Page 1

D-Link DFL-700
Network Security Firewall
Manual
Building Networks for People
Ver.1.02
(20050419)
Page 2

Contents
Introduction ..................................................................................... 7
Features and Benefits ........................................................................... 7
Introduction to Firewalls ........................................................................ 7
Introduction to Local Area Networking .................................................. 8
LEDs ..................................................................................................... 9
Physical Connections............................................................................ 9
Package Contents............................................................................... 10
System Requirements......................................................................... 10
Managing D-Link DFL-700 ............................................................ 11
Resetting the DFL700 ...............................................................................11
Administration Settings................................................................ 12
Administrative Access ......................................................................... 12
Add ping access to an interface ................................................................13
Add Admin access to an interface .............................................................13
Add Read-only access to an interface.......................................................14
Enable SNMP access to an interface ........................................................14
System............................................................................................ 15
Interfaces ............................................................................................ 15
Change IP of the LAN or DMZ interface ....................................................15
WAN Interface Settings – Using Static IP ..................................................16
WAN Interface Settings – Using DHCP .....................................................16
WAN Interface Settings – Using PPPoE....................................................17
WAN Interface Settings – Using PPTP......................................................18
WAN Interface Settings – Using BigPond..................................................19
Traffic Shaping ..........................................................................................19
MTU Configuration....................................................................................20
Routing................................................................................................ 21
Add a new Static Route.............................................................................22
Remove a Static Route..............................................................................22
Logging ............................................................................................... 23
Enable Logging .........................................................................................24
Enable Audit Logging ................................................................................24
Enable E-mail alerting for ISD/IDP events.................................................24
Time .................................................................................................... 26
Changing time zone ..................................................................................27
Using NTP to sync time.............................................................................27
2
Page 3

Setting time and date manually .................................................................27
Firewall ........................................................................................... 28
Policy................................................................................................... 28
Policy modes.............................................................................................28
Action Types..............................................................................................28
Source and Destination Filter ....................................................................29
Service Filter.............................................................................................29
Schedule ...................................................................................................29
Intrusion Detection / Prevention ................................................................29
Traffic Shaping ..........................................................................................30
Add a new policy .......................................................................................31
Change order of policy ..............................................................................32
Delete policy .............................................................................................32
Configure Intrusion Detection....................................................................32
Configure Intrusion Prevention..................................................................33
Port mapping / Virtual Servers ............................................................ 34
Add a new mapping ..................................................................................34
Delete mapping.........................................................................................35
Administrative users............................................................................ 36
Add Administrative User............................................................................36
Change Administrative User Access level .................................................37
Change Administrative User Password .....................................................37
Delete Administrative User ........................................................................38
Users................................................................................................... 39
The DFL-700 RADIUS Support .................................................................39
Enable User Authentication via HTTP / HTTPS.........................................40
Enable RADIUS Support ...........................................................................40
Add User ...................................................................................................41
Change User Password ............................................................................41
Delete User ...............................................................................................42
Schedules ........................................................................................... 43
Add new recurring schedule......................................................................43
Services .............................................................................................. 44
Adding TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP Service ....................................................44
Adding IP Protocol ....................................................................................45
Grouping Services.....................................................................................45
Protocol-independent settings...................................................................46
VPN..................................................................................................... 47
Introduction to IPsec .................................................................................47
Introduction to PPTP .................................................................................48
Introduction to L2TP..................................................................................48
Point-to-Point Protocol ..............................................................................48
Authentication Protocols............................................................................49
PAP ............................................................................................................49
CHAP .........................................................................................................49
Page 4

MS-CHAP v1 ..............................................................................................49
MS-CHAP v2 ..............................................................................................49
MPPE, Microsoft Point-To-Point Encryption ..............................................49
L2TP/PPTP Clients ...................................................................................50
L2TP/PPTP Servers ..................................................................................51
VPN between two networks ......................................................................53
VPN between two networks ......................................................................53
Creating a LAN-to-LAN IPSec VPN Tunnel ...............................................53
VPN between client and an internal network .............................................54
Creating a Roaming Users IPSec VPN Tunnel..........................................54
Adding a L2TP/PPTP VPN Client..............................................................55
Adding a L2TP/PPTP VPN Server ............................................................55
VPN – Advanced Settings ................................................................... 56
Limit MTU..................................................................................................56
IKE Mode ..................................................................................................56
IKE DH Group ...........................................................................................56
PFS – Perfect Forward Secrecy................................................................56
NAT Traversal ...........................................................................................56
Keepalives ................................................................................................56
Proposal Lists............................................................................................57
IKE Proposal List.......................................................................................57
IPSec Proposal List...................................................................................57
Certificates .......................................................................................... 58
Trusting Certificates ..................................................................................58
Local identities ..........................................................................................58
Certificates of remote peers ......................................................................58
Certificate Authorities ................................................................................59
Identities....................................................................................................59
Content Filtering.................................................................................. 60
Active content handling .............................................................................60
Edit the URL Global Whitelist ....................................................................61
Edit the URL Global Blacklist.....................................................................62
Active content handling .............................................................................63
Servers ...........................................................................................64
DHCP Server Settings......................................................................... 64
Enable DHCP Server ................................................................................65
Enable DHCP Relay..................................................................................65
Disable DHCP Server/Relayer ..................................................................65
DNS Relayer Settings ......................................................................... 66
Enable DNS Relayer .................................................................................66
Disable DNS Relayer ................................................................................67
Tools ............................................................................................... 68
4
Page 5

Ping ..................................................................................................... 68
Ping Example............................................................................................68
Dynamic DNS...................................................................................... 69
Add Dynamic DNS Settings ......................................................................69
Backup ................................................................................................ 70
Exporting the DFL-700’s Configuration......................................................70
Restoring the DFL-700’s Configuration .....................................................70
Restart/Reset ...................................................................................... 71
Restarting the DFL-700 .............................................................................71
Restoring system settings to factory defaults ............................................71
Upgrade .............................................................................................. 73
Upgrade Firmware ....................................................................................73
Upgrade IDS Signature-database .............................................................73
Status.............................................................................................. 74
System ................................................................................................ 74
Interfaces ............................................................................................ 75
VPN..................................................................................................... 76
Connections ........................................................................................ 77
DHCP Server ...................................................................................... 78
Users................................................................................................... 79
How to read the logs .....................................................................80
USAGE events .................................................................................... 80
DROP events ...................................................................................... 80
CONN events ...................................................................................... 80
Step by step guides ...................................................................... 82
LAN-to-LAN VPN using IPsec............................................................. 83
Settings for Branch office............................................................................83
Settings for Main office ...............................................................................85
LAN-to-LAN VPN using PPTP ............................................................ 87
Settings for Branch office............................................................................87
Settings for Main office ...............................................................................90
LAN-to-LAN VPN using L2TP ............................................................. 94
Settings for Branch office............................................................................94
Settings for Main office ...............................................................................97
A more secure LAN-to-LAN VPN solution......................................... 101
Settings for Branch office..........................................................................101
Settings for Main office .............................................................................104
Windows XP client and PPTP server ................................................ 105
Page 6

Settings for the Windows XP client ...........................................................105
Settings for Main office .............................................................................113
Windows XP client and L2TP server..................................................115
Settings for the Windows XP client ...........................................................115
Settings for Main office .............................................................................117
Content filtering ..................................................................................119
Intrusion detection and prevention .................................................... 123
Traffic shaping................................................................................... 126
Limit bandwidth to a service......................................................................126
Limit bandwidth to one or more IP addresses...........................................126
Guarantee bandwidth to a service ............................................................127
Appendixes .................................................................................. 129
Appendix A: ICMP Types and Codes ................................................ 129
Appendix B: Common IP Protocol Numbers ..................................... 131
LIMITED WARRANTY .................................................................. 132
6
Page 7

Introduction
The DFL-700 provides three 10/100M Ethernet network interface ports, which are (1)
Internal/LAN, (1) External/WAN, and (1) DMZ port. It also provides easily operated software
WebUI that allows users to set system parameters or monitor network activities using a web
browser.
Features and Benefits
z Firewall Security
z VPN Server/Client Supported
z Content Filtering
z Bandwidth Management
DFL-700 features an extensive Traffic Shaper for bandwidth
management.
z Web Management
Configurable through any networked computer’s web browser using
Netscape or Internet Explorer.
z Access Control supported
Allows you to assign different access rights for different users. Like
Admin or Read-Only User.
Introduction to Firewalls
A firewall is a device that sits between your computer and the Internet that prevents
unauthorized access to or from your network. A firewall can be a computer using firewall
software or a special piece of hardware built specifically to act as a firewall. In most
circumstances, a firewall is used to prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing
private networks or corporate LAN’s and Intranets.
A firewall watches all of the information moving to and from your network and analyzes
each piece of data. Each piece of data is checked against a set of criteria that the
administrator configures. If any data does not meet the criteria, that data is blocked and
discarded. If the data meets the criteria, the data is passed through. This method is called
packet filtering.
A firewall can also run specific security functions based on the type of application or type
of port that is being used. For example, a firewall can be configured to work with an FTP or
Telnet server. Or a firewall can be configured to work with specific UDP or TCP ports to allow
certain applications or games to work properly over the Internet.
Page 8

Introduction to Local Area Networking
Local Area Networking (LAN) is the term used when connecting several computers
together over a small area such as a building or group of buildings. LAN’s can be connected
over large areas. A collection of LAN’s connected over a large area is called a Wide Area
Network (WAN).
A LAN consists of multiple computers connected to each other. There are many types of
media that can connect computers together. The most common media is CAT5 cable (UTP or
STP twisted pair wire.) On the other hand, wireless networks do not use wires; instead they
communicate over radio waves. Each computer must have a Network Interface Card (NIC),
which communicates the data between computers. A NIC is usually a 10Mbps network card, a
10/100Mbps network card or a wireless network card.
Most networks use hardware devices such as hubs or switches that each cable can be
connected to in order to continue the connection between computers. A hub simply takes any
data arriving through each port and forwards the data to all other ports. A switch is more
sophisticated, in that a switch can determine the destination port for a specific piece of data.
A switch minimizes network traffic overhead and speeds up the communication over a
network.
Networks take some time in order to plan and implement correctly. There are many ways
to configure your network. You may want to take some time to determine the best network
set-up for your needs.
8
Page 9

LEDs
Power: A solid light indicates a proper connection to the power supply.
Status: System status indicators, flashes to indicate an active system. If the LED has a
solid light the unit is defective.
WAN, LAN & DMZ: Ethernet port indicators, Green. The LED flickers when the ports are
sending or receiving data.
Physical Connections
Console: Serial access to the firewall software, 9600, 8bit, None Parity, 1Stop bit.
DMZ Port: Use this port to connect to the company’s server(s), which needs direct
connection to the Internet (FTP, SNMP, HTTP, DNS).
Internal Ports (LAN): Use this port to connect to the internal network of the office.
External Port (WAN): Use this port to connect to the external router, DSL modem, or
Cable modem.
Reset: Reset the DFL-700 to the original default settings.
DC Power: connect one end of the power supply to this port, the other end to the
electrical wall outlet.
Page 10

Package Contents
Contents of Package:
• D-Link DFL-700 Firewall
• Manual and CD
• Quick Installation Guide
• AC Power adapter
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included
with the DFL-700 will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
If any of the above items are missing, please contact your reseller.
System Requirements
• Computer with a Windows, Macintosh, or Unix based operating system with an
installed Ethernet adapter
• Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, version 6.0 or above, with JavaScript
enabled.
10
Page 11
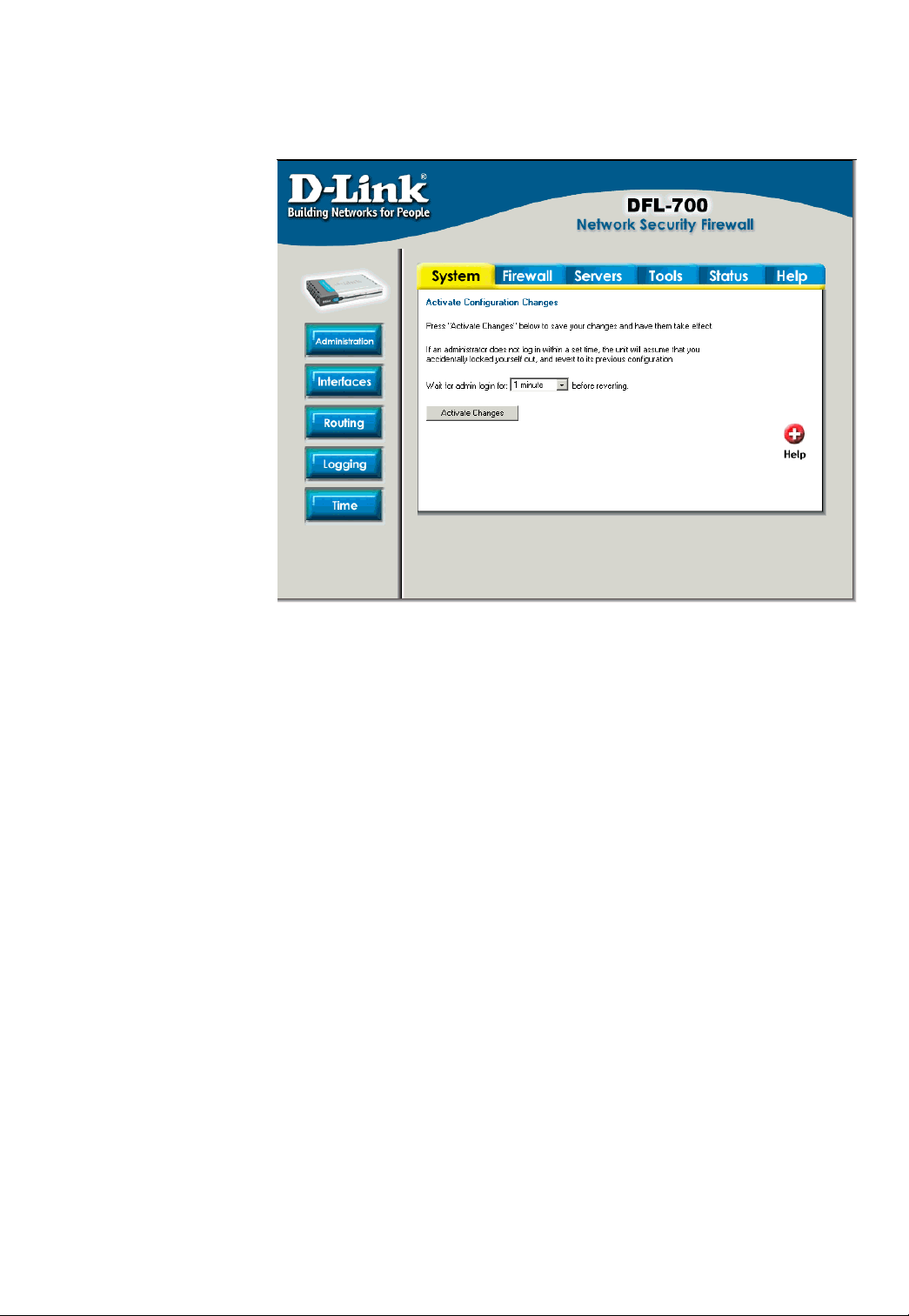
Managing D-Link DFL-700
When a change is
done to the
configuration a new
icon named Activate
Changes
When all changes and
administrator would like
to do is done the
changes need to be
saved and activated to
take effect, this is done
by clicking on the
Activate Changes
button on the Activate
Configuration Changes
page. What will happen
is that the firewall will
save the configuration
and reload it, letting the
new changes take effect.
But for the changes to
become permanent the admin need to login again. This have to be done before a configurable
timeout has been reached, this can be set on the Activate Configuration Changes page, by
choosing the time from the dropdown menu.
will appear.
Resetting the DFL700
To reset the DFL-700 to factory default settings you must hold the reset button down for at
least 15 seconds after powering on the unit. You will first hear one beep, which will indicate
that the firmware have started and the restoring have started, keep the button pressed in until
you hear two consecutive beeps shortly after each other. After this you can release the reset
button and the DFL-700 will continue to load and startup in default mode, i.e. with 192.168.1.1
on the LAN interface.
Page 12

Administration Settings
Administrative Access
Ping – If enabled, specifies who can ping the interface IP of the DFL-700. Default if
enabled is to allow anyone to ping the interface IP.
Admin – If enabled allows all users with admin access to connect to the DFL-700 and
change configuration, can be HTTPS or HTTP and HTTPS.
Read-Only – If enabled allows all users with read-only access to connect to the DFL-700
and look at the configuration, can be HTTPS or HTTP and HTTPS. If there is no Admin
access specified on an interface and only read-only, admin users can still connect but will be
in read-only mode.
SNMP – Specifies if SNMP should be allowed or not on the interface, the DFL-700 only
supports read-only access.
12
Page 13

Add ping access to an interface
To add ping access click on the interface you would like to add it to.
Follow these steps to add ping access to an interface.
Step 1. Click on the interface you would like to add it to.
Step 2. Enable the Ping checkbox.
Step 3. Specify what networks are allowed to ping the interface, for example
192.168.1.0/24 for a whole network or 172.16.0.1 – 172.16.0.10 for a range.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Example:
Add Admin access to an interface
To add admin access click on the interface you would like to add it to. Only users with the
administrator rights can login on an interfaces where there is only admin access enabled.
Follow these steps to add admin access to an interface.
Step 1. Click on the interface you would like to add it to.
Step 2. Enable the Admin checkbox.
Step 3. Specify what networks are allowed to ping the interface, for example
192.168.1.0/24 for a whole network or 172.16.0.1 – 172.16.0.10 for a range.
Step 4. Specify protocol used to access the DFL-700 from the dropdown menu, either
HTTP and HTTPS (Secure HTTP) or only HTTPS.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Example:
Page 14

Add Read-only access to an interface
To add read-only access click on the interface you would like to add it to, note that if you
only have read-only access enable on an interface all users only get read-only access, even if
they are administrators.
Follow these steps to add read-only access to an interface.
Step 1. Click on the interface you would like to add it to.
Step 2. Enable the Read-only checkbox.
Step 3. Specify what networks are allowed to ping the interface, for example
192.168.1.0/24 for a whole network or 172.16.0.1 – 172.16.0.10 for a range.
Step 4. Specify protocol used to access the DFL-700 from the dropdown menu, either
HTTP and HTTPS (Secure HTTP) or only HTTPS.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Example:
Enable SNMP access to an interface
Follow these steps to add read-only SNMP access to an interface.
Step 1. Click on the interface you would like to add it to.
Step 2. Enable the Read-only checkbox.
Step 3. Specify what networks are allowed to ping the interface, for example
192.168.1.0/24 for a whole network or 172.16.0.1 – 172.16.0.10 for a range.
Step 4. Specify the community string used to authenticate against the DFL-700.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Example:
14
Page 15

System
Interfaces
Click on System in the menu bar, and then click interfaces below it.
Change IP of the LAN or DMZ interface
Follow these steps to change the IP of the LAN or DMZ interface.
Step 1. Choose which interface to view or change under the Available interfaces list.
Step 2. Fill in the IP address of the LAN or DMZ interface. These are the address that will
be used to ping the firewall, remotely control it and use as gateway for the internal hosts or
DMZ hosts.
Step 3. Choose the correct Subnet mask of this interface from the drop down menu.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 16

WAN Interface Settings – Using Static IP
If you are using Static IP you have
to fill in the IP address information
provided to you by your ISP. All fields
are required except the Secondary
DNS Server. You should probably not
use the numbers displayed in these
fields, they are only used as an
example.
• IP Address – The IP
address of the WAN
interface. This is the
address that may be used to ping the firewall, remotely control it and be used as
source address for dynamically translated connections.
• Subnet Mask – Size of the external network.
• Gateway IP – Specifies the IP address of the default gateway used to reach for
the Internet.
• Primary and Secondary DNS Server – The IP addresses of your DNS servers,
only the Primary DNS is required.
WAN Interface Settings – Using DHCP
If you are using DHCP there is no
need to enter any values in any of
fields.
16
Page 17

WAN Interface Settings – Using PPPoE
Use the following procedure to
configure the DFL-700 external
interface to use PPPoE (Point-to-Point
Protocol over Ethernet). This
configuration is required if your ISP
uses PPPoE to assign the IP address
of the external interface. You will have
to fill the username and password
provided to you by your ISP.
• Username – The login or
username supplied to you
by your ISP.
• Password – The
password supplied to you by your ISP.
• Service Name – When using PPPoE some ISPs require you to fill in a Service
Name.
• Primary and Secondary DNS Server – The IP addresses of your DNS servers,
these are optional and are often provided by the PPPoE service.
Page 18

WAN Interface Settings – Using PPTP
PPTP over Ethernet connections
are used in some DSL and cable
modem networks.
You need your account details, and
possibly also IP configuration
parameters of the actual physical
interface that the PPTP tunnel runs
over. Your ISP should supply this
information.
•
Username – The login or
username supplied to you
by your ISP.
• Password – The
password supplied to you
by your ISP.
• PPTP Server IP – The IP
of the PPTP server that
the DFL-700 should
connect to.
Before PPTP can be used to connect to you ISP the physical (WAN) interface parameters
need to be supplied, it’s possible to use either DHCP or Static IP, this depends on the type of
ISP used and this information should be supplied by them.
If using static IP, this information need to be filled in.
• IP Address – The IP address of the WAN interface. This IP is used to connect to
the PPTP server.
• Subnet Mask – Size of the external network.
• Gateway IP – Specifies the IP address of the default gateway used to reach for
the Internet.
18
Page 19

WAN Interface Settings – Using BigPond
The ISP Telstra BigPond uses
BigPond for authentication; the IP is
assigned with DHCP.
• Username – The login or
username supplied to you
by your ISP.
• Password – The
password supplied to you
by your ISP.
Traffic Shaping
When Traffic Shaping is enabled and the correct maximum up and downstream
bandwidth is specified it’s possible to control which policies have the highest priority when
large amounts of data are moving through the DFL-700. For example, the policy for the web
server might be given higher priority than the policies for most employees' computers.
You can use traffic shaping to guarantee the amount of bandwidth available through the
firewall for a policy. Guarantee bandwidth to make sure that there is enough bandwidth
available for a high-priority service. You can also use traffic shaping to limit the amount of
bandwidth available through the firewall for a policy. Limit bandwidth to keep less important
services from using bandwidth needed for more important services.
Note: If the limit is set too high, i.e. higher then your Internet connection, the traffic
shaping will not work at all.
Page 20

MTU Configuration
To improve the performance of your Internet connection, you can adjust the maximum
transmission unit (MTU) of the packets that the DFL-700 transmits from its external interface.
Ideally, you want this MTU to be the same as the smallest MTU of all the networks between
the DFL-700 and the Internet. If the packets the DFL-700 sends are larger, they get broken up
or fragmented, which could slow down transmission speeds.
Trial and error is the only sure way of finding the optimal MTU, but there are some
guidelines that can help. For example, the MTU of many PPP connections is 576, so if you
connect to the Internet via PPPoE, you might want to set the MTU size to 576. DSL modems
may also have small MTU sizes. Most ethernet networks have an MTU of 1500.
Note: If you connect to your ISP using DHCP to obtain an IP address for the external
interface, you cannot set the MTU below 576 bytes due to DHCP communication
standards.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
20
Page 21
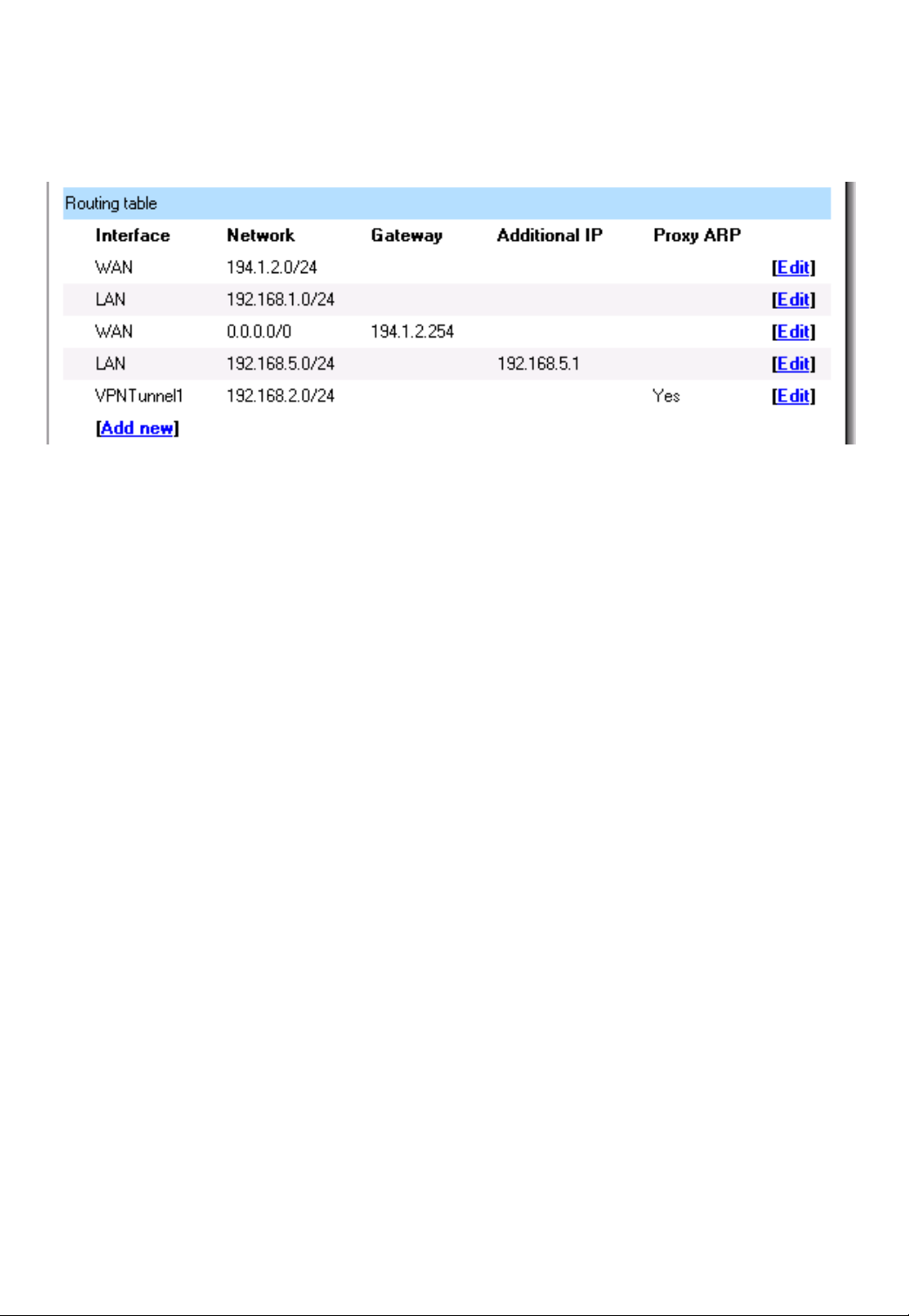
Routing
Click on System in the menu bar, and then click Routing below it, this will give a list of all
configured routes, it will look something like this:
The Routes configuration section describes the firewall’s routing table. DFL-700 uses a
slightly different way of describing routes compared to most other systems. However, we
believe that this way of describing routes is easier to understand, making it less likely for
users to cause errors or breaches in security.
Interface – Specifies which interface packets destined for this route shall be sent through.
Network – Specifies the network address for this route.
Gateway – Specifies the IP address of the next router hop used to reach the destination
network. If the network is directly connected to the firewall interface, no gateway address is
specified.
Local IP Address – The IP address specified here will be automatically published on the
corresponding interface. This address will also be used as the sender address in ARP queries.
If no address is specified, the firewalls own interface IP address will be used.
Proxy ARP – Specifies that the firewall shall publish this route via Proxy ARP.
One advantage with this form of notation is that you can specify a gateway for a particular
route, without having a route that covers the gateway’s IP address or despite the fact that the
route that covers the gateway’s IP address is normally routed via another interface.
The difference between this form of notation and that most commonly used is that there,
you do not specify the interface name in a separate column. Instead, you specify the IP
address of each interface as a gateway.
Note: The firewall does not Proxy ARP routes on VPN interfaces.
Page 22

Add a new Static Route
Follow these steps to add a new route.
Step 1. Go to System and Routing.
Step 2. Click on Add new in the bottom of the routing table.
Step 3. Choose the interface that the route should be sent trough from the dropdown
menu.
Step 4. Specify the Network and Subnet mask.
Step 5. If this network is behind a remote gateway enable the checkbox Network is
behind remote gateway and specify the IP of that gateway
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Remove a Static Route
Follow these steps to add a remove a route.
Step 1. Go to System and Routing.
Step 2. Take Edit after the route you would like to remove.
Step 3. Check the checkbox named Delete this route.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
22
Page 23

Logging
Click on System in the menu bar, and then click Logging below it.
Logging, the ability to audit decisions made by the firewall, is a vital part in all network
security products. The D-Link DFL-700 provides several options for logging its activity. The DLink DFL-700 logs its activities by sending the log data to one or two log receivers in the
network.
All logging is done to Syslog recipients. The log format used for syslog logging is suitable
for automated processing and searching.
The D-Link DFL-700 specifies a number of events that can be logged. Some of those
events, for instance, startup and shutdown events, are mandatory, and will always generate
log entries. Others, for instance to log if when allowed connections are opened and closed, is
Page 24

configurable. It’s also possible to have E-mail alerting for IDS/IDP events to up to three email
addresses.
Enable Logging
Follow these steps to enable logging.
Step 1. Enable syslog by checking the Syslog box.
Step 2. Fill in your first syslog server as Syslog server 1, if you have two syslog servers
you have to fill in the second one as Syslog server 2. You must fill in at least one syslog
server for logging to work.
Step 3. Specify what facility to use by selecting the appropriate syslog facility. Local0 is
the default facility.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Enable Audit Logging
To start auditing all traffic trough the firewall, follow the sets below and the firewall will start
logging all traffic trough the firewall, this is needed for running third party log analyzers on the
logs and to see how much traffic different connections use.
Follow these steps to enable auditing.
Step 1. Enable syslog by checking the Enable audit logging box.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Enable E-mail alerting for ISD/IDP events
Follow these steps to enable E-mail alerting.
Step 1. Enable E-mail alerting by checking the Enable E-mail alerting for IDS/IDP
events checkbox.
Step 2. Choose the sensitivity level.
Step 3. In the SMPT Server field, fill in the SMTP server to which the DFL-700 should
send email.
Step 4. Specify up to three valid email addresses to receive the email alerts.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
24
Page 25

Intrusion attacks will always be logged in the usual logs if IDS is enabled for any of the
rules.
For more information about how to enable intrusion detection and prevention on a policy
or port mapping, read more under Policies and Port Mappings in the Firewall section below.
Page 26
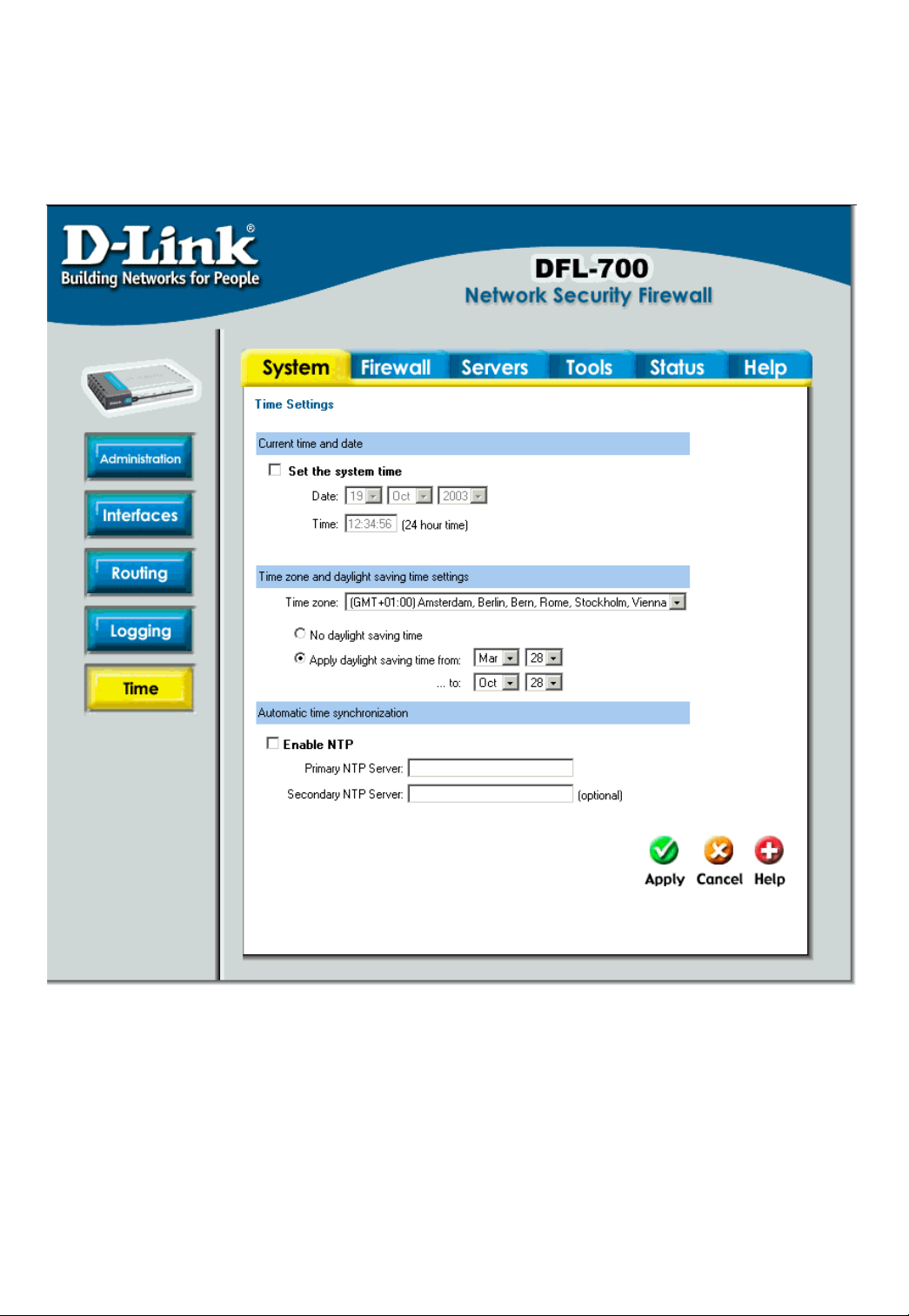
Time
Click on System in the menu bar, and then click Time below it. This will give you the
option to either set the system time by syncing to an Internet Network Time Server (NTP) or
by entering the system time by hand.
26
Page 27

Changing time zone
Follow these steps to change the time zone.
Step 1. Choose the correct time zone in the drop down menu.
Step 2. Specify your daylight time or choose no daylight saving time by checking the
correct box.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Using NTP to sync time
Follow these steps to sync to an Internet Time Server.
Step 1. Enable synchronization by checking the Enable NTP box.
Step 2. Enter the Server IP Address or Server name with which you want to synchronize.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Setting time and date manually
Follow these steps to set the system time by hand.
Step 1. Checking the Set the system time box.
Step 2. Choose the correct date.
Step 3. Set the correct time in 24-hour format.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 28

Firewall
Policy
The Firewall Policy configuration section is the "heart" of the firewall. The policies are the
primary filter that is configured to allow or disallow certain types of network traffic through the
firewall. The policies also regulate how bandwidth management, traffic shaping, is applied to
traffic flowing through the WAN interface of the firewall.
When a new connection is being established through the firewall, the policies are
evaluated, top to bottom, until a policy that matches the new connection is found. The Action
of the rule is then carried out. If the action is Allow, the connection will be established and a
state representing the connection is added to the firewall's internal state table. If the action is
Drop, the new connection will be refused. The section below will explain the meanings of the
various action types available.
Policy modes
The first step in configuring security policies is to configure the mode for the firewall. The
firewall can run in NAT or No NAT (Route) mode. Select NAT mode to use DFL-1000 network
address translation to protect private networks from public networks. In NAT mode, you can
connect a private network to the internal interface, a DMZ network to the dmz interface, and a
public network, such as the Internet, to the external interface. Then you can create NAT mode
policies to accept or deny connections between these networks. NAT mode policies hide the
addresses of the internal and DMZ networks from users on the Internet. In No NAT (Route)
mode you can also create routed policies between interfaces. Route mode policies accept or
deny connections between networks without performing address translation. To use NAT
mode select Hide source addresses (many-to-one NAT) and to use No NAT (Route) mode
choose No NAT.
Action Types
Drop – Packets matching Drop rules will immediately be dropped. Such packets will be
logged if logging has been enabled in the Logging Settings page.
Reject – Reject works in basically the same way as Drop. In addition to this, the firewall
sends an ICMP UNREACHABLE message back to the sender or, if the rejected packet was a
TCP packet, a TCP RST message. Such packets will be logged if logging has been enabled
in the Logging Settings page.
Allow – Packets matching Allow rules are passed to the stateful inspection engine, which
will remember that a connection has been opened. Therefore, rules for return traffic will not be
required as traffic belonging to open connections is automatically dealt with before it reaches
the policies. Logging is carried out if audit logging has been enabled in the Logging Settings
page.
28
Page 29

Source and Destination Filter
Source Nets – Specifies the sender span of IP addresses to be compared to the received
packet. Leave this blank to match everything.
Source Users/Groups – Specifies if an authenticated username is needed for this policy
to match. Either make a list of usernames, separated by , or write Any for any authenticated
user. If it’s left blank there is no need for authentication for the policy.
Destination Nets – Specifies the span of IP addresses to be compared to the destination
IP of the received packet. Leave this blank to match everything.
Destination Users/Groups – Specifies if an authenticated username is needed for this
policy to match. Either make a list of usernames, separated by , or write Any for any
authenticated user. If it’s left blank there is no need for authentication for the policy.
Service Filter
Either choose a predefined service from the dropdown menu or make a custom.
The following custom services exist:
All – This service matches all protocols.
TCP+UDP+ICMP – This service matches all ports on either the TCP or the UDP protocol,
including ICMP.
Custom TCP – This service is based on the TCP protocol.
Custom UDP – This service is based on the UDP protocol.
Custom TCP+UDP – This service is based on either the TCP or the UDP protocol.
The following is used when making a custom service:
Custom source/destination ports – For many services, a single destination port is
sufficient. The source port most often be all ports, 0-65535. The http service, for instance, is
using destination port 80. A port range can also be used, meaning that a range 137-139
covers ports 137, 138 and 139. Multiple ranges or individual ports may also be entered,
separated by commas. For instance, a service can be defined as having source ports 102465535 and destination ports 80-82, 90-92, 95. In this case, a TCP or UDP packet with the
destination port being one of 80, 81, 82, 90, 91, 92 or 95, and the source port being in the
range 1024-65535, will match this service.
Schedule
If a schedule should be used for the policy, choose one from the dropdown menu, these
are specified on the Schedules page. If the policy should always be active, choose Always
from the dropdown menu.
Intrusion Detection / Prevention
The DFL-700 Intrusion Detection/Prevention System (IDS/IDP) is a real-time intrusion
detection and prevention sensor that identifies and takes action against a wide variety of
suspicious network activity. The IDS uses intrusion signatures, stored in the attack database,
to identify the most common attacks. In response to an attack, the IDS protect the networks
behind the DFL-700 by dropping the traffic. To notify of the attack the IDS sends an email to
Page 30

the system administrators if email alerting is converted. There are two modes that can be
configured, either Inspection Only or Prevention. Inspection Only will only inspect the traffic
and if the DFL-700 sees anything it will log, email an alert (if configured) and pass on the
traffic, if Prevention is used the traffic will be dropped and logged and if configured a email
alert will be sent.
D-Link updates the attack database periodically. Since firmware version 1.30.00 automatic
updates are possible. If IDS or IDP is enabled for at least one of the policies or port mappings,
auto updating of the IDS database will be enabled. The firewall will then automatically
download the latest database from the D-Link website.
Traffic Shaping
The simplest way to obtain quality of service in a network, seen from a security as well as
a functionality perspective, is to have the components in the network, not the applications, be
responsible for network traffic control in well-defined choke points.
Traffic shaping works by measuring and queuing IP packets, in transit, with respect to a
number of configurable parameters. Differentiated rate limits and traffic guarantees based on
source, destination and protocol parameters can be created; much the same way firewall
policies are implemented.
There are three different priorities when configuring the traffic shaping, Normal, High and
Critical.
Limit works by limiting the inbound and outbound traffic to the specified speed. This is the
maximum bandwidth that can be used by traffic using this policy. Note however that if you
have other policies using limit; which in total is more then your total internet connection and
have configured the traffic limits on the WAN interface this limit is sometimes lowered to allow
traffic with higher priorities to have precedence.
By using Guarantee, you can traffic using a policy a minimum bandwidth, this will only
work if the traffic limits for the WAN interface are configured correctly.
30
Page 31

Add a new policy
Follow these steps to add a new outgoing policy.
Step 1. Choose the LAN->WAN policy list from the available policy lists.
Step 2. Click on the Add new link.
Step 3. Fill in the following values:
Name: Specifies a symbolic name for the rule. This name is used mainly as a rule
reference in log data and for easy reference in the policy list.
Action: Select Allow to allow this type of traffic.
Source Nets: – Specifies the sender span of IP addresses to be compared to the
received packet. Leave this blank to match everything.
Source Users/Groups: Specifies if an authenticated username is needed for this policy to
match. Either make a list of usernames, separated by , or write Any for any authenticated
user. If it’s left blank there is no need for authentication for the policy.
Destination Nets: Specifies the span of IP addresses to be compared to the destination
IP of the received packet. Leave this blank to match everything.
Destination Users/Groups: Specifies if an authenticated username is needed for this
policy to match. Either make a list of usernames, separated by , or write Any for any
authenticated user. If it’s left blank there is no need for authentication for the policy.
Service: Either choose a predefined service from the dropdown menu or make a custom.
Schedule: Choose what schedule should be used for this policy to match, choose Always
for no scheduling.
Step 4. If using Traffic shaping fill in that information, if not skip this step.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
Page 32

Change order of policy
Follow these steps to change order of a policy.
Step 1. Choose the policy list you would like do change order in from the available policy
lists.
Step 2. Click on the Edit link on the rule you want to delete.
Step 3. Change the number in the Position to the new line, this will after the apply button
is clicked move this policy to this row and move the old policy and all after to one step
down.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
Delete policy
Follow these steps to delete a policy.
Step 1. Choose the policy list you would like do delete the policy in from the available
policy lists.
Step 2. Click on the Edit link on the rule you want to delete.
Step 3. Enable the Delete policy checkbox.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
Configure Intrusion Detection
Follow these steps to configure IDS on a policy.
Step 1. Choose the policy you would like have IDS on.
Step 2. Click on the Edit link on the rule you want to delete.
Step 3. Enable the Intrusion Detection / Prevention checkbox.
Step 4. Choose Intrusion Detection from the mode drop down list.
Step 5. Enable the alerting checkbox for email alerting.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
32
Page 33

Configure Intrusion Prevention
Follow these steps to configure IDP on a policy.
Step 1. Choose the policy you would like have IDP on.
Step 2. Click on the Edit link on the rule you want to delete.
Step 3. Enable the Intrusion Detection / Prevention checkbox.
Step 4. Choose Prevention from the mode drop down list.
Step 5. Enable the alerting checkbox for email alerting.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
Page 34

Port mapping / Virtual Servers
The Port mapping / Virtual Servers configuration section is where you can configure virtual
servers like Web servers on the DMZ or similar. It’s also possible to regulate how bandwidth
management, traffic shaping, is applied to traffic flowing through the WAN interface of the
firewall. It is also possible to use Intrusion Detection / Prevention and Traffic shaping on Port
mapped services, these are done in the same way as on policies, so see that chapter for
more information.
Mappings are read from top to bottom, and the first matching mapping is carried out.
Add a new mapping
Follow these steps to add a new mapping on the WAN interface.
Step 1. Choose the WAN policy list from the available policy lists.
Step 2. Click on the Add new link.
Step 3. Fill in the following values:
Name: Specifies a symbolic name for the rule. This name is used mainly as a rule
reference in log data and for easy reference in the policy list.
Source Nets: Specify the source networks, leave blank for everyone (0.0.0.0/0).
Source Users/Groups: Specifies if an authenticated username is needed for this
mapping to match. Either make a list of usernames, separated by , or write Any for any
authenticated user. If it’s left blank there is no need for authentication for the policy.
Destination Nets: Leave empty for the interfaces own IP or enter a new IP if using Virtual
IP.
Service: Either choose a predefined service from the dropdown menu or make a custom.
Pass To: The IP of the server that the traffic should be passed to.
Schedule: Choose what schedule should be used for this mapping to match, choose
Always for no scheduling.
Step 4. If using Traffic shaping fill in that information, if not skip this step.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes
34
Page 35

Delete mapping
Follow these steps to delete a mapping.
Step 1. Choose the mapping list (WAN, LAN or DMZ) you would like do delete the
mapping from.
Step 2. Click on the Edit link on the rule you want to delete.
Step 3. Enable the Delete mapping checkbox.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 36

Administrative users
Click on Firewall in the menu bar, and then click Users below it. This will show all the
users, and the first section is the administrative users.
The first column show the access levels, Administrator and Read-only. An Administrator
user can add, edit and remove rules, change settings of the DFL-700 and so on. The Read-
only user can only look at the configuration. The second column shows the users in each
access level.
Add Administrative User
Follow these steps to add a new
administrative user.
Step 1. Click on add after the type
of user you would like to add,
Admin or Read-only.
Step 2. Fill in User name; make
sure you are not trying to add one
that already exists.
Step 3. Specify the password for the new user.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Note: The user name and password should be at least six characters long. The user
name and password can contain numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-
z). Special characters and spaces are not allowed.
36
Page 37

Change Administrative User Access level
To change the access lever of a user click on the user name and you will see the following
screen. From here you can change the
access level by choosing the
appropriate level from the drop-down
menu.
Access levels
• Administrator – the user
can add, edit and remove
rules and change all
settings.
• Read-only – the user can
only look at the
configuration of the firewall.
• No Admin Access – The user is only used for user authentication.
Follow these steps to change Administrative User Access level.
Step 1. Click on the user you would like to change level of.
Step 2. Choose the appropriate level from the drop-down menu.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Change Administrative User Password
To change the password of a user click on the user name and you will see the following
screen.
Follow these steps to change
Administrative User password.
Step 1. Click on the user you would
like to change level of.
Step 2. Enable the Change
password checkbox.
Step 3. Enter the new password
twice.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Note: The password should be at least six characters long. The password can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z). Special characters and spaces
are not allowed.
Page 38

Delete Administrative User
To delete a user click on the user name and you will see the following screen.
Follow these steps to delete an
Administrative User.
Step 1. Click on the user you would
like to change level of.
Step 2. Enable the Delete user
checkbox.
Click the Apply button below to
apply the setting or click Cancel to
discard changes.
Note: Deleting a user is
undeleted.
irreversible; once the user is deleted, it cannot be
38
Page 39

Users
User Authentication allows an administrator to grant or reject access to specific users from
specific IP addresses, based on their user credentials.
Before any traffic is allowed to pass through any policies configured with username or
groups, the user must first authenticate him/her-self. The DFL-700 can either verify the user
against a local database or passes along the user information to an external authentication
server, which verifies the user and the given password, and transmits the result back to the
firewall. If the authentication is successful, the DFL.700 will remember the source IP address
of this user, and any matching policies with usernames or groups configured will be allowed.
Specific policies that deal with user authentication can be defined, thus leaving policies that
not require user authentication unaffected.
The DFL-700 supports the RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service)
authentication protocol. This protocol is heavily used in many scenarios where user
authentication is required, either by itself or as a front-end to other authentication services.
The DFL-700 RADIUS Support
The DFL-700 can use RADIUS to verify users against for example Active Directory or Unix
password-file. It is possible to configure up to two servers, if the first one is down it will try the
second IP instead.
The DFL-700 can use CHAP or PAP when communicating with the RADIUS server.
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) does not allow a remote attacker to
extract the user password from an intercepted RADIUS packet. However, the password must
be stored in plaintext on the RADIUS server. PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) might
be defined as the less secure of the two. If a RADIUS packet is intercepted while being
transmitted between the firewall and the RADIUS server, the user password can be extracted,
given time. The upside to this is that the password does not have to be stored in plaintext in
the RADIUS server.
The DFL700 uses a shared secret when connecting to the RADIUS server. The shared
secret enables basic encryption of the user password when the RADIUS-packet is transmitted
from the firewall to the RADIUS server. The shared secret is case sensitive, can contain up to
100 characters, and must be typed exactly the same on both the firewall and the RADIUS
server.
Page 40

Enable User Authentication via HTTP / HTTPS
Follow these steps to enable User
Authentication.
Step 1. Enable the checkbox for User
Authentication.
Step 2. Specify if HTTP and HTTPS or
only HTTPS should be used for the login.
Step 3. Specify the idle-timeout, the time
a user can be idle before being logged out by the firewall.
Step 4. Choose new ports for the management WebUI to listen on as the user
authentication will use the same ports as the management WebUI is using..
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Enable RADIUS Support
Follow these steps to enable RADIUS
support.
Step 1. Enable the checkbox for
RADIUS Support.
Step 2. Fill in up to two RADIUS servers.
Step 3. Specified which mode to use, PAP or CHAP.
Step 3. Specify the shared secret for this connection.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
40
Page 41

Add User
Follow these steps to add a new user.
Step 1. Click on add after the type of
user you would like to add, Admin or
Read-only.
Step 2. Fill in User name; make sure
you are not trying to add one that
already exists.
Step 3. Specified what groups the user
should be a member of.
Step 3. Specify the password for the new user.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Note: The user name and password should be at least six characters long. The user
name and password can contain numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-
z). Special characters and spaces are not allowed.
Change User Password
To change the password of a user click on the user name and you will see the following
screen.
Follow these steps to change a users
password.
Step 1. Click on the user you would like
to change level of.
Step 2. Enable the Change password
checkbox.
Step 3. Enter the new password twice.
Click the Apply button below to apply
the setting or click Cancel to discard
changes.
Note: The password should be at least six characters long. The password can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z). Special characters and spaces
are not allowed.
Page 42

Delete User
To delete a user click on the user name and you will see the following screen.
Follow these steps to delete a user.
Step 1. Click on the user you would like
to change level of.
Step 2. Enable the Delete user
checkbox.
Click the Apply button below to apply
the setting or click Cancel to discard
changes.
Note: Deleting a user is
irreversible;
once the user is deleted, it cannot be
undeleted.
42
Page 43

Schedules
It is possible to
configure a schedule for
policies to take affect.
By creating a schedule,
the DFL-700 is allowing
the firewall policies to
be used at those
designated times only.
Any activities outside of
the scheduled time slot
will not follow the
policies and will
therefore likely not be
permitted to pass
through the firewall. The
DFL-700 can be
configured to have a
start time and stop time,
as well as creating 2
different time periods in
a day. For example, an
organization may only
want the firewall to allow
the internal network
users to access the
Internet during work
hours. Therefore, one may create a schedule to allow the firewall to allow traffic MondayFriday, 8AM-5PM only. During the non-work hours, the firewall will not allow Internet access.
Add new recurring schedule
Follow these steps to add new recurring schedule.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and Schedules and choose Add new.
Step 2. Choose the starting and ending date and hour when the schedule should be active.
Step 3. Use the checkboxes to set the times this schedule should be active. If all boxes
are checked the schedule will be active all the time from the starting to the ending date. If
all boxes are unchecked the schedule never will trigger.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 44

Services
A service is basically a definition of a specific IP protocol with corresponding parameters.
The service http, for instance, is defined as to use the TCP protocol with destination port 80.
Services are simplistic, in that they cannot carry out any action in the firewall on their own.
Thus, a service definition does not include any information whether the service should be
allowed through the firewall or not. That decision is made entirely by the firewall policies, in
which the service is used as a filter parameter.
Adding TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP Service
For many services, a single destination port is sufficient. The http service, for instance, is
using destination port 80. To use a single destination port, enter the port number in the
destination ports text box. In most cases, all ports (0-65535) have to be used as source ports.
The second option is to define a port range, a port range is inclusive, meaning that a range
137-139 covers ports 137, 138 and 139.
Multiple ranges or individual ports may also be entered, separated by commas. For
instance, a service can be defined as having source ports 1024-65535 and destination ports
80-82, 90-92, 95. In this case, a TCP or UDP packet with the destination port being one of 80,
81, 82, 90, 91, 92 or 95, and the source port being in the range 1024-65535, will match this
service.
Follow these steps to add a TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP service.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and Service and choose add new.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the service in the name field. This name will appear in the
service list when you add a new policy. The name can contain numbers (0-9) and upper
and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters - and _. No other special
characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Select TCP/UDP Service.
Step 4. Select the protocol (either TCP, UDP or both TCP/UDP) used by the service.
Step 5. Specify a source port or range for this service by typing in the low and high port
numbers. Enter 0-65535 for all ports, or a single port like 80 for only one source port.
Step 6. Specify a destination port or range for this service by typing in the low and high
port numbers. Enter 0-65535 for all ports, or a single port like 80 for only one destination
port.
Step 7. Enable the Syn Relay checkbox if you want to protect the destination from SYN
flood attacks.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
44
Page 45

Adding IP Protocol
When the type of the service is IP Protocol, an IP protocol number may be specified in the
text field. To have the service match the GRE protocol, for example, the IP protocol should be
specified as 47. A list of some defined IP protocols can be found in the appendix named “IP
Protocol Numbers”.
IP protocol ranges can be used to specify multiple IP protocols for one service. An IP
protocol range is similar to the TCP and UDP port range described previously; the range 1-4,
7 will match the protocols ICMP, IGMP, GGP, IP-in-IP and CBT.
Follow these steps to add a TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP service.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and Service and choose new.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the service in the name field. This name will appear in the
service list when you add a new policy. The name can contain numbers (0-9) and upper
and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters - and _. No other special
characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Select IP Protocol.
Step 4. Specify a comma-separated list of IP protocols.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Grouping Services
Services can be grouped in order to simplify configuration. Consider a web server using
standard http as well as SSL encrypted http (https). Instead of having to create two separate
rules allowing both types of services through the firewall, a service group named, for instance,
Web, can be created, with the http and the https services as group members.
Follow these steps to add a group.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and Service and choose new.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the service in the name field. This name will appear in the
service list when you add a new policy. The name can contain numbers (0-9) and upper
and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters - and _. No other special
characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Select Group.
Step 4. Specify a comma-separated list of existing services.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 46

Protocol-independent settings
Allow ICMP errors from the destination to the source – ICMP error messages are sent
in several situations: for example, when an IP packet cannot reach its destination. The
purpose of these error control messages is to provide feedback about problems in the
communication environment.
However, ICMP error messages and firewalls are usually not a very good combination; the
ICMP error messages are initiated at the destination host (or a device within the path to the
destination) and sent to the originating host. The result is that the ICMP error message will be
interpreted by the firewall as a new connection and dropped, if not explicitly allowed by the
firewall rule-set. Now, allowing any inbound ICMP message to be able have those error
messages forwarded is generally not a good idea.
To solve this problem, DFL-700 can be instructed to pass an ICMP error message only if it
is related to an existing connection. Check this option to enable this feature for connections
using this service.
ALG – Like other stateful inspection based firewalls, DFL-700 filters on information found
in packet headers, for instance in IP, TCP, UDP and ICMP headers.
In some situations though, filtering on header data only is not sufficient. The FTP protocol,
for instance, includes IP address and port information in the protocol payload. In these cases,
the firewall needs to be able to examine the payload data and carry out appropriate actions.
DFL-700 provides this functionality using Application Layer Gateways, also known as ALGs.
To use an Application Layer Gateway, the appropriate Application Layer Gateway
definition is selected in the dropdown menu. The selected Application Layer Gateway will thus
manage network traffic that matches the policy using this service.
Currently, DFL-700 supports two Application Layer Gateways, one is used to manage the
FTP protocol and the other one is a HTTP Content Filtering ALG. For detailed information
about how to configure the HTTP Application Layer Gateway, please see the Content Filtering
chapter.
46
Page 47

VPN
Introduction to IPsec
This chapter introduces IPsec, the method, or rather set of methods used to provide VPN
functionality. IPSec, Internet Protocol Security, is a set of protocols defined by the IETF,
Internet Engineering Task Force, to provide IP security at the network layer.
An IPsec based VPN, such as DFL-700 VPN, is made up by two parts:
• Internet Key Exchange protocol (IKE)
• IPSec protocols (ESP)
The first part, IKE, is the initial negotiation phase, where the two VPN endpoints agree on
which methods will be used to provide security for the underlying IP traffic. Furthermore, IKE
is used to manage connections, by defining a set of Security Associations, SAs, for each
connection. SAs are unidirectional, so there will be at least two SAs per IPSec connection.
The other part is the actual IP data being transferred, using the encryption and authentication
methods agreed upon in the IKE negotiation. This can be accomplished in a number of ways;
by using the IPSec protocol ESP.
To set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN), you do not need to configure an Access Policy
to enable encryption. Just fill in the following settings: VPN Name, Source Subnet (Local Net),
Destination Gateway (If LAN-to-LAN), Destination Subnet (If LAN-to-LAN) and Authentication
Method (Pre-shared key or Certificate). The firewalls on both ends must use the same Preshared key or set of Certificates and IPSec lifetime to make a VPN connection.
Page 48

Introduction to PPTP
PPTP, Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol, is used to provide IP security at the network
layer.
A PPTP based VPN is made up by these parts:
• Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
• Authentication Protocols (PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP v1, MS-CHAP v2)
• Microsoft Point-To-Point Encryption (MPPE)
• Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
PPTP uses TCP port 1723 for it's control connection and uses GRE (IP protocol 47) for
the PPP data. PPTP supports data encryption by using MPPE.
Introduction to L2TP
L2TP, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol, is used to provide IP security at the network layer.
An L2TP based VPN is made up by these parts:
• Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
• Authentication Protocols (PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP v1, MS-CHAP v2)
• Microsoft Point-To-Point Encryption (MPPE)
L2TP uses UDP to transport the PPP data, this is often encapsulated in IPSec for
encryption instead of using MPPE.
Point-to-Point Protocol
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) is a standard for transporting datagram’s over point-to-point
links. It is used to encapsulate IP packets for transport between two peers.
PPP consists of these three components:
• Link Control Protocols (LCP), to negotiate parameters, test and establish the link.
• Network Control Protocol (NCP), to establish and negotiate different network
layer protocols (DFL-700 only supports IP)
• Data encapsulation, to encapsulate datagram’s over the link.
To establish a PPP tunnel, both sides send LCP frames to negotiate parameters and test
the data link. If authentication is used, at least one of the peers has to authenticate itself
before the network layer protocol parameters can be negotiated using NCP. During the LCP
and NCP negotiation optional parameters such as encryption, can be negotiated. When LCP
and NCP negotiation is done, IP datagram’s can be sent over the link.
48
Page 49

Authentication Protocols
PPP supports different authentication protocols, PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP v1 and MSCHAP v2 is supported. Which authentication protocol to use is negotiated during LCP
negotiation.
PAP
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) is a simple, plaintext authentication scheme,
which means that user name and password are sent in plaintext. PAP is therefore not a
secure authentication protocol.
CHAP
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) is a challenge-response
authentication protocol specified in RFC 1994. CHAP uses a MD5 one-way encryption
scheme to hash the response to a challenge issued by the DFL-700. CHAP is better then
PAP in that the password is never sent over the link. Instead the password is used to create
the one-way MD5 hash. That means that CHAP requires passwords to be stored in a
reversibly encrypted form.
MS-CHAP v1
MS-CHAP v1 (Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 1) is
similar to CHAP, the main difference is that with MS-CHAP v1 the password only needs to be
stored as a MD4 hash instead of a reversibly encrypted form. Another difference is that MSCHAP v1 uses MD4 instead of MD5.
MS-CHAP v2
MS-CHAP v2 (Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 1) is more
secure then MS-CHAP v1 as it provides two –way authentication.
MPPE, Microsoft Point-To-Point Encryption
MPPE is used is used to encrypt Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) packets. MPPE uses the
RSA RC4 algorithm to provide data confidentiality. The length of the session key to be used
for the encryption can be negotiated. MPPE currently supports 40-bit, 56-bit and 128-bit RC4
session keys.
Page 50

L2TP/PPTP Clients
General parameters
Name – Specifies a name for
the PPTP/L2TP Client.
Username - Specify the
username to use for this
PPTP/L2TP Client.
Password/Confirm
Password - The password to use
for this PPTP/L2TP Client.
Interface IP.- Specifies if the
L2TP/PPTP Client should try to
use a specified IP or get one from
the server.
Remote Gateway - The IP
address of the PPTP/L2TP
Server. To connect to
Dial on demand is used
when the tunnel should only be used when needed, if diabled the tunnel will always try to be
up.
Authentication protocol
Specify if, and what
authentication protocol to use,
read more about the different
authentication protocols in the
Authentication Protocol
Introduction chapter.
MPPE encryption
If MPPE encryption is going to
be used, this is where the
encryption level is configured.
If L2TP or PPTP over IPSec
is going to be used it has to be
enabled and configured to either
use a Pre-Shared Key or a
Certificate.
50
Page 51

L2TP/PPTP Servers
Name – Specifies a name for
this PPTP/L2TP Server.
Outer IP - Specifies the IP
that the PPTP/L2TP server
should listen on, leave it Blank for
the WAN IP.
Inner IP - Specifies the IP
inside the tunnel, leave it Blank
for the LAN IP.
IP Pool and settings
Client IP Pool - A range,
group or network that the
PPTP/L2TP Server will use as IP
address pool to give out IP addresses to the clients from.
Primary/Secondary DNS - IP of the primary and secondary DNS servers.
Primary/Secondary WINS - IP of the Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) servers
that are used in Microsoft environments which uses the NetBIOS Name Servers (NBNS) to
assign IP addresses to NetBIOS names.
Authentication protocol
Specify if, and what
authentication protocol to use,
read more about the different
authentication protocols in the
Authentication Protocol
Introduction chapter.
Page 52

MPPE encryption
If MPPE encryption is going to
be used, this is where the
encryption level is configured.
If L2TP or PPTP over IPSec
is going to be used it has to be
enabled and configured to either
use a Pre-Shared Key or a
Certificate.
52
Page 53

VPN between two networks
In the following example users on the main
office internal network can connect to the branch
office internal network vice versa. Communication
between the two networks takes place in an
encrypted VPN tunnel that connects the two DFLs
Network Security Firewall across the Internet. Users
on the internal networks are not aware that when
they connect to a computer on the other network
that the connection runs across the Internet.
As shown in the example, you can use the DFL
to protect a branch office and a small main office.
Both of these DFLs can be configured as IPSec
VPN gateways to create the VPN that connects the
branch office network to the main office network.
The example shows a VPN between two
internal networks, but you can also create VPNs
between an internal network behind one VPN
gateway and a DMZ network behind another or
between two DMZ networks. The networks at the
ends of the VPN tunnel are selected when you configure the VPN policy.
Creating a LAN-to-LAN IPSec VPN Tunnel
Follow these steps to add LAN-to-LAN Tunnel.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and VPN and choose Add new in the IPSec tunnels section.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the new tunnel in the name field. The name can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters -
and _. No other special characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Specify your local network, or your side of the tunnel, for example
192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0, in the Local Net field.
Step 4. Choose authentication type, either PSK (Pre-shared Key) or Certificate-based. If
you choose PSK make sure both firewalls use exactly the same PSK.
Step 5. As Tunnel Type choose LAN-to-LAN tunnel and specify the network behind the
other DFL-700 as Remote Net also specify the external IP of the other DFL-700, this can
be an IP or a DNS name.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Repeat this on the firewall on the other site.
Page 54

VPN between client and an internal network
In the following example users can connect to
the main office internal network from anywhere on
the Internet. Communication between the client and
the internal network takes place in an encrypted
VPN tunnel that connects the DFL and the roaming
users across the Internet.
The example shows a VPN between a roaming
VPN client and the internal network, but you can
also create a VPN tunnel that uses the DMZ network.
The networks at the ends of the VPN tunnel are
selected when you configure the VPN policy.
Creating a Roaming Users IPSec VPN Tunnel
Follow these steps to add a roaming users tunnel.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and VPN and choose Add new in the IPSec tunnels section.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the new tunnel in the name field. The name can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters -
and _. No other special characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Specify your local network, or your side of the tunnel, for example
192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0, in the Local Net field. This is the network your roaming VPN
clients should be allowed to connect to.
Step 4. Choose authentication type, either PSK (Pre-shared Key) or Certificate-based. If
you choose PSK make sure the clients use exactly the same PSK.
Step 5. As Tunnel Type choose Roaming User.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
54
Page 55

Adding a L2TP/PPTP VPN Client
Follow these steps to add a L2TP or PPTP VPN Client configuration.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and VPN and choose Add new PPTP client or Add new L2TP
client in the L2TP/PPTP Clients section.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the new tunnel in the name field. The name can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters -
and _. No other special characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Enter the username and password for the PPTP or L2TP Client.
Step 4. Specifies if the IP should be received from the server or if one should be specified.
Should be left blank in most scenarios.
Step 5. Specify the Remote Gateway; this should be the IP of the L2TP or PPTP Server
you are connecting to.
Step 6. If you are using IPSec encryption for the L2TP or PPTP Client choose
authentication type, either PSK (Pre-shared Key) or Certificate-based.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Adding a L2TP/PPTP VPN Server
Follow these steps to add a L2TP or PPTP VPN Server configuration that listens on the WAN
IP.
Step 1. Go to Firewall and VPN and choose Add new PPTP server or Add new L2TP
server in the L2TP/PPTP Server section.
Step 2. Enter a Name for the new tunnel in the name field. The name can contain
numbers (0-9) and upper and lower case letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special characters -
and _. No other special characters and spaces are allowed.
Step 3. Specify the Client IP Pool; this should be a range of unused IP’s on the LAN
interface that should be handed out to the L2TP or PPTP Clients.
Step 4. If you are using IPSec encryption for the L2TP or PPTP Client choose
authentication type, either PSK (Pre-shared Key) or Certificate-based.
Click the Apply button below to apply the change or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 56

VPN – Advanced Settings
Advanced settings for a VPN tunnel is used when one need change some characteristics
of the tunnel when using for example trying to connect to a third party VPN Gateway. The
different settings to set per tunnel is the following:
Limit MTU
Whit this setting it’s possible to limit the MTU (Max Transferable Unit) of the VPN tunnel.
IKE Mode
Specify if Main mode IKE or Aggressive Mode IKE should be used when establishing
outbound VPN Tunnels. Inbound main mode connections will always be allowed. Inbound
aggressive mode connections will only be allowed if this setting is set to aggressive mode.
IKE DH Group
Here it’s possible to configure the Diffie-Hellman group to 1 (modp 768-bit), 2 (modp 1024bit) or 5 (modp 1536-bit).
PFS – Perfect Forward Secrecy
If PFS, Perfect Forwarding Secrecy, is enabled, a new Diffie-Hellman exchange is
performed for each phase-2 negotiation. While this is slower, it makes sure that no keys are
dependent on any other previously used keys; no keys are extracted from the same initial
keying material. This is to make sure that, in the unlikely event that some key was
compromised; no subsequent keys can be derived.
NAT Traversal
Here it’s possible to configure how the NAT Traversal code should behave.
Disabled - The firewall does not send the Vendor ID's that include NAT-T support when
setting up the tunnel.
On if supported and need NAT - Will only use NAT-T if one of the VPN gateways is
NATed.
On if supported - Always tries to use NAT-T when setting up the tunnel.
Keepalives
No keepalives – Keep-alive is disabled.
Automatic keepalives - The firewall will send ICMP pings to IP Addresses automatically
discovered from the VPN Tunnel settings.
Manually configured IP addresses - Configure the source and destination IP addresses
used when sending the ICMP pings
56
Page 57

Proposal Lists
To agree on the VPN connection parameters, a negotiation process is performed. As the
result of the negotiations, the IKE and IPSec security associations (SAs) are established. As
the name implies, a proposal is the starting point for the negotiation. A proposal defines
encryption parameters, for instance encryption algorithm, life times etc, that the VPN gateway
supports.
There are two types of proposals, IKE proposals and IPSec proposals. IKE proposals are
used during IKE Phase-1 (IKE Security Negotiation), while IPSec proposals are using during
IKE Phase-2 (IPSec Security Negotiation).
A Proposal List is used to group several proposals. During the negotiation process, the
proposals in the proposal list are offered to the remote VPN gateway one after another until a
matching proposal is found.
IKE Proposal List
Cipher – Specifies the encryption algorithm used in this IKE proposal. Supported
algorithms are AES, 3DES, DES, Blowfish, Twofish and CAST128.
Hash – Specifies the hash function used to calculate a check sum that reveals if the data
packet is altered while being transmitted. MD5 and SHA1 are supported algorithms.
Life Times – Specifies in KB or seconds when the security associations for the VPN
tunnel need to be re-negotiated.
IPSec Proposal List
Cipher – Specifies the encryption algorithm used in this IPSec proposal. Supported
algorithms are AES, 3DES, DES, Blowfish, Twofish and CAST128.
HMAC – Specifies the hash function used to calculate a check sum that reveals if the data
packet is altered while being transmitted. MD5 and SHA1 are supported algorithms.
Life Times – Specifies in KB or seconds when the security associations for the VPN
tunnel need to be re-negotiated.
Page 58

Certificates
A certificate is a digital proof of identity. It links an identity to a public key in a trustworthy
manner. Certificates can be used to authenticate individual users or other entities. These
types of certificates are commonly called end-entity certificates.
Before a VPN tunnel with certificate based authentication can be set up, the firewall needs
a certificate of its own and that of the remote firewall. These certificates can either be selfsigned certificates, or issued by a CA.
Trusting Certificates
When setting up a VPN tunnel, the firewall has to be told whom it should trust. When using
pre-shared keys, this is simple. The firewall trusts anyone who has the same pre-shared key.
When using certificates, on the other hand, you tell the firewall that it can trust anyone
whose certificate is signed by a given CA. Before a certificate is accepted, the following steps
are taken to verify the validity of the certificate:
• Construct a certification path up to the trusted root CA.
• Verify the signatures of all certificates in the certification path.
• Fetch the CRL for each certificate to verify that none of the certificates have been
revoked.
Local identities
This is a list of all the local identity certificates that can be used in VPN tunnels. A local
identity certificate is used by the firewall to prove its identity to the remote VPN peer.
To add a new local identity certificate, click Add new. The following pages will allow you to
specify a name for the local identity, and upload the certificate and private key files. This
certificate can be selected in the Local Identity field on the VPN page.
This list also includes a special certificate called Admin. This is the certificate used by the
web interface to provide HTTPS access.
Note: The certificate named Admin can only be replaced, not deleted or renamed. This is
used for HTTPS access to the DFL-700.
Certificates of remote peers
This is a list of all certificates of individual remote peers.
To add a new remote peer certificate, click Add new. The following pages will allow you to
specify a name for the remote peer certificate and upload the certificate file. This certificate
can be selected in the Certificates field on the VPN page.
58
Page 59

Certificate Authorities
This is a list of all CA certificates. To add a new Certificate Authority certificate, click Add
new. The following pages will allow you to specify a name for the CA certificate and upload
the certificate file. This certificate can be selected in the Certificates field on the VPN page.
Note: If the uploaded certificate is a CA certificate, it will automatically be placed in the
Certificate Authorities list, even if Add New was clicked in the Remote Peers list. Similiarly, a
non-CA certificate will be placed in the Remote Peers list even if Add New was clicked from
the Certificate Authorities list.
Identities
This is a list of all the configured Identity lists. An Identity list can be used on the VPN
page to limit inbound VPN access from this list of known identities.
Normally, a VPN tunnel is established if the certificate of the remote peer is present in the
Certificates field in the VPN section, or if the remote peer's certificate is signed by a CA
whose certificate is present in the Certificates field in the VPN section. However, in some
cases it might be necessary to limit who can establish a VPN tunnel even among peers
signed by the same CA.
The Identity list can be selected in the Identity List field on the VPN page.
If an Identity List is configured, the firewall will match the identity of the connecting remote
peer against the Identity List, and only allow it to open the VPN tunnel if it matches the
contents of the list.
If no Identity List is used, no identity matching is done.
Page 60

Content Filtering
DFL-700 HTTP content filtering can be configured to scan all HTTP content protocol
streams for URLs or for web page content.
You can configure URL blacklist to block all or just some of the pages on a website. Using
this feature you can deny access to parts of a web site without denying access to it
completely.
The HTTP content filter can also be configured to strip contents like ActiveX, Flash and
cookies.
There is also a URL whitelist for URLs that should be excluded from all Content Filtering.
To have the URL white/black list match entire sites, you will most likely want to use
wildcards before and after the host names, e.g. "*example.com/*". However, this will also
trigger on e.g. "myexample.com/", so you may want to split it up in two patterns, e.g.
"example.com/*" and "*.example.com/*", to catch the domain name by itself as well as
variants with prefixed host names ("www.") without having the filter trigger on domains ending
with the same text.
Note: For HTTP URL filtering to work, all HTTP traffic needs to go trough a policy using a
service with the HTTP ALG, which is the case for the "http-outbound" service by default.
Also note that the HTTP content filter cannot examine HTTPS (encrypted) connections
due to their encrypted nature. If you wish to block access to HTTPS sites, you will need to
configure rules in the firewall policy to block access to port 443 (https) on the IP addresses in
question.
Active content handling
Active content handling can be enabled or disabled by checking the checkbox before each
type you would like to strip. For example to strip ActiveX and Flash enable the checkbox
named Strip ActiveX objects. It is possible to strip ActiveX, Flash, Java, JavaScript and
VBScript. It is also possible to block cookies.
60
Page 61

Edit the URL Global Whitelist
Follow these steps to
add or remove a url.
Step 1. Go to
Firewall and Content
Filtering and choose
Edit global URL
whitelist
Step 2. Add/edit or
remove the URL that
should never be
checked with the
Content Filtering.
Click the Apply
button below to apply
the change or click
Cancel to discard
changes.
Page 62

Edit the URL Global Blacklist
Follow these steps to
add or remove a url.
Step 1. Go to
Firewall and Content
Filtering and choose
Edit global URL
blacklist
Step 2. Add/edit or
remove the URL that
should be checked
with the Content
Filtering.
Click the Apply
button below to apply
the change or click
Cancel to discard
changes.
Note: For HTTP
URL filtering to work, all
HTTP traffic needs to go
trough a policy using a
service with the HTTP
ALG.
62
Page 63

Active content handling
Active content handling can be enabled or disabled by checking the checkbox before each
type you would like to strip. For example to strip ActiveX and Flash enable the checkbox
named Strip ActiveX objects. It’s possible to strip ActiveX, Flash, Java, JavaScript and
VBScript, it’s also possible to block cookies.
Note: For HTTP URL filtering to work, all HTTP traffic needs to go trough a policy using a
service with the HTTP ALG.
Page 64

Servers
DHCP Server Settings
The DFL-700 contains a DHCP server; DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a
protocol that lets network administrators to automatically assign IP numbers to computers on
a network. The DFL-700
DHCP Server helps to
minimize the work
necessary to administer
a network, as there is
no need for another
server running DHCP
Server software.
The DFL-700 DHCP
Server only implements
a subset of the DHCP
protocol necessary to
serve a small network,
these are:
• IP address
• Netmask
• Subnet
• Gateway
address
• DNS
Servers
• WINS
Servers
• Domain
name
The DFL-700 DHCP
Server assigns and manages IP addresses from specified address pools within the firewall to
the DHCP clients.
Note: Leases are remembered over a re-configure or reboot of the firewall.
The DFL-700 also includes a DHCP Relayer. A DHCP relayer is a form of gateway
between a DHCP Server and its users. The relayer intercepts DHCP queries from the users
and forwards them to a DHCP server while setting up dynamic routes based on leases. This
enables the firewall to keep an accurate routing table based on active users and protects the
DHCP server to some degree among other things.
Note: There can only be one DHCP Server or DHCP Relay configured per interface.
64
Page 65

Enable DHCP Server
To enable the DHCP Server on an interface, click on Servers in the menu bar, and then
click DHCP Server below it.
Follow these steps to enable the DHCP Server on the LAN interface.
Step 1. Choose the LAN interface from the Available interfaces list.
Step 2. Enable by checking the Use built-in DHCP Server box.
Step 3. Fill in the IP Span, the start and end IP for the range of IP addresses that the DFL-
700 can assign.
Step 4. Fill in the DNS servers DHCP server will assigns to the clients, at least one should
be provided. If the DNS relayer is configured the DHCP server can assign those.
Step 5. Optionally type in the WINS servers the DHCP server assigns to the clients.
Step 6. Optionally type in the domain that the DHCP server assigns to the clients.
Step 7. Choose for how long the DHCP server will give out leases before the client have
to renew them.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes
Enable DHCP Relay
To enable the DHCP Relay on an interface, click on Servers in the menu bar, and then
click DHCP Server below it.
Follow these steps to enable the DHCP Relayer on the LAN interface.
Step 1. Choose the LAN interface from the Available interfaces list.
Step 2. Enable by checking the Relay DHCP Requests to other DHCP server box.
Step 3. Fill in the IP of the DHCP Server; note that it should be on another interface then
where the DHCP request is coming from, i.e. a server on the DMZ.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes
Disable DHCP Server/Relayer
To disable the DHCP Server on an interface, click on Servers in the menu bar, and then
click DHCP Server below it. Here click on the interface that you want to disable the DHCP
server or relayer on.
Follow these steps to disable the DHCP Server or Relayer on the LAN interface.
Step 1. Choose the LAN interface from the Available interfaces list.
Step 2. Disable by checking the No DHCP processing box.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes
Page 66

DNS Relayer Settings
Click on Servers in the menu bar, and then click DNS Relay below it. The DFL-700
contains a DNS relayer that you can be configured to relay DNS queries from the internal LAN
to the DNS servers used by the firewall itself.
Enable DNS Relayer
Follow these steps to enable the DNS Relayer.
Step 1. Enable by checking the Enable DNS Relayer box.
Step 2. Enter the IP numbers that the DFL-700 should listen for DNS queries on.
Note: If “Use address of LAN interface” is checked, you don’t have to enter an IP in IP
Address 1 as the firewall will know what address to use.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
66
Page 67

Disable DNS Relayer
Follow these steps to disable the DNS Relayer.
Step 1. Disable by un-checking the Enable DNS Relayer box.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 68

Tools
Ping
Click on Tools in the menu bar, and then click Ping below it. This tool is used to send a
specified number of ICMP Echo Request packets to a given destination. All packets are sent
in immediate succession rather than one per second. This behavior is the best one suited for
diagnosing connectivity problems.
• IP Address – Target IP to send the ICMP Echo Requests to.
• Number of packets – Number of ICMP Echo Request packets to send, up to 10.
• Packet size – Size of the packet to send, between 32 and 1500 bytes.
Ping Example
In this example, the IP Address is 192.168.10.1 the Number of packets is five, after
clicking on Apply the firewall will start to send the ICMP Echo Requests to the specified IP.
After a few seconds the result will be shown, in this example only four out of five packets was
received back, a 20% packet loss, and the average time for the packets to travel to and from
the specified IP was 57 ms.
68
Page 69

Dynamic DNS
The Dynamic DNS (require Dynamic DNS Service) allows you to alias a dynamic IP
address to a static hostname, allowing your device to be more easily accessed by specific
name. When this function is enabled, the IP address in Dynamic DNS Server will be
automatically updated with the new IP address provided by ISP.
Click DynDNS in the Tools menu to enter Dynamic DNS configuration.
The firewall provides a list of a few predefined DynDNS service providers; users have to
register with one of these providers before trying to use this function.
Add Dynamic DNS Settings
Follow these steps to enable Dynamic DNS.
Step 1. Go to Tools and DynDNS.
Step 2. Choose what Dynamic DNS service you would like to use, and fill in the needed
information, username and password in all cases and domains in all but cjb.net.
Click the Apply button below to apply the setting or click Cancel to discard changes.
Page 70

Backup
Click on Tools in the
menu bar, and then
click Backup below it.
Here a administrator
can backup and restore
the configuration. The
configuration file stores
system settings, IP
addresses of Firewall’s
network interfaces,
address table, service
table, IPSec settings,
port mapping and
policies. When the
configuration process is
completed, system
administrator can
download the
configuration file into
local disc as a backup.
System Administrators
can restore the firewall’s configuration file with the one stored on disc.
Exporting the DFL-700’s Configuration
Follow these steps to export the configuration.
Step 1. Under the Tools menu and the Backup section, click on the Download
configuration button.
Step 2. When the File Download pop-up window appears, choose the destination place in
which to save the exported file. The Administrator may choose to rename the file if
preferred.
Restoring the DFL-700’s Configuration
Follow these steps to restore the configuration.
Step 1. Under the Tools menu and the Backup section, click on the Browse button next
to the empty field. When the Choose File pop-up window appears, select the file to which
contains the saved firewall settings, then click OK.
Step 2. Click Upload Configuration to import the file into the Firewall.
70
Page 71

Restart/Reset
Restarting the DFL-700
Follow these steps restart the DFL-700.
Step 1. Choose if you want to do a quick or full restart.
Step 2. Click Restart Unit and the unit will restart.
Restoring system settings to factory defaults
Use the following procedure to restore system settings to the values set at the factory.
This procedure will possibly change the DFL-700 firmware version to lower version if it has
been upgraded.
This procedure deletes all of the changes that you have made to the DFL-700
configuration and reverts the system to its original configuration including resetting interface
addresses.
Follow these steps reset the DFL-700 to factory default.
Page 72

Step 1. Under the Tools menu and the Reset section, click on the Reset to Factory
Defaults button.
Step 2. Click OK in the dialog to reset the unit to factory default, or press Cancel to cancel.
You can restore your system settings by uploading a previously downloaded system
configurations file to the DFL-700 if a backup of the device has been done.
72
Page 73

Upgrade
The DFL-700’s
software, IDS
signatures and system
parameters are all
stored on a flash
memory card. The flash
memory card is rewritable and re-readable.
Upgrade
Firmware
To upgrade the
firmware first download
the correct firmware
image from D-Link. After
having the newest
version of software,
please store it on the
hard disk, then connect
to the firewall’s WebUI,
enter Upgrade on the
Tools menu, click
Browse and choose the
file name of the newest
version of the firmware,
then click Upload
firmware image.
The updating process won’t overwrite the system configuration, so it is not necessary but still
a good idea to backup it before upgrading the software.
Upgrade IDS Signature-database
To upgrade the signature-database first download the newest IDS signatures from D-Link.
After having the newest version of software connect to the firewall’s WebUI, enter Upgrade
on the Tools menu, click Browse in the Upgrade Unit’s signature-database section and
choose the file name of the newest version of the IDS signatures, then click Upload
signature database.
Page 74

Status
In this section, the DFL-700 displays the status information about the Firewall.
Administrator may use Status to check the System Status, Interface statistics, VPN,
connections and DHCP Servers.
System
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click System below it. A window will appear
providing some information about the DFL-700.
Uptime – The time
the firewall have been
running, since the last
reboot or start.
CPU Load –
Percentage of cpu used.
Connections –
Number of current
connections trough the
firewall.
Firmware version –
The firmware version
running on the firewall.
Last restart – The
reason for the last
restart.
IDS Signatures –
The IDS signature
versions.
There are also two
graphs on this page,
one showing the CPU
usage during the last 24
hours. The other one is
showing the state table usage during the last 24 hours.
74
Page 75

Interfaces
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click Interfaces below it. A window will appear
providing information about the interfaces in the DFL-700. By default information about the
LAN interface will be show, to see another one click on that interface (WAN or DMZ).
Interface – Name of
the interface shown,
LAN, WAN or DMZ.
Link status –
Displays what link the
current interface has,
the speed can be 10 or
100 Mbps and the
duplex can be Half or
Full.
MAC Address –
MAC address of the
interface.
Send rate – Current
amount of traffic sent
trough the interface.
Receive rate –
Current amount of traffic
received trough the
interface.
There are also two
graphs displaying the
send and receive rate
trough the interfaces
during the last 24 hours.
Page 76

VPN
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click Interfaces below it. A window will appear
providing information about the VPN connections done in the DFL-700. By default information
about the first VPN tunnel will be show, to see another one click on that VPN tunnels name.
The two graphs
display the send and
receive rate trough the
selected VPN tunnel
during the last 24 hours.
On this example a
tunnel named
RoamingUsers is
selected, this is a tunnel
that allows roaming
users. So under the
IPSec SA listing each
roaming user connected
to this tunnel is shown.
76
Page 77

Connections
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click Connections below it. A window will
appear providing information about the content of the state table.
Shows the last 100
connections opened
through the firewall.
Connections are
created when traffic is
permitted to pass via
the policies.
Each connection
has two timeout values,
one in each direction.
These are updated
when the firewall
receives packets from
each end of the
connection. The value
shown in the Timeout
column is the lower of
the two values.
Possible values in
the State column
include: TPC_CLOSE,
TCP_OPEN,
SYN_RECV, FIN_RECV and so on.
The Proto column can have:
TCP - The connection is a TCP connection
PING - The connection is an ICMP ECHO connection
UDP - The connection is a UDP connection
RAWIP - The connection uses an IP protocol other than TCP, UDP or ICMP
The Source and Destination columns show from what ip and port on the source interface
is the connection, and to what interface with what port number is the connection to.
Page 78

DHCP Server
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click DHCP Server below it. A window will
appear providing information about the configured DHCP Servers. By default information
about the LAN interface
will be show, to see
another one click on
that interface.
Interface – Name of
the interface the DHCP
Server is running on.
IP Span – Displays
the configured ranges of
IP’s that are given out
as DHCP leases.
Usage – Display
how much of the IP
range is give out to
DHCP clients.
Active leases are
the current computers
using this DHCP server.
It is also possible to end
a computers lease from
here by clicking on End
lease after that IP.
Inactive leases are leases that are not currently in use but have been used by a computer
before, that computer will get that lease the next time it is on the network. If there is no free IP
in the pool these IP’s will be used for new computers.
78
Page 79

Users
Click on Status in the menu bar, and then click Users below it. A window will appear
providing user information.
Currently authenticated users – users logged in using HTTP/HTTPS authentication,
users logged in on PPTP and L2TP servers will be listed here. Users can be forced to log out
by clicking logout.
Currently recognized privileges – all users and groups that are used in policies are
listed here. These users and groups will be able to use HTTP and HTTPS authentication.
Interfaces where authentication are available – here all interfaces where HTTP and
HTTPS authentication is possible is listed.
Page 80

How to read the logs
Although the exact format of each log entry depends on how your syslog recipient works,
most are very much alike. The way in which logs are read is also dependent on how your
syslog recipient works. Syslog daemons on UNIX servers usually log to text files, line by line.
Most syslog recipients preface each log entry with a timestamp and the IP address of the
machine that sent the log data:
Oct 20 2003 09:45:23 gateway
This is followed by the text the sender has chosen to send. All log entries from DFL-700
are prefaced with "EFW:" and a category, e.g. "DROP:"
Oct 20 2003 09:45:23 gateway EFW: DROP:
Subsequent text is dependent on the event that has occurred.
USAGE events
These events are sent periodically and provide statistical information regarding
connections and amount of traffic.
Example:
Oct 20 2003 09:45:23 gateway EFW: USAGE: conns=1174 if0=core ip0=127.0.0.1
tp0=0.00 if1=wan ip1=192.168.10.2 tp1=11.93 if2=lan ip2=192.168.0.1 tp2=13.27 if3=dmz
ip3=192.168.1.1 tp3=0.99
The value after conns is the number of open connections trough the firewall when the
usage log was sent. The value after tp is the throughput through the firewall at the time the
usage log was logged.
DROP events
These events may be generated by a number of different functions in the firewall. The
most common source is probably the policies.
Example:
Oct 20 2003 09:42:25 gateway EFW: DROP: prio=1 rule=Rule_1 action=drop recvif=wan
srcip=192.168.10.2 destip=192.168.0.1 ipproto=TCP ipdatalen=28 srcport=3572 destport=135
tcphdrlen=28 syn=1
In this line, traffic from 192.168.10.2 coming from the WAN side of the firewall, connecting
to 192.168.10.1 on port 135 is dropped. The protocol used is TCP.
CONN events
These events are generated if auditing has been enabled.
80
Page 81

One event will be generated when a connection is established. This event will include
information about protocol, receiving interface, source IP address, source port, destination
interface, destination IP address and destination port.
Open Example:
Oct 20 2003 09:47:56 gateway EFW: CONN: prio=1 rule=Rule_8 conn=open
connipproto=TCP connrecvif=lan connsrcip=192.168.0.10 connsrcport=3179 conndestif=wan
conndestip=64.7.210.132 conndestport=80
In this line, traffic from 192.168.0.10 on the LAN interface is connecting to 64.7.210.132 on
port 80 on the WAN side of the firewall (internet).
Another event is generated when the connection is closed. The information included in the
event is the same as in the event sent when the connection was opened, with the exception
that statistics regarding sent and received traffic is also included.
Close Example:
Oct 20 2003 09:48:05 gateway EFW: CONN: prio=1 rule=Rule_8 conn=close
connipproto=TCP connrecvif=lan connsrcip=192.168.0.10 connsrcport=3179 conndestif=wan
conndestip=64.7.210.132 conndestport=80 origsent=62 termsent=60
In this line, the connection in the other example is closed.
Page 82

Step by step guides
In the following guides example IPs, users, sites and passwords are used. You will have to
exchange the IP addresses and sites to your own. Passwords used in these examples are not
recommended for real life use. Passwords and keys should be chosen so that they are
impossible to guess or find out by eg a dictionary attack.
In these guides for example Firewall->Users will mean that Firewall first should be
selected from the menu at the top of the screen,
and than the Users button to the left of the screen.
82
Page 83

LAN-to-LAN VPN using IPsec
Settings for Branch office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.10
LAN IP: 192.168.4.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup IPsec tunnel, Firewall->VPN:
Under IPsec tunnels click Add new
Name the tunnel ToMainOffice
Local net: 192.168.4.0/24
PSK: 1234567890 (Note! You should use a key that is hard to guess)
Page 84

Retype PSK: 1234567890
Select Tunnel type: LAN-to-LAN tunnel
Remote Net: 192.168.1.0/24
Remote Gateway: 194.0.2.20
Enable Automatically add a route for the remote network
Click Apply
3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
84
Page 85

4. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart
Settings for Main office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.20
LAN IP: 192.168.1.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup IPsec tunnel, Firewall->VPN:
Under IPsec tunnels click add new
Name the tunnel ToBranchOffice
Local net: 192.168.1.0/24
PSK: 1234567890 (Note! You should use a key that is hard to guess)
Retype PSK: 1234567890
Page 86

Select Tunnel type: LAN-to-LAN tunnel
Remote Net: 192.168.4.0/24
Remote Gateway: 194.0.2.10
Enable “Automatically add a route for the remote network”
Click Apply
3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
4. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart
This example will allow all traffic between the two offices. To get a more secure solution read
the A more secure LAN-to-LAN VPN solution in this chapter.
86
Page 87

LAN-to-LAN VPN using PPTP
Settings for Branch office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.10
LAN IP: 192.168.4.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup PPTP client, Firewall->VPN:
Under PPTP/L2TP clients click Add new PPTP client
Name the tunnel toMainOffice
Page 88

Username: BranchOffice
Password: 1234567890 (Note! You should use a password that is hard to guess)
Retype password: 1234567890
Interface IP: leave blank
Remote gateway: 192.0.2.20
Remote net: 192.168.1.0/24
Dial on demand: leave unchecked
Under authentication MSCHAPv2 should be the only checked option.
88
Page 89

Under MPPE encryption 128 bit should be the only checked option.
Leave Use IPsec encryption unchecked
Click Apply
3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
4. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart.
Page 90

Settings for Main office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.20
LAN IP: 192.168.1.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup PPTP server, Firewall->VPN:
Under L2TP / PPTP Server click Add new PPTP server
Name the server pptpServer
Leave Outer IP and Inner IP blank
Set client IP pool to 192.168.1.100 – 192.168.1.199
Check Proxy ARP dynamically added routes
Check Use unit’s own DNS relayer addresses
Leave WINS settings blank
90
Page 91

Under authentication MSCHAPv2 should be the only checked option.
Under MPPE encryption 128 bit should be the only checked option.
Leave Use IPsec encryption unchecked
Click Apply
3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
Page 92

4. Set up authentication source, Firewall->Users:
Select Local database
Click Apply
5. Add a new user, Firewall->Users:
Under Users in local database click Add new
Name the new user BranchOffice
Enter password: 1234567890
Retype password: 1234567890
Leave static client IP empty (could also be set to eg 192.168.1.200. If no IP is set
here the IP pool from the PPTP server settings are used).
Set Networks behind user to 192.168.4.0/24
92
Page 93

Click Apply
6. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart.
This example will allow all traffic between the two offices. To get a more secure solution read
the A more secure LAN-to-LAN VPN solution section in this chapter.
Page 94

LAN-to-LAN VPN using L2TP
Settings for Branch office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.10
LAN IP: 192.168.4.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup L2TP client, Firewall->VPN:
Under L2TP / PPTP client click Add new L2TP client
Name the server toMainOffice
94
Page 95

Username: BranchOffice
Password: 1234567890 (Note! You should use a password that is hard to guess)
Retype password: 1234567890
Interface IP: leave blank
Remote gateway: 192.0.2.20
Remote net: 192.168.1.0/24
Dial on demand: leave unchecked
Under authentication only MSCHAPv2 should be checked
Page 96

Under MPPE encryption only None should be checked
Check Use IPsec encryption
Enter key 1234567890 (Note! You should use a key that is hard to guess)
Retype key 1234567890
Click Apply
3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
96
Page 97

4. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart
Settings for Main office
1. Setup interfaces, System->Interfaces:
WAN IP: 193.0.2.20
LAN IP: 192.168.1.1, Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
2. Setup L2TP server, Firewall->VPN:
Under L2TP / PPTP Server click Add new L2TP server
Name the server l2tpServer
Leave Outer IP and Inner IP blank
Set client IP pool to 192.168.1.100 – 192.168.1.199
Check Proxy ARP dynamically added routes
Check Use unit’s own DNS relayer addresses
Page 98

Leave WINS settings blank
Under authentication MSCHAPv2 should be the only checked option.
Under MPPE encryption None should be the only checked option.
Check Use IPsec encryption
Enter key 1234567890 (Note! You should use a key that is hard to guess)
Retype key 1234567890
Click Apply
98
Page 99

3. Setup policies for the new tunnel, Firewall->Policy:
Click Global policy parameters
Enable Allow all VPN traffic: internal->VPN, VPN->internal and VPN->VPN
Click Apply
4. Set up authentication source, Firewall->Users:
Select Local database
Click Apply
Page 100

5. Add a new user, Firewall->Users:
Under Users in local database click Add new
Name the new user BranchOffice
Enter password: 1234567890
Retype password: 1234567890
Leave static client IP empty (could also be set to eg 192.168.1.200. If no IP is set
here the IP pool from the L2TP server settings are used).
Set Networks behind user to 192.168.4.0/24
Click Apply
6. Click Activate and wait for the firewall to restart.
This example will allow all traffic between the two offices. To get a more secure solution read
the A more secure LAN-to-LAN VPN solution section in this chapter.
100
 Loading...
Loading...