
Freescale Semiconductor
Data Sheet: Advance Information
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet
Supports MCF5207 & MCF5208
by: Microcontroller Division
MCF5208EC
Rev. 1, 4/2007
The MCF5207 and MCF5208 devices are
highly-integrated, 32-bit microprocessors based on the
version 2 ColdFire microarchitecture. Both devices
contain a 16-Kbyte internal SRAM, an 8-Kbyte
configurable cache, a 2-bank SDR/DDR SDRAM
controller, a 16-channel DMA controller, up to three
UARTs, a queued SPI, a low-power management
modeule, and other peripherals that enable the MCF5207
and MCF5208 for use in industrial control and
connectivity applications. The MCF5208 device also
features a 10/100 Mbps fast ethernet controller.
This document provides detailed information on power
considerations, DC/AC electrical characteristics, and AC
timing specifications of the MCF5207 and MCF5208
microprocessors. It was written from the perspective of
the MCF5208 device. See the following section for a
summary of differences between the two devices.
Table of Contents
1 MCF5207/8 Device Configurations......................2
2 Ordering Information ...........................................2
3 Signal Descriptions..............................................3
4 Mechanicals and Pinouts ....................................8
5 Electrical Characteristics ...................................17
6 Revision History ................................................44
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2007. All rights reserved.
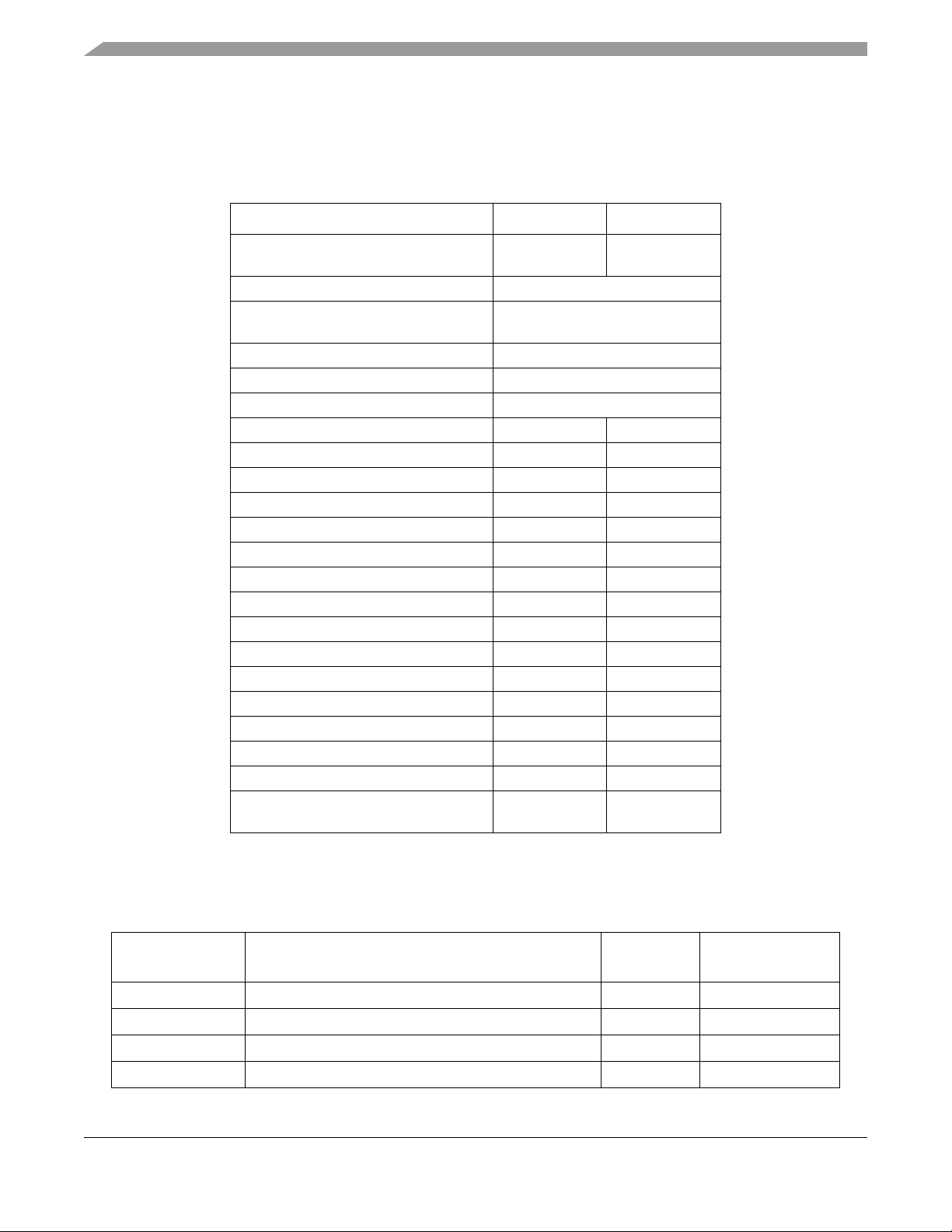
MCF5207/8 Device Configurations
1 MCF5207/8 Device Configurations
The following table compares the two devices described in this document:
Table 1. MCF5207 & MCF5208 Configurations
Module MCF5207 MCF5208
Version 2 ColdFire Core with EMAC
(Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit)
Core (System) Clock up to 166.67 MHz
Peripheral and External Bus Clock
(Core clock ÷ 2)
Performance (Dhrystone/2.1 MIPS) up to 159
Instruction/Data Cache 8 Kbytes
Static RAM (SRAM) 16 Kbytes
SDR/DDR SDRAM Controller • •
Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC) — •
Low-Power Management Module • •
UARTs 3 3
2
C••
I
QSPI • •
32-bit DMA Timers 4 4
Watchdog Timer (WDT) • •
Periodic Interrupt Timers (PIT) 4 4
Edge Port Module (EPORT) • •
Interrupt Controllers (INTC) 1 1
16-channel Direct Memory Access (DMA) • •
FlexBus External Interface • •
General Purpose I/O Module (GPIO) • •
JTAG - IEEE
Package 144 LQFP
®
1149.1 Test Access Port • •
••
up to 83.33 MHz
160 QFP
144 MAPBGA
196 MAPBGA
2 Ordering Information
Table 2. Orderable Part Numbers
Freescale Part
Number
MCF5207CAG166 MCF5207 RISC Microprocessor, 144 LQFP 166.67 MHz –40
MCF5207CVM166 MCF5207 RISC Microprocessor, 144 MAPBGA 166.67 MHz –40
MCF5208CAB166 MCF5208 RISC Microprocessor, 160 QFP 166.67 MHz –40
MCF5208CVM166 MCF5208 RISC Microprocessor, 196 MAPBGA 166.67 MHz –40
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Description Speed Temperature
° to +85° C
° to +85° C
° to +85° C
° to +85° C
Freescale Semiconductor2
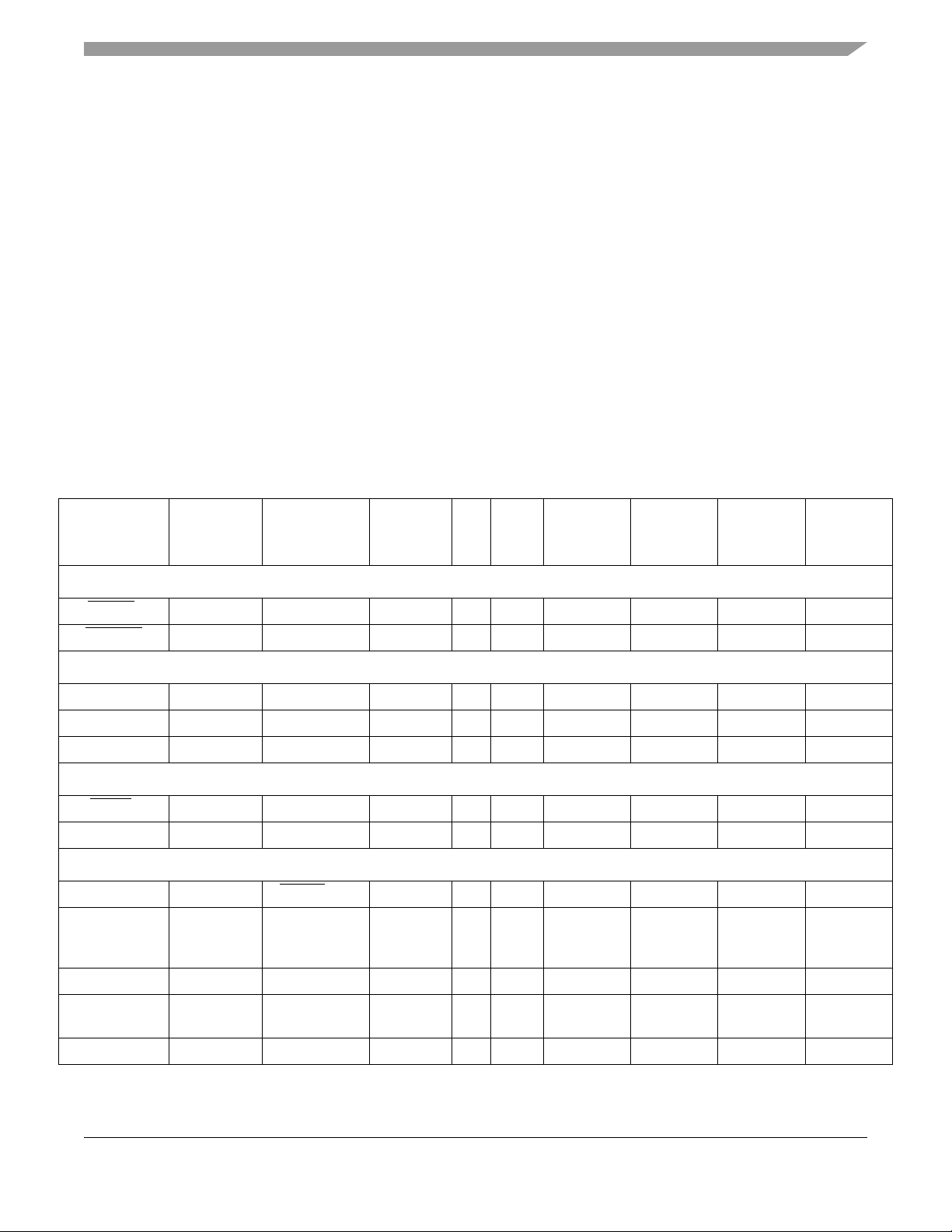
Signal Descriptions
3 Signal Descriptions
The following table lists all the MCF5208 pins grouped by function. The Dir column is the direction for
the primary function of the pin only . Refer to Section 4, “Mechanicals and Pinouts” for package diagrams.
For a more detailed discussion of the MCF5208 signals, consult the MCF5208 Reference Manual
(MCF5208RM).
NOTE
In this table and throughout this document, a single signal within a group is
designated without square brackets (i.e., A23), while designations for
multiple signals within a group use brackets (i.e., A[23:21]) and is meant to
include all signals within the two bracketed numbers when these numbers
are separated by a colon.
NOTE
The primary functionality of a pin is not necessarily its default functionality .
Pins that are muxed with GPIO will default to their GPIO functionality.
Table 3. MCF5207/8 Signal Information and Muxing
Signal Name GPIO Alternate 1 Alternate 2
2
RESET
RSTOUT — — — O
EXTAL — — — I
XTAL — — — O
FB_CLK — — — O
2
RCON
DRAMSEL — — — I
A[23:22] — FB_CS
A[21:16] — — — O
A[15:14] — SD_BA[1:0]
A[13:11] — SD_A[13:11]
A10 — — — O
— — — I
Mode Selection
— — — I
[5:4] — O
3
3
—O
—O
1
Dir.
Reset
Clock
FlexBus
Voltage
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
SDVDD
EVDD
EVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
MCF5207
144
LQFP
Domain
82 J10 90 J14
74 M12 82 N14
78 K12 86 L14
80 J12 88 K14
34 L1 40 N1
144 C4 160 C3
79 H10 87 K11
118, 117 B9, A10 126, 125 B11, A11
116–114,
112, 108,
107
106, 105 B12, C12 114, 113 C14, D12
104–102 D11, E10,
101 C10 109 E12
MCF5207
144
MAPBGA
C9, A11,
B10, A12,
C11, B11
D12
MCF5208
160
QFP
124, 123,
122, 120,
116, 115
112, 111,
110
MCF5208
196
MAPBGA
B12, A12,
A13, B13,
B14, C13
D13, D14,
E11
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Signal Descriptions
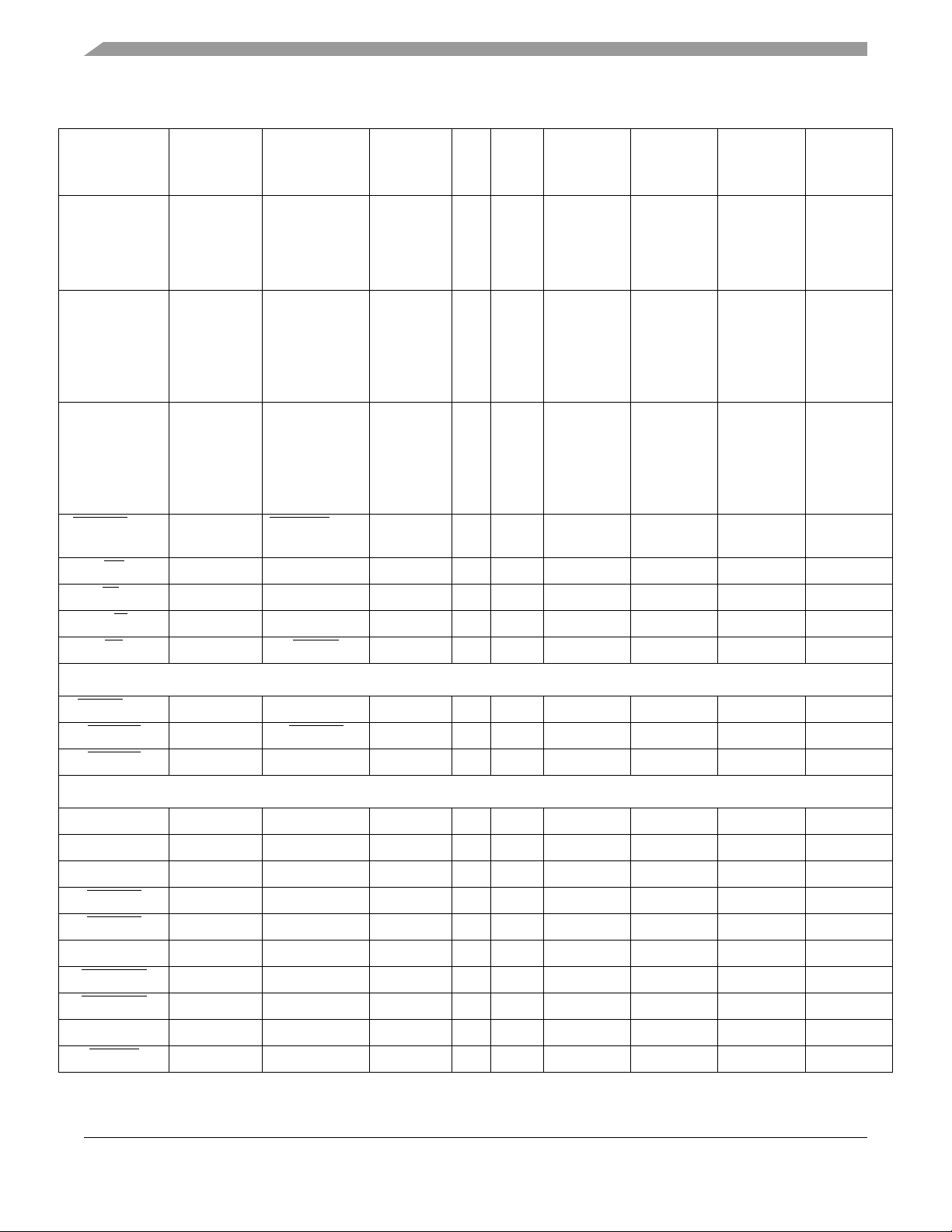
Table 3. MCF5207/8 Signal Information and Muxing (continued)
Signal Name GPIO Alternate 1 Alternate 2
A[9:0] — SD_A[9:0]
D[31:16] — SD_D[31:16]
D[15:0] — FB_D[31:16]
BE/BWE[3:0] PBE[3:0] SD_DQM[3:0]
OE
TA
R/W
2
PBUSCTL3 — — O
PBUSCTL2 — — I
PBUSCTL1 — — O
3
4
4
3
—O
— I/O
— I/O
— O
TS PBUSCTL0 DACK0 —O
1
Dir.
Voltage
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
MCF5207
144
LQFP
Domain
100–91 E11, D9,
MCF5207
144
MAPBGA
E12, F10,
F11, E9,
MCF5208
MCF5208
160
QFP
MAPBGA
108–99 E13, E14,
F11–F14,
G11–G14
F12, G10,
G12, F9
21–28,
40–47
F1, F2, G1,
G2, G4, G3,
H1, H2, K3,
L2, L3, K2,
27–34,
46–53
K4–K1, M3,
N3, M4, N4,
P4, L5, M5,
M3, J4, M4,
K4
8–15, 51–58 B2, B1, C2,
C1, D2, D1,
E2, E1, L5,
K5, L6, J6,
16–23,
57–64
G4–G1, H1,
N6, P6, L7,
M7, N7, P7,
M6, J7, L7,
K7
20, 48, 18, 50F4, L4, E3, J526, 54, 24, 56H2, P5, H4,
60 J8 66 M8
90 G11 98 H14
59 K6 65 L8
4 B3 12 E3
196
J4–J1,
N5
F3–F1,
N8, P8
M6
Chip Selects
FB_CS
[3:2] PCS[3:2] — — O
FB_CS1
FB_CS0
PCS1 SD_CS1 —O
———O
SDRAM Controller
SD_A10 — — — O
SD_CKE — — — O
SD_CLK — — — O
SD_CLK
SD_CS0
———O
———O
SD_DQS[3:2] — — — O
SD_SCAS
SD_SRAS
———O
———O
SD_SDR_DQS — — — O
SD_WE
———O
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
SDVDD
119, 120 D7, A9 — C11, A10
121 C8 127 B10
122 B8 128 C10
37 M1 43 N2
6C314E1
31 J1 37 L1
32 K1 38 M1
7 A1 15 F4
19, 49 F3, M5 25, 55 H3, L6
38 M2 44 P2
39 J2 45 P3
29 H3 35 L3
5D313E2
Freescale Semiconductor4
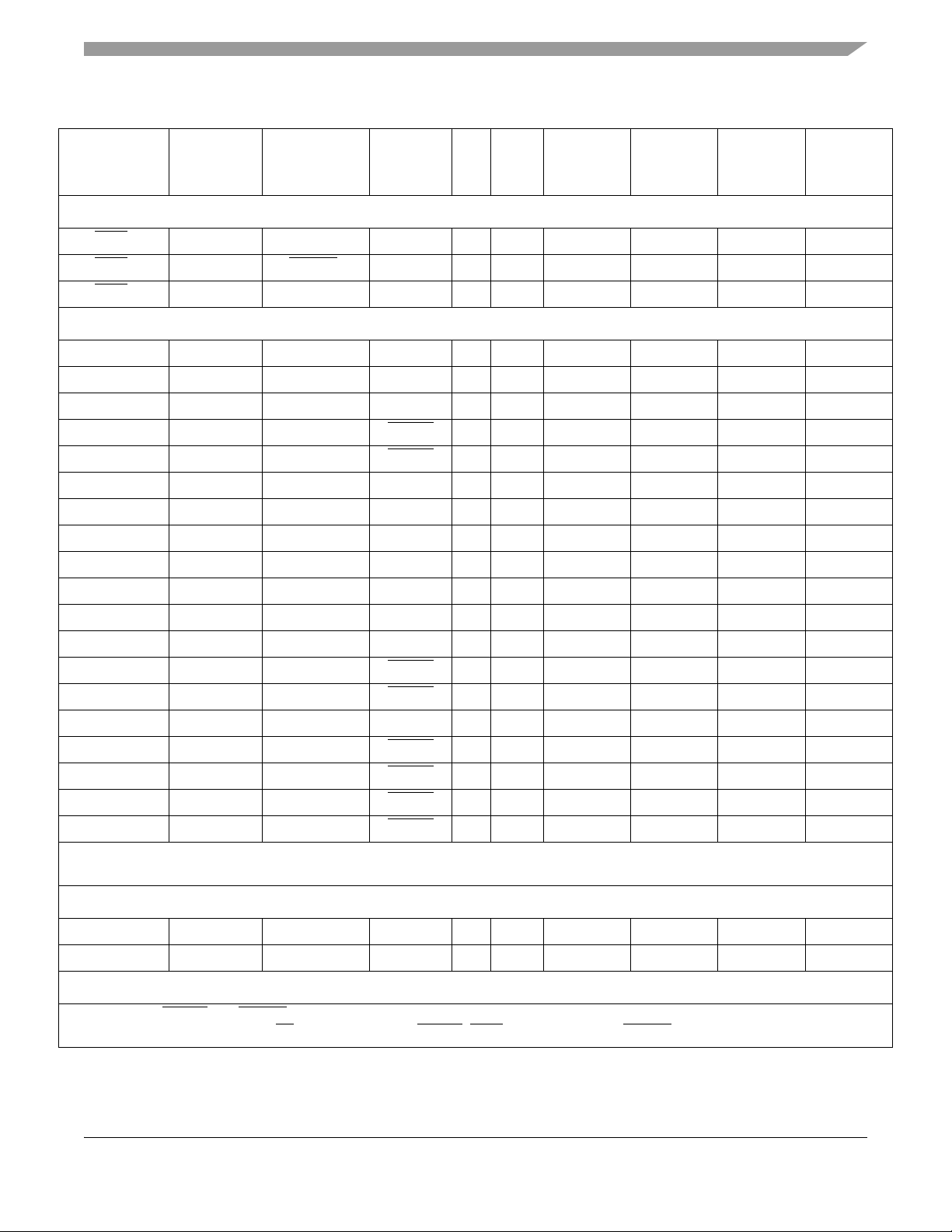
Table 3. MCF5207/8 Signal Information and Muxing (continued)
Signal Descriptions
Signal Name GPIO Alternate 1 Alternate 2
External Interrupts Port
IRQ7
IRQ4
IRQ1
2
2
2
PIRQ7
PIRQ4
PIRQ1
2
2
2
— — I
DREQ0
2
— I
— — I
Voltage
MCF5207
144
LQFP
Domain
5
134 A5 142 C7
133 C6 141 D7
132 B6 140 D8
1
Dir.
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
MCF5207
144
MAPBGA
MCF5208
160
QFP
MCF5208
196
MAPBGA
FEC
FEC_MDC PFECI2C3 I2C_SCL
FEC_MDIO PFECI2C2 I2C_SDA
2
U2TXD O
2
U2RXD I/O
FEC_TXCLK PFECH7 — — I
— PFECH6 — U1RTS O
FEC_TXEN PFECH6 — U1RTS O
FEC_TXD0 PFECH5 — — O
FEC_COL PFECH4 — — I
FEC_RXCLK PFECH3 — — I
FEC_RXDV PFECH2 — — I
FEC_RXD0 PFECH1 — — I
FEC_CRS PFECH0 — — I
FEC_TXD[3:1] PFECL[7:5] — — O
— PFECL4 — U0RTS O
FEC_TXER PFECL4 — U0RTS O
FEC_RXD[3:2] PFECL[3:2] — — I
— PFECL1 — U1CTS I
FEC_RXD1 PFECL1 — U1CTS I
— PFECL0 — U0CTS I
FEC_RXER PFECL0 — U0CTS I
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
— — 148 D6
— — 147 C6
— — 157 B3
142 A2 — —
— — 158 A2
— — 3 B1
— — 7 D3
— — 154 B4
— — 153 A4
— — 152 D5
— — 8 D2
— — 6–4 C1, C2, B2
141 D5 — —
— — 156 A3
— — 149–150 A5, B5
139 B4 — —
— — 151 C5
140 E4 — —
— — 155 C4
Note: The MCF5207 does not contain an FEC module. However, the UART0 and UART1 control signals (as well as their GPIO signals)
are available by setting the appropriate FEC GPIO port registers.
I2C
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
2
2
PFECI2C0
PFECI2C1
2
U2RXD
2
U2TXD
2
2
— I/O
— I/O
EVDD
EVDD
— — —D1
— — —E4
DMA
DACK0 and DREQ0 do not have a dedicated bond pads. Please refer to the following pins for muxing:
and QSPI_CS2 for DACK0, IRQ4 and QSPI_DIN for DREQ0.
TS
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Signal Descriptions
Table 3. MCF5207/8 Signal Information and Muxing (continued)
Signal Name GPIO Alternate 1 Alternate 2
Voltage
Domain
MCF5207
144
LQFP
1
Dir.
MCF5207
144
MAPBGA
MCF5208
160
QFP
MCF5208
196
MAPBGA
QSPI
QSPI_CS2 PQSPI3 DACK0 U2RTS O
QSPI_CLK PQSPI0 I2C_SCL
QSPI_DOUT PQSPI1 I2C_SDA
QSPI_DIN PQSPI2 DREQ0
2
2
2
— O
— O
U2CTS I
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
126 A8 132 D10
127 C7 133 A9
128 A7 134 B9
129 B7 135 C9
Note: The QSPI_CS1 and QSPI_CS0 signals are available on the U1CTS, U1RTS, U0CTS, or U0RTS pins for the 196 and 160-pin
packages.
UARTs
U1CTS PUARTL7 DT1IN QSPI_CS1 I
U1RTS PUARTL6 DT1OUT QSPI_CS1 O
U1TXD PUARTL5 — — O
U1RXD PUARTL4 — — I
U0CTS PUARTL3 DT0IN QSPI_CS0 I
U0RTS PUARTL2 DT0OUT QSPI_CS0 O
U0TXD PUARTL1 — — O
U0RXD PUARTL0 — — I
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
— — 136 D9
— — 137 C8
131 A6 139 A8
130 D6 138 B8
— —76N12
— —77P12
71 L10 79 P13
70 M10 78 N13
Note: The UART2 signals are multiplexed on the DMA Timers, QSPI, FEC, and I2C pins. For the MCF5207 devices, the UART0 and
UART1 control signals are multiplexed internally on the FEC signals.
DMA Timers
DT3IN PTIMER3 DT3OUT U2CTS I
DT2IN PTIMER2 DT2OUT U2RTS I
DT1IN PTIMER1 DT1OUT U2RXD I
DT0IN PTIMER0 DT0OUT U2TXD I
BDM/JTAG
JTAG_EN
DSCLK — TRST
PSTCLK — TCLK
7
— — — I
BKPT — TMS
DSI — TDI
2
2
2
2
— I
— O
— I
— I
DSO — TDO — O
DDATA[3:0] — — — O
PST[3:0] — — — O
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
6
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
EVDD
135 B5 143 B7
136 C5 144 A7
137 A4 145 A6
138 A3 146 B6
83 J1191J13
76 K11 84 L12
64 M7 70 P9
75 L12 83 M14
77 H9 85 K12
69 M9 75 M12
— K9, L9, M11,
M8
— L11, L8,
K10, K8
—P11, N11,
M11, P10
— N10, M10,
L10, L9
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor6
NOTES:
Table 3. MCF5207/8 Signal Information and Muxing (continued)
Signal Descriptions
Signal Name GPIO Alternate 1 Alternate 2
ALLPST — — — O
Voltage
Domain
MCF5207
144
LQFP
67 — 73 —
1
Dir.
EVDD
MCF5207
144
MAPBGA
MCF5208
160
QFP
MCF5208
MAPBGA
Test
7
TEST
— — — I
PLL_TEST — — — I
EVDD
EVDD
109 ——C12
— ——M13
Power Supplies
EVDD — — — — — 1, 33, 63, 66,
72, 81, 87,
125
E5–E6, F5,
G8–G9,
H7–H8
2, 9, 69, 72,
80, 89, 95,
131
E5–E7, F5,
F6, G5, H10,
J9, J10,
K8–K10,
K13, M9
IVDD — — — — — 30, 68, 84,
113, 143
D4, D8, H4,
H11, J9
36, 74, 92,
121, 159
J12, D4,
D11, H11,
L4, L11,
PLL_VDD — — — — — 86 H12 94 H13
SD_VDD — — — — — 3, 17, 35, 61,
89, 110, 123
E7–E8, F8,
G5, H5–H6,
J3
11, 39, 41,
67, 97, 118,
129
E8–E10, F9,
F10, G10,
H5, J5, J6,
K5–K7, L2
VSS — — — — — 2, 16, 36, 62,
65, 73, 88,
111, 124
D10, F6–F7,
G6–G7
1, 10, 42, 68,
71, 81, 96,
117, 119,
130
A1, A14,
F7–F8,
G6–G9,
H6–H9,
J7–J8, L13,
M2, N9, P1,
196
P14
PLL_VSS — — — — — 85 —93H12
1
Refers to pin’s primary function.
2
Pull-up enabled internally on this signal for this mode.
3
The SDRAM functions of these signals are not programmable by the user. They are dynamically switched by the processor when
accessing SDRAM memory space and are included here for completeness.
4
Primary functionality selected by asserting the DRAMSEL signal (SDR mode). Alternate functionality selected by negating the
DRAMSEL signal (DDR mode). The GPIO module is not responsible for assigning these pins.
5
GPIO functionality is determined by the edge port module. The GPIO module is only responsible for assigning the alternate functions.
6
If JTAG_EN is asserted, these pins default to Alternate 1 (JTAG) functionality. The GPIO module is not responsible for assigning
these pins.
7
Pull-down enabled internally on this signal for this mode.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Mechanicals and Pinouts
4 Mechanicals and Pinouts
Drawings in this section show the pinout and the packaging and mechanical characteristics of the
MCF5207 and MCF5208 devices.
NOTE
The mechanical drawings are the latest revisions at the time of publication
of this document. The most up-to-date mechanical drawings can be found at
the product summary page located at http://www.freescale.com/coldfire.
4.1 Pinout—144 LQFP
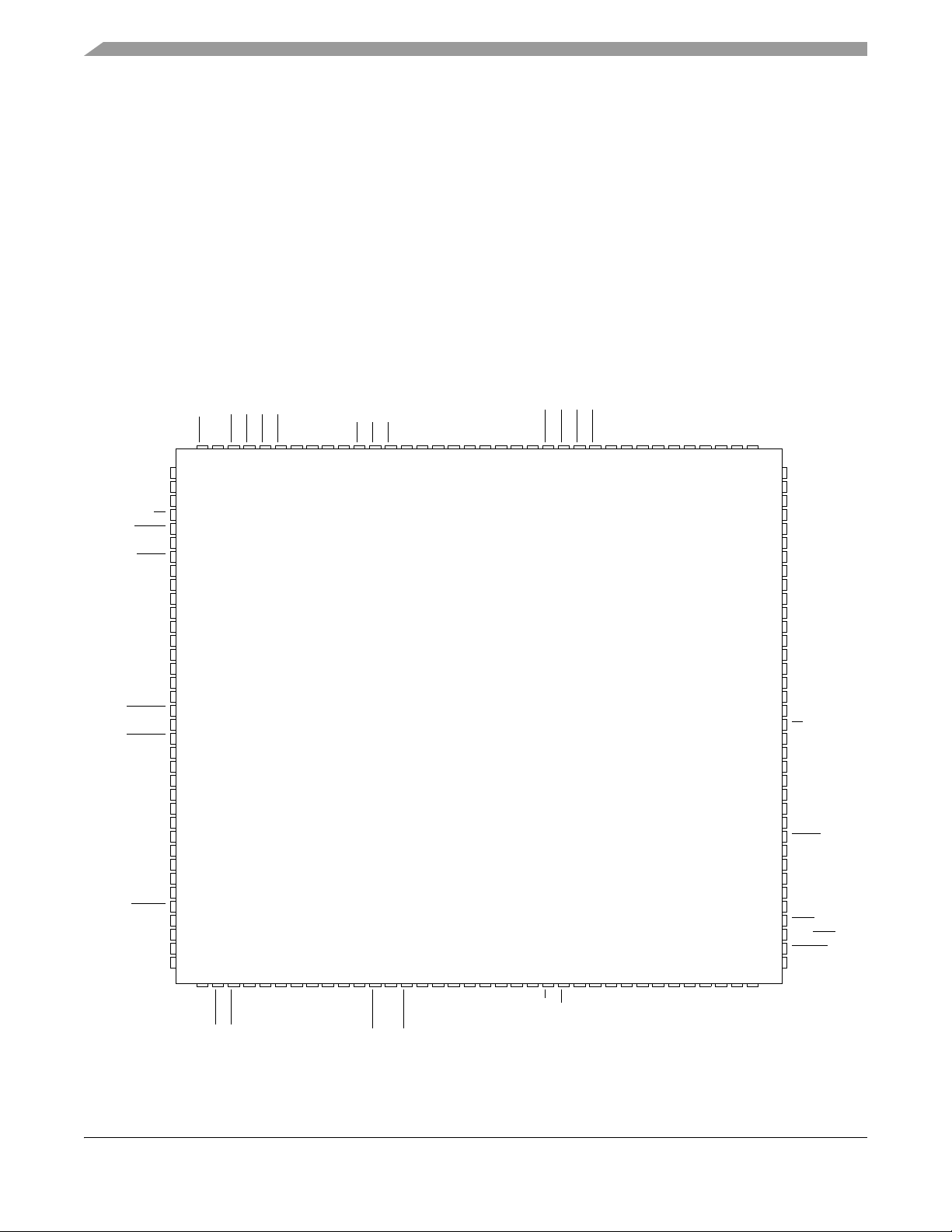
Figure 1 shows a pinout of the MCF5207CAG166 device.
RCON
IVDD
U1RTS
U0RTS
U0CTS
U1CTS
DT0IN
DT1IN
DT2IN
DT3IN
IRQ7
IRQ4
IRQ1
U1TXD
U1RXD
QSPI_DIN
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_CS2
EVDD
VSS
SD_VDD
FB_CS0
FB_CS1
FB_CS2
FB_CS3
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
IVDD
A18
VSS
SD_VDD
TEST
•
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
TDO/DSO
U0TXD
U0RXD
109
72
EVDD
EVDD 1 108 A17
EVSS 2 107 A16
SD_VDD 3 106 A15
TS
SD_WE
SD_CKE 6 103 A12
SD_VDD
BE/BWE1
SD_DQS3
BE/BWE3
SD_SDR_DQS 29 80 XTAL
SD_CLK 31 78 EXTAL
SD_CLK
SD_VDD 33 76 TRST
FB_CLK 34 75 TMS/BKPT
SD_VDD 35 74 RSTOUT
4 105 A14
5 104 A13
SD_CS
7 102 A11
D15 8 101 A10
D14 9 100 A9
D13 10 99 A8
D12 11 98 A7
D11 12 97 A6
D10
13 96 A5
D9
14 95 A4
D8
15 94 A3
EVSS
16 93 A2
17 92 A1
18 91 A0
19 90 TA
20 89 SD_VDD
D31 21 88 VSS
D30 22 87 EVDD
D29 23 86 PLL_VDD
D28 24 85 PLL_VSS
D27 25 84 IVDD
D26 26 83 JTAG_EN
D25 27 82 RESET
D24 28 81 EVDD
IVDD 30 79 DRAMSEL
32 77 TDI/DSI
VSS 36 73 VSS
3738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071
SD_A10
SD_CAS
D23
SD_RAS
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
D17
D16
BE/BWE2
SD_DQS2
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
BE/BWE0
D0
OE
R/W
VSS
SD_VDD
EVDD
VSS
TCLK/PSTCLK
EVDD
IVDD
ALL_PST
Figure 1. MCF5207CAG166 Pinout Top View (144 LQFP)
/DSCLK
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor8
4.2 Package Dimensions—144 LQFP
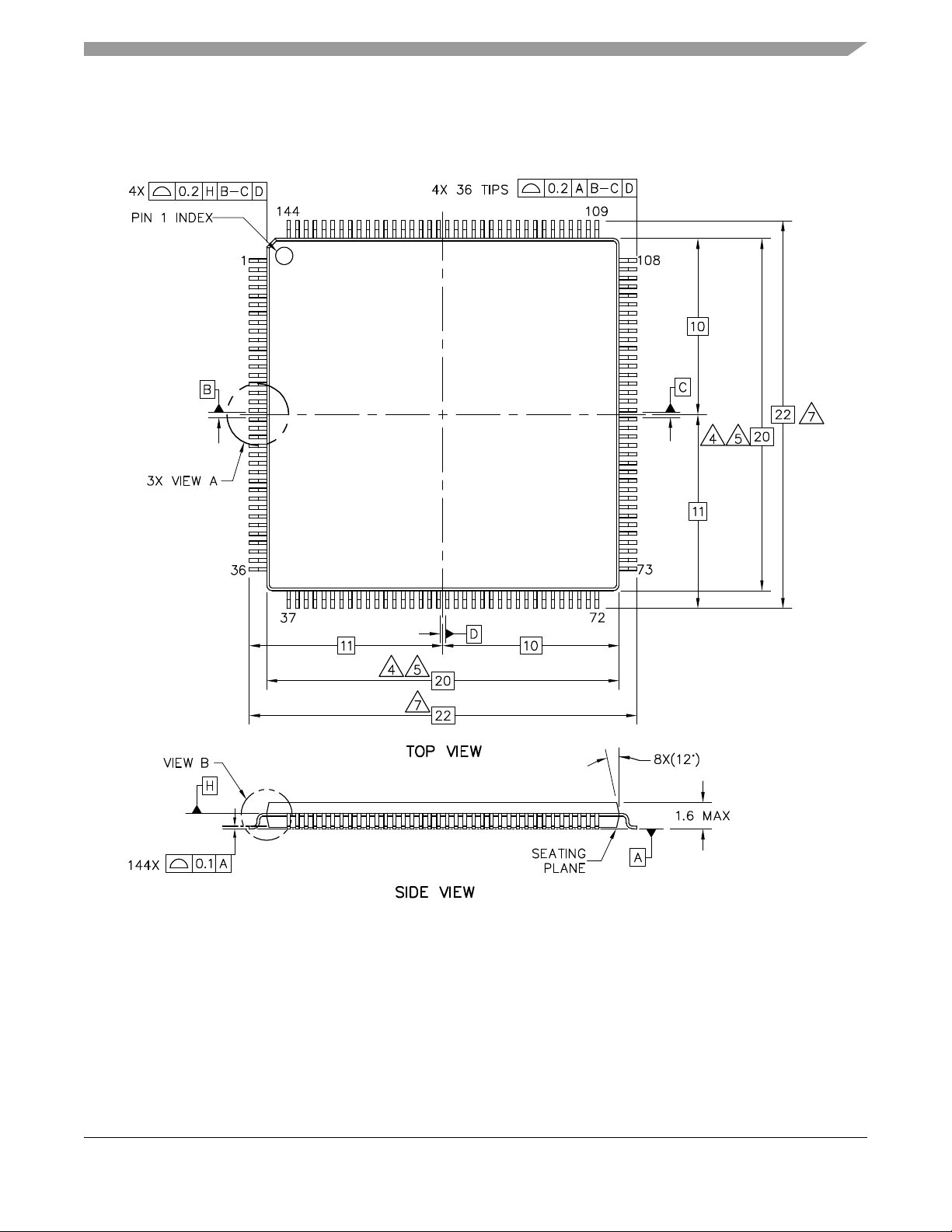
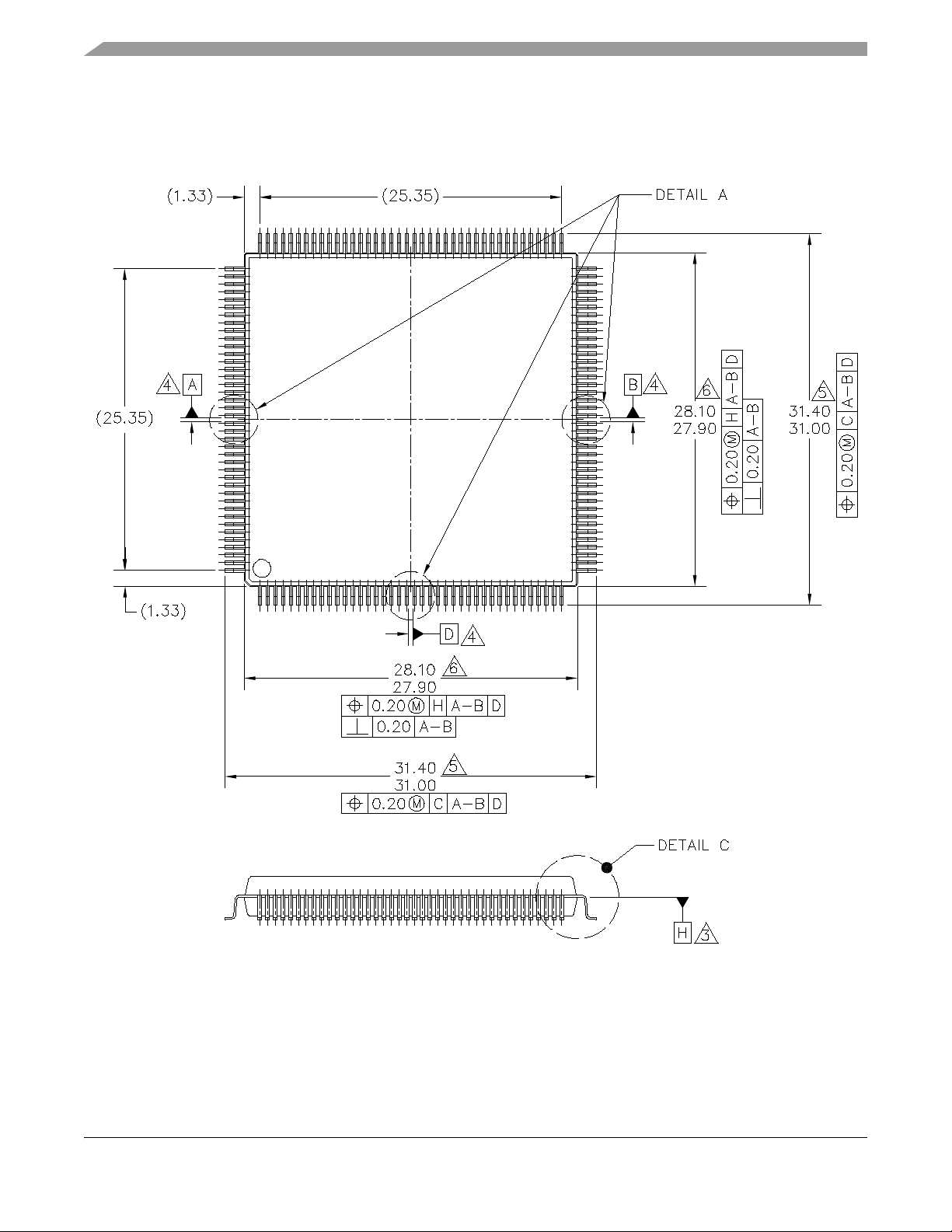
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show MCF5207CAB166 package dimensions.
Mechanicals and Pinouts
Figure 2. MCF5207CAB166 Package Dimensions (Sheet 1 of 2)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 9
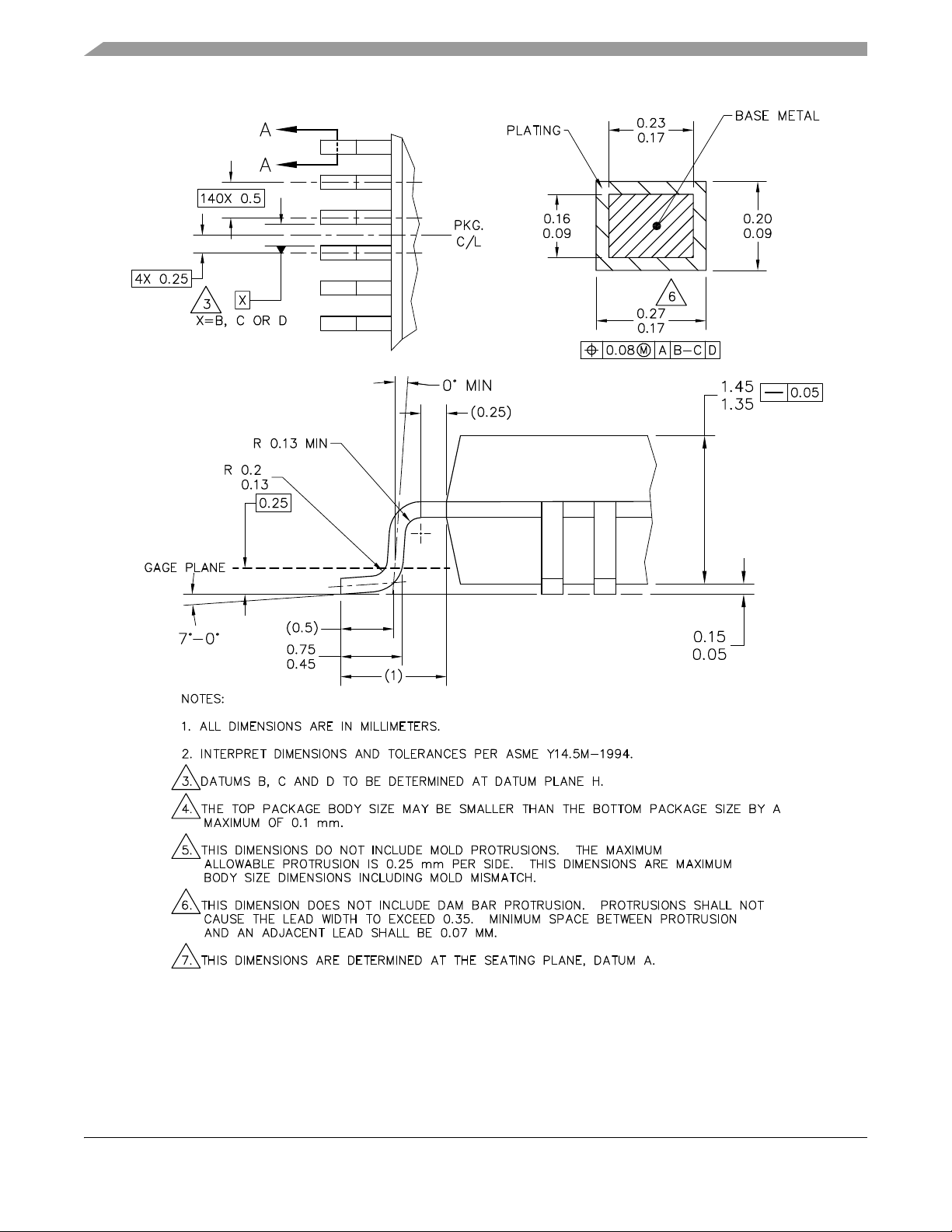
Mechanicals and Pinouts
View A
Section A-A
Rotated 90× CW
144 Places
View B
Figure 3. MCF5207CAB166 Package Dimensions (Sheet 2 of 2)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor10
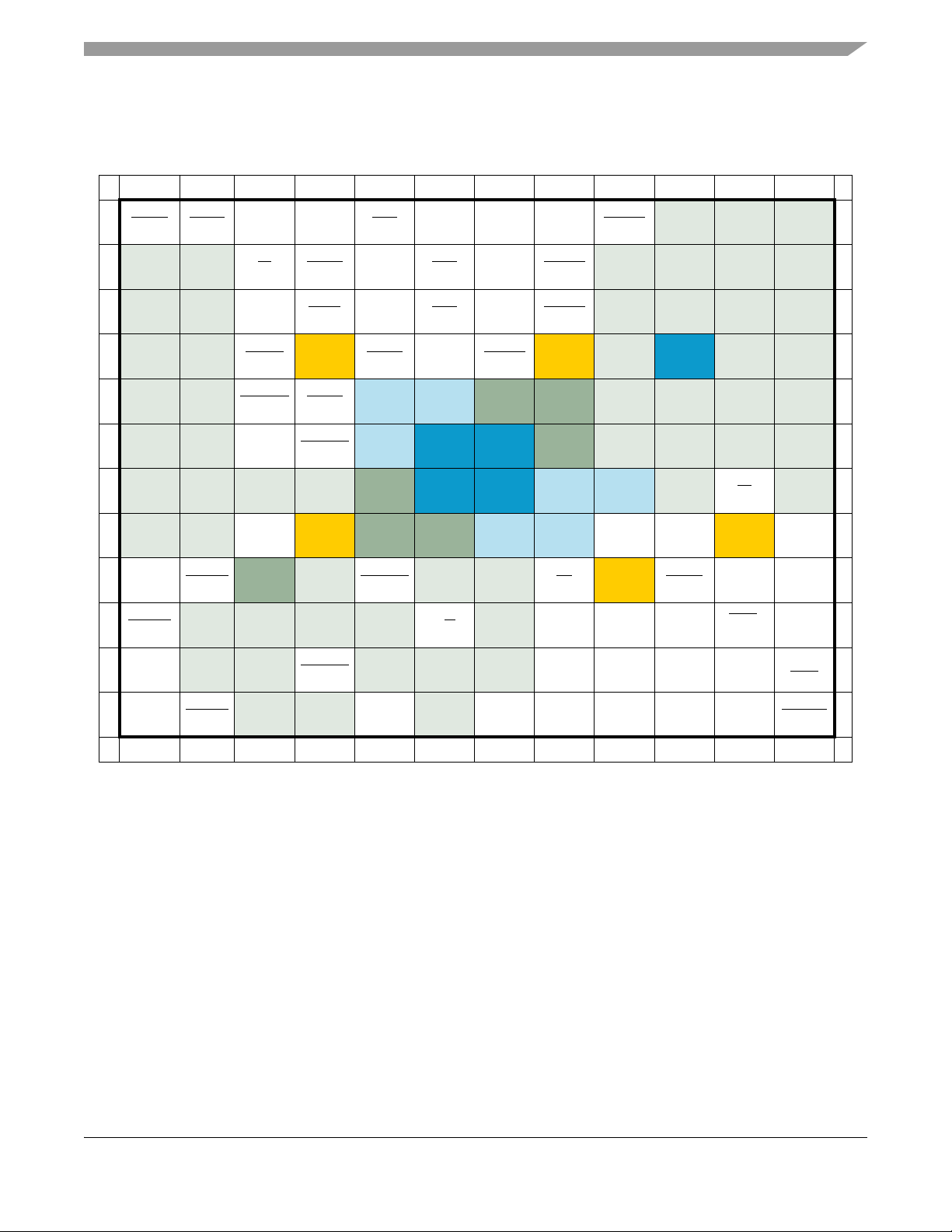
4.3 Pinout—144 MAPBGA
The pinout of the MCF5207CVM166 device is shown below.
123456789101112
Mechanicals and Pinouts
ASD_CS
B
D14 D15 TS U1CTS DT3IN IRQ1 QSPI_DIN FB_CS0 A23 A19 A16 A15 B
C
D12 D13 SD_CKE RCON DT2IN IRQ4
D
D10 D11 SD_WE IVDD U0RTS U1RXD FB_CS3 IVDD A8 VSS A13 A11 D
E
F
D31 D30 SD_DQS3 BE/BWE3 EVDD VSS VSS SD_VDD A0 A6 A5 A3 F
G
D29 D28 D26 D27 SD_VDD VSS VSS EVDD EVDD A2 TA A1 G
H
D25 D24
J SD_CLK SD_RAS
K SD_CLK
LFB_CLK
U1RTS DT0IN DT1IN IRQ7 U1TXD
D8 D9 BE/BWE1 U0CTS EVDD EVDD SD_VDD SD_VDD A4 A12 A9 A7 E
SD_SDR_
DQS
SD_VDD D18 BE/BWE0 D4 D2 OE IVDD RESET JTAG_EN XTAL J
D20 D23 D16 D6 R/W D0 PST0 DDATA3 PST1
D22 D21 BE/BWE2 D7 D5 D1 PST2 DDATA2 U0TXD PST3
IVDD SD_VDD SD_VDD EVDD EVDD TDI/DSI
QSPI_
DOUT
QSPI_
QSPI_CS2 FB_CS2
CLK
FB_CS1
A22 A20 A18 A
A21 A10 A17 A14 C
DRAM
SEL
IVDD PLL_VDD H
TRST
/
DSCLK
EXTAL K
TMS/
BKPT
L
M SD_A10 SD_CAS
123456789101112
D19 D17 SD_DQS2 D3
TCLK/
PSTCLK
DDATA0 TDO/DSO U0RXD DDATA1 RSTOUT M
Figure 4. MCF5207CVM166 Pinout Top View (144 MAPBGA)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 11
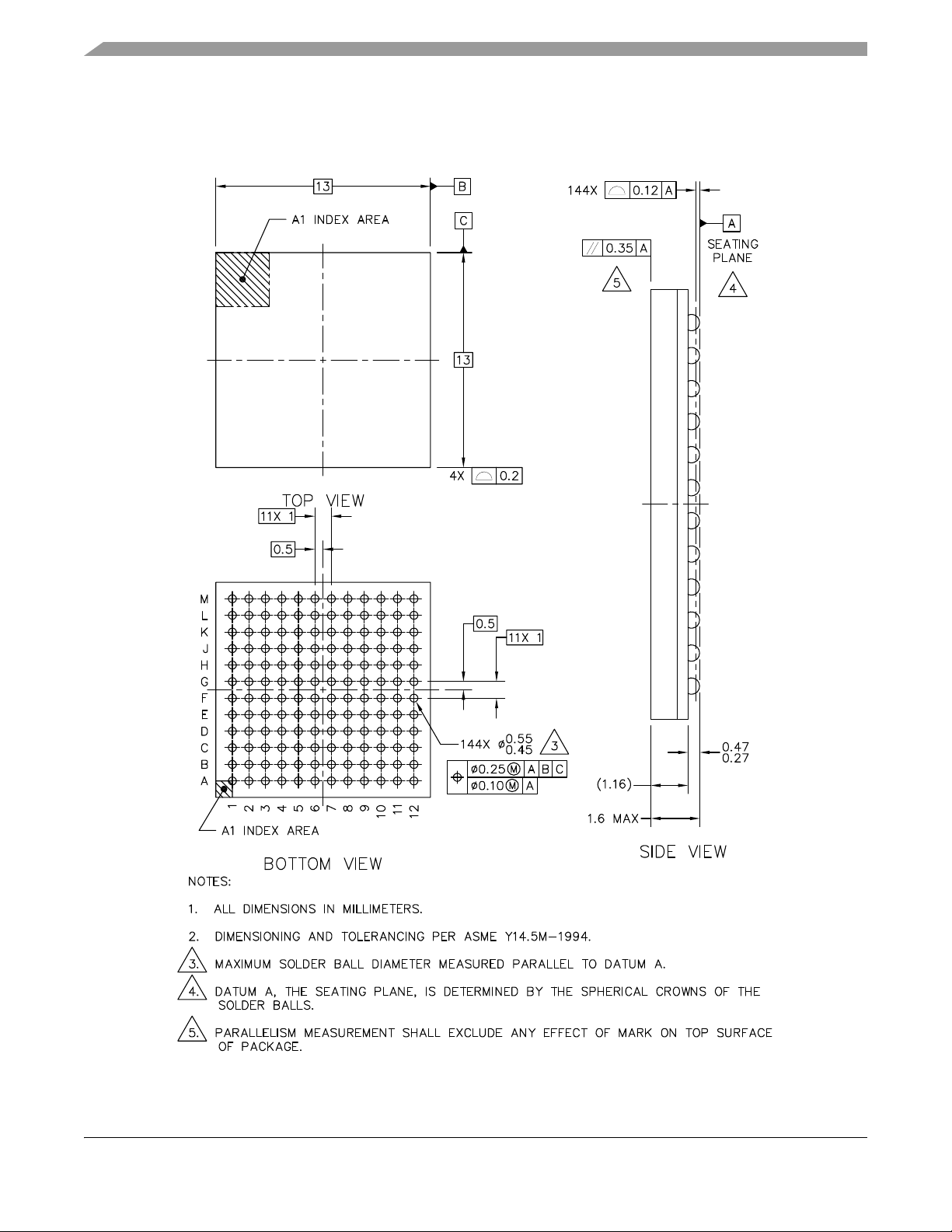
Mechanicals and Pinouts
4.4 Package Dimensions—144 MAPBGA
Figure 5 shows the MCF5207CAB166 package dimensions.
Figure 5. MCF5207CAB166 Package Dimensions (144 MAPBGA)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor12
Mechanicals and Pinouts
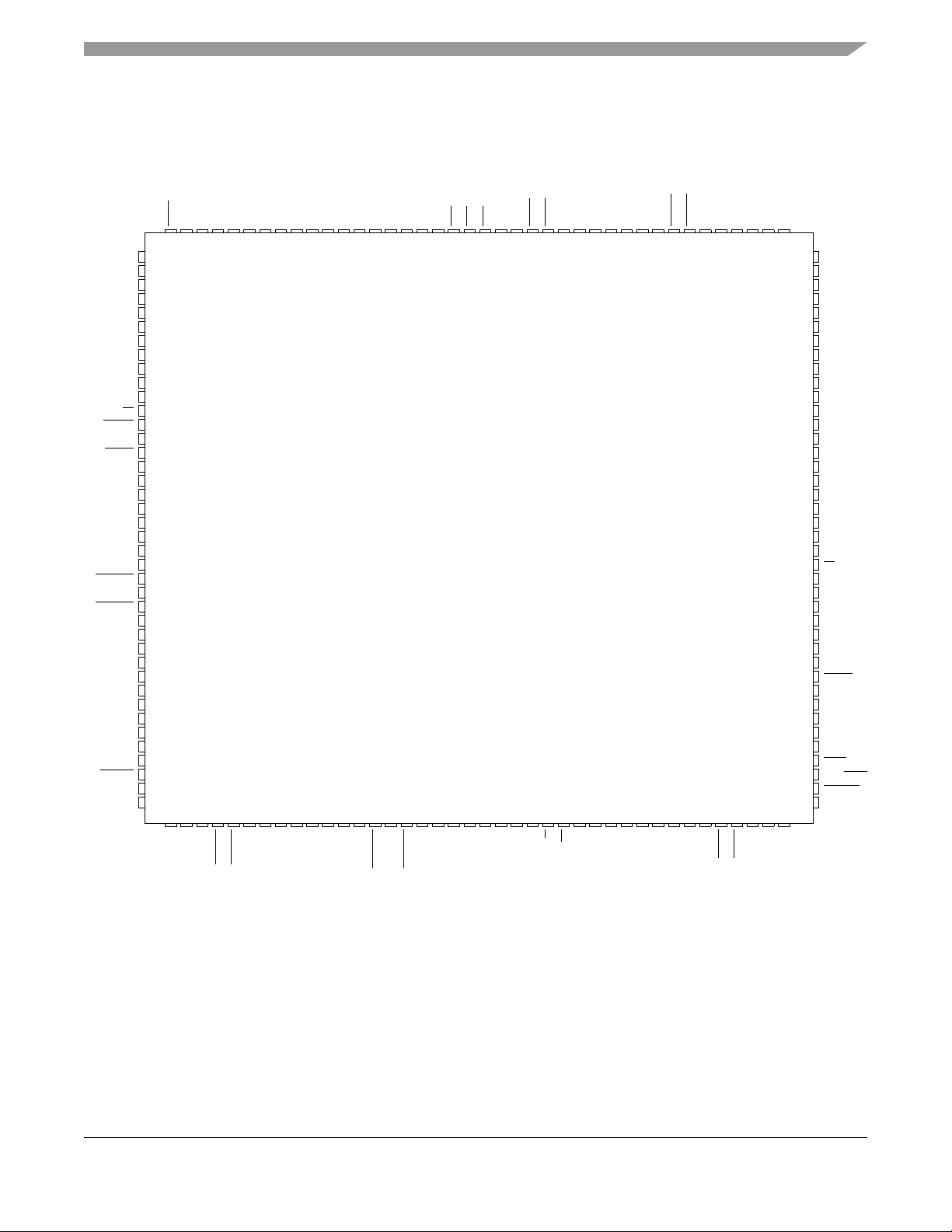
4.5 Pinout—160 QFP
Figure 6 shows a pinout of the MCF5208CAB166 device.
RCON
IVDD
FEC_TXEN
FEC_TXCLK
FEC_TXER
FEC_RXER
FEC_RXCLK
FEC_RXDV
FEC_RXD0
FEC_RXD1
FEC_RXD2
FEC_RXD3
FEC_MDC
FEC_MDIO
DT0IN
DT1IN
DT2IN
DT3IN
IRQ7
IRQ4
IRQ1
U1TXD
U1RXD
U1RTS
U1CTS
QSPI_DIN
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_CS2
EVDD
VSS
SD_VDD
FB_CS0
FB_CS1
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
IVDD
•
160
159
158
157
156
155
154
153
152
151
150
149
148
147
146
145
144
143
142
141
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
133
132
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
U0RTS
U0RXD
121
80
EVDD
U0TXD
VSS 1 120 A18
EVDD 2 119 VSS
FEC_TXD0 3 118 SD_VDD
FEC_TXD1 4 117 VSS
FEC_TXD2 5 116 A17
FEC_TXD3 6 115 A16
FEC_COL 7 114 A15
FEC_CRS 8 113 A14
EVDD 9 112 A13
VSS 10 111 A12
SD_VDD 11 110 A11
TS
SD_WE
SD_CKE
BE/BWE1
SD_DQS3
BE/BWE3
SD_SDR_DQS
SD_CLK
SD_CLK
SD_VDD
FB_CLK
12 109 A10
13 108 A9
14 107 A8
SD_CS
15 106 A7
D15
16 105 A6
D14
17 104 A5
D13
18 103 A4
D12
19 102 A3
D11
20 101 A2
D10
21 100 A1
D9
22 99 A0
D8
23 98 TA
24 97 SD_VDD
25 96 VSS
26 95 EVDD
D31
27 94 PLL_VDD
D30
28 93 PLL_VSS
D29
29 92 IVDD
D28
30 91 JTAG_EN
D27
31 90 RESET
D26
32 89 EVDD
D25
33 88 XTAL
D24
34 87 DRAMSEL
35 86 EXTAL
IVDD
36 85 TDI/DSI
37 84 TRST
38 83 TMS/BKPT
39 82 RSTOUT
40 81 VSS
414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879
VSS
SD_VDD
SD_A10
SD_CAS
D23
SD_RAS
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
D17
D16
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
BE/BWE0
BE/BWE2
SD_DQS2
D0
OE
R/W
VSS
SD_VDD
EVDD
TCLK/PSTCLK
VSS
EVDD
ALL_PST
IVDD
U0CTS
TDO/DSO
Figure 6. MCF5208CAB166 Pinout Top View (160 QFP)
/DSCLK
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 13
Mechanicals and Pinouts
Top Vi ew
4.6 Package Dimensions—160 QFP
The package dimensions of the MCF5208CAB166 device are shown in the figures below.
Figure 7. MCF5208CAB166 Package Dimensions (Sheet 1 of 2)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor14

Mechanicals and Pinouts
DETAIL A
SECTION B-B
Figure 8. MCF5208CAB166 Package Dimensions (Sheet 2 of 2)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 15

Mechanicals and Pinouts
4.7 Pinout—196 MAPBGA
Figure 9 shows a pinout of the MCF5208CVM166 device.
1234567891011121314
A
VSS
FEC_
B
TXD0
FEC_
C
TXD3
D I2C_SDA
E SD_CKE SD_WE
F
D13 D14 D15 SD_CS EVDD EVDD VSS VSS SD_VDD SD_VDD A7 A6 A5 A4 F
G
D9 D10 D11 D12 EVDD VSS VSS VSS VSS SD_VDD A3 A2 A1 A0 G
H
D8
J
D28 D29 D30 D31 SD_VDD SD_VDD VSS VSS EVDD EVDD NC IVDD
K
D24 D25 D26 D27 SD_VDD SD_VDD SD_VDD EVDD EVDD EVDD
L SD_CLK
FEC_
TXEN
FEC_
TXD1
FEC_
TXD2
FEC_
CRS
BE/
BWE3
SD_VDD
FEC_
TXER
FEC_
TXCLK
RCON
FEC_
COL
TS I2C_SCL EVDD EVDD EVDD SD_VDD SD_VDD SD_VDD A11 A10 A9 A8 E
SD_
DQS3
SD_SDR
_DQS
FEC_
RXDV
FEC_
RXCLK
FEC_
RXER
IVDD
BE/
BWE1
IVDD D18
FEC_
RXD3
FEC_
RXD2
FEC_
RXD1
FEC_
RXD0
SD_VDD VSS VSS VSS VSS EVDD IVDD
DT1IN DT2IN U1TXD
DT0IN DT3IN U1RXD
FEC_
MDIO
FEC_
MDC
SD_
DQS2
IRQ7
IRQ4 IRQ1 U1CTS
U1RTS
D5 R/W PST0 PST1 IVDD
QSPI_
CLK
QSPI_
DOUT
QSPI_
DIN
FB_CS2
FB_CS1
FB_CS0
QSPI_
CS2
A22 A20 A19 VSS A
A23 A21 A18 A17 B
FB_CS3 TEST A16 A15 C
IVDD A14 A13 A12 D
DRAM
SEL
PLL_
VSS
TDI/
DSI
TRST
DSCLK
PLL_
VDD
JTAG_
EN
EVDD XTAL K
/
VSS EXTAL L
TA
RESET J
H
M SD_CLK
NFB_CLKSD_A10
P
VSS SD_CAS SD_RAS D19
VSS D23 D21 D17
D22 D20 D16 D7 D3 D1 VSS PST3 DDATA2 U0CTS U0RXD RSTOUT N
BE/
BWE2
1234567891011121314
BE/
BWE0
D6 D2 D0
D4 OE EVDD PST2 DDATA1
TCLK/
PSTCLK
DDATA0 DDATA3 U0RTS U0TXD VSS P
TDO/
DSO
PLL_
TEST
Figure 9. MCF5208CVM166 Pinout Top View (196 MAPBGA)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor16
TMS/
BKPT
M

4.8 Package Dimensions—196 MAPBGA
Top V i e w
Bottom View
The package dimensions for the MCF5208CVM166 device is shown below.
Electrical Characteristics
Figure 10. MCF5208CVM166 Package Dimensions (196 MAPBGA)
5 Electrical Characteristics
The following electrical specifications are preliminary and are from previous designs or design
simulations. These specifications may not be fully tested or guaranteed at this early stage of the product
life cycle; however, for production silicon, these specifications are met. Finalized specifications will be
published after complete characterization and device qualifications have been completed.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 17

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
5.1 Maximum Ratings
Table 4. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
1, 2
Core Supply Voltage IV
CMOS Pad Supply Voltage EV
DDR/Memory Pad Supply Voltage SDV
PLL Supply Voltage PLLV
Digital Input Voltage
Instantaneous Maximum Current
Single pin limit (applies to all pins)
3
3, 4, 5
V
I
Operating Temperature Range (Packaged) T
DD
DD
DD
DD
IN
D
A
– 0.5 to +2.0 V
– 0.3 to +4.0 V
– 0.3 to +4.0 V
– 0.3 to +2.0 V
– 0.3 to +3.6 V
25 mA
– 40 to 85 °C
(TL - TH)
Storage Temperature Range T
1
Functional operating conditions are given in Section 5.4, “DC Electrical Specifications”.
stg
– 55 to 150 °C
Absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only, and functional operation at the maxima is
not guaranteed. Continued operation at these levels may affect device reliability or cause
permanent damage to the device.
2
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage due to high static voltage or
electrical fields; however, it is advised that normal precautions be taken to avoid application of
any voltages higher than maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance circuit. Reliability of
operation is enhanced if unused inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (V
EVDD).
3
Input must be current limited to the value specified. To determine the value of the required
current-limiting resistor, calculate resistance values for positive and negative clamp voltages,
then use the larger of the two values.
4
All functional non-supply pins are internally clamped to VSS and EVDD.
5
Power supply must maintain regulation within operating EVDD range during instantaneous
and operating maximum current conditions. If positive injection current (Vin > EVDD) is greater
than I
, the injection current may flow out of EVDD and could result in external power supply
DD
going out of regulation. Ensure external EVDD load shunts current greater than maximum
injection current. This is the greatest risk when the MCU is not consuming power (ex; no
clock). Power supply must maintain regulation within operating EV
range during
DD
instantaneous and operating maximum current conditions.
SS
or
5.2 Thermal Characteristics
Table 5 lists thermal resistance values
Table 5. Thermal Characteristics
Characteristic Symbol 196MBGA 144MBGA 160QFP 144LQFP Unit
Junction to ambient, natural convection Four layer board
(2s2p)
Junction to ambient (@200 ft/min) Four layer board
(2s2p)
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
θ
θ
JMA
JMA
47
43
1,2
1,2
47
43
1,2
1,2
Freescale Semiconductor18
49
44
1,2
1,2
65
58
1,2
1,2
°C / W
°C / W

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
Table 5. Thermal Characteristics (continued)
Characteristic Symbol 196MBGA 144MBGA 160QFP 144LQFP Unit
3
Junction to board θ
Junction to case θ
Junction to top of package Ψ
Maximum operating junction temperature T
1
θ
and Ψjt parameters are simulated in conformance with EIA/JESD Standard 51-2 for natural convection. Freescale
JMA
recommends the use of θ
and power dissipation specifications in the system design to prevent device junction temperatures
JmA
JB
JC
jt
j
36
4
22
1,5
6
105 105 105 105
from exceeding the rated specification. System designers should be aware that device junction temperatures can be significantly
influenced by board layout and surrounding devices. Conformance to the device junction temperature specification can be
verified by physical measurement in the customer’s system using the Ψ
parameter, the device power dissipation, and the
jt
method described in EIA/JESD Standard 51-2.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-6 with the board horizontal.
3
Thermal resistance between the die and the printed circuit board in conformance with JEDEC JESD51-8. Board temperature is
measured on the top surface of the board near the package.
4
Thermal resistance between the die and the case top surface as measured by the cold plate method (MIL SPEC-883 Method
1012.1).
5
Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the junction temperature
per JEDEC JESD51-2. When Greek letters are not available, the thermal characterization parameter is written in conformance
with Psi-JT.
6
Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the junction temperature
per JEDEC JESD51-2. When Greek letters are not available, the thermal characterization parameter is written in conformance
with Psi-JT.
7
Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the junction temperature
per JEDEC JESD51-2. When Greek letters are not available, the thermal characterization parameter is written in conformance
with Psi-JT.
36
22
6
1,5
3
4
12
40
39
1,6
3
4
50
19
5
3
4
1,7
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
o
C
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 19

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
TJTAP
DΘJMA
×()+=
P
D
K
T
J
273° C+()
-------------------------------- -
=
KPDTA273° C×()Q
JMAPD
2
×+×=
The average chip-junction temperature (TJ) in °C can be obtained from:
Where:
Eqn. 1
T
A
Q
JMA
P
D
P
INT
P
I/O
For most applications P
P
is neglected) is:
I/O
= Ambient Temperature, °C
= Package Thermal Resistance, Jun ction-to-Ambient, ×C/W
=P
INT
+ P
I/O
=IDD × IVDD, Watts - Chip Internal Power
= Power Dissipation on Input and Output Pins — User Determined
I/O
< P
and can be ignored. An approximate relationship between PD and TJ (if
INT
Eqn. 2
Solving equations 1 and 2 for K gives:
Eqn. 3
where K is a constant pertaining to the particular part. K can be determined from Equation 3 by measuring
PD (at equilibrium) for a known TA. Using this value of K, the values of PD and TJ can be obtained by
solving Equation 1 and Equation 2 iteratively for any value of TA.
5.3 ESD Protection
Table 6. ESD Protection Characteristics1,
2
Characteristics Symbol Value Unit
ESD Target for Human Body Model HBM 2000 V
1
All ESD testing is in conformity with CDF-AEC-Q100 Stress Test Qualification for
Automotive Grade Integrated Circuits.
2
A device is defined as a failure if, after exposure to ESD pulses, the device no longer
meets the device specification requirements. Complete DC parametric and functional
testing is performed per applicable device specification at room temperature followed by
hot temperature, unless specified otherwise in the device specification.
5.4 DC Electrical Specifications
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Core Supply Voltage IV
PLL Supply Voltage PLLV
CMOS Pad Supply Voltage EV
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Table 7. DC Electrical Specifications
DD
DD
DD
1.4 1.6 V
1.4 1.6 V
3.0 3.6 V
Freescale Semiconductor20

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
Table 7. DC Electrical Specifications (continued)
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
SDRAM and FlexBus Supply Voltage
SDV
Mobile DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 1.8V)
DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 2.5V)
SDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 3.3V)
CMOS Input High Voltage EV
CMOS Input Low Voltage EV
CMOS Output High Voltage
I
= –5.0 mA
OH
CMOS Output Low Voltage
I
= 5.0 mA
OL
SDRAM and FlexBus Input High Voltage
EV
EV
SDV
Mobile DDR/Bus Input High Voltage (nominal 1.8V)
DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 2.5V)
SDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 3.3V)
SDRAM and FlexBus Input Low Voltage
SDV
Mobile DDR/Bus Input High Voltage (nominal 1.8V)
DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 2.5V)
SDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 3.3V)
SDRAM and FlexBus Output High Voltage
SDV
Mobile DDR/Bus Input High Voltage (nominal 1.8V)
DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 2.5V)
SDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 3.3V)
= –5.0 mA for all modes
I
OH
SDRAM and FlexBus Output Low Voltage
SDV
Mobile DDR/Bus Input High Voltage (nominal 1.8V)
DDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 2.5V)
SDR/Bus Pad Supply Voltage (nominal 3.3V)
I
= 5.0 mA for all modes
OL
Input Leakage Current
= IVDD or VSS, Input-only pins
V
in
Weak Internal Pull Up Device Current, tested at VIL Max.
Input Capacitance
2
1
I
APU
C
All input-only pins
All input/output (three-state) pins
DD
IH
IL
OH
OL
IH
IL
OH
OL
I
in
1.70
2.25
3.0
2EV
1.95
2.75
3.6
+0.3 V
DD
VSS - 0.3 0.8 V
EV
- 0.4 — V
DD
—0.4V
1.35
1.7
2
VSS - 0.3
VSS - 0.3
VSS - 0.3
SDVDD-0.35
2.1
2.4
—
—
—
SDVDD+0.3
SDVDD+0.3
SDVDD+0.3
0.45
0.8
0.8
—
—
—
0.3
0.3
0.5
–1.0 1.0 μA
V
V
V
V
V
-10 - 130 μA
in
—
—
7
7
pF
1
Refer to the signals section for pins having weak internal pull-up devices.
2
This parameter is characterized before qualification rather than 100% tested.
5.4.1 PLL Power Filtering
To further enhance noise isolation, an external filter is strongly recommended for PLL analog VDD pins.
The filter shown in Figure 11 should be connected between the board VDD and the PLLVDD pins. The
resistor and capacitors should be placed as close to the dedicated PLLVDD pin as possible.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 21

Electrical Characteristics
Board V
DD
10 Ω
0.1 µF
PLL V
DD
Pin
10 µF
GND
Figure 11. System PLL V
Power Filter
DD
5.4.2 Supply Voltage Sequencing and Separation Cautions
The relationship between SDVDD and EVDD is non-critical during power-up and power-down sequences.
SDV
5.4.2.1 Power Up Sequence
If EVDD/SDVDD are powered up with IVDD at 0 V, the sense circuits in the I/O pads cause all pad output
drivers connected to the EVDD/SDVDD to be in a high impedance state. There is no limit on how long after
EVDD/SDVDD powers up before IVDD must power up. IVDD should not lead the EVDD, SDVDD, or
PLLVDD by more than 0.4 V during power ramp-up or there will be high current in the internal ESD
protection diodes. The rise times on the power supplies should be slower than 500 us to avoid turning on
the internal ESD protection clamp diodes.
5.4.2.2 Power Down Sequence
If IVDD/PLLVDD are powered down first, sense circuits in the I/O pads cause all output drivers to be in a
high impedance state. There is no limit on how long after IVDD and PLLVDD power down before EVDD
or SDVDD must power down. IVDD should not lag EVDD, SDVDD, or PLLVDD going low by more than
0.4 V during power down or there is an undesired high current in the ESD protection diodes. There are no
requirements for the fall times of the power supplies.
(2.5V or 3.3V) and EVDD are specified relative to IVDD.
DD
The recommended power down sequence is:
1. Drop IV
/PLLVDD to 0 V.
DD
2. Drop EVDD/SDVDD supplies.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor22

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
5.5 Current Consumption
All of the below current consumption data is lab data measured on a single device using an evaluation
board. Table 8 shows the typical current consumption in low-power modes at various f
Current measurements are taken after executing a STOP instruction.
Table 8. Current Consumption in Low-Power Mode
1,2
frequencies.
sys/2
Mode
Stop Mode 3
(Stop 11)
Stop Mode 2
(Stop 10)
Stop Mode 1
(Stop 01)
Stop Mode 0
(Stop 00)
Wait/Doze
5
5
5
5
3
Voltag e
(V)
3.3 1.33
2.5 15.19
1.5 0.519
3.3 1.93
2.5 15.19
1.5 1.25
3.3 1.83
2.5 15.23
1.5 8.24 10.22 9.55 10.61 12.1 12.1
3.3 2.23 2.33 2.41 2.5 2.61 2.61
2.5 16.2 16.47 16.62 16.91 17.24 17.24
1.5 8.32 10.32 9.66 10.73 12.25 12.25
3.3 2.23 2.33 2.41 2..5 2.6 4.07
2.5 16.2 16.48 16.62 16.91 17.24 18.77
1.5 11.53 14.36 14.29 15.92 18.21 35.45
44 MHz 56 MHz 64 MHz 72 MHz 83.33 MHz 83.33 MHz
Typ i cal
(mA)
Peak
4
(mA)
3.3 6.79 9.02 14.56 19.54 29.12 30.43
Run
1
All values are measured with a 3.30V EVDD, 2.50V SDVDD, and 1.5V IVDD power supplies. Tests performed at
room temperature with pins configured for high drive strength.
2
Refer to the Power Management chapter in the MCF5208 Reference Manual for more information on low-power
modes.
3
All peripheral clocks except UART0, FlexBus, INTC, reset controller, PLL, and Edge Port off before entering
low-power mode. All code executed from flash.
4
Peak current measured while running a while(1) loop with all modules active.
5
See the description of the low-power control register (LCPR) in the MCF5208 Reference Manual for more
information on stop modes 0–3.
Freescale Semiconductor 23
2.5 16.17 16.48 16.64 16.89 17.23 18.76
1.5 16.29 20.36 21.13 23.57 27.0 44.1
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1

Electrical Characteristics
0
50
100
150
200
250
44 48 56 64 72 83.33 83.33(peak)
fsys/2 (MHz)
Power Consumption (mW)
Stop 0 - Flash
Stop 1 - Flash
Stop 2 - Flash
Stop 3 - Flash
Wait/Doze - Flash
R un - Fl ash
The figure below illustrates the power consumption in a graphical format.
Figure 12. Current Consumption in Low-Power Modes
Peak
1
3
Active
(mA)
Table 9. Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications
2
Active (mA)
f
sys/2
Frequency
Vol tag e
(V)
Typical
SRAM Flash
3.3 2.042.122.28
1 MHz
2.5 15.24 15.32 15.24
1.5 1.301.411.49
3.3 2.232.403.57
2 MHz
2.5 15.26 15.42 15.26
1.5 1.711.922.09
3.3 2.602.953.58
4 MHz
2.5 15.30 15.61 15.30
1.5 2.492.953.29
3.3 7.61 17.67 25.34
44 MHz
2.5 16.13 19.49 16.95
1.5 24.04 28.72 39.02
3.3 8.16 26.21 34.45
48 MHz
2.5 16.28 20.06 17.17
1.5 26.05 31.13 42.30
56 MHz
3.3 10.09 30.71 38.97
2.5 16.43 20.71 17.65
1.5 30.07 35.90 47.90
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor24

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
Table 9. Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications1 (continued)
2
Active (mA)
Peak3 Active
(mA)
f
sys/2
Frequency
Vol tag e
(V)
Typical
SRAM Flash
3.3 15.72 31.37 42.10
64 MHz
2.5 16.56 21.08 17.95
1.5 32.19 38.72 53.50
3.3 20.97 31.40 48.80
72 MHz
2.5 16.87 21.70 18.20
1.5 35.90 43.20 59.50
3.3 31.37 25.83 48.60
83.33 MHz
2.5 17.21 22.80 18.83
1.5 41.10 49.40 67.50
1
All values are measured with a 3.30V EVDD, 2.50V SDVDD, and 1.5V IVDD power
supplies. Tests performed at room temperature with pins configured for high drive
strength.
2
CPU polling a status register. All peripheral clocks except UART0, FlexBus, INTC,
reset controller, PLL, and edge port disabled.
3
Peak current measured while running a while(1) loop with all modules active.
5.6 Oscillator and PLL Electrical Characteristics
Table 10. PLL Electrical Characteristics
Num Characteristic Symbol
1 PLL Reference Frequency Range
Crystal reference
External reference
2 Core frequency
CLKOUT Frequency
3 Crystal Start-up Time
4 EXTAL Input High Voltage
Crystal Mode
2
3, 4
5
All other modes (External, Limp)
5 EXTAL Input Low Voltage
Crystal Mode
5
All other modes (External, Limp)
7 PLL Lock Time
8 Duty Cycle of reference
3, 6
3
9 XTAL Current I
10 Total on-chip stray capacitance on XTAL C
11 Total on-chip stray capacitance on EXTAL C
f
ref_crystal
f
ref_ext
f
sys
f
sys/2
t
cst
V
IHEXT
V
IHEXT
V
ILEXT
V
ILEXT
t
lpll
t
dc
XTAL
S_XTAL
S_EXTAL
Min.
Val ue
12
12
488 x 10
244 x 10
-6
-6
—10ms
V
+ 0.4
XTAL
/2 + 0.4
E
VDD
—
—
— 50000 CLKIN
40 60 %
13mA
Max.
Val ue
25
40
166.66
83.33
—
—
V
XTAL
/2 - 0.4
E
VDD
1.5 pF
1.5 pF
1
1
- 0.4
Unit
MHz
MHz
MHz
MHz
V
V
V
V
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 25

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
Table 10. PLL Electrical Characteristics (continued)
Num Characteristic Symbol
12 Crystal capacitive load C
L
Min.
Val ue
Max.
Val ue
See crystal
spec
13 Discrete load capacitance for XTAL C
14 Discrete load capacitance for EXTAL C
17 CLKOUT Period Jitter,
3, 4, 7, 8, 9
Measured at f
SYS
Max
Peak-to-peak Jitter (Clock edge to clock edge)
Long Term Jitter
18 Frequency Modulation Range Limit
(f
Max must not be exceeded)
sys
19 VCO Frequency. f
1
The maximum allowable input clock frequency when booting with the PLL enabled is 24 MHz. For higher input clock
frequencies, the processor must boot in LIMP mode to avoid violating the maximum allowable CPU frequency.
2
All internal registers retain data at 0 Hz.
3
This parameter is guaranteed by characterization before qualification rather than 100% tested.
4
Proper PC board layout procedures must be followed to achieve specifications.
5
This parameter is guaranteed by design rather than 100% tested.
6
This specification is the PLL lock time only and does not include oscillator start-up time.
7
C
PCB_EXTAL
8
Jitter is the average deviation from the programmed frequency measured over the specified interval at maximum f
and C
PCB_XTAL
= (f
vco
PFD)/4 f
ref *
are the measured PCB stray capacitances on EXTAL and XTAL, respectively.
3, 10, 11
L_XTAL
L_EXTAL
C
jitter
C
mod
vco
—
—
0.8 2.2 %f
350 540 MHz
2*CL -
C
S_XTAL
C
PCB_XTAL
2*CL -
C
S_EXTAL
C
PCB_EXTAL
10
TBD
-
7
-
7
Measurements are made with the device powered by filtered supplies and clocked by a stable external clock signal.
Noise injected into the PLL circuitry via PLL V
the Cjitter percentage for a given interval.
9
Values are with frequency modulation disabled. If frequency modulation is enabled, jitter is the sum of Cjitter+Cmod.
10
Modulation percentage applies over an interval of 10μs, or equivalently the modulation rate is 100KHz.
11
Modulation range determined by hardware design.
, EVDD, and VSS and variation in crystal oscillator frequency increase
DD
% f
% f
Unit
pF
pF
sys/2
sys/2
sys/2
sys
.
5.7 External Interface Timing Characteristics
Table 11 lists processor bus input timings.
NOTE
All processor bus timings are synchronous; that is, input setup/hold and
output delay with respect to the rising edge of a reference clock. The
reference clock is the FB_CLK output.
All other timing relationships can be derived from these values. Timings
listed in Table 11 are shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor26

Electrical Characteristics
Invalid Invalid
FB_CLK(75MHz)
T
SETUP
T
HOLD
Input Setup And Hold
1.5V
t
rise
Vh = V
IH
Vl = V
IL
1.5V1.5V Vali d
t
fall
Vh = V
IH
Vl = V
IL
Input Rise Time
Input Fall Time
* The timings are also valid for inputs sampled on the negative clock edge.
Inputs
FB_CLK
FB4
FB5
Figure 13. General Input Timing Requirements
5.7.1 FlexBus
FlexBus is a multi-function external bus interface provided to interface to slave-only devices up to a
maximum bus frequency of 83.33 MHz. It can be directly connected to asynchronous or synchronous
devices such as external boot ROMs, flash memories, gate-array logic, or other simple target (slave)
devices with little or no additional circuitry . For asynchronous devices, a simple chip-select based interface
can be used. The FlexBus interface has six general purpose chip-selects (FB_CS
configured to be distributed between the FlexBus or SDRAM memory interfaces. Chip-select FB_CS[0]
can be dedicated to boot ROM access and can be programmed to be byte (8 bits), word (16 bits), or
longword (32 bits) wide. Control signal timing is compatible with common ROM/flash memories.
[5:0]) that can be
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 27

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
FB_CLK
A[23:0]
D[31:0]
R/W
TS
FB_CSn
OE
TA
FB1
A[23:0]
FB2
FB3
FB4
FB5
FB6
FB7
DATA
BE/BWEn
5.7.1.1 FlexBus AC Timing Characteristics
The following timing numbers indicate when data will be latched or driven onto the external bus, relative
to the system clock.
Table 11. FlexBus AC Timing Specifications
Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit Notes
Frequency of Operation 83.33 Mhz f
FB1 Clock Period (FB_CLK) t
FB2 Data, and Control Output Valid (A[23:0], D[31:0],
t
FBCK
FBCHDCV
12 ns t
—7.0 ns
FB_CS[5:0], R/W, TS, BE/BWE[3:0] and OE)
FB3 Data, and Control Output Hold ((A[23:0], D[31:0],
t
FBCHDCI
1— ns
FB_CS[5:0], R/W, TS, BE/BWE[3:0], and OE)
FB4 Data Input Setup t
FB5 Data Input Hold t
FB6 Transfer Acknowledge (T
FB7 Transfer Acknowledge (T
1
Timing for chip selects only applies to the FB_CS[5:0] signals. Please see Section 5.8, “SDRAM Bus” for SD_CS[1:0]
timing.
2
The FlexBus supports programming an extension of the address hold. Please consult the device reference manual for
A) Input Setup t
A) Input Hold t
DVF BCH
DIFBCH
CVFBCH
CIFBCH
3.5 — ns
0— ns
4— ns
0— ns
more information.
sys/2
cyc
1
1, 2
Figure 14. FlexBus Read Timing
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor28

Electrical Characteristics
FB_CLK
A[23:0]
D[31:0]
R/W
TS
FB_CSn
TA
FB1
FB2
FB3
FB3
FB6
FB7
OE
BE/BWEn
Figure 15. Flexbus Write Timing
5.8 SDRAM Bus
The SDRAM controller supports accesses to main SDRAM memory from any internal master . It supports
standard SDRAM or double data rate (DDR) SDRAM, but it does not support both at the same time. The
SDRAM controller uses SSTL2 and SSTL3 I/O drivers. Both SSTL drive modes are programmable for
Class I or Class II drive strength.
5.8.1 SDR SDRAM AC Timing Characteristics
The following timing numbers indicate when data will be latched or driven onto the external bus, relative
to the memory bus clock, when operating in SDR mode on write cycles and relative to SD_DQS on read
cycles. The SDRAM controller is a DDR controller with an SDR mode. Because it is designed to support
DDR, a DQS pulse must remain supplied to the device for each data beat of an SDR read. The ColdFire
processor accomplishes this by asserting a signal called SD_SDR_DQS during read cycles. Take care
during board design to adhere to the following guidelines and specs with regard to the SD_SDR_DQS
signal and its usage.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 29

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
Table 12. SDR Timing Specifications
Symbol Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit Notes
Frequency of Operation TBD 83.33 MHz
SD1 Clock Period (tCK)t
SD3 Pulse Width High (t
SD4 Pulse Width Low (t
)t
CKH
)t
CKL
SD5 Address, SD_CKE, SD_CAS, SD_RAS, SD_WE,
SD_BA, SD_CS[1:0] - Output Valid (t
CMV
)
SD6 Address, SD_CKE, SD_CAS, SD_RAS, SD_WE,
SD_BA, SD_CS[1:0] - Output Hold (t
SD7 SD_SDR_DQS Output Valid (t
DQSOV
SD8 SD_DQS[3:2] input setup relative to SD_CLK (t
SD9 SD_DQS[3:2] input hold relative to SD_CLK (t
)
CMH
)t
DQSIS)tDQVSDCH
DQSIH
SD10 Data (D[31:0]) Input Setup relative to SD_CLK
(reference only) (t
DIS
)
SD11 Data Input Hold relative to SD_CLK (reference only)
(t
)
DIH
SD12 Data (D[31:0]) and Data Mask(SD_DQM[3:0])
t
SDCHACV
t
SDCHACI
)t
DQISDCH
t
DVS DCH
t
t
SDCHDMV
SDCK
SDCKH
SDCKL
DQSOV
DISDCH
Output Valid (tDV)
12 TBD ns
0.45 0.55 SD_CLK
0.45 0.55 SD_CLK
—0.5× SD_CLK
+1.0
2.0 — ns
—Self timedns
0.25 × SD_CLK 0.40 × SD_CLK ns
Does not apply. 0.5 SD_CLK fixed width.
0.25 × SD_CLK — ns
1.0 — ns
—0.75× SD_CLK
+ 0.5
ns
ns
1
2
3
3
4
5
6
7
SD13 Data (D[31:0]) and Data Mask (SD_DQM[3:0]) Output
DH
)
Hold (t
1
The device supports the same frequency of operation for FlexBus and SDRAM as that of the internal bus clock. Please see the
t
SDCHDMI
1.5 — ns
PLL chapter of the MCF5208 Reference Manual for more information on setting the SDRAM clock rate.
2
SD_CLK is one SDRAM clock in (ns).
3
Pulse width high plus pulse width low cannot exceed min and max clock period.
4
SD_DQS is designed to pulse 0.25 clock before the rising edge of the memory clock. This is a guideline only. Subtle variation from
this guideline is expected. SD_DQS only pulses during a read cycle and one pulse occurs for each data beat.
5
SDR_DQS is designed to pulse 0.25 clock before the rising edge of the memory clock. This spec is a guideline only. Subtle
variation from this guideline is expected. SDR_DQS only pulses during a read cycle and one pulse occurs for each data beat.
6
The SDR_DQS pulse is designed to be 0.5 clock in width. The timing of the rising edge is most important. The falling edge does
not affect the memory controller.
7
Because a read cycle in SDR mode continues using the DQS circuit within the device, it is most critical that the data valid window
be centered 1/4 clk after the rising edge of DQS. Ensuring that this happens results in successful SDR reads. The input setup spec
is provided as guidance.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor30

Figure 16. SDR Write Timing
SD_CLK
SDDM
D[31:0]
A[23:0]
SD_BA[1:0]
CMD
ROW
SD1
SD4
COL
SD5
WD1 WD2 WD3 WD4
SD12
SD11
SD_CSn
SD_RAS
SD_WE
SD_CAS
SD2
SD3
SD_CLK
SD_CSn,
SDDM
D[31:0]
A[23:0],
SD_RAS
,
SD_BA[1:0]
CMD
ROW
SD1
SD4
COL
WD1 WD2 WD3 WD4
SD9
3/4 MCLK
SD_SDR_DQS
SD_DQS[3:2]
Delayed
SD10
SD7
Board Delay
SD8
Board Delay
SD6
tDQS
Reference
SD_CLK
from
Memories
(Measured at Output Pin)
(Measured at Input Pin)
SD5
NOTE: Data driven from memories relative
to delayed memory clock.
SD_WE
SD_CAS,
SD2
SD3
Electrical Characteristics
Freescale Semiconductor 31
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Figure 17. SDR Read Timing

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
5.8.2 DDR SDRAM AC Timing Characteristics
When using the SDRAM controller in DDR mode, the following timing numbers must be followed to
properly latch or drive data onto the memory bus. All timing numbers are relative to the four DQS byte
lanes. The following timing numbers are subject to change at anytime, and are only provided to aid in early
board design. Please contact your local Freescale representative if questions develop.
Table 13. DDR Timing Specifications
Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit Notes
— Frequency of Operation — TBD 83.33 Mhz
DD1 Clock Period (SD_CLK) t
DD2 Pulse Width High t
DD3 Pulse Width Low t
DD4 Address, SD_CKE, SD_CAS, SD_RAS, SD_WE,
t
SD_CS[1:0] - Output Valid
DDCK
DDCKH
DDCKL
SDCHACV
12 TBD ns
0.45 0.55 SD_CLK
0.45 0.55 SD_CLK
—0.5× SD_CLK
+1.0
ns
1
2
3
3
4
DD5 Address, SD_CKE, SD_CAS
[1:0] - Output Hold
SD_CS
, SD_RAS, SD_WE,
DD6 Write Command to first DQS Latching Transition t
DD7 Data and Data Mask Output Setup (DQ-->DQS)
t
SDCHACI
CMDVDQ
t
DQDMV
2.0 — ns —
1.25 SD_CLK —
1.5 — ns
Relative to DQS (DDR Write Mode)
DD8 Data and Data Mask Output Hold (DQS-->DQ)
t
DQDMI
1.0 — ns
Relative to DQS (DDR Write Mode)
DD9 Input Data Skew Relative to DQS (Input Setup) t
DD10 Input Data Hold Relative to DQS. t
DVD Q
DIDQ
—1ns
0.25 × SD_CLK
—ns
+0.5ns
DD11 DQS falling edge from SDCLK rising (output hold time) t
DD12 DQS input read preamble width (t
DD13 DQS input read postamble width (t
DD14 DQS output write preamble width (t
DD15 DQS output write postamble width (t
1
The frequency of operation is 2x or 4x the FB_CLK frequency of operation. FlexBus and SDRAM clock operate at the same
frequency as the internal bus clock.
2
SD_CLK is one SDRAM clock in (ns).
3
Pulse width high plus pulse width low cannot exceed min and max clock period.
4
Command output valid should be 1/2 the memory bus clock (SD_CLK) plus some minor adjustments for process, temperature, and
)t
RPRE
)t
RPST
)t
WPRE
)t
WPST
DQLSDCH
DQRPRE
DQRPST
DQWPRE
DQWPST
0.5 — ns —
0.9 1.1 SD_CLK —
0.4 0.6 SD_CLK —
0.25 — SD_CLK —
0.4 0.6 SD_CLK —
voltage variations.
5
This specification relates to the required input setup time of today’s DDR memories. The device’s output setup should be larger
than the input setup of the DDR memories. If it is not larger, the input setup on the memory is in violation.
MEM_DATA[31:24] is relative to MEM_DQS[3], MEM_DATA[23:16] is relative to MEM_DQS[2], MEM_DATA[15:8] is relative to
MEM_DQS[1], and MEM_[7:0] is relative MEM_DQS[0].
6
The first data beat is valid before the first rising edge of DQS and after the DQS write preamble. The remaining data beats are valid
for each subsequent DQS edge.
5
6
7
8
9
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor32

Electrical Characteristics
SD_CLK
SD_CS
n, SD_WE,
DM3/DM2
D[31:24]/D[23:16]
A[13:0]
SD_RAS
, SD_CAS
CMD
ROW
DD1
DD5
DD4
COL
WD1 WD2 WD3 WD4
DD7
SD_DQS3/SD_DQS2
DD8
DD8
DD7
SD_CLK
DD3
DD2
DD6
7
This specification relates to the required hold time of today’s DDR memories. MEM_DATA[31:24] is relative to MEM_DQS[3],
MEM_DATA[23:16] is relative to MEM_DQS[2], MEM_DATA[15:8] is relative to MEM_DQS[1], and MEM_[7:0] is relative
MEM_DQS[0].
8
Data input skew is derived from each DQS clock edge. It begins with a DQS transition and ends when the last data line becomes
valid. This input skew must include DDR memory output skew and system level board skew (due to routing or other factors).
9
Data input hold is derived from each DQS clock edge. It begins with a DQS transition and ends when the first data line becomes
invalid.
Freescale Semiconductor 33
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Figure 18. DDR Write Timing

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
SD_CLK
SD_CS
n, SD_WE,
SD_DQS3/SD_DQS2
D[31:24]/D[23:16]
A[13:0]
SD_RAS
, SD_CAS
CMD
ROW
DD1
DD5
DD4
WD1 WD2 WD3 WD4
SD_DQS3/SD_DQS2
DD9
SD_CLK
DD3
DD2
D[31:24]/D[23:16]
WD1 WD2 WD3 WD4
DD10
CL=2
CL=2.5
COL
DQS Read
Preamble
DQS Read
Postamble
DQS Read
Preamble
DQS Read
Postamble
CL = 2.5 CL = 2
Figure 19. DDR Read Timing
5.9 General Purpose I/O Timing
Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
G1 FB_CLK High to GPIO Output Valid t
G2 FB_CLK High to GPIO Output Invalid t
G3 GPIO Input Valid to FB_CLK High t
G4 FB_CLK High to GPIO Input Invalid t
1
GPIO spec cover: IRQn, UART and Timer pins.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Table 14. GPIO Timing1
CHPOV
CHPOI
PVCH
CHPI
—8ns
1.5 — ns
8—ns
1.5 — ns
Freescale Semiconductor34

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
G1
FB_CLK
GPIO Outputs
G2
G3 G4
GPIO Inputs
R1
R2
FB_CLK
RESET
RSTOUT
R3
R4
R8
R7R6R5
Configuration Overrides*:
R4
(RCON, Override pins)
Figure 20. GPIO Timing
5.10 Reset and Configuration Override Timing
Table 15. Reset and Configuration Override Timing
Num Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
R1 RESET
R2 FB_CLK High to RESET Input invalid t
R3 RESET Input valid Time
R4 FB_CLK High to RSTOUT Valid t
R5 RSTOUT valid to Config. Overrides valid t
R6 Configuration Override Setup Time to RSTOUT invalid t
R7 Configuration Override Hold Time after RSTOUT invalid t
R8 RSTOUT invalid to Configuration Override High Impedance t
1
During low power STOP, the synchronizers for the RESET input are bypassed and RESET is asserted asynchronously to
the system. Thus, RESET
Input valid to FB_CLK High t
1
must be held a minimum of 100 ns.
RVCH
CHRI
t
RIVT
CHROV
ROVCV
COS
COH
ROICZ
9—ns
1.5 — ns
5—t
—10ns
0—ns
20 — t
0—ns
—1t
CYC
CYC
CYC
Figure 21. RESET and Configuration Override Timing
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 35

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
NOTE
Refer to the MCF5208 Reference Manual for more information.
5.11 I2C Input/Output Timing Specifications
Table 16 and Table 17 list specifications for the I2C input and output timing parameters.
Table 16. I2C Input Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
I1 Start condition hold time 2 — t
I2 Clock low period 8 — t
cyc
cyc
I3 I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA rise time (VIL= 0.5 V to VIH= 2.4 V) — 1 ms
I4 Data hold time 0 — ns
I5 I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA fall time (VIH= 2.4 V to VIL= 0.5 V) — 1 ms
I6 Clock high time 4 — t
cyc
I7 Data setup time 0 — ns
I8 Start condition setup time (for repeated start condition only) 2 — t
I9 Stop condition setup time 2 — t
Table 17. I2C Output Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA
cyc
cyc
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
1
I1
I2
I3
I4
I5
I6
I7
I8
I9
Start condition hold time 6 — t
1.
Clock low period 10 — t
2
I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA rise time (V
1.
Data hold time 7 — t
3
I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA fall time (V
1.
Clock high time 10 — t
1.
Data setup time 2 — t
1.
Start condition setup time (for repeated start condition only) 20 — t
1.
Stop condition setup time 10 — t
= 0.5 V to VIH= 2.4 V) — — µs
IL
= 2.4 V to VIL= 0.5 V) — 3 ns
IH
cyc
cyc
cyc
cyc
cyc
cyc
cyc
1
Output numbers depend on the value programmed into the IFDR; an IFDR programmed with the
maximum frequency (IFDR = 0x20) results in minimum output timings as shown in Table A-16. The I
interface is designed to scale the actual data transition time to move it to the middle of the I2C_SCL low
period. The actual position is affected by the prescale and division values programmed into the IFDR;
however, the numbers given in Table A-16 are minimum values.
2
Because I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA are open-collector-type outputs, which the processor can only actively
drive low, the time I2C_SCL or I2C_SDA take to reach a high level depends on external signal
capacitance and pull-up resistor values.
3
Specified at a nominal 50-pF load.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor36
2
C

Electrical Characteristics
I2 I6
I1 I4
I7
I8 I9
I5
I3
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
M1 M2
FEC_RXCLK (input)
FEC_RXD[3:0] (inputs)
FEC_RXDV
FEC_RXER
M3
M4
Figure 22. I2C Input/Output Timings
5.12 Fast Ethernet AC Timing Specifications
MII signals use TTL signal levels compatible with devices operating at 5.0 V or 3.3 V.
5.12.1 MII Receive Signal Timing (FEC_RXD[3:0], FEC_RXDV, FEC_RXER, and FEC_RXCLK)
The receiver functions correctly up to a FEC_RXCLK maximum frequency of 25 MHz +1%. There is no
minimum frequency requirement. In addition, the processor clock frequency must exceed twice the
FEC_RXCLK frequency.
Table 18 lists MII receive channel timings.
Table 18. MII Receive Signal Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M1 FEC_RXD[3:0], FEC_RXDV, FEC_RXER to FEC_RXCLK
setup
M2 FEC_RXCLK to FEC_RXD[3:0], FEC_RXDV, FEC_RXER hold 5 — ns
M3 FEC_RXCLK pulse width high 35% 65% FEC_RXCLK period
M4 FEC_RXCLK pulse width low 35% 65% FEC_RXCLK period
Figure 23 shows MII receive signal timings listed in Table 18.
5— ns
Freescale Semiconductor 37
Figure 23. MII Receive Signal Timing Diagram
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1

Electrical Characteristics
M6
FEC_TXCLK (input)
FEC_TXD[3:0] (outputs)
FEC_TXEN
FEC_TXER
M5
M7
M8
FEC_CRS
M9
FEC_COL
5.12.2 MII Transmit Signal Timing (FEC_TXD[3:0], FEC_TXEN, FEC_TXER, FEC_TXCLK)
Table 19 lists MII transmit channel timings.
The transmitter functions correctly up to a FEC_TXCLK maximum frequency of 25 MHz +1%. In
addition, the processor clock frequency must exceed twice the FEC_TXCLK frequency.
Table 19. MII Transmit Signal Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M5 FEC_TXCLK to FEC_TXD[3:0], FEC_TXEN, FEC_TXER
invalid
M6 FEC_TXCLK to FEC_TXD[3:0], FEC_TXEN, FEC_TXER valid — 25 ns
M7 FEC_TXCLK pulse width high 35% 65% FEC_TXCLK period
M8 FEC_TXCLK pulse width low 35% 65% FEC_TXCLK period
Figure 24 shows MII transmit signal timings listed in Table 19.
Figure 24. MII Transmit Signal Timing Diagram
5— ns
5.12.3 MII Async Inputs Signal Timing (FEC_CRS and FEC_COL)
Table 20 lists MII asynchronous inputs signal timing.
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M9 FEC_CRS, FEC_COL minimum pulse width 1.5 — FEC_TXCLK period
Figure 25 shows MII asynchronous input timings listed in Table 20.
Table 20. MII Async Inputs Signal Timing
Figure 25. MII Async Inputs Timing Diagram
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor38

Electrical Characteristics
M11
FEC_MDC (output)
FEC_MDIO (output)
M12 M13
FEC_MDIO (input)
M10
M14
M15
5.12.4 MII Serial Management Channel Timing (FEC_MDIO and FEC_MDC)
Table 21 lists MII serial management channel timings. The FEC functions correctly with a maximum
MDC frequency of 2.5 MHz.
Table 21. MII Serial Management Channel Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M10 FEC_MDC falling edge to FEC_MDIO output invalid (minimum
propagation delay)
M11 FEC_MDC falling edge to FEC_MDIO output valid (max prop delay) — 25 ns
M12 FEC_MDIO (input) to FEC_MDC rising edge setup 10 — ns
M13 FEC_MDIO (input) to FEC_MDC rising edge hold 0 — ns
M14 FEC_MDC pulse width high 40% 60% FEC_MDC period
M15 FEC_MDC pulse width low 40% 60% FEC_MDC period
Figure 26 shows MII serial management channel timings listed in Table 21.
0— ns
Freescale Semiconductor 39
Figure 26. MII Serial Management Channel Timing Diagram
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1

Electrical Characteristics
QSPI_CS[3:0]
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_DOUT
QS5
QS1
QSPI_DIN
QS3
QS4
QS2
5.13 32-Bit Timer Module AC Timing Specifications
Table 22 lists timer module AC timings.
Table 22. Timer Module AC Timing Specifications
Name Characteristic Unit
Min Max
T1 DT0IN / DT1IN / DT2IN / DT3IN cycle time 3 — t
T2 DT0IN / DT1IN / DT2IN / DT3IN pulse width 1 — t
5.14 QSPI Electrical Specifications
Table 23 lists QSPI timings.
Table 23. QSPI Modules AC Timing Specifications
Name Characteristic Min Max Unit
QS1 QSPI_CS[3:0] to QSPI_CLK 1 510 tcyc
QS2 QSPI_CLK high to QSPI_DOUT valid. — 10 ns
QS3 QSPI_CLK high to QSPI_DOUT invalid. (Output hold) 1.5 — ns
QS4 QSPI_DIN to QSPI_CLK (Input setup) 9 — ns
QS5 QSPI_DIN to QSPI_CLK (Input hold) 9 — ns
The values in Table 23 correspond to Figure 27.
CYC
CYC
Figure 27. QSPI Timing
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor40

5.15 JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing
NOTES:
TCLK
V
IL
V
IH
J3 J3
J4 J4
J2
(input)
Table 24. JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing
Electrical Characteristics
Num Characteristics
J1 TCLK Frequency of Operation f
J2 TCLK Cycle Period t
J3 TCLK Clock Pulse Width t
J4 TCLK Rise and Fall Times t
J5 Boundary Scan Input Data Setup Time to TCLK Rise t
J6 Boundary Scan Input Data Hold Time after TCLK Rise t
J7 TCLK Low to Boundary Scan Output Data Valid t
J8 TCLK Low to Boundary Scan Output High Z t
J9 TMS, TDI Input Data Setup Time to TCLK Rise t
J10 TMS, TDI Input Data Hold Time after TCLK Rise t
J11 TCLK Low to TDO Data Valid t
J12 TCLK Low to TDO High Z t
J13 TRST
J14 TRST
1
JTAG_EN is expected to be a static signal. Hence, specific timing is not associated with it.
Assert Time t
Setup Time (Negation) to TCLK High t
1
Symbol Min Max Unit
JCYC
JCYC
JCW
JCRF
BSDST
BSDHT
BSDV
BSDZ
TAPBST
TAPBHT
TDODV
TDODZ
TRSTAT
TRSTST
DC 1/4 f
4— t
sys/2
CYC
26 — ns
03 ns
4— ns
26 — ns
033 ns
033 ns
4— ns
10 — ns
026 ns
08 ns
100 — ns
10 — ns
Figure 28. Test Clock Input Timing
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 41

Electrical Characteristics
Input Data Valid
Output Data Valid
Output Data Valid
TCLK
Data Inputs
Data Outputs
Data Outputs
Data Outputs
V
IL
V
IH
J5 J6
J7
J8
J7
Input Data Valid
Output Data Valid
Output Data Valid
TCLK
TDI
TDO
TDO
TDO
TMS
V
IL
V
IH
J9 J10
J11
J12
J11
TCLK
TRST
J14
J13
Figure 29. Boundary Scan (JTAG) Timing
Figure 30. Test Access Port Timing
Figure 31. TRST Timing
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor42

Electrical Characteristics
NOTES:
PSTCLK
PSTDDATA[7:0]
D0
D1
D2
Past
Current
DSCLK
DSI
DSO
Next
Current
D5
D3
D4
5.16 Debug AC Timing Specifications
Table 25 lists specifications for the debug AC timing parameters shown in Figure 32.
Table 25. Debug AC Timing Specification
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
D0 PSTCLK cycle time 1 1 t
D1 PSTCLK rising to PSTDDATA valid — 3.0 ns
D2 PSTCLK rising to PSTDDATA invalid 1.5 — ns
DSI-to-DSCLK setup 1 — PSTCLK
D3
1
D4
DSCLK-to-DSO hold 4 — PSTCLK
D5 DSCLK cycle time 5 — PSTCLK
D6 BKPT assertion time 1 — PSTCLK
1
DSCLK and DSI are synchronized internally. D4 is measured from the synchronized
DSCLK input relative to the rising edge of PSTCLK.
SYS
Figure 32. Real-Time Trace AC Timing
Figure 33. BDM Serial Port AC Timing
Freescale Semiconductor 43
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1

Revision History
6 Revision History
Table 26. Revision History
Revision
Number
Date Substantive Changes
0 5/23/2005 • Initial Release
0.1 6/16/2005 • Corrected 144QFP pinout in Figure 1. Pins 139-142 incorrectly showed
FEC functionality, which are actually UART 0/1 clear-to-send and
request-to-send signals.
• Changed maximum core frequency in Ta b l e 1 0 , spec #2, from 240MHz to
-> f
166.67MHz. Also, changed symbols in table: f
core
sys
and f
sys
for consistency throughout document and reference manual.
0.2 8/26/2005 • Changed ball M9 from SD_VDD to EVDD in Figure 9.
• Ta bl e 3 : Pin 33 for 144 LQFP package should be EVDD instead of
SD_VDD. BE/BWE[3:0] for 144 LQFP should be “20, 48, 18, 50“ instead
of “18, 20, 48, 50”
Cleaned up various electrical specifications:
• Ta bl e 4 : Added DDR/Memory pad supply voltage spec, changed “clock
synthesizer supply voltage” to “PLL supply voltage”, changed min PLLV
from -0.5 to -0.3, changed max VIN from 4.0 to 3.6, changed minimum T
from -65 to -55,
• Ta bl e 5 : Changed TBD values in T
entry to 105°C.
j
• Ta bl e 7 : Changed minimum core supply voltage from 1.35 to 1.4 and
maximum from 1.65 to 1.6, added PLL supply voltage entry, added pad
supply entries for mobile-DDR, DDR, and SDR, changed minimum input
high voltage from 0.7xEV
to 2 and maximum from 3.65 to EVDD+0.05,
DD
changed minimum input low voltage from VSS-0.3 to -0.05 and maximum
from 0.35xEV
to 0.8, added input high/low voltage entries for DDR and
DD
mobile-DDR, removed high impedance leakage current entry, changed
minimum output high voltage from EV
-0.5 to EVDD-0.4, added DDR/bus
DD
output high/low voltage entries, removed load capacitance and DC
injection current entries.
• Added filtering circuits and voltage sequencing sections: Section 5.4.1,
“PLL Power Filtering,” and Section 5.4.2, “Supply Voltage Sequencing and
Separation Cautions.”
• Removed “Operating Conditions” table from Section 5.6, “Oscillator and
PLL Electrical Characteristics,” because it is redundant with Ta bl e 7 .
• Ta bl e 1 1 : Changed minimum core frequency to TBD, removed external
reference and on-chip PLL frequency specs to have only a CLKOUT
frequency spec of TBD to 83.33MHz, removed loss of reference frequency
and self-clocked mode frequency entries, in EXTAL input high/low voltage
entries changed “All other modes (Dual controller (1:1), Bypass, External)”
to “All other modes (External, Limp)”, removed XTAL output high/low
voltage entries, removed power-up to lock time entry, removed last 5
entries (frequency un-lock range, frequency lock range, CLKOUT period
jitter, frequency modulation range limit, and ICO frequency)
-> f
sys/2
DD
stg
0.3 9/07/2005 • Corrected DRAMSEL footnote #3 in Ta bl e 3 .
• Updated Ta bl e 3 with 144MAPBGA pin locations.
• Added 144MAPBGA ballmap to Section 4.3, “Pinout—144 MAPBGA.”
• Changed J12 from PLL_VDD to IVDD in Figure 9.
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor44

Table 26. Revision History (continued)
Revision History
Revision
Number
0.4 10/10/2005 • Figure 1 and Ta bl e 3 : Changed pin 33 from EVDD to SD_VDD
0.5 3/29/2006 • Added “top view” and “bottom view” labels where appropriate to
0.6 7/21/2006 • Corrected cross-reference to Figure 9 in Section 4.7, “Pinout—196
1 3/28/2007 • Removed preliminary designation from Section 5, “Electrical
Date Substantive Changes
• Figure 4 and Ta bl e 3 : Changed ball D10 from TEST to VSS
• Figure 6 and Ta bl e 3 : Changed pin 39 from EVDD to SD_VDD and pin 117
from TEST to VSS
mechanical drawings and pinouts.
• Updated mechanical drawings to latest available, and added note to
Section 4, “Mechanicals and Pinouts.”
MAPBGA.”
• Corrected L3 label in Figure 9 from SD_DR_DQS to SD_SDR_DQS.
• Corrected L6 label in Figure 9 from SD_DQS0 to SD_DQS2 and H3 from
SD_DQS1 to SD_DQS3.
• Removed second sentence from Section 5.12.2, “MII Transmit Signal
Timing (FEC_TXD[3:0], FEC_TXEN, FEC_TXER, FEC_TXCLK),”
regarding no minimum frequency requirement for TXCLK.
• Removed third and fourth paragraphs from Section 5.12.2, “MII Transmit
Signal Timing (FEC_TXD[3:0], FEC_TXEN, FEC_TXER, FEC_TXCLK),”
as this feature is not supported on this device.
Characteristics.”
• Updated Section 5.2, “Thermal Characteristics.”
• Updated Section 5.4, “DC Electrical Specifications.”
• Added Section 5.5, “Current Consumption.”
• Updated Section 5.6, “Oscillator and PLL Electrical Characteristics.”
• Made some corrections to the drawings in Section 5.8, “SDRAM Bus.”
• Edited for grammar, punctuation, spelling, style, and format. - JD
MCF5208 ColdFire® Microprocessor Data Sheet, Rev. 1
Freescale Semiconductor 45

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and
software implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are
no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or
fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the
information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further
notice to any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty,
representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any
particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically
disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or
incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be provided in Freescale
Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different
applications and actual perfor mance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer
application by customer’s technical exper ts. Freescale Semiconductor does
not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized
for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body,
or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other
application in which the failure of the Freescale Semic onductor product could
create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended
or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale
Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and
distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of
personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized
use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was negligent
regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale
Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or ser vice names are the property
of their respective owners.© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2007. All rights
reserved.
MCF5208EC
Rev. 1
4/2007
 Loading...
Loading...