Page 1

D-Link ™ DGS-3224SR
High-Density Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
User’s Guide
Page 2

D-Link DGS-3212SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2003 D-Link Corporation. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of D-Link
Corporation is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: D-Link, the D-LINK logo are trademarks of D-Link Computer Corporation; Microsoft and Windows are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or their products.
D-Link Computer Corporation disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
August 2003 P/N 651GS3224015
ii
Page 3

CONTENTS
D-Link ™ DGS-3224SR.......................................................................................................................................... i
Intended Readers................................................................................................................................................ vi
Typographical Conventions ............................................................................................................................... vi
Notes, Notices, and Cautions ................................................................................................................................ vii
Safety Instructions................................................................................................................................................. vii
Safety Cautions ............................................................................................................................................. vii
General Precautions for Rack-Mountable Products ....................................................................................... ix
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge......................................................................................................x
Introduction..............................................................................................................................................................1
Switch Description ...........................................................................................................................................1
Features ................................................................................................................................................................1
Front-Panel Components......................................................................................................................................2
LED Indicators.................................................................................................................................................2
Rear Panel Description.........................................................................................................................................3
Management Options ...........................................................................................................................................4
Installation................................................................................................................................................................2
Package Contents .............................................................................................................................................2
Installing the Switch in a Rack.........................................................................................................................4
Connecting Stacked Switch Groups.....................................................................................................................5
Configuring a Switch Group for Stacking........................................................................................................6
Connecting the Console Port............................................................................................................................9
Password Protection...........................................................................................................................................10
SNMP Settings ...............................................................................................................................................11
IP Address Assignment......................................................................................................................................12
Connecting Devices to the Switch......................................................................................................................13
Introduction to Switch Management......................................................................................................................14
Web-based User Interface ..............................................................................................................................15
Basic Setup.........................................................................................................................................................16
Switch Information.........................................................................................................................................17
Switch IP Settings ..............................................................................................................................................18
Security IP Management Stations Configuration...........................................................................................20
User Accounts Management ..............................................................................................................................21
Admin and User Privileges ............................................................................................................................22
Saving Changes..................................................................................................................................................22
Factory Reset......................................................................................................................................................23
Restart System................................................................................................................................................23
Page 4

Switch Information.........................................................................................................................................24
Advanced Settings..........................................................................................................................................25
Switch Stack Management.....................................................................................................................................27
Stacking Information..........................................................................................................................................27
VLAN Configuration .............................................................................................................................................31
GVRP Setting.................................................................................................................................................32
Understanding VLANs.......................................................................................................................................37
Port Settings Configuration....................................................................................................................................41
Basic Port Configuration....................................................................................................................................41
Link Aggregation Configuration............................................................................................................................44
Forwarding and Filtering........................................................................................................................................46
IGMP Settings................................................................................................................................................49
Static Router Ports..........................................................................................................................................50
New IGMP Snooping Feature ........................................................................................................................52
Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration...............................................................................................................53
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree.........................................................................................................................53
QoS (Quality of Service)........................................................................................................................................58
Traffic Control (Broadcast/Multicast Storm Control)....................................................................................58
Configuring Default Priority ..........................................................................................................................59
Configuring 802.1p User Priority...................................................................................................................60
802.1p User Priority .......................................................................................................................................61
Traffic Segmentation......................................................................................................................................62
Bandwidth Control .........................................................................................................................................63
System Log Server.................................................................................................................................................65
Port Security Settings.............................................................................................................................................67
SNTP Setting..........................................................................................................................................................69
Access Profile Table ..............................................................................................................................................72
Security IP Management........................................................................................................................................76
Port Access Entity..................................................................................................................................................77
802.1X Port-based Network Access Control......................................................................................................77
Configure Authenticator.................................................................................................................................79
Port Authenticating Settings...........................................................................................................................82
Radius Server .................................................................................................................................................82
SNMP.....................................................................................................................................................................84
SNMP User Table ..........................................................................................................................................84
SNMP View Table .........................................................................................................................................86
SNMP Group Table........................................................................................................................................87
SNMP Community Table Configuration........................................................................................................90
SNMP Host Table ..........................................................................................................................................90
Page 5

SNMP Engine ID ...........................................................................................................................................92
System Monitoring and Statistics...........................................................................................................................93
Port Utilization...............................................................................................................................................93
Packets ...........................................................................................................................................................94
Errors..............................................................................................................................................................97
Size...............................................................................................................................................................101
Maintenance .........................................................................................................................................................107
Technical Specifications ......................................................................................................................................112
Glossary ...............................................................................................................................................................114
WARRANTY FOR ALL COUNTRIES AND REGIONS EXCEPT USA ..................................................................................121
WARRANTY INFORMATION FOR USA ONLY..............................................................................................................124
Page 6
D-Link DGS-3224SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Intended Readers
The DGS-3224SR User Guide contains information for setup and management and of the DGS-3224SR switch.
This guide is intended for network managers familiar with network management concepts and terminology.
Typographical Conventions
Convention Description
In a command line, square brackets indicate an optional entry. For
[ ]
Bold font
example: [copy filename] means that optionally you can type copy
followed by the name of the file. Do not type the brackets.
Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu, or menu item. For example:
Open the File menu and choose Cancel. Used for emphasis. May
also indicate system messages or prompts appearing on your
screen. For example: You have mail. Bold font is also used to
represent filenames, program names and commands. For example:
use the copy command.
Boldface Typewriter
Font
Initial capital letter
Italics
Menu Name > Menu Option
Indicates commands and responses to prompts that must be typed
exactly as printed in the manual.
Indicates a window name. Names of keys on the keyboard have
initial capitals. For example: Click Enter.
Indicates a window name or a field. Also can indicate a variables or
parameter that is replaced with an appropriate word or string. For
example: type filename means that you should type the actual
filename instead of the word shown in italic.
Menu Name > Menu Option Indicates the menu structure.
Device > Port > Port Properties means the Port Properties menu
option under the Port menu option that is located under the Device
menu.
vi
Page 7
D-Link DGS-3224SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make
better use of your device.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss
of data and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage,
personal injury, or death.
Safety Instructions
Use the following safety guidelines to ensure your own personal safety and to help protect your system from
potential damage. Throughout this safety section, the caution icon ( ) is used to indicate cautions and
precautions that you need to review and follow.
Safety Cautions
To reduce the risk of bodily injury, electrical shock, fire, and damage to the equipment, observe the following
precautions.
Observe and follow service markings. Do not service any product except as explained in your system
documentation. Opening or removing covers that are marked with the triangular symbol with a lightning bolt
may expose you to electrical shock. Components inside these compartments should be serviced only by a trained
service technician.
If any of the following conditions occur, unplug the product from the electrical outlet and replace the part or
contact your trained service provider:
vii
Page 8

D-Link DGS-3224SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
– The power cable, extension cable, or plug is damaged.
– An object has fallen into the product.
– The product has been exposed to water.
– The product has been dropped or damaged.
– The product does not operate correctly when you follow the operating instructions.
• Keep your system away from radiators and heat sources. Also, do not block cooling vents.
• Do not spill food or liquids on your system components, and never operate the product in a wet
environment. If the system gets wet, see the appropriate section in your troubleshooting guide or contact
your trained service provider.
• Do not push any objects into the openings of your system. Doing so can cause fire or electric shock by
shorting out interior components.
• Use the product only with approved equipment.
• Allow the product to cool before removing covers or touching internal components.
• Operate the product only from the type of external power source indicated on the electrical ratings label.
If you are not sure of the type of power source required, consult your service provider or local power
company.
• To help avoid damaging your system, be sure the voltage selection switch (if provided) on the power
supply is set to match the power available at your location:
– 115 volts (V)/60 hertz (Hz) in most of North and South America and some Far Eastern countries such
as South Korea and Taiwan
– 100 V/50 Hz in eastern Japan and 100 V/60 Hz in western Japan
– 230 V/50 Hz in most of Europe, the Middle East, and the Far East
• Also be sure that attached devices are electrically rated to operate with the power available in your
location.
Safety Instructions (continued)
• Use only approved power cable(s). If you have not been provided with a power cable for your system or
for any AC-powered option intended for your system, purchase a power cable that is approved for use in
your country. The power cable must be rated for the product and for the voltage and current marked on
the product's electrical ratings label. The voltage and current rating of the cable should be greater than
the ratings marked on the product.
• To help prevent electric shock, plug the system and peripheral power cables into properly grounded
electrical outlets. These cables are equipped with three-prong plugs to help ensure proper grounding. Do
not use adapter plugs or remove the grounding prong from a cable. If you must use an extension cable,
use a 3-wire cable with properly grounded plugs.
• Observe extension cable and power strip ratings. Make sure that the total ampere rating of all products
plugged into the extension cable or power strip does not exceed 80 percent of the ampere ratings limit
for the extension cable or power strip.
• To help protect your system from sudden, transient increases and decreases in electrical power, use a
surge suppressor, line conditioner, or uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
• Position system cables and power cables carefully; route cables so that they cannot be stepped on or
tripped over. Be sure that nothing rests on any cables.
• Do not modify power cables or plugs. Consult a licensed electrician or your power company for site
modifications. Always follow your local/national wiring rules.
• When connecting or disconnecting power to hot-pluggable power supplies, if offered with your system,
observe the following guidelines:
viii
Page 9
D-Link DGS-3224SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
– Install the power supply before connecting the power cable to the power supply.
– Unplug the power cable before removing the power supply.
– If the system has multiple sources of power, disconnect power from the system by
unplugging all power cables from the power supplies.
• Move products with care; ensure that all casters and/or stabilizers are firmly connected to the system.
Avoid sudden stops and uneven surfaces.
General Precautions for Rack-Mountable Products
Observe the following precautions for rack stability and safety. Also refer to the rack installation documentation
accompanying the system and the rack for specific caution statements and procedures.
Systems are considered to be components in a rack. Thus, "component" refers to any system as well as to various
peripherals or supporting hardware.
CAUTION: Installing systems in a rack without the front and side stabilizers
installed could cause the rack to tip over, potentially resulting in bodily injury under
certain circumstances. Therefore, always install the stabilizers before installing
components in the rack.
After installing system/components in a rack, never pull more than one component
out of the rack on its slide assemblies at one time. The weight of more than one
extended component could cause the rack to tip over and may result in serious
injury.
• Before working on the rack, make sure that the stabilizers are secured to the rack, extended to the floor,
and that the full weight of the rack rests on the floor. Install front and side stabilizers on a single rack or
front stabilizers for joined multiple racks before working on the rack.
Safety Instructions (continued)
Always load the rack from the bottom up, and load the heaviest item in the rack first.
Make sure that the rack is level and stable before extending a component from the rack.
Use caution when pressing the component rail release latches and sliding a component into or out of a rack; the
slide rails can pinch your fingers.
After a component is inserted into the rack, carefully extend the rail into a locking position, and then slide the
component into the rack.
Do not overload the AC supply branch circuit that provides power to the rack. The total rack load should not
exceed 80 percent of the branch circuit rating.
Ensure that proper airflow is provided to components in the rack.
Do not step on or stand on any component when servicing other components in a rack.
ix
Page 10

D-Link DGS-3224SR Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
NOTE: A qualified electrician must perform all connections to DC power and to
safety grounds. All electrical wiring must comply with applicable local or national
codes and practices.
CAUTION: Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the
absence of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical
inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is
available.
CAUTION: The system chassis must be positively grounded to the rack cabinet
frame. Do not attempt to connect power to the system until grounding cables are
connected. Completed power and safety ground wiring must be inspected by a
qualified electrical inspector. An energy hazard will exist if the safety ground cable
is omitted or disconnected.
Protecting Against Electrostatic Discharge
Static electricity can harm delicate components inside your system. To prevent static damage, discharge static
electricity from your body before you touch any of the electronic components, such as the microprocessor. You
can do so by periodically touching an unpainted metal surface on the chassis.
You can also take the following steps to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD):
1. When unpacking a static-sensitive component from its shipping carton, do not remove the component
from the antistatic packing material until you are ready to install the component in your system. Just
before unwrapping the antistatic packaging, be sure to discharge static electricity from your body.
2. When transporting a sensitive component, first place it in an antistatic container or packaging.
3. Handle all sensitive components in a static-safe area. If possible, use antistatic floor pads and
workbench pads and an antistatic grounding strap.
x
Page 11
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 1
Introduction
Switch Description
Features
Front-Panel Components
Back Panel Description
Plug-in Module Descriptions
Management Options
Switch Description
The DGS-3224SR is a modular Gigabit Ethernet backbone switch designed for adaptability and scalability. The
switch provides a management platform and uplink to backbone for a stacked group of twelve DGS-3224SR
Layer 2 switches in a ring or chain topology arrangement. Alternatively, the switch can utilize up to twelve
Gigabit Ethernet ports to function as a central distribution hub for other switches or switch groups, or routers.
The four built-in combination Gigabit ports have the option of being used as either 1000BASE-T or SFP Gigabit
connections.
Features
• 4 built-in combination 1000BASE-T/SFP ports
• Ring or chain topology switch stacking configuration for up to 12 additional DES-3224SR switches.
• 88 Gbps switching fabric capacity
• Supports 802.1D STP and 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree for redundant back up bridge paths
• Supports 802.1Q VLAN, IGMP snooping, 802.1p Priority Queues, port trunking, port mirroring
• Multi-layer Access Control (based on MAC address, IP address, VLAN, Protocol, 802.1p, DSCP)
• Quality of Service (QoS) customized control
• 802.1x (port-based) access control and Radius Client support
• Administrator-definable port security
• Per-port bandwidth control
• IEEE 802.3z and IEEE 802.3x compliant Flow Control for all Gigabit ports
• SNMP v.1, v.2, v.3 network management, RMON support
• Support optional external Redundant Power Supply
• Supports Web-based management.
• CLI management support
• DHCP and BOOTP Client support.
• Fully configurable either in-band or out-of-band control via RS-232 console serial connection.
• Telnet remote control console
• TFTP upgrade
• Traffic Segmentation
1
Page 12
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• SysLog support
• Simple Network Time Protocol
• Web GUI Traffic Monitoring
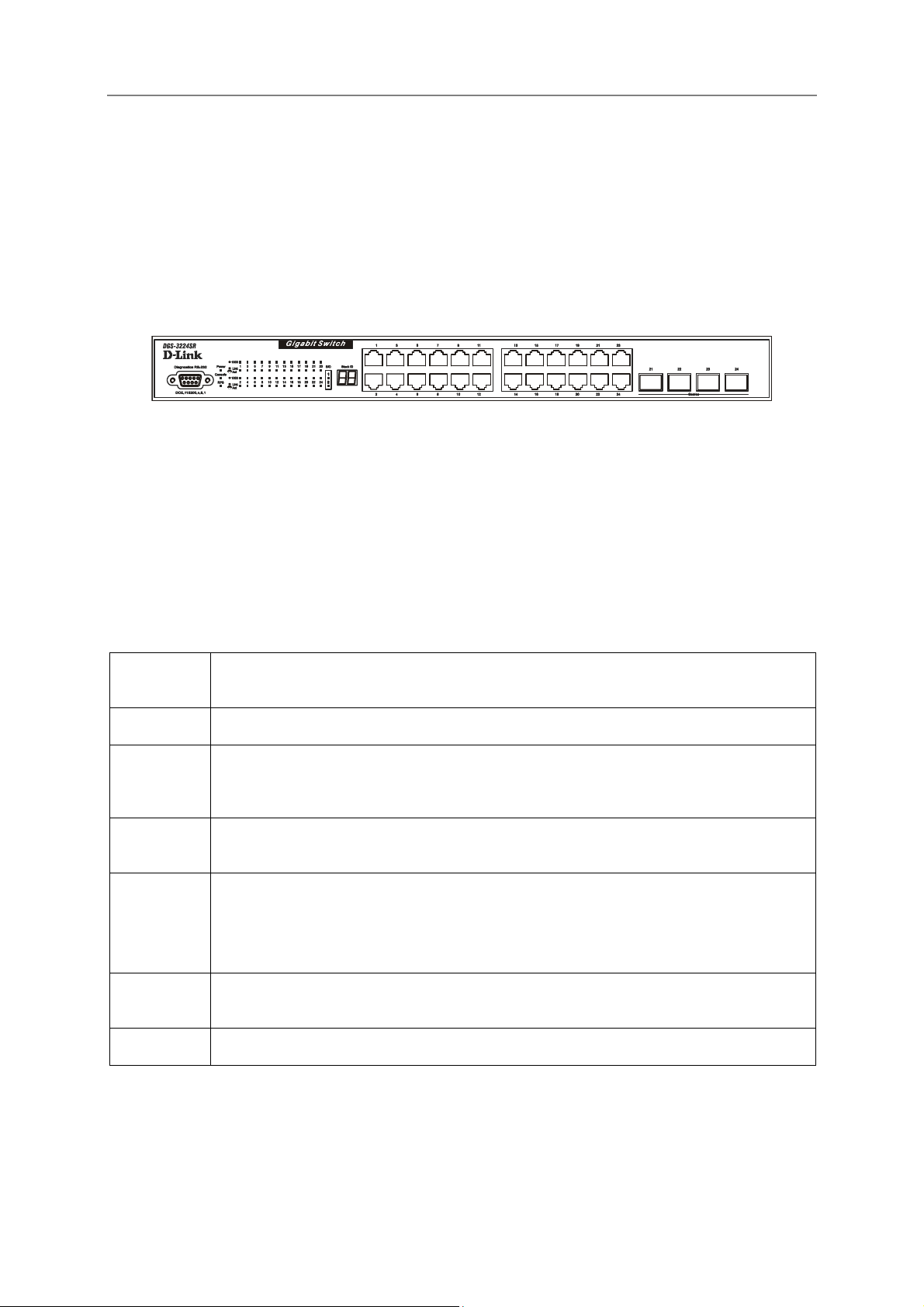
Front-Panel Components
The front panel of the Switch consists of LED indicators, an RS-232 communication port, and four SFP (MiniGBIC) combo ports.
Figure 1 - 1. Front Panel View of the switch
Comprehensive LED indicators display the status of the switch and the network.
An RS-232 DCE console port for setting up and managing the switch via a connection to a console terminal or
PC using a terminal emulation program.
LED Indicators
The LED indicators of the Switch include Power, Master, Console, and RPS (Redundant Power Supply). A bank
of 24 LEDs (2 for each port) indicates link, activity status and connection speed for each port
Power
Master
Console
RPS
1000
Link/Act
Stack ID
It will light green approximately 2 seconds after the switch is powered on to indicate
the ready state of the device.
Lights steady green when the Switch is configured as the Master Switch in a stack.
This indicator on the front panel should be lit during the Power-On Self Test (POST).
Lights green when the switch is being managed via out-of-band/local console
management through the RS-232 console port using a straight-through serial cable.
This indicator will light steady amber when an external power supply is supplying
power. This indicates the internal power supply has failed.
Each on-board Gigabit Ethernet port has a corresponding indicator. This will light
steady green for a valid link and blink whenever there is reception or transmission
(i.e. Activity--Act) of data occurring at a port.
The switch includes a 7-segment LED (labeled STACK ID) to indicate the switch
status in a stacked switch group.
SIO
Indicates which stacking port, if any, is in use.
2
Page 13

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Rear Panel Description
The rear panel of the switch contains an AC power connector, a connector for the Redundant Power Supply
(RPS) and two stacking ports.
Figure 1-2. Rear panel view of the Switch
The AC power connector is a standard three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug the female
connector of the provided power cord into this socket, and the male side of the cord into a power outlet. The
switch automatically adjusts its power setting to any supply voltage in the range from 100 ~ 240 VAC at 50 ~ 60
Hz.
RPS Connector
Connect the optional external redundant power supply to the RPS connector. If the switch’s internal power unit
fails, the redundant power system automatically supplies power to the switch for uninterrupted operation.
The switch supports the D-Link RPS-500 redundant power supply units.
3
Page 14

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Management Options
The system may be managed out-of-band through the console port on the front panel or in-band using Telnet or a
web browser.
Web-based Management Interface
After you have successfully installed the switch, you can configure the switch, monitor the LED panel, and
display statistics graphically using a web browser, such as Netscape Navigator (version 6.2 and higher) or
Microsoft
® Internet Explorer (version 5.0).
NOTE: To access the switch through a web browser, the computer
running the web browser must have IP-based network access to the
switch.
Command Line Console Interface Through the Serial Port or Telnet
You can also connect a computer or terminal to the serial console port or use Telnet to access the switch. The
command-line-driven interface provides complete access to all switch management features. For a full list of
commands, see the Command Line Reference, which is included on the documentation CD.
SNMP-Based Management
You can manage the switch with an SNMP-compatible console program. The switch is supports SNMP version
1.0, version 2.0 and version 3.0. The SNMP agent decodes the incoming SNMP messages and responds to
requests with MIB objects stored in the database. The SNMP agent updates the MIB objects to generate statistics
and counters.
The switch supports a comprehensive set of MIB extensions:
• RFC1213 MIB II
• RFC1493 Bridge
• RFC1757 RMON
• RFC 1643 Ether-like MIB
• D-Link Enterprise MIB
• 802.1p RFC2674
• RFC 2233 Interface MIB
• RFC 2618 (Radius-Auth-Client-MIB)
• RFC 2620 (Radius-Acc-Client-MIB)
• IEEE8021-PAE-MIB
• RFC2575 (VACM for SNMP)
• RFC2576 (Coexistence between SNMPs)
• RFC 1907 (SNMPv2-MIB)
• RSTP-MIB
• RFC2021 (RMON2)
• RFC2571 (SNMP Frameworks)
• RFC2572 (Message Processing for SNMP)
• RFC2573 (SNMP Applications)
• RFC2574 (USM for SNMP)
4
Page 15

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 2
Installation
Package Contents
Before You Connect to the Network
External Redundant Power System
Connecting the Console Port
Password Protection
SNMP Settings
IP Address Assignment
Connecting Devices to the Switch
Package Contents
Before you begin installing the switch, confirm that your package contains the following items:
• One DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Switch
• Mounting kit: 2 mounting brackets and screws
• Four rubber feet with adhesive backing
• One AC power cord
• This User’s Guide
• CLI Reference
• CD-ROM with User’s Guide and CLI Reference
2
Page 16
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Before You Connect to the Network
NOTICE: Do not connect the switch to the network until you have established
the correct IP settings.
Before you connect to the network, you must install the switch on a flat surface or in a rack, set up a terminal
emulation program, plug in the power cord, and then set up a password and IP address.
The switch is supplied with rubber feet for stationing it on a flat surface and mounting brackets and screws for
mounting the switch in a rack.
NOTICE: Do not connect the stacked switch group to the network until you have
properly configured all switches for switch stacking. An improperly configured
switch stack can cause a broadcast storm.
Installing the Switch Without the Rack
1. Install the switch on a level surface that can safely support the weight of the switch and its attached
cables. The switch must have adequate space for ventilation and for accessing cable connectors.
2. Set the switch on a flat surface and check for proper ventilation. Allow at least 5 cm (2 inches) on each
side of the switch and 15 cm (6 inches) at the back for the power cable.
3. Attach the rubber feet on the marked locations on the bottom of the chassis.
4. The rubber feet, although optional, are recommended to keep the unit from slipping.
Figure 2-1. Install rubber feet for installations with or without a rack
3
Page 17
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
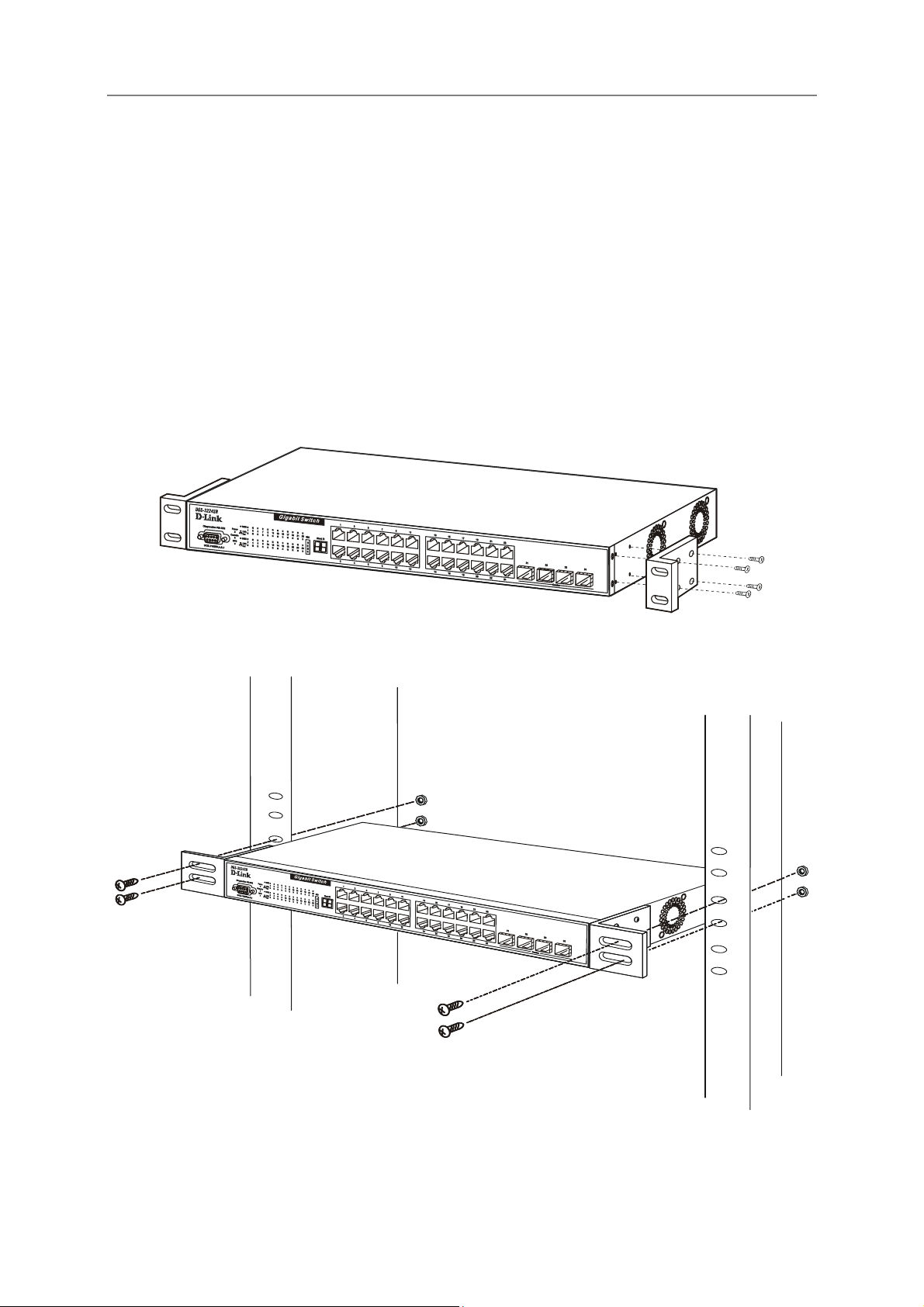
Installing the Switch in a Rack
You can install the switch in most standard 19-inch (48.3-cm) racks. Refer to the illustrations below.
1. Use the supplied screws to attach a mounting bracket to each side of the switch.
2. Align the holes in the mounting bracket with the holes in the rack.
3. Insert and tighten two screws through each of the mounting brackets.
Figure 2-2. Attach mounting brackets
Figure 2-3. Install switch in equipment rack
4
Page 18
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
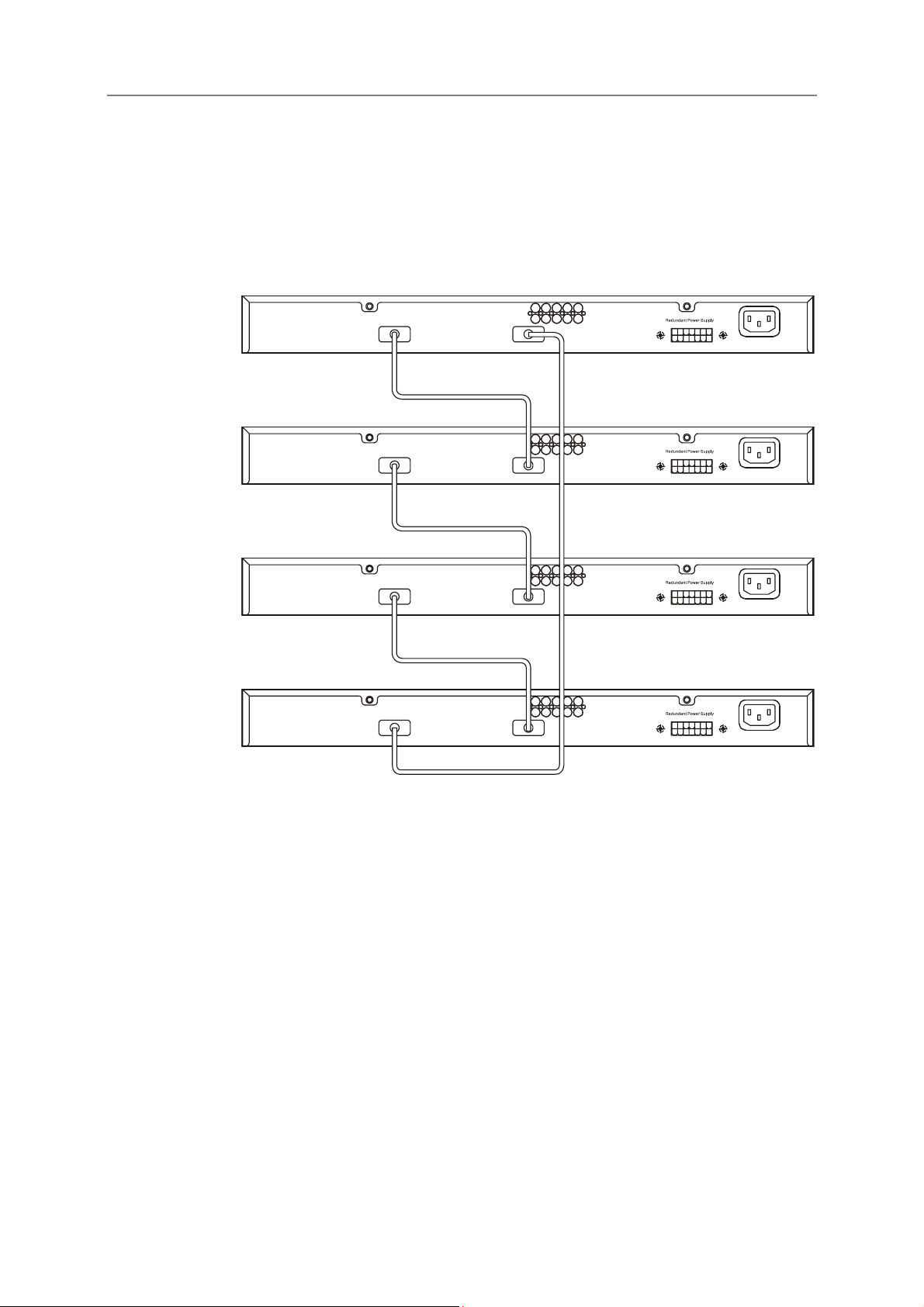
Connecting Stacked Switch Groups
Up to 12 Switches can be stacked together for Ring mode or Chain mode to a Master Unit or in tandem with a
second master unit via the second 10Gig stacking port. Users can add unit to reach maximum 288 GbE ports per
Ring stack or 168 GbE ports per Star stack. Switches are stacked together through a high-speed stack cables that
provide high speed of multiple Gigabit connections, allowing the entire stack to perform as a single IP entity.
User can see the number of switches stacked together from 7-segment display on front panel. Please refer to the
diagram below.
Figure 2-4. Ring (Bus) Topology
Please note that the DGS-3324SRi is needed to connect a group of Switches in the Star topology, as shown
below.
5
Page 19
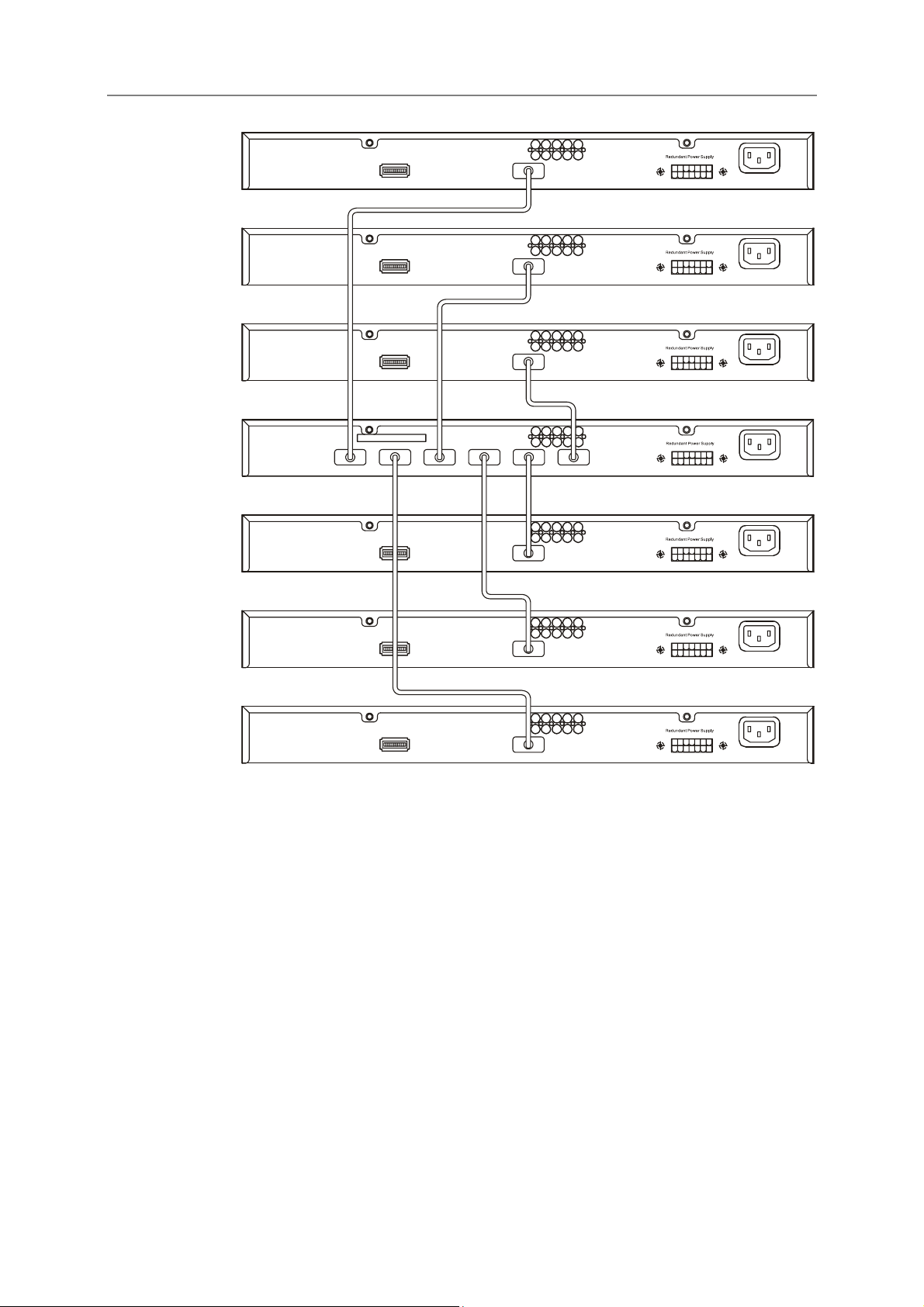
DGS-3224SRi
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 2-5. Star Topology Stacked Switch Group
The stacking ports are designated 1 and 2, and the stacking port being used will have its matching LED (on the
front panel) light a steady green when in use. Connection can be made from any stacking port to any other
stacking port. That is, stacking port 1 may connect to 1 or 2, and stacking port 2 may connect to 2 or 1
Configuring a Switch Group for Stacking
Follow the instructions below to configure the DGS-3224SR as the designated Master, and then to configure the
slave units.
To configure the DES-3224SR to function in a stacked group as a master, do the following:
1. At the CLI login prompt, enter config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 1
and press the Enter key. (Where the lowest priority number in a stack is always the Master, i.e. 2 would
have a higher priority than 5.)
2. Successful configuration will be verified by a Success message. It takes a few seconds for the change to
take effect. See the example below for the DES-3224SR.
3. Be sure to save the configuration change using the CLI command save.
4. Reboot the Switch.
6
Page 20

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
DGS-3223Sr:4#config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 1
Command: config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 1
Success.
DES-3224SR:4#............
DES-3224SR:4#
To configure the same DGS-3224SR to function in a stacked group as the Slave, do the following:
1. At the CLI login prompt, enter config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 2
and press the Enter key.
2. Successful configuration will be verified by a Success message. It takes a few seconds for the change to
take effect. See the example below for the DGS-3224SR.
3. Be sure to save the configuration change using the CLI command save.
DGS-3224SR:4#config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 2
Command: config config box_priority current_box_id 1 priority 2
Success.
DGS-3224SR:4#...................................................................
Note: Make sure that each box has a different ID. No two boxes can have the same ID.
Unit ID Display for Switches in a Switch Stack
The Stack ID. 7-segment LED (as shown below) on the front panel displays the Stack ID of the Switch. Please
also note that the Master LED is lit, indicating that this Switch is the Master unit in the stack.
Gigabit Combo Ports
In addition to the 24 10/100/1000 Mbps ports, the Switch features four Mini-GBIC Combo ports. These four
ports are 10/100/1000BASE-T copper ports (built-in) and Mini-GBIC ports (optional). Please note that the MiniGBIC ports are used instead of the built-in 10/100/1000BASE-T ports. The Mini-GBIC ports will not work
simultaneously with its corresponding 10/100/1000BASE-T port. For example, if port 24x is used on the Mini
GBIC module, port 24 is not available for the 10/100/1000BASE-T built-in port, and vice versa.
7
Page 21
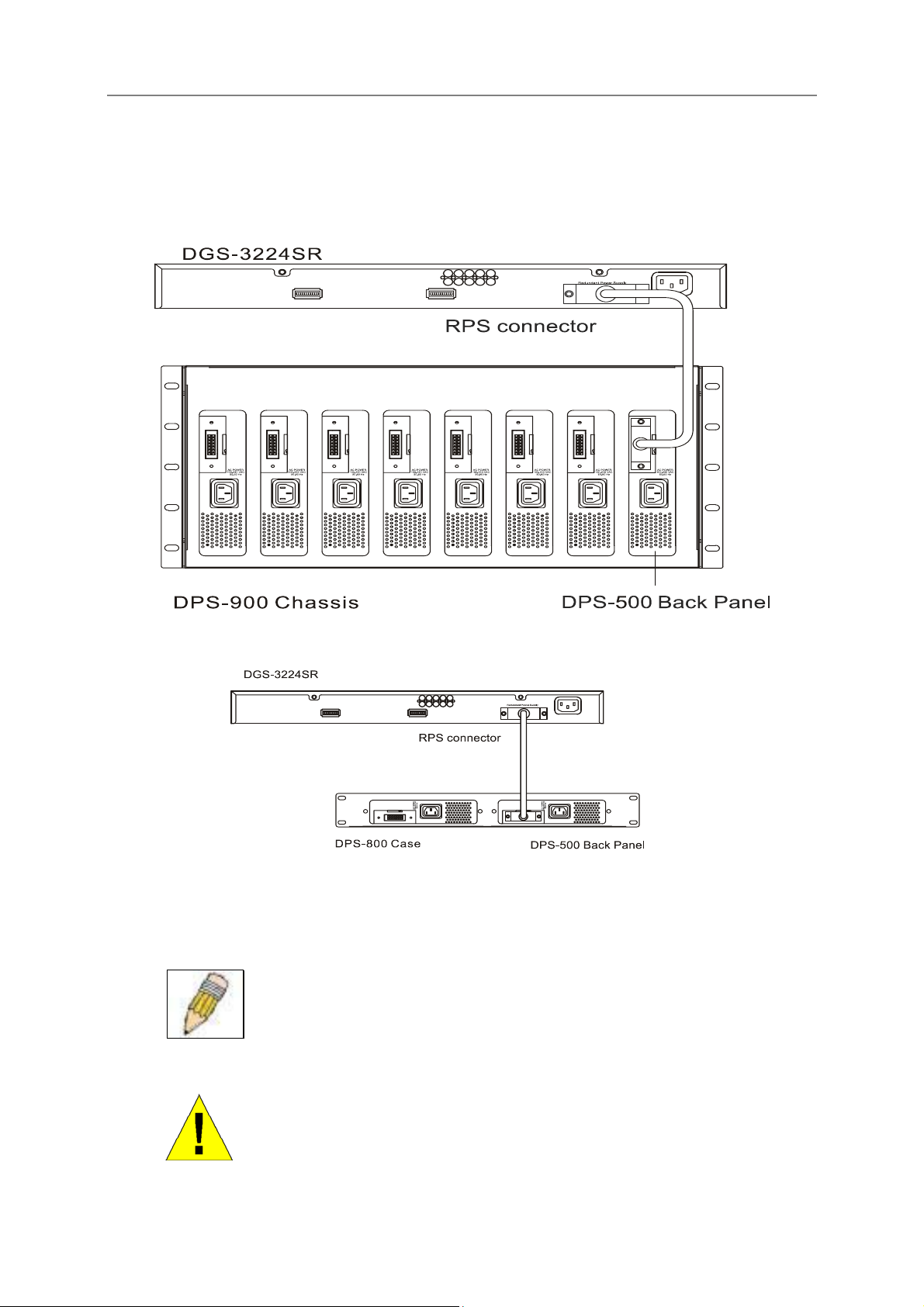
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
External Redundant Power System
The switch supports an external redundant power system.
Figure 2-6. DPS-500 with DES-3224SR
Figure 2-7. DPS-800 with DES-3224SR
NOTE: See the DPS-500 documentation for more information.
CAUTION: Do not use the switch with any redundant power system other than
the DPS-500.
8
Page 22

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Connecting the Console Port
The switch provides an RS-232 serial port that enables a connection to a computer or terminal for monitoring
and configuring the switch. This port is a DB-9 connector, implemented as a DCE connection.
To use the console port, you need the following equipment:
• A terminal or a computer with both a serial port and the ability to emulate a terminal
• A RS-232 cable with a female DB-9 connector for the console port on the switch
To connect a terminal to the console port:
1. Connect the RS-232 cable directly to the console port on the switch, and tighten the captive retaining
screws.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to a terminal or to the serial connector of a computer running
terminal emulation software. Set the terminal emulation software as follows:
1. Select the appropriate serial port (COM port 1 or COM port 2).
3. Set the data rate to 115200 baud.
4. Set the data format to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity.
5. Set flow control to
6. Under Properties, select VT100 for Emulation mode.
7. Select Terminal keys for Function, Arrow, and Ctrl keys. Ensure that you select Terminal
keys (not Windows keys).
none.
NOTICE: When you use HyperTerminal with the Microsoft® Windows® 2000
operating system, ensure that you have Windows 2000 Service Pack 2 or later
installed. Windows 2000 Service Pack 2 allows you to use arrow keys in
HyperTerminal’s VT100 emulation. See www.microsoft.com for information on
Windows 2000 service packs.
8. After you have correctly set up the terminal, plug the power cable into the power receptacle on
the back of the switch. The boot sequence appears in the terminal.
9. After the boot sequence completes, the console login screen displays.
10. If you have not logged into the command line interface (CLI) program, press the Enter key at
the User name and password prompts. There is no default user name and password for the
switch, user names and passwords must first be created by the administrator. If you have
previously set up user accounts, log in and continue to configure the Switch.
11. Enter the commands to complete your desired tasks. Many commands require administratorlevel access privileges. Read the next section for more information on setting up user accounts.
See the Command Line Reference on the documentation CD for a list of all commands and
additional information on using the CLI.
12. When you have completed your tasks, exit the session with the logout command or close the
emulator program.
9
Page 23
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Password Protection
The DGS-3224SR does not have a default user name and password. One of the first tasks when settings up the
switch is to create user accounts. If you log in using a predefined administrator-level user name you have
privileged access to the switch’s management software.
After your initial login, define new passwords for both default user names to prevent unauthorized access to the
switch, and record the passwords for future reference.
To create an administrator-level account for the switch, do the following:
1. At the CLI login prompt, enter create account admin followed by the <user name> and press
the Enter key.
2. You will be asked to provide a password. Type the <password> used for the administrator
account being created and press the Enter key.
3. You will be prompted to enter the same password again to verify it. Type the same password
and press the Enter key.
4. Successful creation of the new administrator account will be verified by a Success message.
User names and passwords can be up to 15 characters in length.
The sample below illustrates a successful creation of a new
administrator-level account with the user name “newmanager”.
NOTE: Passwords
are case sensitive.
DGS-3224SR:4#create account admin newmanager
Command: create account admin newmanager
Enter a case-sensitive new password:********
Enter the new password again for confirmation:********
Success.
NOTICE: CLI configuration commands only modify the running
configuration file and are not saved when the switch is rebooted. To save
all your configuration changes in nonvolatile storage, you must use the
save command to copy the running configuration file to the startup
configuration.
10
Page 24

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
SNMP Settings
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) function designed
specifically for managing and monitoring network devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read
and modify the settings of gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure
system features for proper operation, monitor performance and detect potential problems in the switch, switch
group or network.
Managed devices that support SNMP include software (referred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device.
A defined set of variables (managed objects) is maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device.
These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard presentation of
the information controlled by the on-board SNMP agent. SNMP defines both the format of the MIB
specifications and the protocol used to access this information over the network.
The DGS-3224SR supports the SNMP versions 1, 2c, and 3. You can specify which version of the SNMP you
want to use to monitor and control the switch. The three versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided
between the management station and the network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v.2, user authentication is accomplished using ‘community strings’, which function like
passwords. The remote user SNMP application and the switch SNMP must use the same community string.
SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are:
public - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
private - Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects.
SNMP v.3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts. The first part is to
maintain a list of users and their attributes that are allowed to act as SNMP managers. The second part describes
what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager.
The switch allows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges. The SNMP version
may also be set for a listed group of SNMP managers. Thus, you may create a group of SNMP managers that are
allowed to view read-only information or receive traps using SNMP v.1 while assigning a higher level of
security to another group, granting read/write privileges using SNMP v.3.
Using SNMP v.3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be restricted from
performing specific SNMP management functions. The functions allowed or restricted are defined using the
Object Identifier (OID) associated with a specific MIB. An additional layer of security is available for SNMP v.3
in that SNMP messages may be encrypted. To read more about how to configure SNMP v.3 settings for the
switch read the next section, Management.
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the Switch. The events can be as serious
as a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF the Switch), or less serious like a port status change. The Switch
generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network manager). Typical traps include trap messages
for Authentication Failure, Topology Change and Broadcast\Multicast Storm.
MIBs
Management and counter information are stored by the switch in the Management Information Base (MIB). The
Switch uses the standard MIB-II Management Information Base module. Consequently, values for MIB objects
can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network management software. In addition to the standard MIB-II, the
Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended Management Information Base. The
proprietary MIB may also be retrieved by specifying the MIB Object Identifier. MIB values can be either readonly or read-write.
11
Page 25

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IP Address Assignment
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an SNMP network
manager or other TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The switch’s default IP address is
10.90.90.90. You can change the default Switch IP address to meet the specification of your networking address
scheme.
The switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This MAC address cannot be changed, and
can be found from the initial boot console screen – shown below.
Figure 2 - 4. Boot Screen
The switch’s MAC address can also be found from the Web management program on the Switch Information
(Basic Settings) window on the Configuration menu.
The IP address for the switch must be set before it can be managed with the Web-based manager. The switch IP
address can be automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to
the switch must be known.
The IP address may be set using the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial port as follows:
1. Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP
interface named System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
2. Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s represent
the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the z represents the corresponding
number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask which can then be
used to connect a management station to the switch’s Telnet or Web-based management agent.
Figure 2 - 5. Assigning the Switch an IP Address
In the above example, the switch was assigned an IP address of 10.52.19.13 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0. The
system message Success indicates that the command was executed successfully. The switch can now be
configured and managed via Telnet and the CLI or via the Web-based management.
12
Page 26

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Connecting Devices to the Switch
After you assign IP addresses to the switch, you can connect devices to the switch.
To connect a device to an SFP transceiver port:
1. Use your cabling requirements to select an appropriate SFP transceiver type.
2. Insert the SFP transceiver (sold separately) into the SFP transceiver slot.
3. Use the appropriate network cabling to connect a device to the connectors on the SFP transceiver.
NOTICE: When the SFP transceiver acquires a link, the associated
integrated 10/100/1000BASE-T port is disabled.
13
Page 27

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 3
Introduction to Switch Management
Login to Web Manager
Web-based User Interface
Basic Setup
Switch Information
IP Address
User Accounts
Saving Changes
Factory Reset
Restart System
Introduction
All software functions of the DGS-3224SR can be managed, configured and monitored via the embedded webbased (HTML) interface. The switch can be managed from remote stations anywhere on the network through a
standard browser such as Netscape Navigator/Communicator or Microsoft Internet Explorer. The browser acts as
a universal access tool and can communicate directly with the Switch using the HTTP protocol.
The Web-based management module and the Console program (and Telnet) are different ways to access the same
internal switching software and configure it. Thus, all settings encountered in web-based management are the
same as those found in the console program.
Login to Web Manager
To begin managing your Switch simply run the browser you have installed on your computer and point it to the
IP address you have defined for the device. The URL in the address bar should read something like:
http://123.123.123.123, where the numbers 123 represent the IP address of the switch.
NOTE: The Factory default IP address for the switch is 10.90.90.90.
In the page that opens, click on the Login to make a setup button at the top of the window:
Figure 3-1. Login Page
14
Page 28
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
This opens the management module’s main page.
The switch management features available in the web-based manager are explained below.
Web-based User Interface
The user interface provides access to various switch configuration and management screens, allows you to view
performance statistics, and permits you to graphically monitor the system status.
Areas of the User Interface
The figure below shows the user interface. The user interface is divided into 3 distinct areas as described in the
table.
Area 1
Area 2
Area Function
Presents a graphical near real-time image of the front panel of the switch. This area
displays the switch’s ports and expansion modules, showing port activity, duplex
1
2
mode, or flow control, depending on the specified mode.
Various areas of the graphic can be selected for performing management functions,
including port configuration.
Select the menu or window to be displayed. The folder icons can be opened to
display the hyperlinked menu buttons and subfolders contained within them. Click
the D-Link logo to go to the D-Link website.
Area 3
Figure 3-2. Main Web-Manager Screen
3
Presents switch information based on your selection and the entry of configuration
data.
15
Page 29

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
NOTICE: Any changes made to the switch configuration during the current
session must be saved in the Save Changes web menu (explained below) or use
the command line interface (CLI) command save.
Web Pages
When you connect to the management mode of the switch with a web browser, a login screen is displayed. Enter
a user name and password to access the switch’s management mode.
Below is a list and description of the main folders available in the web interface:
Configuration folder: includes menus for port configuration, bandwidth control, link aggregation, port
mirroring, VLANs configuration, Spanning Tree Protocol setup, forwarding & filtering configuration, Quality of
Service, broadcast/multicast storm controls (Traffic Control), IGMP snooping, static router ports setup, SysLog
server setup, port security, SNTP settings and the access profile table. This also contains the Advanced Settings
menu which is used to configure miscellaneous settings such as for the serial port, MAC address aging time, and
to enable/disable the following: RMON, IGMP snooping, Telnet and web management access, traffic
segmentation, and 802.1x. The Switch Information page is used to enter system contact and physical location
information and lists basic information such as the switch’s MAC address, current firmware version and the
modules installed.
Security Management: contains 802.1x settings including Radius server information and PAE setup and
security management IP station setup.
SNMP Manager: contains menus for establishing the switch IP settings, user accounts configuration and SNMP
setup including SNMP v.3 configuration.
Monitoring: includes menus for monitoring switch performance monitors, MAC address table information,
router port information, IGMP Snooping information and 802.1x related information.
Maintenance: contains menus for upgrading firmware and saving configuration files (TFTP Services), saving
configuration changes, resetting and rebooting the switch, Ping test and logging out of the web manager.
NOTE: Be sure to configure the user name and password in the User
Accounts menu before connecting the switch to the greater network.
Basic Setup
The subsections below describe how to change some of the basic settings for the switch such as changing IP
settings and assigning user names and passwords for management access privileges, as well as how to save the
changes and restart the switch.
16
Page 30
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
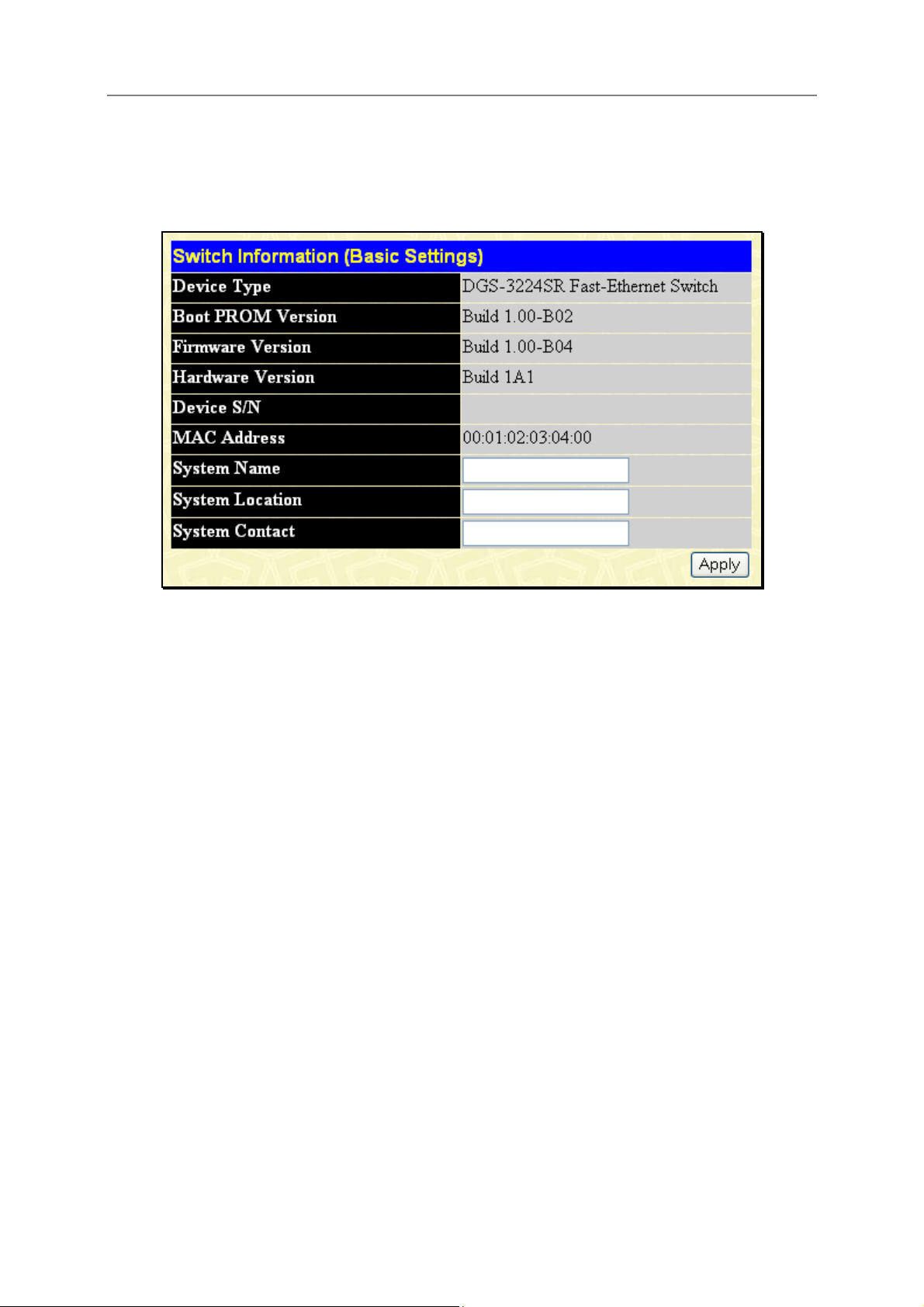
Switch Information
Click the Switch Information link in the Configuration menu.
Figure 3-3. Switch Information – Basic Settings
The Switch Information window shows the switch’s MAC Address (assigned by the factory and
unchangeable). In addition, the Boot PROM and Firmware Version numbers are shown. This information is
helpful to keep track of PROM and Firmware updates and to obtain the switch’s MAC address for entry into
another network device’s address table – if necessary.
You may assign a System Name, System Location, and System Contact. If any changes or additions are made,
click Apply.
17
Page 31

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Switch IP Settings
Switch IP settings may initially be set using the console interface prior to connecting to it through the Ethernet. If
the switch IP address has not yet been changed, read the Introduction of the CLI Reference or skip ahead to the
end of this section for a quick description of how to use the console port and CLI IP settings commands to
establish IP settings for the switch.
To change IP settings using the web manager you must access the IP Address menu located in the
Configuration folder.
To configure the switch’s IP address:
Open the Configuration folder and click the IP Address menu button. The web manager will display the
Switch IP Settings menu below.
Figure 3-4. Configure Switch IP Settings
NOTE: the switch’s factory default IP address is 10.90.90.90 with a subnet
mask of 255.0.0.0 and a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
To manually assign the switch’s IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address:
Select Manual from the Get IP From drop-down menu.
Enter the appropriate IP address and subnet mask.
If you want to access the switch from a different subnet from the one it is installed on, enter the IP address of the
gateway. If you will manage the switch from the subnet on which it is installed, you can leave the default address
(0.0.0.0) in this field.
If no VLANs have been previously configured on the switch, you can use the default VLAN ID (VID) 1. The
default VLAN contains all of the switch ports as members. If VLANs have been previously configured on the
switch, you will need to enter the VLAN ID of the VLAN that contains the port connected to the management
station that will access the switch. The switch will allow management access from stations with the same VID
listed here.
18
Page 32

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
To use the BOOTP or DHCP protocols to assign the switch an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
address:
Use the Get IP From: <Manual> pull-down menu to choose from BOOTP or DHCP. This selects how the
switch will be assigned an IP address on the next reboot.
The Switch IP Settings options are:
Parameter Description
BOOTP The switch will send out a BOOTP broadcast request when it is powered
up. The BOOTP protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default
gateways to be assigned by a central BOOTP server. If this option is set,
the Switch will first look for a BOOTP server to provide it with this
information before using the default or previously entered settings.
DHCP The switch will send out a DHCP broadcast request when it is powered up.
The DHCP protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default
gateways to be assigned by a DHCP server. If this option is set, the switch
will first look for a DHCP server to provide it with this information before
using the default or previously entered settings.
Manual Allows the entry of an IP address, Subnet Mask, and a Default Gateway for
the switch. These fields should be of the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each
xxx is a number (represented in decimal form) between 0 and 255. This
address should be a unique address on the network assigned for use by
the network administrator. The fields which require entries under this
option are as follows:
Subnet Mask A Bitmask that determines the extent of the subnet that the Switch is on.
Should be of the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number
(represented in decimal) between 0 and 255. The value should be
255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and
255.255.255.0 for a Class C network, but custom subnet masks are
allowed.
Default Gateway IP address that determines where packets with a destination address
outside the current subnet should be sent. This is usually the address of a
router or a host acting as an IP gateway. If your network is not part of an
intranet, or you do not want the Switch to be accessible outside your local
network, you can leave this field unchanged.
VID This allows the entry of a VLAN ID from which a management station will
be allowed to manage the switch using TCP/IP (in-band via web manager
or Telnet). Management stations that are on VLANs other than the one
entered in the VID field will not be able to manage the switch in-band
unless their IP addresses are entered in the Security IP Management
menu. If VLANs have not yet been configured for the switch, The default
VID (1) contains all of the switch’s ports. There are no entries in the
Security IP Management table, by default − so any management station
that can connect to the switch can access the switch until either a
management VLAN (see page 31) is specified or Management Station IP
Addresses (see page 20) are assigned.
19
Page 33

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
n
b
d
n
t
k
d
b
d
Setting the Switch’s IP Address using the Console Interface
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with a
SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP application (for example BOOTP, TFTP). The
switch’s default IP address is 10.90.90.90. You can change the default Switch IP address to
meet the specification of your networking address scheme.
The IP address for the switch must be set before it can be managed with the Webmanager. The switch IP address can be automatically set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, i
which case the actual address assigned to the switch must be known.
The IP address may be set using the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial por
as follows:
Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy. Where the x’s represent the IP address to be assigned to the
IP interface named System and the y’s represent the corresponding subnet mask.
Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z. Where the x’s
represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the z represents
the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mas
which can then be used to connect a management station to the switch’s Telnet or Web-base
management agent.
The system message Success indicates that the command was executed successfully. The
switch can now be configured and managed via Telnet and the CLI or via the Webmanagement agent using the above IP address to connect to the switch.
ase
ase
Security IP Management Stations Configuration
Go to the Security Management folder and click on Security IP; the following screen will appear.
Figure 3-5. Security IP Management Setup
Use the Management Station IP Settings to select up to three management stations used to manage the Switch. If
you choose to define one or more designated management stations, only the chosen stations, as defined by IP
address, will be allowed management privilege through the web manager or Telnet session. To define a
management station IP setting, type in the IP address and click on the Apply button.
20
Page 34

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
User Accounts Management
Use the User Accounts Control Table to control user privileges. To view existing User Accounts, open the
Security Management folder and click on the User Accounts link. This will open the User Account
Management page, as shown below.
Figure 3-6. User Accounts Management Table
To add a new user, click on the Add button. To modify or delete an existing user, click on the Modify button for
that user.
Figure 3-7. Add User Accounts Modify Table
Add a new user by typing in a User Name, and New Password and retype the same password in the Confirm
New Password. Choose the level of privilege (Admin or User) from the Access Right drop-down menu. To add
a user account using the CLI commands use create account and config account.
Figure 3-8. Modify User Accounts
21
Page 35

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Modify or delete an existing user account in the User Account Control Table – Edit. To delete the user account,
click on the Delete button. To change the password, type in the New Password and retype it in the Confirm
New Password entry field. Choose the level of privilege (Admin or User) from the Access Right drop-down
menu. To delete a user account using CLI use the command delete account. To change an existing account use
config account.
From the Main Menu, highlight Setup User Accounts and press Enter, then the User Account Management
menu appears.
Admin and User Privileges
There are two levels of user privileges: Admin and User. Some menu selections available to users with Admin
privileges may not be available to those with User privileges.
The following table summarizes the Admin and User privileges:
Management Admin User
Configuration
Network Monitoring
Community Strings and Trap Stations
Update Firmware and Configuration Files
System Utilities
Factory Reset
User Account Management
Add/Update/Delete User Accounts
View User Accounts
Admin and User Privileges
After establishing a User Account with Admin-level privileges, be sure to save the changes (see below).
Yes Read Only
Yes Read Only
Yes Read Only
Yes No
Yes Ping Only
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Saving Changes
Changes made to the switch’s configuration must be saved in order to retain them. Access the Save
Configuration by clicking the Save Changes button located in the Maintenance folder.
Figure 3-9. Save Configuration window
22
Page 36

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The switch has two levels of memory, normal RAM and non-volatile or NV-RAM. To save all the changes made
in the current session to the Switch’s flash memory, click the Save Configuration button. Click the OK button
in the new dialog box that appears to continue. When this is done, the settings will be immediately applied to the
switching software in RAM, and will immediately take effect. Once the switch configuration settings have been
saved to NV-RAM, they become the default settings for the switch. These settings will be used every time the
switch is rebooted.
Some settings, though, require you to restart the switch before they will take effect. Restarting the switch erases
all settings in RAM and reloads the stored settings from the NV-RAM. Thus, it is necessary to save all setting
changes to NV-RAM before rebooting the switch.
To save settings using CLI the command is save.
Factory Reset
Click the Factory Reset link in the Maintenance folder to bring up the reset menu.
Figure 3-10. Factory Reset to Default Value
Reset − returns all configuration settings except the switch’s IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, log, user
account and stack information settings to the factory default settings.
Reset Config − returns all configuration settings except the stack information settings to the factory default
settings, but does not save the settings or reboot the switch. If you select this option the switch configuration will
be returned to the factory default settings for the current session only. When the switch is rebooted, it will return
to the last configuration saved to the switch’s NV-RAM using the Save Changes option.
Reset System − returns switch configuration to the factory default settings and then saves the factory default
configuration to the switch’s NV-RAM. The switch will then reboot. When the switch has rebooted, it will have
the same configuration as when it was delivered from the factory.
Restart System
The following menu is used to restart the switch. Access this menu by clicking on the Reboot Device link in the
Maintenance folder.
Click the Yes after Do you want to save the settings? to instruct the switch to save the current configuration to
non-volatile RAM before restarting the switch.
Clicking the No option instructs the switch not to save the current configuration before restarting the switch. All
of the configuration information entered since the last time Save Changes was executed will be lost.
23
Page 37

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Click the Restart button to restart the switch.
Figure 3-11. Restart System
NOTE: clicking Yes is equivalent to executing Save Changes and then
restarting the switch.
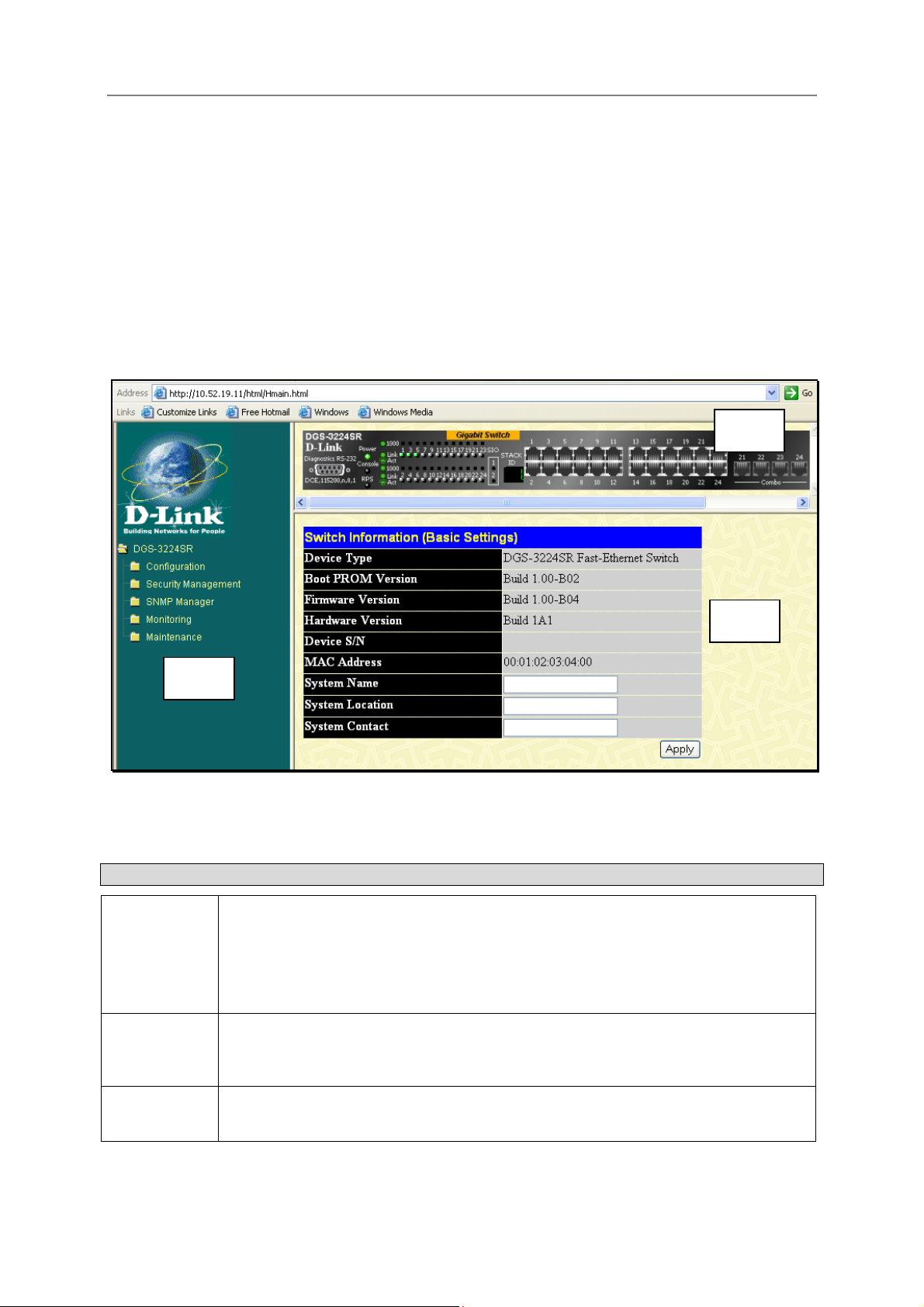
Switch Information
The first page displayed upon logging in presents the System Information menu. This page can be accessed at
any time by clicking the Switch Information button in the Configuration folder.
24
Page 38

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 3-12. Switch Information
The System Information page displays general information about the Switch including its MAC Address,
Hardware Boot PROM and Firmware versions, and other optional information.
You can also enter or change a System Name, System Location, and the name and telephone number of the
responsible administrator in the System Contact. It is recommended that the person responsible for the
maintenance of the network system be listed here. Click on the Apply button to make the changes effective.
To view this information using Telnet use CLI command show switch.
Advanced Settings
Figure 3-13. Switch Information − Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings menu options are summarized in the table below.
25
Page 39

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Variables in the Advanced Settings menu of the Web Manager and their corresponding CLI command groups are
the following:
Parameter Description
Serial Port Auto
Logout
Serial Port Baud
Rate
MAC Address Aging
Time
IGMP Snooping
Multicast Router
Only
Telnet Status
Select the logout time used for the console interface. This automatically
logs the user out after an idle period of time as defined. Choose from the
following options: 2 Minutes, 5 Minutes, 10 Minutes, 15 Minutes or Never.
Fixed at 115200.
This field specifies the length of time a learned MAC Address will remain in
the forwarding table without being accessed (that is, how long a learned
MAC Address is allowed to remain idle). The default age-out time for the
Switch is 300 seconds. To change this, type in a different value
representing the MAC address age-out time in seconds. The Aging Time
can be set to any value between 10 and 1,000,000 seconds.
To enable system-wide IGMP Snooping capability select Enabled. IGMP
snooping is Disabled by default. Enabling IGMP snooping allows you to
specify use of a multicast router only (see below). To configure IGMP
Snooping for individual VLANs, use the IGMP Snooping page under the
IGMP folder.
If this option is enabled and IGMP Snooping is also enabled, the switch
forwards all multicast traffic to a multicast-enabled router only. Otherwise,
the switch will forward all multicast traffic to any IP router.
Telnet configuration is Enabled by default. If you do not want to allow
configuration of the system through Telnet choose Disabled.
Web Status
RMON Status
GVRP
Link Aggregation
Algorithm
Switch 802.1x
Auth Protocol
HOL Prevention
State
Jumbo Frame
Syslog State
Web-based management is Enabled by default. If you choose to disable
this by selecting Disabled, you will lose the ability to configure the system
through the web interface as soon as these settings are applied.
Remote monitoring (RMON) of the switch is Enabled or Disabled here.
Use this pull-down menu to Enable or Disable GVRP on the switch.
The algorithm that the switch uses to balance the load across the ports that
make up the port trunk group is defined by this definition. Choose Source
Address, Destination Address or Both. (See Link Aggregation).
Enables or disables 802.1x VLANs; default is Disabled.
Fixed at Radius Eap.
Enables or disables HOL (Head of Line) prevention; default is Enabled.
Enables or disables Jumbo Frame acceptance; default is Disabled.
Enables or disables Syslog State; default is Disabled.
26
Page 40

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 4
Switch Stack Management
The DGS-3224SR switch can be used as a standalone high-capacity switch or be used in a stacked arrangement.
One stacking module can be installed to stack up to 4 additional slave switch units or two modules can be
installed to stack up to 8 additional slave switch units. Please read the relevant information in Sections 1 and 2
for more information.
Stacking Information
To change a switch’s default stacking configuration (for example, the order in the stack), you must use the
console Command Line Interface.
The number of switches in the switch stack (up to 12 − total) are displayed in the upper right-hand corner of your
web-browser. The icons are in the same order as their respective Unit numbers, with the Unit 1 switch
corresponding to the icon in the upper left-most corner of the icon group.
When the switches are properly interconnected through their optional Stacking Modules, information about the
resulting switch stack is displayed under the Stack Information link.
To view the stacking information, click on the Stacking Information link from the Monitoring folder:
Figure 4-1. Stacking Information
Box ID − displays the switch’s order in the stack.
Type − displays the model name of the corresponding switch in a stack.
User Set – Box ID can be assigned automatically (Auto), or can be assigned statically. Default is Auto.
Exist – Denotes whether a switch does or does not exist in a stack.
27
Page 41

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Priority – Displays the priority ID of the Switch. The lower the number, the higher the priority. The box
(switch) with the lowest priority number in the stack is the Master switch.
PROM Version – Shows the PROM in use for the Switch. This may be different from the values shown in the
illustration.
H/W Version – Shows the hardware version in use for the Switch. This may be different from the values shown
in the ullustration.
Runtime Version – Shows the firmware version in use for the Switch. This may be different from the values
shown in the illustrations.
The switch’s current order in the switch stack is also displayed on the front panel, under the STACK NO.
heading.
Alternatively, the stacking order can be manually assigned using the console’s Command Line Interface (CLI).
You can use the show stack_information command to display the current switch stack information. The syntax
of the show stack_information command is as follows:
show stack_information
Using the optional parameter mode displays only the stacking mode of the switches in the switch stack.
Entering the show stack_information command returns all of the relevant stacking information for all of the
switches in the stack:
Figure 4-2. Console CLI show stack_information command
The same switch stack information is displayed in the console as is displayed in the Web-based management
agent.
To modify the box ID, use the config box_id command, first identifying the current box ID and then assigning a
new box ID, as follows:
28
Page 42

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Use the following command to modify all box_id to become AUTO or static (apply current box id to User Set),
use the following syntax:
Config all_box_id [auto_mode|static_mode]
The config box_priority command allows you to configure the switch stack manually.
The syntax of the config box_priority command is as follows:
config box_priority current_box_id <1-12> priority <1-16>
Where the highest priority is assigned to the lowest value, i.e. 2 is a higher priority than 5.
Note: Box-priority settings will take effect after the switch is rebooted.
Figure 4-3. Config box_priority Command
You can then use the show stack_information command. Or, to see the status of only existing switches, use the
command show device_status. The resulting screen shows the status of internal and external power systems and
also shows the status of the cooling fans on each device. Click on Esc to return to the CLI screen.
29
Page 43

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
30
Page 44

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 5
VLAN Configuration
The first half of this section describes how to use the web manager to configure VLANs in the switch. This is
followed by a review of some of the basic concepts of VLANs in an Ethernet switching environment. For a
detailed list of CLI commands associated with VLAN management, please read the CLI reference guide.
To create or modify an 802.1Q VLAN:
In the Configuration folder, open the VLAN folder and click the Static VLAN Entry link to open the following
window:
Figure 5-1. 802.1Q Static VLANs
The 802.1Q Static VLANs menu lists all previously configured VLANs by VLAN ID and name. To delete an
existing 802.1Q VLAN, click the corresponding Delete button.
To create a new 802.1Q VLAN, click the Add button in the Static VLANs menu. A new menu appears, use this
to configure the port settings and to assign a unique name and number to the new VLAN. See the table below for
a description of the parameters in the new menu.
Figure 5-2. 802.1Q Static VLANs Entry Settings – Add
To change an existing 802.1Q VLAN entry, double-click on the selected entry in the 802.1Q Static VLANs
menu. A new menu appears, use this to configure the port settings and to assign a unique name and number to
the new VLAN. See the table below for a description of the parameters in the new menu.
31
Page 45

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 5-3. 802.1Q Static VLANs Entry Settings – Modify
The following fields can then be set in either the Add or Modify 802.1Q Static VLANs menus:
Parameter Description
VID (VLAN ID) Allows the entry of a VLAN ID in the Add dialog box, or displays the VLAN
ID of an existing VLAN in the Edit dialog box. VLANs can be identified by
either the VID or the VLAN name.
VLAN Name
Port
Tag
Egress
Forbidden
Allows the entry of a name for the new VLAN in the Add dialog box, or for
editing the VLAN name in the Edit dialog box.
Allows an individual port to be specified as member of a VLAN.
Specifies the port as either 802.1Q tagging or 802.1Q untagged. Checking
the box will designate the port as Tagged.
Select this to specify the port as a static member of the VLAN. Egress
member ports are ports that will be transmitting traffic for the VLAN. These
ports can be either tagged or untagged.
Select this to specify the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that
the port is forbidden from becoming a member of the VLAN dynamically.
GVRP Setting
In the Configuration menu, open the VLANs folder and click GVRP Setting.
The Port VLAN ID (PVID) dialog box, shown below, allows you to determine whether the switch will share its
VLAN configuration information with other GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enabled switches. In
addition, Ingress Checking can be used to limit traffic by filtering incoming packets whose PVID does not
match the PVID of the port.
32
Page 46

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 5-4. GVRP Setting
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
Displays the Unit ID of the switch − within the switch stack − that the VLAN
will be created on.
These two fields allow you to specify the range of ports that will be
From/To
included in the Port-based VLAN that you are creating using the 802.1Q
Port Settings page.
A Port VLAN Identifier is a classification mechanism that associates a port
with a specific VLAN and is used to make forwarding decisions for
PVID
untagged packets received by the port. For example, if port #2 is assigned
a PVID of 3, then all untagged packets received on port #2 will be assigned
to VLAN 3. This number is generally the same as the VID# number
assigned to the port in the Edit 802.1Q VLANs menu above.
GVRP State
The Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to
dynamically become a member of a VLAN. GVRP is disabled by default.
This field can be toggled using the space bar between Enabled and
Disabled. Enabled enables the port to compare the VID tag of an incoming
Ingress Check
packet with the PVID number assigned to the port. If the two are different,
the port filters (drops) the packet. Disabled disables Ingress filtering.
Ingress Checking is disabled by default.
33
Page 47

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Configure 802.1Q Static VLANs
The following figures and tables describe how to set up static VLANs on the switch. Click on the Static VLAN
Entry link in the VLANs folder to open the 802.1Q Static VLANs page, as shown below.
Figure 5-5. 802.1Q Static VLANs Page
The Static VLANs menu lists existing VLANs by their VLAN ID (VID) and by name. To create a new VLAN,
click the Add button to the upper left of the table. To edit an existing VLAN, double-click on the VLAN you
want to edit. To eliminate an entire VLAN, click on the “X” button for the VLAN you wish to delete.
The user configurable settings are the same when you Add or Modify a VLAN. Read the next section for a
description of these settings.
Add a Static 802.1Q VLAN
The following figure and table describe the parameters that must be configured to add an 802.1Q VLAN on the
switch. Click the Show All Static VLAN Entries link to return to the 802.1Q Static VLAN Entries table.
Figure 5- 6. 802.1Q Static VLANs Entry Settings – Add Screen
Parameter Description
Unit
VID (VLAN ID)
VLAN Name
Displays the Unit ID of the switch − within the switch stack − that the VLAN
will be created on.
The VLAN ID of the VLAN that is being created.
The name of the VLAN that is being created.
34
Page 48

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Port
Tag
None
Egress
Corresponds to the ports that will be members of the VLAN.
Specifies the port as either 802.1Q tagging or 802.1Q untagging.
Checking the box will designate the port as Tagging.
Specifies the port as not being a static member of the VLAN, but with no
restrictions for joining the VLAN dynamically through GVRP.
Specifies the port as being a static member of the VLAN. Egress Member
Ports are ports that will be transmitting traffic for the VLAN.
Edit 802.1Q VLANs
The following figure and table describe how to edit an existing 802.1Q VLAN entry on the switch.
Figure 5-7. 802.1Q Static VLANs Entry Settings – Edit Screen
The Static VLANs Edit screen presents the current configuration of the VLAN. Use this screen to change
settings for the VLAN as described in the table below. Click the Show All Static VLAN Entries
return to the Current VLAN Entries table.
Parameter Description
Unit
VID (VLAN ID)
VLAN Name
Port
Tag
Displays the Unit ID of the switch − within the switch stack − that the VLAN
will be created on.
The VLAN ID of the VLAN that is being created.
The name of the VLAN that is being created.
Corresponds to the ports that will be members of the VLAN.
Specifies the port as either 802.1Q tagging or 802.1Q untagging.
Checking the box will designate the port as Tagging.
35
hyperlink to
Page 49

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
None
Egress
Click the Apply button to let your changes take effect.
Specifies the port as not being a static member of the VLAN, but with no
restrictions for joining the VLAN dynamically through GVRP.
Specifies the port as being a static member of the VLAN. Egress Member
Ports are ports that will be transmitting traffic for the VLAN.
GVRP Settings
Select VLANs in the Configuration folder, then open GVRP Settings and select the Unit and range of ports to
configure. For the selected port or group of ports, choose to enable or disable Ingress checking and establish an
acceptable packet rule.
The following figure and table describe how to configure the 802.1Q VLAN port settings for the switch.
Figure 5-8. GVRP Settings Screen
Click Apply to let your changes take effect.
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To
Displays the Unit ID of the switch − within the switch stack − that the VLAN
will be created on.
These two fields allow you to specify the range of ports that will be
36
Page 50

Ingress Check
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
included in the Port-based VLAN that you are creating using the 802.1Q
Port Settings page.
This field can be toggled using the space bar between Enabled and
Disabled. Enabled enables the port to compare the VID tag of an incoming
packet with the PVID number assigned to the port. If the two are different,
the port filters (drops) the packet. Disabled disables Ingress filtering.
Ingress Checking is disabled by default.
PVID
GVRP
Shows the current PVID assignment for each port. The switch’s default is
to assign all ports to the Default VLAN with a VID of 1.
The PVID is used by the port to tag outgoing, untagged packets, and to
make filtering decisions about incoming packets. If the port is specified to
accept only tagged frames − as tagging, and an untagged packet is
forwarded to the port for transmission, the port will add an 802.1Q tag
using the PVID to write the VID in the tag. When the packet arrives at its
destination, the receiving device will use the PVID to make VLAN
forwarding decisions.
If a packet is received by the port, and Ingress filtering is enabled, the port
will compare the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are
unequal, the port will drop the packet. If the two are equal, the port will
receive the packet.
The Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to
dynamically become a member of a VLAN. GVRP is disabled by default.
Understanding VLANs
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic rather than physical location. End nodes that frequently
communicate with each other are assigned to the same VLAN, regardless of where they are located physically on
the network. Logically, a VLAN can be equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are forwarded
only to members of the VLAN on which the broadcast was initiated.
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
Some relevant terms:
Tagging - The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
Untagging - The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
Ingress port - A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the switch and VLAN decisions must be made.
Egress port - A port on a switch where packets are flowing out of the switch, either to another switch or to an
end station, and tagging decisions must be made.
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLANs are implemented on the DES-3224SR switch. 802.1Q VLANs require tagging,
which enables the VLANs to span an entire network (assuming all switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Qcompliant).
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging. The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
allow VLANs to work with legacy switches that don’t recognize VLAN tags in packet headers. The tagging
feature allows VLANs to span multiple 802.1Q VLAN compliant switches through a single physical connection
and allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
Packet forwarding decisions are made based upon the following three types of rules:
• Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of received frames belonging to a VLAN.
37
Page 51

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• Forwarding rules between ports – decides filter or forward the packet
• Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
Figure 5-9. IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag. There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC
address. Their presence is indicated by a value of 0x8100 in the EtherType field. When a packet’s EtherType
field is equal to 0x8100, the packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag. The tag is contained in the following
two octets and consists of 3 bits or user priority, 1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier (CFI – used for
encapsulating Token Ring packets so they can be carried across Ethernet backbones) and 12 bits of VLAN ID
(VID). The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p. The VID is the VLAN identifier and is used by the 802.1Q
standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLANs can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets. All of the information
contained in the packet originally is retained.
Figure 5-10. IEEE 802.1Q Tag
The EtherType and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address, but before the original
EtherType/Length or Logical Link Control. Because the packet is now a bit longer than it was originally, the
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) must be recalculated.
38
Page 52

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 5-11. Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q
compliant network device to another with the VLAN information intact. This allows 802.1Q VLANs to span
network devices (and indeed, the entire network – if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
Unfortunately, not all network devices are 802.1Q compliant. These devices are referred to as tag-unaware.
802.1Q devices are referred to as tag-aware.
Prior to the adoption of 802.1Q VLANs, port-based and MAC-based VLANs were in common use. These
VLANs relied upon a Port VLAN ID (PVID) to forward packets. A packet received on a given port would be
assigned that port’s PVID and then be forwarded to the port that corresponded to the packet’s destination address
(found in the switch’s forwarding table). If the PVID of the port that received the packet is different from the
PVID of the port that is to transmit the packet, the switch will drop the packet.
Within the switch, different PVIDs mean different VLANs. (Remember that two VLANs cannot communicate
without an external router). So, VLAN identification based upon the PVIDs cannot create VLANs that extend
outside a given switch (or switch stack).
Every physical port on a switch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assigned a PVID, for use within the switch. If
no VLANs are defined on the switch, all ports are then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1.
Untagged packets are assigned the PVID of the port on which they were received. Forwarding decisions are
based upon this PVID, insofar as VLANs are concerned. Tagged packets are forwarded according to the VID
contained within the tag. Tagged packets are also assigned a PVID, but the PVID is not used to make packetforwarding decisions, the VID is.
Tag-aware switches must keep a table to relate PVIDs within the switch to VIDs on the network. The switch will
compare the VID of a packet to be transmitted to the VID of the port that is to transmit the packet. If the two
VIDs are different, the switch will drop the packet. Because of the existence of the PVID for untagged packets
and the VID for tagged packets, tag-aware and tag-unaware network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID, but can have as many VIDs as the switch has memory in its VLAN table
to store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision must be made at each port on a tag-aware
device before packets are transmitted – should the packet to be transmitted have a tag or not? If the transmitting
port is connected to a tag-unaware device, the packet should be untagged. If the transmitting port is connected to
a tag-aware device, the packet should be tagged.
Tagging and Untagging
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagging or untagging.
Ports with tagging enabled will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the header of all
packets that flow into and out of it. If a packet has previously been tagged, the port will not alter the packet, thus
keeping the VLAN information intact. The VLAN information in the tag can then be used by other 802.1Q
compliant devices on the network to make packet forwarding decisions.
Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that flow into and out of those ports. If
the packet doesn’t have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the port will not alter the packet. Thus, all packets received by
39
Page 53

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
and forwarded by an untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN information. (Remember that the PVID is only
used internally within the switch). Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant network device
to a non-compliant network device.
Ingress Filtering
A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the switch and VLAN decisions must be made is referred to as
an ingress port. If ingress filtering is enabled for a port, the switch will examine the VLAN information in the
packet header (if present) and decide whether or not to forward the packet.
If the packet is tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will first determine if the ingress port itself is a
member of the tagged VLAN. If it is not, the packet will be dropped. If the ingress port is a member of the
802.1Q VLAN, the switch then determines if the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN. If it is not,
the packet is dropped. If the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the packet is forwarded and the
destination port transmits it to its attached network segment.
If the packet is not tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will tag the packet with its own PVID as a
VID (if the port is a tagging port). The switch then determines if the destination port is a member of the same
VLAN (has the same VID) as the ingress port. If it does not, the packet is dropped. If it has the same VID, the
packet is forwarded and the destination port transmits it on its attached network segment.
This process is referred to as ingress filtering and is used to conserve bandwidth within the switch by dropping
packets that are not on the same VLAN as the ingress port at the point of reception. This eliminates the
subsequent processing of packets that will just be dropped by the destination port.
40
Page 54

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 6
Port Settings Configuration
This section contains information for configuring various attributes and properties for individual physical ports,
including port security, traffic segmentation, port bandwidth control, serial port settings and port mirroring.
Basic Port Configuration
To configure basic port settings such as port speed, duplex and learning state use the Port Configuration menu.
Click the Port Configuration link in the Configuration folder:
Figure 6-1. Port Configuration
To configure switch ports:
1. Choose the Unit from the pull-down menu.
2. Choose the port or sequential range of ports using the From…To… port pull-down menus.
3. Use the remaining pull-down menus to configure the parameters described below:
Parameter Description
State <Enabled> Toggle the State <Enabled> field to either enable or disable a given port.
Speed/Duplex
<Auto>
Toggle the Speed/Duplex <Auto> field to either select the speed and
duplex/half-duplex state of the port. Auto – auto-negotiation between 10
and 100 Mbps devices, full- or half-duplex. The Auto setting allows the port
to automatically determine the fastest settings the device the port is
connected to can handle, and then to use those settings. The other options
are Gauto,10/Halfl, 10/Full, 100/Full, 100/Half, 1000/Full_M, and
1000Full_Sf. There is no automatic adjustment of port settings with any
option other than Auto.
41
Page 55

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Flow Control
Learning
Port Mirroring
Displays the flow control scheme used for the various port configurations.
Ports configured for full-duplex use 802.3x flow control, half-duplex ports
use backpressure flow control, and Auto ports use an automatic selection
of the two. The default is Disabled.
Enable or disable MAC address learning for the selected ports. When
Enabled, destination and source MAC addresses are automatically listed in
the forwarding table. When learning is Disabled, MAC addresses must be
manually entered into the forwarding table. This is sometimes done for
reasons of security or efficiency. See the section titled Forwarding and
Filtering for information on entering MAC addresses into the forwarding
table.
Figure 6-2. Port Mirroring window
The Switch allows you to copy frames transmitted and received on a port and redirect the copies to another port.
You can attach a monitoring device to the mirrored port, such as a sniffer or an RMON probe, to view details
about the packets passing through the first port.
To configure a mirror port,
1. Select the Source Port from where you want to copy frames and the Target Port, which receives the
copies from the source port.
2. Select the Source Direction, Ingress, Egress, or Both and change the Status drop-down menu to
Enabled.
3. Click Apply to let the changes take effect.
42
Page 56

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
NOTE: You cannot mirror a fast port onto a slower port. For example, if you try
to mirror the traffic from a 100 Mbps port onto a 10 Mbps port, this can cause
throughput problems. The port you are copying frames from should always
support an equal or lower speed than the port to which you are sending the copies.
Also, the target port for the mirroring cannot be a member of a trunk group.
Please note a target port and a source port cannot be the same port.
43
Page 57

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 7
Link Aggregation Configuration
Link aggregation allows several ports to be grouped together and to act as a single link. This gives a bandwidth
that is a multiple of a single link’s bandwidth.
Link aggregation is most commonly used to link a bandwidth intensive network device or devices – such as a
server – to the backbone of a network.
The switch allows the creation of up to 32 link aggregation groups, each group consisting of up of up to 8 links
(ports). A link aggregation group may not cross a 12-port boundary, starting with port 1 (a group may not contain
ports 12 and 13, for example) and all of the ports in the group must be members of the same VLAN. Further, the
aggregated links must all be of the same speed and should be configured as full-duplex.
Port security and 802.1x should not be enabled on any of the aggregated ports. The static multicast group
member must be identical among aggregated ports, and the STP port state must be identical among aggregated
ports.
The configuration of the Master port in the group becomes the configuration for all of the ports in the
aggregation group.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the ports in the aggregated group, and a link failure within the group
causes the network traffic to be directed to the remaining links in the group.
The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat a link aggregation group as a single link, on the switch level. On the port
level, the STP will use the port parameters of the Master Port in the calculation of port cost and in determining
the state of the link aggregation group. If two redundant link aggregation groups are configured on the switch,
STP will block one entire group – in the same way STP will block a single port that has a redundant link.
To configure port trunking, click on the Link Aggregation hyperlink in the Configuration folder to bring up the
Port Trunk Group Entries table:
Figure 7-1. Port Trunking Group Entry Table
To configure port trunk groups, click the Add button to add a new trunk group and use the menu Port Trunking
Configuration menu (see example below) to set up trunk groups. To modify a port trunk group, double-click on
it to bring up the Port Trunking Configuration menu. To delete a port trunk group, click the Delete option in
the Port Trunk Group Entries table.
44
Page 58

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 7-2. Link Aggregation Group Configuration
The user-changeable parameters are as follows:
Parameter Description
Group ID
Group Name
State
Select an ID number for the group.
Type in a name for the group (optional).
Trunk groups can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled. This is used
to turn a port trunking group on or off. This is useful for diagnostics, to
quickly isolate a bandwidth intensive network device or to have an absolute
backup aggregation group that is not under automatic control.
Type
This pull-down menu allows you to select between Static and LACP (Link
Aggregation Control Protocol.) LACP allows for the automatic detection of
links in a Port Trunking Group.
Master Port
Member Unit
Choose the Master port for the trunk group.
Choose the switch unit on which to set up a trunk group. Trunk groups
must be confined to ports on a single switch.
Flooding Port
A trunking group must designate one port to allow transmission of
broadcasts and unknown unicasts.
45
Page 59

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 8
Forwarding and Filtering
Static Unicast Forwarding
Open the Forwarding & Filtering folder in the Configuration menu and click on the Unicast Forwarding
link. This will open the Setup Static Unicast Forwarding Table, as shown below.
Figure 8-1. Static Unicast Forwarding Setup
To add an entry, define the following parameters in the Add an Entry field:
Parameter Description
VLAN ID
MAC Address
Allowed to Go to
Unit
Port
Click on the Add/Modify button to add a unicast MAC address to the switch’s forwarding table, or to modify a
previous entry.
The VLAN ID number of the VLAN on which the above Unicast MAC
address resides.
The MAC address to which packets will be statically forwarded. This must
be a unicast MAC address.
Allows the designation of the module on which the above MAC address
resides.
Choose the port on which the MAC address resides. Selecting Port 0
means no ports are allowed.
Static Multicast Forwarding
The following figure and table describe how to set up Multicast forwarding on the switch. Open the Forwarding
& Filtering folder and click on the Multicast Forwarding link to see the entry screen below:
46
Page 60

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 8-2. Setup Static Multicast Forwarding Table
The Static Multicast Forwarding Settings page displays all of the entries made into the switch’s static multicast
forwarding table. Click the Add button to open the Setup Static Multicast Forwarding Table, as shown
below.
Figure 8-3. Setup Static Multicast Forwarding Table
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
MAC Address
VID
The MAC address of the static source of multicast packets. This must be a
multicast MAC address.
The VLAN ID of the VLAN the above MAC address belongs to.
Allows the selection of ports that will be members of the static multicast
group and ports that are either forbidden from joining dynamically, or that
can join the multicast group dynamically, using GMRP. The options are;
Port Settings
None – no restrictions on the port dynamically joining the multicast group,
None is chosen, then an end station attached to the port can join the
multicast group using GMRP.
Egress – the port is a static member of the multicast group.
47
Page 61

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
48
Page 62

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 9
IGMP Settings
In order to use IGMP Snooping it must first be enabled for the entire Switch (see Advanced Settings). You may
then fine-tune the settings for each VLAN using the IGMP Snooping link in the Configuration folder. When
enabled for IGMP snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to a specific Multicast group member based on
IGMP messages sent from the device to the IGMP host or vice versa. The Switch monitors IGMP messages and
discontinues forwarding multicast packets when there are no longer hosts requesting that they continue.
Use the IGMP Snooping Group Entry Table to view IGMP Snooping status. To modify settings, click the
Modify button for the VLAN ID you want to change.
Figure 9-4. IGMP Snooping Entry Table
Clicking the Modify button will bring up the IGMP Snooping Settings menu.
Figure 9-5. IGMP Snooping Settings Screen
49
Page 63

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Parameter Description
Query Interval
Max Response Time
Robustness Variable
Last Member Query
Interval
Host Timeout
Route Timeout
The Query Interval field is used to set the time (in seconds) between
transmitting IGMP queries. Entries between 1 and 9,999 seconds are
allowed. Default = 125.
This determines the maximum amount of time in seconds allowed before
sending an IGMP response report. The Max Response Time field allows
an entry between 1 and 25 (seconds). Default = 10.
Adjust this variable according to expected packet loss. If packet loss on
the VLAN is expected to be high, the Robustness Variable should be
increased to accommodate increased packet loss. This entry field allows
an entry of 2 to 255. Default = 2.
Specifies the maximum amount of time between group-specific query
messages, including those sent in response to leave group messages.
Default = 1.
This is the maximum amount of time in seconds allowed for a host to
continue membership in a multicast group without the Switch receiving a
host membership report. Default = 260.
This is the maximum amount of time in seconds a route is kept in the
forwarding table without receiving a membership report. Default = 260.
This specifies the maximum amount of time in seconds between the
Leave Timer
Querier State
State
Switch receiving a leave group message from a host, and the Switch
issuing a group membership query. If no response to the membership
query is received before the Leave Timer expires, the (multicast)
forwarding entry for that host is deleted.
Choose Querier to enable transmitting IGMP Query packets or Non-
Querier to disable. The default value is Non-Querier.
Select Enabled to implement IGMP Snooping. This is Disabled by
default.
Static Router Ports
A static router port is a port that has a multicast router attached to it. Generally, this router would have a
connection to a WAN or to the Internet. Establishing a router port will allow multicast packets coming from the
router to be propagated through the network, as well as allowing multicast messages (IGMP) coming from the
network to be propagated to the router.
A router port has the following behavior:
• All IGMP Report packets will be forwarded to the router port.
• IGMP queries (from the router port) will be flooded to all ports.
• All UDP multicast packets will be forwarded to the router port. Because routers do not send IGMP
reports or implement IGMP snooping, a multicast router connected to the router port of the Layer 3
switch would not be able to receive UDP data streams unless the UDP multicast packets were all
forwarded to the router port.
50
Page 64

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
A router port will be dynamically configured when IGMP query packets, RIPv2 multicast, DVMRP multicast,
PIM-DM multicast packets are detected flowing into a port.
Open the IGMP folder and the click on the Static Router Ports Entry link to open the Current Static Router
Ports Entries page, as shown below.
Figure 9-6. Current Static Router Ports Screen
The Current Static Router Ports Entries page (shown above) displays all of the current entries to the Switch’s
static router port table. To add or modify an entry, click the Modify button. This will open the Static Router
Ports Settings page, as shown below.
Figure 9-7. Static Router Ports Settings Screen
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
VID (VLAN ID)
VLAN Name
Unit
Member Ports
This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN name, identifies the VLAN
where the multicast router is attached.
This is the name of the VLAN where the multicast router is attached.
This is the Unit ID of the switch in a switch stack for which you are creating
an entry into the switch’s static router port table.
There are the ports on the switch that will have a multicast router attached
to them.
51
Page 65

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
New IGMP Snooping Feature
In the DGS-3224SR, the user may configure a forbidden portlist, whose members are not forced to become
router ports.
To activate this feature, please use the console (CLI). The CLI command will be:
Config router_ports_forbidden
To disp[lay the forbidden portlist, the CLI command will be:
Show router_ports
52
Page 66

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 10
Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration
The switch supports 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP).
802.1d STP will be familiar to most networking professionals. However since 802.1w RSTP has been recently
introduced to D-Link managed Ethernet switches, a brief introduction to the technology is provided below
followed by a description of how to set up 802.1 d STP and 802.1w RSTP.
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
The Switch implements two versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol, the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
as defined by the IEE 802.1w specification and a version compatible with the IEEE 802.1d STP. RSTP can
operate with legacy equipment implementing IEEE 802.1d, however the advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) evolved from the 802.1d STP standard. RSTP was
developed in order to overcome some limitations of STP that impede the function of some recent switching
innovations, in particular, certain Layer 3 function that are increasingly handled by Ethernet switches. The basic
function and much of the terminology is the same as STP. Most of the settings configured for STP are also used
for RSTP. This section introduces some new Spanning Tree concepts and illustrates the main differences
between the two protocols.
Port Transition States
An essential difference between the two protocols is in the way ports transition to a forwarding state and the in
the way this transition relates to the role of the port (forwarding or not forwarding) in the topology. RSTP
combines the transition states disabled, blocking and listening used in 802.1d and creates a single state
Discarding. In either case, ports do not forward packets; in the STP port transition states disabled, blocking or
listening or in the RSTP port state discarding there is no functional difference, the port is not active in the
network topology. Table 5-7 below compares how the two protocols differ regarding the port state transition.
Both protocols calculate a stable topology in the same way. Every segment will have a single path to the root
bridge. All bridges listen for BPDU packets. However, BPDU packets are sent more frequently – with every
Hello packet. BPDU packets are sent even if a BPDU packet was not received. Therefore, each link between
bridges are sensitive to the status of the link. Ultimately this difference results faster detection of failed links, and
thus faster topology adjustment. A drawback of 802.1d is this absence of immediate feedback from adjacent
bridges.
802.1d STP 802.1w RSTP Forwarding? Learning?
Disabled Discarding No No
Blocking Discarding No No
Listening Discarding No No
Learning Learning No Yes
Forwarding Forwarding Yes Yes
Comparing Port States
RSTP is capable of more rapid transition to a forwarding state – it no longer relies on timer configurations –
RSTP compliant bridges are sensitive to feedback from other RSTP compliant bridge links. Ports do not need to
wait for the topology to stabilize before transitioning to a forwarding state. In order to allow this rapid transition,
the protocol introduces two new variables: the edge port and the point-to-point (P2P) port.
Edge Port
The edge port is a configurable designation used for a port that is directly connected to a segment where a loop
cannot be created. An example would be a port connected directly to a single workstation. Ports that are
designated as edge ports transition to a forwarding state immediately without going through the listening and
53
Page 67

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
learning states. An edge port loses its status if it receives a BPDU packet, immediately becoming a normal
spanning tree port.
P2P Port
A P2P port is also capable of rapid transition. P2P ports may be used to connect to other bridges. Under RSTP,
all ports operating in full-duplex mode are considered to be P2P ports, unless manually overridden through
configuration.
802.1d/802.1w Compatibility
RSTP can interoperate with legacy equipment and is capable of automatically adjusting BPDU packets to 802.1d
format when necessary. However, any segment using 802.1 STP will not benefit from the rapid transition and
rapid topology change detection of RSTP. The protocol also provides for a variable used for migration in the
event that legacy equipment on a segment is updated to use RSTP.
STP Switch Settings
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) operates on two levels: on the switch level, the settings are globally
implemented. On the port level, the settings are implemented on a per user-defined Group of ports basis.
Figure 10-1. STP Switch Settings
54
Page 68

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Configure the following parameters and click the Apply button to implement them:
Parameter Description
This field can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled using the pull-
Status <Disabled>
down menu. This will enable or disable the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP),
globally, for the switch.
The Max. Age can be set from 6 to 40 seconds. At the end of the Max.
Max Age: (6 - 40 sec)
<20 >
Age, if a BPDU has still not been received from the Root Bridge, your
Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other Switches for permission
to become the Root Bridge. If it turns out that your Switch has the lowest
Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.
Hello Time: (1 - 10
sec) < 2 >
Forward Delay: (4 30 sec) <15 >
The Hello Time can be set from 1 to 10 seconds. This is the interval
between two transmissions of BPDU packets sent by the Root Bridge to
tell all other Switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge.
The Forward Delay can be from 4 to 30 seconds. This is the time any port
on the Switch spends in the listening state while moving from the blocking
state to the forwarding state.
A Priority for the switch can be set from 0 to 61440. This number is used
Priority: (0 - 61440)
<32768>
in the voting process between switches on the network to determine which
switch will be the root switch. A low number indicates a high priority, and a
high probability that this switch will be elected as the root switch.
Choose RSTP (default) or STP Compatibility. Both versions use STP
STP Version<RSTP >
parameters in the same way. RSTP is fully compatible with IEEE 802.1d
STP and will function with legacy equipment.
Tx Hold Count <3 >
Forwarding BPDU
<Enabled >
This is the maximum number of Hello packets transmitted per interval. The
count can be specified from 1 to 10. Default value = 3.
This can enabled or disabled. When it is enabled it allows the forwarding of
STP BPDU packets from other network devices when STP is disabled on
the switch. The default is enabled.
Note: the Hello Time cannot be longer than the Max. Age. Otherwise, a configuration error will occur.
Observe the following formulas when setting the above parameters:
Max. Age ≤ 2 x (Forward Delay - 1 second)
Max. Age ≥ 2 x (Hello Time + 1 second)
55
Page 69

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
STP Port Settings
For stacked switch installations, first select the Unit to be configured.
Figure 10-2. STP Port Settings
In addition to setting Spanning Tree parameters for use on the switch level, the switch allows for the
configuration of groups of ports, each port-group of which will have its own spanning tree, and will require some
of its own configuration settings. An STP Group will use the switch-level parameters entered above, with the
addition of Port Priority and Port Cost.
An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge
concept is replaced with a root port concept. A root port is a port of the group that is elected on the basis of port
priority and port cost, to be the connection to the network for the group. Redundant links will be blocked, just as
redundant links are blocked on the switch level.
The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices). The port
level STP will block redundant links within an STP Group.
It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports.
56
Page 70

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To
State
Cost
Priority <128>
Migration <No>
This is the Unit ID of a switch in a switch stack. 15 indicates a DGS-
3224SR switch in standalone mode.
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected
port.
This drop-down menu allows you to Enable or Disable STP for the
selected group of ports.
A Port Cost can be set from 1 to 200000000. The lower the number, the
greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
Default port cost:
100Mbps port = 200000
Gigabit ports = 20000
A Port Priority can be from 0 to 240. The lower the number, the greater the
probability the port will be chosen as the Root Port.
Select Yes or No. Choosing Yes will enable the port to migrate from 802.1d
STP status to 802.1w RSTP status. RSTP can coexist with standard STP,
however the benefits of RSTP are not realized on a port where an 802.1d
network connects to an 802.1w enabled network. Migration should be
enabled (yes) on ports connected to network stations or segments that will
be upgraded to 802.1w RSTP on all or some portion of the segment.
Edge <No>
P2P <Yes>
Select Yes or No. Choosing Yes designates the port as an edge port. Edge
ports cannot create loops, however an edge port can lose edge port status
if a topology change creates a potential for a loop. An edge port normally
should not receive BPDU packets. If a BPDU packet is received it
automatically loses edge port status. No indicates the port does not have
edge port status.
Select Yes or No. Choosing Yes indicates a point-to-point (p2p) shared
link. These are similar to edge ports however they are restricted in that a
p2p port must operate in full-duplex. Like edge ports, p2p ports transition to
a forwarding state rapidly thus benefiting from RSTP.
57
Page 71

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 11
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS settings allow customization of packet priority in order to facilitate delivery of data traffic that might be
affected by latency problems. The IEEE 802.1p Priority specification uses 8 priority levels to classify data
packets. In 802.1p compliant devices, a tag inserted into the packet header is used to identify the priority level of
data packets.
The Switch implements 802.1p priority using 8 hardware queues. Note:
Individual ports may still be assigned priority using the 8 levels as defined by the 802.1p standard.
It is important to note that changes in a networks QoS scheme should be carefully considered, planned for and if
possible tested for efficiency. When set up properly, it QoS can allow efficient and timely delivery of data for
video conferencing or IP telephony without causing unacceptable delays of other network traffic. If QoS is not
well set up however, significant delays and excessive packet loss may result for data assigned to lower priority
queues.
Traffic Control (Broadcast/Multicast Storm Control)
Use the Traffic Control Setting menu to enable or disable storm control and adjust the threshold for multicast and
broadcast storms, as well as DLF (Destination Look Up Failure). Traffic control settings are applied to individual
Switch modules.
Figure 10-3. Traffic Control Settings
Traffic or storm control is used to stop broadcast, multicast or ARP request storms that may result when a loop is
created. The Destination Look Up Failure control is a method of shutting down a loop when a storm is formed
58
Page 72

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
because a MAC address cannot be located in the Switch’s forwarding database and it must send a packet to all
ports or all ports on a VLAN.
To configure Traffic Control, select the Unit (Unit ID of a switch in a switch) you want to configure. Broadcast
Storm, Multicast Storm and Destination Look Up Failure may be Enabled or Disabled. The Threshold value
is the upper threshold at which the specified traffic control is switched on. This is the number of Broadcast,
Multicast or DLF packets, in Kbps, received by the switch that will trigger the storm traffic control measures.
The Threshold value can be set from 0 to 255 packets. The Default setting is 128.
Configuring Default Priority
The switch allows the assignment of a default 802.1p priority to each port on the switch.
Click on the 802.1p Default Priority link:
Figure 10-4. Priority Based on a Port-group basis
This page allows you to assign a default 802.1p priority to any given port on the switch. The priority queues are
numbered from 0 − the lowest priority − to 7 − the highest priority.
59
Page 73

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Configuring 802.1p User Priority
The DGS-3224SR allows the assignment of a User Priority to each of the 802.1p priorities.
Figure 10-5. User Priority Configuration
Once you have assigned a priority to the port groups on the switch, you can then assign this Class to each of the
8 levels of 802.1p priorities.
QoS Output Scheduling Configuration
QoS can be customized by changing the output scheduling used for the hardware queues in the Switch. As with
any changes to QoS implementation, careful consideration should be given to how network traffic in lower
priority queues is affected. Changes in scheduling may result in unacceptable levels of packet loss or significant
transmission delay. If you choose to customize this setting, it is important to monitor network performance,
especially during peak demand as bottlenecks can quickly develop if the QoS settings are not suitable.
Figure 10-6. QoS Output Scheduling Configuring
60
Page 74

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Scheduling Mechanism − This drop-down menu allows you to select between a Weight Fair and a Strict
mechanism for emptying the priority queues.
Click Apply to let your changes take effect.
802.1p User Priority
The User Priority menu is used to map incoming packets with 802.1p priority tags to one of the 8 hardware
queues used on the Switch.
Note: Level 7 (the highest level) is reserved for internal control packets.
Figure 10-7. Traffic Class Configuration window
This window allows you to configure traffic class priority by specifying the class value, from 0 to 6, of the
Switch’s eight levels of priority.
Click Apply to let your changes take effect.
61
Page 75

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Traffic Segmentation
Traffic segmentation is used to limit traffic flow from a single port to a group of ports on either a single switch
(in standalone mode) or a group of ports on another switch in a switch stack. This method of segmenting the flow
of traffic is similar to using VLANs to limit traffic, but is more restrictive. It provides a method of directing
traffic that does not increase the overhead of the Master switch CPU.
Figure 10-8. Traffic Segmentation Table
Click on the Setup button to open the Setup Forwarding ports page, as shown below.
Figure 10-9. Setup Forwarding Ports
62
Page 76

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
This page allows you to determine which port on a given switch in a switch stack will be allowed to forward
packets to other ports on that switch.
Configuring traffic segmentation on the DGS-3224SR is accomplished in two parts. First you specify a switch
from a switch stack, and then a port from that switch. Then you specify a second switch from the switch stack,
and then you select which ports (or different ports on the same switch,) on that switch that you want to be able to
receive packets from the switch and port you specified in the first part.
In the example above, the switch is Unit 1 and port 5 is selected as the transmitting port. Ports 1-3 and 9-24 are
selected as being able to receive packets from port 5.
Clicking the Apply button will enter the combination of transmitting port and allowed receiving ports into the
switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
The Unit drop-down menu at the top of the page allows you to select a switch from a switch stack using that
switch’s Unit ID. The Port drop-down menu allows you to select a port from that switch. This is the port that
will be transmitting packets.
The Unit drop-down menu under the Setup Forwarding ports heading allows you to select a switch from a switch
stack using that switch’s Unit ID. The Forward Port click boxes allow you to select which of the ports on the
selected switch will be able to forward packets. These are the ports that will be allowed to receive packets from
the port specified above.
Click Apply to enter the settings into the switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
Bandwidth Control
The bandwidth control settings are used to place a ceiling on the transmitting and receiving data rates for any
selected port.
Figure 10-11. Bandwidth Settings
63
Page 77

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The following parameters can be set or are displayed:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To
Type
no_limit
Rate
Allows you to specify a switch in a switch stack using that switch’s Unit ID.
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected
port.
This drop-down menu allows you to select between RX (receive,) TX
(transmit,) and Both. This setting will determine whether the bandwidth
ceiling is applied to receiving, transmitting, or both receiving and
transmitting packets.
This drop-down menu allows you to specify that the selected port will have
no bandwidth limit. Enabled disables the limit.
This field allows you to enter the data rate, in kb/s, that will be the limit for
the selected port.
64
Page 78

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 12
System Log Server
The switch can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers. Use the System Log Server
Figure 13-1. System Log Servers
The parameters configured for adding and editing System Log Server settings are the same. See the table below
for a description.
Figure 13-2. System Log Servers − Add
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Index
Syslog server settings index (1-4).
Server IP
Severity
Facility
The IP address of the Syslog server.
This drop-down menu allows you to select the level of messages that will
be sent. The options are Warning, Informational, and All.
Some of the operating system daemons and processes have been
assigned Facility values. Processes and daemons that have not been
explicitly assigned a Facility may use any of the "local use" facilities or they
may use the "user-level" Facility. Those Facilities that have been
65
Page 79

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
designated are shown in the following: Bold font means the facility values
that the switch currently now.
Numerical Facility
Code
0 kernel messages
1 user-level messages
2 mail system
3 system daemons
4 security/authorization messages
5 messages generated internally by syslog line printer subsystem
7 network news subsystem
8 UUCP subsystem
9 clock daemon
10 security/authorization messages
11 FTP daemon
UDP Port
Status
12 NTP subsystem
13 log audit
14 log alert
15 clock daemon
16 local use 0 (local0)
17 local use 1 (local1)
18 local use 2 (local2)
19 local use 3 (local3)
20 local use 4 (local4)
21 local use 5 (local5)
22 local use 6 (local6)
23 local use 7 (local7)
Type the UDP port number used for sending Syslog messages. The
default is 514.
Choose Enabled or Disabled to activate or deactivate this
66
Page 80

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 13
Port Security Settings
A given port’s (or a range of ports’) dynamic MAC address learning can be locked such that the current source
MAC addresses entered into the MAC address forwarding table can not be changed once the port lock is enabled.
The port can be locked by using the Learn <Disabled> pull-down menu to Enabled, and clicking Apply.
This is a security feature that prevents unauthorized computers (with source MAC addresses unknown to the
switch prior to locking the port (or ports) from connecting to the switch’s locked ports and gaining access to the
network.
Figure 14-1. Port Security Settings
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To
Admin State
Max.Addr(0-64)
Allows you to specify a switch in a switch stack using that switch’s Unit ID.
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected
port.
This pull-down menu allows you to Enable or Disable Port Security
(locked MAC address table for the selected ports.)
The number of MAC addresses that will be in the MAC address forwarding
table for the selected switch and group of ports.
67
Page 81

Mode
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
This pull-down menu allows you to select how the MAC address table
locking will be implemented on the switch, for the selected group of ports.
The options are DeleteOnReset and DeleteOnTimeout.
68
Page 82

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 14
SNTP Setting
The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) (an adaptation of the Network Time Protocol (NPT) is configured
on the switch using the following pages.
Time Settings
Figure 15-1. Time Settings Page
The following parameters can set or are displayed:
Parameter Description
System Boot Time
Time Source
SNTP State
SNTP Primary
Server
SNTP Secondary
Server
SNTP Poll Interval in This is the interval between requests for updated SNTP information.
Displays the current system time.
Displays the time source for the system.
Use this pull-down menu to Enable or Disable SNTP.
This is the primary server the SNTP information will be taken from
This is the secondary server the SNTP information will be taken from
69
Page 83

Seconds
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Year
Month
Day
Time in HH MM SS
Time Zone and DST
Enter the current year, if you want to update the system clock.
Enter the current month, if you want to update the system clock.
Enter the current day, if you want to update the system clock.
Enter the current time in hours, minutes, and seconds, if you want to
update the system clock.
Figure 15-2. Time Zone and DST Settings Page
The following parameters can set:
Parameter Description
Daylight Saving
Time State
Daylight Saving
Use this pull-down menu to Enable or Disable the DST Settings.
Use this pull-down menu to specify the amount of time that will
70
Page 84

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Time Offset in
Minutes
Time Zone Offset
from GMT in +/HH:MM
DST Repeating
Settings
From: Which Day
From: Day of Week
From: Month
From: time in HH:MM
To: Which Day
To: Day of Week
constitute your local DST offset − 30, 60, 90, or 120 minutes.
Use these pull-down menus to specify your local time zone’s offset
from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT.)
Repeating - Using repeating mode will enable DST seasonal time
adjustment. Repeating mode requires that the DST beginning and
ending date be specified using a formula. For example, specify to
begin DST on Saturday during the second week of April and end DST
on Sunday during the last week of October.
Should be From: Which Week. Enter the week of the month that DST
will start.
Enter the day of the week that DST will start on.
Enter the month DST will start on.
Enter the time of day that DST will start on.
Should be be To: Which Week. Enter the week of the month the DST
will end.
Enter the day of the week that DST will end.
To: Month
To: time in HH:MM
Annual Settings
From: Month
From: Day
From: time in HH:MM
To: Month
To: Day
To: time in HH:MM
Enter the month that DST will end.
Enter the time DST will end.
Annual - Using annual mode will enable DST seasonal time
adjustment. Annual mode requires that the DST beginning and ending
date be specified consisely. For example, specify to begin DST on
April 3 and end DST on October 14.
Enter the month DST will start on, each year.
Enter the day of the week DST will start on, each year.
Enter the time of day DST will start on, each year.
Enter the month DST will end on, each year.
Enter the day of the week DST will end on, each year.
Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
71
Page 85

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 15
Access Profile Table
Access profiles allow you to establish criteria to determine whether or not the switch will forward packets based
on the information contained in each packet’s header. These criteria can be specified on a basis of VLAN, MAC
address or IP address.
Creating an access profile is divided into two basic parts. The first is to specify which part or parts of a frame the
switch will examine, such as the MAC source address or the IP destination address. The second part is entering
the criteria the switch will use to determine what to do with the frame. The entire process is described below in
two parts.
To display the currently configured Access Profiles on the switch, open the Configuration folder and click on
the Access Profile Table link. This will open the Access Profile Table page, as shown below.
Figure 16-1. Access Profile Table
To add an entry to the Access Profile Table, click the Add button. This will open the Access Profile
Configuration page, as shown below. There are two Access Profile Configuration pages − one for Ethernet
(or MAC address-based) profile configuration, and one for IP address-based profile configuration. You can
switch between the two Access Profile Configuration pages by using the Type drop-down menu, and clicking
on the Apply button. The page shown below is the Ethernet Access Profile Configuration page.
Figure 16-2. Access Profile Table (Ethernet)
72
Page 86

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Type in a unique identifier number for this profile set or allow an ID to be
Profile ID(1-8)
automatically assigned by checking the Auto Assign option. This value can
be set from 1 – 8.
Select profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address) or IP address. This will
change the menu according to the requirements for the type of profile.
Type
Select Ethernet to instruct the switch to examine the layer 2 part of each
packet header. Select IP to instruct the switch to examine the IP address in
each frame’s header.
Vlan
Source Mac
Destination Mac
Selecting this option instructs the switch to examine the VLAN part of each
packet header and use this as the full or partial criterion for forwarding.
Source MAC Mask - Enter a MAC address mask for the source MAC
address.
Destination MAC Mask - Enter a MAC address mask for the destination
MAC address.
Selecting this option instructs the switch to examine the 802.1p priority
802.1p
value of each packet header and use this as the, or part of the criterion for
forwarding.
Ethernet type
Select permit to specify that the packets that match the access profile are
forwarded by the switch according to any additional rule added (see
Mode
below).
Select deny to specify that packets that do not match the access profile are
not forwarded by the switch and will be filtered.
To add an entry to the Access Profile Table, click the Add button. This will open the Access Profile
Configuration page, as shown below. There are two Access Profile Configuration pages − one for Ethernet
(or MAC address-based) profile configuration, and one for IP address-based profile configuration. You can
switch between the two Access Profile Configuration pages by using the Type drop-down menu, and clicking
on the Apply button. The page shown below is the IP Access Profile Configuration page.
73
Page 87

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 16-3. Access Profile Configuration (IP)
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Type in a unique identifier number for this profile set or allow an ID to be
Profile ID(1-8)
automatically assigned by checking the Auto Assign option. This value can
be set from 1 – 8.
Select profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address) or IP address. This will
change the menu according to the requirements for the type of profile.
Type
Select Ethernet to instruct the switch to examine the layer 2 part of each
packet header. Select IP to instruct the switch to examine the IP address in
each frame’s header.
Vlan
Source IP Mask
Destination IP Mask
Selecting this option instructs the switch to examine the VLAN part of each
packet header and use this as the, or part of the criterion for forwarding.
Source IP Mask - Enter an IP address mask for the source IP address.
Destination IP Mask - Enter an IP address mask for the destination MAC
address.
Dscp
Selecting this option instructs the switch to examine the DiffServ Code part
of each packet header and use this as the, or part of the criterion for
forwarding.
74
Page 88

Protocol
D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Selecting this option instructs the switch to examine the protocol type value
in each frame’s header. You must then specify what protocol(s) to include
according to the following guidelines:
Select ICMP to instruct the switch to examine the Internet Control Message
Protocol (ICMP) field in each frame’s header.
Select Type to further specify that the access profile will apply an ICMP
type value, or specify Code to further specify that the access profile will
apply an ICMP cod value.
Select IGMP to instruct the switch to examine the Internet Group
Management Protocol (ICMP) field in each frame’s header.
Select Type to further specify that the access profile will apply an IGMP
type value
Select TCP to use the TCP port number contained in an incoming packet
as the forwarding criterion. Selecting TCP requires that you specify a
source port mask and/or a destination port mask.
src port mask − Specify a TCP port mask for the source port in hex form
(hex 0x0-0xffff).
dest port mask − Specify a TCP port mask for the destination port in hex
form (hex 0x0-0xffff).
Mode
Select UDP to use the UDP port number contained in an incoming packet
as the forwarding criterion. Selecting UDP requires that you specify a
source port mask and/or a destination port mask.
src port mask − Specify a TCP port mask for the source port in hex form
(hex 0x0-0xffff).
dest port mask − Specify a TCP port mask for the destination port in hex
form (hex 0x0-0xffff).
protocol id − Specify a Layer 4 port mask for the destination port in hex
form (hex 0x0-0xffffffff).
Select permit to specify that the packets that match the access profile are
forwarded by the switch according to any additional rule added (see
below).
Select deny to specify that packets that do not match the access profile are
not forwarded by the switch and will be filtered.
75
Page 89

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 16
Security IP Management
The Security IP Management page allows you to specify the IP addresses of management stations (PCs) on your
network that will be allowed to access the switch’s Web-based management agent.
You can enter up to three IP addresses of local hosts (on the same subnet as the switch) that will be allowed to
manage the switch. It is recommended that the IP address of the local host that will be used to manage the switch
be entered here to avoid possible frequent disconnection from the switch’s Web-based management agent.
Go to the Security Management folder, click on Security IP.
Figure 17-1. Security IP Management
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
IP1 Access to Switch
IP2 Access to Switch
IP3 Access to Switch
Enter the IP address of a management station that will be used to manage
the switch. This IP address must be on the same subnet as the switch.
Enter the IP address of a management station that will be used to manage
the switch. This IP address must be on the same subnet as the switch.
Enter the IP address of a management station that will be used to manage
the switch. This IP address must be on the same subnet as the switch.
76
Page 90

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Port Access Entity
802.1X Port-based Network Access Control
The Switch is an implementation of the server side of IEEE 802.1X-Port Based Network Access Control.
Through this mechanism, users have to be authorized before being able to access the network. See the following
figure:
Figure 17-2. Typical 802.1X Configuration Prior to User Authentication
Once the user is authenticated, the switch unblocks the port that is connected to the user as shown in the next
figure.
77
Page 91

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 17-3. Typical 802.1X Configuration with User Authentication
The user’s information, including account number, password, and configuration details such as IP address and
billing information, is stored in a centralized RADIUS server.
Figure 9 - 1. Typical Configuration with 802.1X Fully Implemented
78
Page 92

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
State Machine Name
Port Timers state machine
Authenticator PAE state machine
The Authenticator Key Transmit state machine
Reauthentication Timer state machine
Backend Authentication state machine
Controlled Directions state machine
The Key Receive state machine
Conformance to IEEE 802.1X Standards
Configure Authenticator
To display the current 802.1X Authenticator Settings on the switch, open the Configuration folder, and then
the Port Access Entity folder and finally click on the Configure Authenticator link. This will open the 802.1X
Authenticator Settings page, as shown below.
Figure 17-4. 802.1X Authenticator Settings
To configure the 802.1X Authenticator settings for a given port, click on the blue port number under the Port
heading. This will open the 802.1X Authenticator Settings page, as shown below.
79
Page 93

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 17-5. 802.1X Authenticator Settings
This window allows you to set the following features:
• From [ ] To [ ] – Enter the port or ports to be set.
• AdmDir [both] – Sets the administrative-controlled direction to either in or both. If in is selected, control is
only exerted over incoming traffic through the port you selected in the first field. If both is selected, control
is exerted over both incoming and outgoing traffic through the controlled port selected in the first field.
• PortControl [auto] – This allows you to control the port authorization state. Select forceAuthorized to
disable 802.1X and cause the port to transition to the authorized state without any authentication exchange
required. This means the port transmits and receives normal traffic without 802.1X-based authentication of
the client. If forceUnauthorized is selected, the port will remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all
attempts by the client to authenticate. The switch cannot provide authentication services to the client through
the interface. The third option is auto. This enables 802.1X and causes the port to begin in the unauthorized
state, allowing only EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port. The authentication process
begins when the link state of the port transitions from down to up, or when an EAPOL-start frame is
received. The switch then requests the identity of the client and begins relaying authentication messages
between the client and the authentication server.
• TxPeriod [30 ] – This sets the TxPeriod of time for the authenticator PAE state machine. This value
determines the period an EAP Request/Identity packet is transmitted to the client.
• QuietPeriod [60 ] – This allows you to set the number of seconds that the switch remains in the quiet state
following a failed authentication exchange with the client.
• SuppTimeout [30 ] – This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the Authenticator
and the client.
• ServerTimeout [30 ] – This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the
Authenticator and the client.
• MaxReq [2 ] – The maximum number of times that the switch will retransmit an EAP Request packet to the
client before it times out the authentication session.
• ReAuthPeriod [3600 ] – A constant that defines a nonzero number of seconds between periodic
reauthentications of the client.
80
Page 94

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
• ReAuth [Disabled] – Determines whether regular reauthentication will take place on this port.
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To
AdmDir
PortControl
TxPeriod
QuietPeriod
SuppTimeout
ServerTimeout
Allows you to specify a switch in a switch stack using that switch’s Unit ID.
15 indicates a switch in standalone mode.
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected
port.
From the pull-down menu, select whether a controlled Port that is
unauthorized will exert control over communication in both receiving and
transmitting directions, or just the receiving direction.
From the pull-down menu, select Force Authorized, Force Unauthorized
or Auto − Force Authorized forces the Authenticator of the port to
become Authorized. Force Unauthorized forces the port to become
Unauthorized.
Select the time to wait for a response from a supplicant (user) to send EAP
Request/Identity packets.
Select the time interval between authentication failure and the start of a
new authentication attempt.
Select the time to wait for a response from a supplicant (user) for all EAP
packets, except for the Request/Identity packets.
Select the length of time to wait for a response from a Radius server.
MaxReq
ReAuthPeriod
ReAuth
Select the maximum number of times to retry sending packets to the
supplicant.
Select the time interval between successive re-authentications.
Enable or disable reauthentication.
81
Page 95

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Port Authenticating Settings
To set the port authenticating settings, open the Configuration folder, and then the Port Access Entity folder, and
then the PAE System Control folder. Finally click on the Port Authenticating Settings link. This will open the
802.1X Capability Settings page, as shown below.
Figure 17-6. 802.1X Authenticator Settings
To set up the Switch’s 802.1X port-based authentication, select which ports are to be configured in the From and
To fields. Next, enable the ports by selecting Authenticator from the drop-down menu under Capability.
Click Apply to let your change take effect.
Radius Server
Use this menu to configure the settings the switch will use to communicate with a Radius server. To add Radius
server settings click the New button, a separate configuration menu appears. To edit an existing Radius settings
index, select it and click the edit button
82
Page 96

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 17-7. 802.1X Authentic Radius Server Setting
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Index
Radius Server
Authentic Port
Accounting Port
Key
Status
Radius server settings index.
Type in the IP address of the Radius server.
This is the UDP port on the Radius server that will be used to authenticate
users. The default is 1812.
This is the UDP port on the Radius server that will be used to log
authentication events. The default is 1813.
Type the shared-secret key used by the Radius server and the switch. Up
to 32 characters can be used. Retype the Key in the Confirm Key field.
This drop-down menu allows you to select Valid or Invalid.
83
Page 97

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Section 17
SNMP
The DGS-3224SR incorporates a flexible SNMP management for the switching environment. SNMP
management can be customized to suit the needs of the networks and the preferences of the network
administrator. Use the SNMP V3 menus to select the SNMP version used for specific tasks.
The DGS-3224SR supports the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 1, 2c, and 3. The
SNMP version used to monitor and control the switch can be specified by the administrator. The three versions
of SNMP vary in the level of security provided between the management station and the network device.
SNMP settings are configured using the menus located on the SNMP V3 folder of the web manager.
Workstations on the network that are allowed SNMP privileged access to the switch can be restricted with the
Management Station IP Address menu.
SNMP User Table
The SNMP User Table displays all of the SNMP Users currently configured on the switch.
Open the SNMP Manager folder and then the SNMP User Table link.
Figure 18-1. SNMP User Table
To delete an existing SNMP User Table entry, click on the X icon below the Delete heading corresponding to the
entry you want to delete.
To display the detailed entry for a given user, click on the blue User Name. This will open the SNMP User
Table Display page, as shown below.
Figure 18-2. SNMP User Table Display
84
Page 98

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
The following parameters are displayed:
Parameter Description
User Name
Group Name
An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the
SNMP users.
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP
messages.
V1 – Indicates that SNMP version 1 will be used.
SNMP Version
V2 – Indicates that SNMP version 2 will be used.
V3 – Indicates that SNMP version 3 will be used.
None − Indicates that no authorization protocol is in use.
Auth-Protocol
MD5 − Indicates that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used.
SHA − Indicates that the HMAC-SHA authentication protocol will be used
.
None − Indicates that no authorization protocol is in use.
Priv-Protocol
DES − Indicates that DES 56-bit encryption is in use based on the CBC-
DES (DES-56) standard.
To add a new entry to the SNMP User Table Configuration, click on the Add button on the SNMP User Table
page. This will open the SNMP User Table Configuration page, as shown below.
Figure 18-3. SNMP User Table Configuration
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
User Name
An alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to identify the
SNMP users.
85
Page 99

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Group Name
SNMP Version
Auth-Protocol
Priv-Protocol
This name is used to specify the SNMP group created can request SNMP
messages.
V1 – Specifies that SNMP version 1 will be used.
V2c – Specifies that SNMP version 2c will be used.
V3 – Specifies that SNMP version 3 will be used.
None − Specifies that no authorization protocol is in use.
MD5 − Specifies that the HMAC-MD5-96 authentication level will be used.
SHA − Specifies that the HMAC-SHA authentication protocol will be used.
None − Specifies that no authorization protocol is in use.
DES − Specifies that DES 56-bit encryption is in use based on the CBC-
DES (DES-56) standard.
SNMP View Table
The SNMP View Table is used to assign views to community strings that define which MIB objects can be
accessed by a remote SNMP manager.
Figure 18-4. SNMP View Table
To delete an existing SNMP View Table entry, click the selection button on the far left that corresponds to the
port you want to configure and click the Delete button. To create a new entry, click the Add button, a separate
menu will appear.
86
Page 100

D-Link DGS-3224SR Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 18-5. SNMP View Table Configuration
The SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views
created in the previous menu.
The following parameters can set:
Parameter Description
View Name
Subtree OID
View Type
Type an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters. This is used to
identify the new SNMP view being created.
Type the Object Identifier (OID) Subtree for the view. The OID identifies an
object tree (MIB tree) that will be included or excluded from access by an
SNMP manager.
Select Included to include this object in the list of objects that an SNMP
manager can access. Select Excluded to exclude this object from the list
of objects that an SNMP manager can access.
SNMP Group Table
An SNMP Group created with this table maps SNMP users (identified in the SNMP User Table) to the views
created in the previous menu.
87
 Loading...
Loading...