Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
UAA3545
Fully integrated DECT transceiver
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC17
2001 Sep 06
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
FEATURES
• Economical solution for a radio in DECT cordless
telephones
• Integrated low phase noise VCO with no production
tuning required
• Fully integrated receiver with high sensitivity
• Dedicated DECT PLL synthesizer
• 3 dBm output preamplifier with an integrated switch
• 3-line serial interface bus
• Low current consumption from a 3.2 V supply
• Compatible with Philips Semiconductors baseband
chips (PCD509xx and PCD80xxx)
• Reduced number of control signals.
APPLICATIONS
• DECT cordless telephones: 1880 to 1930 MHz.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The UAA3545 BiCMOS device is a low power, highly
integrated circuit, for Digital Enhanced Cordless
Telecommunication (DECT) applications.
It features a fully integrated receiver, from antenna filter
output to the demodulated data output, a fully integrated
VCO, a synthesizer to implement a phase-locked loop for
DECT channel frequencies and aTXpreamplifierto drive
the external transmit power amplifier (CGY20xx series or
UAA359x series of Philips integrated circuits).
The synthesizer’s main divider is driven by the prescaler
output in the range of 1880 to 1930 MHz and is
programmed via a 3-wire serial bus. The reference divider
ratio is programmable to 4, 8, 12 or 16. Outputs of the
main and reference dividers drive a phase comparator
whereachargepumpproducesphaseerrorcurrentpulses
for integration in an external loop filter (only a passive loop
filter is necessary). The charge-pump current is set to
4 mA for fast switching.
The VCO is powered from an internally regulated voltage
source and includes integrated variable capacitance
diodesandintegratedcoils.Itstuning range is guaranteed.
The VCO and the synthesizer are switched-on one slot
before the active slot to lock the VCO to the required
channel frequency. Immediately before the active slot, the
synthesizer is switched-off to allow open loop modulation
of the VCO during transmission. When opening the loop,
frequency pulling (due to switching-off the synthesizer)
can be maintained within the DECT specification.
The device is designed to operate from a 3.2 V nominal
supply. Separate power and ground pins are provided for
thedifferentsectionsofthecircuit.Groundleadsshouldbe
short-circuited externally to prevent large currents flowing
across the die and causing damage. All VCC supplies
(V
CC(REG)
, V
CC(SYN)
, V
CC(RX)
and V
) must be at the
CC(TX)
same potential (VCC).
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
UAA3545HL LQFP32 plastic low profile quad flat package; 32 leads; body 5 × 5 × 1.4 mm SOT401-1
2001 Sep 06 2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
VCC= 3.2 V; T
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
CC(syn)
CC(reg)
CC(RX)
CC(TX)
CC(SYN)
CC(REG)
CC(RX)
CC(TX)
CC(pd)
o(RF)
(i)XTAL
PC
amb
,
,
,
V
V
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
f
f
f
T
=25°C; characteristics with a typical value only are not tested; unless otherwise specified.
amb
supply voltage All VCCsupplies
3.0 3.2 3.6 V
must be at the
same potential
)
(V
CC
synthesizer supply current synthesizer ON − 57mA
VCO, buffer and prescaler regulator
VCO ON − 14 17 mA
supply current
receiver supply current − 36 44 mA
transmit preamplifier supply current − 12 15 mA
total supply current in Power-down mode − 10 100 µA
RF output frequency 1880 − 1930 MHz
crystal reference input frequency − 3.456,
− MHz
6.912,
10.368or
13.824
phase comparator frequency − 864 − kHz
ambient temperature −10 − +60 °C
2001 Sep 06 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
15
RFA
14
RFB
20
TXA
21
TXB
VCO_ON
R_ON
1
17
S_CLK
V
CC(RX)
16
LNA
AMP
CONTROL
LOGIC
6
8
S_DATA
S_EN
V
×
CC(TX)
22
RSSI
RXGND
12
DEMODULATORLIMITER
TXGND
13
19
SLIC = 1
UAA3545
PRESCALER
SYNTHESIZER
29
TEST3
18
23
DIVGND
VREGDIV
28 32 25
4
TEST2
TEST1
5
24 3
V
XTAL
CC(SYN)
CP/VCO
SLICER
0
V
tune
1 kΩ
(1)
VCO REGULATOR
MOD
SLIC = 1
V
CC(REG)
SLIC = 1
0
0
2
11
26
10
31
30
27
MGW108
7
9
RDATAP
DATAM
SLCCTR
VREGI
SYNGND
VREGO
REGGND
VCOGND
(1) SLCCTR ‘switches’ shown in position SLCCTR = LOW.
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2001 Sep 06 4
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
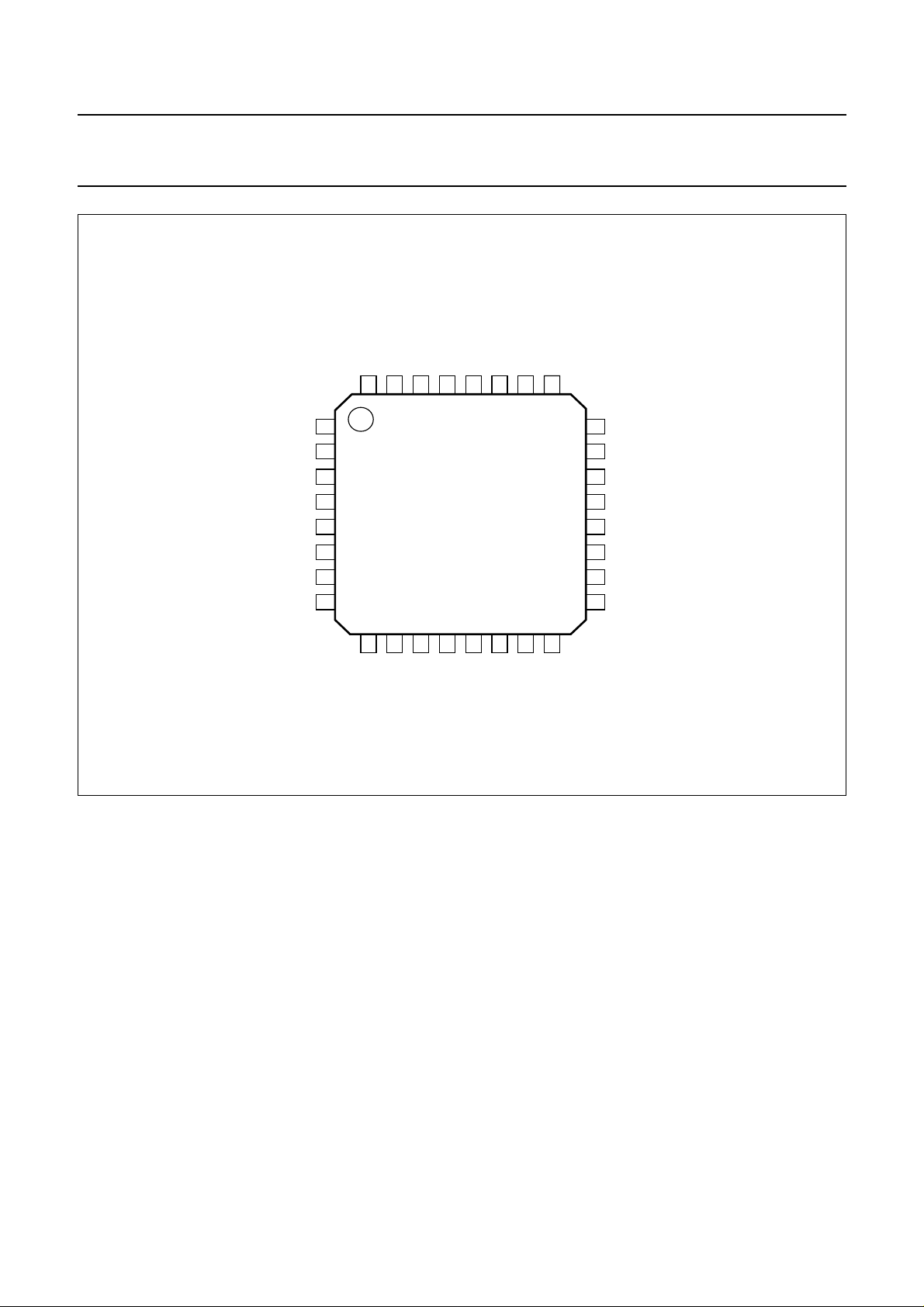
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
VCO_ON 1 VCO section power-on control; note 1
V
CC(REG)
V
CC(SYN)
S_DATA 4 3-wire bus data signal input
XTAL 5 reference frequency input; note 2
S_EN 6 3-wire bus enable signal input
RDATAP 7 demodulator output voltage
S_CLK 8 3-wire bus clock signal input
DATAM 9 switched demodulator output voltage
SYNGND 10 synthesizer ground
SLCCTR 11 DATAM switch control signal (see Fig.1)
RSSI 12 received signal strength intensity voltage output
RXGND 13 receiver ground
RFB 14 received signal input B
RFA 15 received signal input A
V
CC(RX)
R_ON 17 receiver power-on control; note 3
TEST3 18 TEST input 3 (must be connected to GND)
TXGND 19 transmitter ground
TXA 20 transmit amplifier output A
TXB 21 transmit amplifier output B
V
CC(TX)
DIVGND 23 divider ground
VREGDIV 24 divider regulated supply voltage
V
MOD
VREGI 26 VCO regulated voltage input
VCOGND 27 VCO ground
TEST1 28 TEST input 1 (must not be connected)
TEST2 29 TEST input 2 (must not be connected)
REGGND 30 regulator ground
VREGO 31 VCO section regulated voltage output
CP/VCO
tune
2 regulator positive supply voltage
3 synthesizer positive supply voltage
16 receiver positive supply voltage
22 transmitter positive supply voltage
25 VCO analog modulation voltage input
32 charge-pump output/VCO tuning input
Notes
1. Corresponds to the S_PWR of the baseband chip (see Section “Operating modes” for more details).
2. Corresponds to the REF_CLK of the baseband chip.
3. See Section “Operating modes” for more details.
2001 Sep 06 5
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
handbook, full pagewidth
VCO_ON
V
CC(REG)
V
CC(SYN)
S_DATA
RDATAP
S_CLK
XTAL
S_EN
tune
CP/VCO
VREGO
REGGND
TEST2
TEST1
VCOGND
31
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DATAM
30
UAA3545HL
11
10
SLCCTR
SYNGND
29
12
RSSI
28
27
13
14
RFB
RXGND
VREGI
26
15
RFA
MOD
V
25
16
CC(RX)
V
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
FCA242
VREGDIV
DIVGND
V
CC(TX)
TXB
TXA
TXGND
TEST3
R_ON
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
2001 Sep 06 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Transmit chain
VCO AND PRESCALER
The fully integrated VCO operates at a multiple of the
DECT frequency. It is supplied by an on-chip voltage
regulator to minimize frequency disturbances due to
supply voltage variations. The VCO signal is fed into a
prescaler. A large difference between transmitted and
VCO frequencies reduces transmitter-oscillator coupling
problems.
The output of the prescaler drives the synthesizer main
divider. The divider output can also be switched to either
the TX preamplifier or the RX LO output buffer. The high
isolation obtained from the prescaler ensures very small
frequencychangeswhenturning-onthe TX preamplifier or
the RX section. In TX mode, the oscillator can be
modulated directly with GFSK-filtered data at pin V
MOD
.
TX PREAMPLIFIER
The TX preamplifier amplifies the RF signal to a level of
3 dBm (typical) which is suitable for use with Philips
Semiconductors DECT power amplifiers.
Synthesizer
MAIN DIVIDER
The main divider is clocked by the RF signal from the
prescaler at frequencies from 1880 to 1930 MHz. Any
main divider ratio from 2176 to 2303 inclusive can be
programmed.
REFERENCE DIVIDER
PHASE COMPARATOR
The phase comparator is driven by the output of the main
and reference dividers. It produces current pulses at
pin CP/VCO
, the pulse duration being the difference in
tune
arrival time of current pulse edges from the two dividers.
If the main divider edge arrives first, pin CP sinks current.
If the reference divider edge arrives first, pin CP sources
current. The DC value of the charge-pump current is
defined by an internal resistor. Additional circuitry is
included to ensure the gain of the phase detector remains
linear even for small phase errors.
Serial programming bus
A simple 3-line unidirectional serial bus is used to
program the circuit. The three lines are data (S_DATA),
serial clock (S_CLK) and serial bus enable (S_EN). Data
sent to the device are loaded in bursts framed by S_EN.
Programming clock edges and their appropriate data bits
are ignored until S_EN goes active (LOW). The
programmed information is read directly by the main
divider when S_EN returns to HIGH. S_DATA and S_EN
change value on the falling edge of S_CLK.
During synthesizer operation, S_EN should be held
HIGH. Only the last 24 bits clocked into the device are
retained within the serial register. Additional leading bits
are ignored and no check is made on the number of clock
pulses. The data format is shown in Table 1. The first bit
entered is b23, the last bit is b0. For the main divider ratio,
the first bit (b5) is the Most Significant Bit (MSB).
The serial bus enable (S_EN) must be LOW to capture
newprogramming data and must be HIGHto switch on the
synthesizer.
The reference divider is clocked by the signal at pin XTAL.
The circuit operates with levels from 1.2 to 1.8 V (p-p) at a
frequency of 3.456 MHz. By programming the ‘REFD’ bits
of the serial input register (see Table 1) the reference
frequency can be set for 6.912, 10.368 or 13.864 MHz.
2001 Sep 06 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
Receiver
The receiver is a fully integrated RF + IF strip and
demodulatorfor DECT. It provides allthe required channel
filtering over the DECT band and generates analog RSSI
and a switched output for Philips Semiconductors
basebandchip.Veryfewoff-chipcomponentsarerequired
and all of these can be placed without trimming. The chip
is designed to operate with a power supply voltage that
can fall to 3.0 V. The input is the RF antenna signal
derived from the band filter or the antenna switch. The
outputs are the RSSI voltage, representing the
instantaneous signal strength and two HIGH-level
demodulator output signals RDATAP and DATAM, the
latter being switched by SLCCTR to generate the external
slicer threshold. During the blind slot, while the PLL is
settling, an internal voltage source is activated to
precharge the external capacitor (connected to
pin DATAM) to a voltage close to the required slicer
threshold.
Operating modes
The operating modes available are:
• Normal mode (see Fig.3)
• Reduced signal mode (see Fig.4)
• Advanced signal mode (see Fig.5).
Selection of an operating mode is achieved via the serial
interface register (see Table 3).
NORMAL MODE (MODE 1)
In the normal mode, the synthesizer is ON when
S_EN = HIGH and VCO_ON = HIGH, and OFF when
S_EN = LOW. When turned ON, the dividers and phase
detector are synchronized to avoid a random initial phase
error. When turned OFF, the phase detector is
synchronized with the dividers to avoid interrupting a
charge-pump pulse. This feature requires a signal to be
present for a few microseconds on the XTAL pin after
S_EN goes LOW.
The VCO is ON when the input signal VCO_ON is HIGH.
The polarity of VCO_ON is chosen for compatibility with
output S_PWR of the baseband chip. When the VCO is
turned ON, it takes 50 µs (typical) to reach its steady state.
REDUCED SIGNAL MODE (MODE 2)
Inthe reduced signal mode, the parallel control signals are
replaced by serial bus programming. To select this mode,
the bit ‘NEW’ of the internal register must be set to ‘1’ and
the bit ‘SPWR’ must be reset to ‘0’, timing is then
controlled by the S_EN signal.
After the register programming, the S_EN rising edge
programs the PLL, closes the loop, powers-on the VCO
and, if the ‘TRX’ bit = 0, turns ON the TX preamplifier.
On the falling edge of the first S_EN pulse, the loop is
opened (unless the bit ‘PLL’ is set to 1) and the receiver
switches ON if the ‘TRX’ bit = 1. A second pulse on S_EN
is required at the endof the wanted slot to power-down the
application.
The R_ON pin becomes an output in this mode, drives the
RX PIN diode and corresponds to the internal power-on
signal of the receiver.
ADVANCED SIGNAL MODE (MODE 3)
In the advanced signal mode, the parallel control signals
are partly replaced by serial bus programming. To select
this mode, the bit ‘NEW’ and the bit ‘SPWR’ of the internal
register must be set to ‘1’. The S_EN signal will then
control the UAA3545 timing (except for timing of a general
power-down as this is controlled by the VCO_ON input).
The VCO_ON signal should rise at the beginning of the
previous slot. After the serial bus has been programmed,
the S_EN rising edge programs the PLL, closes the loop
and, if the ‘TRX’ bit = 0, turns ON the TX preamplifier.
On the falling edge of the first S_EN pulse, the loop is
opened(unless the ‘PLL’ bitis set to 1) and theRX section
switches ON if bit ‘TRX’ = 1. At the end of the wanted slot,
the VCO_ON goes LOW to power-down the whole IC.
In fact, the second pulse of the S_EN signal in mode 2 is
now replaced by the signal VCO_ON.
The R_ON pin becomes an output in this mode, drives the
RX PIN diode and corresponds to the internal power-on
signal of the receiver.
The TX preamplifier is ON when bit ‘TRX’ is programmed
to ‘0’ and VCO_ON is HIGH. When the TX preamplifier is
turned ON, it takes typically 10 µs to be ready. The
receiver is turned ON when R_ON = HIGH and
VCO_ON = HIGH.
2001 Sep 06 8
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
Programming
Table 1 Serial interface register
REGISTER BIT ALLOCATION
first in last in
b23 to b20 b19 b18, b17 b16 to b10 b9 b8 b7 b6 b5 to b0
TEST
(2)
SLIC
(3)
REFD
(4)
TEST
(2)
SPWR
(5)
PLL
(6)
NEW
(5)
TRX MAIN DIVIDER
Notes
1. Bit b5 is the MSB of the main divider coefficient; this comprises bits b5, b4, b3, b2, b1, b0 and b6 (TRX).
2. Test bits b23, b22, b21, b20, b16, b15, b14, b13, b12, b11, b10 must always be programmed to 0.
3. Bit ‘SLIC’ = 1 forces the internal slicer on. In this mode, pin DATAM is connected to an external capacitor. Together
with an internal 1 kΩ resistor, it defines the low pass time constant for the slicer threshold voltage. When the
bit ‘SLIC’ = 0, the pin RDATAP is connected directly to the demodulator output and delivers an analog signal.
Pin DATAM also reflects the demodulator voltage without the internal 1 kΩ resistor when the SLCCTR pin is HIGH.
4. REFD sets the reference divider ratio to 4, 8, 12 or 16 (corresponding respectively to a reference input frequency of
3.456, 6.912, 10.368 or 13.824 MHz) (see Table 4).
5. Bits ‘NEW’, and ‘SPWR’ select the operating mode (see Table 3).
6. Bit ‘PLL’ = 1 forces the PLL to remain on when the VCO is on.
7. The main divider ratio is equal to 2176 + the programmed value (see Table 2).
(1)
(7)
Table 2 Main divider programming
BIT
b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 b6 (TRX)
MAIN DIVIDER
RATIO
SYNTHESIZED
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Binary equivalent of n 2176 + n 0.864 × (2176 + n)
000000 0 2176 1880.064
010111 1 2223 1920.672
Table 3 Operating mode selection
BIT
OPERATING MODE
b9 (SPWR) b7 (NEW)
0 0 normal mode (mode 1)
0 1 reduced signal mode (mode 2)
1 0 do not use
1 1 advanced signal mode (mode 3)
Table 4 Reference divider ratio programming
BIT
REFERENCE DIVIDER RATIO REFERENCE INPUT FREQUENCY
b18 b17
0 0 4 3.456 MHz
0 1 16 13.824 MHz
1 0 8 6.912 MHz
1 1 12 10.368 MHz
2001 Sep 06 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
,
V
CC(syn)
V
CC(reg)
V
CC(RX)
V
CC(TX)
V
n
P
i(RFA)(max)
P
i(RFB)(max)
supply voltage All VCC supplies must be at
,
,
voltage on any pin −0.3 V
,
maximum input power at
pins RFA and RFB
∆GND difference in ground supply voltage
applied between all ground pins
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
T
j
total power dissipation − 300 mW
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
ambient temperature −10 +60 °C
junction temperature − 150 °C
the same potential (VCC)
note 1 − 0.01 V
−0.3 +3.6 V
CC
V
− 15 dBm
Note
1. Ground pins must be short-circuited externally (this is in addition to being short-circuited internally.
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices.
All pins are compatible with
“EIA/JESD22-A114-A Class1 (October 1997)”
.
LATCH-UP
Pins S_DATA, TXA and TXB are susceptible to latch-up if a negative current greater than 20 mA is drawn from the
respective pin (occurs when the pin voltage is negative with respect to GND).
To avoid latch-up, pins TXA and TXB pins must be connected to VCCthrough coils, and the S_DATA control signal input
from the baseband IC must be kept positive with respect to GND.
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 100 K/W
2001 Sep 06 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
CHARACTERISTICS
VCC= 3.2 V; T
unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
V
V
V
I
I
I
I
I
CC(syn)
CC(reg)
CC(RX)
CC(TX)
CC(SYN)
CC(REG)
CC(RX)
CC(TX)
CC(pd)
,
,
,
Synthesizer
=25°C; f
amb
supply voltage All VCC supplies must be at the
= 288 kHz; f
dev
= 13.824 MHz; characteristics with a typical value only are not tested;
(i)XTAL
3.0 3.2 3.6 V
same potential (VCC)
synthesizer supply
S_EN = HIGH − 57 mA
current
VCO, buffer and
VCO ON − 14 17 mA
prescaler regulator
supply current
receiver supply current RX mode − 36 44 mA
transmit preamplifier
TX mode − 12 15 mA
supply current
total supply current in
− 10 100 µA
Power-down mode
MAIN DIVIDER
f
o(RF)
R
m
RF output frequency 1880 − 1930 MHz
main divider ratio 2176 − 2234
REFERENCE DIVIDER
f
(i)XTAL
crystal reference input
frequency
V
(i)XTAL(p-p)
crystal reference input
voltage (peak-to-peak
value)
R
RD
R
i(XTAL)
reference divider ratio programmed values; see Table 4 − 4, 8, 12
input resistance (real
part of the parallel input
impedance)
C
i(XTAL)
input capacitance
(imaginary part of the
parallel input
impedance)
PHASE COMPARATOR
f
PC
phase comparator
frequency
programmed values; see Table 4 − 3.456,
6.912,
10.368
or
13.824
square wave input;
all f
(i)XTAL
values
1.2 − 1.8 V
or 16
f
= 3.456 MHz − 17 − kΩ
(i)XTAL
f
= 3.456 MHz − 1.5 − pF
(i)XTAL
− 864 − kHz
− MHz
−
2001 Sep 06 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
CHARGE-PUMP OUTPUT
I
o(CP)
VCO
f
VCO
V
CP/VCOtune
G
VCO
G
MOD
Transmit preamplifier
P
o(TXA)
P
o(TXB)
R
o(TXA)
R
o(TXB)
C
o(TXA)
C
o(TXB)
f
VCO(feedthru)
CNR
25
CNR
4686
∆f
o(push)
∆f
o(pull)
∆f
o(drift)
charge-pump output
VCP=1⁄2V
CC
current
oscillator frequency defined at transmit output,
T
= −10 to +60 °C; note 1
amb
charge pump input
voltage and VCO tuning
output voltage
VCO tuning input gain
defined at transmit output; note 2 − 70 − MHz/V
(mean value)
VCO modulation input
defined at transmit output; note 3 − 2.4 − MHz/V
gain
,
transmit output power T
= −10 to +60 °C; f
amb
to 1930 MHz; note 1
,
transmit output
resistance (real part of
balanced; expressed at high signal
level
the parallel output
impedance)
,
transmit output
capacitance (imaginary
balanced; expressed at high signal
level
part of the parallel
output impedance)
VCO frequency
feedthrough at
referred to P
f
= 1900 MHz; note 1
VCO
transmit output
carrier-to-noise ratio at
transmit output
carrier-to-noise ratio at
carrier offset in closed loop;
∆f=25kHz
carrier offset; ∆f = 4686 kHz −−135 −129 dBc/Hz
transmit output
frequency shift due to
supply voltage drop
measured dynamically;
VCCdrop = 100 mV;
V
CP/VCOtune
TX load = 50 Ω; note 1
frequency shift due to
disabling the synthesizer
frequency pulling measured 20 µs
after synthesizer disabled;
V
CP/VCOtune
f
= 1880.064 MHz; V
VCO
TX load = 50 Ω; note 1
transmit output
notes 1 and 4 −−6±12 kHz
frequency drift during a
slot
= 1880
VCO
MOD
;
=0;
o(TXA),Po(TXB)
= 1.2 V; V
set by the PLL on
MOD
− 3.5 − mA
1880 − 1930 MHz
0.3 − VCC− 0.3 V
03−dBm
− 200 −Ω
− 0.3 − pF
−−20 −15 dBc
−−65 −56 dBc/Hz
−+10 ±20 kHz
−+5±10 kHz
=0;
2001 Sep 06 12
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Receiver section
V
RSSI(max)
maximum RSSI output
voltage
V
t
RSSI
on
RSSI output voltage monotonicity over range
wake-up time from the
power-on signal to
correct RSSI output
s
B
input sensitivity BER ≤ 10−3; note 1 −−96 −93 dBm
IM intermodulation
rejection
R
R
co
i(n−1)
co-channel rejection BER < 10−3; wanted channel at
adjacent channel
rejection
R
i(n−2)
bi-adjacent channel
rejection
R
i(n−≥3)
rejection with
≥3 channels separation
RBl rejection of a blocking
signal
R
o(RF)
RF inputresistance(real
part of the parallel input
impedance)
C
o(RF)
RF input capacitance
(imaginary part of the
parallel input
impedance)
under high RX input signal level − 1.9 − V
−96 to −36 dBm
P
i(RFA/B)
P
i(RFA/B)
P
i(RFA/B)
= −33 dBm − 1.7 2.0 V
= −36 dBm − 1.64 − V
= −96 dBm − 0.3 − V
− 25 40 µs
BER ≤ 10
BER < 10
−5
; note 1 −−92 −76 dBm
−3
; wanted signal at
33 42 − dBc
−83 dBm; level of interference in
channels n + 2 and n + 4; note 1
−10 −7.5 − dBc
−76 dBm; note 1
BER < 10−3; wanted channel at
14 20 − dBc
−76 dBm; adjacent levelreferredto
wanted channel level; note1
BER < 10−3; wanted channel at
35 42 − dBc
−76 dBm; bi-adjacent levelreferred
to wanted channel level; note1
BER < 10−3; wanted channel at
40 45 − dBc
−76 dBm; n ≥ 3 adjacent level
referred to wanted channel level;
note 1
BER < 10
−3
; wanted signal at
−83 dBm at channel 5:
f − f
> 6 MHz; note 2 38 55 − dBc
c
(f
1780 MHz < f < (f
+ 5 MHz) < f < 2 GHz;
RFmax
RFmin
48 58 − dBc
− 5 MHz)
; note 1
2GHz<f<4.32 GHz;
38 60 − dBc
notes 1 and 5
balanced; at 1890 MHz − 100 −Ω
balanced; at 1890 MHz − 0.8 − pF
2001 Sep 06 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
f
i(RF)(max)
f
i(RF)(min)
RL
RF
G
DEM
V
DEM
Interface logic input and output pins S_DATA, S_CLK, S_EN, R_ON, VCO_ON, SLCCTR and RDATAP
V
IH
V
IL
I
bias
V
OH(RDATAP)
V
OL(RDATAP)
I
O(RON)
Z
O(RON)
f
SCLK(max)
t
SEN(min)
maximum RF input
−−1930 MHz
frequency
minimum RF input
1880 −− MHz
frequency
return loss on matched
balanced; note 1 11 15 − dB
RF input
demodulator gain mean value of f
DC levelat demodulator
fLO=fRF+ 864 kHz − 1.3 − V
= ±288 kHz − 1.6 − V/MHz
dev
outputs RDATAP and
DATAM
HIGH-level input voltage note 6 1.4 − V
CC
V
LOW-level input voltage) −0.3 − +0.4 V
input bias current HIGH or LOW input levels −5 − +5 µA
HIGH-level output
bit ‘SLIC’ = 1; IOH= 500 µAV
− 0.4 V
CC
CC
− V
voltage (pin RDATAP)
LOW-level output
bit ‘SLIC’ = 1; IOL= −500 µA − 0 0.4 V
voltage (pin RDATAP)
output drive current
(pin R_ON)
output impedance
mode 2 or 3; V
VCC− V
RON
= 0.5 V
mode 2 or 3; V
= HIGH level;
RON
= LOW level − 6 − kΩ
RON
2.5 5 − mA
(pin R_ON)
maximum frequency
− 10 − MHz
(pin S_CLK)
minimum pulse duration
− 1 −µs
(pin S_EN)
Notes
1. Measuredandguaranteedonlyon the Philips evaluation board, including Printed-Circuit Board (PCB) and balun filter
with internal slicer.
2. Mean of the values of transmit frequency at V
3. Measured with V
CP/VCOtune
= 1.5 V, mean of the values of transmit frequency at V
CP/VCOtune
4. Frequency difference measured during 420 µs with V
= 0.3 and 2.7 V.
= 0 and 0.5 V.
MOD
= 0 (no modulation applied), at least 20 µs after disabling
MOD
the synthesizer.
5. Except for three occurrences, as defined in the DECT specification.
6. VIH should never exceed 3.6 V.
2001 Sep 06 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
MODE 1 TIMING
handbook, full pagewidth
EXTERNAL VCO_ON
RECEIVE MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
EXTERNAL R_ON
EXTERNAL XTAL
TRANSMIT MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
EXTERNAL VCO_ON
EXTERNAL R_ON
EXTERNAL XTAL
TRANSMIT
PREAMPLIFIER
STATUS
SIGNAL ON OUTPUTS
TXA, TXB
FCA243
Fig.3 Normal mode timing diagram.
2001 Sep 06 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
MODE 2 TIMING
handbook, full pagewidth
INTERNAL VCO_ON
RECEIVE MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
R_ON OUTPUT
EXTERNAL XTAL
TRANSMIT MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
INTERNAL VCO_ON
EXTERNAL XTAL
SIGNAL ON OUTPUTS
TXA, TXB
Fig.4 Reduced signal mode timing diagram.
2001 Sep 06 16
FCA244
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
MODE 3 TIMING
handbook, full pagewidth
EXTERNAL VCO_ON
RECEIVE MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
R_ON OUTPUT
EXTERNAL XTAL
TRANSMIT MODE
S_DATA
S_CLK
S_EN
EXTERNAL VCO_ON
EXTERNAL XTAL
SIGNAL ON OUTPUTS
TXA, TXB
Fig.5 Advanced signal mode timing diagram.
2001 Sep 06 17
FCA245
Page 18

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
k,
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2001 Sep 06 18
V
CC
XTAL
C58
10 µF
T_GFSK
C57
100 nF
C31
1 nF
VCO_ON
C22
82 pF
S_DATA
S_EN
R_DATAP
S_CLK
SLCCTR
RSSI
560 pF
C18
8.2 nF
NPO
(1)
C13
NPO
C66
100 nF
R11
TEST1
2.2 kΩ
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
1
2
3
4
TEST2
UAA3545
5
6
7
8
9 10111213141516
C40
4.7 nF
C44
27 pF
L9
6.8 nH
6.8 pF
C65
RFB
L8
6.8 nH
C40
8.2 pF
C43
1.5 pF
full pagewidth
RFA
C41
8.2 pF
L10
6.8 nH
C67
6.8 pF
V
CC
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
C62
1.8 pF
TXB
TXA
V
CC
C46
8.2 pF
C42
1.5 pF
C68
8.2 pF
R
470 Ω
L7
12 nH
L6
2.7 nH
PA
C
8.2pF
C32
8.2 pF
C33
0.82 pF
C70
8.2 pF
(2)
470 Ω
L5
2.7 nH
C28
8.2 pF
L4
12 nH
ADDITIONAL
IMPLEMENTATION
R
C
8.2 pF
C23
100 nF
C27
0.82 pF
TX output
T_PWR
C69
8.2 pF
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
RF input
FCA246
(1) S_DATA input (pin 4) is subject to latch-up if a negative voltage is applied. The application circuit should be designed to prevent this occurring.
(2) TXA and TXB outputs(pins 20 and 21) aresubject to latch-up if anegative output voltage occurs. Toprevent this happening, the applicationcircuit should use a DCbiasing arrangement
with L5 and L6 connected to V
as shown.
CC
Fig.6 Evaluation board schematic (mode 3 operation).
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
Internal pin configuration
PIN SYMBOL INTERNAL CIRCUIT
1 VCO_ON
4 S_DATA
6 S_EN
8 S_CLK
11 SLCCTR
7RDATAP
9 DATAM
12 RSSI
1, 4, 6, 8, 11
MGW234
7, 9
MGW235
14 RFB
15 RFA
17 R_ON
12
MGW237
14 15
MGW238
17
MGW239
2001 Sep 06 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
PIN SYMBOL INTERNAL CIRCUIT
20 TXA
21 TXB
20 21
MGW240
25 V
MOD
25
MGW241
31 VREGO
32 CP/VCO
31
MGW242
tune
32
MGW243
2001 Sep 06 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
RECEIVED SIGNAL STRENGTH INTENSITY
handbook, full pagewidth
2
V
RSSI
(V)
1.6
1.2
0.8
0.4
0
−100 −70 −60 −50 −40−80−90 −30 −20
P
i(RFA/B)
(dBm)
−10
MGW233
0
Fig.7 RSSI output as a function of input power at pins RFA and RFB.
2001 Sep 06 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
PACKAGE OUTLINE
LQFP32: plastic low profile quad flat package; 32 leads; body 5 x 5 x 1.4 mm
c
y
X
SOT401-1
24
25
pin 1 index
32
1
e
w M
b
p
D
H
D
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
1.60
A
1A2A3bp
0.15
1.5
1.3
0.25
0.05
cE
0.27
0.18
0.17
0.12
UNIT
17
Z
16
E
A
e
H
E
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
9
8
Z
D
p
detail X
v M
A
B
v M
B
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
5.1
4.9
eH
H
D
5.1
4.9
0.5
7.15
6.85
E
7.15
6.85
LL
p
0.75
1.0
0.45
0.2
0.12 0.1
Z
0.95
0.55
D
(A )
3
L
p
L
Zywv θ
E
0.95
0.55
o
7
o
0
θ
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
SOT401-1 136E01 MS-026
2001 Sep 06 22
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
99-12-27
00-01-19
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
SOLDERING
Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
Thistextgivesaverybriefinsight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering can still be used for
certainsurfacemountICs,butitisnotsuitableforfinepitch
SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is
recommended.
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
tothe printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
convection or convection/infrared heating in a conveyor
type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending
on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 220 °C for
thick/large packages, and below 235 °C for small/thin
packages.
Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemountdevices(SMDs)orprinted-circuitboards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswithleadsonfoursides,thefootprintmust
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
2001 Sep 06 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, HBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, TFBGA not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HBCC, HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
2001 Sep 06 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
DATA SHEET STATUS
PRODUCT
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective specification Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
Preliminary specification Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Product specification Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
(1)
STATUS
(2)
DEFINITIONS
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Changes will be
communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition Limiting values given are in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
attheseorat any other conditions above those given in the
Characteristics sections of the specification is not implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentationorwarrantythatsuchapplicationswillbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury.Philips
Semiconductorscustomersusingorsellingtheseproducts
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuseofanyoftheseproducts,conveysnolicenceortitle
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,andmakes no representations or warranties that
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
2001 Sep 06 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
NOTES
2001 Sep 06 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Fully integrated DECT transceiver UAA3545
NOTES
2001 Sep 06 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2001
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands 403506/01/pp28 Date of release: 2001 Sep 06 Document order number: 9397 750 08151
SCA73
 Loading...
Loading...