Page 1

AVCS GYRO
GY502
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
YAW-AXIS STABILIZER FOR MODEL HELICOPTER
(RATE GYRO)
Page 2

2
Thank you for buying a GY502 AVCS gyro.
Before using your new gyro, please read this manual thoroughly and use the
gyro properly and safely. After reading this manual, store it in a safe place.
FOREWORD
The GY502 is an AVCS (Angular Vector Control System) rate gyro
developed for use with .60 type and other model helicopters.
[Features]
•High-speed arithmetic processing by microcomputer allows high-speed
pulse drive of servos. (Compatible with high-speed digital servos)
•Sensor vibration resistance and neutral characteristics have been improved
by the use of a low back aerofoam case.
•Amplifier mounts an LCD for accurate data setting.
[Applicable servos]
Gyro performance largely depends on the servo used. The higher the speed
and response of the servo, the higher the gyro gain and the better the gyro
performance. From this standpoint, a digital servo is perfectly suited for use
with a gyro. We recommend the use of a high-speed digital servo especially
developed for gyro use.
•No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form without prior permission.
•The contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice.
•This manual has been carefully written. Please write to Futaba if you feel that any
corrections or clarifications should be made.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
FOR SAFETY
•Meaning of Special Markings ---------------------------- 4
•Mounting/Operating Precautions ------------------------ 5
•Fuselage Maintenance Precautions ---------------------- 7
BEFORE USE
•Set Contents------------------------------------------------- 8
•AVCS Gyro ------------------------------------------------- 9
•Digital Servo Compatibility -----------------------------11
DATA SETTING
•Name and Function of Each Part------------------------12
•LCD Display and Edit Keys -----------------------------13
•Function Map ----------------------------------------------14
•GY502 Functions Setting --------------------------------15
•Remote Gain Function------------------------------------21
•Initialization------------------------------------------------30
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
•Installing to Fuselage -------------------------------------32
•Flight Adjustments ----------------------------------------37
3
REFERENCE
•Specifications ----------------------------------------------40
•Definition of Abbreviations------------------------------41
•GY502 Parameters Sheet---------------------------------42
Page 4

FOR SAFETY
4
FOR SAFETY
To ensure safe use, observe the following precautions.
Meaning of Special Markings
Pay special attention to the safety at the parts of this manual that are
indicated by the following marks.
Mark Meaning
Procedures which may lead to a dangerous
condition and cause death or serious injury to
the user if not carried out properly.
Procedures which may lead to a dangerous
condition or cause death or serious injury to
the user if not carried out properly, or procedures where the probability of superficial
injury or physical damage is high.
Procedures where the possibility of serious
injury to the user is small, but there is a
danger of injury, or physical damage, if not
carried out properly.
Symbol:
; Prohibited ; Mandatory
Page 5

FOR SAFETY
Mounting/Operating Precautions
Insert the connectors fully and firmly.
If a connector works loose due to vibration during flight, control may
be lost and result in a dangerous situation.
Always use the accessory sensor tape to install the sensor to the
fuselage.
This is necessary to securely fasten the sensor to the fuselage so that
operation of the gyro does not transmit unwanted fuselage vibrations
directly to the sensor.
When mounting the sensor, provide a little surplus so that the
sensor connection cables are not too taut.
If the sensor cables are too taut, the gyro will not display its full
performance. If the sensor peels, control will be lost and result in a
dangerous situation.
Mount the sensor and control amp so that metals or other
conductive objects do not touch these cases.
The GY502 uses a conductive resin case to reduce electromagnetic
interference. Because the surface of the case is conductive, metal
objects may cause a short circuit.
5
Mount the sensor and servo at least 2cm apart.
When using a GV-1 governor, mount the sensor and GV-1 amp
at least 5cm apart.
When using the GY502 with a motor-driven helicopter, mount
the sensor and drive motor at least 10cm apart.
Noise from the servo motor, GV-1 amp and drive motor may cause
the performance of an erroneously operated gyro to drop.
Page 6

6
FOR SAFETY
Precautions When Turning on the Power Switch
During initialization, the message “-Hello-” appears on the GY502
LCD screen.
Do not move the helicopter until this message disappears (in
about 3 seconds).
Also, do not move the transmitter rudder stick from the neutral
position during this period.
Always check the direction of operation of the servos.
If you attempt to fly the model when a servo operates in the wrong
direction, the fuselage will spin in a fixed direction and enter an
extremely dangerous state.
When the rudder neutral position was changed by the linkage,
the rudder neutral position in the AVCS mode must always be
re-read before use.
Re-reading method:
Turn on the transmitter in the AVCS mode, then turn on the
gyro . Or quickly switch (interval of within 1 second) the
remote gain channel switch between the AVCS mode and
Normal mode at least three times and switch the AVCS side
with the transmitter in the ON state. This memorizes the new
rudder position inside the GY502.
Avoid sudden temperature changes.
Sudden temperature changes will cause the neutral position to
change. For example, in the winter, do not fly immediately after
removing the model from inside a heated car and in the summer, do
not fly immediately after removing the model from inside an air
conditioned car. Allow the model to stand for about 10 minutes and
turn on the power after the temperature inside the gyro has stabilized.
Also, if the gyro is exposed to direct sunlight or is mounted near the
engine, the temperature may change suddenly. Take suitable measures so that the gyro is not exposed to direct sunlight, etc.
Page 7

FOR SAFETY
Check the remaining receiver/gyro/servo nicd battery operating
time during the adjustment stage and decide how many flights
are remaining.
Never use the transmitter rudder trim in the AVCS mode.
When the rudder is trimmed during flight, the neutral position will
change.
When using the GY502 in the AVCS mode, set revolution mixing
to OFF.
Fuselage Maintenance Precautions
Use a tale rotor drive tube or other part with a high torsion
performance for the tail drive.
Take the strength of the tail into account during inspection and
adjustment.
The amount of improvement of gyro performance has a considerable
effect on the fuselage vibration level or the size, type, linkage
method, looseness, etc. of the tail rotor.
7
Since a higher gain than usual can be used then the tail rotor is more
effective, the load on the tail is also greater.
Always perform proper maintenance for ultimate performance.
The rigidity of the fuselage tail has a large effect on gyro performance.
Make the fuselage vibration as small as possible.
Fuselage vibration has an adverse affect on gyro operation.
Page 8
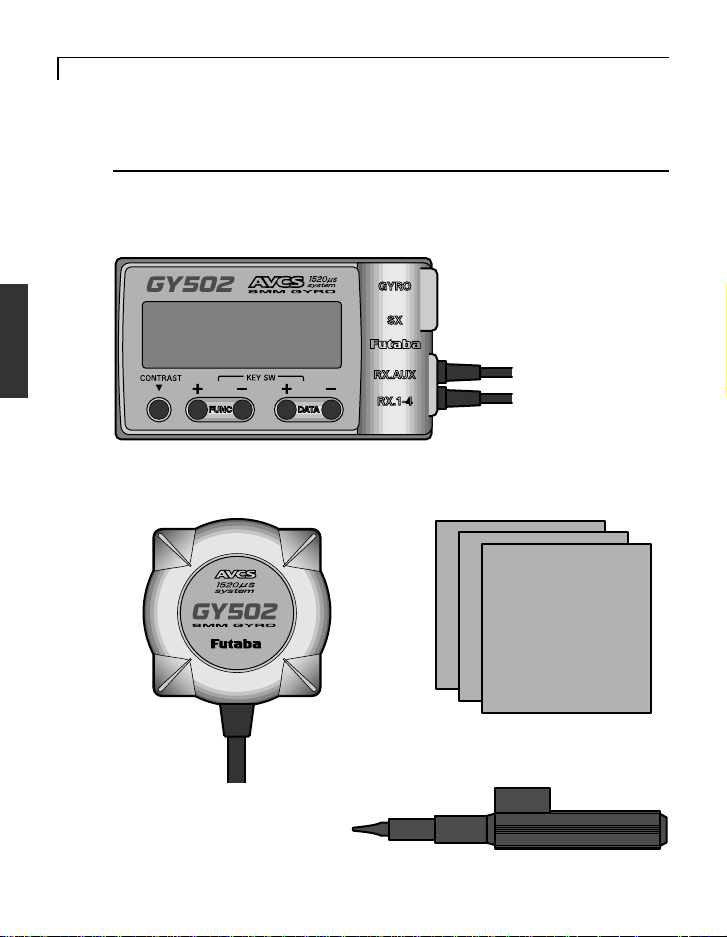
BEFORE USE
8
BEFORE USE
Set Contents
After unpacking the GY502 set, first check if the following parts are
provided:
GY502 control amp
(x1)
GY502 sensor (x1)
Sensor tape (x3)
Mini screwdriver (x1)
Page 9
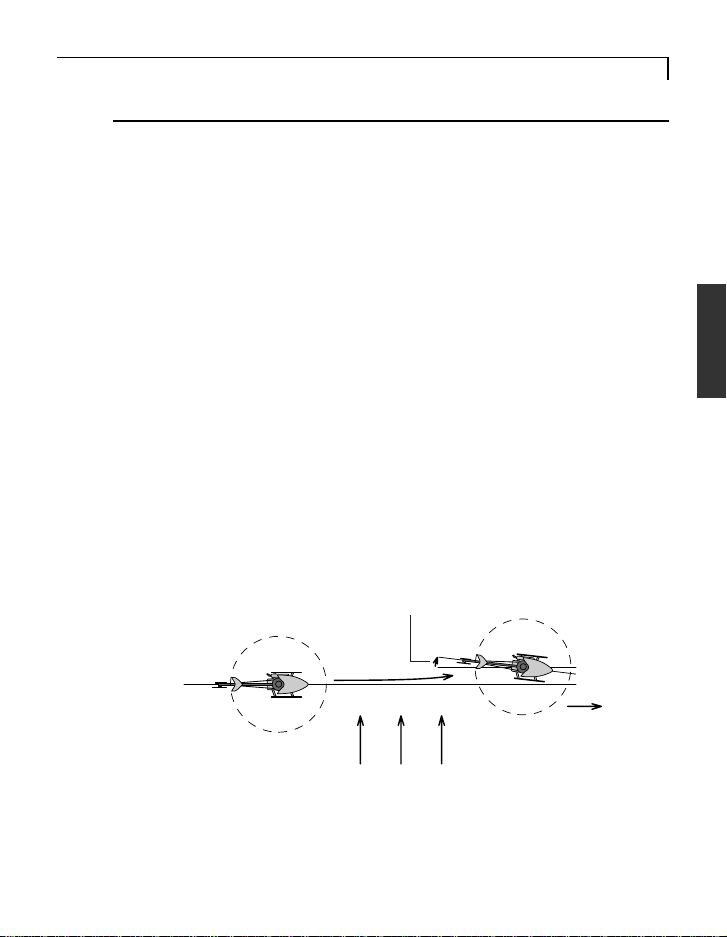
BEFORE USE
• Drifting stop
Forward
Side wind
AVCS Gyro
Differences Between AVCS Gyro and Conventional Gyro
Compared to a convention gyro, the AVCS gyro has a substantially improved tail control capacity. Gyro operation also differs from that of
conventional systems in a number of ways.
The following sequentially describes the conventional gyro and the AVCS
gyro.
Conventional gyro
The conventional gyro detects movement of the helicopter's tail and controls
the rudder servo so that movement of the tail stops.
Now, consider hovering when the helicopter is exposed to a side wind, the
tail drifts. When the tail drifts, the gyro detects the tail rotation angular
velocity and operates the servo in the direction that stops the tail from
moving. Drifting of the tail is stopped by control from the gyro. When the
tail stops drifting, the control amount from the gyro becomes zero. Since the
helicopter is always exposed to side wind, even in this state, the tail starts to
drift again. When the tail drifts, the gyro tries to stop it again. The "drifting
stop" operation is repeated and the tail continues to drift in the wind
direction in this manner. The higher the gyro sensitivity, the smaller the
amount of this drift. However, if the sensitivity is high, hunting will occur
and, therefore, the sensitivity amp has a limit.
9
AVCS gyro
This following describes how the AVCS system works when the helicopter
is exposed to a side wind while hovering, the same as the preceding item.
When the helicopter is exposed to a side wind, the tail begins to drift. The
Page 10

10
BEFORE USE
gyro controls the servo so that the movement of the tail stops, the same as a
conventional gyro. At the same time, a sensor is controlled so that the tail is
rotated in the opposite direction (returns to the original position). In short,
the conventional gyro performs an operation known as "drifting stop", but
the AVCS system performs an operation that "stops drifting and returns to
original position". The "return to original position" operation added to the
AVCS system improves rudder trim operation. In other words, the gyro can
automatically trim the rudder against side winds. This also applies to reverse
flight. When a helicopter is flying in the forward and reverse directions, the
rudder trim is changed to advance, but with the AVCS system, this trim
change is performed automatically and instantaneously so that the tail
remains extremely stable even during high-speed reverse flight.
The AVCS system requires a high-precision angular velocity sensor. The
GY501 realizes a high-precision angular velocity detection function and
extremely small output drift by using a new type of gyro sensor. This
minimizes rudder neutral position drift during flight and eliminates the need
to trim the rudder during flight.
• The tail remains extremely stable.
Forward
Side wind
Differences in rudder control method
The following describes the differences between conventional gyro and
AVCS gyro rudder control.
The conventional gyro sends the rudder control signals from the transmitter
to the rudder servo and starts to move the tail. When the tail moves, the gyro
detects this movement and generates a signal to stop it. If the tail continues
to move even in this state, a rudder control signal larger than the signal from
the gyro must be applied from the transmitter. That is, the difference
between the rudder control signal from the transmitter and the control signal
that attempts to stop this from the gyro becomes the actual amount of
movement of the tail. Ordinarily, the rudder control signal is amplified
Page 11

BEFORE USE
several times over by the gyro amp and is balanced with the gyro control
signal so that the transmitter can be used at the normal steering angle.
The AVCS system uses a different rudder control method. As described in
the preceding section, it has additional functions that "attempt to return
movement by external force to the original position" and that generate an
angular velocity proportional to the rudder control signal. That is, it functionally controls the speed of rotation of the tail. The original AVCS
(Angular Vector Control System) came from this.
•In the AVCS mode, when the transmitter rudder stick is moved when
the helicopter was stopped, the rudder servo controls operation until
the tail reaches the specified rotational speed.
•Trim deviation of the rudder control signal also becomes a signal that
causes the tail to turn so that even a little trim deviation causes the
tail to move. Therefore, the rudder trim is made the same in all flight
states and must match the neutral reference signal at the gyro. The
method of reading the rudder neutral signal at the gyro will be
described separately.
•Since the rudder mixing signals from the transmitter also become a
tail rotation signal, all the rudder mixing functions must be disabled.
•In the AVCS mode, the gyro automatically trims the rudder so that
linkage changes cannot be verified. Initially, the GY502 trims the
rudder by flying in the Normal mode to take the rudder linkage neutral
position. This centers the linkage. At this time, this rudder neutral
reference point is read to the GY502.
Giving the gyro the rudder neutral reference signal and performing
tail operation by referring to this signal in the AVCS mode in this
way is how the AVCS system differs from the conventional system.
11
Digital Servo Compatibility
Gyro performance largely depends on the servo used. The GY502 displays
top performance when used with a digital servo.
When using a digital servo, set the servo frame rate (Frm) function to High.
(For a description of the setting method, see page 19.)
Page 12

DATA SETTING
12
DATA SETTING
Name and Function of Each Part
GY502 control amp
LCD display
Displays the set data. (8 characters X 1 line)
(Input/output terminals)
Gyro sensor input
Rudder servo output
Edit keys
Used when setting data.
Operated by pushing with the
accessory mini screwdriver.
LCD contrast trimmer
Allows adjustment of the contrast so that the LCD display is easiest to see.
It is adjusted with the accessory mini screwdriver.
GY502 gyro sensor
Stick to the body using the accessory
sensor tape.
(Receiver connectors)
Remote gain input
Rudder input
To control amp
Page 13

DATA SETTING
LCD Display and Edit Keys
LCD display
Set data display and operation
status monitoring are possible.
Edit keys
Setup screen call
The setup screens can be sequentially called with the FUNC+ or
FUNC- key. For the order in which
the setup screens are called, see the
function map.
Data setting
Perform data setting with the DATA+
or DATA- key. When setting a value,
the data is increased when the
DATA+ key is pressed and is
decreased when the DATA- key is
pressed. The mode can also be
selected using either the DATA+ or
the DATA- key.
13
Page 14

DATA SETTING
14
FUNC ”-” key
Function Map
Normal screen display
(P15)
FUNC ”+” key
Gyro Reverse
(P16)
Gyro Gain Adjustment
(P16)
Rudder Control Gain
(P17)
Control Delay I
(P17)
Control Delay D
(P17)
Gain Tracking
(P18)
Power ON
Power on screen display
(P15)
Operation Mode Setting
(P18)
Servo Frame Rate
(P19)
AVCS sense
(P20)
Linkage Limit Setting
(P20)
Page 15
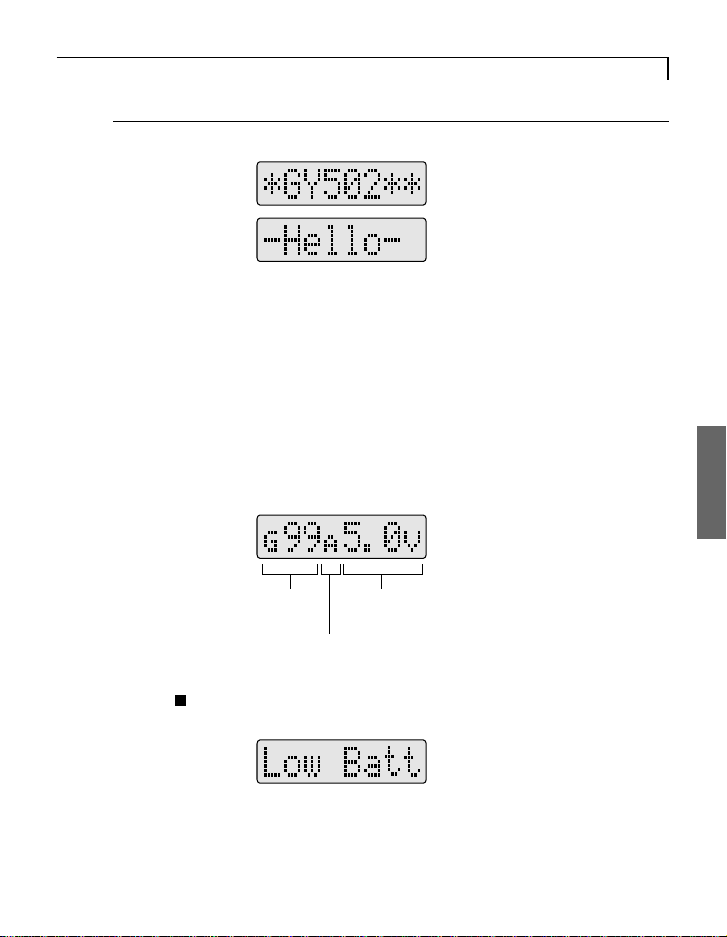
DATA SETTING
GY502 Functions Setting
Power on screen display
When the gyro power is turned on after the transmitter power was
turned on, -Hello- blinks for about three seconds to initialize the data
inside the gyro. During this period, do not move the transmitter
rudder stick or the helicopter. If the transmitter rudder stick or the
helicopter is moved by mistake, the rudder neutral data will not be
correctly read.
Normal screen display
15
•Actual gain (sensitivity)
display
•Operation mode display
N : NOR mode
A : AVCS mode
: Neutral offset
•Power supply voltage display
•During rudder neutral reset operation,
**** is displayed.
•During rudder servo reset operation by
rudder stick, ---- is displayed.
Low battery alarm
When the power supply voltage drops to 3.8V or less,
LOW Batt is displayed. When this message is displayed,
immediately stop use and recharge the Nicd battery.
Page 16

16
DATA SETTING
Gyro Reverse
Initial value: NOR
Sets the gyro operation direction. NOR or REV can be selected.
Set so that when the helicopter is banked right, left correction rudder
is applied and when the helicopter is banked left, right correction
rudder is applied.
Gyro Gain Adjustment
Initial value: 100%
Adjusts the gyro gain. Setting range is 0 to 120%.
Two-point (G:1, G:2) gain adjustment is possible. When A is
displayed, the gyro is in the AVC mode and when N is displayed, the
gyro is in the NOR mode in accordance with the operation mode
setting.
Page 17

DATA SETTING
Rudder Control Gain
Initial value : ACG: 100%, NCG: 120%
Adjusts the rudder stick operation gain. Setting range is 10% to
250%.
AVCS and NOR mode gain can be set independently. In the AVCS
mode, ACG is displayed and in the NOR mode, NCG is displayed.
The display automatically changes to A or B according to the
direction of the rudder stick and the gain of each direction can be set.
This function is used when tracking rudder operation gain between
the AVCS and NOR modes.
Control Delay I
Initial value : 0%
Sets the delay when the rudder stick was pushed operated. Setting
range is 0 to 100%. Rudder stick left and right can be set separately.
17
Control Delay D
Initial value : 0%
Sets the delay when the rudder stick was returned. Setting range is 0
to 100%. Rudder stick left and right can be set separately.
Page 18

18
DATA SETTING
Gain Tracking
Initial value : +0%
Adjusts left and right tail braking tracking. Setting range is -20% to
+20%.
For example, when there is a sense of hunting when stopping left
pirouette or the helicopter drifts when stopping right pirouette, shift
Trk in the + direction. In the opposite case, shift Trk in the - direction.
Operation Mode Setting
Initial : CMT
Sets the gyro operation mode. Settings are NOR, AVC, and CMT. In
the NOR mode, both G1 and G2 operate in the AVCS mode. In the
CMT mode, G1 operates in the AVCS mode and G2 operates in the
NOR mode. In the NOR mode, the GY502 operates the same as an
ordinary gyro. In the AVC mode, the GY502 always operates in the
AVCS mode. In the CM mode, the GY502 can be used in both the
AVCS and NOR modes.
Page 19

DATA SETTING
Servo Frame Rate
Initial value : Low
Switches the servo output pulses.
The Low mode outputs pulses for an ordinary servo. Switch to the
High mode only when using a digital servo.
When using a servo that cannot be driven by high-speed pulses,
other than a digital servo, never set servo frame rate to the High
mode.
The servo may be destroyed.
19
Page 20

20
DATA SETTING
AVCS Sense
Initial value : 100%
Adjusts the rudder control characteristic in the AVCS mode. Setting
range is 50 to 150%.
Adjust by checking the rudder operation feel and stopping characteristic.
Linkage Limit Setting
Initial value : 100%
Sets the rudder servo travel limit.
Operate the rudder stick and adjust the rudder servo travel limit by
pressing the +/- key so that the servo moves to the maximum linkage
position. Use the same procedure to set both the left and right limits .
When setting, move the servo substantially so that the rudder angle
automatically becomes 200% and limit setting is easy. A or B is
displayed for the right and left directions.
Note: When this screen is displayed, the GY502 does not operate as
a gyro. To check operation, return to the initial screen, etc.
Page 21

DATA SETTING
Remote Gain Function
The remote gain function lets operator perform AVCS mode and
Normal mode sensitivity adjustment and operation mode switching
from the transmitter. The channel used here is called the "remote
gain channel". (Channel 5 is used.)
21
(Remote Gain Function)
Transmitter
Gain/Mode Selection
• CH5 switch
• Idle-Up switch (T8Usuper)
• Flight condition (T9Z)
Gain Settings
• ATV function
• Gyro mixing (T8Usuper/T9Z)
• Programmable mixing (T9Z)
Receiver
GY501
Mode Settings
• Normal mode (NOR)
• AVCS mode (AVC)
• Selectable mode (CMT)
Gain Settings
• Gyro Gain Adjustment
Remote Gain Channel (CH5)
Page 22

22
DATA SETTING
When Using a T9Z World Champion Model Transmitter
Gyro Sense Mixing
The Gyro Sense Mixing (GYR) function lets operator perform two-point gain
adjustment at each condition. Set the sensitivity at all conditions.
[GY502 Settings]
Select the gyro operation mode at the GY502 Mode screen. (AVC, NOR, or
CMT)
[Transmitter Settings]
ATV function:
Adjust both the RATE A and RATE B rates to 100% at the transmitter ATV
function setup screen.
Gyro Sense Mixing function:
1. Select the Dual Mode (DUO) at the transmitter Gyro Sense Mixing setup
screen.
2. Set the GAIN1 and GAIN2 gains.
(The following page shows a setting example in the CMT mode.)
[Sensitivity Display]
The gain display indicates the actual gain at the GY502 normal screen
display.
The following shows the relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
when GY502 sensitivity setting is 100% in both the G1 and G2 gain modes.
- Relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
Transmitter
settings
GY502mode
settings
Actual gain
GAIN1
GAIN2
NOR
AVC
CMT
0% - 50% - 100%
Normal mode
AVCS mode
Normal mode AVCS mode
(G2) (G1)
100% - 0% - 100%
Page 23

DATA SETTING
(Setting Example)
Adjust the gyro gain at the Gyro Sense Mixing setup screen at each
condition.
The following shows a setting example in the CMT mode.
Select the Dual Mode (DUO).
GYRO SENCE
DUAL : MODE
85 %
15 %
Use the following values as the sensitivity setting standard:
01 . MODEL-01. NORML HEL PCM 0: 23: 17
: GAIN 1
: GAIN 2
0 20 40 60 80 100
END
Sensitivity rate
Choose the GAIN1 or GAIN2 by the CH5 switch.
23
CH5 switch
Hovering Flight
GAIN1
setting
GAIN2
setting
Actual gain
85%
15%
70% 40%
70%
30%
AVCS side
Normal side
The GY502 sensitivity is 0% at 50%. When set over 50%, the GY502
operates in the AVCS mode and when set under 50%, the GY502
operates in the Normal mode. When setting is changed 1%, the gyro
sensitivity is changed 2%.
Page 24

DATA SETTING
24
When Using a T9Z Transmitter Programmable Mixing
The Programmable Mixing (PMIX) function lets operator perform a gain
adjustment at each condition. Set the sensitivity at all conditions.
[GY502 Settings]
Select the gyro operation mode at the GY502 Mode screen. (AVC, NOR, or
CMT)
[Transmitter Settings]
Function Control:
Set the CH5 (GYR) switch to “NUL” at the transmitter Function Control
(FNC) setup screen.
ATV function:
Adjust both the RATE A and RATE B rates to 120% at the transmitter ATV
function setup screen.
Programmable Mixing function:
1. Select the “ACTIVE” mode (ACT) at the transmitter Programmable Mixing
setup screen.
2. Set the mixing type to “OFS”.
3.Set the slave channel to “GYR”.
4. Set the sensitivity rate (RATE).
(The following page shows a setting example in the CMT mode.)
[Sensitivity Display]
The gain display indicates the actual gain at the GY502 normal screen
display.
The following shows the relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
when GY502 sensitivity setting is 100% in both the G1 and G2 gain modes.
- Relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
Transmitter
settings
GY502mode
settings
NOR
AVC
CMT
-100% - 0% - +100%
Normal mode
AVCS mode
Normal mode AVCS mode
(G2) (G1)
Actual gain
100% - 0% - 100%
Page 25

DATA SETTING
(Setting Example)
Adjust the gyro gain at the Programmable Mixing setup screen at each
condition. The following shows a setting example in the CMT mode.
Select the “ACTIVE”.
PROG MIX 1
ACTIVE : MODE ( ON) TRIM:
GYR
OFS
LIN
OFS
01 . MODEL-01. NORML HEL PCM 0: 23: 17
*** : MASTER
: SLAVE
: MIX TYPE
MSTR MIX MODE:
HOV CRV CTL
******
******
SWT
NXT
END
25
Select the “GYR”.
PROG MIX 1
Select the “OFS”.
01 . MODEL-01. NORML HEL PCM 0: 23: 17
: RATE+ 70 %
0 20 40 60 80 100
END
Sensitivity rate
Use the following values as the sensitivity setting standard:
Hovering Flight
AVCS mode
Normal mode
Actual gain
+70%
-70%
70% 40%
+40%
-40%
When set over 0%, the GY502 operates in the AVCS mode and when
set under 0%, the GY502 operates in the Normal mode.
Page 26

26
DATA SETTING
When Using a T8Usuper Transmitter
The Gyro Mixing (GYRO) function lets operator perform a gain adjustment at
each Idle-Up switch position.
[GY502 Settings]
Select the gyro operation mode at the GY502 Mode screen. (AVC, NOR, or
CMT)
[Transmitter Settings]
Gyro Mixing function:
1. Select the “ON” mode at the transmitter Gyro Mixing (GYRO) setup
screen.
2. Select the Idle-Up switch(SW-E) for the sensitivity selection.
3. Set the “NORM”, “IDL1” and “IDL2” gains.
(The following page shows a setting example in the CMT mode.)
[Sensitivity Display]
The gain display indicates the actual gain at the GY502 normal screen
display.
The following shows the relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
when GY502 sensitivity setting is 100% in both the G1 and G2 gain modes.
- Relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
Transmitter
settings
GY502mode
settings
NORM
IDL1
IDL2
NOR
AVC
CMT
Actual gain
0% - 50% - 100%
Normal mode
AVCS mode
Normal mode AVCS mode
(G2) (G1)
100% - 0% - 100%
Page 27

DATA SETTING
(Setting Example)
Adjust the gyro gain at each the Idle-Up swtch position at the Gyro Mixing
setup screen. The following shows a setting example in the CMT mode.
Select the “ON”
mode.
Select the Idle-Up
switch(SW-E).
27
Switch position
Sensitivity rate
Set the “NORM”, “IDL1” and “IDL2” gains at each setup screen.
Use the following values as the sensitivity setting standard:
(NORM)(IDL1)(IDL2)
SW-E
AVCS mode
Normal mode
Actual gain
Hovering
85%
15%
70% 40%
Flight
70%
30%
When set over 50%, the GY502 operates in the AVCS mode and when
set under 50%, the GY502 operates in the Normal mode.
Page 28

28
DATA SETTING
When Using a Transmitter ATV Function
The ATV function lets operator perform a gain adjustment at each CH5
switch position.
[GY502 Settings]
Select the gyro operation mode at the GY502 Mode screen. (AVC, NOR,
or CMT)
[Transmitter Settings]
ATV function:
Set the ATV rates at the transmitter CH5 ATV function.
[Sensitivity Display]
The gain display indicates the actual gain at the GY502 normal screen
display.
The following shows the relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
when GY502 sensitivity setting is 100% in both the G1 and G2 gain
modes.
- Relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
CH5 Switch CH5 Switch
Transmitter
settings
GY502mode
settings
ATV rates
NOR
AVC
CMT
Forward side Front side
90% - 0% - 90%
Normal mode Normal mode
AVCS mode AVCS mode
Normal mode AVCS mode
(G2) (G1)
Actual gain
100% - 0% - 100%
Page 29

DATA SETTING
When Using a GY502 Gyro Gain Adjustment Function
[Transmitter Settings]
Adjust both the ATV rates to 90% at the transmitter Ch5 ATV function.
[GY502 Settings]
Operation Mode Setting function:
Select the gyro operation mode at the GY502 Mode screen. (AVC, NOR, or
CMT)
Gyro Gain Adjustment function:
Set the G:1 and G:2 gains at the GY502 G:x screen.
- Relationship between transmitter and gyro setting
CH5 Switch CH5 Switch
Transmitter
settings
ATV rates
Forward side Front side
90% (Fixed) 90% (Fixed)
29
GY502mode
settings
NOR
AVC
CMT
Actual gain
Normal mode Normal mode
AVCS mode AVCS mode
Normal mode AVCS mode
(G2) (G1)
100% - 0% - 100%
Page 30

30
DATA SETTING
Initialization
AVCS mode operation is based on the rudder neutral data stored in
the GY502. When using the GY502 for the first time, or when the
internal reference data and the transmitter neutral position differed
when the transmitter neutral trim was adjusted, etc., the rudder
neutral data must be read again.
[At power ON]
When the power switch is turned on, the GY502 automatically
obtains the reference signal for AVCS function correction and
initializes itself.
•When the power was turned on in the Normal mode, the rudder
neutral position already memorized in the GY502 is not updated.
•When the power was turned on in the AVCS mode, the rudder signal
at that point is memorized and updated.
Precautions When Turning on the Power Switch
During initialization, the message “-Hello-” appears on the GY502
LCD screen.
Do not move the helicopter until this message disappears (in
about 3 seconds).
Also, do not move the transmitter rudder stick from the neutral
position during this period.
[During use]
When the rudder was re-trimmed in the Normal mode and the new
trim position also affects the AVCS mode, the rudder trim neutral
position must be memorized in the GY502.
Page 31

DATA SETTING
Re-reading method
In this case, quickly switch (interval of within 1
second) the transmitter remote gain switch between the
Normal and AVCS sides at least three times and
switch the AVCS side at the neutral trim position set in
the Normal mode. This memorizes the new rudder
neutral position in the GY502.
When the transmitter has a function that allows trim
setting for each flight condition, such as the T9Z, the
AVCS mode trim position is fixed and this operation is
unnecessary.
Never use the transmitter rudder trim in the AVCS mode.
When the rudder is trimmed during flight, the neutral position will
change.
When using the GY502 in the AVCS mode, set revolution mixing
to OFF.
When the rudder neutral position was changed by the linkage,
the rudder neutral position in the AVCS mode must always be
re-read before use.
31
Page 32

32
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
Install and adjust the GY502 as described below.
•When making GY502 adjustments, always
use the accessory miniature screwdriver
and do not apply excessive force.
Installing to Fuselage
1 Installing sensor and amp
GY502 sensor
Frame gyro bed
Install the GY502 sensor to the fuselage using the accessory sensor
tape. Also routinely check the sensor tape and replace the tape if it is
saturated with oil or partially peeled.
*Oil on the sensor bottom and the part installed to the frame can be
wiped off with cleaner, etc.
Sensor installation precautions
•Always use the accessory sensor tape to install the sensor. Install the
sensor to the center of the sensor tape.
•Depending on the vibration from the helicopter, the sponge may tear
near the corners of the sensor tape. If the helicopter is flown in this
state, vibrations will not be sufficiently absorbed and the sensor may
fall off. Before flight, always check the sensor installation state. If the
sponge is torn, replace it.
•Install the sensor so that the
bottom of the gyro is perpendicular to the main rotor shaft axial
direction. Offset of this axis will
also react in the roll and pitch
directions.
Installing control amp
•When installing the control amp, after the end of sensitivity adjustment, vibration-proof the amp by wrapping it in sponge, the same as
the receiver.
Page 33

2 Connections
Connect the GY502, receiver
and servo as shown below.
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
33
Insert the connectors fully
and firmly.
If a connector works loose
due to vibration during flight,
control may be lost and result
in a dangerous situation.
•Connect the sensor to the
amp sensor input ("GYRO").
•Connect the amp rudder
input ("RX,1-4") input
connector to the receiver
rudder channel (ch4).
Black Red
To receiver
•Connect the rudder servo to
the amp servo output ("SX").
•Connect the amp remote
3 Servo selection
When using a digital servo (S9253, S9250,
S9450, etc.) as the rudder servo, select High at
the Frm screen.
When using a servo other than a digital servo,
select Low at the Frm screen.
4 Gyro operation mode selection
When using the gyro only in the NOR mode,
select NOR. When using the gyro only in the
AVCS mode. select AVCS. When using the
gyro in both the AVCS and NOR modes,
select CMT.
gain input ("RX,AUX")
connector to the receiver
sensitivity setting channel
(normally ch5).
Page 34

34
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
*However, when using the gyro in the CMT mode, since the AVCS
and NOR mode gain must be set during hovering and in flight, a
transmitter with a gyro mixing function (T9Zwc series, T8Usuper
series) is necessary.
•For a description of transmitter setting, see the remote gain function
(p21).
5 Rudder servo linkage check
Make the initial linkage connections in the NOR mode. In this case,
make adjustments mechanically and make minimum trimmer
adjustments at the transmitter.
In the NOR mode, make the following linkage checks:
•In the rudder neutral position, connect the linkage at the position at
which the servo horn and control wire are perpendicular.
Perpendicular
Control wire
Set the servo horn length based on the
helicopter manufacturer's instructions.
Move the rudder stick to the right and left and check the direction of
operation of the tail rotor. If the tail rotor turns in the wrong direction, reverse the direction with the transmitter reverse function.
6 Gyro operation direction check
If the rudder servo moves to the left when the nose of the helicopter
moves to the right, the gyro direction is correct.
If the rudder servo moves to the right, switch
the direction using the GDir screen.
*If you try to fly the helicopter while the gyro direction is incorrect,
when the rotor rotates clockwise, the helicopter nose will yaw to
the left and cause an extremely dangerous situation.
Page 35

INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
7 Limit setting
Move the rudder stick to the left and right and
perform adjustment at the Lmt screen so that
the servo operation angle becomes the maximum value at which the servo horn does not
strike the linkage.
*When flying, the servo horn does not move beyond this set angle,
thus protecting the linkage. However, if the limit setting is too low,
gyro performance will be effected.
*In this mode, only the stick operates; the gyro does not operate.
8 Gyro gain setting (tentative setting)
The initial gain of the GY502 is 100% for
both G1 and G2. When setting the gain from
the transmitter, leave it at the 100% reference
gain.
Make the following value the gain setting criteria.
A setting example when a T9Zwc series transmitter was used is
described below. When using another transmitter, see "Remote gain
function" on page 21.
(T9Zwc transmitter setting)
•Call the transmitter GYR setting screen.
•Adjust the gain when hovering to 90% at the AVCS side and 10% at
the normal side on the transmitter screen.
•Set the gain in flight to 80% and 20% for the AVCS and NOR mode,
respectively, on the transmitter screen.
•At this time, the GY502 gain display becomes 80% for hovering and
60% for flight.
(*1) In the case of the T9Z GYR function, GY502 gain is 0% for a
transmitter setting of 50%. When the gain is set above 50%, the
GY502 operates in the AVCS mode and when the gain is set below
50%, the GY502 operates in the normal mode. The gyro gain
changes 2% for every 1% gain change.
35
Page 36

36
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
When using a transmitter without a gyro gain switching function,
connect the gain setting connector to an idle channel and set the
GY502 G1 and G2 gains using this gain setting screen. Gain can be
trimmed by means of the transmitter ATV function.
9 Transmitter setting check
Checks the transmitter setting in the ACVS mode. Check that the
transmitter is not set so that the neutral position has shifted.
(Transmitter setting)
•Set all rudder mixings to INH.
•Set all hovering and flight rudder trims to the same position.
•Set rudder ATV to 100% under all conditions.
•Also set the T9Z condition delay function to INH.
If the normal screen operation mode display is “A” under all usage
conditions, neutral offset is OK. If “ ” is displayed, display “A” by
operating the rudder trimmer for that flight condition.
10 Rudder neutral position check
In the AVCS mode, the rudder servo neutral position is unknown.
Check the neutral position by switching the GY502 to the NOR
mode, or by moving the rudder stick to the left and right at least
three times at high speed and immediately returning the stick to the
neutral position. This temporarily resets the rudder servo.
Page 37

INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
Flight Adjustments
1
In the AVCS mode, turn on the transmitter power, then turn on
the gyro and receiver power. This reads the rudder neutral signal at
the GY502.
•Never move the helicopter or rudder stick during the approximately
three seconds that the -Hello- display blinks.
2 Hover in the Normal mode and adjust the rudder neutral position.
•In the AVCS mode, the rudder neutral position is automatically set,
and linkage changes cannot be verified. First, perform rudder neutral
adjustment in the Normal mode.
•Move the transmitter trim lever and reset the neutral position. When
the rudder servo neutral position has changed considerably, readjust
the linkage.
3 When the transmitter rudder trim was adjusted, the rudder neutral
data must be read to the GY502. Therefore, always perform the
following operations:
•Switch the transmitter sensitivity switch quickly (internal of within 1
second) between AVCS and Normal at least three times. "****" is
displayed on the LCD screen to show that data is being memorized.
During this operation, never move the transmitter rudder stick from
the neutral position for at least 1 second immediately after switching
the switch in the state in which the model is on the ground. Memorization and updating is executed only when the sensitivity switch is in
the AVCS mode position.
37
4 Set the sensitivity to the position at which hunting does not occur
during hovering and flight.
•When the helicopter tail hunts, set the gyro sensitivity to a lower
value. When adjusting the gyro sensitivity, increase and decrease the
sensitivity gradually while checking.
Page 38
38
INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
5 Adjust the hovering and flight rudder effect using the transmitter's
D/R or AFR function.
•Do not adjust with the ATV function. If the ATV function is used,
trimming may change.
(If necessary)
6 When you sense a difference in the rudder effect between the
AVCS and Normal modes, adjust using the GY502 rudder control
gain.
•Adjustment method
When the rudder effect in the AVCS is different from the rudder effect
in the Normal mode after adjustment was performed using the
transmitter's D/R or AFR function, adjust the difference using the
NCGx parameter.
7 Adjust the left and right pirouette stopping state by control delay
and tracking.
•Adjustment using the delay function of the T9Z transmitter is also
possible. Since the gyro gain also has a large effect on the stopping
state, make this adjustment after adjusting the sensitivity.
8 Adjust the rudder operation feel using the GY502 AVCS sense in
the AVCS mode.
(Steering angle, neutral suppression, and pirouette stopping)
Page 39

INSTALLATION AND ADJUSTMENT
9 When you want to use rudder mixing in the Normal mode, set the
transmitter so that rudder mixing is applied only during Normal
mode operation. Never use rudder mixing in the AVCS mode.
39
Page 40

40
REFERENCE
REFERENCE
Specifications
GY502 Ratings
Yaw-axis stabilizer for helicopter (rate gyro)
Display device: 8-character dot matrix liquid crystal display
Operating voltage range: DC 3.8V to 6.0V
Current drain: 70mA (@5.0V, including sensor)
Operating temperature range: -10 to +50 degree C
Operating humidity range: 10 to 90%RH (no condensation)
Dimensions: 57 x 32 x 15mm (amp), 34 x 34 x 16.5mm (sensor)
Weight: 34g (amp) + 25g (sensor)
* Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Page 41

REFERENCE
Definition of Abbreviations
The following defines the abbreviations and symbols used in this
manual in alphabetical order. The function names are given on the
description pages.
41
A
ACGA/B Rudder control gain
(AVCS) p17
AFR AFR function.
ATV ATV function. Steering angle
adjustment function.
AVC AVCS mode.
AVCS AVCS system. AVCS mode.
AVS AVCS sense. p20
C
CMT Normal/AVC switching mode.
D
D1DA Control delay. p17
D1IA Control delay. p17
D/R Dual rate function.
DUO T9Z dual gain control mode.
F
Frm Servo frame rate. p19
G
G:1A/N Gyro gain 1 side. p16
G:2A/N Gyro gain 2 side. p16
GDir Gyro reverse. p16
GYRO T9Z gyro sense mixing.
H
Hello Power on screen display.
High High side.
I
IDLE Transmitter power OFF state.
INH Use inhibited state.
L
LCD Liquid crystal display screen.
LmtA/B Linkage limit setting. p20
Low Low side.
LOW BAT Low battery error
display.
M
Mode Operation mode setting. p18
N
NCGA/B Rudder control gain
(Normal) p17
NOR Normal mode. Normal side.
P
PMIX Programmable mixing.
R
REV Reverse side.
T
Trk Gain tracking. p18
Page 42

42
REFERENCE
GY502 Parameters Sheet
* Copy and use.
Helicopter:
Date:
Parameter value value Remarks
GDir
Gyro Reverse
G:xx
Gyro Gain Adjustment
ACGx,NCGx
Rudder Control Gain
D11x
Control Delay I
D1Dx
Control Delay D
Initial Set
NOR NOR/REV
G:1 100% 0-120%
G:2 100% 0-120%
ACGA 100% 10-250%
ACGB 100% 10-250%
NCGA 120% 10-250%
NCGB 120% 10-250%
D1IA 0% 0-100%
D1IB 0% 0-100%
D1DA 0% 0-100%
D1DB 0% 0-100%
Trk
Gain Tracking
Mode
Operation Mode Setting
Frm
Servo Frame Rate
AVS
AVCS Sense
Lmtx
Linkage Limit Setting
+0% -20-+20%
CMT CMT/NOR/AVC
Low Low/High
100% 50-150%
LmtA 100%
LmtB 100%
Page 43

REFERENCE
43
Makuhari Techno Garden Bldg., B6F 1-3 Nakase, Mihama-ku, Chiba 261-8555, Japan
FUTABA CORPORATION
Phone: (043) 296-5118 Facsimile: (043) 296-5124
©FUTABA CORPORATION 2000, 9
 Loading...
Loading...