Page 1

CYBELEC SA Tel. ++ 41 24 447 02 00
Parameters for
Synchronized
Press Brakes
RUE DES UTTINS 27 Fax ++ 41 24 447 02 01
CH - 1400 YVERDON-LES-BAINS E-Mail: info@cybelec.ch
SWITZERLAND
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5
Page 2

Page 3

ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
This manual describes the machine parameters of the ModEva /
ModEva RA numerical controls for synchronized press brakes and
other similar controls like the DNC880, the DNC1200 and the DNC60
and DNC600.
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Copyright © 2009, Cybelec S.A. All rights reserved. All text,
pictures and graphics are protected by copyrights. No copying is
permitted without written permission.
TRAD E MARKS
CYBELEC is a registered trade mark of CYBELEC S.A.
MS-Windows is a registered trade mark of Microsoft Corporation.
All other registered and unregistered trademarks in this document are
the property of their respective owners.
DISCLAIMER
The infor mation contained in this document is s ubject to change
without notice. Great care has been taken to ensure that the
information in this document is accurate yet the information contained
within is supplied “as-is”. Cybelec SA provides no warranty with
regard to this document and hereby expressly disclaims any implied
warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose
with regard to the foregoing.
INTENDED AUDIENCE
This manual is intended for qualified and well trained engineers
involved in the commissi oning and servicing of synchronized press
brakes. A good general knowledge about press brakes and operation
of the Cybelec DNC is assumed.
This manual is not intended for end -users, machine operators, and
other general audience.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 2
Page 4

WARNING
Machine parameters may only be modified by qualified
specialists. Wrong settings can cause damage to the
machine and tools, and might represent a safety risk for
the operator.
DOCUMENT VERSION
This manual has been updated for software version P:
ModEva series SSBFxPx
DNC880S SWBMHPx
Note The software version P introduces a number of additions and
improvements for the beam requiring a reconfiguration of the
beam parameter pages. This version also introduces a final
approach speed instead of a final approach voltage for the
BDC-positioning. Both final approach parameters are
described in this manual. More generally, both the previous
and the new operation of a parameter are described whenever
the basic functioning has been changed in a more recent
software version.
This V5.0 version contains following additional information.
• P45, P45b, P46 additional info + diagrams.
Down diagram corrected and updated (V5.0).
• Tips: how to smooth movement high speed down and arrival
at TDC.
• Description input "pause return beam".
• Sensitive mode, possibility to continuesely move the beam
up/down (se e Operating modes)
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 3
Page 5

CONTENTS
CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT .......................................................................................................... 2
Copyright Notice..................................................................................................................... 2
Trade marks ........................................................................................................................... 2
Disclaimer .............................................................................................................................. 2
Intended audience ................................................................................................................. 2
Warning .................................................................................................................................. 3
Document version .................................................................................................................. 3
CONTENTS ................................................................................................................................... 4
INTRODUCTION / CONVENTIONS ........................................................................................... 14
ABBREVIATIONS ....................................................................................................................... 15
OPTIONS .................................................................................................................................... 16
02 CAD INTERFACE PAGE ......................................................................................................... 17
03 COMMUNICATIONS LINK7000 ................................................................................................ 17
08 MESSAGE INTERPRETER....................................................................................................... 18
30 ANGLE MEASURING DEVICE ................................................................................................... 18
33 FRONT X AXES (X3, X4, X7, X8) .......................................................................................... 19
34 FRONT Z AXES (Z3, Z4) ....................................................................................................... 19
38 BACK SHEET SUPPORT (H, H2) ............................................................................................. 20
41 “SCHRAEGSTELLUNG” .......................................................................................................... 20
42 BENDING ASSISTANCE .......................................................................................................... 21
43 P/PC PRESSE ..................................................................................................................... 22
44 THICKNESS MEAS. BY SERIAL PORT ....................................................................................... 23
51 DIE AXES (M1, M2) ............................................................................................................. 24
52 FRONT SHEET SUPPORTS (H3, H4) ....................................................................................... 25
55 EXTERNAL COMMANDS ......................................................................................................... 26
57 THICKNESS MEAS. BY N2X (MS1, MS2) ............................................................................... 26
60 ANGLE MEASURING DEVICE ................................................................................................... 27
64 CAN ................................................................................................................................... 27
65 SECOND ANGLE MEASURE .................................................................................................... 28
66 CONTINUOUS ANGLE MEASURES ........................................................................................... 28
68 FORCE & CROWNING CALCULAT. V2.0 ................................................................................... 29
74 … 78 COUNTER AXES CAN D0 … D4 ................................................................................... 29
82 SERIAL LINK WITH PLC ......................................................................................................... 31
83 PLUG IN ............................................................................................................................... 32
84 LASERSAFE PCSS LINK ....................................................................................................... 33
86 STRAIN GAUGE..................................................................................................................... 34
89 MACHINE TANDEM ............................................................................................................... 34
90 HAP MECANIC SI MP LIF IED .................................................................................................... 35
91 FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’............................................................................................................. 36
92 FOLLOW-UP BENDING ASSISTANCE ........................................................................................ 36
CONFIGURATION ...................................................................................................................... 37
AUXILIARY PAGE ........................................................................................................................ 38
LINE N° ..................................................................................................................................... 38
MODE ........................................................................................................................................ 39
Axes ..................................................................................................................................... 39
NAME ........................................................................................................................................ 41
EXAMPLE CONFIGURATIONS ........................................................................................................ 42
DECIMALS MM / INCH .................................................................................................................. 51
N2X AXIS N° ............................................................................................................................. 52
N2X NUMBERING ....................................................................................................................... 52
PREFERENCES ......................................................................................................................... 53
PRODUCT PARAMETRIC .............................................................................................................. 54
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 4
Page 6

CONTENTS
GRAPHICAL PROFILE ON PAGE NUMERICAL PRODUCT ................................................................... 56
BEND 2D INTERACTIVE ............................................................................................................... 57
AUTOMATIC DISPLAY OF PRODUCT INFORMATIONS ....................................................................... 58
PROGRAMMING WHILE WORKING ................................................................................................. 59
Double mode ........................................................................................................................ 59
Single mode ......................................................................................................................... 59
PRODUCTION PAGE .................................................................................................................... 61
PRODUCTION-CHECK .................................................................................................................. 63
MANUAL MOVEMENTS WITH QUICKCURSOR ................................................................................. 64
ALLOW SWITCHING OFF AUTOMATIC CALCULATI O NS ..................................................................... 65
KEY 0 BLOCKS UTI LIZATION ......................................................................................................... 66
POSITION Z5 – Z6 ...................................................................................................................... 67
COMPUTE AXES Z ON PRODUCT 2D ............................................................................................. 68
AUTOMATIC CORRECTION OF THE RAM SPEED .............................................................................. 69
RETRACTIONS OF X AXIS ............................................................................................................ 70
RETRACTIONS OF Z AXIS ............................................................................................................ 71
INDEXATION AIDS ....................................................................................................................... 72
USB/RS232 ANGLE MEASUREMENTS ......................................................................................... 73
MACHINE PARKING FEATURE ....................................................................................................... 74
COMPUTING CROWNING CORRECTION ACCORDING TO MEASURED ANGLE ...................................... 75
N2X.............................................................................................................................................. 77
QUICKCURSOR ...................................................................................................................... 78
149 STEP SIZE .......................................................................................................................... 78
150 ACCELERATION FACTOR ..................................................................................................... 78
FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’............................................................................................................... 79
SLAVE ....................................................................................................................................... 80
MASTER .................................................................................................................................... 80
DISTANCE MAX ........................................................................................................................... 80
CAN BUS .................................................................................................................................... 81
MESSAGE VIEWER ................................................................................................................ 82
TOTAL RECORDS ........................................................................................................................ 82
INITIAL DATE AND TI ME ................................................................................................................ 82
MESSAGE VIEW ER ...................................................................................................................... 82
POP UP...................................................................................................................................... 84
RECORDS .................................................................................................................................. 84
RECORDS TO KEEP ..................................................................................................................... 84
MESSAGE FILE IN ....................................................................................................................... 85
COPY MESSAGE FILE TO ............................................................................................................. 85
BEAM PARAMETERS................................................................................................................ 86
INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................... 86
HYDRAULIC SYST EMS ................................................................................................................. 87
Differential - and counter pressure system .......................................................................... 87
Pressure balance ................................................................................................................. 87
Valve overlap ....................................................................................................................... 88
PRESS BRAKE TYPES .................................................................................................................. 89
BEAM MODES ............................................................................................................................ 90
OPERATING MODES .................................................................................................................... 90
CLOSED LOOP MODES ................................................................................................................ 93
TDC regulation mode ........................................................................................................... 95
BDC closed loop regulation mode ....................................................................................... 95
DECOMPRESSION MODES ........................................................................................................... 96
Return mode (open loop mode) ........................................................................................... 96
Bending mode (closed loop mode) ...................................................................................... 96
SLOW RETURN SPEED MODES ..................................................................................................... 98
Reduced return speed mode (open loop mode) .................................................................. 98
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 5
Page 7

CONTENTS
Bending speed mode (closed loop mode) ........................................................................... 98
BEAM CYCLES ........................................................................................................................ 100
DOWN FROM TDC TO BDC ................................................................................................. 101
START FAST APPROACH DOWN .................................................................................................. 102
FAST APPROACH DOWN ............................................................................................................ 102
CHANGE-OVER IN BENDING SPEED ............................................................................................ 102
BENDING ................................................................................................................................. 103
ARRIVAL IN BDC ...................................................................................................................... 103
UP FROM BDC TO TDC ........................................................................................................ 104
Open loop mode return without low speed ........................................................................ 105
Open loop mode return with low speed ............................................................................. 106
Closed loop mode return without low speed ...................................................................... 107
Closed loop mode return with low speed ........................................................................... 108
DECOMPRESSION ..................................................................................................................... 109
RETURN .................................................................................................................................. 109
ARRIVAL IN TDC ...................................................................................................................... 109
BEAM ........................................................................................................................................ 110
01 CONTROL LOOP ................................................................................................................. 112
03 FINAL APPROACH BDC ....................................................................................................... 113
03 FINAL APPROACH TDC ....................................................................................................... 114
05 DECELERATION RAMP DISTANCE ......................................................................................... 115
06 THRESHOLD GV ................................................................................................................. 117
06 THRESHOLD GV2............................................................................................................... 118
07 LIMITS MIN. - MAX. ............................................................................................................. 119
08 REF. IN PRESSURE Y1 - Y2 ................................................................................................. 120
09 INDEX Y1 - Y2 ................................................................................................................... 121
09 POSITION Y1 - Y2 .............................................................................................................. 121
09B INDEXING TYPE ................................................................................................................ 122
Indexing during upward move ............................................................................................ 123
Indexing during downward move ....................................................................................... 123
Indexing during up- or down- movement ........................................................................... 123
Indexing using mechanical stop ......................................................................................... 124
Indexing and indexing zone ............................................................................................... 124
10 SYNCHRONIZATION LIMI T Y ................................................................................................. 125
12 DECEL. DISTANCE HIGH SPEED ............................................................................................ 126
13 MAX BENDING SPEED - ............................................................................................... 127
13 OUTPUT VOLTAGES PRESSURE, Y1, Y2 .............................................................................. 127
20 OFFSET VOLTAGE Y1 - Y2 .................................................................................................. 128
20A MIN. VOLTAGE Y1 - Y2 ..................................................................................................... 129
20B FINAL APPROACH VOLTAGE ........................................................................................... 130
20B FINAL APPROACH SPEED ............................................................................................... 132
20B FINAL APPROACH VOLTAGE ........................................................................................... 133
21 LS VOLTAGE .................................................................................................................. 134
21 LS VOLTAGE .................................................................................................................. 135
22 HS VOLTAGE ................................................................................................................. 136
22 HS VOLTAGE ................................................................................................................. 137
23 HS2 VOLTAGE ............................................................................................................... 138
23 HS DECELERATION VOLTAGE .......................................................................................... 139
24B INDEXATION VOLTAGE ....................................................................................................... 140
25 VOLTAGE COMMUTATION HS .............................................................................................. 141
25 VOLTAGE DECOMPRESSION ................................................................................................ 142
25C MANUAL MODE VOLTAGE .............................................................................................. 143
26 HS SYNCHRONISATION GAIN ........................................................................................... 144
26 HS SYNCHRONISATION GAIN ........................................................................................... 145
27 GAIN BDC ......................................................................................................................... 146
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 6
Page 8

CONTENTS
27 OFFSET AUTO .................................................................................................................... 147
29 ENCODER RESOLUTION ...................................................................................................... 148
29 ENCODER DIRECT. Y1, Y2 .................................................................................................. 149
37 CORRECTION CP ............................................................................................................... 150
37 CORRECTION BDC ............................................................................................................ 151
37 CORRECTION BDC PMAX ................................................................................................... 152
38 STARTING VOLTAGE ....................................................................................................... 153
38 ACCELERATION DISTANCE .............................................................................................. 154
38 DECELERATION DISTANCE .............................................................................................. 155
38 STARTING VOLTAGE ....................................................................................................... 156
38 ACCELERATION DISTANCE .............................................................................................. 157
38 DECELERATION DISTANCE ............................................................................................... 158
39 END OF BEND BEFORE PRESSURE ....................................................................................... 159
40 PINCH POINT BEFORE RETRACTION ..................................................................................... 160
45 COMMUTATION TIME HS-LS ............................................................................................... 161
45 COMMUTATION TIME ................................................................................................... 162
45B DELAY PRESSURE THR ESHOLD LS .................................................................................... 163
46 REGULATION DELAY ........................................................................................................... 165
47 SERVO VALVE DELAY .......................................................................................................... 166
48 DECOMPRESSION TIME MIN. - MAX. .................................................................................... 167
48B DEFAULT DWELL TIME ....................................................................................................... 168
48B MIN. DWEL L TIME.............................................................................................................. 169
49 THRESHOLD FOR BEAM STOP DETECTION ............................................................................ 170
49B ENCODER MONITORING TIME ............................................................................................. 171
52 RAM REGULATION DISTANCE AT TDC .................................................................................. 172
53 TDC MINIMUM V ALUE ......................................................................................................... 173
VERSION ENC ......................................................................................................................... 174
MACHINE N° ............................................................................................................................ 174
54 DISTANCE "START" AF BEF. PINCH PT .................................................................................. 175
55 BEAM DELAY IF BENDING AID ............................................................................................... 176
60 STARTING POINT AXES/AF ................................................................................................. 177
61 AXES START BEFORE/AFTER AF .......................................................................................... 178
62 PRESS ............................................................................................................................... 179
65 SPEED HS ..................................................................................................................... 180
66 GAIN FOR SPEED LIMITATION ........................................................................................... 181
67 SPEED MAX LS AFTER BENDING STOP ............................................................................. 182
68 DISTANCE OUTPUT ADVANCED SCP .................................................................................... 183
MACHINE PARKING FEATURE .............................................................................................. 184
BEAM PARKING POSITION .......................................................................................................... 185
BEAM ABSOLUTE POS ITION ....................................................................................................... 185
REFERENCE + .......................................................................................................................... 186
BOTTOM OF THE DIE’S V + ........................................................................................................ 186
AXES PARKING POSITION .......................................................................................................... 187
SELECTED AXIS ........................................................................................................................ 187
MACHINE TANDEM ................................................................................................................. 188
STRAIN GAUGE ....................................................................................................................... 189
STRAIN GAUGE .................................................................................................................... 190
Y1, Y2 : 0 - 100% .................................................................................................................... 190
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : CTRL ................................................................................................... 191
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : ERR DET .............................................................................................. 191
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : MIN. .................................................................................................... 192
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : POS. .................................................................................................... 192
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : MAX. ................................................................................................... 192
STRAINGAUGE Y1, Y2 : DETECTION .......................................................................................... 194
HIGH PRESSURE MEASURE Y1, Y2 : MIN. .................................................................................. 194
HIGH PRESSURE MEASURE Y1, Y2 : POS. .................................................................................. 195
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 7
Page 9

CONTENTS
HIGH PRESSURE MEASURE Y1, Y2 : MAX. ................................................................................. 195
RAM SPEED FOR THICKNESS M EASURE DETECTIO N .................................................................... 196
MEASURE PRESSUE Y1-Y2 ON ................................................................................................. 196
SWITCH SENSOR THRESHOLD ................................................................................................... 197
SPECIAL CYCLES ................................................................................................................... 198
POSITIONS FOR BACKGAUGE MANUAL TUNING ............................................................ 199
250 X, R, AF GAUGE .............................................................................................................. 199
DIE MOVEMENTS ................................................................................................................. 201
253 AXIS MEAS. M1 CHANGEABLE ON BEND NUM ..................................................................... 201
254 MAX SPACE BETWEEN M1 AND M2 .................................................................................... 201
BACK SHEET SUPPORT ...................................................................................................... 202
255 DISTANCE MIN. R-H ......................................................................................................... 202
256 R CLEARANCE DISTANCE X MOVEMENTS ............................................................................ 203
256 (R CLEARANCE DISTANCE) MVT Z ..................................................................................... 203
PRODUCT QUANTITY REACHED ....................................................................................... 205
260 CYCLE BLOCKING AT REACHED QUANTITY .......................................................................... 205
TEMPERATURE CO MPENSATION ........................................................................................ 206
BDC CORRECTION ACCORDING TO TEMPARATURE ..................................................................... 207
TEMPERATURE MEASURE ......................................................................................................... 208
COMPENSATION ....................................................................................................................... 208
SAFETY .................................................................................................................................... 209
41 RETURN TDC SAFETY ........................................................................................................ 211
42 SAFETY ............................................................................................................................. 212
42B SAFETY POINT TOLERANCE ............................................................................................... 213
43 MATERIAL SAFETY DIST ANCE .............................................................................................. 214
44 DIE SAFETY DISTANCE ........................................................................................................ 215
230 BEAM SPEED IN SAFETY MODE .......................................................................................... 217
231 X POSITION FOR SAFET Y SPEED ........................................................................................ 218
232 AXES SPEED IN SAFETY ZONE ........................................................................................... 220
233 X POS FOR DIE CLEARANCE .............................................................................................. 221
RELEASE DISTANCES X REL. AXES OR AF GAUGE ......................................................... 222
234 DIE - REAR PROTECTION .................................................................................................. 222
50 SAFETY DIST. DIE X - R ...................................................................................................... 223
51 STOPPING DISTANCE Z1 - Z2 .............................................................................................. 224
52 MAX SPACE BETWEEN R1 AND R2 ...................................................................................... 225
57 MAX. SPACE X1 - X2 .......................................................................................................... 226
58 COEFFICIENT FOR Z IN GAP MODE ....................................................................................... 227
95 JITTER ERROR TREATM ENT ................................................................................................. 228
96 DETECTION +/- 15V ........................................................................................................... 229
99 RETRACT X BY DEFAULT ..................................................................................................... 230
99 RETRACT X MIN. ................................................................................................................ 231
DNC SHUT DOWN ................................................................................................................ 232
Example shut down electrical diagram .............................................................................. 232
OUTPUT “DNC SHUT DOWN” BECOMES ACTIVE UPON ................................................................. 233
OUTPUT “DNC SHUT DOWN” BECOMES ACTIVE UPON ................................................................. 233
DELAY BEFORE ACTI VATING OUTPUT “DNC SHUT DOWN” ............................................................ 235
STOPPING TIME AND LEAKAGE ........................................................................................... 236
BEAM SPEED MEASURE ..................................................................................................... 237
177 HS DOWNWARD ............................................................................................................... 237
178 BENDING SPEED ............................................................................................................... 237
179 HS UPWARD .................................................................................................................... 237
BEAM SAFETY CHECK ........................................................................................................ 238
RAM STOPPING TIME CHECK ............................................................................................ 240
184 ACCELERATION DIST. HS .................................................................................................. 241
180 MAX. STOPPING TIME ....................................................................................................... 242
181 MAX. STOPPING DISTANCE ................................................................................................ 243
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 8
Page 10

CONTENTS
LEAKAGE CHECK ................................................................................................................. 244
183 LEAKAGE MEASUREMENT TIME .......................................................................................... 244
182 MAX. JACKS LEAKAGE....................................................................................................... 246
DOUBLE SAFETY CHECK ...................................................................................................... 247
PRESSURE AND CROWNING ................................................................................................ 248
PRESSURE D/A ........................................................................................................................ 249
CROWNING .............................................................................................................................. 250
30 TONNAGE MAX ................................................................................................................... 252
31 PRESSURE HS1 ................................................................................................................. 253
32 PRESSURE HS2 (DECEL.) .............................................................................................. 254
33 PRESSURE .................................................................................................................... 255
33B PRESSURE FA UPWARD ................................................................................................... 256
34 MIN PRESSURE 1 (LS) ........................................................................................................ 257
34B PRESSURE LS > SP ......................................................................................................... 258
35 MIN PRESSURE 2 (DECEL. + FA) ......................................................................................... 259
36 PRESSURE DECOMPRESSION .............................................................................................. 260
30A DISTANCE BE TWEEN JACKS............................................................................................... 261
30B CROWNING FACTOR ......................................................................................................... 262
30C REDUCTION OF CROWNING FOR WIDE BENDS ..................................................................... 263
30D ADAPT FORCE ACCORDING TO MATERIAL POSITION ............................................................ 264
30E SURFACE RATIO CYLINDERS .............................................................................................. 265
38 FORCE CALCULATION AS FUNCTION OF TARGET ANGLE ......................................................... 266
301 R CORRECTION TO MAX CROWNING ................................................................................... 267
302 WIDTH OF R CORRECTION ZONE ....................................................................................... 268
303 PRESSURE ACCELERATION TIME ....................................................................................... 269
304 PRESSURE DECELERATION TIME ....................................................................................... 270
305 THRESHOLD INPUT SYSTEM PRESSURE FOR COMMUTATION SN/SP .................................... 271
306 MAX. PRESSURE IN MANUAL MODE .................................................................................... 272
307 CROWNING RESOLUTION .................................................................................................. 273
308 PUNCH CLAMPING PRESSURE ........................................................................................... 274
309 DIE CLAMPING PRESSURE ................................................................................................. 275
AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS ......................................................................................................... 276
FUNCTION................................................................................................................................ 277
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 277
NATURE................................................................................................................................... 278
Digital ................................................................................................................................. 279
Voltage ............................................................................................................................... 280
Analog. X ............................................................................................................................ 281
Bending aids ...................................................................................................................... 282
Gauge ................................................................................................................................ 284
Die ...................................................................................................................................... 284
A/D - D/A ............................................................................................................................ 285
MIN. AND MAX. RANGE ............................................................................................................. 286
MIN. AND MAX. VALUE .............................................................................................................. 287
Setup min and max value for an auxiliary axis .................................................................. 287
TOLERANCE ............................................................................................................................. 288
LOW SPEED DISTANCE .............................................................................................................. 289
ADVANCED STOP ...................................................................................................................... 290
OVERRUN DISTANCE ................................................................................................................ 291
TIME SP/SN ............................................................................................................................ 292
INPUTS ..................................................................................................................................... 293
Location of input signals on the NIN board ........................................................................ 294
DIGITAL INPUT SIG N ALS ............................................................................................................ 295
ANALOG INPUT SIGNALS............................................................................................................ 304
DECELERATION AXIS X ............................................................................................................. 306
OUTPUTS ................................................................................................................................. 307
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 9
Page 11

CONTENTS
Location of output signals on the NOT board .................................................................... 308
DIGITAL OUTPUT SIGN ALS ......................................................................................................... 309
ANALOG OUTPUT SIGNALS ........................................................................................................ 316
SQUARE SIGNAL ....................................................................................................................... 317
SQUARE SIGNAL - TIME AT 1 ..................................................................................................... 318
SQUARE SIGNAL - TIME AT 0 ..................................................................................................... 318
DIGITAL I/O (DNC880S)........................................................................................................... 319
ANALOG I/O (DNC880S) ......................................................................................................... 320
ANGLE MEASUREMENT SYSTEM ......................................................................................... 321
BENDING ASSISTANCE ......................................................................................................... 323
SPEED FACTOR K ................................................................................................................ 325
BENDING AID RETURN DELAY MIN. – MAX. ................................................................................. 326
START DELAY AFTER RAM STOP ................................................................................................ 326
X AXIS RETRACTION POSITION ................................................................................................... 327
MAX RETURN SPEED ................................................................................................................. 328
BEAM: MAX. BENDING SPEED WITH ASSISTANCE......................................................................... 328
RETURN ACCORDING TO BEND FEATURES .................................................................................. 329
SPEED FACTOR SPRIN GBACK CYCLE .......................................................................................... 329
SPEED FACTOR BEAM ’S FINAL APPROACH .................................................................................. 330
INTERPOLATED BENDING AIDS ................................................................................................... 331
SPEED CORRECTIONS MANAGEMENT ......................................................................................... 331
LINEARITY CORRECTION MANAGEMENT ...................................................................................... 332
HAP SIMPLIFIED MECHANICS ............................................................................................ 333
HAP AXES PAIR ....................................................................................................................... 334
CONFIGURATION PAUSES SP/SN ........................................................................................ 335
PAUSES AXES GROUPS N ......................................................................................................... 336
SIGNAL SP GROUPS AXES N ..................................................................................................... 336
SIGNAL SN GROUPS AXES N ..................................................................................................... 336
QUICKCURSOR ....................................................................................................................... 337
CALIBRATION SELECTORS ......................................................................................................... 338
QuickCursor functions ........................................................................................................ 339
MACHINE DIMENSIONS .......................................................................................................... 340
BEAM - ORIGIN AND WIDTH ....................................................................................................... 341
TOOL GRIP - ORIGIN AND WIDTH ............................................................................................... 341
PUNCHES - REFERENCE ........................................................................................................... 342
PUNCHES - DIST. H2-H1 .......................................................................................................... 343
PUNCHES - L5 ......................................................................................................................... 344
DIMENSIONS OF UPPER BEAM - L1 .. L10 ................................................................................... 345
DIMENSIONS OF LOWER BEAM - L1 .. L7 .................................................................................... 346
SHEET SUPPORT DIMENSIONS - L1 .. L4 .................................................................................... 347
REAR PROTECTION ................................................................................................................... 348
BACKGAUGE CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................... 349
BACKGAUGE CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................... 350
Simple backstop ................................................................................................................. 350
Standard backstop with one additional stop ...................................................................... 350
Multiple stops ..................................................................................................................... 351
Special cases ..................................................................................................................... 352
Height adjustment of the backstop..................................................................................... 353
Backstop change in manual mode ..................................................................................... 353
Automatic backstop selection ............................................................................................ 353
N° ........................................................................................................................................... 354
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 354
MODE ...................................................................................................................................... 355
L1 .. L6 ................................................................................................................................... 356
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 10
Page 12

CONTENTS
L6 MIN, L6 MAX ........................................................................................................................ 357
OX .......................................................................................................................................... 359
AF VALUE................................................................................................................................ 360
WIDTH ..................................................................................................................................... 361
SIM. RETRAC. ........................................................................................................................... 362
STOP CLEARANCE .................................................................................................................... 363
AF TIME ................................................................................................................................... 364
AF QUITTANCE ......................................................................................................................... 365
PREFERRED DISTANCE ............................................................................................................. 366
SIDE STOPS ............................................................................................................................. 367
TYPE ....................................................................................................................................... 368
L1 ........................................................................................................................................... 368
L2 ........................................................................................................................................... 368
R1 .......................................................................................................................................... 369
R2 .......................................................................................................................................... 369
R3 .......................................................................................................................................... 369
PHERIPHERALS ...................................................................................................................... 370
PROGRAMMED PERIPHERALS .......................................................................................... 370
ADDITIONAL PERIPHERALS ............................................................................................... 370
N° ........................................................................................................................................... 371
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 371
TYPE ....................................................................................................................................... 371
PATH ....................................................................................................................................... 372
OPT. NB ................................................................................................................................... 372
CONFIGURATION LINK9000 .................................................................................................. 373
Link9000 for option 8, Message interpreter ....................................................................... 374
Link9000 for LazerSafe PCSS ........................................................................................... 374
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 375
PORT ...................................................................................................................................... 375
BAUD RATE .............................................................................................................................. 375
PROTOCOL .............................................................................................................................. 377
CTS LINE ................................................................................................................................ 377
STOP BITS ............................................................................................................................... 377
DATA BITS ............................................................................................................................... 378
PARITY .................................................................................................................................... 378
SWITCH ................................................................................................................................... 378
POSITION ................................................................................................................................. 379
INSERT CR-LF EACH ................................................................................................................ 379
IGNORE CR-LF AT RECEPT ION .................................................................................................. 379
INITIAL TIMEOUT ....................................................................................................................... 380
TIMEOUT BETWEEN CHARACTERS - RECEIVE ............................................................................. 380
TIMEOUT BETWEEN CHARACTERS - SEND .................................................................................. 380
HEADERS - RECEIVE ................................................................................................................ 381
HEADERS - SEND ..................................................................................................................... 381
TERMINATORS - RECEIVE ......................................................................................................... 381
TERMINATORS - SEND .............................................................................................................. 382
CONFIGURATION LINK7000 .................................................................................................. 383
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 384
PORT ...................................................................................................................................... 384
BAUD RATE .............................................................................................................................. 384
CTS LINE ................................................................................................................................ 385
STOP BITS ............................................................................................................................... 385
DATA BITS ............................................................................................................................... 385
PARITY .................................................................................................................................... 386
TRANSMISSION FILE.................................................................................................................. 386
SWITCH ................................................................................................................................... 386
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 11
Page 13

CONTENTS
POSITION ................................................................................................................................. 387
PROTOCOL .............................................................................................................................. 387
AXES ....................................................................................................................................... 387
CODES 1 .. 4 ............................................................................................................................ 388
PRODUCTS .............................................................................................................................. 388
TOOLS ..................................................................................................................................... 388
TRANSFER TO DNC60 ............................................................................................................ 389
NAME ...................................................................................................................................... 390
PORT ...................................................................................................................................... 390
BAUD RATE .............................................................................................................................. 390
CTS LINE ................................................................................................................................ 391
STOP BITS ............................................................................................................................... 391
DATA BITS ............................................................................................................................... 391
PARITY .................................................................................................................................... 392
TRANSMISSION FILE.................................................................................................................. 392
PROTOCOL .............................................................................................................................. 392
PRODUCTS .............................................................................................................................. 393
TOOLS ..................................................................................................................................... 393
INTERNAL BACKU P (SAVE) ......................................................................................................... 394
INTERNAL RESTORATION OF PMS AND TOOLS ............................................................................ 397
SAFETY CONTROLLER .......................................................................................................... 399
MATERIAL ................................................................................................................................ 400
MATERIAL ............................................................................................................................. 401
UNFOLDED LENGTH .................................................................................................................. 402
PRESSURE - AIR BENDING PRESSURE FACTOR ........................................................................... 403
PRESSURE - BOTTOMING PRESSURE FACTOR ............................................................................ 404
SPRINGBACK COMPENSATION ................................................................................................... 405
THICKNESS CORRECTION FACTOR ............................................................................................. 406
CP TOLERANCE IN % OF THICKNESS ......................................................................................... 407
LINEAR ENC. POSITION Y1 ........................................................................................................ 408
DISTANCE BET WEEN L IN . ENC. Y1 AND LIN. ENC. Y2 ................................................................... 409
SENSITIVITY BDC MIN: 1° CORRESPONDS TO ............................................................................. 410
LOG ........................................................................................................................................... 411
OPERATION .......................................................................................................................... 412
LOG ........................................................................................................................................ 412
RECORDS ................................................................................................................................ 412
CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................................. 413
LOCATION OF LOG .................................................................................................................... 413
RECORDS TO KEEP ................................................................................................................... 413
CONTINUOUS PRINTING ............................................................................................................ 414
COPY OF LOG TO ...................................................................................................................... 414
EVENTS TO RECORD .......................................................................................................... 415
INTERPRETED MESSAGES ......................................................................................................... 415
ERROR MESSAGES ................................................................................................................... 415
PRODUCT TRAFFIC ................................................................................................................... 415
WORKING MODE (ENC) ............................................................................................................ 416
WORKING SEQUENCES (ENC) .................................................................................................. 416
PEDAL AND ++ -- (ENC) ........................................................................................................... 416
MESSAGE INTERPRETER ...................................................................................................... 417
OPERATION .......................................................................................................................... 418
INTERPRETER .......................................................................................................................... 418
INTERPRETED MESSAGES ......................................................................................................... 418
CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................................. 419
SOURCE OF MESSAG ES ............................................................................................................ 419
DESTINATION OF AN SWERS ....................................................................................................... 419
CONFIRMATION ........................................................................................................................ 419
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 12
Page 14

CONTENTS
PATTERN AND SCALES ......................................................................................................... 420
PATTERN ................................................................................................................................. 421
DRAWING SCALES .............................................................................................................. 422
U ............................................................................................................................................ 422
V............................................................................................................................................. 422
TRACKBALL .......................................................................................................................... 423
SENSITIVITY X.......................................................................................................................... 423
SENSITIVITY Y.......................................................................................................................... 423
LANGUAGE .............................................................................................................................. 424
TEXTS AND DRAWINGS ............................................................................................................. 425
PRINTER .................................................................................................................................. 427
DESTINATION ........................................................................................................................... 428
JPEG DESTINATION ................................................................................................................. 429
TRANSLATION ......................................................................................................................... 430
DATE AND TIME ...................................................................................................................... 431
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 13
Page 15

INTRODUCTION / CONVENTIONS
INTRODUCTION / CONVENTIONS
This manual describes the machine parameters of the ModEva
numerical controls for synchronized press brakes and other, similar
controls like the DNC880, the DNC1200 and the DNC60 and
DNC600.
The parameter descriptions correspond to the standard version of the
ModEva software. Note that certain parameters described in this
manual are shown only for specific axes-configurations or selected
options.
N2X- and CAN-axes para meters for X, R and all other digital axes are
not described in this manual. Refer to the specific documentation for
detailed information.
Numerous special options and configurations exist for the Cybelec
numerical controls. Examples include Bending aids, Tool changer,
Angle measurement, Safety PLC data link, Tandem configuration, etc.
This manual contains no or limited information about the particular
parameters for these options and configurations. Refer to the specific
documentation for detailed information.
Most chapters in this manual are dedicated to specific machine
parameter pages, e.g. Auxiliary Functions, Beam,
Configuration, etc.
The titles of these chapters correspond to the titles of the ModEva
parameter pages. Each chapter details the parameters contained in the
corresponding parameter page(s).
A few chapters contain more general information, e.g.
Abbreviations, Beam parameters, Beam modes and Beam
cycles. It is recommended to study this information prior to
consulting specific parameters.
A typical value is given for many parameters. This typical value can
be used in most cases, or at least serve as a good starting point. Note,
however, that optimum parameter values strongly depend on machine
construction, - size, hydraulic configuration, etc.
References to other parameters, DNC pages etc. are shown in bold and
use a different font, e.g. P01, Control loop, DNC page Bend
Numerical. In most cases, reference to “machine parameter xxx” is
written as “Pxxx” since this is shorter and easier to read. The
parameter name is given as well since this avoids having to search for
additional information in most ca ses.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 14
Page 16

ABBREVIATIONS
value exists for the field).
AD
Analog to Digital converter
AF
Auxiliary Function
In this document: End of the closing stroke of the beam
CP
Clamping Point, also PP or SCP
etc
etc
DA
Digital to Analog converter
FA
Final Approach
For the beam: Fast approach speed or fast return speed
For the beam: Fast approach speed or fast return speed
For the beam: Bending speed
LS-
Limit Switch -, minimum axis position
PP
Pinch Point, also CP or SCP
Also designates the safety point in- and output of the DNC
For the beam: Bending speed
Also Speed Commutation Point (Parameter 68)
Enable signal for the co rresponding movement of an axis
Can also mean Safety Point (see PSS)
In this document: End o f t he opening st roke of the beam
ABBREVIATIONS
The following is a list of the abbreviations commonly used throughout
this document:
Symbol used for an undefined (empty, non pro grammed)
data field. An undefined field takes a default value (if such
BDC Bottom Dead Center
D0
D1
GV High speed (French: Grande Vitesse), also HS
HS High Speed, also GV
LS Low Speed (or slow speed), also PV
LS+
PSS Safety point (French: Point d e Sécurité (Suédois))
PV Slow speed (French: Petite Vitesse), also LS
SCP Sheet Clamping Point, also CP or PP
Data bit 0
Data bit 1
Limit Switch +, maxi mum axis position
SN Negative direction (French: Sens Négatif)
SP Positive direction (French: Sens Positif)
TDC Top Dead center
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 15
Enable signal for the co rresponding movement of an axis
Page 17

OPTIONS
OPTIONS
DNC-Options are optional selec ta ble extensions to the standard D NCsoftware. Some options are available as standard, others are available
at extra cost, and a few are exclusive to a specific machine
manufacturer or application.
The selection field in front of the option number selects whether the
option is activated or not: Select – to d eactivate and + to activate the
option.
The choice whether to activate an option or not is determined by the
hardware of the machine. Therefore, no typical values are given in the
description of the options.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 16
Page 18

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Interface page for import
and export of DXF- or IGES-files
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the data exchange via a RS232 data
link using the Link7000 protocol
Page
Options
02 CAD INTERFACE PAGE
Function
This option is only used for the 3D version of the PC-Software.
The CAD-Interface allows to import
unfolded part data from a CAD system,
avoiding time consuming reprogramming of
the part and the risk of data introduction
errors. In the ideal case, the CAD system
exports DXF- or IGES files specifically
adapted for the Cybelec software. In his
case, the import process is very simple and
largely automatic.
Activates the CAD-
03 COMMUNICATIONS LINK7000
Function
This option is only used for the PC-Software.
Link7000 i s us ed to exchange product data with t he non PC based
Cybelec controls such as the DNC7000 and DNC70, which don’t have
a floppy disk drive or an USB port.
For the data exchange with current DNC60 controls, Link7000 has
been replaced by the standard Transfer to DNC 60 feature. Note
that this fea ture is only availabl e when the option Communications
Link7000 is not activated.
Transfer to DNC 60 is available starting with so ftware version
SSBFxN4 and requires DNC60/600 software version SIXFDK /
SVXFDK or later.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 17
Page 19
OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the Message interpreter
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
a real-time, analog measurement interface
Page
Options
08 MESSAGE INTERPRETER
This option allows to remote control a DNC. Commands can be issued
through a ser i al RS232 data link or by command files exchange d over
a network. The message interpreter is mainly used for machine
automation, interfacing to a bending cell robot and interfacing to a
barcode reader.
30 ANGLE MEASURING DEVICE
Function
See also option 60, Angle measuring device, for angle
measurement systems using a serial link interface.
Refer to the specific angle measurement documentation for further
information.
Activates the angle measurement system using
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 18
Page 20

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the front X-axes
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the front Z-axes
Page
Options
33 FRONT X AXES (X3, X4, X7, X8)
Enables the selection of front X-a xes on the Configuration page.
Note Front axes are not calculated by the DNC, and must be
programmed manually. See the chapter Configuration for
further details.
34 FRONT Z AXES (Z3, Z4)
Enables the selection of front Z-axes on the Configuration page.
Note Front axes are not calculated by the DNC, and must be
programmed manually. See the chapter Configuration for
further details.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 19
Page 21

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the rear sheet support axes
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the calculation support for bends
which are not parallel to the edge of the sheet
Page
Options
38 BACK SHEET SUPPORT (H, H2)
Enables the selection of rear sheet support axes on the
Configuration page.
Note Sheet support axes are used to support the sheet prior to
bending. Unlike bending aids, sheet support axes do not follow
the sheet during the bending operation. See also option 42,
Bending assistance.
Note Specific parameters for the rear sheet support axes are
programmed in the parameters Back sheet support on the
parameter page Special cycles.
41 “SCHRAEGSTELLUNG”
Function
This option requires a rear gauge configuration with two X- and two
Z-axes as well as backgauge fingers with a side stop. Note that a
configuration with a backgauge bar driven by two X-motors is not
suitable for this option because the fingers do not remain
perpendicular to the bend line when the X-axes are set to different
positions. See also the chapter Example configurations.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 20
Page 22

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the bending aid axes AP1..AP4
Page
Options
When this option is activated, special calculation parameters for bends
which are not parallel to the edge of the sheet are available on the
Bend Numerical page.
42 BENDING ASSISTANCE
Enables the selection of front (AP3, AP4) and rear (AP1, AP2)
bending aid axes on the Configuration page.
Bending aids are support arms that follow and support the sheet
during the bending process. They ar e synchronized with the
movement of the beam, and intended to support heavy parts during
bending. Bending aids are also used to support very thin material in
order to avoid unwanted folding on the edge of the Vee.
See also option 38, Back sheet support (H, H2), a nd 52, Front
sheet supports (H3, H4).
Example configuration with
AP3 (left) shown in the down
position and AP4 (right)
shown in the up positio n
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 21
Page 23

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the configuration of the DNC for a
“conventional”, non synchronized, press brake
Page
Options
43 P/PC PRESSE
Function
Do not activate this option on a synchronized press brake as this will
adapt the functioning of the DNC for a “conventional” machine.
Except for the beam parameters, all parameters for a conventional P or
PC type press brake are the same as for a synchronized press brake.
Note, however, that a number of functions and options are not
available for P/PC type machines.
This pictur e shows
the first Beam
parameter page for
a PC-press with Y1
and M-axes. The
second Beam
parameter page is
identical with the
synchronized press
brake and there is
no third Beam
parameter page.
This pictur e shows
the first Beam
parameter page for
a P-press with only
an M-axis. There
are no other Beam
parameter pages.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 22
Page 24

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the material thickness measurement
system using a RS232 serial data link
Page
Options
44 THICKNESS MEAS. BY SERIAL PORT
Function
Originally developed for a Krautkramer ultrasonic measurement
system, this option can also be used with a Roland inductive
measureme nt s ystem as well as with other systems using the same
data format.
This option allows automatic c orrection of the bending depth
according t o the measur ed thickness .
Note See also option 57, Thickness meas. by N2X (MS1,
MS2).
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 23
Page 25
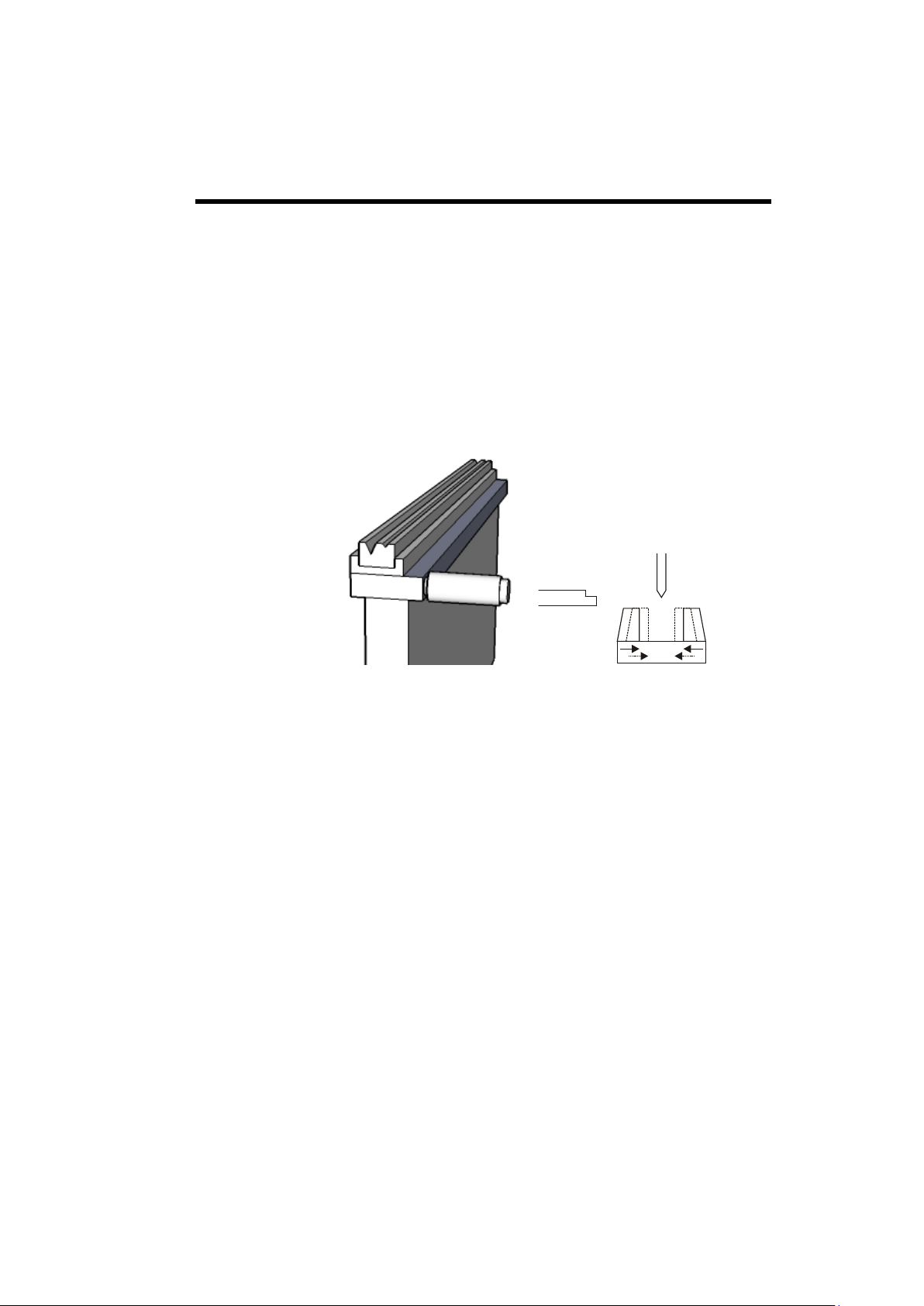
OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
die: X-Positioning (die shifter ) or variable Vee
Page
Options
51 DIE AXES (M1, M2)
Function
Enables the selection of die axes on the Configuration page.
Positioning of selected die Variable Vee die
M-axes are used to position the selected die of a multi-Vee die or
another multiple die system in the be nding position. The positions of
the M-axes are defined in the programmed die data.
Activates the axes for the positioning of the
M-axes can also be used to position variable-Vee dies. In this case the
size of the Vee-opening is adjusted with one or two M-axes.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 24
Page 26

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the front sheet support axes
Page
Options
H
52 FRONT SHEET SUPPORTS (H3, H4)
Enables the selection of front sheet support axes on the
Configuration page.
The DNC calculates the position of the front sheet supports according
to the selected tools and bend conditions.
Note Sheet support axes are used to support the sheet prior to
bending. Unlike bending aids, sheet support axes do not foll ow
the sheet during the bending operation. See also option 38,
Back sheet support (H, H2), as well as option 43,
Bending assistance.
Note The dimensions of the front sheet support arms or –table are
programmed in the parameters Sheet support dimensions
on the parameter page Machine dimensions.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 25
Page 27

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
and outputs required
for external commands
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the material thickness measurement
system using N2X meas urement axes
Page
Options
55 EXTERNAL COMMANDS
Function
Enables the selection of special in- and outputs on the Inputs and
Outputs pages.
Note External commands have become a standard feature for the
ModEva and DNC880S, and this option no longer needs to be
activated.
Activates additional in-
57 THICKNESS MEAS. BY N2X (MS1, MS2)
Function
Enables the selection of material thickness measurement axes on the
Configuration page.
This option allows automatic c orrection of the bending depth
according t o the measur ed thickness . The material thickne s s is
measured with special measurement clamps mounted on or in the
backstop fingers.
See also option 44, Thickness meas. by serial port.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 26
Page 28

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
a serial link measurement interface
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the CAN axes interface
Page
Options
60 ANGLE MEASURING DEVICE
64 CAN
Function
See also option 30, Angle measuring device, for angle
measureme nt s ystems using a real-time analog measurement interface.
See also options 65 and 66 for extensio ns to this option.
Refer to the specific angle measurement documentation for further
information.
Activates the angle meas urement syste m using
This option is required for axes using CAN drives. The CAN bus of
the drive(s) is connected to a NCX board, which replaces the regular
N2X- and NMX/ NSX boards.
A maximum of 2 NCX boards can be mounted in a CNC rack. Each
board can control a maximum of 8 CAN axes.
The maximum number of CAN axes is determined by the options 74
.. 78.
Refer to the specific CAN documentation for further information.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 27
Page 29

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the dual angle measurement option
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the real time angle measurement
option
Page
Options
65 SECOND ANGLE MEASURE
This is an extension to option 60, Angle measuring device.
This option is required to support a dual (left-right) measurement
system.
Refer to the specific angle measurement docu mentation fo r further
information.
66 CONTINUOUS ANGLE MEASURES
Function
This is an extension to option 60, Angle measuring device.
This option is required to support a real-time measure ment system.
Refer to the specific angle measurement documentation for further
information.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 28
Page 30

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
force and crowning
Page
Options
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
78: Activates the CAN axes counter bit D 4
Page
Options 2
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4 Maximum number of CAN Axes
- - - - -
+ - - - -
- + - - -
+ - + - -
+ + + - -
- + - + -
- - - - +
68 FORCE & CROWNING CALCUL AT. V2.0
Function
See P38, Force calculation as functi o n o f target angle.
Activates the alternative calculation met hod for
74 … 78 COUNTER AXES CAN D0 … D4
Function
74: Activates the CAN axes counter bit D0
75: Activates the CAN axes counter bit D 1
76: Activates the CAN axes counter bit D 2
77: Activates the CAN axes counter bit D 3
The number of configurable CAN axes on the machine is limited to
the number defined with the options 74, 75, 76, 77 and 78. So me
examples:
74
75
76
77
78
0 axes
1 axis
2 axes
5 axes
7 axes
10 axes
16 axes
See also option 64, Can, as well as the specific CAN documentation.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 29
Page 31

OPTIONS
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 30
Page 32

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
an external PLC
Page
Options 2
82 SERIAL LINK WITH PLC
Function
This option allows to exchang e digital I/O signals with an external
(safety) PLC (without t he need of physically wiring these signals
between in- and outputs). This option also allows to log and display
PLC operator messages on the DNC screen.
Activates the interface for data exchange with
Refer to the specific documentation for this option for a description of
the machine parameters.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 31
Page 33

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
in support for the
integration of supplementary software
Page
Options 2
83 PLUG IN
Function
The plug-in optio n allows the integration of user tailored software into
in the Cybelec Software.
A typical use for the plug-in is the display of bend simulation images
generated by an external CAD system. Other applications include the
control of particular crowning systems, special axes-calculations, etc.
Activates the DNC plug-
The page Bend - OEM
viewer constitutes the user
interface for the supplementary
software.
The main window (black area
of the image) is available to the
user software to display
pictures, data fields, control
elements etc.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 32
Refer to the specific documentation for this option for a description of
the machine parameters.
Page 34

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the LazerSafe PCSS interface
Page
Options 2
84 LASERSAFE PCSS LINK
This is a special option for machines equipped with a LazerSafe PCSS
safety controller. The DNC and machine interface with the PCSS
controller is configured on the parameter page Safety controller.
The operator configures the PCSS working mode and other PCSS
functions on the operator page Safety controller, accessible from
the Product and Bend menu. This page also shows the current state
of safety system.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 33
Page 35

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Activates the strain gauge deflection
compensation system
Page
Options 2
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the Tandem press interface
Page
Options 2
86 STR AIN GAUGE
Function
See the machine parameters page Strain gauge for further
information.
89 MACHINE TANDEM
This option enables specific in- and outputs for the synchronized
(tandem) operation of 2 or more machines.
Refer to the documentation Tandem_Option89 that co vers this
subject in detail.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 34
Page 36

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
axes with a “simplified” mechanics.
Page
Options 2
HAP
APV
L1
L2
L5
L3
L4
L6
Axis AP
Axis H
90 HAP MECANIC SIMPLIFIED
Function
Activates the use of AP-axes mounted on H-
This option enables the us e of bending a id AP-axes mounted on s heet
support H-axes in a configuration with simplified mechanics. See the
kinematics example of this configuration below:
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 35
Note The option 90, HAP mechanic simplified, neither requires
option 38, Back sheet support (H, H2), nor option 42,
Bending assistance.
Page 37

OPTIONS
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates the use of free axes as slave axes
Page
Options 2
Data type
Selection - / +
Default value
-
Function
Activates follow up bending assistance
Page
Options 2
91 FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’
This option enables the use of free axes as slave axes linked to master
axes. A common application is a backgauge X-axis with two
servodrives. The first s ervodrive is driven by a regular X axis. The
second servodrive is driven by a free axis configured in slave mode of
the X master axis.
92 FOLLOW-UP BENDING ASSISTANCE
Starting with software version P, this option has become a standard
feature for machine configurations with bending aid axes. See the
page Bending assistance.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 36
Page 38

CONFIGURATION
CONFIGURATION
The numerical axes of the DNC are defined in the Configuration
parameters.
The operator pages (e.g. Bend Numerical) show the axes in t he
order defined on the configuration page. Up to 4 configuration pages
may be defined in order to accommodate all axes.
Note An axis may be defined on multiple configuration pages. The
axis settings Name, Decimals, N2X Axis N° are the same on
all pages.
On the operator pages, the function Actions – Auxiliary page
cycles though the defined configuration pages to display the axes.
Note that this function is only availab le if multiple configuration
pages have been defined.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 37
Page 39

CONFIGURATION
Data type
Number
Default value
1
Typical value
1
Value range
1 to 4
Function
Selects the displayed configuration page
Page
Configuration
Data type
Number
Fixed value
1 to 9
table
Page
Configuration
AUXILIARY PAGE
Up to 4 configuration pages may be defined.
On the operator pages, the function Actions – Auxiliary page
cycles though the defined configuration pages to display the axes.
Note that this function is only availab le if multiple configuration
pages have been defined.
LINE N°
Function
Shows the line number in the configuration
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 38
Page 40

CONFIGURATION
Data type
Selection axis typ e
Default value
Typical value
None
Function
Selects the axis type
Page
Configuration
The axes types shown in the selection list depend on
the active options. The first choice in the selection
A given axis type can only be defined once for the
machine. Note, however, that the same axis may be
AP1
First rear bending aid axis (requires option 42)
AP2
Second rear bending aid axis (requires option 42)
AP3
First front bending aid axis (requires option 42)
AP4
Second front bending aid axis (requires option 42)
Free1
First free axis
Free2
Second free axis
Free3
Third free axis
Free4
Fourth free axis
Free5
Fifth free axis
Free6
Sixth free axis
Free7
Seventh free axis
Free8
Eighth free axis
MODE
list specifies “no axis” and clears all the fields on the
current selection line.
defined on multiple configuration pages.
AXES
The following table lists the mo st common axes:
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 39
Page 41

CONFIGURATION
H
First rear sheet support axis (requires option 38)
H2
Second rear sheet support axis (requires option 38)
H3
First front sheet support axis (requires option 52)
H4
Second front sheet support axis (requires option 52)
H7
Third front sheet support axis (requires option 52)
H8
Fourth front sheet support axis (requires option 52)
M
Depth stop for P/PC press (requires option 43)
M1
First die axis (requires option 51)
M2
Second die axis (requires option 51)
MS1
First sheet thickness measurement axis (requires option 57)
MS2
Second sheet thickness measurement axis (requires option 57)
R
First rear gauge height axis
R2
Second rear gauge height axis
R5
Third rear gauge height axis
R6
Fourth rear gauge heigh t axis
X
First rear gauge position axis
X1
First relative gauge position axis (mounted on the X-axis)
X1ABS
X1 mode axis with absolute (instead of relative) position display
X2
Second rear gauge position axis
X2REL
Second rel ative gauge p osition axis (mounted on the X-axis)
X3
First front gauge position axis (requires option 33)
X4
Second front gauge position axis (requires option 33)
X5
Third rear gauge position axis
X6
Fourth rear gauge position axis
X7
Third front gauge position axis (requires option 33)
X8
Fourth front gauge position axis (requires option 33)
Beam position measurement (PC-press, requires option 43)
Y2
Second beam (bending) axis
Z
First rear gauge lateral axis
Z2
Second rear gauge lateral axis
Z3
First front gauge lateral axis (requires option 34)
Z4
Second front gauge lateral axis (requires option 34)
Z5
Third rear gauge lateral axis
Z6
Fourth rear gauge later al axis
Y1
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 40
First beam (bending) axis (synchronized press brake)
Page 42

CONFIGURATION
Data type
Text
Default value
, uses the Mode field te xt as axis name
Typical value
Name of the axis
Value range
0 to 5 characters
Function
User-defined name of the axis.
Page
Configuration
NAME
This name is used to reference the axis on all operator- and parameter
pages. When left blank, the name of t he axis mode is used as the axis
name. In some cases, it is recommended to change this default name.
See the examples below:
Mode Name Display Function
X X1 X1 Le ft X-axis
X2 X2 Right X-axis
Mode Name Display Function
X X X-axis bar with two X-adjustable
fingers
X1 X1 Left backgauge finger X-axis
X2REL X2 X2 Right backgauge finger X-axis
Mode Name Display Function
H3 FH FH Front sheet support
H3 FSUP FSUP Alternative front shee t support name
AP3 FBAID FBAID Front bending aid
Note Always retain the basic mode name as the axis name for H, M,
R, X, Y, and Z axes. These are standard names which should
not be changed. Another common convention is to use a lower
index for axes on the left-hand side (e.g. R1, X1, Y1, Z1) and a
higher index for axes on the right-hand side of the machine
(e.g. R2, X2, Y2, Z2).
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 41
No common names exist for AP, Free, MS and other special
axes. Keep the basic mode name if convenient, or define
another suitable name if this is more suitable for the operator.
Page 43

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Note X X
Manual Z axis
Mode
Name
Note X X
Manual Z axis
R
R
EXAMPLE CONFIGURATIONS
The following examples show a numbe r of common axes
configurations.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 42
Page 44

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X
Z
Z1 R R
Z2
Z2
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X
Z
Z1
Free1
XS
Z2
Z2 R R
The axis Free1 is configured as a slave of the master axis X.
Note Slave axes require option 91, Free axes ‘slaves’.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 43
Page 45

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X1
Z
Z1
X2
X2
Z2
Z2 R R1
R2
R2
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X
R
R1
X1
X1
R2
R2
Z
Z1
Z2
Z2
Note
This configuration is not suitable for option 41,
“Schraegstellung”, because the backgauge fingers are not
perpendicular to the bend line when X1 <> X2.
In this configuration X1 must be on the right side.
Note This configuration is suitable for option 41,
“Schraegstellung”.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 44
Page 46

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X
R
R1
X1
X1
Left side
R2
R2
X2REL
X2
Right side
Z
Z1
Z2
Z2
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X
R R Free1
XS
Z
Z1
X1
X1
Z2
Z2
Note This configuration is suitable for option 41,
“Schraegstellung”.
In this configuration X1 must be on the right side
Note This configuration is suitable for option 41,
“Schraegstellung”.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 45
Page 47

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
Y1
Y1
R
R1
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X3
X3
R3
R3
X4
X4
R4
R4
Y2
X
X2
X5
Y2
X1
X2
X3
R2
Z
Z2
R2
Z1
Z2
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 46
Page 48

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Mode
Name
X
X1
X5
X5
X2
X2
R5
R5
R
R
X5
X6
Z
Z1
R6
R6
Z2
Z2
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 47
Page 49

CONFIGURATION
Mode
Name
Note
AP3
FBAID1
Left bendin g aid axis shown in down p osition
AP4
FBAID2
Right bending aid axis shown in up position
Mode
Name
Note
H3
FSUP1
Left front support axis
H4
FSUP2
Right front support axis
No common names exist for AP axes. Keep the basic mode name if
convenient, or define another suitable name if this is more suitable for
the operator. In this example AP3 and AP4 are named FBAID1 and
FBAID2.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 48
Page 50

CONFIGURATION
Bending aid in down position
Bending aid during fold ing cycle
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 49
Page 51

CONFIGURATION
Motorized H axis
M axis used a s die shifter , shown in two positions
Alternatively, an M-axis can also be used to adjust the opening of the
Vee.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 50
Page 52

CONFIGURATION
Data type
Number
Default value
None, must be defined
Typical value
2 / 3 for Y1-Y2; 1 / 2 for other axes
Value range
0 to 4
imperial (inch) mode shown on the operator
pages.
Page
Configuration
DECIMALS MM / INCH
Function
Normally, the inch setting equals the mm settin g plus one.
The setting of the number of decimal places is used for the operator
pages (e.g. Bend Numerical) only. The number of decimal places is
fixed for the machine parameter pages.
Number of decimal places for metric (mm) and
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 51
Page 53

CONFIGURATION
Data type
Number
Default value
for Y1, Y2; No default for al other axes
Typical value
None
Value range
0 to 15
the Y1 and Y2 axes.
Page
Configuration
Data type
Selection numbering system
Default value
14-15, 0-1, 2-3
Typical value
0-1, 2-3, 4-5 for ModEva
Function
Selects the N2X numbering system
Page
Configuration
N2X AXIS N°
Function
Note The physical axis numbe rs of the N2X axes depend on the
selected numbering system. See parameter N2X-Numbering.
N2X NUMBERING
Physical axis number. Must be undefined for
For the DNC1200, the first N2X slot was reserved for the NLR-board.
This slot corresponds to the N2X-axes 14-15. The next slo ts wer e
numbered N2X 0-1, 2-3, etc.
For the ModEva, the first N2X-Slot is not specifically reserved for an
NLR-board, and the slots are numbered starting from 0-1.
Although either numbering system can be used on a DNC, the selected
system sho uld correspond to the labeling of the DNC in order to avoid
confusion.
The NMX (N2X master) and NSX (N2X slave) board follow the
regular N2X numbers.
Refer to the CAN documentation for the numbering of CAN axes
using the NCX board.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 52
Page 54

PREFERENCES
PREFERENCES
The preference parameters select optional functions.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 53
Page 55

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Numerical Param eters
Page
Preferences
PRODUCT PARAMETRIC
Function Selects to display the page Product
Parametric products offer a fast and easy way to modify preprogrammed 2D profiles. First, 2D product data is entered for a
typical, representative part in the normal way on the Product
Numerical page. Next the bend sequence is determined and the part
is produced and optimized as usual. The final DNC program for the
part is the basis for the parametric product.
On the Product Numeri cal Par amet e rs page, the parameters A to
H can be assigned to various data elements of the basic product. These
parameters are given a meani ngful description (field Caption), and
limit values (fields Min and Max) as well as a default value (field
Suggested) are defined. Finally, the field Parameters is set to
Active to activate parametric programming for this product.
Note Changing the field Parameters requires key level 3.
The picture below illustrates the defined parameters for a simple Uprofile:
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 54
Page 56

PREFERENCES
When the field Parameters is se t t o Active, the Product
Numerical page only shows basic product data and the list of user
defined parameters. See the picture below:
Normal, non parametric programming of the product is restored by
setting the field Parameters to Inactive on the Product
Numerical Parame ters page.
Note Parametric products can only be used in 2D-mode.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 55
Page 57

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
Yes
Typical value
Yes
Selects to display the 2D product profile on the
Product Numerical page
Page
Preferences
Selection No
Selection Yes
GRAPHICAL PROFILE ON PAGE NUMERICAL
PRODUCT
Function
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 56
Page 58

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
Yes
2D
Page
Preferences
Selection No
Selection Yes
BEND 2D INTERACTIVE
Function Selects interactive operation on the page Bend
When this preference is set to Yes, the thickness of the material is
represented and additional options show the part and to define bend
and gauge positions are available on the Bend 2D page.
Note The Bend / Unbend mode selection is no longer available when
this option is set to Yes. Also, the front sheet support axes
(H3, H4) will not be represented in the 2D-image in this case.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 57
Page 59

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
Yes
window when loading a product
in the working me mor y
Page
Preferences
AUTOMATIC DISPLAY OF PRODUCT
INFORMATIONS
Function Selects to automatically display the Product
When this preference is set to Yes, the Product Information
window will be displayed automatically (if product information has
been defined) when loading a product in the working memor y.
Information
Note The Product Information window can be shown any time
by selecting the ? (no product information defined) or !
(product information a vailable) symbol in the top rig ht hand
corner on the screen.
Refer to the chapter Product information in the 2D reference
manual for further information about programming and using product
information.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 58
Page 60

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Selects to enable the programming of a product
on the DNC while producing another product
on the machi ne
Page
Preferences
PROGRAMMING WHILE WORKING
Function
Note It is normally not recommended to set this option to Yes since
the operator(s) can easily be confused by the different mode
changes, and loose the “wrong” product when returning to
SINGLE MODE.
When this preference is set to Yes, the Double mode can be selected.
In this mode, a product can be programmed on the DNC while another
product is produced on the machine:
Change to a ut omatic mode as usual. The LED of the key lights
up and the DNC operates in automatic mode. The product can be
produced on the machine.
DOUBLE MODE
Press the Program mi ng ke y .to switch to DOUBLE MODE.
The LED o f the Automatic key remains li t and the LED of the
Programming key is lit as well. The DNC can now be used to
program another prod uct while cont i nuing prod uction on the machine.
Note The product number shown between
square brackets is the produc t being
produced.
SINGLE MODE
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 59
When in DOUBLE MODE (The LEDs of bo th the Programming
key and the Automatic key are lit), return to SINGLE MODE by
pressing either the
Programming key to keep the product being programmed,
or the
Page 61

PREFERENCES
Automatic key to keep the product being produced.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 60
Page 62

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Order / Production Time pages
Page
Preferences
PRODUCTION PAGE
Function Selects access to the List of Orders and
When this preference is set to Yes, the List of Orders and Order /
Production Time pages can be selected from the main menu:
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 61
Page 63

PREFERENCES
Note It is normally not recommended to activate this option.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 62
Page 64

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Function
Selects access to the Production Check page
Page
Preferences
PRODUCTION-CHECK
When this preference is set to Yes, the Production Check page can
be selected from the main menu:
Note It is normally not recommended to activate this option.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 63
Page 65

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
using the Qui ckCursor
Page
Preferences
MANUAL MOVEMENTS WITH QUICKCURSOR
Function
When this preference is set to Yes, the QuickCursor can be used for
manual posit ioning of the axes.
Note See the machine parameter pages QuickCursor and N2X
page 2 for specific parameters for manual movements with
the QuickCursor.
Note It is normally not recommended to activate this option.
Selects to authorize manual axis-movements
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 64
Page 66

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Selects to allow the operator to disable
automatic calculations
Page
Preferences
Automatic calculations
No automatic calculations
ALLOW SWITCHING OFF AUTOMATIC
CALCULATIONS
Function
When this preference is set to Yes, the automatic calculation of BDC,
Bending force etc. as a function of the material thickness etc. can be
switched on and off wit h a corresponding funct i on on the Actions
menu.
A calculator symbol signals the state of the automatic calculations.
Note Under normal conditions, the a utomatic calculations should
always rema in switched on.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 65
Page 67

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
level 0
Page
Preferences
KEY 0 BLOCKS UTILIZATION
Function
When this preference is set to Yes, the DNC keyboard will be locked
(except for changing the key level) when the curr ent key level is 0.
This effectively disables using any keyboard function of the DNC and
prevents that changes can be made to the current product or DNC
operating mode.
This feature is particularly use ful during exhibitions to prevent that
visitors introduce unwanted changes.
Note Key level 1 or higher is always required to memorize and
delete products.
Selects to lock t he DN C-keyb oar d when in key
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 66
Page 68

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection Z-axes configuration
Default value
No
Typical value
Machine dependent
Function
Selects the physical position of the Z axes
Page
Preferences
Z - Z2 - Z5
Z5 is located to the right of the Z2 axis
Z - Z5 - Z2
Z5 is located between the Z1 and Z2 axes
Z5 - Z - Z2
Z5 is located to the left o f the Z axis
Z - Z2 - Z6
Z6 is located to the right of the Z2 axis
Z - Z6 - Z2
Z6 is located between the Z1 and Z2 axes
Z6 - Z - Z2
Z6 is located to the left of the Z axis
POSITION Z5 – Z6
The preferences Position Z5 and Position Z6 are shown only if the
corresponding Z5 or Z6 axes are configured.
The following settings can be selected:
Preference Position Z5
Preference Position Z6
Note The configuration with a Z5 and/or Z6 axis outside of the Z1-
Z2 axes is used when the Z5 and/or Z6 axes are located outside
of the side frames.
Configure Z5 and/or Z6 axis between the Z1-Z2 axes when the
Z-axes are located between the side frames.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 67
Page 69

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection Z-axes calculation
Default value
No computation
Typical value
Select calculation according to the Z-axes
axes for
products programmed in 2D (or numerical)
Page
Preferences
No computation
No automatic calculation
are not calculated.
Calculate positions for the Z, Z5 and Z2 axes, Z6 is
not calculated
Calculate positions for the Z, Z6 and Z2 axes, Z5 is
not calculated
Z - Z5 - Z6 - Z2
Calculate positions for the Z, Z5, Z6 and Z2 axes
COMPUTE AXES Z ON PRODUCT 2D
Function
When this pr eference is no t set to No computation, the positions of
the Z-axes will not be calculated automatically as a function of the
bending length and material positio n.
The following settings can be selected:
Z - Z2
Z - Z5 - Z2
Z - Z6 - Z2
Note The Z-axes must be physically located on the order defined by
the selection.
Selects the calculation mode of Z-
Calculate positions for the Z and Z2 axes, other Z axes
Note The axes selected for automatic calculation must, of course, be
defined in the machine configurati on.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 68
Page 70

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
Yes if machine has bending aid axes
Selects to automatically limit the bending
speed when us ing bending aid axes
Page
Preferences
AUTOMATIC CORRECTION OF THE RAM SPEED
Function
When bending at nominal speed, the required positioning speed of the
bending aid axes can exceed the maximum positioning spee d. This
situation can occur in particular when using a die with a small Vee
opening.
When this preference is set to No, an error message is shown when
the required positioning speed of the bending aid axes exceeds the
maximum speed.
When this preference is set to Yes, the bending speed of the beam is
automatically reduced in order to limit the positioning speed of the
bending aid axes to the maximum speed.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 69
Page 71

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection Imprecise/Precise/By choice
Default value
Imprecise
Typical value
Imprecise
Function
Selects the retraction mode for the rear X-axes
Page
Preferences
This choice is used to optimize the beam cycle speed.
retraction position before the beam starts to bend.
page
RETRACTIONS OF X AXIS
The following selections are available for this preference:
Imprecise
Precise
By choice The retraction mode is selected on the Bend Numerical
Note In most cases, imprecise retractions are optimal since this
choice minimizes the position time of the rear X-axes for the
retraction. In some cases, however, precise retractions could be
required.
The rear X-axes move in full speed during the pro grammed
retraction distance and then sto ps. The beam starts bending
as soon the X axes reaches the retract position (at full
speed).
In this mode, the stop position is not important, the real stop
position is located somewere after the retraction distance
depending the speed reached at that point.
The rear X-axes position precisely at the programmed
retraction position.
This selection is used if the operator need for a specific
reason to have the X axis a one exact position at the end of
retraction. This mode use more beam cycle time, because
the X axis has to properly terminate its positioning at
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 70
Page 72

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Function
Selects the retraction mode for the rear Z-axes
Page
Preferences
RETRACTIONS OF Z AXIS
When this preference is set to Yes, the retraction direction and distance of the Z1- and Z2 axes can be programmed on the Bend
Numerical page.
In some cases, a lateral retraction of the
Z-axes may be more convenient to use
than the standard backward retraction of
the X-axis.
A positive Z-retraction is interpreted as
a movement to the left (negative
movement) for Z1 and a movement to
the right (positive movement) for Z2.
When both X- and Z-retractions are
defined, the Z-retraction takes place
prior to the X-retraction.
Note This function is not available for Z5 and Z6.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 71
Page 73

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Selects to activate the indexation assistance for
the operator
Page
Preferences 2
INDEXATION AIDS
Function
This preference has been introduced in software version M. The
assistance functionality, however, is implemented starting with
software version N. For software versions prior to N, this parameter
should always be set to Yes to avoid a problem with the indexing
cycle.
When this parameter is set to Yes for software version N, a pop-up
window with user help information is shown when a problem is
detected during the normal indexing procedure of the beam.
Starting with the P version o f the software, add itional beam ind exing
methods and special beam synchronization inputs are available, and
this parameter should be set to Yes for normal operation. See also
P09b, Indexing type and the d igital i nput s ignals Y1 > Y2 and Y2
> Y1.
Note This preference is only used for the traditional indexation
method (P09b, Indexing type set to Indexing during
upward move), and has no importance for the other possible
indexing metho d s.
In some special cases (parameter- and machine set-up, etc.),
this parameter can be set to No to disable error detection and
display of pop-up messages. For the traditional indexation
method, this allows to keep the beam under pressure against
the mechanical limit, in order to adjust the limit pres sure, check
signals, etc. without interruptio n of the indexing cycle due to
the stop detection of the beam.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 72
Page 74

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/RS232/USB
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Defines the interface type for the manual angle
measurement protractor
Page
Preferences 2
USB/RS232 ANGLE MEASUREMENTS
Function
Starting with software version O, a manual Mitutoyo angle protractor
can also be connected to the USB port of the ModEva or DNC880S
control.
The USB interface also permits to use a Mitutoyo protractor equipped
with a special wireless data transceiver.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 73
Page 75

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Function
Selects to activate the machine parking feature
Page
Preferences 2
MACHINE PARKING FEATURE
Selection this preference to Yes activates the feature to easily position
all axes of the machine to predefined parking positions.
The Y1-Y2 axes should always be parked to safe positions prior to
switching off the machine. Parking all other axes is recommended,
and may gain a considerable amount of time at start-up if the
indexation speed (homing speed for CAN axes) is low.
The parking procedure can be initiated by the action Park machine
or by the dedicated digital input signal P ark mach ine.
Note This parameter is available starting with software version P.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 74
Page 76

PREFERENCES
Data type
Selection No/Yes
Default value
No
Typical value
No
Selects to activate the crowning correction
calculation
Page
Preferences 2
Selection Yes
Selection No
COMPUTING CROWNING CORRECTION
ACCORDING TO MEASURED ANGLE
Function
When set to Yes, the action Angle correction on the page
Corrections sho ws the angle mea surement wind ow with data fields
for the measured angle in the center of the material:
Note that the action Angle correction and the angle measurement
window are o nly shown when the following parameters are defined:
Page Material: Parameter Linear enc. position Y1 and Distance
between lin. enc. Y1 and lin. enc. Y2.
Although not strictly required, the parameters Beam origin and
Beam width on the page Machine dimensions should also be
defined.
The data fields for the measured angle in the center of the material are
only shown when this preference is set to Yes and the following
parameters are defined as well:
Page Pressure and crowning 2: P307, Crowning resolution.
Page Pressure and crowning: P30a, Distance between jacks.
Note also that display of the action Angle correction on the page
Corrections (and therefore also the display of the angle
measurement window) also requires that all data for Y1-Y2-, pressureand crowning calculation (tool data, thickness, bend angle, bending
length, etc.) has been programmed on the operator pages.
Note further that that the calculation for mulas have been adapted and
optimized to include the crowning correction calculation. Because of
this, the calculated Y1-Y2 corrections (without crowning correction)
are slightly different from the p revious calculations.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 75
Note This parameter is available starting with software version P.
Page 77

PREFERENCES
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 76
Page 78

N2X
N2X
Note The N2X so ftware versio n is shown at the top of the N2X
parameter pages. Complete software version information for
DNC, ENC, N2X and NLR is shown on the Welcome page.
Refer to the specific N2X documentation for details about the N2X
parameters.
Note The QuickCursor parameters 149 and 150 are only shown
when the preference Manual movements with
QuickCursor is set t o Yes.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 77
Page 79

N2X
Data type
Distance [mm]
Default value
0.10
Typical value
Value range
0.00 to 999.99
Defines the positioning distance of the axis per
increment o f the QuickCursor
Page
N2X page 2
Data type
Factor [%]
Default value
100%
Typical value
Value range
0.0 to 99.9
Defines the acceleration/deceleration of the
axis for QuickC urs or mo ve me nts
Page
N2X page 2
QUICKCURSOR
This section contains QuickCursor parameters for manual axismovements.
See also the chapter QuickCursor for further details.
149 STEP SIZE
Function
Set this parameter to 0.1 mm when precise QuickCursor movements
are required. Set to 1 mm or bigger when the Quic kCursor is only
used to move an axis out of the way.
Note This parameter requires the preference Manual movements
with QuickCursor.
150 ACCELERATION FACTOR
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 78
Function
Note This parameter requires the preference Manual movements
with QuickCursor.
Page 80

FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’
FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’
This page requires option 91, Free axes ‘slaves’ and the
configuration of at least one Free axis.
A slave axis is linked to a master axis. A common application is a
backgauge X-axis with two servodr i ves. The first servodrive is driven
by a regular X axis. The second servodrive is driven by a free axis
configured in slave mode of the X master axis.
Note A bending aid axis cannot have a slave axis.
Note For the ModEva, the master axis and the corresponding slave
axis must be located on the same NMX/NMS group. This
restriction does not apply to the DNC880s
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 79
Page 81

FREE AXES ‘SLAVES’
Data type
Slave axis t ype
Function
Displays configured slave axes
Page
Free axes ‘slaves’
Data type
Selection axis type
Default value
Free axis (not used as a slave axis)
Typical value
Depends on the machine
slave axis
Page
Free axes ‘slaves’
Data type
Distance [mm]
Default value
No master-slave position difference limitation
Typical value
Depends on the machine
and slave axi s .
Page
Free axes ‘slaves’
SLAVE
MASTER
Function
DISTANCE MAX
Function
Selects the master axis for a free axis used as a
Maximum position difference between master-
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 80
Page 82

CAN BUS
field to exit the
viewer
CAN BUS
This page requires option 64, CAN.
Recorded CAN messages are shown with the function Actions –
CAN viewer. This action is available on most DNC pages.
New CAN vi e we r
Old CAN viewer.
Select the cursor fields to scroll
and the Quit
See also the chapter Log.
Use the cur sor keys or the sc roll
bar to scroll. Exit the viewer with
the Exit button or the ESC key
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 81
Page 83

CAN BUS
Shows the total number of recorded CAN
messages
Page
CAN bus
Function
Date and time of the first CAN message
Page
CAN bus
Data type
Selection On/Off
Default value
Off
Typical value
Off
Function
Selects the activation of the message viewer
Page
CAN bus
MESSAGE VIEWER
The functio n Actions – Erase deletes the CAN message file. Note
that this operation also set the parameter Message viewer to Off.
TOTAL RECORDS
Function
Note This information field shows the tota l number of CAN
messages. This value can be reset by the function Actions –
Reset total records.
INITIAL DATE AND TIME
MESSAGE VIEWER
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 82
A confirmation is requested when the setting of this
parameter is changed.
Page 84

CAN BUS
Note First set the parameter Records to keep, sinc e changing this
parameter will set the parameter Message viewer to Off.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 83
Page 85

CAN BUS
Data type
Selection Yes/No
Default value
Yes
Typical value
Yes
Function
Selects if pop-up messages are used
Page
CAN bus
Function
Shows the number of recorded CAN messages
Page
CAN bus
Data type
Number
Default value
None, must be programmed
Typical value
500
Value range
0 to 5000
Limits the number of CAN messages recorded
in the message file
Page
CAN bus
POP UP
When set to Yes, cer tain important CAN errors are shown
immediately to the operator in a pop-up message window. These
messages are also recorded in the CAN message file.
RECORDS
Note This information field shows the total number of recorded
messages in the log file. The function Actions – Erase
deletes the log file and sets the parameter Message viewer to
Off.
RECORDS TO KEEP
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 84
Function
Page 86

CAN BUS
Data type
Selection DNC peripheral
Default value
Internal
Typical value
Internal
Function
Defines where the CAN message file is stored
Page
CAN bus
Data type
Selection DNC peripheral
Default value
Internal
Typical value
Peripheral like Floppy, USB or Network
Defines to which peripheral the CAN message
file will be copied to
Page
CAN bus
Note Changing the setting of t he parameter Records to keep will
set the parameter Message viewer to Off.
MESSAGE FILE IN
COPY MESSAGE FILE TO
Function
Note Use the function Actions – Copy to copy the message file to
the selected peripheral.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 85
Page 87

BEAM PARAMETERS
BEAM PARAMETERS
INTRODUCTION
Many parameters are provided to permit optimal adjustment for all
machine configurations and the various hydraulic systems in use.
Virtually all beam parameters have a single, specific function. A few
exceptions to this rule exist. In these cases, the parameter description
details the particular functions.
Changing the setting of a parameter with a single, specific function
does not directly affect another parameter or function. For example,
changing the high speed voltage down does not directly affect the low
speed down or the return movement of the beam. Note, however, that
this does not mean that c hanging a given parameter will not require to
adapt another parameter: For example, changing the high speed
voltage down normally also requires to adapt the deceleration ramp
and/or –distance parameters.
As a rule, changing a parameter will also require to adapt one or more
other parameters, which in turn could even require further par ameter
changes. Consult the special chapters Beam cycle and Beam
positioning, these chapters provide a global overview and show
many details about the relations between the various parameters.
Note that this document is not intende d as a start-up instruction guide
or user operation manual. The main purpose of this document is to
describe the function of the parameters, their limit values as well as
the default- and usual values. For a number of beam parameters, a
basic adjustment procedure is given, and in some cases also details
about the relation to other parameters. Refer to the specific
documentation for information about start-up procedures,
programming of the DNC, etc.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 86
Page 88

BEAM PARAMETERS
HYDRAULIC SYSTEMS
DIFFERENTIAL - AND COUNTER PRESSURE SYSTEM
The main types of hydraulic systems used for press brakes are the
differential system and the counter-pressure system.
The differential system was the first s ystem used. In this
configuration, the oil from the bottom side of the cylinders is fed to
the top side. This helps to fill the top side during the fast approach,
and increases the bending speed at the expense of a reduction of the
bending force. The differential system requires a minimum pressure
(giving a mi nimum bendi ng force) during bendi ng t o avoid
overspeeding, and is no longer used for new machines.
In the counte r-pressure configuration, the oil from the bottom side
flows through a pressur e relief valve to tank during the bending
operation. This is the most common system in use now. When the
counter pressure is set correctly, overspeeding during bending is not
possible. Note that although not required to avoid overspeeding, a
minimum system pressur e (giving a mi nimum bending force) is
required for proper BDC closed loop position regulation.
PRESSURE BALANCE
The hydraulic system can be equipped with a pressure balance system.
The purpose of this system is to keep a constant, low pressure drop
across the proportional valves by automatic limitation of the system
pressure. Some pressure balance systems are only active during the
return movement of the beam; others are also active during the
bending cycle. Because of the automatic pressure limitation, the
pressure balance system makes it more complicated to set the pressure
parameters. In most cases, the effective pressures set by the pressure
parameters can only been seen when the ram movement is obstructed
(end of stroke of the cylinders, closed tools).
Note that an active pressure b alance system during the bending cyc le
constitutes a second regulation loop. Especially during BDC
regulation, this regulation loop may interfere with the position
regulation loop of the DNC, and require adapting some parameters.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 87
Page 89

BEAM PARAMETERS
Flow
Control
Voltage
Zero overlap
Flow
Control
Voltage
Positive overlap
VALVE OVERLAP
The main types of regulation valves used for press brakes are valves
without overlap (or zero overlap) and valves with a positive overlap.
See the image below:
Zero overlap valves were commonly used in the past. At present,
mainly valves with a positive overlap are used because these valves
are cheaper and easier to integrate in a safety system. Because of the
positive overlap, these valves can be more difficult to adjust and they
usually require higher voltage settings than for zero ove rlap valves.
Throughout this document, the typical values for beam voltage
parameters assume zero-overlap valves. Some valve amplifiers
electrically compensate a positive overlap. In this case, the beam
voltage parameters are very similar to the settings for zero overlap
valves. A positive overlap can also be compensated by P20a, Min.
voltage Y1 - Y2. As a rule, the overlap is only partially
compensated. See the description of this parameter for further details.
When the overlap is not or only partially compensated, the typical
values shown in this document must, of course, be increased to
account for the non compensated overlap. The required increase is
typically 0.5 to 1V.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 88
Page 90

BEAM PARAMETERS
PRESS BRAKE TYPES
Two types of press brakes exist: downstroking and upstroking
machines. The type of press brake can be selected by P62, Press, as
Downstroke or as Upstroke.
For the downstroking machines, the lower beam is fixed. The upper
beam moves down from TDC to BDC during the bend operation, and
then returns back up to TDC.
For the upstr oking machines, the upper beam is fi xed. The lo we r beam
moves up from BDC to TDC during the bend operation, and then
returns back down to BDC.
Basically, all parameters are identical for both types. The main
difference is the inversion of TDC and BDC in the parameter names.
Also, a standard downstroking press does not require hydraulic
pressure during the fast approac h closing movement, whereas the
upstroking press brake requires system pressure to lift the lower beam.
For the opening movement, the pressure requirements are, of course,
inverted. Further, the i ndexatio n cycle of the b eam is different for the
two types.
Unless specifically stated, a downstroking type press brake is assumed
throughout this document.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 89
Page 91

BE AM MO DE S
electrical panel
Regulation
Automatic
Adjustment
Sensitive
Auto
BEAM MODES
OPERATING MODES
The operating mode of the machine is determined by the selection of
the operating mode of the DNC and the selection of the operating
mode on the electrical panel.
The operating modes of the DNC are:
Programming
Manual
Semi-Automatic
Automatic
The operating modes of the electrical panel are defined by the digital
inputs Regulation and Automatic. The s e inputs define the
following modes:
Mode
Note The sensitive mode may not be available on a specific
electrical panel (Machine manufacturer choice).
Input
Active
24V
Not active
0V
Not active
0V
Input
Don’t care
0V or 24V
Not active
0V
Active
24V
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 90
Page 92

BE AM MO DE S
electrical panel
Mode DNC
Function
Beam movement down only in
bending speed, down stroke
P07, Limits Min
No beam down movement
No beam down movement
Beam movement down only in
bending speed, down stroke
limited by P07, Limits Min.
Beam movement down in fast
approach and bending speed.
When BDC has been reached,
adjustment of the beam position
No automatic return to TDC, no
automatic advance to the next
bend in the program.
am movement down in fast
approach and bending speed.
When BDC has been reached, no
automatic advance to the next
bend in the program.
Beam movement down only in
bending speed, down stroke
limited by P07, Limits Min.
Beam movement down in fast
approach and bending speed.
When BDC has been reached,
programmed dwell time. No
automatic advance to the next
bend in the program.
approach and bending speed.
When BDC has been reached,
TDC after the programmed dwell
time.
The following table defines the possible operating modes of the
machine:
Mode
Adjustment Manual
Sensitive
Semi-Auto
Automatic
Manual
Semi-Auto
limited by
allowed.
allowed.
possible with the + and – keys.
.
Auto
Automatic
Manual
Semi-Auto
Automatic
Be
automatic r eturn to TDC and no
automatic return to TDC after the
Beam movement down in fast
advance to the next bend in the
program and automatic return to
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 91
Note Beam movement down is not allowed in DNC mode
Programming. Beam movement up is allowed in all modes.
Page 93

BE AM MO DE S
When the mode on the electrical panel is set to Sensitive
and the mode on the DNC to Semi-Auto or Automatic
, the beam will stay in BDC as long as the down command is
maintained by the operator, and the programmed dwell time is not
taken into account. The ram only returns to TD C when an up
command is given by the o perator.
When the mode on the electrical panel is set to Sensitive
and the mode on the DNC to Semi-Auto the position of the
beam can be adjusted under pressure using the + and – keys:
or : Adjusts the beam position by ±5 measurement
increments (corresponds to ± 0,05 mm with an encoder resolution of
200 I/mm) at each key-press.
or : Adjusts the beam position by ±1 measurement
increment (corresponds to ± 0,005 mm with an encod er resolution of
200 I/mm) at each key-press.
If the manual buttons are maintained pressed more than 2 sec. the
beam will co ntinusely move slowly up or down.
The adjustment of the BDC under pressure is especially useful to
optimize the BDC position for semi-bottoming or hemming bends as
well as to determine the BDC for operations such as material marking
or punching with special tools.
After adjustment, once the beam has returned to TDC, the final BDC
can be copied to the current bend sequence using the actio n Teach.
For a DNC 60 or similar control, the key is used to teach the
final BDC position.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 92
Page 94

BE AM MO DE S
CLOSED LOOP MODES
Depending on machine- and safety requirements, the DNC must react
to an interruption of the machine cycle in differ ent ways. In some
configurations, the beam must automatically return to TDC, while in
other configurations t he beam should remain at the current position. In
some situations, the beam should keep its current position under
pressure, while in other cases the safety requirements do not allow
this. Machine- and safety requirements also determine the appropriate
decompression cycle and the type of slow speed return of the beam.
The machine parameters P01, Closed loop, and P41, Return TDC
Safety, and the input Permanent regulation determine how the
DNC reacts to interruptions of the machine cycle as well as the type of
decompression cycle and slow speed return of the beam.
When the be am is in TDC o r when the down movement is interrupted,
the following situations occur:
• Beam in TDC
When the beam has normally reached TDC, the DNC will keep the
beam in position with TDC regulation. In this mode, the DNC will
automatically move the beam back up, when it has dropped down
too much below the TDC (because of some leakage in the
cylinders or in the hydraulic system). The limit distance can be
adjusted by P52, Ram regulation distance at TDC.
Throughout this document, this type of regulation is referred to as
TDC regulation.
• Down movement interrupted above the safety point
In this case, P41, Return TDC Safety determines if the beam
will automatically return to TDC or stay at the current position.
When set to Yes or when set to External mode and the electrical
panel is not in Sensitive mode, the beam returns to TDC.
Otherwise the beam stays at the current position and the setting of
P01, Closed loop, determines if this position is regulated by the
DNC. When set to 0, the DNC will not regulate the beam position.
Otherwise, the DNC will mainta in the current position as in TDC.
• Down movement interrupted below the safety point
In this case, the beam will stay in the current po sition. When P01,
Closed loop, is set to 0, the DNC will not regulate the beam
position.
Otherwise, the input Permanent regulation determines how to
regulate the beam position.
When the input Permanent regulation is active, the beam is
kept in the current position with reduced pressure and BDC closed
loop position regulation. This means that the SNY and PVY
enable signals as well as the pressure - and proportional valves
remain active.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 93
Page 95

BE AM MO DE S
Throughout this document, this type of regulation is referred to as
BDC closed loop regulation.
Note that the hydraulic system must remain in bending
configuration during the BDC clos ed loop regulation while the
operator has released the down command. Safety regulations
usually do not allow this and restrict the use of the BDC closed
loop regulation. When using a foot pedal, a possible compromise
is the use of a pedal with an intermediate position. In the
intermediate position, the down command is released, while the
input Permanent regulation is active, and the hydraulic system
maintains the bending configurat i on. In this case, the BDC closed
loop regulation is active. When the pedal is fully released, the
input signal Permanent regulation is switched off. This will
switch off the BDC closed loop regulation, and no longer require
the hydraulic system to stay in the bending confi guration.
When the input Permanent regulation is not active, the beam
keeps the current position using T DC regulatio n.
When the input Permanent regulation is switched from active
to not active (switched off), the BDC closed loop regulation is
switched off. This will also switch off the SNY and PVY enable
signals and the pressure - and proportional valves. The beam
continues to keep the current p osition using TDC regulation.
When the input Permanent regulation is switched from not
active to active (switched on), the TDC regulation is maintained.
The BDC closed loop regulation is o nly activate d when
interrupting the down command below the safety point as long as
the input Permanent regulation is active.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 94
Page 96

BE AM MO DE S
The closed loop modes can be summarized as follows:
TDC REGUL ATION MODE
In this mode, the beam is ke pt in positi on with TDC regulatio n. The
DNC will automaticall y move the beam back up, when it has dropped
down too much (because of some leakage in the cylinders or in the
hydraulic system). The limit distance can be adjusted by P52, Ram
regulation distance at TDC.
BDC CLOSED LOOP REGULATION MODE
In this mode, the beam is ke pt in the current position with reduced
pressure and BDC closed loop position regulation. This means that the
SNY and PVY enable signals as well as the pressure - and
proportional valves remain active .
This mode requires that all of the followi ng conditions are met:
P01, Closed loop is set to 1 or 2
Input Permanent regulation is active
DNC operating mode is (semi) a utomatic
Beam is at or below the safety point
If any condition is no longer met, the regulation mode reverts to TDC
regulation. Note that the DNC will not switch from TDC regulation
mode to BDC closed loop regulation mode.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 95
Page 97

BE AM MO DE S
DECOMPRESSION MODES
After reaching the BDC, or when the down move ment is interrupted
below the safety point, a decompression cycle is performed prior to
starting the return to TDC. The purpose of this decompression cycle is
to reduce the (high) pressure on the top side of the cylinder prior to
opening the prefill valves. This avoids a decompression bang due to
the opening of the prefill valves under pressure.
On many systems, the prefill valves open automatically when the
enable signals SNY and PVY for the down movement are switched
off. In this case, especially when the prefill valves open fast, a
decompression bang can occur.
On other systems, the prefill valves are always open in one direction
allowing to fill the top side of the cylinder. In the other direction, from
the cylinder to tank, these valves remain closed unless a pilot pressure
is applied to open them. In this case, the prefill valves remain closed
when the ena ble signals SNY and PVY for the down movement are
switched off (and no decompression bang will occur). The pilot
pressure to open the prefill valves is applied when starting the normal
return to TDC (when the enable signal SPY is switched on).
Depending on the operating conditions, the decompression will be
carried out in one of the following modes:
RETURN MODE (OPEN LOOP MODE)
This mode is used when P01, Closed loop, is set to 0, or when the
input Permanent regulation is not active. Note that once active,
this mode remains active even when the input Permanent
regulation is activated.
In this mode, the enable signal SPY is output as for the normal, high
speed return. During the decompression time, the regulation valves are
set according to P25, Voltage decompression, and the system
pressure valve is set to P36, Pressure decompression. Note that
the prefill valves will open at the start of the decompression cycle.
The opening speed of these valves should be restricted to avoid a
decompression bang.
BENDING MODE (CLOSED LOOP MODE)
This mode is used when P01, Closed loop, is set to 1 or 2, and the
input Permanent regulation is active. Note that the mode will
switch to return mode (open loop mode) when the input Permanent
regulation is deactivated.
In this mode, the hydrau lic system remains in the bending
configuration, and the prefill valves remain closed. The DNC tries to
move the beam up with the speed set in P13, Max bending speed
. The settin g of the regulation valves is limited to the voltage of
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 96
Page 98

BE AM MO DE S
P21, LS voltage , and the system pressure valve is set to P36,
Pressure decompression.
The prefill valves will open after the decompression cycle. A
decompression bang will not occur, provided that the pressure on the
top side of the cylinders has sufficiently decreased during the
decompression cycle.
The closed loop decompression mode provides optimum
decompression control. Note, however, that the hydraulic system must
remain in be nding confi guration d uring the decompression, also when
the operator releases the down command. Safety regulations usually
do not allow this and restrict the use of the closed loop decompression
mode. In some cases, the SPY enable signal can be used instead of
SNY to differ entiate between bendi ng and decompression, resolving
the safety restriction. See P01, Closed loop.
Alternatively, the inp ut Permanent regulation can be active as
long as the operator maintains the down command. While this is the
case, the closed loop decompression mode is permitted. When the
down command is released during the decompression, the
decompression mode will switch from closed loop to open loop mode.
In many cases, this is an acceptable compromise.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 97
Page 99

BE AM MO DE S
SLOW RETURN SPEED MODES
The operator can program a slow speed return from BDC to the pinch
point or during a part of this distance. After the slow speed return, the
DNC switches over to the normal return speed.
Depending on the operating conditions, the slow speed return will be
carried out in one of the following modes:
REDUCED RETURN SPEED MODE (OPEN LOOP
MODE)
This mode is used when P01, Closed loop, is set to 0, or when the
input Permanent regulation is not active. Note that once active,
this mode remains active even when the input Permanent
regulation is activated.
In this mode, the enable signal SPY is output as for the normal, high
speed, return, and the prefill valves are open. Very slow beam speeds
are critical and instable in this hydraulic configuration. Therefore,
P20b, Final approach voltage , is used to set the reduced speed
of the beam, irrespective of the slow return speed programmed by the
operator.
Note that with high return forces (spring l oaded punching tools ,
adiprene dies, high springback material, etc.), the return force may be
sufficient to lift the beam at a high speed. In this case, the beam
movement cannot be controlled by the DNC, because the prefill
valves are open and the oil can freely flow from the top side of the
cylinders t o tank.
BENDING SPEED MODE (CLOSED LOOP MODE)
This mode is used when P01, Closed loop, is set to 1 or 2, and the
input Permanent regulation is active. Note that the mode will
switch to reduced return speed mode (open loop mode) when the input
Permanent regulation is deactivated.
In this mode, the hydrau lic system remains in the bending
configuration, and the prefill valves remain closed. The DNC moves
the beam up with the speed set b y the operator. The maximum speed
is defined by P13, Max bending speed , and the setting of the
regulation valves is limited to the volta ge o f P21, LS voltage .
Note that the speed during the decompression is the slow speed set by
the operator instead of the maximum speed.
Compare to bending, the slow return speed requires a (much) higher
output voltage to the regulating valves. The high cylinder surface ratio
requires this in order to achieve a sufficiently low pressure at the top
side of the cylinders.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 98
Page 100

BE AM MO DE S
The closed loop decompression mode provides optimum slow speed
control. Note, however, that th e hydraulic system must remain in
bending co nfiguration during the slow speed return, also when the
operator has released the down command. Safety regulations usually
do not allow this and restrict the use of t he c losed loop slow return
mode. In some cases, the SPY enable signal can be used instead of
SNY to differentiate between bending and slow speed return,
resolving the safety restriction. Se e P01, Closed loop.
Alternatively, the inp ut Permanent regulation can be active as
long as the operator maintains the down command. While this is the
case, the closed loop slow speed return mode is permitted. When the
down command is released during the slow speed return, the DNC
will switch from closed loop to open loop mode and continue the slow
return as a normal return with a reduced speed. In many cases, this is
an acceptable compromise.
V-DOC-PMPS2EN_V5 99
 Loading...
Loading...