Doosan P158LE, P180LE, P222LE Operator Manual

65.99897-8076C
Operation &
Maintenance Manual
GENERATOR DIESEL ENGINE
P158LE / -1 / - 2 / -S / -III
P180LE / -1 / -S / -II
P222LE / -1 / -S / -II
POWER UNIT DIESEL ENGINE
PU158TI
PU180TI
PU222TI
FOREWORD
This manual is designed to serve as an instruction for Diesel generator engine and Power Unit engine of
DOOSAN series (P158LE /P180LE /P222LE, PU158TI/ PU180TI/ PU222TI).
The engines are 4 strokes, 2 valves per cylinder, V-type, and direct injection mode and thus, are also satisfying
with various features required as generator and power unit engine such as quiet operation, economical fuel
consumption, durability in high speed operation and so forth.
We are very confident that these engine series are quite superior to any high speed engines in economy and
efficiency. However, high performance and long life cycle will be accomplished when a proper handling and
administration of periodic inspections and maintenance should be observed. Readers are desired to know for
your reference that those kinds of maintenance matters are explained here in detail by means of figures and
diagrams.
In this manual, the following symbols are used to indicate the type of service operations to be performed.
Removal Adjustment
Installation Cleaning
Disassembly Pay close attention-Important
Reassembly Tighten to specified torque
Align the marks Use special tools of manufacturer's
Directional Indication Lubricate with oil
Inspection Lubricate with grease
Measurement
If you have any question or recommendation in connection with this manual, please do not hesitate to contact
our head office, dealers or authorized service shops near by your location for any services.
For the last, the contents of this instruction manual may be changed without prior notice for some quality
improvement. Thank you.
Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.
Jan. 2008

CONTENTS
1. Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
1.1. Safety regulations ............................................................................................................................... 1
1.2. Engine Specification ........................................................................................................................... 5
1.3. Engine Assembly .............................................................................................................................. 11
2. Technical Information
2.1. Engine Model and Serial Number ..................................................................................................... 19
2.2. Engines Characteristic ...................................................................................................................... 20
2.3. Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................................ 41
2.4. Operation tip ..................................................................................................................................... 51
3. Disassembly and Reassembly of Major Components
3.1. Engine Disassembly ......................................................................................................................... 52
3.2. Inspection ......................................................................................................................................... 62
3.3. Engine Reassembly .......................................................................................................................... 81
3.4. Breaking-In ....................................................................................................................................... 98
4. Commissioning and Operation
4.1. Preparations ..................................................................................................................................... 99
4.2. Starting ............................................................................................................................................. 99
4.3. Running in ...................................................................................................................................... 100
4.4. During operation ............................................................................................................................. 100
4.5. Shutting down ................................................................................................................................. 100
4.6. Maintenance and Care ................................................................................................................... 101
5. Maintenance of Major Components
5.1. Fuel Injection System ..................................................................................................................... 105
5.2. Cooling System .............................................................................................................................. 126
5.3. Lubricating System ......................................................................................................................... 129
5.4. Turbo Charger ................................................................................................................................ 131
5.5. Installation ...................................................................................................................................... 140
5.6. Air Cleaner ...................................................................................................................................... 143
5.7. Tightening Cylinder Head Bolts ...................................................................................................... 145
5.8. V-belts ............................................................................................................................................ 146
6. Special Tool List
z
Appendix
z
Parts & After Service Center
z
Worldwide Network
................................................................................................................................. 149

1. Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
1.1. Safety Regulations
1.1.1. General notes
Handling diesel engines and the necessary resources is no problem when the personnel commissioned
with operation and maintenance are trained accordingly and use their common sense.
This summary is a compilation of the most important regulations, These are broken down into main
sections which contain the information necessary for preventing injury to persons, damage to property
and pollution. In addition to these regulations those dictated by the type of engine and its site are to be
observed also.
IMPORTANT :
If despite all precautions, an accident occurs, in particular through contact with
caustic acids, fuel penetrating the skin, scalding from oil, antifreeze being splashed
in the eyes etc, consult a doctor immediately.
1.1.2. Regulations designed to prevent accidents
1) During commissioning, starting and operation
z
Before putting the engine into operation for the first time, read the operating instructions carefully
and familiarize yourself with the “critical” points, If you are unsure, ask your DHI representative.
z
For reasons of safety we recommend you attach a notice to the door of the engine room
prohibiting the access of unauthorized persons and that you draw the attention of the operating
personal to the fact that they are responsible for the safety of persons who enter the engine room.
z
The engine must be started and operated only by authorized personnel. Ensure that the engine
cannot be started by unauthorized persons.
z
When the engine is running, do not get too close to the rotating parts. Wear close-fitting clothing.
z
Do not touch the engine with bare hands when it is warm from operation risk of bums.
z
Exhaust gases are toxic. Comply with the instructions for the installation of DHI Diesel engines
which are to be operated in enclosed spaces. Ensure that there is adequate ventilation and air
extraction.
z
Keep vicinity of engine, ladders and stairways free of oil and grease. Accidents caused by slipping
can have serious consequences.
- 1 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications

2) During maintenance and care
z
Always carry out maintenance work when the engine is switched off. If the engine has to be
maintained while it Is running, e.g. changing the elements of change-over filters, remember that
there is a risk of scalding. Do not get too close to rotating parts.
z
Change the oil when the engine is warm from operation.
CAUTION :
There is a rise of burns and scalding. Do not touch oil drain plug or oil filters with
bare hands.
z
Take into account the amount of oil in the sump. Use a vessel of sufficient size to ensure that the
oil will not overflow.
z
Open the coolant circuit only when the engine has cooled down. If opening while the engine is still
warm is unavoidable, comply with the instructions in the chapter “Maintenance and Care”.
z
Neither tighten up nor open pipes and hoses (lube oil circuit, coolant circuit and any additional
hydraulic oil circuit) during the operation. The fluids which flow out can cause injury.
z
Fuel is inflammable. Do not smoke or use naked lights in its vicinity. The tank must be filled only
when the engine is switched off.
z
When using compressed air, e.g. for cleaning the radiator, wear goggles.
z
Keep service products (anti-freeze) only in containers which can not be confused with drinks
containers.
z
Comply with the manufacturer’s instructions when handling batteries.
CAUTION :
Accumulator acid is toxic and caustic. Battery gases are explosive.
3) When carrying out checking, setting and repair work
z
Checking, setting and repair work must be carried out by authorized personnel only.
z
Use only tools which are in satisfactory condition. Worn open-end wrench slip. which could lead to
Injury.
z
When the engine is hanging on a crane, no-one must be allowed to stand or pass under it. Keep
lifting gear in good condition.
z
When working on parts which contain asbestos, comply with the notes at the end of this chapter.
z
When checking injectors do not put your hands under the jet of fuel. Do not inhale atomized fuel.
z
When working on the electrical system disconnect the battery earth cable first. Connect it up
again last in prevent short circuits.
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 2 -

1.1.3. Regulations designed to prevent damage to engine and premature wear
1) Never demand more of the engine than it was designed to yield for its intended purpose.
z
Detailed information on this can be found in the sales literature. The injection pump must not be
adjusted without prior written permission of DHI.
2) If faults occur, find the cause immediately and have it eliminated in order to prevent more serious of
damage.
3) Use only genuine DHI spare parts. DHI will accept no responsibility for damage resulting from the
installation of other parts which are supposedly “just as good”.
4) In addition to the above, note the following points.
z
Never let the engine run when dry, i.e. without lube oil or coolant.
z
Use only DHI-approved service products (engine oil , anti-freeze and anticorrosion agent).
z
Pay attention to cleanliness. The Diesel fuel must be free of water. See “Maintenance and care”.
z
Have the engine maintained at the specified intervals.
z
Do not switch off the engine immediately when it is warm, but let it run without load for about 5
minutes so that temperature equalization can take place.
z
Never put cold coolant into an overheated engine. See “Maintenance and care”.
z
Do not add so much engine oil that the oil level rises above the max. marking on the dipstick. Do
not exceed the maximum permissible tilt of the engine. Serious damage to the engine may result
if these instructions are not adhered to.
z
Always ensure that the testing and monitoring equipment (for battery charge, oil pressure, coolant
temperature) function satisfactorily.
z
Comply with instructions for operation of the alternator. See “Commissioning and operation”.
z
Do not let the raw water pump run dry, If there is a risk of frost, drain the pump when the engine is
switched off.
1.1.4. Regulations designed to prevent pollution
1) Engine oil, filter elements, fuel filters
z
Take old oil only to an oil collection point.
z
Take strict precautions to ensure that oil does not get into the drains or into the ground. The
drinking water supply could be contaminated.
z
Filter elements are classed as dangerous waste and must be treated as such.
2) Coolant
z
Treat undiluted anti-corrosion agent and / or antifreeze as dangerous waste.
z
When disposing of spent coolant comply with the regulations of the relevant local authorities.
1.1.5. Notes on safety in handling used engine oil
Prolonged or repeated contact between the skin and any kind of engine oil decreases the skin.
Drying, irritation or inflammation of the skin may therefore occur. Used engine oil also contains
dangerous substances which have caused skin cancer in animal experiments. If the basic rules of
hygiene and health and safety at work are observed, health risks are not to the expected as a result of
handling used engine oil.
- 3 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications

Health precautions :
z
Avoid prolonged or repeated skin contact with used engine oil.
z
Protect your skin by means of suitable agents (creams etc.) or wear protective gloves.
z
Clean skin which has been in contact with engine oil.
-
Wash thoroughly with soap and water, A nailbrush is an effective aid.
-
Certain products make it easier to clean your hands.
-
Do not use petrol, Diesel fuel, gas oil, thinners or solvents as washing agents.
z
After washing apply a fatty skin cream to the skin.
z
Change oil-soaked clothing and shoes.
z
Do not put oily rags into your pockets.
Ensure that used engine oil is disposed of properly.
- Engine oil can endanger the water supply -
For this reason do not let engine oil get into the ground, waterways, the drains or the sewers.
Violations are punishable.
Collect and dispose of used engine oil carefully. For information on collection points please contact the
seller, the supplier or the local authorities.
1.1.6. General repair instructions
1. Before performing service operation, disconnect the grounding cable from the battery for reducing
the chance of cable damage and burning due to short-circuiting.
2. Use covers for preventing the components from damage or pollution.
3. Engine oil and anti-freeze solution must be handled with reasonable care as they cause paint
damage.
4. The use of proper tools and special tools where specified is important to efficient and reliable service
operation.
5. Use genuine DOOSAN parts necessarily.
6. Used cotter pins, gaskets, O-rings, oil seals, lock washer and self-lock nuts should be discarded and
new ones should be prepared for installation as normal function of the parts can not be maintained if
these parts are reused.
7. To facilitate proper and smooth reassemble operation, keep disassembled parts neatly in groups.
Keeping fixing bolts and nut separate is very important as they vary in hardness and design
depending on position of installation.
8. Clean the parts before inspection or reassembly. Also clean oil ports, etc. using compressed air to
make certain they are free from restrictions.
9. Lubricate rotating and sliding faces of parts with oil or grease before installation.
10. When necessary, use a sealer on gaskets to prevent leakage.
11. Carefully observe all specifications for bolts and nuts torques.
12. When service operation is completed, make a final check to be sure service has been done
property.
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 4 -
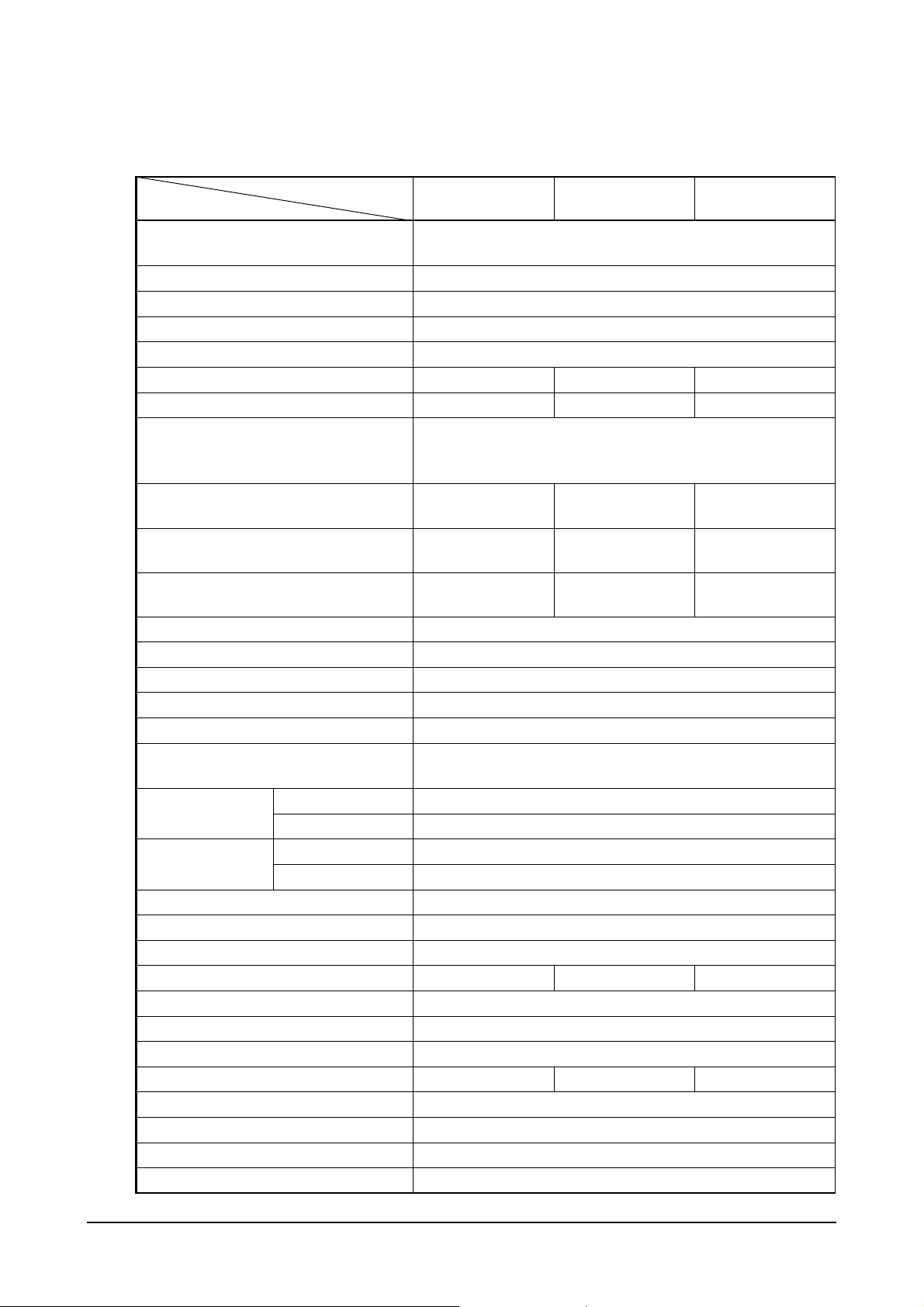
1.2. Engine Specification
1.2.1. Specification for generator engine
Engine Model
Items
Engine type
P158LE series P180LE series P222LE series
Water-cooled, 4 cycle Vee type
Turbo charged & intercooled
Combustion chamber type Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Wet type, chromated or casting liner
Timing gear system Gear driven type
No. of piston ring Compression ring 2, oil ring 1
No. of cylinder-bore × stroke (mm) 8 – 128 × 142 10 – 128 × 142 12 – 128 × 142
Total piston displacement (cc) 14,618 18,273 21,927
P158LE/-1/-2, P180LE/-1, P222LE/-1 => 15.0 : 1
Compression ratio
P158LE-S/-III, P180LE-S/-II, P222LE-S/-II => 14.6 : 1
P222LE-II(EAYQD) => 14.0 : 1
Engine dimension
(length × width × height) (mm)
Engine dry weight (kg)
Fuel injection order
1,484 × 1,389 × 1,161.5
P158LE/-1/-2 : 950
P158LE-S/-III : 961
1-5-7-2-6-3-4-8
1,557 × 1,389 × 1,248 1,717 × 1,389 × 1,288
P180LE/-1 : 1,175
P180LE-S/-II : 1,188
1-6-5-10-2-7-3-8-4-9
P222LE/-1 : 1,575
P222LE-S/-II : 1,591
1-12-5-8-3-10-6-7-
2-11-4-9
Injection pump type Bosch in-line P type
Governor type Electrical type
Injection nozzle type Multi-hole type
Fuel injection pressure (kg/cm
Compression pressure (kg/cm
Intake and exhaust valve clearance
(at cold) (mm)
Open at 24
2
)285
2
) 28 (at 200 rpm)
0.3 / 0.4
°
(B.T.D.C)
Intake valve
Close at 36
Open at 63
°
(A.B.D.C)
°
(B.B.D.C)
Exhaust valve
Close at 27
°
(A.T.D.C)
Lubrication method Fully forced pressure feed type
Oil pump type Gear type
Oil filter type Full-flow, cartridge type
Lubricating oil capacity (max./min.) (lit) 21 / 17 35 / 28 40 / 33
Oil cooler type Water cooled
Water pump Centrifugal type driven by belt
Cooling Method Pressurized circulation
Cooling water capacity (engine only) (lit)
Thermostat type Wax pallet type (71 ~ 85
20 21 23
°
C)
Alternator voltage – capacity (V – A) 24 – 45
Starting Motor voltage – output (V – kW)
24 – 7.0
Battery capacity (V – AH) 24 – 200
- 5 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
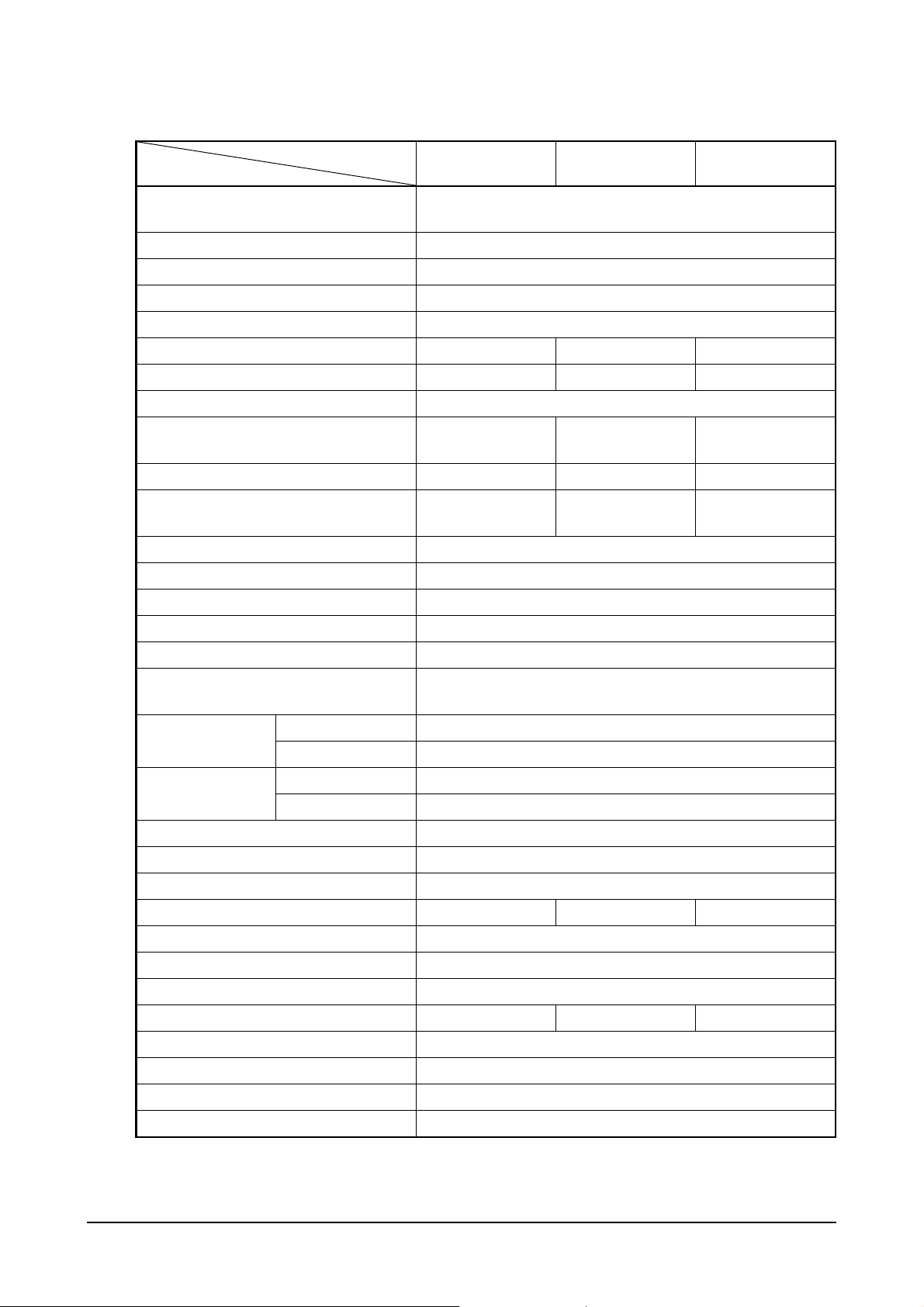
1.2.2. Specification for power unit engine
Engine Model
Items
Engine type
PU158TI PU180TI PU222TI
Water-cooled, 4 cycle Vee type
Turbo charged & intercooled
Combustion chamber type Direct injection type
Cylinder liner type Wet type, chromated or casting liner
Timing gear system Gear driven type
No. of piston ring Compression ring 2, oil ring 1
No. of cylinder-bore × stroke (mm) 8 – 128 × 142 10 – 128 × 142 12 – 128 × 142
Total piston displacement (cc) 14,618 18,273 21,927
Compression ratio 15 : 1
Engine dimension
(length × width × height) (mm)
1,484 × 1,389 × 1,161.5
1,557 × 1,389 × 1,248 1,717 × 1,389 × 1,288
Engine dry weight (kg) 950 1,175 1,575
Fuel injection order 1-5-7-2-6-3-4-8
1-6-5-10-2-7-3-8-4-9
1-12-5-8-3-10-6-7-
2-11-4-9
Injection pump type Bosch in-line P type
Governor type Mechanical type
Injection nozzle type Multi-hole type
2
Fuel injection pressure (kg/cm
Compression pressure (kg/cm
Intake and exhaust valve clearance
(at cold) (mm)
Open at 24
)285
2
) 28 (at 200 rpm)
0.3 / 0.4
°
(B.T.D.C)
Intake valve
Close at 36
Open at 63
°
(A.B.D.C)
°
(B.B.D.C)
Exhaust valve
°
Close at 27
(A.T.D.C)
Lubrication method Pressurized circulation
Oil pump type Gear type
Oil filter type Full-flow, cartridge type
Lubricating oil capacity (max./min.) (lit) 21 / 17 35 / 28 40 / 33
Oil cooler type Water cooled
Water pump Centrifugal type driven by belt
Cooling Method Pressurized circulation
Cooling water capacity (engine only) (lit)
Thermostat type Wax pallet type (71 ~ 85
Alternator voltage – capacity (V – A) 24 – 45
Starting Motor voltage – output (V – kW)
Battery capacity (V – AH) 24 – 200
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
20 21 23
°
C)
24 – 7.0
- 6 -
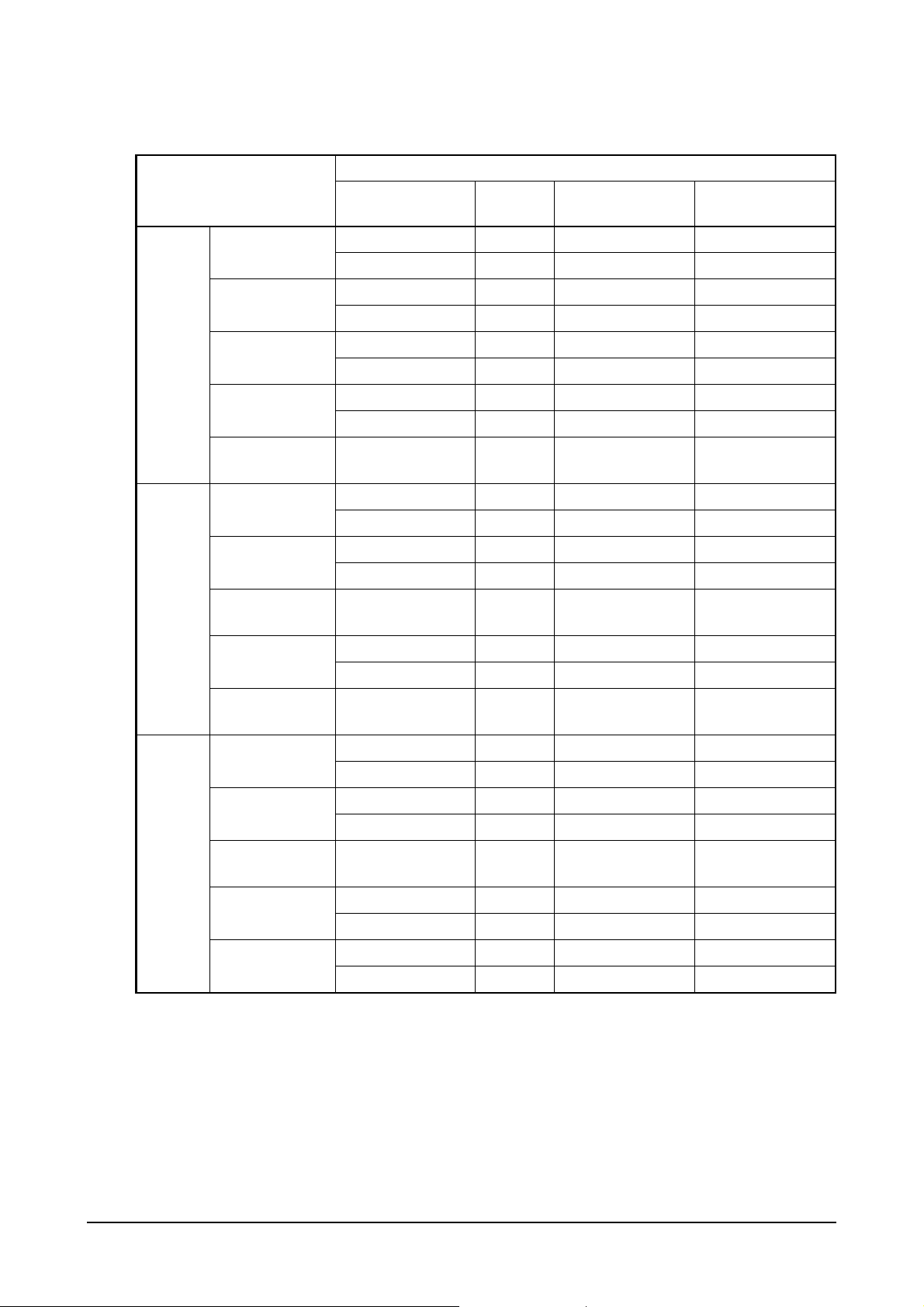
1.2.3. Engine power for generator
Engine model
P158LE-2
(EAZOC/QC)
Production tolerance : ±5%
Condition
HZ
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 399 PS(293 kW) 437 PS(321 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 470 PS(346 kW) 510 PS(375 kW)
Timing
(BTDC)
Prime Stand by
P158LE
P180LE
P158LE-1
(EAZOB/QB)
P158LE
(EAZOA/QA)
P158LE-S
(EAZOG/H/QG)
P158LE-III
(EAZOF)
P180LE-1
(EASOB/QB)
P180LE
(EASOA/QA)
P180LE
(EASOC)
P180LE-S
(EASOE/F/QE)
P180LE-II
(EASOD)
P222LE-1
(EAYOB/QB)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 444 PS(327 kW) 492 PS(362 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 498 PS(366 kW) 546 PS(402 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 494 PS(363 kW) 563 PS(414 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 547 PS(402 kW) 623 PS(458 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 12 546 PS(402 kW) 600 PS(441 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 600 PS(441 kW) 654 PS(481 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 – 690 PS(508 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 548 PS(403 kW) 601 PS(442 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 617 PS(454 kW) 677 PS(498 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 602 PS(443 kW) 674 PS(496 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 676 PS(497 kW) 734 PS(540 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 18 695 PS(511 kW) 764 PS(562 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 615 PS(452 kW) 674 PS(496 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 705 PS(519 kW) 771 PS(567 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 – 827 PS(608 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 696 PS(512 kW) 752 PS(553 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 765 PS(563 kW) 850 PS(625 kW)
P222LE
(EAYOA/QA)
P222LE
* Note : All data are based on operation without cooling fan at ISO 3046
P222LE
(EAYOC)
P222LE-S
(EAYOE/F/QE)
P222LE-II
(EAYOD/QD)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 16 723 PS(532 kW) 781 PS(574 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 16 803 PS(591 kW) 883 PS(649 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 18 803 PS(591 kW) 898 PS(660 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 20 750 PS(552 kW) 820 PS(603 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 19 850 PS(625 kW) 927 PS(682 kW)
50 HZ(1,500 rpm) 13 – 886 PS(652 kW)
60 HZ(1,800 rpm) 19 – 1000 PS(736 kW)
- 7 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
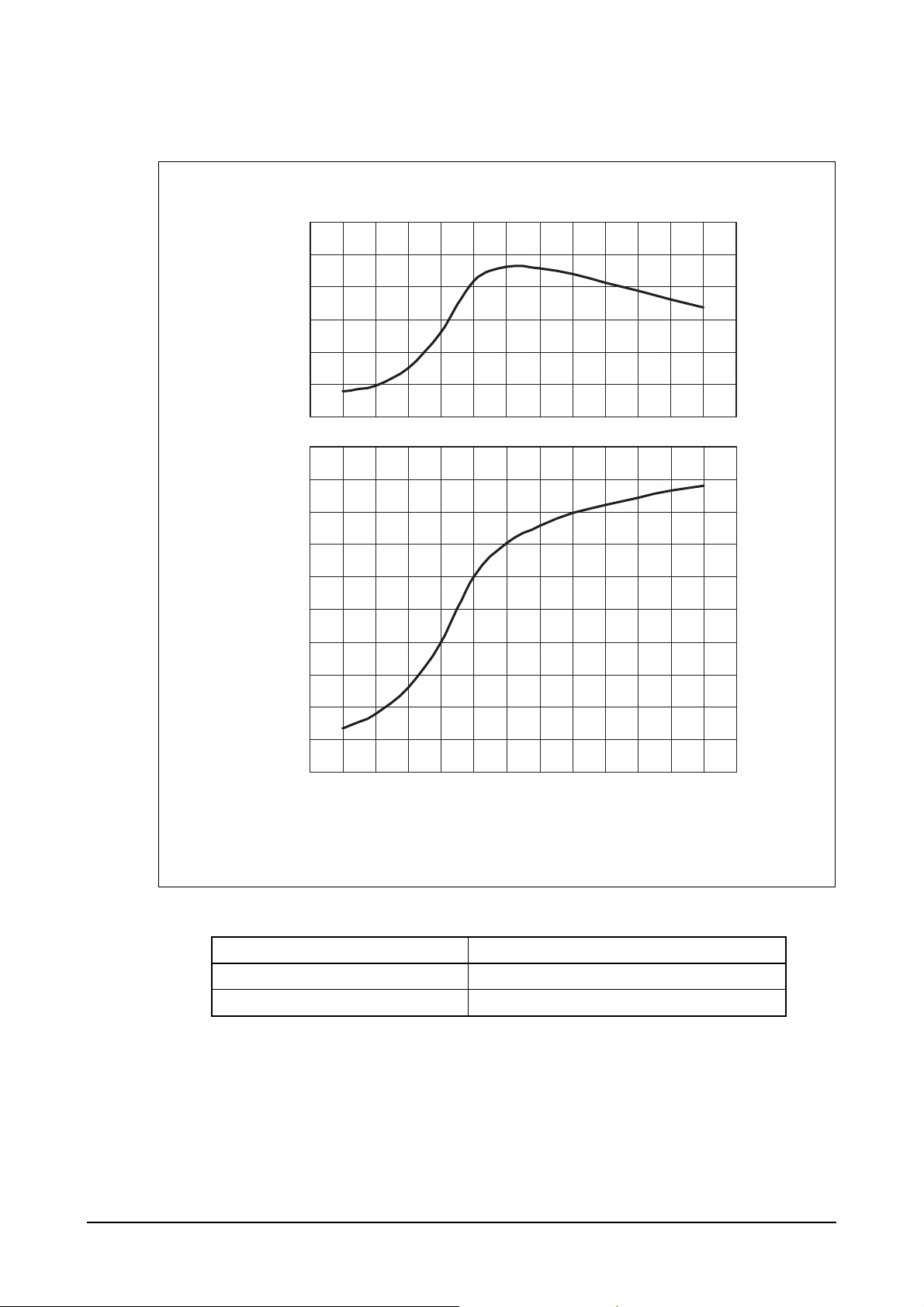
1.2.4. Engine performance curve
1) PU158TI engine
250
225
m)
200
.
175
Torque (kg
150
125
100
600
550
500
450
400
350
Power (PS)
300
250
200
150
100
900 1,000
1,000
1,200 1,300 1,400 1,500 1,600 1,700 1,800 1,900 2,000 2,100 2,200
Engine Speed (rpm)
Performance ISO 3046, DIN 6270B
Output (max.) 397 kW (540 PS) / 2,100 rpm
⋅
Torque (max) 2,117 N
m (216 kg⋅m) / 1,500 rpm
EH5OM001
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 8 -
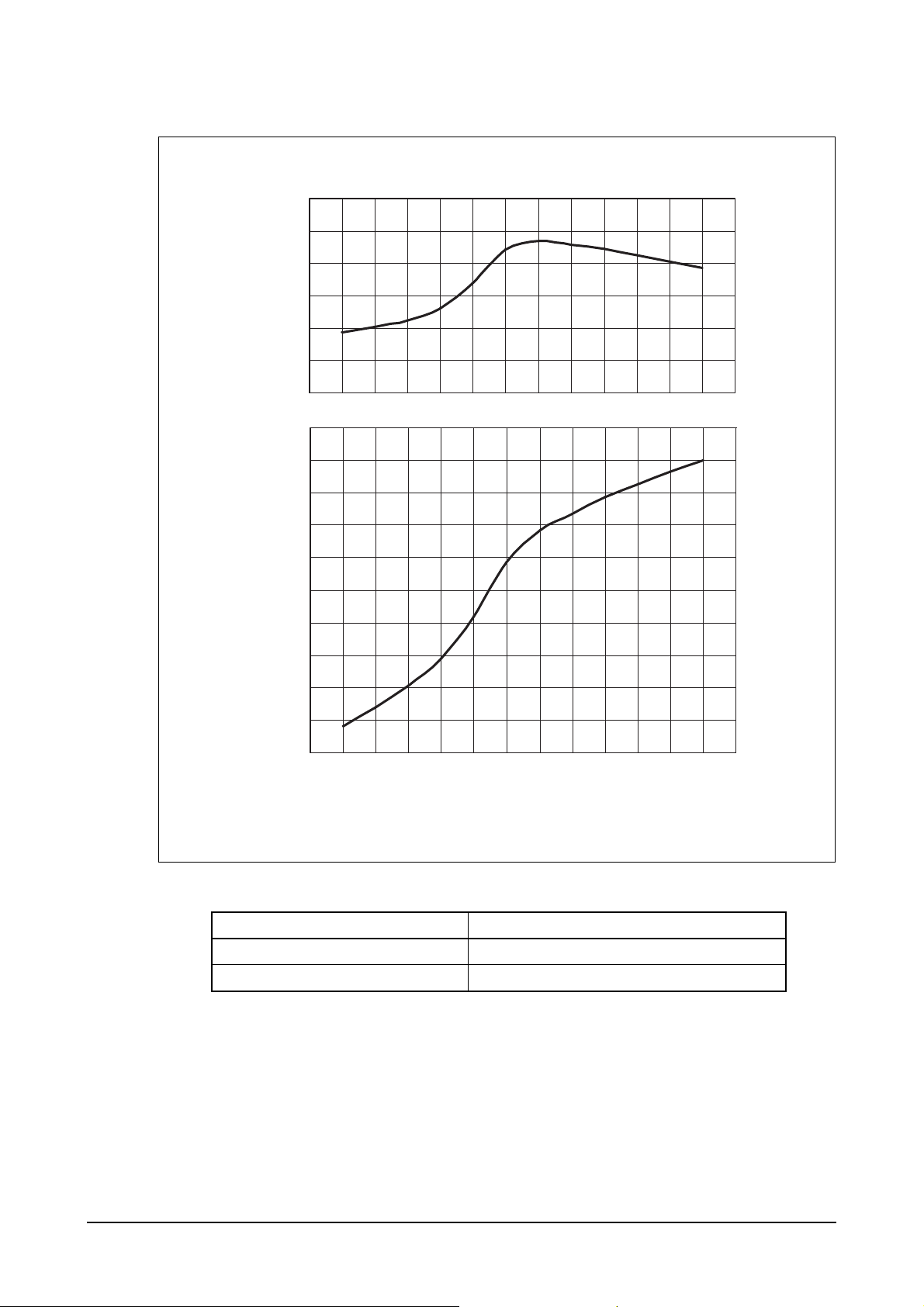
2) PU180TI engine
275
250
m)
225
.
200
Torque (kg
175
150
125
700
650
600
550
500
450
Power (PS)
400
350
300
250
200
900 1,000
1,000
1,200 1,300 1,400 1,500 1,600 1,700 1,800 1,900 2,000 2,100 2,200
Engine Speed (rpm)
Performance ISO 3046, DIN 6270B
Output (max.) 478 kW (650 PS) / 2,100 rpm
Torque (max) 2,303 N
⋅
m (235 kg⋅m) / 1,500 rpm
EH5OM002
- 9 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
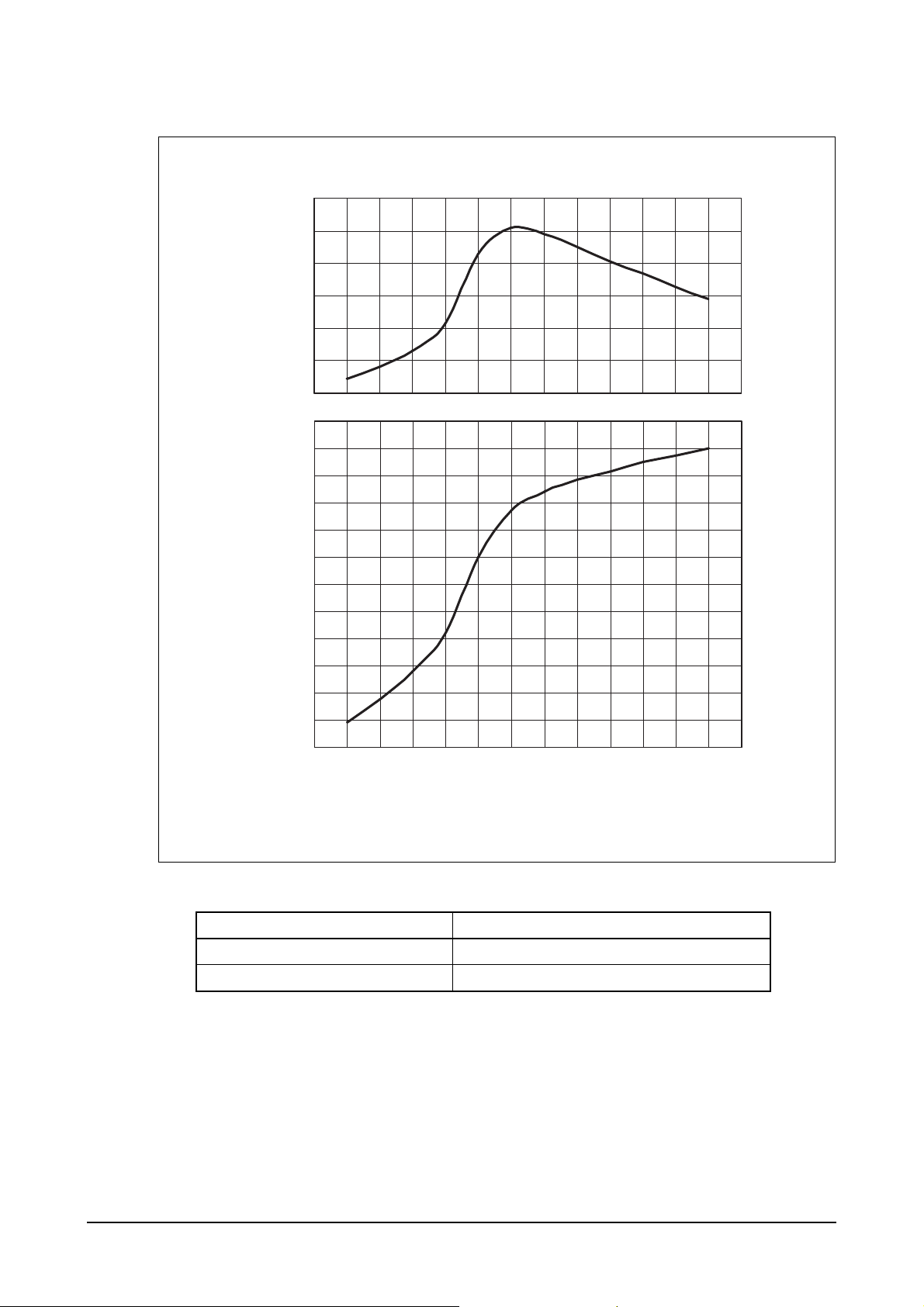
3) PU222TI engine
350
325
m)
300
.
275
Torque (kg
250
225
200
850
800
750
700
650
600
550
Power (PS)
500
450
400
350
300
250
900 1,000
1,000
1,200 1,300 1,400 1,500 1,600 1,700 1,800 1,900 2,000 2,100 2,200
Engine Speed (rpm)
Performance ISO 3046, DIN 6270B
Output (max.) 588 kW (800 PS) / 2,100 rpm
Torque (max) 3,205 N
⋅
m (327 kg⋅m) / 1,500 rpm
EH5OM003
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 10 -
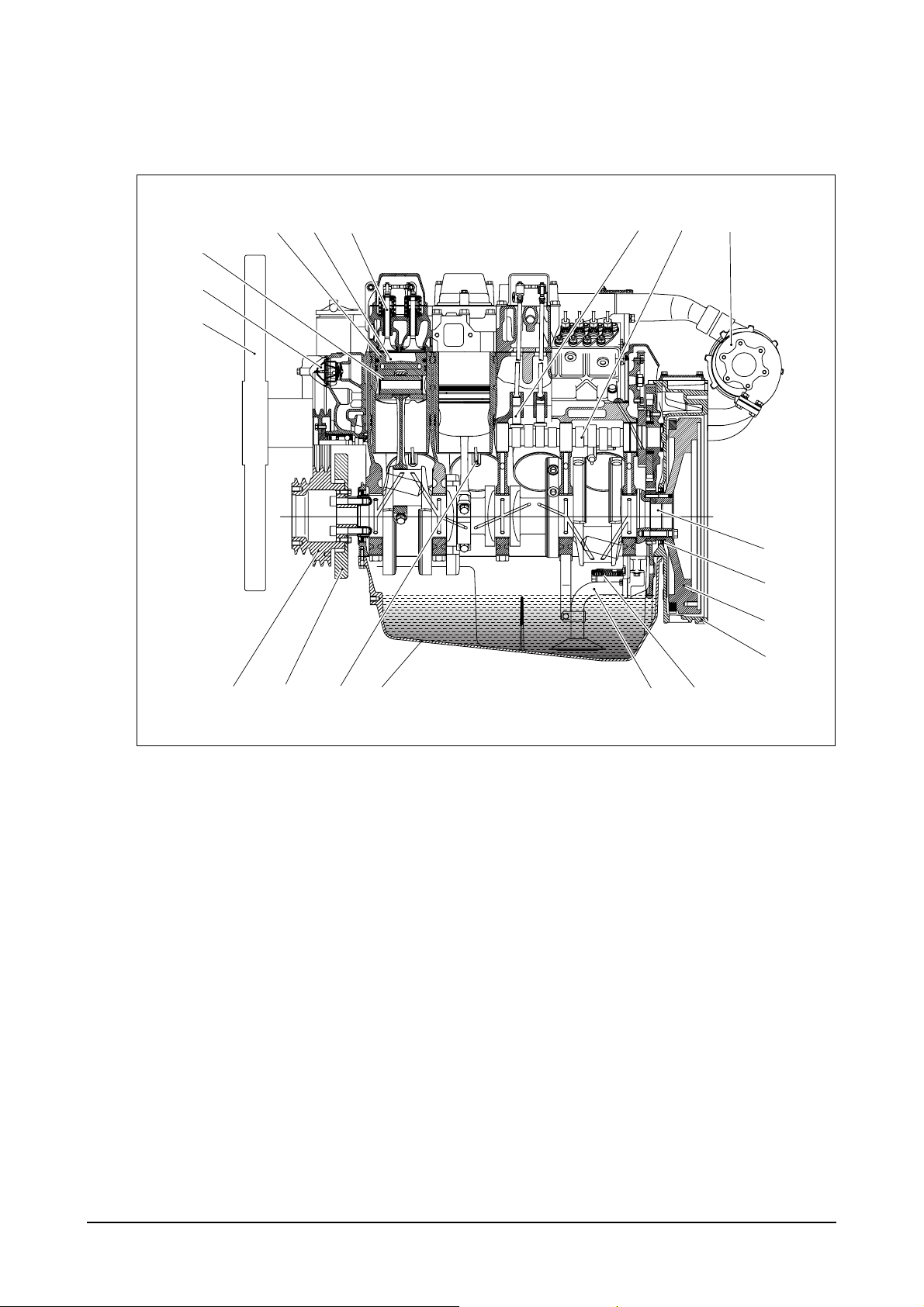
1.3. Engine Assembly
1.3.1. Engine sectional view (Longitudinal)
12 3
7
8
9
45 6
19
18
17
16
1110
10. Crank shaft pulley
12 13
1. Piston 11. Vibration damper
2. Combustion camper 12. Oil spray nozzle
3. Valve 13. Oil pan
4. Tappet 14. Oil suction pipe
5. Cam shaft 15. Oil pump relief valve
6. Turbocharger 16. Flywheel housing
7. Piston pin 17. Flywheel
8. Thermostat 18. Oil seal
9. Cooling fan 19. Crank shaft
14 15
EA6O1004
- 11 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
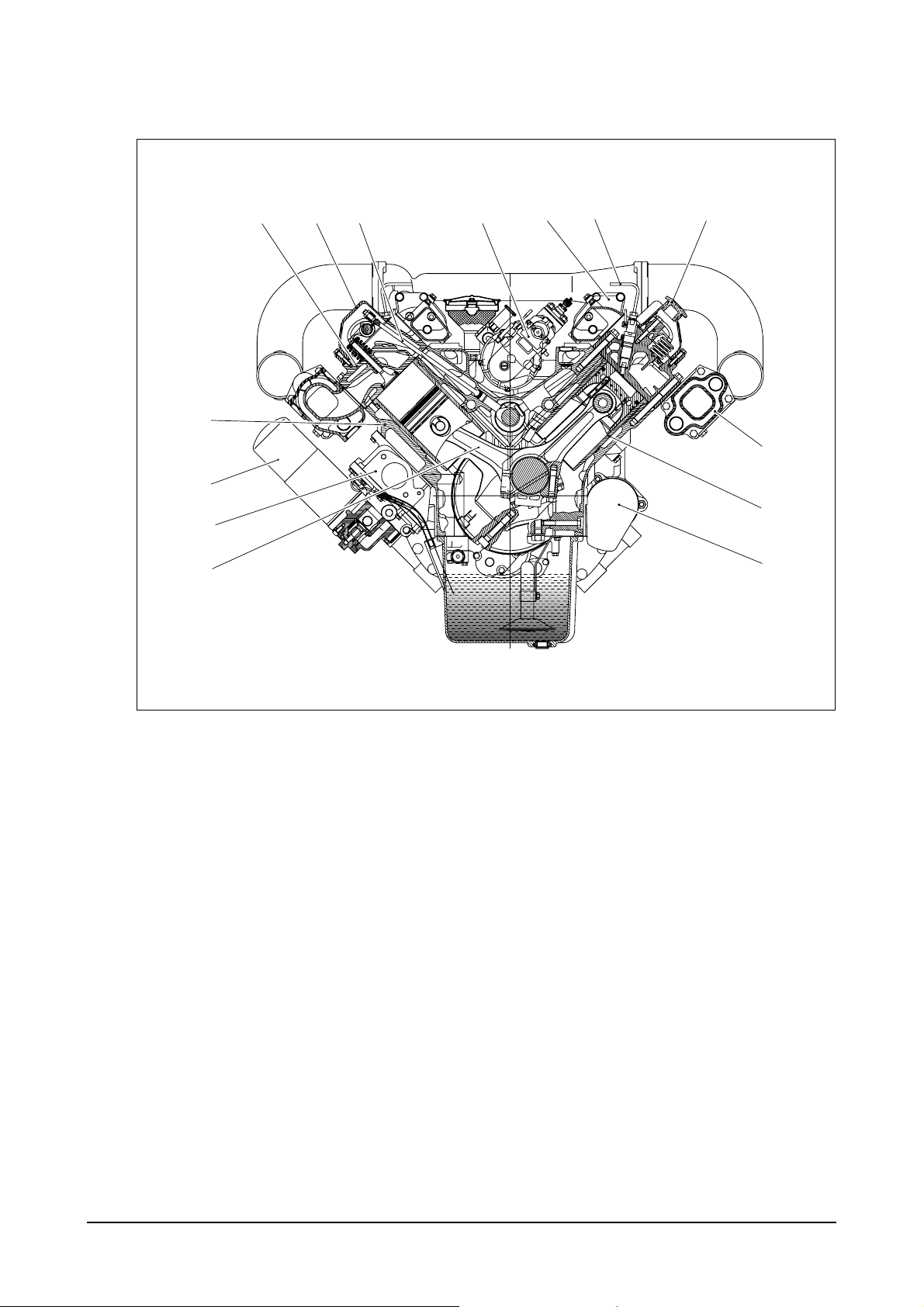
1.3.2. Engine sectional view (Cross)
10
11
12
3
4
56 7
8
12
9
13
14
1. Cylinder head 8. Cylinder block
2. Cylinder head cover 9. Oil filter
3. Push rod 10. Oil cooler
4. Injection pump 11. Connecting rod
5. Intake manifold 12. Exhaust manifold
6. Injection pipe 13. Cylinder liner
7. Oil filler cap 14. Starter
EA6O1005
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 12 -
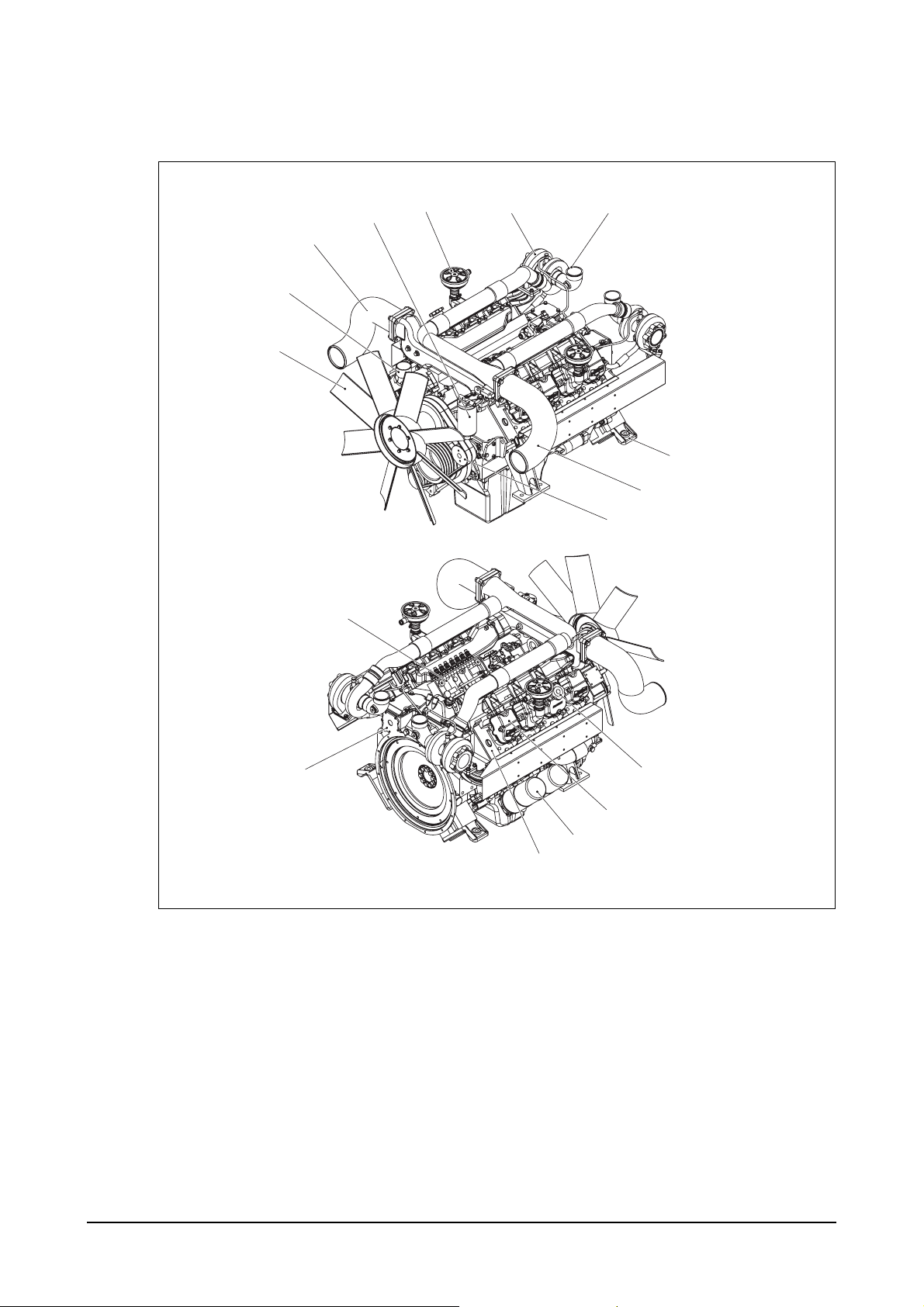
1.3.3. Engine assembly views
1) PU158TI : Power unit engine
4
5
67
3
2
1
8
9
10
11
12
16
15
14
13
1. Cooling fan 9. Air pipe
2. Water outlet (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
3. Air pipe 10. Idle pulley
(Intercooler to intake manifold) 11. Injection pump
4. Fuel filter 12. Fly wheel housing
5. Breather 13. Cylinder head
6. Turbo charger 14. Oil filter
7. Air pipe 15. Cylinder head cover
(
Air cleaner to turbocharger)
16. Oil filler cap
8. Mounting bracket
EH5OM004
- 13 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
2) PU180TI : Power unit engine
5
6
7
4
3
2
1
8
9
10
11
12
13
17
16
15
14
1. Cooling fan 9. Air pipe
2. Water outlet (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
3. Air pipe 10. Starter
(Intercooler to intake manifold) 11. Idle pulley
4. Fuel filter 12. Injection pump
5. Breather 13. Fly wheel housing
6. Turbo charger 14. Cylinder head
7. Air pipe 15. Oil filter
(
Air cleaner to turbocharger)
16. Oil filler cap
8. Mounting bracket 17. Cylinder head cover
EH5OM005
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 14 -
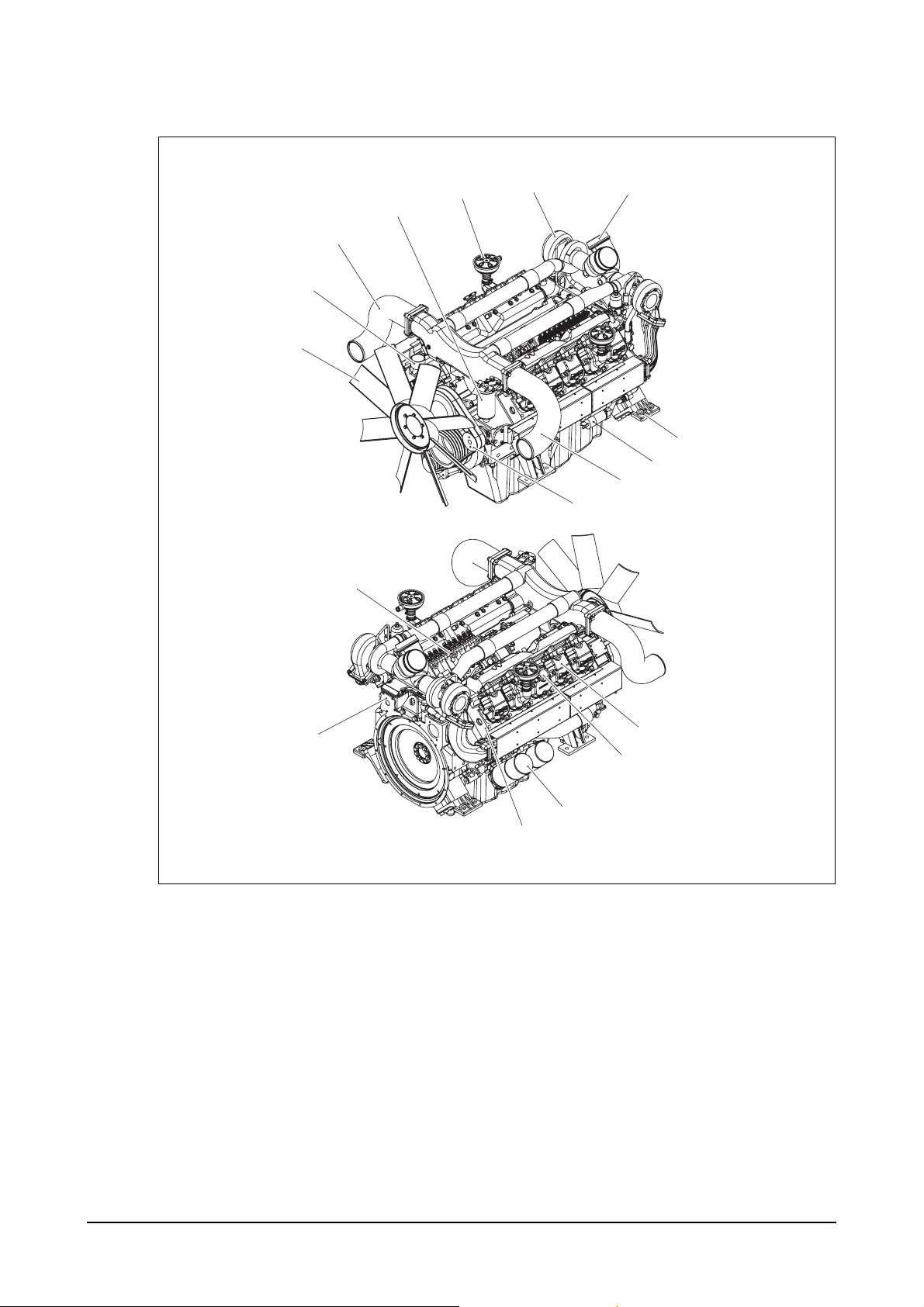
3) PU222TI : Power unit engine
5
6
7
4
3
2
1
8
9
10
11
12
16
15
14
13
1. Cooling fan 9. Air pipe
2. Water outlet (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
3. Air pipe 10. Idle pulley
(Intercooler to intake manifold) 11. Injection pump
4. Fuel filter 12. Fly wheel housing
5. Breather 13. Cylinder head
6. Turbo charger 14. Oil filter
7. Air pipe 15. Oil filler cap
(
Air cleaner to turbocharger)
16. Cylinder head cover
8. Starter
EH5OM006
- 15 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
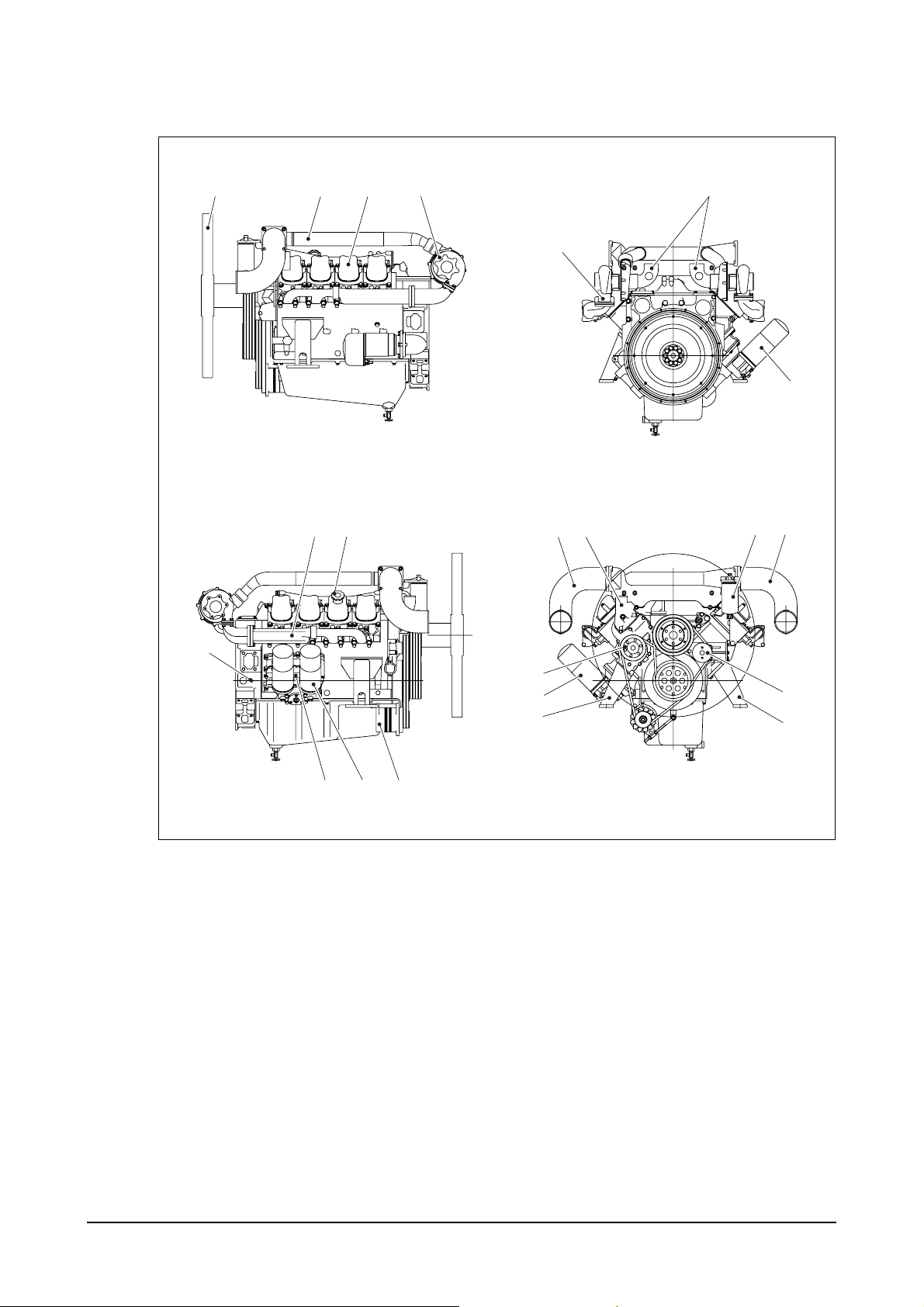
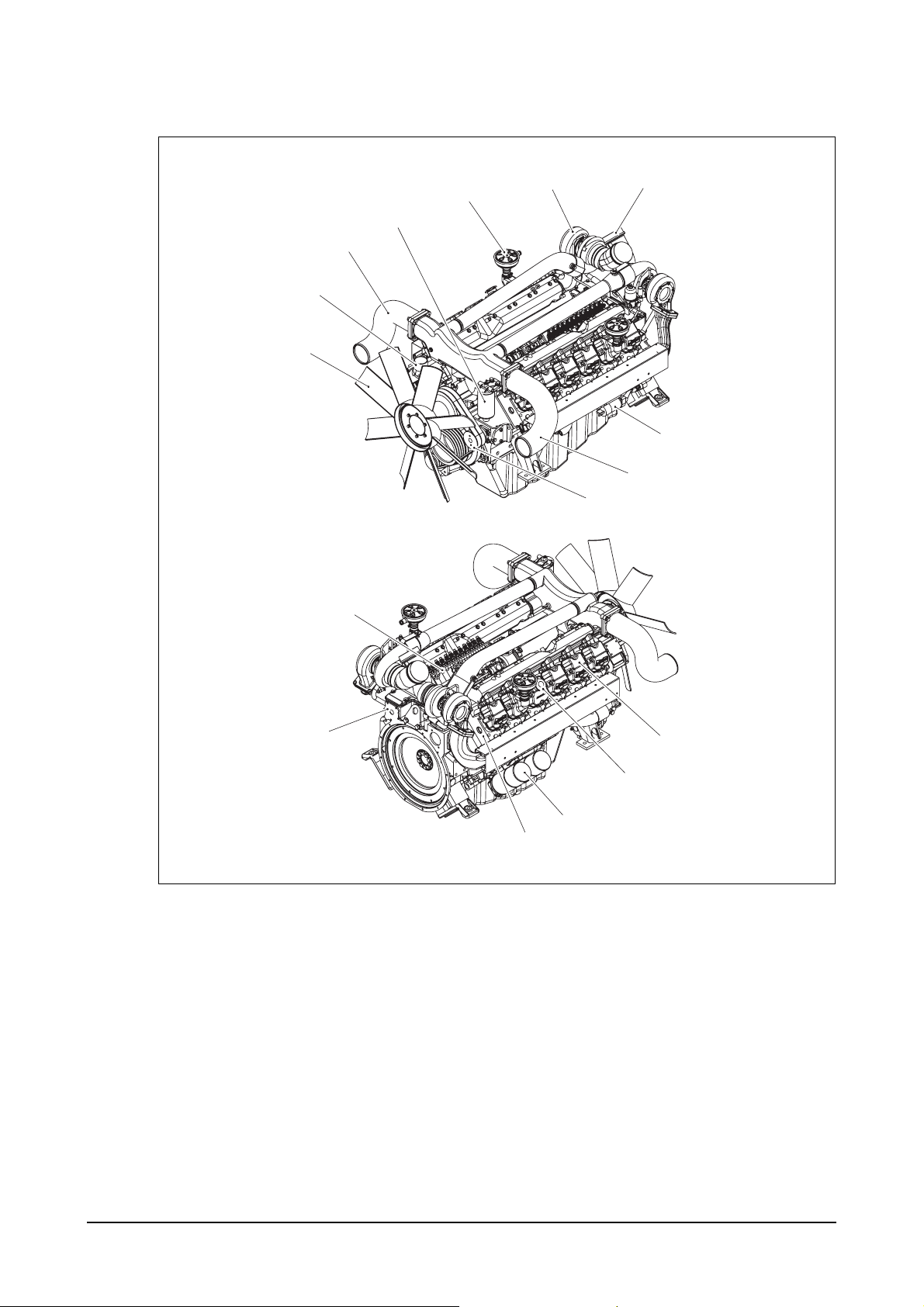
4) P158LE : Generator engine
234
910
14
18 17
151
191620
23
16
22
21
22
121116 13
EA6O1001
1. Cooling fan 10. Oil filler cap 18. Air pipe
2. Air pipe 11. Pick up sensor (Air cleaner to turbocharger)
3. Cylinder head cover 12. Oil cooler 19. Fuel filter
4. Turbocharger 13. Alternator 20. Air pipe
5. Oil drain valve 14. Exhaust elbow (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
6. Oil pan 15. Air pipe 21. Idle pulley
7. Starter (Air cleaner to turbocharger) 22. Engine mounting bracket
8. Flywheel housing 16. Oil filter 23. Water pump
9. Exhaust manifold 17. Cooling water outlet
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 16 -
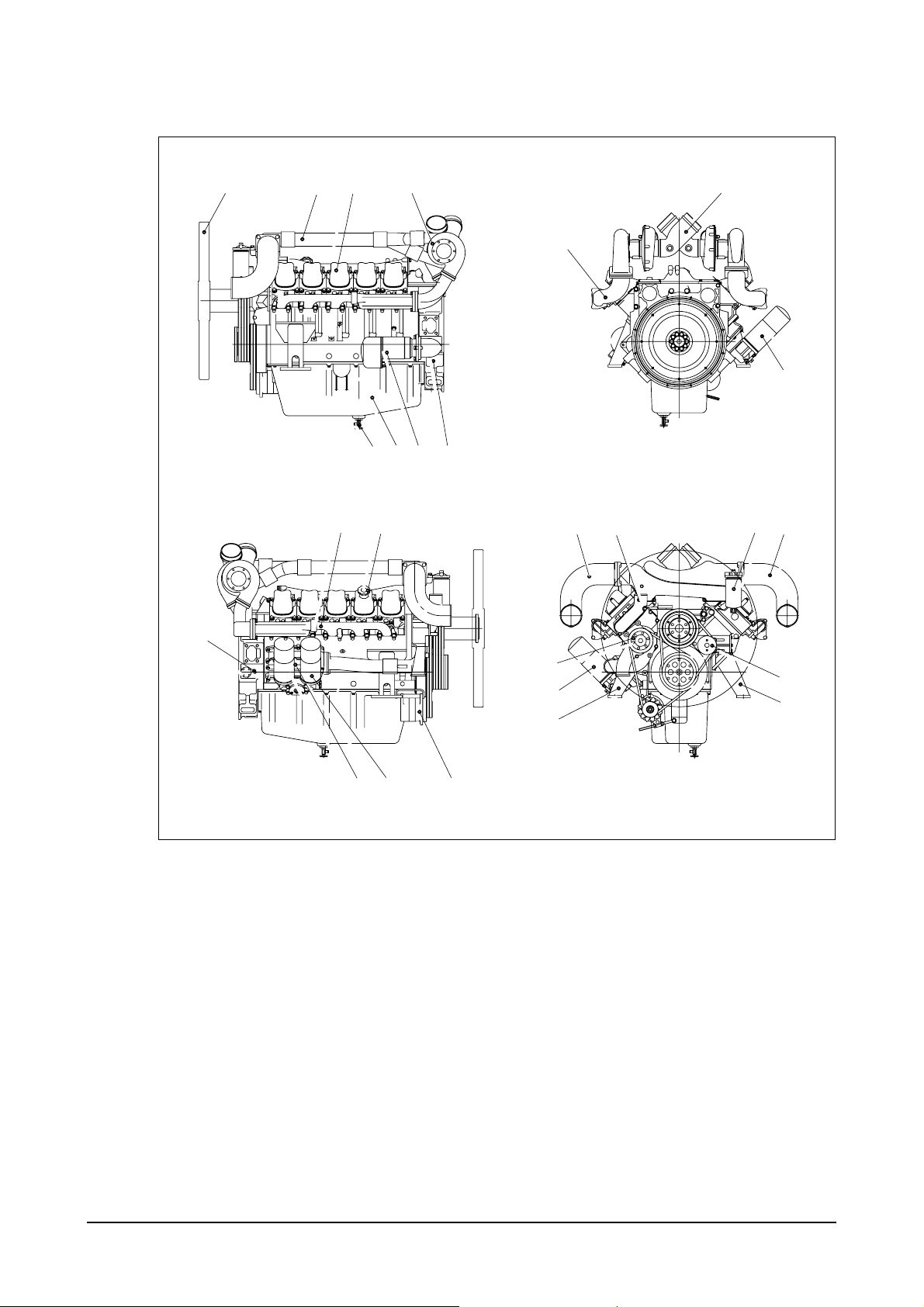
5) P180LE : Generator engine
123
4
5
67 8
910
14
18 17
15
16
19 20
11
23
21
16
22
22
12 16 13
EA6O1002
1. Cooling fan 10. Oil filler cap 18. Air pipe
2. Air pipe 11. Pick up sensor (Air cleaner to turbocharger)
3. Cylinder head cover 12. Oil cooler 19. Fuel filter
4. Turbocharger 13. Alternator 20. Air pipe
5. Oil drain valve 14. Exhaust elbow (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
6. Oil pan 15. Air pipe 21. Idle pulley
7. Starter (Air cleaner to turbocharger) 22. Engine mounting bracket
8. Flywheel housing 16. Oil filter 23. Water pump
9. Exhaust manifold 17. Cooling water outlet
- 17 -
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
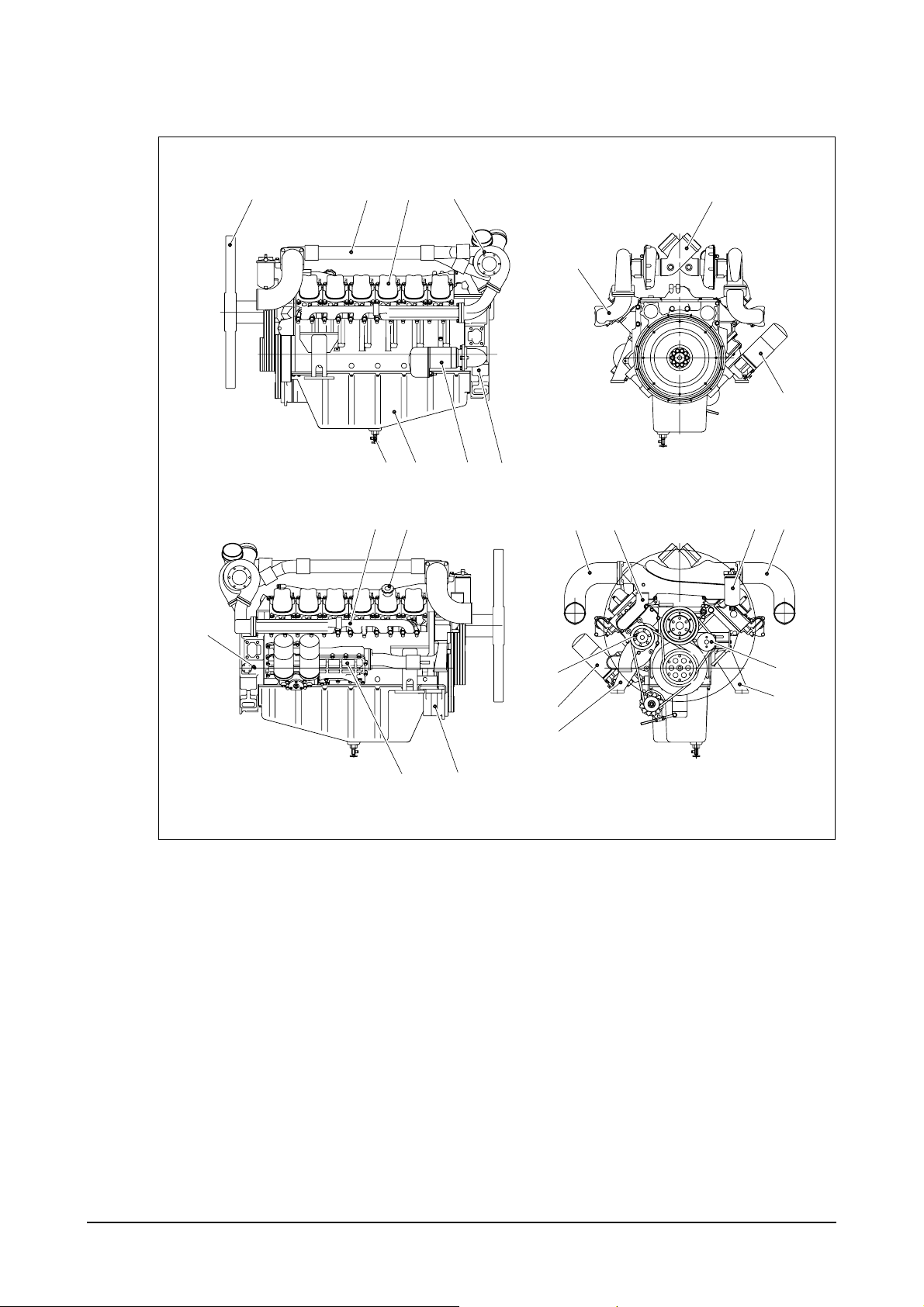
6) P222LE : Generator engine
11
123
4
56 7 8
910 18 17 1920
15
14
16
23
16
21
22
22
12
13
EA6O1003
1. Cooling fan 10. Oil filler cap 18. Air pipe
2. Air pipe 11. Pick up sensor (Air cleaner to turbocharger)
3. Cylinder head cover 12. Oil cooler 19. Fuel filter
4. Turbocharger 13. Alternator 20. Air pipe
5. Oil drain valve 14. Exhaust elbow (Turbocharger to inter cooler)
6. Oil pan 15. Air pipe 21. Idle pulley
7. Starter (Air cleaner to turbocharger) 22. Engine mounting bracket
8. Flywheel housing 16. Oil filter 23. Water pump
9. Exhaust manifold 17. Cooling water outlet
Safety Regulations & Engine Specifications
- 18 -
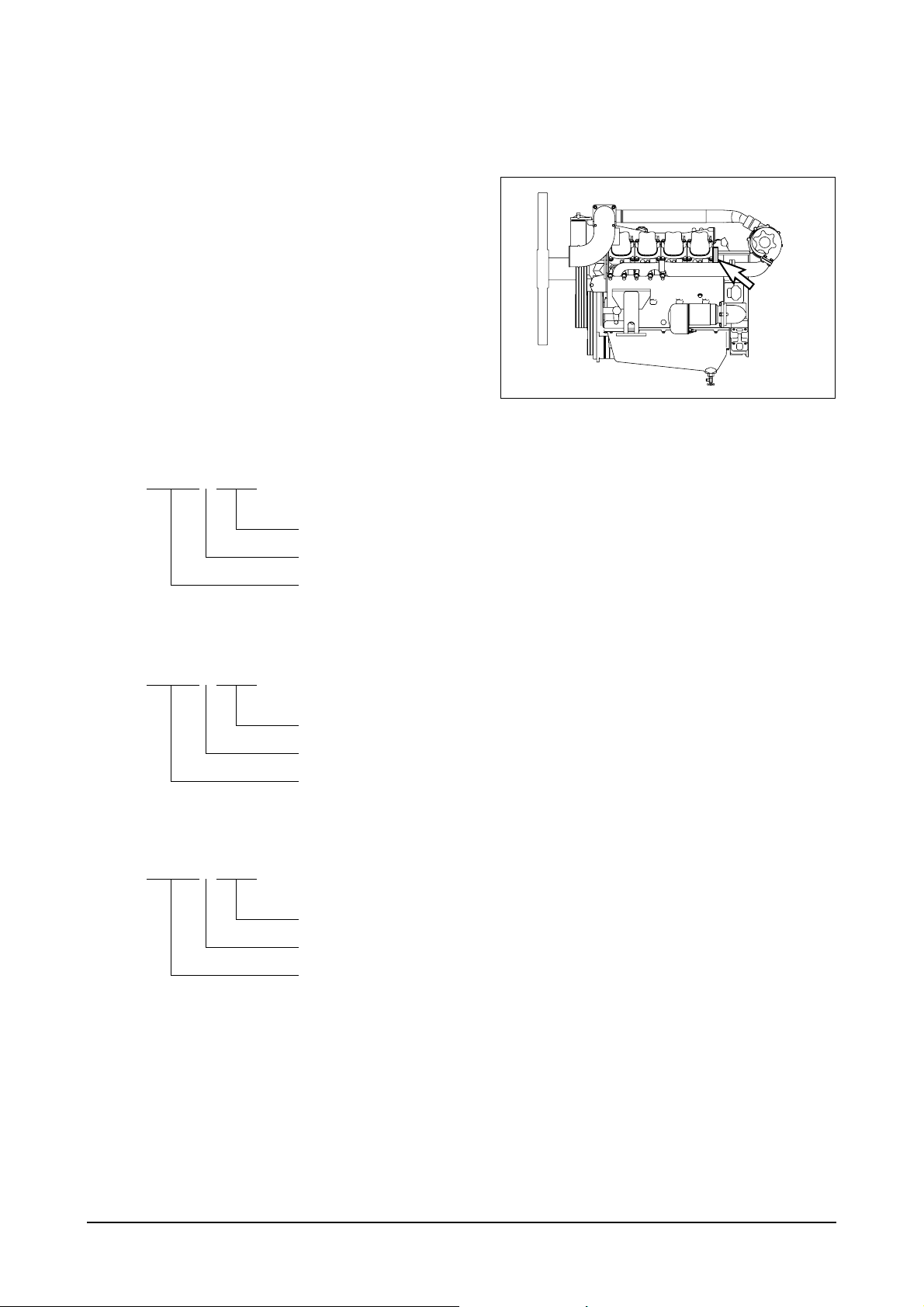
2. Technical Information
2.1. Engine Model and Serial Number
z
The engine model and serial number is
located on the engine as illustrated. These
numbers are required when requesting
warranty and ordering parts. They are also
referred to as engine model and serial
number because of their location.
z
Engine serial No. (example 1 : P158LE)
EAZOA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine
number
EA6O1006
Engine Model Suffix
z
Engine serial No. (example 2 : P180LE)
EASOA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine Model Suffix
z
Engine serial No. (example 3 : P222LE)
EAYOA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine Model Suffix
- 19 -
Technical Information
z
Engine serial No. (example 4 : PU158TI)
EAZPA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine Model Suffix
z
Engine serial No. (example 5 : PU180TI)
EASPA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine Model Suffix
z
Engine serial No. (example 6 : PU222TI)
EAYPA 8 00001
Serial No.
Production Year(2008)
Engine Model Suffix
2.2. Engines Characteristic
z
The generator engine(P158LE/P180LE/P222LE) and power unit engine(PU158TI/PU180TI/PU222TI)
series are V-type liquid-cooled 8/10/12-cylinder four-stroke Diesel engines with direct injection.
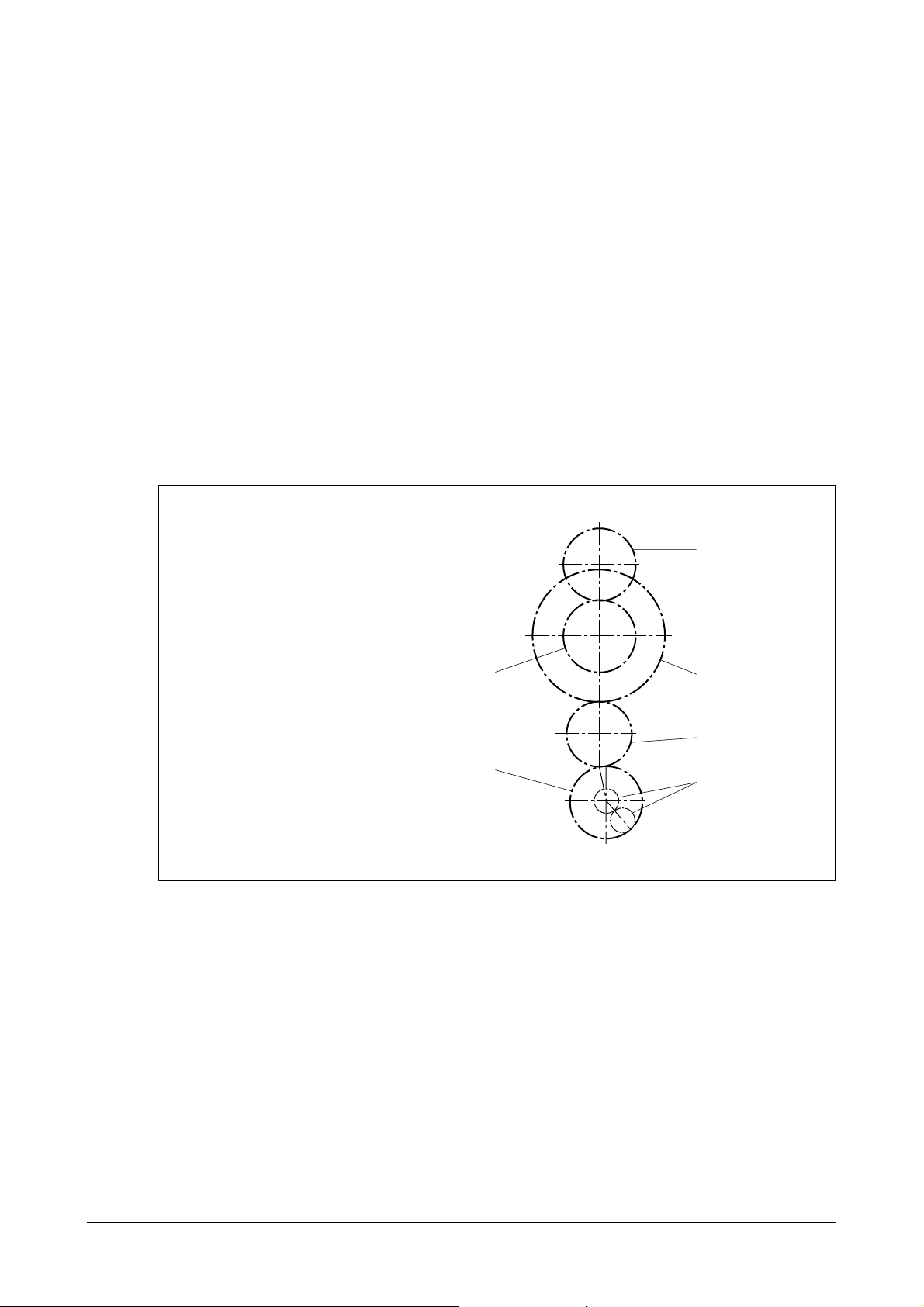
2.2.1. Oil gallery cooling type piston
z
Oil gallery cooling is used for the piston
of the engine.
z
When thermal loading is high, piston
cooling by means of an oil gallery in the
crown is normally necessary to prevent
crown cracking and ring sticking. The
design of the gallery, the design and
location of the oil spray nozzle and the
quantity of oil flowing in the gallery are
critical in order to achieve the desired
temperature reduction.
z
The cross section shape of the gallery should be designed to achieve sufficient oil movement to
maximize cooling efficiency.
ED7OM007
Technical Information
- 20 -
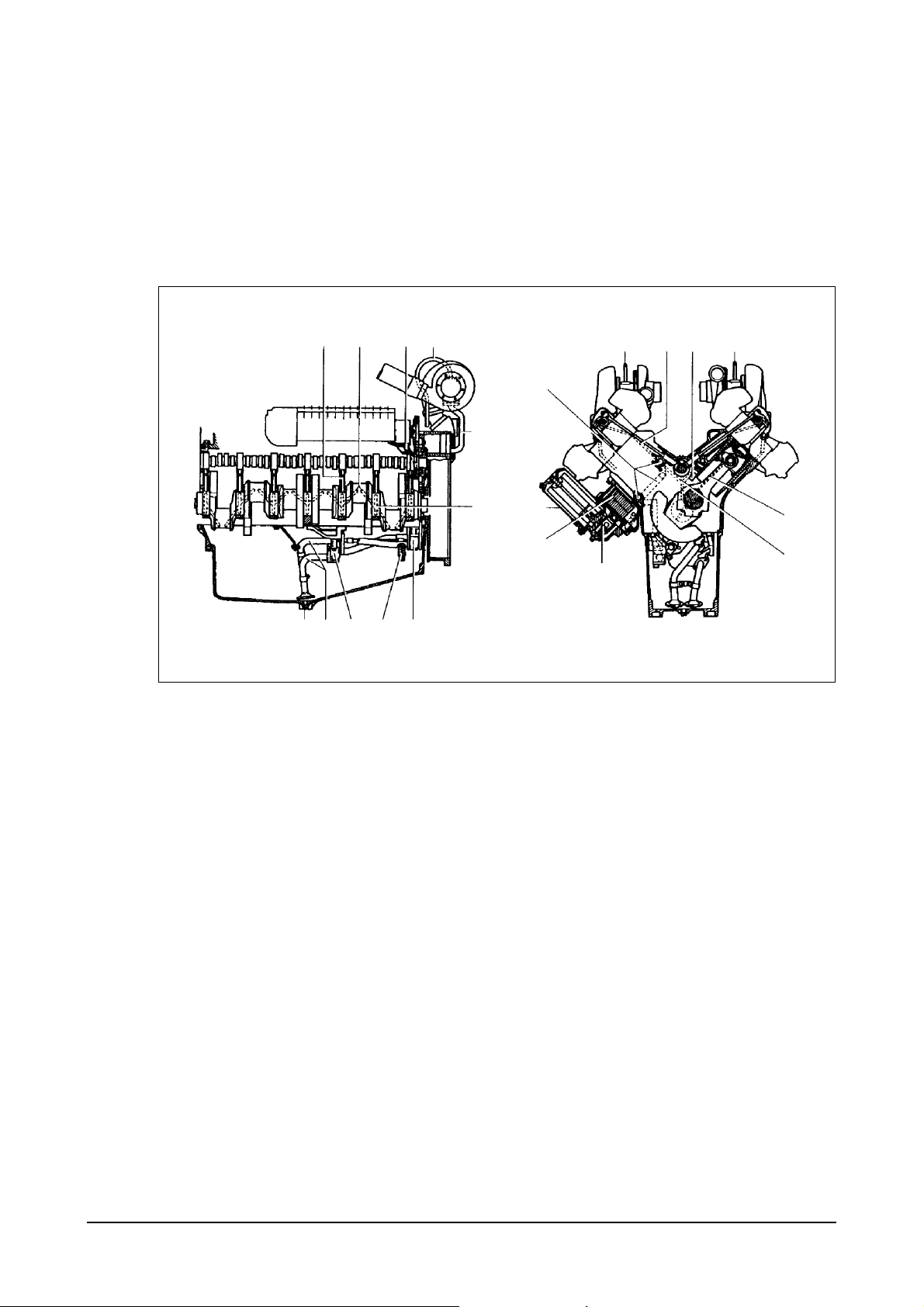
2.2.2. Engine block
z
The cylinder block is a single piece of alloy cast iron. To increase its stiffness, it is extended to a level
below the crankshaft center line. The engine has replaceable wet cylinder liners and individual
cylinder heads with strung-in valve seat rings and replaceable valve guides.
2.2.3. Piston / Connecting rod / Crank assembly
z
The forged crankshaft has screwed-on counterweights. Radial seals with replaceable wearing rings
on crankshaft and flywheel are provided to seal the crankcase penetrations.
z
The connecting rods are die-forged, diagonally split and can be removed through the top of the
cylinders together with the pistons. Crankshaft and connecting rods run in steel-backed lead bronze
ready-to fit type bearings.
2.2.4. Engine timing
z
Camshaft, oil pump and injection pump are driven by a gear train arranged at the flywheel end.
2.2.5. Valves
z
The overhead valves are actuated via chilled cast iron tappets, push rods and rocker arms from the
camshaft.
1. Crankshaft gear
2. Oil pump drive gear
3. Oil pump impeller gears
4. Camshaft drive gear
5. Injection pump drive gear
6
5
2
4
1
3
EA6O3001
- 21 -
Technical Information
2.2.6. Engine lubrication
z
The engine is equipped with force-feed lubrication.
The pressure is produced by a gear pump whose drive gear is in direct mesh with the crankshaft
gear at the flywheel end.
z
The oil pump draws the oil from the oil sump and delivers it through the oil cooler and oil filter to the
main distributor gallery and from there to the main bearings, big-end bearings and camshaft bearings
as well as to the small-end bearings and the rocker arms.
10 15 17
8
17 13 14 17
7
18
9
2
16
1
1. Oil suction pipes 10. Ports for big end bearing lubrication
2. Oil pumps 11. Small end bearing lubrication
3. Oil relief valves 12. Camshaft bearing lubrication
4. Oil cooler 13. Rocker arm lubrication
5. Oil filter 14. Spray nozzle
6. Bypass valve 15. Injection pump lubrication
7. Main oil galleries 16. Oil drain plug
8. Oil gallery to crankshaft 17. Lube oil pipes to turbochargers
9. Ports for main bearing lubrication 18. Oil return from turbochargers
3
2
5
4
6
11
12
EA6O3002
Technical Information
- 22 -
z
The injection pump and the turbocharger are also connected to the engine lubricating system. The
cylinder walls and timing gears are splash-lubricated.
Each cylinder has an oil jet provided for cooling the underside of the pistons.
The lube oil is cleaned in a full-flow oil filter. Depending on the agreed extent of delivery and the
design of the engine, the lube oil circuit can be equipped with oil pressure monitors (advance
warning and cut-off function) which shut the engine down in the event of a sudden loss of pressure.
(1) Oil cooler
An oil cooler is provided between the oil filter and the crankcase. This cooler is of the flat tube
type with turbulence inserts and operated by the coolant.
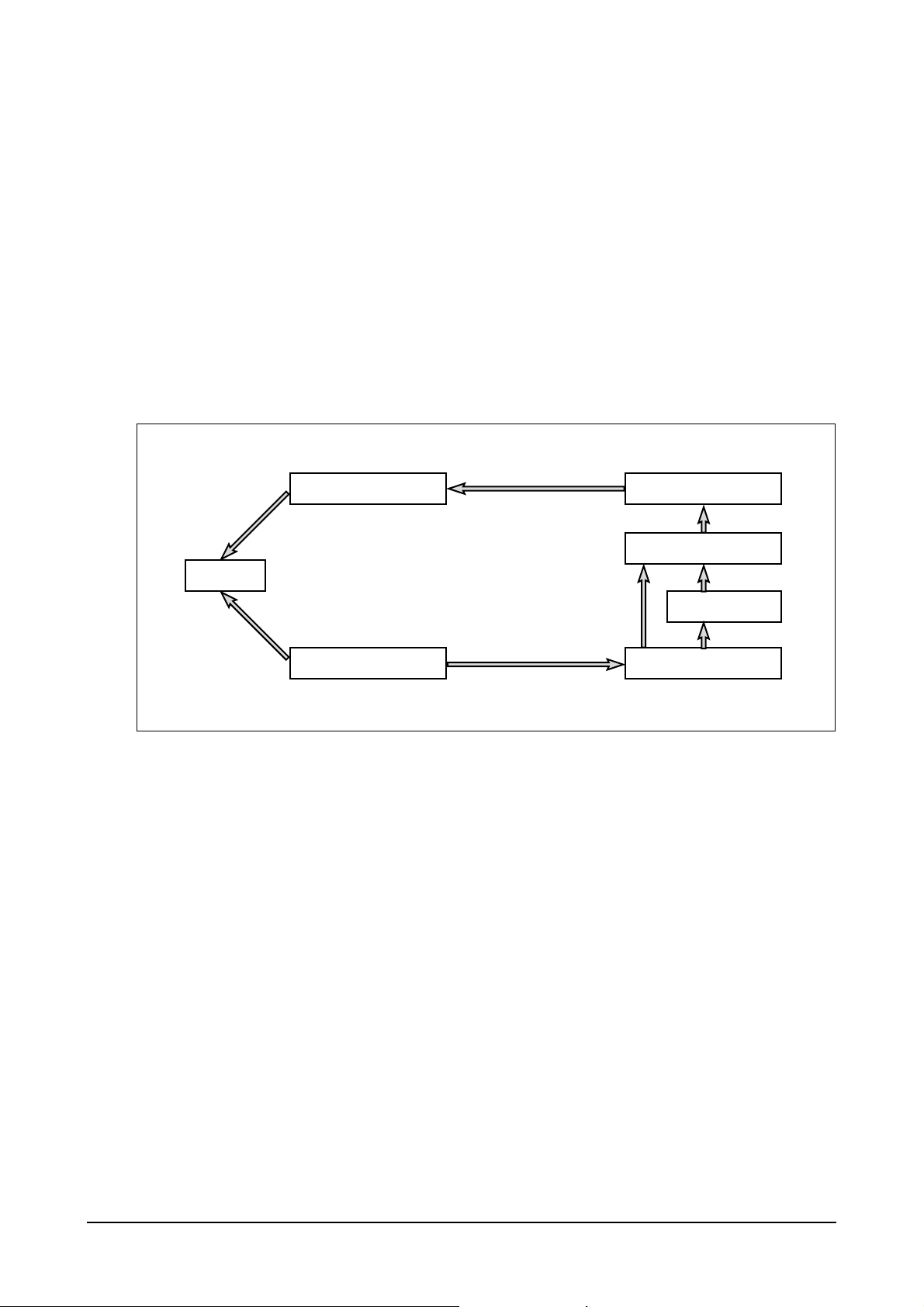
2.2.7. Engine cooling system
Radiator
Thermostat
Water pump
Coolant pipe
Cylinder head
Oil cooler
Coolant pipe
EA6M1001
- 23 -
Technical Information
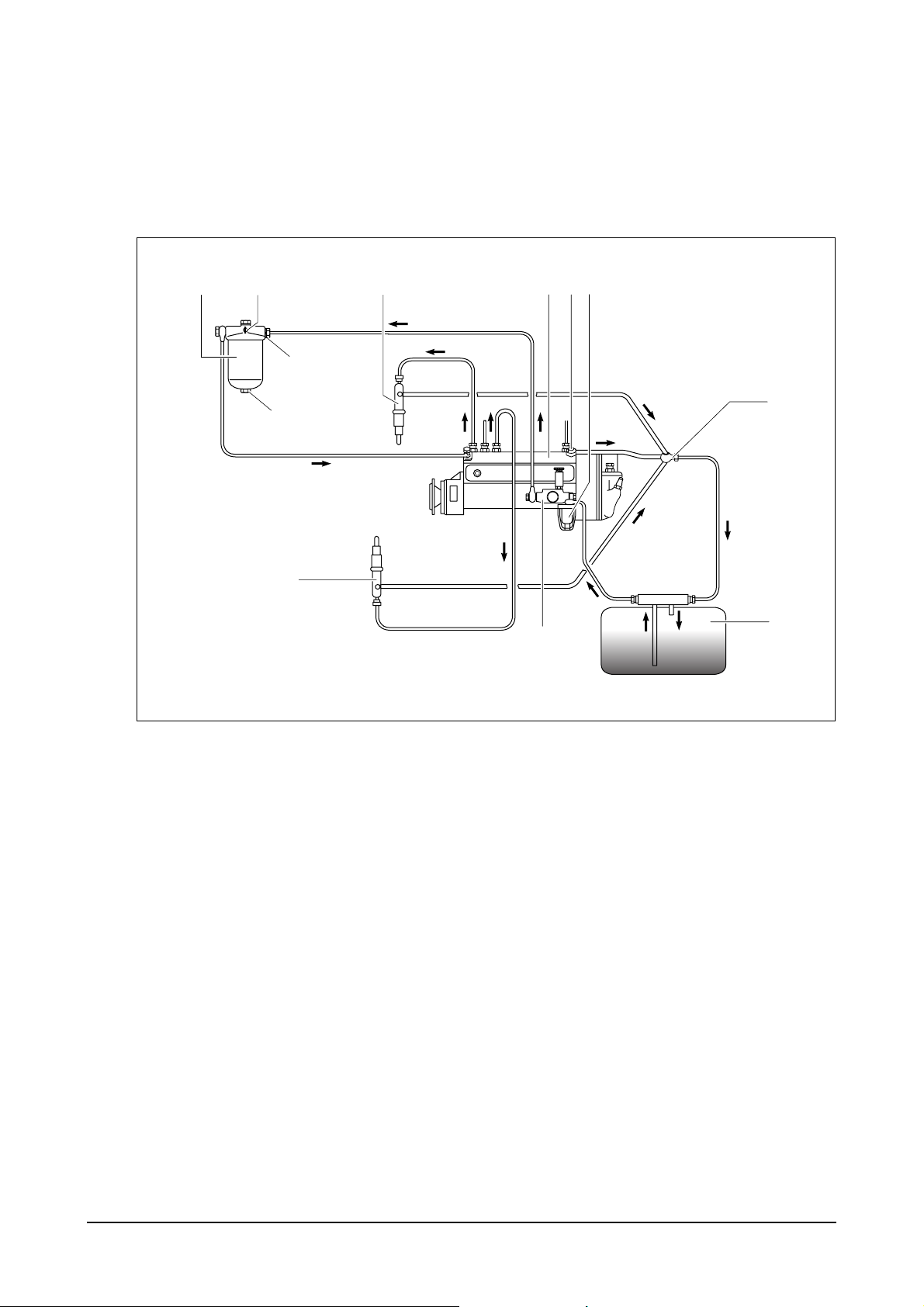
2.2.8. Fuel system
The fuel is delivered by the fuel lift pump via the fuel filter to the injection pump and from there to the
injectors.
The fuel is sprayed into the cylinder through nozzles fitted in screw-fit injections in the cylinder heads.
Excessive fuel delivered and leak fuel from the injectors flow through the return pipe back to the tank.
4
4b
7
682
5
9
4a
7
1
10
EA6O3003
1. Fuel tank 5. Fuel pipe connector
2. Strainer 6. Injection pump
3. Fuel Filter 7. Injector
4. Fuel filter assembly 8. Fuel pressure relief valve
4a. Fuel water drain plug 9. Fuel return pipe
4b. Air bleeding plug
10. Fuel feed pump
(for fuel filter)
Technical Information
- 24 -
If Diesel fuel which contains moisture is used the injection system and the cylinder liners / pistons will be
damaged. This can be prevented to same extent by filling the tank as soon as the engine is switched off
while the fuel tank is still warm (formation of condensation is prevented). Drain moisture from storage
tanks regularly. Installation of a water trap upstream of the fuel filter is also advisable.
z
Fuel oil selection chart
General Fuel
Classification
Gravity, °API
#)
Flash Point
Min. °F (°C)
Viscosity, Kinematic
cST 100 °F (40 °C )
Cloud Point °F
#)
Sulfur Content
wt%, Max.
Carbon Residue
on 10 %, wt%, Max.
ASTM
Test
No. 1
ASTM 1-D
No. 2
ASTM 2-D
D 287 40 ~ 44 33 ~ 37 0.815 ~ 0.855
D 93 100 (38) 125 (52) 131 (55)
D 445 1.3 ~ 2.4 1.9 ~ 4.1 1.8 ~ 10
D 2500 See NOTE 1) See NOTE 1) See NOTE 1)
D 129 0.5 0.5 0.15
D 524 0.15 0.35 0.1
Accelerated Stability
Total Insolubles
mg/100 ml, Max.
#)
D 2274 1.5 1.5
Ash, wt%, Max. D 482 0.01 0.01
Cetane Number, Min.
+)
D 613 45 45 > 45
Distillation
Temperature, °F (°C)
IMP, Typican
10 % Typical
50 % Typical
+)
90 %
End Point
#)
#)
#)
#)
D 86
350(177)
385(196)
45(218)
500(260) Max.
550(288) Max.
375(191)
430(221)
510(256)
625(329) Max.
675(357) Max.
DIN 51601
680(360)
Water & Sediment
%, Max.
D 1796 0.05 0.05 0.05
#) Not specified In ASTM D 975
+) Differs from ASTM D 975
NOTE :
The cloud point should be -12
°
C (10 °F) below the lowest expected fuel temperature
to prevent clogging of fuel fitters by crystals.
- 25 -
Technical Information
2.2.9. Injection pump
No alterations must be made to the injection pump. If the lead seal is damaged the warranty on the
engine will become null and avoid.
z
Faults
We strongly recommend that any faults developing in the injection pump should be taken care of by
authorized specialist personnel.
z
Bleeding the fuel system
Bleeding the fuel filter is by releasing the bleed screws and operating the manual primer.
The suction chamber of the injection pump is continuously bled via the relief valve during operation If
the suction chamber is completely empty, e.g., when fitting a new pump, filling and bleeding it is by
actuating the manual primer.
z
Fuel lift pump
The fuel lift pump is operated by the injection pump camshaft via the roller tappet.
z
Strainer
After every 200 hours of operation the fuel strainer connected upstream of the fuel lift pump should
be cleaned.
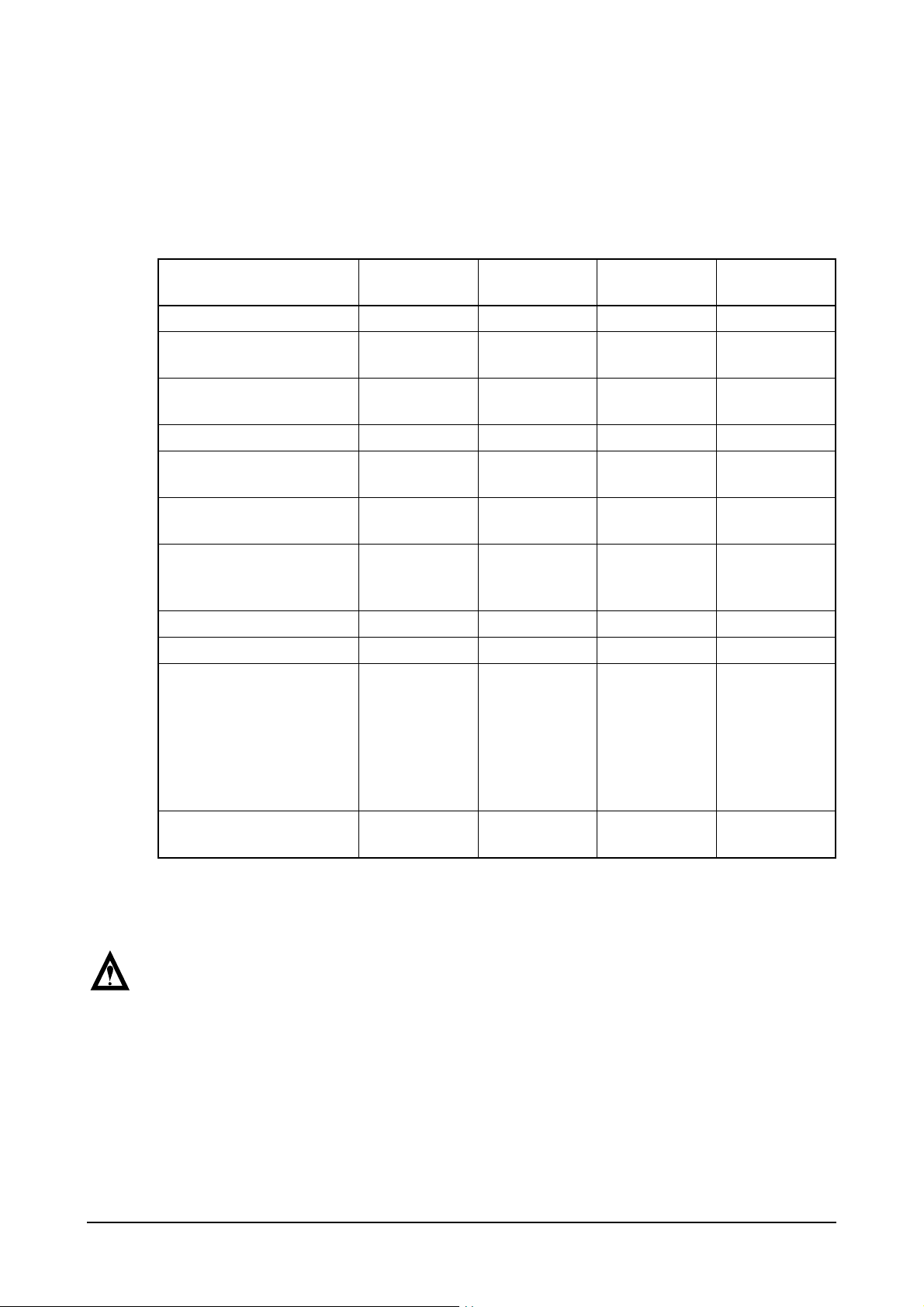
2.2.10. Fuel filter
z
After every 1,200 hour of operation,
drain the water and sediment from the
fuel-water separator.
z
Shut off the engine. Use your hand to
open the drain valve(6).
Turn the valve counter clockwise
approximately 2 ~ 3 turns until draining
occurs. Drain the filter sump of water
until close fuel is visible.
z
Turn the valve clockwise to close the
drain valve. Do not over tighten the
valve, overtightening can damage the
threads.
1
3
4
6
5
2
EA2O4009
Technical Information
- 26 -
2.2.11. Replacement of fuel filter
z
Clean the area around the fuel filter head(3).
z
Remove the fuel filter(2).
z
Remove the fuel filter thread adapter seal ring(4).
Use a clean lint free cloth to clean the gasket surface of the fuel filter head(3).
z
Install the new thread adapter seal ring(4)supplied with the new filter.
Use clean oil to lubricate the filter seal(5), and fill the new filter with clean fuel.
z
Install the filter on the filter head(5).
Tighten the filter until the gasket contacts the filter head surface.
Tighten the filter on additional one-half to three-fourths of a turn, on as specified by the filter
manufacturer.
NOTE :
Mechanical over tightening of the filter can distort the thread or damage the filter
element seal.
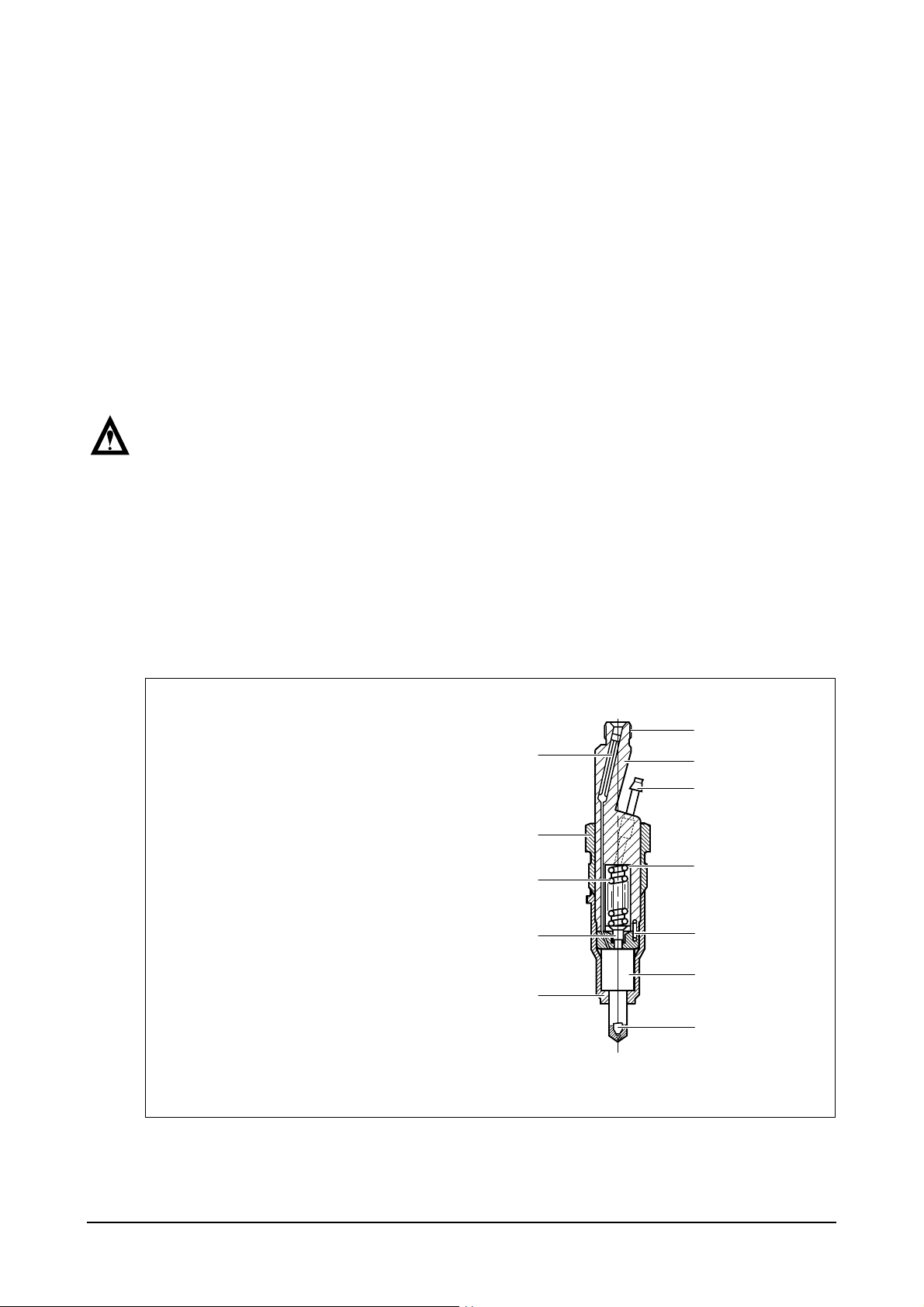
2.2.12. Injector maintenance
The injectors are designed to spray the fuel delivered by the injection pump directly into the spherical
combustion chamber in the piston crown.
The injector consists of the nozzle and the nozzle holder.
A copper gasket fitted to the injector ensures gas-tight seating and good heat dissipation.
The opening pressure of the nozzle is adjusted by means of shims at the compression spring.
1. Rod type filter
2. Cap nut
3. Compression spring
4. Compression pin
5. Cap nut for fixed nozzle
6. Nozzle needles
7. Connect hole for fuel delivery
8. Nozzle holder
9. Connect tube for overflow
10. Shim
11. Pin
12. Nozzle bush
7
1
2
3
4
5
8
9
10
11
12
6
EA6O5006
- 27 -
Technical Information
 Loading...
Loading...