Page 1

D-Link
DI-711
Wireless Broadband Router
Rev. 07062005
User’s Manual
Page 2

Contents
Introduction................................................................................................4
Package Contents .....................................................................................5
Introduction to Broadband Router Technology........................................6
Introduction to Firewalls..........................................................................6
Introduction to Local Area Networking...................................................7
Introduction to Virtual Private Networking..............................................8
Introduction to Wireless Networking .......................................................9
Hardware Installation..............................................................................11
Placement ...............................................................................................11
Safety Precautions..................................................................................11
Side Panel...............................................................................................11
Front Panel .............................................................................................12
Rear Panel...............................................................................................12
Basic DI-711 Configuration & Main Page .............................................13
Start-up and Log in.................................................................................13
Main Page...............................................................................................15
Setup Wizard..........................................................................................15
Device Information.................................................................................16
Device Status..........................................................................................17
Basic Setup.............................................................................................18
Advanced Settings ....................................................................................21
DHCP Server Settings............................................................................21
Virtual Server Settings............................................................................22
DMZ...................................................................................................22
Static Routing.........................................................................................24
Dynamic Settings ...................................................................................25
2
Page 3

Modem String Settings...........................................................................26
System Tools..............................................................................................27
Intruder Detection Log...........................................................................27
Display Routing Table............................................................................28
System Diagnostics ................................................................................30
Load Default Settings.............................................................................31
Upgrade Firmware..................................................................................32
Reset Device...........................................................................................33
Troubleshooting........................................................................................34
Basic Functions ......................................................................................34
LAN Connection Problems....................................................................36
ISP Connection Problems.......................................................................38
Internet Application Problems................................................................39
Wireless Troubleshooting.......................................................................41
Performing a Factory Reset....................................................................42
Using the PING Utility in Windows 95/98/Me......................................43
Using the WINIPCFG Utility in Windows 95/98/Me............................45
Technical Specifications ...........................................................................47
D-Link Offices...........................................................................................49
Limited Wa rranty.....................................................................................50
Registration Card................................................................................59
3
Page 4

Introduction
Congratulations on your purchases of the D-Link Wireless Broadband
Router. Your Wireless Broadband Router enables you to share your DSL or
Cable Internet connection with computers on your network. This guide will
explain the features and functions of the Wireless Broadband Router to
help you get the most out of your Internet experience.
D-Link’s Wireless Broadband Router allows LAN users to share a
single Internet Connection while providing the safety and security of port
blocking, packet filtering, and a natural firewall. Static address support,
integrated DHCP, PPPoE, and device name support will allow it to connect
to nearly any broadband provider whether Cable or DSL based, and at the
same time simplify local area network settings.
The Wireless Broadband Router provides two levels of security
support. First, it masks local users’ IP addresses from others on the Internet
making it much more difficult for a hacker to target a machine on your
network. Secondly, it can block and redirect certain ports to limit the
services that outside users can access. Specific ports can be opened to
ensure that games and other Internet applications will run properly.
The Broadband Router provides special pass through support for
common VPN implementations. The Virtual Server feature allows you to
expose HTTP, FTP, Game Servers and other local services to be accessible
to Internet users located outside of the LAN. The User-Definable
Application Sensing Tunnel feature allows you to define the attributes to
support special applications requiring multiple connections, such as
Internet gaming, video conferencing, and Internet telephony. A DMZ
setting can be applied to a single client behind the Broadband Router to
4
Page 5

expose it to the Internet and ensure complete Internet application
compatibility even if specific ports are not known.
Unlike proxy server or NAT software that requires the software server
to remain visible on the Internet, no local computers are directly externally
visible when using the Broadband Router. Also the Broadband Router, like
broadband, is always on, removing the need to constantly boot a software
server when access is desired from a client.
Integrated DHCP services allow up to 252 users to get their IP address
automatically on boot up from the Broadband Router. Client machines
require no software, simply set them to accept a dynamically assigned IP
address and reboot. Each time they are powered up the Broadband Router
will recognize them and set their IP address to ins tantly connect them to
the LAN.
Package Contents
The D-Link DI-711 package should include the following items.
DI-711 Broadband router
User’s Manual
Quick Install Guide
Power Adapter
CAT-5 UTP Cable
5
Page 6

Introduction to Broadband Router Technology
A router is a device that forwards data packets from a source to a
destination. Routers work on OSI layer 3, which forwards data packets
using an IP addresses and not a MAC address. A router will forward data
from the Internet to a particular computer on your LAN.
The information that makes up the Internet gets moved around using
routers. When you click on a link on a web page, you send a request to a
server to show you the next page. The information that is sent and received
from your computer is moved from your computer to the server using
routers. A router also determines the best route that your information
should follow to ensure that the information is delivered properly.
A router controls the amount of data that is sent through your network
by eliminating information that should not be there. This provides security
for the computers behind your router because computers from the outside
cannot access or send information directly to any computer on your
network. The router determines which computer the information should be
forwarded to and sends it. If the information is not intended for any
computer on your network, the data is discarded. This keeps any unwanted
or harmful information from accessing or damaging your network.
Introduction to Firewalls
A firewall is a device that sits between your computer and the Internet
that prevents unauthorized access to or from your network. A firewall can
be a computer using firewall software or a special piece of hardware built
specifically to act as a firewall. In most circumstances, a firewall is used to
prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks such
as corporate LAN’s and Intranets.
6
Page 7

A firewall watches all of the information moving to and from your
network and analyzes each piece of data. Each piece of data is checked
against a set of criteria that the administrator configures. If any data does
not meet the criteria, that data is blocked and discarded. If the data meets
the criteria, the data is passed through. This method is called packet
filtering.
A firewall can also run specific security functions based on the type of
application or type of port that is being used. For example, a firewall can
be configured to work with an FTP or Telnet server. Or a firewall can be
configured to work with specific UDP or TCP ports to allow certain
applications or games to work properly over the Internet.
Introduction to Local Area Networking
Local Area Networking (LAN) is the term used when connecting
several computers together over a small area such as a building or group of
buildings. LAN’s can be connected over large areas. A collection of LAN’s
connected over a large area is called a Wide Area Network (WAN).
A LAN consists of multiple computers connected to each other. There
are many types of media that can connect computers together. The most
common media is CAT5 cable; UTP or STP twisted pair wire. On the other
hand, wireless networks do not use wires; instead they communicate over
radio waves. Each computer must have a Network Interface Card (NIC),
which communicates the data between computers. A NIC is usually a
10Mbps network card, 10/100Mbps network card, or a wireless network
card.
Most networks use hardware devices such as hubs or switches that
each cable can be connected to in order to continue the connection between
7
Page 8

computers. A hub simply takes any data arriving through each port and
forwards the data to all other ports. A switch is more sophisticated, in that a
switch can determine the port that each piece of data is supposed to be
delivered to. A switch minimizes network traffic and speeds up the
communication over a network.
Networks take some time in order to plan and implement correctly.
There are many types of scenarios to consider which could affect the
operability of a network.
Introduction to Virtual Private Networking
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) uses a publicly wired network (the
Internet) to securely connect two different networks as if they were the
same network. For example, an employee can access the corporate network
from home using VPN, allowing the employee to access files and printers.
Here are several different implementations of VPN that can be used.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP uses proprietary means of connecting two private networks over the
Internet. PPTP is a way of securing the information that is communicated
between networks. PPTP secures information by encrypting the data inside
of a packet.
IP Security (IPSec)
IPSec provides a more secure network-to-network connection across the
Internet or a Wide Area Network (WAN). IPSec encrypts all
communication between the client and server whereas PPTP only encrypts
the data packets.
8
Page 9

Both of these VPN implementations are used because there is not a
standard for VPN server software. Because of this, each ISP or business
can implement their own VPN network making interoperability a
challenge.
Introduction to Wireless Networking
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide
easy to use and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your
home or business. Strictly adhering to IEEE 802.11b the D-Link wireless
family of products will allow you to access the data you want, when and
where you want it. No longer will you be tethered to a workstation or
forced to run new wiring. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that
wireless networking delivers.
Standards Based Technology
Based on IEEE 802.11b, D-Link Air products can throughput data up
to 11 Megabits per second. This means you will be able to transfer large
files quickly or even watch a Movie in MPEG format over your network
without noticeable delays. This technology works by using multiple
frequencies in the 2.4GHz range utilizing Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum (DSSS) technology. D-Link Air products will automatically
sense the best possible connection speed to ensure the greatest speed and
range possible with the technology.
Installation Considerations
Designed to go up to 100 meters indoors and up to 300 meters
9
Page 10

outdoors, D-Link Air lets you access your network from anywhere you
want. Keep in mind, however, that the number of walls, ceilings or other
objects that the wireless signals must pass thru will limit range. Typical
ranges vary depending on the types of materials and background RF noise
in your home or business. The key to maximizing range is to follow these
basic principles:
1. Keep the number of walls and ceilings to a minimum - Each wall or
ceiling can reduce your D-Link Air Wireless products range from 1-30
meters. Position your Access Points, Residential Gateways, and
Computers so that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2. Be aware of the direct line between Access Points, Residential
Gateways, and Computers - A wall that is .5 meter thick, at a 45 degree
angle appears to be almost 1 meter thick. At a 2 degree angle it looks
over 14 meters thick! Try to make sure that the AP and Adapters are
positioned so that the signal will travel straight through a wall or
ceiling for better reception.
3. Building Materials make a difference - A solid metal door or aluminum
studs may have a negative effect on range. Again, try to position
Access Points, Residential Gateways, and Computers so that the signal
passes through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4. Make sure that the antenna is positioned for best reception by using the
software signal strength tools included with your product.
5. Keep your product away (at least 1-2 meters) from electrical devices
that generate RF noise, like microwaves, Monitors, electric motors, etc.
For the average American 4-bedroom home, range should not be a
problem. If you experience low or no signal strength in areas of your
home that you wish to access, consider positioning the Access Point in
10
Page 11

a location directly between the Residential Gateways and/or Computers
that will be connected. Additional Access Points can be connected to
provide better coverage in rooms where the signal does not appear as
strong as desired.
Hardware Installation
Placement
Your Wireless Broadband Router should be placed in a safe and
secure location. To ensure proper operation, please keep the unit away
from water and other damaging elements.
Safety Precautions
Please read the installation guide thoroughly before you install the
DI-711.
The DI-711 should only be repaired by authorized and qualified
personnel.
Please do not try to open or repair the DI-711 yourself.
Do not place the DI-711 in a damp or humid location, i.e. a bathroom.
The DI-711 should be placed in a sheltered and non-slip location within
a temperature range of +5 to +40 Celsius degree.
Please keep the wrap bag of the DI-711 and the clip binding the cable
out of reach of children and babies to avoid choking.
Please do not expose the DI-711 to direct sunlight or other heat sources.
The housing and electronic components may be damaged by direct
sunlight or heat sources.
Side Panel
The power port is located on the right-hand side of the DI-711. Connect the
11
Page 12
AC adapter to this port to supply power.
Front Panel
The front panel provides LED’s for device status. Refer to the
following table for the meaning of each feature.
Power
WLAN
WAN
LAN
STAT
Power status of the DI-711. A steady LED indicates that the
power is on. No LED light indicates lack of power.
Wireless Connection status. The WLAN LED will be ON
indicating any wireless connection on the Local Network.
Wide Area Network status. When connected to the Internet,
the WAN LED should be on.
Local Area Network status. A steady LED indicates a
connection to the wired local network. A flickering LED
indicates data transmission.
System status indicator. A flickering light indicates proper
operation.
Rear Panel
The rear panel features a LAN port, WAN port, Serial port and
Factory Reset button. Refer to the following table for the meaning of each
feature.
Serial
LAN
WAN
Reset
Port used to connect an external analog backup modem.
The RJ-45 Ethernet port used to connect your hub/switch using
Ethernet cables to your DI-711.
The RJ-45 Ethernet port labeled WAN is used to connect your
DI-711 to your DSL or Cable modem.
Resets the configuration to default settings.
12
Page 13

Basic DI-711 Configuration & Main Page
The DI-711 provides a Web Configuration interface that can be
accessed using standard web browsers such as Netscape Communicator or
Microsoft Internet Explorer. Since the interface is web based (HTTP), the
DI-711 can be configured with any java and HTML compliant Internet
browser in any operating system. This section will discuss the Web
Configuration interface and how to use different options and settings.
Although you can change the IP address of the DI-711 to meet your
needs, this manual will assume that the defaults are left in place. This
means that the IP address of your DI-711 will be 192.168.0.1. If you have
changed the IP address scheme, please substitute 192.168.0.1 with the IP
address scheme that you have chosen.
Start-up and Log in
In order to configure the DI-711, you must use your web browser and
manually input 192.168.0.1 into the Address box and press Enter. The
Main Page will appear. The Device Information and Device Status screens
can be seen without logging into the DI-711. However, when the Setup
Wizard, Basic Setup, Advanced Settings and System Tools buttons are
pressed, the log in screen will be shown.
13
Page 14
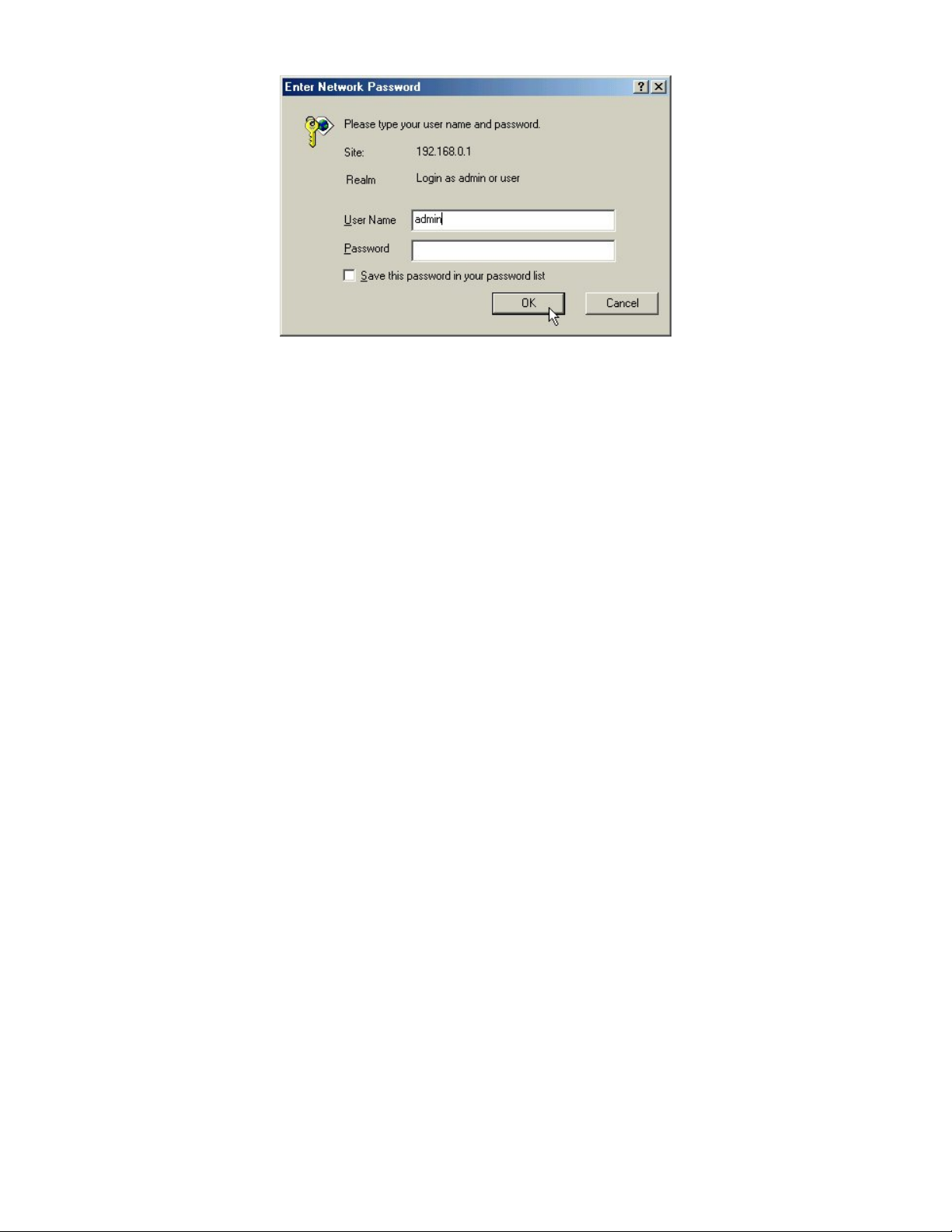
In order to configure the DI-711 you must input the user-name into
the User Name box. Enter the password into the Password box and press
the OK button. The default User Name is “admin”. There is no default
password, leave the Password field blank.
Once you have logged-in as administrator, it is a good idea to change
the administrator password to ensure a secure connection to the DI-711.
The Advanced Settings section described later in this manual describes
how to change the password.
Once you have input the correct password and logged-in, the screen
will change to the Main Page screen.
If you are having problems logging in and you are sure that the
password you are using is correct, check the top right-hand corner of your
keyboard to make sure that the Caps Lock light is not on.
14
Page 15
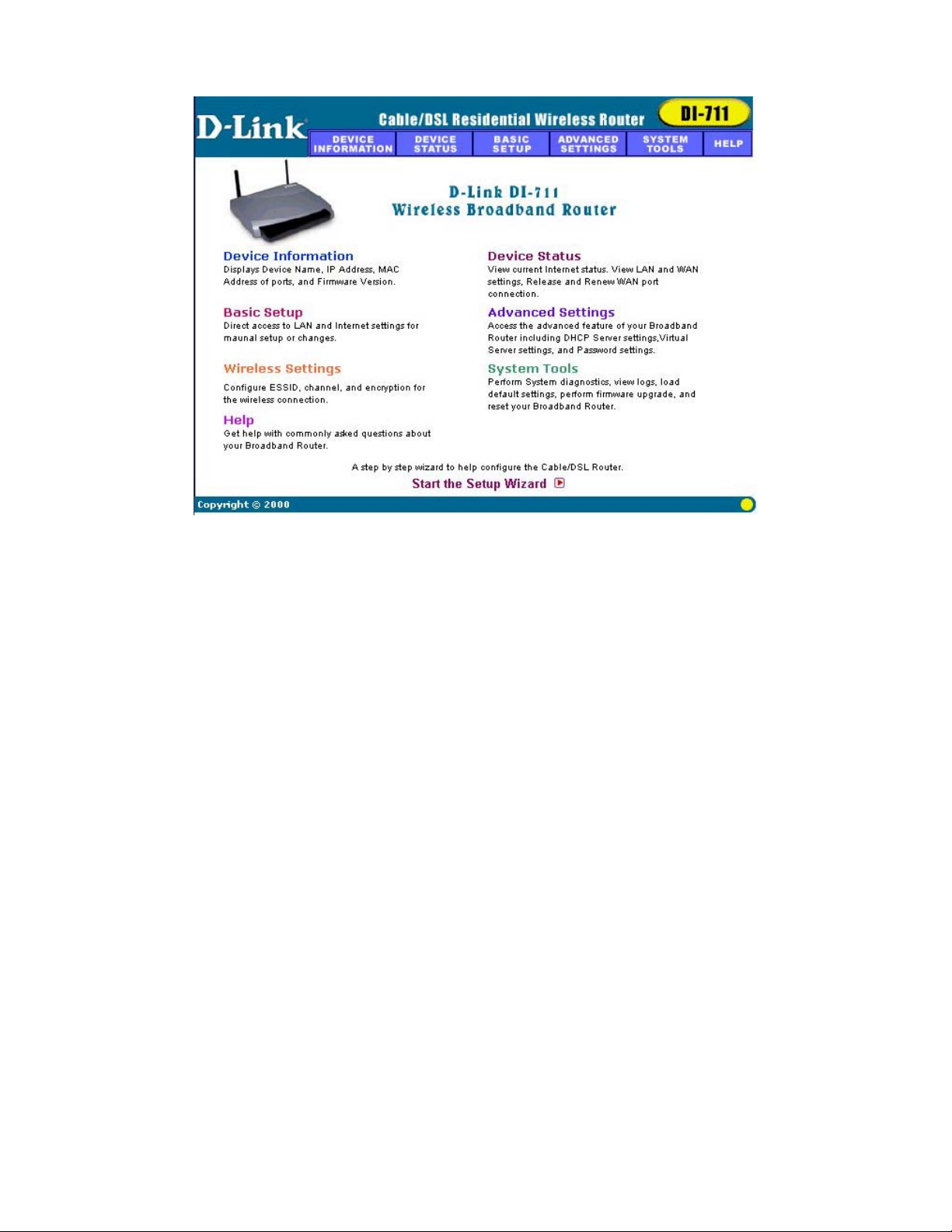
Main Page
The Main Page screen provides links to the main sections of the web
configuration interface.
Setup Wizard
The Setup Wizard is a step-by-step guide to configuring the DI-711 to
work with your ISP provider. Please refer to the quick install guide for
additional instructions.
15
Page 16

Device Information
The Device Information screen displays the basic information of your
DI-711.
The Device Name is the same as the Computer Name that was set in
the Setup Wizard.
The IP Address is the IP Address assigned to LAN side of your
DI-711.
The Private LAN Mac Address the Mac Address assigned to the
LAN side of your DI-711.
The Public WAN (Cable/DSL) Mac Address is the Mac Address
assigned to the WAN port of the DI-711. This Mac Address may be used by
some cable modem connections.
The Firmware Version is the current firmware version used by the
DI-711.
16
Page 17

Device Status
The Device Status screen displays a graphical representation of your
current configuration. The left side of the screen shows your connection
information in regards to WAN and LAN IP Address information. The right
side displays the connection status of each device.
This means that there is a connection.
17
Page 18

This means that there is not a connection.
The DHCP Log displays information about each IP Address assigned
to a computer using the DHCP server built-in to the DI-711.
Basic Setup
The Basic Setup screen enables you to change basic settings related to
accessing the Internet. All of the settings covered in the Basic Setup
section are covered in the Setup Wizard.
The Computer Name is used to give a name to your connection if
you are using a Cable modem.
18
Page 19

The Domain Name (host name) is the name given to you by your ISP
provider if you using the @Home cable Internet service.
Choose the Type of Connection you use by selecting Dynamic IP,
Static IP, or PPPoE.
Select Dynamic IP if your ISP has not given you a unique IP address
and you receive an automatic IP address each time you connect to your ISP.
The rest of the settings related to your connection are retrieved
automatically each time you connect to the Internet.
Select Static IP if your ISP assigns you an IP address. This means that
your ISP has given you an IP address that you will use to connect to the
Internet through their service. If you select Static IP, you will need to enter
the correct values for the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway in the
fields provided.
Select PPPoE if your ISP uses the Point-to-Point over Ethernet
protocol to authenticate a username and password and then automatically
assign you an IP Address. PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a non-standard
method of connecting to your ISP to obtain an IP address. It relies upon a
software client that is provided by the ISP. If you have a broadband
connection and login to your ISP like you would do with a dial-in modem,
then you are probably using PPPoE. If you are simply connected to the
Internet when you turn on your computer, you probably are not. The safest
way to check is to call your ISP or read the documentation provided when
you signed up for your Internet service. If you select PPPoE, you will need
to enter the correct values for your User Name and Password in the fields
provided.
The DNS section needs to be set to the correct option in order for the
DI-711 to resolve domain name information in URL’s.
19
Page 20

Select Dynamic DNS if your ISP provides the DNS information much
in the same way as you receive an IP Address.
Select Static DNS if you were given the DNS server information
when you signed with your ISP.
Click on the Save & Restart button to save your settings.
20
Page 21

Advanced Settings
DHCP Server Settings
By default, the Wireless Broadband Router has DHCP server enabled to
assign an IP address ranging from 192.168.0.100 to 192.168.0.199. In
addition, the router is capable of reserving up to four IP addresses within
the local network for mail, web, or ftp server.
21
Page 22

Virtual Server Settings
Specific application support is enabled in Virtual Server Settings
under Advanced Settings. Click on the arrow to select the common
applications such as FTP, Web server, and mail server. The DI-711
Wireless Broadband Router will detect and automatically open outgoing
ports required by most applications and games. However, some games
and applications such as Netmeeting will require that the computer be
exposed in the DMZ zone to allow incoming ports required by the
application. Click on the “Submit” button to save your settings.
DMZ
The Virtual Server Settings under Advanced Settings also enables one
computer to have full access to the Internet without the protection of the
22
Page 23

firewall. This allows a computer to be exposed to unrestricted two-way
communication outside of your network.
To enable DMZ, click the checkbox to the left and select “All”. Then
type the IP address of the selected computer in the box provided. Click
the “Submit” button to save your changes.
Only one computer can use DMZ at a time. Please note that enabling
DMZ removes the protection of the firewall, which exposes the computer
to intrusion.
Use DMZ only when needed and not for extended periods of time.
In some circumstances with gaming, enabling DMZ may help the
game contact the maximum number of servers, which can improve ping
times. Once the game connects to the game server, disable DMZ to ensure
proper firewall protection.
23
Page 24

Static Routing
In Static Routing, the user has the ability to add a static route to the
routing table by simple entering the destination IP, subnet mask, and
gateway. Clicking on “Add” and then “Submit” which requires a restart
for the IP address to be incorporated into the routing table.
24
Page 25

Dynamic Settings
By default, the Wireless Broadband Router will not send or receive
any routing Internet protocols (RIP) to update the routing table. However,
the user can enable the Wireless Broadband Router to automatically send
and receive RIP packets to establish routes for commonly used paths.
25
Page 26

Modem String Settings
Most dial-up modems are compatible with the standard modem
strings. However for modems that require special modem strings, the
user can enter the information in this screen.
26
Page 27

System Tools
The System Tools section enables you to manage your DI-711 and
view information related to unit functions. The following functions are
described in this chapter.
Intruder Detection Log: View detection logs.
System Diagnostics: Change remote configuration settings.
Load Default Settings: Restore settings to factory default.
Upgrade Firmware: Upgrade the firmware with a latest version.
Reset Device: Reboot the DI-804.
Intruder Detection Log
The Intruder Detection Log displays all information related to
intrusion attempts on your network. If any packets are seen as harmful,
27
Page 28

those packets are blocked and a log is kept about the information related to
that packet.
Index: (1,2,3 etc.) Refers to the row number.
Time: The time that the action was logged.
Protocol: (IP, UDP etc.) The type of protocol detected.
Source IP (Port): The source IP address of the intruding packet.
Dest IP (Port): The IP address assigned to the destination of the
intruding packet.
Event: The type of intrusion.
Display Routing Table
The Display Routing Table screen displays the routing table that the
DI-711 is using. A router uses a routing table to keep track of what IP
addresses there are and where the router should forward packets when it
28
Page 29

receives them.
Type: The type of routing protocol used.
Destination LAN IP Address: Shows the Destination IP Address on
the LAN side.
Subnet Mask: Shows the subnet mask assigned to the Destination
LAN IP Address.
Gateway IP Address: The IP Address of the assigned Gateway.
Hop Count: The number of hops between the Destination LAN IP
Address and the Gateway IP Address.
29
Page 30

System Diagnostics
30
Page 31

The System Diagnostics screen displays current status and connection
information. This screen is similar to the Device Status screen, although
both sections can be used to diagnose problems with your Internet
connection.
The Configuration section shows important information about your
ISP Settings, Modem Settings, and Device Settings as well as the latest
firmware version the DI-711 is using.
The Diagnosis section shows important information about ISP Status,
Link Status, and the current WAN connection.
This information is very useful in troubleshooting connection
problems.
Load Default Settings
The Load Default Settings screen enables you to restore the settings
31
Page 32

that came as default when set by D-Link. Click the Start button to begin the
process.
Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware screen enables you to update the firmware
used in the DI-711. Visit D-Link’s product support site to download an
updated firmware. Updated firmware usually fix problems encountered by
users, but may incorporate new features.
Begin by clicking the “Browse…” button to browse your computer to
select the updated firmware file. Once the firmware file is selected, click
the “Start” button to upgrade the firmware.
Note: When upgrading the firmware, do not try to access the Internet
and do not turn the power off. Doing so may cause the firmware upgrade
process to abort, which may result in a corrupt firmware.
32
Page 33

Reset Device
The Reset Device screen enables you to reboot the DI-711. If any
changes are made and you want them to take effect, you will need to reset
the DI-711 to do so. Click the “Reboot” button to reset the DI-711. Click
the “Cancel” button to cancel.
When you press the “Reboot” button, the DI-71 1 will go through its
shutdown and boot-up process. The Internet will not be accessible until the
DI-711 has finished its reboot process.
33
Page 34

Troubleshooting
In the event that you are unable to connect to or use your
Broadband Router, please refer to the following troubleshooting guide.
After each problem description, a possible cause and problem resolution is
provided. If this section does not help you fix the problem, go to the
D-Link web site (www.dlink.com) for additional troubleshooting tips. If
neither of these helps, please contact D-Link Technical Support for
additional help. The phone numbers for Technical Support are in the
appendix of this manual under D-Link Office Information.
Basic Functions
My Broadband Router will not turn on. No LED’s light up.
Cause
:
The power is not connected or the power switch is set to “Off”.
Resolution:
Connect the power adapter to your Broadband Router and plug it into
the power outlet.
Make sure that the power switch is set to “On”.
Note: Only use the power adapter provided with your Broadband Router.
Using any other adapter may damage your Broadband Router.
LED’s don’t follow the correct boot-up sequence as stated in the Quick
Install Guide.
:
Cause
The unit’s firmware is corrupt.
34
Page 35

The unit is not receiving the correct voltage from the power supply.
Resolution:
Download and upgrade the latest firmware.
Make sure the correct firmware has been used while upgrading. Use
only the firmware provided on D-Link’ s web or FTP sites.
Use only the power adapter provided.
The Link or Act LED’s do not turn on.
Cause:
The network cable is not connected.
The network cable is connected but not the right type, whether it is
patch or straight-through.
Resolution:
Make sure that both ends of the cable are connected.
Try using another cable.
If you are using a straight-through cable, try a patch cable and
vice-versa.
Sometimes my Broadband Router stops working or locks up.
Cause:
Someone has attempted to hack into someone on your LAN.
The Broadband Router has detected harmful data trying to access your
LAN.
The NAT table is full.
Resolution:
Reboot the Broadband Router by turning the power to the unit off and
then on again. Some types of hacker tools use very non-standard data
35
Page 36

streams. Some of these streams may cause the Broadband Router to
lock up. When the Broadband Router locks up, it will not affect the
computers attached to it. You may need to restart the client computers
to regain Internet access.
Although sometimes inconvenient, a lock-up is an indication of an
attack. Part of the design of the Broadband Router is to act as a decoy
for such traffic. If your computer locks up, you may have lost changes
to open files, data, and/or corrupted your operating system or hard
drive.
If you are currently experiencing frequent lock-ups, you may wish to
upgrade the firmware.
LAN Connection Problems
I can’t access my Broadband Router.
Cause:
The unit is not turned on.
There is not a network connection.
The computer you are using does not have a compatible IP Address.
Resolution:
Make sure your Broadband Router is turned on.
Make sure that there is a physical connection between your computer
and the Broadband Router and that the Link light is on.
Use the WINIPCFG utility described in the appendix to make sure that
your computer has a compatible IP Address. If your IP Address is not
set correctly and you are using DHCP, use WINIPCFG to renew your
IP Address. Otherwise, make correct changes to your Windows
36
Page 37

network settings. Make sure that the IP Address used on your computer
is set to the same subnet as the Broadband Router. For example, if the
Broadband Router is set to 192.168.0.1, change the IP address of your
computer to 192.168.0.15 or another unique IP Address that
corresponds to the 192.168.0.X subnet.
Follow the instructions outlined in the Appendix section labeled
“Console Mode” to check the basic settings of your Broadband router.
You can verify the IP Address of the Broadband Router to make sure
that your computers IP Address are set correctly.
Use the Reset button located on the front of your Broadband Router to
revert to the default settings.
I can’t connect to other computers on my LAN.
Cause:
The IP Addresses of the computers are not set correctly.
Network cables are not connected properly.
Windows network settings are not set correctly.
Resolution:
Make sure that each computer has a unique IP Address. If using DHCP
through the Broadband Router, make sure that each computer is set to
“Obtain an IP Address automatically” and restart the computer. Use the
WINIPCFG and PING utilities described in the appendix to make sure
that you can connect to each computer.
Make sure that the Link LED is on. If it is not, try a different network
cable.
Check each computer for correct network settings.
37
Page 38

ISP Connection Problems
I can access the Broadband Router, but I can’t connect to my ISP.
Cause
:
Your DSL or Cable modem is not functioning correctly.
The cable is connected from the WAN port of the Broadband Router to
your DSL or Cable modem.
The wrong connection type is used in Setup.
The username and password is not input correctly.
If using @Home service, the computer name is not input correctly.
Your ISP may only allow one MAC address to access the Internet.
Your ISP may only allow one computer to access their service.
Resolution
:
Make sure that your DSL or Cable modem is running correctly and
connected to the WAN port of the Broadband Router.
Make sure that the right connection type is used in the web
configuration.
Make sure that the username and password used in the connection type
is correct.
If using @Home, make sure that the computer name is input correctly.
Clone the MAC address using the web configuration interface.
Some ISP's do not care if you share your broadband connection among
multiple users. Other ISP's will explicitly restrict this type of activity in
your service contract. It is important that you verify that you are in
accordance with your service agreement before sharing Internet access.
38
Page 39

Internet Application Problems
My online game does not work.
Cause
:
The NAT table has filled up.
The correct settings have not been used to open the correct ports for
your application.
The unit has stopped working or crashed.
Resolution
:
If you are trying to connect to game servers and your connection has
stopped working, wait a few minutes or turn the unit off and then on
again. Games send out many requests to many different servers trying
to find the best game server for your connection. When this is done, the
NAT table used in the Broadband Router can fill up and stop working
temporarily. Try using the DMZ host feature while connecting to game
servers and then disabling DMZ while playing the game.
Turn the Broadband Router off and then on again to reset the NAT
table.
Make sure that the correct ports have been opened in order for your
specific game to operate correctly behind a firewall. Consult your game
documentation or contact technical support for your game to obtain the
correct settings for your game.
Some games just won’t operate correctly behind a firewall. In this case,
use the DMZ host feature while using the game, then turning DMZ off
while the game is not being played to ensure proper firewall protection.
39
Page 40

My E-Mail program doesn’t receive my E-Mail
Cause:
The Domain Suffix is not set correctly.
Resolution:
Some email applications require you to enter the Domain Suffix when
you configure your network and TCP/IP settings. The Domain Suffix is
the unique identifier for your email server.
The Domain Suffix is the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) address of the
email server you are using. Your cable modem or DSL provider usually
lists it somewhere on your invoice. The Domain Suffix address should
appear similar to this: dlink.occa.home.com. Find the Domain Suffix
on your invoice or call your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to obtain it.
I can’t connect to AOL
Cause:
Your AOL software is not set correctly to use the Broadband Router.
Resolution:
Use your AOL software to change the location information to use
TCP/IP in the Network field. Leave the phone number blank. Save your
settings and try to sign on again.
If this does not help, make sure that you can access the Internet in
general. If you can access the Internet, contact AOL technical support
to help you configure your AOL software to work correctly with your
Broadband Router.
40
Page 41

Wireless Troubleshooting
Can’t access the Broadband Router from a wireless network card
Cause
:
Settings are not the same among each wireless adapter.
Out of range.
IP Address is not set correctly.
Resolution
:
Make sure that the Mode, SSID, Channel and encryption settings are
set the same on each wireless adapter. The default SSID and Channel
that the Wireless Broadband Router uses is “default” and “6”
respectively.
Make sure that your computer is within range and free from any strong
electrical devices that may cause interference. Refer to the section
“Introduction to Wireless Networking” for tips to help make a good
connection.
Check your IP Address to make sure that it is compatible with the
Wireless Broadband Router. The default IP Address of the Wireless
Broadband Router is “192.168.0.1”. A compatible IP Address would be
“192.168.0.50”.
41
Page 42

Performing a Factory Reset
Follow these steps to perform a Factory Reset using the Reset button
on the back of the DI-804.
1. With the unit off, press and hold the Reset button with a pen or
paper clip and turn the unit on.
2. Hold the reset button for about 5 or 6 seconds until the Power/Test
LED on the front panel blinks very quickly and then release.
3. Wait a few seconds for the Broadband Router to reboot using
default settings.
A Factory Reset can also be performed through the web configuration
interface. Follow these steps to perform a factory reset using the web
configuration interface.
1. Log-in to the DI-711 web configuration interface.
2. Click on the System Management link at the bottom of the
screen.
3. Click on Restore Default Settings.
4. You will be asked if you want to restore to default settings. Click
OK to restore settings to default configuration or click Cancel to
discard any changes.
42
Page 43

Using the PING Utility in Windows 95/98/Me
In Windows, Microsoft has provided a small utility called PING that
can be used to troubleshoot your IP address and connection. The PING
utility is used mainly to test the connection between your computer and a
client computer. Using the PING utility to check a connection can be
helpful in determining where the problem is, whether it be your Broadband
Router, your DSL or Cable modem, or your ISP.
Use the following steps to use the WINIPCFG utility:
Click on the Start button and click Run.
Type "command" in the Open box.
Click "OK" to get to a DOS prompt.
Type "ping 192.168.0.1", which is the IP address of the Gateway
in this case, and hit the Enter key. The following screen will be
shown.
C:\>ping 192.168.0.1
Pinging 192.168.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time=130ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time=20ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.0.1: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 10ms, Maximum = 130ms, Average = 42ms
This screen shows a successful connection between you and your
Broadband Router. You can use these same steps to ping your DSL
or Cable modem and then your ISP provider and Internet website.
If any one of these attempts results in an unsuccessful PING, your
43
Page 44

connection is not complete.
If a PING is unsuccessful between you and your DSL or Cable
modem, then your connection is not setup correctly. If it is
unsuccessful when PINGing your ISP or an Internet site, your
connection setup maybe correct, but there might be a problem
with your ISP or the Internet site you trying to PING is
unavailable.
The screen shown below is an example of an unsuccessful PING.
C:\>ping 192.168.0.1
Pinging 192.168.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Ping statistics for 192.168.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
44
Page 45

Using the WINIPCFG Utility in Windows 95/98/Me
In Microsoft Windows versions 95 through Me, Microsoft has
provided a small utility called WINIPCFG that can be used to troubleshoot
your IP address and connection. The WINIPCFG utility is used mainly to
view, release and renew your IP Address configuration. Windows NT
(including Windows 2000) has a similar utility called IPCONFIG that can
be used to perform similar tasks.
Use the following steps to use the WINIPCFG utility:
Click on the Start button and click Run
Type "winipcfg" in the Open box.
Click OK. The IP Configuration screen will be displayed.
The IP address will be displayed in the IP Address box. If you have
more than one network card, make sure that the network card that
you are using is displayed in the white dropdown box.
Make sure that the Default Gateway is the IP Address of your
Broadband router. If it is not, you will not be able to connect to the
Internet. If you are using DHCP, click the Release and then the
45
Page 46

Renew buttons to receive the correct settings. If you manually set
your network settings, make sure that the IP Address of your
Broadband Router is set in the Gateway portion of the TCP/IP
settings in your network settings.
Click on "More Info" to display additional IP information.
The important settings to watch for in this screen are in the Host
Information box. Make sure that the DNS Servers box has the
correct DNS information.
Also check the DHCP server box to make sure that you are
connected to the right DHCP server.
46
Page 47

Technical Specifications
Standards:
• IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
• IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
• ANSI/IEEE 802.3 NWay auto-negotiation
Protocols Supported:
• TCP
• IP
• NAT
• UDP
• PPPoE
• DHCP (Client and Server)
Management:
• Web-Based
Ports:
• LAN: NWay 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
• WAN: 10BASE-T
• RS-232 (DB-9) Serial
47
Page 48

Wireless Specifications
General Wireless Specifications:
• IEEE 802.11b W ireless LAN, Wi-Fi Compatible
Access Point Frequency Band:
• 2.4 ~ 2.4835 GHz (subject to local regulation)
Access Point Number of Channel:
• USA & Canada: 11
Access Point Frequency Range:
• 5 Mbps
Access Point Data Rate:
• 11 Mbps*
• 5.5 Mbps
• 2 Mbps
• 1 Mbps
Additional details available at D-Link’ s web site (www.dlink.com).
*Maximum wireless signal rate based on IEEE Standard 802.11b specifications. Actual data throughput will vary.
Network conditions and environmental factors including volume of network traffic, building m ateri als and
construction, and network overhead lower actual data throughput rate.
48
Page 49

D-Link Offices
AUSTRALIA D-LINK AUSTRALASIA
Unit 16, 390 Eastern Valley Way, Roseville, NSW 2069, Australia
TEL: 61-2-9417-7100 FAX: 61-2-9417-1077
TOLL FREE: 1800-177-100 (Australia), 0800-900900 (New Zealand)
URL: www.dlink.com.au E-MAIL: support@dlink.com.au, info@dlink.com.au
CANADA D-LINK CANADA
2180 Winston Park Drive, Oakville, Ontario L6H 5W1 Canada
TEL: 1-905-829-5033 FAX: 1-905-829-5095 BBS: 1-965-279-8732 FREE CALL: 1-800-354-6522
URL: www.dlink.ca E-MAIL: techsup@dlink.ca
CHILE D-LINK SOUTH AMERICA
Isidora Goyenechea #2934 of.702, Las Condes, Santiago, Chile
TEL: 56-2-232-3185 FAX: 56-2-2320923 URL: www.dlink.cl
CHINA D-LINK CHINA
2F., Sigma Building, 49 Zhichun Road, Haidian District, 100080 Beijing, China
TEL: 86-10-88097777 FAX: 86-10-88096789
URL: www.dlink.com.cn
DENMARK D-LINK DENMARK
Naverland 2, DK-2600 Glostrup, Copenhagen, Denmark
TEL:45-43-969040 FAX:45-43-42434 7 URL: www.dlink.dk
E-MAIL: info@dlink.dk
EGYPT D-LINK MIDDLE EAST
7 Assem Ebn Sabet Street, Heliopolis Cairo, Egypt
TEL: 202-2456176 FAX: 202-2456192 U RL: www.dlink-me.com
E-MAIL: support@dlink-me.com
FRANCE D-LINK FRANCE
Le Florilege #2, Allee de la Fresnerie
78330 Fontenay Le Fleury France
TEL: 33-1- 30238688 FAX: 33- 1-3023-8689 URL: www.dlink-france.fr
E-MAIL: info@dlink-france.fr
GERMANY D-LINK GERMANY
Bachstrae 22, D-65830 Kriftel Germany
TEL: 49-(0)6192-97110 FAX: 49-(0)6192-9711-11
URL: www.dlink.de BBS: 49-(0)6192-971199 (Analog) 49-(0)6192-971198 (ISDN)
INFO LINE: 00800-7250-0000 (toll free) HELP LINE: 00800-7250-4000 (toll free)
REPAIR LINE: 00800-7250-8000
INDIA D-LINK INDIA
Plot No.5, Kurla-Bandra Complex Road,
Off Cst Road, Santacruz (E), Bombay - 400 098 India
TEL: 91-22 -652-6696 FAX: 91- 22-652-8914 URL: www.dlink-india.com
E-MAIL: service@dlink.india.com
ITALY D-LINK ITALIA
Via Nino Bonnet No. 6/b, 20154 Milano, Italy
TEL: 39-0 2-2900-0676 FAX: 3 9-02-2900-1723 URL: www.dlink.it
E-MAIL: info@dlink.it
JAPAN D-LINK JAPAN
10F, 8-8-15 Nishi-Gotanda, Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo 141 Japan
TEL: 81-3- 5434-9678 FAX: 81 -3-5434-9868 URL: www.d-link.co.jp
RUSSIA D-LINK RUSSIA
Michurinski Prospekt 49, 117607 Moscow, Russia
TEL: 7-095-737-3389, 7-095-737-3492 FAX: 7-095-737-3390
SINGAPORE D-LINK INTERNATIONAL
1 International Business Park, #03-12 The Synergy, Singapore 609917
TEL: 65-774-6233 FAX: 65-774-6322
URL: www.dlink-intl.com E-MAIL: info@dlink.com.sg
S. AFRICA D-LINK SOUTH AFRICA
Unit 2, Parkside 86 Oak Avenue
Highveld Technopark Centurion, Gauteng, Republic of South Africa
TEL: 27(0)126652165 FAX: 27(0)126652186
SWEDEN D-LINK SWEDEN
P.O. Box 15036, S-167 15 Bromma Sweden
TEL: 46-(0)8564-61900 FAX: 46-(0)8564-61901 E-MAIL: info@dlink.se
URL: www.dlink.se
TAIWAN D-LINK TAIWAN
2F, No. 119 Pao-Chung Road, Hsin-Tien, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
TEL: 886-2-2910-2626 FAX: 886-2-2910-1515 URL: www.dlinktw.com.tw
U.K. D-LINK EUROPE
4
TEL: 44-20-8731-5555 FAX: 44-20-8731-5511
URL: www.dlink.co.uk E-M AIL: info@dlink.co.uk
U.S.A. D-LINK U.S.A.
53 Discovery Drive, Irvine, CA 92618 USA
TEL: 1-949-788-0805 FAX: 1-949-753-7033 INFO LINE: 1-800-326-1688
BBS: 1-949-455-1779, 1-949-455-9616
URL: www.dlink.com E -MAIL: tech@dlink.com, support@dlink.com
Tech Support Hours: 6 A.M. to 6 P.M. Pacific Standar d Time. Monday through Friday
th
Floor, Merit House, Edgware Road, Colindale, London, NW9 5AB, U.K.
49
Page 50

Limited Warranty
D-Link Systems, Inc. (“D-Link”) provides this limited warranty for its
product only to the person or entity who originally purchased the product
from D-Link or its authorized reseller or distributor.
Limited Hardware Warranty: D-Link warrants that the hardware portion
of the D-Link products described below (“Hardware”) will be free from
material defects in workmanship and materials from the date of original
retail purchase of the Hardware, for the period set forth below applicable to
the product type (“Warranty Period”) if the Hardware is used and serviced
in accordance with applicable documentation; provided that a completed
Registration Card is returned to an Authorized D-Link Service Office
within ninety (90) days after the date of original retail purchase of the
Hardware. If a completed Registration Card is not received by an
authorized D-Link Service Office within such ninety (90) day period, then
the Warranty Period shall be ninety (90) days from the date of purchase.
Product Type Warranty Period
Product (excluding power supplies and fans), if
purchased and delivered in the fifty (50) United
States, or the District of Columbia (“USA”)
Product purchased or delivered outside the USA One (1) Year
Power Supplies and Fans One (1) Year
Spare parts and spare kits Ninety (90) days
D-Link’s sole obligation shall be to repair or replace the defective
One (1) Year
Hardware at no charge to the original owner. Such repair or replacement
will be rendered by D-Link at an Authorized D-Link Service Office. The
replacement Hardware need not be new or of an identical make, model or
part; D-Link may in its discretion may replace the defective Hardware (or
50
Page 51

any part thereof) with any reconditioned product that D-Link reasonably
determines is substantially equivalent (or superior) in all material respects
to the defective Hardware. The Warranty Period shall extend for an
additional ninety (90) days after any repaired or replaced Hardware is
delivered. If a material defect is incapable of correction, or if D-Link
determines in its sole discretion that it is not practical to repair or replace
the defective Hardware, the price paid by the original purchaser for the
defective Hardware will be refunded by D-Link upon return to D-Link of
the defective Hardware. All Hardware (or part thereof) that is replaced by
D-Link, or for which the purchase price is refunded, shall become the
property of D-Link upon replacement or refund.
Limited Software Warranty: D-Link warrants that the software portion of
the product (“Software”) will substantially conform to D-Link’s then
current functional specifications for the Software, as set forth in the
applicable documentation, from the date of original delivery of the
Software for a period of ninety (90) days (“Warranty Period”), if the
Software is properly installed on approved hardware and operated as
contemplated in its documentation. D-Link further warrants that, during
the Warranty Period, the magnetic media on which D-Link delivers the
Software will be free of physical defects. D-Link’s sole obligation shall be
to replace the non-conforming Software (or defective media) with software
that substantially conforms to D-Link’s functional specifications for the
Software. Except as otherwise agreed by D-Link in writing, the
replacement Software is provided only to the original licensee, and is
subject to the terms and conditions of the license granted by D-Link for the
Software. The Warranty Period shall extend for an additional ninety (90)
51
Page 52

days after any replacement Software is delivered. If a material
non-conformance is incapable of correction, or if D-Link determines in its
sole discretion that it is not practical to replace the non-conforming
Software, the price paid by the original licensee for the non-conforming
Software will be refunded by D-Link; provided that the non-conforming
Software (and all copies thereof) is first returned to D-Link. The license
granted respecting any Software for which a refund is given automatically
terminates.
What You Must Do For Warranty Service:
Registration Card. The Registration Card provided at the back of this
manual must be completed and returned to an Authorized D-Link Service
Office for each D-Link product within ninety (90) days after the product is
purchased and/or licensed. The addresses/telephone/fax list of the nearest
Authorized D-Link Service Office is provided in the back of this manual.
FAILURE TO PROPERLY COMPLETE AND TIMELY RETURN THE
REGISTRATION CARD MAY AFFECT THE WARRANTY FOR THIS
PRODUCT.
Submitting A Claim. Any claim under this limited warranty must be
submitted in writing before the end of the Warranty Period to an
Authorized D-Link Service Office. The claim must include a written
description of the Hardware defect or Software nonconformance in
sufficient detail to allow D-Link to confirm the same. The original product
owner must obtain a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number from
the Authorized D-Link Service Office and, if requested, provide written
proof of purchase of the product (such as a copy of the dated purchase
invoice for the product) before the warranty service is provided. After an
52
Page 53

RMA number is issued, the defective product must be packaged securely in
the original or other suitable shipping package to ensure that it will not be
damaged in transit, and the RMA number must be prominently marked on
the outside of the package. The packaged product shall be insured and
shipped to D-Link, 53 Discovery Drive, Irvine CA 92618, with all shipping
costs prepaid. D-Link may reject or return any product that is not packaged
and shipped in strict compliance with the foregoing requirements, or for
which an RMA number is not visible from the outside of the package. The
product owner agrees to pay D-Link’s reasonable handling and return
shipping charges for any product that is not packaged and shipped in
accordance with the foregoing requirements, or that is determined by
D-Link not to be defective or non-conforming.
What Is Not Covered:
This limited warranty provided by D-Link does not cover:
Products that have been subjected to abuse, accident, alteration,
modification, tampering, negligence, misuse, faulty installation, lack of
reasonable care, repair or service in any way that is not contemplated in the
documentation for the product, or if the model or serial number has been
altered, tampered with, defaced or removed;
Initial installation, installation and removal of the product for repair, and
shipping costs;
Operational adjustments covered in the operating manual for the product,
and normal maintenance;
Damage that occurs in shipment, due to act of God, failures due to power
surge, and cosmetic damage; and
Any hardware, software, firmware or other products or services provided
53
Page 54

by anyone other than D-Link.
Disclaimer of Other Warranties: EXCEPT FOR THE LIMITED
WARRANTY SPECIFIED HEREIN, THE PRODUCT IS PROVIDED
“AS-IS” WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NON-INFRINGEMENT. IF ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE
DISCLAIMED IN ANY TERRITORY WHERE A PRODUCT IS SOLD,
THE DURATION OF SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTY SHALL BE
LIMITED TO NINETY (90) DAYS. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY
COVERED UNDER THE LIMITED WARRANTY PROVIDED HEREIN,
THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY, SELECTION AND
PERFORMANCE OF THE PRODUCT IS WITH THE PURCHASER OF
THE PRODUCT.
Limitation of Liability: T O T HE MAXIMU M EXTENT PERMITTED BY
LAW, D-LINK IS NOT LIABLE UNDER ANY CONTRACT,
NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHER LEGAL OR
EQUITABLE THEORY FOR ANY LOSS OF USE OF THE PRODUCT,
INCONVENIENCE OR DAMAGES OF ANY CHARACTER, WHETHER
DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL (INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF GOODWILL,
WORK STOPPAGE, COMPUTER FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION,
LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA CONTAINED IN, STORED ON,
OR INTEGRATED WITH ANY PRODUCT RETURNED TO D-LINK
FOR WARRANTY SERVICE) RESULTING FR OM THE USE OF THE
54
Page 55

PRODUCT, RELATING TO WARRANTY SERVICE, OR ARISING OUT
OF ANY BREACH OF THIS LIMITED WA RRANTY, EVEN IF D-LINK
HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
THE SOLE REMEDY FOR A BREACH OF THE FOREGOING
LIMITED WARRANTY IS REPAIR, REPLACEMENT OR REFUND OF
THE DEFECTIVE OR NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT.
GOVERNING LAW: This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws
of the state of California.
Some states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages, or limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts,
so the foregoing limitations and exclusions may not apply. This limited
warranty provides sp ecif ic lega l rights and the product owner may also have
other rights which vary from state to state.
Trademarks
Copyright ©1999 D-Link Corporation. Contents subject to change without
prior notice. D-Link is a registered trademark of D-Link
Corporation/D-Link Systems, Inc. All other trademarks belong to their
respective proprietors.
Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means
or used to make any derivative such as translation, transformation, or
adaptation without permission from D-Link Corporation/D-Link Systems
Inc., as stipulated by the United States Copyright Act of 1976.
CE Mark Warning
55
Page 56

This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may
cause radio interference, in which case the user may be required to take
adequate measures
Warnung!
Dies ist in Produkt der Klasse B. Im Wohnbereich kann dieses Produkt
Funkstoerungen verursachen. In diesem Fall kann vom Benutzer verlangt
werden, angemessene Massnahmen zu ergreifen.
Advertencia de Marca de la CE
Este es un producto de Clase B. En un entorno doméstico, puede causar
interferencias de radio, en cuyo case, puede requerirse al usuario para que
adopte las medidas adecuadas.
Attention!
Ceci est un produit de classe B. Dans un environnement domestique, ce
produit pourrait causer des interférences radio, auquel cas l`utilisateur
devrait prendre les mesures adéquates.
Attenzione!
Il presente prodotto appartiene alla classe B. Se utilizzato in ambiente
domestico il prodotto può causare interferenze radio, nel cui caso è
possibile che l`utente debba assumere provvedimenti adeguati.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
56
Page 57

are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
-Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
-Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
-Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/ TV technician for help.
VCCI Warning
57
Page 58

Contacting Technical Support
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United
States. U.S. customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
web site, e-mail, or by phone.
United States technical support is available Monday through Friday from
6:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. (PST).
Web:
http://www.dlink.com
Email:
support@dlink.com
Phone:
949-788-0805 (option #4)
If you are a customer residing outside of the United States, please refer
to the list of D-Link locations in the Table of Contents.
Thank you for purchasing this product. We like to receive feedback from
our customers concerning our products. Please take a moment to visit our
web site. You can register your purchase on-line, learn more about the
newest networking products, and let us know the things your new network
has empowered you to do.
58
Page 59

Register by mail or online at http://www.dlink.com/sales/reg/
Registration Card
Print, type or use block letters.
Your name: Mr./Ms _____________________________________________________________________________
Organization: ________________________________________________ Dept. ____________________________
Your title at organization: ________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _______________________________________ Fax:________________________________________
Organization's full address: ______________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Country: _____________________________________________________________________________________
Date of purchase (Month/Day/Year): _______________________________________________________________
Product Model Product Serial No. * Product installed in type of
(* Applies to adapters only)
Product was purchased from:
Reseller's name: ______________________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _______________________________________ Fax:________________________________________
Reseller's full address: _______________________________ ___ __ _____________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Answers to the following questions help us to support your product:
1. Where and how will the product primarily be used?
Home Office Travel Company Business Home Business Personal Use
2. How many employees work at installation site?
1 employee 2-9 10-49 50-99 100-499 500-999 1000 or more
3. What network protocol(s) does your organization use?
XNS/IPX TCP/IP DECnet Others_____________________________
4. What network operating system(s) does your organization use?
D-Link LANsmart Novell NetWare NetWare Lite SCO Unix/Xenix PC NFS 3Com 3+Open
Banyan Vines DECnet Pathwork Windows NT Windows NTAS Windows '95
Others__________________________________________
5. What network management program does your organization use?
D-View HP OpenView/Windows HP OpenView/Unix SunNet Manager Novell NMS
NetView 6000 Others________________________________________
6. What network medium/media does your organization use ?
Fiber-optics Thick coax Ethernet Thin coax Ethernet 10BASE-T UTP/ST P
100BASE-TX 100BASE-T4 100VGAnyLAN Others_________________
7. What applications are used on your network?
Desktop publishing Spreadsheet Word processing CAD/CAM
Database management Accounting Others_____________________
8. What category best describes your company?
Aerospace Engineering Education Finance Hospital Legal Insurance/Real Estate Manufacturing
Retail/Chainstore/Wholesale Government Transportation/Utilities/Communication VAR
System house/company Other________________________________
9. Would you recommend your D-Link product to a friend?
Yes No Don't know yet
10.Your comments regarding this product?
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
computer (e.g., Compaq 486)
* Product installed in
computer serial No.
59
Page 60

60
 Loading...
Loading...