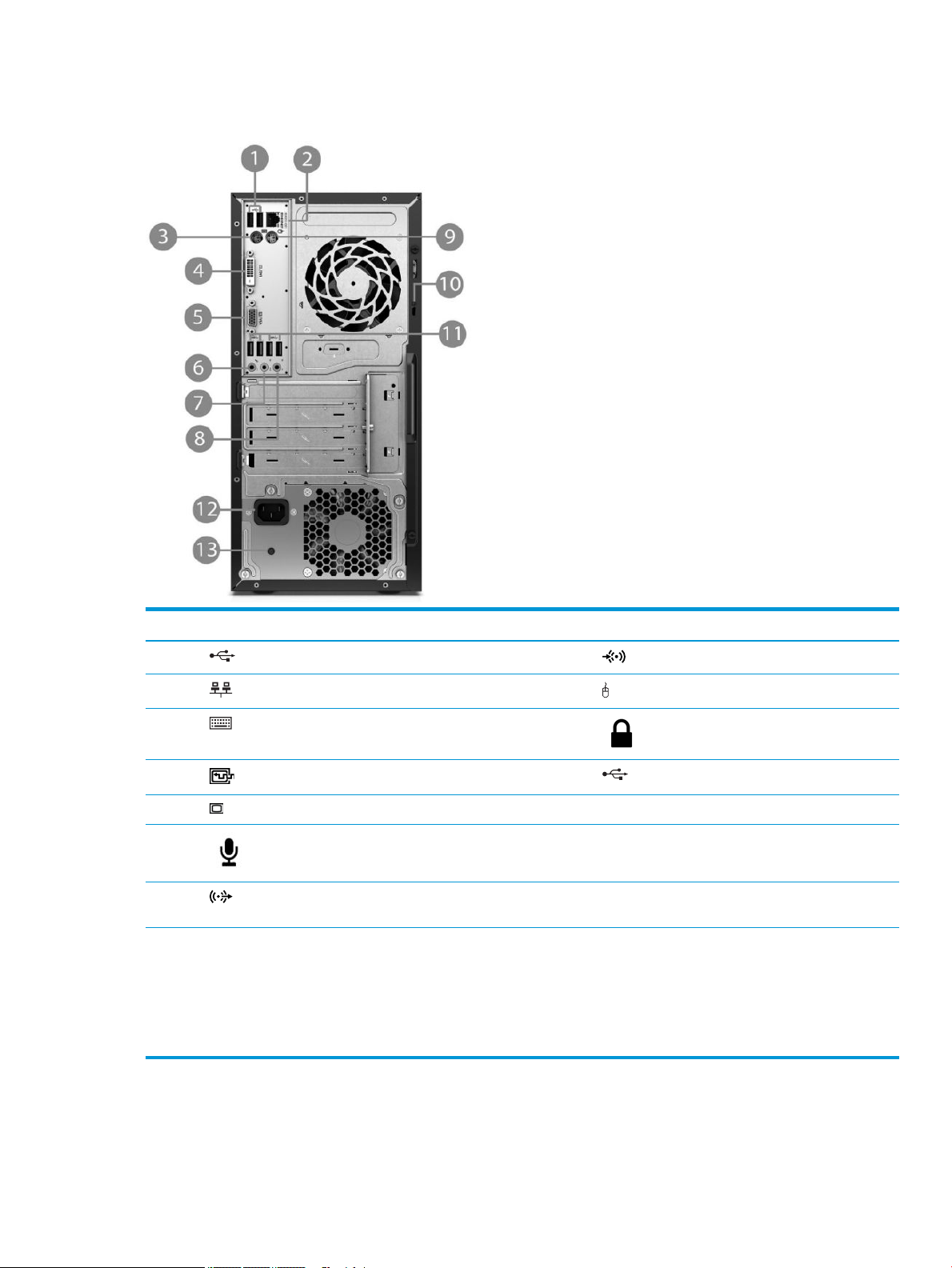
Rear panel components
Item Component Item Component
1 USB 2.0 ports (black) 8 Line-in audio connector (blue)
2 RJ-45 network connector 9 PS/2 mouse connector (green)
3 PS/2 keyboard connector (purple) 10 Security cable slot
4 DVI-D port 11 USB 3.0 ports (blue)
5 VGA monitor connector 12 Power cord connector
6 Microphone connector 13 Power supply activity light
7 Line-out connector for powered audio devices
(
green)
NOTE: When a device is plugged into the blue Line-In Audio Connector, a dialog box will pop up asking if you want to use the connector for a
line-in de
taskbar.
When a graphics card is installed in one of the system board slots, the video connectors on the graphics card and/or the integrated graphics
on the sys
The system board graphics can be disabled by changing settings in Computer Setup.
vice or a microphone. You can recongure the connector at any time by double-clicking the Audio Manager icon in the Windows
tem board may be used. The specic graphics card installed and software conguration will determine the behavior.
2 Chapter 1 Product features
Page 11

Serial number location
Each computer has a unique serial number and a product ID number that are located on the exterior of the
computer. Keep these numbers available for use when contacting customer service for assistance.
Serial number location 3
Page 12
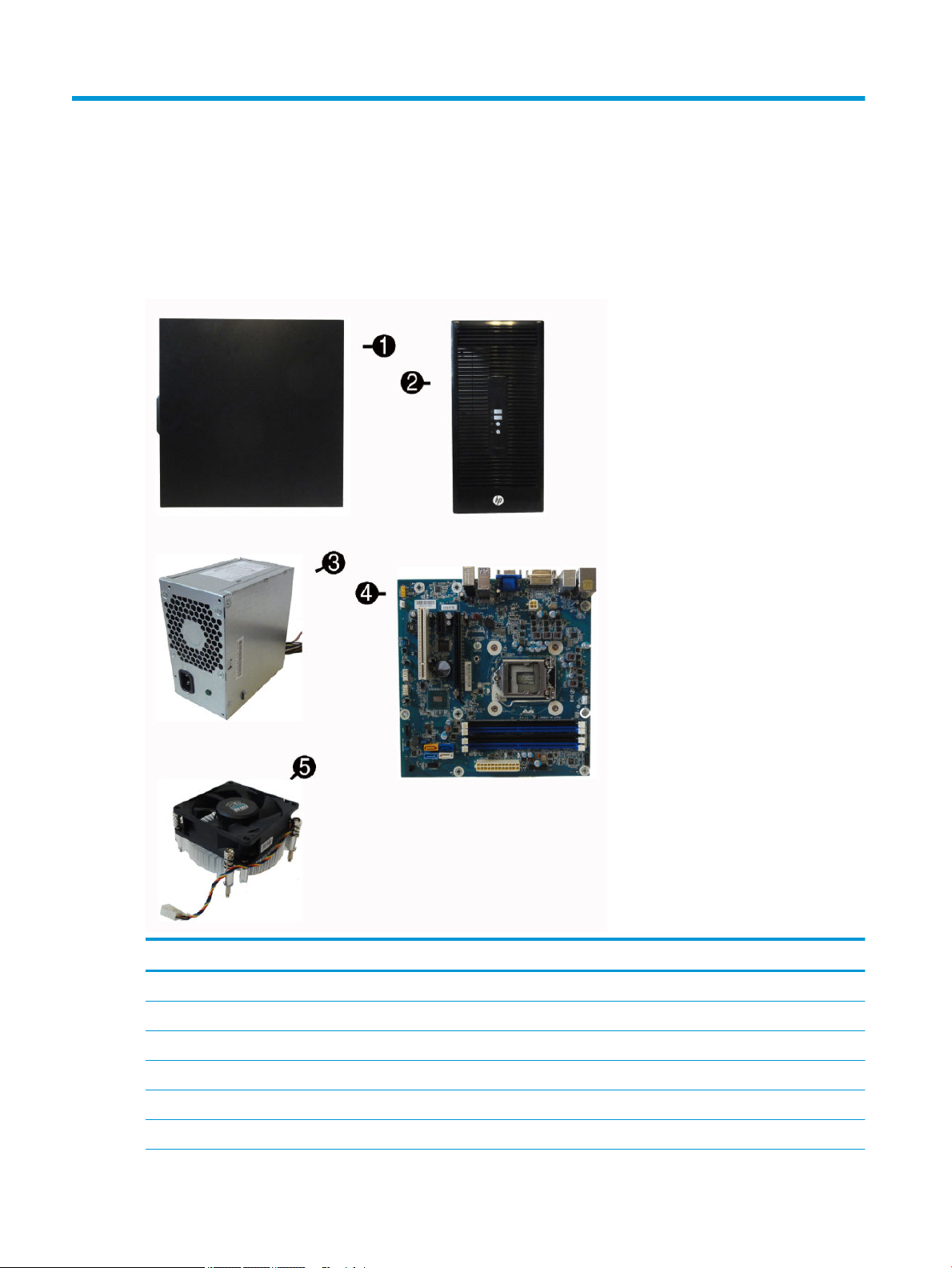
2 Illustrated parts catalog
Microtower (MT) chassis spare parts
Computer major components
Item Description
(1) Access panel
(2) Front bezel
(3) Power supply
300W, APFC
300W, Energy Star
300W, Energy Star 6.0, bronze
4 Chapter 2 Illustrated parts catalog
Page 13

Item Description
(4) System board (includes replacement thermal material)
(5) Fan sink (includes replacement thermal material)
x
Memory modules (PC4-17000)
8-GB
4-GB
x
Processors
(include replacement thermal material)
Intel Core i7 6700 (3.4-GHz, 8-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Core i5 6500 (3.2-GHz, 6-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Core i3 6320 (3.9-GHz, 4-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Core i3 6100 (3.7-GHz, 3-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Pentium G4520 (3.6-GHz, 3-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Pentium G4400 (3.3-GHz, 3-MB L3 cache), 65W
Intel Celeron G3900 (2.8-GHz, 2-MB L3 cache), 65W
x
not illustrated
Drives
Description
Hard drives
2-TB
1-TB
500-GB
Optical drives
DVD±RW drive
DVD-ROM drive
Grommet
, hard drive isolation, blue
Microtower (MT) chassis spare parts 5
Page 14

Misc parts
Item Description
(1) Fan
(2) Front I/O assembly
(3) Speaker
(4) SATA data cable, 10 inch, 1 straight end, 1 angled end
(5) SATA data cable, 11 inch, 1 straight end, 1 angled end
(6) Secure Digital (SD) card reader
x
x
x
x
x
Power cord, 2 meter
Slim optical drive bezel blank
Hard drive conversion bracket, 2.5-inch to 3.5-inch
Grommet, hard drive isolation, blue
Mouse
PS2, optical
HP USB
x
Keyboards
PS/2
PS/2, slim
USB
USB, slim
x
not illustrated
6 Chapter 2 Illustrated parts catalog
Page 15
3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and
disassembly preparation
This chapter provides general service information for the computer. Adherence to the procedures and
precautions described in this chapter is essential for proper service.
CAUTION: When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system
board. You must disconnect the power cord from the power source before opening the computer to prevent
system board or component damage.
Electrostatic discharge information
A sudden discharge of static electricity from your nger or other conductor can destroy static-sensitive
devices or microcircuitry. Often the spark is neither felt nor heard, but damage occurs. An electronic device
exposed to electrostatic discharge (ESD) may not appear to be aected at all and can work perfectly
throughout a normal cycle. The device may function normally for a while, but it has been degraded in the
internal layers, reducing its life expectancy.
Networks built into many integrated circuits provide some protection, but in many cases, the discharge
contains enough power to alter device parameters or melt silicon junctions.
Generating static
The following table shows how humidity aects the electrostatic voltage levels generated by dierent
activities. A product can be degraded by 700 volts.
●
Dierent activities generate dierent amounts of static electricity.
●
Static electricity increases as humidity decreases.
Relative Humidity
Event 55% 40% 10%
Walking across carpet
Walking across vinyl oor
Motions of bench worker
Removing DIPs from plastic tube
Removing DIPs from vinyl tray
Removing DIPs from Styrofoam
Removing bubble pack from PCB
Packing PCBs in foam-lined box
7,500 V
3,000 V
400 V
400 V
2,000 V
3,500 V
7,000 V
5,000 V
15,000 V
5,000 V
800 V
700 V
4,000 V
5,000 V
20,000 V
11,000 V
35,000 V
12,000 V
6,000 V
2,000 V
11,500 V
14,500 V
26,500 V
21,000 V
Electrostatic discharge information 7
Page 16

Preventing electrostatic damage to equipment
Many electronic components are sensitive to ESD. Circuitry design and structure determine the degree of
sensitivity. The following packaging and grounding precautions are necessary to prevent damage to electric
components and accessories.
●
To avoid hand contact, transport products in static-safe containers such as tubes, bags, or boxes.
●
Protect all electrostatic-sensitive parts and assemblies with conductive or approved containers or
packaging.
●
Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free stations.
●
Place items on a grounded surface before removing them from their containers.
●
Always be properly grounded when touching a sensitive component or assembly.
●
Avoid contact with pins, leads, or circuitry.
●
Place reusable electrostatic-sensitive parts from assemblies in protective packaging or conductive
foam.
Personal grounding methods and equipment
Use the following equipment to prevent static electricity damage to equipment:
●
Wrist straps are exible straps with a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance in the ground cords.
To provide proper ground, a strap must be worn snugly against bare skin. The ground cord must be
connected to the banana plug connector on the grounding mat or workstation and t snugly into it.
●
Heel straps/Toe straps/Boot straps can be used at standing workstations and are compatible with
most types of shoes or boots. On conductive oors or dissipative oor mats, use them on both feet with
a maximum of one-megohm ± 10% resistance between the operator and ground.
Static Shielding Protection Levels
Method Voltage
Antistatic plastic
Carbon-loaded plastic
Metallized laminate
Grounding the work area
To prevent static damage at the work area, observe the following precautions:
●
Cover the work surface with approved static-dissipative material. Provide a wrist strap connected to the
work surface and use properly grounded tools and equipment.
●
Use static-dissipative mats, foot straps, or air ionizers to give added protection.
●
Handle electrostatic-sensitive components, parts, and assemblies by the case or PCB laminate. Handle
them only at static-free work areas.
●
Turn o power and input signals before inserting and removing connectors or test equipment.
1,500
7,500
15,000
●
Use xtures made of static-safe materials when xtures must directly contact dissipative surfaces.
●
Keep work area free of nonconductive materials such as ordinary plastic assembly aids and Styrofoam.
●
Use eld service tools, such as cutters, screwdrivers, and vacuums, that are conductive.
8 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation
Page 17

Recommended materials and equipment
The following grounding equipment is recommended to prevent electrostatic damage:
●
Antistatic tape
●
Antistatic smocks, aprons, or sleeve protectors
●
Conductive bins and other assembly or soldering aids
●
Conductive foam
●
Conductive tabletop workstations with ground cords of one-megohm +/- 10% resistance
●
Static-dissipative table or oor mats with hard ties to ground
●
Field service kits
●
Static awareness labels
●
Wrist straps and footwear straps providing one-megohm +/- 10% resistance
●
Material handling packages
●
Conductive plastic bags
●
Conductive plastic tubes
●
Conductive tote boxes
●
Opaque shielding bags
●
Transparent metallized shielding bags
●
Transparent shielding tubes
Operating guidelines
To prevent overheating and to help prolong the life of the computer:
●
Keep the computer away from excessive moisture, direct sunlight, and extremes of heat and cold.
●
Operate the computer on a sturdy, level surface. Leave a 10.2 cm (4-inch) clearance on all vented sides
of the computer and above the monitor to permit the required airow.
●
Never restrict the airow into the computer by blocking any vents or air intakes. Do not place the
keyboard, with the keyboard feet down, directly against the front of the desktop unit as this also
restricts airow.
●
Occasionally clean the air vents on all vented sides of the computer. Lint, dust, and other foreign matter
can block the vents and limit the airow. Be sure to unplug the computer before cleaning the air vents.
●
Never operate the computer with the cover or side panel removed.
●
Do not stack computers on top of each other or place computers so near each other that they are subject
to each other’s re-circulated or preheated air.
●
If the computer is to be operated within a separate enclosure, intake and exhaust ventilation must be
provided on the enclosure, and the same operating guidelines listed above will still apply.
●
Keep liquids away from the computer and keyboard.
Operating guidelines 9
Page 18

●
Never cover the ventilation slots on the monitor with any type of material.
●
Install or enable power management functions of the operating system or other software, including
sleep states.
Routine care
General cleaning safety precautions
1. Never use solvents or ammable solutions to clean the computer.
2. Never immerse any parts in water or cleaning solutions; apply any liquids to a clean cloth and then use
the cloth on the component.
3. Always unplug the computer when cleaning with liquids or damp cloths.
4. Always unplug the computer before cleaning the keyboard, mouse, or air vents.
5. Disconnect the keyboard before cleaning it.
6. Wear safety glasses equipped with side shields when cleaning the keyboard.
Cleaning the computer case
Follow all safety precautions in General cleaning safety precautions on page 10 before cleaning the computer.
To clean the computer case, follow the procedures described below:
●
To remove light stains or dirt, use plain water with a clean, lint-free cloth or swab.
●
For stronger stains, use a mild dishwashing liquid diluted with water. Rinse well by wiping the surface
with a cloth or swab dampened with clear water.
●
For stubborn stains, use isopropyl (rubbing) alcohol. No rinsing is needed; alcohol will evaporate quickly
without leaving a residue.
●
After cleaning, always wipe the unit with a clean, lint-free cloth.
●
Occasionally clean the air vents on the computer. Lint and other foreign matter can block the vents and
limit the airow.
Cleaning the keyboard
Follow all safety precautions in General cleaning safety precautions on page 10 before cleaning the keyboard.
To clean the tops of the keys or the keyboard body, follow the procedures described in Cleaning the computer
case on page 10.
When cleaning debris from under the keys, review all rules in General cleaning safety precautions on page 10
before following these procedures:
CAUTION: Use safety glasses equipped with side shields before attempting to clean debris from under the
keys.
●
Visible debris underneath or between the keys may be removed by vacuuming or shaking.
●
Canned, pressurized air may be used to clean debris from under the keys. Caution should be used as too
much air pressure can dislodge lubricants applied under the wide keys.
10 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation
Page 19
●
If you want to remove a key, use a specially designed key puller to prevent damage to the keys. This tool
is available through many electronics supply outlets.
CAUTION: Never remove a wide, level key (like the space bar) from the keyboard. If these keys are
improperly removed or installed, the keyboard may not function properly.
●
Cleaning under a key may be done with a swab moistened with isopropyl alcohol and then squeezed out.
Be careful not to wipe away lubricants necessary for proper key functions. Use tweezers to remove any
bers or dirt in conned areas. Allow the parts to air dry before reassembly.
Cleaning the monitor
●
Wipe the monitor screen with a towelette designed for cleaning monitors or with a clean cloth
moistened with water. Do not use sprays or aerosols directly on the screen; the liquid may seep into the
housing and damage a component. Never use solvents or ammable liquids on the monitor.
●
To clean the monitor body follow the procedures in Cleaning the computer case on page 10.
Cleaning the mouse
Before cleaning the mouse, ensure that the power to the computer is turned o.
●
Clean the mouse ball by rst removing the retaining plate and the ball from the housing. Pull out any
debris from the ball socket and wipe the ball with a clean, dry cloth before reassembly.
●
To clean the mouse body, follow the procedures in Cleaning the computer case on page 10.
Service considerations
Listed below are some of the considerations that you should keep in mind during the disassembly and
assembly of the computer.
Tools and software requirements
To service the computer, you need the following:
●
Torx T-15 screwdriver
●
Flat-bladed screwdriver (may sometimes be used in place of the Torx screwdriver)
●
Phillips #2 screwdriver
●
Diagnostics software
Screws
The screws used in the computer are not interchangeable. They may have standard or metric threads and may
be of dierent lengths. If an incorrect screw is used during the reassembly process, it can damage the unit. HP
strongly recommends that all screws removed during disassembly be kept with the part that was removed,
then returned to their proper locations.
CAUTION: Metric screws have a black nish. U.S. screws have a silver nish and are used on hard drives only.
CAUTION: As each subassembly is removed from the computer, it should be placed away from the work area
to prevent damage.
Service considerations 11
Page 20

Cables and connectors
Most cables used throughout the unit are at, exible cables. These cables must be handled with care to
avoid damage. Apply only the tension required to seat or unseat the cables during insertion or removal from
the connector. Handle cables by the connector whenever possible. In all cases, avoid bending or twisting the
cables, and ensure that the cables are routed in such a way that they cannot be caught or snagged by parts
being removed or replaced.
CAUTION: When servicing this computer, ensure that cables are placed in their proper location during the
reassembly process. Improper cable placement can damage the computer.
Hard Drives
Handle hard drives as delicate, precision components, avoiding all physical shock and vibration. This applies
to failed drives as well as replacement spares.
●
If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble-pack mailer or other suitable protective packaging
and label the package “Fragile: Handle With Care.”
●
Do not remove hard drives from the shipping package for storage. Keep hard drives in their protective
packaging until they are actually mounted in the computer.
●
Avoid dropping drives from any height onto any surface.
●
If you are inserting or removing a hard drive, turn o the computer. Do not remove a hard drive while the
computer is on or in standby mode.
●
Before handling a drive, ensure that you are discharged of static electricity. While handling a drive, avoid
touching the connector.
●
Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive.
●
Avoid exposing a hard drive to liquids, temperature extremes, or products that have magnetic elds
such as monitors or speakers.
Lithium coin cell battery
The battery that comes with the computer provides power to the real-time clock and has a minimum lifetime
of about three years.
See the appropriate removal and replacement chapter for the chassis you are working on in this guide for
instructions on the replacement procedures.
WARNING! This computer contains a lithium battery. There is a risk of re and chemical burn if the battery is
handled improperly. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts, dispose in water or re, or
expose it to temperatures higher than 140ºF (60ºC). Do not attempt to recharge the battery.
NOTE: Batteries, battery packs, and accumulators should not be disposed of together with general
household waste. In order to forward them for recycling or proper disposal, please use the public collection
system or return them to HP.
12 Chapter 3 Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation
Page 21

SATA hard drives
Serial ATA Hard Drive Characteristics
Number of pins/conductors in data cable 7/7
Number of pins in power cable 15
Maximum data cable length 39.37 in (100 cm)
Data interface voltage dierential 400-700 mV
Drive voltages 3.3 V, 5 V, 12 V
Jumpers for conguring drive N/A
Data transfer rate 6.0 Gb/s
SMART ATA drives
The Self Monitoring Analysis and Recording Technology (SMART) ATA drives for HP personal computers have
built-in drive failure prediction that warns the user or network administrator of an impending failure (crash)
of the hard drive. The SMART drive tracks fault prediction and failure indication parameters such as
reallocated sector count, spin retry count, and calibration retry count. If the drive determines that a failure is
imminent, it generates a fault alert.
SATA hard drives 13
Page 22
4 Removal and replacement procedures –
Microtower (MT) chassis
Adherence to the procedures and precautions described in this chapter is essential for proper service. After
completing all necessary removal and replacement procedures, run the Diagnostics utility to verify that all
components operate properly.
NOTE: Not all features listed in this guide are available on all computers.
Preparation for disassembly
See Routine care, SATA drive guidelines, and disassembly preparation on page 7 for initial safety procedures.
1. Remove/disengage any security devices that prohibit opening the computer.
2. Close any open software applications.
3. Exit the operating system.
4. Remove any compact disc or media card from the computer.
5. Turn o the computer and any peripheral devices that are connected to it.
CAUTION: Turn o the computer before disconnecting any cables.
Regardless of the power-on state, voltage is always present on the system board as long as the system
is plugged into an active AC outlet. In some systems the cooling fan is on even when the computer is in
the “Standby,” or “Suspend” modes. The power cord should always be disconnected before servicing a
unit.
6. Disconnect the power cord from the electrical outlet and then from the computer.
7. As applicable, lay the computer down on its side to achieve a safe working position.
NOTE: During disassembly, label each cable as you remove it, noting its position and routing. Keep all
screws with the units removed.
CAUTION: The screws used in the computer are of dierent thread sizes and lengths; using the wrong screw
in an application may damage the unit.
14 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 23

Access panel
To access internal components, you must remove the access panel:
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the two screws that secure the panel to the chassis (1), slide the panel back to disengage it (2)
and then lift it o the computer (3).
To replace the access panel, reverse the disassembly procedures.
Access panel 15
Page 24

Front bezel
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
3. Lift up the three tabs on the side of the bezel (1), and then rotate the bezel o the chassis (2).
To replace the front bezel, reverse the disassembly procedures.
16 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 25

Front bezel security
The front bezel can be secured in place by installing a screw through the front of the chassis into the front
bezel.
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
3. Install a 6-32 screw through the front of the chassis and into the screw hole located below the center
bezel release tab.
4. Replace the computer access panel.
5. Reconnect the power cord and any external devices, and then turn on the computer.
6. Lock any security devices that were disengaged when the access panel was removed.
Front bezel security 17
Page 26

Slim optical drive bezel blank
On some models, there is a bezel blank covering the slim optical drive bay. Remove the bezel blank before
installing an optical drive. To remove the bezel blank:
1. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
2. Remove the front bezel (Front bezel on page 16)
3. To remove the bezel blank, press upward on the bottom tab and press downward on the top tab on the
side of the blank (1), and then rotate the blank o the front of the bezel (2).
18 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 27
Memory
Description
8-GB, PC4-17000
4-GB, PC4-17000
The computer comes with double data rate 4 synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR4-SDRAM)
dual inline memory modules (DIMMs).
DIMMs
The memory sockets on the system board can be populated with up to four industry-standard DIMMs. These
memory sockets are populated with at least one preinstalled DIMM. To achieve the maximum memory
support, you can populate the system board with up to 64 GB of memory congured in a high-performing
dual channel mode.
DDR4-SDRAM DIMMs
For proper system operation, the DIMMs must be:
●
industry-standard 288-pin
●
unbuered non-ECC PC4-17000 DDR4-2133 MHz-compliant
●
1.2 volt DDR4-SDRAM DIMMs
The DIMMs must also:
●
support CAS latency 15 DDR4 2133 MHz (15-15-15 timing)
●
contain the mandatory JEDEC SPD information
In addition, the computer supports:
●
512-Mbit, 1-Gbit, and 2-Gbit non-ECC memory technologies
●
single-sided and double-sided DIMMs
●
DIMMs constructed with x8 and x16 DDR devices; DIMMs constructed with x4 SDRAM are not supported
NOTE: The system will not operate properly if you install unsupported DIMMs.
Populating DIMM sockets
There are four DIMM sockets on the system board, with two sockets per channel. The sockets are labeled
DIMM1, DIMM2, DIMM3, and DIMM4. Sockets DIMM1 and DIMM2 operate in memory channel B. Sockets DIMM3
and DIMM4 operate in memory channel A.
The system will automatically operate in single channel mode, dual channel mode, or ex mode, depending
on how the DIMMs are installed.
NOTE: Single channel and unbalanced dual channel memory congurations will result in inferior graphics
performance.
Memory 19
Page 28

●
The system will operate in single channel mode if the DIMM sockets are populated in one channel only.
●
The system will operate in a higher-performing dual channel mode if the total memory capacity of the
DIMMs in Channel A is equal to the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in Channel B. The technology and
device width can vary between the channels. For example, if Channel A is populated with two 1 GB
DIMMs and Channel B is populated with one 2 GB DIMM, the system will operate in dual channel mode.
●
The system will operate in ex mode if the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in Channel A is not equal
to the total memory capacity of the DIMMs in Channel B. In ex mode, the channel populated with the
least amount of memory describes the total amount of memory assigned to dual channel and the
remainder is assigned to single channel. For optimal speed, the channels should be balanced so that the
largest amount of memory is spread between the two channels. If one channel will have more memory
than the other, the larger amount should be assigned to Channel A. For example, if you are populating
the sockets with one 2 GB DIMM, and three 1 GB DIMMs, Channel A should be populated with the 2 GB
DIMM and one 1 GB DIMM, and Channel B should be populated with the other two 1 GB DIMMs. With this
conguration, 4 GB will run as dual channel and 1 GB will run as single channel.
●
In any mode, the maximum operational speed is determined by the slowest DIMM in the system.
Installing DIMMs
CAUTION: You must disconnect the power cord and wait approximately 30 seconds for the power to drain
before adding or removing memory modules. Regardless of the power-on state, voltage is always supplied to
the memory modules as long as the computer is plugged into an active AC outlet. Adding or removing
memory modules while voltage is present may cause irreparable damage to the memory modules or system
board.
The memory module sockets have gold-plated metal contacts. When upgrading the memory, it is important
to use memory modules with gold-plated metal contacts to prevent corrosion and/or oxidation resulting from
having incompatible metals in contact with each other.
Static electricity can damage the electronic components of the computer or optional cards. Before beginning
these procedures, ensure that you are discharged of static electricity by briey touching a grounded metal
object.
When handling a memory module, be careful not to touch any of the contacts. Doing so may damage the
module.
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
20 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 29

3. Open both latches of the memory module socket (1), and insert the memory module into the socket (2).
NOTE: A memory module can be installed in only one way. Match the notch on the module with the tab
on the memory socket.
Populate the black DIMM sockets rst.
For maximum performance, populate the sockets so that the memory capacity is spread as equally as
possible between Channel A and Channel B.
4. Push the module down into the socket, ensuring that the module is fully inserted and properly seated.
Make sure the latches are in the closed position (3).
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 to install any additional modules.
6. Replace the computer access panel.
7. Reconnect the power cord and turn on the computer.
8. Lock any security devices that were disengaged when the access panel was removed.
The computer should automatically recognize the additional memory the next time you turn on the computer.
Memory 21
Page 30

Expansion cards
The computer has one PCI Express x1 expansion socket and two PCI Express x16 expansion sockets.
NOTE: You can install a PCI Express x1, x8, or x16 expansion card in the PCI Express x16 socket.
For dual graphics card congurations, the rst (primary) card must be installed in the PCI Express x16 socket
that is NOT downshifted to a x4.
To remove, replace, or add an expansion card:
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
3. Release the slot cover retention latch that secures the slot covers by removing the Torx screw (1), sliding
the latch up (2), and pulling the latch away from the computer (3).
4. Locate the correct vacant expansion socket on the system board and the corresponding expansion slot
on the back of the computer chassis.
5. Before installing an expansion card, remove the expansion slot cover or the existing expansion card.
NOTE: Before removing an installed expansion card, disconnect any cables that may be attached to
the expansion card.
a. If you are installing an expansion card in a vacant socket, you must slide one of the expansion slot
covers up and out of the chassis or use a atblade screwdriver to pry out one of the metal shields
on the rear panel that covers the expansion slot. Be sure to remove the appropriate shield for the
expansion card you are installing.
22 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 31

b. If you are removing a PCI Express x1 card, hold the card at each end and carefully rock it back and
forth until the connectors pull free from the socket. Lift the card straight up (1) then away from the
inside of the chassis (2) to remove it. Be sure not to scrape the card against other components.
Expansion cards 23
Page 32

c. If you are removing a PCI Express x16 card, pull the retention arm on the back of the expansion
socket away from the card and carefully rock the card back and forth until the connectors pull free
from the socket. Lift the card straight up then away from the inside of the chassis to remove it. Be
sure not to scrape the card against other components.
6. Store the removed card in anti-static packaging.
7. If you are not installing a new expansion card, install an expansion slot cover to close the open slot.
CAUTION: After removing an expansion card, you must replace it with a new card or expansion slot
cover for proper cooling of internal components during operation.
24 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 33

Drives
Description
Hard drives
2-TB
1-TB
500-GB
Optical drives
DVD±RW drive
DVD-ROM drive
Grommet, hard drive isolation, blue
When installing drives, follow these guidelines:
●
The primary Serial ATA (SATA) hard drive must be connected to the dark blue primary SATA connector on
the system board labeled SATA0.
●
Connect secondary hard drives and optical drives to one of the remaining SATA connectors on the
system board.
CAUTION: To prevent loss of work and damage to the computer or drive:
If you are inserting or removing a drive, shut down the operating system properly, turn o the computer, and
unplug the power cord. Do not remove a drive while the computer is on or in standby mode.
Before handling a drive, ensure that you are discharged of static electricity. While handling a drive, avoid
touching the connector. For more information about preventing electrostatic damage, refer to Electrostatic
discharge information on page 7.
Handle a drive carefully; do not drop it.
Do not use excessive force when inserting a drive.
Avoid exposing a hard drive to liquids, temperature extremes, or products that have magnetic elds such as
monitors or speakers.
If a drive must be mailed, place the drive in a bubble-pack mailer or other protective packaging and label the
package “Fragile: Handle With Care.”
Drives 25
Page 34

Drive positions
Item Component
1 9.5-mm slim optical drive bay
2 3.5-inch secondary hard drive bay
3 3.5-inch primary hard drive bay
NOTE: The bottom bay supports up to two 2.5-inch hard drives installed using an adapter bracket.
NOTE: The drive conguration on your computer may be dierent than the drive conguration shown above.
To verify the type and size of the storage devices installed in the computer, run Computer Setup.
26 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 35

Removing a 9.5 mm slim optical drive
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14)
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15)
3. Remove the front bezel (Front bezel on page 16)
4. Disconnect the power cable (1) and data cable (2) from the rear of the optical drive.
CAUTION: When removing the cables, pull the tab or connector instead of the cable itself to avoid
damaging the cable.
CAUTION: When removing the cables, pull the tab or connector instead of the cable itself to avoid
damaging the cable.
5. Press upward on the green release latch on the underside of the drive (1), and then slide the drive out of
the drive bay (2).
Drives 27
Page 36

Installing a 9.5 mm slim optical drive
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. If you are installing a slim optical drive in a bay covered by a bezel blank, remove the front bezel and
then remove the bezel blank. See Front bezel on page 16 for more information.
4. Follow the instructions for removing the optical drive if one was installed. Refer to Removing a 9.5 mm
slim optical drive on page 27.
5. Align the small pin on the release latch with the small hole on the side of the drive and press the latch
rmly onto the drive.
6. Slide the optical drive through the front of the chassis (1) all the way into the bay so that the green latch
locks onto the chassis frame (2).
28 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 37

7. Connect the power cable (1) and data cable (2) to the rear of the optical drive.
8. If installing a new drive, connect the opposite end of the data cable to one of the SATA connectors
(labeled SATA1 or SATA2) on the system board.
9. Replace the front bezel if it was removed.
10. Replace the computer access panel.
11. Reconnect the power cord and any external devices, and then turn on the computer.
12. Lock any security devices that were disengaged when the access panel was removed.
Drives 29
Page 38

Removing a hard drive
NOTE: Before you remove the old hard drive, be sure to back up the data from the old hard drive so that you
can transfer the data to the new hard drive.
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Disconnect the power cable (1) and data cable (2) from the rear of the hard drive.
4. Pull the green latch next to the drive outward (1) and slide the drive out of the bay (2).
30 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 39

Installing a hard drive
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. You can install a 3.5-inch hard drive or a 2.5-inch hard drive with a 3.5-inch adapter bracket similar to
the example shown below.
●
Slide the 2.5-inch drive into the bay adapter bracket, ensuring the connector on the drive is fully
inserted into the connector on the adapter bracket.
●
Secure the drive to the bay adapter bracket by installing four black M3 adapter bracket screws
through the sides of the bracket into the drive.
Drives 31
Page 40

4. Install four mounting screws into the sides of the 3.5-inch drive or the 2.5-inch drive adapter bracket
(two on each side).
NOTE: HP has supplied four extra mounting screws installed on the chassis next to the hard drive bays.
Refer to Drives on page 25 for an illustration of the location of the extra mounting screws.
5. Slide the drive into the drive bay, making sure to align the mounting screws with the guide slots, until
the drive snaps into place.
NOTE: 3.5-inch hard drive shown. The bottom bay supports up to two 2.5-inch hard drives installed
using an adapter bracket.
32 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 41

6. Connect the power cable (1) and data cable (2) to the rear of the hard drive.
7. If installing a new drive, connect the opposite end of the data cable to the appropriate system board
connector.
NOTE: You must connect the primary hard drive data cable to the dark blue connector labeled SATA0 to
avoid any hard drive performance problems. If you are adding a second hard drive, connect the data
cable to one of the remaining SATA connectors.
8. Replace the computer access panel.
9. Reconnect the power cord and any external devices, and then turn on the computer.
10. Lock any security devices that were disengaged when the access panel was removed.
Drives 33
Page 42

Front I/O and power switch assembly
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the computer access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Remove the front bezel (Front bezel on page 16).
4. Remove the Torx T15 screw that secures the assembly to the chassis, push the tab on the right side of
the assembly to disengage it from the chassis.
5. Remove the cables from the clips on the base pan.
6. Disconnect the three cables from the following system board connectors:
(1) F_AUDIO (yellow)
(2) F_USB1 (white)
(3) F_PANEL (black)
7. Push the assembly into the chassis (4), and then remove the assembly from the inside of the computer.
To reinstall the assembly, reverse the removal procedure.
34 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 43

Fan sink
CAUTION: The bond between the fan sink and the processor may be very tight.
If the computer will power on, before removing the fan sink, turn on the computer until it warms the fan sink.
Warming the fan sink lessens the bond between the heat sink and the processor, thereby making separating
them easier.
Make sure not to pull the processor out of the socket when you lift the fan sink, especially if you cannot warm
the fan sink prior to removal. Inadvertently removing the processor can damage the pins.
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Disconnect the fan cable from the system board connector labeled CPU_FAN (1).
4. Loosen the four silver captive Torx T15 screws (2) that secure the fan sink to the system board.
CAUTION: Remove fan sink retaining screws in diagonally opposite pairs (as in an X) to even the
downward forces on the processor. The pins on the socket are very fragile and any damage to them may
require replacing the system board.
Fan sink 35
Page 44

5. Lift the heat sink from atop the processor.
When reinstalling the fan sink, make sure that its bottom has been cleaned with an alcohol wipe and fresh
thermal grease has been applied to the top of the processor.
CAUTION: Fan sink retaining screws should be tightened in diagonally opposite pairs (as in an X) to evenly
seat the fan sink on the processor. This is especially important as the pins on the socket are very fragile and
any damage to them may require replacing the system board.
36 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 45

Processor
Description Description
Intel Core i7-6700, 3.4 GHz Intel Pentium G4520, 3.6 GHz
Intel Core i5-6500, 3.2 GHz Intel Pentium G4400, 3.3 GHz
Intel Core i3-6320, 3.9 GHz Intel Celeron G3900, 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i3-6100, 3.7 GHz
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Remove the fan sink (Fan sink on page 35).
4. Rotate the locking lever to its full open position (1).
5. Raise and rotate the microprocessor retainer to its fully open position (2).
6. Lift the processor (3) straight up and remove it.
CAUTION: Do NOT handle the pins in the processor socket. These pins are very fragile and handling
them could cause irreparable damage. Once pins are damaged it may be necessary to replace the
system board.
Reverse the removal procedure to install a new processor.
NOTE: After installing a new processor onto the system board, update the system ROM to ensure that the
latest version of the BIOS is being used on the computer. The latest system BIOS can be found on the Web at:
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/support/les.
Processor 37
Page 46

Speaker
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Remove the front bezel (Front bezel on page 16).
4. From the outside, front of the chassis, remove the two Torx T15 screws that secure the speaker to the
chassis.
5. Disconnect the speaker wire from the system board connector labeled INT_SPKR (1).
6. Remove the speaker from the chassis (2).
To replace the speaker, reverse the removal procedures.
38 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 47

Rear chassis fan
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Remove the three silver Phillips screws that secure the fan to the rear of chassis.
4. Disconnect the fan control cable (1) from the system board connector labeled SYS_FAN.
5. Pull the fan away from the rear wall, and then lift the fan out of the chassis (2).
To install the fan assembly, reverse the removal procedure. Be sure to orient the air ow out of the unit.
Rear chassis fan 39
Page 48

Power supply
Description
Power supply, 300W, APFC
Power supply, 300W, Energy Star
Power supply, 300W, ES6 bronze
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. Remove the four silver Torx T15 screws that connect the power supply to the rear of the chassis.
4. Remove the power cable from the clip on the base pan.
5. Disconnect the power supply cable from the rear of the hard drive (1).
If an optical drive is installed, disconnect the power supply from the rear of the optical drive (not shown).
40 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 49

6. Disconnect the power supply cable from the following system board connectors:
(2) ATX_CPU
(3) ATX_PWR
7. Press the tab (1) on the base pan in front of the power supply that holds it in place.
8. Slide the power supply toward the front of the computer (2), rotate toward the fan so the power supply
clears the lip on the top of the chassis, and then lift the power supply out of the chassis (3).
To install the power supply, reverse the removal procedure.
Power supply 41
Page 50

System board
1. Prepare the computer for disassembly (Preparation for disassembly on page 14).
2. Remove the access panel (Access panel on page 15).
3. When replacing the system board, make sure the following components are removed from the defective
system board and installed on the replacement system board:
●
Memory modules (Memory on page 19)
●
Expansion cards (Expansion cards on page 22)
●
Heat sink (Fan sink on page 35).
●
Processor (Processor on page 37)
4. Disconnect all cables connected to the system board, noting their location for reinstallation.
5. Remove the eight Torx T15 screws (1) that secure the system board to the chassis.
6. Slide the system board toward the power supply (2), and then lift the system board up and out of the
computer (3).
When reinstalling the system board, rst insert the I/O panel back into the slots in the rear of the chassis, and
then align the board with the chassis screw holes.
NOTE: When replacing the system board, you must change the chassis serial number in the BIOS.
42 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures – Microtower (MT) chassis
Page 51

System board callouts
Sys Bd Label Color Component Sys Bd Label Color Component
PCIE_X1_2 White Expansion card F_PANEL Black Front I/O & power switch
PCIE_X1_1 Black Expansion card SATA1 White Any SATA Device other
than the primary hard
drive
PCIE_X16 Black Expansion card SATA2 Light blue Any SATA Device other
than the primary hard
drive
ATX_CPU White Power supply (4 pin) SATA3 Orange Any SATA Device other
than the primary hard
drive
SYS_FAN Red Rear system fan SATA0 Dark blue Hard drive
PROCESSOR Silver Processor CARD_READER White Card reader
CPU_FAN White Processor fan F_USB1 White Front I/O & power switch
XMM4 Black Memory module BAT Black RTC battery
XMM3 Blue Memory module CLR_PSWD Blue Clear system passwords
XMM2 Black Memory module CLR_CMOS Blue Clear CMOS memory
XMM1 Blue Memory module INT_SPKR White Speaker
ATX_PWR White Power supply (24 pin) F_AUDIO Yellow Front I/O & power switch
System board 43
Page 52

5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities
Use Computer Setup (F10) Utility to do the following:
●
Change factory default settings.
●
View the system conguration, including settings for processor, graphics, memory, audio, storage,
communications, and input devices.
●
Modify the boot order of bootable devices such as hard drives, optical drives, or USB ash media devices.
●
Select Post Messages Enabled or Disabled to change the display status of Power-On Self-Test (POST)
messages. Post Messages Disabled suppresses most POST messages, such as memory count, product
name, and other non-error text messages. If a POST error occurs, the error is displayed regardless of the
mode selected. To manually switch to Post Messages Enabled during POST, press any key (except F1
through F12).
●
Establish an Ownership Tag, the text of which is displayed each time the system is turned on or
restarted.
●
Enter the Asset Tag or property identication number assigned by the company to this computer.
●
Enable the power-on password prompt during system restarts (warm boots) as well as during power-on.
●
Establish a setup password that controls access to the Computer Setup (F10) Utility and the settings
described in this section.
●
Secure integrated I/O functionality, including the serial, USB, or parallel ports, audio, or embedded NIC,
so that they cannot be used until they are unsecured.
●
Enable or disable removable media boot ability.
●
Solve system conguration errors detected but not automatically xed during the Power-On Self-Test
(POST).
●
Replicate the system setup by saving system conguration information on a USB device and restoring it
on one or more computers.
●
Enable or disable DriveLock security (when supported by drive).
Using Computer Setup (F10) Utilities
Computer Setup can be accessed only by turning the computer on or restarting the system. To access the
Computer Setup Utilities menu, complete the following steps:
1. Turn on or restart the computer.
2. Repeatedly press F10 when the monitor light turns green to access the utility.
You can also press Esc to a menu that allows you to access dierent options available at startup,
including the Computer Setup utility.
NOTE: If you do not press F10 at the appropriate time, you must restart the computer and again
repeatedly press F10 when the monitor light turns green to access the utility.
44 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 53

3. A choice of four headings appears in the Computer Setup Utilities menu: Main, Security, Advanced, and
UEFI Drivers.
NOTE: Selecting UEFI Drivers restarts the computer into the 3rd party option ROM management
application. You can access this application directly by pressing F3 during startup.
4. Use the arrow (left and right) keys to select the appropriate heading. Use the arrow (up and down) keys
to select the option you want, then press Enter. To return to the Computer Setup Utilities menu, press
Esc.
5. To apply and save changes, select Main > Save Changes and Exit.
●
If you have made changes that you do not want applied, select Ignore Changes and Exit.
●
To reset to factory settings or previously saved default settings (some models), select Apply
Factory Defaults and Exit. This option will restore the original factory system defaults.
NOTE: Not all settings shown in the following sections are available for all models
CAUTION: Do NOT turn the computer power OFF while the BIOS is saving the Computer Setup (F10) changes
because the CMOS could become corrupted. It is safe to turn o the computer only after exiting the F10 Setup
screen.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 45
Page 54

Computer Setup–Main
NOTE: Support for specic Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware conguration.
Table 5-1 Computer Setup—Main
Option Description
System Information Lists all information in following list if Advanced System Information is selected. Lists smaller subset if
Basic System Information is selected.
●
Product name
●
Installed memory size
●
Processor type
●
Processor cache size (L1/L2/L3)
●
Processor speed
●
MicroCode Revision
●
Processor Stepping
●
DIMM size (for each installed module)
●
System BIOS version
●
Integrated Video BiOS Revision
●
Born On Date
●
Serial Number
●
SKU number
●
UUID (Universally Unique Identier)
●
Asset Tracking Number
●
Feature Byte
●
Build ID
●
Product Family
●
System Board ID
●
System Board CT
●
Integrated MAC Address
System Diagnostics Starts HP PC Hardware Diagnostics UEFI.
Lets you perform the following functions:
●
Memory Test
●
Hard Drive Check
●
Language
Update System BIOS Lets you update the system BIOS. BIOS update binary (BIN) les must be located on the system hard drive
or on a removable USB drive under the “Hewlett-Packard\BIOS\New” folder or under the “EFI\HP\BIOS
\New” folder.
Set Machine Unique Data Lets you update the following values:
●
Feature Byte
●
Build ID
46 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 55

Table 5-1 Computer Setup—Main (continued)
Option Description
●
Serial Number
●
SKU Number
●
Product Family
●
System Board CT
●
Product Name
System IDs Lets you clear the following values:
●
Asset Tracking Number
●
Ownership Tag
Replicated Setup Backup current settings to USB device
Saves system conguration to a formatted USB ash media device.
Restore current settings from USB device
Restores system conguration from a USB ash media device.
NOTE: In order to protect system security, this feature does not support replicating passwords. Use the
BIOS Conguration Utility instead.
Save Custom Defaults Saves the current system conguration settings as the default.
Apply Custom Defaults
and Exit
Apply Factory Defaults
and Exit
Ignore Changes and Exit Exits Computer Setup without applying or saving any changes.
Save Changes and Exit Saves changes to system conguration or default settings and exits Computer Setup.
Applies the currently selected default settings and clears any established passwords.
Restores the factory system conguration settings as the default.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 47
Page 56

Computer Setup—Security
NOTE: Support for specic Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware conguration.
Table 5-2 Computer Setup—Security
Option Description
Set up BIOS
Administrator Password
Change BIOS
Administrator Password
(This selection is active
only if a BIOS
administrator password is
set.)
Password Policy Let you set the guidelines for a valid password. Options include:
Lets you set and enable a BIOS administrator password, which includes the following privileges:
●
Manage other BIOS users
●
Full access to BIOS policy and settings
●
Control BIOS access of other users by setting security level
●
Unlock the computer when other BIOS users fail the preboot authentication.
NOTE: Creating a BIOS user disables the Fast Boot option.
NOTE: If the password is set, it is required to change Computer Setup options, ash the ROM, and make
changes to certain plug and play settings under Windows.
Lets you change the BIOS administrator password.
You must know the current password to be able to change it.
●
Password minimum length
●
Requires at least one symbol
●
Requires at least one number
●
Requires at least one upper case character
●
Requires at least one lower case character
●
Allow spaces
Clear Password Jumper
Select ‘Honor’ to engage or ‘Ignore’ to disengage the password jumper. Default is ‘Honor’.
Security Conguration Lets you activate HP SureStart.
Verify Boot Block on ever Boot
Select to enable HP SureStart.
BIOS Data Recovery Policy
Select ‘Automatic’ or ‘Manual’ to determine data recovery process.
TPM Embedded Security TPM Device
Lets you set the Trusted Platform Module as available or hidden.
TPM State
Select to enable the TPM.
TPM Clear
Select to reset the TPM to an unowned state. After the TPM is cleared, it is also turned o. To temporarily
suspend TPM operations, turn the TPM o instead of clearing it.
48 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 57

Table 5-2 Computer Setup—Security (continued)
Option Description
CAUTION: Clearing the TPM resets it to factory defaults and turns it o. You will lose all created keys and
data protected by those keys.
Set Up BIOS Power-On
Password
Change BIOS Power-On
Password
(This selection is active
only if a BIOS power-on
password is set.)
DriveLock Allows you to assign or modify a master or user password for hard drives. When this feature is enabled,
Secure Erase Lets you select a hard drive to completely erase.
Lets you set and enable a BIOS power-on password. The power-on password prompt appears after a
power cycle or reboot. If the user does not enter the correct power-on password, the unit will not boot.
Lets you change the BIOS power-on password.
You must know the current password to be able to change it.
the user is prompted to provide one of the DriveLock passwords during POST. If neither is successfully
entered, the hard drive will remain inaccessible until one of the passwords is successfully provided during
a subsequent cold-boot sequence.
NOTE: This selection will only appear when at least one drive that supports the DriveLock feature is
attached to the system.
CAUTION: Be aware that these settings take place immediately. A save is not necessary.
CAUTION: Be sure to document the DriveLock password. Losing a DriveLock password will render a drive
permanently locked.
After you select a drive, the following options are available:
Set DriveLock Master Password. Sets the drive’s master password but does not enable DriveLock.
Enable DriveLock. Sets the drive’s user password and enables DriveLock.
Once a hard drive has been erased with a program that utilizes Secure Erase rmware commands, no le
recovery program, partition recovery program, or other data recovery method will be able to extract data
from the drive.
Save/Restore MBR of the
system hard drive
Smart Cover Cover Lock (Lock/Unlock)
Enabling this feature will save the Master Boot Record (MBR) of the system hard drive. If the MBR gets
changed, the user will be prompted to restore the MBR. Default is disabled.
The MBR contains information needed to successfully boot from a disk and to access the data stored on
the disk. Master Boot Record Security may prevent unintentional or malicious changes to the MBR, such as
those caused by some viruses or by the incorrect use of certain disk utilities. It also allows you to recover
the "last known good" MBR, should changes to the MBR be detected when the system is restarted.
When MBR Security is enabled, the BIOS prevents any changes being made to the MBR of the current
bootable disk while in MS-DOS or Windows Safe Mode.
NOTE: Most operating systems control access to the MBR of the current bootable disk; the BIOS cannot
prevent changes that may occur while the operating system is running.
Restores the backup Master Boot Record to the current bootable disk. Default is disabled.
Only appears if all of the following conditions are true:
●
MBR security is enabled
●
A backup copy of the MBR has been previously saved
●
The current bootable disk is the same disk from which the backup copy was saved
CAUTION: Restoring a previously saved MBR after a disk utility or operating system has modied the
MBR, may cause the data on the disk to become inaccessible. Only restore a previously saved MBR if you
are condent that the current bootable disk's MBR has been corrupted or infected with a virus.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 49
Page 58

Table 5-2 Computer Setup—Security (continued)
Option Description
Default is ‘Unlock’.
Cover Removal Sensor (Disabled/Notify user/Administrator password)
Lets you disable the cover sensor or congure what action is taken if the computer cover was removed.
Default is ‘Disabled’.
NOTE: Notify user alerts the user that the sensor has detected that the cover has been removed.
Administrator Password requires that the password be entered to boot the computer if the sensor
detects that the cover has been removed.
System Management
Command
Restore Security
Settings to Default
Allows authorized personnel to reset security settings during a service event. Default is enabled.
Restoring settings to default requires the BIOS Administrator password.
Computer Setup—Advanced
NOTE: Support for specic Computer Setup options may vary depending on the hardware conguration.
Table 5-3 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users)
Option Heading
Select Language Lets you select the language of the menus in F10 Setup.
Select Keyboard Layout Lets you select language for the keyboard.
Boot Options Startup Menu Delay(sec)
Enabling this feature will add a user-specied delay to the POST process. This delay is sometimes needed
for hard disks on some PCI cards that spin up very slowly, so slowly that they are not ready to boot by the
time POST is nished. The POST delay also gives you more time to select F10 to enter Computer (F10)
Setup. Default is ‘0’.
Select the devices that the computer can boot from, as well as other options, including:
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
●
Fast Boot. Default is disabled.
CD-ROM Boot. Default is enabled.
Network (PXE) Boot. Default is enabled.
SD Boot. Default is enabled.
Netclone BIOS Boot. Default is disabled.
Prompt on Memory Size Change. Default is enabled.
Prompt on Fixed Storage Change. Default is disabled.
Display Diagnostic URL. Default is enabled.
UEFI Boot Order. Default is enabled.
Specify the order in which UEFI boot sources (such as a internal hard drive, USB hard drive, USB
optical drive, or internal optical drive) are checked for a bootable operating system image. Each
device on the list may be individually excluded from or included for consideration as a bootable
operating system source.
UEFI boot sources always have precedence over legacy boot sources.
Legacy Boot Order
50 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 59

Table 5-3 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
Option Heading
Specify the order in which legacy boot sources (such as a network interface card, internal hard drive,
USB optical drive, or internal optical drive) are checked for a bootable operating system image. Each
device on the list may be individually excluded from or included for consideration as a bootable
operating system source.
Specify the order of attached hard drives. The rst hard drive in the order will have priority in the
boot sequence and will be recognized as drive C (if any devices are attached).
NOTE: To drag a device to a preferred place, press Enter. To remove the device from consideration as a
bootable device, press F5.
You can use F5 to disable individual boot items, as well as disable UEFI boot and/or legacy boot.
NOTE: MS-DOS drive lettering assignments may not apply after a non-MS-DOS operating system has
started.
Shortcut to Temporarily Override Boot Order
To boot one time from a device other than the default device specied in Boot Order, restart the computer
and press Esc (to access the boot menu) and then F9 (Boot Order), or only F9 (skipping the boot menu)
when the monitor light turns green. After POST is completed, a list of bootable devices is displayed. Use
the arrow keys to select the preferred bootable device and press Enter. The computer then boots from the
selected non-default device for this one time.
Secure Boot
Conguration
System Options Onboard RAID (enable/disable)
Congure Legacy Support and Secure Boot
Legacy Support – Lets you turn o all legacy support on the computer, including booting to DOS, running
legacy graphics cards, booting to legacy devices, and so on.
Secure Boot – Lets you make sure an operating system is legitimate before booting to it, making Windows
resistant to malicious modication from preboot to full OS booting, preventing rmware attacks. UEFI and
Windows Secure Boot only allow code signed by pre-approved digital certicates to run during the
rmware and OS boot process.
Default is ‘Legacy Support Enable and Secure Boot Disable’.
Secure Boot Key Management
Lets you manage the custom key settings.
Clear Secure Boot Keys
Lets you delete any previously loaded custom boot keys. Clearing keys will disable secure boot. Default is
disabled.
Reset Security Boot keys to factory defaults
Default is disabled.
Lets you enable onboard RAID. Default is disabled.
Max SATA Speed (6.0 Gbps/3.0Gbps)
Lets you set the maximum SATA drive speed to either 3.0 Gbps or 6.0 Gbps. The default is ‘6.0 Gbps’.
USB 3.0 (XHCI) (enable/disable)
Lets you enable the eXtensible Host Controller Interface (xHCI). If enabled, the USB 3.0 ports are routed to
the xHCI controller before booting to OS. If disabled, the USB 3.0 ports are routed to the EHCI controller
before booting to OS. The default is disabled.
After Power Loss (o/on/previous state). Default is Power o. Setting this option to:
●
Power o—causes the computer to remain powered o when power is restored.
●
Power on—causes the computer to power on automatically as soon as power is restored.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 51
Page 60

Table 5-3 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
Option Heading
●
Previous state—causes the computer to power on automatically as soon as power is restored, if it
was on when power was lost.
SVM CPU VIrtualization (enable/disable)
Controls the virtualization features of the processor. Changing this setting requires turning the computer
o and then back on. Default is disabled.
Allow PCIe/PCI SERR# Interrupt (enable/disable)
Allows PCI devices to report PCI/PCIe System Error signals, such as address parity errors, data parity
errors, and critical errors other than parity. Default is enabled.
Power Button Override (disable/4 sec/15 sec)
Lets you disable or enable and select the number of seconds you have to hold down the power button for
it to override the system. Default is ‘4 sec’.
Built-In Device Options Embedded LAN Controller
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Wake On LAN
Lets you either disable the Wake On LAN feature, or congure where the computer boots, including the
network or hard drive. Default is Boot to Network.
Embedded WWAN Device
Select to enable.
Video Memory Size
Use this option to manage graphics memory allocation. The value you choose is allocated permanently to
graphics and is unavailable to the operating system. For example, if you set this value to 512M on a
system with 2 GB of RAM, the system always allocates 512 MB for graphics and the other 1.5 GB for use by
the BIOS and operating system. Default is ‘Auto’ which sets memory allocation to 512 MB.
Audio Device
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Internal Speakers (does not aect external speakers)
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Integrated Microphone
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Integrated Camera
Use this option to disable the integrated video controller when another video controller is present in the
system. Default is enabled.
Increase Idle Fan Speed(%)
Sets idle fan speed percentage. This setting only changes the minimum fan speed. The fan is still
automatically controlled.
Fingerprint Device
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Touch Panel
Select to show the device in the operating system. Default is enabled.
Port Options Allows you to hide the following ports from the operating system:
52 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 61

Table 5-3 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
Option Heading
●
Serial port A
●
SATA0
●
SATA1
●
SATA2
●
Front USB ports
●
Rear USB ports
●
Media card reader
Restrict USB Devices
Specify the following categories of USB devices to enable:
●
Allow all USB devices
●
Allow only keyboard and mouse
●
Allow all but storage devices and hubs.
Option ROM Launch
Policy
Power Management
Options
These policies control whether the Legacy Option ROM or the UEFI driver is loaded. Default is ‘All UEFI’.
Congure Option ROM Launch Policy
●
All legacy
●
All UEFI
●
All UEFI except video
Runtime Power Management (enable/disable)
Allows certain operating systems to reduce processor voltage and frequency when the current software
load does not require the full capabilities of the processor. Default is enabled.
Extended Idle Power States (enable/disable)
Allows certain operating systems to decrease the processors power consumption when the processor is
idle. Default is enabled.
S5 Maximum Power Savings (enable/disable)
Enabling this feature reduces the power of the system as much as possible in the S5 state. Power is
removed from the wake up circuitry, the expansion slots, and any management features while in S5.
Default is disabled.
SATA Power Management (enable/disable)
Enables or disables SATA bus and/or device power management. Default is enabled.
PCI Express Power Management (enable/disable)
Enabling this option permits the PCI Express links to use Active Power State Management (ASPM) to enter
lower power states while not in use. Default is enabled.
Unique Sleep State Blink Rates (enable/disable)
This feature is designed to provide a visual indication of what sleep state the system is in. Each sleep
state has a unique blink pattern. Default is disabled.
NOTE: A normal shutdown goes to the S4 state.
S0 (On) = Solid white LED.
S3 (Stand By)= 3 blinks at 1Hz (50% duty cycle) followed by a pause of 2 seconds (white LED) — repeated
cycles of 3 blinks and a pause.
Computer Setup (F10) Utilities 53
Page 62

Table 5-3 Computer Setup—Advanced (for advanced users) (continued)
Option Heading
S4 (Hibernation)= 4 blinks at 1Hz (50% duty cycle) followed by a pause of 2 seconds (white LED) —
repeated cycles of 4 blinks and a pause.
S5 (Soft O) = LED is o.
Power On from Keyboard Ports (enable/disable)
Enables or disables waking from S3 due to any keyboard activity. Default is disabled.
USB Charging Port Function (enable/disable)
Enables or disables the charging capability of the USB charging port. Default is enabled.
Congurations Allows you to use F10 Setup to check for BIOS updates and apply them using either a manual selection or
an automatically scheduled check upon boot-up.
NOTE: If Windows BitLocker Drive Encryption (BDE) is enabled, HP requires that BDE be suspended
temporarily before the BIOS is ashed. You must get the BDE recovery password and PIN before
suspending BDE. After updating the BIOS, you can resume BDE.
Update Source (HP/Custom)
Selects hp.com or a locally managed custom address to serve BIOS updates. Default is ‘HP’.
Update Address.
If ‘Custom’ is selected for Update Source, enter the URL of the locally managed server.
Update BIOS via Network (Enabled/Disable)
Enables or disables the network BIOS update scheduler. Default is ‘Enable’.
Automatic Update Frequency (Daily, Weekly, Monthly)
If ‘Enable’ is selected for Update BIOS via Network, sets the frequency of checks to the BIOS update
server. If a newer version of BIOS is available on the network server, the system will prompt to update the
BIOS. Default is ‘Daily’.
Automatic BIOS Update Setting
If ‘Enable’ is selected for Update BIOS via Network, during the next boot, checks whether an updated
BIOS is available and installs only specied updates. This value is independent of the Automatic Update
Frequency setting.
Available congurations include:
●
Check and install all BIOS updates automatically
●
Check and install only important updates automatically
●
Check for BIOS updates but let me decide whether to install them
Default is ‘Check and install all BIOS updates automatically’.
Check for updates now Select to check for the latest BIOS release revision on the network. Lets you decide whether to download
the BIOS image and update the system.
Scheduled Power-On This feature wakes the system up from a powered o state at a specied date and time.
54 Chapter 5 Computer Setup (F10) Utility
Page 63

Recovering the Conguration Settings
This method of recovery requires that you rst perform the Save to Removable Media command with the
Computer Setup (F10) Utility before Restore is needed. (See Computer Setup–Main on page 46 in the
Computer Setup—File table.)
NOTE: It is recommended that you save any modied computer conguration settings to a USB ash media
device and save the device for possible future use.
To restore the conguration, insert the USB ash media device with the saved conguration and perform the
Restore from Removable Media command with the Computer Setup (F10) Utility. (See Computer Setup–Main
on page 46 in the Computer Setup—File table.)
Recovering the Conguration Settings 55
Page 64

6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
This chapter provides information on how to identify and correct minor problems, such as USB devices, hard
drive, optical drive, graphics, audio, memory, and software problems. If you encounter problems with the
computer, refer to the tables in this chapter for probable causes and recommended solutions.
NOTE: For information on specic error messages that may appear on the screen during Power-On Self-Test
(POST) at startup, refer to POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
on page 86.
Safety and comfort
WARNING! Misuse of the computer or failure to establish a safe and comfortable work environment may
result in discomfort or serious injury. Refer to the Safety & Comfort Guide at http://www.hp.com/ergo for
more information on choosing a workspace and creating a safe and comfortable work environment. For more
information, refer to the Safety & Regulatory Information guide.
Before you call for technical support
If you are having problems with the computer, try the appropriate solutions below to try to isolate the exact
problem before calling for technical support.
●
Run the HP diagnostic tool.
●
Run the hard drive self-test in Computer Setup. Refer to Computer Setup (F10) Utility on page 44 for
more information.
●
Check the Power LED on the front of the computer to see if it is ashing red. The ashing lights are error
codes that will help you diagnose the problem. Refer to POST error messages and diagnostic front panel
LEDs and audible codes on page 86 for more information.
●
If the screen is blank, plug the monitor into a dierent video port on the computer if one is available. Or,
replace the monitor with a monitor that you know is functioning properly.
●
If you are working on a network, plug another computer with a dierent cable into the network
connection. There may be a problem with the network plug or cable.
●
If you recently added new hardware, remove the hardware and see if the computer functions properly.
●
If you recently installed new software, uninstall the software and see if the computer functions properly.
●
Boot the computer to the Safe Mode to see if it will boot without all of the drivers loaded. When booting
the operating system, use “Last Known Conguration.”
●
Refer to the comprehensive online technical support at http://www.hp.com/support.
●
Refer to Helpful hints on page 57 in this guide.
To assist you in resolving problems online, HP Instant Support Professional Edition provides you with selfsolve diagnostics. If you need to contact HP support, use HP Instant Support Professional Edition's online chat
feature. Access HP Instant Support Professional Edition at: http://www.hp.com/go/ispe.
Access the Business Support Center (BSC) at http://www.hp.com/go/bizsupport for the latest online support
information, software and drivers, proactive notication, and worldwide community of peers and HP experts.
56 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 65

If it becomes necessary to call for technical assistance, be prepared to do the following to ensure that your
service call is handled properly:
●
Be in front of your computer when you call.
●
Write down the computer serial number, product ID number, and monitor serial number before calling.
●
Spend time troubleshooting the problem with the service technician.
●
Remove any hardware that was recently added to your system.
●
Remove any software that was recently installed.
●
Restore the system from the Recovery Disc Set that you created or restore the system to its original
factory condition in System Software Requirement Disks (SSRD).
CAUTION: Restoring the system will erase all data on the hard drive. Be sure to back up all data les before
running the restore process.
NOTE: For sales information and warranty upgrades (Care Packs), call your local authorized service provider
or dealer.
Helpful hints
If you encounter problems with the computer, monitor, or software, see the following list of general
suggestions before taking further action:
●
Check that the computer and monitor are plugged into a working electrical outlet.
●
Check that the voltage select switch (some models) is set to the appropriate voltage for your region
(115V or 230V).
●
Check that the computer is turned on and the white power light is on.
●
Check that the monitor is turned on and the green monitor light is on.
●
Check the Power LED on the front of the computer to see if it is ashing red. The ashing lights are error
codes that will help you diagnose the problem. Refer to POST error messages and diagnostic front panel
LEDs and audible codes on page 86 for more information.
●
Turn up the brightness and contrast controls of the monitor if the monitor is dim.
●
Press and hold any key. If the system beeps, then the keyboard should be operating correctly.
●
Check all cable connections for loose connections or incorrect connections.
●
Wake the computer by pressing any key on the keyboard or pressing the power button. If the system
remains in suspend mode, shut down the computer by pressing and holding the power button for at
least four seconds then press the power button again to restart the computer. If the system will not shut
down, unplug the power cord, wait a few seconds, then plug it in again. The computer will restart if it is
set to power on automatically as soon as power is restored in Computer Setup. If it does not restart,
press the power button to start the computer.
●
Recongure the computer after installing a non-plug and play expansion board or other option. See
Solving Hardware Installation Problems on page 74 for instructions.
●
Be sure that all the needed device drivers have been installed. For example, if you are using a printer,
you need a driver for that model printer.
●
Remove all bootable media (CD/DVD or USB device) from the system before turning it on.
Helpful hints 57
Page 66

●
If you have installed an operating system other than the factory-installed operating system, check to be
sure that it is supported on the system.
●
If the system has multiple video sources (embedded, PCI, or PCI-Express adapters) installed (embedded
video on some models only) and a single monitor, the monitor must be plugged into the monitor
connector on the source selected as the primary VGA adapter. During boot, the other monitor connectors
are disabled and if the monitor is connected into these ports, the monitor will not function. You can
select which source will be the default VGA source in Computer Setup.
CAUTION: When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, there is always voltage applied to the
system board. You must disconnect the power cord from the power source before opening the computer to
prevent system board or component damage.
Solving general problems
You may be able to easily resolve the general problems described in this section. If a problem persists and you
are unable to resolve it yourself or if you feel uncomfortable about performing the operation, contact an
authorized dealer or reseller.
WARNING! When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system
board. To reduce the risk of personal injury from electrical shock and/or hot surfaces, be sure to disconnect
the power cord from the wall outlet and allow the internal system components to cool before touching.
Cannot access the Computer Setup (F10) Utility when booting the computer.
Cause Solution
The Computer Setup (F10) Utility is set to “fast boot” causing the
F10 access screen to display too briey when booting the
computer.
Computer appears locked up and will not turn o when the power button is pressed.
Cause Solution
Software control of the power switch is not functional. 1. Press and hold the power button for at least four seconds
Computer will not respond to keyboard or mouse.
Cause Solution
Computer is in Sleep state. To resume from Sleep state, press the power button.
Before turning on the computer, press and hold F10. Turn on the
computer and continue to hold F10 until the Computer Setup
(F10) Utility is displayed.
- or –
Follow the Windows instructions for rebooting the computer into
the Computer Setup (F10) Utility.
until the computer turns o.
2. Disconnect the power cord from the electrical outlet.
CAUTION: When attempting to resume from Sleep state, do not
hold down the power button for more than four seconds.
Otherwise, the computer will shut down and you will lose any
unsaved data.
System has locked up. Restart computer.
58 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 67

Computer date and time display is incorrect.
Cause Solution
RTC (real-time clock) battery may need to be replaced.
NOTE: Connecting the computer to a live AC outlet prolongs the
life of the RTC battery.
There is no sound or sound volume is too low.
Cause Solution
System volume may be set low or muted. 1. Check the Computer Setup settings to make sure the
Reset the date and time under Control Panel (Computer Setup
can also be used to update the RTC date and time). If the problem
persists, replace the RTC battery. See the Removal and
Replacement section for instructions on installing a new battery,
or contact an authorized dealer or reseller for RTC battery
replacement.
To access Control Panel in Windows 7, select Start, and then
select Control Panel.
To access Control Panel in Windows 10, type control panel in
the taskbar search box, and then select Control Panel.
ternal system speaker is not muted (this setting does not
in
aect the external speakers).
2. Make sure the external speakers are properly connected and
wered on and that the speakers' volume control is set
po
correctly.
3. Use the system volume control available in the operating
tem to make sure the speakers are not muted or to
sys
increase the volume.
Cannot remove computer cover or access panel.
Cause Solution
Smart Cover Lock, featured on some computers, is locked. Unlock the Smart Cover Lock using Computer Setup.
In case of forgotten password, power loss, or computer
function, you must manually disable the Smart Cover lock . A
mal
key to unlock the Smart Cover Lock is not available from HP. Keys
are typically available from a hardware store.
Poor performance.
Cause Solution
Processor is too hot. 1. Make sure
Hard drive is full. Transfer data from the hard drive to create more space on the
10.2-cm (4-inch) clearance on all vented sides of the
computer and above the monitor to permit the required
airow.
2. Make sure fans are connected and working properly (some
ans only operate when needed).
f
3. Make sure the processor heat sink is installed properly.
ard drive.
h
airow to the computer is not blocked. Leave a
Solving general problems 59
Page 68

Poor performance.
Cause Solution
Low on memory. Add more memory.
Hard drive fragmented. Defragment hard drive.
Program previously accessed did not release reserved memory
back to the system.
Virus resident on the hard drive. Run virus protection program.
Too many applications running. 1. Close unnecessary applications to free up memory.
Restart the computer.
2. Add more memory.
3. Some applications run in the background and can be closed
by right-clicking on their corresponding icons in the task
tray. To prevent these applications from launching at
startup:
In Windows 7:
a. Go to Start > All Programs > Accessories > Run
b. Type msconfig, and then press Enter.
c. On the
In Windows 10:
a. Type
b. On the
c. Select applications that you do not want to launch
Startup tab of the System Conguration Utility,
clear applications that you do not want to launch
automatically, and the click OK.
msconfig in the taskbar search box, and then
select mscong
click Open Task Manager.
aut
omatically, and the click Disable.
.
Startup tab of the System Conguration Utility,
Some software applications, especially games, are stressful on
the graphics subsystem.
Cause unknown. Restart the computer.
Computer powered
Cause Solution
Processor thermal protection activated:
A fan may be blocked or not turning.
OR
The heat sink is not properly attached to the processor.
o automatically and the Power LED ashes red four times and then white two times.
60 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
1. Lower the display resolution for the current application or
c
onsult the documentation that came with the application
for suggestions on how to improve performance by
adjusting parameters in the application.
2. Add more memory.
3. Upgrade the graphics solution.
1. Ensure that the computer air vents are not blocked and the
pr
ocessor cooling fan is running.
2. Open the access panel, press the power button, and see if
the pr
ocessor fan (or other system fan) spins. If the fan does
not spin, make sure the fan cable is plugged onto the system
board header.
3. If fan a plugged in and not spinning, replace it.
Page 69

System does not power on and the LEDs on the front of the computer are not ashing.
Cause Solution
System unable to power on. Press and hold the power button for less than 4 seconds. If the
hard drive LED turns white, then:
1. If equipped with a voltage selector, check that the voltage
selector (located on the rear of the power supply) is set to
the appropriate voltage. Proper voltage setting depends on
your region.
2. Remove the expansion cards one at a time until the 5V_aux
light on the system board turns on.
3. Replace the system board.
OR
Press and hold the power button for less than 4 seconds. If the
hard drive LED does not turn on white then:
1. Check that the unit is plugged into a working AC outlet.
2. Open the access panel and check that the power button
cable is properly connected to the system board.
3. Check that the power supply cables are properly connected
to the system board.
4. Check to see if the 5V_aux light on the system board is
turned on. If it is turned on, then replace the power button
assembly.
5. If the 5V_aux light on the system board is o, then replace
the power supply.
6. Replace the system board.
Solving general problems 61
Page 70

Solving power problems
Common causes and solutions for power problems are listed in the following table.
Power supply shuts down intermittently.
Cause Solution
If equipped with a voltage selector, voltage selector switch on
rear of computer chassis (some models) not switched to correct
line voltage (115V or 230V).
Power supply will not turn on because of internal power supply
fault.
Computer powered o automatically and the Power LED ashes Red two times, once every second, followed by a two second
pause, and the computer beeps two times. (Beeps stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Computer powered o automatically and the Power LED ashes red four times and then white two times.
Cause Solution
Processor thermal protection activated:
A fan may be blocked or not turning.
OR
The heat sink is not properly attached to the processor.
Power LED ashes Red four times, once every second, followed by a two second pause, and the computer beeps four times. (Beeps
stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Computer powered o automatically and the Power LED ashes red three times and then white four times.
Select the proper AC voltage using the selector switch.
Replace the power supply.
1. Ensure that the computer air vents are not blocked and the
processor cooling fan is running.
2. Open the access panel, press the power button, and see if
the processor fan (or other system fan) spins. If the fan does
not spin, make sure the fan cable is plugged onto the system
board header.
3. If fan a plugged in and not spinning, replace it.
Cause Solution
Power failure (power supply is overloaded). 1. If equipped with a voltage selector, check that the voltage
62 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
selector, located on the rear of the power supply (some
models), is set to the appropriate voltage. Proper voltage
setting depends on your region.
2. Open the access panel and ensure the power supply cable is
seated into the connector on the system board.
3. Check if a device is causing the problem by removing ALL
attached devices (such as hard drives or optical drives and
expansion cards). Power on the system. If the system enters
POST, then power o and replace one device at a time and
repeat this procedure until failure occurs. Replace the device
that is causing the failure. Continue adding devices one at a
time to ensure all devices are functioning properly.
4. Replace the power supply.
5. Replace the system board.
Page 71

Solving hard drive problems
Hard drive error occurs.
Cause Solution
Hard disk has bad sectors or has failed. 1. In Windows 7, click Start, click Computer, and right-click on
Disk transaction problem.
Cause Solution
a drive. Select Properties, and then select the Tools tab.
Under Error-checking click Check Now.
In Windows 10, type file in the taskbar search box, and
then select
left column, expand This PC, right-click on a drive, select
Properties, and then select the Tools tab. Under Error
checking click Check.
2. Use a utility to locate and block usage of bad sectors. If
nec
File Explorer from the list of applications. In the
essary, reformat the hard disk.
Either the directory structure is bad or there is a problem with a
le.
Drive not found
Cause Solution
Cable could be loose. Check cable connections.
The system may not have automatically recognized a newly
installed device.
The device is attached to a SATA port that has been hidden in
Computer Setup.
(identied).
In Windows 7, click
drive. Select Properties, and then select the Tools tab. Under
Error-checking click Check Now.
In Windows 10, type file in the taskbar search box, and then
File Explorer from the list of applications. In the left
select
column, expand This PC, right-click on a drive, select Properties,
and then select the Tools tab. Under Error checking click Check.
See reconguration directions in the
Installation Problems on page 74 section. If the system still
doe
s not recognize the new device, check to see if the device is
listed within Computer Setup. If it is listed, the probable cause is a
driver problem. If it is not listed, the probable cause is a hardware
problem.
If this is a newly installed drive, run the Computer Setup utility
and try adding a POST delay under Advanced > Boot Options.
Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure Device Available is
selected for the device's SATA port in Advanced > Port Options.
Start, expand Computer, and right-click on a
Solving Hardware
Drive responds slowly immediately after power-up. Run Computer Setup and increase the POST Delay in Advanced >
Boot Options.
Solving hard drive problems 63
Page 72

Nonsystem disk/NTLDR missing message.
Cause Solution
The system is trying to start from the hard drive but the hard
drive may have been damaged.
System les missing or not properly installed. 1. Insert bootable media and restart the computer.
Hard drive boot has been disabled in Computer Setup. Run the Computer Setup utility and enable the hard drive entry in
Bootable hard drive is not attached as rst in a multi-hard drive
conguration.
Bootable hard drive is not listed rst in the Boot Order. Run the Computer Setup utility and select Advanced > Boot
Computer will not boot from hard drive.
Cause Solution
The device is attached to a SATA port that has been hidden in
Computer Setup.
▲ Perform Drive Protection System (DPS) testing in system
ROM.
2. Boot to the windows installation media and select the
recovery option. If only a restore kit is available, then select
the File Backup Program option, and then restore the
system.
3. Install system les for the appropriate operating system.
the Advanced > Boot Options list.
If attempting to boot from a hard drive, ensure it is attached to
the system board dark blue SATA connector.
Options and ensure the bootable hard drive is listed immediately
under the Hard Drive entry.
1. Check SATA cable connections.
2. Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure Device Available
is selected for the device's SATA port in Advanced > Port
Options.
Boot order is not correct. Run the Computer Setup utility and change boot sequence in
Advanced > Boot Options.
Hard drive is damaged. Observe if the front panel Power LED is blinking RED and if any
beeps are heard. See POST error messages and diagnostic front
panel LEDs and audible codes on page 86 to determine possible
causes for the blinking red and beep codes.
See the Worldwide Limited Warranty for terms and conditions.
Computer seems to be locked up.
Cause Solution
Program in use has stopped responding to commands. 1. Use the task manager to close programs that do not
respond.
2. Attempt the normal Windows “Shut Down” procedure. If this
fails, press the power button for four or more seconds to
turn o the power. To restart the computer, press the power
button again.
64 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 73

Solving media card reader problems
Media card will not work in a digital camera after formatting it in Windows.
Cause Solution
By default, Windows will format any media card with a capacity
greater than 32MB with the FAT32 format. Some digital cameras
use the FAT (FAT16 & FAT12) format and can not operate with a
FAT32 formatted card.
A write-protected or locked error occurs when attempting to write to the media card.
Cause Solution
Media card is locked. Locking the media card is a safety feature
that prevents writing to and deleting from an SD/Memory
Stick/PRO card.
Can not write to the media card.
Cause Solution
The media card is a read-only memory (ROM) card. Check the manufacturer’s documentation included with your card
Media card is locked. Locking the media card is a safety feature
that prevents writing to and deleting from an SD/Memory
Stick/PRO card.
Either format the media card in the digital camera or select FAT
le system to format the media card in a computer with Windows.
If using an SD card, make sure that the lock tab located on the
right of the SD card is not in the locked position. If using a Memory
Stick/PRO card, make sure that the lock tab located on the bottom
of the Memory Stick/PRO card is not in the locked position.
to see if it writable. Refer to the previous section for a list of
compatible cards.
If using an SD card, make sure that the lock tab located on the
right of the SD card is not in the locked position. If using a Memory
Stick/PRO card, make sure that the lock tab located on the bottom
of the Memory Stick/PRO card is not in the locked position.
Unable to access data on the media card after inserting it into a slot.
Cause Solution
The media card is not inserted properly, is inserted in the wrong
slot, or is not supported.
Do not know how to remove a media card correctly.
Cause Solution
The computer’s software is used to safely eject the card. In Windows 7, click Start, select Computer, right-click on the
Ensure that the card is inserted properly with the gold contact on
the correct side. The green LED will light if inserted properly.
corresponding drive icon, and then select Eject. Pull the card out
of the slot.
In Windows 10, type file in the taskbar search box, and then
File Explorer from the list of applications. In the left
select
column, expand This PC, right-click on the corresponding drive
icon, and then select Eject. Pull the card out of the slot.
NOTE: Never remove the card when the green LED is ashing
Solving media card reader problems 65
Page 74

After installing the media card reader and booting to Windows, the reader and the inserted cards are not recognized by the
computer.
Cause Solution
The operating system needs time to recognize the device if the
reader was just installed into the computer and you are turning
the PC on for the rst time.
After inserting a media card in the reader, the computer attempts to boot from the media card.
Cause Solution
The inserted media card has boot capability. 1. If you do not want to boot from the media card, remove it
Solving display problems
If you encounter display problems, see the documentation that came with the monitor and to the common
causes and solutions listed in the following table.
Blank screen (no video).
Cause Solution
Wait a few seconds so that the operating system can recognize
the reader and the available ports, and then recognize the media
inserted in the reader.
during boot or do not select the option to boot from the
inserted media card during the boot process.
2. During POST (Power On Self-Test), press F9 to modify the
boot menu.
3. Change the boot sequence in F10 Computer Setup.
Monitor is not turned on and the monitor light is not on. Turn on the monitor and check that the monitor light is on.
Bad monitor. Try a dierent monitor.
The cable connections are not correct. Check the cable connection from the monitor to the computer and
to the electrical outlet.
You may have a screen blanking utility installed or energy saver
features are enabled.
System ROM is corrupted; system is running in Boot Block
Emergency Recovery Mode (indicated by eight beeps).
You are using a xed-sync monitor and it will not sync at the
resolution chosen.
Computer is in Sleep state. Press the power button to resume from Sleep state.
Monitor cable is plugged into the wrong connector. Systems may have a monitor connection on both the
Monitor settings in the computer are not compatible with the
monitor.
Press any key or click the mouse button and type your password
(if set).
Reash the system ROM with the latest BIOS image.
Be sure that the monitor can accept the same horizontal scan rate
as the resolution chosen.
CAUTION: When attempting to resume from Sleep state, do not
hold down the power button for more than four seconds.
Otherwise, the computer will shut down and you will lose any
unsaved data.
motherboard or an add-in card. Try moving the monitor
connection to a dierent connector on the back of the computer
1. In Control Panel, select Category from the View by list, then
under Appearance and Personalization, select Adjust
screen resolution.
66 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 75

Blank screen (no video).
Cause Solution
To access Control Panel in Windows 7, click Start, and then
select Control Panel.
To access Control Panel in Windows 10, type control
in the taskbar search box, and then select Control
panel
Panel from the list of applications.
2. Expand the
to reset the resolution.
Monitor is congured to use an input that is not active. Use the monitor's on-screen menu controls to select the input
that is being driven by the system. Refer to the monitor's user
documentation for more information on the on-screen controls
and settings.
Resolution box, and then use the sliding control
Blank screen and the power LED
beeps ve times. (Beeps stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Cause Solution
Pre-video memory error.
Blank screen and the power LED
beeps six times. (Beeps stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Cause Solution
Pre-video graphics error. For systems with a graphics card:
ashes Red ve times, once every second, followed by a two second pause, and the computer
1. Reseat DIMMs. Power on the system.
2. Replace DIMMs one at a time to isolate the faulty module.
3. Replace third-party memory with HP memory.
4. Replace the system board.
ashes Red six times, once every second, followed by a two second pause, and the computer
1. Reseat the graphics card (if applicable). Power on the
sys
tem.
2. Replace the graphics card (if applicable).
3. Replace the system board.
For systems with integrated graphics, replace the system board.
Blank screen and the power LED
beeps seven times. (Beeps stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Cause Solution
System board failure (ROM detected failure prior to video). Replace the system board.
ashes Red seven times, once every second, followed by a two second pause, and the computer
Solving display problems 67
Page 76

Monitor does not function properly when used with energy saver features.
Cause Solution
Monitor without energy saver capabilities is being used with
energy saver features enabled.
Dim characters.
Cause Solution
The brightness and contrast controls are not set properly. Adjust the monitor brightness and contrast controls.
Cables are not properly connected. Check that the graphics cable is securely connected to the
Blurry video or requested resolution cannot be set.
Cause Solution
If the graphics controller was upgraded, the correct graphics
drivers may not be loaded.
Monitor is not capable of displaying requested resolution. Change requested resolution.
Graphics card is bad. Replace the graphics card.
Disable monitor energy saver feature.
graphics card (if applicable) or video connector and the monitor.
Install the video drivers included in the upgrade kit.
The picture is broken up, rolls, jitters, or ashes.
Cause Solution
The monitor connections may be incomplete or the monitor may
be incorrectly adjusted.
Monitor needs to be degaussed. Degauss the monitor. Refer to the documentation that came with
Image is not centered.
Cause Solution
Position may need adjustment. Press the monitor's Menu button to access the OSD menu. Select
1. Be sure the monitor cable is securely connected to the
computer.
2. In a two-monitor system or if another monitor is in close
proximity, be sure the monitors are not interfering with each
other’s electromagnetic eld by moving them apart.
3. Fluorescent lights or fans may be too close to the monitor.
the monitor for instructions.
ImageControl/ Horizontal Position or Vertical Position to adjust
the horizontal or vertical position of the image.
68 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 77

“No Connection, Check Signal Cable” displays on screen.
Cause Solution
Monitor video cable is disconnected. Connect the video cable between the monitor and computer.
CAUTION: Ensure that the computer power is o while
connecting the video cable.
“Out of Range” displays on screen.
Cause Solution
Video resolution and refresh rate are set higher than what the
monitor supports.
Restart the computer and enter Safe Mode. Change the settings to
a supported setting then restart the computer so that the new
settings take eect.
To enter Safe Mode in Windows 7:
1. Restart the computer.
2. Press and hold the F8 key as your computer restarts, before
the Windows logo appears. If the Windows logo appears,
you must restart the computer and try again.
3. On the Advanced Boot Options screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the safe mode option you want, and then press
Enter.
4. Log on to your computer with a user account that has
administrator rights.
When your computer is in safe mode, Safe Mode displays in
the corners of your monitor. To exit safe mode, restart your
computer and let Windows start normally.
To enter Safe Mode in Windows 10:
1. Log into the computer using an Administrator account.
2. Type msconfig in the taskbar search box, and then select
mscong from the list of applications.
3. Click the
Boot tab, select Safe boot and then click OK.
High pitched noise coming from inside a
Cause Solution
Brightness and/or contrast settings are too high. Lower brightness and/or contrast settings.
Fuzzy focus; streaking, ghosting, or shadowing
picture on the screen (at panel monitors using an analog VGA input connection only).
Cause Solution
Flat panel monitor’s internal digital conversion circuits may be
unable to correctly interpret the output synchronization of the
graphics card.
at panel monitor.
eects; horizontal scrolling lines; faint vertical bars; or unable to center the
1. Select the monitor’s Auto-Adjustment option in the
2. Manually synchronize the Clock and Clock Phase on-screen
or’s on-screen display menu.
monit
play functions. To download a SoftPaq that will assist you
dis
Solving display problems 69
Page 78

Fuzzy focus; streaking, ghosting, or shadowing eects; horizontal scrolling lines; faint vertical bars; or unable to center the
picture on the screen (at panel monitors using an analog VGA input connection only).
Cause Solution
with the synchronization, go to the following Web site,
select the appropriate monitor, and download either
SP32347 or SP32202: http://www.hp.com/support
Graphics card is not seated properly or is bad (some models). 1. Reseat the graphics card.
2. Replace the graphics card.
Certain typed symbols do not appear correct.
Cause Solution
The font you are using does not support that particular symbol. Use the Character Map to locate and select the appropriate
symbol. You can copy the symbol from the Character Map into a
document.
In Windows 7, click Start, select All Programs, select Accessories,
select System Tools, and then select Character Map.
In Windows 10, type ch in the taskbar search box, and then select
Character Map
from the list of applications.
Solving audio problems
If the computer has audio features and you encounter audio problems, see the common causes and solutions
ted in the following table.
lis
Sound cuts in and out.
Cause Solution
Processor resources are being used by other open applications. Shut down all open processor-intensive applications.
Sound does not come out of the speaker or headphones.
Cause Solution
Software volume control is turned down or muted. Double-click the
Audio is hidden in Computer Setup. Enable the audio in Computer Setup: Advanced > Built-in Device
The external speakers are not turned on. Turn on the external speakers.
The audio device may be connected to the wrong jack. Ensure that the device is connected to the correct jack on the
Speaker icon on the taskbar, then make sure
that Mute is not selected and use the volume slider to adjust the
volume.
Options.
computer. The rear audio jack output is the green receptacle. The
speakers should be plugged into the line-out jack and the
headphones should be plugged into the headphone jack.
External speakers plugged into the wrong audio jack on a recently
installed sound card.
70 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
See the sound card documentation for proper speaker connection.
The rear audio jack output is the green receptacle.
Page 79

Sound does not come out of the speaker or headphones.
Cause Solution
Headphones or devices connected to the line-out connector mute
the internal speaker.
Computer is in Sleep state. Press the power button to resume from Sleep state.
Internal speaker is disabled in Computer Setup. Enable the internal speaker in Computer Setup. Select Advanced >
The application is set to use a dierent audio device than
speakers.
Some applications can select which audio output device is used. Make sure the application has selected the correct audio device.
The operating system controls may be set to use a dierent audio
device as the default output device than what is expected.
Turn on and use headphones or external speakers, if connected,
or disconnect headphones or external speakers.
CAUTION: When attempting to resume from Sleep state, do not
hold down the power button for more than four seconds.
Otherwise, the computer will shut down and you will lose any
unsaved data.
Built-in Device Options.
Some graphics cards support audio over the DisplayPort
connection (if applicable), so multiple audio devices may be listed
in Device Manager. Make sure the correct device is being used.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select Control
Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
Set the operating system to use the correct audio device.
Sound from headphones is not clear or
Cause Solution
Headphones are plugged into the rear audio output connector.
The rear audio output connector is for powered audio devices and
is not designed for headphone use.
Computer appears to be locked up while recording audio.
Cause Solution
The hard disk may be full. Before recording, make sure there is enough free space on the
Line-in jack is not functioning properly.
Cause Solution
Jack has been
software.
recongured in the audio driver or application
mued.
Plug the headphones into the headphone connector on the front
of the computer.
h
ard disk. You can also try recording the audio le in a
compressed format.
In the audio driver or application software, recongure the jack or
set the jack to its default value.
Solving audio problems 71
Page 80

There is no sound or sound volume is too low.
Cause Solution
The application is set to use a dierent audio device than
speakers.
Some applications can select which audio output device is used. Make sure the application has selected the correct audio device.
The operating system controls may be set to use a dierent audio
device as the default output device than what is expected.
Solving printer problems
If you encounter printer problems, see the documentation that came with the printer and to the common
cause
s and solutions listed in the following table.
Printer will not print.
Cause Solution
Printer is not turned on and online. Turn the printer on and make sure it is online.
Some graphics cards support audio over the DisplayPort
connection (if applicable), so multiple audio devices may be listed
in Device Manager. Make sure the correct device is being used.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select Control
Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
Set the operating system to use the correct audio device.
The correct printer drivers for the application are not installed. 1. Install the correct printer driver for the application.
2. Try printing using the MS-DOS command:
DIR C:\ > [printer port]
where
[printer port] is the address of the printer being
used. If the printer works, reload the printer driver.
To run MS-DOS commands, press the Windows key + r, type
Open box, and then click OK.
in the
If you are on a network, you may not have made the connection
to the printer.
Printer may have failed. Run printer self-test.
Printer will not turn on.
Cause Solution
The cables may not be connected properly. Reconnect all cables and check the power cord and electrical
Make the proper network connections to the printer.
utlet.
o
cmd
72 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 81

Printer prints garbled information.
Cause Solution
The correct printer driver for the application is not installed. Install the correct printer driver for the application.
The cables may not be connected properly. Reconnect all cables.
Printer memory may be overloaded. Reset the printer by turning it o for one minute, then turn it back
on.
Printer will not print.
Cause Solution
The printer may be out of paper. Check the paper tray and rell it if it is empty.
Solving keyboard and mouse problems
If you encounter keyboard or mouse problems, see the documentation that came with the equipment and to
the common causes and solutions listed in the following table.
A wireless keyboard/mouse is not working correctly. Symptoms include lagging mouse movement, jumpy mouse/keyboard, or no
function of mouse/keyboard and external drive.
Cause Solution
If your computer is equipped with USB 3.0 ports, connected USB
3.0 devices can interfere with the wireless keyboard USB receiver.
Keyboard commands and typing are not recognized by the computer.
Cause Solution
Keyboard connector is not properly connected. Shut down the computer, reconnect the keyboard to the back of
Program in use has stopped responding to commands. Shut down your computer using the mouse and then restart the
Keyboard needs repairs. See the Worldwide Limited Warranty for terms and conditions.
Computer is in Sleep state. Press the power button to resume from Sleep state.
Connect the wireless keyboard USB receiver to a USB 2.0 port that
is separated from ports with USB 3.0 devices. If you still
experience interference, you may have to place the connectors
farther apart using an external USB hub.
the computer, and then restart the computer.
computer.
CAUTION: When attempting to resume from Sleep date, do not
hold down the power button for more than four seconds.
Otherwise, the computer will shut down and you will lose any
unsaved data.
Solving keyboard and mouse problems 73
Page 82

Mouse does not respond to movement or is too slow.
Cause Solution
Mouse connector is not properly plugged into the back of the
computer.
Program in use has stopped responding to commands. Shut down the computer using the keyboard then restart the
Mouse may need cleaning. Remove the roller ball cover on the mouse and clean the internal
Shut down the computer using the keyboard.
Windows 7:
1. Press the Ctrl and Esc keys at the same time (or press the
Windows logo key) to display the Start menu.
2. Use the arrow keys to select Shut Down and then press
Enter.
3. After the shutdown is complete, plug the mouse connector
into the back of the computer (or the keyboard) and restart.
Windows 10:
1. Press the Ctrl and Esc keys at the same time (or press the
Windows logo key) to display the Start menu.
2. Use the arrow keys to scroll to and select the power icon at
the top right on the menu, and then press Enter.
3. Use the arrow keys to select Shut Down, and then press
Enter.
4. After the shutdown is complete, plug the mouse connector
into the back of the computer (or the keyboard) and restart.
computer.
components.
Mouse may need repair. See the Worldwide Limited Warranty for terms and conditions.
Computer is in Sleep state. Press the power button to resume from Sleep state.
CAUTION: When attempting to resume from Sleep state, do not
hold down the power button for more than four seconds.
Otherwise, the computer will shut down and you will lose any
unsaved data.
Mouse will only move vertically, horizontally, or movement is jerky.
Cause Solution
Mouse roller ball or the rotating encoder shafts that make contact
with the ball are dirty.
Remove roller ball cover from the bottom of the mouse and clean
the internal components with a mouse cleaning kit available from
most computer stores.
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
You may need to recongure the computer when you add or remove hardware, such as an additional drive or
expansion card. If you install a plug and play device, Windows automatically recognizes the device and
congures the computer. If you install a non-plug and play device, you must recongure the computer after
completing installation of the new hardware. In Windows, use the Add Hardware Wizard and follow the
instructions that appear on the screen.
To open the Add Hardware Wizard, open a Command Prompt and open hdwwiz.exe.
74 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 83

WARNING! When the computer is plugged into an AC power source, voltage is always applied to the system
board. To reduce the risk of personal injury from electrical shock and/or hot surfaces, be sure to disconnect
the power cord from the wall outlet and allow the internal system components to cool before touching.
Table 6-1 Solving Hardware Installation Problems
A new device is not recognized as part of the system.
Cause Solution
Device is not seated or connected properly. Ensure that the device is properly and securely connected and
that pins in the connector are not bent down.
Cable(s) of new external device are loose or power cables are
unplugged.
Power switch of new external device is not turned on. Turn o the computer, turn on the external device, then turn on
When the system advised you of changes to the conguration,
you did not accept them.
A plug and play board may not automatically congure when
added if the default conguration conicts with other devices.
USB ports on the computer are disabled in Computer Setup. Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure that Device available
Computer will not start.
Cause Solution
Ensure that all cables are properly and securely connected and
that pins in the cable or connector are not bent down.
the computer to integrate the device with the computer system.
Reboot the computer and follow the instructions for accepting the
changes.
Use Windows Device Manager to deselect the automatic settings
for the board and choose a basic conguration that does not
cause a resource conict. You can also use Computer Setup to
recongure or disable devices to resolve the resource conict.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select Control
Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
is selected for appropriate USB ports under Advanced > Port
Options.
Wrong memory modules were used in the upgrade or memory
modul
es were installed in the wrong location.
1. Review the documentation that came with the system to
det
ermine if you are using the correct memory modules and
to verify the proper installation.
NOTE: DIMM1 or XMM1 must always be installed. DIMM1
mus
t be installed before DIMM2, and DIMM3 must be
installed before DIMM4.
2. Observe the beeps and LED lights on the front of the
c
omputer. Beeps and ashing LEDs are codes for specic
problems.
3. If you still cannot resolve the issue, contact Customer
Sup
port.
Solving Hardware Installation Problems 75
Page 84

Power LED ashes Red three times and then white two times.
Cause Solution
Memory is installed incorrectly or is bad. CAUTION: To avoid damage to the DIMMs or the system board,
Solving Network Problems
Some common causes and solutions for network problems are listed in the following table. These guidelines
do not discuss the process of debugging the network cabling.
Table 6-2 Solving Network Problems
Network driver does not detect network controller.
you must unplug the computer power cord before attempting to
reseat, install, or remove a DIMM module.
1. Reseat DIMMs. Power on the system.
2. Replace DIMMs one at a time to isolate the faulty module.
NOTE: DIMM1 or XMM1 must always be installed. DIMM1
must be installed before DIMM2, and DIMM3 must be
installed before DIMM4
3. Replace third-party memory with HP memory.
4. Replace the system board.
Cause Solution
Network controller is disabled. 1. Run Computer Setup and enable network controller.
2. Enable the network controller in the operating system using
Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select
Control Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
Incorrect network driver. Check the network controller documentation for the correct driver
or obtain the latest driver from the manufacturer’s Web site.
Network status link light never
NOTE: The network status light is supposed to ash when there is network activity.
Cause Solution
No active network is detected. Check cabling and network equipment for proper connection.
Network controller is not set up properly. Check for the device status within Windows, such as Device
ashes.
Man
ager for driver load and the Network Connections applet
within Windows for link status.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select Control
Panel, and then select Device Manager.
76 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 85

Table 6-2 Solving Network Problems (continued)
Network status link light never ashes.
NOTE: The network status light is supposed to ash when there is network activity.
Cause Solution
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
ager from the list of applications.
Man
Network controller is disabled.
Network driver is not properly loaded. Reinstall network drivers.
System cannot autosense the network. Disable auto-sensing capabilities and force the system into the
Diagnostics reports a failure.
Cause Solution
The cable is not securely connected. Ensure that the cable is securely attached to the network
The cable is attached to the incorrect connector. Ensure that the cable is attached to the correct connector.
There is a problem with the cable or a device at the other end of
the cable.
1. Run Computer Setup and enable network controller.
2. Enable the network controller in the operating system using
De
vice Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select
Control Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
correct operating mode.
onnector and that the other end of the cable is securely attached
c
to the correct device.
Ensure that the cable and device at the other end are operating
correctly.
The network controller is defective. Contact an authorized service provider.
Diagnostics passes, but the computer does not communicate with the network.
Cause Solution
Network drivers are not loaded, or driver parameters do not
tch current conguration.
ma
The network controller is not congured for this computer. Select the Network and Sharing Center icon in the Control Panel
Make sure the network drivers are loaded and that the driver
parameters match the conguration of the network controller.
Make sure the correct network client and protocol is installed.
and congure the network controller.
To access Control Panel in Windows 7, click Start, and then select
Control Panel.
To access Control Panel in Windows 10, type control panel in
the taskbar search box, and then select Control Panel from the
t of applications.
lis
Solving Network Problems 77
Page 86

Network controller stopped working when an expansion board was added to the computer.
Cause Solution
The network controller requires drivers. Verify that the drivers were not accidentally deleted when the
drivers for a new expansion board were installed.
Network controller stops working without apparent cause.
Cause Solution
The les containing the network drivers are corrupted. Reinstall the network drivers using the Recovery Disc Set in
Windows 7.
If necessary, download the softpaq from the web (from a dierent
computer).
The cable is not securely connected. Ensure that the cable is securely attached to the network
connector and that the other end of the cable is securely attached
to the correct device.
The network controller is defective. Contact an authorized service provider.
New network card will not boot.
Cause Solution
New network card may be defective or may not meet industrystandard specications.
Cannot connect to network server when attempting Remote System Installation.
Cause Solution
The network controller is not congured properly. Verify Network Connectivity, that a DHCP Server is present, and
System setup utility reports unprogrammed EEPROM.
Cause Solution
Unprogrammed EEPROM. Contact an authorized service provider.
Install a working, industry-standard NIC, or change the boot
sequence to boot from another source.
that the Remote System Installation Server contains the NIC
drivers for your NIC.
78 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 87

Solving memory problems
If you encounter memory problems, some common causes and solutions are listed in the following table.
CAUTION: Power may still be supplied to the DIMMs when the computer is turned o (depending on the
Management Engine (ME) settings). To avoid damage to the DIMMs or the system board, you must unplug the
computer power cord before attempting to reseat, install, or remove a memory module.
For those systems that support ECC memory, HP does not support mixing ECC and non-ECC memory.
Otherwise, the computer will not boot the operating system.
NOTE: The memory count will be aected by congurations with the Management Engine (ME) enabled. The
ME uses 8MB of system memory in single channel mode or 16MB of memory in dual-channel mode to
download, decompress, and execute the ME rmware for Out-of-Band (OOB), third-party data storage, and
other management functions.
System will not boot or does not function properly after installing additional memory modules.
Cause Solution
A memory module is not installed in the DIMM1 or XMM1 socket. Ensure that a memory module is installed in the DIMM1 or XMM1
socket on the system board. This socket must be populated with a
memory module.
Memory module is not the correct type or speed grade for the
system or the new memory module is not seated properly.
Out of memory error.
Cause Solution
You have run out of memory to run the application. Check the application documentation to determine the memory
Memory count during POST is wrong.
Cause Solution
The memory modules may not be installed correctly. Check that the memory modules have been installed correctly and
Integrated graphics may use system memory. No action required.
Insucient memory error during operation.
Replace module with the correct industry-standard device for the
computer. On some models, ECC and non-ECC memory modules
cannot be mixed.
requirements.
that proper modules are used.
Cause Solution
Too many Terminate and Stay Resident programs (TSRs) are
installed.
You have run out of memory for the application. Check the memory requirements for the application or add more
Delete any TSRs that you do not need.
memory to the computer.
Solving memory problems 79
Page 88

Power LED ashes Red ve times, once every second, followed by a two second pause, and the computer beeps ve times. (Beeps
stop after fth iteration but LEDs continue ashing.)
Cause Solution
Memory is installed incorrectly or is bad. 1. Reseat DIMMs. Power on the system.
Solving CD-ROM and DVD problems
If you encounter CD-ROM or DVD problems, see the common causes and solutions listed in the following table
or to the documentation that came with the optional device.
System will not boot from CD-ROM or DVD drive.
Cause Solution
2. Replace DIMMs one at a time to isolate the faulty module.
3. Replace third-party memory with HP memory.
4. Replace the system board.
The device is attached to a SATA port that has been hidden in the
Computer Setup utility.
Removable Media Boot is disabled in the Computer Setup utility. Run the Computer Setup utility and enable booting to removable
Network Boot is enabled in Computer Setup. Run the Computer Setup utility and disable Network Boot in
Non-bootable CD in drive. Try a bootable CD in the drive.
Boot order not correct. Run the Computer Setup utility and change boot sequence in
Drive not found (identied).
Cause Solution
Cable could be loose. Check cable connections.
The system may not have automatically recognized a newly
installed device.
Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure Device Available is
selected for the device's SATA port in Advanced > Port Options.
media in Advanced > Boot Options.
Advanced > Boot Options.
Advanced > Boot Options.
See reconguration directions in the Solving Hardware
Installation Problems on page 74 section. If the system still does
not recognize the new device, check to see if the device is listed
within Computer Setup. If it is listed, the probable cause is a driver
problem. If it is not listed, the probable cause is a hardware
problem.
If this is a newly installed drive, run the Computer Setup utility
and try adding a POST delay under Advanced > Power-On
Options.
The device is attached to a SATA port that has been hidden in
Computer Setup.
Drive responds slowly immediately after power-up. Run Computer Setup and increase the POST Delay in Advanced >
80 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure Device Available is
selected for the device's SATA port in Advanced > Port Options.
Power-On Options.
Page 89

CD-ROM or DVD devices are not detected or driver is not loaded.
Cause Solution
Drive is not connected properly or not properly congured. See the documentation that came with the optional device.
Movie will not play in the DVD drive.
Cause Solution
Movie may be regionalized for a dierent country. See the documentation that came with the DVD drive.
Decoder software is not installed. Install decoder software.
Damaged media. Replace media.
Movie rating locked out by parental lock. Use DVD software to remove parental lock.
Media installed upside down. Reinstall media.
Cannot eject compact disc (tray-load unit).
Cause Solution
Disc not properly seated in the drive. Turn o the computer and insert a thin metal rod into the
emergency eject hole and push rmly. Slowly pull the tray out
from the drive until the tray is fully extended, then remove
the disc.
CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, or DVD-R/RW drive cannot read a disc or takes too long to start.
Cause Solution
Media is corrupt. Try dierent media to conrm whether media is valid.
Media has been inserted upside down. Re-insert the media with the label facing up.
The DVD-ROM drive takes longer to start because it has to
determine the type of media played, such as audio or video.
CD or DVD disc is dirty. Clean CD or DVD with a CD cleaning kit, available from most
Windows does not detect the CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive. 1. Use Device Manager to remove or uninstall the device.
Wait at least 30 seconds to let the DVD-ROM drive determine the
type of media being played. If the disc still does not start, read the
other solutions listed for this topic.
computer stores.
To access Device Manager in Windows 7, click Start, select
Control Panel, and then select Device Manager.
To access Device Manager in Windows 10, type device
manager in the taskbar search box, and then select Device
from the list of applications.
ager
Man
2. Restart the computer and let Windows detect the CD or DVD
driv
er.
Solving CD-ROM and DVD problems 81
Page 90

Recording or copying CDs is dicult or impossible.
Cause Solution
Wrong or poor quality media type. 1. Try using a slower speed when recording.
Solving USB ash drive problems
If you encounter USB ash drive problems, common causes and solutions are listed in the following table.
USB ash drive is not seen as a drive letter in Windows.
Cause Solution
The drive letter after the last physical drive is not available. Change the default drive letter for the ash drive in Windows.
USB ash drive not found (identied).
Cause Solution
2. Verify that you are using the correct media for the drive.
3. Try a dierent brand of media. Quality varies widely
between manufacturers.
The device is attached to a USB port that has been hidden in
Computer Setup.
The device was not properly seated before power-up. Ensure the device is fully inserted into the USB port before
System will not boot from USB ash drive.
Cause Solution
Boot order is not correct. Run the Computer Setup utility and change boot sequence in
Removable Media Boot is disabled in the Computer Setup utility. Run the Computer Setup utility and enable booting to removable
The computer boots to DOS after making a bootable ash drive.
Cause Solution
Flash drive is bootable. Install the ash drive only after the operating system boots.
Flash drive is defective. Try a dierent ash drive.
Run the Computer Setup utility and enable USB ports in Advanced
> Port Options.
applying power to the system
Advanced > Boot Options.
media in Advanced > Boot Options. Ensure USB is enabled in
Storage > Boot Order.
82 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 91

Solving front panel component problems
If you encounter problems with devices connected to the front panel, refer to the common causes and
solutions listed in the following table.
A USB device, headphone, or microphone is not recognized by the computer.
Cause Solution
Device is not properly connected. 1. Turn o the computer.
2. Reconnect the device to the front of the computer and
restart the computer.
The device does not have power. If the USB device requires AC power, be sure one end is connected
to the device and one end is connected to a live outlet.
The correct device driver is not installed. 1. Install the correct driver for the device.
2. You might need to reboot the computer.
The cable from the device to the computer does not work. 1. If possible, replace the cable.
2. Restart the computer.
The device is not working. 1. Replace the device.
2. Restart the computer.
USB ports on the computer are disabled in Computer Setup. Run the Computer Setup utility and ensure that the USB ports are
set to Enabled in Security > USB Security.
Solving Internet access problems
If you encounter Internet access problems, consult your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or refer to the common
causes and solutions listed in the following table.
Unable to connect to the Internet.
Cause Solution
Internet Service Provider (ISP) account is not set up properly. Verify Internet settings or contact your ISP for assistance.
Web browser is not set up properly. Verify that the Web browser is installed and set up to work with
Cable/DSL modem is not plugged in. Plug in cable/DSL modem. You should see a “power” LED light on
Cable/DSL service is not available or has been interrupted due to
bad weather.
The CAT5 UTP cable is disconnected. Connect the CAT5 UTP cable between the cable modem and the
IP address is not congured properly. Contact your ISP for the correct IP address.
Cookies are corrupted. (A “cookie” is a small piece of information
that a Web server can store temporarily with the Web browser.
This is useful for having the browser remember some specic
information that the Web server can later retrieve.)
your ISP.
the front of the cable/DSL modem.
Try connecting to the Internet at a later time or contact your ISP.
(If the cable/DSL service is connected, the “cable” LED light on the
front of the cable/DSL modem will be on.)
computers’s RJ-45 connector. (If the connection is good, the “PC”
LED light on the front of the cable/DSL modem will be on.)
Windows 7:
1. Select Start > Control Panel.
2. Click Internet Options.
Solving front panel component problems 83
Page 92

Unable to connect to the Internet.
Cause Solution
3. In the Browsing history section on the General tab, click the
Delete button.
4. Select the Cookies check box and click the Delete button.
Windows 10:
1. Type control panel in the taskbar search box, and then
Control Panel from the list of applications.
select
2. Click
3. In the
4. Select the
Cannot automatically launch Internet programs.
Cause Solution
You must log on to your ISP before some programs will start. Log on to your ISP and launch the desired program.
Internet Options.
Browsing history section, click the Delete button.
Cookies and website data check box and click the
Delete button.
84 Chapter 6 Troubleshooting without diagnostics
Page 93

Solving software problems
Most software problems occur as a result of the following:
●
The application was not installed or congured correctly.
●
There is insucient memory available to run the application.
●
There is a conict between applications.
●
Be sure that all the needed device drivers have been installed.
●
If you have installed an operating system other than the factory-installed operating system, check to be
sure it is supported on the system.
If you encounter software problems, see the applicable solutions listed in the following table.
Computer will not continue and the HP logo does not display.
Cause Solution
ROM issue - POST error has occurred. Observe the beeps and LED lights on the front of the computer.
See POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and
audible codes on page 86 to determine possible causes.
See the Worldwide Limited Warranty for terms and conditions.
“Illegal Operation has Occurred” error message is displayed.
Cause Solution
Software being used is not Microsoft-certied for your version of
Windows.
Conguration les are corrupt. If possible, save all data, close all programs, and restart the
Verify that the software is certied by Microsoft for your version
of Windows (see program packaging for this information).
computer.
Solving software problems 85
Page 94

7 POST error messages and diagnostic front
panel LEDs and audible codes
This appendix lists the error codes, error messages, and the various indicator light and audible sequences
that you may encounter during Power-On Self-Test (POST) or computer restart, the probable source of the
problem, and steps you can take to resolve the error condition.
POST Message Disabled suppresses most system messages during POST, such as memory count and nonerror text messages. If a POST error occurs, the screen will display the error message. To manually switch to
the POST Messages Enabled mode during POST, press any key (except F10, F11, or F12). The default mode is
POST Message Disabled.
The speed at which the computer loads the operating system and the extent to which it is tested are
determined by the POST mode selection.
Quick Boot is a fast startup process that does not run all of the system level tests, such as the memory test.
Full Boot runs all of the ROM-based system tests and takes longer to complete.
Full Boot may also be enabled to run every 1 to 30 days on a regularly scheduled basis. To establish the
schedule, recongure the computer to the Full Boot Every x Days mode, using Computer Setup.
NOTE: For more information on Computer Setup, see Computer Setup (F10) Utility on page 44.
POST numeric codes and text messages
This section covers those POST errors that have numeric codes associated with them. The section also
includes some text messages that may be encountered during POST.
NOTE: The computer will beep once after a POST text message is displayed on the screen.
Control panel message Description Recommended action
002-Option ROM Checksum Error System ROM or expansion board option ROM
checksum.
003-System Board Failure DMA or timers. 1. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
1. Verify the correct ROM.
2. Flash the ROM if needed.
3. If an expansion board was recently added,
remove it to see if the problem remains.
4. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
5. If the message disappears, there may be a
problem with the expansion card.
6. Replace the system board.
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
2. Remove expansion boards.
3. Replace the system board.
005-Real-Time Clock Power Loss Invalid time or date in conguration memory. Reset the date and time under Control Panel
(Computer Setup can also be used). If the
86 Chapter 7 POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
Page 95

Control panel message Description Recommended action
RTC (real-time clock) battery may need to
be replaced.
008–Microcode Patch Error Processor is not supported by the BIOS. 1. Upgrade BIOS to proper version.
009–PMM Allocation Error during MEBx
Download
100-Front Audio Not Connected Front audio cable has been detached or
00A-Product Information Not Valid The product information programmed into the
00B-MEBx Module did not checksum correctly Memory error during POST execution of the
Memory error during POST execution of the
Management Engine (ME) BIOS Extensions
option ROM.
unseated from system board.
system board is missing or invalid.
Management Engine (ME) BIOS Extensions
option ROM.
problem persists, replace the RTC battery. See
the Removal and Replacement section for
instructions on installing a new battery.
2. Change the processor.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. Unplug the power cord, re-seat the
memory modules, and reboot the
computer.
3. If the memory conguration was recently
changed, unplug the computer, restore
the original memory conguration, and
reboot the computer.
4. If the error persists, replace the system
board.
Reconnect or replace front audio cable.
Use Computer Setup to update this information.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. Unplug the power cord, re-seat the
memory modules, and reboot the
computer.
3. If the memory conguration was recently
changed, unplug the power cord, restore
the original memory conguration, and
reboot the computer.
4. If the error persists, replace the system
board.
00C-PMM Deallocation Error during MEBx
Cleanup
00D-Setup Error during MEBx Execution MEBx selection or exit resulted in a setup
Memory error during POST execution of the
Management Engine (ME) BIOS Extensions
option ROM.
failure.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. Unplug the power cord, re-seat the
memory modules, and reboot the
computer.
3. If the memory conguration was recently
changed, unplug the power cord, restore
the original memory conguration, and
reboot the computer.
4. If the error persists, replace the system
board.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. Unplug the power cord, re-seat the
memory modules, and reboot the
computer.
3. If the memory conguration was recently
changed, unplug the power cord, restore
the original memory conguration, and
reboot the computer.
POST numeric codes and text messages 87
Page 96

Control panel message Description Recommended action
4. If the error persists, replace the system
board.
00E-Inventory Error during MEBx Execution BIOS information passed to the MEBx resulted
in a failure.
00F-Interface Error during MEBx Execution MEBx operation experienced a hardware error
during communication with the ME.
2E1-MemorySize Error Memory amount has changed since the last
boot (memory added or removed).
2E2-Memory Error Memory module conguration failed during
boot up.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. If the error persists, update to the latest
BIOS version.
3. If the error still persists, replace the
system board.
1. Reboot the computer.
2. If the error persists, update to the latest
BIOS version.
3. If the error still persists, replace the
system board.
The system memory size is dierent from the
last startup. The most common reason is the
removal of memory from the system board.
Press the F1 key to save the memory changes.
If this message persists, verify that the
memory modules are installed correctly.
1. Ensure memory modules are correctly
installed.
2. Verify proper memory module type.
3. Remove and replace the identied faulty
memory module(s).
4. If the error persists after replacing
memory modules, replace the system
board.
2E3-Incompatible Memory Module in Memory
Socket(s) X, X, ...
2E4-DIMM Conguration Warning The current memory conguration is not
2E5-ECC Memory Module Detected on
Unsupported Platform
2E6–Memory Not Congured Correctly for
Proper MEBx Execution
300–Conguration Change Warning The storage device conguration will be
301-Hard Disk 1: SMART Hard Drive Detects
Imminent Failure
A memory module in memory socket identied
in the error message is missing critical SPD
information, or is incompatible with the chipset.
optimized.
Recently added memory module(s) support ECC
memory error correction.
DIMM1 is not installed. Make sure there is a memory module in the
updated as shown.
Hard drive is about to fail. (Some hard drives
have a hard drive rmware patch that will x an
erroneous error message.)
1. Verify proper memory module type.
2. Try another memory socket.
3. Replace with a supported module.
Rearrange the DIMMs so that each channel has
the same amount of memory.
1. If additional memory was recently added,
remove it to see if the problem remains.
2. Check product documentation for
memory support information.
DIMM1 socket and that it is properly seated.
Not applicable
1. Determine if hard drive is giving correct
error message. Run the Drive Protection
System test under using F2 Diagnostics
when booting the computer.
2. Apply hard drive rmware patch
if applicable. (Available at
http://www.hp.com/support.)
88 Chapter 7 POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
Page 97

Control panel message Description Recommended action
3. Back up contents and replace hard drive.
302-Hard Disk 2: SMART Hard Drive Detects
Imminent Failure
309 – 30C: Hard Disk 3–6: SMART Hard Drive
Detects Imminent Failure
3F0–Boot Device Not Found Boot device not found. Insert boot device or load operating system.
3F1–Hard Disk 1 Error Hard disk 1 error. 1. Check and/or replace cables.
3F2–Hard Disk 2 Error Hard disk 2 error. 1. Check and/or replace cables.
Hard drive is about to fail. (Some hard drives
have a hard drive rmware patch that will x an
erroneous error message.)
Hard drive is about to fail. (Some hard drives
have a hard drive rmware patch that will x an
erroneous error message.)
1. Determine if hard drive is giving correct
error message. Run the Drive Protection
System test under using F2 Diagnostics
when booting the computer.
2. Apply hard drive rmware patch
if applicable. (Available at
http://www.hp.com/support.)
3. Back up contents and replace hard drive.
1. Determine if hard drive is giving correct
error message. Run the Drive Protection
System test under using F2 Diagnostics
when booting the computer.
2. Apply hard drive rmware patch
if applicable. (Available at
http://www.hp.com/support.)
3. Back up contents and replace hard drive.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
3. Replace the hard disk drive.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
3. Replace the hard disk drive.
400-Serial Port A Address Conict Detected Both external and internal serial ports are
assigned to the same resources.
401-Serial Port B Address Conict Detected Both external and internal serial ports are
assigned to the same resources.
402-Serial Port C Address Conict Detected Both external and internal serial ports are
assigned to the same resources.
403-Serial Port D Address Conict Detected Both external and internal serial ports are
assigned to the same resources.
1. Remove any serial port expansion cards.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
3. Recongure card resources and/or run
Computer Setup or Windows utilities.
1. Remove any serial port expansion cards.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
3. Recongure card resources and/or run
Computer Setup or Windows utilities.
1. Remove any serial port expansion cards.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
3. Recongure card resources and/or run
Computer Setup or Windows utilities.
1. Remove any serial port expansion cards.
2. Clear CMOS. (See Password security and
resetting CMOS on page 93.)
POST numeric codes and text messages 89
Page 98

Control panel message Description Recommended action
3. Recongure card resources and/or run
Computer Setup or Windows utilities.
419-Out of Memory Space for Option ROMs Recently added PCI expansion card contains an
option ROM too large to download during POST.
41A-Front USB1/USB2 Not Connected Front USB cable has been detached or unseated
from system board.
41B-Device in PCI Express Slot Failed To
Initialize
43A-USB Type-C I2C Not Connected Cable is required between I2C on card and USB-
43B-More Than One USB type-C Cards Are
Installed
500–BIOS Recovery A system BIOS recovery has occurred. Not applicable.
60x-HP Battery Alert The system has detected the storage capacity
70x-Wireless Mode Not Supported The system has detected a wireless module
800-Keyboard Error Keyboard failure. 1. Reconnect keyboard with computer
There is an incompatibility or problem with a
PCIe device and the system or PCIe link could
not be congured to a valid bus width or speed.
C on the system board.
More than one USB type-C card is installed. Remove USB type-C card so only one is
of the battery stated below to be very low.
installed in the system that is not supported
and has been disabled.
▲ If a PCI expansion card was recently
added, remove it to see if the problem
remains.
Reconnect or replace front USB cable.
Try rebooting the system. If the error reoccurs,
the device may not work with this system
Install cable between I2C on card and USB-C on
the system board.
installed.
For optimal performance, replace the battery.
Replace with a supported module.
turned o.
2. Check connector for bent or missing pins.
3. Ensure that none of the keys are
depressed.
4. Replace keyboard.
801-Keyboard or System Unit Error Keyboard failure. 1. Reconnect the keyboard with computer
turned o.
2. Ensure that none of the keys are
depressed.
3. Replace the keyboard.
4. Replace the system board.
900-CPU Fan Not Detected CPU fan is not connected or may have
malfunctioned.
901-Chassis, Rear Chassis, or Front Chassis Fan
not Detected
904-SATA Cabling Error One or more SATA devices are improperly
Chassis, rear chassis, or front chassis fan is not
connected or may have malfunctioned.
attached. For optimal performance, the SATA 0
and SATA 1 ports should be used for hard drives
before other ports.
1. Reseat CPU fan.
2. Reseat fan cable.
3. Replace CPU fan.
1. Reseat chassis, rear chassis, or front
chassis fan.
2. Reseat fan cable.
3. Replace chassis, rear chassis, or front
chassis fan.
Ensure SATA connectors are used in ascending
order. For one device, use SATA 0. For two
devices, use SATA 0 and SATA 1. For three
devices, use SATA 0, SATA 1, and SATA 2.
90 Chapter 7 POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
Page 99

Control panel message Description Recommended action
910–Filter Warning Airow lter is dirty. Replace the airow lter.
90B-Fan Failure The system has detected that a cooling fan is
not operating correctly.
90D-System Temperature Thermal shutdown occurred. The system BIOS
has detected your machine was previously shut
down to avoid overheating. Overheating may
occur if the cooling vents are blocked or the
operating temperature exceeds the system
specications. The machine should return to
normal operation once the situation is resolved.
90E-Power Supply Fan Not detected Power supply fan is not connected or may have
malfunctioned.
1. Reseat fan.
2. Reseat fan cable.
3. Replace fan.
Make sure system has proper airow.
1. Reseat power supply fan.
2. Reseat fan cable.
3. Replace power supply fan.
Interpreting system validation diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
During the system validation phase that occurs at system startup, the BIOS validates the functionality of the
following subsystems and conditions:
●
AC adapter
●
System board power
●
Processor failure
●
BIOS corruption
●
Memory failure
●
Graphics failure
●
System board failure
●
BIOS authentication failure
If an error is detected, specic patterns of long and short blinks, accompanied by long and short beeps (where
applicable) are used to identify the error. These patterns will make up a two part code:
●
Major – the category of the error
●
Minor – the specic error within the category
NOTE: Single beep/blink codes are not used.
Number of long beeps/blinks Error category
1 Not used
2 BIOS
3 Hardware
Interpreting system validation diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes 91
Page 100

Number of long beeps/blinks Error category
4 Thermal
5 System board
Patterns of blink/beep codes are determined by using the following parameters:
●
1 second pause occurs after the last major blink.
●
2 second pause occurs after the last minor blink.
●
Beep error code sequences occur for the rst 5 iterations of the pattern and then stop.
●
Blink error code sequences continue until the computer is unplugged or the power button is pressed.
NOTE: Not all diagnostic lights and audible codes are available on all models.
The red LED blinks to represent the major error category (long blinks). The white LED blinks to represent the
minor error category (short blinks). For example, ‘3.5’ indicates 3 long red blinks and 5 short white blinks to
communicate the processor is not detected.
Category Major/minor code Description
BIOS 2.2 The main area (DXE) of BIOS has become corrupted and there is no recovery
binary image available.
2.3 The embedded controller policy requires the user to enter a key sequence.
2.4 The embedded controller is checking or recovering the boot block.
Hardware 3.2 The embedded controller has timed out waiting for BIOS to return from
memory initialization.
3.3 The embedded controller has timed out waiting for BIOS to return from
graphics initialization.
3.4 The system board displays a power failure (crowbar).*
3.5 The processor is not detected.*
3.6 The processor does not support an enabled feature.
Thermal 4.2 A processor over temperature condition has been detected.*
4.3 An ambient temperature over temperature condition has been detected.
4.4 An MXM over temperature condition has been detected.
System board 5.2 The embedded controller cannot nd valid rmware.
5.3 The embedded controller has timed out waiting for the BIOS.
5.4 The embedded controller has timed out waiting for BIOS to return from
system board initialization.
5.5 The embedded controller rebooted the system after a possible lockup
condition had been detected through the use of a System Health Timer,
Automated System Recovery Timer, or other mechanism.
* Indicates hardware triggered event; all other events are controlled by the BIOS.
92 Chapter 7 POST error messages and diagnostic front panel LEDs and audible codes
 Loading...
Loading...