Page 1
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA1015T
0,5 W audio power amplifier
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, ICO1
March 1986
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA1015T is a low-cost audio amplifier which can deliver up to 0,5 W output power into a 16 Ω load impedance at
a supply voltage of 9 V. The amplifier is specially designed for portable applications such as radios and recorders.
The IC has a very low supply voltage requirement (3,6 V min.).
Features
• High input impedance
• Separated preamplifier and power amplifier
• Limited noise behaviour at radio frequencies
• Short-circuit protected
• Miniature encapsulation.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Supply voltage range V
Peak output current I
Output power P
Voltage gain power amplifier G
Voltage gain preamplifier G
Total quiescent current I
Operating ambient temperature range T
Storage temperature range T
PACKAGE OUTLINE
8-lead mini-pack; plastic (SO8; SOT96A); SOT96-1; 1996 July 23.
P
OM
o
tot
amb
stg
V1
V2
3,6 to 12 V
max. 1 A
typ. 0,5 W
typ. 29 dB
typ. 23 dB
max. 22 mA
−25 to +150 °C
−55 to + 150 °C
March 1986 2
Page 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
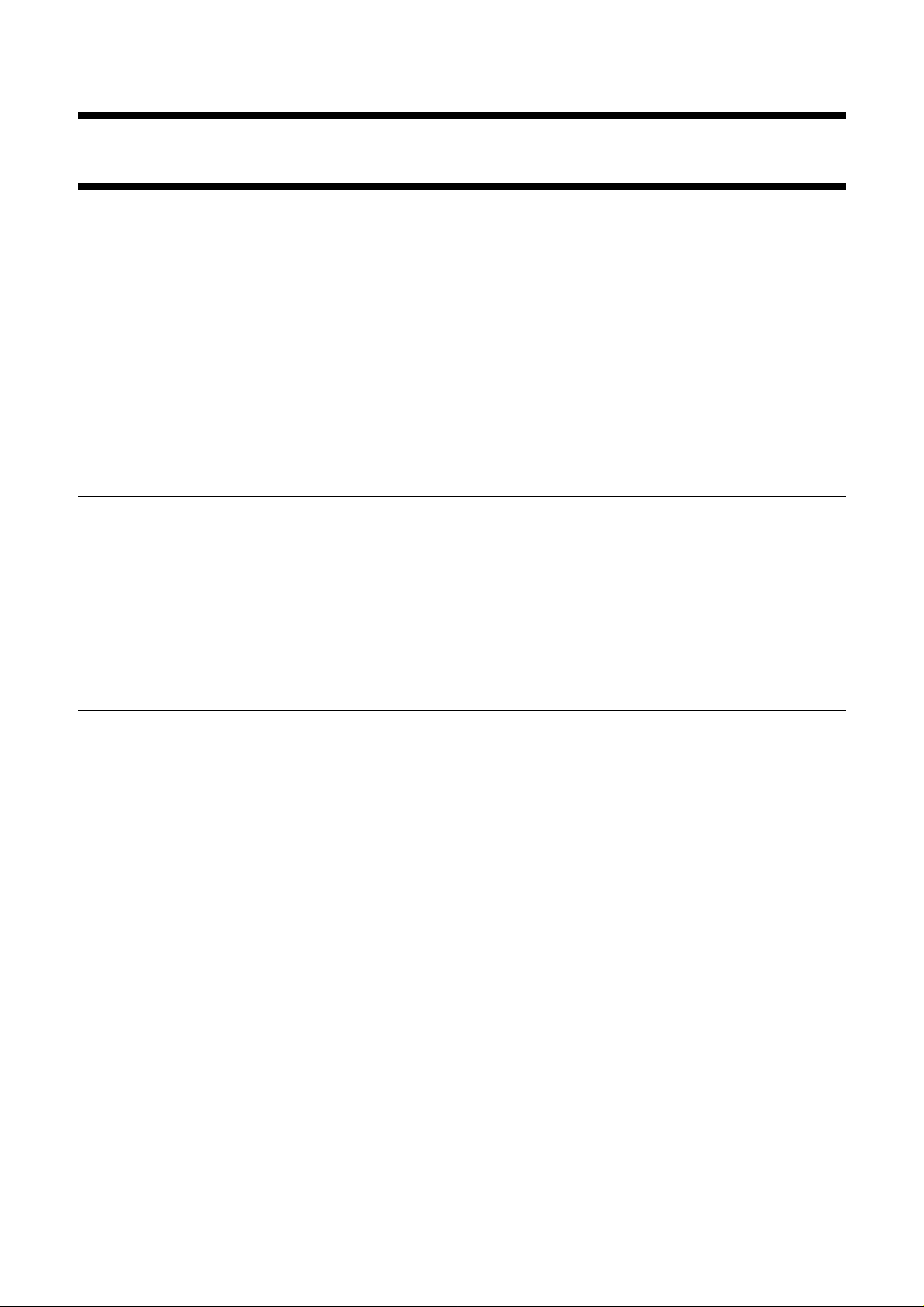
Fig.1 Block diagram.
RATINGS
Limiting values in accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
Supply voltage V
Peak output current I
P
OM
max. 12 V
max. 1 A
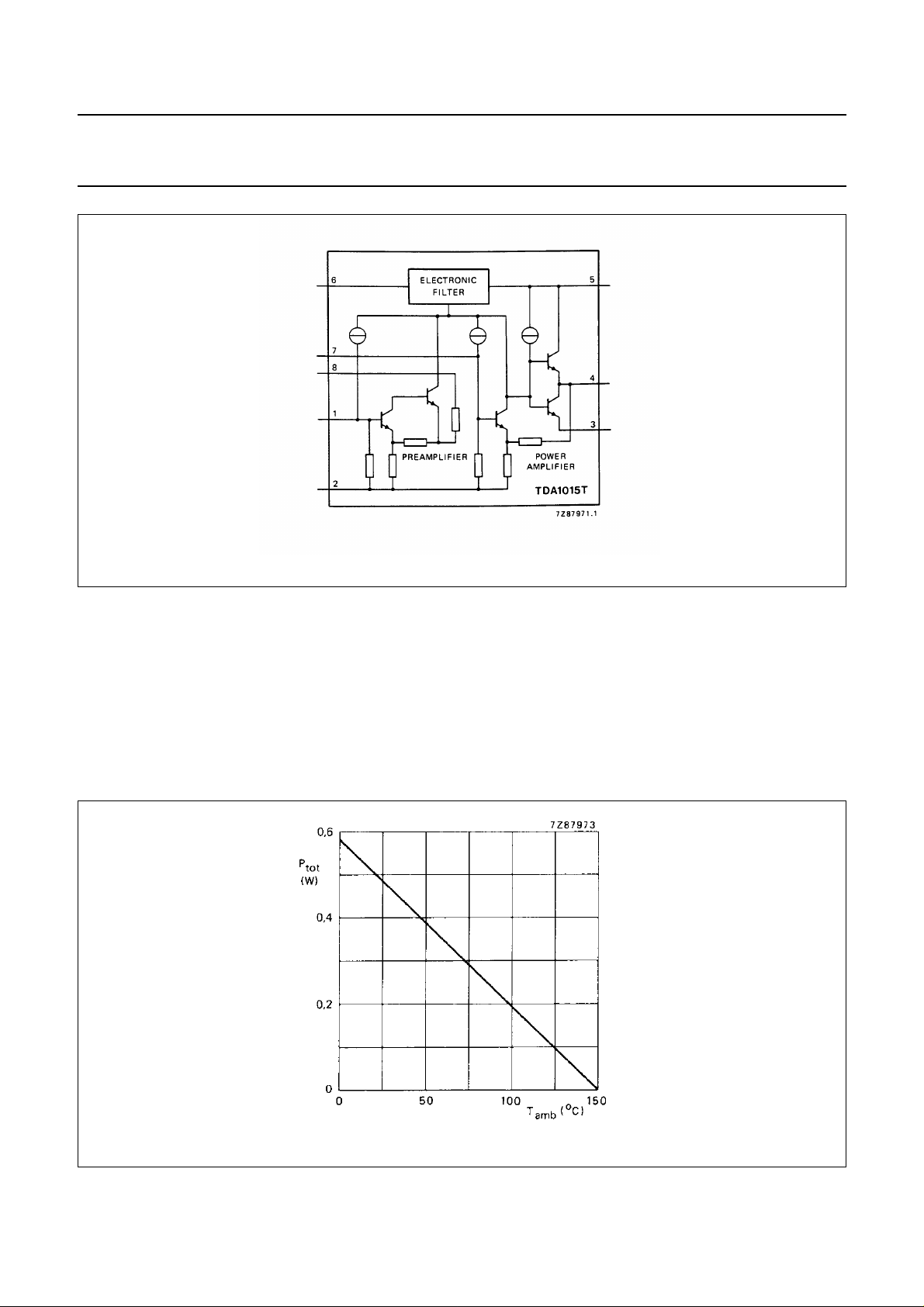
Total power dissipation see derating curve Fig.2
Storage temperature range −55 to + 150 °C
A.C. short-circuit duration of load during sine-wave drive at V
= 9 V t
P
sc
max. 1 hour
Fig.2 Power derating curve.
March 1986 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
CHARACTERISTICS
= 25 °C; VP = 9 V; RL = 16 Ω; f = 1 kHz; see Fig.3; unless otherwise specified
T
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
I
ORM
I
tot
P
o
P
o
G
v1
G
v2
G
tot
B Frequency response at −3 dB (note 3) − 60 to 15 000 − Hz
|Zi1| Input impedance power amplifier − 20 − kΩ
|Z
i2
|Z
o2
V
o2(rms)
V
n(rms)
V
n(rms)
V
n(rms)
RR C2 = 1 µF (note 6) − 38 − dB
Supply voltage 3,6 9 12 V
Repetitive peak output current −−1A
Total quiescent current − 12 22 mA
A.F. output power at d
= 10%; note 1
tot
VP = 9 V; RL = 16 Ω−0,5 − W
VP = 6 V; RL = 8 Ω−0,3 − W
Voltage gain power amplifier − 29 − dB
Voltage gain preamplifier (note 2) − 23 − dB
Total voltage gain 49 52 55 dB
| Input impedance preamplifier (note 4) 100 200 − kΩ
| Output impedance preamplifier 0,5 1 1,5 kΩ
Output voltage preamplifier (r.m.s. value)
d
< 1% (note 2) − 0,7 − V
tot
Noise output voltage (r.m.s. value); note 5
RS = 0 Ω−0,2 − mV
RS = 10 kΩ−0,5 − mV
Noise output voltage (r.m.s. value)
f = 500 kHz; B = 5 kHz; RS = 0 Ω− 8 −µV
Ripple rejection at f = 100 Hz;
Notes to the characteristics
1. Output power is measured with an ideal coupling capacitor to the speaker load.
2. Measured with a load resistance of 20 kΩ.
3. The frequency response is mainly determined by the capacitors, C1, C3 (low frequency) and C4 (high frequency).
4. Independent of load impedance of preamplifier.
5. Effective unweighted r.m.s. noise voltage measured in a bandwidth from 60 Hz to 15 kHz (slopes 12 dB/octave).
6. Ripple rejection measured with a source impedance between 0 and 2 kΩ (maximum ripple amplitude of 2 V).
March 1986 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Fig.3 Test circuit.
______ measured in Fig.3
− − − − measured with a 1,5 MΩ resistor
connected between pins 7 and 2.
Fig.4 Total quiescent current as a function
of supply voltage.
March 1986 5
Fig.5 Output power as a function of supply
voltage; d
= 10%; f = 1 kHz.
tot
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
______ measured in Fig.3
− − − − measured with a 1,5 MΩ resistor connected between pins 7 and 2.
Fig.6 Total distortion as a function of output power; VP = 9 V; RL = 16 Ω; f = kHz.
Fig.7 Application circuit for power stage only and battery power supply; Gv1 = 29 dB; |Zi1| = 20 kΩ.
March 1986 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
Fig.8 Application circuit for preamplifier and power amplifier stages and battery power supply;
G
= 52 dB; |Zi2| = 200 kΩ.
v tot
March 1986 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
PACKAGE OUTLINE
SO8: plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm
D
c
y
Z
8
pin 1 index
1
e
5
A
2
A
4
w M
b
p
SOT96-1
E
H
E
1
L
detail X
A
X
v M
A
Q
(A )
L
p
A
3
θ
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT96-1
A
max.
1.75
0.069
A
1
0.25
0.10
0.010
0.004
A2A
1.45
1.25
0.057
0.049
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
076E03S MS-012AA
0.25
0.01
b
3
p
0.49
0.25
0.36
0.19
0.019
0.0100
0.014
0.0075
UNIT
inches
Notes
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
2. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
(1)E(2)
cD
5.0
4.8
0.20
0.19
REFERENCES
4.0
3.8
0.16
0.15
0.050
March 1986 8
eHELLpQZywv θ
1.27
6.2
5.8
0.244
0.228
1.05
1.0
0.4
0.039
0.016
0.7
0.6
0.028
0.024
0.25 0.10.25
0.010.010.041 0.004
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
(1)
0.7
0.3
0.028
0.012
ISSUE DATE
95-02-04
97-05-22
o
8
o
0
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC
packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when
through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed
on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is
not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for
printed-circuits with high population densities. In these
situations reflow soldering is often used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
“IC Package Databook”
our
Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering techniques are suitable for all SO
packages.
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt. Dwell times vary
between 50 and 300 seconds depending on heating
method. Typical reflow temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder is
10 seconds, if cooled to less than 150 °C within
6 seconds. Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
Repairing soldered joints
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonallyopposite end leads. Use only a low voltage soldering iron
(less than 24 V) applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact
time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C. When
using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in
one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 minutes at
45 °C.
Wave soldering
Wave soldering techniques can be used for all SO
packages if the following conditions are observed:
• A double-wave (a turbulent wave with high upward
pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave) soldering
technique should be used.
• The longitudinal axis of the package footprint must be
parallel to the solder flow.
• The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves at
the downstream end.
March 1986 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
0,5 W audio power amplifier TDA1015T
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
March 1986 10
 Loading...
Loading...