Page 1

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
with HART to Modbus Converter
Safety Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-2
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-3
Workflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-3
Mechanical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-4
Electrical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-4
Establish HART Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-10
Transmitter Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-13
Modbus Communication Protocol Configuration . . . . . .page 1-14
Alarm Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-22
Common Modbus Host Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-25
Specific Modbus Host Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . page 1-30
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-34
HMC Firmware Upgrade in Rosemount Radar Master . .page 1-35
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .page 1-40
This instruction is a supplement to the Rosemount 5300 Series Reference
Manual (Document No. 00809-0100-4530), and the Rosemount 5400 Series
Reference Manual (Document No. 00809-0100-4026).
www.rosemount.com
Page 2
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
October 2010
SAFETY MESSAGES Procedures and instructions in this section may require special precautions to
ensure the safety of the personnel performing the operations. Information that
raises potential safety issues is indicated by a warning symbol ( ). Please
refer to the following safety messages before performing an operation
preceded by this symbol.
Failure to follow safe installation and service guidelines could result in death or
serious injury
• Make sure the transmitter is installed by qualified personnel and in accordance
with applicable code of practice.
• Use the equipment only as specified in the Rosemount 5300 Series Reference
Manual (Document No. 00809-0100-4530), the Rosemount 5400 Series
Reference Manual (Document No. 00809-0100-4026), and in this Manual
Supplement. Failure to do so may impair the protection provided by the
equipment.
• Do not perform any services other than those contained in this manual unless
you are qualified.
Explosions could result in death or serious injury
• Verify that the operating environment of the transmitter is consistent with the
appropriate hazardous locations specifications.
• To prevent ignition of flammable or combustible atmospheres, disconnect
power before servicing.
®
• Before connecting a HART
an explosive atmosphere, make sure the instruments in the loop are installed in
accordance with intrinsically safe or non-incendive field wiring practices.
• To avoid process leaks, only use o-ring designed to seal with the
corresponding flange adapter.
Electrical shock can result in death or serious injury
• Avoid contact with the leads and terminals. High voltage that may be present
on leads can cause electrical shock.
• Make sure the main power to the Rosemount 5300 Series transmitter or
Rosemount 5400 Series transmitter is off and the lines to any other external
power source are disconnected or not powered while wiring the transmitter.
Probes with non-conducting surfaces
• Probes covered with plastic and/or with plastic discs may generate an
ignition-capable level of electrostatic charge under certain extreme conditions.
Therefore, when the probe is used in a potentially explosive atmosphere,
appropriate measures must be taken to prevent electrostatic discharge.
or FOUNDATION™ fieldbus based communicator in
1-2
Page 3
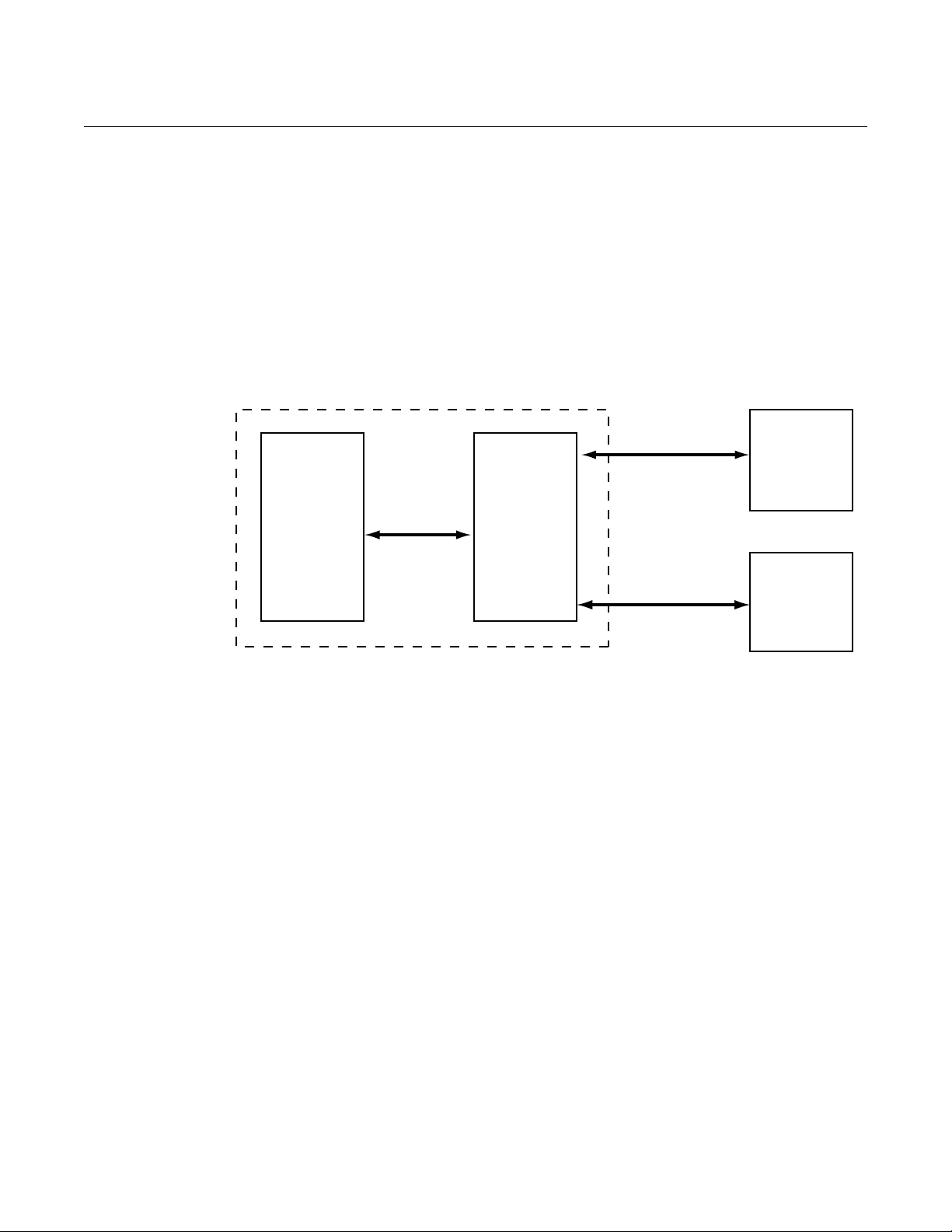
Manual Supplement
5300/5400
transmitter
electronics
HART
signals
HART to
Modbus
Converter
Modbus and
Levelmaster
communication
Remote
Terminal
Unit
Rosemount
Radar Master/
Field
Communicator
HART signals
5300/5400 transmitter enclosure
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
INTRODUCTION The Rosemount 5300 Series and Rosemount 5400 Series transmitters are
Modbus compatible measurement devices that support commun ication with a
Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) using a subset of read, write, and diagnostic
commands used by most Modbus compatible host controllers. The
transmitters also support communication through Levelmaster and Modbus
ASCII protocols.
®
The HART
Rosemount 5300 and Rosemount 5400 transmitter enclosure and provides
power to and communicates with the transmitter through a HART interface.
Figure 1-1. System Overview
to Modbus Converter (HMC) module is located inside the
During normal operation, the HMC “mirrors” the conten t s of process var iables
from the 5300/5400 transmitter to the Modbus registers. To configure the
5300/5400 transmitter, it is possible to connect a configuration tool to the
HMC. See “Transmitter Configuration” on page 1-13 for more information.
WORKFLOW Overview of workflow for commissioning a Rosemount 5300 or a Rosemount
5400 transmitter with Modbus protocol:
1. Mount the transmitter on the tank.
2. Connect the power and communication wires.
3. Establish HART communication with the transmitter through Rosemount
Radar Master , or a Field Communicator. This is done by:
• Connecting to the HART terminals, or
• Connecting to the MA/MB terminals (tunneling mode)
4. Configure the transmitter.
5. Configure the Modbus communication.
6. Configure Modbus host.
7. Verify output values as reported by the transmitter.
1-3
Page 4

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
For instructions on how to mount the Rosemount 5300/5 400 transmitter, refer
to the Rosemount 5300 Series Reference Manual (Document No.
00809-0100-4530), and the Rosemount 5400 Series Reference Manual
(Document No. 00809-0100-4026).
NOTE
For general electrical installation requirements, including grounding
requirements, refer to Rosemount 5300 Series Refere nce Manual (Document
No. 00809-0100-4530), and the Rosemo un t 54 00 Seri es Re fe re nc e Ma n ua l
(Document No. 00809-0100-4026).
To connect the Rosemount 5300/5400:
1. Disconnect/shut off the electrical power to transmitter head and then
open the instrument cover. Do not remove the cover in an explosive
atmosphere with a live circuit.
2. Pull the cable through the cable gland/conduit. For the RS-485 bus, use
shielded twisted pair wiring, preferably with an impedance of 120
(typically 24 AWG) in order to comply with the EIA-485 standard and
EMC regulations. The maximum cable length is 4000 ft/1200 m.
3. Make sure that the transmitter housing is grounded, then connect wires
according to Figure 1-2 and Table 1-1. Connect the lead that originates
from the “A” line from the RS-485 bus to the terminal marked MB, and
the lead that originates from the “B” line to the terminal marked MA.
4. If it is the last transmitter on the bus, connect the 120 termination resistor.
5. Connect the leads from the positive side of the power supply to the
terminal marked POWER +, and the leads from the negative side of the
power supply to the terminal marked POWER -. The power supply
cables must be suitable for the supply volt age and ambien t temperatur e,
and approved for use in hazardous areas, where applicable.
6. Attach and tighten the housing cover. Tighten the cable gland, then plug
and seal any unused terminals, and connect the power supply.
1-4
Page 5
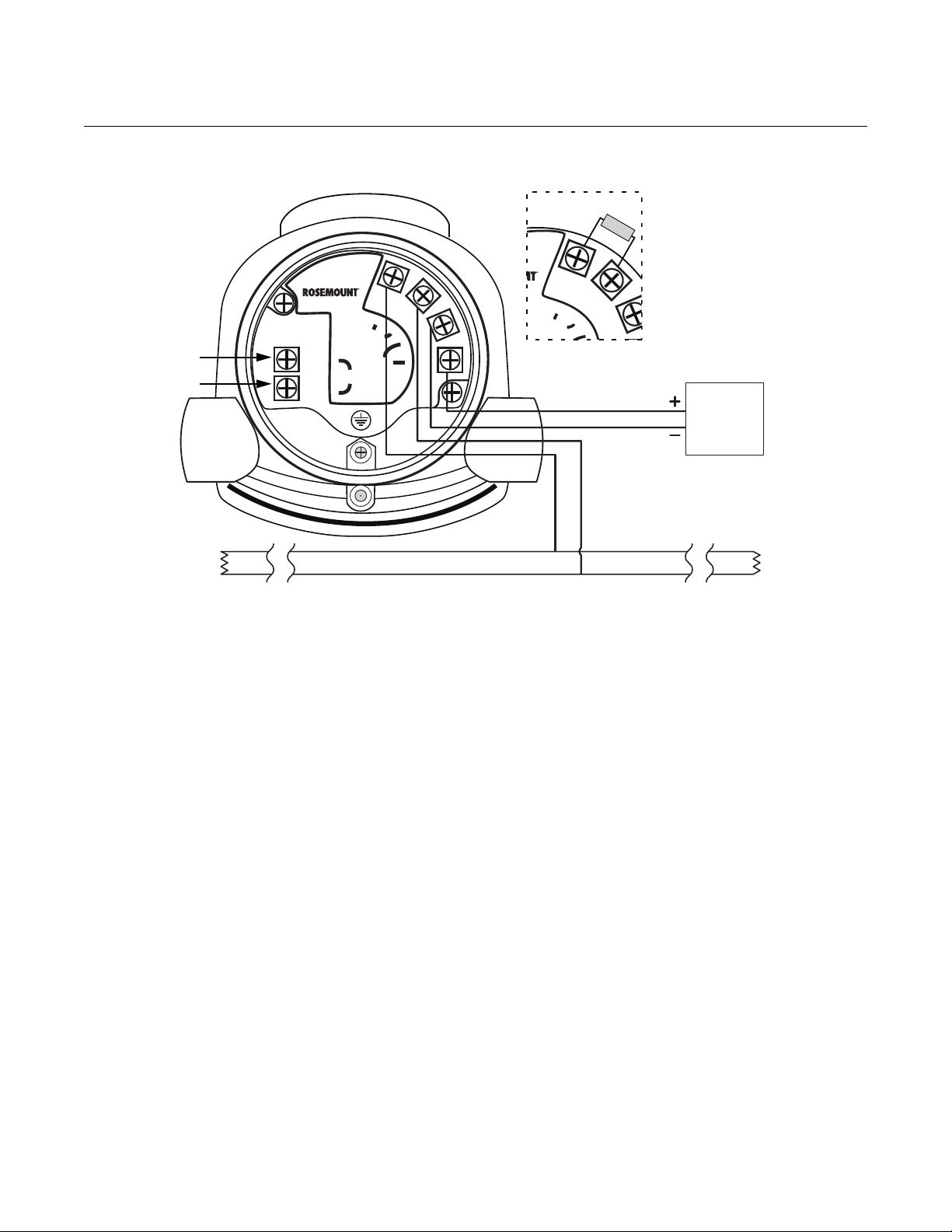
Manual Supplement
RS-485 Bus
B
A
Power
Supply
HART
+
HART -
120
120
In case it is the last
transmitter on the
bus, connect the
120
termination
resistor
v
120
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Figure 1-2. Field Wiring Connections
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
HART to Modbus Converter
-
HART
+
MODBUS
(RS-485)
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
erter
MB
MB
MA
-
+
MODBUS
(RS-485)
MA
-
1-5
Page 6
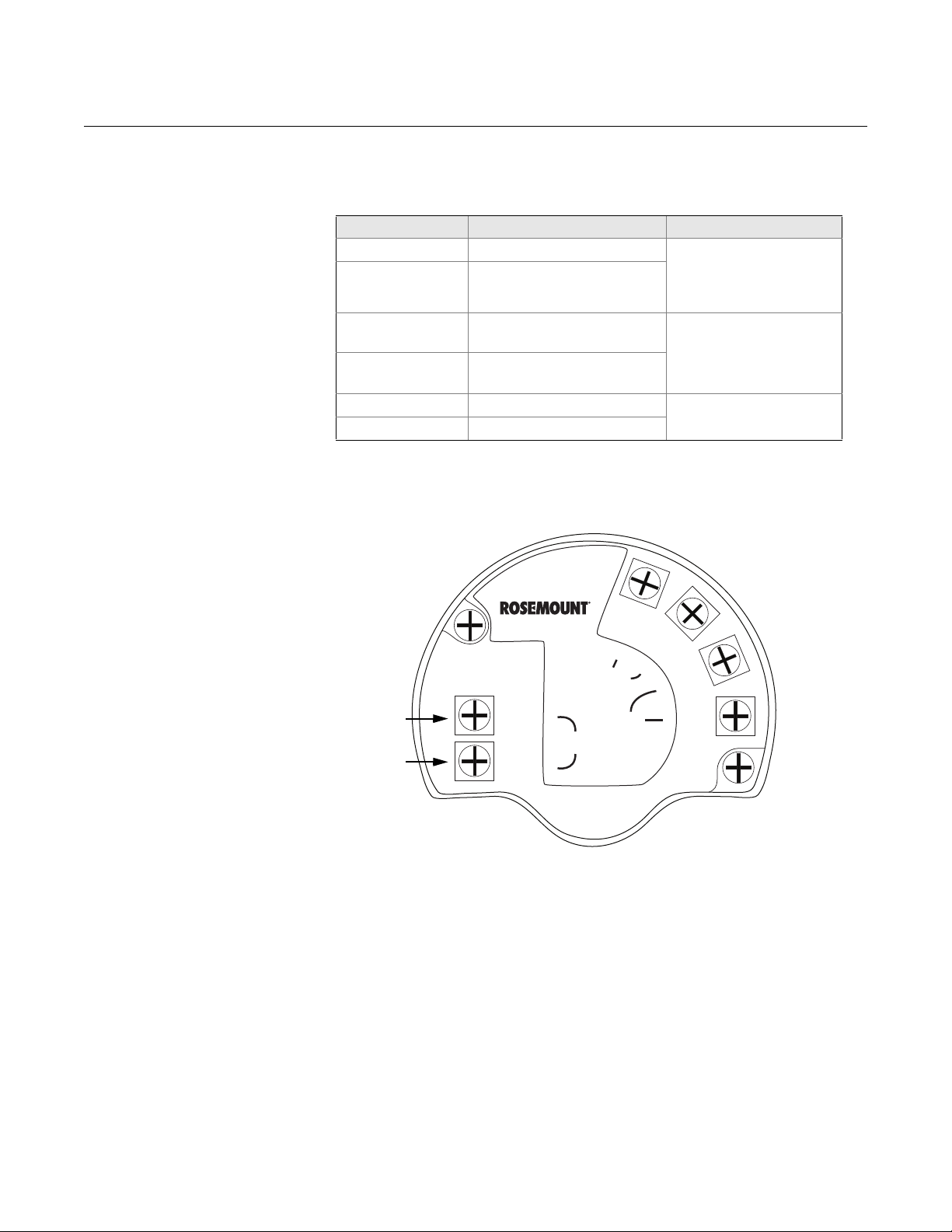
Manual Supplement
MODBUS
POWER
HART
(RS-485)
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
-
-
+
+
HART +
HART -
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Connection Terminals The connection terminals are described in Table 1-1 below:
Table 1-1. Connection Terminals
Connector label Description Comment
HART + Positive HART connector Connect to PC with RRM
software, Field
HART - Negative HART connector
MA
MB
Modbus RS-485 B connection
(RX/TX+)
Modbus RS-485 A connection
(RX/TX-)
(1)
(1)
POWER + Positive Power input terminal
POWER - Negative Power input terminal
(1) The designation of the connectors do not follow the EIA-485 standard, which states
that RX/TX- should be referred to as 'A' and RX/TX+ as 'B'.
Communicator, or other
HART configurators.
Connect to RTU
Apply +8 Vdc to +30 Vdc
(max. rating)
October 2010
Figure 1-3. Connection Terminals
for Rosemount 5300/5400 with
HART to Modbus Converter
1-6
Page 7
Manual Supplement
MODBUS
POWER
HART
(RS-485)
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
-
-
+
+
MODBUS
POWER
HART
(RS-485)
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
-
-
+
+
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
Power
Supply
120
120
RS-485 Bus
BAModbus
Master
Z
External
Ground Screw
Internal
Ground Screw
External
Ground Screw
Internal
Ground Screw
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
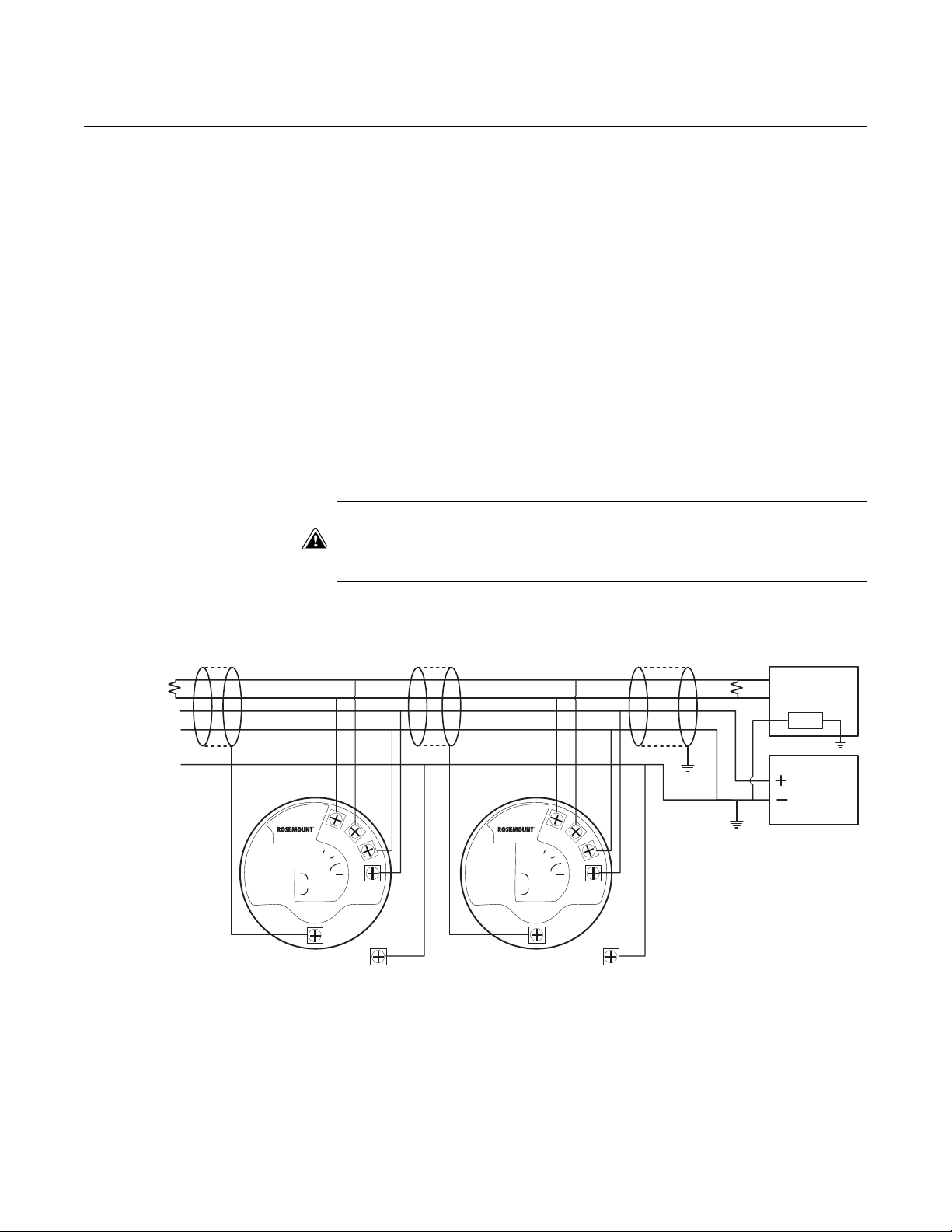
RS-485 Bus • The 5300/5400 transmitters do not provide electrical isolation between
the RS-485 bus and the transmitter power supp ly
• Maintain a bus topology and minimize stub length
• Figure 1-4 identifies multidrop wiring topology, where up to 32 devices
may be wired on one RS-485 bus
• The RS-485 bus needs to be terminated once at each end, but should
not be terminated elsewhere on the bus
Installation cases Install the Rosemount 5300/5400 Series Transmitters as shown in Figure 1-4.
• Use common ground for Modbus Master and Power Supply
• The Power cables and RS-485 Bus are in the same cable installation
• An ground cable is installed and shall be used (cable size ≥4 mm
according to IEC60079-14, or size according to applicable national
regulations and standards). A properly installed threaded conduit
connection may provide sufficient ground.
• The cable shielding is grounded at master site (optional)
NOTE
The HMC equipped transmitter contains intrinsically safe circuits that require
the housing to be grounded in accordance with national and local electrical
codes. Failure to do so may impair the protection provided by the equipment.
Figure 1-4. Multidrop Connection of
5300/5400 Transmitters
1-7
Page 8
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Power
Supply
120
120
RS-485 Bus
BAModbus
Master
Z
External
Ground Screw
External
Ground Screw
Internal
Ground Screw
Internal
Ground Screw
v
For Star Topology
connection,
connect the 120
termination
resistor to the
transmitter with
the longest cable
run.
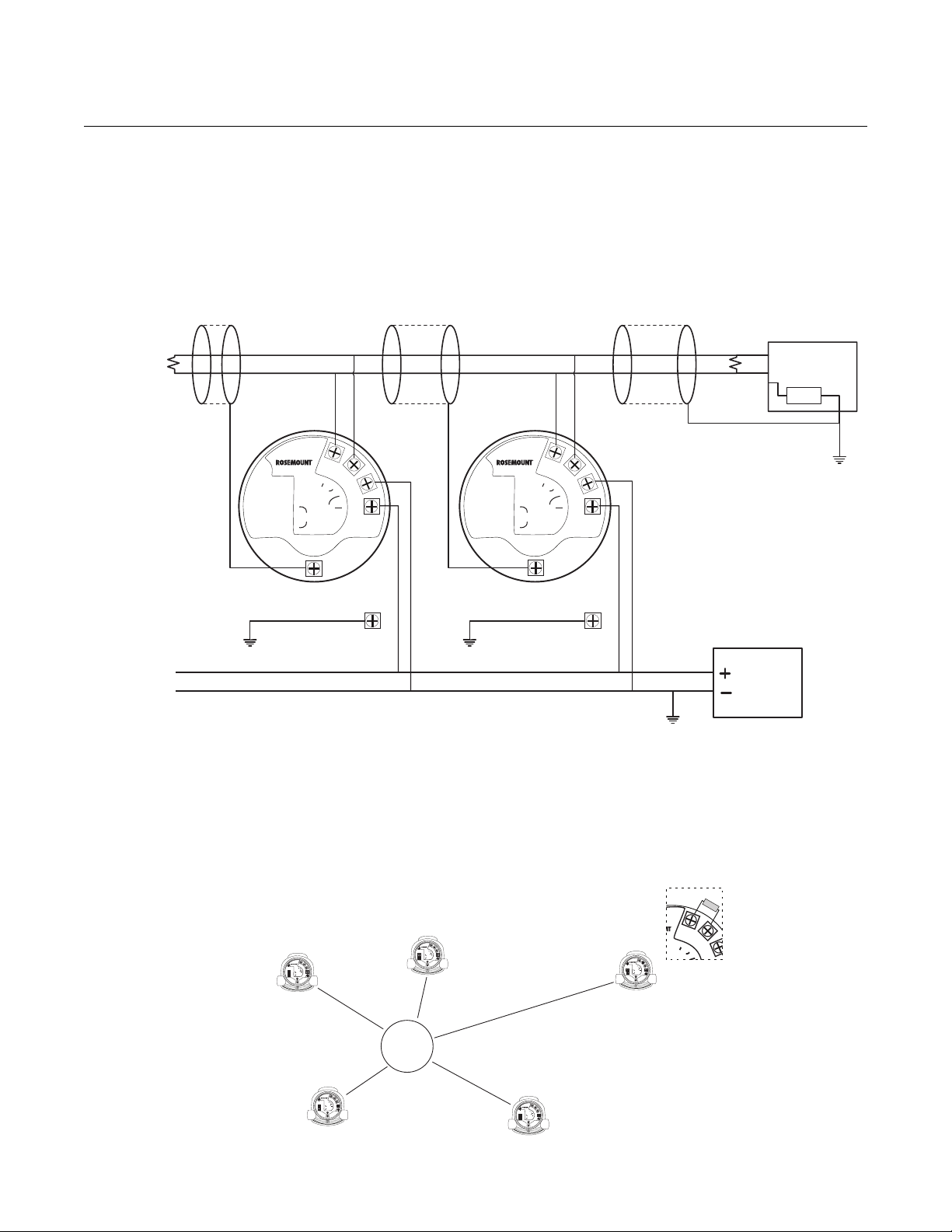
Alternatively, the Rosemount 5300/5400 Series Transmitters can be installed
as shown in Figure 1-5. If this wiring layout is used, there is an increased risk
for communication disturbances due to differences in potential between
grounding points. By using the same grounding point for Modbus Master and
Power Supply, this risk is reduced.
Figure 1-5. Alternative Multidrop
Connection of 5300/5400
Transmitters
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Figure 1-6. Star Topology
Connection of 5300/5400
Transmitters
HART to Modbus Converter
-
HART
+
HART to Modbus Converter
-
HART
+
MODBUS
(RS-485)
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
MB
MA
-
+
MODBUS
(RS-485)
MB
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
MA
-
+
Star Topology
For a St ar Topology Connection of the 5300/5400 transmitters, the transmitter
with the longest cable run needs to be fitted with a 120- termination resistor.
erter
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
-
+
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
HART
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
-
+
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
HART
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
+
+
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
-
+
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
HART
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
+
-
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
-
+
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
HART
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
+
1-8
HART to Modbus Converter
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
-
+
POWER
Ambients > 60 ºC
HART
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
+
Page 9
Manual Supplement
Power
Supply
RS-485
Bus
Up to four
external
devices
External HART
device 2
External HART
device 1
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
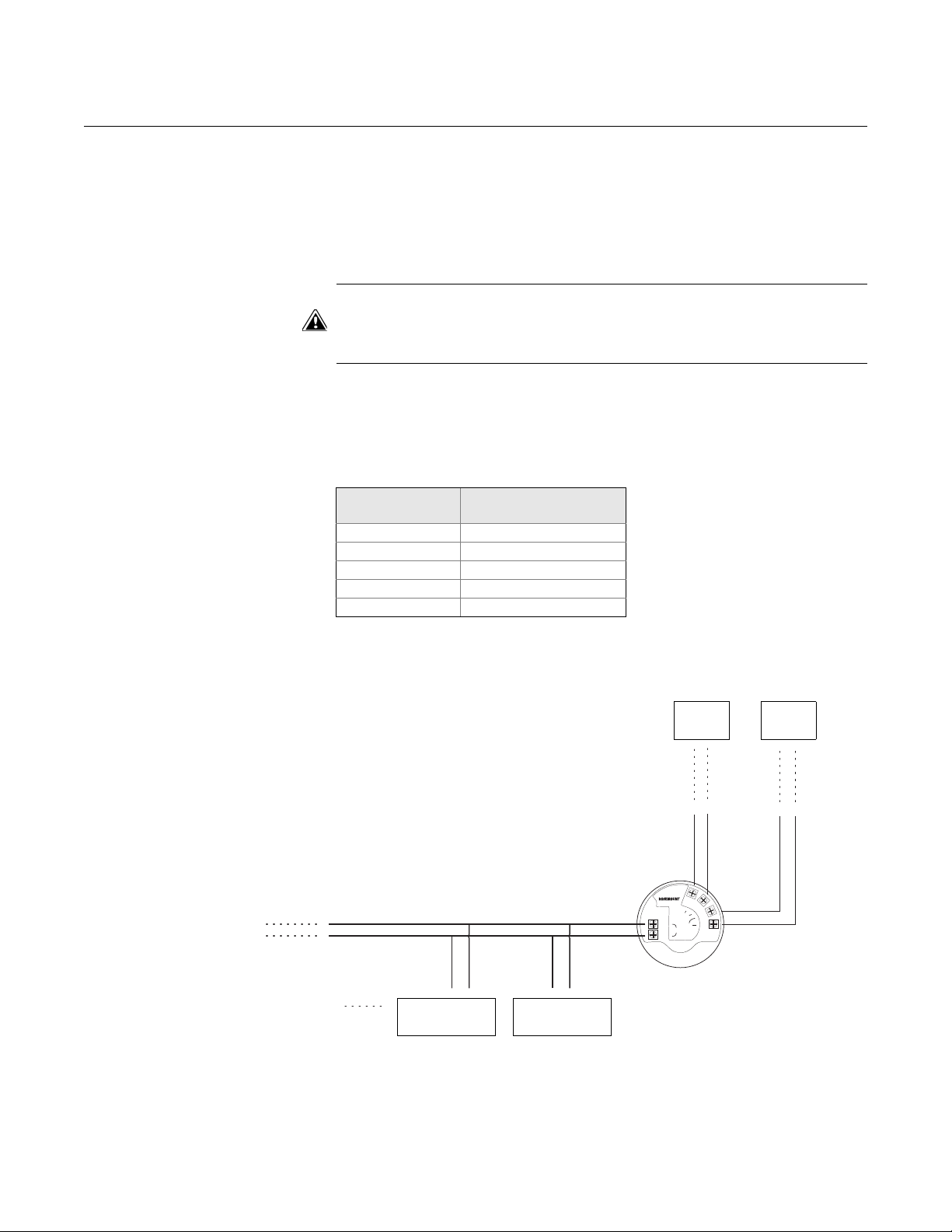
External HART Devices (Slaves)
Table 1-2. Approximate update
rates for measurement values
The HMC supports up to four external HART devices. The external devices
are separated by using the HART address. The address must be different
between the external devices and only addr e sse s 1 to 5 are allo we d for
multiple slaves. Connect the devices one at a time and change the short
address prior to connecting the next device by using a HART Configuration
Tool such as RRM, or a Field Communicator.
NOTE
The power supply from the HMC to external HART devices is not intrinsically
safe. In a hazardous environment, any exter n al HA RT device conn ec te d to
the HMC must have Flameproof/Explosion-proof certification.
The HMC cyclically polls the HART devices for measurement values. The
update rate depends on the number of connected devices and is shown in
Table 1-2.
No. of devices
(slaves)
1 2 seconds
2 3 seconds
3 4 seconds
4 5 seconds
5 5 seconds
Approx. update rate
Figure 1-7. The HMC Module
supports up to four external devices
(slaves)
HART to Modbus Converter
-
+
MB
MA
MODBUS
(RS-485)
-
+
POWER
HART
Ambients > 60 ºC
Use wiring rated
for min 90 ºC
1-9
Page 10
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
HART
20 seconds
Modbus RTU
20 seconds
Configured
protocol
(Modbus RTU,
Levelmaster,
or Modbus
ASCII)
20 seconds
HART
20 seconds
Time
0 s 20 s 40 s 60 s 80 s 100 s
Configured
protocol
(Modbus RTU,
Levelmaster,
or Modbus
ASCII)
20 seconds
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
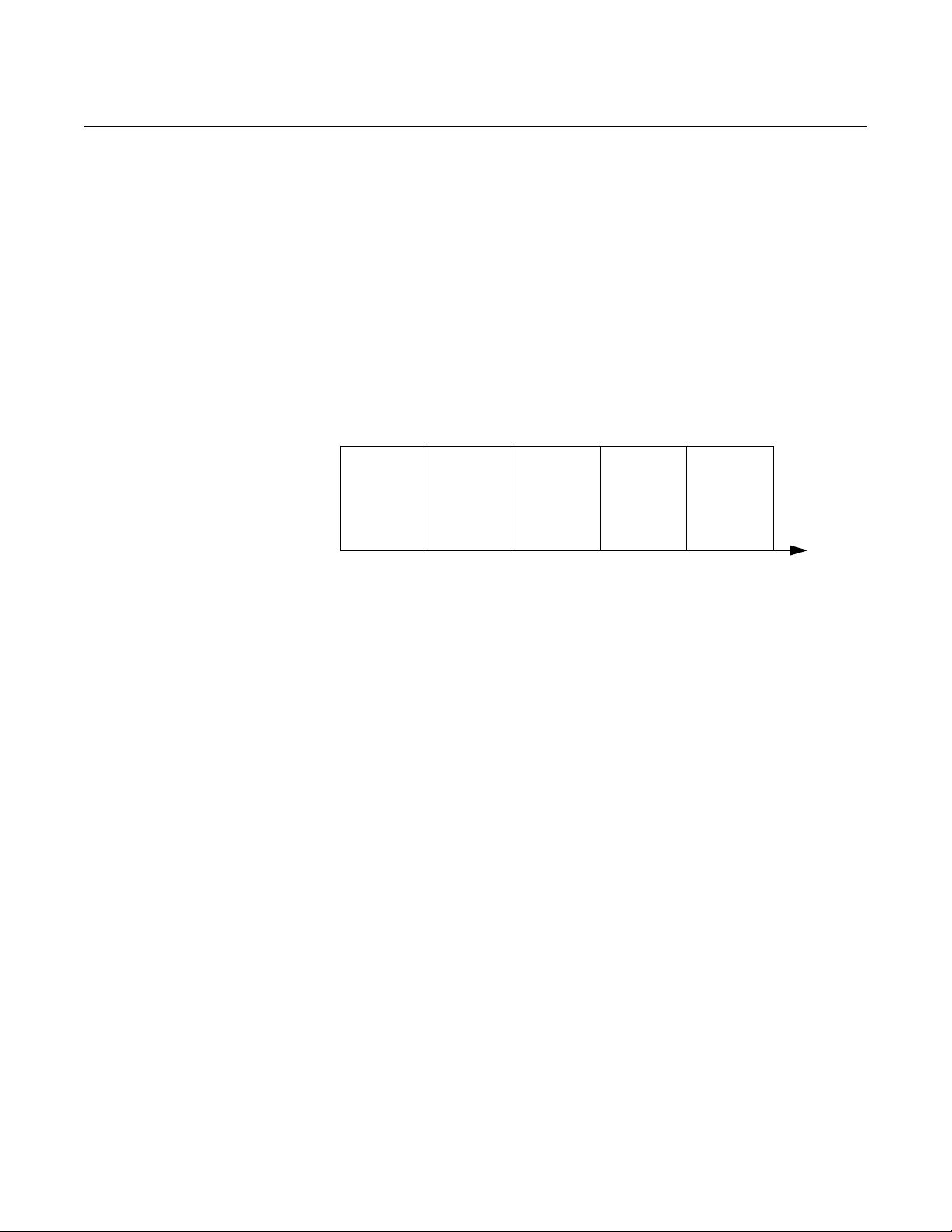
ESTABLISH HART COMMUNICATION
Connect to the MA/MB terminals
Figure 1-8. RS-485 Communication
after startup
The Rosemount 5300 Series and Rosemount 5400 Series can be configured
using the Rosemount Radar Master (RRM) PC software or a Field
Communicator. Configuration is done by sending HART commands through
the HART to Modbus Converter (HMC) to the 5300/5400 transmitter
electronics. To establish HART communication, connect to the MA/MB
terminals, or to the HART terminals. Both alternatives are desc rib ed belo w.
The 5300/5400 level transmitter can be configured with RRM using the MA,
MB terminals.
An RS-485 Converter is required to connect to the transmitter.
The transmitter will try to establish communication using different protocols
during 20 second timeslots from time of startup.
The transmitter will continue to use a communication protocol once
communication has been established.
1-10
Page 11
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
To configure the 5300/5400 level transmitter using RRM and the MA, MB
terminals, do the following:
1. Connect the RS-485 Converter to the MA, MB connectors.
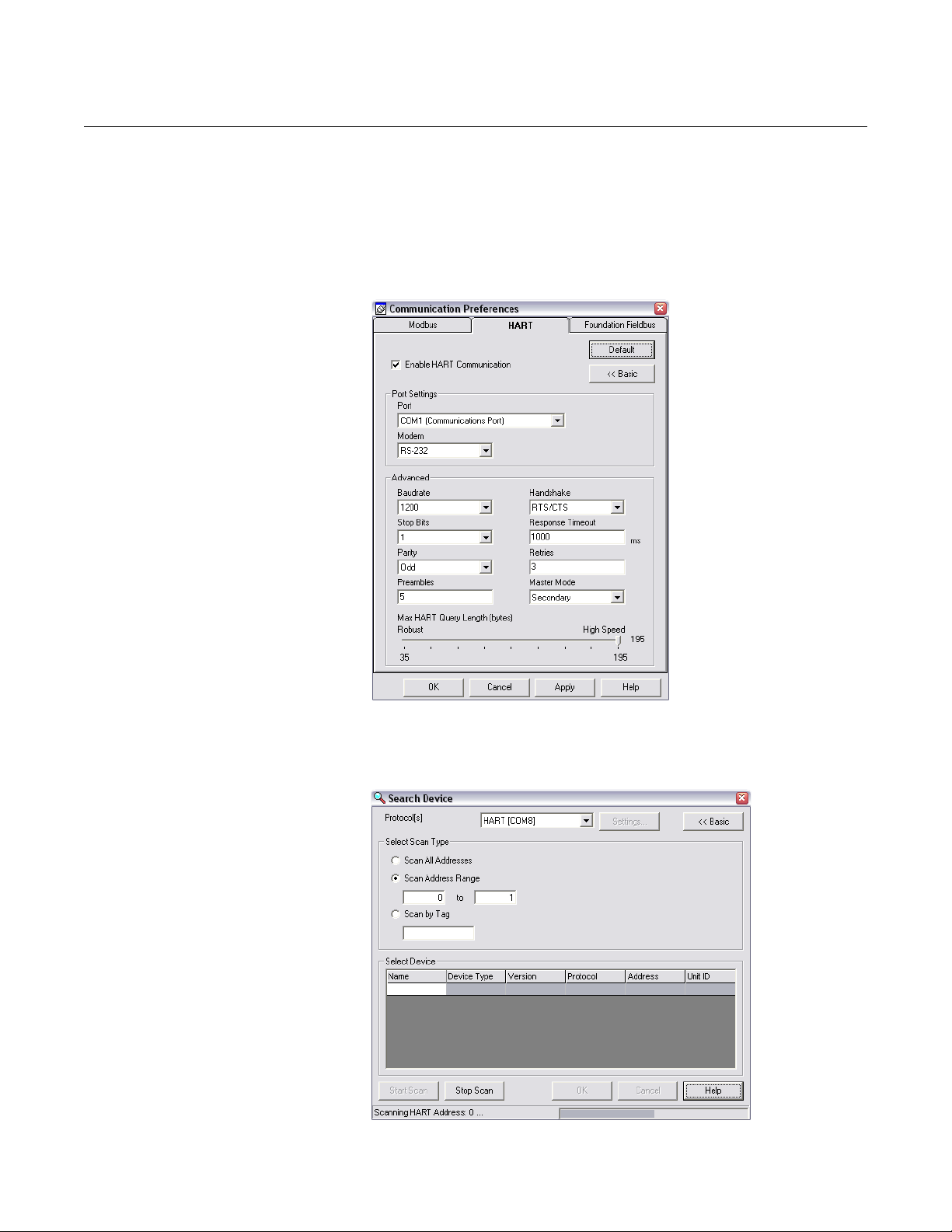
2. Start RRM and open Communication Preferences.
3. Enable HART communication and make sure the port for the RS-485
Converter is selected. Use the following settings:
4. Connect the power wires (or cycle power) to the transmitter.
5. Wait 20 seconds and then open the Sea rch Device windo w in RRM (also
see note below). Make sure HART address 1 is being scanned.
1-11
Page 12

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
6. Connect to the transmitter and perform the necessary configuration.
7. After completing the configuration, disconnect the RS-485 Converter,
connect the Modbus communication wires and cycle power to the
transmitter
8. Verify communication between the transmitter and the RTU is
established (can take up to 60 seconds from startup) .
NOTE
Take the following into consideration if there are multiple 5300/5400 Modbus
units on the bus:
By default, the transmitters have HART address 1. It will not be possible to
establish communication on HART address 1 if several transmitters have the
same address. In this case, there are alternative solutions to establish
communication:
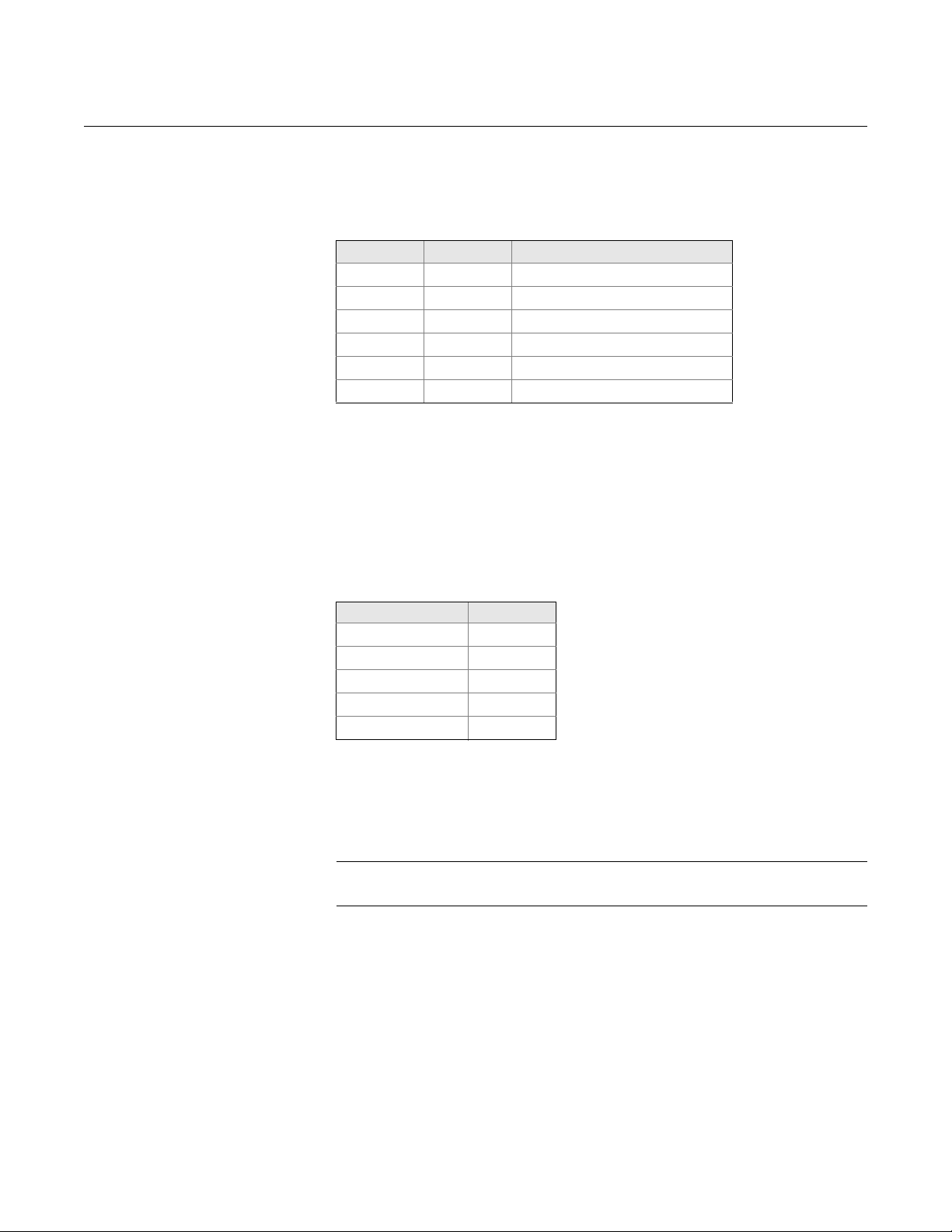
1. Select the Scan by T ag option in the Search Device window in RRM and
enter the HART Device Tag of the transmitter. Communication can now
be established with an individual transmitter even if several devices have
the same HART address.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Connect to the HART terminals
1-12
2. Make sure the 5300/5400 transmitter is alone on bu s. Disconnect or tur n
off power from any other devices.
To configure the 5300/5400 transmitter, connect the communicator or PC to
the HART terminals using a HART modem, see Figure 1-3 on p a ge 1-6. Both
the configuration tool and the RS-485 bus can be connected simultaneously.
Configuration data is sent with HART commands through the HMC to the
5300/5400 transmitter electronics, as illustrated in Figure 1-1 on page 1-3.
Note that the power supply must be connected during configuration, see also
“Electrical Installation” on page 1-4.
NOTE
Measurement data is not updated to the Modbus Master when a configur ation
tool is connected.
Page 13

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
TRANSMITTER CONFIGURATION
Configuration data such as Tank Height, Upper Null Zone, dielectric
constants, and other basic parameters are configured in the same way as for
a standard Rosemount 5300/5400 transmitter. For more information, see the
Rosemount 5300 Series Quick Installation Guide (Document No.
00825-0100-4530), and the Rosemount 5400 Series Quick Installation Guide
(Document No. 00825-0100-4026).
Make sure that the measurement unit of the Primary Variable (PV) matches
the configuration of the Modbus Host since the transmitter output value does
not include any information on associated measurement units.
For further information on basic configuration, see the Rosemount 5300
Series Reference Manual (Document No. 00809-0100-4530), and the
Rosemount 5400 Series Reference Manual (Document No.
00809-0100-4026).
NOTE
The 5300/5400 transmitter with Modbus protocol is configured to HART
address 1 at factory. This reduces power consumption by locking the analog
output at 4 mA.
1-13
Page 14

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL CONFIGURATION
Table 1-3. List of RTUs’ Supported
Protocols
The Rosemount 5300/5400 level transmitter can communicate with RTUs
using Modbus RTU (often referred to as just “Modbus”), Modbus ASCII, and
Levelmaster (also known as “ROS,” “Siemens,” or “Tank” protocol).
RTU Protocols
ABB Totalflow Modbus RTU, Levelmaster
Bristol ControlWave Micro Modbus RTU
Emerson Process
Management ROC800 Series
Emerson Process
Management FloBoss 107
Kimray DACC 2000/3000 Levelmaster
ScadaPack Modbus RTU
Thermo Electron Autopilot Modbus RTU, Levelmaster
(1) Levelmaster protocol should be used when using the Emerson
Process Management Digital Level Sensor (DLS) User Program
or Application Module together with the device. Use Modbus
RTU in other cases.
Modbus RTU, Levelmaster
Modbus RTU, Levelmaster
(1)
(1)
Modbus ASCII is not commonly used, since it doubles the amount of bytes
for the same message as the Modbus RTU.
Using RRM to change communication parameters
If you do not have any of these RTUs, check your RTU manual to see which
protocols it supports.
NOTE
To change Modbus communication parameters, the Rosemount 5300/5400
must use HART address 1, the default address.
NOTE
After changing communication pa rameters, disconnect th e HART modem a nd
wait at least 60 seconds for the change to take effect.
In case the MA/MB terminals are used for connection to the HMC, disconnect
the RS-485 Converter, cycle power to the transmitter and wait up to 60
seconds for the change to take effect.
1-14
Page 15

Manual Supplement
Modbus Setup
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
To change the Modbus address and communication parameters in
Rosemount Radar Master (RRM):
1. Start RRM and connect to the transmitter.
2. In RRM, select Setup>General.
3. Select the Communication tab.
4. Click the Modbus Setup button.
5. In the Modbus Setup window, select Modbus protocol and type the
desired Modbus address.
6. Enter the baud rate, parity, and stop bits, then click the OK button.
It is also possible to enter a user-defined Modbus Message in the Modbus
String area.
See separate sections below for more details regarding each Modbus
protocol.
1-15
Page 16

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Using a Field Communicator to change communication parameters
Modbus RTU Communication Setup
Table 1-4. Modbus RTU
Communication Parameters
NOTE
To change Modbus communication parameters, the Rosemount 5300/5400
must use HART address 1, the default address.
NOTE
After changing communication parameters, disconnect the Field
Communicator and wait up to 60 seconds for the change to t ake effect.
The Modbus communication parameters can be changed by enter ing a text
string in the HART Message parameter. See separate sections below for
details regarding each Modbus protocol and what strings to use.
When using the Field Communicat or, the Message Area is reached using
HART command [2,2,1], and then selecting Message (menu item 11 for
Rosemount 5300 and menu item 10 for Rosemount 5400).
The Rosemount 5300/5400 is configured with the default Modbus RTU
address 246, and with the following Modbus RTU communication parameter
default settings:
Parameter Default Value Configurable Values
Baud Rate 9600 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200
(1)
Start Bits
Data Bits
Parity None None, Odd, Even
Stop Bits One One or Two
Address
range
(1) Start Bits and Data Bits cannot be changed.
One One
(1)
Eight Eight
246 1-255
Table 1-5. Communication
Parameters Used by the Host
(example)
1-16
To reset the communication parameters to default M odbus RTU settings, use
the following Modbus Message:
HMC
Modbus RTU Parameter Configuration Example
You want to use address 44 for the 5300/5400 transmitter, and the following
communication parameters are used by the host:
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 4800
Start Bits One
Data Bits Eight
Parity Odd
Stop Bits Two
Page 17

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
To configure the 5300/5400 transmitter to communicate with the Host in this
example, the following text string is written to the HART Slave 1 Message
Area:
HMC A44 B4800 PO S2.
HMC: These three letters are used for safety and will eliminate the risk of
changing the configuration data by mistake.
A44: A indicates that the following number is the new address (address 44).
Leading zeroes are not needed.
B4800: B indicates that the following number is the new baud rate (1200,
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200).
PO: P identifies the following letter as parity type (O = odd, E = even, and
N = none).
S2: S indicates that the following figure is the number of stop bits (1 = one,
2 = two).
Only values that differ from the current values need to be included. For
example, if only the address is changed, the following text string is written into
the 5300/5400 (HART Slave 1) Message Area:
Levelmaster Communication Setup
Table 1-6. Levelmaster
Communication Parameters
HMC A127,
indicates that 127 is the new address.
The default and configurable parameter values can be found in Table 1-6.
Parameter Default value Configurable value
Baud Rate 9600 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200
Start Bits One One
Data Bits Seven Seven, Eight
Parity None None, Odd, Even
Stop Bits One One or Two
Address 1 1-99
To reset the communication parameters to default Levelmaster settings, use
the following Modbus Message:
HMC M2
1-17
Page 18

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Levelmaster Parameter Configuration Example
You want to use address 2 for the 5300/5400 transmitter and the host uses
the following parameters:
Table 1-7. Parameters Used by the
Host (in case of Levelmaster,
example)
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Start Bits One
Data Bits Seven
Parity None
Stop Bits One
To configure the 5300/5400 transmitter to communicate with the Host in this
example, the following text string is written to the Modbus Message area.
HMC M2 A2 B9600 D7 PN S1.
NOTE
Include all the parameters when writing to the message area.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Note that an address must be unique on the bus.
HMC: These three letters are used for safety and will eliminate the risk of
changing the configuration data by mistake.
M2: This means that the Levelmaster protocol is to be used.
A2: A indicates that the following is the new address (address 2). Leading
zeroes are not needed.
B9600: B indicates that the following number is the new baud rate (1200,
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200).
D7: D indicates that the following data bits are to be used (7 = seven,
8 = eight).
PN: P identifies the following letter as parity type (O = odd, E = even, and
N = none).
S1: S indicates that the following figure is the number of stop bits (1 = one,
2 = two).
Note: Start Bits are not configurable and cannot be set.
1-18
Page 19

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Table 1-8. Implemented Functions
of Levelmaster Protocol
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
In Table 1-8 and Table 1 -9 is a desc rip tio n of th e impl e me nted fun ct i on s of
Levelmaster protocol in the HMC.
Input format Description Output format
UnnN?
UnnNmm
UnnF?
UnnFx?
Unn?
(1) In this case, number of floats is set to 1. If number of floats is set to 2, the Output Format
would be: UnnDddd.ddDddd.ddFfffEeeeeWwwwCcccc
NOTE
If one float is sent, it is “Float1”. If two floats are sent, it is “Float 1” before
“Float 0”.
Return ID number
Set ID number
Return number of floats
Set number of floats
Return floats and other data
UnnNnnCcccc
UnnNOKCcccc
UnnFxCcccc
UnnFOKCcccc
UnnDddd.ddFfffEeeee
WwwwCcccc
(1)
Table 1-9. Letters and Expressions
Used in Previous Tables
Letter Description
nn is used to identify slave to respond,
nn
nn is a number 00-99 or ** (wildcard).
The EmulCtrl Address Holding register can be configured to a higher
value than 99. In that case, the address will be truncated to 99.
mm
x
mm is the new ID number for the slave; mm is a number 00-99
x is the number of floats returned when slave receives Unn?, x is a
number 0-2.
.
cccc Is the 16 bit CRC checksum, cccc are hexadecimal characters.
ddd.dd
ddd.dd is the distance value from slave 1. Note that the first d can also be
a ‘-’ (minus).
Float 1 Slave 1 PV.
Float 0 Slave 1 SV.
fff The temperature value. Configured by Holding Register 3208 in HMC.
An error value.
eeee
Bit 0: Invalid SV value (Float 0).
Bit 8: Invalid Temperature value.
Bit 12: Invalid PV value (Float 1)
.
Wwww A warning value, not used in this implementation.
(1) Any of the four available variables from any of the five HART slaves can be selected as
the temperature source.
The least four significant bits (bit 0-3) select the variable number. Bits 4-7 select the HART
slave address. If invalid values are used, the temperature value will be invalid, with no
Error bit set.
For example, if we want to use FV from HART Slave 3 as temperature source, we have
to write the value 34 Hex (52 decimal).
(1)
1-19
Page 20
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Modbus ASCII Communication Setup
Table 1-10. Modbus ASCII
Communication Parameters
Table 1-11. Parameters Used by
the Host (in case of Modbus ASCII,
example)
The parameter, default, and configurable values are shown in Table 1-10
below.
Parameter Default value Configurable values
Baud Rate 9600 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200
Start Bit s One One
Data Bits Seven Seven, Eight
Parity None None, Odd, even
Stop Bits One One or Two
Address 1 1-255
To reset the communication parameters to default Modbus ASCII settings,
use the following Modbus Message:
HMC M1
Modbus ASCII Parameter Configuration Example
You want to use address 246 for the 5300/5400 transmitter and the h ost uses
the following parameters:
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Start Bits One
Data Bits Seven
Parity None
Stop Bits One
1-20
To configure the 5300/5400 transmitter to communicate with the Host in this
example, the following text string is written to the Modbus Message area.
HMC M1 A246 B9600 D7 PN S1.
NOTE
Include all the parameters when writing to the message area.
Note that an address must be unique on the bus.
HMC: These three letters are used for safety and will eliminate the risk of
changing the configuration data by mistake.
M1: This means that the Modbus ASCII protocol is to be used.
A246: A indicates that the following number is the new address (address
246). Leading zeroes are not needed.
B9600: B indicates that the following number is the new baud rate (1200,
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200).
Page 21

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
D7: D indicates that the following data bits are to be used (7 = seven,
8 = eight).
PN: P identifies the following letter as parity type (O = odd, E = even, and
N = none).
S1: S indicates that the following figure is the number of stop bits (1 = one,
2 = two).
Note: Start Bits are not configurable and cannot be set.
1-21
Page 22

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Modbus Setup
ALARM HANDLING NOTE
If the Modbus communication setup has been changed, but the transmitter
has not yet started to use the new configuration, then yo u need to disconnect
the HART modem and wait up to 60 seconds for the change to take effect.
In case the MA/MB terminals are used for connection to the HMC, disconnect
the RS-485 Converter, cycle power to the transmitter and wait up to 60
seconds for the change to take effect.
The Modbus communication settings will otherwise be lost if you write a new
message to the transmitter.
The output from the Modbus transmitter in case of an error (such as a field
device malfunction) can be configured. The values for Modbus registers
corresponding to PV, SV , TV, and QV will be changed accordingly (applicable
registers in area 1300, 2000, 2100, and 2200).
The default alarm output value for each protocol is defined on the next page.
Configuring alarm output value is optional.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Use the Modbus string to configure the alarm output. To enter a Modbus string
in RRM, do the following (Modbus RTU shown):
1. Start RRM and connect to the transmitter.
2. In RRM, select Setup>General.
1-22
Page 23

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
3. Select the Communication tab.
4. Click the Modbus Setup button.
5. Enter the Modbus string, and click OK.
See below for available Alarm Output Modbus strings.
Modbus RTU
String Alarm Output
HMC EN Not a number (NaN), default
HMC EF Freeze, hold last value
HMC EU U-0.1 User defined value, -0.1 in this example
Levelmaster
String Alarm Output
HMC M2 EH High value, 999.99, default
HMC M2 EL Low value, -99.99
HMC M2 EF Freeze, hold last value
HMC M2 EU U0 User defined value (range -99.99 to 999.99),
0 in this example
Modbus ASCII
String Alarm Output
HMC M1 EN Not a number (NaN), default
HMC M1 EF Freeze, hold last value
HMC M1 EU U-0.1 User defined value (range -99.99 to 999.99),
-0.1 in this example
NOTE
After changing the Alarm Output configuration, disconnect the HART modem
and wait up to 60 seconds for the change to take effect.
In case the MA/MB terminals are used for connection to the HMC, disconnect
the RS-485 Converter, cycle power to the transmitter, and wait up to 60
seconds for the change to take effect.
1-23
Page 24

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Verify Alarm Output To verify the Alarm Output, use RRM to simulate a device failure:
1. Establish HART communication with the transmitter through RRM.
2. Select Simulation Mode in the Tools menu.
3. Click Enable Device Failure Alarm (simulated).
4. Click the Start button.
5. Disconnect HART modem.
6. Verify that the con figured alarm output is available in the Modbus host.
7. Use RRM to turn off simulation mode.
October 2010
Use status information to evaluate measurement validity
Use Heartbeat to detect errors
The transmitter updates status information about the current measurement,
and this status information is available as a bitfield register through Modbus
communication.
By monitoring the status information it is possible to determine if the current
measurement output value is valid. See “Common Modbus Host
Configuration” on page 1-25 for details about the individual status bits.
By reading and evaluating the Heartbeat value from the device, it is possible
to verify that the communication link between the transmitter, HMC, RTU and
even the control system communicating with the RTU is working.
Assign Heartbeat to one of the transmitter variables (SV, TV, or QV).
Heartbeat is increased by one for each measurement cycle in the device (until
it eventually starts over at zero again).
In case this value is not updated, it means that the communication link is
broken.
1-24
Page 25

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
COMMON MODBUS HOST CONFIGURATION
Table 1-12. Byte Transmission
Order is specified by the Floating
Point Format Code
When using Modbus RTU or Modbus ASCII, the registers to receive status
and variables must be configured in the host system.
The transmission of single-precision (4 bytes) IEEE 754 floating point
numbers can be rearranged in different byte orders specified by the Floating
Point Format Code. The format code information, stated for each Remote
Terminal Unit (RTU) respectively, specifies which registers to poll from the
5300/5400 transmitter in order for the R TU to correctly interpret floating point
numbers. The byte transmission order for each format code is demonstrated
in Table 1-12 below.
Format
Code
0 [AB] [CD] Straight word order, most significant byte first
1 [CD] [AB] Inverse word order, most significant byte first
2 [DC] [BA] Inverse word order, least significant byte first
3 [BA] [DC] Straight word order, least significant byte first
Byte transmission
order
Description
NOTE
Some Modbus hosts cannot read the information described here using Input
Registers (Modbus function code 4). The Input Register information can also
be read using Holding Register (Function code 3). In this case, Input Register
number + 5000 is used as Holding Register number.
Between host system and device, it is recommended to use 60 seconds or
less between polls, and three retries.
Input Registers The register area starting with 1300 can be config ured to ha ve an y of the four
format codes. The configuration is done by setting FloatingPointFormatCode
register (holding register 3000) to 0-3, as shown in Table 1-12 . This
configuration can be done with the Rosemount Radar Master program.
NOTE
Depending on the slave number the 5300/5400 transmitter is using, diff erent
registers must be used with the default slave number being 1. Slave number
is determined by the HART address.
1-25
Page 26

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Table 1-13. Output Variables for the
Configurable Floating Point Format
(default code 1)
Register Name
Slave 1 Status
Conf
Slave 1 PV Conf 1302
Slave 1 SV Conf 1304
Slave 1 TV Conf 1306
Slave 1 FV Conf 1308
Slave 2 data 1310-1318 Same data as for Slave 1.
Slave 3 data 1320-1328 Same data as for Slave 1.
Slave 4 data 1330-1338 Same data as for Slave 1.
Slave 5 data 1340-1348 Same data as for Slave 1.
Register
Number
1300
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Note
Bit information in bitfield.
Bit 0: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 PV.
Bit 1: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 Non PV.
Bit 2: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 Non PV.
Bit 3: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 Non PV.
Bit 14: HART bus busy (slave in burst or other
master present)
Bit 15: HTM Task not running (option not
available).
Note: Bit 1-3 is set when Invalid Measurement of
Slave 1 Non PV. i.e. all three bits are set
simultaneously.
Primary variable from slave 1 represented in
IEEE 754 format, using the byte order set in the
FloatingPointFormatCode register.
Secondary variable from slave 1 represented in
IEEE 754 format, using the byte order set in the
FloatingPointFormatCode register.
Tertiary variable from slave 1 represented in
IEEE 754 format, using the byte order set in the
FloatingPointFormatCode register.
Fourth variable from slave 1 represented in IEEE
754 format, using the byte order set in the
FloatingPointFormatCode register.
1-26
The Rosemount 5300/5400 register area starting with register 2000 is used
for hosts that require Floating Point Format Code 0 (see Table 1-14).
Floating Point Format Codes 2 and 3 use register areas 2100 and 2200,
respectively (see Table 1-15 and Table 1-16).
Page 27

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Table 1-14. Output Variables for
Floating Point Format Code 0
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Register Name Register Number Note
Bit information in bitfield:
Bit 0: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 PV.
Bit 1: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 SV.
Bit 2: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 TV.
Bit 3: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 FV.
Slave 1 Status 2000
Slave 1 PV 2002
Slave 1 SV 2004
Slave 1 TV 2006
Slave 1 FV (QV) 2008
Bit 14: HART bus busy (slave in burst or
other master present)
Bit 15: HTM Task not running (option not
available).
Note: Bit 1-3 is set when Invalid
Measurement of Slave 1 Non PV, i.e. all
three bits are set simultaneously.
Primary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 0.
Secondary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 0.
Tertiary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 0.
Fourth variable from slave 1 represented
in IEEE 754 format, using Floating Point
Format Code 0.
Table 1-15. Output Variables for
Floating Point Format Code 2
Register Name Register Number Note
Bit information in bitfield:
Bit 0: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 PV.
Bit 1: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 SV.
Bit 2: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 TV.
Bit 3: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 FV.
Slave 1 Status 2100
Slave 1 PV 2102
Bit 14: HART bus busy (slave in burst or
other master present)
Bit 15: HTM Task not running (option not
available).
Note: Bit 1-3 is set when Invalid
Measurement of Slave 1 Non PV, i.e. all
three bits are set simultaneously.
Primary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 2.
1-27
Page 28

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Register Name Register Number Note
Slave 1 SV 2104
Slave 1 TV 2106
Slave 1 FV (QV) 2108
Table 1-16. Output Variables for
Floating Point Format Code 3
Register Name Register Number Note
Slave 1 Status 2200
Slave 1 PV 2202
Slave 1 SV 2204
Slave 1 TV 2206
Slave 1 FV (QV) 2208
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Secondary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 2.
Tertiary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 2.
Fourth variable from slave 1 represented
in IEEE 754 format, using Floating Point
Format Code 2.
Bit information in bitfield:
Bit 0: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 PV.
Bit 1: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 SV.
Bit 2: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 TV.
Bit 3: Invalid Measurement Slave 1 FV.
Bit 14: HART bus busy (slave in burst or
other master present)
Bit 15: HTM Task not running (option not
available).
Note: Bit 1-3 is set when Invalid
Measurement of Slave 1 Non PV, i.e. all
three bits are set simultaneously.
Primary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 3.
Secondary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 3.
Tertiary variable from slave 1
represented in IEEE 754 format, using
Floating Point Format Code 3.
Fourth variable from slave 1 represented
in IEEE 754 format, using Floating Point
Format Code 3.
1-28
Page 29

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Table 1-17. Measurement units and
corresponding input registers
Table 1-18. Conversion of Unit
Code to Measurement Unit
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Measurement Units
Measurement units for the various HART slaves are stored in input registers
as a Unit Code presented in Table 1-17. Conversion from Unit Code to
measurement unit is given in Table 1-18 on page 1-29.
Register Name Register Number Note
Slave 1 PV Units 104
Slave 1 SV Units 108
Slave 1 TV Units 112
Slave 1 FV (QV) Units 116
Unit Code Measurement Unit Unit Code Measurement Unit
Volume Length
40 US Gallon 44 Feet
41 Liters 45 Meters
42 Imperial Gallons 47 Inches
43 Cubic Meters 48 Centimeters
46 Barrels 49 Millimeters
111 Cub ic Yards Temperature
112 Cubic Feet 33 Degree Fahrenheit
113 Cubic Inches 32 D egree Celsius
See Table 1-18 for conversion from Unit
Code to Measurement Unit.
1-29
Page 30

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
SPECIFIC MODBUS HOST CONFIGURATION
The Remote Terminal Unit needs to be configured to communicate and
correctly interpret data when reading input registers from the Rosemount
5300/5400 transmitter.
Baud Rate
The specified Baud Rates below are recommendations. If other Baud Rates
are used, make sure that the 5300/5400 and the RTU are configured for the
same communication speed.
Floating Point Format Code
See Section “Common Modbus Host Configuration” on page 1-25.
RTU Data Type
The RTU Data Type specifies which configuration to use in the RTU in order
for the RTU to correctly interpret a floating point number transmitted from the
5300/5400 transmitter with Modbus.
Input Register Base Number
Data registers in the 5300/5400 transmitter with Modbus are num bered
exactly as they are transmitted in the Modbus communication. Some RTUs
use different naming conventions and to configure the RTU to poll the correct
registers from the 5300/5400 Modbus, an Input Register Base Number is
stated for each RTU respectively. E.g. if the input register base number is 1
for the RTU, the 5300/5400 Modbus input register 1302 has to be ente red in
the RTU address as input register 1303.
Emerson Process Management ROC800 Series
Figure 1-9. Wiring Diagram for
Connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
Emerson Process Management
ROC800 Series
Table 1-19. Parameter Values (in
case of Emerson Process
Management ROC800 Series)
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 0
RTU Data Type Conversion Code 66
Input Register Base Number 0
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1300 needs to
have 1300 entered as the address.
Parameter Value
1-30
Page 31

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Emerson Process Management FloBoss 107
Figure 1-10. Wiring Diagram for
Connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
Emerson Process Management
FloBoss 107
Table 1-20. Parameter Values (in
case of Emerson Process
Management FloBoss 107)
5300/5400 Modbus
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 0
RTU Data Type Conversion Code 66
Input Register Base Number 0
POWER +
POWER -
Power Supply
+ 8 to + 30 Vdc
(max. rating)
Parameter Value
MA
MB
GND
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
FloBoss 107
RS-485
A
B
NC
NC
PWR
GND
ABB TotalFlow
Figure 1-11. Wiring diagram for
connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
ABB TotalFlow
Table 1-21. Parameter Values (in
case of ABB TotalFlow)
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1300 needs to
have 1300 entered as the address.
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 0
RTU Data Type 16 Bit Modicon
Input Register Base Number 1
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1302 needs to
have 1303 entered as the address etc.
1-31
Page 32

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Com Port 3 (C3) RS-485
1
2
3
4
5
TXDTXD+
GND
6
7
8
9
MA
MB
POWER +
POWER -
ControlWave Micro
5300/5400 Modbus
Power Supply
+ 8 to + 30 Vdc
(max. rating)
GND
DB9 Male
Thermo Electron Autopilot
Figure 1-12. Wiring Diagram for
Connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
Thermo Electron Autopilot
Table 1-22. Parameter Values (in
case of Thermo Electron Autopilot)
5300/5400 Modbus
MA
MB
POWER +
POWER -
Power Supply
+ 8 to + 30 Vdc
(max. rating)
GND
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 1
RTU Data Type IEEE Flt 2R
Input Register Base Number 0
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
AutoPILOT
CEB TB1
1 RX +
2 RX -
Bristol ControlWave Micro
Figure 1-13. Wiring Diagram for
Connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
Bristol ControlWave Micro
Table 1-23. Parameter Values (in
case of Bristol ControlWave Micro)
1-32
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1302 needs to
have 1302 entered as the address etc.
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 2 (FC 4)
RTU Data Type 32-bit registers as 2 16-bit registers
Input Register Base Number 1
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1302 needs to
have 1303 entered as the address etc.
Page 33

Manual Supplement
RS-485 on COM1
1 +5 V
2 RX3 TX4 GND
5 RX+
6 TX+
7 Not Used
8 Not Used
SCADAPack32
MA
MB
POWER +
POWER -
5300/5400 Modbus
Power Supply
+ 8 to + 30 Vdc
(max. rating)
REF
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
ScadaPack
Figure 1-14. Wiring Diagram for
Connecting 5300/5400 Modbus to
SCADAPack 32
Table 1-24. Parameter Values (in
case of SCADAPack 32)
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Floating Point Format Code 0
RTU Data Type Floating Point
Input Register Base Number 30001
Kimray DACC 2000/3000 This table shows input types in Kimray IMI software and the corresponding
T able 1-25. Kimray Input T ypes and
Corresponding Values
The Input Register Base Number needs to be added to the Input Register
address of the 5300/5400 transmitter. In this case, register 1302 needs to
have 31303 entered as the address etc.
value. The communication port must be configured to use “Tank Levels”
protocol.
Kimray Inp type 5300/5400 variable Format
Tank Level1 PV ddd.d d.alt. -dd.dd
Tank Level2 SV ddd.d d.alt -dd.dd
1-33
Page 34

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
TROUBLESHOOTING No communication on RS-485 bus (MA, MB)
• Check that the cables are connected
• Check that PWR+ is connected to + and PWR- is connected to - on the
power supply
• Make sure the 5300/5400 transmitter is supplied with 8-30 Vdc
(max. rating)
• Try alternating MA/MB if you are unsure of the polarity
• If an RS-485 converter is used, make sure it is properly installed and
configured
• The last 5300/5400 transmitter may need a terminating 120-resistor
connected between MA and MB
No 5300/5400 communication in RRM
• Using HART+, HART-
• HART modem is not properly connected
• Polling address is incorrect in RRM (default 1)
• Using MA, MB
• See No communication on RS-485 bus
• Polling address is incorrect in RRM (default 1)
• Cycle the power and wait 20 seconds before polling
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
No communication with Modbus RTU protocol
•See No communication on RS-485 bus
• Make sure the “Modbus Communication Protocol Configuration” is
done properly
• Make sure the Modbus RTU address is unique on the bus
• Cycle the power and try to connect
• Check the RTU communication settings
No communication with Modbus ASCII protocol
•See No communication on RS-485 bus
• Make sure the “Modbus Communication Protocol Configuration” is
done properly
• Make sure the Modbus ASCII address is unique on the bus
• Cycle the power, waiting 40 seconds before communication begins
• Check the RTU communication settings
No communication with Levelmaster protocol
•See No communication on RS-485 bus
• Make sure the “Modbus Communication Protocol Configuration” is
done properly
• Make sure the Levelmaster address is unique on the bus
• Cycle the power, waiting 40 seconds before communication begins
• Check the RTU communication settings
1-34
Page 35

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
HMC FIRMWARE UPGRADE IN ROSEMOUNT RADAR MASTER
The HMC’s firmware is upgraded using Rosemount Radar Master (RRM). A
detailed description on how to carry out the firmware upgrade is shown on the
following pages.
NOTE
All settings in the HMC will be lost after upgrading the transmitter.
Reconfiguration of Modbus communication setup and alarm handling is
required after completing the upgrade.
NOTE
During firmware upgrade, the HMC Modbus RTU address must be 246, the
default address. Make sure to disconnect other Modbus R TU devices th at are
connected and have address 246.
NOTE
Do not interrupt communication between the PC and the 5300/5400 level
transmitter during the firmware upload.
1. Start RRM and select Communication Preferences in the View menu.
2. Navigate to the Modbus tab and use the following settings:
• Modem: RS-485
• Baudrate: According to configuration in HMC (default 9600)
• Stop Bits: According to configuration in HMC (default 1)
• Parity: According to configuration in HMC (default None)
• Handshake: RTS/CTS
• Response Timeout: 1000 ms
•Retries: 3
3. Select Enable Modbus Communication and click OK.
1-35
Page 36

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
4. If the HMC is configured for Modbus ASCII or Levelmaster
communication cycle the power to the transmitter (the HMC will then
communicate using Modbus RTU for 20 seconds and under that time it is
possible to connect with RRM).
5. Open the Search Device window and make sure Modbus is selected in
the Protocol list.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
6. Search for HMCs by selecting “Scan Address Range”, and choose a
start and end address for Modbus. The default HMC Modbus address is
246.
7. Click the Start Scan button.
8. Click OK to connect when the device is found.
9. From the Service menu, choose the Enter Service Mode option.
10. Type password, “admin”.
1-36
Page 37

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
11. From the Service menu, choose the Upload Firmware option.
12. Click Browse.
13. Select the upgrade “.cry” file.
14. Click Open.
1-37
Page 38

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Checksum
15. Click the Upload button to start the firmware upgrade.
16. When upload is finished, select Diagnostics in the Tools menu.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
1-38
17. Click Device Errors and check for “Checksum”.
18. If it is on the list, choose the Factory Settings option from the Tools
menu.
Page 39

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
19. Select All and click OK.
20. Select “Yes”.
NOTE
An error message might be displayed when performing the Reset to Factory
Settings operation. The operation has been successful if the checksum error
has been cleared.
21. Select Restart in the Tools menu to restart the HMC.
22. The checksum error should no longer be present (select Diagnostics in
the Tools menu to verify, see Step 16). If it still persists, follow the next
steps.
23. Select View Holding Registers in the Service menu and write th e value
16760 to register 65510.
24. Restart the HMC.
25. If the HMC is configured for Modbus ASCII or Levelmaster
communication after upload has been completed, proceed with the
following:
1. Close RRM and disconnect the RS-485 converter from the HMC.
2. Cycle the power to the HMC to have it exit Modbus RTU
communication mode.
1-39
Page 40

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1-26. Specifications
Power supply 8-30 Vdc (max. rating)
Power consumption
Signal wiring
Power supply cabling
Ground (common mode)
voltage limit
Bus termination Standard RS-485 bus termination per EIA-485
See the Rosemount 5300 Series Reference Manual (Document No.
00809-0100-4530), and the Rosemount 5400 Series Reference Manual
(Document No. 00809-0100-4026) for further specifications.
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
< 0.5 W (with HART address=1)
< 1.2 W (incl. four HART slaves)
Two-wire half duplex RS-485 Modbus. Use shielded
twisted pair wiring, preferably with an impedance of 120
(typically 24 AWG), in order to comply with EIA-485
standard and EMC regulations.
The power supply cables must be suitable for the supply
voltage and ambient temperature, and approved for use
in hazardous areas, where applicable.
± 7 V
1-40
Page 41

Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
1-41
Page 42

Rosemount 5300/5400 Series
Manual Supplement
00809-0500-4530, Rev AA
October 2010
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson Electric Co.
Rosemount and the Rosemount logotype are registered trademarks of Rosemount Inc.
All other marks are the property of their respective owners.
Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale can be found at www.rosemount.com\terms_of_sale
© 2010 Rosemount Inc. All rights reserved.
Emerson Process Management
Rosemount Measurement
8200 Market Boulevard
Chanhassen MN 55317 USA
Tel (USA) 1 800 999 9307
Tel (International) +1 952 906 8888
F +1 952 949 7001
00809-0500-4530 Rev AA 10/10
Emerson Process Management
Shared Services Ltd
Heath Place
Bognor Regis
West Sussex PO22 9SH
England
Tel +44 (1243) 863 121
Fax +44 (1243) 867 554
Emerson Process Management
Asia Pacific Pte Ltd
1 Pandan Crescent
Singapore 128461
Tel +65 6777 8211
Fax +65 6777 0947
Service Support Hotline: +65 6770 8711
Email: Enquiries@AP.EmersonProcess.com
 Loading...
Loading...