Page 1

53-1001980-01
15 November 2010
Dell M8428-k
Hardware Reference Manual
Page 2

Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2010 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction of these materials in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, Inspiron, Dell Precision, Dimension, OptiPlex, Latitude, PowerEdge, PowerVault,
PowerApp,
PowerConnect, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks of Dell Inc.; Intel, Pentium, and Celeron are registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation in
the U.S. and other countries; Microsof t, Windows, Windows Server, MS-DOS and Windows Vista are either trademarks or
registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming the marks and names or
their products.
Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Regulatory Model Codes: M8428-k
Page 3

Contents
About This Document
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Supported hardware and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
What’s new in this document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Command syntax conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Command examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Notes, cautions, and warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Key terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ix
Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Industry resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Chapter 1 Introducing the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Dell M8428-k overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
NPIV mode and full fabric mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
NPIV mode hardware considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Port side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Top view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Labeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Transceivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
ISL trunking groups. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Optional features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Unpacking and installing the Dell M8428-k . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Chapter 2 Configuring the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Items required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual iii
53-1001980-01
Page 4

Modifying the converged network switch IP address . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Using the CMC CLI to set the IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Using the CMC GUI to set the IP address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Using the Dell M8428-k CLI to set the IP address. . . . . . . . . . .12
Configuring for FCoE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Connecting the switch to the Ethernet management network . . . . 14
Connecting the switch to the fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Changing from NPIV aggregator mode to full fabric mode . . . . . . . . 17
Changing to full fabric mode using the browser-based GUI . . . 17
Changing to full fabric mode using the command line
interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Changing from full fabric mode to NPIV aggregator mode. . . . . . . .18
Changing to NPIV mode using the browser-based GUI . . . . . . . 18
Changing to NPIV mode using the command line interface . . .19
Backing up the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Chapter 3 Operating the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Interoperability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Port negotiation on Fibre Channel ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Accessing the converged network switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Interpreting POST results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Interpreting LED activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Switch module status LEDs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Port status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Locating the serial number. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Removing and replacing the converged network switch . . . . . . . . . 25
Appendix A Dell M8428-k specifications
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
NPIV Mode default port mapping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Processor and memory specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Weight and physical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Facility requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Electrical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Architectural specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Supported mezzanine cards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Fibre Channel standards compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
iv Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 5

Index
Regulatory compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
FCC warning (US only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
KCC Statement (Republic of Korea) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
VCCI statement (Japan) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
BSMI statement (Republic of Taiwan) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
CE statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Canadian requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Laser compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Environmental regulation compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
China RoHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Regulatory certifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual v
53-1001980-01
Page 6

vi Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 7

About This Document
In this chapter
•How this document is organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
•Supported hardware and software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
•What’s new in this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
•Notice to the reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
•Additional information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
How this document is organized
This document is organized to help you find the information that you want as quickly and easily as
possible.
The document contains the following components:
• Chapter 1, “Introducing the Dell M8428-k,” describes the converged network switch and
explains its basic concepts and features. This chapter also provides instructions for unpacking
the switch module from its shipping container, and references to the appropriate publication
for installing the module into the Blade Server Enclosure.
• Chapter 2, “Configuring the Dell M8428-k” describes how to change the converged network
switch’s IP address, connect the module to the Ethernet network and fabric, change between
NPIV mode and full fabric mode, and backing up the switch module configuration.
• Chapter 3, “Operating the Dell M8428-k,” provides details about monitoring and replacing a
switch module.
• Appendix A, “Dell M8428-k specifications,” is a product specification reference.
Supported hardware and software
This document includes information specific to the Dell M8428-k only.
What’s new in this document
This is a new document.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual vii
53-1001980-01
Page 8

Document conventions
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notice formats used in this
document.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
italic text Provides emphasis
code text Identifies CLI output
For readability, command names in the narrative portions of this guide are presented in mixed
lettercase: for example, switchShow. In actual examples, command lettercase is all lowercase.
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords and operands
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Identifies variables
Identifies paths and Internet addresses
Identifies document titles
Identifies command syntax examples
Command syntax conventions
Command syntax in this manual follows these conventions:
command Commands are printed in bold.
--option, option Command options are printed in bold.
-argument, arg Arguments.
[ ] Optional element.
variable Variables are printed in italics. In the help pages, values are underlined
enclosed in angled brackets < >.
... Repeat the previous element, for example “member[;member...]”
value Fixed values following arguments are printed in plain font. For example,
--show WWN
| Boolean. Elements are exclusive. Example:
--show -mode egress | ingress
or
Command examples
This book describes how to perform configuration tasks using the switch module command line
interface, but does not describe the commands in detail.
viii Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 9

Notes, cautions, and warnings
NOTE
ATTENTION
CAUTION
DANGER
The following notices and statements are used in this manual. They are listed below in order of
increasing severity of potential hazards.
A note provides a tip, guidance or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a reference
to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
A Caution statement alerts you to situations that can be potentially hazardous to you or cause
damage to hardware, firmware, software, or data.
A Danger statement indicates conditions or situations that can be potentially lethal or extremely
hazardous to you. Safety labels are also attached directly to products to warn of these conditions
or situations.
Key terms
For definitions of SAN-specific terms, visit the Storage Networking Industry Association online
dictionary at:
http://www.snia.org/education/dictionary
Notice to the reader
This document may contain references to the trademarks of the following corporations. These
trademarks are the properties of their respective companies and corporations.
These references are made for informational purposes only.
Corporation Referenced Trademarks and Products
Dell, Inc. PowerEdge
Microsoft Corporation Windows, Windows 2000, Windows 2003, Windows XP
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Solaris
Red Hat Inc. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
Novell, Inc SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES)
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual ix
53-1001980-01
Page 10

Additional information
This section lists additional industry-specific documentation that you might find helpful.
Industry resources
For additional resource information, visit the Technical Committee T11 Web site. This Web site
provides interface standards for high-performance and mass storage applications for Fibre
Channel, storage management, and other applications:
http://www.t11.org
For information about the Fibre Channel industry, visit the Fibre Channel Industry Association Web
site:
http://www.fibrechannel.org
Getting technical help
Contact your switch support supplier for hardware, firmware, and software support, including
product repairs and part ordering. To expedite your call, have the following information available:
1. General Information
• Switch model
• Switch operating system version
• Software name and software version, if applicable
• Error numbers and messages received
• supportSave command output
• Detailed description of the problem, including the switch or fabric behavior immediately
following the problem, and specific questions
• Description of any troubleshooting steps already performed and the results
• Serial console and Telnet session logs
• syslog message logs
2. Switch Serial Number
The switch serial number and corresponding bar code are provided on the serial number label,
as illustrated below.:
*FT00X0054E9*
FT00X0054E9
3. World Wide Name (WWN)
Use the licenseIdShow command to display the WWN of the chassis.
If you cannot use the licenseIdShow command because the switch is inoperable, you can get
the WWN from the same place as the serial number.
x Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 11

Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual xi
53-1001980-01
Page 12

xii Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 13

Chapter
Introducing the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter
•Dell M8428-k overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•NPIV mode and full fabric mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
•Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
•ISL trunking groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
•Optional features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
•Unpacking and installing the Dell M8428-k . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Dell M8428-k overview
The Dell M8428-k is a 28-port switch module with 8 external Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE)
ports, 4 external Fibre Channel (FC) ports, and 16 internal CEE ports that installs in a Dell
PowerEdge M1000e Blade Server Enclosure. The switch module is designed to be inserted in any
of the bays labeled B1, B2, C1, or C2.
1
The external CEE ports operate at 10 Gbps. The internal CEE ports can operate at either 10 Gbps or
1 Gbps. The FC ports support link speeds up to 8 Gbps.
The 16 internal ports connect to the server utilizing 10GBase-KR (KR) technology.
The Dell M8428-k ships with N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV) mode enabled. This technology
provides the ability to attach more devices to the fabric without having to create more domains.
Management for the converged network switch can be done through Dell Chassis Management
Controller (CMC), the browser based GUI, or the command line interface (CLI).
The switch module contains three (3) temperature sensors. While the sensors will report the
temperature of the switch, they will not initiate shutdown if the temperature is too high. That
decision is made by the CMC.
The switch ships with three licenses installed:
• Fabric license
• Enhanced Group Management license
• FCoE Base license
NPIV mode and full fabric mode
The converged network switch can function in either NPIV mode or full fabric mode.
• The switch module is shipped in NPIV mode by default.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 1
53-1001980-01
Page 14

NPIV mode and full fabric mode
NOTE
1
• NPIV mode simplifies SAN deployment by using N_Port ID Virtualization. NPIV provides Fibre
Features available on the switch module depend on whether the module is configured in NPIV or
full fabric mode.
Tab le 1 lists Fabric OS components that are supported on a switch when NPIV mode is enabled.
“No” indicates that the feature is not provided in NPIV mode. “NA” indicates this feature is not
applicable in NPIV mode of operation. A single asterisk (*) indicates the feature is transparent to
NPIV, that is NPIV forwards the request to the Enterprise fabric. Two asterisks (**) indicates that if
the Enterprise fabric is not of a specific configuration, the feature may not be available.
TABLE 1 Fabric OS components supported in NPIV mode
Feature Support
Access Control Yes (limited roles)
Admin Domains No
Audit Yes
Beaconing Yes
Config Download/Upload Yes
DHCP Yes
Environmental Monitor Yes
Error Event Management Yes
Extended Fabrics No
Fabric Device Management Interface (FDMI) Yes*
Fabric Watch Yes (limited)
FICON (includes CUP) No
Native Interoperability Mode NA
License Yes**
Log Tracking Yes
Management Server NA
Manufacturing Diagnostics Yes
N_Port ID Virtualization Yes
Name Server NA
Network Time Protocol (NTP) No (no relevance from fabric perspective)
Open E_Port NA
Performance Monitor Yes (Basic PM only, no APM support)
Port Mirroring No
Channel switch functions that improve switch module scalability, manageability, and
interoperability.
- For a list of switch module F_Ports mapped to N_Ports in the switch module as shipped
from the factory, refer to
NPIV mode-enabled switches cannot be connected directly into an array; it requires a fabric to
support NPIV.
“NPIV Mode default port mapping” on page 27.
1
2
2 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 15

Hardware description
TABLE 1 Fabric OS components supported in NPIV mode (Continued)
Feature Support
QuickLoop, QuickLoop Fabric Assist No
Security Yes (ADS/DCC Policy)
SNMP Yes
Speed Negotiation Yes
Syslog Daemon Yes
Tru nkin g Yes* *
Zoning NA
1. When a switch is enabled in NPIV mode, RBAC features in the Fabric OS are available, but
there are some limitations.
2. In embedded switches, time should be updated by the server management utility.
NPIV mode hardware considerations
Hardware considerations for NPIV mode are as follows:
1
• Loop devices are not supported.
• Direct connections to SAN target devices are only supported if the NPIV-enabled module is
connected to a fabric.
Hardware description
This section describes the physical switch module as shipped from the factory. For specifications,
such as installed memory, weight and physical dimensions, facility requirements, architectural
specifications, and regulatory compliance, refer to
Port side
Externally accessible ports and LEDs are on the port side of the switch module. The port side faces
out when the switch module is inserted into the I/O bay of the Blade Server enclosure.
details the port side. For a complete description of the locations and interpretations of these LEDs,
see
“Interpreting LED activity” on page 23.
Access the converged network switch handle at the front of the port side of the switch module. By
lifting the handle’s release latch, you can open the handle to remove and insert the unit. To extend
the release lever, gently squeeze the release latch and pull outward.
Appendix A, “Dell M8428-k specifications”
Figure 1
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 3
53-1001980-01
Page 16

Hardware description
M8428 - k
21
7 68
45
3
1
FIGURE 1 Port side view
1 10 GbE CEE ports with bi-color
(green/amber) port status LEDs above
each port
3 8 Gbps FC ports with bi-color
(green/amber) port status LEDs above
each port
5 Power status LED (green) 6 Release latch
7 Server management LED (blue/amber) 8 Release lever
2 RJ45 console port
4Switch status LED (green/amber)
Top view
The nonport side of the switch module (shown in Figure 2) is seated into the enclosure. You do not
need to line up the switch module as it will seat correctly when the release lever is closed.
When the switch module is inserted, the midplane connectors activate a connection port, allowing
the switch module to be configured in the Blade Server Enclosure.
4 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 17
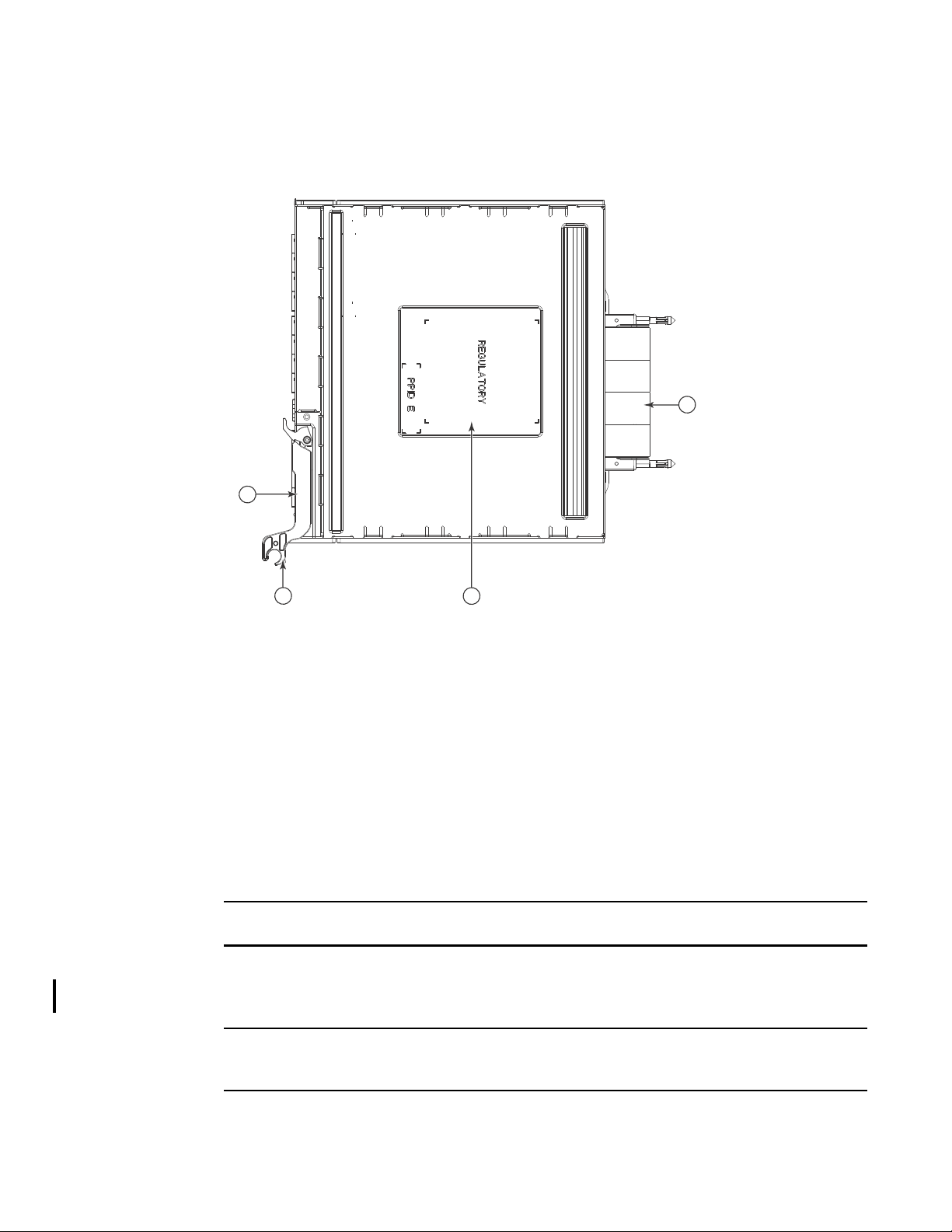
FIGURE 2 Top view
NOTE
NOTE
4
3
2
1
Hardware description
1
1 Switch module release lever
2 Release latch
3 Product label including serial number
4 Midplane connectors
Labeling
Figure 2 shows the labels appearing on the switch module. A second serial label is located beneath
the release lever on the enclosure (visible only when the lever is extended).
Transceivers
You must install Dell-approved transceivers in the switch module.
The converged network switch was designed to work with small form-factor pluggable (SFP) optical
modules. The basic switch module ships with four 8 Gbps Dell-approved transceivers for the Fibre
Channel ports.
You can also install 4 Gbps transceivers in the FC ports of the switch module. All transceivers must
be Dell-approved.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 5
53-1001980-01
Page 18

ISL trunking groups
NOTE
NOTE
1
Transceivers provide optical connections to external devices for both SWL and LWL connections.
Replace transceivers with a new pluggable unit rather than replacing the switch module. Refer to
the manufacturer’s instructions when installing transceivers.
“Removing and replacing the converged network switch” on page 25 provides details about
removing transceivers from the converged network switch.
ISL trunking groups
If you have purchased an ISL Trunking license for your converged network switch, external FC ports
can form trunking groups of ISLs between adjacent switches. Ports that can be used within the
same trunking group are color-coded on the switch module’s port side for easy identification.
All four external FC ports (0, 25-27) can be formed into a single 4-port trunk if the attached switch
supports an 4-port trunk. The ports can also form 2-port or 3-port trunk as well.
Only the external ports are available for trunking.
Optional features
The converged network switch supports the following optional software, which is activated with the
purchase of the corresponding license key. Applicable options depend on whether the switch
module operates in NPIV or full fabric mode.
NPIV mode
• Fabric/Switch License
• NPIV (N_Port) Trunking
• Server Application Optimization
Full fabric mode
• Enhanced Group Management
• ISL Trunking
1. included with the converged network switch
1
• Advanced Performance Monitoring
• Fabric Watch
Unpacking and installing the Dell M8428-k
If the converged network switch is installed in the Blade Server Enclosure as shipped to you, skip
this section. This section applies when installing a new module in an empty bay or replacing an
existing converged network switch.
The converged network switch is designed to work in I/O bays B1/B2 and C1/C2 of the Dell M1000e
Blade Server Enclosure for SAN connectivity. Make sure to comply with installation requirements in
the Blade Server Enclosure Hardware Owner’s Manual.
6 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 19

Unpacking and installing the Dell M8428-k
NOTE
Perform the following steps to remove the switch module from its shipping package.
1. Open the shipping box and inspect the contents, making sure that nothing is missing or
damaged.
Do not insert a damaged converged network switch into the Blade Blade Server Enclosure. If
the converged network switch appears to be damaged, contact your sales representative
before proceeding.
2. Remove the cardboard accessory tray from on top of the converged network switch.
This tray contains the documentation, regulatory statements, product information guide, and
Documentation CD.
3. Remove the switch module from the box.
The protective foam ends will slide out with the switch module.
4. Remove the foam ends from the switch module.
5. Be sure that you have taken the necessary precautions for electrostatic sensitivity; then break
the seal warning.
6. Slide the switch module out of the antistatic sleeve and inspect it carefully for any obvious
defects or shipping damage.
1
7. For complete instructions to install the converged network switch into the Blade Server
Enclosure, refer to the section on installing answitch module in the Blade Server Enclosure
Hardware Owner’s Manual.
Be sure to remove the protective covers from the midplane connectors before installing the
module into the enclosure.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 7
53-1001980-01
Page 20

Unpacking and installing the Dell M8428-k
1
8 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 21

Chapter
NOTE
Configuring the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter
•Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
•Items required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
•Modifying the converged network switch IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
•Configuring for FCoE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
•Connecting the switch to the Ethernet management network. . . . . . . . . . . 14
•Connecting the switch to the fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
•Changing from NPIV aggregator mode to full fabric mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
•Changing from full fabric mode to NPIV aggregator mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
•Backing up the configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Introduction
2
Use procedures in this chapter to configure the switch module to operate on a network and fabric.
Also use steps to change the module’s operating mode (full fabric and NPIV modes) using either
the browser-based GUI or the command line interface.
Although the switch module is configured at the factory for NPIV mode, you can enable it for full
fabric mode. For more information, refer to
mode” on page 17.
This chapter provides configuration procedures that use switch module command line interface
(CLI) and the browser-based GUI application. For details refer to the Dell Converged Enhanced
Ethernet Administrator’s Guide, and Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Command Reference. If
the same operation can be performed using the Blade Server Enclosure’s Chassis Management
Controller (CMC) application, use that application instead.
Items required
The following items are required for configuring and connecting the converged network switch for
use in a network and fabric:
• The converged network switch installed in a Blade Server Enclosure. For instructions, refer to
“Changing from NPIV aggregator mode to full fabric
the steps on installing an I/O module in the Hardware Owner’s Manual for the Blade Server
Enclosure.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 9
53-1001980-01
Page 22

Modifying the converged network switch IP address
NOTE
ATTENTION
NOTE
2
• If required, management workstation (computer) that has a terminal emulator (such as
HyperTerminal) or a keyboard, video, and mouse (KVM) device. Note that this is only required if
not changing the converged network switch IP address through the Blade Server Enclosure GUI
or CLI management programs.
• An unused IP address and corresponding subnet mask and gateway address unless DHCP is
used.
• If required, a serial cable to connect to the switch module serial console port. Note that this is
only required if not changing the switch module IP address through the Blade Server Enclosure
GUI or CLI management programs.
• Transceivers and compatible fibre cables, as required. The switch module can also use twin-ax
copper cables.
Use only Dell-approved transceivers on the external ports of this module.
• Access to an FTP server for backing up the converged network switch configuration.
• Access to these publications:
• Blade Server Enclosure Hardware Owner’s Manual
• Blade Server Enclosure Configuration Guide
• Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator’s Guide
• Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Command Reference
• Dell Fabric OS MIB Reference Manual
Modifying the converged network switch IP address
By default, the IP address for the converged network switch is configured as 10.77.77.77 with a
default Ethernet subnetmask of 255.255.255.0. The default gateway is 0.0.0.0.
You can set the IP address using three methods. If the IP values are set using any of these
methods, the IP values are stored on the switch module.
• Blade Server Enclosure CMC CLI.
• Blade Server Enclosure CMC graphical user interface (GUI).
• Dell M8428-k command line interface (CLI).
After modifying the switch module’s IP address and domain name (if switch module is in full fabric
mode), we recommend that you cable all external ports to fabric connections before bringing the
switch module online.
Do not connect the switch module to the internal network until the IP address is correctly set for your
Ethernet network requirements.
It is recommended that you set the IP address using the Blade Server Enclosure CMC GUI
application because this enables centralized management of the converged network switch.
10 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 23

Modifying the converged network switch IP address
2
Using the CMC CLI to set the IP address
Use the following steps to connect modify the converged network switch IP address through the
CMC CLI.
1. Establish a Telnet session to the CMC CLI.
2. At the command prompt, type connect switch-x where x is the bay where the switch module is
installed. For example, switch-x can be:
• Switch-3 for switch module installed in bay B1.
• Switch-4 for switch module installed in bay B2.
• Switch-5 for switch module installed in bay C1.
• Switch-6 for switch module installed in bay C2.
3. At the login prompt, enter the default user name as “admin” and password as “password”.
4. Use the appropriate CLI commands to change the IP address of the selected switch module.
Refer to your Blade Server Enclosure CLI documentation.
Using the CMC GUI to set the IP address
To change the IP address, use the following steps:
1. Click the I/O Module Overview in the navigation panel of the CMC menu.
2. Open the CMC application’s Setup tab.
3. Enter the new information in the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway fields as appropriate
and click Apply.
4. To enable DHCP, select DHCP Enabled and click Apply.
FIGURE 3 CMC Setup Tab
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 11
53-1001980-01
Page 24

Modifying the converged network switch IP address
NOTE
2
Refer to the documentation for the CMC GUI application for additional detail.
Using the Dell M8428-k CLI to set the IP address
Use the following tasks to change the IP address on the switch module using the module’s CLI.
Follow the first few steps to establish a terminal emulation session between the switch module and
a Blade Server Enclosure management workstation used for managing the switch module. Once
this session is established, you can log into the module and use its CLI commands to manage the
module.
1. Connect a serial cable between the serial console port on the converged network switch and a
Blade Server Enclosure management workstation that can establish a terminal emulation
session with the switch module. For instructions, refer to the Configuration Guide for your
Blade Server Enclosure.
2. Disable any serial communication programs that are running on the workstation.
3. Using a terminal emulator application (such as HyperTerminal on a PC or TERM in a LINUX or
UNIX environment), establish a terminal session to the converged network switch from the
management workstation. You will use this connection if you want to reset the module’s IP
address using CLI commands and perform other configuration tasks.
For Windows 95, 98, 2000, XP, NT, 2003, or 2008
a. Click Start and select Programs -> Accessories -> Communications.
b. Select HyperTerminal and enter a name for the connection.
c. From the Hyper terminal window, click the Connect drop-down menu and select an
available COM port.
12 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 25

Configuring for FCoE
d. Click OK.
e. From the COM Port Properties window, select the following configuration values:
2
• Bits per second: 9600
• Databits: 8
• Parity: None
• Stop bits: 1
• Flow Control: None
For LINUX or UNIX
a. Enter the following at the command prompt:
tip /dev/ttyb -9600
b. When the terminal application stops reporting information, press Enter to display the login
prompt.
c. Log in to the default administrative account using the following identification:
Login: admin
Password: password
d. When prompted either change the administrative password, or press Ctrl-C to bypass.
4. Verify that the switch module has completed POST. When POST is complete, the port status
and switch module power and status LEDs return to a standard healthy state.
5. Enter the CLI ipAddrSet command.
Follow on-screen instructions and supply the correct information, as shown in the following
example.
switch:admin> ipaddrset
Ethernet IP Address [10.77.77.77]:10.32.53.47
Ethernet Subnetmask [255.255.255.0]:255.255.240.0
Fibre Channel IP Addresss [none]:
Fibre Channel Subnetmask [none]:
Gateway IP Address [0.0.0.0]:10.32.48.1
DHCP [Off]:
IP address is being changed...Done.
6. Enter ipAddrShow at the prompt to verify that the address was correctly set.
Configuring for FCoE
The initial configuration of the switch has the CEE ports shut down. In order to configure the ports
for FCoE operation, you must access the CEE command shell and configure both the internal and
external CEE ports. Once you have logged into the switch, use the cmsh command to access the
CEE command shell. Use the following steps to configure the CEE ports.
1. Login to the switch.
2. Enter the following command:
cmsh
3. Once in the command shell, enter the following command:
enable
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 13
53-1001980-01
Page 26

Connecting the switch to the Ethernet management network
NOTE
2
4. Enter the following command:
conf t
5. Enter one of the following commands:
a. interface intengigabitethernet 0/x where x is the internal port you wish to change
b. interface extengigabitethernet 0/x where x is the external port you wish to change
6. The default for internal ports is no shut (enabled) while the default value for external ports is
shut (disabled). To enable the external ports, in the port interface enter the following
commands:
fcoeport
no shut
exit
7. Repeat steps 5-6 for any other module port you wish to configure.
8. Once finished with all of the module ports, type exit and press Enter (you should still be in the
CMSH at this point).
9. Enter the following command:
write mem
Answer yes to overwrite the startup file.
10. Enter the following command:
copy running-config startup-config
Answer yes to overwrite.
See the Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet Administrator’s Guide for information about CEE CLI
interface and configuring switches for FCoE operation and the Dell Converged Enhanced Ethernet
Command Reference for more details on the commands.
Connecting the switch to the Ethernet management network
Once you have successfully set the appropriate IP address of the converged network switch, you
can establish an Ethernet connection through the Chassis Management Controller (CMC) to a
remote management workstation for any additional configuration. The management workstation
must be on the same Ethernet subnet as the CMC.
Ensure that the switch module is not being modified from any other connection until configuration
is complete.
Connecting the switch to the fabric
Before beginning the following steps, determine whether the switch module is in NPIV or full fabric
mode. This affects the configuration process. Using the switch module CLI, enter the ag ––
modeShow command to determine the current operating mode.
14 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 27

Connecting the switch to the fabric
2
1. If the switch module is in full fabric mode, continue with step 2 and step 3. If the module is in
NPIV mode, go on to step 4.
2. Log onto the converged network switch through a Telnet connection, using the admin account.
3. Modify the domain ID if required using switch module CLI commands.
The default domain ID is 1. If the switch module is not powered on until after it is connected to
the fabric and the default domain ID is already in use, the domain ID for the new switch
module is automatically reset to a unique value. If the switch module is connected to the fabric
after it has been powered on and the default domain ID is already in use, the fabric segments.
To find the domain IDs that are currently in use, run the fabricShow command on another
converged network switch or switch in the fabric. Identify an unused domain ID.
a. Disable the converged network switch being configured using the switchDisable
command.
b. Enter the configure command at the root prompt.
The command prompts display sequentially. Enter a new value at the Domain prompt or
press Enter to accept the default value. The converged network switch now has a unique
domain ID and can join the fabric. Following is an example of command output.
Fabric parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no] y
Domain: (1..239) [2]
R_A_TOV: (4000..120000) [10000]
E_D_TOV: (1000..5000) [2000]
WAN_TOV: (0..30000) [0]
MAX_HOPS: (7..19) [7]
Data field size: (256..2112) [2112]
Sequence Level Switching: (0..1) [0]
Disable Device Probing: (0..1) [0]
Suppress Class F Traffic: (0..1) [0]
Per-frame Route Priority: (0..1) [0]
Long Distance Fabric: (0..1) [0]
BB credit: (1..27) [16]
Disable FID Check (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Insistent Domain ID Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Configure edge hold time (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Virtual Channel parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
F-Port login parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Zoning Operation parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
RSCN Transmission Mode (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Arbitrated Loop parameters (yes, y, no, n): [no]
System services (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Portlog events enable (yes, y, no, n): [no]
ssl attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
rpcd attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
cfgload attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
webtools attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
Custom attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
system attributes (yes, y, no, n): [no]
System (yes, y, no, n): [no]
WARNING: The domain ID will be changed. The port level zoning may be
affected
c. Re-enable the switch module by entering the switchEnable command.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 15
53-1001980-01
Page 28

Connecting the switch to the fabric
NOTE
NOTE
ATTENTION
2
It could take a short time (typically a few seconds, but sometimes up to 20 seconds) for the
newly added switch module to appear in the fabric display with its newly assigned domain ID.
4. If you need to install transceivers, install them in the external CEE and FC ports as required.
a. Remove the dust plugs from the ports to be used.
b. If necessary, remove the end caps from the transceiver.
c. Orient the transceiver correctly and insert it into a port until it is firmly seated and the
d. Repeat substeps a, b, and c for the remaining ports, as required.
Use only Dell-approved transceivers in the external optical ports of this module.
5. Connect the cables to the transceivers.
The transceivers are keyed to ensure correct orientation. If a transceiver does not install easily,
ensure that it is correctly oriented and that the end caps have been removed. The cables used
in trunking groups must meet specific requirements.
latching mechanism clicks.
For instructions specific to the type of transceiver, refer to the transceiver manufacturer’s
documentation.
A c able s hould not be bent to a ra dius l ess than 5.08 cm (2 inches) under full tensile load and 3.048
cm (1.2 inches) with no tensile load.
Tie wraps are not recommended for optical cables because they are easily overtightened.
a. Orient a cable connector so that the key (the ridge on one side of connector) aligns with
the slot in the transceiver.
b. Insert the cable into the transceiver until the latching mechanism clicks. For instructions
specific to cable type, refer to the cable manufacturer’s documentation.
c. Repeat for the remaining transceivers as required.
6. Check the LEDs to verify that all components are functional.
For information about LED patterns, see the “Interpreting LED activity” on page 23.
7. Verify the correct operation of the converged network switch by typing the switchShow
command from the workstation.
This command provides information about switch module and port status.
8. Verify the correct operation of the converged network switch in the fabric by entering one of the
following commands:
a. If you are in NPIV mode, enter the ag --show command
b. If you are in full fabric mode, enter the fabricShow command
9. Back up the switch module configuration to an FTP server. See “Backing up the configuration”
on page 20 for specifics.
16 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 29

Changing from NPIV aggregator mode to full fabric mode
NOTE
NOTE
These commands upload the converged network switch configuration to the server, making it
available for downloading to a replacement converged network switch if necessary. Dell
recommends backing up the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a complete
configuration is available for downloading to a replacement switch module.
Changing from NPIV aggregator mode to full fabric mode
If your converged network switch is currently configured in NPIV mode, you can enable the module
for full fabric mode by disabling NPIV mode. When you do this, the module automatically reboots in
full fabric mode.
Determine if the switch module is running in NPIV mode by entering the switchShow CLI command
to display the current switch configuration. If running in NPIV aggregator mode, the switchMode
parameter will display Access Gateway.
Disabling NPIV mode is disruptive because the switch is disabled and rebooted. Always back up the
current configuration before enabling or disabling NPIV mode. Enabling NPIV mode clears the
security and zone databases. Disabling NPIV mode clears the F_Port to N_Port mapping.
2
Changing to full fabric mode using the browser-based GUI
Complete the following steps to enable full fabric mode using the browser-based GUI.
1. From the management console, open a Web browser.
2. Enter the IP address of the converged network switch into the Address field of the Web
browser.
3. Log into the browser-based GUI using the default administrative account.
Login: admin
Password: password
4. From the Fabric Tree, select the converged network switch.
The selected switch module appears in the Switch View.
5. Click the Switch Admin button in the browser-based GUI Manage task box.
The Switch Administration window opens.
You should save the configuration file if you are converting an converged network switch to NPIV
mode. To save your current configuration, click the Show Advanced Mode button in the top
right-hand corner of the Switch Administration window. Select the Configure tab, then select the
Upload/Download tab. Enter the relevant information to upload the configuration file.
6. From the Switch Status section, click Disable.
7. From the NPIV Mode section, click Disable.
8. Click Apply.
9. When prompted, click Yes to restart the switch module in full fabric mode.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 17
53-1001980-01
Page 30

Changing from full fabric mode to NPIV aggregator mode
NOTE
2
The current browser-based GUI session closes; relaunch browser-based GUI after the switch
module reboots.
Changing to full fabric mode using the command line interface
Complete the following steps to enable NPIV mode using the CLI.
1. Log in using the default administrative account.
Login: admin
Password: password
2. Enter the following command to disable the switch.
switchDisable
3. Back up the switch configurations. See “Backing up the configuration” on page 20 for
specifics.
4. Enter the following command to enable full fabric mode:
ag ––modeDisable
The switch module automatically reboots and comes back online in full fabric mode. The NPIV
parameters, such as port mapping and failover and failback, are automatically removed.
You can enter the ag ––modeShow command to ensure that the module is in NPIV mode.
ag ––modeShow
The response should say:
Access Gateway mode is NOT enabled.
Changing from full fabric mode to NPIV aggregator mode
If your converged network switch is currently configured in full fabric mode you can enable NPIV
mode using the following instructions. You can log into the switch module and enable NPIV mode
using either the browser-based GUI or the switch module command line interface (CLI).
Determine if the converged network switch is running in full fabric mode by entering the
switchShow CLI command to display the current switch configuration. If running in full fabric mode,
the switchMode parameter should display Native.
Enabling NPIV mode is a disruptive process because the switch is disabled and rebooted.Always
back up the current configuration before enabling or disabling NPIV mode. Enabling NPIV mode
clears the security and zone databases. Disabling NPIV mode clears the F_Port to N_Port mapping.
Once you enable the converged network switch in NPIV mode, only a limited subset of the fabric
operating system commands are available and all fabric-related service requests are forwarded to
the fabric switches.
18 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 31

Changing from full fabric mode to NPIV aggregator mode
NOTE
2
Changing to NPIV mode using the browser-based GUI
Complete the following steps to enable NPIV mode using the browser-based GUI.
1. From the management console, open a Web browser.
2. Enter the IP address of the converged network switch into the Address field of the Web
browser.
3. Log into the browser-based GUI using the default administrative account.
Login: admin
Password: password
4. From the Fabric Tree, select the converged network switch.
The selected switch module appears in the Switch View.
5. Click the Switch Admin button in the browser-based GUI Manage task box.
The Switch Administration window opens.
You should save the configuration file if you are converting an converged network switch to NPIV
mode. To save your current configuration, click the Show Advanced Mode button in the top
right-hand corner of the Switch Administration window. Select the Configure tab, then select the
Upload/Download tab. Enter the relevant information to upload the configuration file.
6. From the Switch Status section, click Disable.
7. From the NPIV Mode section, click Enable.
8. Click Apply.
9. When prompted, click Yes to restart the switch module in NPIV mode.
The current browser-based GUI session closes; relaunch browser-based GUI after the switch
module reboots.
Changing to NPIV mode using the command line interface
Complete the following steps to enable NPIV mode using the CLI.
1. Log in using the default administrative account.
Login: admin
Password: password
2. Enter the following command to disable full fabric mode.
switchDisable
3. Back up the switch configurations. See “Backing up the configuration” on page 20 for
specifics.
4. Enter the following command to enable NPIV mode:
ag ––modeEnable
The switch module automatically reboots and comes back online in NPIV mode using a factory
default F_Port to N_Port mapping.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 19
53-1001980-01
Page 32

Backing up the configuration
2
5. You can enter the ag ––modeShow command to ensure that the module is in NPIV mode.
ag --modeShow
The response should be:
Access Gateway mode is enabled.
You can also enter the ag ––mapshow command to display the F_Port to N_Port mapping.
Enter ag ––help command to display a list of all NPIV actions.
Backing up the configuration
Perform these steps to back up the switch module configuration to an FTP server.
1. Open a Telnet or SSH session to the switch module.
2. Enter the following command to upload the basic configuration of the switch module:
configUpload
You are then presented with a series of prompts.
3. Follow the prompts to upload the configuration.
4. When the upload completes, enter the following command to access the CEE CLI:
cmsh
5. Enter the following command to upload the current CEE configuration:
copy running-config ftp://[username@server/path]
You are then prompted for a password.
When you enter the password, the copy procedure begins.
These commands upload the switch module configurations to the server, making it available for
downloading to a replacement switch module if necessary.
Dell recommends backing up the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a complete
configuration is available for downloading to a replacement switch module.
20 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 33

Chapter
NOTE
Operating the Dell M8428-k
In this chapter
•Interoperability. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
•Accessing the converged network switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
•Interpreting POST results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
•Interpreting LED activity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
•Locating the serial number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
•Removing and replacing the converged network switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Interoperability
The converged network switch supports interoperability for the following functions:
• link initialization
• principal converged network
switch selection
• routing (FSPF)
• Simple Name Service
• state change notification
3
• soft WWN zoning
• SNMP facilities
• translative mode (private target support on fabrics)
• trunking (between two Dell switches)
• Advanced Performance Monitoring
Port negotiation on Fibre Channel ports
The converged network switch has been designed to be highly interoperable. 8 Gbps ports support
2, 4, and 8 Gbps transmit and receive rates with autonegotiation using SFP+ transceivers. You can
also install 4 Gbps SFP transceivers, which allow 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, and 4 Gbps transmit and receive
rates with autonegotiation. The actual data signaling rate used on a port is automatically sensed
and set to the rate supported by the device or devices attached to the port.
You must install Dell-approved transceivers in the switch module.
If the converged network switch is connected to a device, but is unable to negotiate the signaling
rate, the operator can manually set the speed of each port through the management interfaces.
The converged network switch is compliant with current Fibre Channel standards, including most
current-generation switch N_Ports, NL_Ports, and E_Ports as well as host adapters, Redundant
Array of Independent Disks (RAID) storage devices, hubs, Fibre-SCSI bridge devices, and older
switch families.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 21
53-1001980-01
Page 34

Accessing the converged network switch
3
Accessing the converged network switch
The converged network switch is managed as a single element. It has a single IP address and
appears as a separate entity to the Telnet protocol and the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP).
When SNMP devices send SNMP messages to a management console running SAN management
software, the information is stored in a Management Information Base (MIB). The switch module
OS supports the FibreAlliance Fibre Channel Management (FCMGMT) MIBs, allowing the provision
of needed information to a SAN administrator.
Secure Telnet access is available using Secure Shell (SSH), a network security protocol for secure
remote login and other secure network services over an insecure network.
Browser-based GUI management is available through a secure browser using Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL). The SSL security protocol provides data encryption, server authentication, message integrity,
and optional client authentication for a TCP/IP connection. Because SSL is built into all major
browsers and Web servers, installing a digital certificate enables the SSL capabilities.
Interpreting POST results
The power-on self test (POST) system check is performed each time the converged network switch
is powered on, rebooted, or reset.
Example POST Output
POST1: Started running Fri Oct 8 13:39:25 GMT 2010
POST1: Test #1 - Running ceeturboramtest
POST1: Running diagshow
POST1: Script PASSED with exit status of 0 Fri Oct 8 13:39:54 GMT 2010 took
(0:0:29)
POST2: Started running Fri Oct 8 13:39:54 GMT 2010
POST2: Test #1 - Running ceeportloopbacktest (SERDES)
POST2: Test #1 - Running ceeportloopbacktest (BACKPLANE)
During POST, the LEDs are activated in various indicator patterns.
Perform the following steps to determine POST completion status.
1. Verify that the LEDs on the converged network switch indicate a healthy converged network
switch. LED patterns are described in
If one or more LEDs do not display a healthy state, verify that the LEDs are not set to beacon.
Use the switch module CLI switchShow command or the browser-based GUI to verify the LED
state.
2. Use the Blade Server Enclosure’s Chassis Management Controller (CMC) GUIto verify that the
converged network switch is working correctly.
For details, refer to the Hardware Owner’s Manual for the Blade Server Enclosure.
“Interpreting LED activity,” next.
3. Review the system log for errors.
Any errors detected during POST are written to the system log. Access this log through the
Module’s CLI errShow command.
22 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 35

Interpreting LED activity
NOTE
M8428 - k
3
4
5
1
2
Each converged network switch uses LEDs to indicate status. These LEDs are shown in Figure 4.
FIGURE 4 LED Locations
Interpreting LED activity
3
1 Bi-color (green/amber) LEDs for 10 GbE
CEE ports
3 Server management LED (blue/amber) 4 Power status LED (green)
5 Switch status LED (green/amber)
The front panel of the switch module has two sets of LEDs. The power and status/fault LEDs on the
right of the switch module indicate the switch module status. The fault/activity LEDs on the CEE
ports and the fault/activity LEDs on the FC ports indicate the status of the external ports. Each port
has one bi-color LED.
See Figure 4 on page 23 for the locations of the LEDs on the switch module. These LEDs are
described in “Switch module status LEDs” on page 23 and “Port status LEDs” on page 24.
Any errors that are detected during POST are written to the system log.
When POST errors are written to the system log, these errors are also written to the BladeCenter
management module event log. If a hardware error, such as a current fault occurs, the
management module displays it. If a software error occurs, the management module displays the
“Module did not complete POST” message and a post error code that indicates the test that was
running when the error was detected.
You can also use the management module to make sure that the switch module is operating
correctly. For more information, see the documentation for the BladeCenter unit.
2 Bi-color (green/amber) LEDs for 8 Gbps FC ports
Switch module status LEDs
The following table provides descriptions of the switch module status LEDs on the front panel of the
switch module.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 23
53-1001980-01
Page 36

Locating the serial number
3
TABLE 2 System Status LEDs
Location Indicator Color Description
Power Green Off - no power
On - power is on
Status Green/Amber Off - Switch is off
Green - OK
Amber - boot-up state or one or more ports are offline
or reset state
Blinking (green/amber alternating) - error
CMC Management Blue/Amber Steady blue - Normal/Stack Master
Flashing blue - Module identify
Steady amber - Not used
Flashing amber - Fault
Off - on fault/Stack Slave
Port status LEDs
The following table provides descriptions of the port status LEDs on the front panel of the switch
module.
TABLE 3 CEE and FC port status LEDs
Location Port type Color Description
CEE ports Bi-color LED
FC ports Bi-color LED
Locating the serial number
Before contacting service support, be sure to obtain the module’s serial number. Use one of these
methods to locate the number:
• Use the switch module CLI and enter the ChassisShow command. The converged network
switch serial number is displayed along with other data.
• Locate the serial number on the label attached to the converged network switch. Refer to
Figure 2 on page 5 for location.
green/amber
green/amber
Off - no link or unlicensed
Steady green - link is present
Flashing green - activity over the link
Steady amber - fault
Off - no link
Steady green - link is present
Flickering green - normal activity
Slowly flashing green - segmented
Rapidly flashing green - loopback
Steady amber - no sync
Slowly flashing amber - disabled
Rapidly flashing amber - fault
24 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 37

Removing and replacing the converged network switch
NOTE
Removing and replacing the converged network switch
Complete the following steps to remove and replace a failed converged network switch.
Before beginning this procedure, ensure that you have a replacement converged network switch or
filler panel available because you should not leave the slot on the Blade Server Enclosure open for
an extended period of time. The slot must be filled with either a replacement converged network
switch or a filler panel to maintain proper airflow.
1. Back up the converged network switch configuration to an FTP server by using the switch
module’s configUpload CLI command and following the prompts as well as the cmsh copy
command to upload the CEE configuration. See
more details.
This commands upload the converged network switch configurations to the server, making it
available for downloading to a replacement converged network switch if necessary. It is
recommended that you back up the configuration on a regular basis to ensure that a complete
configuration is available for downloading to a replacement converged network switch.
2. Stop all SAN activity requiring the ports used by the converged network switch.
“Backing up the configuration” on page 20 for
3
For details about port management, refer to your Blade Server EnclosureHardware Owner’s
Manual. Verify that there is no activity by viewing the converged network switch LEDs. For
details about LED activity on the converged network switch, see “Interpreting LED activity” on
page 23.
3. Remove all cables from the transceiver modules.
4. Remove the transceiver modules according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Figure 5 on page 26 details the generic process for removing a cable from an transceiver and
an transceiver from a port.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 25
53-1001980-01
Page 38

Removing and replacing the converged network switch
ATTENTION
SFP
Bale
3
1
Cable
Release
2
SFP
4
3
FIGURE 5 Removing a cable and transceiver from a port
5. Refer to the Hardware Owner’s Manual for the Blade Server Enclosure to remove and replace
the switch module from the enclosure.
.
If you are not replacing the converged network switch, use a filler panel to fill the empty slot to
maintain proper air flow. Do not leave the slot empty.
26 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 39

Appendix
Dell M8428-k specifications
In this chapter
•NPIV Mode default port mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
•Processor and memory specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
•Weight and physical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
•Facility requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
•Electrical. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
•Architectural specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
•Supported mezzanine cards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
•Fibre Channel standards compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
•Regulatory compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
•Environmental regulation compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
A
NPIV Mode default port mapping
The switch module contains 28 total ports. Of these, F_Ports are ports 1-24 and N_Ports are ports
0 and 25-27.
In NPIV mode, the switch module F_Ports are mapped to N_Ports. The following table lists the
factory-default F_Port to N_Port mapping for NPIV mode.
TABLE 4 NPIV mode port mapping
F_Ports mapped to N_Ports
1-4, 17, 18 25
5-8, 19, 20 26
9-12, 21, 22 27
13-16, 23, 24 0
Ports 17-24 are the eight external CEE ports.
Processor and memory specifications
The processor and memory installed in the switch module are shown in Table 5.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 27
53-1001980-01
Page 40

Weight and physical dimensions
A
TABLE 5 Memory specifications
Memory type Value
PowerPC MPC8548 processor 1.33 GHz
SDRAM 1 GB DDR2
Boot flash 4 MB
Compact flash 1 GB
Weight and physical dimensions
Tab le 6 lists the weight and physical dimensions of the switch module.
TABLE 6 Switch module specifications
Dimension Measurements
Height 32.48 mm (1.27 in)
Width 272.75 mm (10.74 in)
Depth 307.24 mm (12.09 in)
Weight 2.10 kg (4.65 lb) — without media
Facility requirements
The information in Tab le 7 shows the operating and non-operating limitations of the Dell M8428-k.
TABLE 7 Environmental requirements
Condition Operating Non-operating
Temperature 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F) -20°C to 70°C (-4°F to 158°F)
Humidity 10% to 90%, non-condensing at
Altitude Up to 3,048 m (10,000 ft) 10,668 m (35,000 ft)
Shock 20 G for 6 ms 50G with velocity change of 4216
Vibration 0.4 G at 5-500 Hz for 60 minutes 0.5 G at 2-200 Hz for 15 minutes
Air flow 30°C (86 °F) Ambient: Approx. 3CFM
29°C (84.2°F)
40°C (104°F) Ambient: Approx. 9CFM
5% to 95%, non-condensing at
38°C (100.4 °F)
mm/sec
None required
2
28 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 41

Electrical
Tab le 8 lists switch module electrical specifications.
TABLE 8 Electrical specifications and requirements
Dimension Measurements
DC input 12 V and 3.3 V from chassis
Power consumption About 60 W normally and 70 W maximum measured
Architectural specification
The switch module meets the specifications shown in Table 9.
TABLE 9 Architecture
Feature Description
Electrical
A
Scalability Refer to the current scalability guidelines publication
Certified maximum Refer to the current scalability guidelines publication
Performance -FC ports 1.063 Gbps line speed, full duplex
2.125 Gbps line speed, full duplex
4.25 Gbps line speed, full duplex
8.50 Gbps line speed, full duplex
Performance -CEE ports 1 Gbps line speed, or
10 Gbps line speed
Fabric latency
(full fabric mode only)
Maximum frame size Fibre Channel - 2112-byte payload
Class of service Class 2
Port types FL_Port
Fabric services
(full fabric mode only)
Supported software Telnet, RADIUS, SNMP, Web Tools, Enhanced Group Management,
700 nanosecond with no contention, cut-through routing @ 8 Gbps
Ethernet - 9048 -byte frame
Class 3
Class F (interswitch frames)
F_Port
E_Port
N_Port
Simple Name Server, Registered State Change Notification (RSCN),
Alias Server (multicast),;
Zoning, Web Tools, Enhanced Group Management, Fabric Watch
(optional), ISL Trunking, Advanced Performance Monitor
Fabric Watch, Advanced Zoning, ISL Trunking, Advanced
Performance Monitoring, Data Center Fabric Manager (DCFM)
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 29
53-1001980-01
Page 42

Supported mezzanine cards
A
Supported mezzanine cards
The Dell M8428-k currently supports the BR1741M-k 2P mezzanine card.
Fibre Channel standards compliance
The switch module switch meets or exceeds the Fibre Channel standards for compliance,
performance, and feature capabilities as defined in the standards compliance list below.
FC-AL-2 INCITS 332: 1999
FC-GS-5 ANSI INCITS 427: (includes the following.)
FC-GS-4 ANSI INCITS 387: 2004
FC-IFR INCITS 1745-D, revision 1.03 (under development)
FC-SW-4 INCITS 418:2006 (includes the following)
FC-SW-3 INCITS 384: 2004
FC-VI INCITS 357: 2002
FC-TAPE INCITS TR-24: 1999
FC-DA INCITS TR-36: 2004 (includes the following)
FC-FLA INCITS TR-20: 1998
FC-PLDA INCIT S TR-19: 1998
FC-MI-2 ANSI/INCITS TR-39-2005
FC-PI INCITS 352: 2002
FC-PI-2 INCITS 404: 2005
FC-PI-4 INCITS 1647-D, revision 7.1 (under development)
FC-FS-2 ANSI/INCITS 424:2006 (includes the following)
FC-FS INCITS 373: 2003
FC-LS INCITS 433: 2007
FC-BB-3 INCITS 414: 2006 (includes the following)
FC-BB-2 INCITS 372: 2003
FC-SB-3 INCITS 374: 2003 (replaces FC-SB ANSI X3.271: 1996; FC-SB-2 INCITS 374: 2001)
RFC 2625 IP and ARP Over FC
RFC 2837 Fabric Element MIB
MIB-FA INCITS TR-32: 2003
FCP-2 INCITS 350: 2003 (replaces FCP ANSI X3.269: 1996)
SNIA Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S) Version 1.2 (includes the following)
SNIA Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S) Version 1.03 ISO standard
IS24775-2006. Replaces (ANSI INCITS 388: 2004)
30 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 43

SNIA Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S) Version 1.1.0
SNIA Storage Management Initiative Specification (SMI-S) Version 1.2.0
Regulatory compliance
This section describes the regulatory compliance requirements for the Dell M8428-k.
FCC warning (US only)
This equipment has been tested and complies with the limits for a Class A computing device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, might cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference, in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at the user’s own
expense.
Regulatory compliance
A
KCC Statement (Republic of Korea)
VCCI statement (Japan)
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by
Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this equipment is used in a domestic environment,
radio disturbance might arise. When such trouble occurs, the user might be required to take
corrective actions.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 31
53-1001980-01
Page 44

Regulatory compliance
A
BSMI statement (Republic of Taiwan)
32 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 45

Regulatory compliance
ATTENTION
CAUTION
A
CE statement
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product might cause radio interference,
and the user might be required to take corrective measures.
The standards compliance label on the Switch contains the CE mark which indicates that this
system conforms to the provisions of the following European Council directives, laws, and
standards:
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 89/336/EEC and the Complementary Directives
92/31/EEC and 93/68/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 73/23/EEC and the Complementary Directive 93/68/EEC
• EN50082-2/EN55024:1998 (European Immunity Requirements)
• EN61000-3-2/JEIDA (European and Japanese Harmonics Spec)
• EN61000-3-3
Canadian requirements
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing
Equipment Regulations, ICES-003 Class A.
Laser compliance
This equipment contains Class 1 laser products and complies with FDA Radiation Performance
Standards, 21 CFR Subchapter I and the international laser safety standard IEC 825-2.
Use only optical transceivers that are supported by Dell and comply with the FDA Class 1
radiation performance requirements defined in 21 CFR Subchapter I, and with IEC 825-2. Optical
products that do not comply with these standards might emit light that is hazardous to the eyes.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 33
53-1001980-01
Page 46

Environmental regulation compliance
⦃ֱՓ⫼ᳳ䰤 (EPUP) ܡ䋷ໄᯢ˖
EPUP ᖫϡӮߎ⦄ѻક FRU ⱘᬍ㺙ѻકЁˈгϡӮᇍ Brocade
᠔ᦤկⱘⳌ݇ѻકֱׂᴵℒ˄䆹ֱׂᴵℒ Brocade
ঞ݊ᅶ᠋䯈䖒៤ⱘ䗖⫼ড়ৠЁ߫ߎ˅䖯㸠㸹DŽᇍѢℸ CD
ϞࣙⱘⳌֵ݇ᙃˈབ䗖䫔ᗻǃ䩜ᇍ⡍ᅮ⫼䗨ⱘ䗖⫼ᗻ䴲։ᴗᗻⱘᱫ⼎ֱ䆕ˈBr
ocade ℸ䚥䞡ໄᯢᴀ݀ৌᇍѢϢϞ䗄ֵᙃⳌ݇ⱘ᠔᳝݊Ҫֱ䆕䰜䗄ὖϡ䋳䋷DŽ
EPUP ؛䆒Āѻક᪡ݠāЁ⊼ᯢⱘᐌ㾘ᴵӊϟՓ⫼䆹ѻકDŽ
A
Environmental regulation compliance
This section describes the China ROHS environmental regulatory compliance requirements for the
switch module.
China RoHS
The contents included in this section are per the requirements of the People's Republic of ChinaManagement Methods for Controlling Pollution by Electronic Information products.
䙉ᅜ⦃๗⊩㾘
Ё RoHS
ᴀ㡖Ёࣙⱘݙᆍ䛑䙉ᅜњЁҎ⇥݅lj⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩NJⱘ
㽕∖DŽ
Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) Disclaimer
In no event do the EPUP logos shown on the product and FRUs alter or expand that warranty that
Dell provides with respect to its products as set forth in the applicable contract between Dell and
its customer. Dell hereby disclaims all other warranties and representations with respect to the
information contained on this CD including the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a
particular purposes and non-infringement.
The EPUP assumes that the product will be used under normal conditions in accordance with the
operating manual of the product.
34 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 47

Environmental regulation compliance
A
TS/HS Dual Language Sheet
In accordance with China's Management Measures on the Control of Pollution caused by Electronic
Information products (Decree No. 39 by the Ministry of Information Industry), the following
information is provided regarding the names and concentration level of Hazardous substances (HS)
which may be contained in this product.
China ROHS Hazardous Substances/Toxic Substances (HS/TS) Concentration Chart
Name of the
Component
Fibre Channel
Switch
PCBA cards X O O O O O
transceivers
(optical cable
connectors)
Sheet Metal X O O O O O
Mechanical
brackets and
Slides
Software/
Documentation
CDs
Hazardous/Toxic Substance/Elements
Lead (PB) Mercury
(Hg)
XOOO O O
XOOO O O
XOOO O O
OO O O O O
Cadmium
(Cd)
Hexavalent
Chromium
(CR6+)
Polybrominated
Biphenyl (PBB)
Polybrominated
Diphenyl Ether
(PBDE)
X indicates that the concentration of such hazardous/toxic substance in all the units of
homogeneous material of such component is higher than the SJ/T11363-2006 Requirements for
Concentration Limits.
O indicates that no such substances are used or that the concentration is within the
aforementioned limits.
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 35
53-1001980-01
Page 48

Environmental regulation compliance
CHINA ROHS᳝ᆇ⠽䋼/᳝↦⠽䋼(HS/TS)䰤䞣߫㸼
᳝↦Ϣ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼ܗ㋴ⱘৡ⿄ঞ䞣
ḍЁⱘ<<⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩>>
(ֵᙃѻϮ䚼39োҸ)ˈᴀ݀ৌᦤկҹϟ᳝݇ѻકЁৃ㛑᳝ⱘ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼(HS)ⱘৡ⿄ঞ䞣∈ᑇⱘ
ֵᙃDŽ
᳝ᆇ/᳝↦⠽䋼ܗ㋴Џ㽕䚼ӊৡ⿄
䪙
˄PB
˅
∲
Hg
˅
䬝
CD
˅
݁Ӌ䫀
˄C
R6+˅
⒈㘨㣃
˄PBB˅
⒈Ѡ㣃䝮
PB
DE˅
˅
ܝ㑸䗮䘧Ѹᤶᴎ
XOO O O O
XOO O O O
㒓䏃ᵓ䚼ӊ
XOO O O O
SFP˄ܝ㑸
༈˅
XOO O O O
䩷䞥ӊ
OOOOOO
XOO O O O
ᴎẄᬃᶊঞ⒥䔼
䕃ӊ/᭛ḷܝⲬ
X 㸼⼎ℸ㉏䚼ӊݙৠ䋼ᴤ᭭Ёⱘ᳝ᆇ/᳝↦䞣催ѢSJ/T11363-2006ⱘ䰤䞣㽕∖DŽ
O 㸼⼎Փ⫼ℸ㉏⠽䋼݊䞣ԢѢϞ䗄䰤䞣㽕∖DŽ
˄
˄
A
Regulatory certifications
Tab le 10 lists the safety and EMC (electromagnetic compatibility) specifications for which the
Switch is certified.
TABLE 10 EMC certifications
Country Safety specification EMC specification
Argentina IEC 60950-1:2001
IEC 60825-1:1993+A1+A2
Australia and New Zealand EN55022:2006 Class A
Canada CSA60950-1-03 1st Ed. CSA 108.8 Class A
China (power supply only) GB4943-1995 GB9254-1998
GB17625.1
European Union
(Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech
Republic, Denmark, Estonia,
Finland, France, Germany,
Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy,
Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg,
Malta, Poland, Portugal,
Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain,
Sweden, The Netherlands, and
United Kingdom)
International IEC 60950+A1+A2+A3+A4+A11 EN55022 Class A
Japan IEC 60950+A1+A2+A3+A4+A11 EN55022 Class A
36 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
EN 60950:92
+A1:93+A2:93+A3:95+A4:96+A11:97
73/23/EEC
EN60825-1:1994/A11, -2
TUV (Germany only)
IEC 60950+A1+A2+A3+A4+A11
(NEMKO CB Report) (Norway only)
EN55022:2006 Class A
EN 55024 (Immunity)
EN 61000-4-2 Electrostatic Discharge
EN 61000-4-3 Radiated Fields
EN 61000-4-4 Electrical Fast Transients
EN 61000-4-5 Surge Voltage
EN 61000-4-6 Conducted Emissions
EN 61000-4-8 Magnetic Fields
EN 61000-4-11 Voltage Dips and Interruptions
EN 61000-3-2 Limits for Harmonic Current Emissions
EN 61000-3-3 Flicker
EN 61000-3-2 Harmonics (JEIDA Limits)
53-1001980-01
Page 49

Environmental regulation compliance
TABLE 10 EMC certifications (Continued)
Country Safety specification EMC specification
Republic of Korea KN24
KN22
Russia GOST R IEC 60950-2002 GOST R 51318.22-99 (Class A)
GOST R 51318.24 -99
GOST R 51317.3.2-99
GOST R 51317.3.3-99
Taiwan (power supply only) CNS13438
United States UL 60950-1 1st Ed. EN55022 Class A
FCC Part 15, Subpart B (CFR title 47), Class A
A
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 37
53-1001980-01
Page 50

Environmental regulation compliance
A
38 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
Page 51

Index
A
ag --help command, 20
ag --mapshow command
ag --modeEnable command
air flow
architectural specifications
, 28
, 20
B
backing up
CEE configuration
FC configuration
beacon
boot flash
BSMI statement (Chinese)
, 22
, 27
, 20
, 20
C
cabling guidelines, 10
Canadian requirements
CEE command shell
CEE ports, configuring
China RoHS
cmsh command
, 34
, 13, 20
, 33
, 13
, 13
, 18, 19
, 29
, 32
commands
ag --help
ag --mapshow
ag --modeEnable
cmsh
conf t
configUpload
configure
connect
connect switch-x
copy running-config
enable
errShow
exit
fcoeport
interface extengigabitethernet
interface intengigabitethernet
ipAddrSet
no shut
switchDisable
switchShow
write mem
compact flash
conf t command
configUpload command
configuration
backing up
FCoE
configure command
connect command
connect switch-x command
converged network switch
accessing
cabling guidelines
characteristics
connecting to Ethernet
connecting to fabric
hardware description
physical dimensions and weight
removing and replacing
serial number
status
unpacking and installing
, 20
, 20
, 18, 19
, 13, 20
, 14
, 20
, 15
, 11
, 11
, 14, 20
, 13
, 22
, 14
, 14
, 13
, 14
, 15, 18, 19
, 22
, 14
, 27
, 14
, 20
, 20
, 13
, 15
, 11
, 22
, 10
, 3
, 14
, 14
, 3
, 24
, 23
, 14
, 14
, 11
, 28
, 25
, 6
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 39
53-1001980-01
Page 52

copy running-config command, 20
D
dimensions, 28
E
IP address
modify using CMC CLI
modify using module CLI
modifying default
ipAddrSet command
ISL
trunking groups
ISL trunking
, 6
, 6
, 11
, 12
, 10
, 13
E_Ports, 2
enable command
errShow command
exit command
external CEE ports, configuring
, 13
, 22
, 14
, 13
F
F_Ports, 2
facility requirements
FCC warning (US only)
fcoeport command
Fibre Channel standards compliance
FL_Ports
flash
FTP server
full fabric mode
, 2
, 27
, 20
changing from NPIV mode
enable through browser-based GUI
enable through CLI
, 28
, 31
, 14
, 17
, 18
, 30
, 17
K
kernel, 27
kernel flash
, 27
L
labeling, 5
laser compliance
LED
, 22, 23
LED activity
interpreting
LEDs
information
port status
switch status
limitations
direct connections to target devices
loop devices not supported
LWL
, 6
, 33
, 23
, 23
, 24
, 23
, 3
, 3
H
humidity, 28
M
management tool, 22
memory
MIC statement (Republic of Korea)
, 27
, 31
I
interface extengigabitethernet command, 14
interface intengigabitethernet command
internal CEE ports, configuring
interoperability
interpreting
LED activity
POST results
40 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
, 21
, 23
, 22
, 13
, 14
N
no shut command, 14
NPIV mode
default port mapping
enable through browser-based GUI
enable through CLI
limitations
, 3
, 27
, 19
, 18
53-1001980-01
Page 53

O
T
operating requirements, 28
optional features
full fabric mode
NPIV mode
, 6
, 6
, 6
P
port management, 25
port negotiation
port side of the converged network switch
port status LEDs
POST
, 2, 22
results
processor
protective foam
, 21
, 24
, 22
, 27
, 7
R
regulatory certifications, 36
regulatory compliance
release lever
removing and replacing
, 4
, 31
, 25
, 3
Telnet, 20
temperature
terminal session with switch module
transceivers
trunking
, 28
, 12
, 5
, 6
U
unpacking the converged network switch, 6
V
VCCI statement, 31
vibration
, 28
W
weight, 28
write mem command
, 14
S
SDRAM, 27
SEEPROM
serial cable
serial number
shipping package
shock
specifications
SSH
supported HBAs
supported transceivers
switch module OS
switch status LEDs
switchDisable command
switchShow command
SWL
, 27
, 12
, 24
, 7
, 28
, 28
, 20
, 30
, 22
, 23
, 22
, 6
, 5
, 15, 18, 19
Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual 41
53-1001980-01
Page 54

42 Dell M8428-k Hardware Reference Manual
53-1001980-01
 Loading...
Loading...