Page 1
® U.S. Registered Trademark
Copyright © 2000 Honeywell Inc. • All Rights Reserved EN0B-0090GE51 R1200
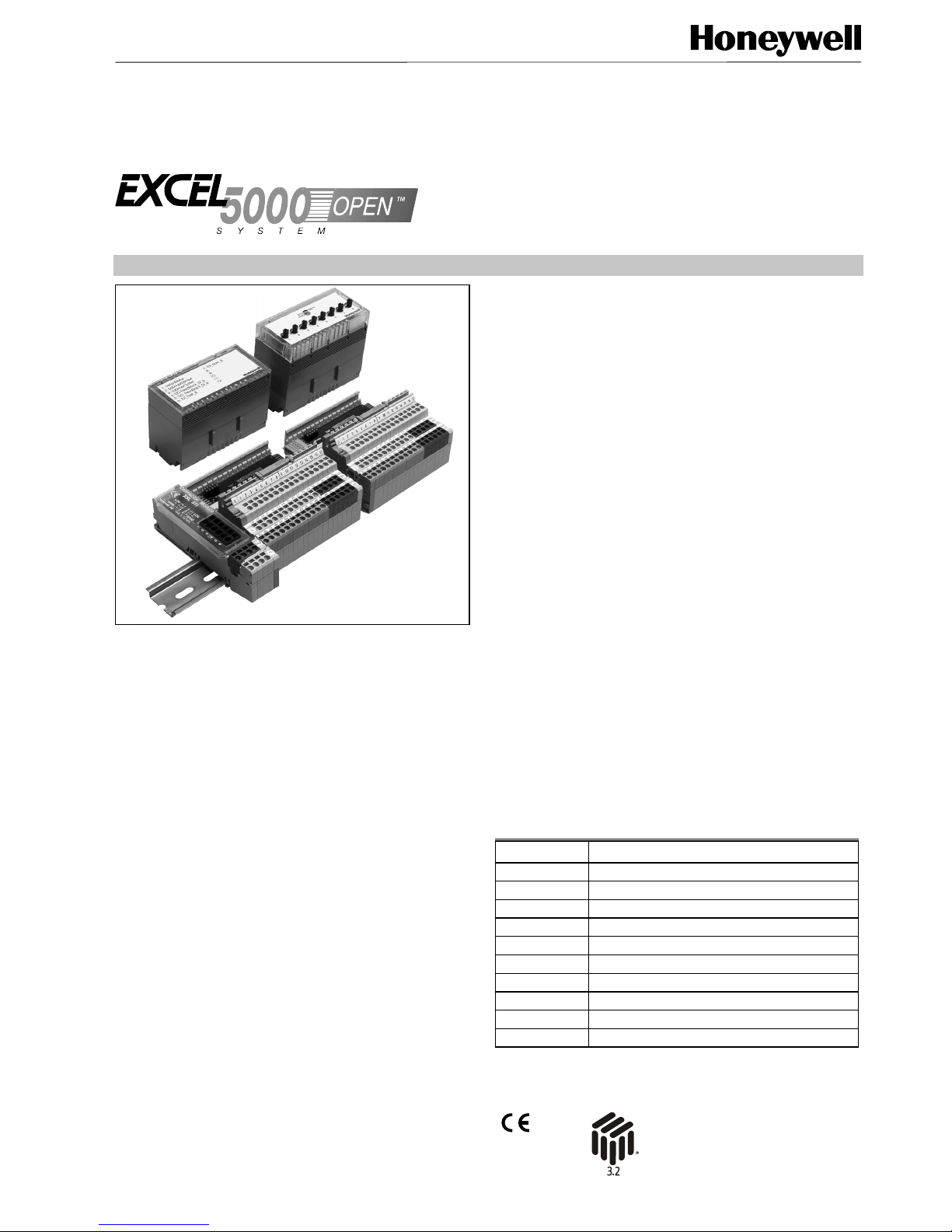
Distributed I/O
XFL521B, 522B,
523B, AND 524B MODULES
PRODUCT DATA
FEATURES
• LONMARK™ compliant
• 2-wire LONWORKS® bus interface between controller
and I/O
• No additional field terminals required
• May be used with Excel 500 controllers in conjunction
with standard I/O modules
• Automatic binding and commissioning with Excel 500
• Connector module with sliding bus connector (thus
eliminating the need to wire together neighboring
modules)
• Fast connection due to spring clamp terminals
• Module exchange during operation
• Optional manual override with feedback
• Alarm in case of defective module
• Mechanical coding prevents mismatching of modules
• Power LED (L1, green) and L
ONWORKS service LED
(L2, red) on all electronics modules.
• Status LEDs for analog outputs and digital in- and
outputs
• Optional manual override modules for analog and
digital output modules
GENERAL
The XFL521B, 522B, 523B, and 524B modules are LONMARK
compliant digital and analog I/O modules which can be
installed at strategic locations within a building. These
modules convert sensor readings and provide output signals
used for operating actuators via L
ONWORKS standard network
variables (SNVTs). Each Distributed I/O module plugs into a
base terminal block allowing communication with controllers
via the built-in Echelon
®
LONWORKS bus interface. The terminal block provides spring clamp terminals for easy connection of field cables from the various sensors and actuators.
The modular system allows Distributed I/O modules to be
removed from the system without disturbing other modules.
The module with terminal block mounts easily onto a DIN-rail.
The Excel 500 CPU (XC5010C, XC5210C, XCL5010) is
capable of automatically binding and commissioning the Distributed I/O modules via the L
ONWORKS bus. When the
modules are used by other controllers, plug-ins are provided
so that the modules can be commissioned by any LNS or
non-LNS installation or network management tool.
DESCRIPTION
The XFL521B, 522B, 523B, and 524B are Distributed I/O
modules that use a Neuron® chip and an FTT-10A free
topology transceiver for communication on a L
ONWORKS bus.
The modules are compliant with L
ONMARK Application Layer
Guidelines V3.2.
Table 1. Modules and accessories.
Module Description
XFL521B Analog Input module
XFL522B Analog Output module
XFL523B Digital Input module
XFL524B Digital Output module
XSL511 LONWORKS connector module
XSL512 Manual terminal disconnect module
XSL513 Terminal block for XFL521/522/523
XSL514 Terminal block for XFL524
XFR522A Analog Output manual override module
XFR524A Digital Output manual override module
Page 2
DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 2
INTEROPERABILITY
The Distributed I/O modules are compliant to the LONMARK
Application Layer Interface Guidelines, version 3.2. The
modules contain a L
ONMARK Node Object to allow monitoring
and setting the status of the various Sensor / Actuator Objects, as well as a L
ONMARK Sensor Object for each input or
an Actuator Object for each individual output.
Upon receiving an update to the NViRequest network vari-
able, the NVoStatus network variable is updated. The definition of SNVT_obj_request includes an object ID field to allow
the Node Object to report status conditions for all objects on
a node.
All network variables have the NV names in their self-documentation strings. This allows a network management node
or tool to display meaningful information on a Distributed I/O
module even if it is installed by an EXCEL 5000 controller
and not by the tool itself.
The Distributed I/O modules use the standard 6-byte location
string (see Table 2) in the Neuron® chip’s EEPROM to store
the module address (0...15 as set using the rotary HEX
switch) and the module type.
Location String
‘0’ Y Y
Module type
Set to '0'
Module
address
Module Type:
0 = XFL521B Analog Input
1 = XFL522B Analog Output
2 = XFL523B Digital Input
3 = XFL524B Digital Output
Table 2. Location string for storing module address
The node self-documentation string contains the module type
and revision in the optional part after the semicolon.
Example:
#pragma set_node_sd_string &3.2@0,3[6;XDO2_2_00
In this example, the module type is "XDO2" ("2" means that
the 3120E5 chip is used) and the revision is "2.00".
LONMARK Node Object
Setting the Node Object to “DISABLE” via nviRequest
suppresses updating of all output NVs and handling of input
NVs. Setting the Node Object to “ENABLE” via nviRequest
returns the module to normal operation.
The Node Object also contains the optional NV nciNetConfig
which is initialized to “CFG_LOCAL” by default. This allows
the Distributed I/O module to set its location string. If a
network management node commands this nci to
“CFG_EXTERNAL”, then the module will no longer modify its
Location String. This nci is stored in EEPROM and remains
there even in the event of a power failure.
LONMARK Sensor/Actuator Objects
All Actuator Objects (contained in the output modules) have
an output NV showing the actual state of the physical output
and whether it is in the automatic or manual override mode.
Note that the output modules have a manual override panel
which can be plugged on or off.
All Sensor Objects (contained in the input modules) have a
configuration property, MaxSendTime, defining the heartbeat
time, i.e. the interval in which output NVs belonging to the
physical inputs will be sent even if their values do not
change.
All Sensor Objects also have a configuration property,
MinSendTime, defining the minimum time which must elapse
before a changed value of an output NV belonging to a
physical input will be sent. This is to limit the network traffic
when sensor values change rapidly.
Node Object
Type #0
Mandatory
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv2
nvoStatus
SNVT_obj_status
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv8
nvoFileDirectory
SNVT_address
Optional
Network
Variables
Optional
Configuration
Properties
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc25
nciNetConfig
SNVT_config_src
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc49
SCPTMaxSendTime
SNVT_time_sec
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc52
SCPTMinSendTime
SNVT_time_sec
Figure 1. Distributed I/O LONMARK Node Object profile.
Page 3
DISTRIBUTED I/O
3 EN0B-0090
Table 3. Node Object network variables.
NV Name Type Range Description
nviRequest SNVT_obj_request RQ_NORMAL
RQ_DISABLE
RQ_ENABLE
RQ_UPDATE_STATUS
RQ_REPOPRT_MASK
RQ_SELF_TEST
Upon receiving an update to nviRequest, nvoStatus is
updated.
RQ_SELF_TEST is used only in the XFL522 analog
output module for outputs configured as a motor. In
this case, a synchronization is performed to set the
actuator in the 0% position.
nvoStatus SNVT_obj_status Reports the status of the node upon request through
nviRequest.
nciNetConfig SNVT_config_src CFG_LOCAL (default)
CFG_EXTERNAL
This configuration variable is set to CFG_LOCAL at
the factory and whenever the rotary HEX switch is
reset. If it is set to CFG_EXTERNAL, a network
manager will assign a network address for the node. In
this case, the module will not modify its location string
as long as the rotary HEX switch is not reset.
nvoFileDirectory SNVT_address Points to a file directory in the address space of the
Neuron® chip containing descriptors for the files in the
module. It is used to access the configuration properties stored in configuration parameter files
accessed by network management read/write
messages.
SCPTminSendTime SNVT_time_sec 1.0 to 10.0s
(default = 1.0)
Defines the minimum period of time between output
variable transitions. This configuration property is
applicable only to output NVs of the input modules.
SCPTmaxSendTime SNVT_time_sec 1.0 to 6553.4s
(default = 60.0s)
Defines the maximum time period of time before output NVs are automatically updated. It must be set to a
higher number than SCPTminSendTime. This configuration property is applicable only to output NVs of
the input modules.
XFL52xB Module Response Times
The response time of Distributed I/O modules is defined as
the period of time between the updating of the physical signal
and the updating of the NV (or vice versa). The response
time varies somewhat due to certain factors and is also
dependent upon the module type (refer also to Table 4).
The total system response time represents the sum of the
response times of all involved devices. When operating in the
open mode, a fast response time of 40 ms can be achieved,
thus enabling them to be employed in time-critical
applications.
Table 4. Response time (RT)
Module Typical RT
(sec)
Max. RT
(sec)
Min. time between
2 updates
XFL521B 0.8 1.6 SNVTMinSendTime
(default: 1 sec)
XFL522B 0.2 0.4 n.a.
XFL523B 0.3 0.5 SNVTMinSendTime
(default: 1 sec)
XFL524B 0.2 0.4
Page 4
DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 4
TECHNICAL DATA
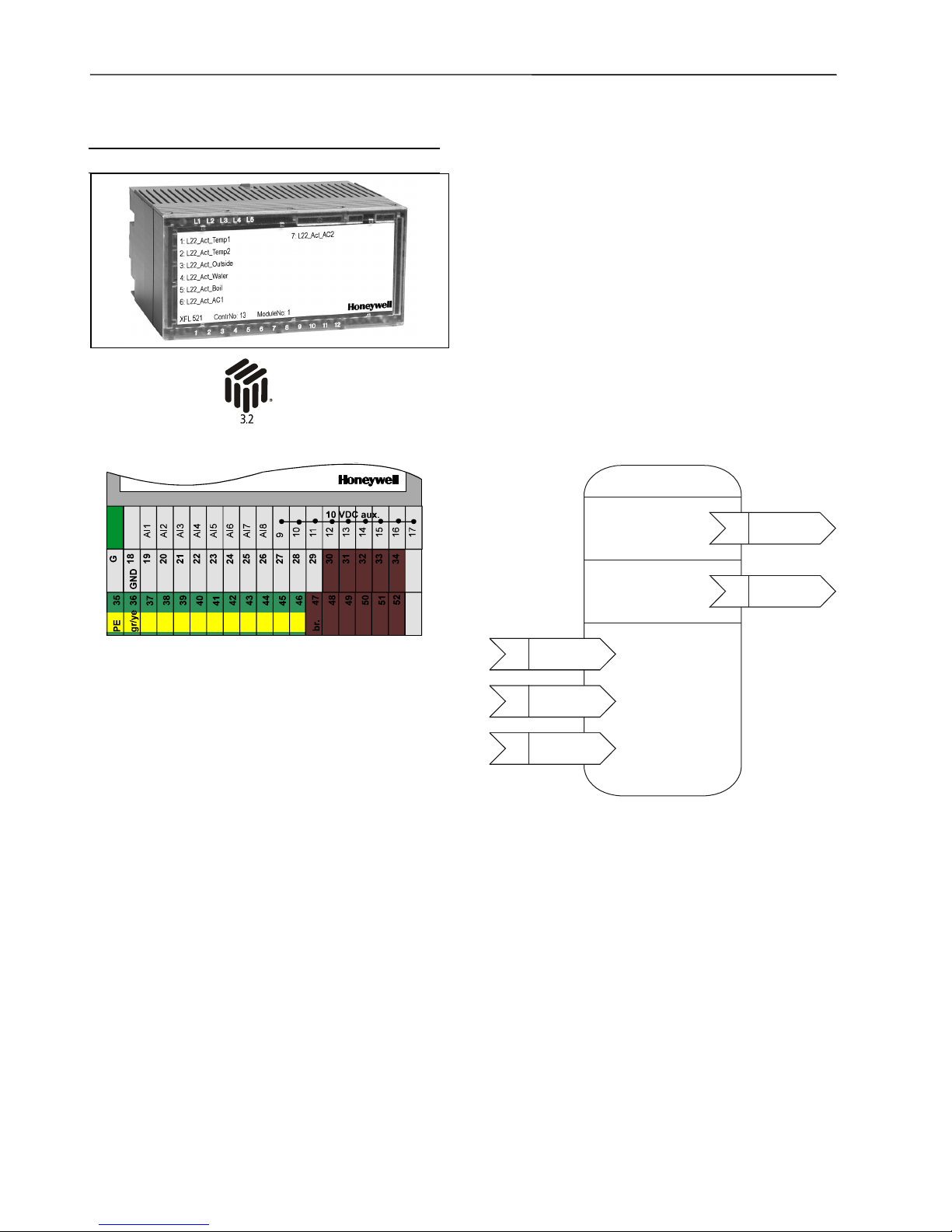
Analog Input Module XFL521B
• Eight inputs (AI1 – AI8)
0 to 10 Vdc (see EN1R-1047 for impedance
information)
0 to 20 mA (via external 500-ohm resistor)
4 to 20 mA (via external 500-ohm resistor)
NTC 20K ohm (-50°C to +150°)
PT1000 (-50°C to +150°C)
• Protected inputs up to 40 Vdc / 24 Vac
• 12-bit resolution
• ± 75 mV accuracy (0 to 10 V)
• 10 Vdc auxiliary voltage supply (9 – 17) , I
max
= 5 mA
• 1 sec polling time with CPU
• Green power LED (L1) and red LONWORKS status LED
(L2)
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x70 mm
The analog input module has eight input channels which
can be used for connecting sensors or any device providing an analog output. The input values are read by the
CPU and can then be used for monitoring or as parameters for controlling other devices.
The unit plugs into the XSL513 Terminal Block and can be
inserted and removed without disturbing other units on the
bus. Terminals AI1 through AI8 are the analog inputs and
terminals 9 through 17 are wired together and provide an
auxiliary voltage of 10 Vdc. The module address is set
using the rotary HEX switch.
NOTE: When the input is identified as a DI point, the
internal pull-up resistor is disabled.
Open Loop Sensor
Object Type #1
Mandatory
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoAiValue
SNVT_volt_f
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoAiTemp
SNVT_temp_p
Optional
Network
Variables
Optional
Configuration
Properties
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc1
UCPTSensorConfig
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc2 UCPTSendOnDelta
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc3 UCPTWireOffset
Figure 2. LONMARK Object for each analog input.
For each Sensor Object, the XFL521 Analog Input Module
provides an additional output NV, SNVT_temp_p, which
communicates the temperature in °C. This allows this
module to be used as a true temperature sensor in an
open L
ONMARK integration. If the Sensor Object is con-
figured as 0 to 10V, this NV will be invalid (0x7FFF).
Page 5

DISTRIBUTED I/O
5 EN0B-0090
Table 5. LONMARK Object NVs for the XFL521B.
NV Name Type Range Description
nvoAiValue SNVT_volt_f 0x000 (0.00 mV) to
0x461C4000 (10V)
The value of the input channel connected to a 0
to 10V signal after it has been filtered. Voltage
is transmitted in mV. When configured for a
temperature sensor, the channel transmits the
measured resistance.
nvoAiTemp SNVT_temp_p 0xEC78 (-50°C) to
0x3A98 (150°C)
Invalid = 0x7FFF
The value of the input connected to either an
NTC20 or PT1000 sensor with a resolution of
0.1°C. If the sensor channel is configured as a
voltage input, the temperature value is invalid
(0x7FFF).
UCPTSensorConfig 0 = not used,
9 = 0 to 10V with pull-up resistor
4 = NTC20
5 = PT1000
10 = 0 to 10V without pull-up
resistor (default = 8)
Specifies the type of sensor for a particular
input channel.
UPCTSendOnDelta SNVT_count 0 to 4095 (default = 2) Specifies the difference in the raw value
measured by the A/D converter is required
before the value of the sensor is transmitted.
UCPTWireOffset SNVT_res 0 to 6553.5 ohm (default = 0) Specifies a resistance value to add to the
resistance measured for a temperature sensor.
Page 6
DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 6
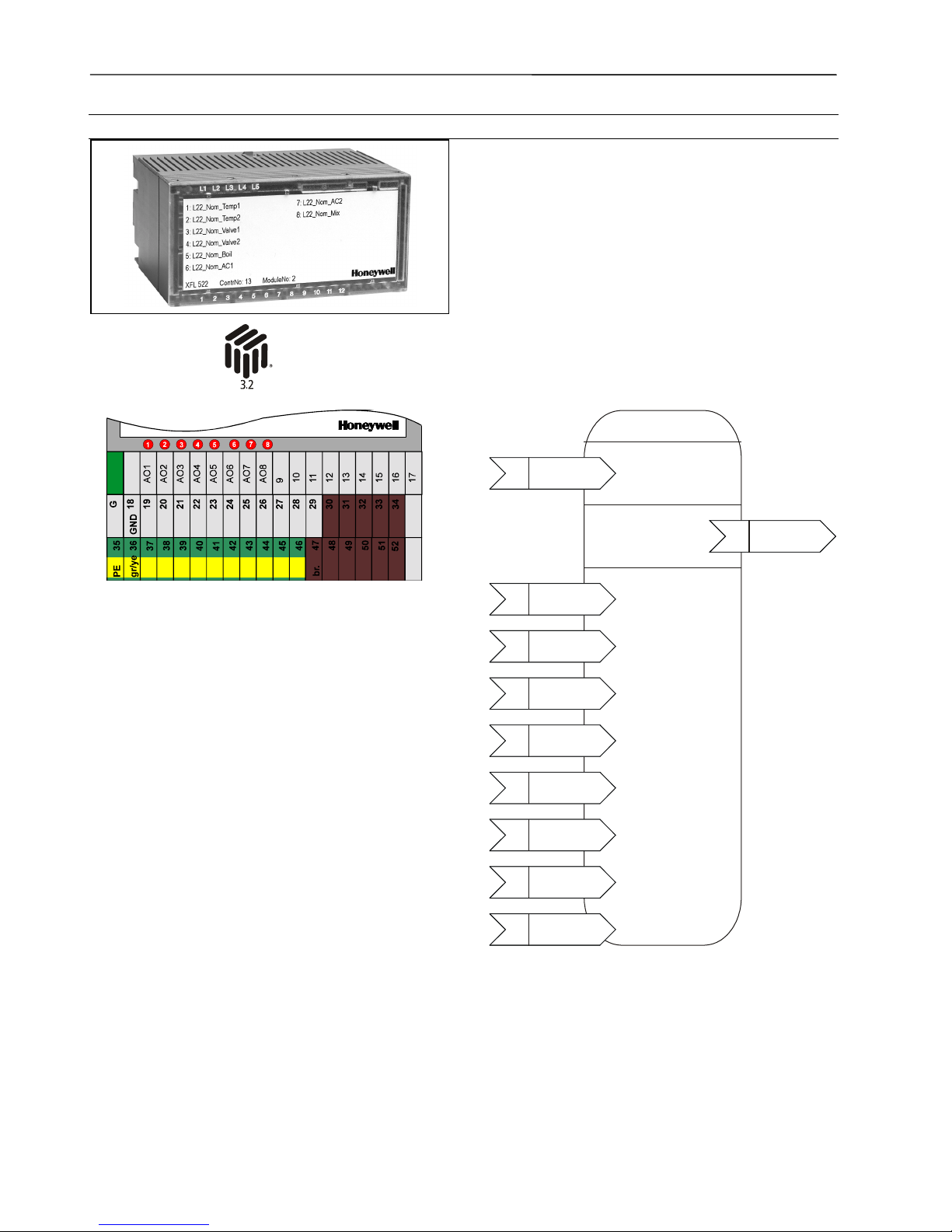
Analog Output Module XFL522B
• Eight outputs (AO1 – AO8), short-circuit proof
• Signal levels 0 to 10 Vdc
U
max
= 11 Vdc, I
max
= +1 mA, -1 mA
• Protected outputs up to 40 Vdc / 24 Vac
• 8-bit resolution
• Zero point < 200 mV
• Accuracy ± 150 mV deviation from output voltage
• One red LED per channel (light intensity proportional to
output voltage)
• Green power LED (L1) and red L
ONWORKS status LED
(L2)
• Control updating every 1 sec with CPU
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x70 mm
This analog output module has eight output channels
which can be connected to actuators or other suitable
analog devices.
The unit plugs into the XSL513 Terminal Block and can be
inserted and removed without disturbing other units on the
bus. Terminals AO1 through AO8 are the analog outputs.
Terminals 9 through 17 are connected to ground. Eight red
LEDs are located on top of the module. The brightness of
each LED is proportional to the output level of the corresponding channel. The module address is set using the
rotary HEX switch.
Open Loop Actuator
Object Type #3
Mandatory
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nviValue
SNVT_switch
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv3
nvoFeedback
SNVT_switch
Optional
Network
Variables
Optional
Configuration
Properties
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc1
UCPTSensorConfig
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc2
UCPTdriveTimeClose
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc3
UCPTdriveTimeOpen
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc4
UCPTsyncMin
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc5
UCPTsyncMax
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc6
UCPTsyncCharge
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc88
UCPTminDeltaLevel
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc96
UCPTdelayTime
Figure 3. LONMARK Object for each analog output.
Page 7

DISTRIBUTED I/O
7 EN0B-0090
Table 6. LONMARK Object NVs for the XFL522B.
NV Name Type Range Description
nviValue SNVT_switch Receives the value for the output channel.
nvoFeedback SNVT_switch Transmits the feedback value of the actuator output. If
the manual override switch is set to 0, or if the manual
override module is not plugged in, the feedback output
reflects the value of nviValue. As soon as the manual
override switch is set at the 20% threshold, the
Actuator Objects adopts this manual value. In this
case, the nvoFeedback state field will be 0xFF (invalid)
and the value field will contain the actuator position.
If the actuator is configured as a motor, the position
commanded with the manual override switch will be
reflected in the open/close commands for a floating
actuator.
If the manual override switch is in the automatic position, data is transmitted whenever nviValue is written.
If the manual override switch is in the manual position,
data is transmitted whenever the manual position is
changed.
UCPTSensorConfig none 0 = not used
6 = 0 to 10V (default)
7 = motor (floating)
Specifies the actuator output type for an output
channel.
UCPTdriveTimeClose SNVT_time_sec 10.0 to 1000s
(default = 90.0s)
Specifies a floating actuator’s runtime from 100% to
0%.
UCPTdriveTimeOpen SNVT_time_sec 10.0 to 1000s
(default = 90.0s)
Specifies a floating actuator’s runtime from 0% to
100%.
SCPTdelayTime SNVT_time_sec 0.0 to 10.0s
(default = 5.0s)
Specifies the delay time before a floating actuator
changes its direction. This avoids mechanical
problems that could occur when the run direction
changes due to an update to nviValue while the
actuator is still moving.
SCPTminDeltaLevel SNVT_lev_cont. Specifies the delta level for an update to nviValue to
be exceeded before a new position is calculated for
the floating motor model. This is applicable only if the
actuator is configured as a motor.
UCPTsyncMin SNVT_lev_cont 0 to10%
(default = 2%)
Specifies the lower synchronization threshold. If the
actuator is configured as a motor and the value
commanded through nviValue approaches 0%, the
actuator is synchronized to 0% as soon as nviValue
reaches the percentage specified by UCPTsyncMin.
UCPTsyncMin SNVT_lev_cont 90 to 100%
(default = 98%)
Specifies the upper synchronization threshold. If the
actuator is configured as a motor and the value
commanded through nviValue approaches 100%, the
actuator is synchronized to 100% as soon as nviValue
reaches the percentage specified by UCPTsyncMin.
UCPTsyncCharge SNVT_lev_cont 0 to 127.5%
(default = 100%)
Specifies the additional runtime when an actuator performs a synchronization. This is to ensure that the
actuator reaches the end position even if the actuator
position is not what it should be due to inaccuracy.
For example, with UCPTsyncCharge at 100%, an
actuator with a theoretical current position of 20%
would be forced to run 120% of the runtime specified
by UCPTdriveTimeClose if it starts a synchronization
from this point of operation.
Page 8
DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 8
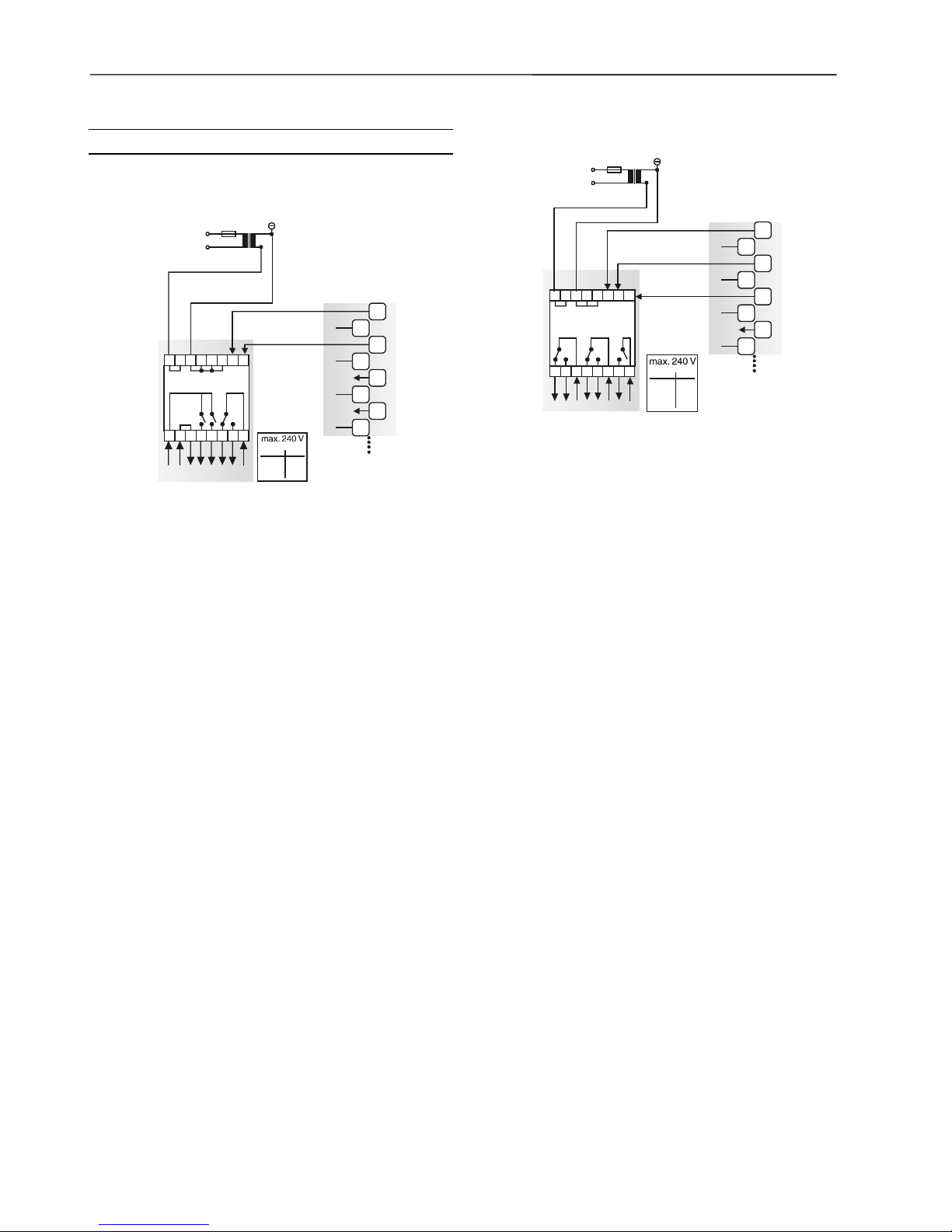
Relay Modules MCD 3 and MCE 3
The relay modules facilitate the control of peripheral devices
with high load via the analog outputs. Figure 4 and Figure 5
present connection examples for the relay modules MCD 3
and MCE 3, respectively.
230 Vac / 12 0 V ac
FUSE
0.2 A
K 1
K 2
K 3
3 A
11121314 15161718
1223K345
K1
LN
678
MCD 3
A
O1
18
A
O2
19
A
O3
20
A
O4
21
00000001
Figure 4. Analog Outputs, Connection of Relay MCD 3.
MCD 3
Relay terminal 17 controls the changeover contact K3. Relay
terminal 18 controls the ON contacts K1, K2. Ground can be
looped through terminals 2/3.
230 Vac / 12 0 V ac
FUSE
A
O1
18
A
O2
19
A
O3
20
A
O4
21
00000002
1112 13 14 15 16 17 18
123
K1 K2
K3
45678
MCE 3
0.2 A
K 1
K 2
2 A
K 3
Figure 5. Analog Outputs, Connection of Relay MCE 3.
MCE 3
Relay terminal 16 controls the ON contact K3. Relay terminal
17 controls the changeover contact K2. Relay terminal 18
controls the changeover contact K1.
Power Supply
Several relay modules can be connected in series via the
bridged terminal pair:
24 Vac: Terminals 11/12 of the relay
24 Vac (-): Terminals 13 to 16 of the relay
Page 9
DISTRIBUTED I/O
9 EN0B-0090
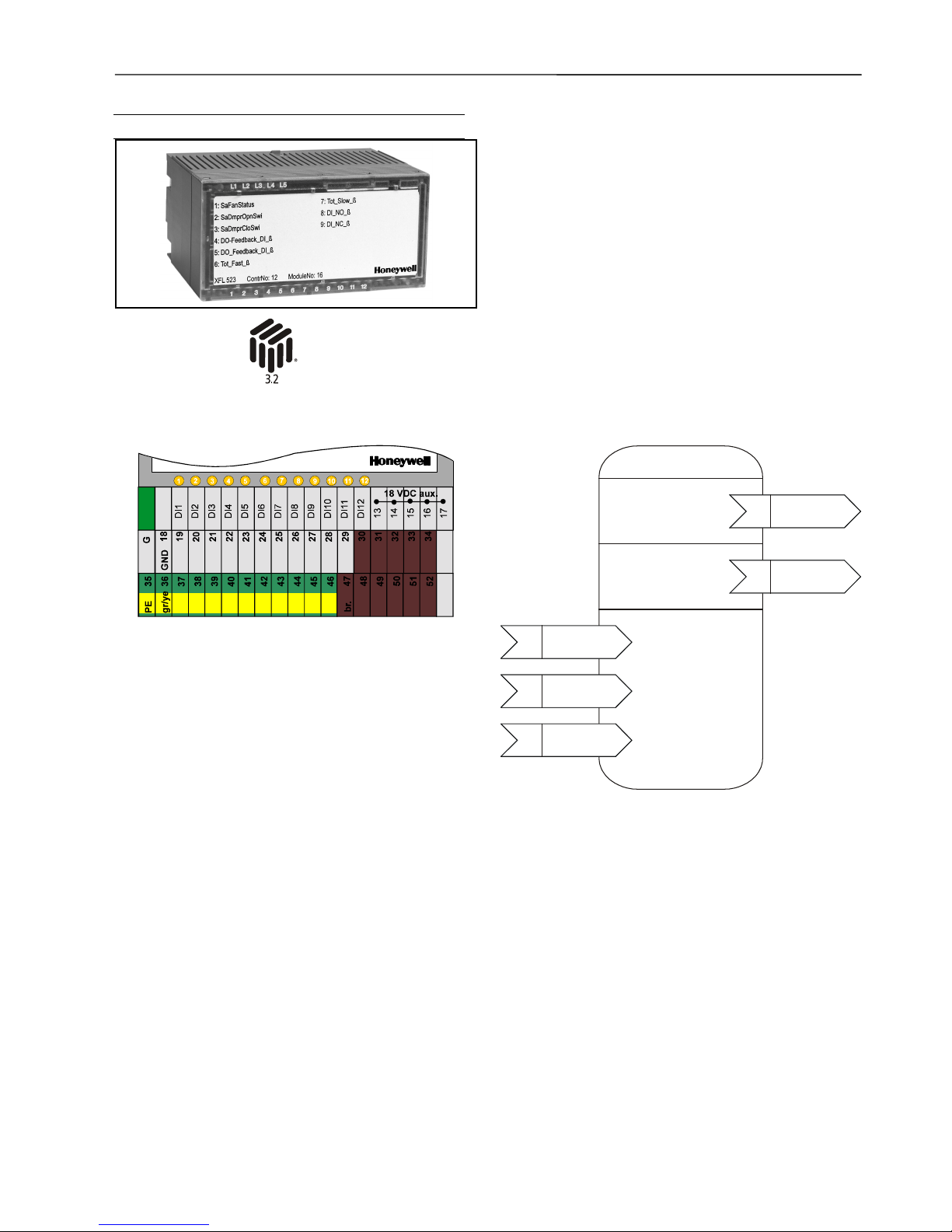
Digital Input Module XFL523B
• Twelve inputs (DI1 – DI12)
• Ri = 10K ohm
• Max. 20 Hz input frequency
• Switching conditions: OFF: Ui ≤ 2.5 V; ON: Ui ≥ 5 V
• Protected switching up to 40 Vdc / 24 Vac
• LED per channel, color selectable in two groups (SW1: DI
1 – 6; SW2 DI: 7 – 12); color combinations: see Table 7
• 18 Vdc auxiliary voltage supply (unregulated)
• 1 sec polling time with CPU
• Green power LED (L1) and red L
ONWORKS status LED
(L2)
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x70 mm
The digital input module has twelve input channels which can
be used for connecting sensors or any device providing a
digital output. The input values are read by the CPU and can
then be used for monitoring or as parameters for controlling
other devices
The unit plugs into the XSL513 Terminal Block and can be
inserted and removed without disturbing other units on the
bus. Terminals DI1 through DI12 are the digital inputs and
terminals 13 through 17 are wired together and provide an
auxiliary voltage of 18 Vdc. The module address is set using
the rotary HEX switch.
Beginning with V2.04.00 Excel 500 controller firmware, the
online point attribute Normally Open / Normally Closed
(NO/NC) defines the relation between the physical state
(contact position) and its logical status. See Table 7.
Open Loop Sensor
Object Type #1
Mandatory
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoDiValue
SNVT_switch
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoDiValueCnt
SNVT_count
Optional
Network
Variables
Optional
Configuration
Properties
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc1
UCPTSensorConfig
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc2 UCPTSendOnDelta
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc27 SCPTSendOnDelta
Figure 6. LONMARK Object for each digital input.
For each Sensor Object, the XFL523 Digital Input Module
provides an additional output NV, SNVT_switch. For an open
L
ONMARK integration, this offers a more convenient way of
accessing the sensor value compared to using the NV
SNVT_count. If the Sensor Object is configured as
“Totalizer”, this NV is invalid (switch.state = 0xFF,
switch.value = 0).
Page 10

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 10
Table 7. Relation between physical state and logical status as defined by the point attribute NO/NC for the XFL523B.
Contact Position NO/NC Attribute Logical Status Input Voltage LED Switch On LED Switch Off
Open NO 0 ≤ 2.5 V Off Green
Closed NO 1 ≥ 5 V Yellow Red
Open NC 1 ≤ 2.5 V Yellow Red
Closed NC 0 ≥ 5 V Off Green
Table 8. LONMARK Object NVs for the XFL523B.
NV Name Type Range Description
nvoDiValue SNVT_switch Transmits the state of the input channel every time
there is a state change or if SCPTMaxSendTime in
the Node Object has expired.
nvoDiValueCnt SNVT_count binary: 0, 1
totalizer: 0 to 65534
(65534 initial value)
Transmits the state of the input channel every time
there is a state change or if SCPTMaxSendTime in
the Node Object is expired. If configured as a
totalizer, this NV transmits the number of transitions
from 0 to 1.
UCPTSensorConfig 0 (not used)
1 = binary (default)
2 = totalizer
Specifies the setting for a sensor channel.
UCPTSendOnDelta SNVT_count 0 to 65535 Specifies the difference in totalizer count required
before a transmission of the value output of the
Sensor Object takes place.
SCPTDirection SNVT_state Used to define the relation between the logical status
of the input and the state of the LED. One bit corresponds to one input channel (bit 4 = input channel
12, bit 15 (MSB) = input channel 1). If a bit is clear,
the LED for the channel will be 0=green and 1=red. If
the bit is set, then 0=red and 1=green.
Page 11

DISTRIBUTED I/O
11 EN0B-0090
Digital Output Module XFL524B
• Six isolated change-over contacts
• Max. voltage U
max
= 230 Vac per output
• Max. current I
max
= 2 A per output
• LED per channel
OFF: LED off
ON: LED illuminated (yellow)
• Green power LED (L1) and red L
ONWORKS status LED
(L2)
• Cycle time 1 sec with CPU
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x70 mm
The digital output module has six isolated change-over contacts which can be connected to actuators or other switchable devices.
The unit plugs into the XSL514 Terminal Block and can be
inserted and removed without disturbing other units on the
bus. Terminals 1 through 18 are switched according to the
adjacent figure. Six LEDs are located on top of the module.
The module address is set using the rotary HEX switch.
Beginning with V2.04.00 Excel 500 controller firmware, the
online point attribute Normally Open / Normally Closed
(NO/NC) defines the relation between the physical state
(relay on/off) and its logical status. See Table 9.
NOTE: The digital outputs can be used as status contacts
or as alarm contacts, depending upon how they are
defined in CARE. All outputs from a single module
must be used for the same purpose.
Table 9. Physical state and logical status as defined by
the point attribute NO/NC for the XFL524B.
Relay
On/Off
NO/NC
attribute
Logical
Status
Output
Voltage
LED
Status
On NO 1 24V On
Off NO 0 0V Off
On NC 0 0V Off
Off NC 1 24V On
Open Loop Actuator
Object Type #3
Mandatory
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nviValue
SNVT_switch
Optional
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoDiagnose
SNVT_count
1
1
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv3
nvoFeedback
SNVT_switch
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nv1
nvoManCnt
SNVT_count
User-Defined
Network
Variables
input
NV 1
nviRequest
SNVT_obj_request
nc1
UCPTSensorConfig
Optional
Configuration
Properties
This output NV appears only once for the node.
Figure 7. LONMARK Object for each digital output.
Page 12

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 12
Table 10. LONMARK Object NVs for the XFL524B.
NV Name Type Range Description
nviValue SNVT_switch Receives the value for the output channel.
nvoFeedback SNVT_switch Transmits the feedback value of the Actuator Object. If
the manual override switch is set to auto, or if the
manual override module is not plugged in, the
feedback output reflects the value of nviValue. As
soon as the manual override switch is set to either
manual position, the Actuator Object adopts this
manual value. In this case, the nvoFeedback state
field will be 0xFF (invalid) and the value field will
contain the actuator position.
If the manual override switch is in the automatic position, data is transmitted whenever nviValue is written.
If the manual override switch is in the manual position,
data is transmitted whenever the manual position is
changed.
nvoManCnt SNVT_count 0 to 65535 Transmits the number of manual switching operations.
Each transition from the state auto/manual on/manual
off to any other statue is counted by incrementing this
NV.
nvoDiagnose SNVT_count 0 to 65535 Counts the number of times the internal filter for
smoothing the signal from the manual override switch
board has been active.
UCPTSensorConfig 0 = not used
1 = binary (default)
Specifies whether an Actuator Object is processed or
not. If set to 0, the value is not updated.
Page 13

DISTRIBUTED I/O
13 EN0B-0090
Terminal Block XSL513 for XFL521B/522B/523B
• Mechanical coding prevents mounting of improper
modules
• Mounts on a DIN-rail (top-hat rail)
• Spring-clamp terminals
• Safety latch secures XFL module in its position
The XSL513 Terminal Block has three rows of terminals:
Top row: 18 signal terminals (gray); function depending
upon the electronics module used (see the
respective Distributed I/O module descriptions).
Middle row: Twelve signal ground terminals (gray), con-
nected internally to electronics modules. Five
interconnected auxiliary terminals (brown)
Bottom row: Twelve PE terminals (green/yellow), connected
together to the DIN-rail. Six interconnected
auxiliary terminals (brown)
NOTE: Both rows of brown terminals are connected
internally but are not connected to the module.
Terminal Block XSL514 for XFL524B
• Mechanical coding prevents mounting of improper
modules
• Mounts on a DIN-rail (top-hat rail)
• Spring-clamp terminals
• Safety latch secures XFL module in its position
The XSL514 Terminal Block is intended for use only with the
XFL524B Digital Output module. It has three rows of
terminals.
Top row: 18 signal terminals (gray); function as
described for XFL524B.
Middle row: Eight interconnected auxiliary terminals
(brown), not connected to the module. Eight
interconnected auxiliary terminals (blue), not
connected to the module.
Bottom row: Seven PE terminals (green/yellow), connected
together to the DIN-rail.
Page 14

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 14
Manual Override Module XFR522A for XFL522B (Analog Output)
• Mounts on top of the XFL522B module
• Potentiometer settings
automatic or variable 0 – 100%
• XFL 522 LEDs remain visible
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x20 mm
• Feedback signal including point name, status (manual,
auto), and point value provided to CPU
The XFR522A manual override module mounts directly on
top of the XFL522B. Eight potentiometers on top of the
module can be used to independently vary the output of each
channel from 0 to 100%. Each potentiometer also has an
automatic setting which causes the channel to operate
normally. The LEDs of the XFL522B are also visible.
The manual override module works even if the CPU
XC5010C or XCL5010 is not working.
An optional label is available showing the functional
description generated by CARE.
Manual Override Module XFR524A for XFL524 (Digital Output)
• Mounts on top of the XFL524B module
• Switch settings:
automatic, off (0) and on (1)
• XFL524B LEDs remain visible
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 47x97x20 mm
• Feedback signal including point name, status (manual,
auto), and point value provided to CPU
The XFR524A manual override module mounts directly on
top of the XFL524B. Six switches on top of the module can
be used to independently switch each of the digital outputs
OFF (0) or ON (1). Each switch also has an automatic setting
which causes the channel to operate normally. The LEDs of
the XFL524B are also visible.
The manual override module works even if the CPU
XC5010C or XCL5010 is not working.
An optional label is available showing the functional description generated by CARE.
LONWORKS Connector Module XSL511
• LONWORKS network connection to CPU
• 24 Vac voltage supply for distribution to connected
modules
• Electronic fuse for 24 Vac
• Connection to Distributed I/O modules via sliding bus
connector (L
ONWORKS bus and voltage supply for ten
Distributed I/O modules)
• Bus data: speed: 78 Kbaud; length: depending on cable
type, e.g. 1,200 m, free topology 500 m, node-to-node 300
m
The XSL511 L
ONWORKS connector module provides ter-
minals for connecting to the L
ONWORKS bus wiring, as well as
terminals for the 24 Vac supply voltage for the other
modules. The part number for the L
ONWORKS bus termination
module is 209541B.
Page 15

DISTRIBUTED I/O
15 EN0B-0090
Manual Terminal Disconnect Module XSL512
• Mounts between terminal blocks and Distributed I/O
modules
• Manual terminal disconnect switches
• 18 disconnect switches
• Dimensions (WxLxH): 58x97x55 mm
• Safety latch secures XFL module in its position
The XSL512 Manual Terminal Disconnect module allows
each of the input connections of the Terminal Block to be
manually disconnected from the plugged-in module. This is
particularly useful for troubleshooting and installation.
Terminal Block Connection
Figure 8. Dimensions of XSL511 LONWORKS connector
module in inches (mm).
NOTE: The terminal blocks are to be mounted on 1.5-inch
(35-mm) DIN-rails (DIN/EN 50 022 35x15). The
mounting panel should have a minimum thickness of
0.08 inch (2 mm) to provide reference potential for
proper grounding and shielding. The maximum
distance between the fastening points of the rail
should be 5.9 inches (150 mm).
The L
ONWORKS connector module is required as an interface
between the L
ONWORKS bus and the Distributed I/O modules.
See section "L
ONWORKS Connector Module XSL511" for
information on determining how many Distributed I/O
modules can be connected to each L
ONWORKS connector
module. The terminal blocks may be fitted alongside one
another.
IMPORTANT
The L
ONWORKS transceiver can be affected by
electromagnetic fields generated by frequency
converters. If possible, locate frequency converters
in a different cabinet, or allow a minimum distance of
18 inches (50 cm) between frequency converters
and their respective cabling, and Distributed I/0
Modules.
Terminal blocks XSL513 and XSL514 can be combined in
any order on the rail.
1. Mount the DIN-rail at the desired location (vertically or
horizontally).
NOTE: It is recommended that when mounting vertically,
the XSL511 L
ONWORKS connector module be
mounted at the bottom to insure a good connection
of the bus in case any slippage occurs on the DINrail.
2. Install the 3
rd
-party DIN-rail end bracket onto the left end
of the rail.
3. Install the connector module onto the left end of the rail
next to the end bracket by first hooking the terminal end of
the module onto the rail and snapping it into place.
4. Install the first terminal block onto the rail.
NOTE: To avoid damage, ensure that the sliding bus con-
nector does not extend past the left edge of the
module.
Page 16

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 16
Figure 9. Terminal blocks with LONWORKS connector.
5. Push the sliding bus connector to the left until it locks onto
the matching circuit board section on the adjacent connector module (see Figure 10).
6. Lock in all other modules and connect them using the
sliding bus connector. Slide each sliding bus connector as
far to the left as possible.
NOTE: The electronics module or the manual terminal dis-
connect module will not fit properly on the terminal
block if the sliding bus connector is not on the left
side.
7. Fit the end cover included with the XSL511 onto the last
module.
8. Install 3
rd
-party DIN-rail end bracket close to end cover of
the last module.
NOTE: It is recommended to use solid standard 3
rd
-party
DIN-rail end brackets on both ends of the terminal
block to prevent any movement of the terminal
blocks. Terminal blocks must abut each other to
insure proper contact at the sliding bus connector.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Connector Module
XSL 511
Honeywell AG
Made in Germany
123
LON
shield shield
LON4
5
6
DIN RAIL
END BRACKET
DIN RAIL
END BRACKET
Figure 10. Sliding bus connector connects adjacent modules.
9. Insert clamps provided with electronics modules into slots
as shown in Figure 11 to provide extra assurance that
adjacent terminal blocks will not become separated.
NOTE: If the manual disconnector XSL512 is installed per-
manently in all terminal blocks, the clamps are to be
inserted into the respective XSL512 slots.
Page 17

DISTRIBUTED I/O
17 EN0B-0090
Figure 11. Clamps hold adjacent terminal blocks
together.
Page 18

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 18
Coding the Terminal Block
Figure 12. Coding comb patterns.
The terminal block is coded with pins to prevent mixing the
module types during commissioning or servicing.
CAUTION
Mixing the modules can destroy them.
Coding the terminal block is achieved by inserting pins into
designated location holes on the terminal block in the base.
This codes the electronics modules to their respective
terminal blocks.
1. Break off the coding pins on the coding comb such that
the comb is left with the coding combinations shown in
Figure 12.
2. The comb side corresponding to the respective terminal
block is inserted into the location holes in the terminal
block and broken off (positions 1 to 9 are printed on the
circuit board of the terminal block for alignment).
Figure 13. Inserting coding comb into terminal block.
3. Next, the other side of the comb is inserted into the elec-
tronics module location holes and likewise broken off. If
one or more opposing location holes both contain pins,
then the module cannot be mounted onto the terminal
block. The module can be mounted only if the single
coding pin corresponds to the missing pin in the terminal
block.
Figure 14. Inserting coding comb into I/O module.
Page 19

DISTRIBUTED I/O
19 EN0B-0090
Setting the Module Address
All modules will report the setting of the 16-position rotary
HEX switch as a 2-byte ASCII number in the lowest 2 bytes
of the Neuron® chip’s location string. Changing the rotary
HEX switch setting causes the module to reset its application
configuration (sensor selection, output selection, motor
runtime, etc.) and go unconfigured. Modules will run their
application in the unconfigured state so that another change
of the DIP switch will be recognized.
To remove the cover or a manual override module from the
Distributed I/O module, do the following:
1. Insert the opening tool XAL2 into the corresponding slots
in the electronics module to release the locking tabs. The
tool should be inserted such that the marking is on the
right-hand side.
Figure 15. Inserting opening tool.
2. Lift off the cover as is depicted in Figure 16.
Figure 16. Lifting the cover off.
IMPORTANT
Always use the XAL2 tool to remove the cover or a
manual override module from an output module. Lift
off manual override modules carefully to avoid
tearing the attached flat strip cable.
Figure 17. Rotary HEX switch location.
3. The module address is set by turning the HEX switch to
the appropriate address code using a screwdriver.
CAUTION
Do not plug an XFL module without a cover or manual
override module into the terminal block.
Installing the I/O Modules
locking procedure locked latch
Figure 18. Safety latch type A
locking procedure locked latch
Figure 19. Safety latch type B
The electronic I/O modules can be installed either on top of
the terminal blocks or on top of the manual terminal disconnect modules.
1. Make sure the sliding bus connector on the terminal block
is on the left side.
2. Mount the module onto the terminal block (or the manual
terminal disconnect module if installed) and make sure the
spring clip snaps on the little hook on the module housing.
3. Lock the safety latch on the terminal block (type A) (and
the manual terminal disconnect module, if installed; for the
safety latch on the manual disconnect module (type B) it is
recommended to use a screwdriver or similar for locking)
as is shown in the figure.
Installing the Manual Override Modules
XFR522A and XFR524A
The manual override modules are installed on top of their
respective output modules. The XFR522A and XFR524A are
connected to the output modules via flat strip cable; this
allows opening the housing and setting the rotary HEX switch
under power without disconnecting the manual override
module.
The manual override modules are installed using the
following procedure:
Page 20

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 20
1. Switch off the power to the output module or, unlock the
safety latch and unplug the module from the terminal block
as described in “Removing Modules and Terminal Blocks”.
2. Remove the standard cover of the module housing
(XFL522A/XFL524A) as is described in "Setting the
Module Address".
3. Plug the manual override connector situated at the end of
the flat strip cable into the socket in the output module.
NOTE: By mechanical design, the plug can be inserted in
only one orientation, thus preventing wrong connection.
Figure 20. Manual override connector socket location.
1. Slightly push back the locking tabs with the XAL2 tool to
bring them behind the edge of the module housing.
Figure 21. Pushing back locking tabs.
2. Snap the override module onto the electronics module
housing such that the power, L
ONWORKS service, and out-
put LEDs in the electronics module are aligned with their
respective view windows on the manual override face
plate. Make sure that all tabs of the manual override
module are snapped into the slots of the output module.
Figure 22. Snap override module into place.
IMPORTANT
Avoid tearing on the flat strip cable if you need to
remove a manual override module. Always use a
cover release tool XAL2 to remove the manual
override module and disconnect the plug carefully
(see also "Setting the Module Address"
3. Remount the module as is described in the previous
section.
Installing the Manu al Terminal Disconnect
Module XSL512
Figure 23. Installing the manual terminal disconnect
module.
The manual terminal disconnect module is installed between
the terminal block and the electronics module. If the right
side of the XSL512 is accessible (no other modules are
mounted to the right), then the end cover provided with the
XSL512 must be used.
1. Remove the electronics module as described in
"Removing Modules and Terminal Blocks"
2. Mount the XSL512 module onto the terminal block with the
switches on the terminal side of the terminal block as
depicted and lock the safety latch as described previously.
3. Mount the electronics module onto the top of the XSL512
and lock the safety latch as described in "Installing the I/O
Modules".
The individual inputs to the electronics module can now be
connected and disconnected manually.
Page 21

DISTRIBUTED I/O
21 EN0B-0090
Applying CARE Printout Labels
Figure 24. XAL1 swivel label holder.
Normally, CARE labels can be used on electronics modules.
When using electronics modules with manual override units,
CARE labels cannot be applied to the face of the manual
override unit. In this case, the XAL1 swivel label holder is required (package of 10). The XAL1 swivel label holder is
mounted to the terminal block as shown in Figure 24.
Removing Modules and Terminal Blocks
The electronics modules and terminal blocks can be removed
by carrying out the following steps:
1. Unlock the safety latch(es) as is depicted in Figure 25.
on terminal blocks on XSL512
Figure 25. Unlocking the safety latches.
2. Remove the electronics module from the terminal block (or
manual terminal disconnect module) by pushing a screwdriver between the electronics module and the spring clip
on the terminal block (or manual terminal disconnect
module).
Figure 26. Unlocking the module spring clip.
3. Unlock the spring clip by lightly bending upwards with the
screwdriver.
4. Unplug the electronics module.
5. When installed, dismount the manual terminal disconnect
module as is described for the electronics module.
6. Disconnect the power to the connector module before
removing the terminal block.
Figure 27. Releasing the sliding bus link.
7. Now release the sliding bus link with a screwdriver and
push the sliding bus link to the right into its terminal block.
Make sure that it is drawn back completely!
NOTE: Do not dismount the terminal block until both sliding
bus links are drawn back completely.
8. The sliding bus link of the terminal block to the right (if one
exists) can be released without removing the electronics
module by pushing a screwdriver into one of the notches
of the sliding bus link and sliding it backwards into its
home position (terminal block) with small sideways movements.
Figure 28. Removing the terminal block.
9. Lift the terminal block from the rail by inserting a screw-
driver tip into the two mounting feet - one after the other and lifting up the terminal block with small levering movements.
LONWORKS Network Interface
Distributed I/O modules contain an FTT-10A Free Topology
Twisted Pair Transceiver allowing communication with other
devices on a L
ONWORKS network. FTT-10A transceivers
communicate at 78 Kbaud and provide transformer isolation
so that the bus wiring does not have a polarity; that is, it is
not important which of the two bus terminals are connected
to each wire of the twisted pair.
FTT devices can be wired in daisy chain, star, loop or any
combination thereof as long as the maximum wire length requirements given below are met. The recommended configuration is a daisy chain with two bus terminations. This
layout allows for maximum bus length, and its simple structure presents the least number of possible problems, particularly when adding on to an existing bus.
NOTE: A doubly-terminated bus may have stubs of up to
10 ft (3 m) from the bus to each node.
Page 22

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 22
Table 11. Doubly-terminated bus specifications.
Cable Type Max. bus length
Belden 85102 8,900 ft (2,700m)
Belden 8471 8,900 ft (2,700m)
Level IV, 22 AWG 4,600 ft (1,400m)
JY (St) Y 2x2x0.8 3,000 ft (900m)
TIA568A Categ. 5 24AWG, twisted pair 3,000 ft (900m)
NOTE: The cable types listed above are as recommended
by Echelon® in their FTT-10A User Guide. The
cable recommended by Honeywell is the level IV, 22
AWG, solid core, nonshielded cable. Belden part
numbers are 9H2201504 (plenum) and 9D220150
(non-plenum).
TERMINATION
MODULE
DEVICE
DEVICE DEVICE DEVICE
DEVICE
TERMINATION
MODULE
Figure 29. Doubly-terminated bus configuration
(recommended).
Free topology requires only one bus termination and allows a
variety of bus configurations (see Figure 30):
TERMINATION
MODULE
DEVICE
DEVICE DEVICE DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
SINGLY TERMINATED
DEVICE
DEVICE
TERMINATION
MODULE
DEVICE
DEVICE
STAR
Figure 30. Possible bus configurations
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
TERMINATION
MODULE
DEVICE
DEVICE
DEVICE
MIXED
TERMINATION
MODULE
DEVICE
DEVICEDEVICE
DEVICEDEVICE
LOOP
Figure 31. Free topology examples.
The FTT specification includes two components that must be
met for proper system operation. The distance from each
transceiver to all other transceivers and to the termination
must not exceed the maximum node-to-node distance. If
multiple paths exist, the maximum total wire length is the total
amount of wire used.
Table 12. Free topology (singly-terminated)
specifications.
Cable type Maximum node-
to-node distance
Maximum total
wire length
Belden 85102 1,650 ft (500m) 1,650 ft (500m)
Belden 8471 1,300 ft (400m) 1,650 ft (500m)
Level IV, 22AWG 1,300 ft (400m) 1,650 ft (500m)
JY (St) Y 2x2x0.8 1,050 ft (320m) 1,650 ft (500m)
TIA568A Category 5
24AWG, twisted pair
825 ft (250m) 1,500 ft (450m)
IMPORTANT
Do not use different wire types or gauges on the
same L
ONWORKS network segment. The step
change in line impedance characteristics would
cause unpredictable reflections on the bus.
Page 23

DISTRIBUTED I/O
23 EN0B-0090
Examples of free topology schemes (1 allowed, 2 not
allowed) for cable JY (St) Y 2x2x0.8 are shown below.
Device
Device
Device
CPU
Termination
module
ALLOWED
Node-to-node = 656 ft (200m)
Total wire length = 328 ft (400m)
NOT ALLOWED
Node-to-node = 1287 ft (400m)
Total wire length = 1640 ft (500m)
Device
656 ft
(200m)
656 ft
(200m)
Device
Device
Termination
module
328 ft
(100m)
328 ft
(100m)
328 ft (100m)
328 ft (100m)
328 ft (100m)
Figure 32. Free topology examples (max. node-to-node
320 m, max. wire length 500m)
NOT ALLOWED
Node-to-node = 656 ft (200m)
Total wire len
g
th = 1969 ft (600m
)
Termination
module
328 ft
(100m)
328 ft
(100m)
Device Device
Device
Device
Device
656 ft
(200m)
Figure 33. Additional free topology example (max. node-
to-node: 320 m, max. wire length: 500 m)
NOTE: In the event that the limit on the total wire length is
exceeded, then FTT physical layer repeaters
(FTT 10A) can be added to interconnect segments
and increase the overall length by an amount equal
to the original specification for that cable type and
bus type for each repeater used. For example,
adding repeaters for a doubly-terminated bus using
JY (St) Y 2x2x0.8 cable increases the maximum
length 3000 ft (900m) for each repeater.
LONWORKS Bus Termination
One or two Termination Modules, part no. 209541B, are required for a L
ONWORKS bus with FTT devices on it, de-
pending upon the configuration. The maximum lengths described in "L
ONWORKS Network Interface" must be adhered to
for either a daisy chain or free topology L
ONWORKS bus
layout. See Figure 34 and Figure 35 for connection details for
the 2095401B Termination Module.
Figure 34. Termination Module connections for doubly-
terminated FTT network.
Figure 35. Termination Module connections for a singly-
terminated FTT network.
Page 24

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 24
Commissioning Distributed I/O Modules
Previous to V2.04.x controller firmware, Distributed I/O
modules were used only on a local L
ONWORKS bus con-
nected to a single Excel 500 controller. Concurrent with the
release of V2.04.x firmware is the release of the XFL52xB
Distributed I/O modules with updated firmware and with a
new Neuron chip which make them fully L
ONMARK compliant.
This means that multiple Excel 500 controllers, each with its
own Distributed I/O modules, as well as third-party L
ONMARK
compliant devices, can coexist and interoperate on the same
L
ONWORKS bus. Furthermore, the XFL52xB modules can be
used as third-party devices with other L
ONMARK compliant
products, independently of an Excel 500 controller.
IMPORTANT:
Full L
ONMARK functionality requires an Excel 500
controller with V2.04.x firmware, a 3120E5 Neuron
chip, and Distributed I/O modules XFL52xB.
An Excel 500 controller with V2.4.x firmware and
3120E5 Neuron chip will commission earlier versions of Distributed I/O modules (XFL52x,
XFL52xA), but only in the local mode (max 16
modules per CPU and no other controllers on the
L
ONWORKS bus).
Distributed I/O modules XFL52xB can be used with
older versions of Excel 500 that support Distributed
I/O, but only if the modules are switched into a
different mode. This is accomplished by pressing the
service pin while simultaneously turning the HEX
address switch. This mode can be cancelled by
pressing the service pin for more than three
seconds.
Table 13. Controller compatibility.
Operating mode
2
of
Distributed I/O modules
Controller type CPU / Application modules Controller
firmware
Open LONWORKS
functionality?
XFL52x XFL52xB
Excel 500 XC5010C / XCL5010 V2.0.x to V2.3.x not possible local local
Excel 500 XC5010C / XCL5010 V2.4.x not possible local local/shared
Excel 500 XC5010C1 / XCL50101 / XC5210C1V2.0.x to V2.3.x not possible local local
Excel 500 XC5010C1 / XCL50101 / XC5210C1V2.4.x in use --- shared/open
Excel 500 XC5010C1 / XCL50101 / XC5210C1V2.4.x not in use local local/shared
1
When bearing the LONMARK™ logo on the module/CPU.
2
The term "local" refers to an operating mode in which a maximum of 16 modules are assigned (automatically) to each controller and only a single controller is connected to each L
ONWORKS bus.
The term "shared" means that a maximum of 16 modules are assigned (manually) to each controller, but that multiple controllers can be connected to a single L
ONWORKS bus.
The term "open" refers to an open L
ONWORKS system, i.e. the use of CARE to generate a LONMARK compliant network
interface file (XIF) capable of providing NVs which can be bound to other devices (Excel 50 or Excel 10 controllers, thirdparty devices); further, the limitation of max. 16 modules per controller can also be exceeded.
Table 14. Distributed I/O module compatibility.
L
ONWORKS Functionality, by Controller Firmware VersionDistributed I/O modules
V2.0.x to V2.3.x V2.4.x
XFL521
XFL522A
XFL523
XFL524A
One controller to which Distributed I/O modules
are assigned on a single L
ONWORKS bus
One controller to which Distributed I/O modules
are assigned on a single LONWORKS bus
XFL521B
XFL522B
XFL523B
XFL524B
One controller to which Distributed I/O modules
are assigned on a single L
ONWORKS bus (press
the L
ONWORKS service pin while turning HEX
switch to enable this backwards-compatible
mode)
1
Full LONWORKS functionality: Multiple
Distributed I/O modules and multiple controllers
possible on a single L
ONWORKS bus
2
1
To cancel the backwards-compatible mode for Distributed I/O modules (allowing full LONWORKS functionality), press and hold
down the L
ONWORKS service pin for at least 3 seconds.
2
Excel 500 controller with Neuron 3120E5 chip required!
NOTE: Compatibility of XFR522A and XFR524A Manual Override modules is affected by neither firmware nor Neuron chip
version.
Page 25

DISTRIBUTED I/O
25 EN0B-0090
Operating Modes
It is important to remember the following definitions:
Local
The term "local" refers to an operating mode in which a max.
of 16 Distributed I/O modules are connected to a single host
Excel 50/500 controller via a L
ONWORKS bus, and in which no
other devices co-exist on that bus. In this mode, the Distributed I/O modules are assigned to their host Excel 50/500
controller automatically, and autobinding is performed.
Shared
The term "shared" means that, aside from the host Excel 500
controller and its Distributed I/O modules, other devices
(which may include other Excel 500 controllers with their own
Distributed I/O modules, Excel 50 or Excel 10 controllers, or
3
rd
-party devices) co-exist on the LONWORKS bus. In the
shared mode, autobinding may still be used for the NVs of a
maximum of 16 Distributed I/O modules assigned (manually)
exclusively to the host Excel 500 controller.
NOTE: It is recommended that you use CARE to assign the
Distributed I/O modules to the host Excel 500 controller (i.e. to enter the Distributed I/O modules'
Neuron IDs). The alternative is to assign them using
the MMI.
Open
The term "open" refers to an interoperable LONWORKS sys-
tem in which CARE has been used to generate a L
ONMARK
compliant network interface file capable of providing NVs
which can be bound to other devices (which may include
other Excel 500 controllers with their own Distributed I/O
modules, Excel 50 or Excel 10 controllers, or third-party
devices). In the open operating mode, the NVs of the Distributed I/O modules exceeding 16 must be bound manually
using a L
ONWORKS network management tool (an LNS-based
tool capable of using Honeywell plug-ins is recommended).
Combined Shared and Open Mode
The shared and the open operating modes can be in effect
simultaneously. In this case, autobinding is performed for the
NVs of a maximum of 16 Distributed I/O modules, while the
data points of additional Distributed I/O modules must be
mapped with shared NVs, and the NVs of the additional Distributed I/O modules must be bound manually (e.g. using an
LNS-based tool).
Autobinding
When Distributed I/O modules are used exclusively by
Honeywell Excel 500 controllers, it is possible to automatically bind their NVs to the controller. This is referred to
as "autobinding." In autobinding, each controller on the bus
finds the Distributed I/O modules assigned to it and binds the
required NVs.
IMPORTANT:
Autobinding does not work across routers. Distributed I/O modules must be located within the
same router segment as the controller to which their
NVs are to be bound. However, autobinding is
possible across repeaters.
IMPORTANT:
The autobound NVs of a controller are not visible to
a L
ONWORKS network management tool, and there is
hence no danger that a careless user will attempt to
re-bind them. However, the NVs of the Distributed
I/O modules are visible to a L
ONWORKS network
management tool. Any attempt to re-bind the autobound NVs of Distributed I/O modules will corrupt
the autobindings. In such a case, the Excel 500 controller will restore the autobindings automatically, but
there will be numerous system and application
alarms as a result.
If, prior to autobinding, the Distributed I/O modules
have been accessed by a L
ONWORKS network
management tool, the modules will remain in the
“configured” mode. In this state, they cannot be
found by the controller during autobinding, and they
do not appear in the list of modules on the controller
MMI. Such modules must be decommissioned using
the L
ONWORKS network management tool, or the
L
ONWORKS service pin must be pressed for at least
three seconds.
If an Excel 500 controller in the shared/open mode is deleted
from the LonMaker project, all of its bindings will also be
deleted. In this case, the Excel 500 controller will restore all
of the autobindings (if any) automatically after 3 minutes
(provided no bindings are performed or changed in LonMaker
in the meantime), but there will be numerous system and
application alarms as a result.
Assignment
There are two methods of assigning Distributed I/O modules
to a particular Excel 500 controller.
Recommended assignment method
The Ideal approach is to know the Neuron IDs of the Distributed I/O modules when engineering the application using
CARE, thus enabling you to enter the Neuron ID during the
CARE terminal assignment. When this is done, every module
will be fully identified and assigned automatically by the Excel
500 controller after the application is downloaded.
Alternate assignment method
If the Neuron ID is not available when engineering the
application using CARE, it will be possible to correctly assign
the Distributed I/O modules to their controller(s) only after
having downloaded the application. In this case, assignment
is performed via the MMI as described in detail in the
XI581/XI582 User Guide, EN2B-0126.
IMPORTANT:
It is essential that Distributed I/O modules not be
assigned simultaneously via different MMIs. When
using the alternative assignment method, work on
only one MMI at a time so as to avoid competing
network accesses. Disregarding this will result in
contradictory and unreliable assignments. There will
be incomplete Distributed I/O module lists displayed,
and there is the danger that one controller will take
away an existent assignment from another
controller.
Page 26

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 26
Regardless of which of these two methods is employed,
assignment requires that the modules' rotary HEX switches
be set according to the CARE terminal assignment.
Priority of Distributed I/O Module Assignments
Assignments made via an MMI always have priority over
assignments made using CARE. Thus, in the event of a conflict (e.g. when the Neuron ID entered using CARE differs
from the Neuron ID entered via the MMI), the assignment
carried out using the MMI will have priority.
Flashing of Distributed I/O Module Assignment
The Distributed I/O module assignment that was made in
CARE or via the controller MMI has to be saved to Flash
memory manually. When Distributed I/O module assignment
has been made during the test mode, the assignments are
saved in Flash memory automatically. These assignments
can be reused for the application after the application has
been downloaded.
Controller Reset
IMPORTANT:
Resetting a controller will erase the Distributed I/O
module assignment. After a reset, one of the
following procedures must be performed.
— Restore the application (including the assignments) from
Flash (this is the simplest method).
— Restore the assignments during the "start-up" sequence
(this requires somewhat more effort).
— Download the application and re-assign the Distributed
I/O modules (this method requires the most effort).
Manual Binding
There are several cases in which it is necessary to manually
bind the NVs of the Distributed I/O modules to their
respective controller(s). This is done using a L
ONWORKS
network management tool (e.g. LonMaker).
More than 16 modules per Excel 50/500
Autobinding can be used to bind the NVs of a maximum of 16
Distributed I/O modules per controller, only. If the application
requires more than 16 Distributed I/O modules per controller,
you must use CARE to allocate those additional NVs
requiring mapping with data points, and you will also have to
use a L
ONWORKS network management tool to bind the NVs
of the additional modules to the controller.
Binding of NVs of other devices to Distributed I/O modules
(Using XFL52xB Modules as 3
rd
-Party Devices)
When the NVs of other devices on the LONWORKS bus (other
than the host Excel 50/500 controller) require binding to
Distributed I/O modules, autobinding cannot be used. A
L
ONWORKS network management tool (e.g. LonMaker) is
required to (manually) bind all of the Distributed I/O modules'
NVs.
Double-mapping a data point
It is possible to preserve the autobinding by mapping the
data point with a second NV. However, the second NV must
then be bound (using a L
ONWORKS network management
tool) to another L
ONWORKS device. While this method
preserves autobinding, it does require one controller NV
more than if all binding is performed using a L
ONWORKS
network management tool (e.g. LonMaker).
Troubleshooting (Autobinding, only)
Wiring Check
Beginning with controller firmware V2.04.x, Distributed I/O
modules can be checked out without even having an
application loaded in the controller using a special test mode
previously active only for internal I/O modules. This test
mode, accessible through the “Data Point Wiring Check”
option on the second screen of the Start-up sequence, allows
manually setting outputs and reading inputs to verify the I/O
wiring. The procedure is described in detail in the XI581/582
User Guide, EN2B-0126.
Figure 36. Distributed I/O module faceplate and LEDs.
Each Distributed I/O module has a green Power ON LED (L1)
and a red L
ONWORKS service LED (L2) at the upper left of the
faceplate. The L
ONWORKS service LED (L2) is used for
diagnosing the state of the Distributed I/O module (see
below).
Figure 37. Distributed I/O module troubleshooting
example.
If you have more than one module connected to one XSL511,
you should check the modules to the left and to the right of
the defect module (status of green power LED L1 and red
L
ONWORKS status LED L2). A module is "working" in Table 15
if L1 illuminates green and if the L
ONWORKS communication
is working.
Page 27

DISTRIBUTED I/O
27 EN0B-0090
Table 15. Troubleshooting of Distributed I/O modules.
Modules to the left side
working
Modules to the right
side working
Possible Causes
no no
• Power OFF
• CPU not working
• Incorrect wiring
• Sliding bus connector on XSL511 not closed properly
• Defective hardware → contact your Honeywell dealer
yes no
• Sliding bus connector on the left side not closed properly
• Defective hardware → contact your Honeywell dealer
yes yes
• Wrong LONWORKS address (HEX switch setting)
• Defective hardware → contact your Honeywell dealer
In case of problems, check if the behavior is changed if you:
1. Push the LONWORKS service button to reconfigure the
Distributed I/O module. The L
ONWORKS service LED will
light as long as you push the L
ONWORKS service button.
The hardware is defective if this is not the case.
2. Switch the power ON / OFF.
3. Set the HEX switch to an unused address for a few
seconds and select the correct address afterwards. This
procedure will cause a reset of the Distributed I/O module.
Please contact Honeywell if the above actions do not solve
the problem.
Service Pin and LED
A service pin message is sent when
— powering-up or resetting,
— transitioning to the configured/online state, or
— turning the DIP switch.
In the case of a power-up or reset, the service pin message
is delayed a random time between 1 and 5 seconds to avoid
an overload of a network management node receiving these
messages when a large number of Distributed I/O modules
are powered up simultaneously.
The service LED indicates the status of the Neuron® chip.
Normally, the LED will blink a few times during the powerup/reset phase and then remain off. During normal commissioning, the LED will stay on briefly and then flash briefly
before remaining off. The time required for commissioning is
variable, lasting from approximately 10 to 60 seconds, depending upon the amount of network information being downloaded from the installation tool and the installation tool itself.
For additional information on LED behavior, see Table 16
and Figure 38.
LONWORKS Service LED L2
This LED is used to diagnose the state of the Distributed I/O
module. In general:
• The module is applicationless if the LED illuminates con-
tinuously.*
• The module has an application but it is not configured if
the LED is blinking.
• The module is running normally if L2 is off.
*Pushing the L
ONWORKS service button will force a new
commissioning of the module. While commissioning, LED L2
continuously illuminates red for less than 1 minute and then
returns to the normal state (L2 = OFF).
A more detailed diagnosis can be carried out by observing
the duration of the ON and OFF states of the service LED in
connection with power ON / OFF. Figure 38 illustrates the
different service LED behaviors. These are the most common
behaviors, but others are possible since the state of the
service LED is under firmware control and can be affected
both by hardware and software anomalies.
IMPORTANT
In Table 16, the words ”configured”, “unconfigured”,
“application”, and “applicationless” refer only to the
communication layer running on the Neuron® chip and not to
the controller application.
1 sec
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
S
ervice L
E
D Behavior
2 sec 3 sec 4 sec 5 sec
Time
(at 10 MHz,
approx.)
Power
applied
to node
Continuous
* Does not scale with the Neuron chip.
Continuous
Continuous
Continuous
Repeated
Repeated*
see table
= ON = OFF
see table
Figure 38. Service LED behavior.
Page 28

DISTRIBUTED I/O
EN0B-0090 28
Table 16. Service LED behavior descriptions.
Behavior Context Likely Explanation
1 Power-up of the node Bad node hardware. For Distributed I/O modules, perform the tests shown in
the previous section.
2 Power-up of the node Bad node hardware. For Distributed I/O modules, perform the tests shown in
the previous section.
3 Power-up / Reset of the node The module is applicationless. May be caused by the Neuron chip firmware
when a mismatch occurs on application checksums. This behavior is normal if
the application was exported to come up applicationless.
4 Anytime Possible corrupt EEPROM. For a Neuron 3150 Chip-based node, use a newly
programmed PROM, or EEBLANK and follow bring-up procedure.
5 Anytime The module is unconfigured.
Connect the Distributed I/O module to the CPU. The CPU will configure the
Distributed I/O module.
6 First power-up, Applicationless
firmware state exported
The OFF duration is approximately 1 second. Service LED should then turn
ON and stay on indicating an applicationless state.
6 First power-up, Unconfigured
firmware state exported
The OFF duration is 1-15 seconds depending on the application size and
system clock. Service LED should then begin flashing as in behavior 5,
indicating an unconfigured state.
Connect the Distributed I/O module to the CPU. The CPU will configure the
Distributed I/O module.
6 First power-up, Configured
firmware state exported
The OFF duration is indefinite (1-15 seconds to load internal EEPROM; stays
OFF indicating configured state.) The module is configured and running
normally.
7 Anytime The module is configured and running normally.
Page 29

DISTRIBUTED I/O
29 EN0B-0090
Accessories, Standards, Rating s, and Literature
Accessories:
— XAL 1 Swivel Label (required for Manual Override
Modules).
— 209541B Termination Module (one or two required,
depending on L
ONWORKS bus layout; see Excel 500
Installation Instructions, EN1R-1047 for details).
— XAL 2 Cover Release Tool (required for opening the
module housing to set the module address using the
rotary HEX switch).
Approvals and Standards:
• CE and EN 50082-1
Environmental Ratings:
• Operating temperature: 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C)
• Shipping/storage temperature: -13° to 150°F (-25° to
65°C)
• Relative humidity (operation and storage): 5% to 90%,
non-condensing
Applicable Literature:
• EN0B-091 Excel 100/500/600 System Overview
• EN1R-1047 Excel 500/600 Installation Instructions
• EN0B-270 Excel 50/500 LONWORKS Mechanisms
Figure 39. Terminal block XSL513/514 (top view) Figure 40. Terminal block XSL513/514 (side view)
Page 30

DISTRIBUTED I/O
Home and Building Control Home and Building Control Home and Building Control Products
Honeywell Inc. Honeywell Limited-Honeywell Limitee Honeywell AG
Honeywell Plaza 155 Gordon Baker Road Böblinger Straβe 17 Manufacturing
P.O. Box 524 North York, Ontario D-71101 Schönaich location certif i ed t o
Minneapolis, MN 55408-0524 M2H 3N7 Germany
USA Canada http://europe.hbc.honeywell.com
EN0B-0090GE51 R1200 printed in Germany Subject to change without notic e
ELECTRONIC MODULE
XFL 521, 522,
523, 524
XSL512
X
FR522,
XFR524
4-41/64
(118)
5-43/64 (144)
WITH MANUAL DISC ONNECT MODULE
6-27/64 (163)
WITH MANUAL DISCONNECT MODULE
AND OVERRIDE MODULE
XSL511
1
1
Figure 41. Outside dimensions of XSL513/514 terminal blocks and mounted modules in inches (mm) (side view).
Maximum length is with XSL511 LON Connector
module attached.
 Loading...
Loading...