Page 1
SERVICE MANUAL
This Service Manual is for the
LT6-M19WB(A8CNBFP) model.
For the LT6-M19WB(A8CNBFP)
model, the letter (A8CNBFP) is
printed on the Serial No. Label.
Refer to the Serial No. Label on the
right.
Serial No. Label
"A8CNBFP"
19″ COLOR LCD TELEVISION
LT6-M19WB
Page 2

19″ COLOR LCD TELEVISION
LT6-M19WB
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Important Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Standard Notes for Servicing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Cabinet Disassembly Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Electrical Adjustment Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
How to Initialize the LCD Television. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Block Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Schematic Diagrams / CBA and Test Points . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
Wiring Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
Exploded View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-1
Mechanical Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-1
Electrical Parts List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-1
The LCD panel is manufactured to provide many years of useful life.
Occasionally a few non active pixels may appear as a tiny spec of color.
This is not to be considered a defect in the LCD screen.
Page 3
SPECIFICATIONS
< TUNER >
VHS/UHF Input ----------- 75Ω unbal., IEC Connector
Center IF ------------------- SECAM-L 38.9MHz, SECAM-L’ 33.9MHz
Description Condition Unit Nominal Limit
1. Video S/N 80 dB --- 40
2. Audio S/N --- dB --- 40/40
< LCD PANEL >
Description Condition Unit Nominal Limit
1. Number of Pixels
2. Viewing Angle
<DVB-T>
Description Condition Unit Nominal Limit
1. RECEIVED
FREQ.RANGE
(-60dBm, 45ch.) *1
2. INPUT DYNAMIC
RANGE (mix./max) *1
3. C/N PERFORMANCE
*1
4 . M U LTI PAT H
a. Performance with
short delay echoes
b. Performance with
long delay echoes
c. C/N Performance on
0dB echo channel
(14µs)
Horizontal
Ver t i cal
Horizontal
Ver t i cal
+
-
VHF HIGH 7ch.
UHF 45ch.
VHF HIGH 7ch.
UHF 45ch.
UHF 45ch.
c:*2
d:*3
c:*2
d:*3
c:*1
pixels
pixels
kHz
kHz
dBm
dBm
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
1440
900
°
°
-85 to 85
-80 to 80
1000
900
-82.5/2
-81.1/2
15
15
18.7
14.0
19.1
13.0
20.7
---
---
---
---
500
-150
-75/-10
-75/-10
≦18
≦18
≦23
≦20
≦23
≦18
≦24
*1: modulation parameters = [8k 64QAM CR=2/3 GI=1/32]
*2: modulation parameters = [2k 64QAM CR=2/3 GI=1/32]
*3: modulation parameters = [2k 16QAM CR=3/4 GI=1/32]
< VIDEO >
Description Condition Unit Nominal Limit
1. Over Scan
2. Color Temperature
3. Resolution
4. Brightness AT 100% WHITE FIELD cd/m
Horizontal
Ver t i cal
AT 80% WHITE FIELD
x
y
Horizontal
Ver t i cal
line
line
%
%
°K 12000
2
5
5
0.272
0.278
400
350
250 ---
---
---
--±0.005
±0.005
---
---
1-1 A8CN0SP
Page 4
< AUDIO >
All items are measured across 8 Ω load at speaker output terminal.
Description Condition Unit Nominal Limit
1. Audio Output Power 10% THD: Lch/Rch W 1.0/1.0 0.8/0.8
2. Audio Distortion 500mW: Lch/Rch % 1.5/1.5 3.0/3.0
-
3. Audio Freq. Response
6dB: Lch
-
6dB: Rch
Hz
Hz
70 to 8 k
70 to 8 k
---
---
4. Audio S/N
Note: Nominal specifications represent the design specifications. All units should be able to approximate these.
Some will exceed and some may drop slightly below these specifications. Limit specifications represent
the absolute worst condition that still might be considered acceptable. In no case should a unit fail to meet
limit specifications.
VIDEO
Component
dB
dB
---
---
>45/45
>45/45
1-2 A8CN0SP
Page 5
IMPORTANT SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Prior to shipment from the factory, our products are strictly inspected for recognized product safety and electrical
codes of the countries in which they are to be sold. However, in order to maintain such compliance, it is equally
important to implement the following precautions when a set is being serviced.
Safety Precautions for LCD TV
Circuit
1. Before returning an instrument to the
customer, always make a safety check of the
entire instrument, including, but not limited to, the
following items:
a. Be sure that no built-in protective devices are
defective and have been defeated during
servicing. (1) Protective shields are provided
on this chassis to protect both the technician
and the customer. Correctly replace all missing
protective shields, including any removed for
servicing convenience. (2) When reinstalling
the chassis and/or other assembly in the
cabinet, be sure to put back in place all
protective devices, including but not limited to,
nonmetallic control knobs, insulating
fishpapers, adjustment and compartment
covers/shields, and isolation resistor/capacitor
networks. Do not operate this instrument or
permit it to be operated without all
protective devices correctly installed and
functioning. Servicers who defeat safety
features or fail to perform safety checks
may be liable for any resulting damage.
b. Be sure that there are no cabinet openings
through which an adult or child might be able to
insert their fingers and contact a hazardous
voltage. Such openings include, but are not
limited to, (1) spacing between the LCD module
and the cabinet mask, (2) excessively wide
cabinet ventilation slots, and (3) an improperly
fitted and/or incorrectly secured cabinet back
cover.
c. Antenna Cold Check - With the instrument AC
plug removed from any AC source, connect an
electrical jumper across the two AC plug
prongs. Place the instrument AC switch in the
on position. Connect one lead of an ohmmeter
to the AC plug prongs tied together and touch
the other ohmmeter lead in turn to each tuner
antenna input exposed terminal screw and, if
applicable, to the coaxial connector. If the
measured resistance is less than 1.0 megohm
or greater than 5.2 megohm, an abnormality
exists that must be corrected before the
instrument is returned to the customer. Repeat
this test with the instrument AC switch in the off
position.
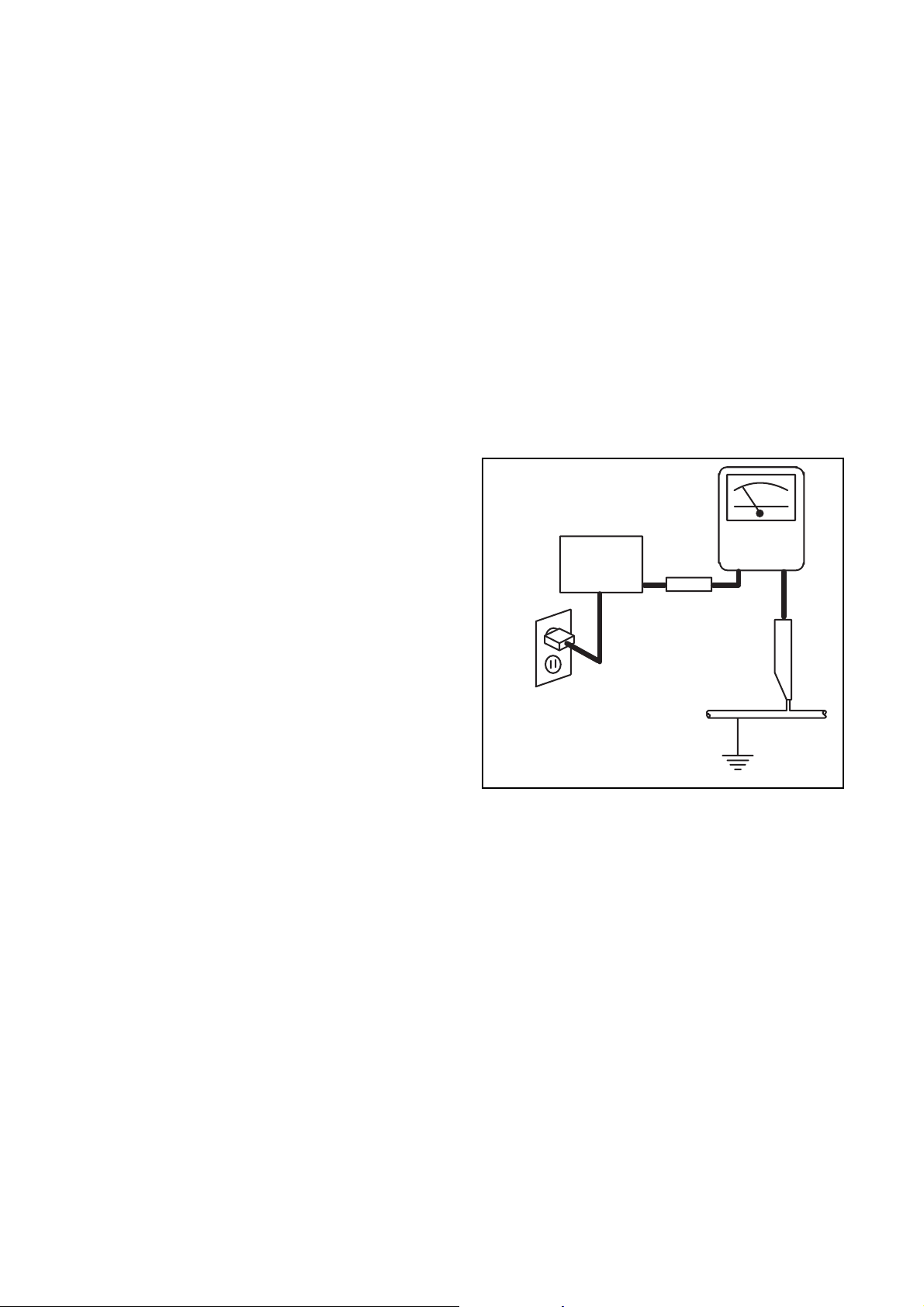
d. Leakage Current Hot Check - With the
instrument completely reassembled, plug the
AC line cord directly into a 230 V AC outlet. (Do
not use an isolation transformer during this
test.) Use a leakage current tester or a
metering system that complies with American
National Standards Institute (ANSI) C101.1
Leakage Current for Appliances and
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 1410, (50.7).
With the instrument AC switch first in the on
position and then in the off position, measure
from a known earth ground (metal water pipe,
conduit, etc.) to all exposed metal parts of the
instrument (antennas, handle brackets, metal
cabinet, screw heads, metallic overlays, control
shafts, etc.), especially any exposed metal
parts that offer an electrical return path to the
chassis. Any current measured must not
exceed 0.5 milli-ampere. Reverse the
instrument power cord plug in the outlet and
repeat the test.
READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE 0.5 mA
LEAKAGE
DEVICE
BEING
TESTED
TEST ALL EXPOSED
METAL SURFACES
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
USING AC
ADAPTER PLUG
AS REQUIRED
ANY MEASUREMENTS NOT WITHIN THE
LIMITS SPECIFIED HEREIN INDICATE A
POTENTIAL SHOCK HAZARD THAT MUST
BE ELIMINATED BEFORE RETURNING THE
INSTRUMENT TO THE CUSTOMER OR
BEFORE CONNECTING THE ANTENNA OR
ACCESSORIES.
2. Read and comply with all caution and safety-
related notes on or inside the receiver cabinet, on
the receiver chassis, or on the LCD module.
3. Design Alteration Warning - Do not alter or add
to the mechanical or electrical design of this LCD
TV receiver. Design alterations and additions,
including, but not limited to circuit modifications
and the addition of items such as auxiliary audio
and/or video output connections, might alter the
safety characteristics of this receiver and create a
hazard to the user. Any design alterations or
additions will void the manufacturer's warranty and
may make you, the servicer, responsible for
personal injury or property damage resulting
therefrom.
CURRENT
TESTER
+
EARTH
GROUND
_
2-1 LTVP_ISP
Page 6

4. Hot Chassis Warning -
a. Some TV receiver chassis are electrically
connected directly to one conductor of the AC
power cord and maybe safety-serviced without
an isolation transformer only if the AC power
plug is inserted so that the chassis is
connected to the ground side of the AC power
source. To confirm that the AC power plug is
inserted correctly, with an AC voltmeter,
measure between the chassis and a known
earth ground. If a voltage reading in excess of
1.0 V is obtained, remove and reinsert the AC
power plug in the opposite polarity and again
measure the voltage potential between the
chassis and a known earth ground.
b. Some TV receiver chassis normally have 85V
AC(RMS) between chassis and earth ground
regardless of the AC plug polarity. This chassis
can be safety-serviced only with an isolation
transformer inserted in the power line between
the receiver and the AC power source, for both
personnel and test equipment protection.
c. Some TV receiver chassis have a secondary
ground system in addition to the main chassis
ground. This secondary ground system is not
isolated from the AC power line. The two
ground systems are electrically separated by
insulation material that must not be defeated or
altered.
5. Observe original lead dress. Take extra care to
assure correct lead dress in the following areas: a.
near sharp edges, b. near thermally hot parts-be
sure that leads and components do not touch
thermally hot parts, c. the AC supply, d. high
voltage, and, e. antenna wiring. Always inspect in
all areas for pinched, out of place, or frayed wiring.
Check AC power cord for damage.
6. Components, parts, and/or wiring that appear to
have overheated or are otherwise damaged
should be replaced with components, parts, or
wiring that meet original specifications.
Additionally, determine the cause of overheating
and/or damage and, if necessary, take corrective
action to remove any potential safety hazard.
7. Product Safety Notice - Some electrical and
mechanical parts have special safety-related
characteristics which are often not evident from
visual inspection, nor can the protection they give
necessarily be obtained by replacing them with
components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc..
Parts that have special safety characteristics are
identified by a ! on schematics and in parts lists.
Use of a substitute replacement that does not
have the same safety characteristics as the
recommended replacement part might create
shock, fire, and/or other hazards. The product's
safety is under review continuously and new
instructions are issued whenever appropriate.
Prior to shipment from the factory, our products
are strictly inspected to confirm they comply with
the recognized product safety and electrical codes
of the countries in which they are to be sold.
However, in order to maintain such compliance, it
is equally important to implement the following
precautions when a set is being serviced.
2-2 LTVP_ISP
Page 7

Precautions during Servicing
A. Parts identified by the ! symbol are critical for
safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
B. In addition to safety, other parts and assemblies
are specified for conformance with regulations
applying to spurious radiation. These must also be
replaced only with specified replacements.
Examples: RF converters, RF cables, noise
blocking capacitors, and noise blocking filters, etc.
C. Use specified internal wiring. Note especially:
1) Wires covered with PVC tubing
2) Double insulated wires
3) High voltage leads
D. Use specified insulating materials for hazardous
live parts. Note especially:
1) Insulation Tape
2) PVC tubing
3) Spacers
4) Insulators for transistors.
E. When replacing AC primary side components
(transformers, power cord, etc.), wrap ends of
wires securely about the terminals before
soldering.
F. Observe that the wires do not contact heat
producing parts (heat sinks, oxide metal film
resistors, fusible resistors, etc.)
G. Check that replaced wires do not contact sharp
edged or pointed parts.
H. When a power cord has been replaced, check that
5~6 kg of force in any direction will not loosen it.
I. Also check areas surrounding repaired locations.
J. Use care that foreign objects (screws, solder
droplets, etc.) do not remain inside the set.
K. When connecting or disconnecting the internal
connectors, first, disconnect the AC plug from the
AC supply outlet.
L. When installing parts or assembling the cabinet
parts, be sure to use the proper screws and
tighten certainly.
2-3 LTVP_ISP
Page 8
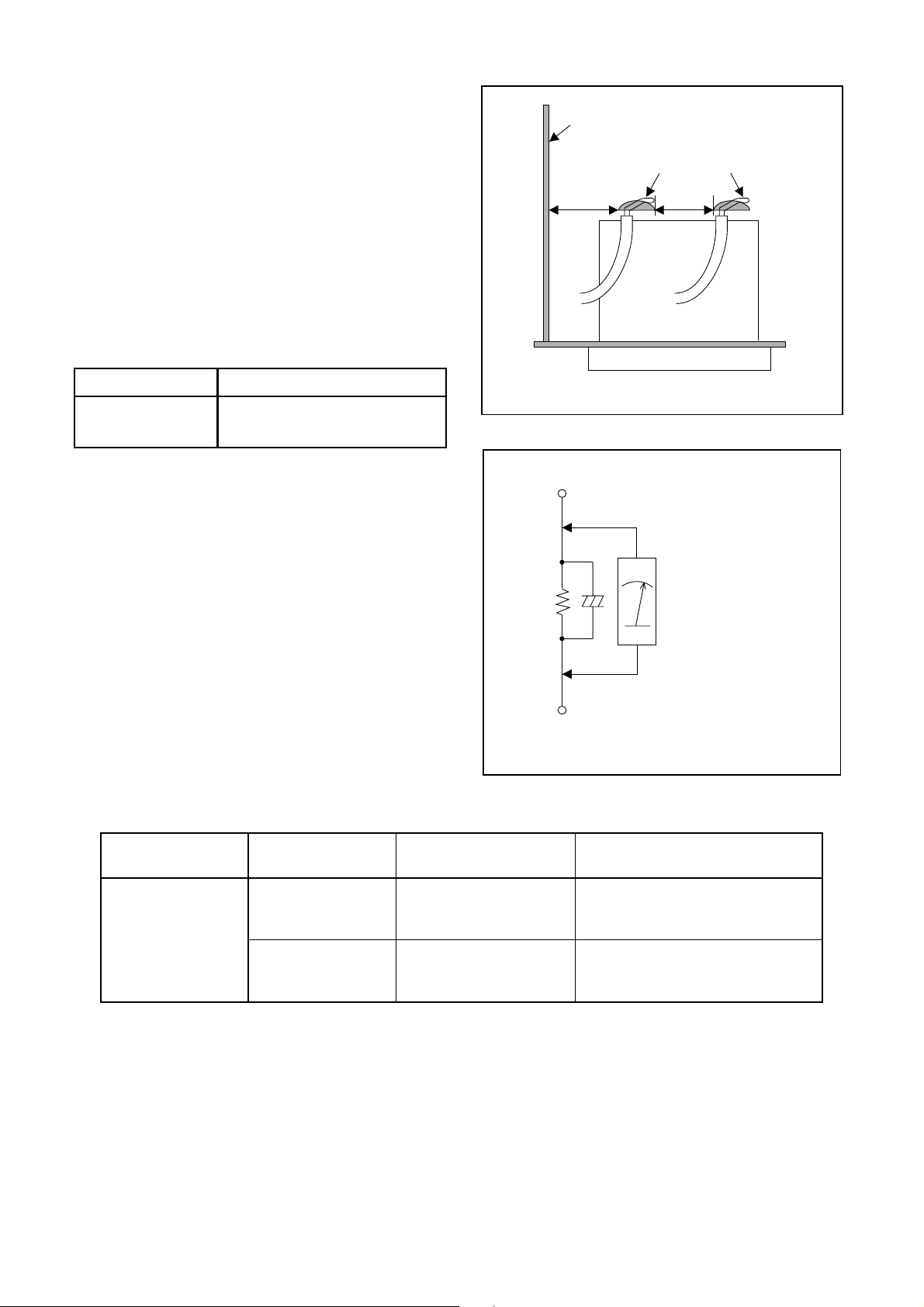
Safety Check after Servicing
Examine the area surrounding the repaired location
for damage or deterioration. Observe that screws,
parts and wires have been returned to original positions. Afterwards, perform the following tests and confirm the specified values in order to verify compliance
with safety standards.
1. Clearance Distance
When replacing primary circuit components, confirm
specified clearance distance (d) and (d') between soldered terminals, and between terminals and surrounding metallic parts. (See Fig. 1)
Table 1 : Ratings for selected area
AC Line Voltage Clearance Distance (d), (d’)
220 to 240 V
Note: This table is unofficial and for reference only.
Be sure to confirm the precise values.
≥ 3mm(d)
≥ 8mm(d’)
2. Leakage Current Test
Confirm the specified (or lower) leakage current between B (earth ground, power cord plug prongs) and
externally exposed accessible parts (RF terminals, antenna terminals, video and audio input and output terminals, microphone jacks, earphone jacks, etc.).
Chassis or Secondary Conductor
Primary Circuit
d' d
Exposed Accessible Part
Z
AC Voltmeter
(High Impedance)
Fig. 1
Measuring Method : (Power ON)
Insert load Z between B (earth ground, power cord
plug prongs) and exposed accessible parts. Use an
AC voltmeter to measure across both terminals of load
Z. See Fig. 2 and following table.
Table 2: Leakage current ratings for selected areas
AC Line Voltage Load Z Leakage Current (i)
2kΩ RES.
Connected in
parallel
220 to 240 V
50kΩ RES.
Connected in
parallel
Note: This table is unofficial and for reference only. Be sure to confirm the precise values.
i≤0.7mA AC Peak
i≤2mA DC
i≤0.7mA AC Peak
i≤2mA DC
One side of
B
Power Cord Plug Prongs
One side of power cord plug
prongs (B) to:
Antenna terminals
A/V Input, Output
Fig. 2
RF or
2-4 LTVP_ISP
Page 9
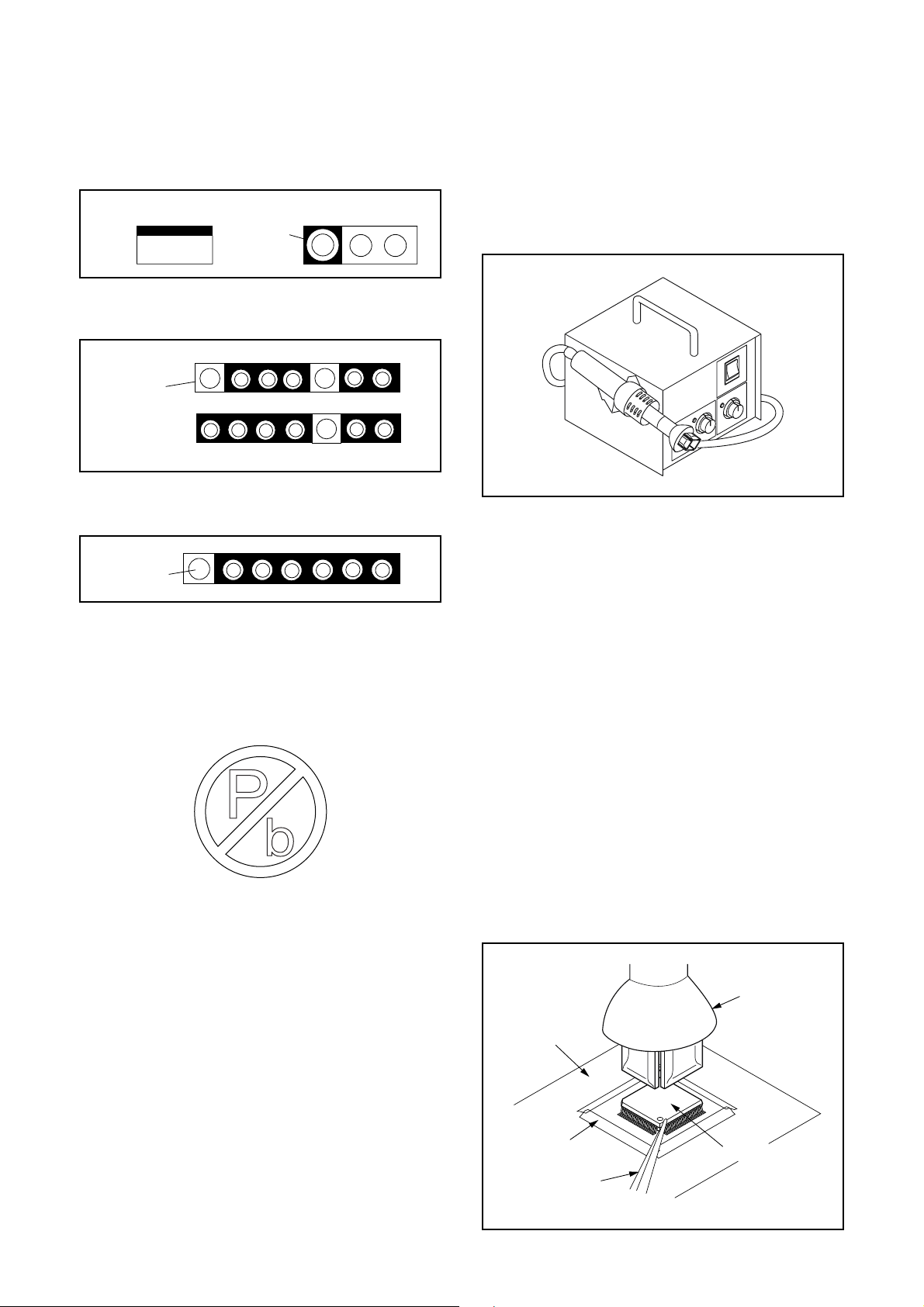
STANDARD NOTES FOR SERVICING
Circuit Board Indications
1. The output pin of the 3 pin Regulator ICs is
indicated as shown.
Top View
Out
2. For other ICs, pin 1 and every fifth pin are
indicated as shown.
Pin 1
3. The 1st pin of every male connector is indicated as
shown.
Pin 1
Input
In
Bottom View
5
10
Pb (Lead) Free Solder
Pb free mark will be found on PCBs which use Pb
free solder. (Refer to figure.) For PCBs with Pb free
mark, be sure to use Pb free solder. For PCBs
without Pb free mark, use standard solder.
Pb free mark
How to Remove / Install Flat Pack-IC
1. Removal
With Hot-Air Flat Pack-IC Desoldering Machine:
1. Prepare the hot-air flat pack-IC desoldering
machine, then apply hot air to the Flat Pack-IC
(about 5 to 6 seconds). (Fig. S-1-1)
Fig. S-1-1
2. Remove the flat pack-IC with tweezers while
applying the hot air.
3. Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
4. Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using
tweezers. (Fig. S-1-6)
CAUTION:
1. The Flat Pack-IC shape may differ by models. Use
an appropriate hot-air flat pack-IC desoldering
machine, whose shape matches that of the Flat
Pack-IC.
2. Do not supply hot air to the chip parts around the
flat pack-IC for over 6 seconds because damage
to the chip parts may occur. Put masking tape
around the flat pack-IC to protect other parts from
damage. (Fig. S-1-2)
3. The flat pack-IC on the CBA is affixed with glue, so
be careful not to break or damage the foil of each
pin or the solder lands under the IC when
removing it.
Hot-air
Flat Pack-IC
Desoldering
CBA
Masking
Tape
Tweezers
3-1 TVP_SN
Machine
Flat Pack-IC
Fig. S-1-2
Page 10
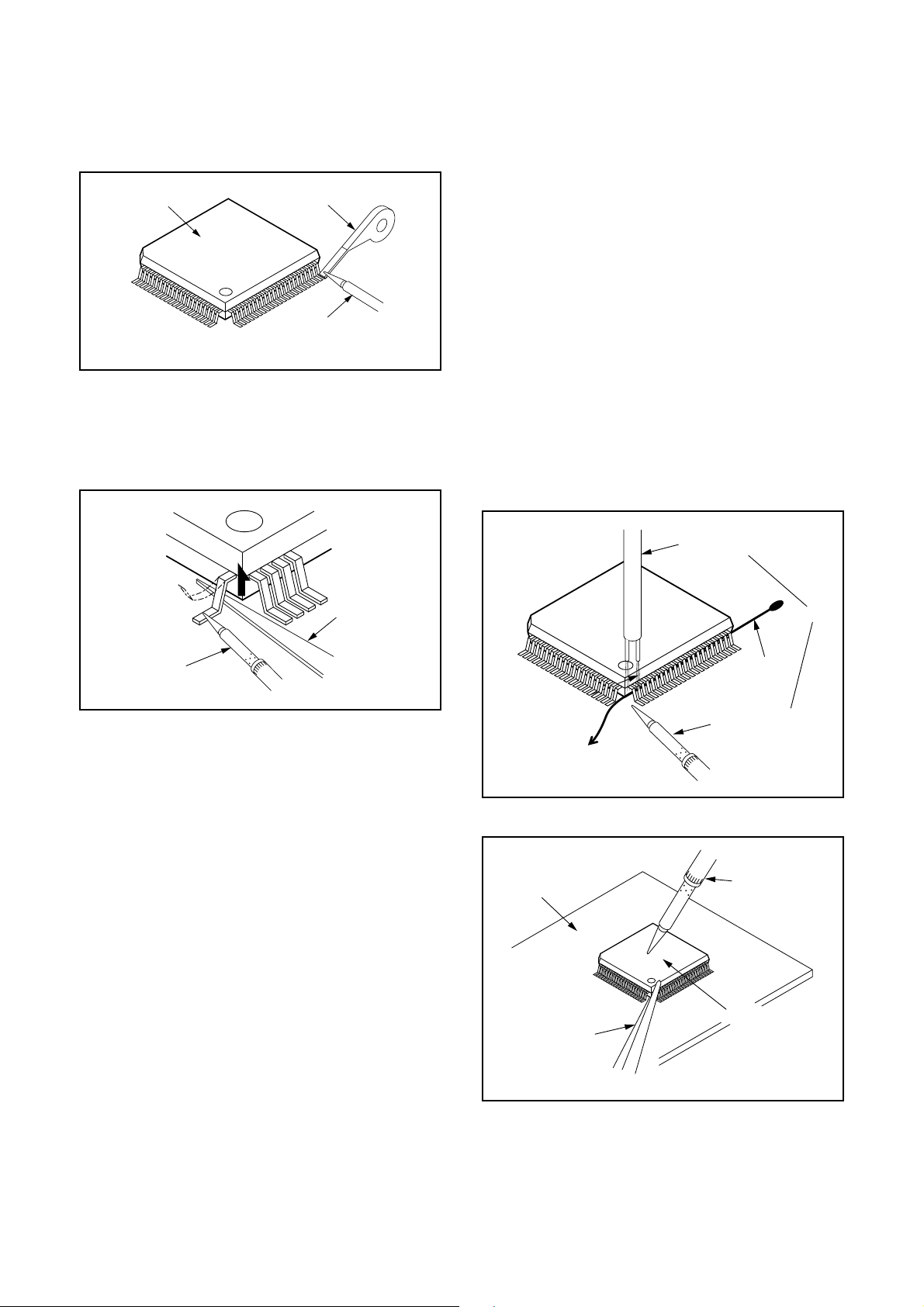
With Soldering Iron:
1. Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from
all pins of the flat pack-IC. When you use solder
flux which is applied to all pins of the flat pack-IC,
you can remove it easily. (Fig. S-1-3)
Flat Pack-IC
Desoldering Braid
Soldering Iron
Fig. S-1-3
2. Lift each lead of the flat pack-IC upward one by
one, using a sharp pin or wire to which solder will
not adhere (iron wire). When heating the pins, use
a fine tip soldering iron or a hot air desoldering
machine. (Fig. S-1-4)
With Iron Wire:
1. Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from
all pins of the flat pack-IC. When you use solder
flux which is applied to all pins of the flat pack-IC,
you can remove it easily. (Fig. S-1-3)
2. Affix the wire to a workbench or solid mounting
point, as shown in Fig. S-1-5.
3. While heating the pins using a fine tip soldering
iron or hot air blower, pull up the wire as the solder
melts so as to lift the IC leads from the CBA
contact pads as shown in Fig. S-1-5.
4. Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
5. Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using
tweezers. (Fig. S-1-6)
Note: When using a soldering iron, care must be
taken to ensure that the flat pack-IC is not
being held by glue. When the flat pack-IC is
removed from the CBA, handle it gently
because it may be damaged if force is applied.
Sharp
Pin
Fine Tip
Soldering Iron
3. Bottom of the flat pack-IC is fixed with glue to the
CBA; when removing entire flat pack-IC, first apply
soldering iron to center of the flat pack-IC and heat
up. Then remove (glue will be melted). (Fig. S-1-6)
4. Release the flat pack-IC from the CBA using
tweezers. (Fig. S-1-6)
Fig. S-1-4
To Solid
Mounting Point
CBA
Hot Air Blower
or
Iron Wire
Soldering Iron
Fig. S-1-5
Fine Tip
Soldering Iron
Flat Pack-IC
Tweezers
Fig. S-1-6
3-2 TVP_SN
Page 11
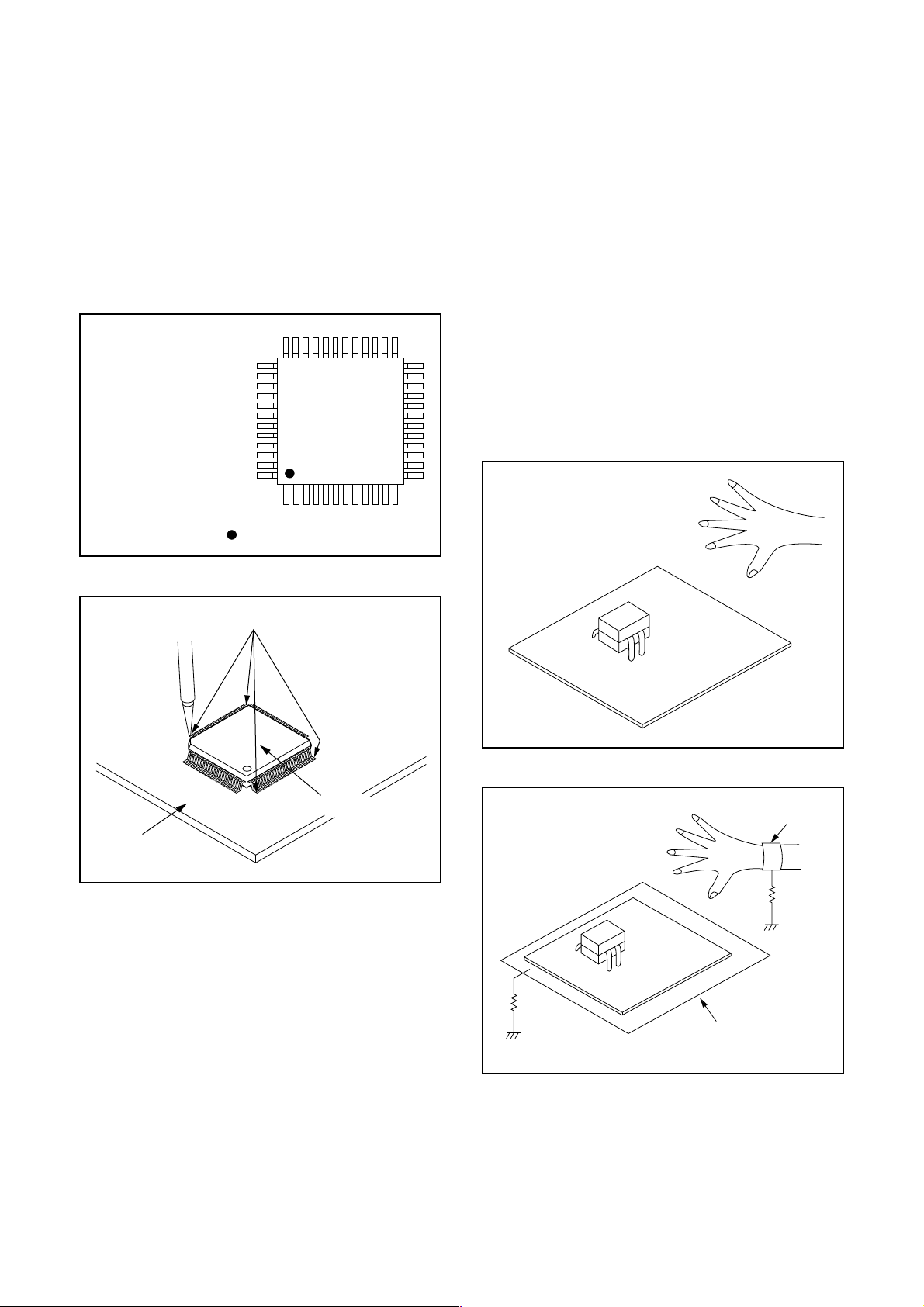
2. Installation
1. Using desoldering braid, remove the solder from
the foil of each pin of the flat pack-IC on the CBA
so you can install a replacement flat pack-IC more
easily.
2. The “●” mark on the flat pack-IC indicates pin 1.
(See Fig. S-1-7.) Be sure this mark matches the
pin 1 on the PCB when positioning for installation.
Then presolder the four corners of the flat pack-IC.
(See Fig. S-1-8.)
3. Solder all pins of the flat pack-IC. Be sure that
none of the pins have solder bridges.
Example :
Pin 1 of the Flat Pack-IC
is indicated by a " " mark.
Fig. S-1-7
Instructions for Handling Semiconductors
Electrostatic breakdown of the semi-conductors may
occur due to a potential difference caused by
electrostatic charge during unpacking or repair work.
1. Ground for Human Body
Be sure to wear a grounding band (1 MΩ) that is
properly grounded to remove any static electricity that
may be charged on the body.
2. Ground for Workbench
Be sure to place a conductive sheet or copper plate
with proper grounding (1 MΩ) on the workbench or
other surface, where the semi-conductors are to be
placed. Because the static electricity charge on
clothing will not escape through the body grounding
band, be careful to avoid contacting semi-conductors
with your clothing.
<Incorrect>
CBA
Presolder
Flat Pack-IC
Fig. S-1-8
<Correct>
1MΩ
CBA
Grounding Band
1MΩ
CBA
Conductive Sheet or
Copper Plate
3-3 TVP_SN
Page 12
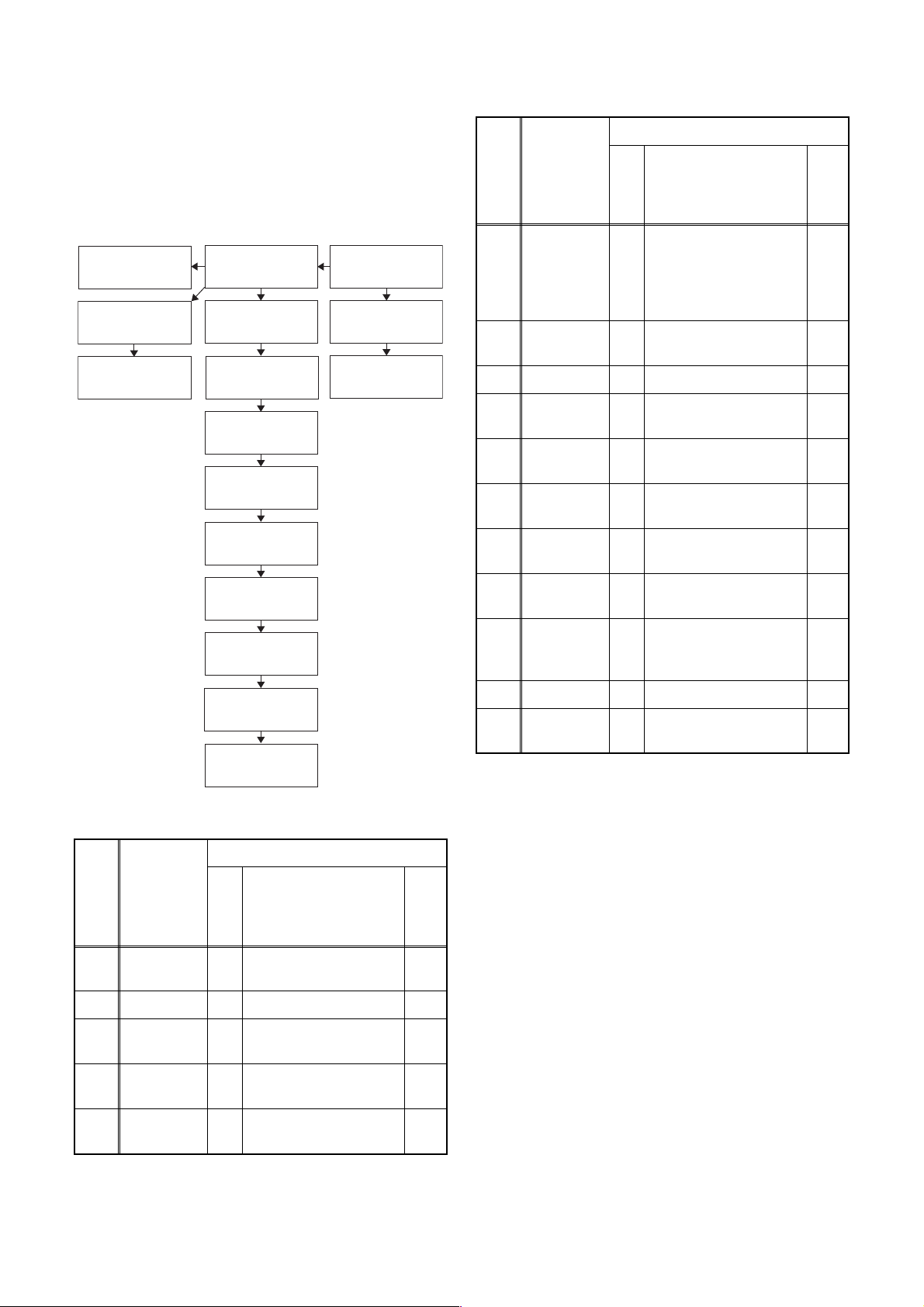
CABINET DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
1. Disassembly Flowchart
This flowchart indicates the disassembly steps for the
cabinet parts, and the CBA in order to gain access to
item(s) to be serviced. When reassembling, follow the
steps in reverse order. Bend, route and dress the
cables as they were.
[15] Speaker(s)
[12] IR Sensor CBA
[13] Function CBA
[4] Rear Cabinet
[5] Jack CBA
[6] Shield Box
[7] Digital Main
CBA Unit
[8] Shield(T)
[9] Main CBA
[1] Stand Cover
[2] Stand Neck
[3] Stand Hinge
Removal
Step/
Loc.
No.
Part
Remove/*Unhook/
Fig.
No.
Unlock/Release/
Unplug/Unclamp/
Desolder
2(H-1), (S-6), 5(S-7),
6(S-8), *CN101A,
[6] Shield Box
D2
*CN102A, *CN103A,
D3
*CN104A, *CN4501,
*CN4502, FFC Shield
Digital Main
[7]
CBA UnitD2D3
2(S-9), Connector IC
Card OSU
[8] Shield(T) D2 (S-10), 2(S-11) ---
[9] Main CBA
Junction
[10]
CBA
Inverter
[11]
CBA
IR Sensor
[12]
CBA
D2D36(S-12), *CN106,
*CN105A, *CN802
D2
*CN403A ---
D3
D2D34(S-13), *CN401,
*CN402, *CN451
D2
*CN301 ---
D3
Note
---
---
---
---
[10] Junction CBA
[11] Inverter CBA
[14] LCD Module
Assembly
[16] Front Cabinet
2. Disassembly Method
Removal
Step/
Loc.
Part
No.
Stand
[1]
Cover
[2] Stand Neck D1 2(S-2) ---
Stand
[3]
Hinge
Rear
[4]
Cabinet
[5] Jack CBA
Remove/*Unhook/
Fig.
No.
Unlock/Release/
Unplug/Unclamp/
Desolder
D1 2(S-1) ---
D1 --------------- ---
2(S-3), 5(S-4),
D1
*7(L-1)
D2
2(S-5), *CN107 ---
D3
Note
---
[13]
Function
CBA
D2
--------------- ---
D3
LCD
[14]
Module
D2 --------------- ---
Assembly
[15] Speaker(s) D2 4(S-14) ---
Front
[16]
↓
(1)
Cabinet
↓
(2)
D2 --------------- ---
↓
(3)
↓
(4)
(5)
↓
Note:
(1) Order of steps in procedure. When reassembling,
follow the steps in reverse order. These numbers
are also used as the Identification (location) No. of
parts in figures.
(2) Parts to be removed or installed.
(3) Fig. No. showing procedure of part location
(4) Identification of parts to be removed, unhooked,
unlocked, released, unplugged, unclamped, or
desoldered.
P = Spring, L = Locking Tab, S = Screw,
H = Hex Screw, CN = Connector
* = Unhook, Unlock, Release, Unplug, or Desolder
e.g. 2(S-2) = two Screws (S-2),
2(L-2) = two Locking Tabs (L-2)
(5) Refer to the following "Reference Notes in the
Ta bl e ."
4-1 A8CNBDC
Page 13
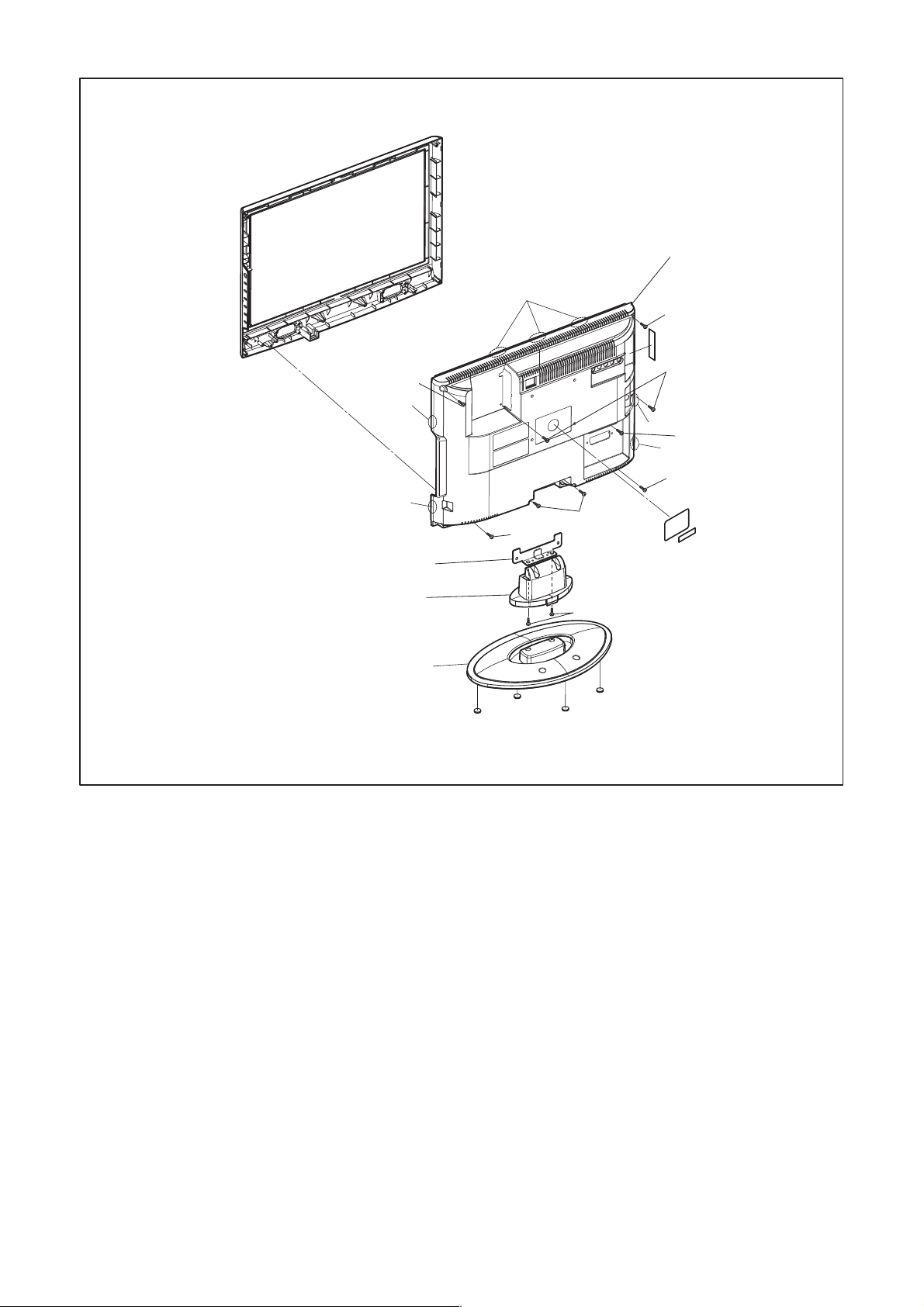
(S-4)
(L-1)
(L-1)
[3] Stand Hinge
(L-1)
(S-4)
(S-1)
[4] Rear Cabinet
(S-4)
(S-3)
(L-1)
(S-4)
(L-1)
(S-4)
[2] Stand Neck
[1] Stand Cover
(S-2)
Fig. D1
4-2 A8CNBDC
Page 14
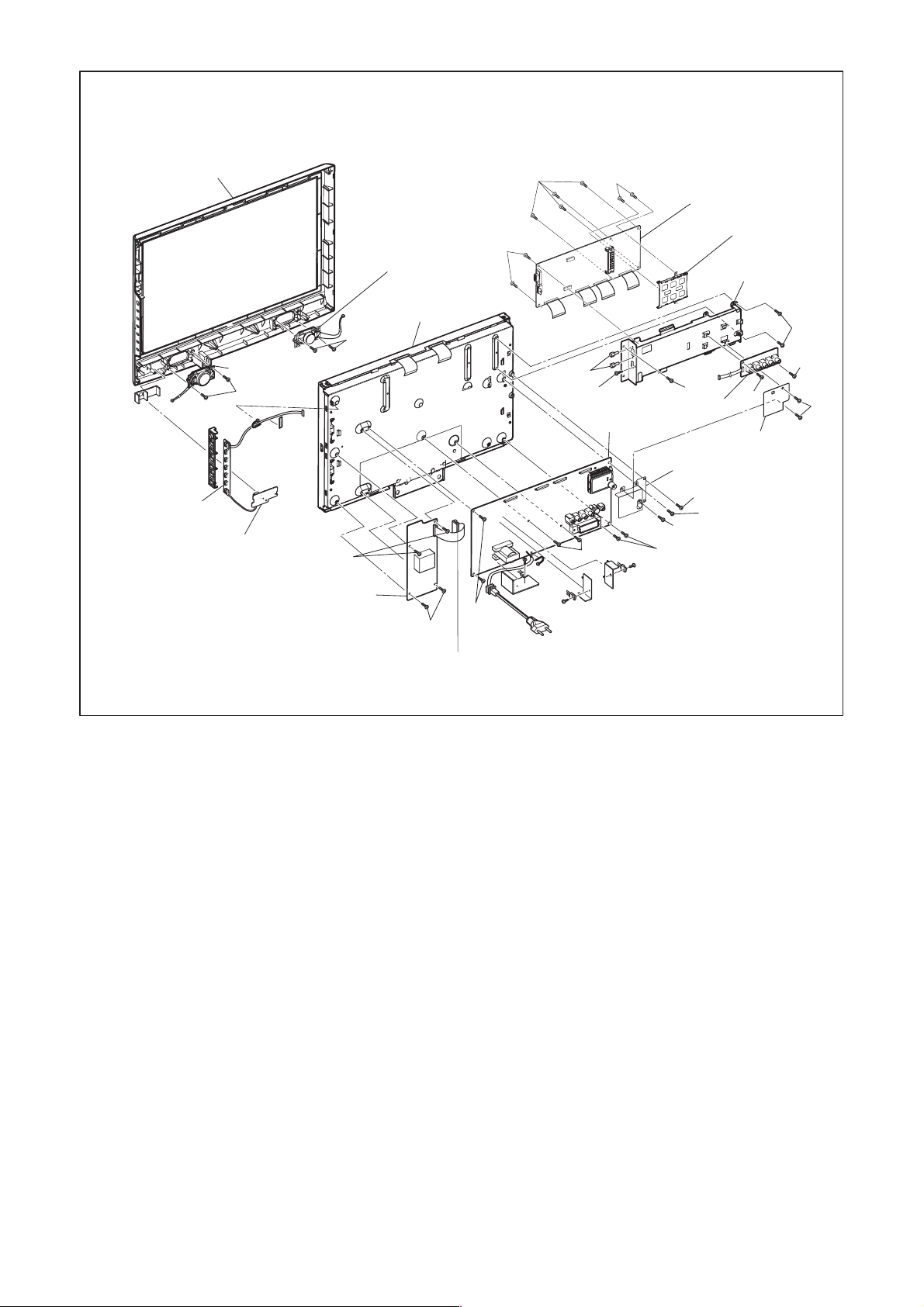
[16] Front Cabinet
[13] Function
CBA
[12] IR Sensor
CBA
[15] Speaker
(S-14)
(S-13)
[15] Speaker
[14] LCD Module
Assembly
(S-14)
(S-8)
(S-8)
(S-9)
(H-1)
(S-6)
[5] Jack CBA
[9] Main CBA
(S-12)
[7] Digital Main
CBA Unit
Connector IC
Card OSU
[6] Shield Box
(S-7)
(S-5)
FFC Shield
[8] Shield(T)
(S-11)
(S-10)
(S-11)
(S-12)
(S-7)
(S-5)
(S-7)
[11] Inverter CBA
(S-12)
(S-13)
[10] Junction CBA
Fig. D2
4-3 A8CNBDC
Page 15

TV Cable Wiring Diagram
To LCD Module
Assembly
Inverter CBA
To Speaker
CN401
CN402
CN451
CN403B
Junction
CBA
CN403A
CN106
CN105A
CL403
To LCD Module
Assembly
CN4501 CN4502
Jack CBA
CN11
Digital Main CBA Unit
CN3704CN4503CN3701CN3601
Main CBA
CN103ACN102ACN101ACN104A
CN107
CN201
CN202
Function
CBA
IR Sensor CBA
CN301
CN802
To Speaker
Fig. D3
4-4 A8CN6DC
Page 16

ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTIONS
General Note: “CBA” is abbreviation for
“Circuit Board Assembly.”
Note: Electrical adjustments are required after
replacing circuit components and certain
mechanical parts. It is important to perform
these adjustments only after all repairs and
replacements have been completed.
Also, do not attempt these adjustments unless
the proper equipment is available.
Test Equipment Required
1. DC Voltmeter
2. Pattern Generato
3. Color Analyzer
How to make the Service remote
control unit:
Cut “A” portion of the attached remote control unit as
shown in Fig. 1.
service button
How to set up the service mode:
Service mode:
1. Use the service remote control unit.
2. Turn the power on.
3. Press the service button on the service remote
control unit as shown in Fig.1.
A
Fig. 1
5-1 A8CN0EA
Page 17

1. Purity Check Mode
2. VCOM Adjustment.
This mode cycles through full-screen displays of red,
green, blue, and white to check for non-active pixels.
1. Enter the Service mode.
2. Each time pressing [7] button on the service
remote control unit, the display changes as
follows.
Purity Check Mode
White mode
[7] button
[7] button
Black mode
[7] button
Red mode
[7] button
Green mode
[7] button
Blue mode
Test Point
Screen
Adj. Point
[P / ]
buttons
M. EQ. Spec.
Color analyzer
See below
Figure
It carries out in a darkroom.
Perpendicularity
L = 3 cm
Color Analyzer
1. Operate the unit for more than 20 minutes.
2. Set the color analyzer and bring the optical
receptor to the center on the LCD-Panel surface
after zero point calibration as shown above.
Note: The optical receptor must be set
perpendicularly to the LCD Panel surface.
3. Enter the Service mode.
4. [VCOM1]
Press [2] button on the service remote control unit.
[VCOM2]
Press [3] button on the service remote control unit.
5. Press [P / ] buttons on the service remote
control unit so that the color analyzer value
becomes minimum.
Note:
When entering this mode, the default setting is White mode.
5-2 A8CN0EA
Page 18
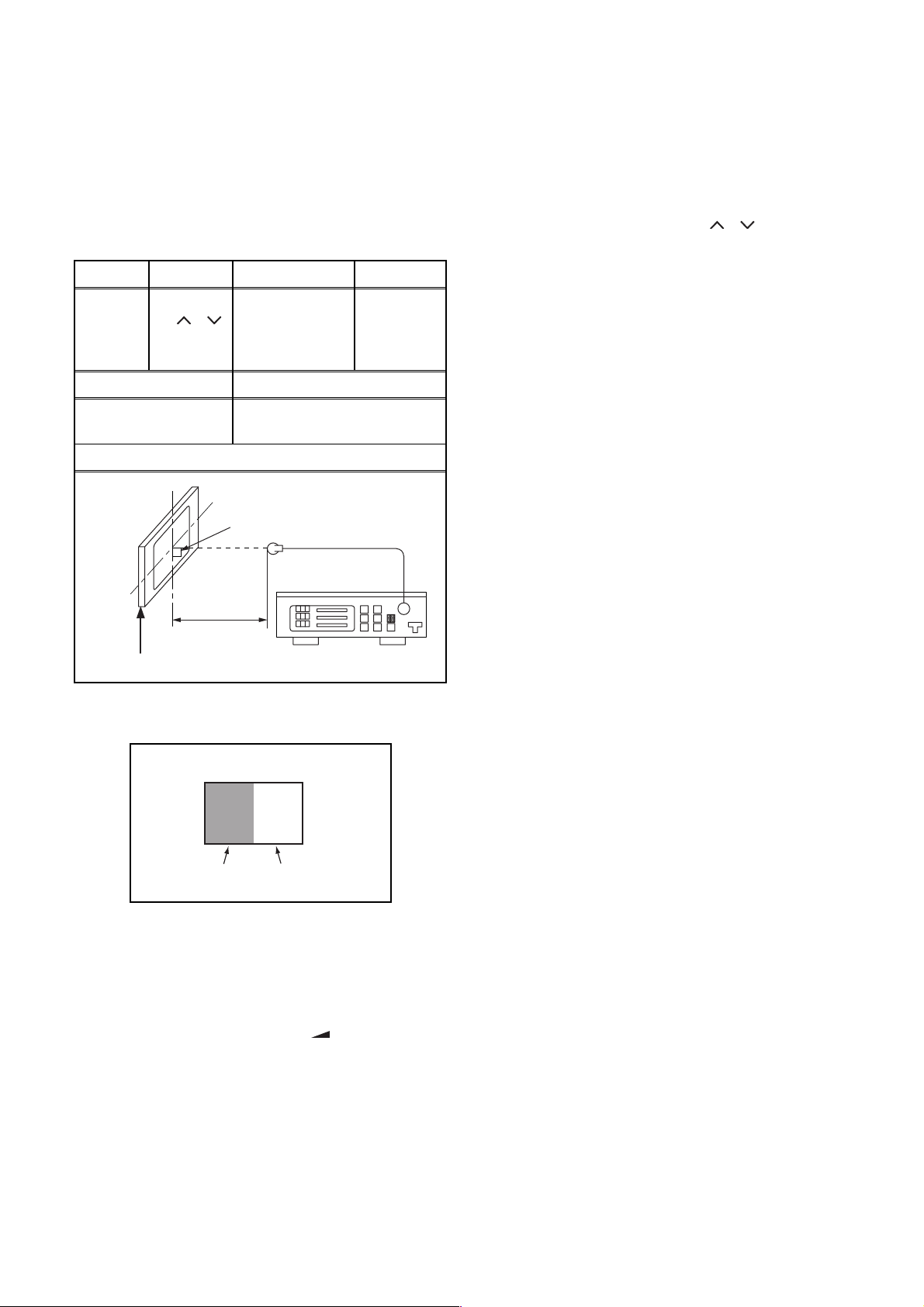
The following adjustment normally are not attempted in
the field. Only when replacing the LCD Panel then adjust
as a preparation.
3. White Balance Adjustment
Purpose: To mix red, green and blue beams correctly
for pure white.
Symptom of Misadjustment: White becomes bluish
or reddish.
Test Point
Screen
Adj. Point Mode Input
[P / ]
buttons
[VIDEO]
C/D
M. EQ. Spec.
White Raster
(APL 70%)
or
(APL 25%)
5. [CUTOFF]
Press [3] button to select “COB” for Blue Cutoff
adjustment. Press [1] button to select “COR” for
Red Cutoff adjustment.
[DRIVE]
Press [6] button to select “DB” for Blue Drive
adjustment. Press [4] button to select “DR” for Red
Drive adjustment.
6. In each color mode, press [P / ] buttons to
adjust the values of color.
7. Adjust Cutoff and Drive so that the color
temperature becomes 12000°K (x
=
0.272 / y
=
0.278 ±0.005).
Pattern Generator,
Color analyzer
x= 0.272 ± 0.005
y= 0.278 ± 0.005
Figure
It carries out in a darkroom.
Perpendicularity
L = 3 cm
INPUT: WHITE 70%, 25%
Color Analyzer
1. Operate the unit for more than 20 minutes.
2. Input the White Raster(70%=70IRE, 25%=25IRE).
INPUT SIGNAL
25%=25IRE
70%=70IRE
3. Set the color analyzer to the CHROMA mode and
bring the optical receptor to the center on the
LCD-Panel surface after zero point calibration as
shown above.
Note: The optical receptor must be set
perpendicularly to the LCD Panel surface.
4. Enter the Service mode. Press [ -] button on the
service remote control unit and select “C/D” mode.
5-3 A8CN0EA
Page 19

HOW TO INITIALIZE THE LCD TELEVISION
How to initialize the LCD television:
1. Turn the power on.
2. To enter the service mode, press the service
button on the service remote control unit. (Refer to
page 5-1.)
- To cancel the service mode, Press [ ] button on
the remote control unit.
3. Press [ ] button on the service remote control
unit to initialize the LCD television.
4. "INITIALIZED" will appear in the upper right of the
screen. "INITIALIZED" color will change to green
from red when initializing is complete.
6-1 A8CN0INT
Page 20

BLOCK DIAGRAMS
System Control Block Diagram
+3.3V
SENSOR
REMOTE
RS301
CN301
D303
LED144
REMOTE22
P-ON-H155
STANDBY
D302
POWER
IR SENSOR CBAFUNCTION CBAMAIN CBA
TO
INVERTER
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
PROTECT3
8
CN105A
BACKLIGHT-SW
9
(CL403)
TO POWER
SUPPLY
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
RESET
PROTECT1
PROTECT2
MAIN CBA
CN202
KEY SWITCH
CN201
LED144
REMOTE22
P-ON-H155
KEY-IN166
CN106
TO POWER
P-ON-H1
CN104ACN3601
REMOTE22 4
CN101A
P-ON-H1125
P-ON-H213 13
KEY-IN125 1
CN3701
LED118 8
SUPPLY
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
P-ON-H2
(SUB MICRO CONTROLLER)
IC4700
X3101
6
XOUT
4MHz
OSC
LED1
12
8
XIN
KEY-IN1
24
IC3102 (MEMORY)
P-ON-H1
P-ON-H2
14
13
CN101ACN3701
PROTECT2
RESET
PROTECT1
PROTECT3
20 6
17 9
21 5
19 7
TO DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
SDA
SCL
5
6
VCOM-PWM
4
3
22
PROTECT1
AMP-MUTE-SUB
18
23
RESET
PROTECT2
PROTECT3
TO AUDIO-2
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
AMP-MUTE
TXD
16
RESET-MAIN
5
21
VCOM-PWM
19
20
SCL
SDA
REMOTE
RXD
11
15
3
CN104ACN3601
BACKLIGHT-SW
23
IC4513
(MAIN MICRO CONTROLLER)
SDA
SCL
TO VIDEO
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
SCL
SCL
AF12
SDA
AE12
SDA
INPUT0
NICAM-RESET
SCART-MUTE
B2
A11
B11
Q3819
Q3823
INPUT0
NICAM-RESET
SCART-MUTE
INPUT1
TO AUDIO-1
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
INPUT2
INPUT1
E12
D12
Q3822
INPUT2
SLOW-SW1E1FBIN1
D1
SLOW-SW1
INPUT2
TO VIDEO
S-SW
C12
S-SW
FBIN1
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
R22
REMOTE
P22
TXD1
N22
RXD1
V24
RESET-MAIN
AA2
AMP-MUTE-MAIN
SPI-CLK
SPI-DO
Y25
Y24
652
SI
SCK
IC3706 (MEMORY)
SPI-DI
SPI-CS
W25
W24
1
CS
SO
X3301
CLKOUT
CLKIN
U25
U26
25MHz
OSC
A2
BACKLIGHT-SW
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
7-1
A8CNBBLS
Page 21

Video Block Diagram
TO DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
TO DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
TO DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
AUDIO SIGNAL
TS-DATA
VIDEO SIGNAL
IC3824 (DEMODULATOR)
58
DIF-OUT1
20 4
CN103A CN3704
SCL
13
MPEG2-TS
INTERFACES
DEMODULATOR
57
IF-AGC18 6
DIF-OUT2
22 2
25
SCL
SCL
64
SCL15 9
SDA
26
SDA
SDA2IF-AGC
63
SDA16 8
TU-CVBS11 13
VIDEO
CN102A CN4503
WF7WF6WF5
VIDEO-B
VIDEO-R
VIDEO-G
TU-CVBS
DTV-CVBS
VIDEO-R323
VIDEO-B521
VIDEO-G422
VIDEO125
TU-VIDEO13 13
SLOW-SW123 3
3
IC3823
(INPUT SELECT)
4
FBIN122 4
WF4
5
SW CTL
109 11
INPUT2
SLOW-SW1
FBIN1
S-SW
CN3704
S-SW123
INPUT2618
CN103A
WF3WF2
S-VIDEO-Y
S-VIDEO-C
S-VIDEO-Y23 3
S-VIDEO-C25 1
CN101A CN3701
COMP-Y
COMP-Pb
COMP-Pb20 6
COMP-Y18 8
COMP-Pr
COMP-Pr21 5
17
DIF-OUT1
TU501
(TUNER UNIT)
8
16
15
SCL
IF-AGC
DIF-OUT2
BUFFER
Q505
6
9SDA
VIDEO-OUT
15
IC851
(INPUT SELECT)
1
2
JK722
VIDEO-IN
SW CTL
MAIN CBA DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
109 11
CN107CN11
COMP-Y11
COMP-Pb22
COMP-Pr44
JACK CBA
JK11
JK12
JK13
COMPONENT
-Y-IN
COMPONENT
-Pb-IN
COMPONENT
-Pr-IN
A8CNBBLV
JK751
15
20VIDEO-IN
VIDEO-R
11
VIDEO-G
7-2
BUFFER BUFFER
Q726 Q744
7
19
VIDEO-B
VIDEO-OUT
8
SLOW-SW
Q734
Q731
16
RAPID-SW
CY
JK721
S-VIDEO-IN
Page 22

Audio-1 Block Diagram
TO
DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
AUDIO SIGNAL
ACLK
BCLK
LRCLK
AD ATA 1
AUX-ADATA
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
INPUT0
INPUT1
INPUT2
DIAGRAM
Q3831
BUFFER
BUFFER
Q3832
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
SCART-MUTE
IC3825
(AUDIO A/D CONVERTER)
111015
12
A/D
CONVERTER
(L-CH)
(R-CH)
1
2
CN3704CN103A
AUDIO(L)321
AUDIO(R)420
INPUT0816
IC3822
(AUDIO D/A CONVERTER)
INPUT2618
INPUT1717
8
(L-CH)
15
7
D/A
6
CONVERTER
(R-CH)
14
5
IC3823
CN4503CN102A
TU-AUDIO(L)10 16
TU-AUDIO(R)11 15
Q3833
15
(INPUT SELECT)
1
2
Q3834
14
109 11
SW CTL
13
12
24
22
(L-CH)
(R-CH)
AUDIO SIGNAL
PROCESS
IC3821 (SOUND PROCESSOR)
3
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
I2C BUS
I/F
RESET
19
18
21
IC850
(INPUT SELECT)
CN107CN11
COMP-AUDIO(L)
COMP-AUDIO(R)
66
77
JK14
JK15
JACK CBA
COMPONENT
AUDIO(L)-IN
COMPONENT
AUDIO(R)-IN
124
3
(L-CH)
5
IC851
(INPUT SELECT)
JK723
4
3
5
AUDIO(L)-IN
121114
(L-CH)
12
JK724
13
15
14
(R-CH)
13
AUDIO(R)-IN
(R-CH)
SW CTL
SW CTL
SCL
SDA
NICAM-RESET
9 10
MAIN CBA
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
CN3704CN103A
SIF915
109 11
4
6
JK751
AUDIO(L)-IN2AUDIO(R)-IN
3
1
AUDIO(L)-OUT
AUDIO(R)-OUT
JK725
PC-AUDIO
-IN
SIF-OUT
TU501
(TUNER UNIT)
DIAGRAM
7-3
A8CNBBLA1
Page 23

Audio-2 Block Diagram
SP802
SPEAKER
L-CH
JK801
HEADPHONE
JACK
CL451
SP451
SPEAKER
R-CH
AUDIO SIGNAL
SP(L) 1
CN802 CL802
IC801 (AUDIO AMP)
SP(R) 1
CN451
SP-GND 2
SP-GND 2
INVERTER CBA
CN403B
WF1
11
AMP
(L-CH)
6
VOLUME
MUTE
/STANDBY
14
AMP
7
2
CONTROL
(R-CH)
1
+9V
SP(R)11 11SP(R)11 11
CN403ACN105A
CL403
JUNCTION
CBA
IC802
(AUDIO D/A CONVERTER)
15
(L-CH)
8
CN101ACN3701
LRCLK11 15
BCLK
LRCLK
TO
DIGITAL
(R-CH)
D/A
CONVERTER
AD ATA13 13
BCLK12 14
A DATA
SIGNAL
PROCESS
BLOCK
14
567
ACLK14 12
AMP-MUTE
917
ACLK
DIAGRAM
AMP-MUTE
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
AMP MUTE
Q805
SWITCHING
Q802
MAIN CBA
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
7-4
A8CNBBLA2
Page 24

Digital Signal Process Block Diagram
LCD MODULE
ASSEMBLY
BRSB2(+)52
CN4501
AUDIO SIGNAL
757473727170666564
VIDEO SIGNAL
IC4201(LCD DRIVE)
BRSB2(-)51
BRSB1(+)50
BRSB1(-)49
BRSB0(+)48
BRSB0(-)47
BRSG2(+)46
BRSG2(-)45
BRSG1(+)44
BRSG1(-)43
BRSG0(+)42
BRSG0(-)41
BRSR2(+)17
63
62616059585756556968907778
D-RSDS
OUTPUT
LVD S
RX
242522232021161718
AF20
AE20
AD19
AD20
AE19
AF19
AF18
AE18
BRSR2(-)16
AE21
BRSR1(+)15
19
AF21
BRSR1(-)14
BRSR0(+)13
BRSR0(-)12
BRSCLK(+)22
BRSCLK(-)21
VCOM7
STH-S11
TP119
POL18
STV5
81
LVD S
FRSB2(+)53
FRSB2(-)52
FRSB1(+)51
FRSB1(-)50
FRSB0(+)49
FRSB0(-)48
FRSG2(+)47
FRSG2(-)46
FRSG1(+)45
VCOM9
CN4502
52515049484744434140393837363534333246
DATA
MAPPING
TX
FRSG1(-)44
D-RSDS
LVD S
9107856123
AF25
AF24
AE25
AD25
AD26
FRSG0(+)43
FRSG0(-)42
OUTPUT
RX
AE24
AD23
FRSR2(+)18
AD24
FRSR2(-)17
AF26
FRSR1(+)16
4
AE26
FRSR1(-)15
FRSR0(+)14
FRSR0(-)13
FRSCLK(+)23
FRSCLK(-)22
STH-F55
CPV6
OE15
STV7
TP120
POL19
DRIVE
IC4511,Q4511,
(SDRAM)
IC3201
B1,B9,C2,C8,
A13-15,A18,
Q4512,Q4513
VCOM-PWM
TO SYSTEM
CONTROL
BLOCK
DATA(0-15)
ADDESS(0-12)
H1,H3,H7,H9
F1,F9,G2,G8,
M2,M3,M7,M8,
N2,N3,N7,N8,
D1,D3,D7,D9,
A21-23,B13-15,
B17,B19-23
C15,C17-19,
C23,C24,D14,
DIAGRAM
P2,P3,P7,P8,R2
D15,D17-19,
D22,D23
145
808284
IC4202 (MEMORY)
SCL
87
6
SCL
SDA
88
5
SDA
IC4513 (DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESS)
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
T4
Y3
TU-CVBS
T3
U4
COMP-Y
COMP-Pb
COMP-Pr
U3
W3
VIDEO
S-VIDEO-Y
TO VIDEO
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
A/D
CONVERTER
SW
V3V4Y2
S-VIDEO-C
VIDEO-R
Y1
AA1
VIDEO-G
VIDEO-B
JK3701
T5
1
RED
R4R3R5
3
2
BLUE
GREEN
VGA-HSYNC
K5
14
13
VSYNC
HSYNC
D-SUB
VGA-VSYNC
L5
SDA
IC3701 (MEMORY)
5
12
15
DATA
CLOCK
AB25
SCL
6
TS I/F
AB12
TS-DATA
DTV-CVBS
TO VIDEO
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
DIGITAL
SIGNAL
PROCESS
AUDIO I/F
AF15
AE15
AE16
AC17
AD15
AUX-ADATA
AD ATA 1
TO AUDIO-1
BCLK
LRCLK
BLOCK
ACLK
DIAGRAM
AD ATA
AD16
BCLK
LRCLK
TO AUDIO-2
BLOCK
ACLK
DIAGRAM
A9
TMDS-D0(+)
JK4001
79461
AUDIO
DECODER
B9
C8
C9
TMDS-D0(-)
TMDS-D1(+)
TMDS-D1(-)
HDMI
I/F
B8
A8
B10
TMDS-CLOCK(+)
TMDS-D2(+)
TMDS-D2(-)
3
101216
HDMI-IN1
VIDEO
DECODER
E9
A10
C10
Q4001
BUFFER
Q4002
BUFFER
TMDS-CLOCK(-)
SDA
SCL
15
Y22,Y23,AA21-23,
AB21-23,AF7-11,
AE9,AE10,AD10
D(0-7)
3,4,7,8,
13,14,
(LATCH)
LATCH
IC3826
2,5,6,
D(0-15)
A(8-13)
CI
CARD
17,18
9,12,15
SLOT
V21,W21,Y21,
AA20,AC20,AC21
AE14,AF14
A(0-7)
A(0-13)
7-5
A8CNBBLD
Page 25

Inverter Block Diagram
BACK
LIGHT
1
2
CN401
BACK
1
CN402
LIGHT
2
LCD MODULE
ASSEMBLY
12
8
3
Q405
OVER CURRENT
PROTECTOR
Q412
JS411
Q404
Q410
OVER VOLTAGE
Q403
PROTECTOR
T401
14
9
4
13
5
7
10
2
CURRENT
CONTROL
Q408
11
1
SWITCH
6
INVERTER CBA
Q406
SW+22V
OVER CURRENT
PROTECTOR
Q411
Q401
Q402
JUNCTION
CBA
2
CN403B
FEEDBACK2
2
CL403 CN403A
FEEDBACK
TO POWER
SUPPLY
1
3,4
INV+22V3,4
+35V1
1
3,4
INV+22V
+35V
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
(CN105A)
CN403B
CL403 CN403A
TO SYSTEM
7-6
8
9
PROTECT38
BACKLIGHT-SW
9
8
9
PROTECT3
BACKLIGHT-SW
CONTROL
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
(CN105A)
A8CNBBLINV
Page 26

Power Supply Block Diagram
NOTE:
The voltage for parts in hot circuit is measured using
hot GND as a common terminal.
CAUTION !
For continued protection against fire hazard,
replace only with the same type fuse.
LCD+24.5V
LCD-6.8V
LCD+13V
P-ON+3.3V
TO
INVERTER
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
(CL403)
18
16
9-11
19-21
+35V1
FEEDBACK2
INV+22V3,4
CN105A
LCD+24.5V8
CN104A CN3601
LCD-6.8V10
LCD+13V5-7
P-ON+3.3V
15-17
+3.5V
2-4
+3.5V
22-24
+3.0V
LCD+3.3V
7,8
14
LCD+3.3V12
+3.0V
18,19
AL+3.3V
AL+3.3V323P-ON+5V1,2
CN101A CN3701
P-ON+5V
24,25
CN102A CN4503
P-ON+9V
12
P-ON+9V14
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
AL+3.3V
P-ON+9V
P-ON+5V
AL+12V
P-ON+3.3V
TO SYSTEM
PROTECT-1
PROTECT-2
CONTROL
BLOCK
P-ON-H1
P-ON-H2
DIAGRAM
RESET
MAIN CBA
SW+25V
Q911,Q912
T601
HOT COLD
Q922,D936
SW+3.3V
Q902,D920
+5V REG.
IC900
19
5
SW+13V
+3.3V REG.
IC902
18
1 2 4
Q901,D916
13
+3.3V REG.
12
3
+9V REG.
Q906,D926
Q903
SW-6.8V
+5V REG.
Q936,D985
14
17
7
Q908
16
15
8
Q907
11
Q904
IC601
RESET
Q920
Q900
FEED
BACK
14
3 2
CAUTION !
Fixed voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F601) is blown , check to see that all components in the power supply
circuit are not defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply.
Otherwise it may cause some components in the power supply circuit to fail.
HOT CIRCUIT. BE CAREFUL.
BRIDGE
D611,D613,
D614,D616
LINE
L601
F601
T4A H 250V
AC601
AC CORD
RECTIFIER
FILTER
SWITCHING
Q600
7-7
Q601
SWITCHING
CONTROL
A8CNBBLP
Page 27

SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS / CBA AND TEST POINTS
Standard Notes
WARNING
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis
have special characteristics. These characteristics
often pass unnoticed and the protection afforded by
them cannot necessarily be obtained by using
replacement components rated for higher voltage,
wattage, etc. Replacement parts that have these
special safety characteristics are identified in this
manual and its supplements; electrical components
having such features are identified by the mark “!” in
the schematic diagram and the parts list. Before
replacing any of these components, read the parts list
in this manual carefully. The use of substitute
replacement parts that do not have the same safety
characteristics as specified in the parts list may create
shock, fire, or other hazards.
Notes:
1. Do not use the part number shown on these
drawings for ordering. The correct part number is
shown in the parts list, and may be slightly
different or amended since these drawings were
prepared.
2. All resistance values are indicated in ohms
(K = 10
3. Resistor wattages are 1/4W or 1/6W unless
otherwise specified.
4. All capacitance values are indicated in µF
(P = 10
5. All voltages are DC voltages unless otherwise
specified.
3
, M = 106).
-6
µF).
8-1 LC6P_SC
Page 28

LIST OF CAUTION, NOTES, AND SYMBOLS USED IN THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS ON
THE FOLLOWING PAGES:
1. CAUTION:
FOR CONTINUED PROTECTION AGAINST FIRE HAZARD, REPLACE ONLY WITH THE SAME TYPE
FUSE.
2. CAUTION:
Fixed Voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F601) is blown, first check to see that all components in the power supply circuit are not
defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply. Otherwise it may cause some components
in the power supply circuit to fail.
3. Note:
1. Do not use the part number shown on the drawings for ordering. The correct part number is shown in the
parts list, and may be slightly different or amended since the drawings were prepared.
2. To maintain original function and reliability of repaired units, use only original replacement parts which are
listed with their part numbers in the parts list section of the service manual.
4. Voltage indications on the schematics are as shown below:
Plug the TV power cord into a standard AC outlet.:
2
(Unit: Volt)
1
5.0 5.0
3
Power on mode
5. How to read converged lines
1-D3
Distinction Area
Line Number
(1 to 3 digits)
Examples:
1. "1-D3" means that line number "1" goes to the line number
"1" of the area "D3".
2. "1-B1" means that line number "1" goes to the line number
"1" of the area "B1".
6. Test Point Information
: Indicates a test point with a jumper wire across a hole in the PCB.
: Used to indicate a test point with a component lead on foil side.
: Used to indicate a test point with no test pin.
: Used to indicate a test point with a test pin.
Voltage
Indicates that the voltage
is not consistent here.
3
2
1
AREA D3
1-B1
AREA B1
1-D3
ABCD
8-2 LC6P_SC
Page 29
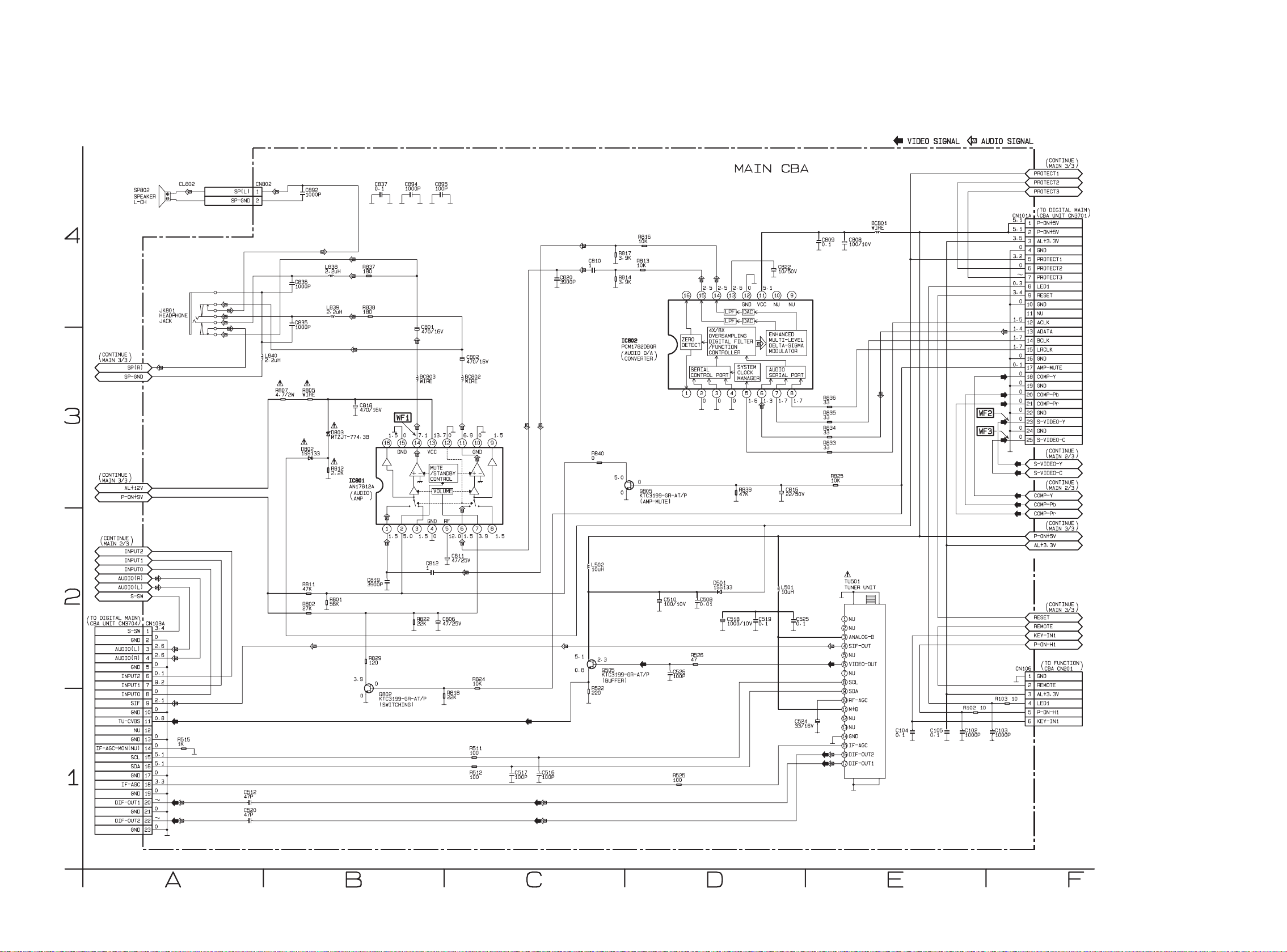
Main 1/3 Schematic Diagram
8-3
A8CNBSCM1
Page 30

Main 2/3, Jack Schematic Diagram
8-4
A8CNBSCM2
Page 31

Main 3/3 Schematic Diagram
NOTE:
The voltage for parts in hot circuit is measured using
hot GND as a common terminal.
CAUTION !
Fixed voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F601) is blown , check to see that all components in the power supply
circuit are not defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply.
Otherwise it may cause some components in the power supply circuit to fail.
CAUTION !
For continued protection against fire hazard,
replace only with the same type fuse.
8-5 A8CNBSCM3
Page 32

Inverter & Junction Schematic Diagram
8-6
A8CNBSCINV
Page 33

Function Schematic Diagram
8-7
A8CNBSCF
Page 34

IR Sensor Schematic Diagram
8-8
A8CNBSCIR
Page 35

Digital Main 1/6 Schematic Diagram
1 NOTE:
The order of pins shown in this diagram is different from that of actual IC4513.
IC4513 is divided into five and shown as IC4513 (1/5) ~ IC4513 (5/5) in this Digital Main Schematic Diagram Section.
8-9
A8CNBSCD1
Page 36

Digital Main 2/6 Schematic Diagram
1 NOTE:
The order of pins shown in this diagram is different from that of actual IC4513.
IC4513 is divided into five and shown as IC4513 (1/5) ~ IC4513 (5/5) in this Digital Main Schematic Diagram Section.
8-10
A8CNBSCD2
Page 37

Digital Main 3/6 Schematic Diagram
1 NOTE:
The order of pins shown in this diagram is different from that of actual IC4513.
IC4513 is divided into five and shown as IC4513 (1/5) ~ IC4513 (5/5) in this Digital Main Schematic Diagram Section.
8-11
A8CNBSCD3
Page 38

Digital Main 4/6 Schematic Diagram
1 NOTE:
The order of pins shown in this diagram is different from that of actual IC4513.
IC4513 is divided into five and shown as IC4513 (1/5) ~ IC4513 (5/5) in this Digital Main Schematic Diagram Section.
8-12
A8CNBSCD4
Page 39

Digital Main 5/6 Schematic Diagram
8-13
A8CNBSCD5
Page 40

Digital Main 6/6 Schematic Diagram
1 NOTE:
The order of pins shown in this diagram is different from that of actual IC4513.
IC4513 is divided into five and shown as IC4513 (1/5) ~ IC4513 (5/5) in this Digital Main Schematic Diagram Section.
8-14
A8CNBSCD6
Page 41

Main CBA Top View
Because a hot chassis ground is present in the power
supply circut, an isolation transformer must be used.
Also, in order to have the ability to increase the input
slowly, when troubleshooting this type power supply
circuit, a variable isolation transformer is required.
CAUTION !
For continued protection against fire hazard,
replace only with the same type fuse.
NOTE:
The voltage for parts in hot circuit is measured using
hot GND as a common terminal.
CAUTION !
Fixed voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F601) is blown , check to see that all components in the power supply
circuit are not defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply.
Otherwise it may cause some components in the power supply circuit to fail.
8-15
BA8CN6F01013-1
Page 42

Main CBA Bottom View
Because a hot chassis ground is present in the power
supply circut, an isolation transformer must be used.
Also, in order to have the ability to increase the input
slowly, when troubleshooting this type power supply
circuit, a variable isolation transformer is required.
CAUTION !
For continued protection against fire hazard,
replace only with the same type fuse.
NOTE:
The voltage for parts in hot circuit is measured using
hot GND as a common terminal.
CAUTION !
Fixed voltage (or Auto voltage selectable) power supply circuit is used in this unit.
If Main Fuse (F601) is blown , check to see that all components in the power supply
circuit are not defective before you connect the AC plug to the AC power supply.
Otherwise it may cause some components in the power supply circuit to fail.
WF1
PIN 14 OF
IC801
WF4
PIN 5 OF
CN102A
WF5
PIN 4 OF
CN102A
WF6
PIN 3 OF
CN102A
WF7
PIN 1 OF
CN102A
WF3
PIN 25 OF
CN101A
WF2
PIN 23 OF
CN101A
8-16
BA8CN6F01013-1
Page 43

Inverter CBA Top View
8-17
BA8CN0F01023-1
Page 44
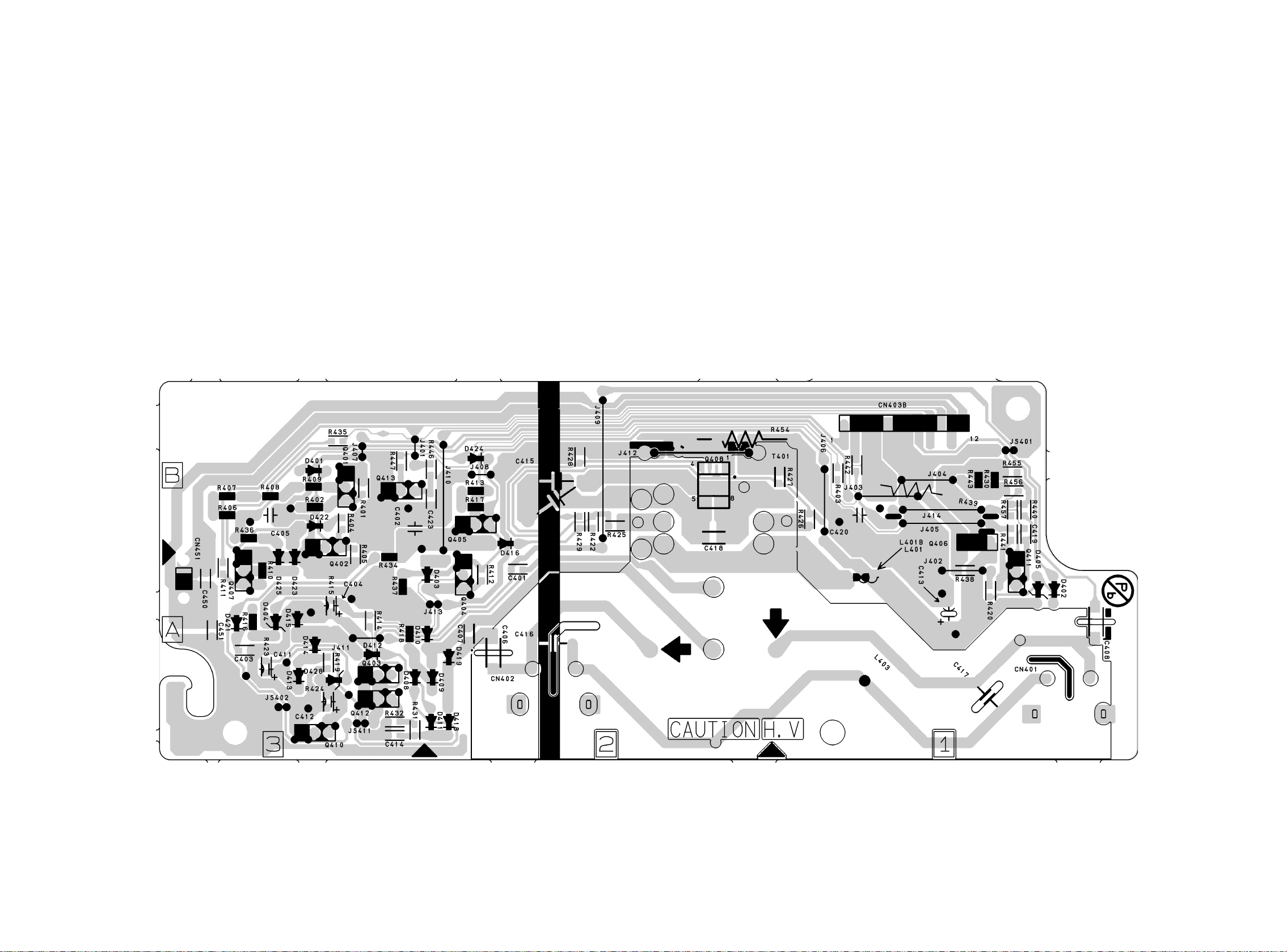
Inverter CBA Bottom View
8-18
BA8CN0F01023-1
Page 45

IR Sensor CBA Top ViewFunction CBA Top View
Function CBA Bottom View
BA8CN6F01013-2
IR Sensor CBA Bottom View
BA8CN6F01013-3
8-19
Page 46

Jack CBA Top View
Junction CBA Top & Bottom View
Jack CBA Bottom View
BA8CN0F01023
BA8CN6F01013-4
8-20
Page 47

WAVEFORMS
WF1 ~ WF7 = Waveforms to be observed at
Waveform check points.
(Shown in Schematic Diagram.)
Input: PAL Color Bar Signal (with 1kHz Audio Signal)
WF1 Pin 14 of IC801
AUDIO 0.1V 0.5ms
WF2 Pin 23 of CN101A
WF4 Pin 5 of CN102A
VIDEO-B 0.5V
B 0.5V 5µs
WF5 Pin 4 of CN102A
WF7 Pin 1 of CN102A
20
µ
s
VIDEO 0.2V 20
µ
s
S-VIDEO-Y 0.2V 10µs
WF3 Pin 25 of CN101A
S-VIDEO-C 0.2V 20µs
VIDEO-G 0.5V
G 0.5V 20µs
WF6 Pin 3 of CN102A
VIDEO-R 0.5V
R 0.5V 10µs
9-1
20
µ
s
20
µ
s
LC6PWF
Page 48

CN4501CN4502
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
GND
GND
VEEG
BRSB2(-)
BRSB1(-)
BRSB2(+)
BRSB1(+)
STH-F
GND53FRSB2(+)52FRSB2(-)51FRSB1(+)50FRSB1(-)49FRSB0(+)48FRSB0(-)47FRSG2(+)
55
54
46
48
47
BRSB0(-)
BRSB0(+)
BRSG2(+)
FRSG2(-)
46
4544434241
BRSG2(-)
BRSG1(-)
BRSG1(+)
BRSG0(+)
FRSG1(+)
FRSG1(-)
FRSG0(+)
FRSG0(-)
4544434241
WIRING DIAGRAMS
30
403938
GND
GMA14
GMA1337GMA1236GMA1135GMA10
BRSG0(-)
GND
GMA14
GMA13
GMA1237GMA1136GMA1035GMA934GMA833VDDA32VDDA31GMA7
403938
34
GMA933GMA8
32
VDDA31VDDA
2928272625
GMA7
GMA6
GMA5
GMA6
GMA5
GMA4
30
2928272625
GMA4
GMA3
242322
GND
GMA3
GMA2
GMA1
BRSCLK(+)
GMA2
GMA1
GND
FRSCLK(+)
FRSCLK(-)21GND20TP119POL18FRSR2(+)17FRSR2(-)16FRSR1(+)15FRSR1(-)
242322
21
20
19
TP1
GND
BRSCLK(-)
18
17
POL
BRSR2(+)
16
15
BRSR2(-)
BRSR1(+)
12
11
STH-S
BRSR0(-)
10
GND
9
VDDD8VDDD
14
13
BRSR1(-)
BRSR0(+)
FRSR0(+)13FRSR0(-)12GND11VDDD10VDDD9VCOM8VEEG
14
765
GND
VCOM
STV
CPV
765
4
STV
GND3GND
OE14XA03GND
2
GND
VGH
2
1
GND
GND
1
LCD MODULE
ASSEMBLY
BACK
BACK
SP451
SPEAKER
R-CH
LIGHT
LIGHT
CL451
CN101A
P-ON+5V
25 1
CN3701
3
4
AL+3.3V
GND
P-ON+5V
232120
24 2
22
2
1
2
1
2
SP-GND
1
SP(R)
5
6
PROTECT2
PROTECT1
CN3704CN103A
CN402
CN401
CN451
8
9
7
PROTECT3
LED1
RESET
18
17
19
232120
22
INVERTER CBA
12
101513
11
GND
14
161113
15
18
19
14
AD ATANUACLK
BCLK
12
161113
17
12
1111
10
9
8
77
6
5
CN403B
4
3
2
1
17
18
16
AMP-MUTE
LRCLK
GND
COMP-Y
9
8
10
14
12
15
21
192422
20
COMP-Pr
GND
COMP-Pb
724
6
9
10
SP-GND
SP(R)
NU
BACKLIGHT-SW
PROTECT3
GND
GND
GND
INV+22V
INV+22V
FEEDBACK
+35V
23
GND
S-VIDEO-Y
724
8
9
8
6
5
4
3
2
1
6
12
10
GND
CN403A
JUNCTION CBA
CN102A
25
S-VIDEO-C
153
CN4503
GND
VIDEO
24 2
25 1
153
CL403
3
VIDEO-R
232120
CN3601CN104A
8
7
6
GNDNUNU
18
19
232120
22
SP-GND
SP(R)
NU
BACKLIGHT-SW
PROTECT3
GND
GND
GND
INV+22V
INV+22V
FEEDBACK
+35V
9
GND
17
1212
11
10
9
8
77
6
5
4
3
2
1
5
4
VIDEO-G
VIDEO-B
22
242
251
11
10
9
8
6
5
CN105A
4
3
2
1
12
101513
11
TU-AUDIO(L)
TU-AUDIO(R)
GND
14
161113
15
18
17
19
14
TU-VIDEO
P-ON+9VNUGNDNUNU
12
14
161113
15
D-SUB
CONNECTOR
17
18
16
9
8
10
12
HDMI-
CONNECTOR-1
21
192422
20
GND
GNDNUFBIN1
724
6
9
724
8
10
CI
CARD SLOT
MAIN CBA
23
SLOW-SW1NUNU
6
25
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
153
153
TU501 TUNER UNIT
AC CORD
AC601
CN802
1
SP(L)
CL802
SP802
S-SW
2
SP-GND
SPEAKER
L-CH
GND
AUDIO(L)
2
AUDIO(L)
VIDEO-IN
AUDIO(R)
GND
513
4
-IN
INPUT2
INPUT1
INPUT0
SIF
6
8
9
7
AUDIO(R)
-IN
PC-AUDIO-IN
CN301
IR SENSOR
CBA
TU-CVBS
GND
NU
10
12
11
S-VIDEO
HEADPHONE
JACK
5
4
3
2
1
SCL
GND
IF-AGC-MON(NU)
15
14
13
-IN
SDA
GND
172220
16
SCART
JACK
P-ON-H1
LED1
AL+3.3V
REMOTE
GND
10-1
5
4
3
2
1
IF-AGC
18
GND
19
CN202
DIF-OUT1
GND
DIF-OUT2
21
13245
CN106
GND
REMOTE
1
CN201
BACKLIGHT-ADJ(NU)
KEY-IN1
GND
23
AL+3.3V
P-ON-H16KEY-IN1
LED1
62453
FUNCTION
CBA
BACKLIGHT-SW
REMOTE
4
LCD+13V
LCD+13V
LCD+13V
735
6
COMPONENT
LCD+24.5V
GND
8
9
-Y-IN
COMPONENT
LCD-6.8V
GND
LCD+3.3V
12
101513
11
-Pb-IN
COMPONENT
-Pr-IN
P-ON-H2
GND
P-ON+3.3V
P-ON+3.3V
16
14
COMPONENT-
AUDIO(L)-IN
COMPONENT-
JACK
CBA
P-ON+3.3V
+3.0V
+3.0V
17
192422
18
CN107CN11
1
AUDIO(R)-IN
COMP-Y
1
GND
GND
+3.5V
+3.5V
+3.5V
21
23
20
24365
GND
COMP-Pr
GND
COMP-Pb
2
COMP-AUDIO(L)
67534
A8CNBWI
P-ON-H1
25
7
COMP-AUDIO(R)
Page 49

Cabinet
A21
EXPLODED VIEWS
L10
L36
A1
A11
B46
B46
A5
CL451
SP802
SP451
L30
Function CBA
L30
B46
B46
CL802
CL4501
CL4502
LCD1
L10
B36
CL3601
Main CBA
L29
CL3701
L28
L10
CL4503
CL3704
B8
B9
Digital Main CBA Unit
CL107
L10
Jack CBA
CN3802
L10
B10
L10
L10
B3
L30
B3
L3
L30
B3
A4
L3
A27
A10
L25
A7
IR Sensor CBA
See Electrical Parts List
for parts with this mark.
L10
Inverter CBA
L10
L10
L10
Junction CBA
B21
AC601
L9
L10
L9
B22
B20
B29
L9
L10
L10
L37
L37
A9
L3
L5
B15
L17
A24
B30
L3
A6
S5
A12
11-1 A8CNBCEX
Page 50

Packing
Some Ref. Numbers are
not in sequence.
X4
Packing Tape
S6
X3
X2-4
S2
Packing Tape
Tape
S5
Packing Tape
FRONT
S4
S3
Packing Tape
X1
S3
FRONT
S1
11-2 A8CNBPEX
Page 51

MECHANICAL PARTS LIST
PRODUCT SAFETY NOTE: Products marked with a
! have special characteristics important to safety.
Before replacing any of these components, read
carefully the product safety notice in this service
manual. Don't degrade the safety of the product
through improper servicing.
NOTE: Parts that are not assigned part numbers
(---------) are not available.
Ref. No. Description Part No.
A1 FRONT CABINET A8CN3FP 1EM122753A
A4 REAR CABINET A8CN7EP 1EM122973
A5 DECORATION PLATE A8CN3FP 1EM222483
A7 FUNCTION KNOB A8CN3FP 1EM324537A
A9 STAND COVER A8CN3FP 1EM222443
A10 REAR COVER A8CN3FP 1EM427321
A11 SENSOR LED LENS A8CN0FP 1EM323959
A12 STAND RUBBER FOOT A8AN0UH 1EM426377
A24 STAND NECK A8CN3FP 1EM324517
B3 WALL MOUNT BRACKET A84N0UH 1EM323797
B8 SHIELD BOX A8CN0FP 1EM122473
B9 SHIELD (T) A8CN6EP 1EM325219
B10 FFC SHIELD A8CN6EP 1EM427320
B15 STAND HINGE A8CN0FP 1EM323940
B29 CLOTH(10X30XT0.5) B5900UA 0EM404486
B30 CLOTH(10X90XT1.0) A7120UH 1EM424258
B36 GASKET A8AF0UH 1EM425861
B46 CLOTH(B) L5201U0 15X10X1.0T 0EM400076
CL107 WIRE ASSEMBLY 7PIN WX1A8CN0-012 WX1A8CN0-012
CL451 WIRE ASSEMBLY 2PIN WX1A8CN0-013 WX1A8CN0-013
CL802 WIRE ASSEMBLY 2PIN WX1A8CN0-013 WX1A8CN0-013
CL3601 WIRE ASSEMBLY 25PIN WX1A8CN0-006 WX1A8CN0-006
CL3701 WIRE ASSEMBLY 25PIN WX1A8CN0-006 WX1A8CN0-006
CL3704 WIRE ASSEMBLY 23PIN WX1A8CN0-005 WX1A8CN0-005
CL4501 WIRE ASSEMBLY FFC 55PIN FFC WIRE/
CL4502 WIRE ASSEMBLY FFC 55PIN FFC WIRE/
CL4503 WIRE ASSEMBLY 25PIN WX1A8CN0-006 WX1A8CN0-006
CN3802 CONNECTOR IC CARD OSU SLOT 2013858-1 J620680AP001
L10 SCREW S-TIGHT M3X6 BIND HEAD+ GBJS3060
L17 DOUBLE SEMS SCREW M4X9 + BLACK
L28 HEX SCREW #4-40 7MM 1EM422042
L29 DOUBLE SEMS SCREW M2X10+ M2X10 FPJ32100
L30 SCREW P-TIGHT M3X10 BIND HEAD+ GBJP3100
L36 DOUBLE SEMS SCREW M2X6+ M2X6 FPJ32060
LCD1 LCD MODULE 19INCH WIDE CMO 19INCH
SP451 SPEAKER MAGNETIC S0306N01 or DSD0806XQ001
SP802 SPEAKER MAGNETIC S0306N01 or DSD0806XQ001
55PIN/42MM
55PIN/42MM
L0130UA
WXGA
SPEAKER MAGNETIC YDP36-16FN DSD0806EFU01
SPEAKER MAGNETIC YDP36-16FN DSD0806EFU01
PACKING
S4 SET BAG A81N0UH 1EM322872A
S6 STAND BAG A81N0UH 1EM424597
ACCESSORIES
X3 REMOTE CONTROL NF031RD 170/
ECPLC6.501/NF031
WX1A8A70-101
WX1A8A70-101
0EM408146A
UG190EB
NF031RD
Ref. No. Description Part No.
A6! RATING LABEL A8CNBFP ----------
A21 POP LABEL A8CNAFP ----------
A27 CARD LABEL A8CN0FP ----------
L3 SCREW P-TIGHT 3X10 BIND HEAD+ GBHP3100
L5 SCREW P-TIGHT M4X18 BIND HEAD+ GBHP4180
L10 SCREW S-TIGHT M3X6 BIND HEAD+ GBJS3060
L25 S-TIGHT SCREW M3X6 BIND HEAD+BLACK GBHS3060
L37 SCREW S-TIGHT M3X4 BIND HEAD+BLK GBHS3040
PACKING
S1 CARTON A8CNBFP 1EM428320
S2 STYROFORM TOP A8CN0FP 1EM022465
S3 STYROFORM BTM A8CN0FP 1EM022466
S5 SERIAL NO. LABEL L9750UA ----------
ACCESSORIES
X1 BAG POLYETHYLENE 235X365XT0.03 0EM408420A
X2-4! OWNERS MANUAL(FR-7) FR ES PT IT DE NL EN1EMN23880B
X4 BATTERY R6DB/2PA XB0M601MS003
20090407 12-1 A8CNBCA
Page 52

ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
PRODUCT SAFETY NOTE: Products marked with a
! have special characteristics important to safety.
Before replacing any of these components, read
carefully the product safety notice in this service
manual. Don't degrade the safety of the product
through improper servicing.
NOTES:
1. Parts that are not assigned part numbers (---------)
are not available.
2. Tolerance of Capacitors and Resistors are noted
with the following symbols.
C.....±0.25% D.....±0.5% F.....±1%
G.....±2% J......±5% K.....±10%
M.....±20% N.....±30% Z.....+80/-20%
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT
Ref. No. Description Part No.
DIGITAL MAIN CBA UNIT 1ESA19248
MMA CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
MMA CBA
Consists of the following:
MAIN CBA
IR SENSOR CBA
FUNCTION CBA
JACK CBA
MAIN CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
MAIN CBA
Consists of the following:
CAPACITORS
C102 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C103 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C104 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C105 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C508 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 0.01µF/50V CHD1JK30B103
C510 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 100µF/10V M CE1AMASDL101
C512 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 47pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH470
C516 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C517 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C518 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 1000µF/10V M CE1AMASDL102
C519 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C520 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 47pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH470
C524 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 33µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL330
C525 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C526 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C600! METALIZED FILM CAP. 0.22µF/250V or CT2E224MS037
! CAP METALIZED FILM 0.22µF/300V K 3.5MM CT2F224DC004
C601! ACROSS THE LINE CAP. 0.1µF/250V or CT2E104DC017
! METALIZED FILM CAP. 0.1µF/250V or CT2E104MS037
! CAP METALIZED FILM 0.1µF/300V K 3.5MM CT2F104DC004
C615! CAP ELECTROLYTIC 180µF/400V M CA2H181DYG10
C621 CERAMIC CAP. 470pF/2KV or CA3D471PAN04
CERAMIC CAP. BL 470pF/2KV CA3D471XF003
C623 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.01µF/
100V J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.01µF/100V J CA2A103SER02
1ESA18248
----------
----------
----------
----------
----------
CA2A103DT018
Ref. No. Description Part No.
C624 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.0015µF/
C625 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.047µF/
C642! SAFTY CAP. 3300pF/250V KX or CA2E332MR101
! CAP CERAMIC 3300pF/250V/M or CA2E332MR086
! SAFETY CAP. 3300pF/250V KX CA2E332MR050
C702 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C703 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C707 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C710 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C711 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C712 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C714 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C716 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C718 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C720 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C721 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C722 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C723 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C731 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C732 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C733 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C734 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C741 CHIP CERAMIC CAP. B K 2200pF/50V CHD1JK30B222
C742 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C744 CHIP CERAMIC CAP. B K 2200pF/50V CHD1JK30B222
C745 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C747 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C751 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C753 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C756 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C758 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/16V M H7 CE1CMAVSL470
C788 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 100µF/16V M CE1CMASDL101
C789 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 330µF/6.3V M H7 or CE0KMAVSL331
C791 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C792 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C793 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C794 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C795 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C796 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C797 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C801 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 470µF/16V M CE1CMASDL471
C802 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 470µF/16V M CE1CMASDL471
C806 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/25V M CE1EMASDL470
C808 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 100µF/10V M CE1AMASDL101
C809 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C810 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C811 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/25V M CE1EMASDL470
C812 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C816 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 22µF/50V M CE1JMASDL220
C818 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 470µF/16V M CE1CMASDL471
C819 CHIP CERAMIC CAP. B K 3900pF/50V CHD1JK30B392
C820 CHIP CERAMIC CAP. B K 3900pF/50V CHD1JK30B392
C822 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C823 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C824 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C825 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C826 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C827 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C835 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
100V J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.0015µF/100V J CA2A152SER02
100V J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.047µF/100V J CA2A473SER02
ALUMINUM ELECTROLYTIC CAP 330µF/6.3V H7CE0KMAVSM331
CA2A152DT018
CA2A473DT018
20090407 13-1 A8CNBEL
Page 53

Ref. No. Description Part No.
C836 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C837 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C883 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C884 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1µF/10V CHD1AK30B105
C892 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C894 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 1000pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH102
C895 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C896 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) CH J 100pF/50V CHD1JJ3CH101
C900 ELECTROLYTIC CAP 3300µF/10V or CE1AMZNDL332
ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 3300µF/10V M CE1AMZPDL332
C901 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 2.2µF/50V M CE1JMASDL2R2
C902 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 2200µF/25V M or CE1EMZPDL222
ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 2200µF/25V M CE1EMZNDL222
C903 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 100µF/50V M CE1JMASDL101
C904 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 330µF/25V M CE1EMASDL331
C905 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/25V M CE1EMASDL470
C907 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 2200µF/6.3V M CE0KMASDL222
C909 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.0027µF/
C910 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 22µF/50V M CE1JMASDL220
C911 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 470µF/16V M CE1CMASDL471
C912 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 1µF/50V M CE1JMASDL1R0
C914 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C916 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C917 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 1000µF/16V M CE1CMASDL102
C920 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C921 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C922 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C923 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C924 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 470µF/16V M CE1CMASDL471
C925 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C926 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C927 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C940 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C941 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C951 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 220µF/16V M CE1CMASDL221
C952 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C953 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 330µF/10V M CE1AMASDL331
C958 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C999 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
100V J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.0027µF/100V J CA2A272SER02
CA2A272DT018
CONNECTORS
CN101A FMN CONNECTOR TOP25P 25FMN-BTK-
CN102A FMN CONNECTOR TOP25P 25FMN-BTK-
CN103A FMN CONNECTOR TOP 23P 23FMN-BTK-
CN104A FMN CONNECTOR TOP25P 25FMN-BTK-
CN105A 242 SERIES CONNECTOR 224202112W1 J322C12TG001
CN106 CONNECTOR PRINT OSU S6B-PH-K-
CN107 FPC/FFC CONNECTOR IMSA-9615S-07A-PP-
A(LF)(SN) or
FFC CONNECTOR IMSA-9615S-25A-PP-A or JC96J25ER007
CONNECTOR PRINT MES 00 6232 025 006
800+
A(LF)(SN) or
FFC CONNECTOR IMSA-9615S-25A-PP-A or JC96J25ER007
CONNECTOR PRINT MES 00 6232 025 006
800+
A(FL)(SN) or
FFC CONNECTOR IMSA-9615S-23A-PP-A or JC96J23ER007
CONNECTOR PRINT MES 00 6232 023 006
800+
A(LF)(SN) or
FFC CONNECTOR IMSA-9615S-25A-PP-A or JC96J25ER007
CONNECTOR PRINT MES 00 6232 025 006
800+
S(LF)(SN) or
CONNECTOR PRINT OSU C R 440055-6 or J344C06AP006
CONNECTOR PRINT OSU JS-1125R-06 J3JT06CHY003
A or
FMN CONNECTOR TOP 7P 07FMN-BTK-
A(LF)(SN) or
JCFNG25JG019
JC62G25UG026
JCFNG25JG019
JC62G25UG026
JCFNG23JG019
JC62G23UG026
JCFNG25JG019
JC62G25UG026
J3PHC06JG030
JC96J07ER007
JCFNG07JG019
Ref. No. Description Part No.
CONNECTOR PRINT MES 00 6232 007 006
800+
CN802 CONNECTOR PRINT OSU
008283021200000S+ or
CONNECTOR PRINT OSU 2P 292161-2 J31FC02AP001
JC62G07UG026
J383C02UG004
DIODES
D501 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D610! ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7722B QDTB00MTZJ22
D611! DIODE 1N5399-B/P or NDLZ001N5399
! DIODE 1N5399BE NDL1001N5399
D612 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
D613! DIODE 1N5399-B/P or NDLZ001N5399
! DIODE 1N5399BE NDL1001N5399
D614! DIODE 1N5399-B/P or NDLZ001N5399
! DIODE 1N5399BE NDL1001N5399
D615 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D616! DIODE 1N5399-B/P or NDLZ001N5399
! DIODE 1N5399BE NDL1001N5399
D621 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D622 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D624 DIODE ZENER 1ZC18(Q) or QDLZ001ZC18Q
DIODE ZENER RD18F-T7-AZ-B or QDJB0RD18FAZ
DIODE ZENER 1ZB18BB NDWZ0001ZB18
D629! ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7733B QDTB00MTZJ33
D701 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7713B QDTB00MTZJ13
D702 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7713B QDTB00MTZJ13
D755 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-773.3B QDTB0MTZJ3R3
D758 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7713B QDTB00MTZJ13
D802! SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
! DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D803! ZENER DIODE MTZJT-774.7B QDTB0MTZJ4R7
D900! SCHOTTKY BARRIER DIODE SB360 or NDQZ000SB360
! DIODE SCHOTTKY SB360BH NDWZ000SB360
D901 DIODE FR104BB or NDL1000FR104
DIODE FR104-B NDLZ000FR104
D903! DIODE FR104BB or NDL1000FR104
! DIODE FR104-B NDLZ000FR104
D904! DIODE FR154 or NDLZ000FR154
! DIODE FR154BD NDL1000FR154
D905! DIODE FR104BB or NDL1000FR104
! DIODE FR104-B NDLZ000FR104
D906! SCHOTTKY BARRIER DIODE SB340 or NDQZ000SB340
! SCHOTTKY BARRIER DIODE SB340 NDWZ000SB340
D908 DIODE 1ZC43(Q) or QDLZ001ZC43Q
DIODE ZENER RD43F-T7-AZ-B or QDJB0RD43FAZ
DIODE ZENER 1ZB43BB NDWZ0001ZB43
D909 RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 or NDQZ001N4005
RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 NDWZ001N4005
D910 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D911 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D912 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D913! ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
D914 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
D915 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7733B QDTB00MTZJ33
D916 IC SHUNT REGULATOR KIA431-AT/P or NSZBA0TJY036
IC SHUNT REGULATOR SL431A-AT or NSZBA0TAUK01
IC SHUNT REGULATOR AS431BZTR-E1 NSZBA0TBCD01
D918 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7712B QDTB00MTZJ12
D919 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D920 IC SHUNT REGULATOR KIA431-AT/P or NSZBA0TJY036
20090407 13-2 A8CNBEL
Page 54

Ref. No. Description Part No.
IC SHUNT REGULATOR SL431A-AT or NSZBA0TAUK01
IC SHUNT REGULATOR AS431BZTR-E1 NSZBA0TBCD01
D922 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D923 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7724B QDTB00MTZJ24
D924! SCHOTTKY BARRIER DIODE SB270-B/P NDWZ000SB270
D925 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D926 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7710B QDTB00MTZJ10
D927 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D928 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-776.8B QDTB0MTZJ6R8
D929 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D930 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D931 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D935 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D936 IC SHUNT REGULATOR KIA431-AT/P or NSZBA0TJY036
IC SHUNT REGULATOR SL431A-AT or NSZBA0TAUK01
IC SHUNT REGULATOR AS431BZTR-E1 NSZBA0TBCD01
D942 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D944 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D947 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D948 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D951 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7715B QDTB00MTZJ15
D953 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D954 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D955 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7739B QDTB00MTZJ39
D956 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D966 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D967 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D970 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D973 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D974 RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 or NDQZ001N4005
RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 NDWZ001N4005
D975 RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 or NDQZ001N4005
RECTIFIER DIODE 1N4005 NDWZ001N4005
D985 IC SHUNT REGULATOR KIA431-AT/P or NSZBA0TJY036
IC SHUNT REGULATOR SL431A-AT or NSZBA0TAUK01
IC SHUNT REGULATOR AS431BZTR-E1 NSZBA0TBCD01
D986 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D987 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D988 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D989 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D990! DIODE SCHOTTKY 30PHA20 QDLZ030PHA20
ICS
IC601! PHOTO COUPLER PS2561L1-1-A-V(L) QPEL561L11AV
IC801 IC AN17812A or QSZBA0SMS017
IC AUDIO SA7412 NSZBA0SQ0007
Ref. No. Description Part No.
IC802 IC(AUDIO D/A) PCM1782DBQR NSZBA0TTY192
IC850 IC SWITCHING TC4052BF(ELNF) or QSZBA0TTS162
IC SWITCHING CD4052BNSR or NSZBA0TTY091
IC SWITCH HCF4052M013TR/SOP/16 NSZBA0TSS301
IC851 IC SWITCH TC4053BF(EL N F) or QSZBA0TTS163
IC SWITCH 4053L-S16-R or NSZBA0TUTC04
IC ANALOG MULTIPLEXERS
HCF4053M013TR or
IC ANALOG MULTIPLEXER CD4053BNSR NSZBA0TTY093
IC900 IC VOLTAGE REGULATOR 5V KIA7805API/P or NSZBA0SJY041
IC REGULATOR L7805CV/TO-220/3PIN or NSZBA0SSS304
IC REGULATOR AS7805T-E1/TO-220-3 NSZBA0SBCD03
IC902 IC REGULATOR KIA278R00PI-U/P NSZBA0SJY062
NSZBA0SSS002
COILS
L501 INDUCTOR 10µH-K-5FT LLARKBSTU100
L502 INDUCTOR 10µH-K-5FT LLARKBSTU100
L601! COIL LINE FILTER JLB20108 LLEG0Z0XB008
L701 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
L702 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
L703 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
L781 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
L838 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
L839 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
L840 INDUCTOR 2.2µH-J-26T LLAXJATTU2R2
TRANSISTORS
Q505 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q600! FET 2SK3566(Q) or QFWZ02SK3566
! FET 2SK3566(Q M) QFQZSK3566QM
Q601! TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-O(TE2 F T) or QQS02SC2120F
! TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SC2120F
! TRANSISTOR KTC3203-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTC3203P
! NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5344 Y NQSY02SC5344
Q726 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q727 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q731 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q734 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q744 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q802 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
20090407 13-3 A8CNBEL
Page 55

Ref. No. Description Part No.
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q805 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q900 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q901 TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-O(TE2 F T) or QQS02SC2120F
TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SC2120F
TRANSISTOR KTC3203-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTC3203P
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5344 Y NQSY02SC5344
Q902 TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-O(TE2 F T) or QQS02SC2120F
TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SC2120F
TRANSISTOR KTC3203-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTC3203P
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5344 Y NQSY02SC5344
Q903 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q904 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q906 TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-O(TE2 F T) or QQS02SC2120F
TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SC2120F
TRANSISTOR KTC3203-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTC3203P
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5344 Y NQSY02SC5344
Q907 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q908 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q911 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q912 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q920 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q922 TRANSISTOR KTD2059-O/P or NQE0KTD2059P
TRANSISTOR KTD2059-Y/P NQEYKTD2059P
Q936 NPN TRANSISTOR POWER 2SC4881F HFE
MAX320 or
TRANSISTOR(PB FREE) KTC2026-Y/P or NQEYKTC2026P
NPN TRANSISTOR STC403 NQEZ00STC403
QQWZ2SC4881F
Ref. No. Description Part No.
RESISTORS
R102 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0100
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10 Ω RRXA100YF002
R103 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0100
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10 Ω RRXA100YF002
R511 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R512 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R515 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0102
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.0k Ω RRXA102YF002
R522 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 220 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0221
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 220 Ω RRXA221YF002
R525 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R526 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0470
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47 Ω RRXA470YF002
R600! GLASS GLAZE RES. 1/2W J 1M Ω or RXX2JZLZ0105
! RES CARBON 1/2W J 1M Ω RCX2105DP006
R610! CEMENT RESISTOR 5W K 1.2 Ω or RW051R2PG001
! CEMENT RESISTOR 5W J 1.2 Ω H 10MM RW051R2PAK10
R620 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4JATZ0824
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4824T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 820k Ω RCX4824FS002
R621 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4JATZ0824
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4824T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 820k Ω RCX4824FS002
R622 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4JATZ0824
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4824T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 820k Ω RCX4824FS002
R623 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4JATZ0824
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 820k Ω or RCX4824T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 820k Ω RCX4824FS002
R624 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 390k Ω or RCX4JATZ0394
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 390k Ω or RCX4394T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 390k Ω RCX4394FS002
R632 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 390 Ω or RCX4JATZ0391
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 390 Ω or RCX4391T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 390 Ω RCX4391FS002
R633 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 390 Ω or RCX4JATZ0391
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 390 Ω or RCX4391T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 390 Ω RCX4391FS002
R634 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 330 Ω or RCX4JATZ0331
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 330 Ω or RCX4331T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 330 Ω RCX4331FS002
R635 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R636! METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.68 Ω or RN02R68ZU001
! METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.68 Ω RN02R68DP004
R637 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 150 Ω or RCX4JATZ0151
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 150 Ω or RCX4151T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 150 Ω RCX4151FS002
R638 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 5.6k Ω or RCX4JATZ0562
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 5.6k Ω or RCX4562T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 5.6k Ω RCX4562FS002
R639 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R701 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R702 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R704 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4JATZ0471
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4471T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 470 Ω RCX4471FS002
20090407 13-4 A8CNBEL
Page 56

Ref. No. Description Part No.
R707 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R708 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R713 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R714 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R716 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R717 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R718 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R719 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R720 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R721 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R722 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R723 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R729 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0102
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.0k Ω RRXA102YF002
R730 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4JATZ0471
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4471T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 470 Ω RCX4471FS002
R732 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 470 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0471
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 470 Ω RRXA471YF002
R737 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4JATZ0471
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4471T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 470 Ω RCX4471FS002
R738 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R739 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R740 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0470
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47 Ω RRXA470YF002
R741 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 560 Ω or RCX4JATZ0561
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 560 Ω or RCX4561T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 560 Ω RCX4561FS002
R746 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 560 Ω or RCX4JATZ0561
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 560 Ω or RCX4561T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 560 Ω RCX4561FS002
R751 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R752 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R756 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 4.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0472
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 4.7k Ω or RCX4472T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 4.7k Ω RCX4472FS002
R757 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 6.8k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0682
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 6.8k Ω RRXA682YF002
R758 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R759 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R761 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4JATZ0471
Ref. No. Description Part No.
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4471T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 470 Ω RCX4471FS002
R762 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R763 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R764 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 75 Ω or RCX4JATZ0750
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 75 Ω or RCX4750T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 75 Ω RCX4750FS002
R765 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R766 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R767 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1.2k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0122
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.2k Ω RRXA122YF002
R768 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4JATZ0471
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 470 Ω or RCX4471T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 470 Ω RCX4471FS002
R770 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 75 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0750
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 75 Ω RRXA750YF002
R771 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R775 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R776 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R777 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R778 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R779 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R780 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R781 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R782 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0102
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.0k Ω RRXA102YF002
R783 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R784 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R785 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R786 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R787 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R788 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R793 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 39k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0393
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 39k Ω RRXA393YF002
R794 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0102
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.0k Ω RRXA102YF002
R797 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0102
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.0k Ω RRXA102YF002
R801 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 56k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0563
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 56k Ω RRXA563YF002
R802 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 27k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0273
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 27k Ω RRXA273YF002
R805! PCB JUMPER D0.6-P15.0 JW15.0T
R807! METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 4.7 Ω or RN024R7ZU001
! METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 4.7 Ω RN024R7DP004
20090407 13-5 A8CNBEL
Page 57

Ref. No. Description Part No.
R808 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R809 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R811 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R812! CHIP RES. 1/10W J 2.2k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0222
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 2.2k Ω RRXA222YF002
R813 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 10k Ω or RCX4JATZ0103
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 10k Ω or RCX4103T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 10k Ω RCX4103FS002
R814 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.9k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0392
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.9k Ω RRXA392YF002
R816 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R817 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.9k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0392
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.9k Ω RRXA392YF002
R818 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 22k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0223
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 22k Ω RRXA223YF002
R822 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 22k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0223
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 22k Ω RRXA223YF002
R824 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R825 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 10k Ω or RCX4JATZ0103
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 10k Ω or RCX4103T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 10k Ω RCX4103FS002
R829 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 120 Ω or RCX4JATZ0121
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 120 Ω or RCX4121T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 120 Ω RCX4121FS002
R830 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R831 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R832 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R833 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 33 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0330
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 33 Ω RRXA330YF002
R834 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 33 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0330
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 33 Ω RRXA330YF002
R835 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 33 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0330
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 33 Ω RRXA330YF002
R836 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 33 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0330
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 33 Ω RRXA330YF002
R837 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 180 Ω or RCX4JATZ0181
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 180 Ω or RCX4181T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 180 Ω RCX4181FS002
R838 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 180 Ω or RCX4JATZ0181
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 180 Ω or RCX4181T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 180 Ω RCX4181FS002
R839 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R840 CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W 0 Ω or RRXAZR5Z0000
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 0 Ω RRXA000YF002
R842 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R843 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R844 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R845 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R846 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
Ref. No. Description Part No.
R847 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R848 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R849 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R850 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R852 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R854 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R855 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R856 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R857 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R858 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R859 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R890 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R891 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R892 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R893 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R894 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R895 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4JATZ0104
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100k Ω or RCX4104T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100k Ω RCX4104FS002
R896 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 27k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0273
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 27k Ω RRXA273YF002
R897 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 27k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0273
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 27k Ω RRXA273YF002
R900 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 3.3 Ω or RCX4JATZ03R3
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 3.3 Ω or RCX43R3T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 3.3 Ω RCX43R3FS002
R904 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 12k Ω or RCX4JATZ0123
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 12k Ω or RCX4123T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 12k Ω RCX4123FS002
R906! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 4.7k Ω or RRXAFR5H4701
! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 4.7k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0472
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 4.70k Ω RTW4701YF002
R907! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 4.7k Ω or RRXAFR5H4701
! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 4.7k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0472
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 4.70k Ω RTW4701YF002
R908! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.9k Ω or RRXAFR5H3901
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 3.9k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3901
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.90k Ω RTW3901YF002
R909! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.9k Ω or RRXAFR5H3901
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 3.9k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3901
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.90k Ω RTW3901YF002
R910 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 820 Ω or RRXAFR5H8200
CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 820 Ω or RRXAFR5Z8200
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 820 Ω RTW8200YF002
R911 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5H5601
20090407 13-6 A8CNBEL
Page 58

Ref. No. Description Part No.
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0562
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 5.60k Ω RTW5601YF002
R912! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5H2400
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5Z2400
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 240 Ω RTW2400YF002
R913! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5H2400
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5Z2400
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 240 Ω RTW2400YF002
R914! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5H2400
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5Z2400
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 240 Ω RTW2400YF002
R915! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5H2400
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5Z2400
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 240 Ω RTW2400YF002
R916 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 180 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0181
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 180 Ω RRXA181YF002
R917 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R918 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 6.8k Ω or RCX4JATZ0682
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 6.8k Ω or RCX4682T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 6.8k Ω RCX4682FS002
R919 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 1W J 470 Ω or RN01471ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 1W 470 Ω RN01471DP003
R920 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R921 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 68k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0683
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 68k Ω RRXA683YF002
R922 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 12 Ω or RN02120ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 12 Ω RN02120DP004
R923 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1k Ω or RCX4JATZ0102
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.0k Ω or RCX4102T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1k Ω RCX4102FS002
R925 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.3k Ω or RRXAFR5H3301
CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 3.3k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3301
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.30k Ω RTW3301YF002
R926 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 9.1k Ω or RRXAFR5H9101
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 9.1k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0912
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 9.10k Ω RTW9101YF002
R928 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0272
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4272T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 2.7k Ω RCX4272FS002
R929 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R930 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3k Ω or RRXAFR5H3001
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.0k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3001
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.00k Ω RTW3001YF002
R931 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 9.1k Ω or RRXAFR5H9101
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 9.1k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0912
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 9.10k Ω RTW9101YF002
R936 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 150 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0151
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 150 Ω RRXA151YF002
R937 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 2.7k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0272
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 2.7k Ω RRXA272YF002
R938 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R939 METAL RESISTER. 2W J 0.82 Ω or RN02R82ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.82 Ω RN02R82DP004
R940 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R941 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R942 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R943 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R944 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0272
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4272T1001
Ref. No. Description Part No.
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 2.7k Ω RCX4272FS002
R945 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R947 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 47k Ω or RCX4JATZ0473
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 47k Ω or RCX4473T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 47k Ω RCX4473FS002
R948 METAL RESISTER. 2W J 0.82 Ω or RN02R82ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.82 Ω RN02R82DP004
R949 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.8k Ω or RCX4JATZ0182
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.8k Ω or RCX4182T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.8k Ω RCX4182FS002
R950 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R953 METAL RESISTOR 2W J 39 Ω or RN02390ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 39 Ω RN02390DP004
R954 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 12 Ω or RN02120ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 12 Ω RN02120DP004
R955 METAL RESISTOR 2W J 39 Ω or RN02390ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 39 Ω RN02390DP004
R958 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R959 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 12k Ω or RRXAFR5H1202
CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 12k Ω or RRXAFR5Z1202
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 12.0k Ω RTW1202YF002
R960 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 620 Ω or RRXAFR5H6200
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 620 Ω or RRXAFR5Z6200
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 620 Ω RTW6200YF002
R961 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3k Ω or RRXAFR5H3001
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.0k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3001
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.00k Ω RTW3001YF002
R962 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R963 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 6.8k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0682
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 6.8k Ω RRXA682YF002
R964 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R965 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 27k Ω or RCX4JATZ0273
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 27k Ω or RCX4273T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 27k Ω RCX4273FS002
R966 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 3.3k Ω or RCX4JATZ0332
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 3.3k Ω or RCX4332T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 3.3k Ω RCX4332FS002
R967 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R968 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0272
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4272T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 2.7k Ω RCX4272FS002
R969 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.3k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0332
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.3k Ω RRXA332YF002
R970 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.3k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0332
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.3k Ω RRXA332YF002
R971 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 8.2k Ω or RRXAFR5H8201
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 8.2k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0822
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 8.20k Ω RTW8201YF002
R972 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.1k Ω or RRXAFR5H5101
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.1k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0512
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 5.10k Ω RTW5101YF002
R973 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R974 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R975 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4JATZ0271
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 270 Ω or RCX4271T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 270 Ω RCX4271FS002
R976 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5H5601
20090407 13-7 A8CNBEL
Page 59

Ref. No. Description Part No.
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0562
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 5.60k Ω RTW5601YF002
R977 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 2.7k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0272
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 2.7k Ω RRXA272YF002
R978 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 8.2k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0822
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 8.2k Ω RRXA822YF002
R980 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1k Ω or RCX4JATZ0102
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.0k Ω or RCX4102T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1k Ω RCX4102FS002
R982 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5H5601
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 5.6k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0562
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 5.60k Ω RTW5601YF002
R983 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 6.8k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0682
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 6.8k Ω RRXA682YF002
R985 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0272
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 2.7k Ω or RCX4272T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 2.7k Ω RCX4272FS002
R986! CHIP RES. 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5H2400
! CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 240 Ω or RRXAFR5Z2400
! RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 240 Ω RTW2400YF002
R987 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0101
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100 Ω RRXA101YF002
R992 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R994 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 3.3k Ω or RRXAFR5H3301
CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W F 3.3k Ω or RRXAFR5Z3301
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 3.30k Ω RTW3301YF002
R995 CHIP RES. 1/10W F 43k Ω or RRXAFR5H0433
CHIP RES. 1/10W F 43.0 k Ω or RRXAFR5Z0433
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W F 43.0k Ω RTW4302YF002
R997 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.22 Ω or RN02R22ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.22 Ω RN02R22DP004
MISCELLANEOUS
AC601! AC CORD W/O A GND WIRE CEE/ 1700/ NO/
! AC CORD P205-1516-1 WAE9172K5002
B20 POW HEAT SINK A7120UH 1EM423993
B21 HEAT SINK PMR ASSEMBLY A8CN0FP 1EM425837A
B22 HEAT SINK PMS ASSEMBLY A8CN0FP 1EM426337A
BC601 BEADS INDUCTOR FBR07HA121SB-00 LLBF00STU030
BC603 BEADS INDUCTOR FBR07HA121SB-00 LLBF00STU030
BC750 BEADS INDUCTOR FBR07HA121SB-00 LLBF00STU030
BC801 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
BC802 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
BC803 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
F601! FUSE 4A/250V(PB FREE) 0215004.MXP PBGZ20BAG021
FH601 FUSE HOLDER MSF-015 LF (B110) XH01Z00LY002
FH602 FUSE HOLDER MSF-015 LF (B110) XH01Z00LY002
JK721 JACK SW DIN PCB S 04/DIN-417HA-01 or JYEJ040YUQ03
JK722 JACK RCA PCB S YELLOW 01/RCA-101H(YL) orJXRJ010YUQ05
JK723 JACK RCA PCB S WHITE 01/RCA-101H(WH) or JXRJ010YUQ02
JK724 JACK SW RCA PCB S RED RCA-102H(RD) or JYRJ010YUQ03
JK725 JACK HPEP SML PCB S PJ-358H or JXSJ020YUQ01
JK751 JACK RGB PCB S 21PIN / MRC-021H-02 JXGJ210LY001
JK801 JACK SE HPEP SML PCM S MSJ-035-04A LF orJYSJ020LY002
JS901 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
L9 SCREW B-TIGHT D3X8 BIND HEAD+ GBJB3080
SA601! SURGE ABSORBER 470V+-10PER or NVQZ10D471KB
! VARISTOR 10D 471K SVR NVQZVR10D471
WHITE or
JACK SW DIN PCB S 04 MDC-076H-A LF JYEJ040LY002
JACK RCA PCB S (YELLOW) 01 MTJ-032-04B-
40 FE
JACK RCA PCB S (WHITE) 01 MTJ-032-04B-41 FEJXRJ010LY031
JACK SW RCA PCB S(RED) 01 MTJ-032-04A-
75 FE
JACK HPEP SML PCB S 02 MSJ-035-29D
(ABS)
JACK SW HPEP SML PCB S PJ-362H-7 JYSJ020YUQ02
WAE9172LW001
JXRJ010LY032
JYRJ010LY031
JXSJ020LY001
Ref. No. Description Part No.
T601! TRANS POWER 8729 or LTT2PE0KT047
! TRANS POWER BCK-28-9943 LTT2PE0XB036
TM601 EYELET TYPE D-1 0VM406868
TM602 EYELET TYPE D-1 0VM406868
IR SENSOR CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
IR SENSOR CBA
Consists of the following:
----------
CAPACITOR
C301 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 2.2µF/50V M H7 CE1JMAVSL2R2
DIODES
D301 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
D302 LED(GREEN) LTL-4234 or NPWZ0LTL4234
LED GREEN 333GT/E(FNA) NPWZ33GTEFNA
D303 LED L-53HT or NP4Z000L53HT
LED 333HT/E-L or NPHL00333HTE
LED 333HT/E-K NPHK00333HTE
RESISTORS
R301 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 120 Ω or RCX4JATZ0121
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 120 Ω or RCX4121T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 120 Ω RCX4121FS002
R302 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 330 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0331
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 330 Ω RRXA331YF002
R303 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 330 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0331
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 330 Ω RRXA331YF002
R304 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.3k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0332
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.3k Ω RRXA332YF002
MISCELLANEOUS
RS301 SENSOR REMOTE RECEIVER KSM-712TH2E USESJRSKK044
FUNCTION CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
FUNCTION CBA
Consists of the following:
CAPACITORS
C201 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
C202 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) F Z 0.1µF/50V CHD1JZ30F104
CONNECTORS
CN201 WIRE ASSEMBLY 6PIN 6PIN/250MM/AWG26 WX1A8CN0-008
CN202 WIRE ASSEMBLY 5PIN WX1A8CN0-002 WX1A8CN0-002
DIODES
D201 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
D202 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
D203 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
RESISTORS
R201 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 10k Ω or RCX4GATZ0103
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 10k Ω RCX4103T1002
R202 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 220 Ω or RCX4JATZ0221
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 220 Ω or RCX4221T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 220 Ω RCX4221FS002
R203 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 1.5k Ω or RCX4GATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 1.5k Ω RCX4152T1002
R204 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 1.5k Ω or RCX4GATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 1.5k Ω RCX4152T1002
R205 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 2.2k Ω or RCX4GATZ0222
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 2.2k Ω RCX4222T1002
R206 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 2.7k Ω or RCX4GATZ0272
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 2.7k Ω RCX4272T1002
R207 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 4.7k Ω or RCX4GATZ0472
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 4.7k Ω RCX4472T1002
R208 CARBON RES. 1/4W G 6.8k Ω or RCX4GATZ0682
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W G 6.8k Ω RCX4682T1002
SWITCHES
SW201 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
----------
20090407 13-8 A8CNBEL
Page 60

Ref. No. Description Part No.
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW202 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW203 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW204 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW205 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW206 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
SW207 TACT SWITCH SKQSAB or SST0101AL038
TACT SWITCH TC-1104(H=5.0) or SST0101DNG02
TACT SWITCH KSM0612B SST0101HH003
JACK CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
JACK CBA
Consists of the following:
CAPACITORS
C14 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
C15 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 5600pF/50V CHD1JK30B562
CONNECTORS
CN11 CONNECTOR FPC/FFC IMSA-9615S-07C-PP-
A or
FMN CONNECTOR SIDE 7P 07FMN-STK-
A(LF)(SN)
RESISTORS
R14 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R15 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0473
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47k Ω RRXA473YF002
R16 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R17 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R18 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
R19 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R20 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4JATZ0152
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.5k Ω or RCX4152T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.5k Ω RCX4152FS002
R21 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R22 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R23 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R24 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
MISCELLANEOUS
JK11 JACK RCA PCB S GREEN 01/RCA-101H(GN) orJXRJ010YUQ03
JACK RCA PCB S(GREEN) 01 MTJ-032-04B-73 FEJXRJ010LY030
JK12 JACK RCA PCB S BLUE 01/RCA-101H(BL) or JXRJ010YUQ04
JACK RCA PCB S(BLUE) 01 MTJ-032-04B-74 FEJXRJ010LY033
JK13 JACK RCA PCB S RED 01/RCA-101H(RD) or JXRJ010YUQ01
JACK RCA PCB S(RED) 01 MTJ-032-04B-75 FE JXRJ010LY028
JK14 JACK RCA PCB S WHITE 01/RCA-101H(WH) or JXRJ010YUQ02
JACK RCA PCB S (WHITE) 01 MTJ-032-04B-41 FEJXRJ010LY031
JK15 JACK SW RCA PCB S RED RCA-102H(RD) or JYRJ010YUQ03
----------
JC96J07ER009
JCFNG07JG021
Ref. No. Description Part No.
JACK SW RCA PCB S(RED) 01 MTJ-032-04A75 FE
JYRJ010LY031
MUT CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
MUT CBA
Consists of the following:
INVERTER CBA
JUNCTION CBA
INVERTER CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
INVERTER CBA
Consists of the following:
CAPACITORS
C401 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 4700pF/50V CHD1JK30B472
C402 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.1µF/100V
C404 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 220µF/16V M CE1CMASDL221
C405 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.1µF/100V
C406 CAP CHIP CERAMIC 5pF/3.15KV/DJ CA3F5R0MR060
C407 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 4700pF/50V CHD1JK30B472
C408 CAP CHIP CERAMIC 5pF/3.15KV/DJ CA3F5R0MR060
C411 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 10µF/50V M CE1JMASDL100
C412 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 47µF/25V M CE1EMASDL470
C413 ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 1000µF/25V M or CE1EMZNDL102
C414 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 0.01µF/50V CHD1JK30B103
C415 CAP METALIZED FILM 0.11µF 250V H MPEF CT2E114DT065
C416 CAP CERAMIC HV 12P 3KV SL J or CCD3FJPSL120
C417 CAP CERAMIC HV 12P 3KV SL J or CCD3FJPSL120
C418 CHIP CERAMIC CONDENSER
C419 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 0.01µF/50V CHD1JK30B103
C420 POLYESTER FILM CAP. (PB FREE) 0.1µF/100V
C450 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1000pF/50V CHD1JK30B102
C451 CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(1608) B K 1000pF/50V CHD1JK30B102
CN401 CONNECTOR PRINT OSU KW04-800-0200 J30402KET001
CN402 CONNECTOR PRINT OSU KW04-800-0200 J30402KET001
CN451 CONNECTOR PRINT OSU
D402 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D403 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D405 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-7715B QDTB00MTZJ15
D408 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D409 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D410 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D411 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D412 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
D413 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.1µF/100V J CA2A104SER02
J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.1µF/100V J CA2A104SER02
ELECTROLYTIC CAP. 1000µF/25V M CE1EMZPDL102
CAP CERAMIC-HV 12pF/3.15KV/SL/J CCD3FJASL120
CAP CERAMIC-HV 12pF/3.15KV/SL/J CCD3FJASL120
X7R_K_3300pF/630V or
CHIP CERAMIC CAP.(3216) X7R_K_3300pF/
630V
J or
CAP POLYESTER FILM 0.1µF/100V J CA2A104SER02
CONNECTORS
008283021200000S+ or
CONNECTOR PRINT OSU 2P 292161-2 J31FC02AP001
DIODES
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
1ESA18306
----------
----------
----------
CA2A104DT018
CA2A104DT018
CA2K332MR054
CA2K332TE012
CA2A104DT018
J383C02UG004
20090407 13-9 A8CNBEL
Page 61
Ref. No. Description Part No.
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D414 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D415 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D416 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D418 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D419 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D422 SWITCHING DIODE 1SS133(T-77) or QDTZ001SS133
DIODE SWITCHING HSS4148TE-E QDTZ0HSS4148
D428 ZENER DIODE MTZJT-775.6B QDTB0MTZJ5R6
COILS
L401B POWER INDUCTER RCR1616-471K or LLC471KSF009
COIL RADIAL LH L 13NB471K 470µH or LLF4710TU012
COIL SEALED INDUCTOR A71116008 LLF4710KV013
L403 CHOKE COIL 22µH-K or LLBD00PKV021
CHOKE COIL 22µH-K or LLBD00PU6011
CHOKE COIL 22µH-K LLBD00PKT002
TRANSISTORS
Q401 TRANSISTOR 2SA950-O (TE2 F T) or QQS002SA950F
TRANSISTOR 2SA950-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY02SA950F
TRANSISTOR (PB FREE) KTA1271-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTA1271P
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1981Y-AT NQSY02SA1981
Q402 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q403 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
Q404 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
Q405 TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-O(TE2 F T) or QQS02SC2120F
TRANSISTOR 2SC2120-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SC2120F
TRANSISTOR KTC3203-Y-AT/P or NQSYKTC3203P
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5344 Y NQSY02SC5344
Q406 NPN TRANSISTOR POWER 2SC4881F HFE
Q408! FET MOS SMD HAT2215R01-EL-E QF2ZHAT2215R
Q410 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
Q411 TRANSISTOR KTA1267-GR-AT/P or NQS1KTA1267P
Q412 TRANSISTOR KTC3199-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3199P
MAX320
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
TRANSISTOR KTA-1266-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTA1266P
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-Y(TE2 F T) or QQSY2SA1015F
TRANSISTOR 2SA1015-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SA1015F
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980 G or NQSG02SA1980
PNP TRANSISTOR 2SA1980MG-AT NQSG2SA1980M
TRANSISTOR KTC3198-GR-AT/P or NQS4KTC3198P
TRANSISTOR 2SC1815-GR(TE2 F T) or QQS12SC1815F
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343G-AT or NQSG02SC5343
NPN TRANSISTOR 2SC5343MG-AT NQSG2SC5343M
QQWZ2SC4881F
RESISTORS
R401 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 1.5k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0152
Ref. No. Description Part No.
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 1.5k Ω RRXA152YF002
R402 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 27k Ω or RCX4JATZ0273
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 27k Ω or RCX4273T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 27k Ω RCX4273FS002
R404 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 3.3k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0332
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 3.3k Ω RRXA332YF002
R405 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R406 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R407 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R408 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R409 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4JATZ0101
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 100 Ω or RCX4101T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 100 Ω RCX4101FS002
R412 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R413 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 1.2k Ω or RCX4JATZ0122
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 1.2k Ω or RCX4122T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 1.2k Ω RCX4122FS002
R414 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 47 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0470
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 47 Ω RRXA470YF002
R415 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 10k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0103
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 10k Ω RRXA103YF002
R417 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 5.6k Ω or RCX4JATZ0562
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 5.6k Ω or RCX4562T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 5.6k Ω RCX4562FS002
R418 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 330 Ω or RCX4JATZ0331
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 330 Ω or RCX4331T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 330 Ω RCX4331FS002
R419 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 330 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0331
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 330 Ω RRXA331YF002
R420 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 8.2k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0822
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 8.2k Ω RRXA822YF002
R422 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 820k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0824
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 820k Ω RRXA824YF002
R423 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 22k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0223
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 22k Ω RRXA223YF002
R424 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 9.1k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0912
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 9.1k Ω RRXA912YF002
R425 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 56 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0560
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 56 Ω RRXA560YF002
R426 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 56 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0560
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 56 Ω RRXA560YF002
R427 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 560k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0564
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 560k Ω RRXA564YF002
R428 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 560k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0564
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 560k Ω RRXA564YF002
R429 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 820k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0824
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 820k Ω RRXA824YF002
R430 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 3.3 Ω or RCX4JATZ03R3
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 3.3 Ω or RCX43R3T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 3.3 Ω RCX43R3FS002
R431 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 18k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0183
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 18k Ω RRXA183YF002
R432 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 820 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0821
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 820 Ω RRXA821YF002
R435 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 2.2k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0222
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 2.2k Ω RRXA222YF002
R437 CARBON RES. 1/4W J 4.7k Ω or RCX4JATZ0472
RES CARBON FILM T 1/4W J 4.7k Ω or RCX4472T1001
RES CARBON FILM 1/4W J 4.7k Ω RCX4472FS002
20090407 13-10 A8CNBEL
Page 62

Ref. No. Description Part No.
R438 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 560 Ω or RRXAJR5Z0561
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 560 Ω RRXA561YF002
R439 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.68 Ω or RN02R68ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.68 Ω RN02R68DP004
R440 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 100k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0104
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 100k Ω RRXA104YF002
R441 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 130k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0134
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 130k Ω RRXA134YF002
R442 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 22k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0223
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 22k Ω RRXA223YF002
R454 METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.33 Ω or RN02R33ZU001
METAL OXIDE FILM RES. 2W J 0.33 Ω RN02R33DP004
R455 CHIP RES. 1/10W J 22k Ω or RRXAJR5Z0223
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 22k Ω RRXA223YF002
R456 CHIP RES.(1608) 1/10W 0 Ω or RRXAZR5Z0000
RES CHIP 1608 1/10W J 0 Ω RRXA000YF002
MISCELLANEOUS
JS402 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
JS411 PCB JUMPER D0.6-P5.0 JW5.0T
T401! TRANS INVERTER ETJV26ZE11BC LTZ3PC0MS003
JUNCTION CBA
Ref. No. Description Part No.
JUNCTION CBA
Consists of the following:
CONNECTOR
CN403A WIRE ASSEMBLY 12PIN WX1A8CN0-101 WX1A8CN0-101
MISCELLANEOUS
CL403 242 SERIES CONNECTOR TUC-P12X-B1 WHT STJCTUB12TG002
----------
Ref. No. Description Part No.
TU501! TUNER UNIT DTV TDAG4-B04A UTUNPSGAL013
20090407 13-11 A8CNBEL
Page 63

LT6-M19WB
A8CNBFP
2009-05-14
 Loading...
Loading...