Page 1
GE
Data Sheet
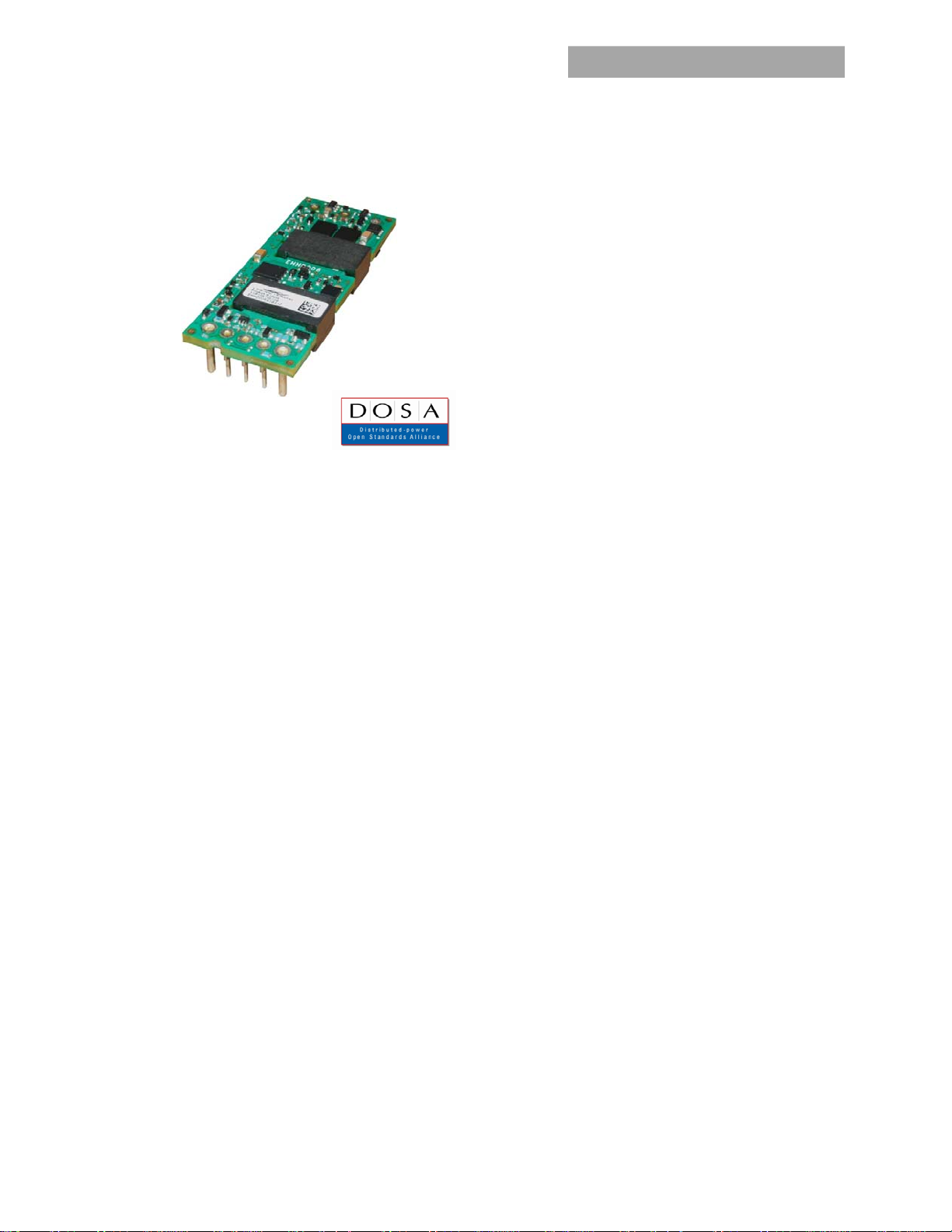
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead* Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Features
Compliant to RoHS II EU “Directive 2011/65/EU (-Z versions)
Compliant to REACH Directive (EC) No 1907/2006
Flat and high-efficiency curve
RoHS Compliant
Applications
Distributed Power Architectures
Wireless Networks
Access and Optical Network Equipment
Industrial Equipment
Options
Negative Remote On/Off logic (preferred)
Overcurrent/Overtemperature/Overvoltage protections
(Auto-restart) (preferred)
Heat plate version (-H)
Surface Mount version (-S)
Industry standard, DOSA compliant footprint
57.9mm x 22.8mm x 7.6mm
(2.28 in x 0.9 in x 0.30 in)
Low-profile height and reduced component skyline
Ultra-wide input voltage range: 18-75 V
Tightly regulated output
Remote sense
Output voltage adjust: 90% to 110% of V
Constant switching frequency
Positive remote On/Off logic
Input under/overvoltage protection
Output overcurrent and overvoltage protection
Overtemperature protection
No reverse current during output shutdown
Wide operating temperature range (-40°C to 85°C)
Suitable for cold wall cooling using suitable Gap Pad applied
directly to top side of module
#
ANSI/UL
60950-1-2011 and CAN/CSA† C22.2 No. 60950-107, Second Edition + A1:2011 (MOD), dated March 19, 2011;
and DIN EN 60950-1 (VDE
1:2006 + A11:2009 + A1:2010, DIN EN 60950-1/A12 (VDE
0805-1/A12):2011-08; EN 60950-1/A12:2011-02, IEC 609501(ed.2);am1:2009
CE mark meets 2006/95/EC directive
Meets the voltage and current requirements for ETSI 300-
132-2 and complies with and licensed for basic insulation
rating per EN60950-1
2250 Vdc Isolation tested in compliance with IEEE 802.3
PoE standards
**
ISO
9001 and ISO 14001 certified manufacturing facilities
dc
O,nom
‡
0805 Teil 1):2011-01; EN 60950-
§
¤
Description
The EHHD006A0B Series, eighth-brick, low-height power modules are isolated DC-DC converters that provide a single, precisely
regulated output voltage over an ultra-wide input voltage range of 18-75V
voltage rated for 6A
output current. The module incorporates GE’s vast heritage for reliability and quality, while also using the
dc
. The EHHD006A0B provides 12Vdc nominal output
dc
latest in technology and component and process standardization to achieve highly competitive cost. The open frame module
construction, available in both surface mount and through-hole packaging, enables designers to develop cost and space efficient
solutions. The module achieves typical full load efficiency greater than 92% at V
=24Vdc and greater than 90% at VIN=48Vdc.
IN
Standard features include remote On/Off, remote sense, output voltage adjustment, overvoltage, overcurrent and
overtemperature protection. An optional heat plate allows for external standard, eighth-brick heat sink attachment to
achieve higher output current in high temperature applications.
*
Trademark Of General Electric Company
UL is a registered trademark of Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
#
CSA is a registered trademark of Canadian Standards Association.
†
VDE is a trademark of Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker e. V.
‡
§ This product is intended for integration into en d-user equipment . All of the required procedures of end-use equipment should be followed.
¤ IEEE and 802 are registered trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated.
** ISO is a registered trademark of the Internat ional Organization of Standards
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 1
Page 2
GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses in excess of the absolute maximum ratings can cause permanent damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings
only, functional operation of the device is not implied at these or any other conditions in excess of those given in the operations
sections of the data sheet. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods can adversely affect the device reliability.
Parameter Device Symbol Min Max Unit
Input Voltage
Continuous All V
Transient, operational (≤100 ms) All V
Operating Ambient Temperature All T
(see Thermal Considerations section)
Storage Temperature All T
Altitude All
I/O Isolation Voltage (100% factory Hi-Pot tested) All
IN
IN,trans
A
stg
-0.3 80 Vdc
-0.3 100 Vdc
-40 85 °C
-55 125 °C
4000 m
2250 Vdc
* For higher altitude applications, contact your GE Sales Representative for alternative conditions of use.
Electrical Specifications
Unless otherwise indicated, specifications apply over all operating input voltage, resistive load and temperature conditions.
Parameter Device Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Operating Input Voltage All VIN 18 24/48 75 Vdc
Maximum Input Current
(VIN= V
Input No Load Current
(VIN = 48V, IO = 0, module enabled)
Input Stand-by Current All
(VIN = 48V, module disabled)
Inrush Transient All I2t 0.5 A2s
IN, min
to V
IN, max
, VO= V
O, set
, IO=I
O, max
)
All I
All I
IN,No load
I
IN,stand-by
IN
4.4 5.0 Adc
80 mA
5 8 mA
Input Reflected Ripple Current, peak-to-peak
(5Hz to 20MHz, 1μH source impedance; V
test configuration section)
Input Ripple Rejection (120Hz) All 50 dB
IN, min
to V
IN, max, IO
= I
Omax
; See
All 30 mA
p-p
CAUTION: This power module is not internally fused. An input line fuse must always be used.
This power module can be used in a wide variety of applications, ranging from simple standalone operation to an integrated part
of sophisticated power architectures. To preserve maximum flexibility, internal fusing is not included; however, to achieve
maximum safety and system protection, always use an input line fuse. The safety agencies require a fast-acting fuse with a
maximum rating of 10 A (see Safety Considerations section). Based on the information provided in this data sheet on inrush energy
and maximum DC input current, the same type of fuse with a lower rating can be used. Refer to the fuse manufacturer’s data
sheet for further information.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 2
Page 3
GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Electrical Specifications (continued)
Parameter Device Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Nominal Output Voltage Set-point
VIN= 24V to 48V IO=I
O, max
, TA=25°C)
All V
O, set
Output Voltage
(Overall operating input voltage, resistive load, and temperature
All V
O
conditions until end of life)
Output Regulation
Line (VIN=V
Load (IO=I
Temperature (T
IN, min
O, min
to V
to I
O, max
ref=TA, min
) All
IN, max
)
to T
) All
A, max
All
Output Ripple and Noise
(VIN=V
IN, min
to V
IN, max
, IO= I
O, max
, TA=T
A, min
to T
)
A, max
RMS (5Hz to 20MHz bandwidth) All
Peak-to-Peak (5Hz to 20MHz bandwidth) All
External Capacitance All C
Output Current All I
Output Current Limit Inception (Hiccup Mode )
(VO= 90% of V
O, set
)
Output Short-Circuit Current
(VO≤250mV) ( Hiccup Mode )
All
All I
O, max
I
O, lim
O, s/c
O
Efficiency
VIN=24V, TA=25°C, IO=3A, VO = 12V All η 90.0 %
VIN=24V, TA=25°C, IO=6A, VO = 12V All η 92.5 %
VIN=48V, TA=25°C, IO=3A, VO = 12V All η 90.0 %
VIN=48V, TA=25°C, IO=6A, VO = 12V All η 90.5 %
Switching Frequency All f
sw
Dynamic Load Response
(dIo/dt=0.1A/s; VIN = 24V or 48V; TA=25°C; CO>100μF)
Load Change from Io= 50% to 75% or 25% to 50% of I
o,max
Peak Deviation All V
Settling Time (Vo<10% peak deviation)
All t
pk
s
11.80 12.00 12.24 V
11.64
0
25 50 mV
75 200 mV
12.36 V
±0.2 % V
±0.2 % V
±1.0
2,000 μF
% V
dc
dc
O, set
O, set
O, set
rms
pk-pk
0 6 Adc
6.6 7.8 9.0 Adc
5 A
rms
280 kHz
3
200
% V
s
O, set
Isolation Specifications
Parameter Device Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Isolation Capacitance All C
Isolation Resistance All R
I/O Isolation Voltage (100% factory Hi-pot tested) All All
iso
iso
100
1000
2250 Vdc
pF
MΩ
General Specifications
Parameter Device Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Calculated Reliability based upon Telcordia SR-332 Issue 3: Method I
=80%I
Case 3 (I
O
Weight (Open Frame) All 19 (0.7) g (oz.)
Weight (with Heat Plate) All 30 (1.1) g (oz.)
, TA=40°C, airflow = 200 lfm, 90% confidence)
O, max
9
All FIT 169.9 10
All MTBF 5,887,341 Hours
/Hours
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 3
Page 4
GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Feature Specifications
Unless otherwise indicated, specifications apply over all operating input voltage, resistive load and temperature conditions. See
Feature Descriptions for additional information.
Parameter Device Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Remote On/Off Signal Interface
(VIN=V
Signal referenced to V
Negative Logic: device code suffix “1”
Logic Low = module On, Logic High = module Off
Positive Logic: No device code suffix required
Logic Low = module Off, Logic High = module On
Turn-On Delay and Rise Times
(IO=I
Case 1: Input power is applied for at least 1 second
then the On/Off input is set from OFF to ON
(T
Case 2: On/Off input is set to Logic Low (Module
ON) then input power is applied
(T
Output voltage Rise time (time for Vo to rise from 10%
of V
Output Voltage Overshoot – Startup
IO= I
Remote Sense Range All V
Output Voltage Adjustment Range All 90 110 % V
Output Overvoltage Protection
Overtemperature Protection – Hiccup Auto Restart
Heat Plate
Input Undervoltage Lockout All V
to V
IN, min
Logic Low - Remote On/Off Current All I
Logic Low - On/Off Voltage All V
Logic High Voltage – (Typ = Open Collector) All V
Logic High maximum allowable leakage current All I
O, max , VIN=VIN, nom, TA
= On/Off pin transition until VO = 10% of V
delay
= VIN reaches V
delay
to 90% of V
o,set
; VIN=V
O, max
Turn-on Threshold
Turn-off Threshold
; open collector or equivalent,
IN, max
terminal)
IN-
on/off
on/off
on/off
on/off
-0.7
2.5
0.15 mA
0.6 Vdc
6.7 Vdc
25 μA
= 25oC)
IN, min
until Vo=10% of V
IN, min
)
o, set
to V
IN, max
)
O, set
All T
All T
)
O,set
All T
, TA = 25 oC
All
All V
Open
frame
Heat
Plate
— 12 — msec
delay
— 25 35 msec
delay
rise
SENSE
O, limit
T
ref
T
ref
UVLO
— 15 25 msec
— 3 % V
10 % V
13.8
16.5 Vdc
135 OC
120 OC
17 18 V
14 15.5 16 Vdc
dc
O, set
O, set
O, set
Hysteresis 1 2.0 Vdc
Input Overvoltage Lockout All V
Turn-on Threshold 76 77
Turn-off Threshold
Hysteresis 1 2
OVLO
Vdc
Vdc
79 81 Vdc
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 4
Page 5
GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
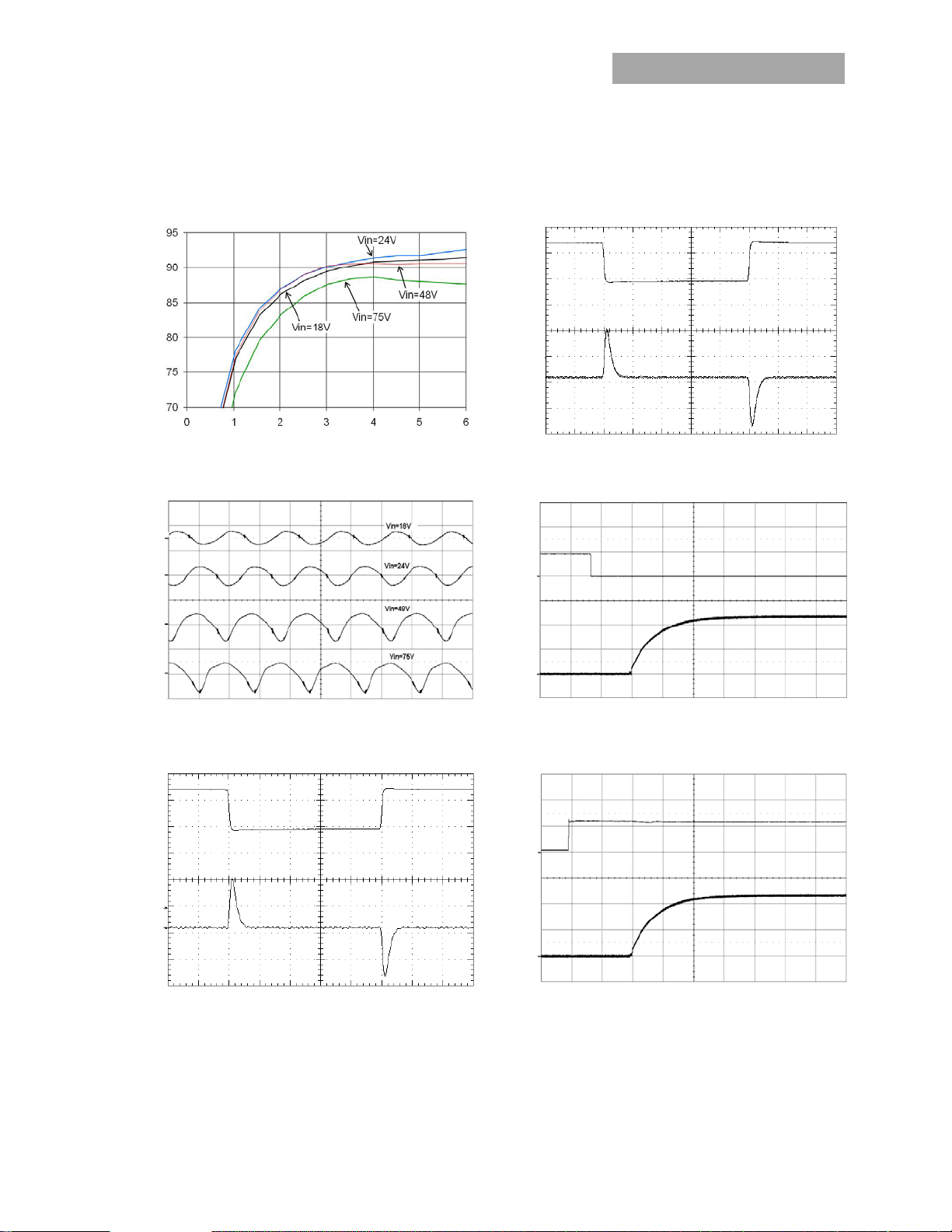
Characteristic Curves
The following figures provide typical characteristics for the EHHD006A0B (12.0V, 6A) at 25oC. The figures are identical for either
positive or negative remote On/Off logic.
Io(A) (1A/div)
(V) (200mV/div)
EFFICIENCY, (%)
OUTPUT CURRENT, IO (A)
Figure 1. Converter Efficiency versus Output Current. Figure 4. Transient Response to 0.1A/µS Dynamic Load
O
OUTPUT VOLTAGE OUTPUT CURRENT
V
TIME, t (200µs/div)
Change from 50% to 75% to 50% of full load, Vin=48V,
>100μF.
C
O
(V) (100mV/div)
O
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
V
TIME, t (2s/div)
Figure 2. Typical output ripple and noise (I
(V) (200mV/div) Io(A) (1A/div)
O
V
OUTPUT VOLTAGE OUTPUT CURRENT
TIME, t (200µs/div)
o = Io,max).
Figure 3. Transient Response to 0.1A/µS Dynamic Load Change
from 50% to 75% to 50% of full load, Vin=24V, C
>100μF.
O
(V) (5V/div)
On/Off
(V) (5V/div) V
O
OUTPUT VOLTAGE On/Off VOLTAGE
V
TIME, t (10ms/div)
Figure 5. Typical Start-up Using Remote On/Off, negative
logic version shown (V
(V) (20V/div)
IN
(V) (5V/div) V
O
OUTPUT VOLTAGE INPUT VOLTAGE
V
IN = 24V or 48V, Io = Io,max).
TIME, t (10ms/div)
Figure 6. Typical Start-up Using Input Voltage (V
o = Io,max).
I
IN
= 24V,
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 5
Page 6
GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
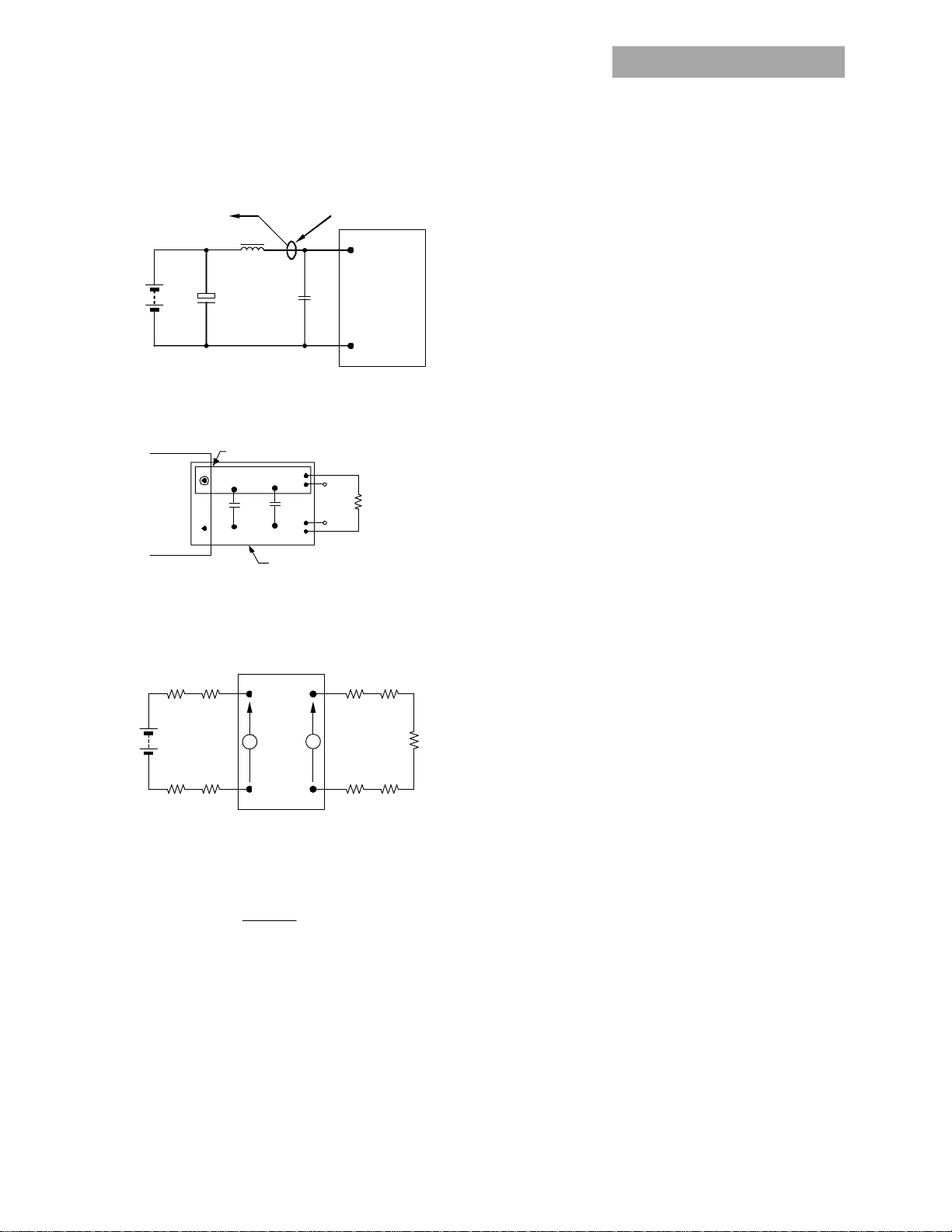
Test Configurations
Vout+
Vout-
33-10 0μF
V
CURRENT PR OBE
SCOP E
R
contact Rdistribution
O
R
contact Rdistribution
x 100 %
Vin +
Vin-
RESISTIVE
LOAD
R
LOAD
TO OSCILL OSCOPE
L
TEST
12μH
CS 220μF
BATTERY
NOTE: M easure i nput r eflected ri pple curr ent with a simula ted
E.S .R.<0 .1
@ 20° C 100kHz
source i nductance (L
possible battery impedance. Measure current as shown
abov e.
) of 12μH. Capacitor CS offs ets
TEST
Figure 7. Input Reflected Ripple Current Test Setup.
COPPER STRIP
V O (+)
V O ( – )
NOTE: A ll vol tage measurem ents to be taken at the module
1uF
10uF
GROUND PLANE
termin als, a s shown ab ove. If sockets are use d then
Kel vin conn ections are requ ired at the mo dule termin als
to av oid measureme nt errors due to socket conta ct
resistance.
Figure 8. Output Ripple and Noise Test Setup.
R
R
contact
distribution
R
R
contact
distribution
NOTE: All voltage measurements to be taken at the module
terminals, as shown above. If sockets are used then
Kelvin connections are require d at the module terminals
to avoid measurement errors du e to socket contact
resistance.
Vin+
V
IN
Vin-
Figure 9. Output Voltage and Efficiency Test Setup.
. I
V
O
Efficiency
=
VIN. I
O
IN
Design Considerations
Input Filtering
The power module should be connected to a low AC
impedance source. Highly inductive source impedance can
affect the stability of the power module. For the test
configuration in Figure 7, a 33-100μF electrolytic capacitor
(ESR<0.7 at 100kHz), mounting close to the power module
helps ensure the stability of the unit. Consult the factory for
further application guidelines.
Safety Considerations
For safety-agency approval of the system in which the
power module is used, the power module must be installed
in compliance with the spacing and separation
requirements of the end-use safety agency standard, i.e.,
UL60950-1, CSA C22.2 No.60950-1, and VDE08051(IEC60950-1).
If the input source is non-SELV (ELV or a hazardous voltage
greater than 60 Vdc and less than or equal to 75Vdc), for the
module’s output to be considered as meeting the
requirements for safety extra-low voltage (SELV), all of the
following must be true:
The input source is to be provided with reinforced
insulation from any other hazardous voltages, including
the AC mains.
One V
pin and one V
IN
pin are to be grounded, or
OUT
both the input and output pins are to be kept floating.
The input pins of the module are not operator
accessible.
Another SELV reliability test is conducted on the whole
system (combination of supply source and subject
module) as required by the safety agencies to verify
that under a single fault, hazardous voltages do not
appear at the module’s output.
Note: Do not ground either of the input pins of the module
without grounding one of the output pins. This may
allow a non-SELV voltage to appear between the
output pins and ground.
The power module has extra-low voltage (ELV) outputs when
all inputs are ELV.
All flammable materials used in the manufacturing of these
modules are rated 94V-0 or tested to the UL60950 A.2 for
reduced thickness.
For input voltages exceeding –60 Vdc but less than or equal
to –75 Vdc, these converters have been evaluated to the
applicable requirements of basic insulation between
secondary DC mains distribution input (classified as TNV-2 in
Europe) and unearthed SELV outputs.
The input to these units is to be provided with a maximum
10 A fast-acting fuse in the ungrounded lead.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 6
Page 7

GE
E
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Feature Descriptions
Remote On/Off
Two remote On/Off options are available. Positive logic turns
the module on during a logic high voltage on the On/Off pin
and off during a logic low. Negative logic remote On/Off,
device code suffix “1”, turns the module off during a logic
high and on during a logic low.
Vin+
I
on/off
V
on/off
ON/OFF
Vin-
Figure 10. Remote On/Off Implementation.
To turn the power module on and off, the user must supply a
switch (open collector or equivalent) to control the voltage
) between the On/Off terminal and the VIN(-) terminal
(V
on/off
(see Figure 10). Logic low is -0.7V ≤ V
maximum I
during a logic low is 0.15mA and the switch
on/off
should maintain a logic low level while sinking this current.
During a logic high, the typical maximum V
by the module is 5.6V and the maximum allowable leakage
current at V
= 5.6V is 25μA.
on/off
If not using the remote On/Off feature:
For positive logic, leave the On/Off pin open.
For negative logic, short the On/Off pin to V
Remote Sense
Remote sense minimizes the effects of distribution losses by
regulating the voltage at the remote-sense connections (See
Figure 11). The voltage between the remote-sense pins and
the output terminals must not exceed the output voltage
sense range given in the Feature Specifications table:
(+) – VO(–)] – [SENSE(+) – SENSE(–)] 0.5 V
[V
O
Although the output voltage can be increased by both the
remote sense and by the trim, the maximum increase for
the output voltage is not the sum of both. The maximum
increase is the larger of either the remote sense or the trim.
≤ 0.6V. The
on/off
Vout+
TRIM
Vout-
generated
on/off
(-).
IN
The amount of power delivered by the module is defined as
the voltage at the output terminals multiplied by the output
current. When using remote sense and trim, the output
voltage of the module can be increased, which at the same
output current would increase the power output of the
module. Care should be taken to ensure that the maximum
output power of the module remains at or below the
maximum rated power (maximum rated power = Vo,set x
Io,max).
SENSE(+)
SENSE(–)
V
I(+)
VO(+)
SUPPLY
CONTACT
RESISTANCE
I
I
V
I(-)
V
O(–)
IO
LOAD
CONTACT AND
DISTRIBUTION LOSS
Figure 11. Circuit Configuration for Remote Sense .
Input Undervoltage Lockout
At input voltages below the input undervoltage lockout limit,
the module operation is disabled. The module will only
begin to operate once the input voltage is raised above the
undervoltage lockout turn-on threshold, V
UV/ON
.
Once operating, the module will continue to operate until
the input voltage is taken below the undervoltage turn-off
threshold, V
UV/OFF
.
Overtemperature Protection
To provide protection under certain fault conditions, the unit
is equipped with a thermal shutdown circuit. The unit will
shutdown if the thermal reference point, Tref, exceeds
O
C (Figure 13, typical) or 120OC (Figure 14, typical), but
135
the thermal shutdown is not intended as a guarantee that
the unit will survive temperatures beyond its rating. The
module will automatically restart upon cool-down to a safe
temperature.
Output Overvoltage Protection
The output overvoltage protection scheme of the modules
has an independent overvoltage loop to prevent single point
of failure. This protection feature latches in the event of
overvoltage across the output. Cycling the On/Off pin or
input voltage resets the latching protection feature. If the
auto-restart option (4) is ordered, the module will
automatically restart upon an internally programmed time
elapsing.
Overcurrent Protection
To provide protection in a fault (output overload) condition,
the unit is equipped with internal
current-limiting circuitry and can endure current
limiting continuously. At the point of current-limit
inception, the unit enters hiccup mode. If the unit is
not configured with auto–restart, it will latch off following
the overcurrent condition. The module can be restarted by
cycling the DC input power for at least one second or by
toggling the remote On/Off signal for at least one second.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 7
Page 8

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
If the unit is configured with the auto-restart option (4), it will
remain in the hiccup mode as long as the overcurrent
condition exists. Once the output current is brought back
into its specified range, the unit will operate normally. The
average output current during hiccup is 10% I
O, max
.
Output Voltage Programming
Trimming allows the output voltage set point to be
increased or decreased from the default value. This is
accomplished by connecting an external resistor between
the TRIM pin and either the V
VIN(+)
ON/OFF
VIN(-)
VO(+)
VOTRIM
VO(-)
Figure 12. Circuit Configuration to Trim Output Voltage.
Connecting an external resistor (R
pin and the V
(-) (or Sense(-)) pin decreases the output
O
voltage set point. To maintain set point accuracy, the trim
resistor tolerance should be ±1.0%.
The following equation determines the required external
resistor value to obtain a percentage output voltage change
of ∆%
R
downtrim
0.12
Where
%
For example, to trim-down the output voltage of the module
by 6% to 11.28V, Rtrim-down is calculated as follows:
(+) pin or the VO(-) pin.
O
trim-down
511
%
VV
desired
V
0.12
100
R
trim-up
LOAD
R
trim-down
) between the TRIM
22.10
6%
511
R
downtrim
6
R
downtrim
Connecting an external resistor (R
pin and the V
(+) (or Sense (+)) pin increases the output
O
voltage set point. The following equation determines the
required external resistor value to obtain a percentage
output voltage change of ∆%:
R
Where
uptrim
V
desired
0.12
%
For example, to trim-up the output voltage of the module by
4% to 12.48V, R
is calculated is as follows:
trim-up
%225.1
0.12
22.10
9.74
) between the TRIM
trim-up
511
%)100(0.1211.5
%
100
4%
22.10
R
uptrim
The voltage between the V
)4100(0.1211.5
4225.1
MRuptrim
(+) and VO(–) terminals must not
O
4
16.1
22.10
511
exceed the minimum output overvoltage protection value
shown in the Feature Specifications table. This limit includes
any increase in voltage due to remote-sense compensation
and output voltage set-point adjustment trim.
Although the output voltage can be increased by both the
remote sense and by the trim, the maximum increase for
the output voltage is not the sum of both. The maximum
increase is the larger of either the remote sense or the trim.
The amount of power delivered by the module is defined as
the voltage at the output terminals multiplied by the output
current. When using remote sense and trim, the output
voltage of the module can be increased, which at the same
output current would increase the power output of the
module. Care should be taken to ensure that the maximum
output power of the module remains at or below the
maximum rated power (maximum rated power = V
).
I
O,max
O,set
x
Thermal Considerations
The power modules operate in a variety of thermal
environments; however, sufficient cooling should be
provided to help ensure reliable operation.
Considerations include ambient temperature, airflow,
module power dissipation and the need for increased
reliability. A reduction in the operating temperature of the
module will result in an increase in reliability.
The thermal data presented here is based on physical
measurements taken in a wind tunnel, using automated
thermo-couple instrumentation to monitor key component
temperatures: FETs, diodes, control ICs, magnetic cores,
ceramic capacitors, opto-isolators, and module pwb
conductors, while controlling the ambient airflow rate and
temperature. For a given airflow and ambient temperature,
the module output power is increased, until one (or more) of
the components reaches its maximum derated operating
temperature, as defined in IPC-9592. This procedure is then
repeated for a different airflow or ambient temperature until
a family of module output derating curves is obtained.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 8
Page 9

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Thermal Considerations (continued)
The thermal reference points, T
for open frame modules is shown in Figure 13. For reliable
operation, these temperatures should not exceed 125
used in the specifications
ref,
o
C.
(A)
O
OUTPUT CURRENT, I
AMBIENT TEMEPERATURE, TA (oC)
Figure 15. Output Current Derating for the Open Frame
Module; Airflow in the Transverse Direction from V
V
(+); VIN =48.
out
(A)
O
OUTPUT CURRENT, I
out
(-) to
AIRFLOW
Figure 13. T
Open Frame Module.
The thermal reference point, T
for modules with a heat plate is shown in Figure 14. For
reliable operation, this temperature should not exceed
O
C.
115
Figure 14. T
Module with Heat plate.
Temperature Measurement Locations for
ref
used in the specifications
ref,
AIRFLOW
Temperature Measurement Location for
ref
Heat Transfer via Convection
Increased airflow over the module enhances the heat
transfer via convection. Derating curves showing the
maximum output current that can be delivered by
each module versus local ambient temperature (T
for natural convection and up to 2m/s (400 ft./min) forced
airflow are shown in Figures 15 - 18.
A
)
AMBIENT TEMEPERATURE, TA (oC)
Figure 16. Output Current Derating for the Module with
Heat plate; Airflow in the Transverse Direction from V
to V
(+);VIN =48V.
out
(A)
O
OUTPUT CURRENT, I
AMBIENT TEMEPERATURE, TA (oC)
Figure 17. Output Current Derating for the Open Frame
Module; Airflow in the Transverse Direction from V
V
(+); VIN =24V.
out
out
out
(-) to
(-)
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 9
Page 10

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Thermal Considerations (continued)
(A)
O
OUTPUT CURRENT, I
Figure 18. Output Current Derating for the Module with
Heat plate; Airflow in the Transverse Direction from V
(+);VIN =24V.
to V
out
Please refer to the Application Note ‘Thermal
Characterization Process For Open-Frame Board-Mounted
Power Modules’ for a detailed discussion of thermal aspects
including maximum device temperatures.
Heat Transfer via Conduction
The module can also be used in a sealed environment with
cooling via conduction from the
module’s top surface through a gap pad material to a
cold wall, as shown in Figure 19. This capability is achieved
by insuring the top side component skyline profile achieves
no more than 1mm height difference between the tallest
and the shortest power train part that benefits from contact
with the gap pad material. The output current derating
versus cold wall temperature, when using a gap pad such as
Bergquist GP2500S20, is shown in Figure 20.
Figure 19. Cold Wall Mounting
AMBIENT TEMEPERATURE, TA (oC)
out
(-)
Through-Hole Soldering Information
Lead-Free Soldering
The EHHD006A0Bxx RoHS-compliant through-hole products
use SAC (Sn/Ag/Cu) Pb-free solder and RoHS-compliant
components. They are designed to be processed through
single or dual wave soldering machines. The pins have a
RoHS-compliant finish that is compatible with both Pb and
Pb-free wave soldering processes. A maximum preheat rate
of 3C/s is suggested. The wave preheat process should be
such that the temperature of the power module board is
kept below 210C. For Pb solder, the recommended pot
temperature is 260C, while the Pb-free solder pot is 270C
max.
Paste-in-Hole Soldering
The EHHD006A0Bxx module is compatible with reflow
paste-in-hole soldering processes shown in Figures 23-25.
Since the EHHD006A0BxxZ module is not packaged per JSTD-033 Rev.A, the module must be baked prior to the
paste-in-hole reflow process. EHHD006A0Bxx-HZ modules
are not compatible with paste-in-hole reflow soldering.
Please contact your GE Sales Representative for further
information.
Surface Mount Information
MSL Rating
The EHHD006A0B-SZ module has a MSL rating of 2a.
Storage and Handling
The recommended storage environment and handling
procedures for moisture-sensitive surface mount packages
is detailed in J-STD-033 Rev. A (Handling, Packing, Shipping
and Use of Moisture/Reflow Sensitive Surface Mount
Devices). Moisture barrier bags (MBB) with desiccant are
provided for the EHHD006A0Bxx-SZ modules. These sealed
packages should not be broken until time of use. Once the
original package is broken, the floor life of the product at
conditions of 30°C and 60% relative humidity varies
according to the MSL rating (see J-STD-033A). The shelf life
for dry packed SMT packages is a minimum of 12 months
from the bag seal date, when stored at the following
conditions: < 40° C, < 90% relative humidity
.
Pick and Place
The EHHD006A0Bxx-S modules use an open frame
(A)
O
OUTPUT CURRENT, I
construction and are designed for a fully automated
assembly process. The modules are fitted with a label
designed to provide a large surface area for pick and place
operations. The label meets all the requirements for surface
mount processing, as well as safety standards, and is able
to withstand reflow temperatures of up to 300
also carries product information such as product code,
serial number and the location of manufacture.
o
C. The label
Figure 20. Derated Output Current versus Cold Wall
Temperature with Local Ambient Temperature Around
Module at 85C; V
COLDPLATE TEMEPERATURE, T
=24V or 48V.
IN
(oC)
C
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 10
Page 11

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Surface Mount Information (continued)
cause damage to the modules, and can adversely affect
long-term reliability.
Tin Lead Soldering
The EHHD006A0Bxx-S power modules are lead free modules
and can be soldered either in a lead-free solder process or
in a conventional Tin/Lead (Sn/Pb) process. It is
recommended that the customer review data sheets in
order to customize the solder reflow profile for each
application board assembly. The following instructions must
Figure 21. Pick and Place Location.
Nozzle Recommendations
The module weight has been kept to a minimum by using
open frame construction. Even so, these modules have a
relatively large mass when compared to conventional SMT
components. Variables such as nozzle size, tip style,
vacuum pressure and placement speed should be
considered to optimize this process. The minimum
recommended nozzle diameter for reliable operation is
6mm. The maximum nozzle outer diameter, which will safely
fit within the allowable component spacing, is 9 mm.
Oblong or oval nozzles up to 11 x 9 mm may also be used
within the space available.
Reflow Soldering Information
The surface mountable modules in the EHHD006A0Bxx-S
family use our newest SMT technology called “Column Pin”
(CP) connectors. Figure 22 shows the new CP connector
before and after reflow soldering onto the end-board
assembly. The CP is constructed from a solid copper pin with
an integral solder ball attached, which is composed of
tin/lead (Sn/Pb) solder for non-Z codes, or Sn/Ag
solder for –Z codes.
EHHD Board
Insulator
Solder Ball
End assembly PCB
Figure 22. Column Pin Connector Before and After Reflow
Soldering.
The CP connector design is able to compensate for large
amounts of planarity and still ensure a reliable SMT solder
joint. Typically, the eutectic solder melts at 183°C (Sn/Pb
solder) or 217-218°C (SAC solder), wets the land, and
subsequently wicks the device connection. Sufficient time
must be allowed to fuse the plating on the connection to
ensure a reliable solder joint. There are several types of SMT
reflow technologies currently used in the industry. These
surface mount power modules can be reliably soldered
using natural forced convection, IR (radiant infrared), or a
combination of convection/IR. The following instructions
must be observed when SMT soldering these units. Failure to
observe these instructions may result in the failure of or
/Cu (SAC)
3
be observed when soldering these units. Failure to observe
these instructions may result in the failure of or cause
damage to the modules, and can adversely affect long-term
reliability.
In a conventional Tin/Lead (Sn/Pb) solder process, peak
reflow temperatures are limited to less than 235°C.
Typically, the eutectic solder melts at 183°C, wets the land,
and subsequently wicks the device connection. Sufficient
time must be allowed to fuse the plating on the connection
to ensure a reliable
solder joint. There are several types of SMT reflow
technologies currently used in the industry. These surface
mount power modules can be reliably soldered using
natural forced convection, IR (radiant infrared), or a
combination of convection/IR. For reliable soldering, the
solder reflow profile should be established by accurately
measuring the modules CP connector temperatures.
Lead Free Soldering
The –Z version of the EHHD006A0B modules are lead-free
(Pb-free) and RoHS compliant and are both forward and
backward compatible in a Pb-free and a SnPb soldering
process. Failure to observe the instructions below may
result in the failure of or cause damage to the modules and
can adversely affect long-term reliability.
300
250
200
15 0
10 0
REFLOW TEMP (C)
50
0
Peak Temp 235oC
Heat zone
oCs-1
max 4
Soak zone
30-240s
Preheat zone
oCs-1
max 4
REFLOW TIME (S)
T
lim
205
Cooling
zo ne
1- 4
above
o
C
oCs-1
Figure 23. Reflow Profile for Tin/Lead (Sn/Pb) process.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 11
Page 12

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Surface Mount Information (continued)
240
235
230
225
220
215
210
MAX TEMP SOLDER (C)
205
200
0 10 203040 5060
Figure 24. Time Limit Curve Above 205oC for Tin/Lead
(Sn/Pb) process
Pb-free Reflow Profile
Power systems will comply with J-STD-015 Rev. C
(Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification for Nonhermetic
Solid State Surface Mount Devices) for both Pb-free solder
profiles and MSL classification procedures. This standard
provides a recommended forced-air-convection reflow
profile based on the volume and thickness of the package
(table 4-2). The suggested Pb-free solder paste is Sn/Ag/Cu
(SAC). The recommended linear reflow profile using
Sn/Ag/Cu solder is shown in Figure 25.
300
Per J-STD-020 Rev. C
250
200
150
Heating Zone
1°C/Second
100
Reflow T emp (°C )
50
0
Figure 25. Recommended linear reflow profile using
Sn/Ag/Cu solder.
Peak Temp 260°C
* Min. Time Above 235°C
15 Seconds
*Time Above 217°C
60 Seconds
Reflow Time (Seconds)
Cooling
Zone
Post Solder Cleaning and Drying Considerations
Post solder cleaning is usually the final circuit board
assembly process prior to electrical board testing. The result
of inadequate cleaning and drying can affect both the
reliability of a power module and the testability of the
finished circuit board assembly. For guidance on
appropriate soldering, cleaning and drying procedures, refer
to GE Board
Mounted Power Modules: Soldering and Cleaning Application
Note (AN04-001).
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 12
Page 13

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
EMC Considerations
The circuit and plots in Figure 26 shows a suggested configuration to meet the conducted emission limits of EN55022 Class B.
Figure 26. EMC Considerations
For further information on designing for EMC compliance, please refer to the FLT007A0 data sheet (DS05-028).
VIN = 48V, Io = I
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 13
o,max
, L Line
VIN = 48V, Io = I
, N Line
o,max
Page 14

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Mechanical Outline for Through-Hole Module
Dimensions are in millimeters and [inches].
Tolerances: x.x mm 0.5 mm [x.xx in. 0.02 in.] (unless otherwise indicated)
x.xx mm 0.25 mm [x.xxx in 0.010 in.]
*Top side label includes GE name, product designation and date code.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 14
Page 15

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Mechanical Outline for Surface Mount Module (-S Option)
Dimensions are in millimeters and [inches].
Tolerances: x.x mm 0.5 mm [x.xx in. 0.02 in.] (unless otherwise indicated)
x.xx mm 0.25 mm [x.xxx in 0.010 in.]
* Top side label includes GE name, product designation and date code.
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 15
Page 16

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Mechanical Outline for Through-Hole Module with Heat Plate (-H Option)
Dimensions are in millimeters and [inches].
Tolerances: x.x mm 0.5 mm [x.xx in. 0.02 in.] (unless otherwise indicated)
x.xx mm 0.25 mm [x.xxx in 0.010 in.]
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 16
Page 17

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Recommended Pad Layout
Dimensions are in millimeters and [inches].
Tolerances: x.x mm 0.5 mm [x.xx in. 0.02 in.] (unless otherwise indicated)
x.xx mm 0.25 mm [x.xxx in 0.010 in.]
Pin Function
1 Vi(+)
2 ON/OFF
3 Vi(-)
4 Vo(-)
5 SENSE(-)
6 TRIM
7 SENSE(+)
8 Vo(+)
SMT Recommended Pad Layout (Component Side View)
Pin Function
1 Vi(+)
2 ON/OFF
3 Vi(-)
4 Vo(-)
5 SENSE(-)
6 TRIM
7 SENSE(+)
8 Vo(+)
NOTES:
FOR 0.030” X 0.025”
RECTANGULAR PIN, USE
0.050” PLATED THROUGHHOLE DIAMETER
FOR 0.62 DIA” PIN, USE
0.076” PLATED THROUGHHOLE DIAMETER
TH Recommended Pad Layout (Component Side View)
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 17
Page 18

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Packaging Details
The surface mount versions of the EHHD006A0B (suffix –S) are
supplied as standard in the plastic trays shown in Figure 27.
Tray Specification
Material Antistatic coated PVC
Max surface resistivity 10
Color Clear
Capacity 12 power modules
Min order quantity 48 pcs (1 box of 4 full trays + 1
12
/sq
empty top tray)
Each tray contains a total of 12 power modules. The trays are
self-stacking and each shipping box for the EHHD006A0B
(suffix –S) surface mount module contains 4 full trays plus one
empty hold-down tray giving a total number of 48 power
modules.
Figure 27. Surface Mount Packaging Tray
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Page 18
Page 19

GE
Data Sheet
EHHD006A0B Hammerhead
Series; DC-DC Converter Power Modules
18-75Vdc Input; 12Vdc, 6.0A, 72W Output
Ordering Information
Please contact your GE Sales Representative for pricing, availability and optional features.
Table 1. Device Codes
Product Codes Input Voltage
EHHD006A0B41Z 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Through-hole CC109159364
EHHD006A0B641Z 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Through-hole 150024112
EHHD006A0B41-HZ 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Through-hole CC109167755
EHHD006A0B641-HZ 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Through-hole 150024113
EHHD006A0B841-HZ 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Through-hole CC109171443
EHHD006A0B41-SZ 24/48V (18-75Vdc) 12.0V 6A Negative Surface mount CC109167763
Table 2. Device Coding Scheme and Options
Output
Voltage
Output
Current
On/Off Logic
Connector
Type
Comcodes
Contact Us
For more information, call us at
USA/Canada:
+1 888 546 3243, or +1 972 244 9288
Asia-Pacific:
+86.021.54279977*808
Europe, Middle-East and Africa:
+49.89.878067-280
India:
+91.80.28411633
July 12, 2013 ©2012 General Electric Company. All rights reserved. Version 1.07
www.ge.com/powerelectronics
 Loading...
Loading...