Page 1
KAM-XM-SERIES
KAM-XM-UDC/UPC/UNC/DNC MODULES
Instruction Manual
SOFTWARE VERSION 1.4.1
071833002
AUGUST 2005
Page 2

Contacting Grass Valley
Region Voice Fax Address Web Site
North America (800) 547-8949
Support: 530-478-4148
Pacific Operations +852-2585-6688
Support: 852-2585-6579
U.K., Asia, Middle East +44 1753 218 777 +44 1753 218 757
France +33 1 45 29 73 00
Germany, Europe +49 6150 104 782 +49 6150 104 223
Copyright © Thomson Broadcast and Media Solutions All rights reserved.
Grass Valley Web Site
Sales: (530) 478-3347
Support: (530) 478-3181
+852-2802-2996
Grass Valley
P.O. Box 599000
Nevada City, CA 959597900 USA
www.thomsongrassvalley.com
The www
Online User Documentation
.thomsongrassvalley.com web site offers the following:
— Current versions of product catalogs, brochures,
data sheets, ordering guides, planning guides, manuals, and release notes
in .pdf format can be downloaded.
FAQ Database
— Solutions to problems and troubleshooting efforts can be
found by searching our Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) database.
Software Downloads
— Software updates, drivers, and patches can be down-
loaded.
2 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 3

Contents
Preface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
KAM-XM Series
Up/Down Conversion Modules
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Module Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Supported Up/Down Conversion Rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Quick Start Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Module Placement in the 2000 Frame. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Cabling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
KAM-XM-R Rear Module Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
GPI0 Connections for GPI Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Power Up and Module Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configuration and Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Configuration Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Up and Down Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Format Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Aspect Ratio Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Proc Amp Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Detail Enhance Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Noise Reduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Spike Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Brickwall Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Temporal Recursive Filtering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Color Legalizer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
GPI and E-MEM Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Configuration Summary Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Newton Control Panel Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Web Page Operations and Functional Elements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Links and Web Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Status Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
License Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Setup Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Format Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Aspect Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Proc Amp Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Detail Enhance Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Spike Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Brickwall Web Page. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 3
Page 4

Contents
Temporal Recursive Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Mosquito Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Advanced Aperture Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Color Legalizer Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Grain Insertion Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
GPI Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
E-MEM Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Slot Config Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Software Update Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Power-up Diagnostics Failure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Module Repair. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Index
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
4 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 5

Preface
About This Manual
This manual describes the features of a specific 2000 Series module in the
Kameleon Media Processing System. As part of this module family, it is
subject to Safety and Regulatory Compliance described in the 2000 Series
frame and power supply documentation (see the 2000 Series Frames Instruc-
tion Manual
).
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 5
Page 6

Preface
6 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 7
KAM-XM Series Up/Down Conversion Modules
Introduction
This manual covers installation, configuration and operation of the following Kameleon KAM-XM Series modules:
• KAM-XM-UDC – HDTV Up/Down Converter
• KAM-XM-UPC – HDTV High Quality Up Converter
• KAM-XM-UNC – HDTV Up Converter with Advanced SDTV Noise
Reduction
• KAM-XM-DNC – HDTV Down Converter
Module functionality is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. KAM-XM Up and Down Converter Module Summary
Function KM-XM-UDC KM-XM-UPC KM-XM-UNC KM-XM-DNC
Aspect Ratio Control X X X X
Proc Amp Adjustments (for video processing) X X X X
Color Space Conversion X X X X
Detail Enhancement X X X X
Spike Filter (Adaptive Median filtering) X
Brickwall Filter X
Temporal Recursive Filter (Auto or Manual mode) X
GPI Control (3 external GPI inputs controlling E-MEMs) X X X X
Color Legalizer Control X X X X
First 2 audio groups of HD video are re-embedded into SDI
stream
First 2 audio groups of SDTV video re-embedded into HD output stream with compensating delay.
Re-insertion of Closed Caption data into HD output stream X X X
XX
XXX
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 7
Page 8

Module Descriptions
The KAM-XM Up/Down conversion series modules also feature:
• Proprietary Teranex™ PixelMotion™ De-interlacing,
• Support of SD and HD video with embedded audio, including
Dolby-E,
• Hot-swap capability,
• Operates in the same frame with other 2000 and Kameleon modules,
• Three external GPI inputs to trigger selectable Preset 1-10 registers,
• Network control with the Newton Control Panel or Kameleon web control, and
• Support of NetConfig™ configuration tool and NetCentral™
SNMP-based monitoring system.
Module Descriptions
Each KAM-XM module uses the same circuit board with the application
software enabled for the particular module type. The module type is identified by a sticker on the circuit board and the Model name is identified in
the web page header. For up/down conversion rates supported, refer to
Table 2 on page 9.
The modules described in this manual include the following:
• KAM-XM-UDC – supports broadcast quality up and down conversion
of SD and HD video with embedded audio with the standard conversion controls. This application utilizes de-interlacing on a
pixel-by-pixel basis for preserving fine detail from the original image.
Down conversion offers an anti-aliasing filter.
• KAM-XM-UNC – supports broadcast quality HD up conversion for
SDI video with or without embedded audio with the standard conversion controls. In addition, this module also offers advanced noise
reduction with adaptive median spike, brickwall, and temporal recursive filter controls. This application utilizes de-interlacing on a
pixel-by-pixel basis for preserving fine detail from the original image.
• KAM-XM-UPC – supports broadcast quality HD up conversion for SDI
video with or without embedded audio with the standard conversion
controls. This application utilizes de-interlacing on a pixel-by-pixel
basis for preserving fine detail from the original image.
• KAM-XM-DNC – this broadcast quality down converter application
also utilizes de-interlacing on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Once the image
has been de-interlaced and down converted, detail enhancement can be
applied to the image to further shape the output. The first two groups
of audio from the HD video are re-embedded into the standard definition SDI video signal.
8 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 9
Supported Up/Down Conversion Rates
The modules support the conversion rates summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. Format Conversion Input/Output Combinations
Input Format Output Format UNC UPC DNC UDC
480i59.94 480i59.94 X X X
480i59.94 720p59.94 X X X
480i59.94 1080i59.94 X X X
576i50 576i50 X X X
576i50 720p50 X X X
576i50 1080i50 X X X
720p50 576i50 X X
720p59.94 480i59.94 X X
1080i50 576i50 X X
1080i59.94 480i59.94 X X
Module Descriptions
KAM-XM-
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 9
Page 10

System Requirements
System Requirements
Operation of the KAM-XM modules in 2000 Series frames has the following
hardware and software requirements:
• Modules must be installed in a 2000T1DNG or 2000T3DNG Kameleon
2000 Series frame containing a a 2000GEN module.
• The frame must have a 2000NET module with assembly number
671-5231-01 or later running software version 3.2.2 or later.
Note
All KAM-XM module sets require two vertical module slots of frame space.
Frame density for the 1 RU frame is two module sets and six module sets
for a fully stuffed 3 RU frame. Both dual and single height Kameleon and
2000 modules can be mixed in the frames.
These requirements are necessary for proper cooling support and interface
to the Newton Control Panel configuration, NetConfig and GUI control, and
SNMP monitoring.
Existing Kameleon frames can be upgraded with the necessary
modules and software for proper operation. Contact your sales representative for more information.
10 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 11

Quick Start Guide
This Quick Start Guide is provided for an overview of installing the
KAM-XM modules. Each step gives you a link to a more detailed description of each process.
1.
3.
2.
4.
6.
7.
Install the KAM-XM modules in the 2000 Kameleon frame. Install the
XM-IO-1 Rear module first, then install the front module in the
corresponding front slot ( Module Placement in the 2000 Frame on
page 12).
Connect the 2000 frame to the network and navigate the web browser
to the frame. This process is described in detail in the 2000NET
Instruction Manual available on-line.
Navigate to the module you would like to configure and click on the
appropriate slot to access the module links ( Links and Web Pages on
page 38).
Quick Start Guide
Click on the Slot Config link on the left side of the page ( Slot Config Web
Page on page 65). This page allows you to assign a name to this module.
Assigning easily recognizable names will help later in the configuration
process.
5.
Cable the rear module signal connections ( Cabling on page 16).
Configure the input and output formats on the Format web page
( Format Web Page on page 44).
Configure the Reference source on the Setup web page ( Setup Web Page
on page 42). Select the type of reference from either the input signal or
an external reference (2000GEN module installed in the 2000 frame).
8.
Continue with module configuration depending on the module type.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 11
Page 12

Installation
Installation
Module Placement in the 2000 Frame
Installation of a KAM-XM module set is a process of:
• Placing the KAM-XM rear module in a frame slot,
• Placing the front media module in the corresponding front slot, and
• Cabling signal ports.
There are twelve slot locations in both the front and rear of a Kameleon
3 RU frame to accommodate KAM-XM modules. A KAM-XM module set
consists of a front media module and a dual height rear module that
requires two module slots.
Each KAM-XM front media module plugs into the front of the 2000 frame
mid-plane. The rear module plugs into the corresponding rear slot to
provide the input and output interface connectors.
A 3 RU 2000T3 frame fully stuffed with KAM-XM front and rear modules
will accommodate up to six module sets. A 1 RU 2000T1 frame will accommodate up to 2 module sets.
The KAM-XM front and rear module can be plugged in and removed from
a Kameleon 2000 Series frame with power on. When power is applied to the
module, LED indicators reflect the initialization process (see
Module Status
To install a KAM-XM module set in a frame:
For fully stuffing a 3 RU frame with KAM-XM modules, locate a vacant
1.
slot in slot 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, or 12 of the rear of the frame (Figure 1 on
page 13). The rear module uses two slots.
Note
on page 19).
This configuration (using slots 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) is only suggested when fully
stuffing the frame with KAM-XM modules. There are no restrictions on which
slot to use as long as there is room in the frame. You may use any two slots
(odd or even numbered) for a KAM-XM module with any Kameleon or 2000
module combination.
Power Up and
12 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 13
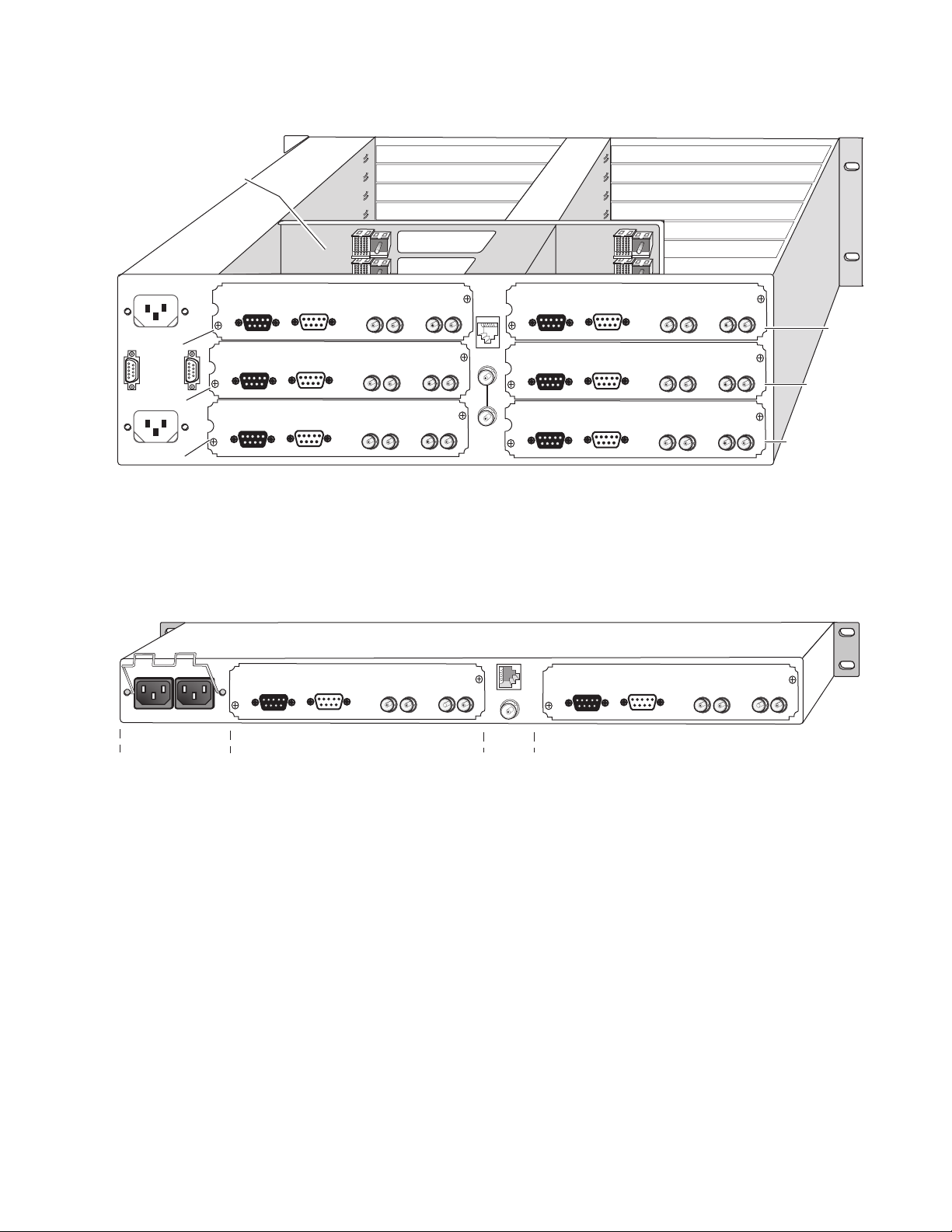
Mid-frame motherboard
with power and
communication buses
Slot 8
Slot 10
Figure 1. 2000T3NG Frame, Rear View
Installation
Slot 2
Slot 4
Slot 12
Power connections
Slot 6
Use rear media module slots 2, 4, and 6Use rear media module slots 8, 10, and 12
For a 1 RU frame, place the rear module in the lower slot as shown in
Figure 2.
Figure 2. 2000T1DNG Frame, Rear View
1
3
J101
J102
2
4
Media section
rear slots 3-4
Network
and reference
input connections
Media section
rear slots 1-2
8330_05r1
8330_17
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 13
Page 14
Installation
Insert the rear module into the vacant rear slot of the frame as
illustrated in Figure 3.
Verify that the module connector seats properly against the midplane.
Using a crossblade screwdriver, tighten the two screw locks to secure
the module in the frame.
Figure 3. Installing KAM-XM Rear Module
2000 frame (rear view)
Alignment post
and receptacle
Board edge guides
(both sides)
Screw locks
(both sides)
2.
3.
4.
5.
RS-232
J7
Locate the front slot 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, or 12 in the frame corresponding to the
rear module circuit board. The 3 RU frame front view is illustrated in
Figure 4 and the 1 RU frame is shown in Figure 5 on page 15.
Note
Figure 4. 2000T3 Frame, Front Slots
Network Slot (13)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
Module slots where the KAM-XM should be installed are highlighted in gray
for a fully stuffed 2000T3 frame and for any 2000T1 frame.
(13)
(15)
GP10
LOOPINOUT2OUT1
J5
J4J5
J1
J2
8330_03r1
Reference Distribution Slot (15)
Main Power Supply Slot (18)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
Fan Sled
Slot (19)
8173-04r1
Secondary Power
Supply Slot (20)
Front Media Slots (1-12)
14 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 15
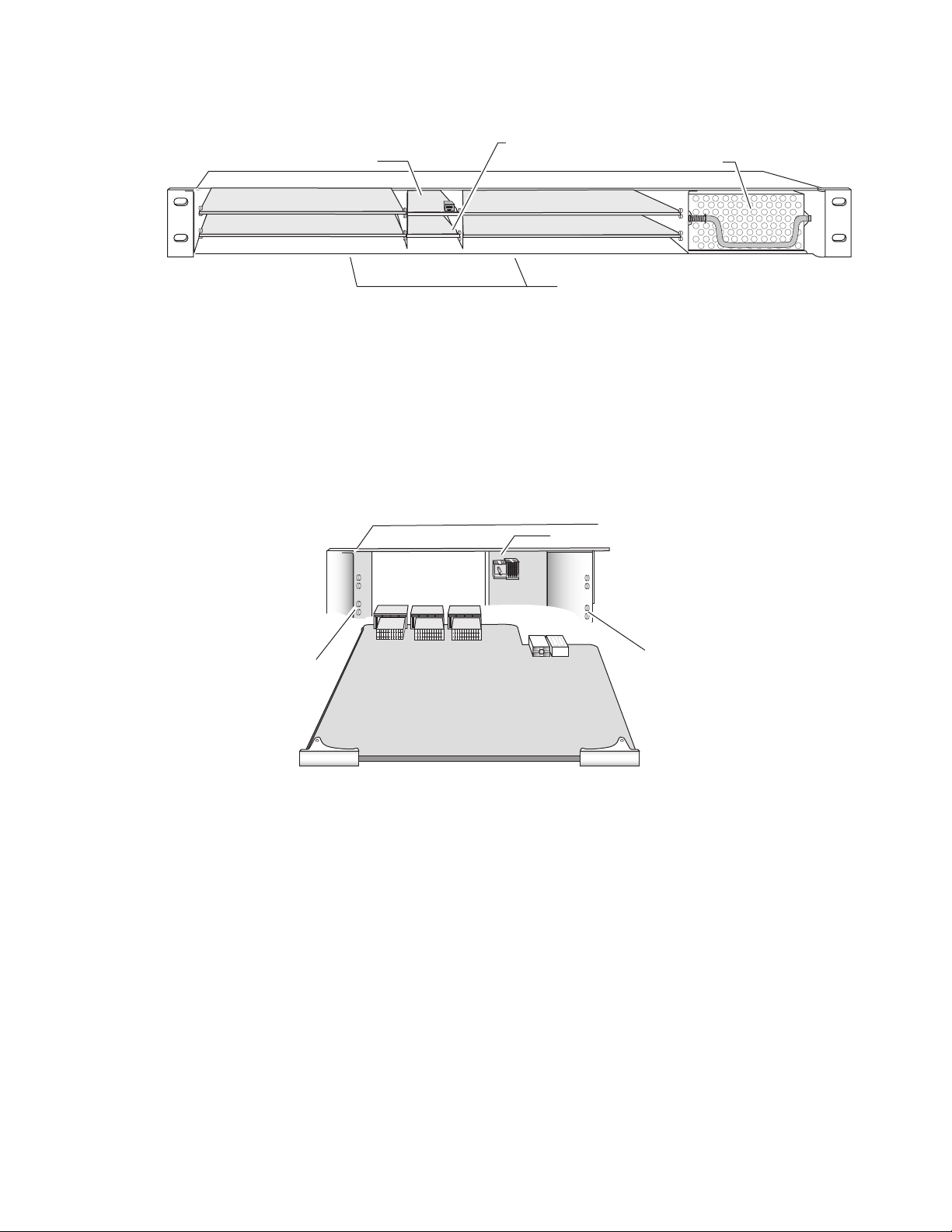
Figure 5. 2000T1 Frame, Front Slots
Network Slot (5)
Reference Distribution Slot (6)
Power Supply Slot (7)
Installation
6.
8.
(1)
(2)
(5)
(6)
(3)
(4)
Front Media Slots (1-4)
With the component side up, insert the front media module in the
corresponding front slot (see Figure 6).
7.
Verify that the module connector seats properly against the midplane
and rear module connector.
Press firmly on both ejector tabs to seat the module.
Figure 6. Installing Front Media Module
2000 Frame (front view)
Alignment post and receptacle
8039-21
Board edge
guides
Board edge
guides
8330-10
KAM-XM
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 15
Page 16

Installation
Cabling
All cabling to the KAM-XM module set is done on the corresponding Dual
Height KAM-XM-R rear module (XM-IO-1) at the back of the 2000 frame.
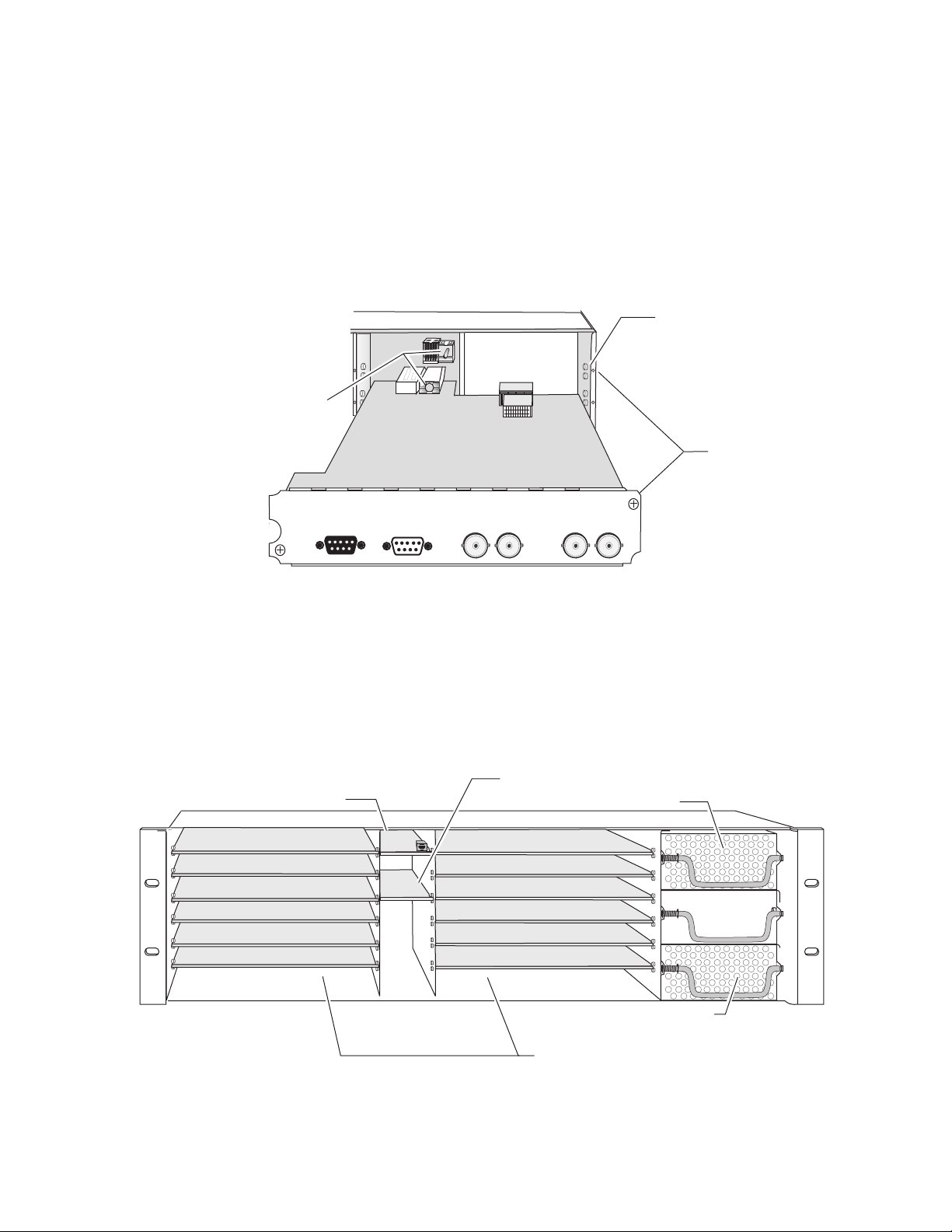
KAM-XM-R Rear Module Connections
Refer to Figure 7 for an illustration of the KAM-XM rear module.
The KAM-XM rear module provides the following input and output and
control connections.
• IN (BNC)– a serial digital input that may be either standard definition
(SD) or high definition (HD) video depending on the front module
type.
• LOOP (BNC)– provides an output for the input signal to be looped to
another destination.
XM-IO-1
RS-232
• OUT1 (BNC)– this serial digital output connection can be either SD or
HD depending on the front module type and the output format
selected.
• OUT2 (BNC)– this serial digital output connection can be either SD or
HD depending on the front module type and the output format
selected.
• RS-232 Port (DB-9, Male) – this serial port allows a direct interface to the
module for testing and configuration purposes. This port is not normally used.
• GPI0 Port (DB-9, Female) – this port allows connection of external GPI
(General Purpose Interface) signals to the module as described in GPI0
Connections for GPI Control on page 18.
Figure 7. KAM-XM Rear Module Input/Output Connectors
GPI0
LOOPINOUT2OUT1
J7
16 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
J6
J4J5
J2
J1
8330_02
Page 17

Installation
KAM-XM-UPC
For a KAM-XM-UPC HDTV Up Converter, connect the SD signal to be up
converted to the IN (J2) BNC. Loop the signal from the LOOP (J1) BNC to
another destination if required.
Connect the OUT1 (J5) and OUT2 (J4) BNCs to the HDTV device.
KAM-XM-UDC
For a KAM-XM-UDC HDTV Up/Down Converter, connect the SD signal
to be up converted or the HD signal to be down converted to the IN (J2)
BNC. Loop the signal from the LOOP (J1) BNC to another destination if
required.
Connect the OUT1 (J5) and OUT2 (J4) BNCs to the HDTV device if up converting or the SDTV device if down converting.
KAM-XM-UNC
For a KAM-XM-UNC HDTV Up Converter with advanced SDTV noise
reduction, connect the SD signal to be up converted to the IN (J2) BNC.
Loop the signal from the LOOP (J1) BNC to another destination if required.
Connect the OUT1 (J5) and OUT2 (J4) BNCs to the HDTV device.
KAM-XM-DNC
For a KAM-XM-DNC Down Converter, connect the HDTV signal to be
down converted to the IN (J2) BNC. Loop the signal from the LOOP (J1)
BNC to another destination if required.
Connect the OUT1 (J5) and OUT2 (J4) BNCs to the SDTV device.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 17
Page 18
Installation
GPI0 Connections for GPI Control
The KAM-XM modules can receive up to three General Purpose Interface
(GPI) external triggers to automatically activate specific user preset
E-MEM registers configured on the GPI (page 58) and E-MEM web pages
(page 59). Customer-supplied external GPI triggers are wired through connector J6 (GPIO) on the rear module.
Inputs to the GPI are held high and expect a contact closure to ground to
activate the programmed presets. There is a 100 mA maximum sink to
ground.
Table 3 provides pinouts for the GPI I/O control port, connector J6.
Table 3. Connector GP10 Wiring for GPI Control
GPIO Control Pin Connector J6
1 GPI Input 1
Pin 1
D-9 Female
Pin 6
Pin 5
Pin 9
2 GPI Input 2
3 GPI Input 3
4 Reserved
5 System Ground
6 System Ground
7 Not Connected
8 Reserved
8330_12
9 Reserved
18 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 19
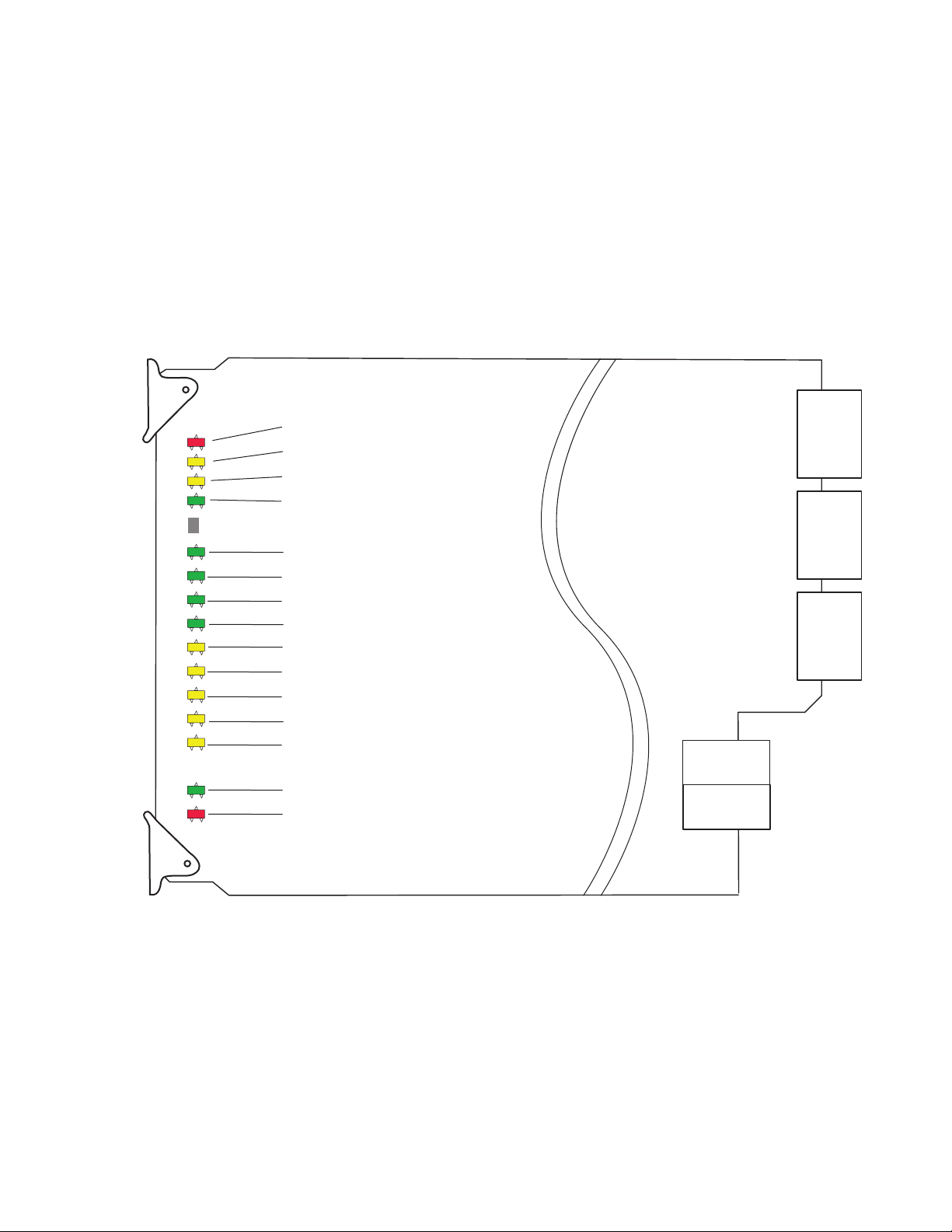
Power Up and Module Status
The front LED indicators are illustrated in Figure 8.
Upon power-up, the green PWR LED should light.
Note The KAM-XM module will take approximately 25 seconds to boot up.
Refer to Table 4 on page 20 to see a complete list of possible operating con-
ditions and the resulting indicator status.
Figure 8. Front Edge LEDs Indicators
Power Up and Module Status
FAULT
COMM
CONF
PWR
+3.3
SEQ
ACT
TC
PRSNT
AUD
PRSNT
FRM
LOCK
FBREF
ERR
UCREF
ERR
OFF
ERR
IFF
ERR
VOLT
TRIP
CH2
STAT
CH1
STAT
RESET
GND
FAULT (red)
COMM (yellow)
CONF (yellow)
PWR +3.3 (green)
SEQ ACT (green)
TC PRSNT (green)
AUD PRSNT (green)
FRM LOCK (green)
FBREF ERR (red)
UCREF ERR (red)
OFF ERR (red)
IFF ERR (red)
VOLT TRIP (red)
CH1 STAT (yellow)
RESET (green)
8269_07
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 19
Page 20
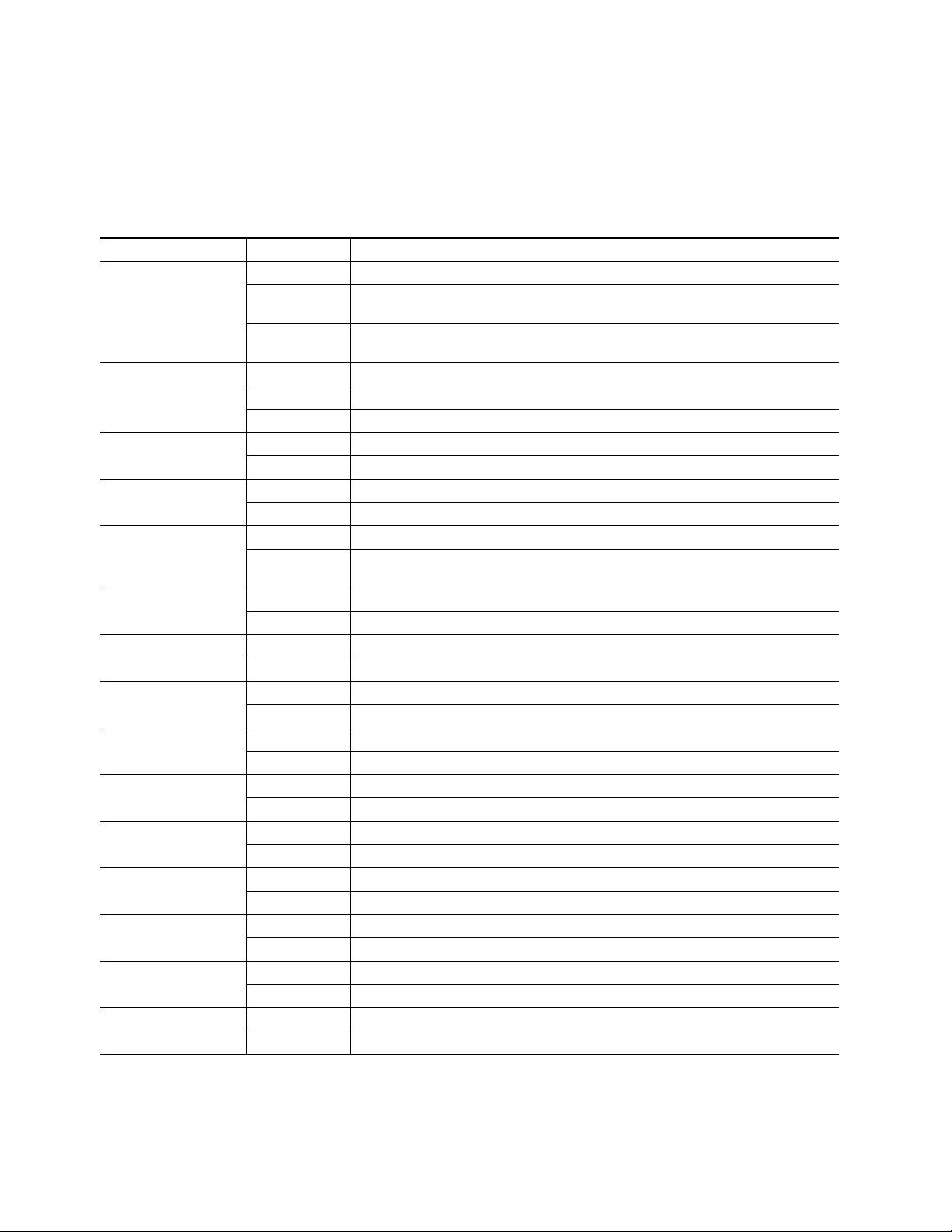
Power Up and Module Status
LED Indication Condition
FAULT
(red)
COMM
(yellow)
CONF
(yellow)
PWR +3.3
(green)
SEQ ACT
(green)
TC PRSNT
(green)
AUD PRSNT
(green)
FRM LOCK
(green)
FBREF ERR
(yellow)
UCREF ERR
(yellow)
OFF ERR
(yellow)
IFF ERR
(yellow)
VOLT TRIP
(yellow)
CH1 STAT
(green)
RESET
(red)
On continuously
Long flash
3 Short Flashes Location Command received by the module from a remote control system.
Short flash Activity present on the frame communication bus.
On continuously Normal operation, module is powered.
A red FAULT LED indicates an error situation and, when noted with the
other indicator LEDs, can indicate a specific problem area. Table 4 describes
signal output and LED indications for the various input combinations and
user settings.
Table 4. Indicator LEDs and Conditions Indicated
Off Normal operation.
Module has detected an Optic 1 or Optic 2 internal fault from the submodule or a write failure has
occurred on the front module.
No input is detected for the input or the input does not match the format selected manually, no rear
module is present, or the wrong rear module is present.
Off No activity on frame communication bus.
On Module is initializing, changing operating modes, or updating firmware.
Off Module is in normal operating mode.
Off No power to module, fuse blown, or module’s DC/DC converter failed.
Off Input video not detected or PLL unlocked.
Blinking
Off No timecode or bad timecode.
On Good timecode is detected.
Off No embedded audio detected.
On Embedded audio detected.
Off Input to output frame rates are not locked.
On Normal operation, input to output frame rates are locked.
Off No FrameBuilder refresh error detected.
On FrameBuffer refresh error detected, output could be corrupted such as bad output image.
Off No Microcode refresh error detected.
On Microcode refresh error detected, Microcode memory could be corrupted.
Off Normal operation, no Output FIFO underflow/overflow error detected.
On Output FIFO underflow/overflow error condition detected.
Off Normal operation, no input FIFO underflow/overflow error condition detected.
On Input FIFO is detecting underflow/overflow error condition.
Off Normal state, no under voltage trip detected.
On Under voltage trip detected, one or more supply voltages is below specification.
Off No input detected or bad input.
On Normal operation, good input detected.
Off Normal operation, board is not in Reset mode.
On Module is in reset mode, including FPGA configuration sequence.
Normal operation, Sequencer Active LED should be blinking to Indicate good video input and PLLs
locked.
20 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 21

Configuration and Adjustments
The KAM-XM modules are configured remotely using the 2000NET
network interface GUI and/or a networked Newton Control Panel.
Refer to the following sections for configuration instructions:
• Configuration Summary (page 21)
• Newton Control Panel Configuration (page 33)
• Web Browser Interface (page 34)
Operation of these control types is explained in detail in their respective
sections of this manual.
Note Before configuration, verify that system requirements have been met as
described in System Requirements on page 10.
Configuration Summary
Configuration and Adjustments
This section provides a summary of all available filters and controls that
can be adjusted on the KAM-XM module. Use this section for a summary
of what adjustments can be made. Table 5 on page 30 provides a summary
in table format of all controls and their ranges, default values, and remote
and control panel function names and locations for setting each value.
Up and Down Conversion
Up and down conversion in today’s facilities is required for interconnection between video formats that have different numbers of pixels/line,
lines/field, and in some cases, a different number of fields or
frames/second. This interconnection requires the use of up and down
format conversion devices.
Up conversion involves a three dimensional process for dealing with conversion of a moving image. Moving images exist in three dimensions. The
horizontal dimension is made up of individual pixels. The vertical dimension is made up of lines contained in the field or frame. These exist in what
is referred to as the spatial domain. The number of fields or frames per
second is known as the temporal domain.
Generally, the process of up conversion deals with changing the number of
pixels and lines in a format (spatial domain). This process is a form of
sample rate conversion. One main issue with this process is that of resolution. Resolution cannot be created so the resolution of the original input
signal must be carefully recovered and passed to the up converted output.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 21
Page 22

Configuration and Adjustments
This is done by a process of de-interlacing the input signal so that the full
vertical detail of the input is retained. On the KAM-XM modules this is
basically accomplished by using an enhanced version of motion compensated de-interlacing which generates a motion vector for every pixel in the
image.
In the process of up conversion, several factors must be addressed and the
following controls are provided on the modules for these considerations:
Format Conversion
The video input to the module and the video output from the module can
be selected as desired. On the Format web page (Figure 22 on page 45), the
currently detected input is reported, the desired format pulldown is available and the status of the desired conversion format is reported as available.
The available input/output format combinations are summarized in
Table 2 on page 9.
Two additional controls are included in format selection described below:
• Source Material – this control is provided to further distinguish the
type of input signal to the module. Two choices are available, Auto or
Video.
When set to Auto, the module will determine if the input material originated as video or film and adjust the filtering accordingly. In some situations, such as broadcast applications, where the input material
cannot be as easily interpreted by the module, the user can force the
mode to Video to prevent artifacts from occurring.
• Deinterlace Type – two types of de-interlacing are provided, PixelMotion and Vert Interpolation.
PixelMotion is a combination of motion-adaptive de-interlacing and
diagonal filtering. When using this technique, the image is analyzed to
determine if there is any motion. This information is used to determine
the filter characteristics used to de-interlace.
Vert Interpolation de-interlacing combines the two fields of video to
create a progressive frame regardless of the amount of motion content
in the image.
22 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 23

Aspect Ratio Modes
Most SD material is in a 4:3 aspect ratio while HD material is 16:9. Aspect
ratio in this case refers to the ratio of an image width to height, not related
to image size. The effect of aspect ratio in up conversion (4:3 to 16:9) is a
process of cropping, stretching, or squeezing the image. To address these
issues, the module provides a control for selecting one of three standard
aspect ratio conversion options:
• Anamorphic – this mode is designed to be used with material originally
captured with an anamorphic lens. It ensures that the top and bottom
edges of the input aspect ratio match the top and bottom edges of the
output aspect ratio. When used with standard 4:3 material, it will have
the effect of stretching the material horizontally as illustrated in
Figure 9. This results in a distortion of the geometry of the image, par-
ticularly causing circles to appear as ovals when present in the image.
Figure 9. 16:9 Anamorphic Mode
Configuration and Adjustments
16:9 conversion with horizontal stretch4:3 Original
• Common Top & Bottom – this mode ensures that the top and bottom
edges of the input image match the top and bottom edges of the output
aspect ratio. A 4:3 image set to this mode will appear centered in a 16:9
display with black bars, or pillars (pillarbox), on the left and right sides
as illustrated in Figure 10.
Figure 10. Common Top and Bottom Mode
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 23
Page 24

Configuration and Adjustments
• Common Side (Common Left & Right) – this mode ensures that the left
Figure 11. Common Sides Mode
and right edges of the input image match the left and right edge of the
output aspect ratio. As illustrated in the Anamorphic example (Figure 9
on page 23), for a 4:3 image, the left and right edges are stretched to
match the left and right edges of the output.
In order to maintain correct geometry of the image, in Common Side
mode the input image is stretched vertically as well, creating a zoom
effect (Figure 11). This method results in correct geometry of the image
but also results in overall loss of approximately 33% of the input information in the vertical domain. This loss of information means less vertical information is available to the interpolation process resulting in
lowering the overall resolution of the output image.
Stretched
vertically
• FlexView – (currently only available in 480i/59.94 to 1080i/59.94 up
conversion) is a non-linear anamorphic aspect ratio designed for use
when converting 4:3 material to 16:9 without the traditional distortion
of a normal anamorphic stretch. FlexView leaves the center portion of
the image untouched and then applies increasing amounts of stretch
closer to the edges of the image, giving a more realistic conversion.
Other aspect ratio controls include the following:
• Zoom Crop – when turned on, will zoom the image by 3 pixels and then
crop the image by 3 pixels. This corrects issues that arise on the top or
bottom edge or on the left or right side of an image.
• Edge Trim – this control adjust the amount of border cropping in the X
and Y directions. It is adjustable from 0-50 or 0-20 pixels, depending on
the conversion currently in use.
• Fill Shade – this control is used when input the aspect ratio is smaller
than the output aspect ratio and there are areas in the output display
that are filled with black. The Fill Shade control adjusts the luminance
level (Y) and color (Cb and Cr) of these areas from 64 (digital black) to
940 (digital white).
24 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 25

Configuration and Adjustments
Proc Amp Controls
Proc Amp controls are provided for making adjustments to the output
video signal. Each Proc Amp function must be enabled before adjustments
can be made.
The following Proc Amp controls are available:
• Video Gain – sets the overall amplitude with a range of ± 6 dB.
• Black Level – adjusts the black level with a range of ± 30 IRE.
• Hue – adjusts the phase with a range of ± 9 degrees.
• Saturation – adjusts the chroma saturation with a range of ± 6 dB.
• RP 177 checkbox – check this box when using video converted from
film production as specified by SMPTE Recommended Practice RP 177.
Detail Enhance Controls
Once the image has been de-interlaced and up converted, detail enhancement can be applied to the image to further sharpen the output detail. This
process utilizes an industry standard film compositing technique called
unsharp masking. The filtering process adds an additional level of image
detail by detecting the edges of objects and adjusting the contrast ratio
around these objects to help separate them from the background. This edge
sharpening filter allows for both positive and negative aperture correction.
The following user adjustable controls are available in Detail Enhance:
• Horizontal – enabling the horizontal control allows the user to soften or
sharpen the horizontal detail in the image. The range of this control is
± 7.0 dB.
• Vertical – enabling the vertical control allows the user to soften or
sharpen the vertical detail in the image. The range of this control is
± 7.0 dB.
• Anti-Alias Filter – in down conversion modes only, an anti-alias filter
can be enabled in the down conversion process to smooth edges such
as graphics.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 25
Page 26

Configuration and Adjustments
Noise Reduction
Two of the modules covered in this manual (KAM-XM-UNC – Up Converter with Noise Reduction and KAM-XM-UDC– Up/Down Converter)
provide the additional noise filtering and reduction controls described
below.
Spike Filtering
This is an adaptive median filter that works well in removing random
impulse noise. This type of filtering performs spatial processing to determine which pixels in an image have been affected by impulse noise. The
adaptive median filter classifies pixels as noise by comparing each pixel in
the image to its surrounding neighbor pixels. The size of the neighborhood
is adjustable, as well as the threshold for the comparison.
A pixel that is different from a majority of its neighbors, as well as being not
structurally aligned with those pixels to which it is similar, is labeled as
impulse noise. These noise pixels are then replaced by the median pixel
value of the pixels in the neighborhood that have passed the noise labeling
test. This results in a prime benefit of not eroding edges or other small
structures in the image with repeated application of the adaptive median
filter.
This type of filtering provides controls for setting the adaptive threshold of
the luminance and the chroma channels. The filter must be enabled to allow
processing.
Brickwall Filtering
This is a low pass filter with a sharp cutoff. This type of high-order low pass
filter attenuates high frequencies (image detail) while leaving low frequency information unaffected. Impulse and Gaussian noise contain high
frequency components and will be diminished with this filter is on.
This filter is primarily intended for pre-compression processing, to attenuate high frequency information that will normally be quantized away in
the compression process. When used for pre-compression, it can improve
the efficiency and quality of the compression process. By controlling the
manner in which the detail is removed, compression artifacts can be minimized. A boost can be applied after the brickwall filter to accentuate the
remaining edges in the filtered image.
One of the benefits of removing high frequency noise before compression
is that there are more bits to spend when generating the compressed stream
since there is less information to compress. In addition, the potential for
loss of desirable information due to the compression of small details is
decreased, resulting in a more consistent output.
26 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 27

Controls for this filter type include the following:
• Enable – the filter must be enabled.
• Boost – sets the amount of amplitude prior to the cutoff frequency. This
boosting of the amplitudes gives the appearance of sharpening in the
image to help compensate for blurring that occurs when filtering out
high frequency information.
• Cutoff – sets the cutoff frequency so that information greater than this
value will be filtered. Information less than the cutoff value will be left
alone.
• Direction Control – allows setting the filter to affect both the horizontal
and vertical axes or just the horizontal or vertical axis.
Temporal Recursive Filtering
This noise reducer is a motion adaptive temporal recursive filter that works
well in removing random and Gaussian noise. Each pixel in the filter
process is labeled as motion, no motion, or noise.
Configuration and Adjustments
Each of these classes of pixels is treated differently in the noise reduction
process as follows:
• For pixels in which there is no motion, low Gaussian noise may be
reduced via temporal processing by a weighted averaging over successive frames.
• For pixels labeled as random noise, spatial processing replaces these
pixels.
• Pixels labeled as being in motion are left as is to avoid artifacts that may
be introduced through temporal processing.
Controls for temporal filtering include the following:
• Enable – the filter must be enabled.
• Red Overlay – when turned on, the filter superimposes a red overlay
onto areas in the input image where the temporal recursive filter identifies motion. This red overlay will display what area is not being filtered.
• Auto – when Auto mode is turned on, a feedback controller is engaged
that dynamically sets the distance, no motion, and motion slider controls based on noise and motion measurements. The pixels determined
to be in motion will be shown in red as shown in Figure 12 on page 28.
These pixels will not have any noise reduction applied to them.
The Bias control in Auto mode adjusts the noise set point in the temporal recursive controller. The higher the bias, the more aggressive the
controller is towards the noise in the scene. The lower the bias setting,
the more sensitive the controller is towards motion in the scene.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 27
Page 28

Configuration and Adjustments
• Manual mode – when Auto mode is turned off, the temporal recursive
filter is in Manual mode. This will activate a number of controls for
manual temporal filtering.
The Distance control is set to determine the sensitivity to motion
between the current frame and historical frames. This threshold represents a percentage of the current pixel value that the historical pixel
value must be within in order to be considered unchanged. Therefore,
a setting of zero would detect motion at every pixel, applying no filtering occurring. A setting of 40 would be less sensitive to motion, temporally filtering every pixel which could result in blurring or any
objects or areas that are in motion. If the Distance control is set too low,
too little filtering may occur, whereas, if set too high, too much filtering
will be applied.
The No Motion control sets the historical weighting factor for areas in
the frame where no motion has been detected. A setting of 100% forces
the filter to use only historical data in areas where no motion has been
detected. A setting of zero forces the filter to use only current data in
areas where no motion has been detected.
The Motion control sets the historical weighting factor for areas in the
frame where motion has been detected. A setting of 100% forces the
filter to use only historical data in areas where motion has been
detected. A setting of zero forces the filter to use only current data in
areas where motion has been detected.
Red Overlay showing
pixels in motion
Figure 12. Temporal Recursive Filter Red Overlay
28 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 29

Color Legalizer
Color legalizer controls are provided to set the upper and lower limits for
luma and chroma values to be within legal limits for broadcasting and
downstream equipment.
Each luma and chroma value is a 10-bit value making the minimum limit 0
and the maximum limit 1019. High and low luma and chroma limit controls are provided for setting the upper and lower limits that the module
will output. By default, these controls will cut off values outside of the legal
range.
GPI and E-MEM Controls
Configuration is provided for setting up GPI triggers from external
devices. Up to ten different module preset configurations can be defined
then assigned to the three external GPIs or recalled on the E-MEM web
page.
Configuration and Adjustments
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 29
Page 30

Configuration and Adjustments
Configuration Summary Table
Table 5 provides a complete summary of the KAM-XM functions and a
comparison of the functionality available with each control type along with
the ranges and default values for each parameter.
Table 5. Summary of KAM-XM Configuration Functions
Function
Type
Reference input selection Input Input or External
Adjust Genlock Offset when
external reference selected
Closed Caption Line select Line 9 Line 9 to 19
Ignore bad video control Don’t Ignore
Blank VBI lines
(525 line rate only)
Format Conversion Input
selection
Current Input Format 480i59.94 See list above
Input Available – Yes or No
Format Conversion Output
Current Output Format 480i59.94 See list above
Output Available – Yes or No
Apply format control _ _
Source Material selection Video Video or Auto
Deinterlace Type selection PixelMotion
Default
0 µs ± 2000 µs
Not Blanked Blank or Not Blanked
Up Converter:
480i59.94
Down Converter:
720p50
Up Converter:
480i59.94
Down Converter:
576i50
Range/Choices
Resolution
Ignore or
Don’t Ignore
480i59.94
576i50
720p50
720p59.94
1080i50
1080i59.94
See list above
PixelMotion or
Vert Interpolation
Web Page/
Function Name
Setup/
Reference pulldown
Setup/
Genlock Offset (microseconds)
Setup/
Closed Caption Line
Setup/
Bad Video Ignore checkbox
Setup/
Blank Line checkboxes
(525: Line 20, 21, 22, 23, 283,
284, 285, 286)
Format/
Input pulldown
Format/
Current read-only column
Format Conversion/
Available read-only column
Format/
Output pulldown
Format/
Current read-only column
Format/
Available read-only column
Format/
Apply button
Format/
Source Material pulldown
Format/
Deinterlace Type pulldown
Newton
Panel
Ref All modules.
–
CCLine
– All modules
Blank20
Blank283
Blank21
Blank284
Blank22
Blank285
Blank23
Blank286
InDesired All modules.
InCurrent
InAvailable
OutDesired
OutCurrent
Available
ApplyFmt
–
–
Notes/
Conditions
Up conversion
modes.
Up conversion
modes.
All modules.
Changing formats
in some cases will
cause application to
reload. Wait for
module to reload.
Up conversion
modes.
30 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 31

Table 5. Summary of KAM-XM Configuration Functions
Configuration and Adjustments
Function
Type
Current Aspect selection Anamorphic
Zoom Crop enable Off On or Off
Edge Trim – X or Y Trim 0 pixels
Fill Shade – Y/Cb/Cr Channels
Video Gain Enable Off On or Off
Video Gain adjustment 0 dB ± 6.0 dB
Black Level Enable Off On or Off
Black Level adjustment 0 IRE ± 30 IRE
Hue Enable Off On or Off
Hue adjustment 0 degrees ± 9.0 degrees
Saturation Enable Off On or Off
Saturation adjustment 0 dB ± 6 dB
RP 177 enable Off On or Off
Horizontal Detail Enhance
Enable
Horizontal Detail Enhance 0 dB ± 7 dB
Vertical Detail Enhance
Enable
Vertical Detail Enhance 0 dB ± 7 dB
Anti-aliasing filter enable Off On or Off
Default
64 64-940
Off On or Off
Off On or Off
Range/Choices
Resolution
Anamorphic,
Common Top,
Common Side, or
FlexView
(480i/59.94 to
1080i/59.94 only)
0 to 50 pixels
0 to 20 pixels
Web Page/
Function Name
Aspect/
Current Aspect pulldown
Aspect/
Zoom Crop On checkbox
Aspect/
Edge Trim X or Y Trim control
Aspect/
Fill Shade Y, Cb or Cr control
ProcAmp/
Video Gain Enabled checkbox
ProcAmp/
Video Gain control
ProcAmp/
Black Level Enabled checkbox
ProcAmp/
Black Level control
ProcAmp/
Hue Enabled checkbox
ProcAmp/
Hue control
ProcAmp/
Saturation Enabled checkbox
ProcAmp/
Saturation control
ProcAmp/
RP 177 On checkbox
Detail Enhance/
Horizontal Enable checkbox
Detail Enhance/
Horizontal (dB) control
Detail Enhance/
Vertical Enable checkbox
Detail Enhance/
Vertical control
Detail Enhance/
Anti-Alias Filter checkbox
Newton
Panel
Aspect
Crop
XTrim
YTrim
FillY
FillCb
FillCr
GainEn
Gain
BlackEn
Black
HueEn
Hue
SaturEn
Satur
_
EnhHorEn
EnhHorDB
EnhVerEn
EnhVerDB
AntiAlias
Notes/
Conditions
All modules
All modules.
Each control must
be enabled,
All modules.
Each control must
be enabled
Down conversion
modes only
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 31
Page 32

Configuration and Adjustments
Table 5. Summary of KAM-XM Configuration Functions
Function
Type
Luma Limit High 4 4 to 1019
Luma Limit Low 979 4 to 979
Chroma Limit High 4 4 to 1019
Chroma Limit Low 979 4 to 979
Available on KAM-XM-UNC only:
Spike filter enable Off On or Off
Spike Luma/Chroma control 90% 1 to 100%
Brickwall filter enable Off On or Off
Brickwall Boost control 0 dB 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 dB
Brickwall Cutoff setting 3.5 MHz
Brickwall direction Horizontal & Vertical
Temporal Recusive filter
enable
Temporal Recursive Red
Overlay enable
Temporal Recursive Auto On On or Off
Temporal Recursive Bias 0 ± 6
Temporal Recursive Distance 15% 0 to 40%
Temporal Recursive No
Motion
Temporal Recursive Motion 0% 0 to 100%
Default
Off On or Off
Off On or Off
50% 0 to 100%
Range/Choices
Resolution
0.9, 1.0, 1.25, 1.50,
1.75, 2.0, 2.25, 2.5,
2.75, 3.0, 3.25, 3.5,
3.75, 4.0, 4.25, 4.5,
4.75, 5.0, 5.25, 5.5
MHz
Horizontal & Vertical
Horizontal
Vertical
Web Page/
Function Name
Color Legalizer/
Color Legalizer Levels/
Luma Limit High control
Color Legalizer/
Color Legalizer Levels/
Luma Limit Low control
Color Legalizer/
Color Legalizer Levels/
Chroma Limit High control
Color Legalizer/
Color Legalizer Levels/
Chroma Limit Low control
Spike/
Enable pulldown
Spike/
Luma & Chroma control
Brickwall/
Enable pulldown
Brickwall/
Boost control
Brickwall/
Cutoff control
Brickwall/
Direction pulldown
Temporal Recursive/
Enable pulldown
Temporal Recursive/
Red Overlay pulldown
Temporal Recursive/
Auto pulldown
Temporal Recursive/
Auto pulldown
Temporal Recursive/
Distance control
Temporal Recursive/
No Motion control
Temporal Recursive/
Motion control
Newton
Panel
LumaLmtH
LumaLmtL
ChromaLmtH
ChromaLmtL
SpikeEn
SpkLuma
SpkChroma
BrickEn
Boost
Cutoff
Dir
RcrsvEn
RedOvEn
Auto
Bias Auto mode only
Distance
Motion
(PID 1096)
NoMotion
Conditions
All modules.
Control must be
enabled.
Control must be
enabled
Manual mode only
(Auto off)
Notes/
32 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 33

Newton Control Panel Configuration
A Newton Control Panel (hard or soft version) can be interfaced to the
Kameleon 2000 Series frame over the local network. Control panel access
offers the following considerations for module configuration and monitoring:
• Ability to separate system level tasks from operation ones, minimizing
the potential for on-air mistakes.
• Ability to group modular products—regardless of their physical locations—into logical groups (channels) that you can easily manipulate
with user-configured knobs.
• Update software for applicable modules and assign frame and panel IP
addresses with the NetConfig Networking application.
• Recommended for real-time control of module configuration parameters, providing the fastest response time.
Note Not all module functions are available with the control panel, such as E-MEM
and factory default recalls. The available control panel controls for the
module are listed in Table 5 on page 30.
Configuration and Adjustments
An example of the Newton Configurator is shown in Figure 13.
Figure 13. Newton Configurator Example
Refer to the documentation that accompanies the Newton Modular Control
System for installation, configuration, and operation information.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 33
Page 34

Configuration and Adjustments
Web Browser Interface
The web browser interface provides a graphical representation of module
configuration and monitoring.
Use of the web interface offers the following considerations:
• Provides complete access to all module status and configuration func-
• Web access will require some normal network time delays for pro-
tions, including naming of inputs and outputs, factory parameter and
name default recalls, E-MEM functions, slot configuration, and SNMP
monitoring controls.
cessing of information.
• Configuration parameter changes may require pressing the
button or
become effective.
• Web interface recommended for setting up module signal and slot
names, E-MEMS, and reporting status for SNMP and monitoring.
Refer to the Frame Status page shown in Figure 14 on page 35. The Kameleon and 2000 modules can be addressed by clicking either on a specific
module icon in the frame status display or on a module name or slot
number in the link list on the left.
Note The physical appearance of the menu displays on the web pages shown in
Enter, upload processing time, and a manual screen refresh to
this manual represent the use of a particular platform, browser and version
of 2000NET module software. They are provided for reference only. Displays
will differ depending on the type of platform and browser you are using and
the version of the 2000NET software installed in your system. This manual
reflects 2000NET software version 4.0.0.
Apply
34 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 35

Configuration and Adjustments
Figure 14. 2000NET GUI
The Links section lists the frame and its current modules. The selected link's Status
page is first displayed and the sub-list of links for the selection is opened. The sub-list
allows you to select a particular information page for the selected device.
Content display section displays the information page
for the selected frame or module (frame slot icons are also
active links).
Refresh button for manual
update of page
8330_11r2
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 35
Page 36

Configuration and Adjustments
Web Page Operations and Functional Elements
The following conventions and functional elements (shown at left) are used
in KAM-XM web page operations. (The examples shown throughout this
manual represent 2000NET software version 4.0.0 or later):
Pulldown Menus
Button
Radio button
Check box
Refresh button
Coarse Adjust
Fine Adjust
Enter
Low Limit
Status Indicator
Entry Field
Status LED
High Limit
• Pulldown menus allow you to choose selections from a list.
• Clicking on a button performs an immediate action such as recall of
defaults, clearing of states, learning configurations, and selecting all or
none of a selection.
• Radio buttons are used to make a choice of one parameter in a group.
• Check boxes are used when a selection can be enabled or included in a
group. Multiple checkbox selections or enables can be made.
•A
Refresh button (circular arrow) is provided at the top of each web page
for manual refresh to view recently changed parameters.
• Each numerical adjustment control has a
Coarse adjust button (left and
right top double arrows) which increases or decreases the step value by
a factor of 10. The
Fine adjust button (left and right inside single arrows)
increases or decreases the step value by 1.
To change a value, use the arrow button controls or enter a value into
the number field and select the
Enter button (*) or use the Enter key on
your keyboard. The Status Indicator bar will follow the value selected.
Use the
Low and High Limit buttons to go directly to the lowest and
highest limits for the parameter.
• An entry field allows naming of various module functions such as
input or output signals, asset tag, and slot identification.
8341_13
• The Status LED is explained below.
Status LED icon
The Status LED icon reports communication status for the frame slot and is
a link to the module Status page where Warnings and Faults are displayed.
LED colors indicate:
• Green = Pass – no problems detected
• Yellow = Configuration error warning
• Red = Fault condition detected
Variables:
• Model and Description are read-only generated by the module
• Frame Location is entered in 2000 Series Frame configuration
• Slot number reports the module’s location in the frame
• Last Recalled E-MEM reports the name of the last E-MEM recalled
36 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 37

Configuration and Adjustments
An example of the Status page for each of the modules covered in this
manual are shown in Figure 15 (UDC), Figure 16 (UPC), Figure 17 (UNC),
and Figure 18 (DNC).
Figure 15. KAM-XM-UDC Status Header
Figure 16. KAM-XM-UPC Status Header
Figure 17. KAM-XM-UNC Status Header
Figure 18. KAM-XM-DNC Status Header
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 37
Page 38

Configuration and Adjustments
Links and Web Pages
The Kameleon 2000 GUI provides the following links (see graphic at left) to
configuration web pages for all of the modules covered in this manual
unless otherwise specified:
• Status – reports input signal status, warnings, and module information
• License – reports the module type (page 41)
• Setup – provides controls for selecting the video reference for the
• Format – provides controls for setting input and output format
• Aspect – provides aspect ratio conversion options (page 46)
• ProcAmp – provides processing amplifier controls (page 48)
• Detail Enhance – provides horizontal and vertical detail enhancement
including part number, serial number and software versions (page 39)
module, the genlock offset, closed captioning lines and blanking controls (page 42)
(page 44)
controls (page 49)
• The following web pages are available only with the KAM-XM-UNC
module:
• Spike – provides adaptive median filter for random noise removal
(page 50)
• Brickwall – provides a low pass filter with a sharp cutoff for
impulse and gaussian noise conditions (page 51)
• Temporal Recursive – provides a motion adaptive filter for
removing random and gaussian noise (page 52)
• Mosquito – is not available in this application (page 55)
• Advanced Aperture – is not available in this application (page 55)
• Color Legalizer – provides luma and chroma high and low limit controls for setting legal color limits (page 56)
• Grain Insertion – is not available in this application (page 57)
• GPI – enable and assign E-MEM registers to GPI Inputs 1-3 for external
recall (page 58)
• E-MEM – provides ten Preset registers for store and recall of module
configuration (page 59)
• Slot Config – provides Slot ID and Memory functions, Frame Health
reporting and SNMP reporting enable/disable controls (page 65)
• Software Update – gives software update information (page 68)
A summary of all configuration value ranges, defaults, and control types is
given in Table 5 on page 30.
38 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 39

Status Web Page
Configuration and Adjustments
Use
this
link
The Status web page (Figure 19 on page 40) provides an overall indication
of the health of the system in the following sections:
• Status Header – the same on all KAM-XM configuration pages (see Web
Page Operations and Functional Elements on page 36),
• Color-coded communication status for each component and path,
• Summary of all fault/warning conditions, and
• Identification, Version and Download Status reporting.
Color-coded Status Indicators and Links
Each box on the Status page represents a KAM-XM module. Arrows represent signal paths that may or may not be monitored. These elements act as
links when their function is active (indicated by underlined function
name).
Color code:
• Green = Pass – operating as expected.
• Yellow = Warning – signal is absent, has errors, or is misconfigured.
• Red = Fault – a component has failed.
• Grey = Not monitored.
Identification
The Identification section lists the following information about the module:
• Part Number
• Serial Number
• Hardware Version
• License Tag
Version
The Version section lists currently loaded Program, Software, and Video
and Audio firmware.
Download Status
The current software version is listed in the Download Status area for all
download components. The version for each of these components should
be the same.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 39
Page 40

Configuration and Adjustments
Figure 19. KAM-XM Status Web Page
Warning/Fault
reporting area
40 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 41

License Web Page
Configuration and Adjustments
Use
this
link
The License web page (Figure 20) displays read-only values for identifying
the License Tag and Key and the type of module in the Licensed Packages
area.
Note This information is set at the factory to determine module type and options.
Figure 20. KAM-XM License Web Page
Module version
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 41
Page 42

Configuration and Adjustments
Setup Web Page
The Setup web page (Figure 21 on page 43) provides the following controls
Use
this
link
for the module:
•
Reference – set the module reference to either Input (from the currently
selected video input) or
frame).
External (from the 2000GEN module in the
When
the amount of offset in microseconds as needed to match the external
reference.
•
Closed Caption Line – select the line on which to place closed captioning.
•
Bad Video Input – when the Ignore checkbox is selected, the module will
not perform an application restart and will only lose the output for 2
frames. Under normal circumstances if a video switch/error occurs in
the input SDI signal, the module will perform an application restart to
recover, resulting in a 3 second loss of video output.
Note This mode requires that the source and frame be synchronized via an external
• Blank Line – Select the On checkbox to blank the corresponding line in the
vertical interval.
External is selected, the Genlock Offset control will be available. Set
reference.
42 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 43

Figure 21. KAM-XM Setup Web Page.
Configuration and Adjustments
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 43
Page 44

Configuration and Adjustments
Format Web Page
The Format web page (Figure 22 on page 45) provides the following con-
Use
this
link
trols for the module:
•
Note Changing the input or output format will cause the module to reload the appli-
Note All possible input and output values will be listed and can be selected in the
Format Conversion – in the Format Conversion display, the Current input
and output format are displayed. To change the input, use the Input
Desired pulldown and select the format. If it is available a Yes will appear
in the
Available column. Possible input and output formats, as well as the
defaults for an up and down converter are summarized in Table 2 on
page 9.
cation. This will take approximately 60 seconds and a reloading message will
appear during this time. Select the Refresh button at the top of the page to
see the new settings after this time has elapsed.
Select the Apply button to set the values.
pulldowns. If the value does not apply to the application it will be reported as
not available.
• Source Material – select the type of source material being fed to the
module (
Video or Auto). When set to Auto, the module will determine if
the input material is video or film originated and adjust the filtering
accordingly. In some situations, such as broadcast applications, where
the input material cannot be as easily interpreted by the module, the
user can force the mode to
•
Deinterlace Type – select the type of deinterlacing for the module (PixelMotion or Vert Interpolation). Select PixelMotion for material that has motion or
Vert Interpolation for images where motion is not a concern. Refer to
Video to prevent artifacts from occurring.
Format Conversion on page 22 for more explanation on using a partic-
ular de-interlace type.
44 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 45

Figure 22. KAM-XM Format Web Page.
Configuration and Adjustments
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 45
Page 46

Configuration and Adjustments
Aspect Web Page
The Aspect web page (Figure 23 on page 47) provides the following con-
Use
this
link
trols for selecting and adjusting the aspect ratio mode for the module:
•
Note Changing the aspect from Common Sides or to Common Sides will cause the
• Zoom Crop – when enabled by checking the On checkbox, zooms the
Current Aspect – Set the desired Aspect mode to one of the following:
• Anamorphic
• Common Side (Common Left & Right)
• Common Top & Bottom
Refer toAspect Ratio Modes on page 23 for an overview for setting the
aspect ratio mode.
module to reload the application. This will take approximately 60 seconds and
the module will display a message stating that the application is reloading.
Select the Refresh button to see the new settings after this time has elapsed.
image by 3 pixels and then crops the image by 3 pixels. This allows correction of issues that occur on the top and bottom or left and right edges
of an image.
•
Fill Shade – when the input aspect ratio is smaller than the output aspect
ratio there are areas in the output display filled with black. The Fill
Shade controls adjust the luminance (Y) and color (Cb and Cr) of the
black display areas.
•
Edge Trim – use the X Trim and Y Trim controls to adjust the amount of
border cropping in pixels in the X and Y directions performed on the
image.
46 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 47

Figure 23. KAM-XM Aspect Web Page
Configuration and Adjustments
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 47
Page 48

Configuration and Adjustments
Proc Amp Web Page
The Proc Amp web page (Figure 24) provides the controls for adjusting the
Use
this
link
video processing parameters for the output of the module. Ranges and
default values are summarized in Table 5 on page 30.
Each control must be enabled by checking the
Use the Proc Amp controls to set the following parameters:
•
•
•
•
Enabled checkbox.
Video Gain – sets the overall amplitude of the output video signal from
± 6 dB.
Black Level – adjusts the black level of the video output signal ±30 IRE.
Hue – adjusts the phase of the output video signal ± 9 degrees.
Saturation – adjusts the chroma saturation of the output video signal
± 6 dB.
Check the
duction as required by SMPTE Recommended Practice RP 177.
Figure 24. KAM-XM ProcAmp Web Page
RP 177 On checkbox when using video converted from film pro-
48 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 49

Use
this
link
Detail Enhance Web Page
The Detail Enhance web page (Figure 25) provides the controls for determining the amount of detail enhancement applied to the signal.
Each control must be enabled by checking the corresponding
checkbox.
Use the following controls to perform detail enhancement:
•
Horizontal – this control is used to soften or sharpen the horizontal detail
in the image (± 6 dB).
•
Vertical – this control is used to soften or sharpen the vertical detail in
the image (± 6 dB).
•
Anti-Alias Filter – (active in modules with down conversion capability
only) turn anti-aliasing
Figure 25. KAM-XM Detail Enhance Web Page
Configuration and Adjustments
Enable
On or Off with the pulldown.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 49
Page 50

Configuration and Adjustments
Spike Web Page
The Spike web page (Figure 26) is active only on the KAM-XM-UNC
Use
this
link
module.
This web page provides noise reduction with an adaptive median filter that
works well in reducing random impulse noise. Refer to Spike Filtering on
page 26 for a discussion of the Spike filter.
•
•
Figure 26. KAM-XM Spike Web Page
Enable – enable or disable the Spike control with the Enable pulldown.
Luma & Chroma – sets the adaptive threshold of the filter in the luminance
and chrominance channels. This threshold represents a percentage of
the central pixel value that surrounding neighbors must be within in
order to be considered similar.
Setting the filter to 100 (maximum) forces the filter on for every pixel,
resulting in a standard median filter being applied to the entire luminance and chrominance channels.
50 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 51

Use
this
link
Configuration and Adjustments
Brickwall Web Page
The Brickwall web page (Figure 27) is active only on the KAM-XM-UNC
module.
This web page provides noise reduction by using a low pass filter with a
sharp cutoff to attenuate high frequencies. This type of filter is best for
diminishing Gaussian and impulse noise. Refer to Brickwall Filtering on
page 26 for a discussion on using the Brickwall filter.
Enable the control by selecting
lowing controls for the Brickwall filter:
•
Boost – sets the amount of boosting in dB of amplitudes prior to the
cutoff frequency. This gives the appearance of sharpening the image to
help compensate for blurring that occurs when filtering out high frequency information.
•
Cutoff – sets the cutoff frequency in MHz above which information will
be filtered while information below the cutoff will be left untouched.
•
Direction – this control allows the user to set the direction in which the
filters above will affect the picture.
•
Vertical applies the filters to the vertical axis only.
•
Horizontal applies the filters to the horizontal axis only.
•
Horizontal & Vertical applies the filters to the both axes.
Figure 27. KAM-XM Brickwall Web Page
On in the Enable pulldown then use the fol-
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 51
Page 52

Configuration and Adjustments
Temporal Recursive Web Page
The Temporal Recursive web page is active only on the KAM-XM-UNC
Use
this
link
module.
This is a motion adaptive temporal recursive filter that works well in
removing random and Gaussian noise. Refer to Temporal Recursive Filtering
on page 27 for a discussion on using this filter.
Enable the Temporal Recursive control by selecting
down.This filter can operate in either
Auto or Manual mode.
On in the Enable pull-
Auto Mode
Use the following controls for removing noise:
•
Red Overlay – when enabled (On), a red overlay is superimposed onto
areas in the input image where the temporal recursive filter identifies
motion.
•
Auto – enabling this mode (Figure 28) engages a feedback controller that
dynamically sets the
able in
from the scene.
•
Bias – is active only in Auto mode. This control adjusts the noise set point
in the temporal recursive controller. The higher the bias the more
aggressive the controller is towards noise in the scene. The lower the
bias setting the more sensitive the controller is towards motion.
Figure 28. KAM-XM Temporal Recursive – Auto Mode
Manual mode based on noise and motion measurement extracted
Distance, No Motion and Motion control setting avail-
52 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 53

Configuration and Adjustments
Manual Mode
Enable Manual control by turning Auto off. The web page will appear as
shown in Figure 29.
Use the controls below in Manual Mode:
•
Red Overlay – when enabled (On), a red overlay is superimposed onto
areas in the input image where the temporal recursive filter identifies
motion.
•
Auto – disabling Auto (Off) puts the Temporal Recursive filter in Manual
mode.
Figure 29. KAM-XM Temporal Recursive – Manual Mode
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 53
Page 54

Configuration and Adjustments
• Distance – sets the distance threshold to determine the sensitivity to
•
•
motion between the current frame and historical frames. The range of
this control is from 0 – 40, with the nominal value for the distance
threshold at 15. A setting of 0 will detect motion at every pixel, causing
no filtering to occur. A setting of 40 will be less sensitive to motion, temporally filtering every pixel, which may result in blurring of any
objects/areas in motion.
In summary, if the distance is set too low, the module detects everything as moving and applies no filtering. If set too high, no motion is
detected, and everything is filtered.
No Motion – sets the historical weighting factor for areas in the frame
where no motion has been detected. A high setting forces the filter to
use only historical data in areas where no motion as been detected. A
low setting forces the filter to use only current data in areas where no
motion has been detected.
Motion – sets the historical weighting factor for areas in the frame where
motion has been detected. A low setting forces the filter to use only
current data in areas where motion has been detected.
54 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 55

Use
this
link
Use
this
link
Configuration and Adjustments
Mosquito Web Page
The Mosquito web page (Figure 30) indicates it is not available on these
module types.
Figure 30. KAM-XM Mosquito Web Page
Advanced Aperture Web Page
The Advance Aperture web page (Figure 31) indicates it is not available on
these module types.
Figure 31. KAM-XM Advanced Aperture Web Page
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 55
Page 56

Configuration and Adjustments
Color Legalizer Web Page
The Color Legalizer web page (Figure 32) provides the controls for setting
Use
this
link
the high and low legal limits for the luma and chroma values as described
in Color Legalizer on page 29.
Use the following controls to set
•
•
Figure 32. KAM-XM Color Legalizer Web Page
High and Low limits for Luma and Chroma:
Luma – set the legal limits for the Luma signal with the High and Low
controls.
Chroma – set the legal limits for the Chroma signal with the High and
Low controls.
56 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 57

Use
this
link
Configuration and Adjustments
Grain Insertion Web Page
The Grain Insertion web page (Figure 33) indicates it is not available on
these module types.
Figure 33. KAM-XM Grain Insertion Web Page
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 57
Page 58

Configuration and Adjustments
GPI Web Page
The GPI web page (Figure 34) allows enabling and selection of E-MEM registers to be recalled by three external GPI inputs (Input 1-3). The E-MEM
Use
this
link
presets are defined on the E-MEM web page (E-MEM Web Page on page 59).
• Select the desired E-MEM register to be recalled from the pulldown list
for each GPI input.
• Check the
External GPI connection is explained in GPI0 Connections for GPI Control on
page 18.
Figure 34. KAM-XM GPI Web Page
Enabled check box to enable the GPI input.
58 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 59

Use
this
link
E-MEM Web Page
The E-MEM web page provides local operations for learning and recalling
configurations into E-MEM registers. File operations are also available for
saving or loading the learned E-MEM files to and from a hard disk or other
accessible media. These registers can be selected in the GPI 1-3 Inputs to be
recalled when the GPI is fired (see GPI Web Page on page 58).
Factory default settings for all channels can be recalled by selecting the
Recall factory settings button. To return the module to the factory signal
names (such as the signal inputs), select the
Configuration and Adjustments
Recall factory names button.
There are two E-MEM view selections:
Standard and Advanced.
In Standard view (Figure 35 on page 60), any one of ten learned E-MEMs
can be recalled by selecting the corresponding
Recall button in the Local
Operations window. This will place the configuration learned into that
E-MEM into the module. This change will occur immediately upon recall.
To learn an E-MEM, select the
Advanced button in the View Selection section.
This will open the Advanced view (Figure 36 on page 61).
Note The existing configuration of the module is also saved automatically to an
internal module register called Preset 0 once a minute. This feature of
KAM-XM models only, allows the module to recover from a power cycle to
the same configuration it had when powered down. This is not the same as
Slot Memory on the 2000NET module as explained on page 65.
The Advanced View (Figure 36 on page 61) includes a File Operations
section to Learn a configuration into E-MEM (
location (
Save to...) or load a file from a disk location (Load from...).
Learn), save a file to a disk
To learn an E-MEM:
1. Open the Advanced view.
2. When the configuration is complete for the module, type a descriptive
name for the configuration into an unused E-MEM register (or
overwrite an existing one).
3. Learn the E-MEM to memory by selecting the corresponding Learn
button. All module parameters are learned at once and stored in the
same register. This register is now learned and ready for recall.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 59
Page 60

Configuration and Adjustments
Figure 35. KAM-XM E-MEM Web Page – Standard View
60 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 61

Figure 36. KAM-XM E-MEM Web Page – Advanced View
Configuration and Adjustments
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 61
Page 62

Configuration and Adjustments
To save an E-MEM configuration to a file on a hard drive or other accessible
media:
1. Select the corresponding Save to... button in the File Operations section.
2. This will bring up a File Download screen (not shown), select Save to
Figure 37. E-MEM Save to Operation
bring up the Save As screen shown in Figure 37.
3. In the Save As dialog box, the file name will default to the
E-MEM name. Browse to the folder where you want to save the
configuration and select
file type. Other Kameleon module types save as a .mcm file type.
Note You may rename the file during the Save process but the E-MEM name
entered into the Local Operations window will not change on the web page to
match the Save As name. Best practice is to leave the Save As file name the
same as the E-MEM name.
Save. The KAM-XM module files save as a .bin
62 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 63

Configuration and Adjustments
To load a saved E-MEM from a location:
1. Select the Load from ... button in the File Operations section.
2. This will bring up the Load E-MEM page (Figure 38).
Figure 38. Load E-MEM Page
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 63
Page 64

Configuration and Adjustments
3. Select Browse to open the Choose File window (Figure 39). Browse to the
Figure 39. Choose File Window
location of the file you wish to load and select the .bin file then the
button to load the file or enter the filename and path in the Enter
filename box.
Open
4. Once the correct path and filename is loaded, select the Load button on
the Load E-MEM page.
5. This should place the recalled E-MEM file into the corresponding
E-MEM window.
6. Select the corresponding Recall button to invoke this configuration.
Note After a power cycle (module is removed and replaced), E-MEM will default to
Power On Default regardless of the last E-MEM recalled.
64 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 65

Use
this
link
Slot Config Web Page
Use the Slot Config web page (Figure 40) to perform the following functions on the module:
•
Slot Identification – You may identify the module by typing a specific
name in the
module and travels with the 2000NET module if it is moved to another
frame. Select
•
Locate Module – selecting Flash from the Locate Module pulldown flashes
the yellow COMM and CONF LEDs on the front of the module so it can
be located in the frame.
Figure 40. Slot Config Web Page
Configuration and Adjustments
Name field. The assigned name is stored on the 2000NET
Default to enter the factory default module name.
• Slot Memory – the slot configuration for each media module is automati-
cally saved periodically (once an hour) to the 2000NET module in that
frame. You may also select the
save the current configuration for this slot. The configuration is saved
on the 2000NET module. If the 2000NET module is removed or
powered down, the stored configurations are not saved.
Learn Module Config button at any time to
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 65
Page 66

Configuration and Adjustments
• When the Restore upon Install box has been checked, the current configu-
Note Uncheck the Restore Upon Install button before downloading new software.
• Frame Health Reports Link – will appear only on a module installed in a
ration saved to this slot is saved as slot memory. When the current
module is removed and another module of the same type and software
version is installed, the configuration saved to the 2000NET module
will be downloaded to the new module. The box must be checked
before the current module with the saved configuration is removed.
If a different type of module is installed in this slot, a warning message
will state that the original module type has been replaced with another
module type. In this case, a
clear the stored configuration from the previous module.
2000T3 (3 RU) frame. Select the Frame Health Reports link to open the
2000NET module Frame Alarm Reporting web page. This web page
allows configuration of what alarms and warnings are reported to the
external Frame Health Alarm connector on the rear of the frame.
Clear button will appear allowing you to
Note This page is only present on the 2000T3 frame. The 2000T1 frame does not
have an external Frame Health alarm.
This web page contains the following sections:
•
Hardware Switch Status – the Hardware Switch Status section of this
web page displays the current settings of the alarm and warning
configuration DIP switches, S1 and S2, on the 2000NET circuit
board in this frame. These switches allow enabling and disabling of
what overall status reporting information is provided to the
external Frame Alarm.
•
Output Format for Warnings – set the Output Format for Warnings on the
external RS-232 Frame Alarm output on the rear of the frame. When
the
Open radio button is selected, warnings are not reported to the
external frame alarm. Selecting the
warnings to be reported in the same manner as alarms.
•
Frame Health Reporting – this section provides a table showing the
presence and status of all frame devices such as modules, power
supplies, and fans and other frame functions such as Module
Health and Frame Bus status. Use the corresponding
boxes to indicate which alarms and warnings should be reported to
the Frame Health alarm for the following conditions:
Closed radio button, causes
Report check-
• Faults
• Signal Loss
• Reference Loss
• Config Error
66 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 67

Configuration and Adjustments
• SNMP Trap Reports Link – select the SNMP Trap Reports link to open the
2000NET SNMP Reporting web page. This link will only be present
when SNMP Agent software has been installed on the 2000NET
module. This web page allows configuration of what alarms and warnings are reported to the SNMP management software.
•
Hardware Switch Status – the Hardware Switch Status section of this
web page displays the current settings of the alarm and warning
configuration DIP switches, S1 and S2, on the 2000NET circuit
board in this frame. These switches allow enabling and disabling of
what overall status reporting information is provided to the SNMP
traps.
Note Slot SNMP traps can be enabled only when the hardware switches for Module
Fault reporting and Asynchronous Status reporting are in enabled on the
2000NET module (dipswitch S1 segment 7 and dipswitch S2 segment 1).
• SNMP Trap Reporting – this section provides a table showing the pres-
ence and/or status of all frame devices such as modules, power
supplies, power and fan sleds and other frame functions such as fan
and Frame Bus status.
Use the corresponding
warnings and alarms should be reported to the SNMP manager for
the following conditions:
• Faults
• Devices removed
• Signal Loss
• Reference Loss
• Config Error
The enabled SNMP traps will be reported to any SNMP manager
that is identified as an SNMP Report Destination in 2000NET configuration. Trap severity is read-only hard-coded information that
is interpreted and responded to by the SNMP Manager software
configuration.
Refer to the 2000NET Instruction Manual for complete details on using
the 2000NET web pages.
Report checkboxes to indicate what trap
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 67
Page 68

Configuration and Adjustments
Software Update Page
The Software update page (Figure 41) allows updating of software from
remote locations such as a CD-ROM or the Grass Valley web site. Updating
with this method requires the use of an ftp server application also available
from the Grass Valley web site. Refer to the 2000NET Network Interface
Instruction Manual for instructions for installing and using the ftp server
Use
this
link
application.
The preferred method for updating software is done using the NetConfig
PC application option available from Grass Valley. Refer to Software
Updating With NetConfig on page 69 or the NetConfig Networking Application
Instruction Manual available with the application or on-line.
Note Uncheck the Restore Upon Install button on the Slot Config page before
Figure 41. Software Update Web Page
downloading new software.
68 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 69

Configuration and Adjustments
Acquiring the Latest Software
To acquire the latest Kameleon software, connect to the Grass Valley Customer Service FAQ database from the following URL:
http://gvg.custhelp.com
This will take you to the Grass Valley Customer Service FAQ data base. The
information provided here is the most up-to-date. You may also subscribe
to software updates through the FAQ site. This is recommended so that
when new versions of software are released, you are notified by email.
To download the latest Kameleon HD software for either the FTP or NetConfig methods, do the following:
1. Navigate to the FAQ site and click on the first FAQ, DOWNLOAD THE
LATEST SOFTWARE?
2. Select the 2000 Series link.
3. Select the link to the latest Kameleon module software.
4. Follow the instructions to download the files to your PC.
If you cannot find the software you need, go directly to the Grass Valley
Customer FTP site at the following URL:
ftp://ftp.thomsongrassvalley.com/pub/modular
Software Updating With NetConfig
To use this method, your 2000NET module must be running version 3.2.2
or later and you must have the NetConfig Networking Application option
running on a networked PC on the same subnet as the frame with the
2000NET module. Seven files are required for updating software, six .fld
files and an .sw2 for the module being updated.
To use NetConfig for software updating, follow the steps below:
1. Begin the upgrade procedure by moving the KAM-XM files you have
downloaded into your Temp directory into the correct NetConfig
directories (these steps apply to all versions of NetConfig).
2. Copy all KAM-XM software download files from the C:\temp
directory into the main NetConfig directory on your PC. This is
normally in the default location in C:\Program Files\Grass Valley
Group\NetConfig.
If you have installed NetConfig in another location, find the location of
the NetConfig directory by right-clicking on the NetConfig shortcut.
Select
Properties and note the location in the Start In field. Download the
package to the NetConfig directory.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 69
Page 70

Configuration and Adjustments
3. In the main NetConfig directory, locate a folder named modular. If this
4. Move the six .fld files you copied into the main NetConfig directory
5. Verify that the KAM-XM_X.X.X.sw2 file is somewhere in the main
Note NetConfig reads each .sw2 file in its main directory and navigates to the
6. Locate the module to be upgraded in your frame and unplug it. Plug it
CAUTION During the download, the module will have no video output, so be sure the
folder does not exist, create a folder called
modular in the main
NetConfig directory.
into this
NetConfig directory (not in the
modular directory.
modular directory).
directory given in these files to find the .fld files available. The .sw2 file should
not have a .txt extension or NetConfig will not recognize it. There may be a
number of .sw2 and .fld files in your NetConfig directory for other modular
products. These will not interfere with the update.
back in to begin the upgrade.
module is off-air before upgrading.
7. Open NetConfig.
8. Navigate to the frame containing the KAM-XM module you wish to
upgrade on the left of the screen.
Note If you have not used NetConfig before, refer to the NetConfig Instruction
Manual included during installation in the main NetConfig directory in pdf
format (NetConfig.pdf).
9. Click on the Load SW button on the top of the NetConfig toolbar.
10. This will bring up the Load Software screen (Figure 42 on page 71). This
screen shows NetConfig version 2.0.6. If you are using an earlier
version of NetConfig, the file structure is slightly different, but the files
versions are the same.
The following files should appear under Device Type, all reporting the
same software version represented here by X.X.X:
• apps_X.X.X.fld
• firmware_X.X.X.fld
• ucode1_X.X.X.fld
• ucode2_X.X.X.fld
• ucode3_X.X.X.fld
• uvc_X.X.X.fld
70 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 71

Configuration and Adjustments
11. Highlight the apps Device Type. All KAM-XM modules accessible on
this subnet will be displayed in the window on the right with their
current software version and frame IP Address.
Figure 42. NetConfig Load Software Screen – First .fld Download
Select apps and a
KAM-XM Client Name.
12. Find the KAM-XM module you are updating in the Client Name list.
Check the corresponding checkbox in the window on the right to
indicate you wish to update this device.
Note You may upgrade all modules at once with this application by checking all of
the Client Name checkboxes. We recommend upgrading one module first to
understand the process before attempting to upgrade all of the modules at
once.
13. Check the Re-Boot when complete checkbox in the lower left corner of the
screen.
14. Click on the Load button to begin the update.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 71
Page 72

Configuration and Adjustments
15. If the load has been successful, a popup will appear as shown in
Figure 43. Load Successful Popup
16. Allow the reboot to complete.
17. Bring up NetConfig again and click on the Discover button in the top
18. Select the firmware Device Type on the left (Figure 42 on page 71).
Figure 43. Click the
menu bar. Then click on the
OK button.
Load SW button.
19. Select the same Client Name as the first download.
20. Check the Re-Boot when complete checkbox in the lower left corner of the
screen.
21. Press the Load button to download the firmware to the KAM-XM
module selected.
22. If the load has been successful, a popup will appear as shown in
Figure 43. Click the
23. Allow the reboot to complete.
24. Bring up NetConfig again and click on the Discover button in the top
menu bar. Then click on the
25. Select the ucode1 Device Type on the left.
26. Select the same Client Name as the first download.
27. Complete the same steps for the rest of the .fld files listed, allowing the
reboot to complete each time.
28. Verify that all downloads were successful by checking the Download
Status table on the Status web page (Figure 19 on page 40).
OK button.
Load SW button.
For more information on using NetConfig, refer to the NetConfig Networking Application Instruction Manual which is included with the option,
available on the Thomson Grass Valley web site, and may also be present
in the NetConfig directory during some NetConfig installations (Newton
Control Panel installation is one example).
72 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 73

Specifications
Table 6. KAM-XM Series Specifications
Parameter Value
SD/HD Video Input
Standard
KAM-XM-UNC
KAM-XM-UPC
KAM-XM-UDC SMPTE 259-C (270 Mb/s), SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s), SMPTE 274M, SMPTE 296M,
KAM-XM-DNC SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s), SMPTE 274M, SMPTE 296M, SMPTE 349M
Number of inputs 1 with active loop-through
Connector BNC per IEC 60169-8 Amendment 2
Equalization
KAM-XM-UNC
KAM-XM-UPC
KAM-XM-UDC Automatic to 100 m @ 1.5 Gb/s/300 m @ 270 Mb/s with Belden 1694 or equivalent
KAM-XM-DNC Automatic to 100 m @ 1.5 Gb/s with Belden 1694 or equivalent cable
Return Loss > 15 dB @ 270 Mb/s (and 1.5 Gb/s)
Active Input Loop-through Output
Standard
KAM-XM-UNC
KAM-XM-UPC
KAM-XM-UDC
KAM-XM-DNC SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s), SMPTE 274M, SMPTE 296M, SMPTE 349M
Number of outputs 1
Connector BNC per IEC 60169-8 Amendment 2
DC offset 0 V ± 0.5 V
Rise and fall time 750 ps nominal for SD
Overshoot < 10% of amplitude
Return loss > 9 dB @ 1.5 Gb/s
Wideband jitter < 0.2 UI
Up/Down Converted Serial Video Output
Standard
KAM-XM-UNC
KAM-XM-UPC
KAM-XM-DNC
KAM-XM-UDC SMPTE 259-C (270 Mb/s) or SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s)
Number of outputs 2
Connector BNC per IEC 60169-8 Amendment 2
DC offset 0 V ± 0.5 V
Rise and fall time 750 ps nominal for SD
Overshoot < 10% of amplitude
Return loss > 15 dB @ 270 Mb/s, > 9 dB @ 1.5 Gb/s
SMPTE 259-C (270 Mb/s)
SMPTE 349M
Automatic to 300 m @ 270 Mb/s with Belden 1694 or equivalent cable
SMPTE 259-C (270 Mb/s)
SMPTE 259-C (270 Mb/s), SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s), SMPTE 274M, SMPTE 296M,
SMPTE 349M
SMPTE 292M (1.5 Gb/s)
Specifications
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 73
Page 74

Specifications
Table 6. KAM-XM Series Specifications - (continued)
Parameter Value
Wideband jitter < 0.2 UI
Input to Output Processing Delay
Video delay
KAM-XM-UNC
KAM-XM-UPC
KAM-XM-UDC
KAM-XM-UDC
KAM-XM-DNC
Audio delay Delayed and re-embedded in time with the output video
Electrical
Power 27 W
EMI/RFI Complies with FCC Part 15 Class A, EU EMC Directive
Physical
Number of slots 2, installation in even numbered frame slots recommended for maximum frame
Environmental
Operating temperature
range
Non-operating
Temperature
Operating Humidity Range 10 to 90% non condensing
4 frames (up conversion)
2 frames (down conversion)
density
See specifications for Kameleon 2000 frame
-10 to 70 ° C
74 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 75

Service
Power-up Diagnostics Failure
Troubleshooting
Service
The KAM-XM modules make extensive use of surface-mount technology
and programmed parts to achieve compact size and adherence to
demanding technical specifications. Circuit modules should not be serviced in the field unless as directed by Grass Valley Customer Service.
If the module has not passed self-diagnostics, do not attempt to troubleshoot. Return the unit to Grass Valley (see Module Repair).
If your module is not operating correctly, proceed as follows:
• If module power is not present, check fuse F1 (see Figure 44).
• Check for presence and quality of input signals.
• Verify that source equipment is operating correctly.
• Check cable connections.
Figure 44. KAM-XM Voltage Testpoints and Fuse Location
GRASS VALLEY
KAM-XM-DNC
115-0079-02 B
Module Type Label
Fuse: 2.5 A FAST, 125 V
F1
8330_08
Module Repair
If the module is still not operating correctly, replace it with a known good
spare and return the faulty module to a designated Grass Valley repair
depot. Call your Grass Valley representative for depot location. Refer to
Contacting Grass Valley at the front of this document for the Grass Valley
Customer Service Information number.
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 75
Page 76

Service
76 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
Page 77

Index
Numerics
2000GEN module 10
2000NET module
requirements
10
A
Advanced Aperture web page 55
anti-alias filter
overview
remote control 49
summary table 31
application loading message 44, 46
aspect ratio
anamorphic
definition
common sides
definition
common top & bottom
definition
FlexView
definition
overview 23
remote control 46
summary table 31
Aspect web page 46
AUD PRSNT LED 20
25
23
24
23
24
C
cabling 16
CH1 STAT LED 20
Clear button 66
closed caption
setting line
summary table 30
Coarse adjust button
overview
color legalizer
overview
remote control 56
summary table 32
Color Legalizer web page 56
COMM LED 20
configuration
overview
summary table 30
control panel
mneumonics
conversion rates 9
conversion, format
overview
summary table 30
conversion, up and down
overview
42
36
29
21
30
22
21
B
Blanking
VBI lines
Boost
overview
summary table 32
boot up time 19
brickwall filter
overview
remote controls 51
summary table 32
Brickwall web page 51
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 77
42
26
26
D
deinterlace type 44
overview 22
summary table 30
Detail Enhance web page 49
detail enhancement
overview
remote controls 49
summary table 31
documentation online 2
25
Page 78

Index
E
E-MEM
advanced view
description 59
load from file 63
save to file 62
standard view 59
web page 59
environmental 74
59
F
factory defaults
recall factory defaults
recall factory names 59
summary table 30
FAQ database 2
FAULT LED 20
fault table 20
FBREF ERR LED 20
Fine adjust button
overview
FlexView
aspect ratio, overview
format conversion 44
Format web page 44
Frame Health Reporting 66
frame, 1 RU 13
frame, 3RU 12
frequently asked questions 2
FRM LOCK LED 20
front module
installation
front panel LEDs 19
fuse
location and type
36
15
59
24
75
GPI web page 58
Grain Insertion web page 57
Grass Valley web site 2
GUI 38
I
IFF ERR LED 20
input
cabling
installation 12
16
K
KAM-XM module
descriptions
functionality summary 7
KAM-XM-DNC
cabling
description 8
KAM-XM-UDC
cabling
description 8
KAM-XM-UNC
cabling
description 8
KAM-XM-UPC
cabling
description 8
8
17
17
17
17
L
LEDs
meanings
License web page 41
locate module 65
20
M
G
Genlock Offset
remote control
summary table 30
GPI (General Purpose Interface)
configuring inputs
Connector J5 wiring 18
overview 29
78 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
42
58
media module 12
midplane 15
Mosquito web page 55
N
NetConfig
Page 79

Index
software updating 68
Newton Control Panel
overview
O
OFF ERR LED 20
online documentation 2
operational modes 20
outputs
cabling
16
P
passive rear module 12
installation 12
PixelMotion
deinterlace type
Preset 0 59
presets
overview
proc amp
overview
remote control 48
summary table 31
ProcAmp web page 48
PWR LED 20
Q
Quick Start guide 11
33
29
25
30, 44
proc amp control 48
summary table 31
S
SEQ ACT LED 20
Setup web page 42
Slot Config web page 65
slot identification 65
slot memory 66
SNMP reporting
enabling
software download from web 2
Software Update web page 68
software version 39
source material
input selection
summary table 30
spike filter
overview
remote control 50
summary table 32
Spike web page 50
status indicators
color codes
meanings 39
Status LEDs
meaning
Status web page 39
system requirements 10
67
44
26
39
36
R
T
rear module
cabling
red overlay
overview
remote control 52
reference
selecting
Refresh button 36
repair depot 75
RESET LED 20
RP 177
overview
KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual 79
16
27
42
25
TC PRSNT LED 20
Temporal Recursive filter
auto mode
Manual mode 53
overview 27
summary table 32
Temporal Recursive web page 52
testpoints 75
troubleshooting 75
52
U
UCREF ERR LED 20
Page 80

Index
V
VBI blanking
selecting lines
summary table 30
Vert Interpolation
deinterlace type
VOLT TRIP LED 20
42
30, 44
W
web browser overview 34
web site
documentation
FAQ database 2
Grass Valley 2
software download 2
2
80 KAM-XM-SERIES Instruction Manual
 Loading...
Loading...