Page 1
Instruction Manual
D102684X012
May 2017
299H Series
299H Series Pressure Reducing Regulators
WARNING
!
Failure to follow these instructions or
to properly install and maintain this
equipment could result in an explosion
and/or fire causing property damage and
personal injury or death.
Fisher™ regulators must be installed,
operated and maintained in accordance
with federal, state and local codes, rules
and regulations and Emerson Process
Management Regulator Technologies, Inc.
(Emerson) instructions.
If the regulator vents gas or a leak
develops in the system, service to the unit
may be required. Failure to correct trouble
could result in a hazardous condition.
Call a gas service person to service the
unit. Only a qualified person must install
or service the regulator.
Introduction
Scope of the Manual
This Instruction Manual provides installation,
adjustment and maintenance instructions and parts
ordering information for the 299H Series regulators.
Instructions and parts list for the 67C Series
Instrument Supply Regulators are found in Instruction
Manual D102601X012. Instructions and parts list
for the P590 Series Filters are found in Instruction
Manual D101555X012. Instructions and parts list for
the Type VSX2 slam-shut are found in Instruction
Manual D103695X012. Instructions and parts list for
the Type VSX8 slam-shut are found in Instruction
Manual D103127X012.
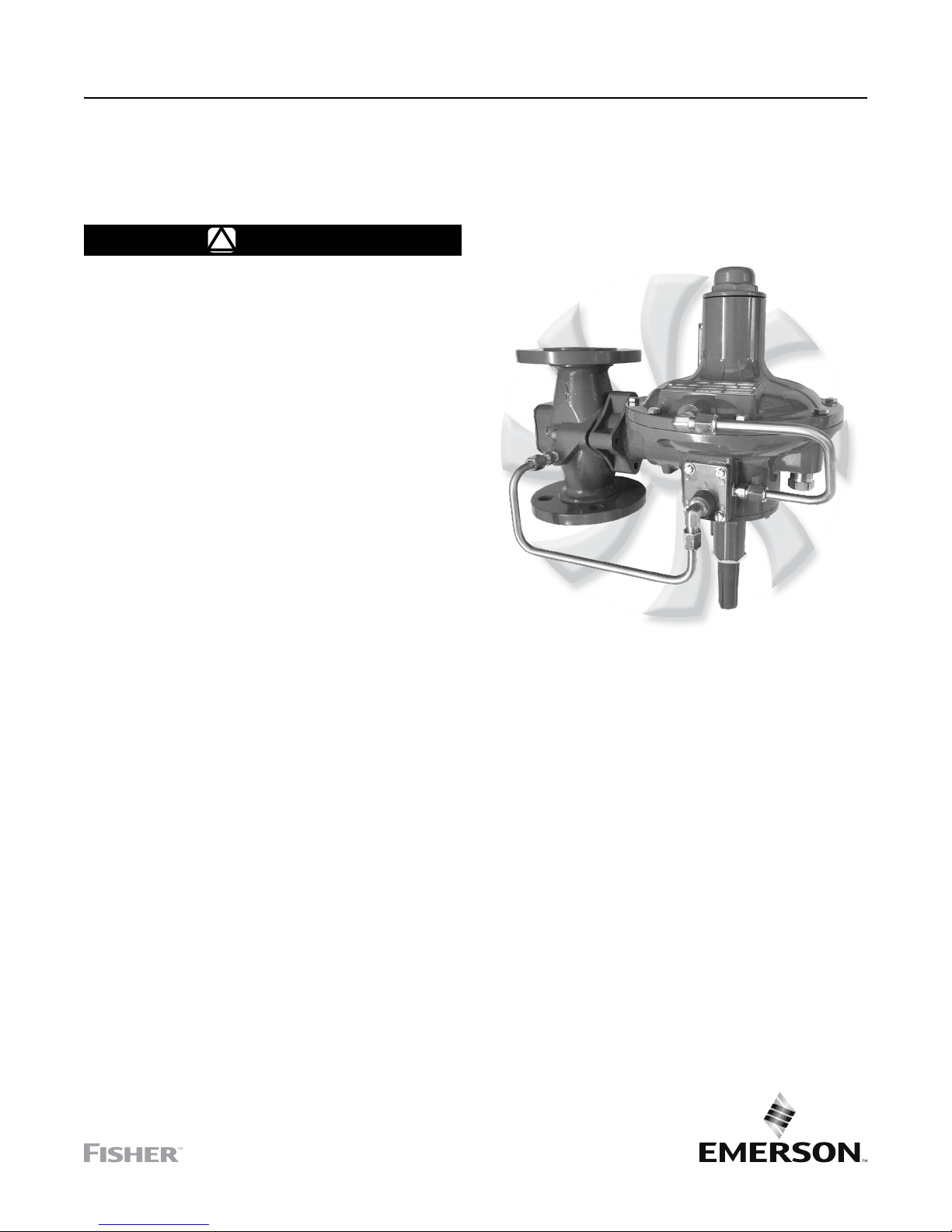
Description
The 299H Series pressure reducing regulators provide
a broad capacity of controlled pressure ranges and
capacities in a wide variety of distribution, industrial
and commercial applications. A 299H Series regulator
has a pilot integrally mounted to the actuator casing.
Figure 1. 299H Series Pressure Reducing Regulator
The 299H Series regulators can handle inlet pressures
up to 175 psi / 12.1 bar depending on orifice size.
The integral token relief on the Types 299HR and
299HSR regulators is located in the pilot and opens to
relieve minor overpressure.
The Types 299HS and 299HV provide overpressure
or overpressure and underpressure protection
by completely shutting off the ow of gas
to the downstream system. It comes with a
Type VSX2 (299HS) or VSX8 (299HV) slam-shut
device which can be congured for Ovepressure
Shutoff (OPSO) or Overpressure and Underpressure
Shutoff (OPSO/UPSO). The slam-shut device’s actions
are independent of the main valve and of variations
to the inlet pressure. The Type VSX2 (299HS) or
VSX8 (299HV) slam-shut device has internal or
external registration. External registration requires a
downstream sensing line.
Page 2
299H Series
Specifications
Specifications for 299H Series constructions are given below. Some specifications for a given regulator as it
originally comes from the factory are stamped on a nameplate located on the actuator upper casing.
Available Constructions
Type 299H: Pilot-operated pressure reducing
regulator with a pilot integrally mounted to the
actuator casing.
Type 299HR: A Type 299H with a token internal
relief valve to relieve minor overpressure caused
by thermal expansion.
Type 299HS: Same as the Type 299H
with a Type VSX-2 slam-shut valve which
provides overpressure or overpressure and
underpressure protection.
Type 299HV: Same as the Type 299H
with a Type VSX8 slam-shut valve which
provides overpressure or overpressure and
underpressure protection.
Type 299HSR: Same as the Type 299HS with an
internal token relief valve.
Type 299HVR: Same as the Type 299HV with an
internal token relief valve.
Body Size and End Connection Styles
See Table 1
Maximum Operating Inlet Pressure by Orifice Size
(1)
1/4 x 3/8 in. / 6.4 x 9.5 mm .......175 psig / 12.1 bar
3/8 in. / 9.5 mm ................175 psig / 12.1 bar
1/2 in. / 13 mm ................175 psig / 12.1 bar
3/4 in. / 19 mm ................150 psig / 10.3 bar
7/8 in. / 22 mm
1 in. / 25 mm
1-3/16 in. / 30 mm
Maximum Casing and Emergency Outlet Pressure
(5)
...............125 psig / 8.6 bar
(5)
.................100 psig / 6.9 bar
(5)
........... 80 psig / 5.5 bar
(1)
66 psig / 4.5 bar
Outlet (Control) Pressure Ranges
(1)(2)
See Table 2
Maximum Set Pressure for Types 299HS and 299HV
16 psig / 1.1 bar
Maximum Set Pressure for Slam-Shut Device
See Table 2
Minimum and Maximum Trip Pressure Ranges
See Type VSX2 slam-shut Instruction Manual
D103695X012 or Type VSX8 slam-shut Instruction
Manual D103127X012.
Types VSX2 and VSX8 Sensing Line Connection
1/4 NPT
Pressure Control Accuracy (Fixed Factor)(PFM)
(3)
±1%
of absolute control pressure
Minimum Differential Pressure For Full Stroke
1.5 psid / 0.10 bar d
Control Line Connections
3/4 NPT
Temperature Capabilities
(1)(6)
-20 to 150°F / -29 to 66°C
Approximate Weight
21 lbs / 10 kg
Pressure Registration
Internal, External or Dual Registration
See Figure 2
Fixed Restriction Sizes
0.044 in. / 1.1 mm, Red (standard gain)
0.071 in. / 1.8 mm, Green (low gain)
0.082 in. / 2.1 mm, Blue (lower gain)
Options
• Filter
(3)
: A P590 Series filter installed in the pilot
supply tubing between main body and pilot
• Filtered pilot supply regulator
(3)(4)
: A Type 67CF
supply regulator with integral 5 micron
Polyethylene filter
(1)
(1)
1. The pressure/temperature limits in this Instruction Manual and any applicable standard or code limitation should not be exceeded.
2. For optimum performance, a pilot supply regulator may be installed in the pilot supply tubing between the main valve and pilot.
3. A pilot supply regulator or a P590 Series lter (only one may be used, not both) may be ordered with the Type 299H, but not both.
4. For in. w.c., use a pilot supply regulator if actual inlet pressure varies more than ±20 psi / ±1.4 bar and published accuracy is required.
5. This orice size is not available for Types 299HS, 299HV, 299HSR and 299HVR.
6. Product has passed Emerson testing for lockup, relief start-to-discharge and reseal down to -40°.
2
Page 3
299H Series
Table 1. Body Sizes and End Connection Styles
BODY SIZE,
IN. / DN
1-1/4
1-1/2
2 / 50 NPT and CL125
1. This ange is available with a face-to-face dimension of 7.5 in. / 190 mm or 10 in. / 254 mm.
OUTLET (CONTROL)
PRESSURE RANGE
In. w.c. mbar In. mm In. mm
(1)
3.5 to 6
(1)
5 to 9
(1)
7 to 20
(1)
16 to 40
1 to 3.25 psig
2.75 to 6 psig
5 to 16 psig
14 to 35 psig
30 to 60 psig
1. Use a pilot supply regulator if actual inlet pressure varies more than ±20 psi / ±1.4 bar and the published accuracy is required.
Cast Iron (For Types 299H and 299HR only) Ductile Iron Steel (For Types 299H and 299HR only)
NPT
NPT
FF(1)
flanged
TYPE PILOT CONTROL SPRING
299HR,
299HS,
299HSR,
299HV
299HVR
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
- - - -
- - - -
(1)
9 to 15
(1)
12 to 22
(1)
17 to 50
(1)
40 to 99
69 mbar to 0.22 bar
0.19 to 0.41 bar
0.34 to 1.1 bar
0.97 to 2.4 bar
2.1 to 4.1 bar
299H
BODY MATERIAL AND END CONNECTION STYLE
- - - NPT
NPT, CL125 FF and CL250 RF flanged
and PN 10/16 flanged
Table 2. Outlet Pressure Ranges
Part Number Color
and
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
T13707T0012
T13589T0012
1N3112X0012
1B413727222
T13593T0012
T13671T0012
T13600T0012
19B0432X012
19B0432X022
Black
Yellow
Unpainted
Purple
Light blue
Orange
Red
Zinc
Green
- - - NPT
NPT and CL150 RF flanged
Free Length Wire Diameter
1.86
2.05
2.18
2.12
2.12
2.40
2.10
2.15
2.75
47.2
52.1
55.4
53.8
53.8
61.0
53.3
54.6
69.8
0.055
0.051
0.075
0.092
0.105
0.120
0.142
0.207
0.225
1.40
1.30
1.90
2.34
2.67
3.05
3.61
5.26
5.71
Principle of Operation
WARNING
!
Since a pilot-operated regulator is
constructed of both a pilot and a main
valve, do not exceed the maximum inlet
pressure shown on the nameplate.
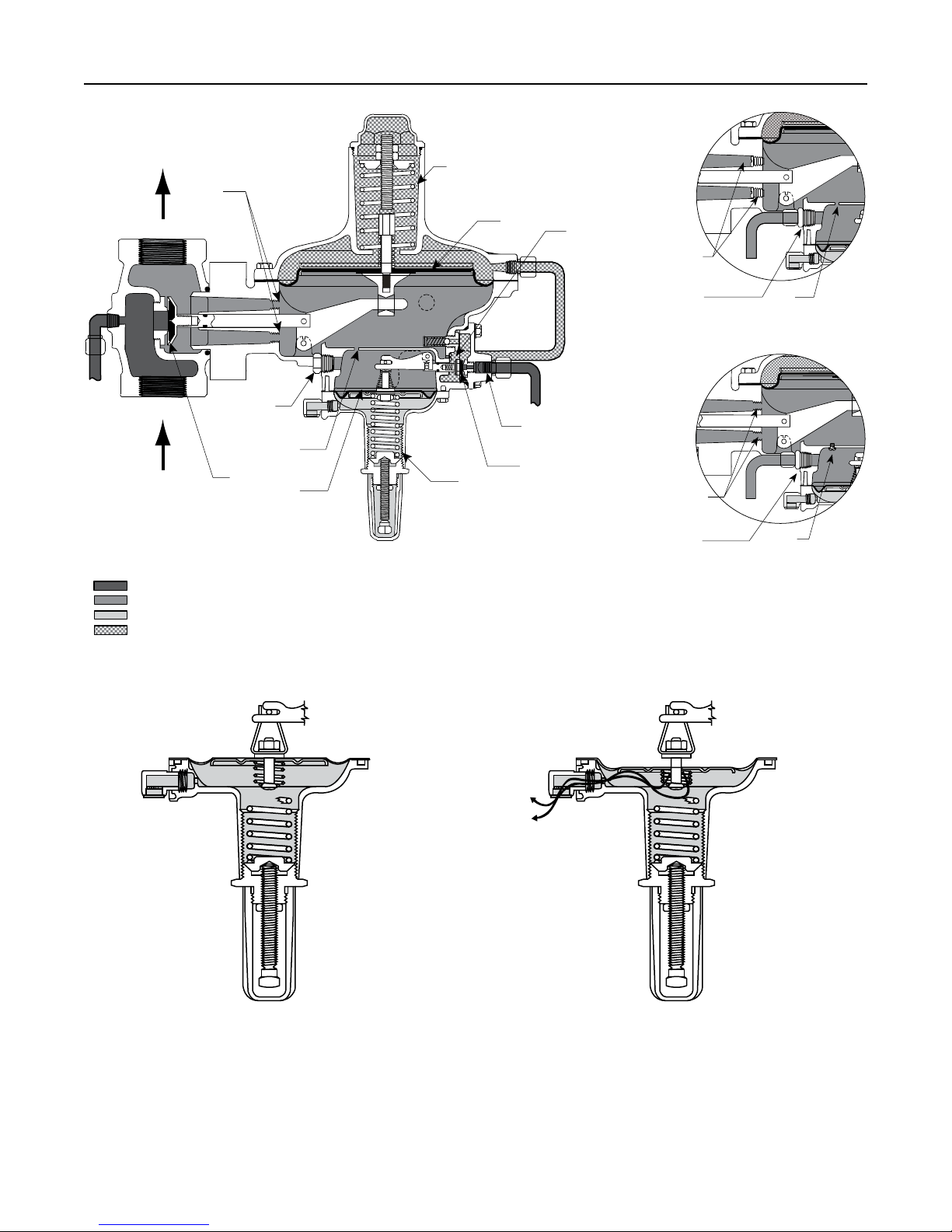
Letter keys in this section refer to Figure 2 unless
otherwise noted. Fast response and accuracy are
made possible by the amplifying effect of the pilot
and by the two-path control system. The function of
the pilot is to sense change in the controlled pressure
and amplify it into a larger change in the loading
pressure. Any changes in outlet pressure act quickly
on both the actuator diaphragm and the loading pilot,
thus providing the precise pressure control that is
characteristic of a two-path control system.
Upstream or inlet pressure is utilized as the operating
medium, which is reduced through pilot operation to
load the main diaphragm chamber. Tubing connects
the inlet pressure to the pilot. Downstream or outlet
pressure registers underneath the main diaphragm (E)
and on top of pilot diaphragm (F). There are three
different versions of pressure registration for the
299H Series.
Internal registration—Outlet pressure is registered
through the throat (J) to the main diaphragm chamber
and then through a small port (G) to the top of the
pilot diaphragm.
External registration—The throat (J) is blocked and a
downstream control line is connected to the pilot upper
diaphragm chamber or the actuator lower diaphragm
chamber. A small port (G) connects the two chambers.
Dual registration—The lower main diaphragm chamber
registers outlet pressure through the throat (J) and the
upper pilot diaphragm chamber registers downstream
pressure by using a downstream control line. The port (G)
between the chambers is blocked.
Type 299H
In operation, assume the outlet pressure is less than
the setting of the pilot control spring (A). The top side
of pilot diaphragm assembly (F) will have a lower
pressure than the setting of the control spring (A).
The control spring (A) forces the diaphragm assembly
upward, opening the pilot orifice (C). Additional loading
pressure is supplied from the pilot orifice to the top
side of the main diaphragm (E).
3
Page 4
Type 299H
Type 299H with Dual Registration
November 2008
Type 299H Internal Registration
July 2008
Type 299H
OUTLET
INLET
K
G
C
A
B
E
H
F
J
3/4 NPT
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
PILOT SUPPLY
SCREEN
299H Series
J
B
OUTLET
3/4 NPT
INLET
E0070
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
K
G
F
INTERNAL
REGISTRATION
E
A
H
PILOT SUPPLY
SCREEN
C
TYPE 299H
J
3/4 NPT
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
3/4 NPT
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
J
DUAL REGISTRATION
G
G
A7272
TOKEN RELIEF CLOSED TOKEN RELIEF OPEN
TYPE 299HR (TOKEN RELIEF DETAIL)
Figure 2. 299H Series Operational Schematics
A7272
4
Page 5
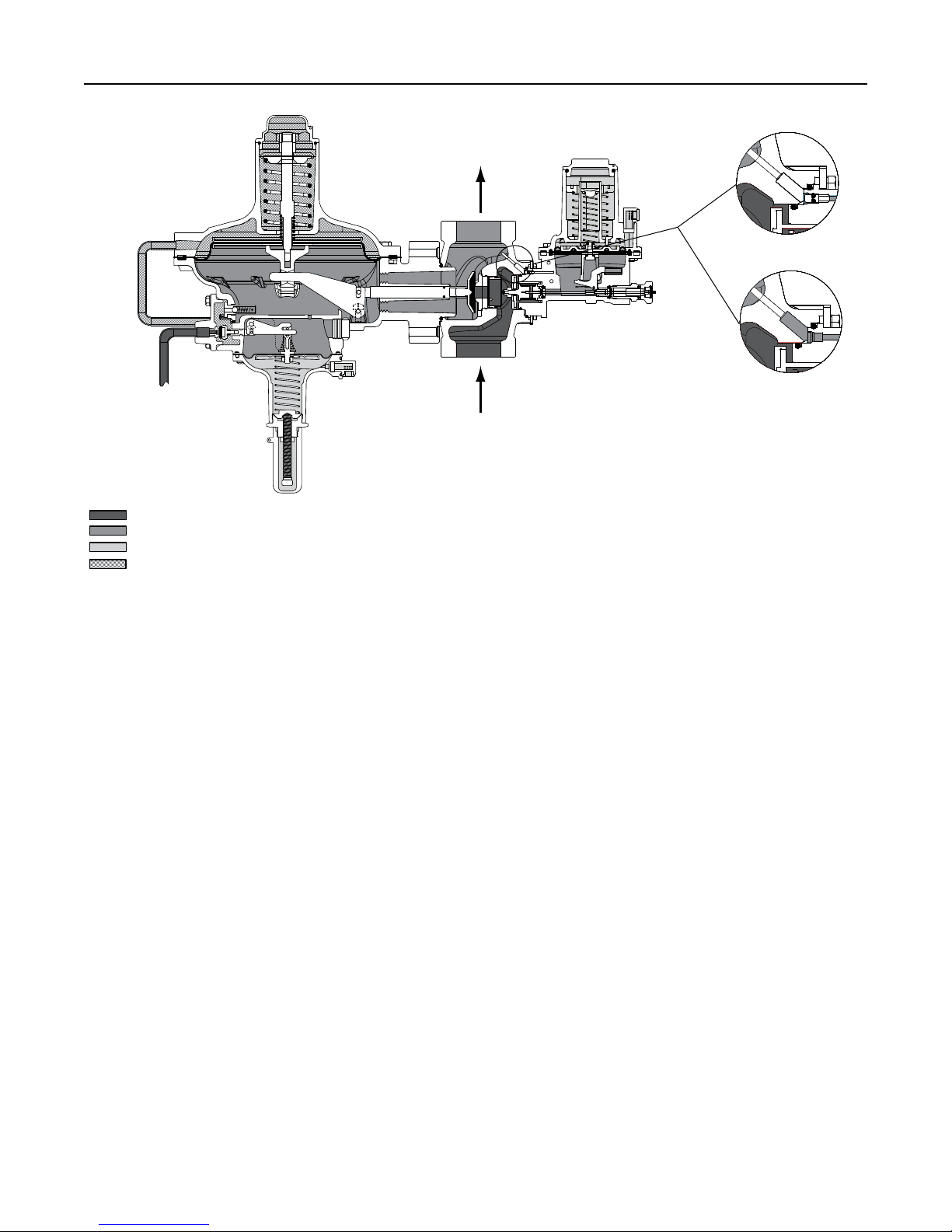
Type 299HV
Type 299HV
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
INTERNAL REGISTRATION
September 2016
Type 299HV
Type 299HV
September 2016
Type 299HV
Type 299HS
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
INTERNAL REGISTRATION
299H Series
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
E0072_09/2016
This creates a higher pressure on the top side of the
main diaphragm (E) than on the bottom side, forcing
the diaphragm downward. This motion is transmitted
through a lever, which pulls the valve disk (K) open,
allowing inlet pressure to flow through the valve.
When the demand in the downstream system has been
satisfied, the outlet pressure increases. The increased
pressure is transmitted through the downstream control
line (for external or dual registration) or through the
port (G) (for internal registration) and acts on top of the
pilot diaphragm (F). This pressure exceeds the pilot
spring setting and forces the diaphragm down, closing
the orifice (C). The loading pressure acting on the
main diaphragm (E) bleeds to the downstream system
through a bleed restriction (H).
With a decrease in loading pressure on top of the
main diaphragm (E), the main closing spring (B)
exerts an upward force on the diaphragm post which
is connected to the main diaphragm (E), pulling it
upward. This moves the main valve disk (K) toward its
seat, decreasing flow to the downstream system.
INLET PRESSURE
OUTLET PRESSURE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE
LOADING PRESSURE
TYPE 299HV
Figure 2. 299H Series Operational Schematics (continued)
Type 299HR
During normal operation the Type 299HR performance
is identical to the Type 299H. If an overpressure
condition occurs, the pilot diaphragm head will
separate from the pilot diaphragm post and travel until
it contacts the pilot spring case. The movement of the
diaphragm head creates a path and a token or small
amount of gas will be released.
When the overpressure condition ceases, the pilot
diaphragm head will return to the diaphragm post and
the regulator will return to normal operation.
Type 299HS or 299HV
The Type VSX2 (299HS) or VSX8 (299HV) slam-shut
device on the Type 299HS or 299HV regulator is a fast
acting slam-shut valve which provides overpressure or
overpressure and underpressure protection by completely
shutting off the flow of gas to the downstream system.
The slam-shut module’s actions are independent of
the Type 299HS or 299HV main regulator and of the
variations to the inlet pressure. The Types VSX2 and
VSX8 have internal or external registration. External
registration requires a downstream sensing line.
5
Page 6

299H Series
The slam-shut disk is held in the open position (reset
position) by an internal latching mechanism that holds
the valve stem and disk assembly. If the pressure
below the diaphragm increases (or decreases)
reaching the Types VSX2 and VSX8 setpoint, the
diaphragm will travel upwards (or downwards)
operating a lever which in turn releases the valve
stem assembly.
Once released, the spring force on the stem will push
the stem and disk to the closed position against the seat
shutting off all gas flow. The pilot supply pressure is also
shut off when the Type VSX2 or VSX8 is closed. The
manual reset has an internal bypass to equalize the
reset pressure on either side on the slam-shut disk.
In order for the Underpressure Shutoff (UPSO) of
any slam shut to be triggered, the downstream pipe
pressure must drop below the UPSO setpoint. In the
case of a downstream line break, numerous factors
can prevent the downstream pipe pressure from
decreasing below the slam-shut UPSO setpoint. These
factors include the distance of pipe to the break, the
diameter of the pipe, size of the break and the number
of restrictions, such as valves, elbows and bends,
downstream of the regulator and/or slam-shut device.
Due to these factors additional protections should be
installed to stop flow in the event of a line break.
Overpressure Protection
Like most regulators, the Type 299H has outlet
pressure ratings lower than the inlet pressure ratings.
Complete downstream overpressure protection is
needed if the actual inlet pressure exceeds the outlet
pressure rating.
Overpressure protection for internal parts is built
into the main and pilot diaphragms by means of a
small spring on each post. The springs will allow
the diaphragm heads to move farther on the posts
avoiding damage to or bending of the valve trim.
Overpressuring any portion of a regulator or
associated equipment may cause leakage, parts
damage or personal injury due to bursting of
pressure-containing parts or explosion of accumulated
gas. Regulator operation within ratings does not
preclude the possibility of damage from external
sources or from debris in the pipeline. A regulator
should be inspected for damage periodically and after
any overpressure condition.
The pilot vent is provided with a 1/4 NPT tapped
connection in the spring case.
Installation
!
WARNING
Personal injury, equipment damage or
leakage due to escaping gas or bursting
of pressure-containing parts might result
if this regulator is overpressured or is
installed where service conditions could
exceed the limits for which the regulator
was designed or where conditions exceed
any ratings of the adjacent piping or
piping connections. To avoid such injury
or damage, provide pressure-relieving
or pressure-limiting devices (as required
by the appropriate code, regulation or
standard) to prevent service conditions
from exceeding those limits.
A regulator may vent some gas to the
atmosphere in hazardous or flammable
gas service. Vented gas might accumulate
and cause personal injury, death or
property damage due to fire or explosion.
Vent a regulator in hazardous gas service
to a remote, safe location away from air
intakes or any hazardous location. Protect
the vent line or stack opening against
condensation or clogging.
If the regulator is exposed to an
overpressure condition, it should be
inspected for any damage that may have
occurred. Operation below these limits
does not preclude the possibility of
damage from external sources or from
debris in the pipeline.
If the Type VSX2 or VSX8 is exposed
to an overpressure condition, it should
be inspected for any damage that may
have occurred. Operation below these
limits does not preclude the possibility
of damage from external sources or from
debris in the pipeline.
In the case of a downstream line break,
numerous factors affect the capability
to evacuate gas from the pipeline.
These factors include the distance of
pipe to the break, the diameter of the
pipe, size of the break and the number
of restrictions, such as valves, elbows
and bends, downstream of the regulator
6
Page 7

299H Series
and/or slam-shut device. Due to these
factors additional protections should be
installed to stop flow in the event of a
line break.
Like most regulators, the 299H Series regulators have
an outlet pressure rating lower than its inlet pressure
rating. Complete downstream overpressure protection
is needed if the actual inlet pressure can exceed the
regulator outlet pressure rating or the pressure ratings
of any downstream equipment. Regulator operation
within ratings does not preclude the possibility of
damage from external sources or from debris in the
lines. A regulator should be inspected for damage
periodically and after any overpressure condition.
Clean out all pipelines before installation. Check for
damage which might have occurred during shipment.
Also, check for and remove any dirt or foreign material
which may have accumulated in the regulator body.
Apply pipe compound to the external pipe threads of
threaded bodies or use suitable line gaskets and good
bolting practices with a flanged body. This regulator
may be installed in any position desired as long as the
flow through the body is in the direction indicated by the
arrow on the body. Install a three-valve bypass around
the regulator if continuous operation is necessary during
maintenance or inspection.
Although the standard orientation of the actuator and
pilot to the main valve body is as shown in Figure 1,
this orientation may be changed in 90° intervals by
rotating the actuator lower casing (key 1, Figure 4) and
the elbow fitting (key 19) by 90° and then reinstalling
the cap screws.
To keep the pilot spring case from being plugged or the
spring case from collecting moisture, corrosive chemicals
or other foreign material, the vent must be pointed down
oriented to the lowest possible point on the spring case
or otherwise protected. Vent orientation may be changed
by rotating the pilot spring case with respect to the
pilot body.
To remotely vent the pilot, remove the screwed-in vent
assembly (key 27, Figure 3) from the pilot spring case
and install obstruction-free tubing or piping into the
1/4 NPT vent tapping. Provide protection on a remote
vent by installing a screened vent cap into the remote
end of the vent pipe.
An upstream pilot supply line is not required
because of the integral pilot supply tubing (key 21,
Figure 4). However, as long as the 1/4 NPT tapping
in the main valve body is plugged, this tubing may
be disconnected from the main valve (key 17) in
order to install a pilot supply line from a desired
remote location into the pilot.
If using a control line, attach the control line from
the pilot tap 2 to 3 ft. / 0.61 to 0.91 m downstream of
the regulator in a straight run of pipe. If impossible
to comply with this recommendation due to the pipe
arrangement, it may be better to make the control line
tap nearer the regulator outlet rather than downstream
of a block valve. Do not make the tap near any elbow,
swage or nipple which might cause turbulence. For
optimal performance, use as large of a control line
as practical.
In many instances, it will be necessary to enlarge the
downstream piping to keep flow velocities within good
engineering practices. Expand the piping as close to
the regulator outlet as possible.
!
WARNING
Adjustment of the pilot control spring to
produce an outlet pressure higher than
the upper limit of the outlet pressure
range for that particular spring can cause
personal injury or equipment damage due
to bursting of pressure-containing parts
or the dangerous accumulation of gases
if the maximum actuator emergency
casing pressure is exceeded. If the
desired outlet pressure is not within the
range of the pilot control spring, install a
spring of the proper range according to
the Maintenance section.
Each regulator is factory-set for the pressure setting
specified on the order. If no setting was specified,
the outlet pressure is set midrange of the pilot control
spring. In all cases, check the control spring setting to
make sure it is correct for the application.
Registration Conversion
To convert the 299H Series regulators from one type of
registration to another, all that is required is adding or
removing screws and O-rings.
To change an internal registration regulator to an
external registration regulator with a downstream
control line, block the two ports in the throat with
screws and O-rings (J in Figure 2). Remove either the
3/4 NPT pipe plug in the pilot casing or the 3/4 NPT
pipe plug in the lower casing and add a downstream
control line.
7
Page 8

299H Series
To convert an external registration regulator to a dual
registration regulator, remove the two screws and
O-rings (J in Figure 2) from the throat and use a screw
and an O-ring to block the port (G in Figure 2) between
the lower diaphragm chamber and pilot diaphragm
chamber. Remove the 3/4 NPT pipe plug in the pilot
lower casing and add a downstream control line.
Type VSX2 Slam-Shut Device
Refer to the Instruction Manual for Type VSX2
slam-shut, document D103695X012, for Adjustment
and Maintenance of the Slam-shut.
Type VSX2 Installation Startup
Note
The Type VSX2 slam-shut module should
be mounted so that the spring case vent
points towards the ground.
The overpressure and underpressure
trip points can only be reset if the
Type 299HS outlet pressure is between
the overpressure and underpressure
trip points.
Startup
With proper installation completed and downstream
equipment properly adjusted, perform the following
procedure while monitoring the pressure with gauges.
1. Very slowly open the upstream block valve.
2. On a Type 299HS, the Type VSX2 is shipped in
the tripped position and will need to be reset. If the
Type VSX2 is a high trip only, it can be reset before
starting the regulator. If the Type VSX2 is a high
and low trip, the regulator will need to be started
and the downstream system pressurized before
the Type VSX2 can be reset. See the section for
Type VSX2 reset.
3. Use the following procedure to reset the
Type VSX2:
a. Unscrew the brass resetting knob to open the
equalizing bypass.
b. Pull out the knob until it stops. This resets the
tripping mechanism.
c. Push in and tighten the knob.
4. Slowly open the hand valve (if used) in the
control line. The regulator will control downstream
pressure at the pilot control spring setting. See
the Adjustment section following these numbered
steps if changes in the setting are necessary
during the start-up procedure.
5. Slowly open the downstream block valve.
6. Slowly close the bypass valve, if used.
7. Check all connections for leaks.
Type VSX8 Slam-Shut Device
Refer to the Instruction Manual for Type VSX8
Slam-shut, document D103127X012, for Adjustment and
Maintenance of the Slam-shut.
Type VSX8 Installation Startup
Note
The Type VSX8 slam-shut device can
be rotated 360° for easy installation
and maintenance.
Equipment installed downstream the
Type VSX8 slam shut device can be
damaged if the following procedure
for resetting the Type VSX8 slam shut
device is not followed. This equipment
includes the integral Type VSX8
regulator configurations.
Before proceeding with the adjustment
of the slam-shut device springs, the
operator must ensure upstream and
downstream valves are closed and
adjusting screws are unscrewed.
With proper installation completed and downstream
equipment properly adjusted, perform the following
procedure while monitoring the pressure with gauges.
1. Very slowly open the upstream block valve.
2. On a Type 299HV, the Type VSX8 is shipped in
the tripped position and will need to be reset. If the
Type VSX8 is OPSO only, it can be reset before
starting the regulator. If the Type VSX8 is OPSO/
UPSO, the regulator will need to be started and
the downstream system pressurized before the
Type VSX8 can be reset. See the section for
Type VSX8 reset.
8
Page 9

299H Series
3. Use the following procedure to reset the
Type VSX8:
a. To properly reset the Type VSX8 slam shut
after it has been tripped to the closed position,
a flat-head screwdriver must be inserted into
the backside of the reset button.
b. The screwdriver should be slowly rotated to
gradually pull the reset button away from the
Type VSX8 device. This slow movement allows
for a slow bleed of the pressure across the
Type VSX8 slam shut’s disk and seat area. The
operator should be able to hear the pressure
bleeding through the system.
c. When the pressure has equalized and the
air bleeding sound has dissipated, the reset
button should be pulled completely away from
the Type VSX8 slam shut device by hand
until the internal shut-off mechanism has
been re-latched.
d. Once the operator feels the click of the re-latch
occurring, the reset button should be pushed
completely back into its original position.
4. Slowly open the hand valve (if used) in the
control line. The regulator will control downstream
pressure at the pilot control spring setting. See
the Adjustment section following these numbered
steps if changes in the setting are necessary
during the start-up procedure.
5. Slowly open the downstream block valve.
6. Slowly close the bypass valve, if used.
7. Check all connections for leaks.
299H Series Adjustment
Keys are referenced in Figure 5. The only adjustment
on a 299H Series regulator is the reduced pressure
setting of the pilot control spring (key 32). Remove
the closing cap (key 29) and turn the adjusting screw
(key 36). Turning the adjusting screw clockwise into
the spring case increases the controlled or reduced
pressure setting. Turning the screw counterclockwise
decreases the reduced pressure setting. Always
tighten the locknut (key 35) and replace the closing
cap after making adjustments.
Shutdown
Installation arrangements may vary, but in any installation
it is important to open and close valves slowly and the
outlet pressure be vented before venting inlet pressure to
prevent damage caused by reverse pressurization of the
regulator. Isolate the regulator from the system. Vent the
downstream pressure; then vent inlet pressure to release
any remaining pressure in the regulator.
Maintenance
Regulator parts are subject to normal wear and must
be inspected periodically and replaced as necessary.
The frequency of inspection and replacement depends
upon the severity of service conditions and upon
applicable codes and government regulations.
Due to the care Emerson takes in meeting all
manufacturing requirements (heat treating,
dimensional tolerances, etc.), use only replacement
parts manufactured or furnished by Emerson.
!
WARNING
Avoid personal injury or damage
to property from sudden release
of pressure or uncontrolled gas or
other process fluid. Before starting
to disassemble, carefully release all
pressures according to the Shutdown
procedure. Use gauges to monitor inlet,
loading and outlet pressures while
releasing these pressures.
On reassembly of the regulator, it is recommended
that a good quality pipe thread sealant be applied to
pressure connections and fittings and a good quality
lubricant be applied to all O-rings. Also apply an anti-
seize compound to the adjusting screw threads and
other areas as needed.
Note
The regulator body may remain in the
pipeline during maintenance procedures.
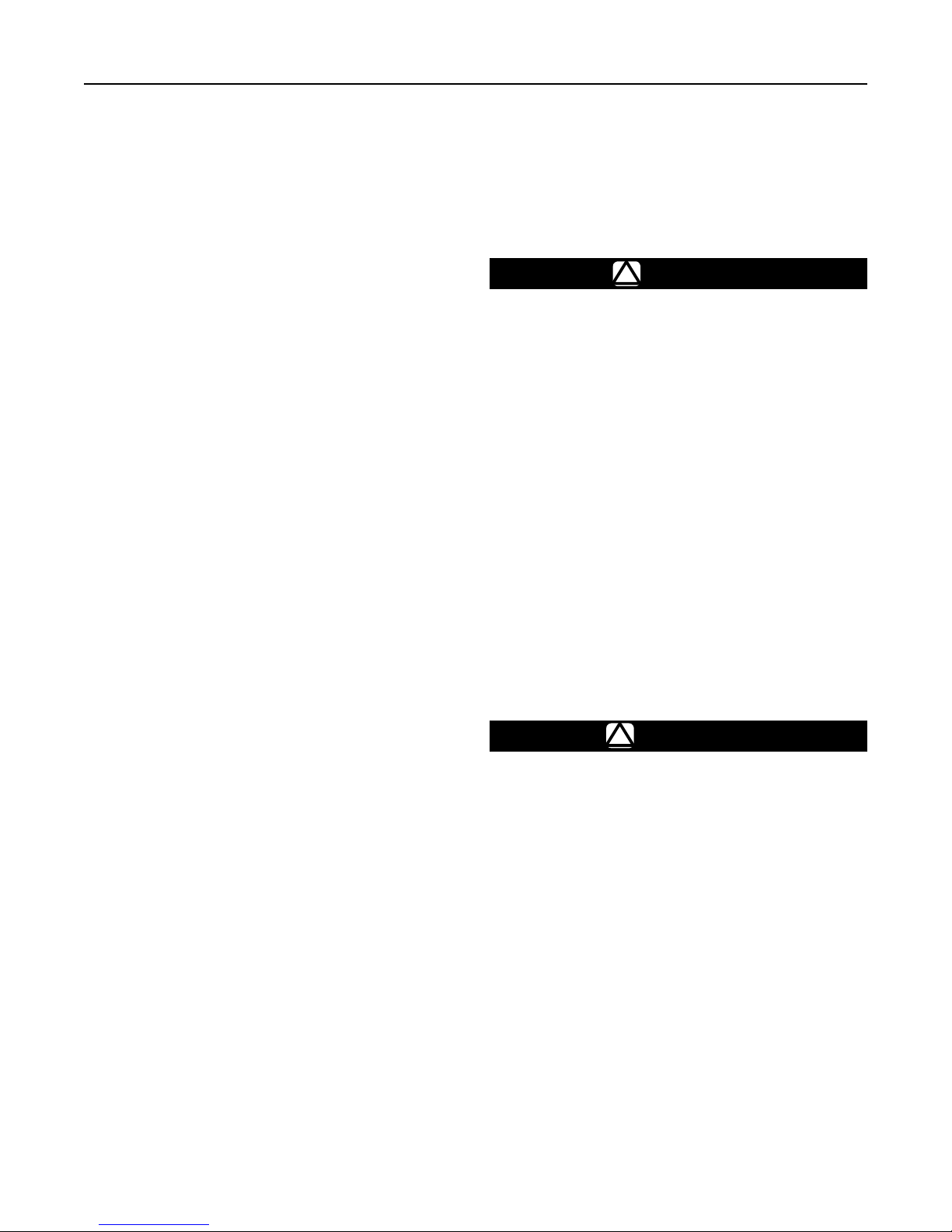
Main Actuator Diaphragm
Follow this procedure to change the actuator
diaphragm or to inspect, clean or replace any other
parts in the main actuator. Part key numbers are
referenced in Figures 3 and 4.
9
Page 10
299H Series
1. Cut the wire seal (key 68) (being careful not to
lose the warning tag) and remove the closing cap
(key 3). Inspect the O-ring (key 9) and replace
if necessary.
2. Carefully loosen and remove the double nuts
(key 5) on the actuator diaphragm post (key 10).
When removing the adjusting nuts, do not twist
or unscrew the diaphragm post, as this action will
loosen the joint between the diaphragm post and
the pusher post (keys 10 and 11).
3. Remove the spring seat (key 4) and closing
spring (key 6).
4. Remove the eight hex head cap screws (key 23)
and lift off the upper casing (key 2).
5. Remove the diaphragm assembly (key 8) by
tipping it so that the lever (key 26) slips out of the
pusher post (key 11).
6. Separate the diaphragm assembly by
unscrewing the diaphragm post (key 10) from the
pusher post (key 11) and remove the diaphragm
post, pressure equalization spring (key 7),
diaphragm head (key 81), diaphragm (key 8), the
second diaphragm head (key 81) and diaphragm
pad (key 80). Inspect the diaphragm parts for
damage and replace if necessary.
7. Inspect the lever (key 26) and replace if
necessary. To replace the valve stem (key 16),
also perform Main Body Valve Disk and Orifice
maintenance procedure steps 1, 2 and 3, remove
disk (key 13) and pull the stem out of the lower
casing assembly (key 1). Lightly lubricate the
replacement stem O-ring (key 14) and install it on
the valve stem. Reinstall the valve stem into the
lower casing assembly. Reinstall the body (key 17)
or continue with the reassembly of the diaphragm.
Note
When assembling the diaphragm assembly
(keys 8, 80 and 81), lubricate the actuator
diaphragm post (key 10) threads.
10. Install the upper casing (key 2) and secure it to the
lower casing (key 1) with the eight hex head screws
(key 23). Tighten the hex head screws evenly using
a crisscross pattern to avoid placing an uneven
strain on the regulator. Tighten the screws to a final
bolt torque of 10 to 13 ft-lbs / 13 to 17 N•m to avoid
crushing the diaphragm.
CAUTION
In step 11, the spring seat (key 4) is
under spring pressure. Use constant
hand pressure to hold the spring down
when installing the hex nuts (key 5),
see Figure 3.
11. Install the closing spring (key 6) and the spring seat
(key 4). Push and hold down on the spring seat,
cocking it to one side until the seat catches onto the
threads of the diaphragm post (key 10). Then, pull
up on the diaphragm post allowing access to the
post threads so that the two adjusting hex nuts
(key 5) can be installed. Install the adjusting hex
nuts as shown in Figure 3. The closing spring must
be adjusted down to a depth of 1/2 in. / 13 mm
from the top of the upper case opening to the top
of the spring seat. When tightening the two hex
nuts, use care not to rotate the diaphragm post,
which may damage the post.
12. Lightly lubricate the O-ring (key 9) on the closing
cap and reinstall the closing cap (key 3).
!
WARNING
The wire seal and warning tag (keys 68
and 69) contain important safety
information, make sure they are attached
when maintenance is completed.
13. Install the wire seal and warning tag (keys 68
and 69).
Main Body Valve Disk and Orifice
8. Loosely reassemble the diaphragm and diaphragm
post parts so that the bolt holes in the diaphragm
align with the corresponding holes in the lower
casing (key 1) when the lever (key 26) is fitted
properly into the pusher post. When this orientation
is made, tighten the diaphragm post into the pusher
post (keys 10 and 11).
9. Reinstall the diaphragm assembly using the
reverse order of step 5.
10
Follow this procedure to inspect, clean or replace
the main body valve disk or to inspect or replace the
orifice. Part key numbers are referenced in Figures 3
and 4.
Note
The regulator body may remain in the
pipeline during maintenance procedures.
Page 11

299H Series
1. Disconnect the pilot supply tubing (key 21) from
the main body (key 17).
2. Remove the two hex head cap screws (key 18)
which hold the lower casing (key 1) to the body.
Separate the lower casing from the body. Inspect
the body O-ring (key 15) and replace if worn
or damaged.
3. Examine the valve disk (key 13) and orifice (key 12)
for nicks, cuts and other damage. Unscrew the disk
holder assembly from the valve stem assembly
(key 16) and replace it with a new part if necessary.
For the Type 299HS, also examine the insert and
O-ring (keys 82 and 83, Figure 6) for any damage.
Replace if needed.
4. If the orifice is being replaced with a new or
differently sized orifice, change the nameplate
(key 63) to state the new size and maximum inlet
pressure. Lubricate the threads and flat face of the
orifice with a good grade of anti-seize lubricant.
Install the orifice using 100 to 120 ft-lbs / 136 to
163 N•m of torque.
5. After replacing all damaged parts, slide the
entire assembly into the valve body (key 17) and
secure with the two hex head cap screws (key 18).
6. Connect the pilot supply tubing (key 21), then refer
to the Startup section for putting the regulator
into operation.
Integral Pilot Valve Disk and Orifice
Follow this procedure to inspect, clean or replace the
integral pilot valve disk or orifice. Part key numbers are
referenced in Figures 3 and 4.
1. Remove or loosen the pilot supply tubing (key 21).
2. Remove the inlet fitting (key 47) and the four
machine screws (key 46).
3. Examine the valve disk (key 52) for nicks, cuts and
other damage. Unscrew the disk holder assembly
from the valve stem (key 48) and replace
if necessary.
4. If the seating edge of the orifice (key 50) is nicked
or rough, use a thin-walled socket to remove the
orifice from the inlet fitting (key 47). Install a new
orifice and a lightly lubricated O-ring (key 49) when
reassembling the regulator.
5. Inspect the check valve assembly (key 45) and
the bleed restriction (key 70) for damage and
replace if necessary.
6. The Type 299H has a wire inlet screen (key 51)
in the pilot supply inlet fitting (key 47). If clogging
is suspected in the pilot supply, remove the elbow
fitting (key 19) and clean the wire screen.
7. Lightly lubricate the O-ring (key 54) on the inlet
fitting (key 47) and reinstall using the four machine
screws (key 46). Torque the machine screws to
30 to 40 in-lbs / 3.4 to 4.5 N•m. Then install and
tighten the pilot supply tubing.
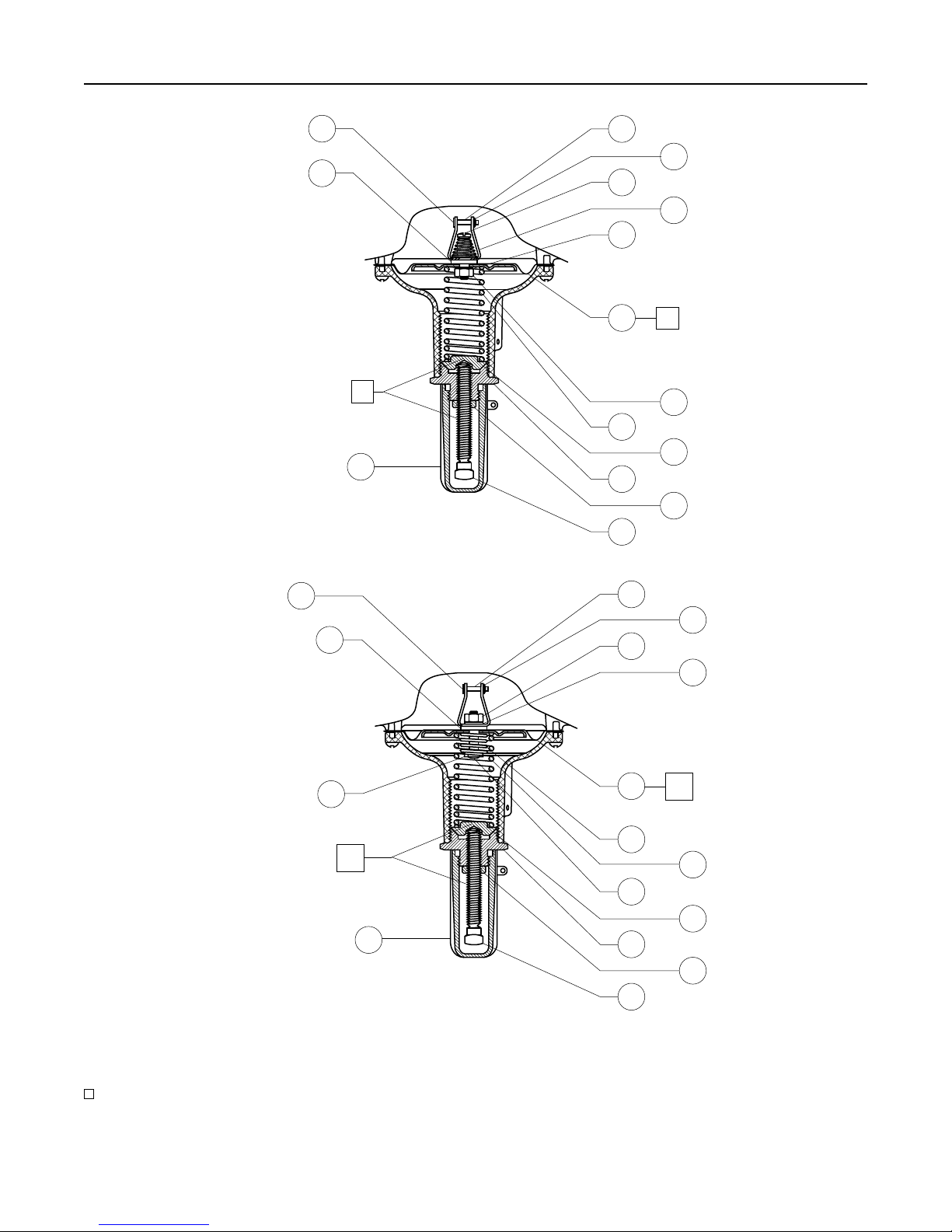
Integral Pilot Control Spring
and Diaphragm
Follow this procedure to change the pilot control spring
or to inspect, clean or replace the diaphragm. Part
key numbers are referenced in Figures 3, 4 and 5.
1. Remove the pilot closing cap (key 29) and
loosen the hex lock nut (key 35). Turn the
adjusting screw (key 36) counterclockwise to
ease spring compression.
2. Unscrew the bonnet (key 34).
3. Remove the bonnet (key 34), spring seat
(key 33) and control spring (key 32).
4. If only replacing the control spring (key 32),
sparingly apply lubricant to the control spring seat
(key 33) and reassemble in the reverse order.
Note
When replacing the control spring with
a different spring range, be sure to
delete the spring range appearing on the
nameplate and indicate the new range.
5. Remove the machine screws (key 30) and spring
case (key 31) from the lower casing (key 1).
6. Remove the diaphragm assembly (key 28) by tilting
them so that the pusher post (key 40) slips off the
lever (key 57). To separate the diaphragm from the
attached parts, unscrew the hex nut (key 37) and
separate the parts: washer (key 38), diaphragm
post (key 39), pusher post (key 40), overtravel
spring (key 41), machine screw (key 42), spring
seat (key 88) (Types 299HR and 299HSR), rivet
(key 43) and retaining ring (key 44).
7. To replace the lever assembly (key 57), remove the
lever pin (key 25). To replace the valve stem
(key 48), also perform Integral Pilot Valve Disk and
Orifice maintenance procedure steps 1, 2 and 3
and pull the stem (key 48) out of the lower casing
assembly (key 1). Lightly lubricate the replacement
stem O-ring (key 53) and install it on the valve stem.
11
Page 12

299H Series
8. Install the valve stem (key 48) into the lower
casing assembly (key 1). Be careful not to cut the
O-ring (key 53) when sliding the valve stem into
the lower casing.
9. Reinstall the diaphragm (key 28) assembly using
the reverse order of step 6.
10. Place the spring case (key 31) on the lower casing
(key 1) with the vent (key 27) oriented downwards
to prevent clogging or entrance or moisture. Install
the machine screws (key 30) and tighten in a
crisscross pattern using 12 to 18 in-lbs /
1.4 to 2.0 N•m of torque.
11. When all maintenance is complete, refer to the
Startup section to put the regulator back into
operation and adjust the pressure setting. Tighten
the locknut (key 35) and install the closing cap
(key 29).
Types VSX2 and VSX8 Maintenance
Maintenance instructions for the Type VSX2 slam-shut
are found in Instruction Manual D103695X012.
Maintenance instructions for the Type VSX8 slam-shut
are found in Instruction Manual D103127X012.
Refer to the Instruction Manual for Type VSX2
slam-shut, document D103695X012, for Adjustment
and Maintenance of the Slam-shut. Refer to the
Instruction Manual for Type VSX8 Slam-shut,
document D103127X012, for Adjustment and
Maintenance of the Slam-shut.
Note
The Type VSX2 is not interchangeable
with the Type VSX8 module. Each
slam-shut module requires a mating
valve body. Both slam-shut and body can
be replaced in the field. See parts list for
part numbers.
Optional P590 Series Filter
For complete installation, maintenance and parts
list refer to the P590 Series Filters Instruction
Manual D101555X012.
Optional Type 67CF Pilot
Supply Regulator
Parts Ordering
The type number, orifice size, spring range and date of
manufacture are stamped on the nameplate. Provide
this information along with the eleven-character part
number to your local Sales Office when ordering parts.
If construction changes are made in the field, be sure
that the nameplate is also changed to reflect the most
recent construction.
Note
It is recommended that the 299H Series
regulator use a complete matching
casing set that includes an upper case,
a lower case and spring case in the
old blank configuration or new swirl
configuration. However, these parts are
interchangeable with each other.
Parts List
299H Series Regulator (Figures 3, 4 and 5)
Key Description Part Number
Parts Kit (Includes keys 8, 9, 13, 14, 15, 28,
49, 52, 53, 54, 60, 61 and 80) R299X000012
1 Lower Casing, Aluminum
Types 299HS and 299HSR T80447T0012
Types 299H, 299HV and 299HVR ERAA10462A1
2 Upper Casing, Aluminum
Type 299HS T40577T0012
Type 299HV ERAA10463A1
3 Closing Cap, Aluminum 1L928308012
4 Spring Seat
Delrin® (standard) ERAA21736A0
Steel (High vibration or engine applications -
used with key 93) T13831T0012
5 Adjustment Nut, Steel (2 required) 1A341224122
6 Closing Spring, Steel T13918T0012
7 Pressure Equalization Spring, Steel T13463T0012
8* Diaphragm, Nitrile (NBR) T20986T0012
9* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) 1F914106992
10 Diaphragm Post, Steel T13814T0012
11 Pusher Post, Aluminum 1L143311992
12 Orifice, Aluminum
1/4 x 3/8 in. / 6.4 x 9.5 mm T13833T0012
3/8 in. / 9.5 mm 1H979309022
1/2 in. / 13 mm 1H979409022
3/4 in. / 19 mm 1H979509022
7/8 in. / 22 mm
(for Types 299H and 299HR only) T14098T0012
1 in. / 25 mm
(for Types 299H and 299HR only) 1H979609022
1-3/16 in. / 30 mm
(for Types 299H and 299HR only) 1H979709022
13* Disk, Nitrile (NBR) 1P7349000A2
14* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) 1E216306992
For complete installation, maintenance and
parts list refer to the 67C Series Instruction
Manual D102601X012.
12
* Recommended spare part.
Delrin® is a mark owned by E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.
Page 13

15* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) T12587T0012
16 Valve Stem Assembly 1L1426000A2
17 Valve Body
Cast Iron, For Types 299H and 299HR only
1-1/4 NPT T40578T0012
1-1/2 NPT 1J190419012
2 NPT 1H968919012
NPS 2 / DN 50
CL125 FF flanged
7.5 in. / 90 mm face-to-face dimension T80445T0012
10 in. / 254 mm face-to-face dimension 2L425119012
Ductile Iron, For all 299H Series
1-1/2 NPT ERAA11740A0
2 NPT ERAA11741A0
NPS 2 / DN 50
CL125 FF flanged ERAA11742A0
CL250 RF flanged ERAA11743A0
PN 10/16 flanged ERAA11744A0
Steel, For Types 299H and 299HR only
1-1/2 NPT 1J1904T0022
2 NPT 1H9689T0022
NPS 2 / DN 50
CL150 RF flanged T80415T0012
18 Cap Screw, Steel (2 required)
Types 299H and 299HR T14034T0012
Types 299HS, 299HSR, 299HV and 299HVR T14082T0012
19 Elbow (3 required for Cast Iron or Steel bodies;
2 required for Ductile Iron Bodies) - - - - - - - - - - -
20 Connector
(1)
- - - - - - - - - - 21 Pilot Supply Tubing, Without filter - - - - - - - - - - 22 Loading Tubing - - - - - - - - - - 23 Cap Screw, Steel (8 required) 1C379124052
24 Machine Screw, Steel (2 required) 1B420428982
25 Lever Pin, Stainless steel (2 required) 1H972935032
26 Lever, Steel T13813T0012
27 Vent Hood (Type Y602-12 Vent Assembly) 27A5516X012
28 Diaphragm Assembly, Nitrile (NBR) diaphragm
and steel diaphragm head T14259T0012
29 Closing Cap, Plastic 24B1301X012
30 Machine Screw, Steel (8 required) T14069T0012
31 Spring Case, Aluminum T14097T0012
Spring Case, Aluminum ERAA10464A1
32 Control Spring See Table 2
33 Spring Seat, Steel T13917T0012
34 Bonnet, Steel T14135T0012
35 Locknut, Steel 1A352224122
36 Adjusting Screw, Steel T14133T0012
37 Hex Nut, Steel 1E985324142
38 Washer, Steel 1F230328992
39 Diaphragm Post, Stainless steel
Types 299H, 299HS and 299HV T13915T0012
Types 299HR, 299HSR and 299HVR T14033T0012
40 Pusher Post, Steel T13914T0012
41 Overtravel Spring, Stainless steel
Types 299H, 299HS and 299HV T14136T0012
Types 299HR, 299HSR and 299HVR T14031T0012
42 Machine Screw, Steel 1A954828992
43 Rivet, Flat head, Stainless steel T13916T0012
299H Series
Key Description Part NumberKey Description Part Number
44 Retaining Ring, Steel 16A6977X012
45 Check Valve Assembly T14258T0012
46 Machine Screw, Steel (4 required) T13920T0012
47 Inlet Fitting, Aluminum T13824T0012
48 Stem Assembly, Aluminum 1H9666T0012
49* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) T13939T0012
50 Pilot Orifice, Aluminum T13825T0012
51 Inlet Screen, Stainless steel T13791T0012
52* Pilot Disk Assembly, Hydrogenated Nitrile (NBR)
and Aluminum disk holder T13955T0012
53* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) 1D682506992
54* O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) 13A2331X022
56 Screw, Steel (External Registration - 2 required
or Dual Registration - 1 required) 1E175828982
57 Lever, Steel T14134T0012
58 Pipe Plug, Steel 1A7715T0012
59 Pipe Plug, Internal Registration only, Steel
3/4 NPT 1A7715T0012
1/4 NPT 1A767524662
61 O-ring, Nitrile (NBR) (External Registration - 2 required
or Dual Registration - 1 required) 17A0960X012
62 Drive Screw, Steel (2 required) 1E501728982
63 Nameplate, Aluminum - - - - - - - - - - 68* Wire Seal T14088T0012
69 Warning Tag, Aluminum - - - - - - - - - - 70 Bleed Restriction, Steel
0.044 in. / 1.1 mm, Red (standard) 17A2029X012
0.071 in. / 1.8 mm, Green 17A2030X012
0.082 in. / 2.1 mm, Blue 17A7277X012
72 Filter Assembly, See P590 Series
Type P593-1 AJ5004T0012
Type P594-1 AJ5004000A2
78 Pilot Supply Tubing, Long (for constructions with
filter or pilot supply option) - - - - - - - - - - 79 Pilot Supply Tubing, Short (for constructions with
filter or pilot supply option) - - - - - - - - - - 80 Pad, Nitrile (NBR) T13830T0012
81 Diaphragm Head, Steel (2 required) T13812T0012
82 Insert (for Types 299HS, 299HSR, 299HV
and 299HVR only, see Figure 6) Aluminum
83 O-ring (for Types 299HS, 299HSR, 299HV
and 299HVR only, see Figure 6) Nitrile (NBR)
84 Plate (for Types 299H and 299HR only), Steel
85 O-ring (for Types 299H and 299HR only),
Nitrile (NBR)
86 O-ring (for Types 299H and 299HR only),
Nitrile (NBR)
87 Set Screw (for Types 299H and 299HR only)
(4 required)
88 Spring Seat, Types 299HR and 299HSR T14030T0012
89 Label
(2)
T13769T0012
(2)
T13772T0012
(2)
1C629828992
(3)
Types 299H and 299HS T1215806032
Types 299HR and 299HSR T1215906032
92 Tee, Stainless steel - - - - - - - - - - 93 Spring Seat Washer, Delrin
(high vibration and engine applications -
94 Plastic Plugs
used with key 4)
(3)
T13543T0042
®
(3)
19B0553X012
(2)
T14013T0012
(2)
T1072606562
(2)
T14039T0012
* Recommended spare part
Delrin® is a mark owned by E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.
1. Cast iron or steel bodies without lter and pilot supply regulator require 1 connector; all other combinations of lter and/or pilot supply regulator require 3 connectors. Ductile iron
bodies without lter and pilot supply regulator require 2 connectors; all other combinations of lter and/or pilot supply regulator require 4 connectors.
2. Ductile iron bodies only.
3. Not shown.
13
Page 14

299H Series
HEX NUTS
APPLY CONSTANT
HAND PRESSURE
SPRING SEAT
UPPER
SPRING CASE
CLOSING SPRING
DIAPHRAGM POST
LOCKING DOWN THE SPRING SEAT TO
FACILITATE INSTALLING THE HEX NUTS
T80391-2
T80391-3
61
25
27
56 24 26
L1
EXTERNAL REGISTRATION
25
26
2724 59
APPLY MULTI-PURPOSE LUBRICANT (L1) / MULTI-PURPOSE POLYTETRAFLUOROETHYLENE (PTFE) THREAD SEALANT (S1)
14
S1
INTERNAL REGISTRATION
Figure 3. 299H Series Interior Assembly
Page 15
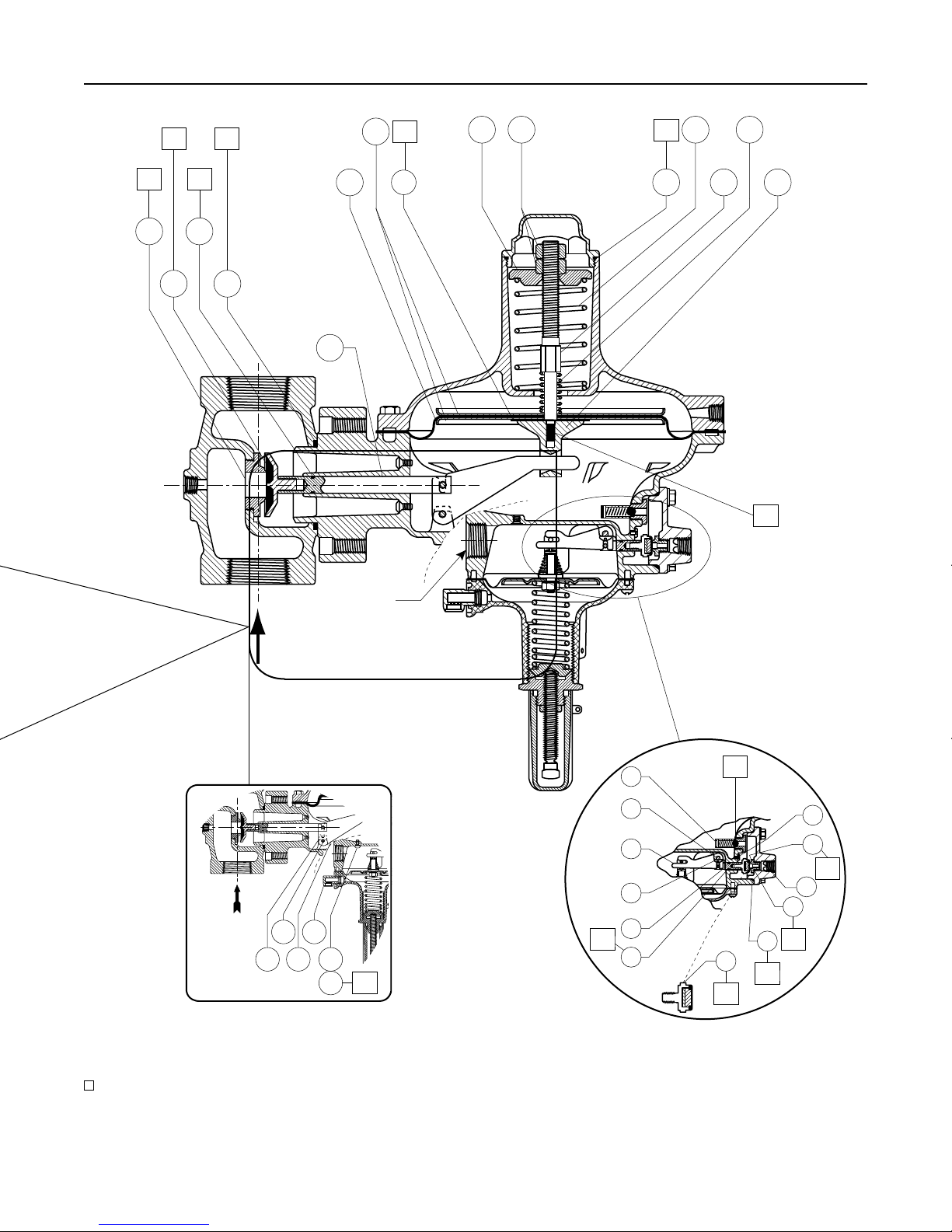
299H Series
L2 L1
L2
12 14
13 15
L1
8 80
16
81
A
4 5 6 7
L1
11109
S2
T80391-4
T80391
24
25
27
26
3/4 NPT
DOWNSTREAM
CONTROL LINE
CONNECTION
56
L1
61
T80391-7
L1
45
25
57
56
48
53
52
L2
L2
54
L1
70
50
L2
51
49
L1
DUAL REGISTRATION
APPLY MULTI-PURPOSE LUBRICANT (L1) / ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND (L2) / THREAD LOCK SEALANT (S1) / ADHESIVE (A)
299H SERIES PILOT TRIM
Figure 3. 299H Series Interior Assembly (continued)
15
Page 16

299H Series
S1
84
85
86
87
20
21
T80391-1
S1
19
18
17
68
69
23
1
2
21
29
3 L2
89
30
19
31
S1
63
62
19
22
46
20
58
47
S1
S1
S1
16
299H SERIES EXTERIOR VIEW
Figure 4. 299H Series Exterior Assembly
Page 17

79
20762078
S1
TYPE 67CF PILOT
SUPPLY REGULATOR
299H Series
T80391-5
78 20 72 20
S1
TUBING AND FITTINGS WITH
OPTIONAL TYPE P590 FILTER
79
20762078
79
APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND (L2) / MULTI-PURPOSE PTFE THREAD SEALANT (S1).
Figure 4. 299H Series Exterior Assembly (continued)
TYPE 67CF PILOT
SUPPLY REGULATOR
T80391-5
TUBING AND FITTINGS WITH OPTIONAL
TYPE 67CF PILOT SUPPLY REGULATOR
S1
17
Page 18
L2
A
40
43
42
38
28
32
34
36
35
33
88
29
37
41
44
39
299H Series
40
39
L2
29
TYPE 299H PILOT WITHOUT RELIEF VALVE
38
32
34
43
42
28
36
44
41
A
37
33
35
40
39
88
L2
29
TYPE 299HR PILOT WITH TOKEN RELIEF VALVE
43
37
28
41
42
34
36
44
38
A
32
33
35
T80391-6
APPLY ANTI-SEIZE COMPOUND (L2) / ADHESIVE (A)
18
Figure 5. 299H Series Pilot Assemblies
Page 19
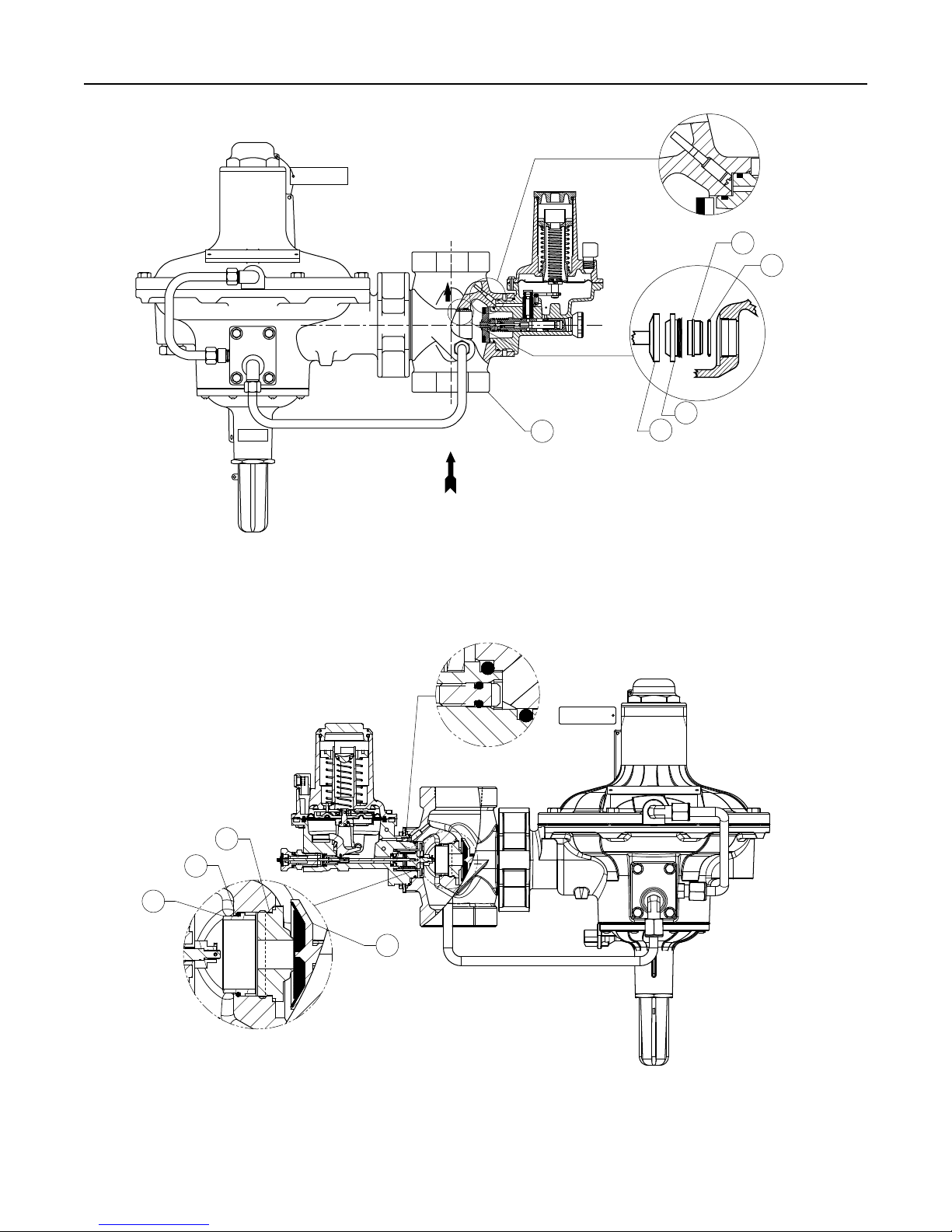
TYPE VSX2
17
299H Series
82
83
12
13
T80423
82
83
12
Figure 6a. Type VSX2 Assembly (for Types 299HS and 299HSR)
TYPE VSX8
TYPE VSX8
13
Figure 6b. Type 299HV with Type VSX8 Assembly
19
Page 20

299H Series
Webadmin.Regulators@emerson.com
Fisher.com
Emerson Automation Solutions
Regulator Technologies
Americas
McKinney, Texas 75070 USA
T +1 800 558 5853
Asia Pacic
Singapore 128461, Singapore
T +65 6770 8337
+1 972 548 3574
Europe
Bologna 40013, Italy
T +39 051 419 0611
Middle East and Africa
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
T +971 4 811 8100
The distinctive swirl pattern cast into every actuator casing
uniquely identies the regulator as part of the Fisher™ brand
Commercial Service Regulator family and assures you of the
highest-quality engineering, performance, and support traditionally
associated with Fisher™, Francel™ and Tartarini™ regulators. Visit
www.fishercommercialservice.com to access interactive applications.
Facebook.com/EmersonAutomationSolutions
LinkedIn.com/company/emerson-automation-solutions
Twitter.com/emr_automation
D102684X012 © 1999, 2017 Emerson Process Management Regulator
Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. 05/17.
The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of Emerson
Electric Co. All other marks are the property of their prospective owners.
Fisher™ is a mark owned by Fisher Controls International LLC, a
business of Emerson Automation Solutions.
The contents of this publication are presented for information purposes
only, and while effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are
not to be construed as warranties or guarantees, express or implied,
regarding the products or services described herein or their use or
applicability. All sales are governed by our terms and conditions, which
are available on request. We reserve the right to modify or improve the
designs or specications of our products at any time without notice.
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. does not
assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any
product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any
Emerson Process Management Regulator Technologies, Inc. product
remains solely with the purchaser.
 Loading...
Loading...