Page 1

Page 2

Contents
Package Contents..........................................................................................................iv
Introduction.....................................................................................................................1
Connections ....................................................................................................................2
LEDs.................................................................................................................................3
Features...........................................................................................................................4
Wireless Basics............................................................................................................... 6
Standards-Based Technology ..................................................................................... 7
Installation Considerations...........................................................................................7
Getting Started................................................................................................................8
Using the Configuration Wizard..................................................................................10
Home > Wireless .......................................................................................................11
Home > WAN.............................................................................................................16
Home > LAN..............................................................................................................24
Home > DHCP...........................................................................................................25
Advanced > Virtual Server.........................................................................................26
Advanced > Applications ...........................................................................................29
Advanced > Filters.....................................................................................................30
Advanced > Parental Control.....................................................................................33
Advanced > Firewall .................................................................................................. 36
Advanced > DMZ.......................................................................................................38
Advanced > DDNS.....................................................................................................39
Advanced > QoS........................................................................................................41
ii
Page 3

Advanced > Performance..........................................................................................49
Tools > Admin............................................................................................................52
Tools > Time..............................................................................................................54
Tools > System..........................................................................................................55
Tools > Firmware.......................................................................................................56
Tools > Misc...............................................................................................................58
Tools > Cable Test.....................................................................................................60
Status > Device Info...................................................................................................61
Status > Log...............................................................................................................63
Status > Statistics......................................................................................................65
Status > Wireless Info................................................................................................66
Status > Printer Info...................................................................................................67
Status > Active Session.............................................................................................68
Help............................................................................................................................70
Technical Specifications.............................................................................................. 71
Appendix........................................................................................................................75
WCN and the Wireless Setup Wizard........................................................................75
Installing a Printer on your DI-524UP for Windows XP.............................................78
Installing a Printer on your DI-524UP for Windows 2000..........................................84
iii
Page 4

Package Contents
Contents of Package:
• D-Link DI-524UP Wireless Router
• Power Adapter-DC 5V, 2A
• Manual and Warranty on CD
• Quick Installation Guide
• Ethernet Cable (All the DI-524UP’s Ethernet ports are
Auto-MDIX)
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the
DI-524UP will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
iv
Page 5

Introduction
The D-Link DI-524UP Wireless Router is an 802.11b/g high-performance, wireless
router that supports high-speed wireless networking at home, at work or in public
places.
The 802.11g standard is backwards compatible with 802.11b products. This means that
you do not need to change your entire network to maintain connectivity. You may
sacr ifice some of 802.11g’s speed when you mix 802.11b and 802.11g devices, but you
will not lose the ability to communicate when you incorporate the 802.11g standard into
your 802.11b network. You may choose to slowly change your network by gradually
repl acing the 802.11b devices with 802.11g devices.
In addition to offering faster data transfer speeds when used with other 802.11g
products, the DI-524UP has the newest, strongest, most advanced security features
available today. When used with other 802.11g WPA or WPA2 (WiFi Protected Access)
and 802.1x compatible products in a network with a RADIUS server, the security
features include:
• WPA Wi-Fi Protected Access authorizes and identifies users based on a secret
key that changes automatically at a regular interval. WPA uses TKIP (Temporal
Key Integrity Protocol) to change the temporal key every 10,000 packets (a packet
is a kind of message transmitted over a network.) This insures much greater
security than the standard WEP security. (By contrast, the older WEP encryption
required the keys to be changed manually.)
• WPA2, based on the IEEE 802.1i Wi-Fi certified standard, goes a level beyond
the previous WPA by enhancing security with a new encryption code.
Employing AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), and yet still backwards
compatible with WPA, WPA2 utilizes 802.1X and EAP (Extensible
Authentication Protocol) to verify users on the wireless network using a
Pre-Shared Key. Once all users on the LAN have been authenticated, there can
be a securely encrypted flow of information between all parties on the LAN.
For home users that will not incorporate a RADIUS server in their network, the security for
the DI-524UP, used in conjunction with other 802.11g products, will still be much
stronger than ever before. Utilizing the Pre Shared Key mode of WPA, the DI-524UP will
obtain a new security key every time it connects to the 802.11g network. You only need
to input your encryption information once in the configuration menu. No longer will you
have to manually input a new WEP key frequently to ensure security, with the DI-524UP,
you will automatically receive a new key every time you connect, vastly increasing the
safety of your communications.
The DI-524UP also comes equipped with one USB 1.1 port on the rear panel that
supports printer sharing.
1
Page 6
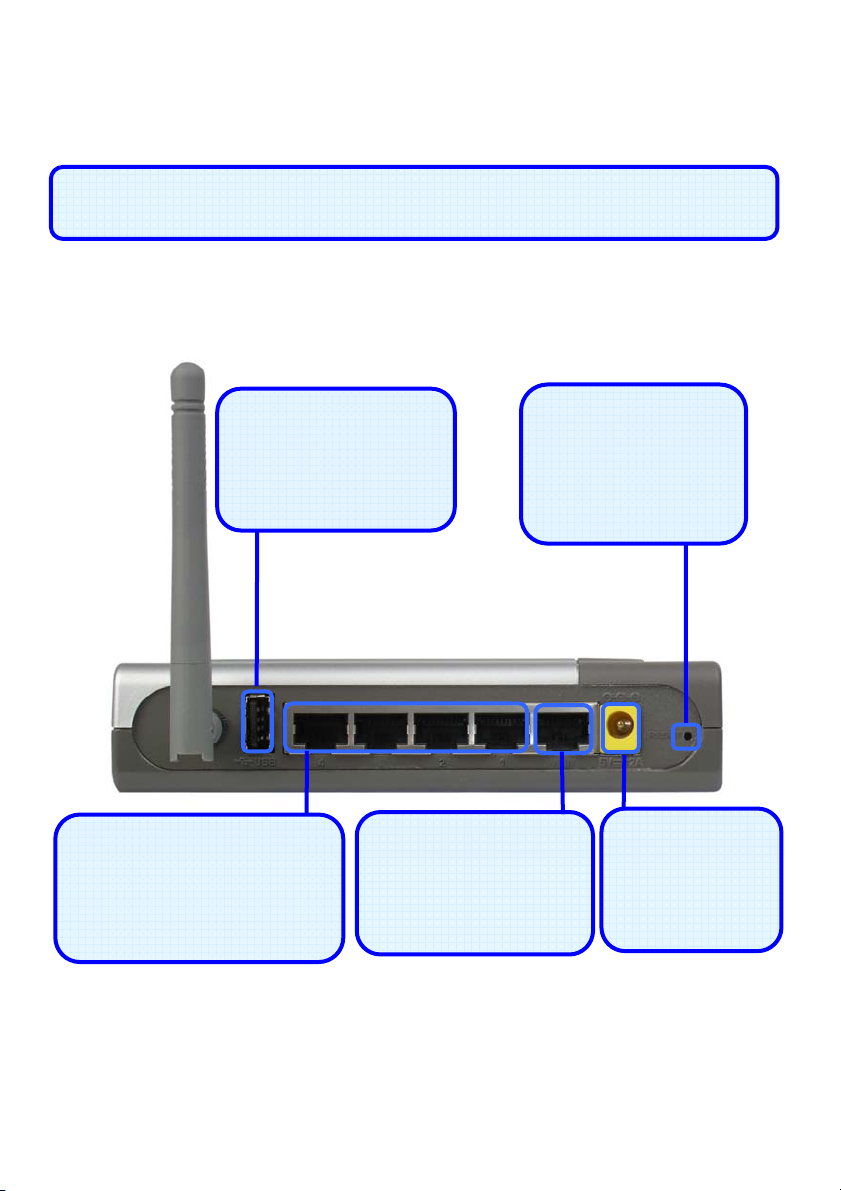
Connections
g
All Ethernet Ports (WAN and LAN) are auto MDI/MDIX, meaning you can
use either a strai
ht-through or a crossover Ethernet cable.
Auto MDI/MDIX LAN Ports
Connect the Ethernet
cable from computers on
your LAN to these ports.
USB 1.1 Connection
Use this port to
connect your USB
printer.
WAN Port
Connect the Ethernet
cable from your ADSL
modem to this port.
Factory Reset Button
Pressing this button
will restore the router
to its factory default
settings.
Power Adapter
Connect your
5V 2A power
adapter here.
2
Page 7
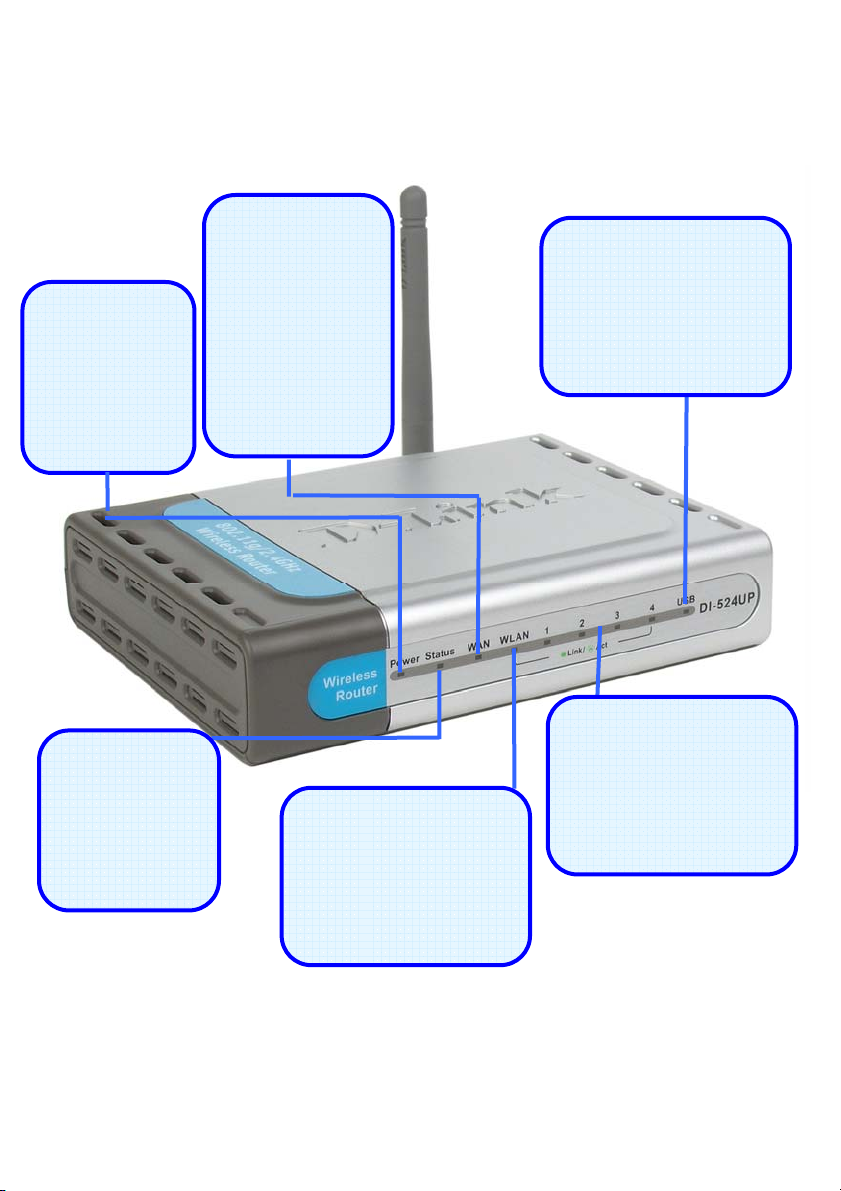
LEDs
p
Power LED
A solid light
indicates a valid
connection to
the power
supply.
Status LED
A blinking LED
indicates the
DI-524UP is
functioning
properly.
WAN LED
An active LED
indicates a link
has been
established. A
blinking LED
indicates
activity on the
WAN port.
WLAN LED
An active LED indicates
a link has been
established. A blinking
LED indicates activity
on the WLAN
ort.
USB LED
An active LED indicates
a link has been
established. A blinking
LED indicates activity
on the USB port.
LAN LEDs
An active LED indicates
a link has been
established. A blinking
LED indicates activity on
the LAN port.
3
Page 8

Features
• Fully compatible with the 802.11g standard to provide a wireless data rate of up
to 54Mbps
• Backwards compatible with the 802.11b standard to provide a wireless data rate
of up to 11 Mbps
• WPA authorizes and identifies users based on a secret key that changes
automatically at a regular interval, for example, TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity
Protocol), in conjunction with a RADIUS server, changes the temporal key every
10,000 packets, ensuring greater security
• Pre Shared Key mode means that the home user, without a RADIUS server, will
obtain a new security key every time the he or she connects to the network,
vastly improving the safety of communications on the network
• New WPA2 enhanced wireless security authenticates using 802.1X and a
Pre-Shared key, and encrypts the data with the AES encryption standard. Wi-Fi
certified, WPA2 is also compatible with WPA and can be used for a large
network or for the SOHO environment
• 802.1x Authentication in conjunction with the RADIUS server verifies the identity
of would be clients
• Utilizes OFDM technology (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
• User-friendly configuration and diagnostic utilities
• Operates in the 2.4GHz frequency range
• Connects multiple computers to a Broadband (Cable or DSL) modem to share
the Internet connection
• Advanced Firewall features
• Supports NAT with VPN pass-through, providing added security
• MAC Filtering
4
Page 9

• IP Filtering
• URL Filtering
• Domain Blocking
• Scheduling
• DHCP server supported enables all networked computers to automatically
receive IP addresses
• Web-based interface for Managing and Configuring
• Access Control to manage users on the network
• Supports special applications that require multiple connections
• Equipped with four 10/100Mbps Ethernet ports, one WAN port, Auto MDI/MDIX
• Equipped with one USB 1.1 port at the rear of the router used to connect with a
USB printer
• VPN Pass-Through
• DMZ and DDNS functions
• Stateful Packet Inspection for protection against unwanted packets
• Quality of Service (QoS) for prioritizing ports and IP addresses
• Supports IGMP
• Multiple users and administrators with configurable privileges for each
• Intrusion detection for ICMP, SYN, UDP flood, Land, IP spoof, Ping of Death,
Port Scan, Smurf, Steal Fin, Syn with data, Tear Drop, and UDP bomb attacks
• Statistics for all main functions on the router
5
Page 10

Wireless Basics
D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-to-use and
compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home, business or public
access wireless networks. D-Link wireless products will allow you access to the data
you want, when and where you want it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that
wireless networking brings.
A WLAN is a cellular computer network that transmits and receives data with radio signals
instead o f w ires. WLANs are used i n c r e a s i ngly in both home and office environment s , and
public areas such as airports, coffee shops and universities. Innovative ways to utilize
WLAN technology are helping people to work and communicate more efficiently.
Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other fixed infrastructure have proven to
be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network. Wireless
adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems support the same protocols as
Ethernet adapter cards.
People use wireless LAN technology for many different purposes:
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any location
within the operating range of the WLAN. Management decisions based on real-time
information can significantly improve worker efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs – WLANs are easy to set up, manage, change and
relocate. Networks that frequently change can benefit from WLANs ease of
implementation. WLANs can operate in locations where installation of wiring may be
impractical.
Installation and Network Expansion - Installing a WLAN system can be fast and
easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and ceilings. Wireless
technology allows the network to go where wires cannot go - even outside the home or
office.
Scalability – WLANs can be configured in a variety of topologies to meet the needs
of specific applications and installations. Configurations are easily changed and range
from peer-to-peer networks suitable for a small number of users to larger infrastructure
networks to accommodate hundreds or thousands of users, depending on the number of
wireless devices deployed.
Inexpensive Solution - Wireless network devices are as competitively priced as
conventional Ethernet network devices.
6
Page 11

Standards-Based Technology
The DI-524UP Wireless Router utilizes the new 802.11g standard.
The IEEE 802.11g standard is an extension of the 802.11b standard. It increases the
data rate up to 54 Mbps within the 2.4GHz band, utilizing OFDM technology.
This means that in most environments, within the specified range of this device, you will
be able to transfer large files quickly or even watch a movie in MPEG format over your
network without noticeable delays. This technology works by transmitting high speed
digital data over a radio wave utilizing OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing) technology. OFDM works by splitting the radio signal into multiple smaller
sub-signals that are then transmitted simultaneously at different frequencies to the
receiver. OFDM reduces the amount of crosstalk (interference) in signal transmissions.
The DI-524UP is backwards compatible with 802.11 b devices. This means that if you
have an existing 802.11 b network, the devices in that network will be compatible with
802.11g devices at speeds of up to 11 Mbps in the 2.4GHz range.
Installation Considerations
The D-Link DI-524UP lets you access your network, using a wireless connection, from
virtually anywhere within its operating range. Keep in mind, however, that the number,
thickness and location of walls, ceilings, or other objects that the wireless signals must
pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges vary depending on the types of
materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise in your home or business. The
key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic guidelines:
1. Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the DI-524UP and other
network devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your D-Link
wireless product’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position your devices so
that the number of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2. Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick
(.5 meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a
2-degree angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Position devices so that
the signal will travel straight through a wall or ceiling ( instead of at an angle) for
better reception.
3. Building Materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or
aluminum studs may have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless
devices and computers with wireless adapters so that the signal passes
through drywall or open doorways and not other materials.
4. Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical
devices or appliances that generate extreme RF noise.
7
Page 12
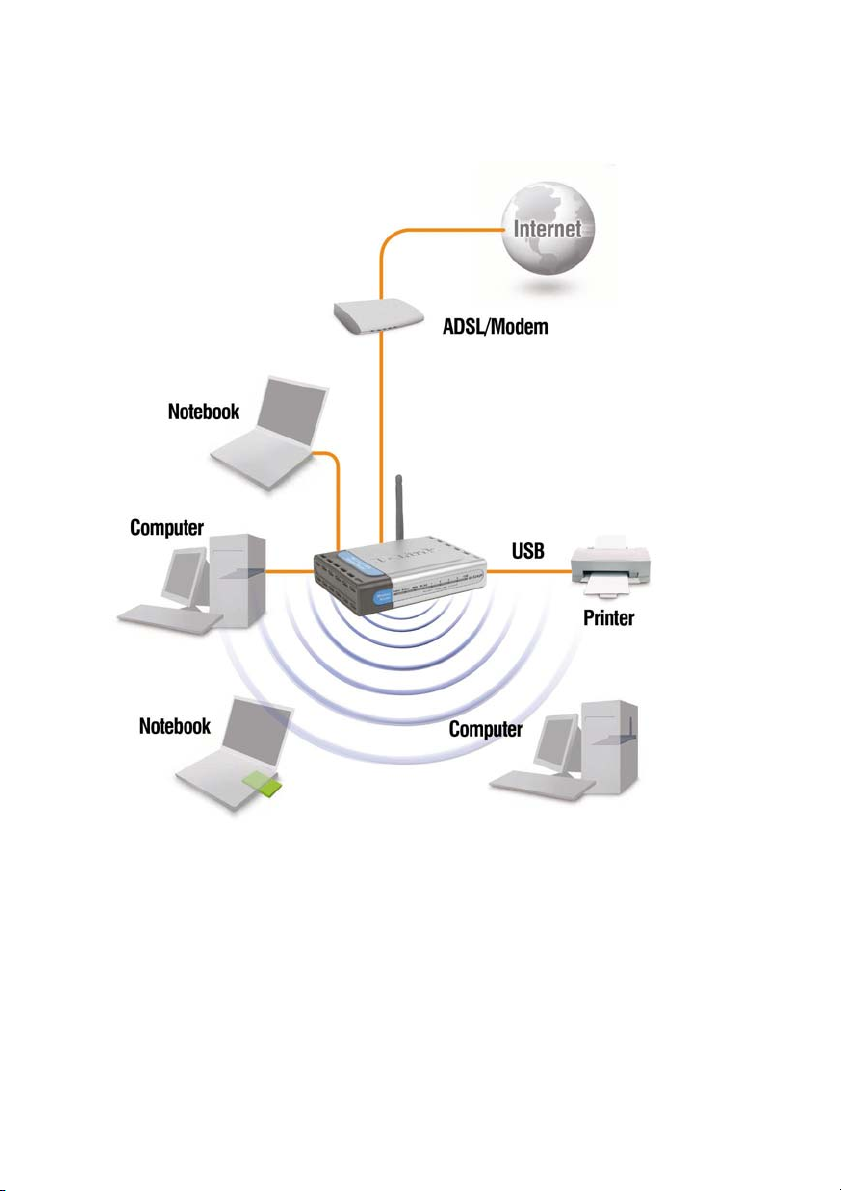
Getting Started
Setting up a Wireless Infrastructure Network
Please remember that D-Link AirPlus G wireless devices are pre-configured to connect
together, right out of the box, with their default settings. For a typical wireless setup at
home (as shown above), please do the following:
1. You will need broadband Internet access (a Cable or DSL-subscriber line
into your home or office)
8
Page 13

2. Consult with your Cable or DSL provider for proper installation of the
modem
3. Connect the Cable or DSL modem to the DI-524UP Wireless Router (see
the printed Quick Installation Guide included with your router.)
4. If you are connecting a desktop computer to your network, install the D-Link
AirPlus G DWL-G520 wireless PCI adapter into an available PCI slot on
your desktop computer. You may also install the DWL-G520. (See the
printed Quick Installation Guide included with the network adapter.)
5. Install the D-Link DWL-G650 wireless Cardbus adapter into a laptop
computer. (See the printed Quick Installation Guide included with the
DWL-G650.)
6. Install the D-Link DFE-530TX+ adapter into a desktop computer. The four
Ethernet LAN ports of the DI-524UP are Auto MDI/MDIX and will work with
both Straight-Through and Cross-Over cable. (See the printed Quick
Installation Guide included with the DFE-530TX+.)
Connect your printer to the printer port on the DI-524 UP. Please refer to t he qu ic k
installation guide for loading the print server software.
9
Page 14
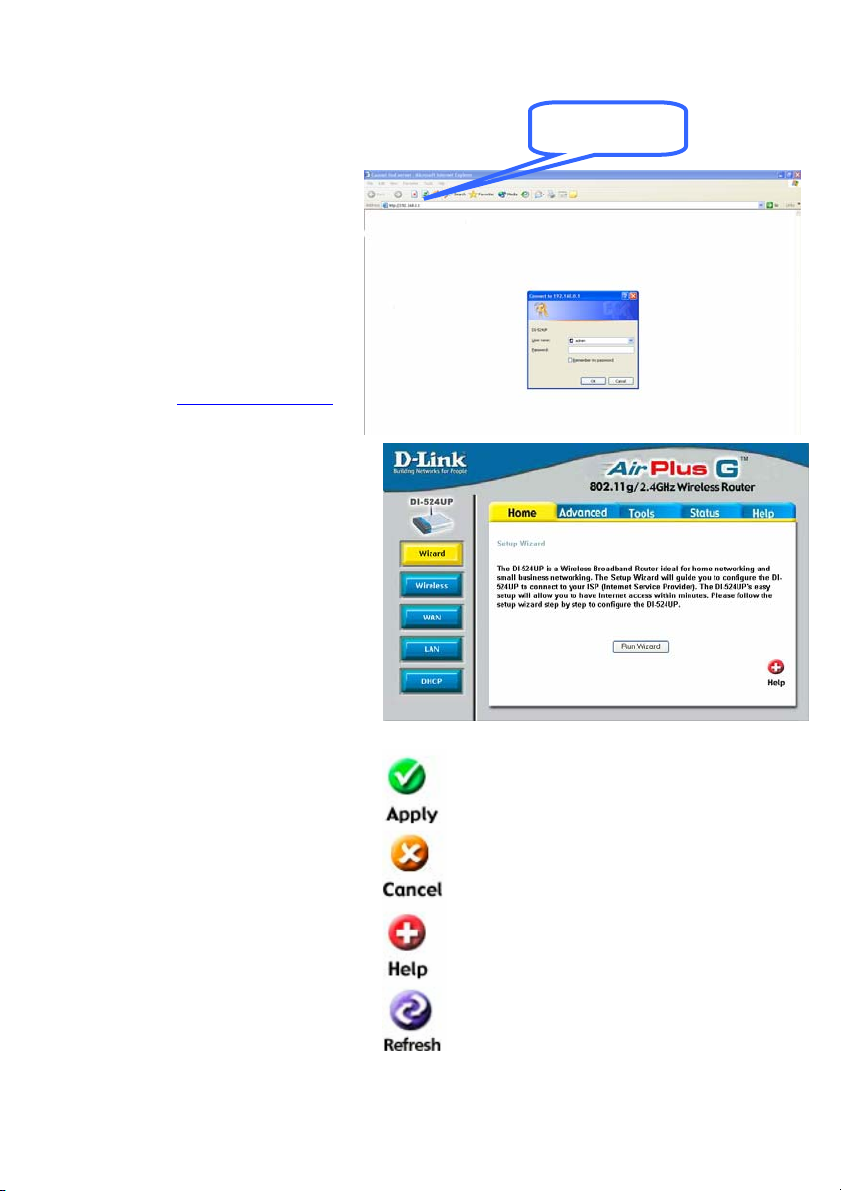
Using the Configuration Wizard
Whenever you want to configure
your network or the DI-524UP, you
can access the Configuration Menu
by opening the web-browser and
typing in the IP Address of the
DI-524UP. The DI-524UP default IP
Address is shown to the right:
• Open the web browser.
• Type in the IP Address of the
Router (http://192.168.0.1
).
• Type “admin” in the User
Name field.
• Leave the Password blank.
• Click OK.
The Home > Wizard window will
appear. Please refer to the Quick
Installation Guide for more information regarding the Setup
Wizard.
These buttons appear on most o f th e
configuration windows in this
section. Please click on the
appropriate button at the bottom of
each window after you have made a
configuration change.
NOTE: If you have changed the
default IP Address assigned to the
DI-524UP, make sure to enter the
correct IP Address.
Clicking Apply will save configured
settings to the router.
Clicking Cancel will clear changes
made to the current page.
Clicking Help will provide the user with
helpful information about the current
window.
Clicking Refresh will refresh the
statistics of the current window.
10
192.168.0.1
Page 15
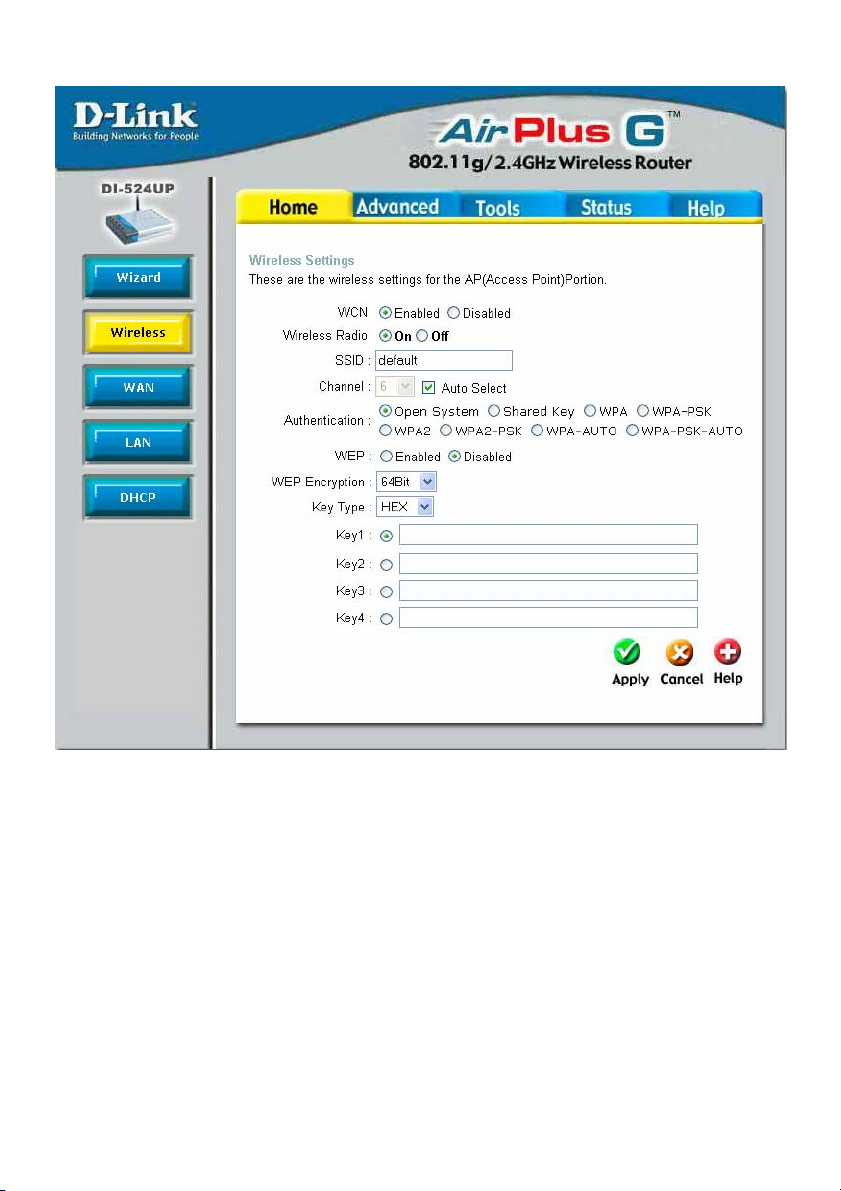
Home > Wireless
WCN WCN or Windows Connect Now Technology is used to
automatically configure the wireless settings for this device. The
WCN must be previously configured on computer running a
Windows XP operating system, which has Service Pack 2
installed. Once the configuration has been completed by
running the Wireless Network Setup Wizard, it must be saved
to a USB enabled memory device and then uploaded
automatically to the router and any other device to be put on
this wireless network, using this method. No configuration will
be necessary except for ensuring that this WCN radio button is
enabled before connecting the memory drive to the router. For
a concise explanation on configuring the WCN on Windows XP,
see the Appendix at the back of this manual. (NOTE: For the
11
Page 16

client implementation of this function, please see the user
manual for the associated client PC)
Wireless Radio Click the appropriate radio button to enable or disable the
Wireless Access part of this device.
SSID Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name designated for a spe-
cific wireless local area network (WLAN). The SSID’s factory
default setting is DI-524UP. The SSID can be easily changed to
connect to an existing wireless network or to establish a new
wireless network. This field will be automatically configured for
users who have uploaded a WCN configuration.
Channel What channels are available for use by the access point
depends on the local regulatory environment. Remember that
all devices communicating with the device must use the same
channel (and use the same SSID). Use the drop-down menu to
select the channel used for your 802.11b wireless LAN.
Authentication This router employs three basic types of Authentication for
access to the router’s wireless network, Open System/Shared
Key 802.1X (RADIUS) and PSK (Pre-Shared Key), which can
be selected by clicking the corresponding radio button. Each
selection will alter the window to accommodate the entry of the
selected Authentication. See the explanation below for more
information.
Open System/Shared Key
The Open System/Shared Key choice for Authentication will produce the same window
for the user’s configuration. The Open System choice is for general use and utilizes the
basic WEP encryption. The Shared Key choice is used between cooperating devices
that share a common encryption key. WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol or Wired
Equivalent Privacy) encryption can be enabled for security and privacy. WEP encrypts
the data portion of each frame transmitted from the wireless adapter using one of the
predefined keys. Decryption of the data contained in each packet can only be done if
the both the receiver and transmitter have the correct shared key.
12
Page 17
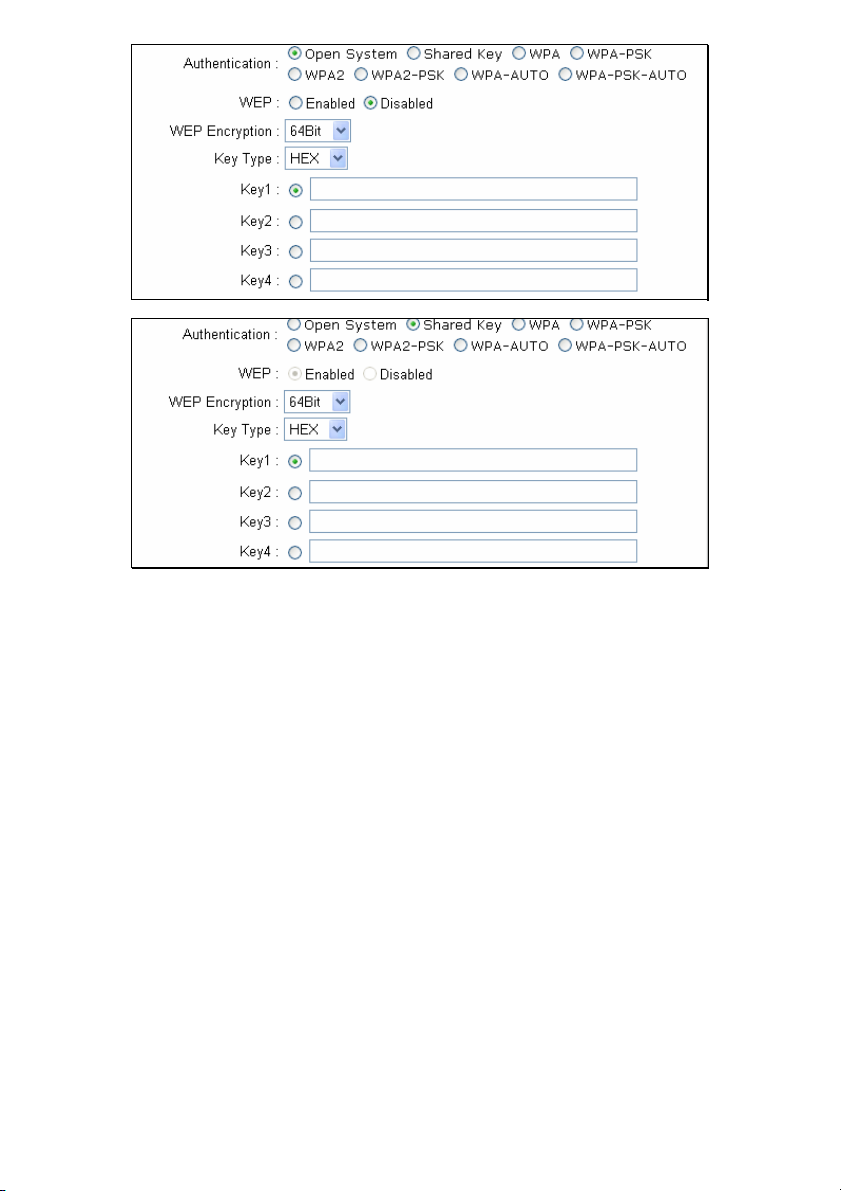
WEP – Click the Enabled radio button to employ WEP encryption on the router.
WEP Encryption – Use the drop-down menu to select the type of WEP encryption.
Select 64 Bit to enabled 64 bit Hexadecimal encryption, 128 Bit to enable 128 bit
Hexadecimal encryption. For 64-bit encryption, the (ASCII) characters are converted
automatically and listed as 10-digit hexadecimal keys. 64-bit encryption allows you to
select one of four active keys. For 128-bit encryption, the characters are converted and
listed as a 26 digit hexadecimal key. 128-bit encryption allows you to select one of four
active keys. 128-bit keys are to be from 5-13 inputted characters in length and 256-bit
keys must be from 10-26 inputted characters in length. Failing to have the same key on
the server and its clients will result in the clients not receiving any information from the
router or its connected devices.
Key Type – Use the pull-down menu to select the type of Key to be used for encryption.
The user may choose HEX (Hexidecimal) or ASCII (American Standard Code for
Information Interchange). Both will require the user to enter a key in the following field.
Key – The user may enter up to four keys to be used for encryption. Only the key
selected using the corresponding radio button will be used for encryption.
Click Apply to set the information in the router’s memory. (NOTE: For the client
implementation of this function, please see the user manual for the associated client
13
Page 18

PC)
WPA/WPA2
WPA or Wireless Protection Access is a new an improved standard of wireless security.
WPA offers encryption keys of up to 256-bits that automatically change frequently. On
this router, the WPA utilizes the RADIUS protocol, which utilizes a server to authorize
the user by matching a Shared Secret password listed in its RADIUS database. There
are two choices for the user to choose from. WPA and WPA2, both use the Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES). In order to use this function, a RADIUS server must be
established on a computer on the LAN. This RADIUS server must be configured to have
the same key as the users on the LAN accessing it.
RADIUS Server IP – Enter the IP address of the remote RADIUS server through which
you will be authenticated.
Port – Enter the virtual port number to which to connect through the RADIUS server.
Common port numbers for RADIUS are 1812 and 1813.
Shared Secret – Enter the password that will be used to authenticate you on the
wireless network. This pass word must be the same on the RADIUS se rver in order for
you to be authorized. (NOTE: For the client implementation of this function, please see
the user manual for the associated client PC.)
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) uses the same encryption as the WPA but is implemented
differently. All devices on the wireless network share the same key (Passphrase) to
activate the WPA security. There are two choices for the user to choose from.
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK, which both use the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
To utilize, select one of the previous choices, enter the Passphrase, confirm it in the
14
Page 19

second field and click Apply. (NOTE: For the client implementation of this function,
please see the user manual for the associated client PC.)
WPA-AUTO/WPA-PSK-AUTO
In addition to standard Wireless Protection Access and WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
functions, the DI-524UP allows users an automatic option for both WPA and WPA-PSK.
In order to use the WPA-Auto function, a RADIUS server must be established on a
computer on the LAN. This RADIUS server must be configured to have the same key as
the users on the LAN accessing it
To utilize the WPA-PSK-Auto function, select one of the previous choices, enter the
Passphrase, confirm it in the second field, and then click Apply.
(NOTE: For the client implementation of this function, please see the user manual for
the associated client PC.)
15
Page 20
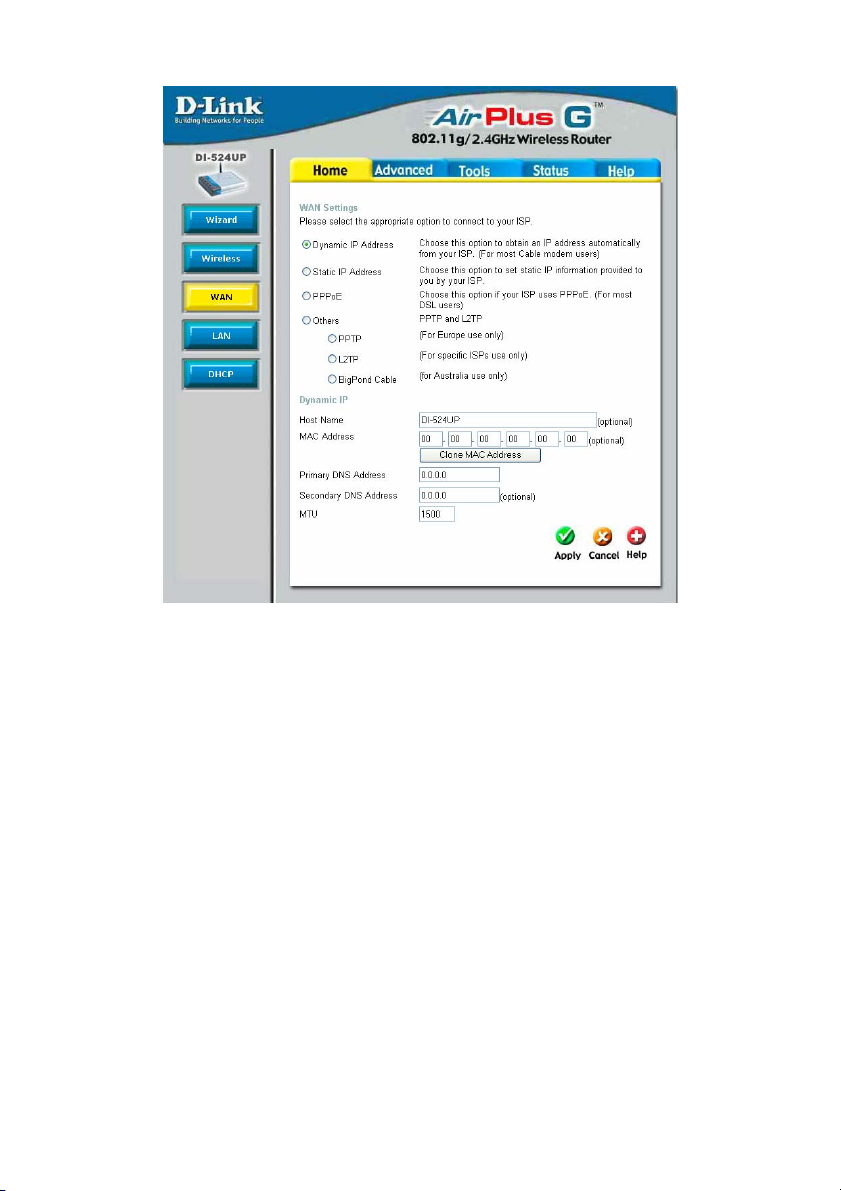
Home > WAN
Dynamic IP Address Choose Dynamic IP Address to obtain IP address information
automatically from your ISP. This option should be selected if
your ISP has not supplied you with an IP address. This option is
commonly used for Cable modem services.
Host Name The Host Name is optional but may be required by some ISPs.
The default host name is the device name of the Router and
may be changed.
MAC Address The default MAC Address is set to the WAN ’s physical interfac e
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
your ISP.
Clone MAC Address The default MAC address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. You can use the Clone
MAC Address button to copy the MAC address of the Ethernet
Card installed by your ISP and replace the WAN MAC address
with the MAC address of the router. It is not recommended that
Primary/Secondary
DNS Address
16
Page 21

you change the default MAC address unless required by your
ISP.
Enter a DNS Address if you wish not to use the address
provided by your ISP.
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
Home > WAN > Static IP Address
Static IP Address Choose Static IP Address if all WAN IP information is provided
to you by your ISP. You will need to enter in the IP address,
subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS address(es) provided
to you by your ISP. Each IP address entered in the fields must
be in the appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated
by a dot (x.x.x.x). The Router will not accept the IP address if it
is not in this format.
IP Address Input the public IP Address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask Input your Subnet mask. (All devices in the network must have
the same subnet mask.)
ISP
Gateway Address Input the public IP address of the ISP to which you are
connecting.
MAC Address The default MAC Address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
17
Page 22
your ISP.
Primary
DNS Address Input the primary DNS (Domain Name Server) IP address
provided by your ISP
Secondary DNS
Address This is an optional DNS Address entry to be used if the primary
DNS fails.
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
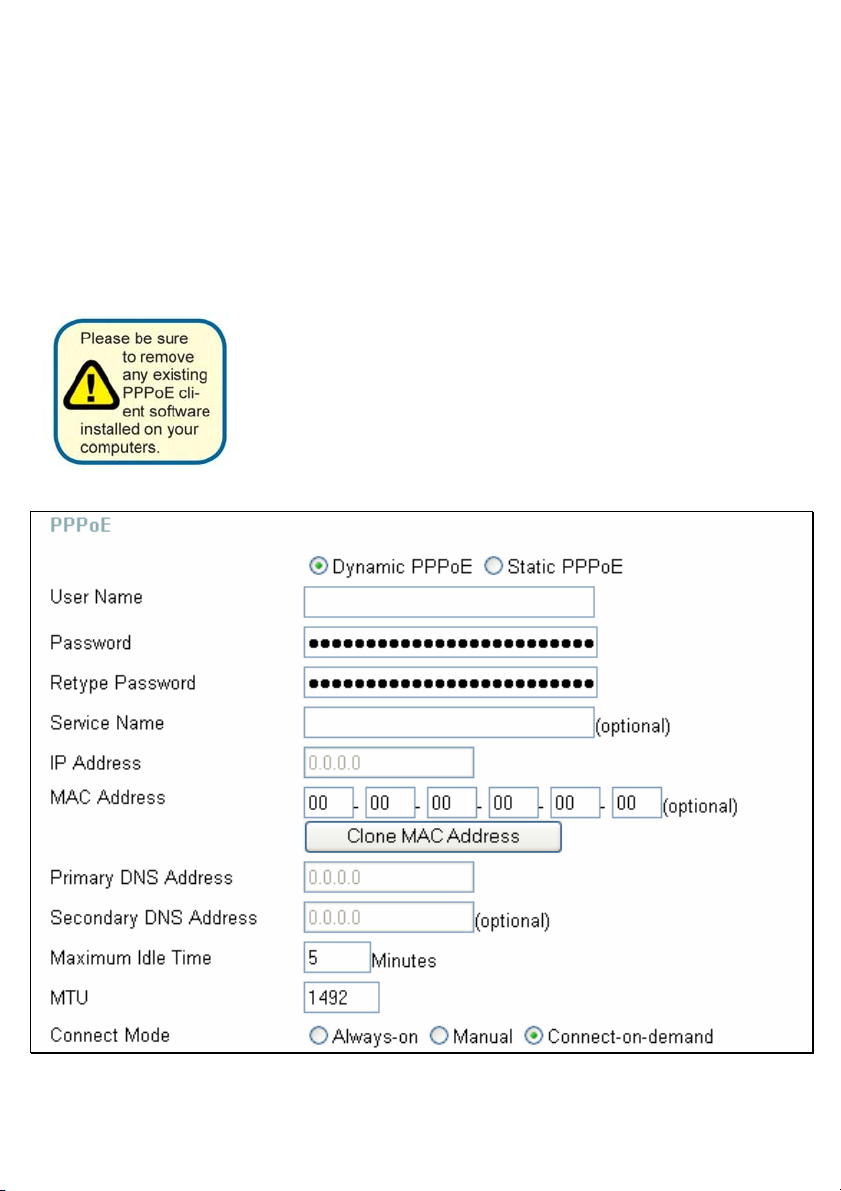
Home > WAN > PPPoE
Choose PPPoE (Point to Point Pr otoco l over Ether net) i f your
ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will provide you
with a username and password. This option is typically used
for DSL services. Select Dynamic PPPoE to obtain an IP
address automatically for your PPPoE connection. Select
Static PPPoE to use a static IP address for your PPPoE
connection.
18
Page 23

PPPoE Choose this option if your ISP uses PPPoE. (Most DSL users
will select this option.)
Dynamic PPPoE Choose this option to rece ive an IP A ddress
automatically from your ISP.
Static PPPoE Choose this option to you have an assigned
(static) IP Address.
Password Enter The PPPoE user name provided to you by your ISP.
Retype Password Retype the password entered in the previous field.
Service Name Enter the Service Name provided by your ISP (optional).
IP Address This option is only available for Static PPPoE. Enter the static
IP address for the PPPoE connection.
MAC Address The default MAC Address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
your ISP.
Clone MAC Address The default MAC address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. You can use the Clone
MAC Address button to copy the MAC address of the Ethernet
Card installed by your ISP and replace the WAN MAC address
with the MAC address of the router. It is not recommended that
you change the default MAC address unless required by your
ISP.
Primary
DNS Address Input the primary DNS (Domain Name Server) IP address
provided by your ISP
Secondary
DNS Address This is an optional DNS Address entry to be used if the primary
DNS fails.
Maximum Idle Time The amount of time of inactivity before the device will
disconnect time your PPPoE session. Enter a Maximum Idle
Time (in minutes) to define a maximum period of time for which
the Internet connection is maintained during inactivity. If the
connection is inactive for longer than the defined Maximum Idle
Time, then the connect ion will be dropped. Either set the value
for idle time to zero or enable Auto-reconnect to disable this
feature.
19
Page 24
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
Connect Mode Allows the user to choose a method of connecting to the ISP.
Always-On will keep the router connected through Idle times.
Manual will require the user to connect manually using the
router anytime a connection to the ISP has timed out.
Connect-on-demand will instruct the router to connect to the
ISP anytime information is sent from the connected computer
on the LAN.
Click Apply to set any changes made to the memory of the router.
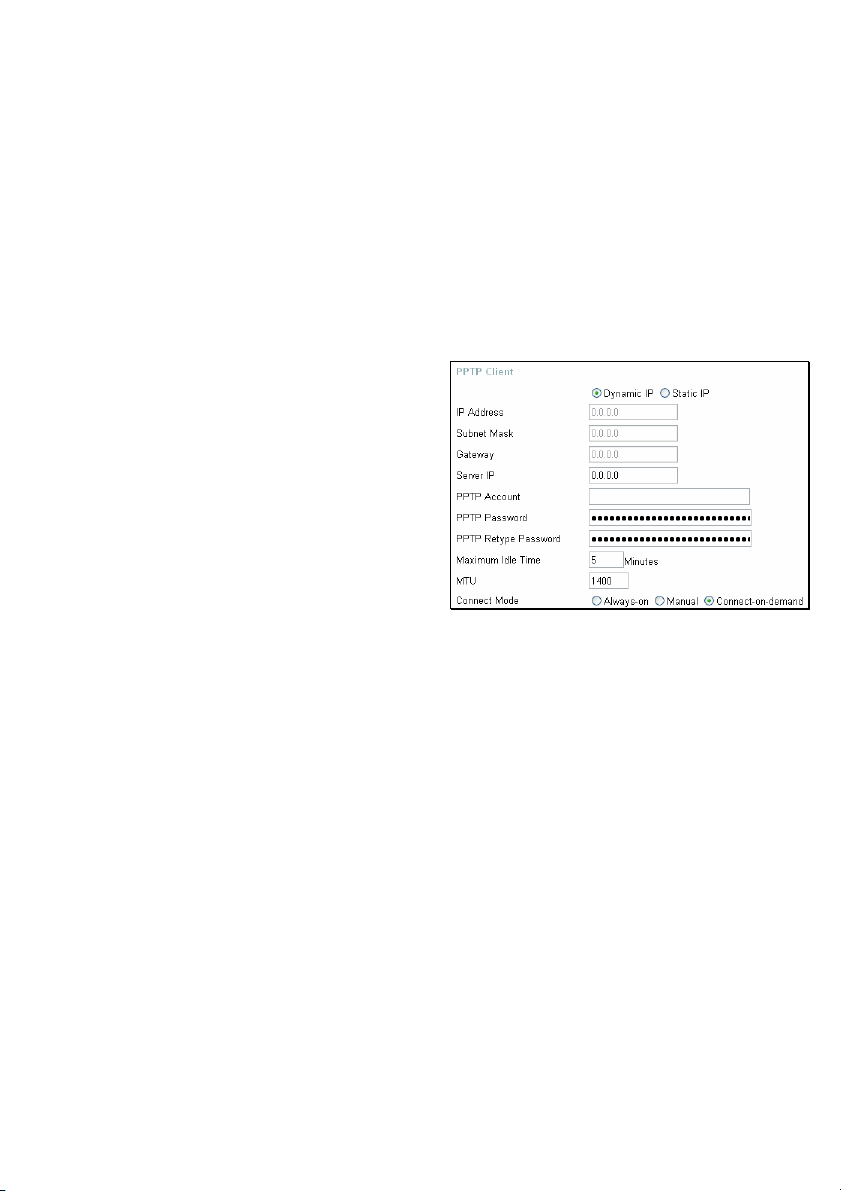
Home > WAN > Others > PPTP
PPTP or Point-to-Point Protocol is a safe
method of sending information between
VPN’s securely using encryption over PPP.
You, as the client, need to enter the correct
information that the server has in order to
create that secure tunnel. Using Dynamic IP,
the router will set your basic IP parameters
for you, such as the IP Address, Subnet
Mask and Gateway. For Static IP, this
information must be set manually by the
user. All information in this window should be
provided by your ISP.
PPTP Choose between Dynamic and Static IP.
IP Address Enter the IP address of the router for a static IP entry. Dynamic
IP requires no input here.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask address of the router for a static IP
entry. Dynamic IP requires no input here.
Gateway Enter the gateway address here. This is the IP address of the
ISP server.
Server IP Enter the IP address of the PPTP’s server computer. This is
how the user will become authenticated to use PPTP.
PPTP Account Enter the name of the PPTP account as provided to you by
your ISP.
PPTP Password Enter the PPTP password as provided to you by your ISP.
20
Page 25
PPTP Retype Retype the password entered in the PPTP Password field.
Password
Maximum Idle Time A value of 0 means that the PPP connection will remain
connected. If your network account is billed according to the
amount of time the Router is actually connected to the Internet,
enter an appropriate Idle Time value (in seconds). This will
disconnect the Router after the WAN connection has been idle
for the amount of time specified. The default value = 5.
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
Connect Mode This function, with Connect-on-demand selected, will allow the
router to connect any workstation on your LAN to the Internet
upon request. If this function is set at Always-on, no request
from the workstation will be needed to connect to the Internet. If
Manual is selected, it will be necessary for the workstation on
the LAN to manually connect to the Internet through this router.
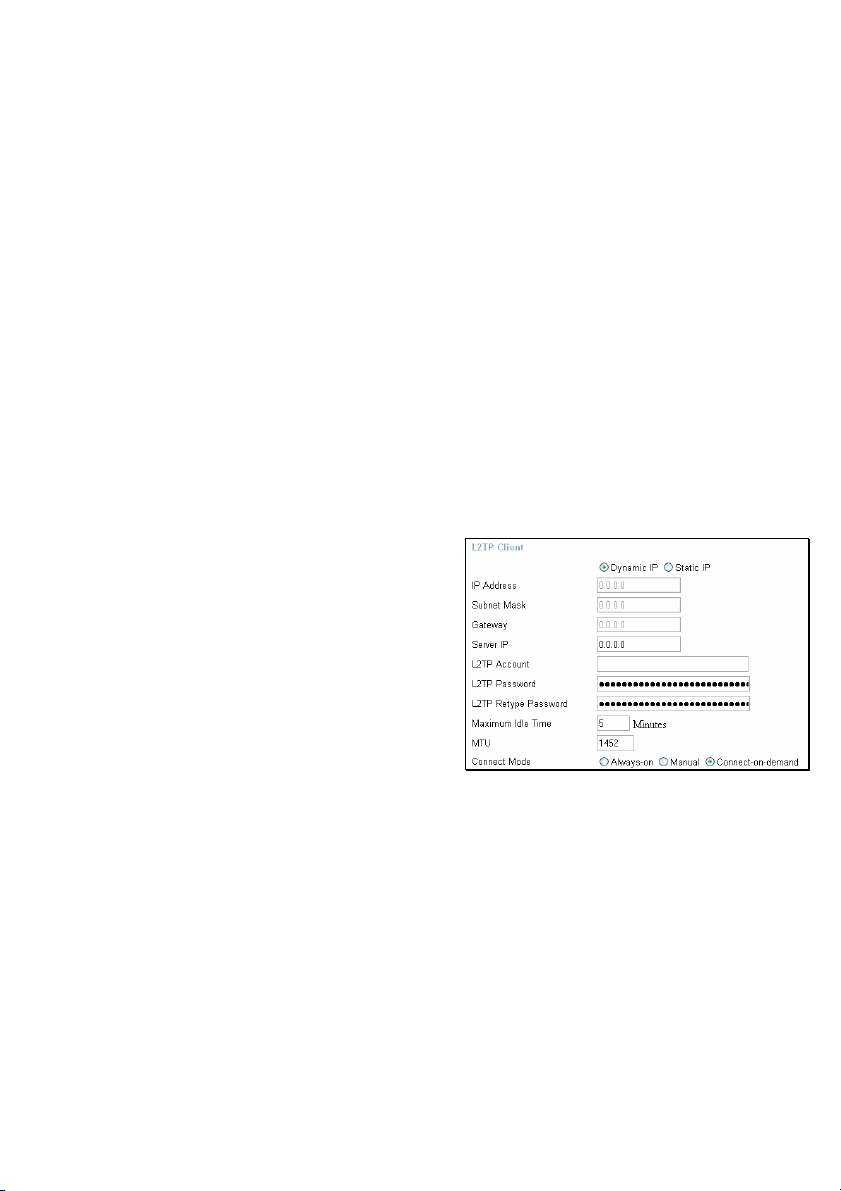
Home > WAN > Others > L2TP
Some ISPs may require the user to uplink
using the Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
method. L2PT is a VPN protocol that will
ensure a direct connection to the server
using an authentication process that
guarantees the data originated from the
claimed sender and was not damaged or
altered in transit. Once connected to the VPN
tunnel, it seems to the user that the client
computer is directly connected to the internal
network. To set up your L2PT connection,
enter the following data that was provided to
you by your ISP.
L2PT Choose between Dynamic and Static IP. Using Dynamic IP, the
router will set your basic IP parameters, such as the IP Address,
Subnet Mask and Gateway. For Static IP, this information must
be set manually by the user.
IP Address The IP address that will be assigned to your router for this
connection, as stated by your ISP. Dynamic IP requires no
input here.
Subnet Mask The IP address of the corresponding Subnet Mask, as stated to
21
Page 26

you by your ISP. Dynamic IP requires no input here.
Gateway The IP address of the gateway device, as stated to you by your
ISP. Dynamic IP requires no input here.
Server IP The IP address of your ISP’s server computer, as stated to you
by your ISP.
L2PT Account The account name of the L2PT account that has been assigned
to you by your ISP.
L2PT Password The password of the L2PT account that was supplied to you by
your ISP.
L2PT Retype Password Retype the password that was entered in the L2PT field.
Ensure that these two passwords are identical or an error will
occur.
Maximum Idle Time A value of 0 means the PPP connection will remain connected.
If your network account is billed according to the amount of time
the Router is actually connected to the Internet, enter an
appropriate Idle Time value (in seconds). This will disconnect
the Router after the WAN connection has been idle for the
amount of time specified. The default value = 5.
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
Connect Mode If Connect-on-demand is selected, will allow the router to
connect any workstation on your LAN to the Internet upon
request. If Always-on, no request from the workstation will be
needed to connect to the Internet. If Manual is selected, the
workstation on the LAN must manually connect to the Internet
through this router.
Home > WAN > Others > BigPond Cable
This selection is for users having Big Pond Cable as their ISP. Enter the following
information, as provided to you by your ISP.
22
Page 27
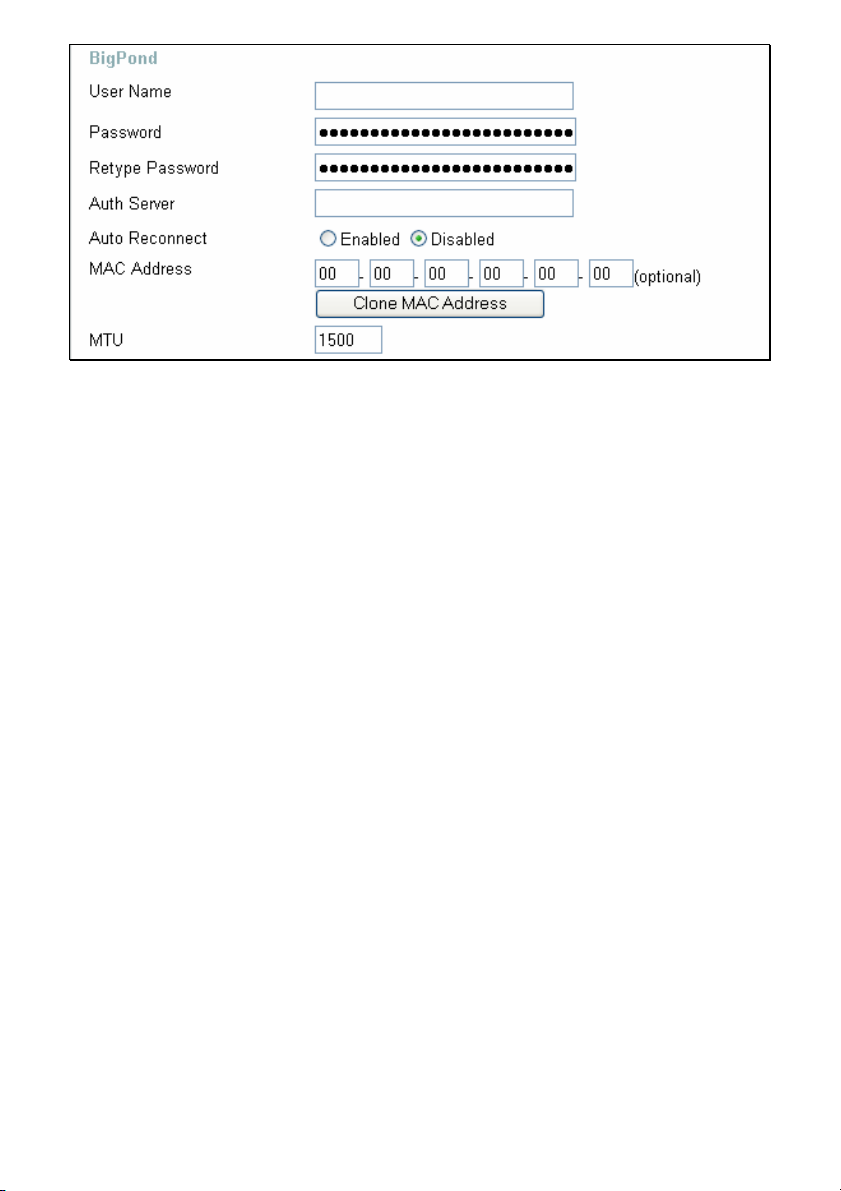
User Name Enter the user name as provided to you by your ISP.
Password Enter The PPPoE user name provided to you by your ISP.
Retype Password Retype the password entered in the previous field.
Auth Server Enter the name of the Authentication Server as provided to you
by your ISP. This is the computer that will accept your user
name and password to be authenticated on the network.
Auto Reconnect Checking the Enabled radio button will allow the router to
reconnect to the network automatically if it becomes
disconnected.
MAC Address The default MAC Address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. It is not recommended
that you change the default MAC address unless required by
your ISP.
Clone MAC Address The default MAC address is set to the WAN’s physical interface
MAC address on the Broadband Router. You can use the
Clone MAC Address button to copy the MAC address of the
Ethernet Card installed by your ISP and replace the WAN MAC
address with the MAC address of the router. It is not
recommended that you change the default MAC address unless
required by your ISP.
MTU Enter an MTU value only if required by your ISP. Otherwise,
leave it at the default setting.
23
Page 28
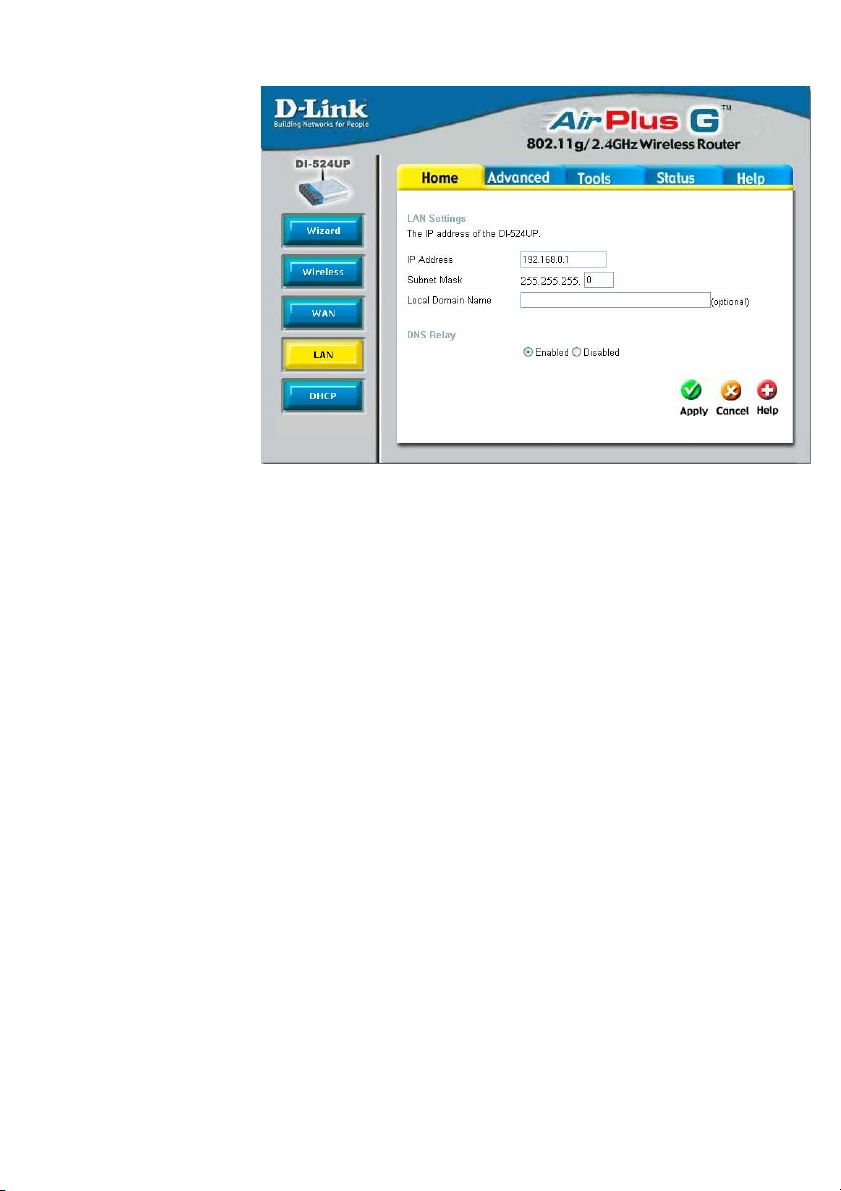
Home > LAN
LAN is short for Local
Area Network. This is
considered your
internal network.
These are the IP
settings of the LAN
interface for the
DI-524UP and may be
referred to as Private
settings. You may
change the LAN IP
address if needed.
The LAN IP address is
private to your internal
network and cannot be
seen on the Internet.
IP Address The IP address of the LAN interface. The default IP address is
192.168.0.1.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask of the LAN interface. The default subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0.
Local Domain Name This entry is for the local Domain set on your network, if you
have given it a name previously. This field is for your personal
use and unnecessary for proper configuration of this window.
DNS Relay The Router can be configured to relay DNS from your ISP or
another available service to workstations on your LAN. When
using DNS relay, the Router will accept DNS requests from
hosts on the LAN and forward them to the ISP (or alternative)
DNS servers. DNS relay can use auto discovery or the DNS IP
address can be manually entered by the user. Alternatively, you
may also disable the DNS relay and configure hosts on your
LAN to use DNS servers directly. Most users who are using the
Router for DHCP service on the LAN and are using DNS
servers on the ISP’s network, will leave DNS relay enabled
(either auto discovery or user configured).
24
Page 29

Home > DHCP
Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol
(DHCP) allows the gateway
to automatically obtain the
IP address from a DHCP
server on the service
provider’s network. The
service provider assigns a
global IP address from a
pool of addresses available
to the service provider.
Typically the IP address
assigned has a long lease
time, so it will likely be the
same address each time
the Router requests an IP
address. If DHCP is not
enabled on the Router, it is
necessary for the user to
assign a static IP address
to each computer on your
LAN.
To setup DHCP for your LAN, first enable the Router as a DHCP server by clicking the
corresponding Enabled radio button in the window above. The next step is to set a
range of IP addresses that you wish to allot to the devices on your LAN by entering a
Starting IP Address and an Ending IP Address. This may be in a range from 2 to 254
(192.168.0.2 – 192.168.0.254). Computers on your LAN will have an IP address within
this range then automatically assigned to them. Finally, using the pull-down menu,
choose the Lease Time, which is the time the Server will set for devices using DHCP to
re-request an IP Address. Clients authorized for DHCP will be listed in the table at the
bottom of the page. Click Apply to implement information set in this table. The DHCP
Server is enabled by default.
DHCP may also be statically configured as well. This method allows the router to assign
the same IP address information to a specific computer on the network, defined by its
MAC address. This computer will get the same DHCP implemented IP address
information every time the computer is turned on and this IP address will be specific to
that computer’s IP address on the local network. No other computer can be assigned
this address. This is useful for computers on the LAN that are hosting applications such
as HTTP or FTP. First, the user must enable the Static DHCP function by clicking the
25
Page 30

corresponding Enabled radio button. Next the user must enter the host name and the IP
address for that computer by entering the last numbers into the space provided in the IP
Address field. Next, the user is to enter the MAC address of the computer into the space
provided. Click Apply to implement these static settings.
The DHCP Client field will allow users to Clone the settings from their computer that
were learned from the DHCP server. Simply use the pull down menu to select the MAC
address of the computer to be cloned and then click the Clone button. The settings from
this computer will be implemented in the Static DHCP configuration area. Click Apply to
implement these static settings.
Advanced > Virtual Server
To view the following window, click on the Advanced tab at the top of the window and
then click the Virtual Server button to the left. The Virtual Server will allow remote users
access to various services outside of their LAN through a public IP address, such as
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or HTTPS (Secure Web). After configuring the Router for
these features, the Router will redirect these external services to an appropriate server
on the users LAN. The Router has 13 pre-configured external services already set, but
the user may add alternate services using the window below. The Virtual Servers listed
in the following window are:
26
Page 31

• FTP – File Transfer Protocol, used to transfer large files over the Internet
• HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol, the basic protocol of the World Wide Web
• HTTPS – HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure, the basic protocol of the World
Wide Web with added security provided by the Secure Shell feature (SSH)
• DNS – Domain Name Server, a server that translates website addresses into IP
addresses
• SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, used to transmit e-mail messages
between parties
• POP3 – Post Office Protocol version 3, used to retrieve e-mail from a mail
server
• Telnet – A terminal emulation program used for remote configuration
• IPSec – IP Security, used for a secure transfer of information over the network.
If one end of the transmission is using IPSec, so must the other end
• PPTP – Point to Point Tunneling Protocol, used to transfer information securely
between VPNs (Virtual Private Routers)
• NetMeeting – An application that allows teleconferences over the Internet
• DCS –1000 – A D-Link internet camera used for security monitoring
• DCS –2000 – A D-Link internet camera used for security monitoring
• DVC –1000 – A D-Link VideoPhone used for video conferencing
External services may be modified by clicking the corresponding edit icon, or they may
be deleted by clicking the corresponding delete icon. Though there are seven fields
available to configure the Virtual Server, in most cases, only the IP address of the
Virtual Server will be needed for implementation. To enable an already existing Virtual
Server, click its corresponding Edit button, configure the appropriate fields listed below
and set the Status fields to Enabled by clicking the radio button. To configure other
virtual servers for the Router, configure the following fields and click Apply.
Virtual Server Click the radio button to enable or disable the selected Virtual
27
Page 32

Server.
Name Enter the name of the Virtual Server. If you have chosen a
pre-configured Virtual Server from the list, its name will appear
in this field.
Private IP Enter the IP address of the Virtual Server.
Protocol Type The protocol type used for the Virtual Server. The user may
select TCP, UDP or Both, depending on the type of Virtual
Server implemented.
Private Port Enter the port number of the Virtual Server’s computer. Existing
Virtual Servers listed already have their well-known port
number listed yet this may need to be changed in certain
circumstances.
Public Port Enter the port number of the device on the WAN side of the
network that will be accessing the Virtual Server currently being
configured. Commonly, this port number is identical to the
Private Port number. Existing Virtual Servers listed already
have their well-known port number listed yet this may need to
be changed in certain circumstances.
Schedule Configure the time schedule you wish these Virtual Servers to
be accessed. Clicking the Always radio button will allow access
to these servers at any time. The user may set a strict time
period by clicking the From radio button and configuring a time
period for access.
28
Page 33

This window is used to
configure applications
that require multiple
connections, such as
Internet Telephony,
video conferencing and
Internet gaming. The
following window lists six
Special Applications that
commonly use more than
one connection. To
configure one of these
applications, click the
corresponding edit icon
and then modify the
fields listed below the
following figure, and then
click Enabled. The user
may add a new
application by modifying
the fields listed and then
clicking Enabled. New
entries will be listed at
the bottom of the page in
the Special Application
List. To delete a
particular application,
click its corresponding
delete icon.
Advanced > Applications
Applications Click the appropriate corresponding radio button to enable or
disable the Applications feature.
Trigger Port Enter the port associated with the Name entered above. This is
the port that will “trigger” this application to accept multiple
connections.
Trigger Type Choose the protocol type of the Special Application from the
pull-down menu. The choices available to the user are TCP,
UDP or Both.
Public Port Enter the port number on the WAN side of the connection that
will access the Special Application. This field will accept a port,
multiple ports which are to be separated by a comma upon
entry, or a range of ports, which are to be separated by a dash.
29
Page 34

Public Type This entry will trigger the public port on the WAN side of the
connection for the specified application. The choices available
to the user are TCP, UDP or Both.
Advanced > Filters
Packet filtering is a basic security measure that should be used on any network that is
exposed to a security risk. A packet filter system examines data packets and scrutinizes
them in order to control network access. Filtering rules determine whether packets are
passed through the Router from either side of the gateway. The rules are created and
controlled by the network administrator and can be precisely defined. These rules are
used to block access to the LAN from outside the network and/or to deny access to the
WAN from within the network. The Router uses filtering rules to examine data packet
headers for specific information. Packets passing through the Router that do not meet
30
Page 35

the criteria specified by the rule set are dropped.
Effective implementation of packet filtering requires detailed knowledge of network
services and communication protocols. An overly complicated filtering scheme can
adversely affect the Router’s performance, while an inadequate set of rules may
needlessly compromise security.
This Router has two fields to configure for filtering which are IP Filters and MAC Filters.
Advanced > Filters > IP Filters
This window will aid
the use in configuring
filters for IP
addresses. This will
deny specified LAN
IP addresses or
specific ports
associated with these
LAN IP address from
accessing the
Internet. Well known
ports have already
been previously set
in the IP Filters List
and can be modified
by clicking their
corresponding edit
icon, and simple
adding an IP address
to the configuration.
To access this
window, click the
Advanced tab along
the top of the
configuration window
and then the Filters
tab to the left hand
side.
IP Filters Choose whether to enable or disable this configuration for IP
filtering.
IP Address An IP address or range of IP addresses that will be denied
access to the Internet.
31
Page 36

Port A port or range of ports that will be denied access to the
Internet. If no port is entered, all ports in this IP range will be
denied access to the Internet.
Protocol Type The protocol associated with this IP filter. The user may choose
between TCP, UDP or Both.
Schedule The user may configure time intervals that these IP filters will
become active. Clicking the Always radio button will not allow
access to these IP filters at any time. The user may set a strict
time period by clicking the From radio button and configuring a
time period to deny these IP addresses from accessing the
Internet.
All computers are
uniquely identified by
Advanced > Filters > MAC Filters
their MAC (Media
Access Control)
address. The
following window will
allow users to deny
computers access to
the Internet or only
allow certain
computers access to
the Internet, based on
their MAC address.
To access this
window, click the
Advanced tab along
the top of the
configuration window,
then the Filters tab to
the left hand side and
finally click the
corresponding radio
button for MAC
Filters.
Disabled MAC Filters Click this radio button to disable MAC filtering on the
Router.
Only Allow Click this radio button if you wish to allow specific
computers access to the network, based on MAC
address.
32
Page 37

Only Deny Click this radio button if you wish to deny specific
computers access to the network, based on MAC
address.
Name A Name defined by the user to identify this MAC
address filter setting.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address to be filtered.
DHCP Client This field will display the DHCP client’s host name and
MAC address here. You may clone this MAC address
by simply clicking the Clone button. The cloned entry
will be displayed in the MAC Filters List.
Advanced > Parental Control
Parental Control is used to deny access to certain websites and domains on the Internet.
This is beneficial for users who want to deny computers on the LAN entry to websites,
33
Page 38

especially for parents who want to guard against questionable content for their
children’s computers. The administrator has two choices in this window, URL blocking
(websites) and Domain Blocking. See the following for more information on Parental
control and its implementation.
Advanced > Parental Control > URL Blocking
URL or Uniform Resource Locator is a specially formatted text string that uniquely
defines an Internet website. This window will allow users to block computers on the LAN
from accessing certain URLs. This may be accomplished by simply entering the URL to
be blocked in the URL Keyword field. The user may also use this field to block certain
websites by entering a keyword into the URL Keyword field. So, if any website’s URL
contains this word, it will automatically be denied access to users on the LAN.
For example, if you wish to block users from accessing shopping websites, enter the
keyword “shopping” into the URL Keyword field. Websites having “shopping” in their
URL (such as http://www.yahoo.com/shopping/stores.html or
http://www.msn/search/shopping-spree.html) will now be denied access from computers
on the LAN. This feature may be beneficial to parents wanting to stop their kids from
accessing certain websites or for companies who want their employees to stop surfing
the Internet on company time.
To configure this window for URL blocking, enter the website’s address or a keyword
into the URL Keyword field and click the radio button to enable URL Blocking and then
click Apply to save this configuration into the Router’s memory. Configured URL
blocking entries will be displayed in a list at the bottom of the window. To modify a URL
blocking entry in the list, click its corresponding edit icon. To delete a URL blocking entry
in the list, click its corresponding delete icon.
34
Page 39

Advanced > Parental Control > Domain Blocking
Domain blocking is a method of denying or allowing computers on the LAN access to
specific domains on the Internet. There are two available methods available to the user
to institute Domain blocking on the router. Under the Domain Blocking header in the
screen pictured above, the user has three choices, one of which is to disable Domain
blocking. The second choice is Allow users to access all domains except “Blocked
Domains”. This option is for users who wish to block certain domains from being
accessed by local users on the LAN, but leave the rest open for use. To specify which
Domains you wish to exclude from use by computers on the LAN, enter the Domain’s
URL (ex. yahoo.com, google.com) into the Blocked Domains field and then click Apply.
The blocked entry will appear in the Blocked Domains List at the bottom of the screen.
To modify an entry in this list, click its corresponding edit icon. To delete an entry from
this list, click its corresponding delete icon.
For users wishing to allow computers on the LAN access to only specified domains,
choose option three under the Domain Blocking heading, Deny users to access all
domains except “Permitted Domains”. To specify which domains you wish to include for
this option, enter the Domain’s URL (ex. yahoo.com, google.com) into the Permitted
Domains field and then click Apply. The permitted entry will appear in the Permitted
Domains List at the bottom of the window. To modify an entry in this list, click its
corresponding edit icon. To delete an entry from this list, click its corresponding delete
35
Page 40

icon.
NOTE: Choosing the Deny users to access all domains except “Permitted
Domains” option will block access to all other Internet traffic except the
Domains specified. Be careful not to misuse this option or users on the LAN
will have difficulty accessing network resources.
Advanced > Firewall
This Router comes equipped with a firewall. The Firewall Rules window allows the
Router to enforce specific predefined policies intended to protect against certain
common types of attacks. To configure the Router’s firewall, click the Advanced tab at
the top of the window and then the Firewall tab to the left. To configure rules for the
firewall, modify the following fields and click Apply to set the rule in the Routers memory.
Newly configured firewall rules will be displayed in the Firewall Rules List at the bottom
36
Page 41

of the page. To modify an entry in this list, click its corresponding edit icon. To delete an
entry from this list, click its corresponding delete icon.
Firewall Click the corresponding radio button if you wish to enable or
disable the firewall function on the Router.
Name Enter a name that will define the firewall rule to be configured.
This entry is dependant on how the user wishes to classify this
rule.
Action Click whether to Allow or Deny traffic to pass through the
Router by checking the corresponding radio button. Users may
configure only specific traffic to pass through the router by
checking Allow or users may stop specific traffic from passing
through the Router by checking Deny.
Source Enter the IP address or range of IP addresses that you wish to
block or allow to pass through the router. The Source may be
identified on the LAN side, the WAN side or both by using the
pull-down menu for the Interface heading.
Dest Enter the IP address or range of IP addresses that you wish to
deny or allow access to the Internet. The Destination may be
identified on the LAN side, the WAN side or Both by using the
pull-down menu for the Interface heading. The type of protocol
may also be chosen by using the pull-down menu. The user
may choose between TCP, UDP, ICMP or (*) Any. The user
may also select a range of ports of the destination IP addresses
by entering the range under the Port Range heading.
Schedule Clicking Always will set the firewall permanently, unless
changed by the user. Alternately, the user may set up a time
schedule to implement the firewall, on a week-to-week basis by
clicking the From radio button and setting the appropriate times
to begin and end the firewall function.
37
Page 42

Advanced > DMZ
Firewalls may conflict with certain interactive applications such as video conferencing or
playing Internet video games. For these applications, a firewall bypass can be set up
using a DMZ IP address. The DMZ IP address is a “visible” address and does not
benefit from the full protection of the firewall function. Therefore it is advisable that other
security precautions be enabled to protect the other computers and devices on the LAN.
It may be wise to use isolate the device with the DMZ IP address from the rest of the
LAN.
For example, if you want to use video conferencing and still use a firewall, you can use
the DMZ IP address function. In this case, you must have a PC or server through which
video conferencing will take place. The IP address of this PC or server will then be the
DMZ IP address. You can designate the server’s IP address as the DMZ by typing in the
IP address in the IP Address space provided and then enabling its status by clicking the
Enabled radio button and then click Apply.
For the system that uses the DMZ IP address, you may want to manually assign an IP
38
Page 43

address to it and adjust your DHCP server addresses so that the DMZ IP address is not
included in the DHCP server range. This way you avoid possible IP address problems if
you reboot the DMZ system. To configure the Router’s DMZ IP address, click the
Advanced tab at the top of the window and then the DMZ tab to the left
.
Advanced > DDNS
The DI-524UP supports Dynamic Domain Name Service. Dynamic DNS allows a
dynamic public IP address to be associated with a static host name in any of the many
domains, allowing access to a specific host from various location s on the Internet. With
this function enabled, remote access to a host will be allowed by choosing a URL by
using the pull-down menu. Because many ISPs assign public IP addresses using DHCP,
it can be difficult to locate a specific host on the LAN using the standard DNS. For
example, if you are running a public web server or VPN server on your LAN, DDNS
ensures that the host can be located from the Internet if the public IP address changes.
39
Page 44

NOTE: DDNS requires that an account be setup with one of the supported DDNS
servers prior to engaging it on the router. This function will not work without an
accepted account with a DDNS server.
DDNS Click the Enabled button to enable the DDNS feature
on the router.
Server Address Choose the DDNS server address from the pull-down
menu. Available servers include DynDns.org,
No-IP.com, hn.org and zoneedit.com.
Host name Enter the host name of the DDNS server.
Username Enter the username given to you by your DDNS server.
Password Enter the password given to you by your DDNS server.
Click Apply to set this information in the Router
.
40
Page 45

Advanced > QoS
QoS or Quality of Service is used to allot bandwidth and priority from the router. To allot
bandwidth per port on the router, click the appropriate QoS radio button and configure
the parameters. QoS may be configured per Physical Port, MAC address, IP address or
specified application. See the following explanation for more detailed information on
each type of QoS setting.
41
Page 46

Advanced > QoS > Physical Port
To enable QoS per port, first click the Physical Port radio button which will reveal the
preceeding window for the user to configure. Simply click the Enable check box of the
corresponding port to enable QoS. You may also set the bandwidth for that port by
using that corresponding pull-down menu. The user may choose a bandwidth between
128 Kbps to 32 Mbps. FULL denotes that the port will have the maximum transfer speed
allowed at any given time, up to 100Mbps. Click Apply to confirm your settings.
42
Page 47

Advanced > QoS > MAC
The user may also set QoS by specific MAC address. To enable QoS per MAC address,
first click the MAC radio button which will reveal the preceeding window for the user to
configure. Ensure that the Bandwidth configured does not exceed the incoming
bandwidth from the ISP or it will cause other devices on the LAN to slow down due to
decreased bandwidth. Check with your ISP for more information on the bandwidt h
allotted to your account.
WAN Uplink Bandwidth Use the pull-down menu to set the WAN Uplink Bandwidth. The
user may choose a speed from 64kbps to Full (100Mbps).
Ensure that the Bandwidth does not exceed the incoming
bandwidth from the ISP or it will cause other devices on the
43
Page 48

LAN to slow down due to decreased bandwidth. Check with
your ISP for more information on the bandwidth allotted to your
account.
QoS Control by MAC Click the Enabled radio button to enable QoS priority by MAC
address. Information coming from this MAC address will have
the highest priority on the LAN. This means that information
originating from this device will be sent to other devices on the
LAN requesting it, first. Other devices will have a lower priority
in sending information through the router.
Source MAC Enter the source MAC address that will be set for high priority
QoS in the router.
DHCP Client The user may use the DHCP client to aid in choosing the MAC
address to be implemented for QoS. All devices connected to
the router will be listed in the pull-down menu. Simply choose
the correct device and click the Clone button, which will
produce that devices MAC address in the Source MAC field.
Bandwidth Use the pull-down menu to select the best bandwidth for the
QoS Setting on this router. The user may set a bandwidth
between 1Kbps to 32Mbps. Choosing Best Effort will set the
router to allow the first user to access the source MAC address
to have the total bandwidth needed for the file being transferred.
Choosing Full will denote that the router will allot 100Mbps of
bandwidth for the specified QoS implementation. Only one QoS
implementation can be set at Full.
Click Apply to set the QoS for MAC
.
44
Page 49

Advanced > QoS > IP
The user may also set QoS by specific IP address. To enable QoS per IP address, first
click the IP radio button which will reveal the preceeding window for the user to
configure. Ensure that the bandwidth does not exceed the incoming bandwidth from the
ISP or it will cause other devices on the LAN to slow down due to decreased bandwidth.
Check with your ISP for more information on the bandwidth allotted to your account.
45
Page 50

Upstream Bandwidth Use the pull-down menu to set the Upstream Bandwidth. The
user may choose a speed from 64kbps to Full (100Mbps).
Ensure that the bandwidth does not exceed the incoming
bandwidth from the ISP or it will cause other devices on the
LAN to slow down due to decreased bandwidth. Check with
your ISP for more information on the bandwidth allotted to your
account.
QoS Control by IP Click the enabled radio button to enable QoS priority by MAC
address. Information coming from this IP address will have the
highest priority on the LAN. This means that information
originating from this device will be sent to other devices on the
LAN requesting it, first. Other devices will have a lower priority
in sending information through the router.
Source IP Address Enter the source IP address or range of IP addresses that will
be set for high priority QoS in the router.
Reserved Bandwidth Use the pull-down menu to select the best bandwidth for the
QoS setting on this router. The user may set a Bandwidth
between 1Kbps to 32Mbps. Choosing Best Effort will set the
router to allow the first user to access the source IP address to
have the total bandwidth needed for the file being transferred.
Choosing Full will denote that the router will allot 100Mbps of
bandwidth for the specified QoS implementation. Only one QoS
implementation can be set at Full.
Click Apply to set the QoS for IP
.
46
Page 51

Advanced > QoS > Application
The user may also set QoS by specific protocol. To enable QoS per protocol, first click
the Application radio button which will reveal the preceeding screen for the user to
configure. Ensure that the bandwidth does not exceed the incoming bandwidth from the
ISP or it will cause other devices on the LAN to slow down due to decreased bandwidth.
Check with your ISP for more information on the bandwidth allotted to your account.
QoS Control by Protocol Click the Enabled radio button to enable QoS priority by
application. Information coming from this application will have
the highest priority on the LAN. This means that information
originating from this device will be sent to other devices on the
47
Page 52

LAN requesting it, first. Other devices will have a lower priority
in sending information through the router.
Name Enter a user-defined name to define this application for users
on the LAN.
Protocol Choose the protocol to be enabled for QoS from the pull-down
menu. The user may choose TCP, UDP or Both.
Port Range Enter a virtual port range that will use this application.
Remember these are virtual ports and not physical ports on the
router.
Bandwidth Use the pull-down menu to select the best bandwidth for the
QoS setting on this router. The user may set a bandwidth
between 1Kbps to 32Mbps. Choosing Best Effort will set the
router to allow the first user to access the set application to
have the total bandwidth needed for the file being transferred.
Choosing Full will denote that the router will allot 100Mbps of
bandwidth for the specified QoS implementation. Only one QoS
implementation can be set at Full.
Click Apply to set the QoS for IP
.
48
Page 53

Advanced > Performance
The Wireless Performance window is used to configure settings for the Access Point
feature of this device. Configuring these settings may increase the performance of your
router but if you are not familiar with networking devices and protocols, this section
should be left at its default settings. Below is a list of the functions associated with the
Access Point feature of the router. Click Apply when you have completed your
changes.
TX Rate Use the pull-down menu to select the transfer data rate,
in Mbps. The default setting of Auto will automatically
adjust the transfer rate to the highest possible rate
allowed.
49
Page 54

Transmit Power Allows the user to adjust the transmit power of the
router. A high transmit power allows a greater area
range of accessibility to the router.
Beacon Interval Beacons are emitted from the router in order to
synchronize the wireless network. You may set the
range between 20-100 microseconds per beacon sent.
The default is 100.
RTS Threshold The RTS (Request to Send) Threshold controls the size
of data packets issued to a RTS packet. A lower level
will send packets more frequently which may consume
a great amount of the available bandwidth. A high
threshold will allow the router to recover from
interference or collisions which is more prevalent in a
network with high traffic or high electromagnetic
interference. The default setting is 2346.
Fragmentation The fragmentation threshold will determine if packets
are to be fragmented. Packets over the 2346 byte limit
will be fragmented before transmission. 2346 is the
default setting.
DTIM Interval DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) is a
countdown informing clients of the next window for
listening to broadcast and multicast messages. The
default setting is 3.
Preamble Type Select Short or Long Preamble. The Preamble defines
the length of the CRC block (Cyclic Redundancy Check
is a common technique for detecting data transmission
errors) for communication between the wireless router
and the roaming wireless network adapters. NOTE:
High network traffic areas should use the shorter
preamble type.
SSID Broadcast Choose Enabled to broadcast the SSID across the
network. All devices on a network must share the same
SSID (Service Set Identifier) to establish
communication. Choose Disabled if you do not wish to
broadcast the SSID over the network.
802.11g Only Mode Select this mode to restrict your network to only those
devices that employ the 802.11g standard. Enabling
this mode will ensure that you maintain the highest
connectivity rate, unhampered by any connection to an
802.11b device.
50
Page 55

CTS Mode CTS (Clear To Send) is a function used to minimize
collisions among wireless devices on a wireless local
area network (LAN). CTS will make sure the wireless
network is clear before a wireless client attempts to
send wireless data. Enabling CTS will add overhead
and may lower wireless throughput.
Auto - CTS will monitor the wireless network and
automatically decide whether to implement CTS based
on the amount of traffic and collisions that occurs on
the wireless network.
Always - CTS will always be used to make sure the
wireless LAN is clear before sending data.
None - CTS is typically used in a pure 802.11g
environment. If CTS is set to “None” in a mixed mode
environment populated by 802.11b clients, wireless
collisions may
51
Page 56

Tools > Admin
With this window, the DI-524UP administrator can change the system password. There
are two accounts that can access the Broadband Router’s Web-Management interface.
They are admin and user. Admin has read/write access while user has read-only access.
User can only view the settings but cannot make any changes.
Administrator “admin” is the Administrator login name.
Password Enter the password here and the same password in the
Confirm Password field. This will be the password that
the administrator will use to gain access to the
configuration menu of the device. There is no default
password for this device.
User “user” is the User login name
Password Enter the password here and the same password in the
52
Page 57

Confirm Password field. This will be the password that
the users will use to gain access to the configuration
menu of the device. Users will have limited privileges
on this device. There is no default password for this
device.
Remote Management
IP Address
Port The port number used to access the Broadband Router.
The Internet IP address of the computer that has
Remote management allows the DI-524UP to be
configured from the Internet by a web browser. A
username and password is still required to access the
Web-Management interface. In general, only a member
of your network can browse the built-in web pages to
perform Administrator tasks. This feature enables you
to perform Administrator tasks from the remote
(Internet) host.
access to the Broadband Router. If you input an
asterisk (*) into this field, then any computer will be
able to access the Router. Putting an asterisk (*) into
this field would present a security risk and is not
recommended.
The default port number for web management is 8080.
53
Page 58

Tools > Time
The system time is the time used by the DI-524UP for scheduling services. You can
manually set the time, connect to a NTP (Network Time Protocol) server or synchronize
the time on the router with your PC. If an NTP server is set, you will only need to set the
time zone and the update Interval. You may also set the time from the clock on your
computer by checking the corresponding radio button. To manually set the time, you will
need to input the value into the fields provided. If you manually set the time, you may
also set the Daylight Saving Time by clicking the corresponding Enabled radio button
and the system time will automatically adjust on those dates. Click Apply to set cha nges
made.
54
Page 59

Tools > System
The System Settings window has three basic functions for the DI-524UP administrator.
Configuration settings can be saved to a local hard drive on your computer by clicking
the Save button. This will produce a new window from your operating system inquiring
you about the location where you would like to save your files. The administrator may
also upload configuration settings saved to a local hard drive by entering the path into
the open field or by clicking the Browse button and searching for its location the
computer. Once found, click Load to upload these settings to the DI-524UP. The
administrator may also restore the router back to its default configurations by clicking
the Restore button.
Save Click Save to save the current settings to the local
drive.
Browse / Load Click Browse to find the settings, then click Load.
Restore Click Restore to restore the factory default settings.
Reboot Click Reboot to reboot the Router.
55
Page 60

Tools > Firmware
You can upgrade the firmware of the Router here. Make sure the firmware you want to
use is on the local hard drive of the computer. Click on Browse to browse the local hard
drive and locate the firmware to be used for the update. Please check the D-Link
Support site for firmware updates at http://support.dlink.com. You can download
firmware upgrades to your hard drive from the D-Link support site.
Firmware Upgrade Click on the link in this window to find out if there is an
updated firmware; if so, download the new firmware to
your hard drive.
Browse After you have downloaded the new firmware, click
Browse in this window to locate the firmware update
on your hard drive.
Click Apply to complete the firmware upgrade. The following window will open to
indicate the DI-524UP is writing flash:
56
Page 61

Click Continue to proceed.
NOTE: Please avoid turning off the DI-524UP when it is in the middle of updating
firmware as this action may cause serious damage to the device.
57
Page 62

Tools > Misc.
58
Page 63

Ping Test The Ping Test is used to send Ping packets to test if a
computer is on the Internet. Enter the IP Address that
you wish to Ping, and click Ping.
Block WAN Ping Discard Ping from WAN side If you choose to block
WAN Ping, the WAN IP Address of the DI-524UP will
not respond to pings. Blocking the Ping may provide
some extra security from hackers. Click Enabled to
block the WAN ping.
SPI Mode SPI or Stateful Packet Inspection is a type of firewall
that protects your network against hacker attacks by
analyzing packets to ensure that only authorized
packets will be allowed to enter your network. To
enable this function, click the Enabled radio button.
This function is enabled by default.
IGMP Proxy The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
snooping allows the Router to recognize IGMP queries
and reports sent between PCs on your LAN and an
IGMP host. When the IGMP Proxy is enabled, the
Router can open or close a port to a specific PC based
on IGMP messages passing through the Router.
UPNP Settings You may enable the Universal Plug n’ Play function
here by clicking the Enabled radio button.
VPN Pass-Through The DI-524UP supports VPN (Virtual Private Network)
pass-through for both PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling
Protocol) and IPSec (IP Security). Once VPN
pass-through is enabled, there is no need to open up
virtual services. Multiple VPN connectio ns c a n be ma de
through the DI-524UP. This is useful when you have
many VPN clients on the LAN network.
PPTP Select enabled or disabled.
IPSec Select enabled or disabled.
WAN Select This section allows the user to set the wire speed over
which the router will transmit packets. The user has
three options:
100 Mbps – Clicking this radio button will set the wire
speed at 100 megabytes per second.
10 Mbps – Clicking this radio button will set the wire
speed at 10 megabytes per second.
59
Page 64

10/100 Mbps Auto – Clicking this radio button will allow
the wire speed to be automatically set by the router
depending on the wire speed available at any given
time.
Tools > Cable Test
The above window is a Virtual Cable Tester and it shows the user the current status of
the ports of the Router. In this window, we can see that LAN 3 port is connected at a
speed of 100Mbps Full (duplex) and all the other connections do not have a valid link.
Clicking the More Info button will open an additional window with more information
about this connection, as shown below.
60
Page 65

Status > Device Info
This window displays the current information for the DI-524UP. It will display the LAN,
WAN, and Wireless 802.11g statistics.
If your WAN connection is set up for a Dynamic IP address then a Release button and a
Renew button will be displayed. Use Release to disconnect from your ISP and use
Renew to connect to your ISP.
If your WAN connection is set up for PPPoE, a Connect button and a Disconnect button
61
Page 66

will be displayed. Use Disconnect to drop the PPPoE connection and use Connect to
establish the PPPoE connection.
This window will show the DI-524UP’s working status:
LAN MAC Address: MAC address of the DI-524UP
IP Address: LAN/Private IP Address of the DI-524UP
Subnet Mask: LAN/Private Subnet Mask of the
DI-524UP
DHCP Server: DHCP Server Status
WAN MAC Address: MAC address of the DI-524UP
Connection: Displays the current connection for DHCP.
This field also has two buttons for resetting the DHCP
server on the Router. DHCP Release – Clicking this
button will release and reset the DHCP server. All
settings configured by DHCP will be lost. DHCP
Renew – Clicking this button will allow the router to
renew the DHCP server and automatically configure
new DHCP settings for the connection.
IP Address: WAN/Public IP Address
Subnet Mask: WAN/Public Subnet Mask
Default Gateway: WAN/Public Gateway IP Address
Domain Name Server: WAN/Public DNS IP Address
Wireless 802.11g MAC Address: MAC address of the DI-524UP
SSID: Displays the current SSID
Channel: Displays the current wireless channel in use
Encryption: indicates whether wireless encryption is
enabled or disabled
62
Page 67

Status > Log
The Router keeps a running log of events and activities occurring on the Router. If the
device is rebooted, the logs are automatically cleared. You may save the log fi les un der
Log Settings.
View Log First Page - The first page of the log
Last Page - The last page of the log
Previous - Moves back one log page
Next - Moves forward one log page
Clear - Clears the logs completely
Log Settings - Brings up the page to configure the log
Refresh – Refreshes the View Log window
63
Page 68

Status > Log > Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings window allows a log to be saved by sending it to either an
admin e-mail address or a Syslog server. Once you have completed your settings, click
Apply to let your changes take effect.
Log Type Choices include System Activity, Debug Information,
Attacks, Dropped Packets, and Notice.
E-Mail Alert Enter the appropriate e-mail information in this section.
64
Page 69

Syslog Account To send a log to a syslog server, click the Enable
button and enter the IP address of the syslog server.
Status > Statistics
The window above displays the Traffic Statistics. Here you can view the amount of packets that pass through the DI-524UP on the WAN, LAN, and Wireless ports. The traffic
counter will reset if the device is rebooted or can be reset by clicking the Reset button.
To refresh current statistics, click the Refresh button.
65
Page 70

Status > Wireless Info
The wireless client table displays a list of current connected wireless clients. This table
also displays the MAC address and mode of the connected wireless client.
Click on Help at any time, for more information.
66
Page 71

Status > Printer Info
The Printer Server Information window displays a list of Printers that are using the
DI-524UP as a print server. These printers are defined by Queue Name and Printer
Name. The status of these printers is located to the right under the heading Printer
Server Status.
To use this window, simply plug your USB printer into the DI-524UP. The USB LED on
the front of the DI-524UP will light up and the printer will automatically appear in the
window above. The default Printer Name is “lp1.”
If you have not done so already, it is necessary to add the printer before you can start
using it. Please see the “Installing a Printer on your DI-524UP” section in the Appendix.
67
Page 72

Status > Active Session
The Active Session window allows users to view the packets passing through the
router, whether from the source or to the destination. This window displays the total
TCP and UDP packets in the NAPT Session section. This is a total of the Active
Session section on the bottom of the screen. The Active Session section will sub-divide
the NAPT session section into separate IP addresses and their TCP and UDP packets.
For more details regarding a separate IP address on the LAN, click the detail button of
the corresponding IP address, which will display the following window for the user to
view.
68
Page 73

Sub-divided again, this window displays more detailed information on the TCP/UDP
actions taken by the specific IP address, as stated below.
Protocol Displays the protocol used by the corresponding IP address,
whether it be TCP or UDP.
Source IP Displays the IP address of the device sending information.
Source Port Displays the virtual port used by the source IP address.
Dest IP Displays the IP addres s of the destination of the packets sent
from the Source IP.
Dest Port Displays the virtual port receiving information for the
Destination IP.
Age Time Displays the total time the particular UDP session was ongoing,
in seconds.
69
Page 74

Help
The Help tab will give basic information referring to various windows located in the
Router. To view a specific section, click on its hyperlinked name. A new window of
information will appear.
70
Page 75

Technical Specifications
Standards
• IEEE 802.11g
• IEEE 802.11b
• IEEE 802.3
• IEEE 802.3u
VPN Pass Through/ Multi-Sessions
• PPTP
• L2TP
• IPSec
Device Management
• Web-Based- Internet Explorer v6 or later; Netscape
Navigator v6 or later
• DHCP Server and Client Advanced Firewall Features
• NAT with VPN Passthrough (Network Address
Translation)
• MAC Filtering
• IP Filtering
• URL Filtering
• Domain Blocking
• Scheduling
Wireless Operating Range
• Indoors – up to 328 feet (100 meters)
• Outdoors – up to 1312 feet (400 meters)
Operating Temperature
• 32
º
F to 113 ºF (0ºC to 45ºC)
71
Page 76

Humidity:
• 95% maximum (non-condensing)
Safety and Emissions:
• EMI: FCC Class B, CE Class B, C-Tick
• Safety: CSA International
Wireless Frequency Range:
• 2.4GHz to 2.462GHz
LEDs:
• Power
• Status
• WAN
• WLAN (Wireless Connection)
• LAN (10/100)
• USB
Status Physical Dimensions:
• L = 5.59 inches (142 mm)
• W = 4.29 inches (109 mm)
• H = 1.22 inches (31 mm)
Wireless Transmit Power:
• 11g: 13dBm Typical
• 11b: 17dBm Typical
Security:
• 802.1 x
• WPA - WiFi Protected Access
• WPA2 – WiFi Certified Security with AES encryption
• (64, 128-bit WEP with TKIP, MIC, IV Expansion, Shared
Key Authentication)
72
Page 77

External Antenna Type:
• Single detachable reverse SMA Modulation Technology:
• Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Power Input:
• Ext. Power Supply DC 5V, 2A
• Weight: 7.83 ounces (222 grams)
Warranty:
• 3 year (depends on D-Link global warranty policy)
Wireless Data Rates with Automatic Fallback:
• 54 Mbps
• 48 Mbps
• 36 Mbps
• 24 Mbps
• 22 Mbps
• 18 Mbps
• 12 Mbps
• 11 Mbps
• 9 Mbps
• 6 Mbps
• 5.5 Mbps
• 2 Mbps
• 1 Mbps
Receiver Sensitivity:
• 54Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -72dBm
• 48Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -74dBm
• 36Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -78dBm
• 24Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -80dBm
73
Page 78

• 18Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -83dBm
• 12Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -84dBm
• 11Mbps CCK, 8% PER, -85dBm
• 9Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -84dBm
• 6Mbps OFDM, 10% PER, -84dBm
• 5.5Mbps CCK, 8% PER, -88dBm
• 2Mbps QPSK, 8% PER, -89dBm
• 1Mbps BPSK, 8% PER, -92dBm
74
Page 79

Appendix
WCN and the Wireless Setup Wizard
WCN or Windows Connect Now technology has been recently incorporated by D-Link to quickly
aid the user in setting up a secure wireless environment. Combining the new WCN technology
incorporated by Windows and only available through a PC that has a wireless NIC card and is
running the Windows XP Operating System with Service Pack 2 installed, the user will configure
the wireless settings only once and then save it to a USB flash drive. Once saved, the user may
insert this flash drive into any device on the network that is running wirelessl y and the settings will
automatically upload to that device. No more configurations are necessary and all devices will
have the identical access information and wireless information necessary to work smoothly over
your internal LAN. See the explanation below for a better understanding of how to set up your
WCN wireless function.
In Windows XP SP2, click Start >
All Programs > Accessories >
Communications > Windows
Network Setup Wizard to open
the wizard’s front page, as seen
below.
75
Page 80

Choose “Set up a new wireless network”.
Click Next.
Enter a network name of up to 32
characters to identify your wireless
network. This name will be common to all
users on the wireless LAN.
Choose “Manually assign a network key”
which will be configured in the next
window.
Click Next.
Choose a key that will be shared among
users on your LAN. There are certain
guidelines to choosing this key, as stated
on the screen to the left.
Confirm the network key by retyping it in
the following field.
Once entered, click Next.
76
Page 81

Insert the USB drive into a USB port on
the computer, choose “Use a USB flash
drive”.
Click Next.
The settings will the automatically be uploaded to your USB flash drive. Once saved the
user is to unplug the device, in the proper method, and then plug that USB flash drive
into all devices that will be accessing the wireless LAN. Each device will upload the
configurations automatically and be instantly accessible on the wireless LAN.
77
Page 82

Installing a Printer on your DI-524UP for Windows XP
The DI-524UP can be used as a print server for devices on your LAN. Once you have
installed the USB printer through the router, the user must set up the computer on the
LAN for the printer as well. The following explanation will guide you through the steps
needed to do this. Remember to enter the same Queue Name on the PC as your router
displays or the printer will not function properly.
Go to
Start >
Printers
and
Faxes.
Click on
Add a
printer.
Click
Next.
78
Page 83

Select Local printer
attached to the
computer.
(Deselect
Automatically detect
and install my Plug
and Play printer if it
has been selected.)
Click Next.
Select Create a port:
and from the pull-down
menu select the correct
port for your printer.
(Most users will want to
select Standard TCP/IP
Port, as shown in the
illustration.)
Click Next.
The Add Standard
TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard window opens.
Click Next.
79
Page 84

Enter the IP Address of
the DI-524UP (default:
192.168.0.1) in the
Printer Name or IP
Address field. Add a
name to the router IP
address to differentiate
it from other devices in
the Port Name field.
Click Next.
The Wizard requires
additional information
to complete the
process. In the
Additional Port
Information Required
window, select the
Custom radio dial and
click the Settings
button.
.
In the Configure
Standard TCP/IP Port
Monitor window, first
select the LPR radio
dial in the Protocol
section.
Next, add a Queue
Name, such as “lp1.”
Click OK.
.
80
Page 85

The Wizard will return
to the Additional Port
Information Required
window after the
settings have been
entered in the Port
Settings tab on the
Configure Standard
TCP/IP Port Monitor
window.
Click Next.
Please confirm the
printer port information.
Click Finish.
Select and highlight the
correct driver for your
printer.
(If the correct driver is
not displayed, insert
the CD or floppy disk
that came with your
printer and click Have
Disk.)
Click Next.
81
Page 86

At this screen, you can
change the name of the
printer (optional).
Click Next.
At this screen, you
must enter a share
name if you want to
share the printer with
other network users.
Click Next.
At this screen, you
have the option of
entering a location and
description of your
printer.
Click Next.
82
Page 87

Select Yes, to print a
test page. A successful
printing will confirm that
you have chosen the
correct driver.
Click Next.
This screen gives
you information
about your printer.
Click Finish.
When the test page has
printed, click OK.
Go to Start
> Printers
and Faxes.
A successful
installation
will display
the printer
icon as
shown at
right.
You have successfully added a printer.
83
Page 88

Installing a Printer on your DI-524UP for Windows 2000
The DI-524UP can be used as a print server for devices on your LAN. Once you have
installed the USB printer through the router, the user must set up the computer on the
LAN for the printer as well. The following explanation will guide you through the steps
needed to do this. Remember to enter the same Queue Name on the PC as your router
displays or the printer will not function properly. To begin the process, open the Printer
window on your PC by clicking Start > Settings > Printers, which will open the
following window.
Double-click Add Printer, which
will open the Welcome to the
Add Printer Wizard.
Click Next.
84
Page 89

In the Local or Network Printer
window, choose “Local printer
attached to this computer.”
Click Next.
Then the user must choose the
type of installation for the wizard.
Choose “Create a new port” and
use the pull-down menu to select
“Standard TCP/IP Port”.
85
Click Next.
The next window to appear is the
Welcome to the Add Standard
TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard.
Make sure that the printer is
turned on and the network is
properly configured.
Click Next.
Page 90

Enter the IP address (default:
192.168.0.1) of the DI-524UP to the
“Printer Name or IP Address” field.
In the Port Name field, be sure to
add a name to the router IP
address to differentiate it from other
devices (ex: IP_192.168.0.1dlink).
Click Next.
After clicking Next, the Wizard
requires additional information to
complete the process. In the
Additional Port Information
Required window, click Custom >
Settings. In the following window,
the user will add the Queue Name.
In the Configure Standard TCP/IP
Port Monitor window, first select
LPR in the Protocol section.
Next, add the Queue Name that
was automatically generated for
you by your DI-524UP (in this case,
lp1).
Click OK to continue.
86
Page 91

The final window will be the
Completing the Add Standard
TCP/IP Printer Port Wizard
window, as shown to the left. Here
you can view the properties of the
added printer, including the IP
address, protocol and queue name.
Click Finish to complete the wizard.
87
Page 92

Technical Support
You can find software updates and user documentation on the D-Link website.
D-Link provides free technical support for customers within the United States
and within Canada for the duration of the warranty period on this product.
U.S. and Canadian customers can contact D-Link technical support through our
website, or by phone.
Tech Support for customers within the United States:
D-Link Technical Support over the Telephone:
(877) 453-5465
24 hours a day, seven days a week
D-Link Technical Support over the Internet:
http://support.dlink.com
email:support@dlink.com
Tech Support for customers within Canada:
88
 Loading...
Loading...