Page 1

Title page
IISO9001:2000
G
E
M
U
L
T
I
L
I
N
R
E
G
I
S
T
E
R
E
D
GE Digital Energy
Multilin
MX350
Automatic Transfer Control
System
Low voltage power transfer control
MX350 revision: 1.2x
Manual P/N: 1601-9071-A2
GE publication code: GEK-113497A
Copyright © 2010 GE Multilin
GE Digital Energy
Power Quality / Zenith
830 W. 40th Street
Chicago IL, 60609
USA
Tel: 800-637-1738
email: GEPQSales@ge.com
Internet: http://www.gedigitalenergy.com/ats
*1601-9071-A2*
Instruction manual
GE Multilin's Quality
Management System is
registered to ISO9001:2000
QMI # 005094
Page 2

© 2010 GE Multilin Incorporated. All rights reserved.
GE Multilin MX350 Automatic Transfer Control System instruction manual for revision 1.2x.
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control System, EnerVista, EnerVista Launchpad, EnerVista
MX350 Setup, and FlexLogic are registered trademarks of GE Multilin Inc.
The contents of this manual are the property of GE Multilin Inc. This documentation is
furnished on license and may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the permission
of GE Multilin. The content of this manual is for informational use only and is subject to
change without notice.
Part number: 1601-9071-A2 (April 2010)
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCTION Overview ............................................................................................................1 - 1
Cautions and warnings............................................................................................................... 1 - 1
Description of the Automatic Transfer Controller system.......................................... 1 - 2
ATS types ........................................................................................................................................... 1 - 5
Specifications ....................................................................................................1 - 6
Timing specifications ................................................................................................................... 1 - 6
Protection specifications............................................................................................................ 1 - 6
User interface specifications.................................................................................................... 1 - 7
Metering and monitoring specifications............................................................................. 1 - 7
Inputs specifications .................................................................................................................... 1 - 7
Outputs specifications ................................................................................................................ 1 - 8
Power supply specifications.....................................................................................................1 - 8
Communications specifications ............................................................................................. 1 - 9
Testing and certification............................................................................................................. 1 - 9
Physical specifications ..............................................................................................................1 - 10
Environmental specifications.................................................................................................1 - 10
Order codes for MX350................................................................................. 1 - 11
Example of an MX350 order code .......................................................................................1 - 11
2. INSTALLATION Mechanical installation ...................................................................................2 - 1
Dimensions....................................................................................................................................... 2 - 1
Product identification .................................................................................................................. 2 - 2
Mounting ........................................................................................................................................... 2 - 2
Module withdrawal and insertion .......................................................................................... 2 - 4
Module and terminal identification....................................................................................... 2 - 6
Electrical installation .......................................................................................2 - 7
Power supply module.................................................................................................................. 2 - 8
CPU module...................................................................................................................................... 2 - 9
Input/Output modules...............................................................................................................2 - 10
Dielectric strength testing .......................................................................................................2 - 14
3. INTERFACING WITH
THE MX350 AT
CONTROLLER
Graphical control panel...................................................................................3 - 1
Introduction to the graphical control panel...................................................................... 3 - 1
MX350 graphical display pages.............................................................................................. 3 - 6
MX350 programming techniques........................................................................................3 - 13
EnerVista™ MX350 Setup Software............................................................ 3 - 17
Software requirements.............................................................................................................3 - 17
Troubleshooting the USB driver............................................................................................3 - 17
Installing the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software........................................................3 - 20
Connecting EnerVista MX350 Setup to the relay .........................................................3 - 20
Working with setpoints and setpoint files........................................................................3 - 23
Upgrading relay firmware .......................................................................................................3 - 29
Power analysis ............................................................................................... 3 - 30
Waveform capture......................................................................................................................3 - 30
Data logger.....................................................................................................................................3 - 34
4. ACTUAL VALUES Actual values overview....................................................................................4 - 1
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL toc–i
Page 4

Metering ............................................................................................................ 4 - 2
Current metering............................................................................................................................4 - 2
Voltage metering............................................................................................................................4 - 2
Power metering ..............................................................................................................................4 - 3
PQ metering......................................................................................................................................4 - 3
Status................................................................................................................. 4 - 4
Status messages ............................................................................................................................4 - 4
Input and output status ..............................................................................................................4 - 4
System Page.....................................................................................................................................4 - 5
Flex Page............................................................................................................................................4 - 5
5. SETPOINTS Understanding setpoints................................................................................ 5 - 1
Setpoint text abbreviations .......................................................................................................5 - 2
Configuration setpoints ................................................................................. 5 - 3
ATS setpoints....................................................................................................................................5 - 3
ATS types............................................................................................................................................5 - 4
Chicago Transfer Alarm Panel (CTAP) option ....................................................................5 - 7
Common ATS setpoints ...............................................................................................................5 - 8
Current and voltage transformers .........................................................................................5 - 9
Inputs................................................................................................................................................ 5 - 10
Outputs ............................................................................................................................................ 5 - 10
Communications setpoints.....................................................................................................5 - 10
System..............................................................................................................................................5 - 12
Events ...............................................................................................................................................5 - 13
Zenith................................................................................................................................................5 - 13
Operation setpoints ...................................................................................... 5 - 14
Timers ............................................................................................................................................... 5 - 15
Control............................................................................................................. 5 - 16
General............................................................................................................................................. 5 - 16
Interlock...........................................................................................................................................5 - 18
Alarms ..............................................................................................................................................5 - 19
Security............................................................................................................ 5 - 20
6. EXERCISER Information....................................................................................................... 6 - 1
Setup....................................................................................................................................................6 - 2
Test........................................................................................................................................................6 - 2
7. DIAGNOSTICS Events ................................................................................................................ 7 - 1
Statistical information.................................................................................... 7 - 3
Phasors.............................................................................................................. 7 - 4
Product information........................................................................................ 7 - 5
Reports .............................................................................................................. 7 - 6
Waveform ......................................................................................................... 7 - 7
Datalog.............................................................................................................. 7 - 8
8. FLEXLOGIC™ FlexLogic™ overview....................................................................................... 8 - 1
Introduction to FlexLogic™........................................................................................................8 - 1
9. COMMUNICATIONS Communications interfaces .......................................................................... 9 - 1
toc–ii MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 5

Digital Energy
NOTE
CAUTION
DANGER
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 1: Introduction
Introduction
Overview
The MX350 is a modular control and monitoring system designed specifically for lowvoltage transfer switch application. The MX350 provides the following key benefits.
• Flexible control and communication options to suit any low-voltage transfer switch
application.
• Small footprint.
• Modular design reduces the number of spare components for maintenance and
testing.
• Integrated pushbuttons and LED indicators reduce external components and wiring.
• DIN rail and Panel Mounting.
• Multiple communication protocols allows simple integration into monitoring and
control systems.
• Graphical control panel interface provides local control and access to system
information.
• Automation FlexLogic™ with interlocking and programmable logic control.
Cautions and warnings
Before attempting to install or use this device, it is imperative that all caution and danger
indicators in this manual are reviewed to help prevent personal injury, equipment damage,
or downtime. The following icons are used to indicate notes, cautions, and dangers.
Figure 1: Note icons used in the documentation
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–1
Page 6
OVERVIEW CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Graphical display
• Large metering values
• Wide viewing angle
Soft key navigation
• Graphical module control
Front port access
• USB for laptop connection
Integrated functionality
• Metering, control
• Event recorder
LED indication
• Time delay indication
• Alarm indication
• Transfer inhibit indication
• Source available & connected
indication
Ease of use
• Graphical interface
• Self-description
Mounting options
•DIN Rail
• Through door
889723A1.CDR
Front panel control
• Integrated device control
• Dedicated control keys
The standard note icon emphasizes a specific point or indicates minor problems that may
occur if instructions are not properly followed.
The caution icon indicates that possible damage to equipment or data may occur if
instructions are not properly followed.
The danger icon provides users with a warning about the possibility of serious or fatal
injury to themselves or others.
Description of the Automatic Transfer Controller system
The MX350 is equipped with a graphical control panel:
• Includes a 89 mm (3.5-inch) 320 by 240 pixel backlit colour LCD screen, 15
pushbuttons, and 7 LED indicators, which provide access to actual values, fault and
alarm lists, event records, and setting configuration. A USB port is provided for laptop
computer connection.
Figure 2: MX350 feature overview
1–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
The MX350 includes the following input/output capabilities:
• 5 to 25 contact outputs
• 5 to 32 contact inputs
The following option packages are available:
Option A:
• Full function ATS control with full sensing and control capabilities, depending on order
option.
• Expanded diagnostics, high-speed 256-event capture, 365-day exerciser, EnerVista
launchpad, USB interface for uploading and downloading setup parameters
• 4 programmable inputs and 4 outputs assignable to additional ATS features
• Full complement of programmable ATS control switches (AUTO/MAN, Preferred Source
selector, Commit/No Commit Xfer, Transition Mode Select (for Closed Transition switch
models).
Option B:
Option Package A plus:
• 10 customer programmable digital and 10 analog alarms
Page 7

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION OVERVIEW
• 20 channel data logger, customer configurable sample period from 1 cycle to 60
minutes
• Waveform capture, 10 channels, up to 256 cycles each 16 samples/sec
• Auto Load Shed with voltage, frequency and kW triggers
Option C:
Option Package B plus:
• 4 additional inputs and outputs (total 8 in, 8 out
Option D:
Option Package C plus:
• 4 additional inputs and outputs (total - 12 in, 12 out)
• FlexLogic for user-customized control logic
Option M:
• Configuration for Manual operation only (non-Automatic)
A single-line diagram for the MX350 is shown below.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–3
Page 8

OVERVIEW CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
GEN
X1
H1
H1
X1
METERING
V, A, W, VAR, VA, PF, HZ
TO LOAD
UTA
UTILITY
(SOURCE-1)
VOLTAGE
CARD
SOURCE
2
POWER
SUPPLY
1
SOURCE
CARD
VOLTAGE
METERING
NEUTRAL
CT CARD
ATS
CONTROLLER
170VDC
RS485 - MODBUS RTU
ETHERNET - MODBUS TCP/IP
NOTE:1
K
CARD
P
ENGINE START CONTACT
I/O
CARD
24VDC
TO K CARD
AND
I/O CARD
SUPPLIED BY OTHERS
(3)
CT'S
(1)
CT
NOTE:1
TO
SOURCE-2
NOTE:1- FOURTH POLE/NEUTRAL POLE IS AN OPTIONAL FEATURE.
NOTE:1
NOTE:1
27 59 47
25
475927
46
51R
50G 51G
889739A1.CDR
Figure 3: Single line diagram
Table 1: MX350 protection functions
ANSI device Description
25 Synch check
27 Undervoltage
46 Current balance
47 Voltage phase reversal
50G (option) Ground instantaneous overcurrent
51G (option) Ground time overcurrent
51 (option) Overcurrent
59 Overvoltage
1–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 9
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION OVERVIEW
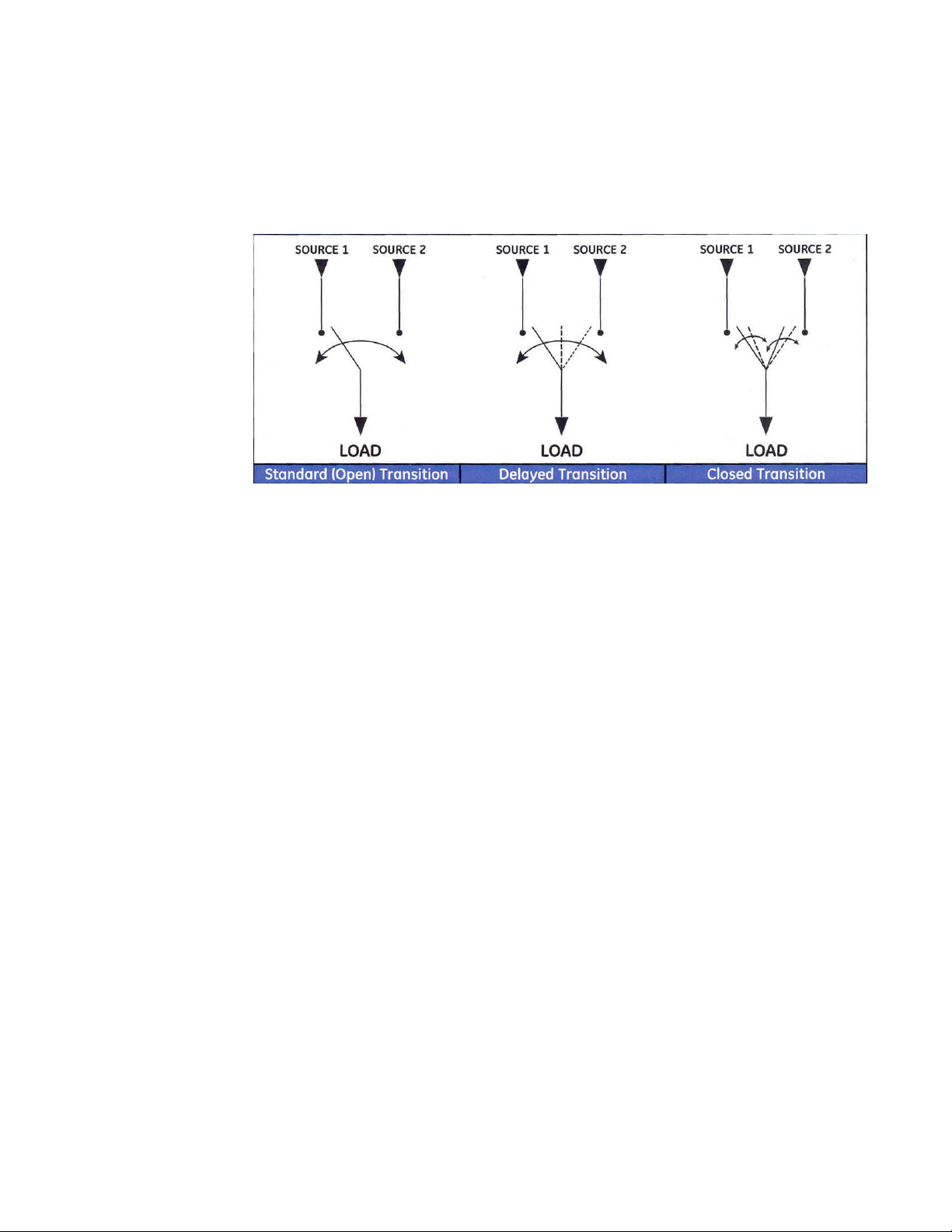
ATS types
Automatic Transfer switch types to be controlled by the Controller are Standard (Open)
Transition, Delayed Transition, and Closed Transition. The figure below shows the one-line
diagram for all three types.
Figure 4: Automatic transfer switch types
In addtion, the MX350 can control the Bypass/Isolation type version of the three basic ATS
types.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–5
Page 10

SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
NOTE
Specifications
NOTE:
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Timing specifications
GENERAL TIMING ACCURACY
Accuracy:................................................................±500 ms
Protection specifications
OVERVOLTAGE
Pickup level:........................................................... 1.05 to 1.10 × VT in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. 1.03 to 1.08 × VT in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ No programmable time delay
UNDERVOLTAGE
Pickup level:........................................................... 0.75 to 0.99 × VT in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. 0.85 to 1.00 × VT in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ No programmable time delay
OVERFREQUENCY
Pickup level:........................................................... 50.1 to 63.0 Hz in steps of 0.1 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. 50.0 to 62.9 Hz in steps of 0.1 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ No programmable time delay
Accuracy:................................................................±0.05 Hz
UNDERFREQUENCY
Pickup level:........................................................... 45.0 to 59.9 Hz in steps of 0.1 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. 45.1 to 60.0 Hz in steps of 0.1 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ No programmable time delay
Accuracy:................................................................±0.05 Hz
POWER FACTOR
Pickup level:........................................................... 0.99 lag to 0.99 lead in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. pickup + hysteresis
Time delay:............................................................ 0 to 65535 seconds in steps of 1
Accuracy:................................................................±0.05
VOLTAGE IMBALANCE
Pickup level:........................................................... 0.05 to 0.20 in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Dropout:.................................................................. 0.03 to 0.18 in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ 1 to 60 seconds in steps of 1
CURRENT IMBALANCE
Range:......................................................................4 to 40% in steps of 1
Pickup level:........................................................... 0.04 to 0.40 in steps of 0.01 (programmable)
Time delay:............................................................ 1 to 60 seconds in steps of 1 s
Timing accuracy:................................................±500 ms
Elements:................................................................alarm
Accuracy:................................................................±2%
1–6 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 11

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
CALCULATION METHOD
( [I
- IAV] / IAV ) x 100%
M
Where:
I
= average phase current
AV
I
= current in a phase with maximum deviation from I
M
AV
THD ALARM (CURRENT/VOLTAGE)
Pickup level:...........................................................0.1% to 100.0% in steps of 0.1% (programmable)
Time delay:.............................................................0 to 65535 seconds in steps of 1
OVERCURRENT (PER PHASE/NEUTRAL)
Pickup level:...........................................................0.01 to 2.00 × Nominal Current in steps of 0.01%
(programmable)
Time delay:.............................................................0 to 65535 seconds in steps of 1
User interface specifications
GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
Size: ...........................................................................height 102mm, width 153mm, depth 35mm
LCD: ...........................................................................89 mm (3.5-inch) colour, 320 by 240 pixels
LED indicators: .....................................................7 LEDs
Pushbuttons:.........................................................Alarm Reset, Test, Ctrl, Info, plus 11 LCD screen display
control keys
Ports:.........................................................................USB 2.0 type Mini-B for laptop computer connection
Metering and monitoring specifications
EVENT RECORDER
Capacity: .................................................................256 events
Data storage:........................................................non-volatile memory
FREQUENCY METERING
Range: ......................................................................40.00 to 70.00 Hz in steps of 0.01
Accuracy:................................................................±0.05 Hz
POWER METERING
Real power range: ..............................................–2000.0 to 2000.0 kW in steps of 0.1
Apparent power range:....................................0.0 to 2500.0 kVA in steps of 0.1
Accuracy:................................................................±2.0% of full scale with 5 A CT
POWER FACTOR METERING
Range: ......................................................................–0.99 to +0.99 in steps of 0.01
Accuracy:................................................................±0.05
Inputs specifications
CONTROL VOLTAGE INPUT
Input range:...........................................................60 V to 300 V AC
Nominal frequency: ...........................................50 or 60 Hz
DIGITAL INPUTS
Nominal input voltage:.....................................24 V DC
Recognition time:................................................2 cycles
Continuous current draw:...............................4 mA
Type:..........................................................................opto-isolated inputs
External switch: ...................................................wet contact
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–7
Page 12

SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
NOTE
PHASE CURRENT INPUTS
Range:......................................................................2.5 to 7.5 A (1.5 × CT)
Input type:.............................................................. 5 A
Frequency: ............................................................. 50 or 60 Hz
Accuracy:................................................................ ±2.0% of Full Scale, where Full Scale = 1.5 × CT Primary
Withstand (at 5A nominal):............................. 0.2 s at 100×
1.0 s at 50×
2.0 s at 40×
continuous at 3× rated current
PHASE VOLTAGE INPUTS (THREE-PHASE VOLTAGE)
Input range:........................................................... 120 to 600 V (nominal)
Nominal frequency:...........................................50 or 60 Hz
Accuracy:................................................................ ±2% of reading, or ±1 V, whichever is greater
NOTE:
Phase current Input Type of 1 A is not supported.
Outputs specifications
FORM-C RELAY
Contact material:................................................silver-alloy
Operate time:........................................................ 10 ms
Maximum contact load: ..................................10 mA at 5 V DC
Maximum switching rate:...............................300 operations per minute (no load), 30 operations per
minute (load)
Mechanical life:.................................................... 10 000 000 operations
Continuous current:........................................... 10 A
Make and carry for 0.2s:.................................. 30 A per ANSI C37.90
FORM-C OUTPUT RELAY BREAK CAPACITY
AC resistive, 120 V AC:......................................10 A normally-open, 5 A normally-closed
AC resistive, 240 V AC:......................................10 A normally-open, 8 A normally-closed
AC inductive, PF = 0.4 pilot duty:..................2.5 A
DC resistive, 30 V DC:........................................10 A
SOLID STATE OUTPUT RELAY
Operate time:........................................................ < 1 ms
Nominal voltage:................................................. 24 V DC
Maximum current:.............................................. 0.5 A
Power supply specifications
POWER SUPPLY
Nominal:.................................................................. 120 to 240 V AC
125 to 250 V DC
Range:......................................................................60 to 300 V AC (50 and 60 Hz)
84 to 250 V DC
Ride-Through:....................................................... 35 ms
ALL RANGES
Voltage withstand:.............................................2 × highest nominal voltage for 10 ms
Power consumption: ......................................... 16 W typical, 25 W maximum
1–8 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 13

CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION SPECIFICATIONS
Communications specifications
ETHERNET (COPPER)
Modes:......................................................................10/100 MB (auto-detect)
Connector:..............................................................RJ-45
SNTP clock synchronization error: ..............<200 ms (typical)
Protocol: ..................................................................Modbus TCP
RS485 PORT
Port: ...........................................................................opto-isolated
Baud rates:.............................................................up to 115 kbps
Protocol: ..................................................................Modbus RTU, half-duplex
Maximum distance: ...........................................1200 m
Isolation:..................................................................2 kV
USB PORT
Standard specification: ....................................Compliant with both USB 2.0 and USB 1.1
Data transfer rate:..............................................USB device emulating serial communications port at
115 kbps
Connector:..............................................................USB2.0 Mini-B
Testing and certification
TESTING AND CERTIFICATION
Test Reference Standard Test Level
Dielectric Voltage Withstand: EN60255-5 2.0 KV
Impulse Voltage Withstand: EN60255-5 5 KV
Insulation Resistance: EN60255-5 500 V DC > 100 Mohm
Damped Oscillatory: IEC61000-4-18/IEC60255-22-1 2.5 KV CM, 1 KV DM
Electrostatic Discharge: EN61000-4-2/IEC60255-22-2 Level 4
RF Immunity: EN61000-4-3/IEC60255-22-3 Level 3
Fast Transient Disturbance: EN61000-4-4/IEC60255-22-4 Level 4
Surge Immunity: EN61000-4-5/IEC60255-22-5 Level 3 & 4
Conducted RF Immunity: EN61000-4-6/IEC60255-22-6 Level 3
Power magnetic Immunity: IEC61000-4-8 Level 4
Voltage Dip & Interruption: IEC61000-4-11 0,40,70% dips 250/300cycle
Radiated & Conducted Emissions: CISPR11 /CISPR22/ IEC60255-25 Class A
Ingress Protection: IEC60529 IP20 (base unit) IP54 (Control
Environmental (Cold): IEC60068-2-1 -20
Environmental (Dry heat): IEC60068-2-2 85
Relative Humidity Cyclic: IEC60068-2-30 6-day variant 2
Fast Transient Disturbance: IEEE C37.90.1 4 KV CM & DM
SWC Damped Oscillatory: IEEE C37.90.1 2.5 KV CM
Electrostatic Discharge: IEEE C37.90.3 8 KV CD, 15 KV AD
interrupts
Panel)
o
C 16 hrs
o
C 16hrs
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–9
Page 14

SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
APPROVALS
Applicable Council Directive According to
CE compliance: Low voltage directive EN60255-5, EN60947-1, EN60947-6-1
EMC Directive EN61000-6-2/ EN61000-6-4
ISO: Manufactured under a registered
quality program
Physical specifications
DIMENSIONS
Size: ........................................................................... Base: 62 mm [2.44"] (W) × 90 mm [3.54"] (H) × 113 mm [4.45"]
Weight (Base):....................................................... 0.75 kg [1.65 lb]
Environmental specifications
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS
Ambient temperatures:
Storage/shipping: - 40
Operating: -20
* 1" around Base Unit
ISO9001
(D) (+ terminals 10mm [0.39"])
Expansion: 62 mm [2.44"] (W) × 90 mm [3.54"] (H) × 113 mm
[4.45"] (D)
GCP: 153 mm [6.02"] (W) × 102 mm [4.02"] (H) × 35 mm [1.38"]
(D)
o
C to 90oC *
o
C to 60oC * (Base Unit and Basic Control Panel)
o
-20
C to 50oC * (Graphical Control Panel)
o
Humidity: Operating up to 95% (non condensing) @ 55
per IEC60068-2-30 Variant 2, 6days)
Altitude: 2000 m (max)
Overvoltage Category: II
Ingress Protection: IP20 (Base Unit), IP54 (Control Panel)
1–10 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
C (As
Page 15
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION ORDER CODES FOR MX350
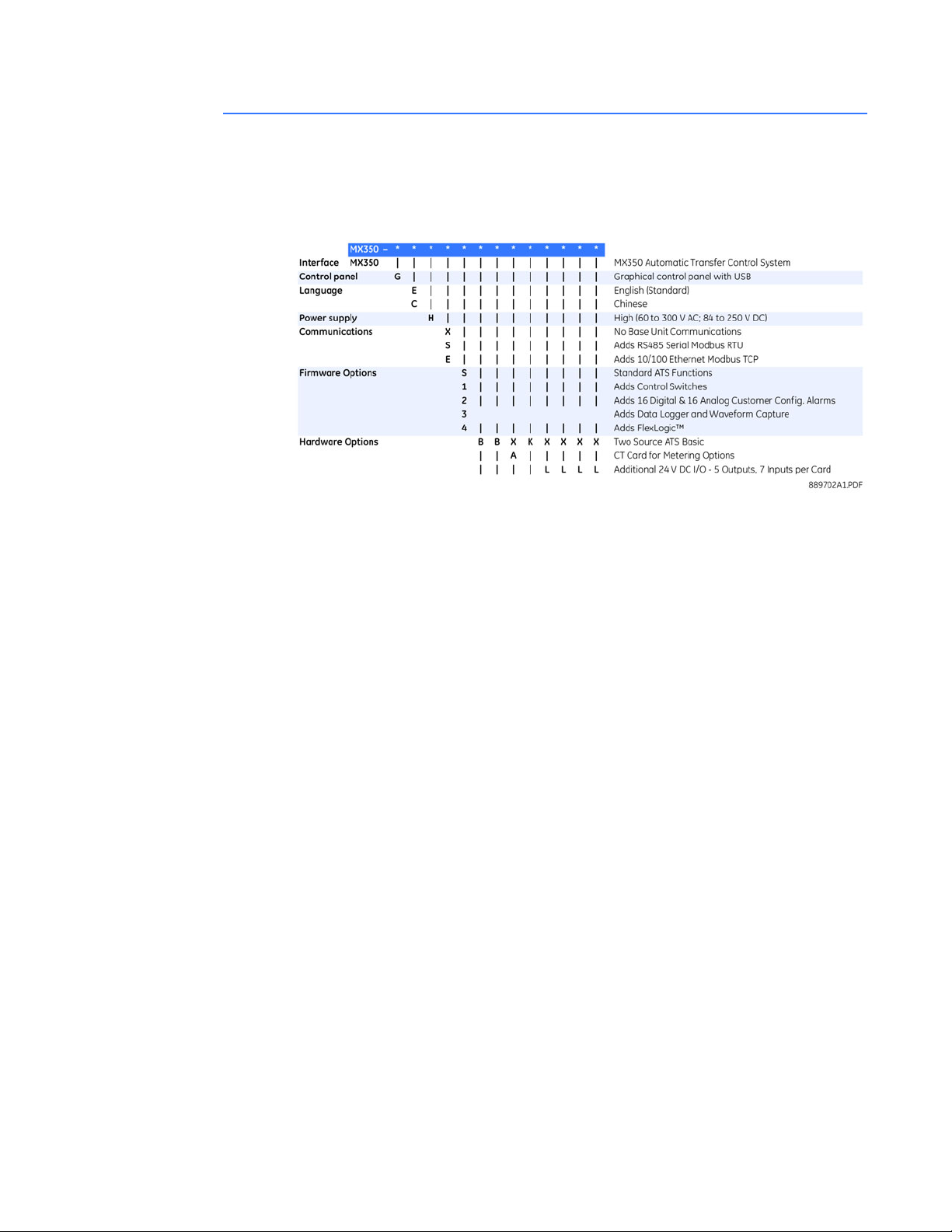
Order codes for MX350
The information to specify an MX350 relay is provided in the following order code figure.
Figure 5: MX350 order codes
Example of an MX350 order code
MX350-GEHE3BBAKLL: MX350 with graphical control panel incl. USB port, English
language display, high voltage control power supply (84 to 250 VDC or 60 to 300VAC), RS485 Modbus RTU port and 10/100 Modbus TCP/IP Ethernet port), data logger and
waveform capture, source 1 voltage sensing, source 2 voltage sensing, load current
sensing, P relay function, and two input/output cards.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 1–11
Page 16

ORDER CODES FOR MX350 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1–12 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 17

Digital Energy
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 2: Installation
Installation
Mechanical installation
This section describes the mechanical installation of the MX350 system, including
dimensions for mounting and information on module withdrawal and insertion.
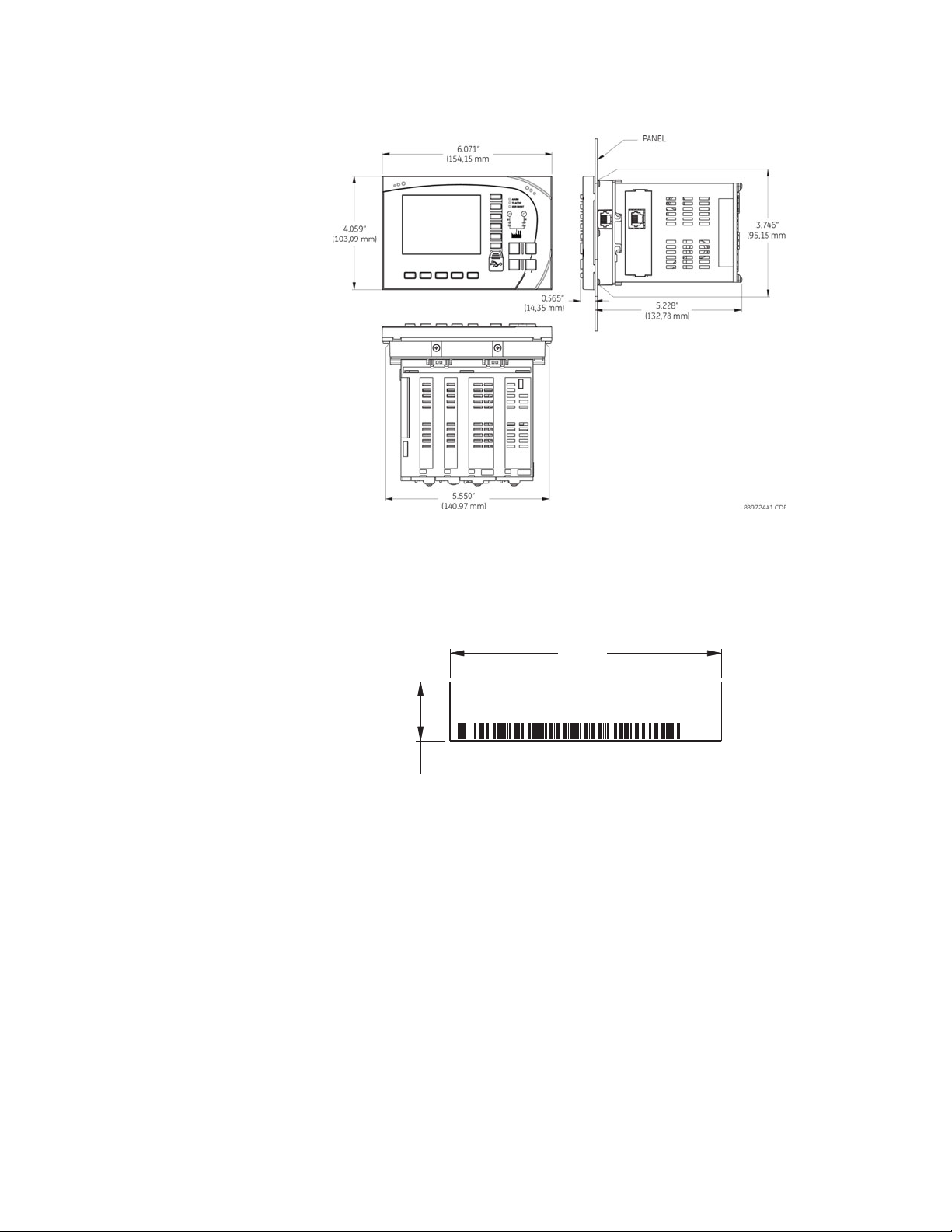
Dimensions
The MX350 is packaged in a modular arrangement.
The dimensions of the MX350 are shown below. Additional dimensions for mounting and
panel cutouts are shown in the following sections.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–1
Page 18
MECHANICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
2.425”
(61.6 mm)
0.525”
(13.3 mm)
889748A1.CDR
Model:
Serial Number:
Firmware:
Mfg. Date:
Figure 1: MX350 dimensions
Product identification
The product identification label is located on the side panel of the MX350. This label
indicates the product model, serial number, firmware revision, and date of manufacture.
Figure 2: MX350 label
Mounting
The MX350 can be mounted three ways: standard panel mount, DIN rail mount, and screw
mount for high vibration environments.
The standard panel mount and cutout dimensions are illustrated below.
2–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 19
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
CAUTION
#4 - 40x3/8in SELF-TAP PAN HD PHILIPS
QTY: 6 (SUPPLIED); GE PART NO. 1402-0017
TIGHTENING TORQUE: 8 lb-in
REAR OF PANEL
CUTOUT AND
MOUNTING HOLES
INSTALL RELAY
FROM FRONT
OF THE PANEL
3.775”
(95,89 mm)
5.580”
(141,73 mm)
0.105”
(2,67 mm)
0.138”
(3,49 mm)
3.500”
(88,90 mm)
0.130”
(3,30 mm)
(QTY: 6)
5.790”
(147,07 mm)
1.750”
(44,45 mm)
889725A1.CDR
SNAP-IN THE DIN CLIPS (QTY: 4)
FOR DIN RAIL MOUNTING
0.30”
(7,6 mm)
1.38”
(35,1 mm)
DIN 3 RAIL
889726A1.CDR
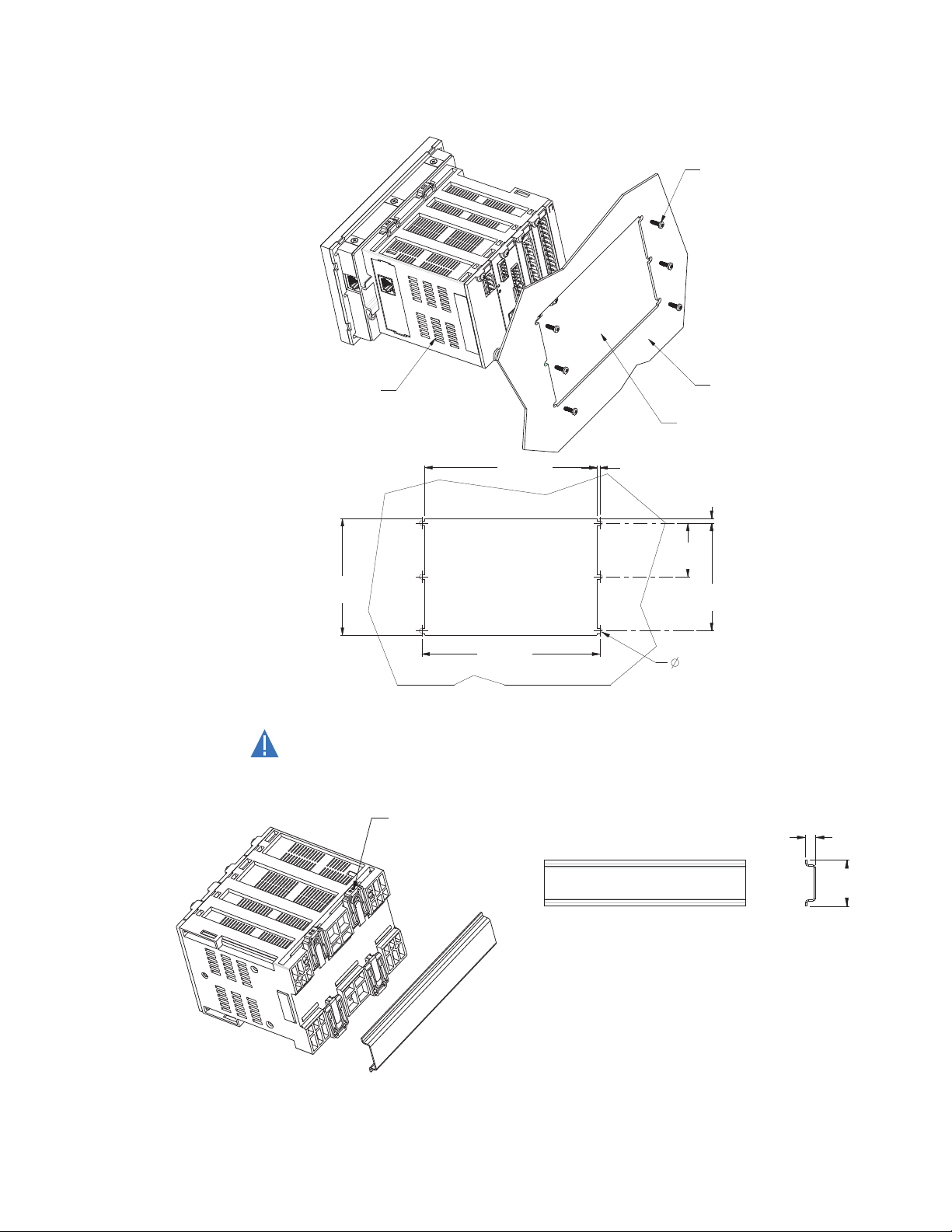
Figure 3: Panel mounting and cutout dimensions
CAUTION:
The DIN rail mounting is illustrated below. The DIN rail conforms to EN 50022.
To avoid the potential for personal injury due to f ire hazards, ensure the unit is
mounted in a safe location and/or within an appropriate enclosure.
Figure 4: DIN rail mounting
The screw mount for high vibration environments is illustrated below.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–3
Page 20
MECHANICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
DANGER
CAUTION
MEETS VIBRATION REQUIREMENT OF
IEC 60255 SEC 21.1, 21.2, & 21.3
2.250”
(57,15 mm)
#6 -32 THREADED HOLE
QTY: 2
4.100”
(104,14 mm)
889727A1.CDR
Figure 5: Screw mounting
DANGER:
CAUTION:
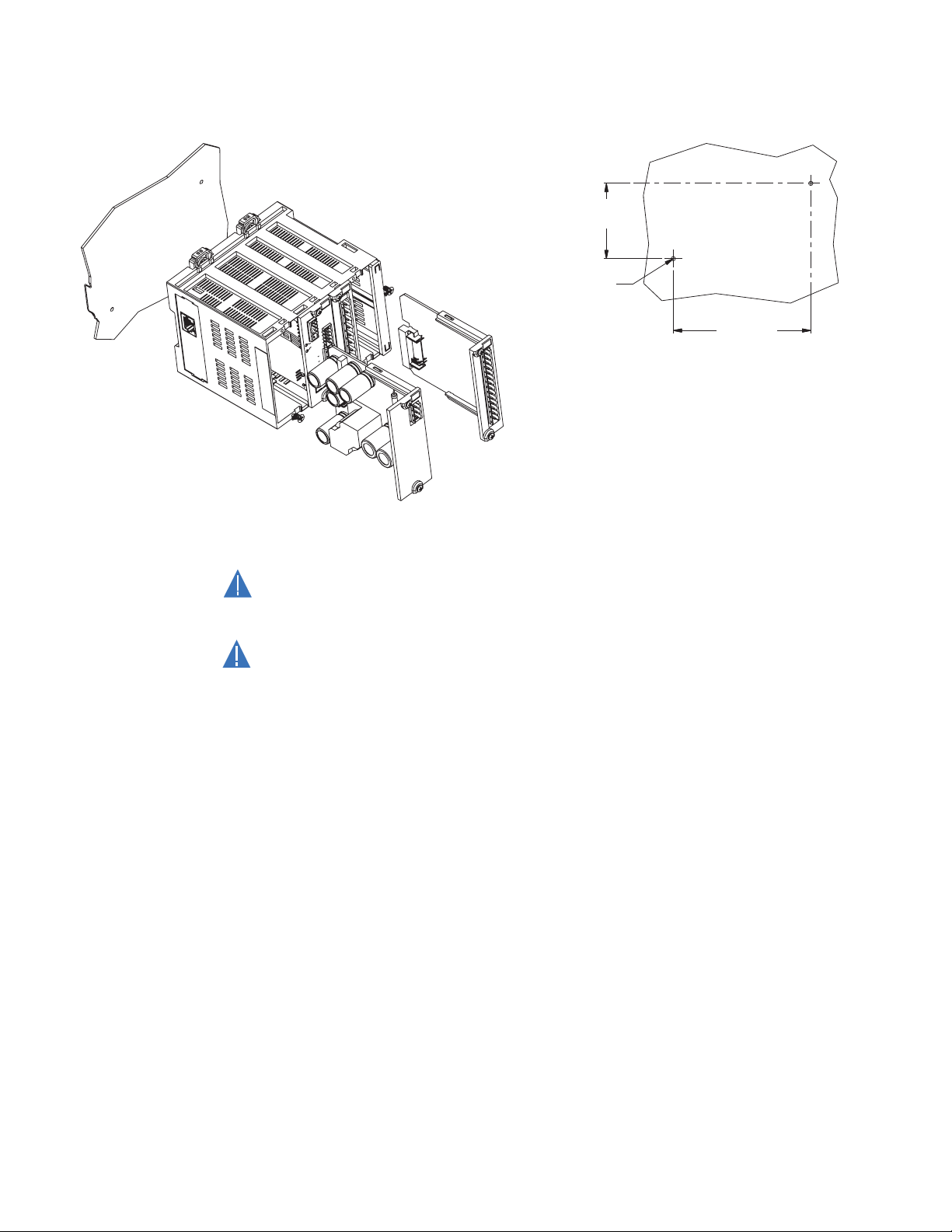
Module withdrawal and insertion
Module withdrawal and insertion may only be performed when control power has been
removed from the unit. Inserting an incorrect module type into a slot may result in
personal injury, damage to the unit or connected equipment, or undesired operation!
Proper electrostatic discharge protection (for example, a static strap) must be used
when coming into contact with modules while they are removed from the MX350.
The MX350 is a modular protection system. This allows for easy withdrawal and insertion
of modules for fast replacement. Modules must only be replaced in their original factory
configured slots.
Use the following procedure to withdraw a module.
1. Ensure that control power has been removed from the MX350.
2. Record the slot location of the module to ensure that the same or replacement
module is inserted into the correct slot.
3. Remove the two captive screws at the top and bottom of the module.
4. Slide a flat-blade screwdriver into the opening above the module marked by the two
arrows on top of the MX350 case.
5. Press down on the screwdriver and pivot towards the unit to unlatch the module from
the MX350 case.
2–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 21
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
889733A1.CDR
889734A1.CDR
Figure 6: Removing a module from the MX350
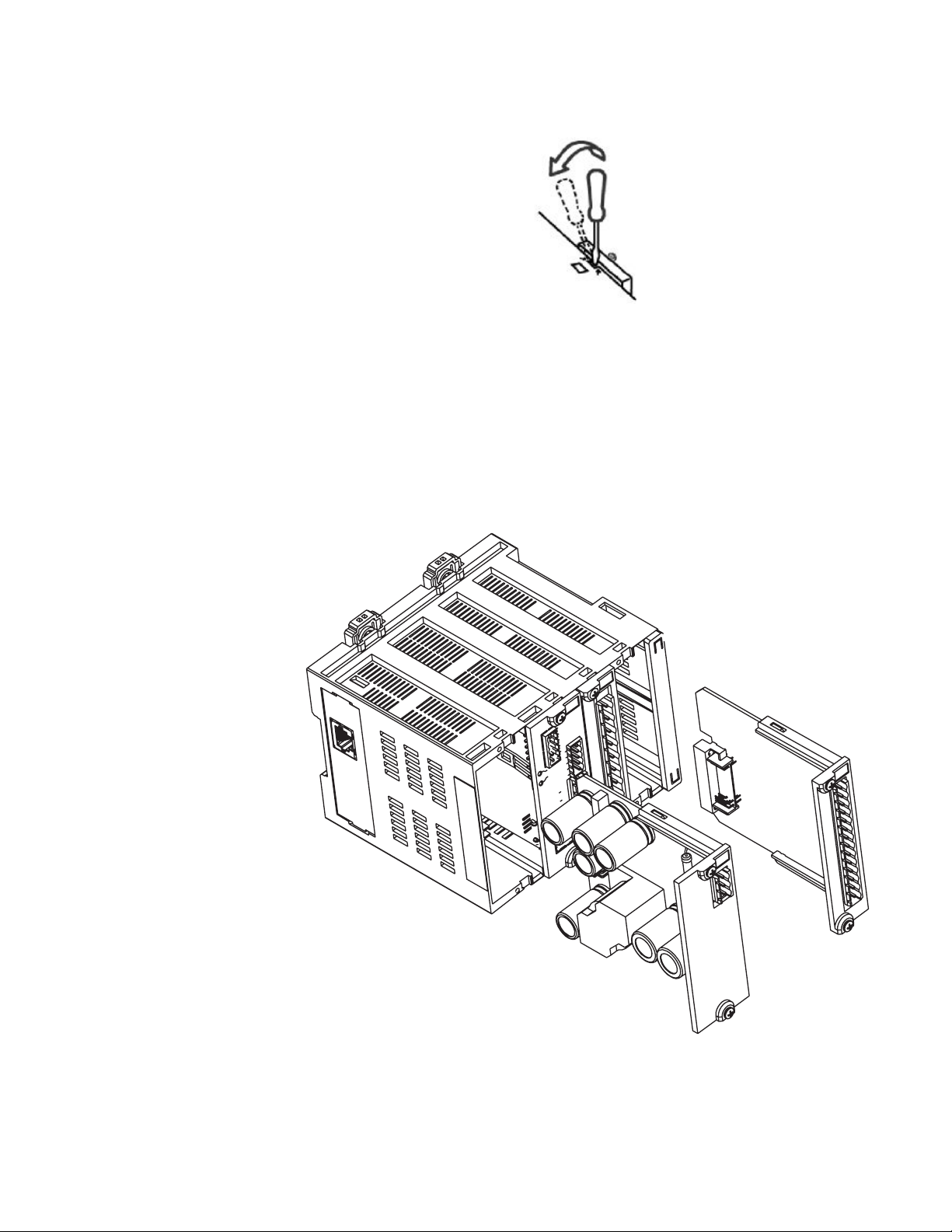
Use the following procedure to insert a module.
1. Ensure that control power has been removed from the MX350.
2. Ensure that the module is being inserted into the correct slot.
3. Align the module card edges with the slot track as shown in the diagram below.
4. Gently slide the modules into the slot until the modules latch into the opening marked
by the two arrows on top of the MX350 case.
5. Attach the two captive screws to anchor the module to the case (use a tightening
torque of 3.5 lb.-in.).
Figure 7: Inserting modules into the MX350
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–5
Page 22

MECHANICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
NOTE
Module and terminal identification
The MX350 input/output and metering modules are labeled with the “IO_” prefix followed
by a one-character identifier as follows.
Table 1: Input/output and metering module nomenclature
Module Description
IO_A CT module
IO_B VT module
IO_K 4 inputs, 4 outputs, plus relay for engine control
IO_L 7 inputs, 5 outputs
The MX350 terminals are labeled with a two-character identifier. The first character
identifies the module slot position and the second character identifies the terminals within
the module. For example, the first terminal in a module in slot F is identified as “F1”.
NOTE:
Do not confuse the slot designation with the module ordering designation. That is, terminal
“F1” does not imply an IO_F module. Rather, it indicates the first terminal of whatever
module is in slot F, which can only be an IO_K module.
2–6 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 23
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
CAUTION
Expansion module
Expansion module
to base unit with a
single connector
CT Input
Three-phase plus
ground/neutral
VT inputs
Optional TCP/IP
Ethernet
RS485 communications
Switched power supply
allows AC or DC control
voltage
889740A2.CDR
K Card
Expansion module
to base/expansion unit
with a single connector
LCard LCard
Expansion module
Reserved
Reserved
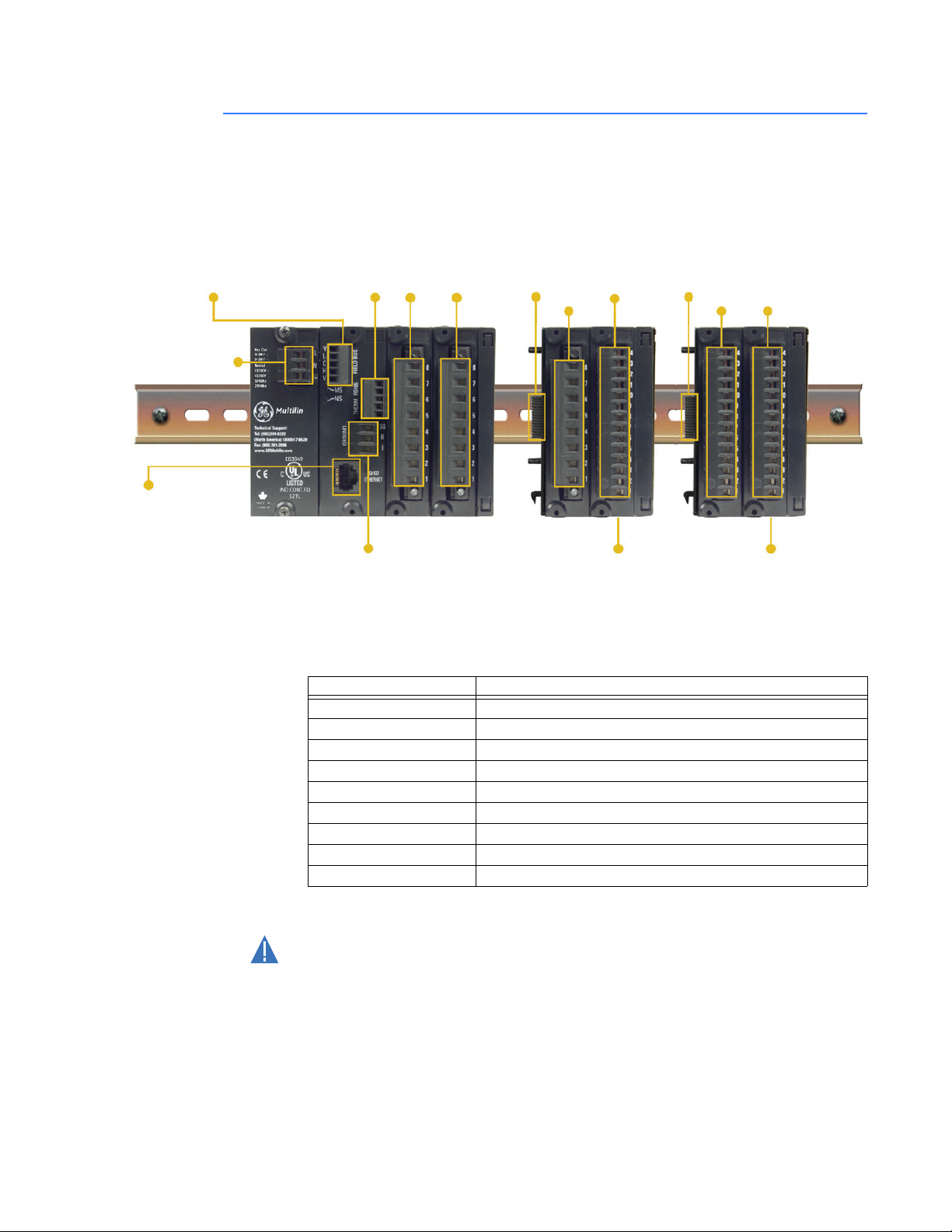
Electrical installation
This section describes the electrical installation of the MX350 system. An overview of the
MX350 terminal connections is shown below.
Figure 8: MX350 terminal connection overview
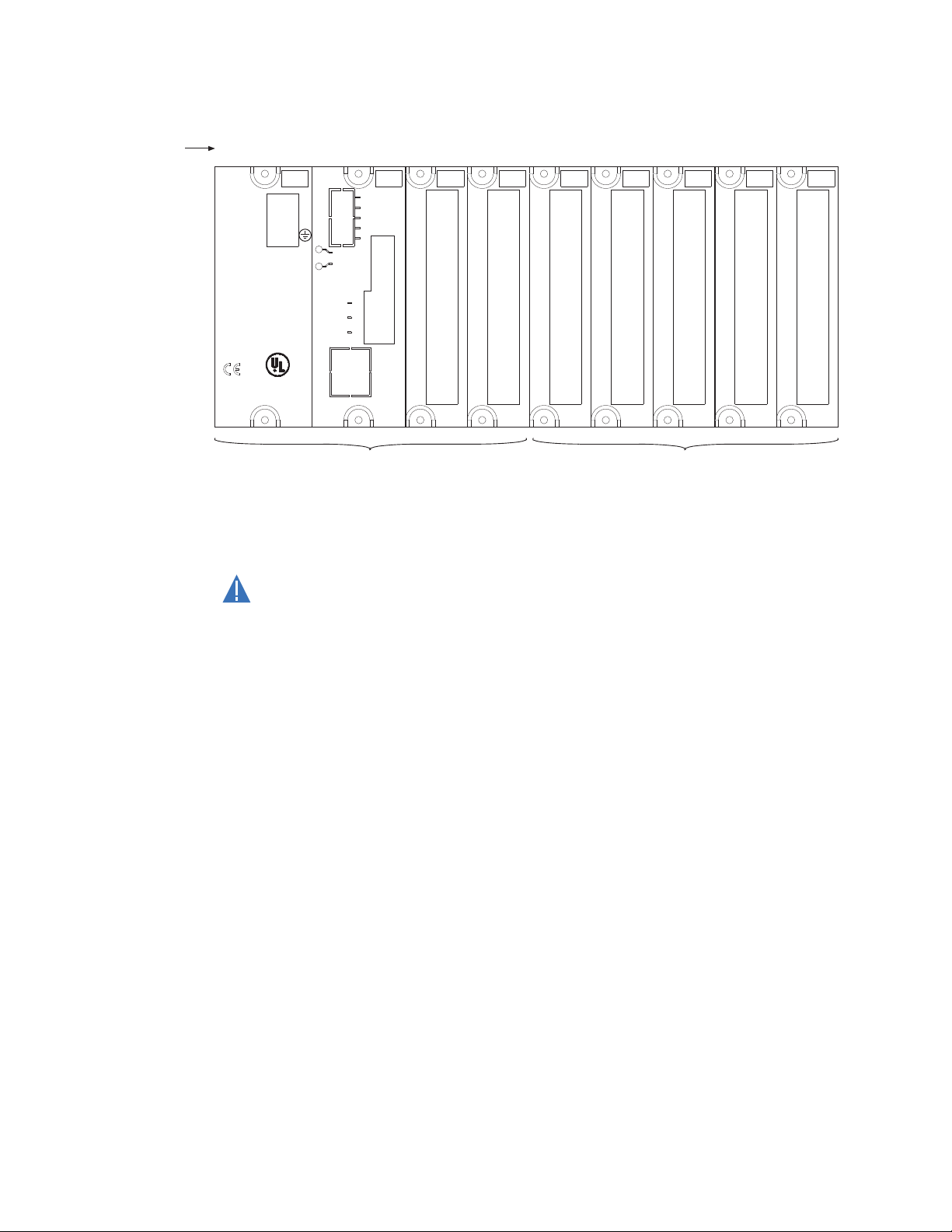
CAUTION:
The MX350 can contain up to ten modules. The first four modules (slots A through D) reside
in the base unit while all subsequent modules (slots E and J) reside in expansion units.
Each expansion unit can contain up to two modules. Slots A through G make up the basic
MX350. The next three modules (slots H through J) are optional I/O modules.
Table 2: Module slot position
Slot Module types
A Power supply module
B CPU module with communications
CIO_B module
DIO_B module
E IO_A module (optional)
FIO_K module
GIO_L module
H IO_L module (optional)
I IO_L module (optional)
The following figure shows a typical module arrangement for an expanded unit .
Use gauge size appropriate for the voltage and current draw of the device.
The MX350 is not to be used in any way other than described in this manual.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–7
Page 24
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
CAUTION
PSU
60-300 VAC
84-250 VDC
L
LISTED
IND.CONT.EQ.
52TL
E200434
N
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
MS
NS
THERM RS485
V-
10/100
ETHERNET
GROUND
CT I/P
I
L
C
H
V+
+
–
C
+
–
FIELD BUS
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH
Slot position
Base unit Expansion modules
889749A1.CDR
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
R
SG
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
I
Figure 9: Typical module arrangement
Power supply module
The power supply module in slot A supplies control power to the MX350 system. A supply
voltage between 60 to 300 V AC or 84 to 250 V DC is required to power the MX350
CAUTION:
Check the voltage rating of the unit before applying control power! Control power
outside of the operating range of the power supply will damage the MX350.
2–8 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 25
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
CAUTION
SCADA, PLC, OR
PERSONAL COMPUTER
COM
OPTOCOUPLER
DATA
IED
SHIELD
889745A1.CDR
UP TO 32 IEDs,
MAXIMUM CABLE
LENGTH OF
1200 m (4000 ft .)
LAST
DEVICE
(*) TERMINATING IMPEDANCE AT E ACH END
(typically 120 ohms and 1 nF)
TWISTED PAIR
ZT(*)
RS485 +
RS485 -
COMMON
RS485 +
RS485 -
COMMON
IED
RS485 +
IED
RS485 -
COMMON
GROUND THE SHIELD AT THE
SCADA/PLC/COMPUTER ONLY
OR THE UNIT ONLY
DATA
OPTOCOUPLER
B1
B2
B3
ZT(*)
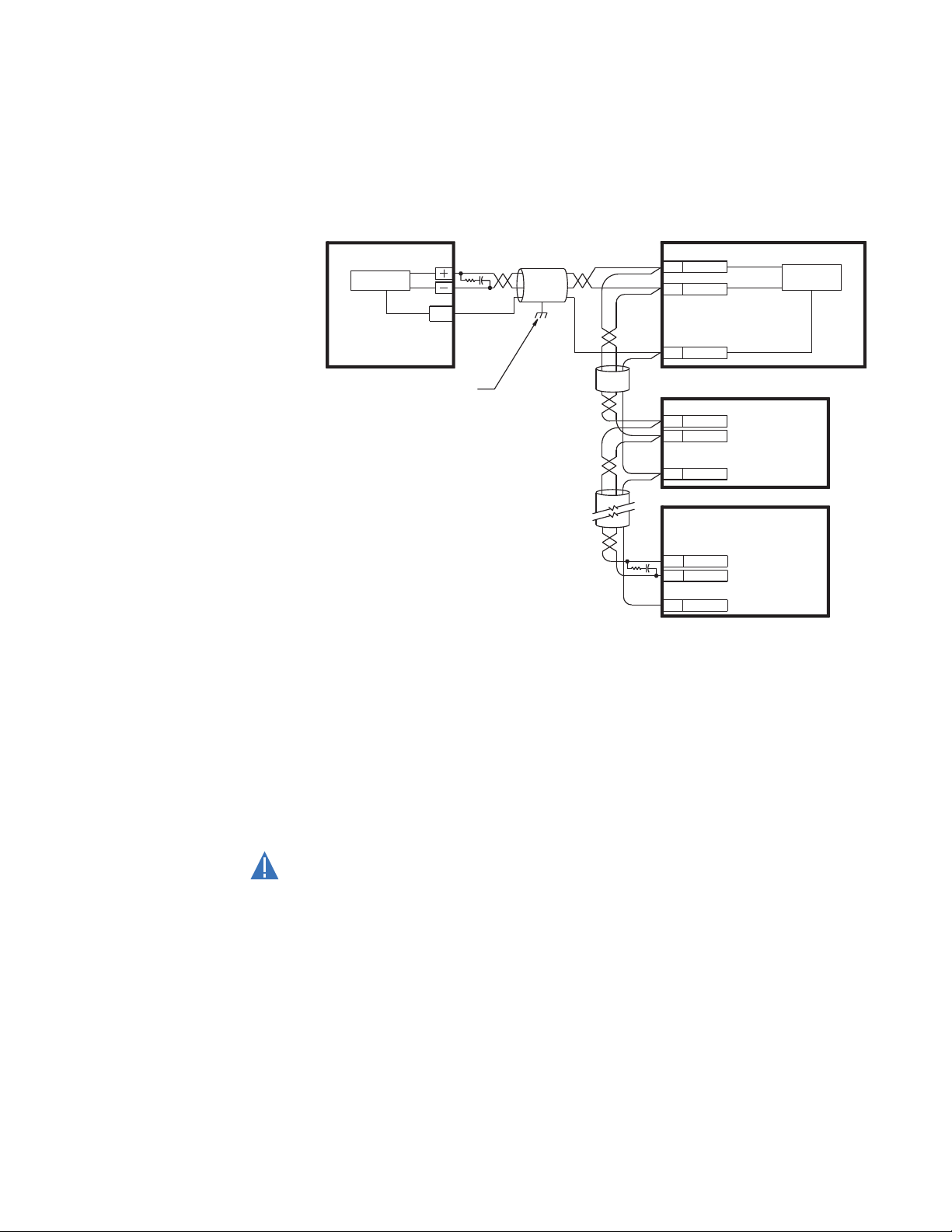
CPU module
The main CPU module and optional communications board is contained in slot B. The main
CPU module provides a Modbus RTU RS485 port. The optional communications board
provides an Ethernet port.
RS485 connections Figure 10: Typical RS485 connection
CAUTION:
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–9
One two-wire RS485 port is provided. Up to 32 MX350 IEDs can be daisy-chained together
on a communication channel without exceeding the driver capability. For larger systems,
additional serial channels must be added. Commercially available repeaters can also be
used to add more than 32 relays on a single channel. Suitable cable should have a
characteristic impedance of 120 ohms (for example, Belden #9841) and total wire length
should not exceed 1200 meters (4000 ft.). Commercially available repeaters will allow for
transmission distances greater than 1200 meters.
Voltage differences between remote ends of the communication link are not uncommon.
For this reason, surge protection devices are internally installed across all RS485 terminals.
Internally, an isolated power supply with an optocoupled data interface is used to prevent
noise coupling.
To ensure that all devices in a daisy-chain are at the same potential, it is imperative
that the common terminals of each RS485 port are tied together and grounded only
once, at the master or at the MX350. Failure to do so may result in intermittent or failed
communications.
The source computer/PLC/SCADA system should have similar transient protection devices
installed, either internally or externally. Ground the shield at one point only, as shown in the
figure above, to avoid ground loops.
Correct polarity is also essential. The MX350 IEDs must be wired with all the positive (+)
terminals connected together and all the negative (–) terminals connected together. Each
relay must be daisy-chained to the next one. Avoid star or stub connected configurations.
The last device at each end of the daisy-chain should be terminated with a 120 ohm
¼ watt resistor in series with a 1 nF capacitor across the positive and negative terminals.
Observing these guidelines will ensure a reliable communication system immune to
system transients.
Page 26
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
CAUTION
A
C
B
Power flow
–
+
E1
E2
E4E3
Phase current inputs
Automatic Transfer Control System
To switchgear
ground bus
889744A1.CDR
E5
E6 E7
CT1 CT2 CT3
Control power
LN
E8
G/F
N
Input/Output modules
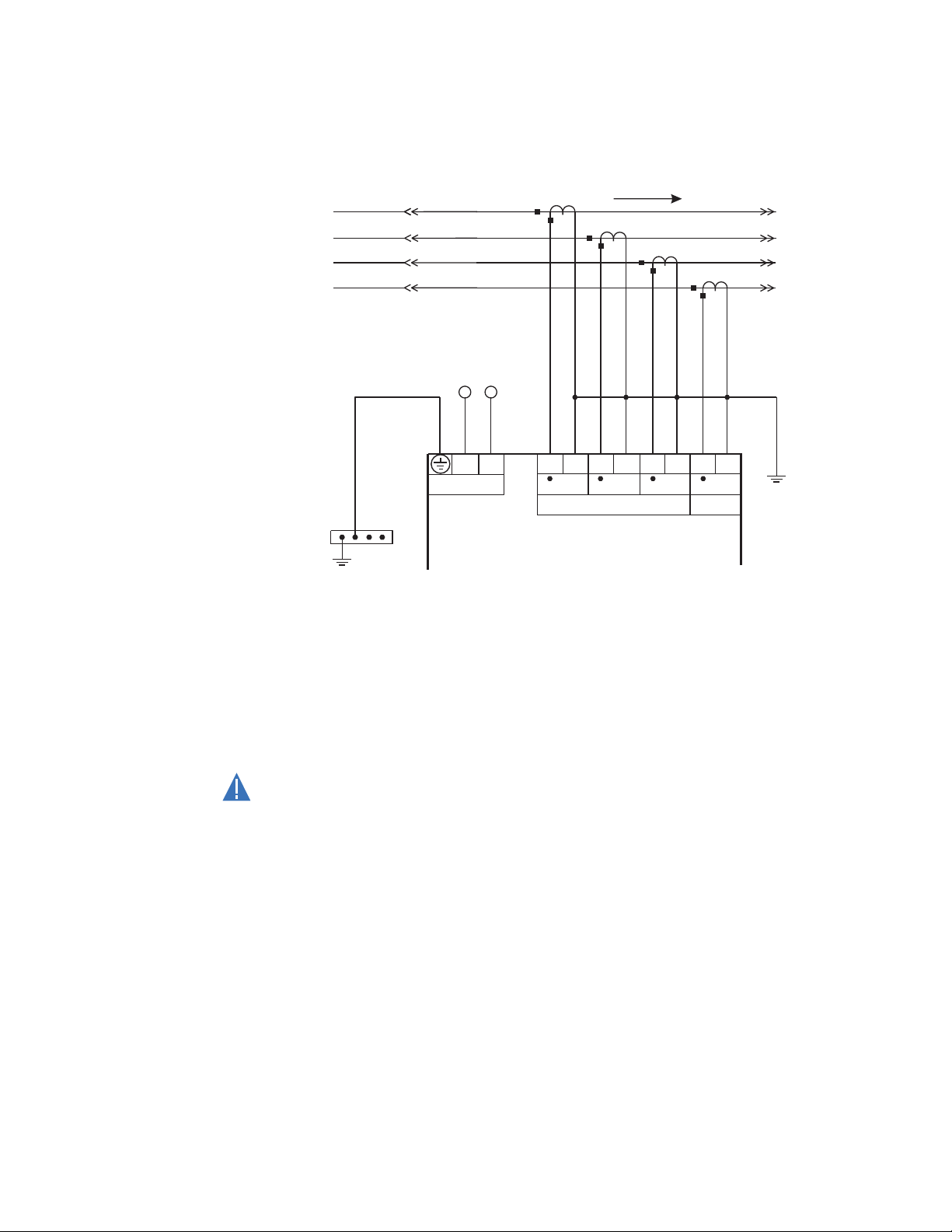
Phase current inputs
(IO_A module)
CAUTION:
Figure 11: Typical phase current input connections
The MX350 has three channels for phase current inputs, plus an additional channel input
for ground/neutral current, each with an isolating transformer. The phase CTs should be
chosen so the nominal current is not less than 50% of the rated phase CT primary. Ideally,
the phase CT primary should be chosen such that the nominal current is 100% of the
phase CT primary or slightly less, never more. This will ensure maximum accuracy for the
current measurements. The maximum phase CT primary current is 4000 A.
The MX350 measures up to 1.5 times the phase current nominal rating. CTs with 1 A or 5 A
secondaries must be used if the FLA is greater than 5 A. The chosen CTs must be capable
of driving the MX350 phase CT burden.
Polarity of the phase CTs is critical for negative-sequence unbalance calculation,
power measurement, and residual ground current detection (if used).
2–10 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 27
CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
A
C
B
–
+
D1
D2 D4D3
Phase voltage inputs
Auto Transfer Control
D5
D6 D7
VT1 VT2 VT3
Control power
LN
D8
N/C
–
+
C1
C2 C4C3
Phase voltage inputs
Auto Transfer Control
889735A1.CDR
C5
C6 C7
VT1 VT2 VT3
Control power
LN
C8
N/C
N
Typically
generator
Typically
utility
LOAD
A
C
B
–
+
D1
D2 D4D3
Phase voltage inputs
Auto Transfer Control
D5
D6
VT1 VT2 VT3
Control power
LN
D7 D8
N/C
–
+
C1
C2 C4C3
Phase voltage inputs
Auto Transfer Control
889736A1.CDR
C5
C6
VT1 VT2 VT3
Control power
LN
C7 C8
N/C
From
Source 2
(generator)
From
Source 1
(utility)
LOAD
Phase voltage inputs
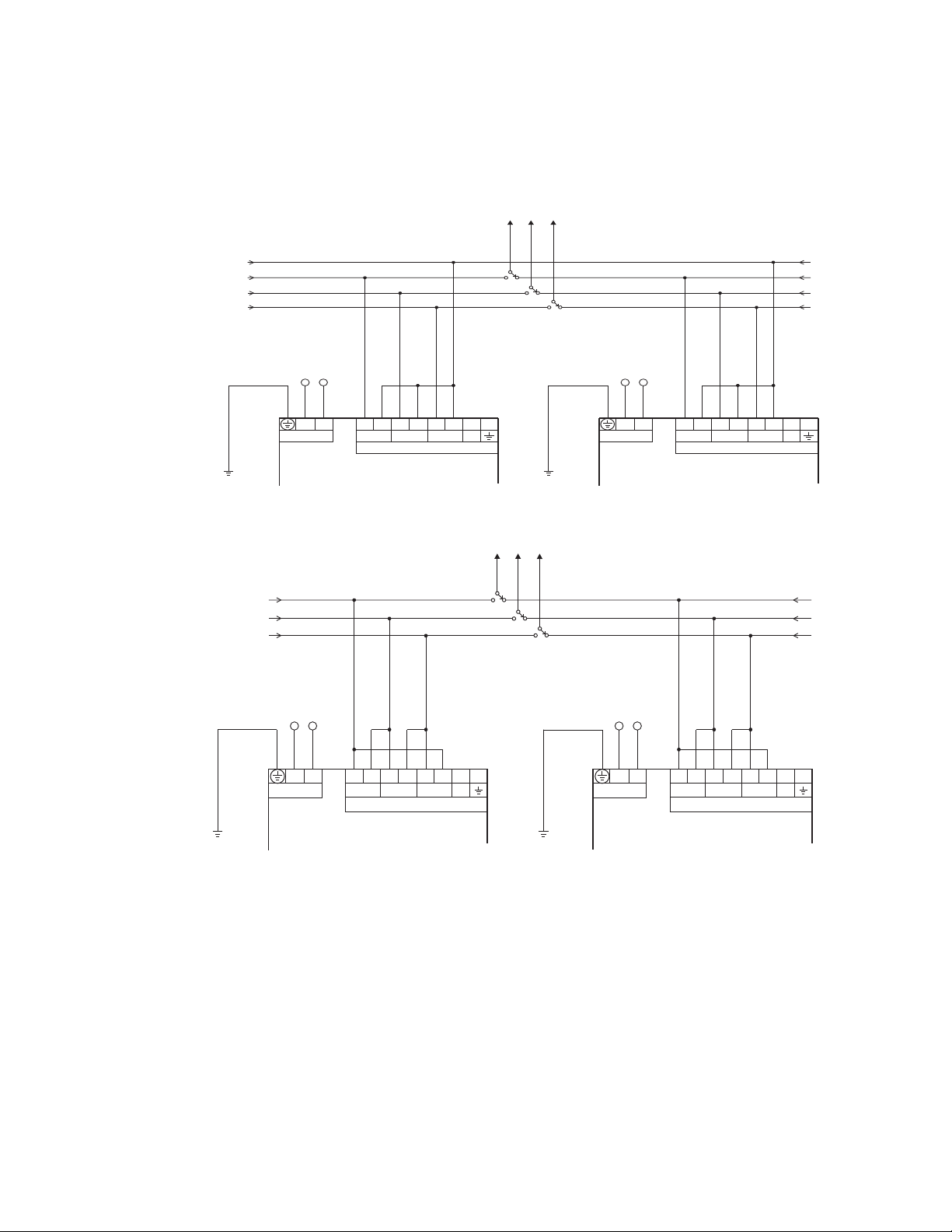
(IO_B module)
The MX350 has three channels for AC voltage inputs. There are no internal fuses or ground
connections on the voltage inputs. Polarity is critical for correct power measurement and
voltage phase reversal operation.
Figure 12: Wye voltage connection
Figure 13: Delta voltage connection
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–11
Page 28
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
~1
~2
~4
~3
~5
~6
Auto Transfer Control
~8
~9
~11
~10
~12
~13
~7
~14
INPUT COMMON
Inp
com
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SW
DELAYED INPUT
Inp 4
Inp 3
Inp 2
Inp 1
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SW
DELAYED INPUT
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SW
INPUT
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SW
INPUT
P. RELAY - ENGINE
START - N.C.
P. RELAY - COMMON
P. RELAY - ENGINE
START - N.O.
COIL CONTROL REL AYS
3&4COMMON
COIL CONTROL REL AY
DEL (OPEN SRC 2)
COIL CONTROL REL AY
DEL (OPEN SRC 1)
COIL CONTROL REL AYS
1&2COMMON
COIL CONTROL REL AY
SOURCE 2
COIL CONTROL REL AY
SOURCE 1
SSR 3&4
COM
SSR 1&2
COM
SSR
SSR
SSR
SSR
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SWITCH (+24 V DC ACTIVE)
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SWITCH (+24 V DC ACTIVE)
NC
NC
NC
24VDC
24VDC
TO SOLENOID
TO SOLENOID
~1
~2
~4
~3
889741A1.CDR
~5
~6
Auto Transfer Control
~8
~9
~11
~10
~12
~13
~7
~14
INPUT COMMON
Inp
com
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SW
DELAYED INPUT
Inp 4
Inp 3
Inp 2
Inp 1
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SW
DELAYED INPUT
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SW
INPUT
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SW
INPUT
P. RELAY - ENGINE
START - N.C.
P. RELAY - COMMON
P. RELAY - ENGINE
START - N.O.
COIL CONTROL REL AYS
3&4COMMON
COIL CONTROL REL AY
DEL (OPEN SRC 2)
COIL CONTROL REL AY
DEL (OPEN SRC 1)
COIL CONTROL REL AYS
1&2COMMON
COIL CONTROL REL AY
SOURCE 2
COIL CONTROL REL AY
SOURCE 1
SSR 3&4
SSR 1&2
SOURCE 2 LIMIT SWITCH (+24 V DC ACTIVE)
SOURCE 1 LIMIT SWITCH (+24 V DC ACTIVE)
NC
NC
NC
0 VDC
0 VDC
24VDC
24VDC
TO SOLENOID
TO SOLENOID
STARTER
CCTRY
GEN
A
B
C
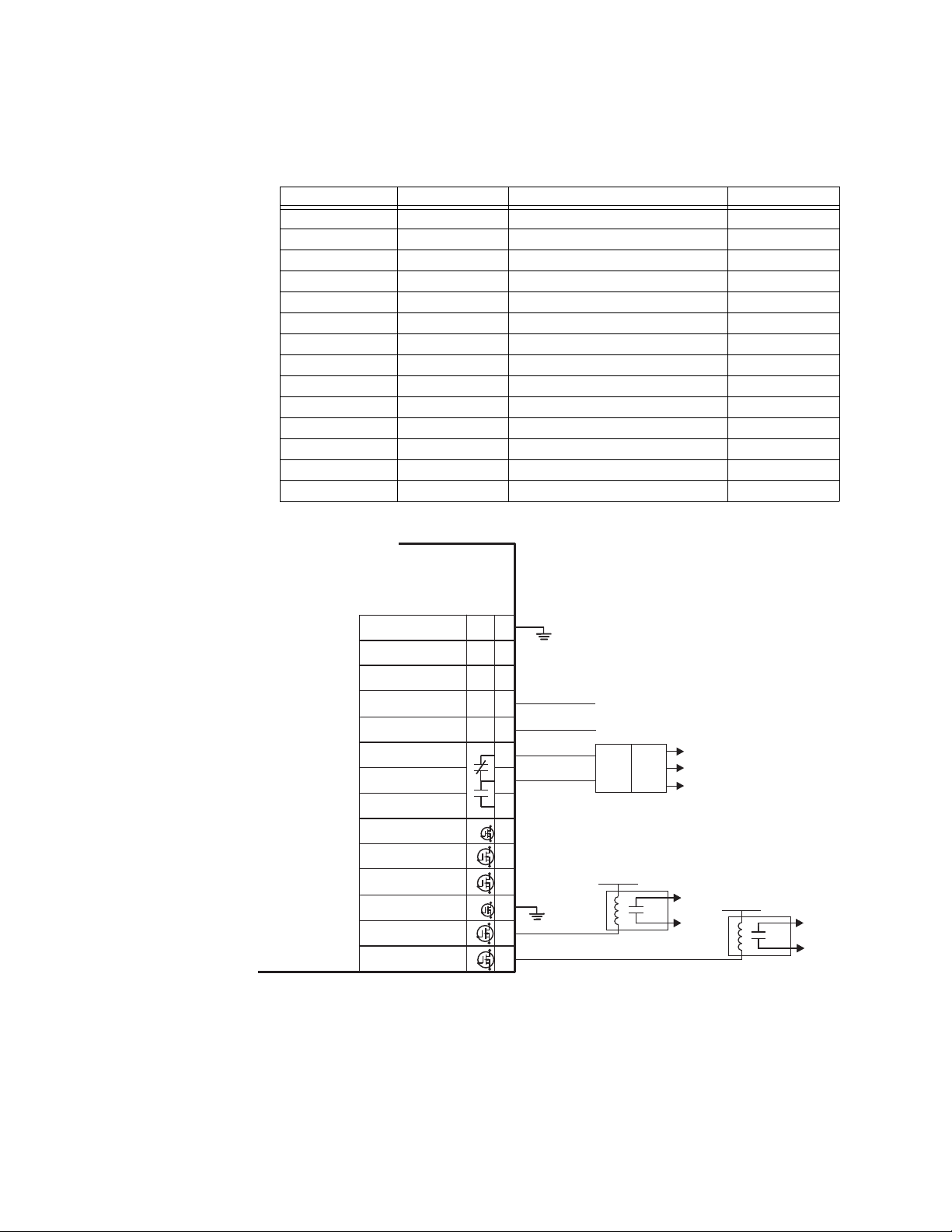
Type IO_K module
connections
The IO_K module handles the automatic delayed start of the engine in case there is a total
power outage, i.e. Source 1 power fails and the MX350 is not powered by an auxiliary
power source. The terminal assignments are as follows:
Terminal Type Function Type
F1 Output S1 Sol Relay N.O.
F2 Output S2 Sol Relay N.O.
F3 N/A Common F1, F2 N/A
F4 Output S1 Del Sol Relay N.O.
F5 Output S2 Del Sol Relay N.O.
F6 N/A Common F4, F5 N/A
F7 Output Engine Start Signal (P Relay) N.O.
F8 N/A Engine Start Signal, Common N/A
F9 Output Engine Start Signal (P Relay) N.C.
F10 Input SN Limit Switch pos.
F11 Input SE Limit Switch pos.
F12 Input SNO Limit Switch pos.
F13 Input SEO Limit Switch pos.
F14 N/A Input Common N/A
Figure 14: IO_K module connections - standard ATS
2–12 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 29

CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
NOTE
~1
~2
~4
~3
~5
~6
Auto Transfer Control
~8
~9
~11
~10
~12
~13
~7
~14
Inp
com
Inp 7
Inp 6
Inp 5
Inp 4
LOAD SHED FROM S2
TEST WITH LOAD
DISCONNECT SW
LOAD SHED FROM S2
SSR
COM
SSR3
SSR5
SSR4
SSR2
SSR1
NO
~1
~2
~4
~3
889742A1.CDR
~5
~6
Auto Transfer Control
~8
~9
~11
~10
~12
~13
~7
~14
Inp
com
In
SSR
SSR
NC
Inp 3
Inp 2
Inp 1
LOAD SHED
HARDWARE
FOR LOCAL
OPTION
TO BREAKER
24VDC
0 VDC
0 VDC
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
USER DEFINED
Type IO_L module
connections
NOTE:
IO_L modules provide all user configurable I/O. Additionally, some of the I/O points on the
first L module in slot G are used for some factory configured I/O. The terminal
configuration is as follows:
Terminal Terminal Terminal Type Function
G1 H1 J1 Output Output 1
G2 H2 J2 Output Output 2
G3 H3 J3 Output Output 3
G4 H4 J4 Output Output 4
G5 H5 J5 Output Output 5
G6 H6 J6 Common Common, Ouputs 1 to 5
G7 H7 J7 Input Input 1
G8 H8 J8 Input Input 2
G9 H9 J9 Input Input 3
G10 H10 J10 Input Input 4
G11 H11 J11 Input Input 5
G12 H12 J12 Input Input 6
G13 H13 J13 Input Input 7
G14 H14 J14 Common Common, Inputs 1 to 7
Terminals G7 and G8 are always used as DS and Q2, respectively. Depending on the type
of switch and the features ordered, Terminals G1 through G5 as well as G9 through G13
may not be available for customer configuration.
Figure 15: IO_L module - standard ATS
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 2–13
Page 30

ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION CHAPTER 2: INSTALLATION
Do not HI-POT test
HI-POT test at 1.9 kV AC for 1 second, or
1.6 kV AC for 1 minute (per UL 508)
LINE FAULT
ON
POWER
FAULT
RESET
kV
VOLTAGEADJUST
HV ON
DIELECTRIC STRENGTHTESTER
BLACK RED
Remove surge ground during test
*
CPU module
C8
C7
C6
C5
C4
C3
C2
C1
Surge Ground
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
CT Module
CT1
CT2
CT3
CT4
Power
supply
L
N
G
Automatic Transfer Control System
VT1 module
VT1
VT3
RS485
Thermistor
VT2
Core
balance
Surge Ground
889738A1.CDR
+
–
C
+
–
R
ISG
*
*
*
*
*
D8
D7
D6
D4
D3
D2
D1
Surge Ground
D5
VT1
VT3
VT2
VT2 module
*
*
*
*
*
Dielectric strength testing
Figure 16: Testing for dielectric strength
2–14 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
It may be required to test for dielectric strength (“flash” or “HI-POT”) with the MX350
installed. The MX350 is rated for 1.9 kV AC for 1 second, or 1.6 kV AC for 1 minute (per UL
508) isolation between relay contacts, CT inputs, VT inputs and the surge ground terminal
SG. Some precautions are required to prevent damage to the MX350during these tests.
Filter networks and transient protection clamps are used between VT input and the surge
ground terminal. This is intended to filter out high voltage transients, radio frequency
interference (RFI), and electromagnetic interference (EMI). The filter capacitors and
transient suppressors may be damaged by continuous high voltage. Disconnect the surge
ground terminals (C8 and D8) during testing of VT inputs. The CT inputs, control power, and
output relays do not require any special precautions. Low voltage inputs (less than
30 volts), and RS485 communication ports are not to be tested for dielectric strength under
any circumstance (see above).
Page 31

Digital Energy
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 3: Interfacing with the
MX350 AT Controller
Interfacing with the MX350 AT Controller
There are four methods of interfacing with the MX350 ATS Controller.
• Interfacing via the graphical control panel.
• Interfacing via remote inputs.
• Interfacing via communicated inputs.
• Interfacing via the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software.
This section provides an overview of the interfacing methods available with the MX350. For
additional details on interface parameters (for example, settings, actual values, etc.), refer
to the individual chapters.
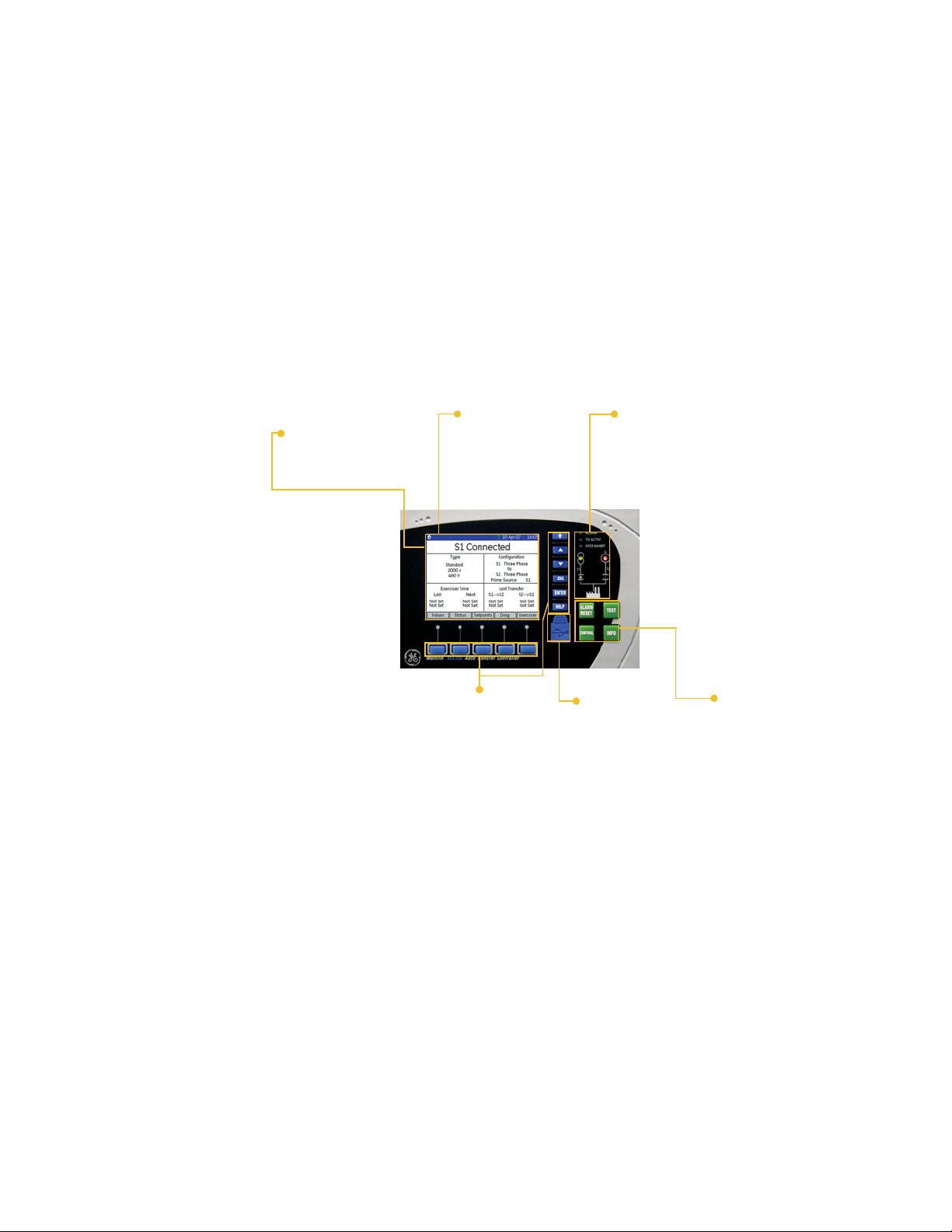
Graphical control panel
The MX350 graphical control panel provides the operator with rapid access to relevant
information and controls using intuitive sequences. It also provides all available
information and setting control, again with intuitive sequences.
Introduction to the graphical control panel
The central feature of the graphical control panel is a 89 mm (3.5-inch) 320 by 240 pixel
backlit color LCD screen. The panel also contains keys (pushbuttons) that control the
display and perform commands. In addition, the interface contains ALARM RESET, TEST,
CONTROL, and INFO direct acting control pushbuttons.
The display also contains several LED indicators that provide a summary of the machine
status. Details are displayed on the screen when the user navigates to the appropriate
page.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–1
Page 32

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
889700A1.CDR
LED indicators
Soft-keys
Graphical
display
Control keys
Function keys
USB port
Header bar
Selected page
Soft-key labels
Path indication Date and timeAccess level
Color convention
for soft-key labels
(blue)
(grey)
(red)
(grey / grey text)
(orange)
Commands
Active Tab
Inactive Tab
Status
Unavailable Feature
Figure 1: MX350 front panel with example default display
Graphical display Each display page consists of the three components shown below.
Figure 2: Graphical display overview
The header bar (white text on a blue background) displays the hierarchical path name, the
date and time in 24-hour format, and the current password access level. The hierarchical
path is always displayed on the left top side of the graphical display. The present time is
displayed on the right top side.
The soft-key labels are indicated on the bottom line. The soft-keys are used for navigation,
performing functions, and for acknowledgement.
• Navigation: soft-keys can be used to traverse across and down the hierarchy of
pages.
• Functional: soft-keys can be used to perform page-specific functions.
• Acknowledgement: soft keys can be used to acknowledge popup windows.
Soft-keys labels change to show relevant selections for the displayed screen. The color of
each soft-key label indicates its functionality. Soft-keys are highlighted for the displayed
page, unauthorized keys are “greyed-out”, and unused keys are not displayed.
3–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 33

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
Header bar
Selected page
Soft-key labels
Path indication Date and timeAccess level
Color convention
for soft-key labels
(blue)
(grey)
(red)
(grey / grey text)
(orange)
Commands
Active Tab
Inactive Tab
Status
Unavailable Feature
The remainder of the screen shows the selected page. Pages are organized in a
hierarchical or tree-based menu structure. To improve readability, some pages are labeled
with rectangular outlines or colored backgrounds. Some pages contain too many fields to
display at once. These pages display arrows bars at the right edge to indicate that the
page continues below the screen. When recalled, scrolled pages are re-positioned at the
top of the page.
Fields display actual value or setting information, and have behaviours that allow help
display, editing, and control.
Each Actual Value analog field displayed on the home page has an associated alarm limit
and changes color to orange when that limit is exceeded. Fields with an associated trip
limit change their color to red when that limit has tripped. Fields that are disabled or
unavailable are greyed-out.
Keypad The function keys perform the labeled functionality. The summary of function key
operation is shown below.
Table 1: Summary of function key operations
Key Operation
HOME Single press recalls the home page; double press recalls the default display
UP Scroll up page, select field, tab to next field, increment value
DOWN Scroll down page, select field, tab to previous field, decrement value
ESC Single press closes pop-up, cancels editing, deselects field, moves to previous page;
ENTER Single press freezes scrolling and selects field, edits selected field, saves edited value;
HELP Displays context sensitive help and Modbus address
sustained press logs out (cancels security passcode entry)
double press sets the selected field/page as default; sustained press logs in (enter
security passcode)
The HOME key always recalls the root or home page. The home page allows access to all
sub-pages and also contains a status and process values summary. Double pressing the
HOME key recalls the default display. Like a screen-saver, the default display appears after
a period of inactivity and displays user-selected information. A typical display is shown
below, indicating that the system load is connected to the utility.
Figure 3: Typical default display (actual size)
The UP and DOWN keys function in different ways depending on their context.
• Where a scroll bar is displayed, the UP and DOWN keys scroll the page up and down.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–3
Page 34

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
• Where there is no scroll bar or it is greyed-out, the first press of the UP and DOWN
keys selects the first field. Subsequent presses tab up and down through the fields,
scrolling as required.
• When a field is open for editing, the UP and DOWN keys increment/decrement the
value of that field.
The ENTER key functions in different ways depending on its context.
• If there are no selected fields, the ENTER key will freeze any scroll bars and select the
first field on the display.
• If a field is selected, pressing ENTER will attempt to open it for editing.
• If a field is opened for editing, pressing enter will exit the edit sequence.
• Double pressing the ENTER key at any time selects the displayed page as the default
display.
• A sustained press on ENTER prompts the security passcode and displays a dialog box
that allows passcode entry.
For example, pressing and holding the ENTER key, or attempting a control where a
password is required, displays the following page.
Figure 4: Passcode entry dialog box
The ESC key functions in different ways depending on its context.
• If a pop-up dialog box is displayed, the ESC key closes it.
• If an edit sequence is in progress, the ESC key cancels the edit.
• If a field is selected, the ESC key de-selects it.
• In all other instances, the ESC key moves back one page in the menu structure.
• A sustained press on the ESC key clears the security passcode and prompts for
confirmation.
The HELP key functions in different ways depending on its context.
• If a field is selected, the HELP key displays a help window for the field.
• If a help window is displayed, the HELP key closes it.
Help windows are also closed when any other key is pressed. A typical help window is
shown below.
Figure 5: Typical MX350 help window
3–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 35

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
Pressing an invalid key displays a message explaining the problem and recommending a
solution. Where the keypress is invalid because a security passcode is required, the dialog
window will be a passcode entry window.
Control keys The MX350 has four large direct control keys: ALARM RESET, TEST, CONTROL, and INFO.
• ALARM RESET: allows the user to silence any audible alarm.
• TEST: takes the user directly to the System Test Screen.
• CONTROL: takes the user directly to the Control Screen that allows the user to select
certain modes of operation.
• INFO: takes the user directly to the Event Report screen.
LED indicators The control panel LEDs summarize the status of the transfer switch:.
• ALARM: indicates that there is a problem with the ATS, or that a user configurable
alarm condition is active, or that the ATS is not in AUTO mode.
• TD ACTIVE: indicates that the controller is timing before taking the next control action.
• XFER INHIBIT: indicates that the controller will not automatically transfer to the other
source and that operator intervention is required.
• S1 (Source-1, typically utility power) Available LED: indicates that S1 is present and
within user defined limits.
• S2 (Source-2, typically generator power) Available LED: indicates that S2 is present and
within user defined limits.
• S1 (Utility) Status LED: indicates that the load is connected to S1 power.
• S2 (Generator) Status LED: indicates that the load is connected to S2 power.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–5
Page 36

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Amps
Power
Volts
PQ
Values
Inputs
Outputs
System
Message
Flex
Summary
Status
Reset
Operation
Control
Security
Config
Setpoints
Phase B
Phase C
Phase A
Phase A
Phase B
Phase C
Phase A
Phase B
Outputs
Comms
System
Events
Zenith
Waveform
Faults
Alarms
Control
Stats
Phasors
About
Events
Report
Diag
ATS
CT-VT
Inputs
Virtual
Waveform
Datalog
Phase C
V1 Harm
V2 Harm
I Harm
Summary
V1 Harm
V2 Harm
I Harm
Summary
V Inputs
V Outputs
S1 Setting
S2 Setting
Timers
General
Interlock
Alarms
Reset
Setup
889701A1.CDR
Main menu
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4
ExerCancel
Info
Exerciser
Datalog
Test
MX350 graphical display pages
A summary of the MX350 page hierarchy is shown below.
Figure 6: MX350 display page hierarchy
3–6 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 37

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
Header bar
Selected page
Soft-key labels
Path indication Date and timeAccess level
Color convention
for soft-key labels
(blue)
(grey)
(red)
(grey / grey text)
(orange)
Commands
Active Tab
Inactive Tab
Status
Unavailable Feature
Home display page The home page represents the root of the entire menu structure. An overview of the
system status is displayed which indicates the following items:
• Load connected to Source 1 or Source 2
• Type of ATS being controlled
• Amperage rating of ATS
• Voltage rating of ATS
•Source 1 type
•Source 2 type
• Preferred source selection
• Information on the System Exerciser
• Information regarding the last load transfer.
Figure 7: Typical MX350 home display
The Values, Status, Setpoints, Diag, and Exerciser soft-keys are displayed on the home
page. The Status soft-key will be highlighted if any alarm condition is present.
Pressing any of the soft-keys displays the first sub-page in the hierarchy. Pressing the ESC
key within any of these sub-pages returns directly to the home page.
Default display The default display is automatically shown when no control key has been pressed for five
minutes. It can also be recalled at any time by double-clicking the HOME key.
The default display can be set to the home page, any actual values page, or any status
page. A page can be set to be the default display by navigating to that page and doublepressing the ENTER key. The default display setting is saved in non-volatile memory.
If a page is set as the default display, the soft-keys will be those of the selected page.
Actual values pages The actual values pages are divided into five sections.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–7
• Summary (overview of primary actual values)
• Amps (metered current values)
• Volts (metered voltage values)
• Power (metered power values)
• PQ (metered power quality values)
The actual values summary page displays a summary of the analog actual values. The
current, voltage, power, and PQ actual values pages are accessible from the summary
page through the corresponding soft-keys at the bottom of the screen.
Page 38

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Some typical actual values screens are shown below.
Figure 8: Typical actual values summary page
Figure 9: Typical actual values current page
Figure 10: Typical actual values voltage page
Status pages The status pages provide the user with up-to-date information on the current status of the
ATS that the MX350 is controlling.
Status pages are divided into five sections.
• Message (displays all locked out conditions plus conditions such as alarms, internal
faults, control status, etc.).
• Inputs (displays the present state of assigned contact inputs).
• Outputs (displays the present state of assigned contact outputs).
• System (displays the present state of the communications interface).
3–8 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 39

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
• Flex (displays the present state of the FlexLogic™ engine and number of lines used.)
A typical display is shown below:
Figure 11: Typical status message page
Message types are classified by color and associated icon type, as follows::
• Red Triangle = Alarm
• Orange Square = Status
• Black Text = Information Message
Message can have an associated countdown timer, if applicable.
When the controller is first powered up, the status page will display any parameters that
must be entered for proper operation of the associated ATS.
Inhibits
These include Transfer Inhibits like Q3 or Q7.
Faults / Alarms
These trigger depending on the respective protection setpoints. A typical example would
be “S1 Failure.”
Information Messages
Information can be one of two types:
– information only
– information with navigation (marked on the Status page with an Enter symbol on
the right)
By pressing the Enter key when an information message with navigation is highlighted, the
Grapical Control Panel will take the user directly to the respective page.
Setpoints pages The Setpoints pages are divided into five sections.
• Config (contains basic configuration setpoints)
• Operation (contains range limits for both power sources and timer values for transfer
operations)
• Control (contains basic control function setup, also accessible via the green CONTROL
key)
• Security (contains the password security setpoints)
• Factory (for access by GE only)
The Home > Setpoints page displays a warning message concerning unexpected
performance if setpoints are improperly changed. It is recommended that all relay outputs
capable of causing damage or harm be blocked before a setpoints change is made and it
is clear the relay is performing as intended with the new setpoints.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–9
Page 40

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Figure 12: setpoints home page
To streamline the setpoint entry process, the graphical control panel will not display
setpoints that are not relevant at the specific instance. For instance, if a process interlock
function is disabled, the six setpoints associated with that interlock function will not be
displayed. If all ten process interlock functions are disabled, the MX350 will display only 10
successive “Disabled” list items. If one of the interlock functions were then enabled, then
room is made on the display for the six setpoints which are now functional.
The setpoint pages are in a common format of up to twelve lines. Each line has a column
that displays the setpoint name and unit, and another column displaying the value
entered.
The Home > Setpoints > Config > CT-VT page is shown below.
Figure 13: Typical setpoints page
Diagnostics pages The diagnostic pages are divided into five sections.
• Events (event recorder data for up to 256 events)
• Stats (statistical data on the last transfer event)
• Phasors (metered phasor data)
• About (product information)
Typical diagnostic pages for Events, Stats, Phasors, and Product Information are shown
below.
3–10 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 41

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
NOTE
Figure 14: Typical Events page
Figure 15: Typical Stats page
Figure 16: Typical Phasors page
NOTE:
Voltage metering displayed on this page is L-N for a 3-phase system. L-L values are shown
on the Voltage Metering page. See the Voltage Metering section in the Actual Values
chapter of this manual.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–11
Page 42

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Control page This page is used to view the active control modes. For example, selection of primary
source, automatic vs manual initialization of transfer, etc.
Figure 17: Typical control page display
Refer to the Control chapter for details on control page functionality.
Popup windows There are three types of popup windows:
• Setpoint editor popup windows.
• Help popup windows.
• Invalid operation popup windows.
Refer to the Setpoints chapter for details on setpoint editor popup windows.
Help popup windows are initiated by pressing the HELP key. This will display help text for
the active setpoint field.
Figure 18: Typical help popup window
Invalid operation popups explain the problem and provide direction on how to rectify it.
This may also include invalid features or uninstalled options. Where a keypress is illegal
because a security passcode is required, the popup is a passcode entry dialog box.
3–12 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 43

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
CAUTION
Figure 19: Typical invalid operation popup window
Help and illegal action popup windows remain open until they are acknowledged by
clicking any soft or hard key, or until a pre-determined period of inactivity has passed.
MX350 programming techniques
To streamline the setting entry process, the graphical control panel omits non-functional
settings from the display.
CAUTION:
Settings may be changed while the Automatic Transfer switch panel associated with
the Controller is energized. However, appropriate measures must be taken to limit the
consequences of entering unintended or misunderstood setting values. Consequences
of inappropriate settings to the specific application at hand include loss of protection,
loss of control, and undesired starting or stopping.
Enumeration
setpoints
Enumeration settings select from a limited set of values (for example, enabled or disabled).
The following procedure describes how to edit an enumeration setting.
1. Use the soft-keys to select the relevant setting page.
2. Use the UP and DOWN keys to select the relevant setting field.
3. Press the ENTER key. A popup window will appear with a list of available values.
4. Use the UP and DOWN keys to select from the available values. If there are more than
seven available values, then an arrow indicator will appear on the lower right of the
popup to indicate additional selections.
5. Press the ENTER key when complete to exit the edit sequence. The selection will be
automatically saved.
6. Press Esc to cancel the edit and leave the setpoint unchanged.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–13
Page 44

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Figure 20: Enumeration setpoint editing
Numeric setpoints Numeric setpoints accept a numerical value within a specific range. The numeric setpoint
editor is a numeric input panel, with the current value shown on the number display. The
minimum, maximum, step, and default values are shown on the left of the keypad, and the
label of the setpoint being edited is displayed on the menu bar of the setpoint editor.
Figure 21: Numeric setpoint editor window
The navigational soft keys change the numeric key in focus, which is highlighted in orange.
There are also five functional soft-buttons in the popup window.
• BkSpc: This key performs the backspace function, clearing the last digit or decimal
from the display.
• CLR: This key clears the field’s value from the display
• Default: This key returns the setpoint value to its default value.
• OFF: This key disables the setpoint and is visible only for setpoints that can be
disabled.
In order to activate the functions offered by these buttons, the user has to highlight the
appropriate button and press "Select".
The UP and DOWN front panel keys can also be used to increment and decrement the
setpoint by its step value. Clicking the ENTER key verifies the displayed value. If the
setpoint value is valid, it is stored as the new setpoint value and the editor is closed.
Otherwise, an error statement is displayed and the Default soft-button is brought to focus.
Clicking HOME before the value is stored cancels the edit sequence and recalls the home
page.
The following procedure describes how to edit a numeric setting.
1. Use the navigation keys to select the relevant setting page.
2. Use the navigation keys to select the relevant setting field.
3–14 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 45

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL
3. Press the ENTER key to open the numeric setpoint editor.
4. Use the navigational soft-keys to highlight the first digit of the new setpoint value.
5. Press the SELECT soft-key to select the highlighted digit .
6. Use the navigational soft-keys to highlight the next digit, then press SELECT.
7. When the new value has been fully entered, press the ENTER key to store the value
and close the window.
Alphanumeric
setpoints
Alphanumeric setpoints accept any alphanumeric value of a specified size and are
generally used for labeling and identification purposes. When an alphanumeric setpoint is
selected, the MX350 displays an alphanumeric setpoint editor window.
Figure 22: Alphanumeric setpoint editor
A flashing underline marks the current character. The “<” and “>” soft-keys shift the cursor
left and right. When the cursor is at the extreme right hand side of the field and the field
has not reached its maximum length of string input, the “>” key shifts the cursor to the
right and sets the selected character to the space character. Up to 20 characters can be
stored for alphanumeric setpoints. A long click of the “<” and “>” soft keys move the cursor
to the first or last character in the string.
The up and down soft-keys increment and decrement the selected character through the
character set. A long click of the up or down soft-keys sets the selected character to “a”
and “Z”, respectively. The shift soft-key toggles the case of the character set. Pressing
ENTER stores the selected value, while pressing ESC cancels the editing sequence and
closes the popup editor.
The following procedure describes how to edit an alphanumeric setting.
1. Use the soft-keys to select the relevant setting page.
2. Use the ARROW soft-keys to select the relevant alphanumeric setpoint field.
3. Press the ENTER key to open the alphanumeric setpoint editor.
4. The first character of the alphanumeric setting value will be marked with a flashing
cursor (underline).
5. Use the UP, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT, SHIFT, and SPACE soft-keys to change the indicated
character.
6. Use the LEFT and RIGHT ARROW soft-keys to select and change more characters.
7. Press the ENTER key when complete to exit the edit sequence. The changes are
automatically saved.
Date, time, and IP
entry
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–15
The entry process for date, time, and IP setpoints follows the same convention as numeric
setpoints, where the day, month, year, hour, minute, second, and each octet of the IP
address are entered as separate fields. Input verification is performed for all fields of the
setpoint when the ENTER key is pressed. As these are standard formats, the minimum,
maximum and step value displays are removed. For date and time setpoints, a format
string of DD/MM/YYYY or HH:MM:SS is included as a part of the setpoint label for reference
when entering a new value.
Page 46

GRAPHICAL CONTROL PANEL CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Figure 23: IP address setpoint editor
Security access There are three levels of security access allowing write access to setpoints, lockout reset,
and firmware download. When there are no pop-ups present, a sustained press on the ESC
key clears the security passcode. When operations are performed that require a higher
level of security, a passcode entry dialog box automatically opens (for example, in entering
factory page at read only security access).
Figure 24: Password entry dialog box
The encrypted key information appears only when the current security access level is 0.
3–16 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 47

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
EnerVista™ MX350 Setup Software
Although settings can be entered manually using the control panel keys, a PC can be used
to download values through the communications port . The EnerVista™ MX350 Setup
software is available from GE Multilin to make this as convenient as possible. With
EnerVista™ MX350 Setup running, it is possible to:
• Program and modify settings
• Load and save setting files to and from a disk
• Read actual values
• Monitor status
• Read pre-trip data and event records
• Get help on any topic
• Upgrade the MX350 firmware
The EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software allows immediate access to all MX350 features
with easy to use pull down menus in the familiar Windows environment. This section
provides the necessary information to install EnerVista™ MX350 Setup upgrade the relay
firmware, and write and edit setting files.
The EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software can run without a MX350 connected to the
computer. In this case, settings may be saved to a file for future use. If an MX350 is
connected to a PC and communications are enabled, the MX350 can be programmed from
the setting screens. In addition, measured values, status and trip messages can be
displayed with the actual value screens.
Software requirements
The following requirements must be met for the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software.
• Microsoft Windows™ XP / 2000 is installed and running properly.
• At least 20 MB of hard disk space is available.
• At least 128 MB of RAM is installed.
The EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software can be installed from either the GE EnerVista CD or
the GE Multilin website at http://www.GEmultilin.com.
Troubleshooting the USB driver
When the Setup Software is installed on the Windows 2000 or XP operating system, and
the device is power recycled while the native USB port is still connected to the PC, the USB
driver in the PC Program may get lost and the setup software may fail to recognize the USB
device. If this happens, the ‘MX350 USB Serial Emulation (COM #)’ will be missing in the
Setup Software’s Device Setup window. To overcome the problem:
1. Remove the USB cable from the native port of the device.
2. Wait for 20 Seconds and connect the cable back to the native port of the device.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–17
Page 48

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
3. Check the Setup Software for the availability of the USB Device on the Device setup
Window. It will automatically reappear on the ‘USB Device’ list as ‘MX350 USB Serial
Emulation (COM #)’ as shown in the image below.
4. If the USB Device is not recognized automatically in the Setup Software, repeat the
same procedure 2 or 3 times until the PC Program recognizes the USB device (and
‘MX350 USB Serial Emulation (COM #)’ reappears in dropdown of ‘USB Device’ list).
5. If problem still persists, uninstall the USB driver from Computer’s ‘Device Manager ’
under tree-branch modems from the Installation folder. To uninstall it, right click on
MX350 USB Serial Emulation and select Uninstall.
3–18 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 49

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
6. After the uninstall, remove the USB cable from the Device’s native USB port, wait for at
least 10 Seconds and reconnect it.
7. Now the ‘Found New Hardware Wizard’ will open, select No, not this time and press
the Next button.
8. Select Install the software automatically (Recommended) and press the Next
button.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–19
Page 50

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
9. Press Continue Anyway.
10. At the end press Finish.
11. Check in the Setup Software for the availability of the USB Device on the Device setup
Window. Now the device will reappear on the ‘USB Device’ list.
For the current version, the USB driver can not be installed on Windows Vista Operating
System and communication to the Device via the Native USB port is not supported.
Installing the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software
Connecting EnerVista MX350 Setup to the relay
Configuring serial
communications
After ensuring the minimum PC requirements indicated earlier, use the following procedure
to install the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software from the enclosed GE EnerVista CD.
1. From the CD, run the MX350Setup.exe file on your computer.
2. Follow the installation instructions to install the EnerVista software on the local PC.
3. When installation is complete, start the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup application.
Before starting, verify that the cable is properly connected to either the USB port on the
front panel of the device (for USB communications) or to the Serial port on the rear of the
device. This example demonstrates a Serial connection.
1. Install and start the latest version of the software (available from the GE EnerVista
CD). See the previous section for the installation procedure.
2. Click on the Device Setup button to open the Device Setup window and click the Add
Site button to define a new site.
3. Enter the desired site name in the "Site Name" field. If desired, a short description of
the site can also be entered. In this example, we will use “Substation 1” as the site
name.
4. The new site will appear in the upper-left list in the window.
5. Click the Add Device button to define the new device.
6. Enter the desired name in the "Device Name" field and a description (optional) of the
device.
7. Select “Serial Device” from the Interface drop-down list.
3–20 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 51

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
Using the Quick
Connect feature
8. Select the relay as the USB device.
9. Click the Read Order Code button to connect to the device and upload the order
code.
10. Click OK when the relay order code has been received. The new device will be added
to the Site List window (or Online window) located in the top left corner of the main
window.
The Site Device has now been configured for USB communications. Proceed to Connecting
to the Relay below, to begin communications.
The Quick Connect button can be used to establish a fast connection through the front
panel USB port of a relay. The following window will appear when the QuickConnect
button is pressed:
As indicated by the window, the "Quick Connect" feature can quickly connect the software
to a front port if the USB is selected in the interface drop-down list . Select " Relay" and
press the Connect button.
When connected, a new Site called “Quick Connect” will appear in the Site List window.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–21
Page 52

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
The Site Device has now been configured via the Quick Connect feature for either USB or Serial communications. Proceed to Connecting to the Relay below, to begin communications.
Connecting to the
relay
Now that the communications parameters have been properly configured, the user can
easily communicate with the relay.
1. Expand the Site list by double clicking on the site name or clicking on the «+» box to
list the available devices for the given site.
2. Desired device trees can be expanded by clicking the «+» box. The following list of
headers is shown for each device:
Device Definition
Setpoints
Values
Diagnostics
Device Summary
Status
Exerciser
Maintenance.
3. Expand any list item and double click on any item contained in the expanded list to
open that item, as shown below:
4. The window related to that item will open with a corresponding status indicator tab on
the lower left of the EnerVista SR3 Setup window.
5. If the status indicator is red, verify that the seria or USB cable is properly connected to
the relay, and that the relay has been properly configured for communications (steps
described earlier).
The "item" settings can now be edited, printed, or changed. Other windows can be
displayed and edited in a similar manner. These windows can be arranged, and resized at
will.
3–22 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 53

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
Working with setpoints and setpoint files
Engaging a device The software may be used in on-line mode (relay connected) to directly communicate with
a relay. Communicating relays are organized and grouped by communication interfaces
and into sites. Sites may contain any number of relays selected from the product series.
Entering setpoints The System Setup page will be used as an example to illustrate the entering of setpoints. In
this example, we will be changing the current sensing setpoints.
1. Establish communications with the relay.
2. Select the Setpoint > Configure > CT-VT menu item.
3. Select the CT Primary setpoint by clicking anywhere in the parameter box. This will
display three arrows: two to increment/decrement the value and another to launch
the numerical keypad.
4. Clicking the arrow at the end of the box displays a numerical keypad interface that
allows the user to enter a value within the setpoint range displayed near the top of the
keypad: Click = to exit from the keypad and keep the new value. Click on X to exit from
the keypad and retain the old value.
5. For setpoints requiring non-numerical pre-set values (e.g. CT Primary below), clicking
anywhere within the setpoint value box displays a drop-down selection menu arrow.
Select the desired value from this list.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–23
Page 54

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
6. For setpoints requiring an alphanumeric text string (e.g. "relay name"), the value may
be entered directly within the setpoint value box.
7. In the Setpoint > Config > CT-VT dialog box, click on Save to save the values into the .
Click YES to accept any changes and exit the window. Click Restore to retain previous
values. Click Default to restore Default values.
File support Opening any file will automatically launch the application or provide focus to the already
opened application. If the file is a Settings file (has a ‘SR3’ extension) which had been
removed from the Settings List tree menu, it will be added back to the Settings List tree.
New files will be automatically added to the tree.
Using setpoints files The software interface supports three ways of handling changes to relay settings:
• In off-line mode (relay disconnected) to create or edit relay settings files for later
download to communicating relays.
• Directly modifying relay settings while connected to a communicating relay, then
saving the settings when complete.
• Creating/editing settings files while connected to a communicating relay, then saving
them to the relay when complete.
Settings files are organized on the basis of file names assigned by the user. A Settings file
contains data pertaining to the following types of relay settings:
•Configure
•Operation
• Control
• Security Settings
• Modbus User Map
•FlexLogic
Factory default values are supplied and can be restored after any changes.
The MX350 displays relay setpoints with the same hierarchy as the front panel display.
Downloading and
saving setpoints files
3–24 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Setpoints must be saved to a file on the local PC before performing any firmware
upgrades. Saving Setpoints is also highly recommended before making any Setpoint
changes or creating new Setpoint files.
The Setpoint files in the window are accessed in the Files Window. Use the following
procedure to download and save Setpoint files to a local PC.
1. Ensure that the site and corresponding device(s) have been properly defined and
configured as shown in Connecting to the Relay, above.
2. Select the desired device from the site list.
3. Select the Online > Read Device Settings from Device menu item (at the top of the
page), or right-click on the device and select Read Device Settings to obtain settings
information from the device.
Page 55

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
4. After a few seconds of data retrieval, the software will request the name and
destination path of the setpoint file. The corresponding f ile extension will be
automatically assigned. Press Receive to complete the process. A new entry will be
added to the tree, in the File pane, showing path and file name for the setpoint file.
Adding setpoints files
to the environment
The software provides the capability to review and manage a large group of setpoint files.
Use the following procedure to add an existing file to the list.
1. In the files pane, right-click on Files and select the Add Existing Setting File item as
shown:
2. The Open dialog box will appear, prompting the user to select a previously saved
setpoint file. As for any other MS Windows® application, browse for the file to be
added then click Open. The new file and complete path will be added to the file list.
Creating a new
setpoints file
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–25
The software allows the user to create new setpoints files independent of a connected
device. These can be uploaded to a relay at a later date. The following procedure illustrates
how to create new setpoints files.
Page 56

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
1. In the File pane, right click on File and select the New Setpoints File item. The
following box will appear, allowing for the configuration of the setpoints file for the
correct firmware version. It is important to define the correct firmware version to
ensure that setpoints not available in a particular version are not downloaded into the
relay.
Upgrading setpoint
files to a new revision
2. Select the Firmware Version, and Order Code options for the new setpoints file.
3. For future reference, enter some useful information in the Description box to facilitate
the identification of the device and the purpose of the file.
4. To select a file name and path for the new file, click the button beside the File Name
box.
5. Select the file name and path to store the file, or select any displayed file name to
replace an existing file. All MX350 setpoints files should have the extension ‘M30’ (for
example, ‘ExerciserStatus.M30’).
6. Click OK to complete the process. Once this step is completed, the new file, with a
complete path, will be added to the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software environment.
It is often necessary to upgrade the revision for a previously saved setpoint file after the
firmware has been upgraded. This is illustrated in the following procedure:
1. Establish communications with the relay.
2. Select the Online > Device Setup menu item and record the Firmware Revision from
the Device Setup window.
3. Load the setpoint file to be upgraded into the EnerVista SR3 Setup environment as
described in the section, Adding Setpoints Files to the Environment.
4. In the File pane, right-click on the saved setpoint file.
5. Note the File Version of the setpoint file. If this version is different from the Firmware
Revision noted in step 2, select a New File Version that matches the Firmware Revision
from the pull-down menu.
3–26 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 57

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
6. For example, if the firmware revision is MAMO3MA120.000 (Firmware Revision 1.20)
and the current setpoint file revision is 1.10, change the setpoint file revision to “1.2x”.
Printing setpoints and
actual values
7. Enter any special comments about the setpoint file in the "Description" field.
8. Select the desired firmware version from the "New File Version" field.
9. When complete, click OK to convert the setpoint file to the desired revision. See
Loading Setpoints from a File below, for instructions on loading this setpoint file into
the MX350.
The software allows the user to print partial or complete lists of setpoints and actual
values. Use the following procedure to print a list of setpoints:
1. Select a previously saved setpoints file in the File pane or establish communications
with a device.
2. From the main window, select the Offline > Export Settings File menu item.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–27
Page 58

ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
3. The Print/Export Options dialog box will appear. Select Settings in the upper section
and select either Include All Features (for a complete list) or Include Only Enabled
Features (for a list of only those features which are currently used) in the filtering
section and click OK.
4. The process for Offline > Print Preview Settings File is identical to the steps above.
5. Setpoint lists can be printed in the same manner by right clicking on the desired file (in
the file list) or device (in the device list) and selecting the Print Device Information or
Print Settings File options.
Printing actual values
from a connected
device
3–28 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
A complete list of Actual Values can also be printed from a connected device with the
following procedure:
1. Establish communications with the desired device.
2. From the main window, select the Online > Print Device Information menu item.
3. The Print/Export Options dialog box will appear. Select Actual Values in the upper
section and select either Include All Features (for a complete list) or Include Only
Enabled Features (for a list of only those features which are currently used) in the
filtering section and click OK.
Actual Values lists can be printed in the same manner by right clicking on the desired
device (in the device list) and selecting the Print Device Information option.
Page 59

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER ENERVISTA™ MX350 SETUP SOFTWARE
CAUTION
Loading setpoints
from a file
CAUTION:
An error message will occur when attempting to download a setpoint file with a
revision number that does not match the relay firmware. If the firmware has been
upgraded since saving the setpoint file, see Upgrading Setpoint Files to a New Revision,
above, for instructions on changing the revision number of a setpoint file.
The following procedure illustrates how to load setpoints from a file. Before loading a
setpoints file, it must first be added to the environment as described in the section, Adding
Setpoints Files to the Environment.
1. Select the previously saved setpoints file from the File pane of the EnerVista™ MX350
Setup software main window.
2. Select the Offline > Edit Settings File Properties menu item and verify that the
corresponding file is fully compatible with the hardware and firmware version of the
target relay. If the versions are not identical, see Upgrading Setpoint Files to a New
Revision, above, for details on changing the setpoints file version.
3. Right-click on the selected file and select the Write Settings File to Device item.
4. Select the target relay from the list of devices shown and click Send. If there is an
incompatibility, an "Incompatible Device" error message will occur:
If there are no incompatibilities between the target device and the settings file, the data
will be transferred to the relay. An indication of the percentage completed will be shown at
the bottom of the main window.
Upgrading relay firmware
For firmware updates contact GE Zenith Service Group at 1-800-637-1738 x3.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–29
Page 60

POWER ANALYSIS CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
Power analysis
Waveform capture
The EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software can be used to capture waveforms (or view trace
memory) from the MX350 at the instance of a trip, activation of a virtual output, or other
conditions. A maximum of 64 cycles (32 samples per cycle) can be captured and the trigger
point can be adjusted to anywhere within the set cycles.
If the trigger mode is set to "ONE-SHOT," then the trace memory is triggered once; if it is set
to "RETRIGGER," then it automatically retriggers and overwrites the previous data.
The following waveforms can be captured:
• Phase A, B, and C currents (Ia, Ib, and Ic)
• Ground/Neutral current (Ig)
• Phase A-N, B-N, and C-N voltages (Van, Vbn, and Vcn) if wye-connected. Phase A-B, BC, and C-A voltages (Vab, Vbc, and Vca) if delta-connected.
• Digital data for output relays and contact input states.
1. With EnerVista™ MX350 Setup running and communications established, select the
Diagnostics > Waveform menu item to open the Waveform Capture setup window.
2. Click on Trigger Waveform to trigger a waveform capture. Waveform file numbering
starts with the number zero in the MX350, so that the maximum trigger number will
always be one less than the total number of triggers available.
3. Click on the Save to File button to save the selected waveform to the local PC. A new
window will appear, requesting the file name and path. One file is saved as a
COMTRADE file, with the extension "CFG." The other file is a "DAT" file, required by the
COMTRADE file for proper display of waveforms
3–30 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 61

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER POWER ANALYSIS
4. To view a previously-saved COMTRADE file, click the Open button and select the
corresponding COMTRADE file.
5. To view the captured waveforms, click on the Launch Viewer button. A detailed
Waveform Capture window will appear as shown below.
6. The red vertical line indicates the trigger point.
7. The date and time of the trigger is displayed at the top left corner of the window. To
match the captured waveform with the event that triggered it, make note of the time
and date shown in the graph. Then find the event that matches the same time and
date in the event recorder. The event record will provide additional information on the
cause and the system conditions at the time and date of the event.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–31
Page 62

POWER ANALYSIS CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
8. From the window main menu bar, press the Preference button to open the COMTRADE
Setup page, in order to change the graph attributes.
9. The following window will appear:
3–32 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 63

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER POWER ANALYSIS
10. Change the color of each graph as desired, and select other options as required, by
checking the appropriate boxes. Click OK to store these graph attributes and to close
the window. The Waveform Capture window will reappear with the selected graph
attributes available for use.
11. To view a vector graph of the quantities contained in the waveform capture, press the
Vector Display button to display the following window:
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–33
Page 64

POWER ANALYSIS CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
12. Use the graph attribute utility described in step 10, to change the vector colors.
Data logger
The data logger feature is used to sample and record up to ten actual values at a
selectable interval. The datalogger can be run with Continuous mode Enabled, which will
continuously record samples until stopped by the user; or with Continuous mode Disabled,
which will trigger the datalog once without overwriting previous data.
3–34 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 65

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER POWER ANALYSIS
Setting Parameter
Sample Rate 1 Second
Continuous Mode Disabled
Data Log Trigger Position 25%
Data Log Trigger Source None
Channel 1 Source Phase A Current
Channel 2 Source Phase B Current
Channel 3 Source Phase C Current
Channel 4 Source Disabled
Channel 5 Source Disabled
Channel 6 Source Disabled
Channel 7 Source Disabled
Channel 8 Source Disabled
Channel 9 Source Disabled
Channel 10 Source Disabled
Viewing and saving of the Datalogger is performed as follows:
1. With EnerVista™ MX350 Setup running and communications established, select the
Diagnostics > Datalog menu item to open the datalog setup window:
2. If Continuous mode is enabled, click on Stop to stop the datalog
3. Click on the Save to File button to save the datalog to the local PC. A new window will
appear requesting for file name and path.
4. One file is saved as a COMTRADE file, with the extension ‘CFG’. The other file is a DAT
file, required by the COMTRADE file for proper display of data.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–35
Page 66

POWER ANALYSIS CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
5. To view a previously saved COMTRADE file, click the Open button and select the
corresponding COMTRADE file.
6.
7. To view the datalog, click the Launch Viewer button. A detailed Datalog window will
appear as shown below.
3–36 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 67

CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER POWER ANALYSIS
8. The method of customizing the datalog view is the same as the Waveform Capture
described above.
9. The datalog can be set to capture another buffer by clicking on Run (when Continuous
mode is enabled), or by clicking on Release (when Continuous mode is disabled).
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 3–37
Page 68

POWER ANALYSIS CHAPTER 3: INTERFACING WITH THE MX350 AT CONTROLLER
3–38 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 69

Digital Energy
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 4: Actual values
Actual values
Actual values overview
Measured values, maintenance and fault analysis information are accessed in the actual
values screens. Actual values may be accessed via one of the following methods.
• Through the graphical control panel, using the keys and display.
• With the EnerVista™ MX350 Setup software supplied with the relay.
• Through the RS485 or Ethernet ports and a PLC/SCADA system running user-written
software.
Actual value messages are organized into logical groups, or pages, for easy reference.
Pressing the Values soft-key displays the actual values summary window. All phase
voltages for both sources as well as power, apparent power, reactive power, and power
factor for the load are shown in the summary window.
Figure 1: Actual values summary window
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 4–1
Page 70

METERING CHAPTER 4: ACTUAL VALUES
NOTE
Metering
Current metering
Select the Values > Amps page to display the metered current for all three phases and
ground/neutral.
Figure 2: Current metering page
Voltage metering
Select the Values > Volts page to display the metered voltage for all three phases of both
sources, as well as their respective frequencies.
Figure 3: Voltage metering page
NOTE:
Voltage metering displayed on this page is L-L for a 3-phase system. L-N values are shown
on the Phasor page. See the Phasor section in the Diagnostics chapter of this manual.
4–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 71

CHAPTER 4: ACTUAL VALUES METERING
Power metering
Select the Values > Power page to display the power and energy metering values.
Figure 4: Power metering display
PQ metering
Select the Values > PQ > Summary page to display the metered power quality values.
Figure 5: Temperature metering page
From the Values > PQ > Summary page the user can access detailed information screens
for the voltage harmonics of Source 1, and Source 2, as well as the current harmonics of
the switch load. A typical page for the voltage harmonics of Source 2 can be seen in the
figure below.
Figure 6: Source 2 voltage harmonics
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 4–3
Page 72

STATUS CHAPTER 4: ACTUAL VALUES
Status
The MX350 status messages are categorized as alarm, or status messages.
Status messages
Figure 7: Typical status message display
Color indicates message type:
• Red Triangle = Alarm
• Orange Square = Status
• Black Text = Information Message
Messages can have an associated countdown timer.
Select the Status > Msg page to display a list of Status messages. Trips, alarms, and
control messages are displayed as Status messages. The up and down keys can be used to
scroll through large lists of Status messages.
Input and output status
Select the Status > Inputs page to display a list of the current state of each input. Similarly,
selects the Status > Outputs page to display a list of the current state of each output.
Figure 8: Typical input status message page
4–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 73

CHAPTER 4: ACTUAL VALUES STATUS
System Page
Shows the communication status of configuration interfaces (serial and Ethernet)..
Figure 9: Typical system page
Flex Page
Shows the status of Flex engine and the number of 512 lines in use.
Figure 10: Typical flex page
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 4–5
Page 74

STATUS CHAPTER 4: ACTUAL VALUES
4–6 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 75

Digital Energy
CAUTION
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 5: Setpoints
CAUTION:
Setpoints
Great care has to be used when switching the standard mode of operation to “Delayed
Transition”. In this mode, the controller will not synchronize the two sources.
Adequate time delay for the DW and DT timers has to be selected to make sure any
rotating loads have enough time to coast to a stop before selecting the Delayed
Transition mode. If this is not taken into account, severe damage to rotating
equipment can occur!
Understanding setpoints
Any of the ATS setpoints may be viewed or altered by pressing the Setpoints soft-key.
Setpoints data is divided into four pages.
• Configuration page: Information about the ATS configuration as well as system setup,
inputs, outputs, communications, CTs, and VTs, events, and data log.
• Operation page: Information about the two power sources, such as failure points for
voltage and frequency, and failure time delays.
• Control page: Operator access to different modes of operation.
• Security page: Information about the security and password features.
Press the Setpoint soft-key to scroll through the setpoints pages. When pressed for the
first time, the following screen is displayed.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–1
Page 76

UNDERSTANDING SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
CAUTION
Figure 1: Setpoints home page
The soft-keys on the Home > Setpoints page open pages two levels down, since the pages
immediately below this page are blank. For example, the Config soft-key opens the Home
> Setpoints > Config > ATS page.
The pages containing setpoint fields, except for the inputs and outputs pages, are in a
common format. This is a simple tabular format with two columns: setpoint name and
units, and setpoint value. Setpoints for features that are not enabled are omitted from the
page.
CAUTION:
Setpoints may be changed while the ATS is in operation; however it is not
recommended to change parameters while the ATS load is fed from Source 2.
Setpoints will remain stored indefinitely in the internal non-volatile memory even when
control power to the is removed. Protection parameters are based on the entered data.
This data must be complete and accurate for the given system for reliable protection and
operation of the ATS.
Setpoint text abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in the setpoints pages.
• A, Amps: amperes
•AUX: auxiliary
• COM, Comms: communications
•CT: current transformer
• GND: ground
•Hz: Hertz
• MAX: maximum
• MIN: minimum
• SEC, s: seconds
• UV & U/V: undervoltage
•VT: voltage transformer
•Ctrl: control
• Hr & hr: hour
• UTC: co-ordinated universal time
• ops: operations
5–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 77

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
NOTE
Configuration setpoints
The configuration setpoints contain data on ATS configuration as well as system setup,
inputs, outputs, communications, CTs, and VTs. The following sub-pages are available.
• ATS (setpoints related to ATS configuration).
• CT-VT (setpoints related to CT and VT configuration).
• Inputs (setpoints related to digital input conf iguration)
• Outputs (setpoints related to digital output configuration)
• Comms (setpoints related to communications configuration)
• System (setpoints related to MX350 system configuration)
• Events (setpoints related to the event recorder)
• Counters (setpoints related to the digital counters)
ATS setpoints
The MX350 can control the following types of transfer switch:
1. Standard (Open) Transition (with or without bypass panel)
2. Delayed Transition (with or without bypass panel)
3. Closed Transition (with or without bypass panel)
The home screen tells the user for which application a particular MX350 is suitable. The
figure below shows the home screen for a Closed Transition type controller.
NOTE:
It is important not to confuse the type of ATS being controlled, with the mode in which it is
being operated. For example, a Closed Transition type switch can be operated in Closed
Transition Mode or in Delayed Transition Mode.
Select the Home > Setpoints > Config > ATS page to edit the ATS data settings.
Figure 2: Closed Transition home screen
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–3
Page 78

CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
ATS types
The following is a brief description of how each type of switch works in a typical setup. i.e.
S1 is utility power and S2 is engine generator power:
Name on Status/
Outputs Screen
SCR-N S1 Sol Relay Connect load to S1 Yes Yes
SCR-NO S1 Delay Relay Disconnect load from S1 N/A Yes
SCR-E S2 Sol Relay Connect load to S2 Yes Yes
SCR-EO S2 Delay Relay Disconnect load from S2 N/A Yes
Standard transition SOURCE 1 POWER FAILURE:
When the Source 1 voltage or frequency has fallen below the values as set up in the
Setpoints > Operations > S1 Settings screen, the controller initiates the P timer (engine
start delay timer). Upon the completion of the P time delay, an Engine Start signal is sent to
Source 2, typically an engine generator set. When frequency and voltage of S2 reach the
values as set up in the Setpoints > Operations > S2 Settings screen, the W timer (time
delay to S2) begins timing. The W time delay ensures that source 2 is stable before actually
transferring to this source. If desired, the operator can bypass this timer from the Status
screen, or through a remote signal. After the W time delay, the MX350 energizes SCR-E to
move the switch to the S2 position, transferring the load to Source 2.
SOURCE 1 POWER RESTORATION:
When Source 1 is recovering and reaches the presets as set up in the Setpoints >
Operations > S1 Settings screen, the controller initiates a re-transfer to Source 1. In order
to ensure that the utility voltage and frequency are stable before transferring back to
Source 1, the delay to Source 1 (T) timer begins to time for a period of time as set up by the
user, typically set to 30 minutes. If the user wishes to re-transfer before the T timer has
expired, he or she can highlight the timing message on the Status screen and bypass the
timer by depressing the Bypass soft key. When the T timer has timed out or the Bypass key
has been depressed, the ATS will transfer the load back to Source 1.
The controller maintains the engine start signal for the time period specified as the U timer
(delay to stop engine) in order to ensure proper cooling of the engine before shutting it
down. If the operator desires to turn off the engine before the U timer has expired, he can
highlight the timing message on the Status screen and bypass the timer by depressing the
Bypass soft key. When the U timer has timed out or the Bypass key has been depressed,
the engine start signal will be removed, causing the engine to shut down.
Associated Function Standard/Open
Transition
Delay/Closed
Transition
Delayed transition SOURCE 1 POWER FAILURE:
When the Source 1 voltage or frequency has fallen below the values as set up in the
Setpoints > Operations > S1 Settings screen, the controller initiates the P timer (engine
start delay timer). Upon the completion of the P time delay, an Engine Start signal is sent to
Source 2, typically an engine generator set. When frequency and voltage of S2 reach the
values as set up in the Setpoints > Operations > S2 Settings screen, the W timer (time
delay to S2) begins timing. The W time delay ensures that source 2 is stable before actually
transferring to this source. If desired, the operator can bypass this timer from the Status
screen or through a remote signal. After the W time delay, the MX350 energizes SCR-NO to
move the switch to the open position, where the load is connected to neither source.
Once the switch is in the open position, the delay to Source 2 (DW) timer starts its timing
cycle. Upon completion of the DW timer, the energizes SCR-E in order to transfer the load
to source 2.
5–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 79

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
SOURCE 1 POWER RESTORATION:
When Source 1 is recovering and reaches the presets as set up in the Setpoints >
Operations > S1 Settings screen, the controller initiates a re-transfer to Source 1. In order
to ensure that the utility voltage and frequency are stable before transferring back to
Source 1, the delay to Source 1 (T) timer begins to time for a period of time as set up by the
user, typically set to 30 minutes. If the user wishes to re-transfer before the T timer has
expired, he or she can highlight the timing message on the Status screen and bypass the
timer by depressing the Bypass soft key. When the T timer has timed out or the Bypass key
has been depressed, the controller will energize SCR-EO and the ATS will move to the
open/neutral position.
Once the switch is in the open position, the delay to Source 1 (DT) timer starts its timing
cycle. Upon completion of the DT timer, the energizes SCR-N in order to transfer the load
back to Source 1.
The controller maintains the engine start signal for the time period specified as the U timer
(delay to stop engine) in order to ensure proper cooling of the engine before shutting it
down. If the operator desires to turn off the engine before the U timer has expired, he or
she can highlight the timing message on the Status screen and bypass the timer by
depressing the Bypass soft key. When the U timer has timed out or the Bypass key has
been depressed, the engine start signal will be removed, causing the engine to shut down.
Closed transition GE Zenith Controls Closed Transition Transfer Switches are designed to transfer a load
between two available sources without interrupting power to the load, i.e. in a makebefore-break type manner. The actual paralleling of the two sources typically occurs
within a time period of 100 ms.
Closed Transition Transfer Switches are designed to transfer a load between two available
sources without interrupting power to the load, i.e. in a make-before-break type manner.
The actual paralleling of the two sources typically occurs within a time period of 100 ms.
In order for the controller to consider both sources synchronized, the following criteria
have to be met:
• Phase Rotation: match
• Voltage difference: < 10%
• Phase Angle difference: < 10 degrees
• Frequency difference: < 0.2 Hz
SOURCE 1 POWER FAILURE:
When the Source 1 voltage or frequency has fallen below the values as set up in the
Setpoints > Operations S1 > Settings screen, the controller initiates the P timer (engine
start delay timer). Upon the completion of the P time delay, an Engine Start signal is sent to
Source 2, typically an engine generator set. When frequency and voltage of S2 reach the
values as set up in the Setpoints > Operations > S2 Settings screen, the W timer (time
delay to S2) begins timing. The W time delay ensures that source 2 is stable before actually
transferring to this source. If desired, the operator can bypass this timer from the Status
screen or through a remote signal. After the W time delay, the MX350 controller energizes
SCR-NO to move the switch to the open position, where the load is connected to neither
source.
Once the switch is in the open position, the delay to Source 2 (DW) timer starts its timing
cycle. Upon completion of the DW timer, the controller energizes SCR-E in order to transfer
the load to source 2.
SYSTEM TEST (S1 AVAILABLE):
When the system is performing a test , the MX350 controller sends an engine start signal to
Source 2. When frequency and voltage of S2 reach the values as set up in the Setpoints >
Operations > S2 Settings screen, the W timer (time delay to S2) begins timing. The W time
delay ensures that source 2 is stable before actually transferring to this source. If desired,
the operator can bypass this timer from the Status screen or through a remote signal.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–5
Page 80

CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
CAUTION
NOTE
Once the W timer has expired, the controller will wait until both sources are within the
allowable synchronization limits and then it will energize SCR-E to connect the load with
Source 2 while it is still connected to Source 1. Once both sources are connected to the
load, the controller will immediately energize SCR-NO and the load will be disconnected
from Source 1. The actual time during which both sources are paralleled is typically less
than 100 ms.
1. The two sources don't become synchronized within 60 seconds while attempting to
transfer to the other source.
2. If the ATS fails to disconnect from the source from which it is transferring away and
both sources remain paralleled for more than 100ms (Open Last Closed feature is
being activated).
3. The Open Last Closed feature fails and the controller issues a shunt trip command to
the generator breaker.
SOURCE 1 POWER RESTORATION:
When Source 1 is recovering and reaches the presets as set up in the
Setpoints > Operations S1 > Settings screen, the controller initiates a re-transfer to
Source 1. In order to ensure that the utility voltage and frequency are stable before
transferring back to Source 1, the delay to Source 1 (T) timer begins to time for a period of
time as set up by the user, typically set to 30 minutes. If the user wishes to re-transfer
before the T timer has expired, he or she can highlight the timing message on the Status
screen and bypass the timer by depressing the Bypass soft key. When the T timer has
timed out or the Bypass key has been depressed, the controller will wait until both sources
are within the allowable synchronization limits and then will energize SCR-N to connect the
load with Source 1 while it is still connected to Source 2. Once both sources are connected
to the load, the controller will immediately energize SCR-EO and the load will be
disconnected from Source 2. The actual time during which both sources are paralleled is
typically less than 100 ms.
The controller maintains the engine start signal for the time period specified as the U timer
(delay to stop engine) in order to ensure proper cooling of the engine before shutting it
down. If the operator desires to turn off the engine before the U timer has expired, he or
she can highlight the timing message on the Status screen and bypass the timer by
depressing the Bypass soft key. When the U timer has timed out or the Bypass key has
been depressed, the engine start signal will be removed, causing the engine to shut down.
If both sources do not synchronize within 60 seconds, the alarm light will come on, the
banner message will display "Sync Fail - Bypass Wait", and the status screen will display
the message "Sources Out of Phase". If that is the case, the user can either continue to
wait for the sources to sync at which the controller will transfer in Closed Transition mode,
or he or she can highlight the message and then press the 'Bypass' button. In that case,
the switch will transfer back in Delayed Transition mode, meaning the load will be out of
power for the time period specified as 'Delay - Neutral to Preferred Source' or 'Delay Neutral to Non-Preferred Source', respectively, on the Config/Operation/Timers screen.
CAUTION:
The user has to make sure that the values entered for 'Delay - Neutral to Preferred
Source' and/or 'Delay - Neutral to Non-Preferred Source' are sufficient to allow rotating
loads to coast to a stop. Severe dammage to connected rotating equipment can occur
if too small of a time value is selected.
NOTE:
If the ATS fails to open the source from which it is transferring away during a closed
transition transfer and both sources remain paralleled for more than 100ms, an alarm
message with be triggered, and the source that had just been connected to the load in
parallel with the other source will attempt to open once more (a.k.a the open-last-closed
feature).
5–6 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 81

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
If the sources remain paralleled for 500ms, another alarm message will be triggered. This
alarm can be programmed to trigger a programmable output which, in turn, can be used
to shunt trip, and thus disconnect, either source. If enabled and wired into the customer
circuit, the shunt trip will ensure that the two sources will not remain paralleled for an
extended period of time.
All Closed Transition type switches are equipped with an audible alarm (horn). This output
is activated when:
1. The two sources don't become synchronized within 60 seconds while attempting to
transfer to the other source.
2. If the ATS fails to disconnect from the source from which it is transferring away and
both sources remain paralleled for more than 100ms (Open Last Closed feature is
being activated).
3. The Open Last Closed feature fails and the controller issues a shunt trip command to
the generator breaker.
In order to silence the horn, the operator must navigate to the Status screen, highlight the
'Audible Alarm' message, and then press the Horn Silence softkey . Alternatively, the user
may press the ALARM RESET key located on the front panel.
Figure 3: Front Panel Alarm Reset key
The table below describes the different timers that are active during the different switch
transition types.
Chicago Transfer Alarm Panel (CTAP) option
If a switch has been ordered with the CTAP option, the Alarm light will illuminate and the
horn will sound when the load is connected to the non-preferred source. In order to
silence the horn, the operator must navigate to the Status screen, highlight the 'Audible
Alarm' message, and then press the Horn Silence softkey . Alternatively, the user may
press the ALARM RESET key (see above) located on the front panel.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–7
Page 82

CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
Common ATS setpoints
Several setpoints are dependent on the chosen ATS type. The setpoints shown below are
common for all ATS types. They are accessible as Modbus registers as well as through the
Setpnt/Config/ATS screen.
ATS name
Range: Up to 20 alphanumeric characters
Default: ATS
This setpoint specifies a name for the ATS. This name will appear with the actual values,
sequence of events record, and other reports
Load control type (for up to 6 loads - LC1 through LC6)
Range: Not Set/Elevator Pre-Signal (T3/W3)/Load Disconnect
Default: Not Set
Load control signals are used to protect certain loads during a transfer of the switch
from one active source to the other. The following picture shows the screen that is used
to activate load control outputs
.
Elevator Pre-Signal (T3/W3) contacts open prior to transfer in either direction. The user can
specify the time period during which the signal is activated. It can range from 0 seconds to
60 minutes on the Setpoints\Operation\Timers screen. Load Control outputs selected as
‘Pre Elevator Signal’ will only be activated when both sources are available.
Load Control outputs selected as type Load Disconnect will close a contact prior to the
load transfer. The operator can specify the time period during which the signal is activated
by entering the desired value as ‘Pre Load Control x (LCx) Timer’. Unlike the Elevator PreSignal, Load Disconnect signals will stay active after the load transfer has occurred for the
time specified as ‘Post Load Control x (LCx) Timer’. Timer presets are selected for each
load on the Setpoints\Operation\Timers screen and can range from 0 sec to 60 minutes.
When one or more Load Control outputs have been activated, the following will happen
during a transfer sequence with both sources available (e.g. load test):
• Immediately after the W or T timer expires, the Load Control output is energized.
• If several Load Control outputs have been selected by the user, the Load Control with
the longest ‘Pre Load Control x (LCx) Time’ is activated, followed by the one with the
second longest Pre Load Control Time, etc.
• All load control pre-timers expire at the same time. When that happens, the controller
transfers the ATS from S1 to S2 or S2 to S1.
• The Load control outputs selected as ‘Pre Elevator Signal’ are de-energized
immediately after the transfer.
• Load Control outputs for each Load Control output selected as ‘Load Disconnect’
remain energized for the time specified as ‘Post Load Control Time’ for the respective
load.
5–8 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 83

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
NOTE
NOTE
• The total time that a given Load control output is active, thus, is the sum of the ‘Pre
Load Control x (LCx) Timer’ and ‘the Post Load Control x (LCx) Timer’.
• Unlike the Elevator Pre-Signal, the Load Disconnect outputs will be energized,
regardless whether one or two sources are available, i.e. they will be activated even
during a transfer of the load due to a source failure.
Current and voltage transformers
The figure below shows the CT-VT screen that allows the user to specify the kind of CT used
in conjunction with the A card in slot E of the controller (if applicable) and the type of
connection for the voltage sensing for both sources.
Figure 4: Typical current and voltage transformer setpoints window
Valid selections for the CT are “None”, “1A secondary”, “5A secondary”, or “Direct Connect”.
If the user enters “1A secondary” or “5A secondary”, another entry field comes up to enter
the primary current of the corresponding current transformer.
This screen is also used to enter the 3 Phase voltage connection type for both Source 1 and
Source 2. Possible selections are Wye and Delta.
NOTE:
Although it is possible to enter different connection types for both sources, both wiring
schemes and selected connection type have to match. Unexpected results and possible
damage to the switch can result if this is not observed.
NOTE:
Only 5 A secondary connections are supported.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–9
Page 84

CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
NOTE
Inputs
The following figure shows the screen that lists all assignable inputs. The user can
highlight any of these input signals and hit enter to see to which available terminal input
the signal can be assigned.
Figure 5: Input configuration setpoint page
Each function can be assigned to only one input. Once an input is assigned, its status can
be monitored from the Status > Inputs screen.
NOTE:
Only inputs to L cards are user programmable, with the exception of the input terminals for
G7 and G8. These inputs are hard coded for basic ATS functions.
Outputs
The following figure shows the screen that lists all assignable outputs. The user can
highlight any of these output signals and hit enter to see to which available terminal
output terminal the signal can be assigned.
Figure 6: Output configuration setpoint page
Each function can be assigned to only one output. Once an output is assigned, its status
can be monitored from the Status > Outputs screen .
Communications setpoints
The MX350 has one RS485 serial communnicatios port supporting a subset of the Modbus
protocol.
Select the Home > Setpnts > Cfg > Comms page to edit the communications setpoints.
5–10 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 85

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
NOTE
NOTE
Figure 7: Communications setpoints page
The following setpoints are available.
Slave Address
Range: 1 to 254 in steps of 1
Default: OFF
For RS485 communications, each MX350 IED must have a unique address from 1 to 254.
Address 0 is the broadcast address detected by all IEDs in the serial link. Addresses do
not have to be sequential, but no two units can have the same address or errors will
occur. Generally, each unit added to the link uses the next higher address starting at 1.
RS485 Baud Rate
Range: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, or 115200 baud
Default: 115200 baud
This setpoint selects the baud rate for the RS485 port. The data frame is fixed at 1 start ,
8 data, and 1 stop bits, while parity is optional.
NTP IP Address
This setpoint is set to the IP address of the external clock source.
NOTE:
Setting of the NTP IP Address will not function unless Comms Security is set to Disabled.
Ethernet IP Address
Range: standard IP address format
Default: 0.0.0.0
This setpoint specifies the dedicated IP address provided by the network administrator.
NOTE:
When changing the IP address, power to the relay must be cycled in order for the new IP
address to become active.
Ethernet Subnet Mask
Range: standard IP address format
Default: 255.255.252.0
This setpoint specifies the subnet IP mask provided by the network administrator.
Ethernet Gateway Address
Range: standard IP address format
Default: 0.0.0.0
This setpoint specifies the gateway IP address provided by the network administrator.
Comms OK Evaluation
Range: Serial, Serial + Ethernet, Ethernet, All
Default: Serial
Specifies the operands for the Comms OK flag.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–11
Page 86

CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
NOTE
Comm Failure Trip
Range: Off, 5 to 25 step 5s
Default: Off
Specifies the time without comms before a trip will be generated.
Comm Failure Alarm
Range: Off, 5 to 25 step 5s
Default: Off
Specifies the time without comms before an alarm will be generated.
NOTE:
Timing delay commences 5 seconds after failure is detected.
System
The System screen lets the user select important system parameters, such as date and
time, LED light intensity, and others.
Figure 8: System screen
System trouble For relay self-test, the MX350 runs a series of self-tests, including data and program
memory integrity and program execution watchdogs. If any of these tests fail, a self-test
fault or alarm is generated depending on the value of the Self Test Action setpoint.
The following setpoints are available for the system trouble element.
Self-Test Action
Range: Fault, Alarm
Default: Fault
This setpoint defines whether a self-test failure will cause a fault or an alarm.
LED indicators These setpoints allow the user to control the display characteristics of the front panel LEDs.
The following setpoints are available.
Green LED Intensity
Range: 1 to 6
Default: 1
Selects brightness level (1 to 6) for Control Panel LEDs.
Red LED Intensity
Range: 1 to 6
Default: 1
Selects brightness level (1 to 6) for Control Panel LEDs.
5–12 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 87

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONFIGURATION SETPOINTS
DANGER
Screensaver The user can select whether or nor the screen save mode is enabled or disabled. When
enabled, the screen will change to displaying a picture of the controller after being idle for
one minute. After two minutes, the pictures will disappear and the screen will go
completely dark.
The Screensaver is enabled by default. If desired, the user can disable it in order to have
the screen visible at all times. GE discourages disabling the Screensaver in order to avoid
the screen being burned-in with a screen image.
Events
The Events screen allows the user to enable or disable certain functions relating the
recording of events as seen in the picture below.
Figure 9: Events screen
DANGER:
The event recorder can be enabled to record alarm, fault, and/or control events. It can
also be used to record changes made to the real time clock of the controller.
Zenith
The Zenith screen gives an overview of the factory setup of the MX350 controller.
Parameters on this screen are not accessible to the user. Only Zenith authorized personnel
can make changes to this screen.
Unauthorized changes made to this screen can lead to damage or destruction of the
ATS and can result in personal injuries or death!
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–13
Page 88

OPERATION SETPOINTS CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
Operation setpoints
Operation setpoints define the acceptable electrical and time limits for both Source 1 and
Source 2. These setpoints define dropout and restore values for over and undervoltage,
over and under frequency, as well as the associated time delays.
In addition, the screen for Source 2 (usually an engine generator set) has a setpoint for
Auto Loadshed Underfrequency. If this feature is enabled, a programmed output can be
used to shed part of the switch load via a downstream breaker. Also, if it is enabled the
user has to setup the variables for the corresponding parameters.
NOTE:
Additional customer wiring is required to use the Auto Load Shed feature.
5–14 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 89

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS OPERATION SETPOINTS
Figure 10: User settings table
Timers
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–15
Page 90

CONTROL CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
NOTE
NOTE
Control
General
Select the Home > Setpoints > Control > General page to edit the controller setpoints.
The general control screen allows the user to set up the following operating parameters:
• Selection of Preferred Source: typically S1 (utility power) is the preferred power source.
• Auto/Manual: An Automatic Transfer Switch can be set up for the following types of
transfers:
– Automatic (both from S1 to S2 and from S2 to S1)
– Manual S1 to S2, S2 to S1, also known as S12
– Manual S2 to S1 Only, also known as S5
NOTE:
These selections are not available on a switch that is designed for manual operation only!
Figure 11: General control configuration setpoints
Commit transfer to S2 (S13): If this option is enabled, then the switch will transfer to
Source 2 once the W timer has begun timing, even if Source 1 returns before the transfer
takes place. This feature can be used to ensure that the transfer takes place, because one
brief outage may be followed by another outage.If this option is disabled, the switch will
only transfer if the duration of the outage is still present when the W timer has expired.
This option should be disabled, when empirical data suggests that a typical outage is an
isolated event.
Preferred source The Preferred Source is the source of power that the controller will try to connect to the
load, if both sources are available. Either source 1 (generally utility power) or source 2
(generally generator power) can be selected as Preferred Source. Typically, utility power is
the preferred source to power the ATS load.
Auto-Manual select
NOTE:
5–16 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
This is not available for Manual type switches.
Three choices are presented for the Auto Manual Select:
• Automatic: In Automatic mode the MX350 will automatically control all load transfers
from S1 to S2, or from S2 to S1.
Page 91

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONTROL
NOTE
• Manual S1-S2, S2-S1 (S12): In this mode, the controller will not automatically initiate a
transfer of the load from one source to the other. It will always wait for an operator
input before automatically transferring the load.
• Manual S2-S1 Only (S5): In this mode, the controller will automatically transfer the
load from S1 to S2, e.g. when a power outage occurs. However, it will only start the retransferring from S2 to S1 after it receives an operator input, or upon Source 2 failure.
Commit transfer to S2
(S13)
Transition mode
select
NOTE:
Depending on empirical data, a customer may want to assume that a brief outage is an
isolated event or that it is likely to be followed by another outage.
If the former is the case, the user should set the 'Commit Transfer to S2' to OFF. This will
start the generator, but the ATS will not transfer to the alternate source unless the outage
is still present the generator power has reached its nominal voltage and frequency and
when the 'Delay - Transfer to Nonpreferred Source' timer (W timer) has expired.
If the latter is the case, the user should set the 'Commit Transfer to S2' to ON. This will
ensure that the ATS will transfer to the alternate source if the outage is still present when
the generator power has reached its nominal voltage and frequency and the 'Delay Transfer to Nonpreferred Source' timer (W timer) has started timing.
Applicable only to Closed Transition types of ATS
If a power outage occurs, the MX350 controller will transfer the load to the alternate
source, once that source has become available. An interruption of power cannot be
avoided in this case. However, after the utility has returned and the T time has expired,
another brief power interruption due to the load transfer from one source to the other may
be undesirable.
If this is the case, the switch needs to be operated in Closed Transition mode. The
controller will then ensure that power to the load is not interrupted during the re-transfer
process.
Closed Transition may also be desirable for testing and exercising the switch so that power
interruptions to the switch load can be avoided during the transfer.
Alternatively, the user can select Delayed Transition mode as the normal mode of
operation.
Auto load shed Auto load shed
Range: Enabled, Disabled
Default: Disabled
Source 2 (normally the generator source) can be protected with the Auto Load Shed
feature.
By factory default this feature is disabled. If desired, it can be activated by changing the
parameter ‘S2 Auto Load Shed Underfrequency Set’ on the Settings > Operations > S2
Set screen from OFF to a valid frequency set point. For example, the user could enter a
value of 59.0 Hz as the trigger point for the Auto Load Shed feature.
Once a valid set point has been entered, the user will be presented with three more entry
fields. For example, the parameters could be set up as follows:
S2 Auto Load Shed Underfrequency Set (Hz) 59.0
S2 Auto Load Shed Underfrequency Delay (s) 3
S2 Auto Load Shed Undervoltage Set (%) 95
S2 Auto Load Shed Overpower Set (%) 103
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–17
Page 92

CONTROL CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
Once this feature is enabled, the user can assign one of the configurable outputs to be
turned on when the Auto Load Shed logic in the controller senses a condition that warrants
a load shed. This is done on the setpoints > config > outputs > alarms screen. The user
can then wire this output to trip a downstream breaker.
In the example above, the Auto Load Shed output will be triggered when the frequency
falls below 59.0Hz for more than 3 seconds, when the voltage drops to less than 95% of
nominal, or when the power of the switch increases to 103% of nominal. If this output is
used to trip a downstream load breaker, a part of the load fed by the switch can be shed in
order to stabilize the generator and keep the system from failing due to overload.
If desired, the user can also bypass the load shedding due to a KW overload condition. To
do so, the ‘Auto Load Shed KW Bypass’ parameter on the Control screen needs to be
changed from ‘Disabled’ to ‘Enabled’.
The output will remain energized until the user manually clears the Load Shed on the
Status screen of the controller.
If the ATS has been ordered with the R15 option, the user will be presented with the Auto
Load Shed Mode selector on the Control screen. If the mode is set to ‘Remote’, the logic of
the controller will trip a downstream breaker as indicated above. If, however, the mode is
set to ‘Local’, the whole switch will disconnect from the S2 power source and the complete
switch load will be without power.
Auto Load Shed Mode, Auto Load Shed KW Bypass, and Auto Load Shed Reset can also be
controlled by hardwired or communicated inputs.
NOTE:
If either the hardwired user configurable input or the selector on the control switch has
been set to ‘Local’, the ATS will disconnect from the S2 power source when the controller
detects a Auto Load Shed condition. In order to have the Auto Load Shed trip a
downstream breaker, the mode selector on the Control screen has to be set to ‘Remote’
and the hardwired input (if configured by user) has to be OFF.
NOTE:
Sync phase angle limit
NOTE:
Interlock
Great care has to be used by the customer to properly apply the Auto Load Shed feature in
order to avoid unintentional power loss to the switch load.
This is applicable only to Closed Transition type switches.
With this variable, the user can select the allowable phase angle difference between
Source 1 and Source 2 for Closed Transition transfer. The default is 10°.
5–18 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 93

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS CONTROL
NOTE
The Interlock screen lets the user enable interlock functions and define their parameters.
Programmable parameters for each interlock are a corresponding name, a function (fault
or alarm), an associated time delay, and the definition of the interlocks healthy state. Once
an interlock has been enabled on this screen, a corresponding input can be set up for this
element on Setpoints\Config\Inputs screen.
The following picture shows a typical interlock setup:
Figure 12: Typical interlock setup
Alarms
The Alarms screen lets the user enable alarm features and define the setpoints for
triggering these alarms as well as associated time delays. Any configured alarm can be
linked to a programmable output on the Setpoints\Config\Outputs\Alarms screen for
customer use.
NOTE:
.
When a Power Factor alarm activates, you can determine whether it is a lead or lag Power
Factor alarm by going to either the Home > Values > Summary, or Home > Values >
Power screen.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–19
Page 94

SECURITY CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
Security
Hardware and passcode security features are designed to restrict user access. This can
deter inappropriate employee action and curtail errors. Security against hackers or others
with malicious intent should be provided by other means. Security for the external hardwired and field controls should also be externally provided as required.
Three security levels above the default level are recognized. Each security level can also be
set for passcode access. The passcode is programmed as a five-digit number, using only
digits 1 through 5. The security access levels are:
• Default - reset faults
• Level 1 - default privileges plus setpoint access
• Level 2 - level 1 privileges plus lockout reset and reset counters
• Level 3 - level 2 privileges plus factory page.
The system passcode can be entered at any time by a sustained press on the ENTER key.
displays a dialog box prompting for a new passcode. Alternatively, the systempasscode
can be entered by pressing a currently unauthorized (grayed-out) control/selection key.
This will display an error message detailing the required security levels and whether access
switch or passcode entry is required. If only a passcode is required to complete the control/
selection, the error message displays a passcode entry dialog box.
Figure 13: Passcode entry dialog box
Passcodes are automatically canceled after five minutes of inactivity. The system
passcode access can also be canceled by a sustained press on the ESC key, which clears
any previously entered passcode. Communications passcode access can be cancelled by
writing zero to the passcode register.
Figure 14: Security page
The following system security setpoints are programmed in the security page.
5–20 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 95

CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS SECURITY
NOTE
Passcode Level 1, Passcode Level 2, Passcode Level 3
Range: any five-digit number using digits 1 through 5 only or Disabled
Default value: 11111 (level 1), 22222 (level 2)
Access is granted if a passcode has been correctly entered matching the value of this
setpoint.
Access Switch Level
Range: 1, 2, 3
Default value: 1
Sets the access level provided by the access switch being closed. The contact input for
the access switch is configured on the contact inputs page.
Comms security
Range: Enabled, Disabled
Default: Disabled
Sets whether the security feature applies to the communications ports.
NOTE:
Setting of the NTD IP Address will not function unless Comms Security is set to Disabled.
Setpoint access
Range: Enabled, Disabled
Default: Enabled
Sets whether the setpoint access is allowed from the control panel display.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 5–21
Page 96

SECURITY CHAPTER 5: SETPOINTS
5–22 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 97

Digital Energy
Multilin
MX350 Automatic Transfer Control
System
Chapter 6: Exerciser
Exerciser
Information
The MX350 has a built-in exerciser that can be enabled and set up from the Exerciser\Info
screen. This feature allows the user to test the system periodically or to setup a schedule
for operating the system periodically in order to minimize utility costs.
Figure 1: Exerciser information screen
From Excerciser > Info screen the operator can access all required setup parameters for
scheduling exercises. It also indicates as to when the last exercise took place and when
the next exercise will be performed.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 6–1
Page 98

INFORMATION CHAPTER 6: EXERCISER
Setup
The Home > Exercise > Setup page displays the MX350 Exerciser parameters as shown
below.
Figure 2: Exerciser values
Exercise type and schedule can be selected on the Excerciser > Setup screen as seen
above. The mode of operation of the exerciser function can be selected with a time base
of 1 day, 1 week, 14 days, 28 days, or 365 days. With a time base of 365 days, up to 24
events can be scheduled. With all other time bases, the number of exercise events is
limited to 7.
For each exercising event, the operator enters a start time as well as a duration. The
exercise duration range is 0 to 60 minutes. In addition, the operator can select the type of
exercise as ‘Genstart and Transfer’ or as ‘Genstart only’.
NOTE:
Do not program two or more CDT events for the same time.
Test
When the ‘Gen Start only’ mode is selected, the controller will start the engine, but does not
actually transfer the load. In this mode, the readiness for the engine generator set is
tested. It does not test the functionality of the Automatic Transfer Switch itself.
In the ‘Gen Start and Transfer’ mode, the controller starts the engine and actually transfers
the load to the alternative source. This mode can be used to test the integrity of the
emergency power system. It can also be used to setup a schedule for times of operation
when the switch load will run on an alternative power supply. This could be done, e.g., to
avoid power demand charges from a utility company.
If the operator chooses to abort an ongoing test , there is a ‘Test Cancel’ button on the
Exerciser > Info screen. This screen also contains a ‘Test’ button that will take the user
directly to the Test screen.
The Home > Exerciser > Test page displays the MX350 sytem test choices, as shown
below.
From the Test screen the user can perform the same operations as performed by the
exerciser. Whereas exercises are performed automatically, a Test always has to be
initiated by the user.
6–2 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Page 99

CHAPTER 6: EXERCISER INFORMATION
NOTE
Figure 3: System test choices
There are three types of tests: Fast Test, Xfer Load, and No Xfer. The screen also provides
an ‘End’ button to abort any of the three test types.
To test the functionality of the switch the operator can use the Fast Test option. With this
kind of test, the engine generator will start and the load will transfer without going through
any time delays.
In order to simulate a load transfer as if an outage was occurring, the operator can select
the Xfer Load test. With this test type, the engine will start up and the load will transfer
according the time delay of the W timer. When the test is ended by depressing the END
button, the switch will go through the U timer delay before actually transferring back to the
utility.
NOTE:
Once a Fast Test, or a Xfer Load command has been issued and the alternative source has
reached an acceptable level of voltage and frequency, the test cannot be aborted. If the
user tries to end the test at this point, the load will still be transferred to the alternative
source, but the return sequence will immediately activated.
For testing the functionality of the engine generator set only, the operator can initiate a
NoXfer test. In this case will engine will start up, but the load will not be transferred.
MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL 6–3
Page 100

INFORMATION CHAPTER 6: EXERCISER
6–4 MX350 AUTOMATIC TRANSFER CONTROL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Loading...
Loading...