ElmoMC Multi-Axis Motion Controller-Maestro User Manual

Maestro
Software Manual
September 2008 – Ver. Q
www.elmomc.com

Important Notice
This guide is delivered subject to the following conditions and restrictions:
This guide contains proprietary information belonging to Elmo Motion Control Ltd. Such information is supplied solely for the purpose of assisting users of Maestro motion supervisor.
The text and graphics included in this manual are for the purpose of illustration and reference only. The specifications on which they are based are subject to change without notice.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Doc. No. MAN-MASSW
Copyright © 2008
Elmo Motion Control
All rights reserved
Revision History
Version |
Release Date |
Status |
|
Changes/Remarks |
Ver Q |
September 2008 |
|
|
MTCR 00-100-28: Changed output_num range to |
|
|
|
|
0…7, ainput_num range to 0…3. (Applies to m_dout |
|
|
|
|
and m_ain functions in Ch 4, page 4-41.) |
Ver. P |
Early August 2008 |
|
|
Changes to chapters 4, 5, 9 and 13 |
|
|
|
|
Added chapter 14 |
Elmo Motion Control Ltd. |
Elmo Motion Control Inc. |
Elmo Motion Control GmbH |
|
64 Gissin St., P.O. Box 463 |
1 Park Drive, Suite 12 |
Steinkirchring 1 |
|
Petach Tikva 49103 |
Westford, MA 01886 |
D-78056, Villingen-Schwenningen |
|
Israel |
USA |
Germany |
|
Tel: +972 (3) 929-2300 |
Tel: +1 (978) 399-0034 |
Tel: +49 (0) 7720-85 77 60 |
|
Fax: +972 (3) 929-2322 |
Fax: +1 (978) 399-0035 |
Fax: +49 (0) 7720-85 77 70 |
|
info-il@elmomc.com |
info-us@elmomc.com |
info-de@elmomc.com |
www.elmomc.com |
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
i |
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction |
.................................................................................................................. |
1-1 |
||
1.1 |
Maestro Highlights ................................................................................................ |
1-1 |
||
1.2 |
Supplementary ................................................................................Documents |
1-2 |
||
1.3 |
Command ......................................................................................Specification |
1-3 |
||
1.4 |
Scope |
..................................................................................................................... |
|
1-3 |
Chapter 2: Functional Overview................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
|||
2.1 |
Functional ..................................................................................Block Diagram |
2-1 |
||
2.2 |
Host Communications .........................................................................Services |
2-2 |
||
2.3 |
Command .................................................................................Line Interpreter |
2-2 |
||
2.4 |
The Kernel ............................................................................................................ |
|
2-2 |
|
2.5 |
Motion Manager .................................................................................................. |
2-3 |
||
2.6 |
CANopen Network ................................................Communications Services |
2-3 |
||
Chapter 3: Host Communications................................................................................................. |
3-1 |
|||
3.1 |
Setting Up ......................................................the Host through Elmo's Studio |
3-1 |
||
3.2 |
Verifying or .........................................................................Changing the Host |
3-1 |
||
3.3 |
Choosing the .......................................................Host through the Composer |
3-2 |
||
Chapter 4: General and ........................................Motion Instructions; Configuration Tools |
4-1 |
|||
4.1 |
General Functions................................................................................................ |
4-4 |
||
4.2 |
Axis ..................................................................................................................... |
|
|
4-12 |
|
4.2.1 |
Axis Motion ........................................................................Commands |
4-12 |
|
|
4.2.2 |
Axis .......................................................................................Properties |
4-12 |
|
|
4.2.3 |
Axis ........................................................................................Functions |
4-16 |
|
4.3 |
Vector.................................................................................................................. |
|
4-18 |
|
|
4.3.1 |
Vector ....................................................................Motion Commands |
4-18 |
|
|
4.3.2 |
Vector ....................................................................................Properties |
4-18 |
|
|
4.3.3 |
Vector ...............................................................................2D Functions |
4-24 |
|
|
4.3.4 |
Vector ...............................................................................3D Functions |
4-29 |
|
4.4 |
Group.................................................................................................................. |
|
4-34 |
|
|
4.4.1 |
Group ....................................................................Motion Commands |
4-34 |
|
|
4.4.2 |
Group ....................................................................................Properties |
4-34 |
|
|
4.4.3 |
Group .....................................................................................Functions |
4-36 |
|
|
4.4.4 |
Group ..........................................................................................Arrays |
4-37 |
|
4.5 |
CAN Bus Configuration ............................................Tools (for DSP 305 support) |
4-37 |
||
4.6 |
I/O Functions..................................................................................................... |
4-40 |
||
|
4.6.1 |
Maestro ..........................................................................I/O Functions |
4-40 |
|
|
4.6.2 CAN .................................I/O Functions (DS 401 Object Properties) |
4-42 |
||
|
4.6.2.1 ........................................................................................ |
Digital Input |
4-42 |
|
|
4.6.2.2 ..................................................................................... |
Digital Output |
4-43 |
|
Chapter 5: MAXL Program ..........................................................................................Language |
5-1 |
|||
5.1 |
Lexical Conventions ............................................................................................ |
5-1 |
||
|
5.1.1 |
Comments ................................................................................................. |
5-1 |
|
|
5.1.2 |
Identifiers .................................................................................................. |
5-2 |
|
|
5.1.3 |
MAXL ......................................................................................Keywords |
5-2 |
|
Maestro Software Manual |
|
Contents |
ii |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.1.4 |
...............................................................................................Punctuators |
5-3 |
|
|
|
5.1.5 |
Operators................................................................................................... |
5-3 |
|
|
|
5.1.6 |
Literals....................................................................................................... |
5-5 |
|
|
|
5.1.6.1 |
Integer Constant................................................................................... |
5-5 |
|
|
|
5.1.6.2 Named Constant - #define and const. ............................................... |
5-6 |
|
||
|
5.1.6.3 |
Floating-Point Constant ...................................................................... |
5-7 |
|
|
|
5.1.6.4 |
String Literals ....................................................................................... |
5-8 |
|
|
5.2 |
Basic Concepts ..................................................................................................... |
5-8 |
|
||
|
5.2.1 |
Declarations and Definitions................................................................... |
5-8 |
|
|
|
5.2.1.1 |
Declarations.......................................................................................... |
5-8 |
|
|
|
5.2.1.2 |
Array Declarations............................................................................... |
5-9 |
|
|
|
5.2.1.3 |
Definitions ........................................................................................... |
5-10 |
|
|
|
5.2.2 |
Program................................................................................................... |
5-10 |
|
|
|
5.2.3 |
Startup and Termination ....................................................................... |
5-10 |
|
|
|
5.2.3.1 Program Startup – the run Function ................................................. |
5-10 |
|
||
|
5.2.3.2 |
Program Termination ......................................................................... |
5-10 |
|
|
|
5.2.4 |
Types........................................................................................................ |
5-11 |
|
|
|
5.2.4.1 |
Fundamental Types ............................................................................ |
5-11 |
|
|
|
5.2.4.2 |
Object Types ........................................................................................ |
5-11 |
|
|
|
5.2.4.3 |
Debug string........................................................................................ |
5-12 |
|
|
5.3 |
Standard Conversions ....................................................................................... |
5-12 |
|
||
5.4 |
Expressions |
......................................................................................................... |
5-13 |
|
|
|
5.4.1 |
Types of Expressions.............................................................................. |
5-13 |
|
|
|
5.4.1.1 |
MAXL Primary Expressions .............................................................. |
5-13 |
|
|
|
5.4.1.2 |
Postfix Expressions ............................................................................. |
5-14 |
|
|
|
5.4.1.3 Expressions with Unary Operators ................................................... |
5-15 |
|
||
|
5.4.1.4 Expressions with Binary Operators .................................................. |
5-16 |
|
||
|
5.4.1.5 |
MAXL Logical Operators ................................................................... |
5-21 |
|
|
|
5.4.1.6 |
Simple Assignment............................................................................. |
5-22 |
|
|
|
5.4.1.7 |
Size of Array........................................................................................ |
5-22 |
|
|
|
5.4.2 |
Semantics of Expressions....................................................................... |
5-23 |
|
|
|
5.4.2.1 |
Order of Evaluation ............................................................................ |
5-23 |
|
|
5.5 |
Statements .......................................................................................................... |
|
5-24 |
|
|
|
5.5.1 |
Labeled Statements ................................................................................ |
5-24 |
|
|
|
5.5.1.1 Using Labels with the goto Statement .............................................. |
5-24 |
|
||
|
5.5.1.2 Using Labels in the case Statement ................................................... |
5-25 |
|
||
|
5.5.2 |
Selection Statements............................................................................... |
5-25 |
|
|
|
5.5.2.1 The MAXL if Statement...................................................................... |
5-25 |
|
||
|
5.5.2.2 The MAXL switch Statement ............................................................. |
5-26 |
|
||
|
5.5.3 |
Iteration Statements ............................................................................... |
5-27 |
|
|
|
5.5.3.1 The MAXL while Statement............................................................... |
5-27 |
|
||
|
5.5.3.2 The MAXL for Statement ................................................................... |
5-28 |
|
||
|
5.5.4 |
Jump Statements..................................................................................... |
5-28 |
|
|
|
5.5.4.1 The MAXL break Statement............................................................... |
5-29 |
|
||
|
5.5.4.2 The MAXL continue Statement ......................................................... |
5-29 |
|
||
|
5.5.4.3 The MAXL return Statement.............................................................. |
5-29 |
|
||
|
5.5.4.4 |
The goto Statement ............................................................................. |
5-29 |
|
|
|
5.5.4.5 |
Declaration Statements....................................................................... |
5-30 |
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
Contents |
iii |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
5.6 |
............................................................................................................Functions |
5-30 |
|
|
|
5.6.1 |
Function Definition ................................................................................ |
5-30 |
|
|
5.6.2 |
Built-in Functions ................................................................................... |
5-33 |
|
|
5.6.3 |
Callback (interrupt) Functions.............................................................. |
5-34 |
|
5.7 |
Virtual Machine Control Statements ............................................................... |
5-36 |
|
|
|
5.7.1 |
wait control statement ............................................................................ |
5-36 |
|
|
5.7.2 |
waitvar control statement ......................................................................... |
5-36 |
|
|
5.7.3 |
until control statement.............................................................................. |
5-37 |
|
|
5.7.4 |
TRACE control statement ...................................................................... |
5-37 |
|
|
5.7.5 |
reset control statement............................................................................ |
5-37 |
|
5.8 |
Difference Between Static and Dynamic Group............................................. |
5-37 |
|
|
|
5.8.1 Recommendations on using dynamic groups ..................................... |
5-38 |
|
|
5.9 |
Static Variables................................................................................................... |
5-40 |
|
|
|
5.9.1 |
Static Variable Definition....................................................................... |
5-40 |
|
|
5.9.2 Elmo Studio User Interface for Static Variables .................................. |
5-40 |
|
|
5.9.3Working with Static Variables in the Maestro Command Interpreter5-41
5.9.4Working with Static Variables in the Maestro Program Interpreter. 5-42
5.10 |
Maestro User Program Priority........................................................................ |
5-44 |
Chapter 6: The Maestro API .......................................................................................................... |
6-1 |
|
6.1 |
MAC_Initialize..................................................................................................... |
6-1 |
6.2 |
MAC_Uninitialize................................................................................................ |
6-2 |
6.3 |
MAC_CreateTCPConnection ............................................................................. |
6-3 |
6.4 |
MAC_CreateRS232Connection .......................................................................... |
6-4 |
6.5 |
MAC_CloseConnection....................................................................................... |
6-5 |
6.6 |
MAC_SendCommand ......................................................................................... |
6-5 |
6.7 |
MAC_LocateDevices ........................................................................................... |
6-6 |
6.8 |
MAC_GetDevice .................................................................................................. |
6-7 |
6.9 |
MAC_GetIpByName ........................................................................................... |
6-7 |
6.10 |
MAC_IsDevicePresent ........................................................................................ |
6-8 |
6.11 |
MAC_LocateObjects............................................................................................ |
6-8 |
6.12 |
MAC_GetObject................................................................................................... |
6-9 |
6.13 |
MAC_DownloadTrajectory .............................................................................. |
6-11 |
6.14 |
MAC_RemoveTrajectory .................................................................................. |
6-11 |
6.15 |
MAC_DownloadProgram................................................................................. |
6-12 |
6.16 |
MAC_RemoveProgram..................................................................................... |
6-12 |
6.17 |
MAC_DownloadResources .............................................................................. |
6-13 |
6.18 |
MAC_DownloadResourcesEx .......................................................................... |
6-14 |
6.19 |
MAC_UploadLog .............................................................................................. |
6-14 |
6.20 |
MAC_DownloadSimpleIQFirmware............................................................... |
6-15 |
6.21 |
MAC_GetLastError ........................................................................................... |
6-16 |
6.22 |
MAC_InitEvents ................................................................................................ |
6-16 |
6.23 |
MAC_DeinitEvents............................................................................................ |
6-17 |
6.24 |
MAC_RegCloseCallback................................................................................... |
6-17 |
6.25 |
MAC_RegInterruptCallback............................................................................. |
6-17 |
6.26 |
MAC_DownloadSimpleIQProgram ................................................................ |
6-18 |
6.27 |
MAC_DownloadSimpleIQParams................................................................... |
6-19 |
6.28 |
MAC_DownloadSimpleIQApp........................................................................ |
6-20 |
Chapter 7: RS-232 Protocol Specification...................................................................................... |
7-1 |
|
7.1 |
Send Command to Maestro ................................................................................ |
7-1 |
Maestro Software Manual |
|
Contents |
iv |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
...........................................................................7.2 Receive Answer from Maestro |
7-1 |
|
|||
Chapter 8: The Recorder |
................................................................................................................ |
8-1 |
|
||
8.1 |
Accessing the Recorder ....................................................................................... |
8-1 |
|
||
Chapter 9: The CANopen Configurator....................................................................................... |
9-1 |
|
|||
9.1 Microsoft .Net Framework Installation Notes.................................................. |
9-1 |
|
|||
9.2 |
CANopen Configurator GUI .............................................................................. |
9-3 |
|
||
9.3 Connecting to a Maestro ..................................................................................... |
9-3 |
|
|||
9.4 Create a Configuration Set.................................................................................. |
9-4 |
|
|||
|
9.4.1 |
Method 1: Online Configuration Set ...................................................... |
9-4 |
|
|
|
Adding and Deleting Nodes ............................................................................... |
9-5 |
|
||
|
9.4.2 |
Method 2: Configuration Set from an Existing File .............................. |
9-5 |
|
|
|
9.4.3 |
Exporting a Node Set ............................................................................... |
9-6 |
|
|
9.5 Identifying and Resolving Network Problems................................................. |
9-6 |
|
|||
9.6 |
Configuration Status Report............................................................................... |
9-8 |
|
||
9.7 |
CANopen Configurator Options ....................................................................... |
9-9 |
|
||
|
9.7.1 |
Changeable Properties ............................................................................. |
9-9 |
|
|
Chapter 10: Axis DS402 Command Reference .......................................................................... |
10-1 |
|
|||
10.1 |
Modes of Operation........................................................................................... |
10-1 |
|
||
|
10.1.1 |
Device State Machine Control............................................................... |
10-3 |
|
|
|
10.1.2 |
State Machine Operation Reactions...................................................... |
10-7 |
|
|
|
10.1.3 |
Parameter limits ..................................................................................... |
10-9 |
|
|
|
10.1.4 |
The Motor Manipulation Macro Command MO .............................. |
10-11 |
|
|
10.2 Profile Position (PP) Mode ............................................................................. |
10-12 |
|
|||
|
10.2.1 |
Profile Position (PP) Commands ........................................................ |
10-12 |
|
|
|
10.2.2 |
Profile Position Commands Usage ..................................................... |
10-14 |
|
|
|
10.2.2.1 Profile Position Motion Implementation ........................................ |
10-14 |
|
||
|
10.2.2.2 Profile position Mode Commands description .............................. |
10-16 |
|
||
|
10.2.2.3 |
Features of Profile Position Operating Mode Using for Group |
|
||
|
(Vector) |
10-17 |
|
|
|
10.3 Profile Velocity (PV) Mode............................................................................. |
10-20 |
|
|||
|
10.3.1 |
Profile Velocity (PV) COMMANDS ................................................... |
10-20 |
|
|
|
10.3.2 |
Profile Velocity Commands ................................................................ |
10-21 |
|
|
|
10.3.3 |
Profile Velocity Mode Commands Description ................................ |
10-22 |
|
|
|
10.3.4 |
Features of Profile Velocity operating Mode Using for Group (Vector)10-22 |
|||
10.4 Interpolated Position (IP) Mode..................................................................... |
10-24 |
|
|||
|
10.4.1 |
Interpolated Position (IP) Commands................................................ |
10-26 |
|
|
|
10.4.2 |
Using Interpolated Position Commands............................................ |
10-28 |
|
|
|
10.4.2.1 Implementing Interpolated Position Motion ................................. |
10-28 |
|
||
|
10.4.2.2 Interpolated Position Mode Commands Description.................... |
10-30 |
|
||
|
10.4.2.3 |
Features of Interpolated Position Operating Mode Using for Group |
|
||
|
(Vector) |
10-35 |
|
|
|
10.5 |
Homing (HM) mode........................................................................................ |
10-36 |
|
||
|
10.5.1 |
Homing (HM) Commands .................................................................. |
10-36 |
|
|
|
10.5.2 |
Using Homing Commands.................................................................. |
10-37 |
|
|
|
10.5.2.1 |
Homing Implementation.................................................................. |
10-37 |
|
|
|
10.5.2.2 Description of Homing Mode Commands ..................................... |
10-38 |
|
||
|
10.5.2.3 Features of Homing Operating Mode Using for Group (Vector).10-38 |
|
|||
Maestro Software Manual |
|
Contents |
v |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
.............................................................................Profiled Torque (PT) Mode |
10-39 |
|
||
|
10.6.1 Profiled Torque (PT) Commands........................................................ |
10-39 |
|
||
|
10.6.2 Using Profiled Torque Commands..................................................... |
10-40 |
|
||
|
10.6.2.1 |
Profiled Torque Implementation ..................................................... |
10-40 |
|
|
|
10.6.2.2 Description of the Profiled Torque Mode Command.................... |
10-41 |
|
||
|
10.6.2.3 Using the Profiled Torque Mode for a Group (Vector) ................. |
10-42 |
|
||
10.7 |
DS402 Command List...................................................................................... |
10-42 |
|
||
10.8 |
DS402 PDO Mapping table............................................................................. |
10-57 |
|
||
Chapter 11: Ethernet IP Communication................................................................................... |
11-1 |
|
|||
11.1 |
Terms and Abbreviations ................................................................................. |
11-2 |
|
||
11.2 |
Types of Ethernet/IP Messages ....................................................................... |
11-2 |
|
||
11.3 |
Product Classes.................................................................................................. |
11-3 |
|
||
11.4 |
Ethernet/IP Module Activation ....................................................................... |
11-3 |
|
||
|
11.4.1 Ethernet/IP Scanner (Rockwell) Activation ........................................ |
11-3 |
|
||
|
11.4.2 Ethernet/IP Adapter (Maestro) Activation ......................................... |
11-6 |
|
||
11.5 |
UCMM (Unconnected) Messaging .................................................................. |
11-7 |
|
||
|
11.5.1 Server (Maestro) UCMM (Unconnected) Messaging.......................... |
11-7 |
|
||
|
11.5.1.1 User interface to create communication objects............................... |
11-7 |
|
||
|
11.5.1.2 |
Using syntax ........................................................................................ |
11-8 |
|
|
|
11.5.2 Client (Rockwell) Messaging Support................................................ |
11-10 |
|
||
|
11.5.2.1 User interface to create communication objects............................. |
11-11 |
|
||
|
11.5.2.2 |
Using syntax ...................................................................................... |
11-12 |
|
|
11.6 |
Class 1 (I/O) connection server ..................................................................... |
11-14 |
|
||
|
11.6.1 User interface to create communication objects................................ |
11-15 |
|
||
|
11.6.2 |
Using syntax ......................................................................................... |
11-15 |
|
|
11.7 |
Class 3 (connected) messaging server ........................................................... |
11-16 |
|
||
|
11.7.1 User interface to create communication objects................................ |
11-16 |
|
||
|
11.7.2 |
Using syntax ......................................................................................... |
11-17 |
|
|
|
11.7.2.1 |
Command interpreter ....................................................................... |
11-17 |
|
|
|
11.7.2.2 |
Maestro Program .............................................................................. |
11-18 |
|
|
Chapter 12: MODBUS Implementation..................................................................................... |
12-1 |
|
|||
12.1 |
Master (Client) functionality implementation................................................ |
12-2 |
|
||
|
12.1.1 |
Ethernet media........................................................................................ |
12-2 |
|
|
|
12.1.1.1 |
TCP communication parameters ....................................................... |
12-2 |
|
|
12.2 |
Serial RS-232 media ........................................................................................... |
12-3 |
|
||
|
12.2.1 Communication parameters for ASCII or RTU................................... |
12-3 |
|
||
12.3 |
MODBUS Master functionality ........................................................................ |
12-3 |
|
||
|
12.3.1 MODBUS Master Object Communication Control Functions ........... |
12-4 |
|
||
|
12.3.2 MODBUS Master Object Bit Access Functions.................................... |
12-4 |
|
||
|
12.3.3 MODBUS Master Object 16-bit Access Functions............................... |
12-7 |
|
||
12.4 |
Slave (Server) functionality implementation ................................................ |
12-10 |
|
||
12.5 |
MODBUS objects configuration by Elmo Studio: User Interface |
|
|
||
implementation |
.......................................................................................................... |
12-13 |
|
||
|
12.5.1 Elmo .........................................................Studio MODBUS window |
12-13 |
|
||
|
12.5.2 |
MODBUS ..........................................................................TCP master |
12-14 |
|
|
|
12.5.3 |
MODBUS .......................................................................Serial Master |
12-15 |
|
|
|
12.5.4 |
MODBUS ............................................................................TCP Slave |
12-15 |
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
|
Contents |
vi |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
12.5.5 |
..........................................................................MODBUS Serial Slave |
12-16 |
|
||
12.6 |
MODBUS communication workflow............................................................. |
12-17 |
|
||
12.7 |
MODBUS Protocol Errors ............................................................................... |
12-18 |
|
||
Chapter 13. Node DS301 Command Reference ........................................................................ |
13-1 |
|
|||
13.1 |
NMT Service....................................................................................................... |
13-1 |
|
||
13.2 |
Sync and Timestamp .......................................................................................... |
13-2 |
|
||
13.3 |
Emergency Handling ........................................................................................ |
13-2 |
|
||
13.4 |
Send PDO |
............................................................................................................ |
13-2 |
|
|
13.5 |
Initialization of Callback Functions: Receive PDO ........................................ |
13-3 |
|
||
13.6 |
Callback Functions: ....................................................................Receive PDO |
13-3 |
|
||
13.7 |
Download .......................................................................................SDO - 8 bit |
13-4 |
|
||
13.8 |
Download .....................................................................................SDO - 16 bit |
13-5 |
|
||
13.9 |
Download .....................................................................................SDO - 32 bit |
13-5 |
|
||
13.10 |
Upload SDO ............................................................................................- 8 bit |
13-6 |
|
||
13.11 |
Upload SDO ...........................................................................................- 16 bit |
13-6 |
|
||
13.12 |
Upload SDO ...........................................................................................- 32 bit |
13-7 |
|
||
13.13 |
Heartbeat ...........................................................................................Handling |
13-7 |
|
||
Chapter 14: Maestro Message .........................................................................................Queue |
14-1 |
|
|||
14.1 |
User Message .....................................................................................Methods |
14-1 |
|
||
14.2 |
Using the ...............................................Maestro Message Queue: Examples |
14-2 |
|
||
Appendix A: Setting up .....................................................................................the Demo Case |
A-1 |
|
|||
A.1 |
Setting Up ................................................................................the CAN nodes |
A-1 |
|
||
A.2 |
Checking ....................................................................the CANOpen Network |
A-2 |
|
||
Appendix B: Sample Programs .................................................................................................... |
B-1 |
|
|||
B.1 |
Graphic Primitives............................................................................................... |
B-3 |
|
||
B.1.1 |
Line ................................................................................................Sample |
B-3 |
|
||
B.1.2 |
Circle ...........................................................................................Samples |
B-3 |
|
||
|
B.1.2.1 ........................................................................................ |
Circle Sample |
B-3 |
|
|
|
B.1.2.2 ................................................................................ |
Add Point Sample |
B-4 |
|
|
B.1.3 Line .................................................................................to Line Samples |
B-5 |
|
|||
|
B.1.3.1 ........................................................................... |
Line _ to _ Line Sample |
B-5 |
|
|
B.1.4 Line ..............................................................................to Circle Samples |
B-5 |
|
|||
|
B.1.4.1 ........................................................................................ |
Line to Circle |
B-5 |
|
|
|
B.1.4.2 ................................................................Line to Circle with Homing |
B-6 |
|
||
B.1.5 Circle ..............................................................................to Line Samples |
B-7 |
|
|||
|
B.1.5.1 ........................................................................................ |
Circle to Line |
B-7 |
|
|
|
B.1.5.2 ..................................................Circle-to-Line with Homing Sample |
B-8 |
|
||
B.1.6 |
Polygon .........................................................................................Sample |
B-8 |
|
||
|
B.1.6.1 ................................................................................................. |
Polygon |
B-8 |
|
|
B.2 |
Motion Mathematics............................................................................................ |
B-9 |
|
||
B.3 |
Basic Programming ............................................................................................. |
B-9 |
|
||
B.3.1 |
Break ...............................................................-Continue-Return Sample |
B-9 |
|
||
B.3.2 |
Function ................................................................................Call Sample |
B-9 |
|
||
B.3.3 |
For Sample ................................................................................................. |
B-9 |
|
||
B.3.4 |
Global ..........................................................................Variable Sample |
B-10 |
|
||
B.3.5 |
If Sample................................................................................................... |
B-10 |
|
||
B.3.6 |
If-Else ..........................................................................................Sample |
B-11 |
|
||
B.3.7 |
If-Else ......................................................................................-If Sample |
B-11 |
|
||
Maestro Software Manual |
|
Contents |
vii |
||
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
B.3.8 |
Label and GoTo Sample.......................................................................... |
B-11 |
|
|
|
B.3.9 |
Order of Processing Sample ................................................................... |
B-11 |
|
|
|
B.3.10 |
Program Call............................................................................................ |
B-12 |
|
|
|
B.3.11 |
Switch Sample.......................................................................................... |
B-12 |
|
|
|
B.3.12 |
While Sample........................................................................................... |
B-12 |
|
|
|
B.3.13 |
Array Samples ......................................................................................... |
B-13 |
|
|
|
B.3.13.1 |
Array ................................................................................................... |
B-13 |
|
|
|
B.3.13.2 |
GroupAsArray ................................................................................... |
B-13 |
|
|
|
B.3.13.3 |
Int Array2D ........................................................................................ |
B-13 |
|
|
|
B.3.13.4 |
VectorAsArray ................................................................................... |
B-13 |
|
|
|
B.3.13.5 |
Drill Machine...................................................................................... |
B-14 |
|
|
B.4 |
Callbacks Functions........................................................................................... |
B-15 |
|
||
|
B.4.1 |
PerrorCallBack......................................................................................... |
B-15 |
|
|
|
B.4.2 |
EmcyCallback .......................................................................................... |
B-15 |
|
|
|
B.4.3 |
HeartbeatCallBack................................................................................... |
B-15 |
|
|
|
B.4.4 |
EmitCallback Samples ............................................................................ |
B-16 |
|
|
|
B.4.4.1 |
Emit ..................................................................................................... |
B-16 |
|
|
|
B.4.4.2 |
EmitCallback ...................................................................................... |
B-17 |
|
|
|
B.4.5 |
InputCallBack Samples........................................................................... |
B-17 |
|
|
|
B.4.5.1 |
InputCallBack..................................................................................... |
B-17 |
|
|
|
B.4.5.2 |
InputOutputTest1 .............................................................................. |
B-19 |
|
|
|
B.4.5.3 |
InputOutputTest2 .............................................................................. |
B-20 |
|
|
|
B.4.6 |
Motion Completed Callback Samples ................................................... |
B-21 |
|
|
|
B.4.6.1 |
MCompleteCallback .......................................................................... |
B-21 |
|
|
|
B.4.6.2 |
MotionCompleteTest ......................................................................... |
B-23 |
|
|
B.5 |
Homing............................................................................................................... |
|
B-23 |
|
|
|
B.5.1 |
Wall Homing............................................................................................ |
B-23 |
|
|
B.6 |
Inputs .................................................................................................................. |
|
B-24 |
|
|
|
B.6.1 |
MaestroAnalogInputs ............................................................................. |
B-24 |
|
|
|
B.6.2 |
Input Callback ......................................................................................... |
B-26 |
|
|
|
B.6.3 |
InputOutputTest1.................................................................................... |
B-26 |
|
|
|
B.6.4 |
InputOutputTest2.................................................................................... |
B-26 |
|
|
B.7 |
Motion Objects ................................................................................................... |
B-26 |
|
||
|
B.7.1 |
Group Objects .......................................................................................... |
B-26 |
|
|
|
B.7.1.1 |
GroupCommonBg.............................................................................. |
B-26 |
|
|
|
B.7.1.2 |
GroupCommonInit ............................................................................ |
B-27 |
|
|
|
B.7.1.3 |
GroupTrj ............................................................................................. |
B-28 |
|
|
B.8 |
Etc........................................................................................................................ |
|
|
B-29 |
|
|
B.8.1 |
Adddwell Sample.................................................................................... |
B-29 |
|
|
|
B.8.2 |
Elmo Logo Outline Sample .................................................................... |
B-30 |
|
|
|
B.8.3 |
SendMessage............................................................................................ |
B-31 |
|
|
|
B.8.4 |
Poin2Point ................................................................................................ |
B-32 |
|
|
|
B.8.5 |
VectorAxisMove ...................................................................................... |
B-33 |
|
|
Appendix C: Performance Considerations................................................................................. |
C-1 |
|
|||
Appendix D: Maestro System Errors.......................................................................................... |
D-1 |
|
|||
D.1 |
Error Structure: ................................................................................................... |
D-1 |
|
||
D.2 |
Common Zone Errors......................................................................................... |
D-2 |
|
||
|
D.2.1 |
Root-level Error Codes:............................................................................ |
D-2 |
|
|
|
D.2.2 |
Root-level Warning Codes: ..................................................................... |
D-2 |
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
|
|
Contents |
viii |
|
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
D.2.3 |
Top-level Error Codes:............................................................................. |
D-2 |
|
||
D.3 CAN Communication Zone Errors................................................................... |
D-4 |
|
|||
D.3.1 |
Root-level Error Codes:............................................................................ |
D-4 |
|
||
D.3.2 |
Root-level Warning Codes: ..................................................................... |
D-5 |
|
||
D.3.3 |
Top-level Error Codes:............................................................................. |
D-5 |
|
||
D.4 Virtual Machine Zone Errors............................................................................. |
D-5 |
|
|||
D.4.1 |
Root-level Error Codes:............................................................................ |
D-5 |
|
||
D.4.2 |
Fatal Errors |
................................................................................................ |
D-8 |
|
|
D.4.3 |
Root-level Warnings ....................................................................Codes: |
D-8 |
|
||
D.4.4 |
Top-level Error .............................................................................Codes: |
D-9 |
|
||
D.5 Mathematical Library ...................................................................Zone Errors |
D-9 |
|
|||
D.5.1 |
Root-level Error ............................................................................Codes: |
D-9 |
|
||
D.5.1.1 |
Error ........................................................................................... |
0001 |
D-9 |
|
|
D.5.1.2 |
Error ........................................................................................... |
0003 |
D-9 |
|
|
D.5.1.3 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0005 |
D-10 |
|
|
D.5.1.4 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0006 |
D-10 |
|
|
D.5.1.5 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0010 |
D-10 |
|
|
D.5.1.6 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0011 |
D-10 |
|
|
D.5.1.7 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0012 |
D-11 |
|
|
D.5.1.8 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0013 |
D-11 |
|
|
D.5.1.9 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0014 |
D-11 |
|
|
D.5.1.10 |
Error 0015........................................................................................... |
D-11 |
|
||
D.5.1.11 |
Error 0017........................................................................................... |
D-12 |
|
||
D.5.1.12 |
Error ..........................................................................................0021 |
D-12 |
|
||
D.5.1.13 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0022 |
D-12 |
|
|
D.5.1.14 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0023 |
D-13 |
|
|
D.5.1.15 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0028 |
D-13 |
|
|
D.5.1.16 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0030 |
D-13 |
|
|
D.5.1.17 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0040 |
D-13 |
|
|
D.5.1.18 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0041 |
D-14 |
|
|
D.5.1.19 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0047 |
D-14 |
|
|
D.5.1.20 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0050 |
D-14 |
|
|
D.5.1.21 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0051 |
D-14 |
|
|
D.5.1.22 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0061 |
D-14 |
|
|
D.5.1.23 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0062 |
D-15 |
|
|
D.5.1.24 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0063 |
D-15 |
|
|
D.5.1.25 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0067 |
D-15 |
|
|
D.5.1.26 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0068 |
D-15 |
|
|
D.5.1.27 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0074 |
D-16 |
|
|
D.5.1.28 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0075 |
D-16 |
|
|
D.5.1.29 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0076 |
D-16 |
|
|
D.5.1.30 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0077 |
D-17 |
|
|
D.5.1.31 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0079 |
D-17 |
|
|
D.5.1.32 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0080 |
D-17 |
|
|
D.5.1.33 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0081 |
D-17 |
|
|
D.5.1.34 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0082 |
D-18 |
|
|
D.5.1.35 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0084 |
D-18 |
|
|
D.5.1.36 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0085 |
D-18 |
|
|
D.5.1.37 |
Error ......................................................................................... |
0089 |
D-18 |
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
|
|
|
Contents |
ix |
|
MAN-MAMSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D.5.1.38 |
Error |
0096......................................................................................... |
D-19 |
|
||
D.5.1.39 |
Error |
0098......................................................................................... |
D-19 |
|
||
D.5.1.40 |
Error |
0100......................................................................................... |
D-19 |
|
||
D.5.1.41 |
Error |
0101......................................................................................... |
D-20 |
|
||
D.5.1.42 |
Error |
0102......................................................................................... |
D-20 |
|
||
D.5.1.43 |
Error |
0103......................................................................................... |
D-20 |
|
||
D.5.1.44 |
Error |
0104......................................................................................... |
D-20 |
|
||
D.5.1.45 |
Error |
0105......................................................................................... |
D-21 |
|
||
D.5.2 |
Root-Level Warning Codes ................................................................... |
D-21 |
|
|||
D.5.2.1 |
Warning |
0001................................................................................... |
D-21 |
|
||
D.5.2.2 |
Warning |
0002................................................................................... |
D-21 |
|
||
D.5.2.3 |
Warning |
0003................................................................................... |
D-21 |
|
||
D.5.2.4 |
Warning |
0004................................................................................... |
D-22 |
|
||
D.5.2.5 |
Warning |
0005................................................................................... |
D-22 |
|
||
D.5.2.6 |
Warning |
0006................................................................................... |
D-22 |
|
||
D.5.2.7 |
Warning |
0007................................................................................... |
D-22 |
|
||
D.5.2.8 |
Warning 0008.................................................................................... |
D-22 |
|
|||
D.5.2.9 |
Warning |
0009................................................................................... |
D-23 |
|
||
D.5.3 |
Additional Errors ................................................................................... |
D-23 |
|
|||
D.5.3.1 |
Error 0202 0007................................................................................. |
D-23 |
|
|||
D.5.3.2 |
Error 0202 0018................................................................................. |
D-23 |
|
|||
D.5.3.3 |
Error 0202 0048................................................................................. |
D-23 |
|
|||
D.5.3.4 |
Error 0202 0049................................................................................. |
D-24 |
|
|||
D.5.3.5 |
Error 0202 0052................................................................................. |
D-24 |
|
|||
D.5.3.6 |
Error 0202 0069................................................................................. |
D-24 |
|
|||
D.5.3.7 |
Error 0202 0086................................................................................. |
D-24 |
|
|||
D.5.3.8 |
Error 0202 0092................................................................................. |
D-25 |
|
|||
D.5.3.9 |
Error 0202 0093................................................................................. |
D-25 |
|
|||
D.5.3.10 |
Error 0202 0095................................................................................. |
D-25 |
|
|||
D.5.3.11 |
Error 0202 0112................................................................................. |
D-25 |
|
|||
D.5.3.12 |
Error 0202 0113................................................................................. |
D-26 |
|
|||
D.5.3.13 |
Error 0016 |
........................................................................................... |
D-26 |
|
||

Maestro Software Manual |
1-1 |
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
||
|
||
|
|
Chapter 1: Introduction
Elmo’s Maestro is a network-based multi-axis motion supervisor that operates in conjunction with Elmo intelligent servo drives to provide a full multi-axis motion control solution. The Maestro and the SimplIQ servo drives share the motion processing workload in a distributed motion control architecture.
1.1Maestro Highlights
The Maestro operates as a Multi-Axis Motion Supervisor to:
coordinate motion between various axes in synchronized interpolated mode
integrate event handling into motion control procedures
The Maestro operates as a CANopen Network Node Master for:
Network management (NMT)
Clock synchronization
Network Configuration
The Maestro operates as an Ethernet - CAN gateway
The Maestro acts as a file archiver and distributor of:
Firmware – Maestro and intelligent drives
Multi-Axis User Applications – Maestro and intelligent drives
System Resources
The Maestro operates as a Multi-Axis Motion Analysis & Development tool:
Multi-Axis recording and analysis tools
Multi-Axis application development environment
The Maestro can be monitored through a web browser.
Machine
Programming
And Control
Multi-Axis
Motion Control
Single-Axis
Motion Control
Figure 1-1 Maestro Multi-Axis Supervisor Architecture

Maestro Software Manual |
Introduction |
1-2 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
1.2Supplementary Documents
This manual is part of a documentation set that, together, can be used to set up and program the motion of any machine whose motors are controlled by Elmo SimplIQ servo drives. Before you can use this manual you will need to carefully follow the instructions in the Maestro Installation Guide to set up your Maestro.
The software described in this manual is provided on the CD that accompanies the Maestro or as a download from Elmo's web site. In this manual it is assumed that you have followed the software setup instructions in the Maestro Installation Guide and have successfully installed the software.
At least one drive needs to be connected to the Maestro in order for it to function as a motion controller. The SimplIQ manuals shown below explain how to set up and program servo drives. Please read the Installation Guide that arrived with your servo drive before setting it up. Servo drives are power devices so be careful.
Maestro
Setup
Maestro
Programming
Drive
Installation
Drive
Setup
Drive/Axis
Programming
Tuba
Cornet
Maestro
Installation Guide
Maestro
Software Manual
SimplIQ
Digital Servo Drive
Installation Guide(s)
Composer User Manual
CANopen Implementation Guide
SimplIQ Software Manual
SimplIQ Command Reference Manual
Figure 1-2: Elmo Documentation Hierarchy
Maestro Software Manual |
Introduction |
1-3 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
1.3Command Specification
Commands for SimplIQ drives may be specified from the following sources:
|
User program |
A program loaded to the servo drive via one of the |
|
|
communication options. After program execution begins, the |
|
|
program is managed by the drive. |
|
RS-232 |
Serial, point-to-point, short-range communication. Although this |
|
|
method is rather slow, RS-232 is very easy to use and |
|
|
requirements are minimal: a standard PC with serial port and |
|
|
ASCII terminal software. |
|
CANopen |
Serial, multi-drop, medium speed and medium-range |
|
|
communication. This type of communication requires special- |
|
|
purpose host hardware and software. |
This manual describes the Maestro commands that can be specified from each of these sources. Most of the commands are equally available for all three sources. Certain commands, however, are limited in scope according to type of program or communication.
All the commands are available to CAN communication in text form through the OS service, objects 0x1023 and 0x1024. In addition, the numerical set/get commands are available to CAN users in short PDO form, called the “binary interpreter.” The binary and the OS SCAN interpreters are described fully in the CAN manual.
CANopen may also be used to manipulate the drive using the object dictionary (OD) method, which is the native CAN method. This manual does not cover OD manipulations with CANopen; refer to the “Object Dictionary” section of the CANopen manual for full explanations.
The Maestro drive responds to many privileged commands — such as those used by the Composer setup wizard — that are not documented in this manual.
1.4Scope
This manual includes the complete list of commands used by the Maestro servo drives.
The commands are presented in two ways:
A task-related listing
Alphabetically
In the task-related reference, the commands are sorted into groups of related commands. Each group is presented in a table listing the commands with basic descriptions. The alphabetical command listing provides a detailed explanation of each command, with examples and references to the SimplIQ Software Manual when necessary.

Maestro Software Manual |
2-1 |
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
||
|
||
|
|
Chapter 2: Functional Overview
This chapter takes a look at the organization of Maestro software.
2.1Functional Block Diagram
The Maestro’s functionality can be organized into the 5 groups shown below.
The first group (Host Communications Services) contains the standard interfaces and protocols that enable the Maestro to communicates with the “outside world”.
The Command Line Interpreter is a utility that enables individual commands to be executed immediately by either the Maestro or by a SimplIQ drive on a specified axis.
The Kernel is the part of the Maestro that executes user programs.
The Motion Manager sends commands and information to all axes and receives information so that it can coordinate motion between all the axes.
The Maestro is designed to manage multiple axes on a CAN Open network. The CAN Network Communication Server contains the CAN Open interfaces and protocols that enable the Maestro to do so.
|
|
|
RS - 232 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethernet |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Host |
|
|
|
|
TelNet |
|
WEB |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
API |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Command Line Interpeter |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Virtual |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Machine |
|
Machine |
|
Kernel |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Virtual |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Machine |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O |
|
Group |
|
|
Vector |
|
|
|||||||
|
CAN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axis Manager |
|||||||||
Services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CANopen (DS-301) |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CANopen Master |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CANopen API |
|||||||||
Gateway
Key:
Host Communication Services
Command Line Interpeter
Virtual Machines
(for executing User Programs)
Motion Manager
CAN Network
Communications Server
Figure 2-1 The Maestro's Building Block
Maestro Software Manual |
Functional Overview |
2-2 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
2.2Host Communications Services
A host application can access the Maestro using either a TCP/IP or RS-232 services. Processes carried out through host communication include:
Transfer of operating instructions (e.g. for running a program or killing it) to the Maestro
Transfer operational data (such as the trajectory of the next motion)
Status requests
Debugging
Generation of a “transparent path” from a Composer program to any single end-unit
Host communication is used to execute different tasks, including:
Processing of interpreter commands
Maintenance and file download/upload
Processing of direct-axis interpreter commands
CANopen gateway
2.3Command Line Interpreter
CLI commands that are sent to the Maestro are either executed by the Maestro itself or are forwarded directly to the specified axis for immediate execution.
The CLI currently supports the following commands:
Initialization commands
Commands for collect information
Axis commands
Vector commands
Group command
2.4The Kernel
One of the main Kernel functions is running Maestro User Programs. The part of the Kernel which executes the User Programs is the Virtual Machine which enables multiaxis programming. Each task (program) can work independently of the other tasks by running a separate virtual machine. Communication and synchronization between tasks can be performed by using global variables. Multiple tasks can be used to run different machine functions in parallel.
Maestro Software Manual |
Functional Overview |
2-3 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
2.5Motion Manager
The Motion Manager is the portion of the Kernel which provides services for the I/O and the following motion objects:
Axis
Group
Vector
2.6CANopen Network Communications Services
The CANopen Network Communication is the portion of the Kernel which provides the following functionality:
CANopen Bus services
CANopen DS 301 Protocol
CANopen Master
CANopen API
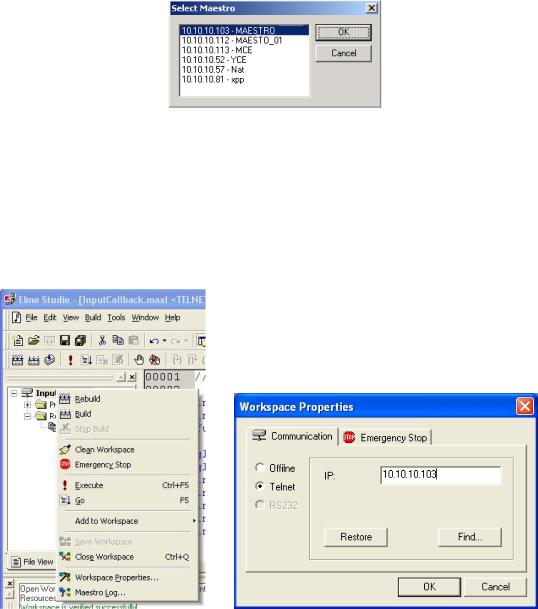
Maestro Software Manual |
3-1 |
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
||
|
||
|
|
Chapter 3: Host Communications
This chapter explains how to set up the Workspace to work with a specific Maestro as a host.
3.1Setting Up the Host through Elmo's Studio
A Select Maestro pick list pops up when starting a new worksheet for the first time. The window contains a list of Maestros currently attached to the network. The IP Address of the Maestro and its name are listed. Select the Maestro you plan to work with and click OK.
Figure 3-1 The Maestro Selection Window
3.2Verifying or Changing the Host
To verify that you have set up the correct Maestro as the host, or to change to another Maestro, move the cursor into the File Viewer and click on the right mouse button. When the menu pops up select Workspace Settings. This will cause the Workspace Settings window to open. If the IP Address is wrong, click the Find button to open the Select Maestro window.
Figure 3-2 Right Mouse Button |
Figure 3-3 The Workspace Settings Window |
Selection Options |
|

Maestro Software Manual |
Host Communications |
3-2 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
3.3Choosing the Host through the Composer
Select Start/Programs/Elmo/Composer to start Elmo's Composer and check the setup.
1.In the Welcome menu select the Open Communication Directly option.
2.In the Application Name and Communication Type dialog box check the TCP/IP Gateway option and click the Properties button.
3.In the Select Drive dialog you should see at least one Maestro in the Gateway list. Select it.
4.Go to the drive window, select one of the drives and click OK to open communications with the selected drive.
5.If the Composer has no information about the device that was selected, it will upload the device info. That could take a minute or two.
6.If all is connected properly, the Smart Terminal window in the Composer will open.
Maestro Software Manual |
4-1 |
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
||
|
||
|
|
Chapter 4: General and Motion
Instructions; Configuration Tools
This chapter describes the Maestro input/output and motion objects, instructions and CAN configuration tools.
The Maestro Multi-Axis Controller supports the following set of Input/Output Objects:
•Internal Maestro I/O Objects: the Maestro has eight Digital Inputs, eight Digital Outputs and four Analog Inputs.
•External CAN I/O: the Maestro can control external I/Os that conform to the CANopen DS 401 protocol and use the I/Os on Elmo SimplIQ devices.
The Maestro Multi-Axis Controller supports the following set of Motion Objects:
•Axis is the most basic Maestro motion object and it is used to control the motion of a single motor/axis.
•Vector2D: This object is comprised of two axes of the same type and it is used to define two dimensional trajectories.
•Vector3D: This object is comprised of three axes of the same type and it is used to define two dimensional trajectories.
•Group is a composite Maestro motion object that is comprised of two or more Maestro axes of the same type. This object can be used to synchronize the operation of all the axes in the group.
All motion objects use the same set of Motion Instructions, which include:
•Commands – instructions sent to an axis (these are similar to the commands used by SimplIQ drives and are described in the SimplIQ Command Reference).
•Properties – system parameters used to set the behavior of the Maestro.
•Functions – a pre-defined set of motion functions.
There is also a unique set of functions called CAN Bus Configuration Tools that are used to set up an LSS slave.
Motion instructions can be sent from a terminal or from a Maestro user program.
Maestro Software Manual |
|
|
|
General and Motion Instructions |
4-2 |
||||
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Table 4-1 Motion Properties and Functions |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Axis |
Vector |
Group |
|
CAN Input |
|
General |
|
|
|
Properties |
Properties |
Properties |
|
Properties |
|
Functions |
|
|
|
|
VAC |
|
|
flr |
|
backup |
|
|
|
|
VAE |
|
|
irq |
|
businfo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VBT |
GBT |
|
mhl |
|
bye, quit, or exit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VCR |
|
|
mlh |
|
command |
|
|
|
|
VDC |
|
|
msk |
|
date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADI |
|
|
|
plr |
|
dynamicip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ADT |
VDT |
|
|
|
|
errlevel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AEL |
|
GEL |
|
|
|
error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AEH |
|
GEH |
|
|
|
find |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AEM |
|
GEM |
|
|
|
format |
|
|
|
AFP |
VFP |
|
|
|
|
halt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AID |
VID |
GID |
|
CAN Output |
|
hbperiod |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALN |
VLN |
|
|
Properties |
|
hbrem |
|
|
|
AMC |
VMC |
GMC |
|
erm |
|
ipconfig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VNT |
|
|
erv |
|
isok |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APE |
|
|
|
flr |
|
kill |
|
|
|
|
VPE |
|
|
plr |
|
list |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
APP |
VPP |
|
|
|
|
load |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSC |
|
|
|
|
message |
|
|
|
|
VSD |
|
|
|
|
messageex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSE |
|
|
|
|
name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSM |
GSM |
|
|
|
nodeguard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VSP |
|
|
|
|
nodeinfo |
|
|
|
|
VSR |
|
|
|
|
property |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ATM |
VTM |
GTM |
|
|
|
restart |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ATP |
|
|
|
|
|
restarta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VTT |
|
|
|
|
restartd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VUM |
|
|
|
|
restarte |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VVE |
|
|
|
|
resauto |
|
|
|
|
VXT |
|
|
|
|
save |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
staticip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sync |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
systime |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
systimex |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tstamp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tstampver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
umauto |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
umstart |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
umstatus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
umstop |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-3 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2D, 3D & |
Group |
Axis |
Group |
|
Functions |
Vector |
Functions |
|
Functions |
|
|
addcircle |
|
|
adddwell |
|
|
addline |
|
addpoint |
addpoint |
|
|
addsplinep |
|
|
attach |
attach |
|
circle |
|
|
clears |
|
|
detach |
detach |
dotrj |
dotrj |
|
ends |
ends |
|
error |
error |
error |
isok |
isok |
isok |
|
line |
|
startstp |
splinee |
|
|
splinep |
|
trj |
splines |
|
|
startp |
|
|
starts |
|
|
trj |
|
|
|
|
CAN Configuration
Tools (Functions)
plss_activate_bt
plss_config_bt
plss_config_nid
plss_inq_addr
plss_inq_nid
plss_inq_product
plss_inq_rev_num
plss_inq_ser_num
plss_inq_vendor
plss_master_bt
plss_start
plss_store_config
plss_stop
plss_sw_glb
plss_sw_sel
Maestro I/O
Functions
m_din
m_din[]
m_dout
m_dout[]
m_ain[]
m_ain[].offset
m_din.polarity,
m_din.plr
m_dout.polarity,
m_dout.plr
Maestro Software Manual |
4-4 |
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
||
|
||
|
|
4.1General Functions
Note: Entering a question mark from the terminal before any function name opens the help text for the function. (Terminal only)
Function |
backup - restart the Maestro with the previous configuration |
Call Format |
backup |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
Function |
baudrate - get the CAN bus baud rate |
Call Format |
baudrate(BusID) |
|
|
Parameters |
BusId - CAN bus ID number |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
Example |
baudrate(0) |
|
|
|
|
Function |
businfo - get CAN Bus information |
Call Format |
businfo <bus_number> - CAN bus number (default value = 0) |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
Example |
businfo 1 |
|
|
|
|
Function |
bye, quit or exit - close the current session |
Call Format |
bye |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
Function |
command - gets help text with the general structure for the motion |
|
object commands. |
Call Format |
?command |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
Function |
date - get (or set) the current date |
Call Format |
date - To change the date, enter a date according to the format |
|
DD.MM.YYYY. |
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
Example |
date 16.11.2005. |
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-5 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
dynamicip – configures the Maestro Network Parameters to work with |
|
|
|
|
a DHCP Server (dynamic IP addressing) |
|
|
|
Call Format |
dynamicip |
|
|
|
Return Value |
EnableDHCP: 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only. Restart (power off/on) the Maestro controller to apply a |
|
|
|
|
new dynamic IP address |
|
|
|
Example |
dynamicip |
|
|
|
|
EnableDHCP: 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
errlevel - |
set the error stack level |
|
|
Call Format |
errlevel( <level> ) |
|
|
|
|
<level> - preferred error level |
|
|
|
Example |
errlevel(3) – set error level 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
error - get the error stack from the Maestro Multi-Axis Controller |
|
|
|
Call Format |
error |
- get all errors with the current error level |
|
|
|
error <level> - get all errors with the specified error level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
error 3 – get all errors with error level 3 only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
find - Search for an object according to the object’s logical name. If the |
|
|
|
|
object exists, the information is displayed as a “list”. If the object does |
|
|
|
|
not exist, the Maestro returns “Object not found”. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call Format |
find <object_name> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
find axis_1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
format – displays the help text that defines how to format a binary, |
|
|
|
|
hexadecimal or floating-point number. |
|
|
|
Call Format |
?format. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
halt - halt the virtual machine |
|
|
|
Call Format |
<name of virtual machine>.halt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
vm.halt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-6 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
hbperiod - |
set heartbeat control period |
|
|
Call Format |
hbperiod(int <bus_number>,int<period>) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
<bus_number> - the CAN bus number to use to send heartbeat |
|
|
|
|
messages |
|
|
|
|
<period> - the interval between heartbeat messages in milliseconds (0– |
|
|
|
|
for cancel). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK or FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
hbperiod(0,1000) – the system uses bus number 0 to send a heartbeat |
|
|
|
|
message every 1000 ms. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
hbrem - remove the node from heartbeat control |
|
|
|
Call Format |
hbrem(int <bus_number>,int<node number>) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
<bus_number> - CAN bus number |
|
|
|
|
<node number> - the CAN node number of the node to remove from |
|
|
|
|
heartbeat control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK or FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
hbrem(0,1) – on CAN bus 0, remove node 1 from heartbeat control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
ipconfig – display the current network configuration type, IP address |
|
|
|
|
and subnet mask |
|
|
|
Call Format |
ipconfig |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
Displays the network configuration type, IP address and subnet mask |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
ipconfig |
|
|
|
|
EnableDHCP: 1 |
|
|
|
|
DhcpIPAddress: 10.10.20.57 |
|
|
|
|
DhcpSubnetMask: 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
isok - verify the Maestro Multi-Axis Controller status |
|
|
|
Call Format |
Isok |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK: Ok |
FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
kill - kill all programs |
|
|
|
Call Format |
Kill |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK: the number of killed programs, or FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-7 |
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
list - gets a list of all the Maestro objects. An object can be a motion |
|
|
object (axis, vector, etc.) or a virtual machine. |
|
|
|
|
Call Format |
list [-key:attribute] … [-key:attribute] |
|
|
Parameters: |
|
|
[-b:id] |
- get information for the specified CAN Bus |
|
[-n] |
- get information about nodes DS301 |
|
[-i] |
- get information about IO DS401 |
|
[-a[:attribute]] - get information about axes. Attributes: target object type. Can be: |
|
|
e[lmo] |
- Elmo motion drivers only |
|
402 |
- DS402 profile motion drivers only |
|
[-v[:attribute]] - get information about vectors. Attributes: target object type. Can be: |
|
|
e[lmo] |
- vectors of Elmo motion drivers only |
|
402 |
- vectors of DS402 profile motion drivers only |
|
[-g[:attribute]] - get information about groups. Attributes: target object type. Can be: |
|
|
e[lmo] |
- groups of Elmo motion drivers only |
|
402 |
- groups of DS402 profile motion drivers only |
|
[-t] |
- get information about trajectories |
|
[-p[:attribute]] - get information about programs. Attributes: target object type. Can |
|
|
be: |
|
|
r[un] |
- running programs only |
|
p[ause] |
- paused programs only |
|
h[alt] |
- halted programs only |
|
a[bort] |
- aborted programs only |
|
f[ile] |
- all programs in the device file |
|
[-u] |
- get information about unrecognized objects |
|
[-f] |
- get full information about current query |
|
[-s] |
- get status of current motion object |
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
Example |
list |
|
|
list –b:0 -a |
|
|
list -p:r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
load - loads the values of all global variables and arrays saved during |
|
|
the previous save() function |
|
Call Format |
load() |
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Program only |
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-8 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
message - post a message to the host computer (no timestamp) |
|
|
|
Call Format |
message(msgID, wParam, lParam) – posts a message without a |
|
|
|
|
timestamp |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
msgID – user-defined message ID |
|
|
|
|
wParam, lParam – user’s message data (Unsigned integer type) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
message ( 0, a1.px, a2.px ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
messageex - post a message to the host computer (with time stamp) |
|
|
|
Call Format |
messageex(msgID, wParam, lParam) – posts a time-stamped message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
msgID – user-defined message ID |
|
|
|
|
wParam, lParam – user’s message data (Unsigned integer type) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
messageex( 0, a1.px, a2.px ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
name - get (or set) the logical device name |
|
|
|
Call Format |
name – gets the device name |
|
|
|
|
name <device_name> - sets the device name |
|
|
|
Return Value |
Device name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
nodeguard – set the nodeguard control period |
|
|
|
Call Format |
nodeguard(int <bus_number>,int <node number>,int<period>) |
|
|
|
|
bus_number - CAN bus ID |
|
|
|
|
node number – CAN node ID |
|
|
|
|
period - the interval between nodeguard messages in milliseconds (0–to |
|
|
|
|
cancel). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
nodeguard (0,1,500) – On CAN bus 0, sets the interval between |
|
|
|
|
nodeguard messages arriving at CAN node 1 to 500 milliseconds. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
nodeinfo – gets the CAN node information |
|
|
|
Call Format |
nodeinfo(int <bus_number>,int < node number >) |
|
|
|
|
bus_number - CAN bus ID |
|
|
|
|
node number – CAN node ID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
nodeinfo(0,1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
property - |
gets the help text for the motion object property |
|
|
Call Format |
? property |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-9 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
restart - Restarts the Maestro and: |
|
|
|
|
• Closes all existing objects |
|
|
|
|
• Kills all virtual machines |
|
|
|
|
• Restarts the Maestro kernel |
|
|
|
|
• Applies the sessions and objects according to the existing |
|
|
|
|
configuration file. |
|
|
|
Call Format |
restart |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
restarta - Restarts the Maestro and: |
|
|
|
|
• Closes all existing objects |
|
|
|
|
• Kills all virtual machines |
|
|
|
|
• Restarts the Maestro kernel |
|
|
|
|
• Applies the sessions and objects according to the existing |
|
|
|
|
configuration file. |
|
|
|
|
• Starts the AUTOEXEC program (if it exists). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call Format |
restarta |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
restartd - restarts the |
Maestro kernel with the default |
|
|
|
configuration and sets the baud rate for each CAN bus. |
|
|
|
Call Format |
restartd() – for baud rate 500 (default setting) |
|
|
|
|
restartd(baudrate1, baudrate2) –baud rate 0 is not used. If the default |
|
|
|
|
baud rate is not selected, a separate baud rate for each CAN bus must |
|
|
|
|
be specified. If a baud rate for one bus is omitted, an error message is |
|
|
|
|
displayed. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
restartd(1000, 1000) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
restarte - restarts the Maestro kernel without running the CAN |
|
|
|
|
bus. |
|
|
|
Call Format |
restarte() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-10 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
rsauto - get (or set) the RS-232 autorun parameter |
|
|
|
Call Format |
rsauto() – to get the current autorun parameter |
|
|
|
|
rsauto(val) – to set the current autorun parameter |
|
|
|
|
val can be 0 or1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
rsauto(1) – allows the RS-232 bus to access the Command Interpreter |
|
|
|
|
rsauto(0) – does not allow the RS-232 bus to access the Command |
|
|
|
|
Interpreter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
save - to save the values of all the global variables and arrays |
|
|
|
Call Format |
save() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Program only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
staticip – configures the Maestro Network parameters to work with |
|
|
|
|
a static IP address |
|
|
|
Call Format |
staticip(ip_address, subnet_mask) |
|
|
|
|
ip_address - new IP Address of Maestro device |
|
|
|
|
subnet_mask |
- new Subnet Mask of Maestro device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
IP Address and Subnet Mask, Network configuration type, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only. Restart (power off/on ) Maestro to apply Static IP |
|
|
|
|
address. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
staticip (10.10.20.57, 255.255.255.0) |
|
|
|
|
IPAddress: 10.10.20.57 |
|
|
|
|
SubnetMask: 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
|
EnableDHCP: 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
sync - begin sending SYNC messages to a CAN bus |
|
|
|
Call Format |
sync (int <bus_number>,float<sync_period>) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
<bus_number> - which CAN bus to send the SYNC messages to |
|
|
|
|
<sync_period> - the value of the SYNC period, in milliseconds |
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK or FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
sync(0,20) – for bus number 0 activate the send sync every 20 |
|
|
|
|
milliseconds. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
systime - returns the system-defined time in milliseconds |
|
|
|
Call Format |
systime() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
systimex - |
returns the CAN bus time in microseconds |
|
|
Call Format |
systimex() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maestro Software Manual |
General and Motion Instructions |
4-11 |
|
|
MAN-MASSW (Ver. Q) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
time - get (or set) the current time |
|
|
|
Call Format |
Time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
tstamp - set the timestamp period |
|
|
|
Call Format |
tstamp(int <bus_number>,int<period>) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parameters |
<bus_number> which CAN bus sends the timestamp |
|
|
|
|
<period> - specifies how many sync periods must pass before the new |
|
|
|
|
timestamp is set. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Return Value |
OK or FAILED: Error message |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example |
tstamp(0,5) |
– for bus number 0, send a timestamp message after each |
|
|
|
5 sync periods. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
umauto - get (or set) the user module autorun parameter |
|
|
|
Call Format |
umauto() – to get the current autorun parameter |
|
|
|
|
umauto(val) – to set the current autorun parameter |
|
|
|
|
val can be 0 or 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
umstart - |
run the user module |
|
|
Call Format |
umstart() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
umstatus - get the user module status |
|
|
|
Call Format |
umstatus() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
umstop - terminate the user module |
|
|
|
Call Format |
umstop() |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
ver - get current Maestro version |
|
|
|
Call Format |
Ver |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations |
Terminal only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Loading...
Loading...