Page 1

REFRIGERATION AND
AIR CONDITIONING
Pulse Motor
Expansion Valves
Type KV
TECHNICAL LEAFLET
Page 2

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Contents
Page
Introduction .....................................................................................................................................................................................3
Features ..............................................................................................................................................................................................3
Explanation of Action ...................................................................................................................................................................4
Operation Principles .................................................................................................................................................................. 4-5
Common Refrigerant Valve and Coil Specifications...........................................................................................................6
Application Examples ...................................................................................................................................................................7
Selection Method .......................................................................................................................................................................8-9
Capacity R410A ............................................................................................................................................................................10
Applications .......................................................................................................................................................................... 11
CO
2
Dimensions ....................................................................................................................................................................................12
2 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
Page 3
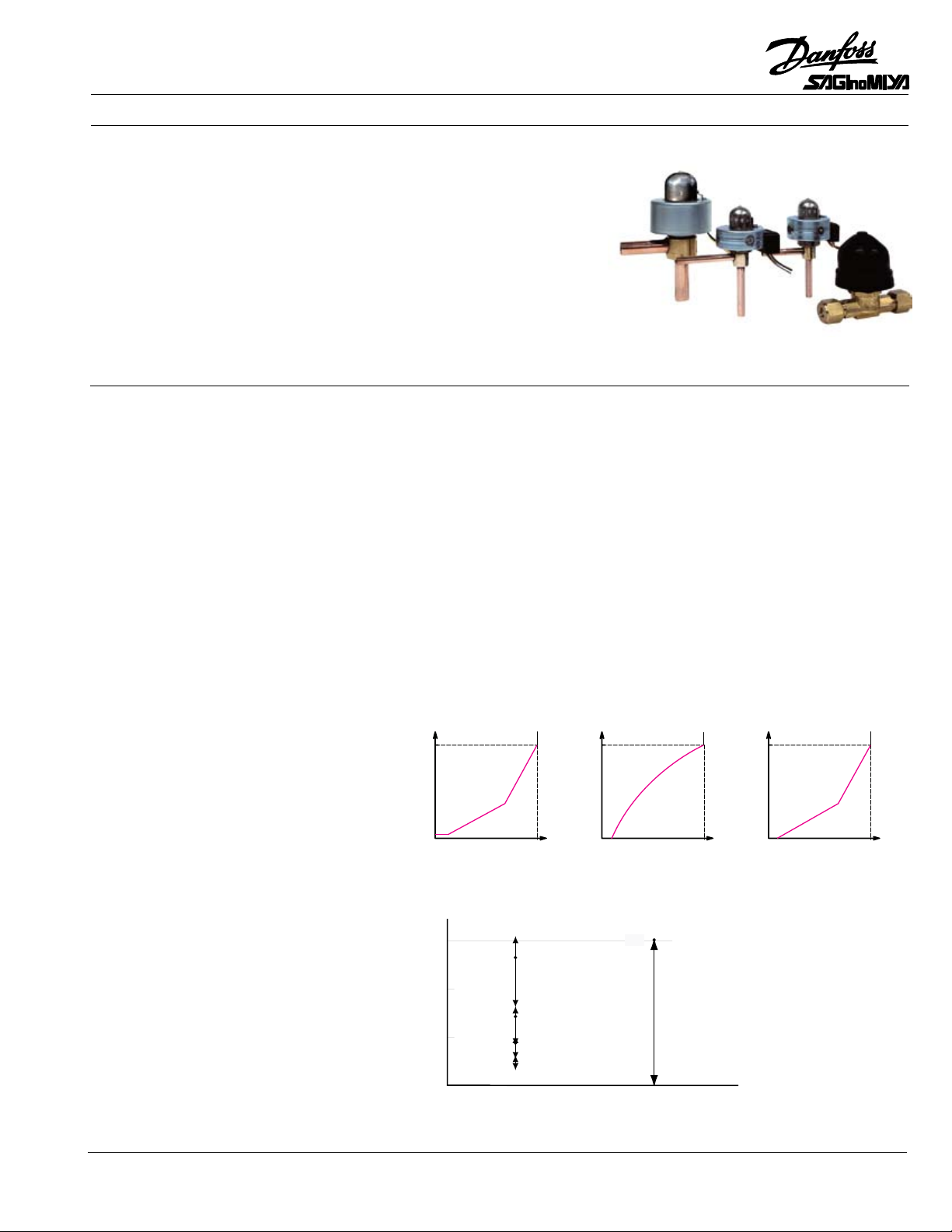
Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
4800
Pulse
Flow
Max
4800
Pulse
Flow
Max
4800
Pulse
Flow
Max
a b c
VPX-3415BPC
2.62
PKV-18BS
Capacity (U.S.R.T)
0
3
VPX-3408BPC
1.40
VPX-3405BPC
0.87
VPX-3403BPC
0.52
Our mechanical
expansion valves
Our pulse motor
expansion valves
(capacity ..... R407C)
3.0
Introduction As environmental consciousness is being raised
and global warming concerns are bringing ever
more stringent regulations, the demand is
quickly growing for energy-saving cooling and
heating devices in household and commercial
applications, including cold storage warehouses
and, rapid freezing devices.
The KV series of stepper motor expansion valves
have been solidly respected in Japanese markets
since 1982. Danfoss Saginomiya offers KV series
pulse motor expansion valves for numerous
applications. KV reliability has been extensively
field proven.
Features
Wide selection for refrigeration and air •
conditioning applications
Compatible with various refrigerants: •
R-410A, R-407C, R-134a, R-404A, R-22
Stepper motor drive provides high-precision •
flow control
A range of full closing valve types is available •
that generally require no solenoid valve
Compact and lightweight design•
Power-saving design requires no energy for •
stopping.
Ideally suited for microcomputer control•
Unipolar drive system (for bipolar drive, please •
contact us)
Bi-flow design for heat pump applications•
UKV, SKV, VKV, AKV: UL recognized•
High resolution: 480 steps from fully closed •
to fully open
KV valves have excellent flow characteristics, including high resolution at low load. •
In KV valves that have an inflected flow characteristic as shown in (a) and (c), the flow per pulse
has one rate for low flow and a higher rate for greater flow. With these valves, fine control can be
accomplished with a low load (low flow). Full closing KV valves having a flow characteristic (b), (c)
are available with inflected flow characteristic or continuous flow characteristic, the latter having
very nearly the same change in flow rate per pulse.
© Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 3
As can be seen in the diagram above, pulse motor expansion valves have a much greater range than
mechanical valves.
Long valve lift range results in a wider range of controllable capacity•
Page 4
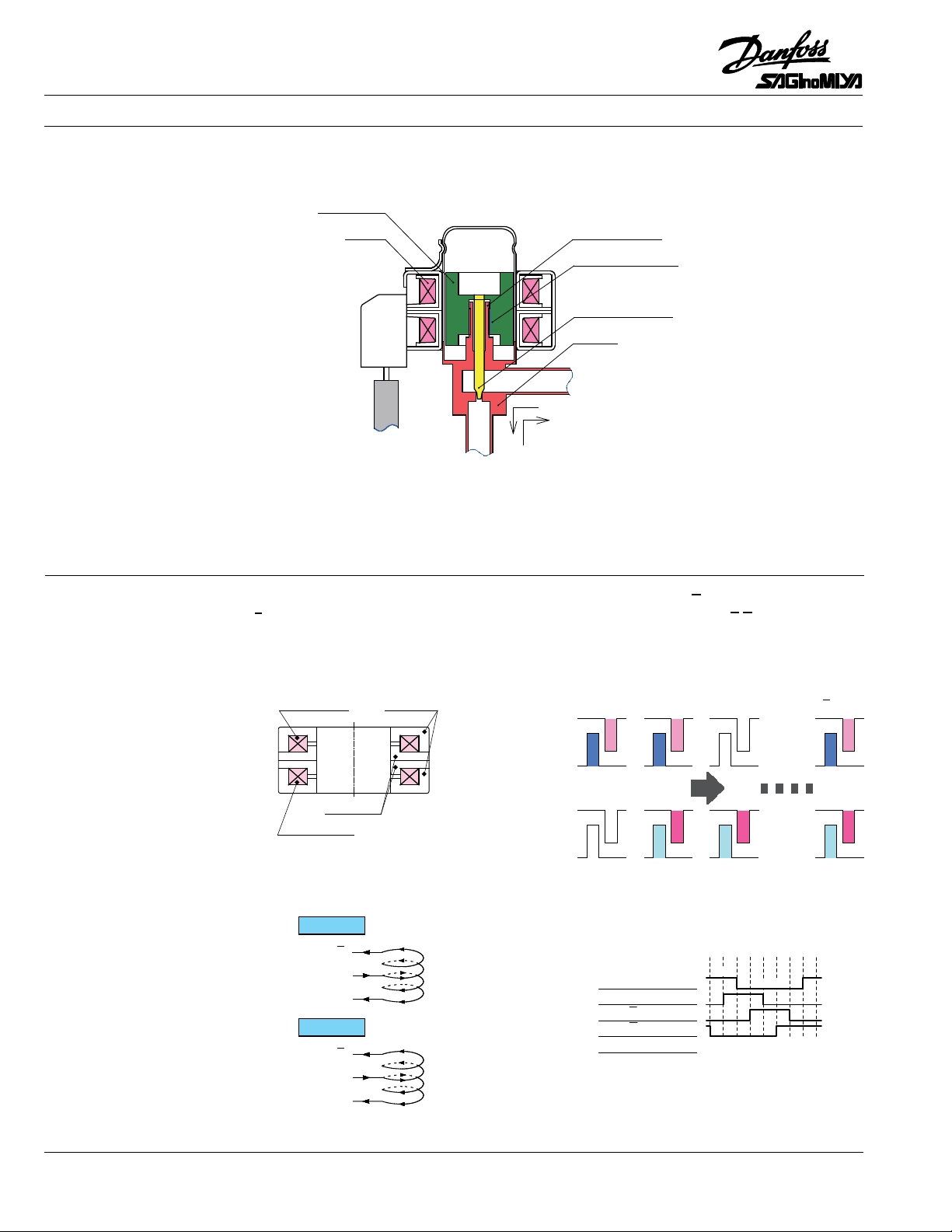
Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Sectional diagram of KV series
B
A
Magnet
Coil Male screw
Female screw
Needle valve
Body
Fluid direction
Lower coil
Stator
Upper coil
Housing
SS
NN
COM
COM
A
A
B
B
A Phase A,B Phase A,B PhaseB Phase
Upper coil
Lower coil
S
N
S
N
N
S
N
S
S
N
S
N
Fig.1-1
Fig.1-2
Fig.1-3
Connector No.
ON
OFF
1
A Phase
2
B Phase
A Phase
B Phase
3
4
5 COM.(+)
Fig.1-4 Excitation sequence
(1-2 phase excitation)
Valve operation Valve opens
Valve is closed
Explanation of Action
In operation of the KV valve, the magnet-needle valve assembly is rotated by the stepper motor
(principle described in next paragraph) and by means of a screw structure has linear motion, opening
and closing to regulate refrigerant flow. This simple structure results in compact products.
Operation Principle I
Figs.1-1 and 1-2 show a vertical cross section of the coils (upper coil (A and A) and lower coil (B and
B). Each coil comprises a clockwise winding A, B and a counterclockwise winding A, B. Each coil has 3
terminals. Fig.1-3 shows the arangement of the stators that surround the armature. The polarities of the
magnetic poles change depending on the direction of current flow.
4 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
Page 5

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Fig.2-1
A Phase
Upper tooth
Lower tooth
B Phase
Upper tooth
Lower tooth
N
N N
S
N
S
S
A Phase
S
N
N
S
S
S
S
N
N
AB Phase
N
N
S
S
S
S
N
N
AB Phase
S
S
N
N
N
N
S
S
N
N
S
S
AB Phase
N
N
S
S
S
N
N
S
N
S
N
N
N
S
S
B Phase
S
S
S
N
N
AB Phase
N
N
S
S
S
S
N
N
S
N
S
N
S
N
N
A Phase
S
N
N
S
S
S
N
N
B Phase
S
Fig.2-2
Operation Principle II
This section explains the rotation of the permanent magnet rotor. The rotor has 24 poles, but the
following explanation is simplified by dealing with only 4 of the poles.
Fig.2-1 shows a vertical cross section through the stator. It shows the positional relation of the stator
magnetic poles with the horizontal sectional diagram in Fig.2-2. In Fig.2-1, j shows the upper teeth of
phase A, k shows the lower teeth of phase A, l shows the upper teeth of phase B, and m shows the
lower teeth of phase B.
Assume that a current flows to phase A as a pulse. The polarities in Fig. (I) are generated in the stator to
stabilize the rotor with an arrow facing upward. When feeding a current to phase AB by sending a pulse,
the polarities are as shown in Fig. (II) causing the rotor to turn 22.5 degrees. When a subsequent current
pulse is sent to phase B, the polarities are as shown in Fig. (III) causing the rotor to turn a further 22.5
degrees. By feeding pulses sequentially, one cycle is composed of 8 pulses, and the rotor rotates 180
grees in this figure. (A KV valve, remember, actually has 24 poles, so that the rotor rotates one sixth as far
as in our example, or 30 degrees with every cycle. )
© Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 5
Page 6

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
0.31 OD 0.31 OD
0 to 3.5 {0 to 507}
0.28
0.23
0.18
2.4 {348} or less
1.0 {145} or less
VKV–25D
0 to 2.5 {0 to 362}
1.5 {217} or less
0.37 OD
0.50 OD
0.63 OD 0.63 OD
0 to 2.5 {0 to 362} 0.7 {101} or less
2.2 {319} or less
2.8 {406} or less
1.5 {217} or less
2.2 {319} or less
3/8"
0 to 2.3 {0 to 333}
0 to 2.8 {0 to 406}
0.5
0.8
0.3
PKV-24BS
0.09
0 to 2.2 {0 to 319} 0.7
1/2"(Flare)
5.0 {17.5} 3.9 {13.7} 3.5 {12.3} 5.1 {18.0}
PKV-14BS 0.06 1.5 {5.2} 1.1 {4.0} 1.0 {3.6} 1.5 {5.3} 1.7 {6.1}
2.9 {10.3}PKV-18BS 0.07 2.3 {8.1} 2.1 {7.3} 3.0 {10.6} 3.4 {12.1}
5.9 {20.6}
5.3 {18.5} 4.1 {14.5} 3.7 {13.1} 5.4 {19.0} 6.2 {21.8}
PKV-30BS
0.12
7.9 {27.8} 6.2 {21.7} 5.6 {19.6} 8.1 {28.5} 9.3 {32.7}
Catalog No.
Port
Size
(
inch)
Capacity
(U.S.R.T.) {kW}
Connection (Solder)
(inch)
Operating Pressure
Differential, B to A
(MPa) {psi}
Wt.
(kg)
R22 R134a R407C R410A B side A side
0.31 OD 0.31 OD
0.25 OD 0.25 OD
0.31 OD 0.31 OD
0 to 3.5 {0 to 507}
0 to 3.5 {0 to 507}
Valve shut press.
on, A to B
flow directionflow direction
(MPa) {psi}
R404A
2.5 {362} or less
2.4 {348} or less
Capacity: Based on CT=38°C
[100˚F]
, ET=5°C
[41˚F]
, SC=0°C
[0˚K]
and SH=0°C
[0˚K]
(Flare)
3/8"
(Flare)
*1
*1 Refer to the following fig. *2 Weight includes a coil.
*1*1 *2
2.3 {8.2} 1.8 {6.4} 2.4 {8.5} 2.8 {9.7}SKV–16D 1.7 {5.8}0.06
SKV–18D 2.9 {10.3} 2.3 {8.1} 3.0 {10.6} 3.4 {12.1}2.1 {7.3}0.07
2.9 {10.3} 2.3 {8.1} 2.1 {7.3} 3.0 {10.6} 3.4 {12.1}UKV–18D 0.07
VKV–20D 2.5 {8.7}3.5 {12.4} 2.7 {9.7} 3.6 {12.7} 4.1 {14.5}0.08
0.09
VKV–30D 7.0 {24.7} 5.5 {19.3} 5.0 {17.4} 7.2 {25.4} 8.3 {29.1}0.12
5.6 {19.6} 4.4 {15.3} 3.9 {13.8} 5.7 {20.1} 6.5 {23.0}UKV–25D 0.09
7.6 {26.8} 6.0 {20.9} 5.4 {18.9} 7.8 {27.5} 9.0 {31.5}UKV–30D 0.12
VKV–32D 5.8 {20.3}8.2 {28.8} 6.4 {22.5} 8.4 {29.6} 9.6 {33.9}0.125
AKV–55D 27.9 {98.1}16.7 {58.8}0.22 23.7 {83.4} 18.5 {65.2} 24.4 {85.6}
0.38A / Phase
AKV
0.26A / Phase
Current (at 20˚C[68˚F])
12V DC
±10%
Rated voltage
UKV,SKV,VKV,PKV
Type
32 ± 3 Ω
(at 20˚C[68˚F])
46 ± 3 Ω
(at 20˚C[68˚F])
Direct current resistance
IP66
Enclosure
Class E MoldedInsulation class
115˚C[239˚F] or less by rated voltage,
temperature - resistance method.
Max. coil temperature
B Side
Conn.
A Side
Conn.
*1
B to A flow direction
A to B flow direction
Common Refrigerant Models
Specifications
Motor and Drive Specifications
Valve Specifications
Maximum working pressure: 609 psi (4.2 MPa)
Ambient temperature: -22 to 140oF (-30 to 60oC)
Type PKV: -58 to 140
o
Fluid Temperature: -22 to 248
F (-30 to 12oC)
o
F (-50 to 60oC)
Type AKV: -22 to 266oF (-30 to 130oC)
Type PKV: -58 to 140oF (-50 to 60oC)
Ambient humidity 95% RH or less
Modulation: Permanent magnet type direct operating stepper motor
Excitation method: 1-2 phase
Excitation speed: 31.3 pps +10%
Operating range: 0 to 480 pulses
Intialization: Phase A COM (+)
Coil Specifications
6 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
Page 7

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Comp.
Remote Controller
Main PC Board
Anti Freeze Heater
Pulse Motor Expansion Valve
KV series
4-Way
Reversing Valve
Type STF
Pressure Sensor
Type XSK
High Pressure Controls
Type HNS
Aircoil Temperature
Sensor
Type TEK
Inlet Temperature Sensor
Type TEK
Outlet Temperature Sensor
Type TEK
Flow Switch
Type FQS
Comp.
Cooling
Indoor Unit
Outdoor Unit
Controller
Accumulator
Pressure Sensor
Type NSK
4-way reversing
valve
Type STF
Pulse Motor Expansion Valve
KV series
Application Examples Multi-type heat pump unit
Chiller unit
© Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 7
Page 8

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Selection Method
If the operating conditions of the unit are known, a KV valve can be selected easily according to the
capacity – valve opening graph given on the next page.
Let’s select an optimum pulse motor expansion valve for the operating conditions shown at the bottom of
this page.
1) Calculate the required maximum refrigerating capacity of the unit (normally, the capacity just after
starting).
Enter the R-407C correction factor table in the row for evaporating temperature (-22˚F) and condensing
temperature (72˚F) , and in the column for the subcool temperature (54˚F) , and at their intersection
find the correction factor (1.39). Then calculate the required maximum capacity (19.1kW) of the unit by
dividing the refrigerating capacity (26.5kW) by the correction factor.
2) Calculate the required minimum refrigerating capacity of the unit (normally, the capacity just after
stopping operation).
Enter the table in the row for the evaporating temperature (-58˚F) and condensing temperature
(104˚F) , and in the column for the subcool temperature (72˚F) , and at their intersection find the
correction factor (1.47). Then calculate the required minimum capacity (10.6kW) of the unit by dividing the
refrigerating capacity (15.6kW) by the correction factor.
3) Selection of pulse motor expansion valves
Pulse motor expansion valves PKV-30BS and PKV-24BS can have refrigerating capacity larger than the
required maximum capacity of the unit at maximum opening 480 pulses. When comparing the valve
opening width between the maximum load and the minimum load with each other, it is 80 pulses in
PKV-30BS and 200 pulses in PKV-24BS. Select PKV-24BS in this case because the valve opening width
between the maximum load and minimum load is wider (high resolution).
Aimed refrigerating temperature: - 40oF
Kind of refrigerant used: R407C
Operating
conditions of unit
Condensing temp
(CT)
Sub cool (SC) 54
Evaporating temp
(ET)
Required capacity
Just after starting operation Just after terminating operation
o
F 104oF
104
o
F 72oF
o
F -58oF
-22
26.5kW
(with the maximum load)
15.6kW
8 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
Page 9

PKV -14BS
PKV -18BS
PKV -24BS
PKV -30BS
0.0
5.0
[1.42]
10.0
[2.84]
15.0
[4.27]
20.0
[5.69]
25.0
[7.11]
30.0
[8.53]
kW
[U.S.R.T]
0 50 100 150 250 300 350 4 00 450200
R407C Correction factor table
Superheat=9
˚F
Sub cool[
˚F]
[˚F] [˚F]
0 18 36 54 72 90 108
-58
0.88 1.04 1.20 1.35 1.51 1.66 1.81
0.90 1.05 1.20 1.35 1.49 1.63 1.77
0.92 1.06 1.20 1.33 1.47 1.60 1.73
0.93 1.06 1.19 1.31 1.44 1.57 1.69
0.93 1.05 1.17 1.29 1.41 1.52 1.64
-40
0.92 1.08 1.24 1.39 1.55 1.70 1.85
0.94 1.09 1.24 1.38 1.53 1.67 1.81
0.95 1.09 1.23 1.37 1.50 1.63 1.76
0.96 1.09 1.22 1.34 1.47 1.59 1.71
0.96 1.08 1.20 1.31 1.43 1.54 1.66
-22
0.95 1.11 1.27 1.43 1.58 1.73 1.88
0.97 1.12 1.27 1.41 1.55 1.69 1.83
0.98 1.12 1.25 1.39 1.52 1.65 1.78
0.98 1.11 1.24 1.36 1.48 1.60 1.73
0.97 1.09 1.21 1.32 1.44 1.55
-
-13
0.97 1.13 1.28 1.44 1.59 1.74 1.89
0.98 1.13 1.28 1.42 1.56 1.70 1.84
0.99 1.13 1.26 1.39 1.53 1.66 1.79
0.99 1.12 1.24 1.36 1.48 1.61
-
0.98 1.09 1.21 1.32 1.44 1.55
-
-4
122
0.98 1.14 1.29 1.45 1.60 1.74 1.89
113
0.99 1.14 1.28 1.43 1.56 1.70 1.84
104
1.00 1.13 1.27 1.40 1.53 1.66
-
95
0.99 1.12 1.24 1.36 1.48 1.60
-
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
0.98 1.09 1.21 1.32 1.43
- -
Pulse
[PKV]
19.1
10.6
Refrigerant : R407C
Evaporating temp : 5˚F
Condensing temp : 104˚F
Sub cool : 0˚F
Superheat : 9˚F
Capacity – valve opening graph
Evaporating
temp.
Condensing
temp.
Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
Selection Method, continued
© Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 9
Page 10

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
[˚F] [˚F]
0 18 36 54 72 90 108
-76
122
0.87 1.06 1.23 1.40 1.57 1.73 1.89
113
0.91 1.08 1.24 1.40 1.56 1.71 1.86
104
0.94 1.09 1.24 1.39 1.54 1.68 1.82
0.95 1.10 1.24 1.37 1.51 1.64 1.77
86
95
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
86
95
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
95
86
122
113
104
86
95
122
113
104
95
86
0.96 1.09 1.22 1.35 1.48 1.60 1.72
-58
0.91 1.09 1.27 1.44 1.60 1.77 1.93
0.94 1.11 1.27 1.43 1.59 1.74 1.89
0.97 1.12 1.27 1.42 1.56 1.70 1.84
0.98 1.12 1.26 1.40 1.53 1.66 1.79
0.98 1.11 1.24 1.37 1.49 1.62 1.74
-40
0.93 1.12 1.29 1.46 1.63 1.79 1.95
0.97 1.14 1.30 1.45 1.61 1
.76 1.91
0.99 1.14 1.29 1.44 1.58 1.72 1.86
1.00 1.14 1.28 1.41 1.54 1.67 1.80
1.00 1.13 1.25 1.38 1.50 1.62 1.74
-22
0.96 1.14 1.31 1.48 1.64 1.80 1.96
0.98 1.15 1.31 1.46 1.61 1.76 1.91
1.00 1.15 1.30 1.44 1.58 1.72 1.85
1.00 1.14 1.28 1.41 1.54 1.67 1.79
1.00 1.12 1.25 1.37 1.49 1.61 -
-13
0.96 1.14 1.31 1.48 1.64 1.80 1.95
0.99 1.15 1.31 1.46 1.61 1.76 1.90
1.00 1.15 1.29 1.44 1.57 1.71 1.84
1.00 1.14 1.27 1.40 1.53 1.65 -
0.99 1.12 1.24 1.36 1.48 1.59 -
-4
0.96 1.14 1.31 1.48 1.64 1.79 1.95
0.99 1
.15 1.31 1.46 1.60 1.75 1.89
1.00 1.15 1.29 1.43 1.56 1.70 -
1.00 1.13 1.26 1.39 1.51 1.64 -
0.98 1.10 1.22 1.34 1.46 - -
5
0.96 1.14 1.31 1.47 1.63 1.78 1.93
0.98 1.14 1.30 1.45 1.59 1.73 -
0.99 1.14 1.28 1.41 1.55 1.68 -
0.98 1.12 1.24 1.37 1.49 - -
0.97 1.09 1.20 1.32 1.43 - -
0.96 1.14 1.30 1.46 1.61 1.77 -
0.98 1.13 1.28 1.43 1.57 1.71 -
0.98 1.12 1.26 1.39 1.52 - -
0.97 1.10 1.22 1.34 1.46 - -
0.94 1.06 1.17 1.28 - - -
0.95 1.12 1.29 1.44 1.59 1.74 -
0.96 1.12 1.26 1.41 1.55 - -
0.96 1.10 1.23 1.36 1.49 - -
0.94 1.07 1.19 1.31 - - -
0.92 1.03 1.13 1.24 - - -
32
23
0.94 1.11 1.27 1.42 1.57 - -
0.95 1.10 1.24 1.38 1.51 - -
0.94 1.07 1.20 1.32 - - -
0.91 1.03 1.15 1.26 - - -
0.88 0.98 1.09 - - - -
41
0.92 1.08 1.24 1.38 1.53 - -
0.92 1.07 1.20 1.34 - - -
0.91 1.03 1.16 1.28 - - -
0.87 0.99 1.10 - - - -
0.83 0.93 1.02 - - - -
0.0
10.0
(2.84)
20.0
(5.69)
30.0
(8.53)
[kW]
([U.S.R.T])
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
[Pulse]
SKV-16D46
SKV-18D49
VKV-20D32
VKV-25D34
VKV-30D36
VKV-32D38
Refrigerant : R410A
Evaporating temp. : -13˚F
Condensing temp. : 104˚F
Sub cool : 0˚F
Superheat : 9˚F
R410A Correction factor table
Superheat=9˚F
Sub cool[˚F]
Evaporating
temp.
Condensing
temp.
14
Capacity - R410A
10 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
Page 11

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
0.18
Catalog No.
Port
Size
(
inch)
Capacity
kW {U.S.R.T.}
Connection (Solder)
(inch)
Operating Pressure
Differential, B to A
psi {MPa}
Wt.
(kg)
R744 B side A side
0.25 OD 0.25 OD 0 to 1450 {0 to 10}
Valve shut press.
on, A to B
flow directionflow direction
(MPa) {psi}
Capacity: Based on inlet temp.=100°F
[38˚C]
, ET=41°F
[5˚F],
inlet pressure=
1378psi[
9.5MPa
] andSH=0°K[0°C]
*1
*1*1 *2
5.95{1.69}UKV–J14D 0.06
UKV-J
0.26A / Phase
Current (at 68˚F[20˚C])
12V DC
±10%
Rated voltage
Type
46 ± 3 Ω
(at 68˚F[20˚C])
Direct current resistance
IP66
Enclosure
Class E MoldedInsulation class
239˚F[115˚C] or less by rated voltage,
temperature - resistance method.
Max. coil temperature
B Side
Conn.
A Side
Conn.
*1
*1 Refer to the following fig. *2 Weight includes a coil.
B to A flow direction
A to B flow direction
Hot water storage unit side
Relief valve
Type VSV/WSV
Pressure
reducing valve
Type CRV
Hydrothermal
exchanger
Air heat
exchanger
Tank
Comp.
Defrost
Solenoid valve
Pressure control
Type CCB
Type HPV
Motorized
control valve
Type UKV-J
Heat pump unit side
Mixing
valve
Water
Supply
Hot Water
Supply
Pump
Hot water
irrigation
Water
irrigation
CO
Application
2
Specifications
Maximum working pressure: 2175 psi (15 MPa)
Ambient temperature: -22 to 158oF (-30 to 70oC)
Fluid temperature: -22 to 148oF (-30 to 70oC)
Ambient humidity 95% RH or less
Motor and Drive Specifications
Valve Specifications
Coil Specifications
Application Examples
CO2 Hot Water Supply Unit
Modulation: Permanent magnet type direct operating stepper motor
Excitation method: 1-2 phase
Excitation speed: 31.3 pps +10%
Operating range: 0 to 480 pulses
Intialization: Phase A COM (+)
© Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 11
Page 12

Technical leaflet Pulse Motor Expansion Valves, Type KV
1.50[38]
1.89
[ 48]
[ 7.94±0.1 t=0.8]
0.31±0.004 t=0.031
1.39±0.08[49±2]
4.06±0.12[103±2]
7.94±0.1 t=0.8
2.44±0.08[62±2]
Conn.
Conn.
A Side
B Side
0.31±0.004
t=0.031
[ 15.88±0.15 t=1.2]
Conn.
[( 67)]( 2.64)
(2.58)[(65.5)]
(2.54)[(64.5)]
(5.91)[(150)]
Conn.
A side
B side
[ 15.88±0.15 t=1.2]
0.63±0.006 t=0.047
0.63±0.006 t=0.047
1.46 [37]
1.89
Conn.
2.52±0.08[64±2]
1.93±0.08[49±2]
4.41±0.12[112±3]
Conn.
B side
A side
[ 48]
[ 7.94±0.1 t=0.8]
0.31±0.004
t=0.031
[ 7.94±0.1 t=0.8]
0.31±0.004
t=0.031
1.46[37]
1.89
Conn.
2.60±0.08[66±2]
2.52±0.08[64±2]
5.12±0.12[130±3]
Conn.
[ 12.7±0.15 t=0.8]
[ 9.52±0.15 t=0.8]
[ 48]
A side
B side
0.5±0.006 t=0.031
0.37±0.006 t=0.031
Inlet
Flow direction
Outlet
1.18[30]
0.71[85]
( 2.17)[( 55)]
(3.62)[(92)]
19.69[500]
5/8 - 18UNF 5/8 - 18UNF
Inlet
Flow direction
M14×1
Outlet
1.42 [ 36]
( 2.17)[( 55)]
(4.13)[(105)]
19.69[500]
3.82[97]
5/8 - 18UNF 3/4 - 16UNF
0.250±0.039
t=0.047
1.54 [39]
1.85±0.079
[47±2]
Conn.
Conn.
B side
A side
1.97±0.079[50±2]
(3.90)[(99)]
[6.35±0.1 t=1.2]
[6.35±0.1 t=1.2]
1.28[32.5]
0.250±0.039 t=0.047
Catalog No.
A
B
UKV–18D
0.250±0.039 t=0.028
[ 6.35±0.1 t=0.7]
UKV–30D
UKV–25D
[ 7.94±0.1 t=0.8]
0.313±0.039 t=0.031
1.97±0.079[50±2]
(3.88)[(98.6)]
1.85±0.079
[47±2]
A
B
(1.85)[(47)]
Conn.
Conn.
Catalog No.
A
B
UKV–18D
0.250±0.039 t=0.028
[ 6.35±0.1 t=0.7]
UKV–30D
UKV–25D
(1.69)[(43)]
(1.26)[(32)]
B side
A side
[ 7.94±0.1 t=0.8]
0.313±0.039 t=0.031
Dimensions
Unit: inch[mm]
Type VKV-20D to 30D
Type UKV
Type UKV-J
Type VKV-32D
Type SKV
Type AKV
Type PKV-14BS to 24BS
Type PKV-30BS
Danfoss, Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning Division, 7941 Corporate Drive, Baltimore, MD 21236 Tel. 410-931-8250, Fax 410-931-8256, www.danfoss.us
12 USCO.PD.V1.A1.22 / 521U0082 © Danfoss Inc (USCO / mks), 1-2008
 Loading...
Loading...