Page 1

Fluke Digital Multimeters
Solutions for every need
Page 2
Service
Entrance
Meter
Meter
Service
Entrance
Meter
Outbuilding
Outbuilding
Transformer
Underground Service
Underground Service
Service
Entrance
How to choose the best
DMM for your job
Choosing the right digital multimeter (DMM) requires thinking
about what you’ll be using it for.
Evaluate your basic measurement needs and job requirements
and then take a look at special
features/functions built into many
multimeters. Think about whether
you need to do basic measurements, or if you need the more
advanced troubleshooting options
offered by special features.
Factors to consider:
Your work environment (voltage
•
level, types of equipment, types
of measurements, applications)
Specialty features/functions
•
(capacitance, frequency, temperature, non-contact voltage,
low impedance mode, min-max
record, data logging, trending)
Resolution and accuracy
•
(6,000, 20,000, or 50,000
count resolution)
Safety
The increased occurrence and
levels of transient overvoltages
in today’s power systems have
given rise to more stringent
safety standards for electrical
measurement equipment.
Transients that ride on top of
power sources (mains, feeder
or branch circuits) can trigger
a sequence of events that
may lead to serious injury. Test
equipment must be designed
to protect people working in
this high-voltage, high-current
environment.
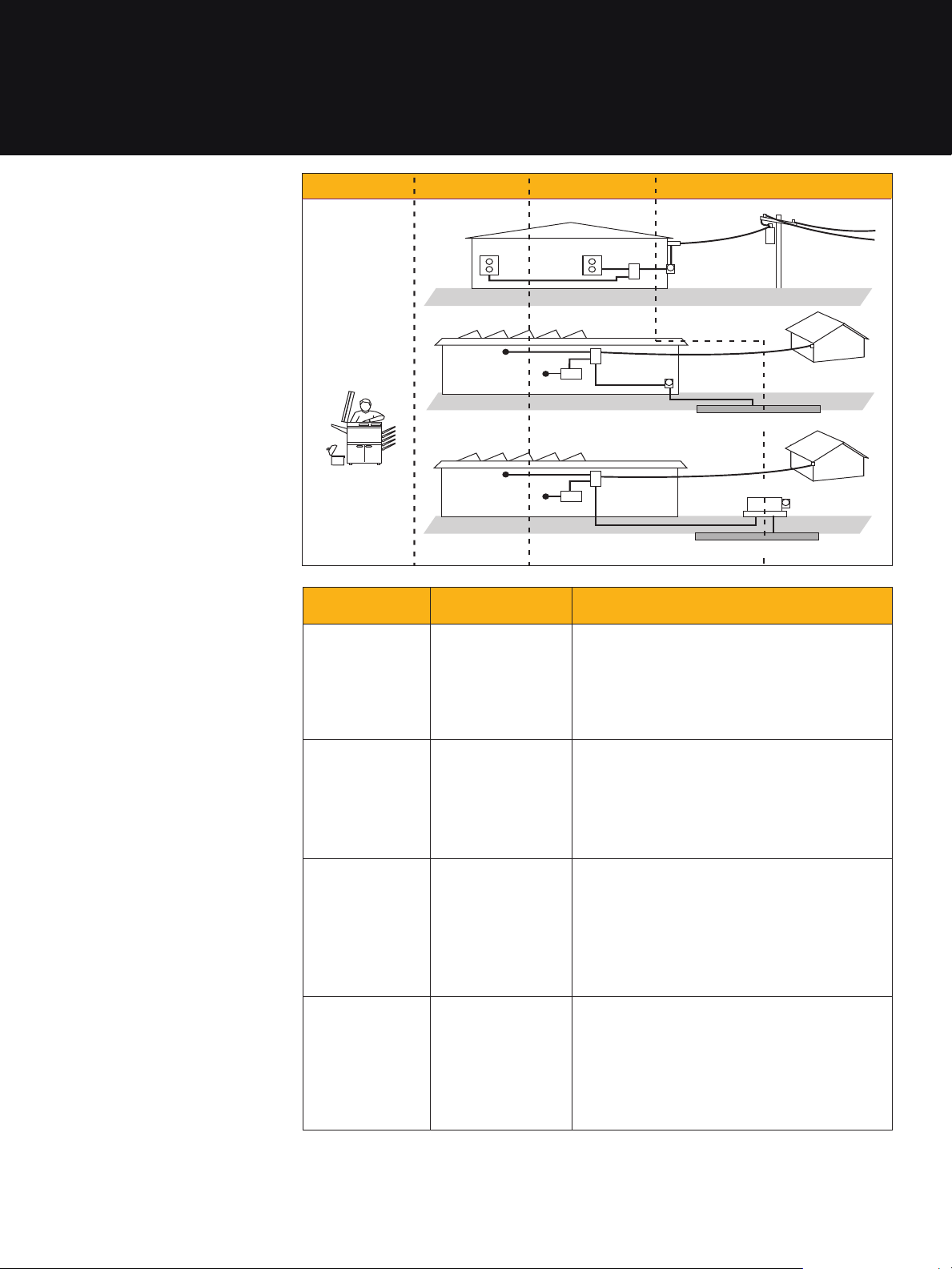
CAT 0 CAT II CAT III CAT IV
Measurement
category
CAT 0 Electronic (Not directly
CAT II Appliances, PCs,
CAT III MC panels, etc. • Equipment in fixed installations, such as switchgear
CAT IV Three-phase at utility
In brief Examples
connected to mains)
and TVs
connection, any
outdoor conductors
• Protected electronic equipment
• Equipment connected to (source) circuits in which
measures are taken to limit transient overvoltages to
an appropriately low level
• Any high-voltage, low-energy source derived from
a high-winding resistance transformer, such as the
high-voltage section of a copier
• Appliance, portable tools, and other household
and similar loads
• Outlet and long branch circuits
• Outlets at more than 10 meters (30 feet) from
CAT III source
• Outlets more than 20 meters (60 feet) from
CAT IV source
and polyphase motors
• Bus and feeder in industrial plants
• Feeders and short branch circuits, distribution panel
devices
• Lighting systems in larger buildings
• Heavy appliance outlets with short connections to
service entrance
• Refers to the “origin of installation,” i.e., where lowvoltage connection is made to utility power
• Electricity meters, primary overcurrent protection
equipment
• Outside and service entrance, service drop from
pole to building, run between meter and panel
• Overhead line to detached building, underground
line to well pump
Page 3

Meters designed for the way you work
Advanced meters Wireless meters General purpose
Models
Basic features
Counts 20000 50000 50000 6000 6000 6000 6000
True-rms readings ac ac+dc ac+dc ac ac ac
Basic dc accuracy 0.05
Wide bandwidth 20 kHz 100 kHz 100 kHz
Auto/manual ranging •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/•
Digits 4-1/2 4-1/2 4-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2
ATEX II 2G Eex ia IICT4 safety rating
Zone 1 and Zone 2
Measurements
Voltage ac/dc 1000V 1000V 1000V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V
Current ac/dc 10 A 10 A 10 A 10 A 400 mA 10 A 10 A
Resistance 50 MW 500 MW 500 MW 40 MW 50 MW 50 MW 50 MW
Frequency 200 kHz 1 MHz 1 MHz 50 kHz 100 kHz 100 kHz 100 kHz
Capacitance 10,000 µF 50,000 µF 50,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF
Temperature (+) 1090 °C (+) 1350 °C (+) 1350 °C (+) 400 °C (+) 400 °C
dB 60 dB 60 dB
Conductance 50 nS 50 nS 50 nS
Duty cycle/pulse width •/– •/• •/•
Continuity/diode test
Motor Drive (ASD) Measurements
VoltAlert™, non-contact voltage
detection
VCHEK™
LoZ: low input impedance
Lo Ohms
Microamps
Display
Wireless capabilities Removable Wire-
Dot matrix display
Dual display
Analog bargraph
Backlight Two level Two level Two level
Graphical trend display
Diagnostics and data
Min Max recording/with time stamp •/– •/• •/• •/– •/– •/– •/–
Fast Min Max 250 µs 250 µs 250 µs
Display Hold/Auto (Touch) Hold •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/•
Relative reference
Stand alone logging
Trend Capture
Readings memories 10,000 10,000
USB interface
Other features
Automatic selection, ac/dcvolts
Real time clock
Overmolded case, integrated holster
Removable holster
Closed case calibration
Separate battery/fuse access •/– •/• •/•
Completely sealed/ watertight
Automatic power off
Low battery indication
Operating temperature range -20 °C, +55 °C -20 °C, +55 °C -20 °C, +55 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C
Warranty and electrical safety
Warranty (years) Lifetime Lifetime Lifetime 3 3 Lifetime Lifetime
Input alert
Dangerous voltage indication
IP Rating IP30 IP42 IP42 IP54
EN61010-1 CAT III 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V
EN61010-1 CAT IV 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V
87 V 289 287 233 3000 FC 179 77 IV
% 0.025 % 0.025 % 0.25 % 0.09 % 0.09 % 0.3 %
• • • • • • •
• •
•
•
• • •
less Display
• • •
• • •
• • • • •
• • • •
• •
• • •
• •
• •
• •
• •
• • • • • •
•
• • • • • • •
• • • •
• • • • • • •
• • • • • • •
• • •
• • • • • • •
Remote wireless
readings. Connect
to smart phone.
Page 4

Compact meters Specialty meters
Models
Basic features
Counts 6000 6000 6000 6000 6000 20000 6000 20000
True-rms readings ac ac ac ac ac ac ac
Basic dc accuracy 0.5
Wide bandwidth 20 kHz 30 kHz 20kHz
Auto/manual ranging •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/• •/•
Digits 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 3-1/2 4-1/2
ATEX II 2G Eex ia IICT4 safety rating
Zone 1 and Zone 2
Measurements
Voltage ac/dc 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000V
Current ac/dc 10 A 600 µA 10 A 10 A 10 A 10 A
Resistance 40 MW 40 MW 40 MW 40 MW 60 kW 50 MW 50 MW 50 MW
Frequency 100 kHz 100 kHz 100 kHz 200 kHz 200 kHz 200 kHz
Capacitance 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF 10,000 µF
Temperature (+) 400 °C (+) 1090 °C (+) 1090 °C
dB
Conductance 60 nS 60 nS 60 nS
Duty cycle/pulse width •/– •/– •/–
Continuity/diode test
Motor Drive (ASD) Measurements
VoltAlert™, non-contact voltage
detection
VCHEK™
LoZ: low input impedance
Lo Ohms
Microamps
Display
Wireless capabilities
Dot matrix display
Dual display
Analog bargraph
Backlight
Graphical trend display
Diagnostics and data
Min Max recording/with time stamp •/– •/– •/– •/– •/– •/– •/– •/–
Fast Min Max 250 µs 250 µs
Display Hold/Auto (Touch) Hold •/– •/– •/– •/– •/– •/• •/• •/•
Relative reference
Stand alone logging
Trend Capture
Readings memories
USB interface
Other features
Automatic selection, ac/dcvolts
Real time clock
Overmolded case, integrated holster
Removable holster
Closed case calibration
Separate battery/fuse access
Completely sealed/ watertight
Automatic power off
Low battery indication
Operating temperature range -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -10 °C, +50 °C -40 °C, +55 °C -40 °C, +55 °C -15 °C, +50 °C
Warranty and electrical safety
Warranty (years) 3 3 3 3 3 Lifetime Lifetime 3
Input alert
Dangerous voltage indication
IP Rating IP42 IP42 IP42 IP42 IP42 IP67 IP67 IP67
EN61010-1 CAT III 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V 1000 V 1000 V 1000 V
EN61010-1 CAT IV 600 V 600 V 600 V 600 V
117 116 115 114 113 28 II 27 II 28IIEX
% 0.5 % 0.5 % 0.5 % 0.5 % 0.05 % 0.1 % 0.05 %
•
• • • • • • • •
• •
•
•
• • • •
• • • •
• • • • • • • •
• • • • •
• • • •
• • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • •
• • • • •
• • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • •
Two level Two level Two level
• • •
•/•
• • •
• • •
·
•/–
Page 5

Digital Multimeter selection chart
Best for Applications Recommended DMM
Advanced
industrial
troubleshooting,
including
data logging
and graphing
intermittent
problems
Advanced
electronic
applications,
including
data logging
and graphing
intermittent
problems
Industrial
Advanced meters
troubleshooting
Remote Display
Digital Multimeter
Logging: For unattended monitoring of signals over time, to detect intermittent
problems.
Graphing: View logged values graphically in the field right on the meter, without a PC.
Working on VSDs: Take accurate voltage, current and frequency measurements on the
output side of the drive at either the drive itself or the motor terminals.
Testing motor windings or contact resistance: Allows testing of resistance up to 50
ohms with one milliohm (0.001 ohm) resolution.
Logging: For unattended monitoring of signals over time, characterize device
performance.
Graphing: View logged values graphically in the field right on the meter, without a PC.
Monitoring two parameters at the same time: Dual display allows for monitoring of
two selectable parameters.
Performance testing: Testing the frequency response of amplifiers and audio
transmission line.
Working on VSDs: Take accurate voltage, current and frequency measurements on the
output side of the drive at either the drive itself or at the motor terminals.
Industrial troubleshooting: All of the resolution and accuracy you need to solve more
problems on motor drives, in-plant automation, power distribution, and electromechanical equipment.
Checking power quality: Capture glitches and spikes as short as 250 μs. Identify
irregular signals.
Take measurements in hard to reach places: With its removable display, you have
the flexibility to take measurements in hard to reach places or in areas with restricted
access. You can be in two places at once and reduce the risk of arc flash by separating
yourself from hazardous measurement situations.
289
287
87V
233
Fluke FC wireless
test tools work
together to help
you troubleshoot
faster
Wireless meters
Every day use
requiring true-rms,
accurate, rugged
meter
Every day use
requiring average
responding,
accurate, rugged
meter
General purpose meters
Work more productively: Now one person can complete a test that would have
required two people using ordinary test tools.
Work faster, safer and easier with FC Wireless Test Tools: The 3000 FC Multimeter
displays the meter measurement, plus readings from up to three wireless modules, connect
to your smart phone to see reading directly on your phone.
Build the system as your needs grow: Start with the multimeter and future proof
your investment.
Industrial troubleshooting: Applications requiring exceptional ease-of-use,
ruggedness and reliability.
Electrical maintenance and troubleshooting: Variety of commercial electrical
troubleshooting, installation and maintenance.
Temperature measurements: Built-in thermometer conveniently allows you to take
temperature readings without having to carry a separate instrument.
Industrial troubleshooting: Applications requiring exceptional ease-of-use,
ruggedness and reliability.
Electrical maintenance and troubleshooting: Variety of commercial electrical
troubleshooting, installation and maintenance.
3000
FC
179
77 IV
Page 6

Best for Applications Recommended DMM
Wide variety of electrical
work
Electrical maintenance troubleshooting: When you need to eliminate false or
“ghost” voltages or perform continuity, connection or basic wiring checks.
Non-contact voltage detection: Integrated non-contact voltage detection
simplifies many tasks.
117
HVAC troubleshooting Residential HVAC maintenance: Lower voltage HVAC residential maintenance,
installation and troubleshooting.
Temperature and microamp measurements: Troubleshooting problems with
HVAC equipment and flame sensors.
Electronic and field
service applications
Electronic troubleshooting: Troubleshoot a wide variety of measurement
parameters, including frequency and capacitance.
Compact meters
Utility applications
involving basic electrical
tests
Harsh environments
requiring dustproof and
waterproof test equipment
Revenue meter tests: Involving meter sets and reconnects, capacitor checks,
detection of absence or presence of voltage, and for continuity, connections or
basic wiring checks.
Simultaneous voltage and continuity checks: Check LoZ low impedance
function allows users to check voltage and continuity simultaneously.
Industrial troubleshooting in indoor and outdoor harsh environments:
Dustproof, waterproof, shockproof multimeter designed to withstand the
toughest environments.
116
115
113
28 II/
27 II
Working on VSDs: Take accurate voltage, current and frequency measurements
on the output side of the drive at either the drive itself or at the motor
terminals. (28 II only)
Industrial troubleshooting
in explosive environments
Safety and compliance: The Fluke 28 II Ex The Model MX57EX TRMS is an
intrinsically safe digital multimeter designed for use in dangerous or explosive
atmospheres. Agency Approvals: IECEx Ex ia IIC T4 Gb, Ex ia IIIC T130 °C Db, I
M1 Ex ia I Ma
Industrial troubleshooting: Completely sealed, IP67 rated case; Withstands
Specialty meters
drops up to 10 feet or 3 meters (with holster); Dustproof per IEC60529 IP6x;
Waterproof per IEC60529 IPx7; Meets IEC Overvoltage Electrical Safety
Standard No. 61010-1:2001
Fluke. Keeping your world up and running.
Fluke Corporation
PO Box 9090, Everett, WA 98206 U.S.A.
Fluke Europe B.V.
PO Box 1186, 5602 BD
Eindhoven, The Netherlands
For more information call:
In the U.S.A. (800) 443-5853 or
Fax (425) 446-5116
In Europe/M-East/Africa +31 (0) 40
2675 200 or Fax +31 (0) 40 2675 222
In Canada (800)-36-FLUKE or
Fax (905) 890-6866
87V Ex
®
From other countries +1 (425) 446-5500 or
Fax +1 (425) 446-5116
Web access: http://www.fluke.com
©2008-2014 Fluke Corporation.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
Printed in U.S.A. 3/2012 3272127C-en
Modification of this document is not permitted
without written permission from Fluke Corporation.
 Loading...
Loading...