User Manual
v1.0 2021.03
Searching for Keywords
Search for keywords such as “battery” and “install” to find a topic. If you are using Adobe
Acrobat Reader to read this document, press Ctrl+F on Windows or Command+F on Mac to
begin a search.
Navigating to a Topic
View a complete list of topics in the table of contents. Click on a topic to navigate to that
section.
Printing this Document
This document supports high resolution printing.

Using this Manual
Legend
Warning Important Hints and Tips Reference
Read Before the First Flight
Read the following documents before using DJITM FPV.
1. User Manual
2. Quick Start Guide
3. Disclaimer and Safety Guidelines
It is recommended to watch all tutorial videos on the official DJI website and read the disclaimer and safety
guidelines before using for the rst time. Prepare for your rst ight by reviewing the quick start guide and refer to
this user manual for more information.
Video Tutorials
Visit the address below or scan the QR code to watch the DJI FPV tutorial videos, which
demonstrate how to use DJI FPV safely:
https://www.dji.com/dji-fpv/video
Download the DJI Fly App
Scan the QR code on the right to download DJI Fly.
The Android version of DJI Fly is compatible with Android v6.0 and later. The iOS version of DJI Fly
is compatible with iOS v11.0 and later.
* For increased safety, ight is restricted to a height of 98.4 ft (30 m) and a range of 164 ft (50 m) when not connected
or logged into the app during ight. This applies to DJI Fly and all apps compatible with DJI aircraft.
Download the DJI Virtual Flight App
Scan the QR code on the right to download DJI Virtual Flight.
The iOS version of DJI Virtual Flight is compatible with iOS v11.0 and later.
Download DJI Assistant 2 (DJI FPV series)
Download DJI ASSISTANTTM 2 (DJI FPV Series) at https://www.dji.com/dji-fpv/downloads.
The operating temperature of this product is 0° to 40° C. It does not meet the standard operating
temperature for military grade application (-55° to 125° C), which is required to endure greater
environmental variability. Operate the product appropriately and only for applications that it meets the
operating temperature range requirements of that grade.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
3

Contents
Using this Manual 3
Product Prole 6
Aircraft 16
Legend 3
Read Before the First Flight 3
Video Tutorials 3
Download the DJI Fly App 3
Download the DJI Virtual Flight App 3
Download DJI Assistant 2 (DJI FPV series) 3
Introduction 6
Preparing the Aircraft 7
Preparing the Goggles 8
Preparing the Remote Controller 10
Diagram 10
Linking 14
Activation 15
Flight Modes 16
Aircraft Status Indicator 17
Return to Home 18
Vision Systems and Infrared Sensing System 20
Flight Recorder 23
Propellers 23
Intelligent Flight Battery 25
Gimbal and Camera 29
Goggles 31
Remote Controller 39
DJI Fly App 45
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
4
Power Supply 31
Operation 32
Home Screen 32
Menu Bar 34
Operation 39
Optimal Transmission Zone 43
Stick Adjustment 44

DJI FPV
User Manual
Flight 47
Flight Environment Requirements 47
Flight Limits and GEO Zones 47
Pre-Flight Checklist 48
Starting/Stopping the Motors 49
Flight Test 50
Maintenance 51
Goggles 51
Aircraft 52
Appendix 61
Specications 61
Calibrating the Compass 65
Updating Firmware 66
After-Sales Information 66
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
5
Product Prole
Introduction
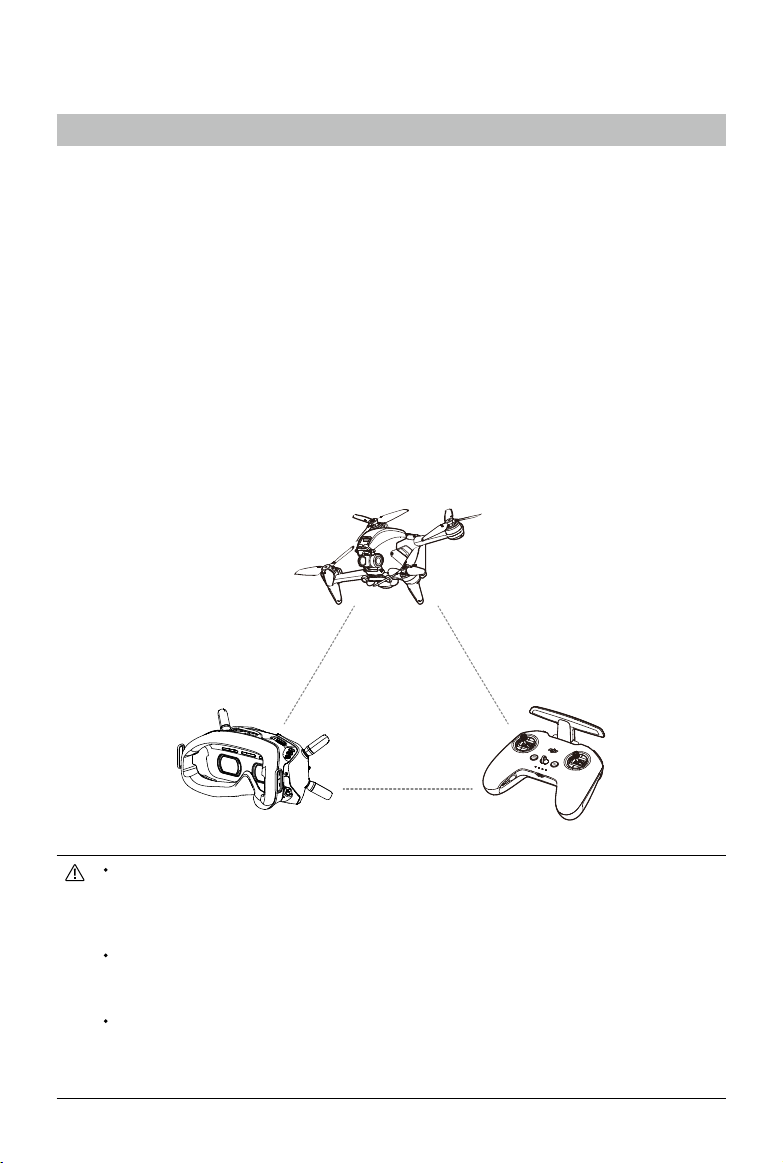
DJI FPV consists of an aircraft, goggles, and remote controller, which all feature DJI’s O3 technology that provides
video transmission with a maximum transmission range of 6 mi (10 km), bit rate of up to 50 Mbps, and minimum
end-to-end latency within 28 ms. DJI FPV works at both 2.4 and 5.8 GHz and is capable of selecting the best
transmission channel automatically. The enhanced anti-interference ability greatly improves the smoothness and
stability of the video transmission, providing an integrated and immersive ight experience.
Featuring a Forward and Downward Vision System and Infrared Sensing System, the aircraft can hover and y
indoors as well as outdoors and automatically initiate Return to Home (RTH). With a gimbal and 1/2.3” sensor
camera, the aircraft stably shoots 4K 60fps ultra-HD video and 4K photos. The aircraft has a maximum ight
speed of 87 mph (140 kph) and a maximum ight time of approximately 20 minutes.
The DJI FPV Goggles V2 are equipped with a high-performance display and support 810p 120fps HD display and
real-time audio transmission. By receiving the video signal from the aircraft, users can enjoy a rst-person view of
their aerial experience in real time. The goggles have a maximum runtime of approximately 1 hour and 50 minutes
when used with DJI FPV Goggles Battery and where the ambient temperature is 25° C and the screen brightness
is set to 6.
The DJI FPV Remote Controller 2 is equipped with a range of function buttons, which can be used to control the
aircraft and operate the camera. The maximum runtime of the remote controller is approximately 9 hours.
Aircraft
Goggles Remote Controller
The remote controller reaches its maximum transmission distance (FCC) in a wide-open area with no
electromagnetic interference when the aircraft is at an altitude of approximately 400 ft (120 m). The
maximum transmission distance refers to the maximum distance that the aircraft can still send and
receive transmissions. It does not refer to the maximum distance the aircraft can y in a single ight.
The end-to-end latency is the total time from camera sensor input to screen display. The DJI FPV
can reach its minimum latency in Low Latency mode (810p 120fps) in a wide open area with no
electromagnetic interference.
Maximum ight time was tested in an environment with no wind while ying at a consistent 24.9 mph
(40 kph) and the maximum ight speed was tested in Manual mode at sea level altitude with no wind.
These values are for reference only. The maximum ight speed of the aircraft varies depending on
national and regional regulations.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
6
DJI FPV
User Manual
5.8 GHz is not supported in some regions. This frequency band will automatically be disabled when
the aircraft is activated or connected to DJI Fly in these regions. Observe local laws and regulations.
Using the goggles does not satisfy the requirement of visual line of sight (VLOS). Some countries
or regions require a visual observer to assist by observing the ight. Make sure to comply with local
regulations when using the goggles.
Preparing the Aircraft
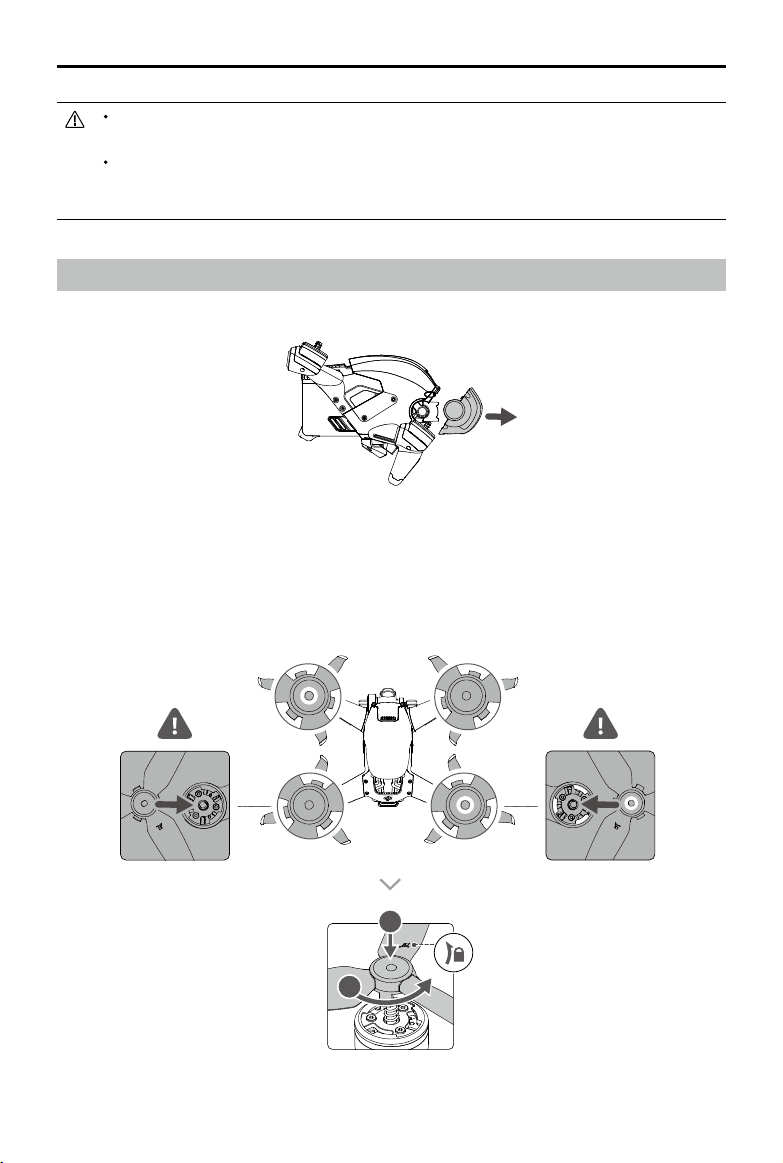
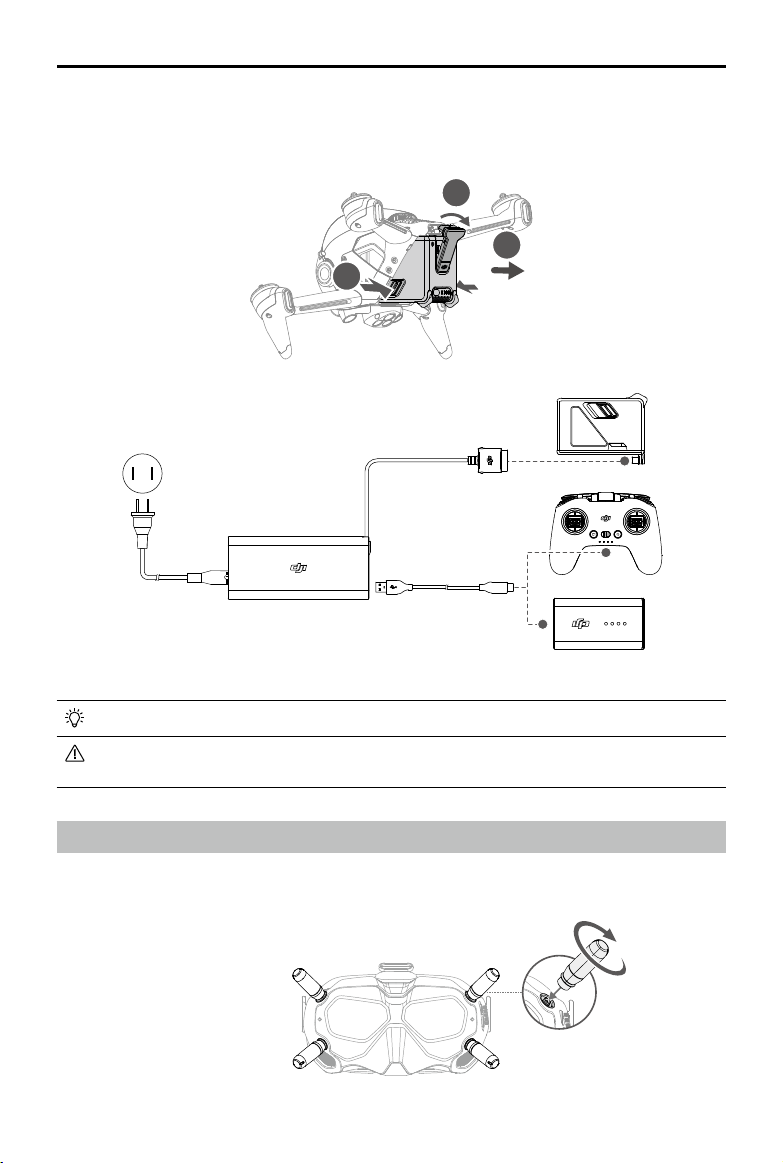
1. Remove the gimbal protector from the camera.
2. Attach the propellers.
Propellers with and without marks indicate dierent directions of rotation. Attach the propellers with marks to
the motors with marks and the unmarked propellers to the motors without marks. Hold the motor, press the
propeller down, and rotate in the direction marked on the propeller until it pops up and locks in place.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
7
BA
B A
1
2
DJI FPV
3. All Intelligent Flight Batteries are in hibernation mode before shipping to ensure safety. Remove the Intelligent
User Manual
Flight Battery and use the provided charger to charge and activate the Intelligent Flight Batteries for the rst
time. It takes approximately 50 minutes to fully charge an Intelligent Flight Battery.
1
3
2
It is recommended to attach a gimbal protector to protect the gimbal when the aircraft is not in use.
Make sure the gimbal protector is removed before powering on the aircraft. Otherwise, it may aect the
aircraft self-diagnostics.
Preparing the Goggles
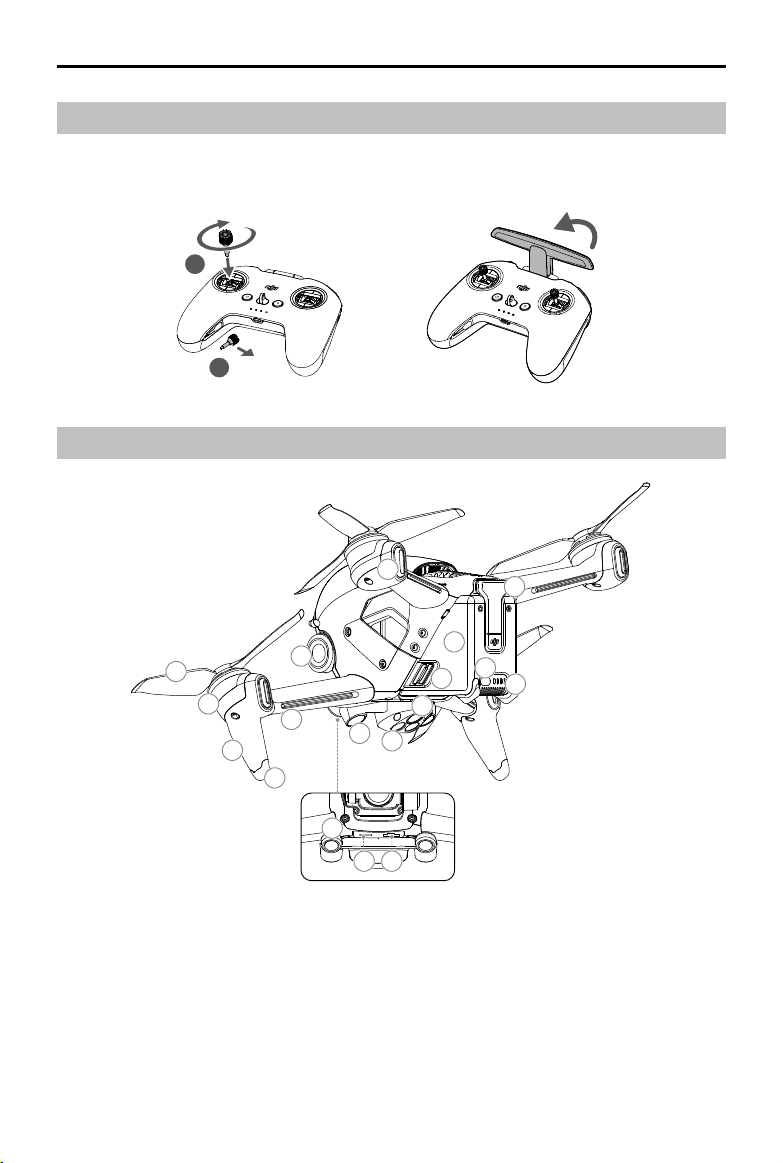
1. Install the four antennas to the mounting holes on the front of the goggles. Make sure that the antennas are
installed securely.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
8

DJI FPV
2. Attach the strap to the headband attachment on the top and sides of the goggles.
3. Use the included power cable to connect the power port of the goggles to the goggles battery.
4. Align the lenses over your eyes and pull the headband down. Adjust the headband size until the goggles t
User Manual
securely and comfortably on your face and head.
5. Turn the Interpupillary Distance (IPD) slider to adjust the distance between the lenses until the images are
properly aligned.
58 – 70 mm
The goggles can be worn over glasses.
DO NOT use the goggles battery to power other mobile devices.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
9
DJI FPV
User Manual
Preparing the Remote Controller
1. Remove the control sticks from the storage slots on the remote controller and screw them into place.
2. Unfold the antennas.
2
1
Diagram
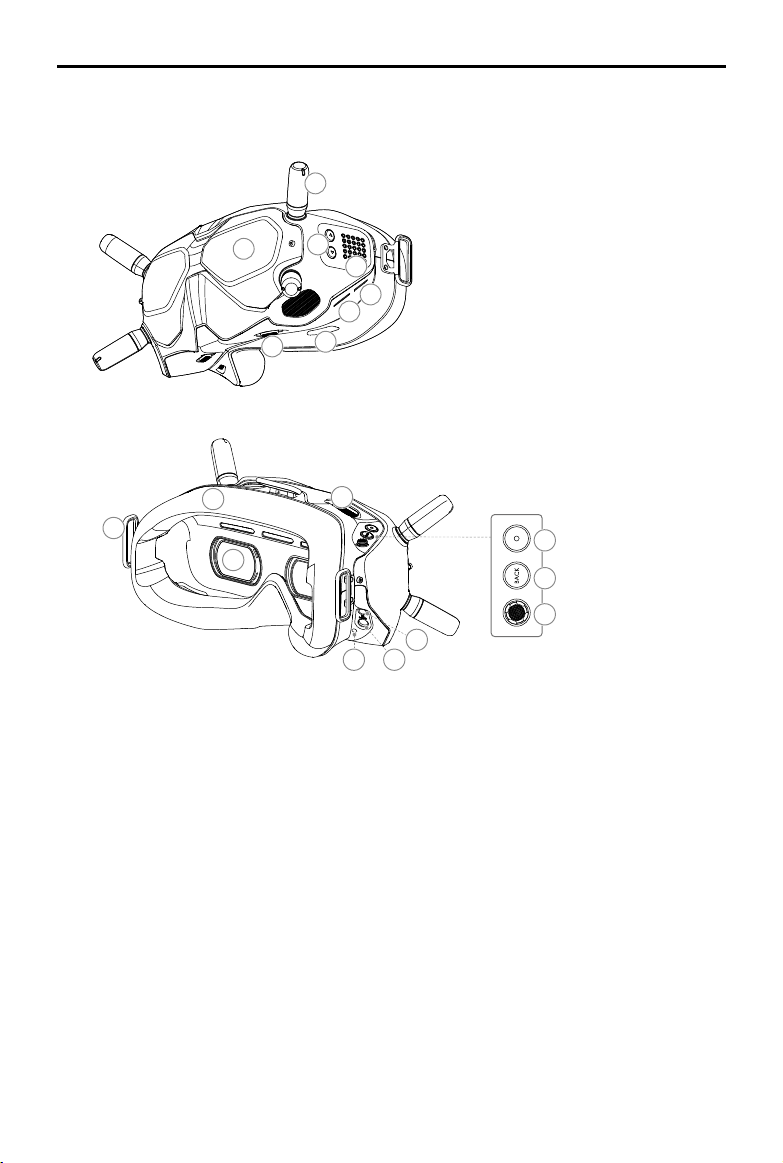
Aircraft
1
2
3
4
1. Propellers
2. Motors
3. Front LED
4. Landing Gears (Built-in antennas)
5. Frame Arms LED
6. Gimbal and Camera
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
10
7
6
5
16
7. Aircraft Status Indicator
8. Downward Vision System
9. Infrared Sensing System
10. Auxiliary Bottom Light
11. Intelligent Flight Battery
12. Battery Buckles
8
17 18
10
9
15
11
13
12
14
13. Power Button
14. Battery Level LEDs
15. Power Port
16. Forward Vision System
17. USB-C Port
18. microSD Card Slot
DJI FPV
Goggles
User Manual
1
2
10
3
4
5
6
7
8
12
9
1. Antennas
2. Front Cover
3. Channel Adjustment Buttons
4. Channel Display
5. USB-C Port
6. microSD Card Slot
7. Air Intake
8. IPD Slider
13
11
14
15
16
1718
9. Headband Attachment
10. Foam Padding
11. Lens
12. Air Vent
13. Shutter/Record Button
Press once to take photos or start or stop recording. Press and hold to switch between photo and video
mode.
14. Back Button
Press to return to the previous menu or exit the current mode.
15. 5D Button
Toggle the button to scroll through the menu. Press the button to conrm.
On the main screen, toggle left or right to adjust the screen brightness and toggle up or down to adjust the
volume. Press the button to enter the menu.
16. Audio/AV-IN Port
17. Power Port (DC5.5×2.1)
18. Link Button
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
11
8 13
10
9
12
14
11
DJI FPV
User Manual
Remote Controller
5
3
4
7
1
2
6
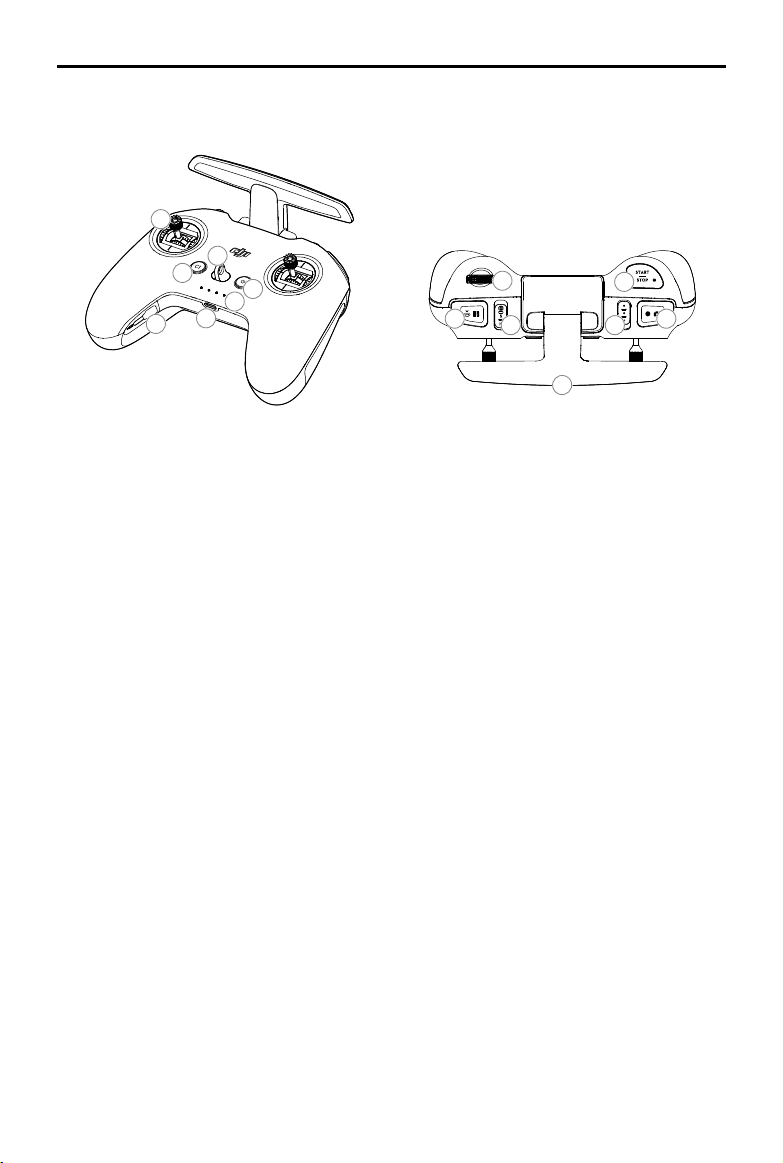
1. Power Button
Press once to check the current battery level. Press once, then again, and hold to power the remote
controller on or o.
2. Battery Level LEDs
Displays the current battery level of the remote controller.
3. Lanyard Attachment
4. C1 Button (Customizable)
The function of this button can be adjusted in the goggles. By default, press once to adjust or disable
Coordinated Turn (S Mode). Press twice to enable or disable ESC Beeping.
5. Control Sticks
Used to control the movements of the aircraft. The control sticks mode can be set in the goggles. The control
sticks are removable and easy to store.
6. USB-C Port
For charging and connecting the remote controller to the computer.
7. Control Sticks Storage Slot
For storing the control sticks.
8. Flight Pause/RTH Button
Press once to make the aircraft brake and hover in place (only when GPS or Downward Vision System are
available). Press and hold the button to initiate RTH. The aircraft returns to the last recorded Home Point.
Press again to cancel RTH.
9. Gimbal Dial
Controls the tilt of the camera.
10. Flight Mode Switch
Switch between Normal, Sport, and Manual mode. Manual mode is disabled by default and must be enabled
in the goggles.
11. C2 Switch (Customizable)
The function of this switch can be adjusted in the goggles. By default, toggle the switch to recenter the
gimbal and adjust up and down.
9
8 13
10
14
12
11
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
12

DJI FPV
User Manual
12. Start/Stop Button
When using Sport mode, press once to enable or disable cruise control.
When using Manual mode, press twice to start or stop the motor.
When using Normal or Sport mode, press once to cancel Low Battery RTH when the countdown appears in
the goggles.
13. Shutter/Record Button
Press once to take photos or start or stop recording. Press and hold to switch between photo and video
mode.
14. Antennas
Relays aircraft control wireless signals.
15
16
18
17
15. F1 Right Stick Resistance Adjustment Screw (Vertical)
Tighten the screw clockwise to increase the vertical resistance of the corresponding stick. Loosen the screw
to decrease vertical resistance.
16. F2 Right Stick Recentering Adjustment Screw (Vertical)
Tighten the screw clockwise to disable the vertical recentering of the corresponding stick. Loosen the screw
to enable vertical recentering.
17. F1 Left Stick Resistance Adjustment Screw (Vertical)
Tighten the screw clockwise to increase the vertical resistance of the corresponding stick. Loosen the screw
to decrease vertical resistance.
18. F2 Left Stick Recentering Adjustment Screw (Vertical)
Tighten the screw clockwise to disable the vertical recentering of the corresponding stick. Loosen the screw
to enable vertical recentering.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
13
DJI FPV
User Manual
Linking
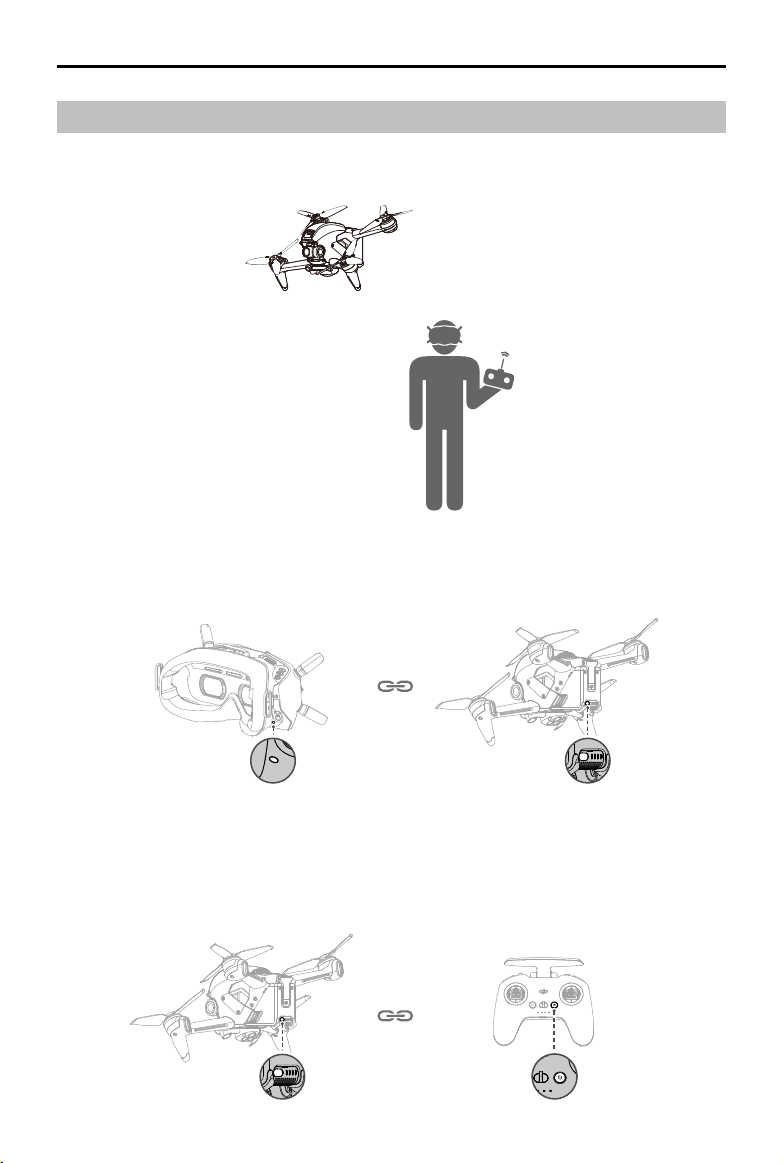
The devices are all linked before shipping. Linking is only required when using a new device for the rst time.
Follow the steps below to link the aircraft, goggles, and remote controller:
1. Power on the aircraft, goggles, and remote controller.
2. Press the link button on the goggles. The goggles will start to beep continually.
3. Press and hold the power button of the aircraft until the battery level LEDs start to blink in sequence.
4. The battery level LEDs of the aircraft turn solid and display the battery level. The goggles stop beeping when
they are successfully linked and the video display is normal.
5. Press and hold the power button of the aircraft until the battery level LEDs start to blink in sequence.
6. Press and hold the power button of the remote controller until it starts to beep continually and the battery level
LEDs blinks in sequence.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
14
DJI FPV
User Manual
7. Once linking is successful, the remote controller stops beeping and both the battery level LEDs turn solid and
display the battery level.
Make sure the goggles and the remote controller are within 0.5 m of the aircraft during linking.
The aircraft must be linked with the goggles before the remote controller.
Activation
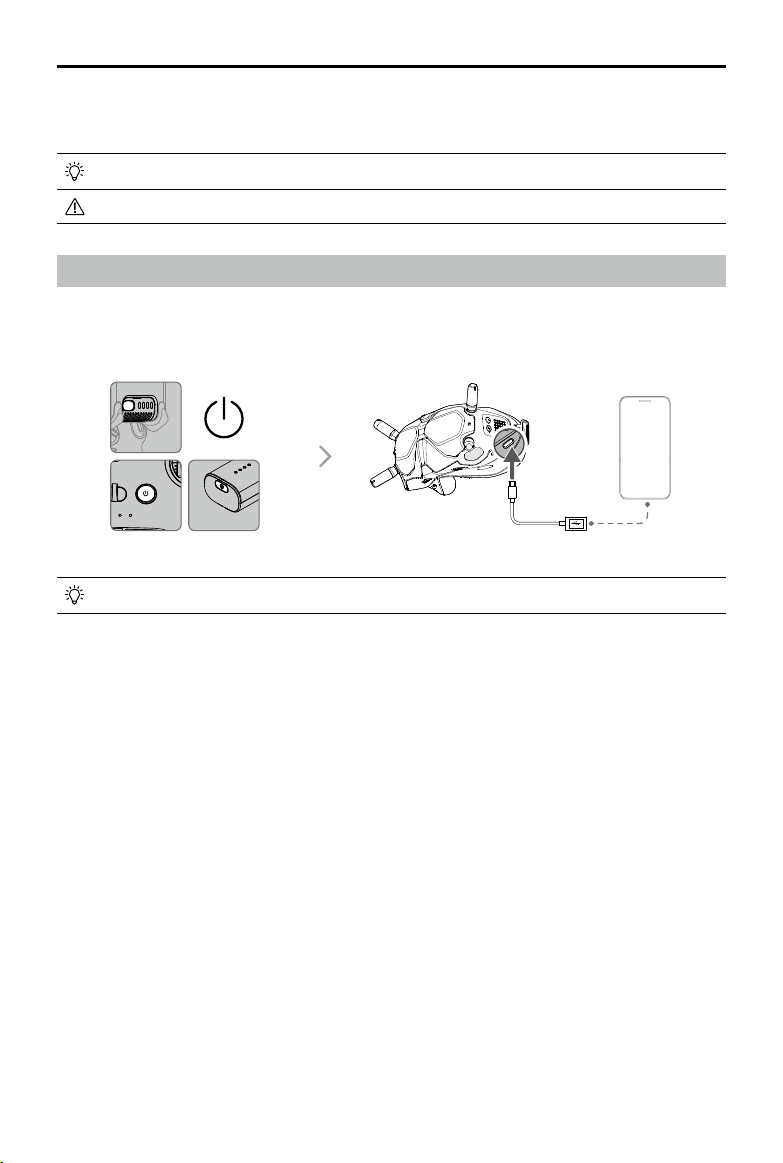
DJI FPV must be activated before using for the rst time. Make sure all devices are linked after powering on the
aircraft, goggles, and remote controller. Connect the USB-C port of the goggles to the mobile device, run DJI Fly,
and follow the prompts to activate. An internet connection is required for activation.
DJI Fly
App
Press and then press and hold to power devices on or o.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
15

Aircraft
DJI FPV contains a flight controller, a gimbal and camera, video downlink system, vision system, propulsion
system, and an Intelligent Flight Battery.
Flight Modes
DJI FPV has three ight modes, plus a fourth ight mode that the aircraft switches to in certain scenarios. Flight
modes can be switched via the ight mode switch on the remote controller.
Normal Mode: The aircraft utilizes GPS, the Forward and Downward Vision Systems, and the Infrared Sensing
System to locate itself and stabilize. The aircraft will use GPS to locate itself when the GPS signal is strong and
use the Downward Vision System to locate and stabilize itself when the lighting conditions are sucient. When the
Downward Vision System is enabled and lighting conditions are sucient, the maximum ight attitude angle is 25°
and the maximum ight speed is 15 m/s.
Sport Mode: The aircraft uses GPS and the Downward Vision System for positioning. In Sport mode, aircraft
responses are optimized for agility and speed making it more responsive to control stick movements. The
maximum ight speed is 27 m/s, maximum ascent speed is 15 m/s, and maximum descent speed is 10 m/s.
Manual Mode: Classic FPV aircraft control mode with the highest maneuverability, which can be used for racing
and freestyle ying. In Manual mode, all ight assistance functions such as automatic stabilization are disabled and
procient control skills are required. The throttle stick can be adjusted in this mode.
In Normal or Sport mode, when the Downward Vision System is unavailable or disabled and when the GPS
signal is weak or the compass experiences interference, the aircraft cannot position itself or brake automatically,
which increases the risk of potential ight hazards. At this time, the aircraft may be more easily aected by its
surroundings. Environmental factors such as wind can result in horizontal shifting, which may present hazards,
especially when ying in conned spaces.
When using Manual mode, move the remote control stick to directly control the throttle and attitude
of the aircraft. The aircraft has no ight assistance functions such as automatic stabilization and
can reach any attitude. Only experienced pilots should use Manual mode. Failure to operate in this
mode properly is a safety risk and may even lead to the aircraft crashing.
Manual mode is disabled by default. Make sure that the switch is set to Manual mode in the goggles
before switching to Manual mode. The aircraft will remain in Normal or Sport mode if the switch is
not set to Manual mode in the goggles. Go to Settings, Control, Remote Control, and then Button
Customization and set the Custom Mode to Manual Mode.
Before using Manual mode, it is recommended to adjust the screw on the rear of the throttle stick so
that the stick does not recenter and to practice ying in the mode using DJI Virtual Flight.
When using Manual mode for the rst time, the maximum attitude of the aircraft will be limited. After
you are familiar with ying in Manual mode, the attitude restriction can be disabled in the goggles. Go
to Settings, Control, Remote Control, RC Exp, and then M Mode Attitude Limit.
The maximum speed and braking distance of the aircraft significantly increase in Sport mode. A
minimum braking distance of 30 m is required in windless conditions.
Descent speed signicantly increases in Sport mode. A minimum braking distance of 10 m is required
in windless conditions.
The responsiveness of the aircraft signicantly increases in Sport mode, which means a small control
stick movement on the remote controller translates into the aircraft moving a large distance. Be vigilant
and maintain adequate maneuvering space during ight.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
16
DJI FPV
User Manual
Aircraft Status Indicator
DJI FPV has a front LED, frame arm LED, and aircraft status indicator.
Aircraft Status Indicator
Frame Arm LED
Front LED
The front LED shows the orientation of the aircraft and the frame arm LED is for decoration. The LEDs turns solid
blue when the aircraft is powered on. The colors and lighting methods of the front LED and frame arm LED can be
customized in the goggles.
The aircraft status indicator shows the status of the ight control system of the aircraft. Refer to the table below for
more information about the aircraft status indicator.
Aircraft Status Indicator States
Normal States
Blinks red, yellow, and green alternately Powered on and performing self-diagnostic tests
Blinks purple slowly Warming up
Blinks green slowly GPS enabled
×2 Blinks green twice repeatedly Forward and Downward Vision Systems enabled
Blinks yellow slowly
Blinks green quickly Braking
Warning States
Blinks yellow quickly Remote controller signal lost
Blinks red slowly Low battery
Blinks red quickly Critically low battery
Blinks red IMU error
—
Solid red Critical error
Blinks red and yellow alternately Compass calibration required
GPS and Forward and Downward Vision System
disabled
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
17

DJI FPV
User Manual
Return to Home
The Return to Home (RTH) function brings the aircraft back to the last recorded Home Point and lands when
the GPS is signal is strong. There are three types of RTH: Smart RTH, Low Battery RTH, and Failsafe RTH. If the
aircraft successfully recorded the Home Point and the GPS signal is strong, the RTH will be triggered when either
Smart RTH is initiated, the aircraft battery level is low, or the signal between the remote controller and the aircraft
is lost. RTH will also be triggered in other abnormal scenarios such as if there is a loss of video transmission.
Description
Home Point
GPS
The default Home Point is the rst location where the aircraft received a strong or
moderately strong GPS signal (where the icon shows white). The aircraft status
20
indicator blinks green quickly and a prompt appears in the goggles to conrm the
Home Point has been recorded.
Smart RTH
If the GPS signal is sucient, Smart RTH can be used to bring the aircraft back to the Home Point. Smart RTH is
initiated by pressing and holding the RTH button on the remote controller. Exit Smart RTH by pressing the RTH
button.
Low Battery RTH
When the Intelligent Flight Battery level is too low and there is not enough power to return home, land the aircraft
as soon as possible. Otherwise, the aircraft will fall when it runs out of power, resulting in the aircraft being
damaged and other potential hazards.
To avoid unnecessary danger due to insucient power, DJI FPV will intelligently determine whether the current
battery level is sucient to return to the Home Point based on the current location. Low Battery RTH is triggered
when the Intelligent Flight Battery is depleted to the point that the safe return of the aircraft may be aected.
RTH can be cancelled by pressing the RTH button on the remote controller. If RTH is cancelled following a low
battery level warning, the Intelligent Flight Battery may not have enough power for the aircraft to land safely, which
may lead to the aircraft crashing or being lost.
The aircraft will land automatically if the current battery level can only support the aircraft long enough to descend
from its current altitude. Auto landing cannot be canceled, but the remote controller can be used to alter the
direction of the aircraft during the landing process.
Failsafe RTH
If the Home Point was successfully recorded and the compass is functioning normally, Failsafe RTH automatically
activates after the remote controller signal is lost for more than 3.5 seconds.
The aircraft will y backwards for 50 m on its original ight route and enter Straight Line RTH. The aircraft enters
Straight Line RTH if the remote controller signal is restored during Failsafe RTH.
The response of the aircraft when the wireless signal is lost can be changed in the goggles. The aircraft will not
execute Failsafe RTH if land or hover has been selected in the settings.
Other RTH Scenarios
A prompt will appear in the goggles and RTH will be initiated if the video download signal is lost during ight while
the remote controller can still be used to control the movements of the aircraft.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
18
DJI FPV
User Manual
RTH (Straight Line)
1. The Home Point is recorded.
2. RTH is triggered.
3. If the aircraft is less than 5 m from the Home Point when RTH begins, it lands immediately.
If the aircraft is more than 5 m and less than 50 m from the Home Point when RTH begins, it will return home
at the current altitude with a maximum horizontal speed of 3 m/s.
If the aircraft is further than 50 m from the Home Point when RTH begins, it will ascend to the RTH altitude
and return home at a speed of 13.5 m/s. The aircraft ies to the Home Point at the current altitude if the RTH
altitude is lower than the current altitude.
4. After reaching the Home Point, the aircraft lands and the motors stop.
Obstacle Avoidance During RTH
1. The aircraft brakes when an obstacle is sensed from in front and ascends to a safe distance. After ascending
another 5 m, the aircraft will continue to y forward.
2. The aircraft brakes when an obstacle is sensed from below and ascends until obstacles are no longer sensed
before ying forward.
During RTH, the aircraft cannot sense obstacles to the side, rear, or from above.
The aircraft cannot avoid obstacles during RTH if the Forward and Downward Vision Systems are
unavailable.
The aircraft cannot return to the Home Point if the GPS signal is weak or unavailable. If the GPS signal
becomes weak or unavailable after RTH is triggered, the aircraft will hover in place for a while before
landing.
Before each ight, it is important to enter Settings and then Safety on the goggles and set a suitable
RTH altitude.
During RTH, if the aircraft is flying forward and the remote controller signal is normal, the remote
controller can be used to control the speed of the aircraft, but cannot control the orientation or y left
or right. The orientation and horizontal position of the aircraft can be controlled when it is descending.
When the aircraft is ascending or flying forward, push the control stick completely in the opposite
direction to exit RTH.
GEO zones will aect RTH. If the aircraft ies into a GEO zone during RTH, it will either descend until it
exits the GEO zone and continue to y to the Home Point or hover in place due to altitude limits.
The aircraft may not be able to return to a Home Point when the wind speed is too high. Fly with
caution.
Landing Protection
Landing Protection will activate during Smart RTH.
1. During Landing Protection, the aircraft will automatically detect and carefully land on suitable ground.
2. If the ground is determined unsuitable for landing, the aircraft will hover and wait for pilot conrmation.
3. If Landing Protection is not operational, the goggles will display a landing prompt when the aircraft descends
to 0.3 m. Pull down on the throttle stick to land.
Vision Systems are disabled during landing. Make sure to land the aircraft with caution.
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
19
DJI FPV
User Manual
Precision Landing
The aircraft automatically scans and attempts to match the terrain features below during RTH. The aircraft will land
when the terrain matches the terrain of the Home Point. A prompt will appear in the goggles if the terrain fails to
match.
Landing Protection is activated during Precision Landing.
The performance of Precision Landing is subject to the following:
a) The Home Point must be recorded upon takeo and must not be changed during ight. Otherwise,
the aircraft will have no record of the terrain features of the Home Point.
b) During takeo, the aircraft must ascend vertically to at least 7 m before moving horizontally.
c) The terrain features of the Home Point must remain largely unchanged after it is recorded.
d) The terrain features of the Home Point must be suciently distinctive.
e) The lighting conditions must not be too light or dark.
The following actions are available during Precision Landing:
a) Pull the throttle stick down to accelerate landing.
b) Pull the throttle stick up or move the other control stick to stop Precision Landing. Landing
Protection remains active while the aircraft descends vertically.
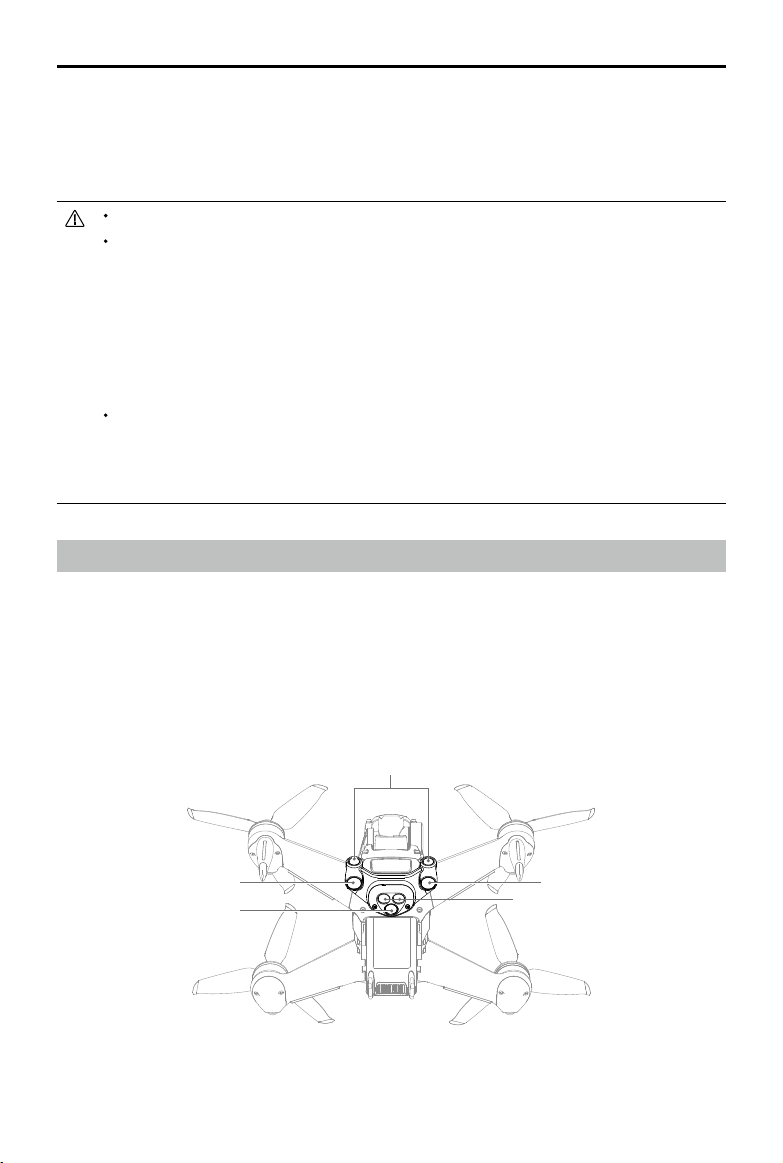
Vision Systems and Infrared Sensing System
DJI FPV aircraft is equipped with both an Infrared Sensing System and Forward and Downward Vision Systems.
The Forward and Downward Vision Systems consist of two cameras each and the Infrared Sensing System
consists of two 3D infrared modules.
The Downward Vision System and Infrared Sensing System help the aircraft maintain its current position, hover
in place more precisely, and to y indoors or in other environments where GPS is unavailable. In addition, the
auxiliary bottom light located on the underside of the aircraft improves visibility for the Downward Vision System in
weak light conditions.
Downward Vision System
Auxiliary Bottom Light
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
20
Forward Vision System
Downward Vision System
Infrared Sensing System
DJI FPV
User Manual
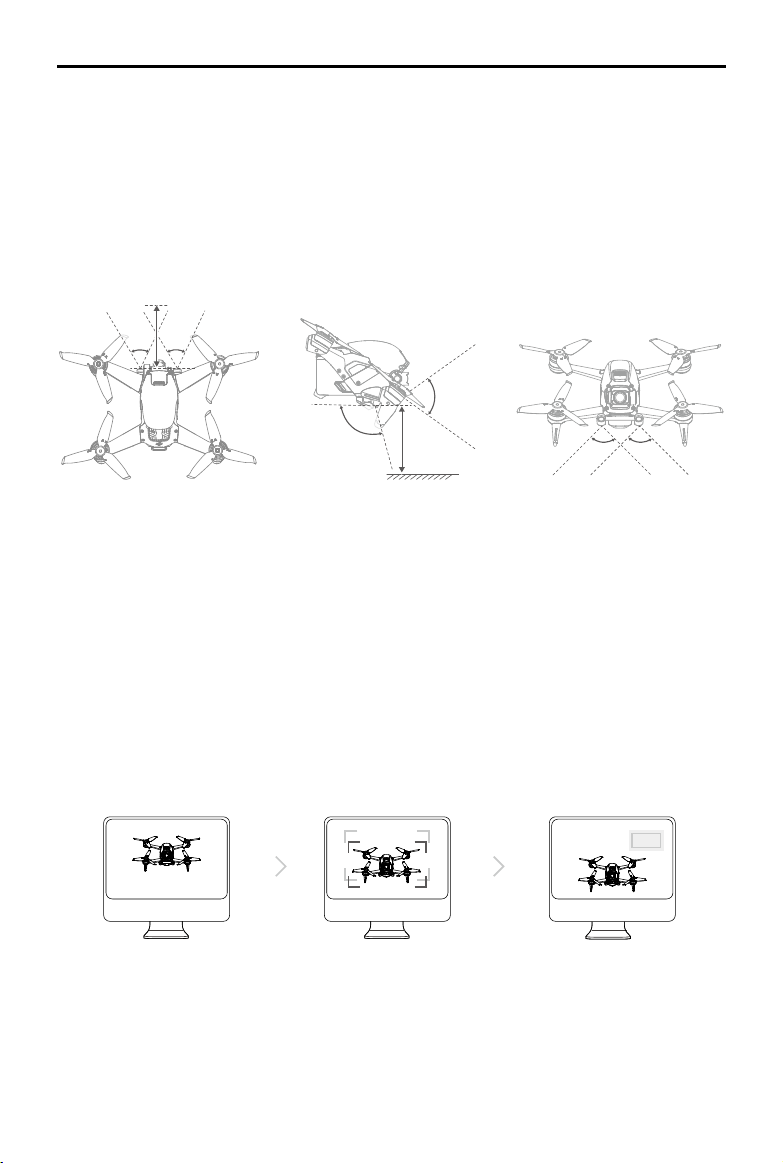
Detection Range
Forward Vision System
The Forward Vision System has a detection range of 0.5 to 18 m, horizontal FOV of 56°, and vertical FOV of 71°.
Downward Vision System
The Downward Vision System works best when the aircraft is at an altitude of 0.5 to 15 m and its operating range
is 0.5 to 30 m. The FOV to the front and rear is 106° and 90° to the right and left.
0.5-18 m
56° 56°
71°
106°
0.5-30 m
90°
90°
Calibrating Vision System Cameras
Auto Calibration
The Vision System cameras installed on the aircraft are calibrated before shipping. If any abnormality is detected
with a Vision System camera, the aircraft will automatically calibrate and a prompt will appear in the goggles. No
further action is required to address the issue.
Advanced Calibration
If the abnormality persists after auto calibration, a prompt appears in the goggles that advanced calibration is
required. Advanced calibration can only be performed using DJI Assistant 2 (DJI FPV series). Follow the steps
below to calibrate the Forward Vision System cameras and repeat the steps to calibrate the other Vision System
cameras.
1
Point the aircraft toward the screen. Align the boxes. Pan and tilt the aircraft.
2
3
© 2021 DJI All Rights Reserved.
21
 Loading...
Loading...