Page 1

™
AS9100 Rev B / ISO9001:2000 Registered Company
Comtech EF Data is an
MDX420 SkyWire
Satellite Network Gateway
Installation and Operation Manual
IMPORTANT NOTE: The information in this do cument supersedes all prev iously published
information for this product. This manual is subject to change without notice.
Part Number MN-MDX420 Revision 6
Page 2

Page 3

Comtech EF Data is an
AS9100 Rev B / ISO9001:2000 Registered Company
MDX420 SkyWire™
Satellite Network Gateway
Installation and Operation Manual
Part Number MN-MDX420
Revision 6
Comtech EF Data, 2114 West 7th Street, Tempe, Arizona 85281 USA, 480.333.2200, FAX: 480.333.2161
Copyright © 2013 Comtech EF Data. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA.
Page 4

Blank Page
Page 5

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
Table of Contents
About this Manual ....................................................................................................................................... i
Warranty Policy .......................................................................................................................................... v
Product Support ......................................................................................................................................... vi
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION ................................................................................... 1–1
1.1 SkyWire Product Overview ....................................................................................................... 1–1
1.2 MDX420 Simple Block Design ................................................................................................... 1–2
1.3 Understanding TDMA ................................................................................................................ 1–3
1.4 SkyWire TDMA Network .......................................................................................................... 1–4
1.4.1 SkyWire Network Share Group ............................................................................................ 1–5
1.4.2 SkyWire Eight Site Mesh Network Example ........................................................................ 1–6
1.4.3 SkyWire Sixteen Site Mesh Network Example .................................................................... 1–7
1.4.4 SkyWire Eight Site Hub / Spoke (Star) Network Example .................................................. 1–8
1.5 IP Ethernet Data Port ................................................................................................................. 1–9
1.5.1 Quality of Service (QoS) ....................................................................................................... 1–9
1.5.2 CRC Control Satellite Packet Error Checking .................................................................... 1–10
CHAPTER 2. SKYWIRE HARDWARE & SOFTWARE CONFIGURATIONS ............. 2–1
2.1 SkyWire Features and Options .................................................................................................. 2–1
2.2 Standard Configuration ............................................................................................................. 2–1
2.3 Hardware Options ...................................................................................................................... 2–1
2.4 Software Options ......................................................................................................................... 2–2
2.5 Hardware Field Upgrades .......................................................................................................... 2–2
CHAPTER 3.
UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION ..................................................... 3–1
3.1 Installation Requirements .......................................................................................................... 3–1
3.2 Unpacking .................................................................................................................................... 3–2
3.3 AC Power Requirements ............................................................................................................ 3–2
3.4 Installation Considerations ........................................................................................................ 3–2
iii
Page 6

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
CHAPTER 4. FRONT & REAR PANEL INTERFACES .............................................. 4–1
4.1 Front Panel .................................................................................................................................. 4–1
4.1.1 Front Panel Status Indicators ................................................................................................ 4–1
4.2 Front Panel LED Status Indicators ........................................................................................... 4–2
4.3 Rear Panel Connections.............................................................................................................. 4–3
4.3.1 Compact Flash (J5) ............................................................................................................... 4–3
4.3.2 Power Input Modules ............................................................................................................ 4–3
4.3.2.1 AC Power Input Module ................................................................................................... 4–3
4.3.2.2 DC Power Input (Optional) ............................................................................................... 4–3
4.3.3 Chassis Connections (Standard) ............................................................................................ 4–3
4.3.3.1 TX IF (J9) ......................................................................................................................... 4–3
4.3.3.2 RX IF (J8) ......................................................................................................................... 4–4
4.3.3.3 Alarm (J6) ......................................................................................................................... 4–4
4.3.3.4 Service Port (J7) ................................................................................................................ 4–5
4.3.3.5 Control Port, Ethernet 10/100 (J1 & J2) ........................................................................... 4–5
4.3.3.6 Data Port, Ethernet 10/100/1000 (J3 & J4) ....................................................................... 4–6
CHAPTER 5. CONFIGURING THE MDX420 SKYWIRE ............................................ 5–1
5.1 Initial Setup of the MDX420 SkyWire ...................................................................................... 5–1
5.2 Function Accessibility ................................................................................................................. 5–1
5.3 Initial Configuration Check ....................................................................................................... 5–1
5.3.1 Standard Factory Configuration Settings .............................................................................. 5–2
5.4 Initial Power-Up .......................................................................................................................... 5–2
5.5 Monitor and Control ................................................................................................................... 5–2
5.5.1 Ethernet Control Port Factory Defaults: ............................................................................... 5–2
5.5.2 Control Port (J1 & J2) ........................................................................................................... 5–2
5.5.3 Service Port (J7) .................................................................................................................... 5–2
CHAPTER 6. TERMINAL SCREENS .......................................................................... 6–1
6.1 Service Port User Interface ........................................................................................................ 6–1
6.2 Description of the Service Port (J7) ........................................................................................... 6–1
6.2.1 Terminal Screens .................................................................................................................. 6–1
6.2.2 Reserved ................................................................................................................................ 6–2
6.2.3 Connecting to the Service Port (J7) ...................................................................................... 6–2
6.2.4 Terminal Screens .................................................................................................................. 6–3
6.2.4.1 Main Menu ........................................................................................................................ 6–3
6.2.4.2 Demodulator Menu Options and Parameters .................................................................... 6–4
6.2.4.3 Modulator Menu Options and Parameters ........................................................................ 6–6
6.2.4.4 System Controls ................................................................................................................ 6–8
iv
Page 7

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
6.2.4.5 Demodulator Alarms ......................................................................................................... 6–9
6.2.4.6 Modulator Alarms ........................................................................................................... 6–10
6.2.4.7 System Alarms ................................................................................................................ 6–11
6.2.4.8 TCP/IP/FTP Controls ...................................................................................................... 6–12
6.2.4.9 SNMP V1 & V2 Controls ............................................................................................... 6–14
6.2.4.10 SNMP V3 Controls ......................................................................................................... 6–15
6.2.4.11 Event Log ........................................................................................................................ 6–17
6.2.4.12 Test Diagnostics .............................................................................................................. 6–18
CHAPTER 7. SKYWIRE CONTROLLER GUI ............................................................. 7–1
7.1 SkyWire Controller Graphical User Interface (GUI) .............................................................. 7–1
7.2 Installing the SkyWire Controller GUI .................................................................................... 7–2
7.3 Connect and Login ...................................................................................................................... 7–4
7.3.1 Destination Configuration Screen ......................................................................................... 7–4
7.3.1.1 Destination Name .............................................................................................................. 7–5
7.3.1.2 IP Address ......................................................................................................................... 7–5
7.3.1.3 SNMP Version .................................................................................................................. 7–5
7.3.1.3.1 SNMPV2 ........................................................................................................................... 7–5
7.3.1.3.2 SNMPV3 ........................................................................................................................... 7–6
7.3.1.4 Polling Interval .................................................................................................................. 7–6
7.4 SkyWire Controller Configure Tab .......................................................................................... 7–7
7.4.1 Configure Satellite Link ........................................................................................................ 7–8
7.4.1.1
Modulator Configuration .................................................................................................. 7–8
7.4.1.2 Demodulator Configuration .............................................................................................. 7–9
7.4.1.3 BUC and LNB Configuration ......................................................................................... 7–10
7.4.1.4 AUPC Configuration ....................................................................................................... 7–11
7.4.2 Configure Terrestrial Interface ............................................................................................ 7–14
7.4.3 Configure Network Configuration ...................................................................................... 7–16
7.4.4 Configure Test and Diagnostics .......................................................................................... 7–19
7.4.5 Configure System Configuration ........................................................................................ 7–20
7.4.6 Configure Alarms ................................................................................................................ 7–22
7.4.7 Configure Share Group ....................................................................................................... 7–25
7.4.8 Configure TCP/IP Settings .................................................................................................. 7–28
7.5 Tools Tab ................................................................................................................................... 7–30
7.5.1 Options ................................................................................................................................ 7–30
7.5.2 Firmware Status .................................................................................................................. 7–31
7.6 Main Screen / Home Screen ..................................................................................................... 7–32
7.6.1 Demodulator Status Screen ................................................................................................. 7–32
7.6.2 Network Status Screen ........................................................................................................ 7–34
7.6.3 Alarm Status Screen ............................................................................................................ 7–35
7.6.4 Events Log Screen .............................................................................................................. 7–35
7.7 Defining User Access Controls (SNMPv3) .............................................................................. 7–36
7.7.1 Setup Terminal Access parameters ..................................................................................... 7–36
v
Page 8

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
7.7.2 Setup SkyWire Controller Access Parameters .................................................................... 7–38
7.7.3 The SNMPv3 Login Menus ................................................................................................ 7–39
7.7.4 SNMPv3 User Profile Configuration .................................................................................. 7–39
CHAPTER 8. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................... 8–1
APPENDIX A. UPGRADE PROCEDURE .................................................................... A–1
A.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................ A–1
A.2 Required Equipment ................................................................................................................. A–1
A.3 Permanent Upgrade Procedure ................................................................................................ A–1
A.4 Demonstration Upgrade Procedure ......................................................................................... A–2
A.5 Canceling Demonstration Mode ............................................................................................... A–3
APPENDIX B. TCP/IP ETHERNET SETUP ................................................................. B–1
B.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................ B–1
B.2 TCP/IP Network Configuration ............................................................................................... B–1
B.3 Network Co nfiguration Summary ............................................................................................ B–3
B.4 Ethernet Test .............................................................................................................................. B–3
B.4.1 Connecting the Gateway Ethernet Cable to a Network Link ............................................... B–3
B.4.2 Connecting the Gateway Ethernet Cable Directly to a Computer (without a Network) ..... B–3
B.4.3 Testing the Ethernet connection using the Ping Program (Optional) ................................... B–6
APPENDIX C. SKYWIRE QUALITY OF SERVICE ..................................................... C–1
C.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................ C–1
C.2 The Relationship Between IP and Other Protocols ................................................................ C–1
C.2.1 IEEE Tagged Packets ........................................................................................................... C–2
C.2.2 IPv4 Packets with a Type of Service field (RFC 791) ......................................................... C–3
C.2.3 IPv4 Packets with a Differentiated Services field (RFC 2474) ............................................ C–4
C.2.4 IPv6 Traffic Class (RFC 2460) ............................................................................................ C–5
C.3 Programmable Ingress Policies ................................................................................................. C–6
C.3.1 Normal QOS ........................................................................................................................ C–6
C.3.2 Port Based QOS ................................................................................................................... C–6
C.3.3 Programmable Egress Policies ............................................................................................. C–7
C.3.4 Fair Weighted Queuing ........................................................................................................ C–7
C.3.5 Strict Priority Queuing ......................................................................................................... C–7
C.4 Additional capabilities ............................................................................................................... C–8
vi
Page 9

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
C.4.1 Automatic Learning and Aging ............................................................................................ C–8
C.4.2 Satellite Packet Error Checking ........................................................................................... C–8
C.4.3 A Daisy Chain Capability .................................................................................................... C–9
C.4.4 In-band Control .................................................................................................................... C–9
C.4.5 Internal Buffer and Flow Control Throttle ........................................................................... C–9
C.4.6 Auto Everything Ethernet ports ......................................................................................... C–10
C.4.6.1 Auto Crossover .............................................................................................................. C–10
C.4.6.2 Auto Polarity .................................................................................................................. C–10
C.4.6.3 Auto Negotiation ............................................................................................................ C–10
C.4.6.4 Transparent Operation .................................................................................................... C–10
C.4.7 Adding Acceleration, Compression, Network Security, and Traffic Shaping ................... C–10
vii
Page 10

MDX420 SkyWire Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Table of Contents MN-MDX420
Blank Page
viii
Page 11

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
PREFACE
About this Manual
This manual gives installation and operation information for the Comtech EF Data
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway. This manual is intended for anyone who
installs or operates the unit.
Patents and Trademarks
See all of Comtech EF Data’s Patents and Patents Pending at
http://patents.comtechefdata.com.
Comtech EF Data acknowledges that all trademarks are the property of the trademark
owners.
Copyright
2013 Comtech EF Data Corp. All rights reserved.
Cautions and Warnings
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury.
CAUTION indicates a hazardous situation that, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury. CAUTION may also be used to indicate other unsafe practices or
risks of property damage.
IMPORTANT or NOTE indicates information critical for proper equipment function, or a
statement that is associated with the task being performed.
i
Page 12

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
Electrical Safety
The MDX420 has been shown to comply with the EN 60950-1 Safety of Information
Technology Equipment (including electrical business machines) safety standard.
The equipment is rated for a nominal operating range of 100 - 240 volts AC or an appropriately
equipped DC option, nominal operating range is 48+/-5 volts DC . The unit has a maximum power
consumption of 250 watts.
Battery
WARNING
The modem contains a Lithium Battery. DANGER OF EXPLOSION EXISTS if the
battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or equivalent type
recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries in accordance
with local and national regulations.
Grounding
Fuses
CAUTION
CORRECT GROUNDING PROTECTION REQUIRED: The installation instructions
require that the integrity of the protective earth must be ensured and that the
equipment shall be connected to the protective earth connection at all times.
Therefore, it is imperative during installation, configuration, and operation that
the user ensures that the unit has been properly grounded using the ground
stud provided on the rear panel of the unit.
In Finland: "Laite on liitettävä suojamaadoituskoskettimilla varustettuun
pistorasiaan."
In Norway: “Apparatet må tilkoples jordet stikkontakt.”
In Sweden: “Apparaten skall anslutas till jordat uttag.”
The MDX420 contains no Fuses.
ii
Page 13

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
Environmental
The MDX420 must not be operated in an environment where the unit is exposed to precipitation;
condensation; humid atmospheres above 95% RH; altitudes (unpressurized) greater than 2000
metres; excessive dust or vibration; flammable gases, corrosive or explosive atmospheres; or
extremes of temperature outside the ambient range 0 to +50°C. Maximum storage temperature
allowed is -20 to +70°C.
Operation in vehicles or other transportable installations that are equipped to provide a stable
environment is permitted. If such vehicles do not provide a stable environment, safety of the
equipment to EN 60950 may not be guaranteed.
Installation
CAUTION
PROPER GROUNDING PROTECTION IS REQUIRED – REFER TO THE
GROUNDING ‘CAUTION’ NOTE PROVIDED ON THE PREVIOUS PAGE. The
MDX420 is designed for connection to a power system that has separate ground,
line and neutral conductors. The equipment is not
power system that has no direct connection to ground.
designed for connection to a
The installation and connection to the line supply must be made in compliance to local or national
wiring codes and regulations.
The MDX420 is shipped with a line inlet cable suitable for use in the country of operation. If it is
necessary to replace this cable, ensure the replacement has an equivalent specification.
Examples of acceptable ratings for the cable include HAR, BASEC and HOXXX-X. Examples of
acceptable connector ratings include VDE, NF-USE, UL, CSA, OVE, CEBEC, NEMKO, DEMKO,
BS1636A, BSI, SETI, IMQ, KEMA-KEUR and SEV.
International Symbols
Symbol Definition Symbol Definition
Alternating Current
Fuse
Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive
In accordance with the Telecommunications Terminal Equipment Directive 91/263/EEC, this
equipment should not be directly connected to the Public Telecommunications Network.
Protective Earth
Chassis Ground
CE Mark
Comtech EF Data declares that the MDX420 modem meets the necessary requirements for the
CE Mark.
iii
Page 14

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
RoHS Compliance
This unit satisfies (with exemption s) the requirem ents specifie d in the European Uni on Directive on th e
Restriction of Hazardous Substances, Directive 2002/95/EC (EU RoHS).
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
In accordance with European Directive 2004/108/EEC, the MDX420 has been shown, by
independent testing, to comply with the following standards:
Emissions: EN 55022 Class B - Limits and methods of measurement of radio interference
characteristics of Information Technology Equipment.
(Also tested to FCC Part 15 Class B.)
Immunity: EN 55024 – Information Technology Equipment: Immunity Characteristics,
Limits, and Methods of Measurement.
Additionally, the MDX420 has been shown to comply with the following standards:
EN 61000-3-2 – Harmonic Currents Emission;
EN 61000-3-3 – voltage Fluctuations and Flicker.
Connections to the transmit and receive IF ports should be made using a good quality
coaxial cable. For example, RG58 or RG59 for BNC IF connectors and LMR200,
LMR240 or equivalent for the L-band SMA IF ports.
All 'D' type connectors attached to the rear panel must have back-shells that provide
continuous metallic shielding. Cable with a continuous outer shield (either foil or braid, or
both) must be used, and the shield must be bonded to the back-shell.
The equipment must be operated with its cover on at all times. If it becomes necessary to
remove the cover, the user should ensure that the cover is correctly re-fitted before
normal operation commences.
iv
Page 15

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
Warranty Policy
Comtech EF Data products are warranted against defects in material and workmanship for a specific period from the date of shipment, and
this period varies by product. In most cases, the warranty period is two years. During the warranty period, Comtech EF Data will, at its
option, repair or replace products that prove to be defective. Repairs are warranted for the remainder of the original warranty or a 90 day
extended warranty, whichever is longer. Contact Comtech EF Data for the warranty period specific to the product purchased.
For equipment under warranty, the owner is responsible for freight to Comtech EF Data and all related customs, taxes, tariffs, insurance,
etc. Comtech EF Data is responsible for the freight charges only for return of the equipment from the factory to the owner. Comtech EF
Data will return the equipment by the same method (i.e., Air, Express, Surface) as the equipment was sent to Comtech EF Data.
All equipment returned for warranty repair must have a valid RMA number issued prior to return and be marked clearly on the return
packaging. Comtech EF Data strongly recommends all equipment be returned in its original packaging.
Comtech EF Data Corporation’s obligations under this warranty are limited to repair or replacement of failed parts, and the return shipment
to the buyer of the repaired or replaced parts.
Limitations of Warranty
The warranty does not apply to any part of a product that has been installed, altered, repaired, or misused in any way that, in the opinion of
Comtech EF Data Corporation, would affect the reliability or detracts from the performance of any part of the product, or is damaged as the
result of use in a way or with equipment that had not been previously approved by Comtech EF Data Corporation.
The warranty does not apply to any product or parts thereof where the serial number or the serial number of any of its parts has been
altered, defaced, or removed.
The warranty does not cover damage or loss incurred in transportation of the product.
The warranty does not cover replacement or repair necessitated by loss or damage from any cause beyond the control of Comtech EF
Data Corporation, such as lightning or other natural and weather related events or wartime environments.
The warranty does not cover any labor involved in the removal and or reinstallation of warranted equipment or parts on site, or any labor
required to diagnose the necessity for repair or replacement.
The warranty excludes any responsibility by Comtech EF Data Corporation for incidental or consequential damages arising from the use of
the equipment or products, or for any inability to use them either separate from or in combination with any other equipment or products.
A fixed charge established for each product will be imposed for all equipment returned for warranty repair where Comtech EF Data
Corporation cannot identify the cause of the reported failure.
Exclusive Remedies
Comtech EF Data Corporation’s warranty, as stated is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed, implied, or statutory, including those of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. The buyer shall pass on to any purchaser, lessee, or other user of Comtech EF Data
Corporation’s products, the aforementioned warranty, and shall indemnify and hold harmless Comtech EF Data Corporation from any
claims or liability of such purchaser, lessee, or user based upon allegations that the buyer, its agents, or employees have made additional
warranties or representations as to product preference or use.
The remedies provided herein are the buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. Comtech EF Data shall not be liable for any direct, indirect,
special, incidental, or consequential damages, whether based on contract, tort, or any other legal theory.
v
Page 16
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Revision 6
Preface MN-MDX420
Product support
On the web
http://www.comtechefdata.com
Support business hours
Support Business Hours: Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (MST)
After hours and weekends
Brand: Comtech EF Data Tel: +1.480.333.4357
Brand: Radyne Tel: +1.602.980.5220
Comtech EF Data and Radyne support contacts
Products Contact
Satellite Modems
Modem Accessories
Amplifiers
Converters
Transceivers
Terminals
IP-Enabled Satellite Modems
IP-Based Modem Accessories
Encapsulators, Receivers, Filtering & Encryption
turboIP® Performance Enhancement Proxies (PEP)
SkyWire™ MDX420 Satellite Network Gateway
Vipersat Network Products
IP-Enabled Satellite Modems used with VMS
Tel: +1.480.333.4357
Fax: +1.480.333.2500
Email:techsupport@comtechefdata.com
Tel: +1.480.333.2433
Fax: +1.480.333.2161
Email:cdmipsupport@comtechefdata.com
Tel: +1.510.252.1462 - select option #2
Fax: +1.510.252.1695
Email:supportcvni@comtechefdata.com
vi
Page 17

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 SkyWire Product Overview
This manual provides detailed information for the Radyne SkyWire MDX420 Satellite Network Gateway.
When describing the SkyWire gateway, it will be referred to as “the MDX420”, “the gateway”, “the network
gateway”, or “the satellite gateway”. The next few sections will describe theory of operation, setup,
accessing and monitoring the gateway.
The Radyne SkyWire MDX420 Satellite Network Gateway (
Gateway
designed for satellite IP networks.
) is a Closed Network Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Satellite Gateway specifically
Figure 1-1 SkyWire Satellie Network
Figure 1-1 SkyWire Satellie Network Gateway
This satellite gateway combines unsurpassed performance with user-friendly remote access. Monitor and
Control (M&C) functions are available through a secure SNMP V1, V2 or V3 interface. Operating
parameters, such as symbol and data rates, FEC code rate, modulation type, IF/RF frequencies, and
three levels of capacity management can be readily set and changed through the user interface by
authorized earth station operations personnel.
The gateway operates over a data rate range of 328kbps to 21.6Mbps with a symbol rate range of
256ksps to 10Msps.
The gateway's data interface is an Ethernet Bridge 10/100/1000 Base-T interface.
The gateway supplies DC power to the LNB. The gateway has an optional feature to supply 24 or 48
volts to the BUC and an optional feature for a high stability 10MHz reference to the BUC and LNB. The
capability to enable and disable the BUC/LNB voltages and 10MHz reference is available via the Ethernet
SNMP control port. In addition, the gateway monitors both the current and the voltage at the output of the
Tx and Rx Ports, thus providing the user verification of overall system status.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–1
Page 18
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
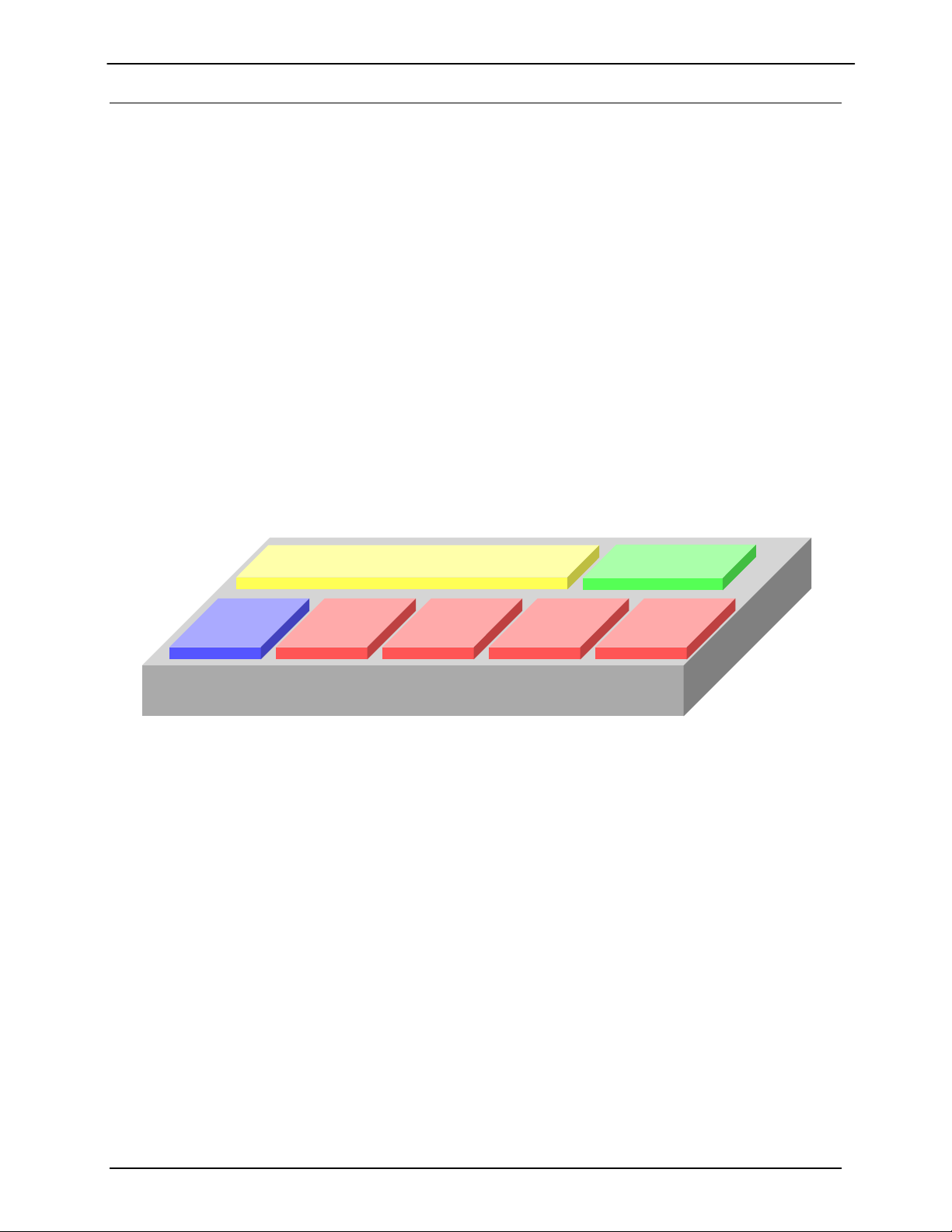
1.2 MDX420 Simple Block Design
The MDX420 satellite gateway is based on a single signal processing printed circuit card desi gned with
one to four optional plug in burst demodulator daughter cards. The minimum configuration consists of a
single signal processing card and a single burst demodulator daughter card with the option to add three
additional burst demodulators for a total of four burst demodulators. The single signal processing printed
circuit board consists of an L-Band burst modulator, the Ethernet interface, and a digital baseband
processor.
Within a SkyWire TDMA satellite network, a gateway has the ability to communicate with up to 32 full
mesh remote sites in a single 1 RU chassis. All units at all locations are based on this sin gle hardware
platform.
Each gateway supports:
One burst Modulator (MOD)
Up to four burst Demods (DEMOD)
Network Control Module for distributed intelligence (NCM)
All gateway IP data traffic passes through a common 10/100/1000 bridge interface.
Optional BUC Power and 10Mhz Reference
MOD DEMOD 1 DEMOD 4DEMOD 3DEMOD 2
Each gateway can:
Transmit one carrier
Simultaneously receive four carriers that do not need to be of the same configuration.
Support a distributed leaderless TDMA network, meaning that there is no HUB and no
single point of failure. The network administrator can log-in through any gateway in a
share group and change the network parameters of any gateway in the share group
10/100/1000 Switch
MDX420
Figure 1-2 MDX420 Block Design
NCM
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–2
Page 19
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
X
L
N
B
B
U
C
X
L
N
B
B
U
C
X
L
N
B
B
U
C
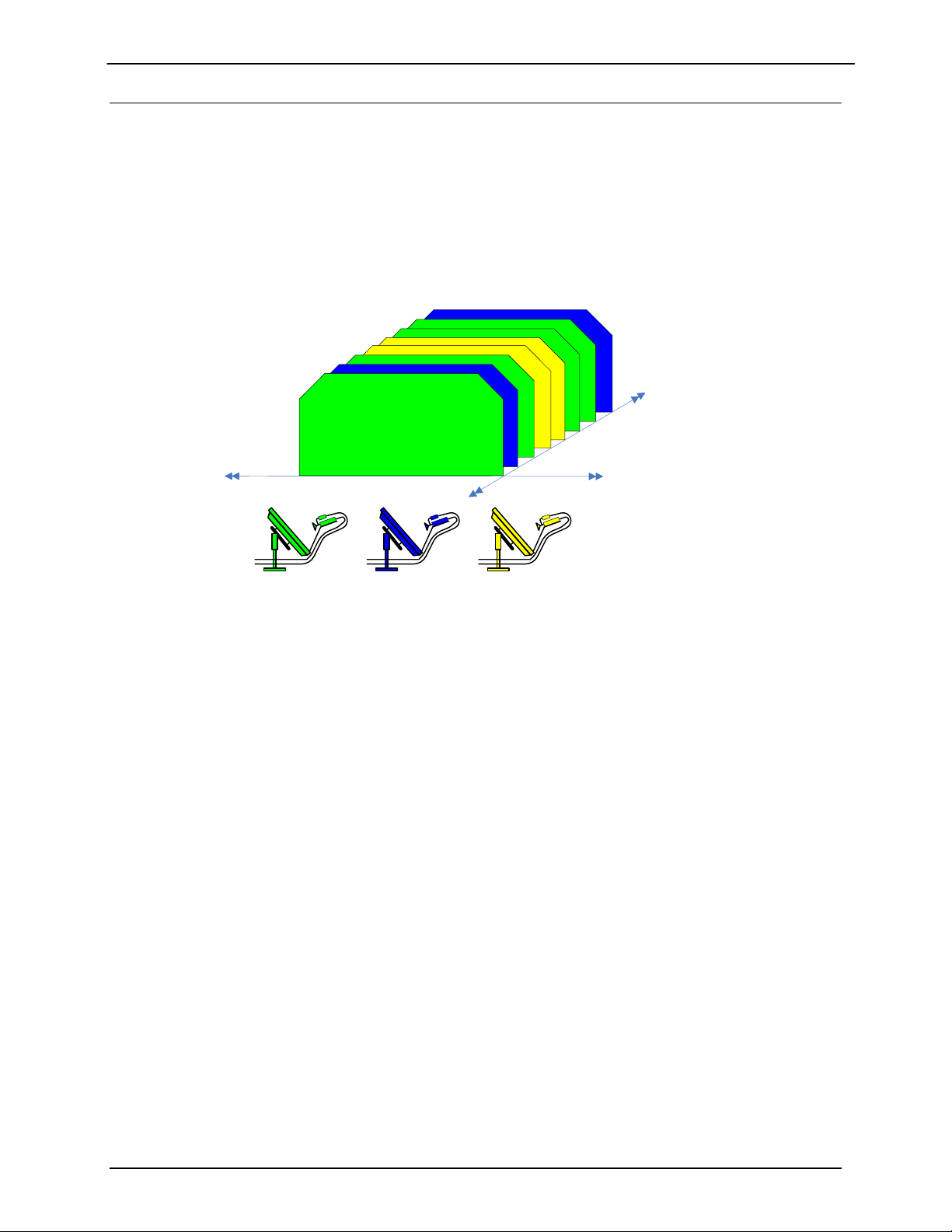
1.3 Understanding TDMA
In a traditional Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) system, a transponder resource is shared
between a number of earth stations based on frequency allocations. In a FDMA system, an earth station
will continuously transmit a single carrier on specific frequency broadcasting to a single receiver or
multiple receivers at different earth stations.
In a TDMA system, a frequency allocation is shared between a number of earth stations based on time
‘slots’. Within a TDMA system, the transponder receives a sequential burst of transmissions from multiple
earth stations broadcasting out to multiple receivers. In traditional “non-skywire” TDMA systems, the time
plan for each earth station’s burst is determined by a central control system at a central location.
Time
Frequency
T
RX
T
RX
T
RX
Figure 1-3 TDMA Access Example
Figure 1-3 shows an example of TDMA access of the satellite frequency allocation. In the example
above, 3 remote sites are sharing a frequency allocation with each site transmitting sequentially. As
stated above, in a TDMA platform, multiple sites “time share” their transmission on the same frequency
carrier and data rates. The aggregate transmission will be received by a hub or participating remotes
allowing each remote to determine which data they need to pass on to the local LAN. The aggregate
transmission reflects multiple bursts from all 3 earth stations transmitting their IP data over satellite to the
all sites in the network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–3
Page 20
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
1.4 SkyWire TDMA Network
The MDX420 gateway is designed for mesh communications. The gateway will transmit on a fixed carrier
frequency and has the capability to receive up to 4 other carriers either on the same satellite or other
satellites. A TDMA shared carrier can support up to 8 gateways all communicating on the same
frequency allocation.
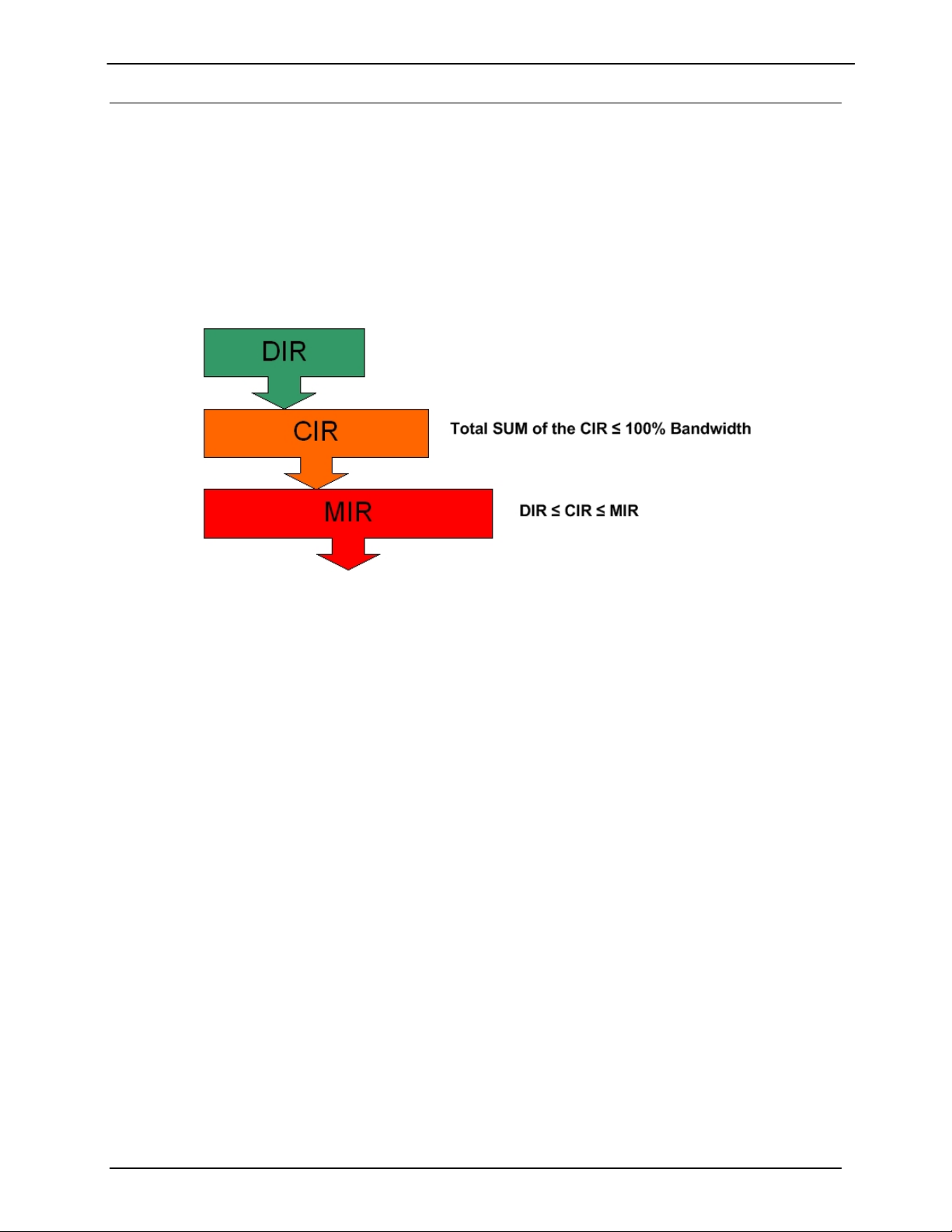
A SkyWire gateway determines the number of bursts it will transmit over satellite. The number of burst
slots per frame is based on the local LAN needs and the needs of the other remotes in the share group.
The gateway uses this information in conjunction with the operator specified Dedicated Information Rate
(DIR), Committed Information Rate (CIR), and Maximum Information Rate (MIR) to determine how many
burst slots it is allocated per frame.
Dedicated Information Rate - throughput in Kbits per second that cannot be used by anyone except the
assigned gateway.
Committed Information Rate – throughput that is available to the user when ever requested, but is pooled
when not in needed by the assigned gateway.
Maximum Information Rate – maximum throughput allowed by the gateway also referred to as the
burstable throughput.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–4
Page 21
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
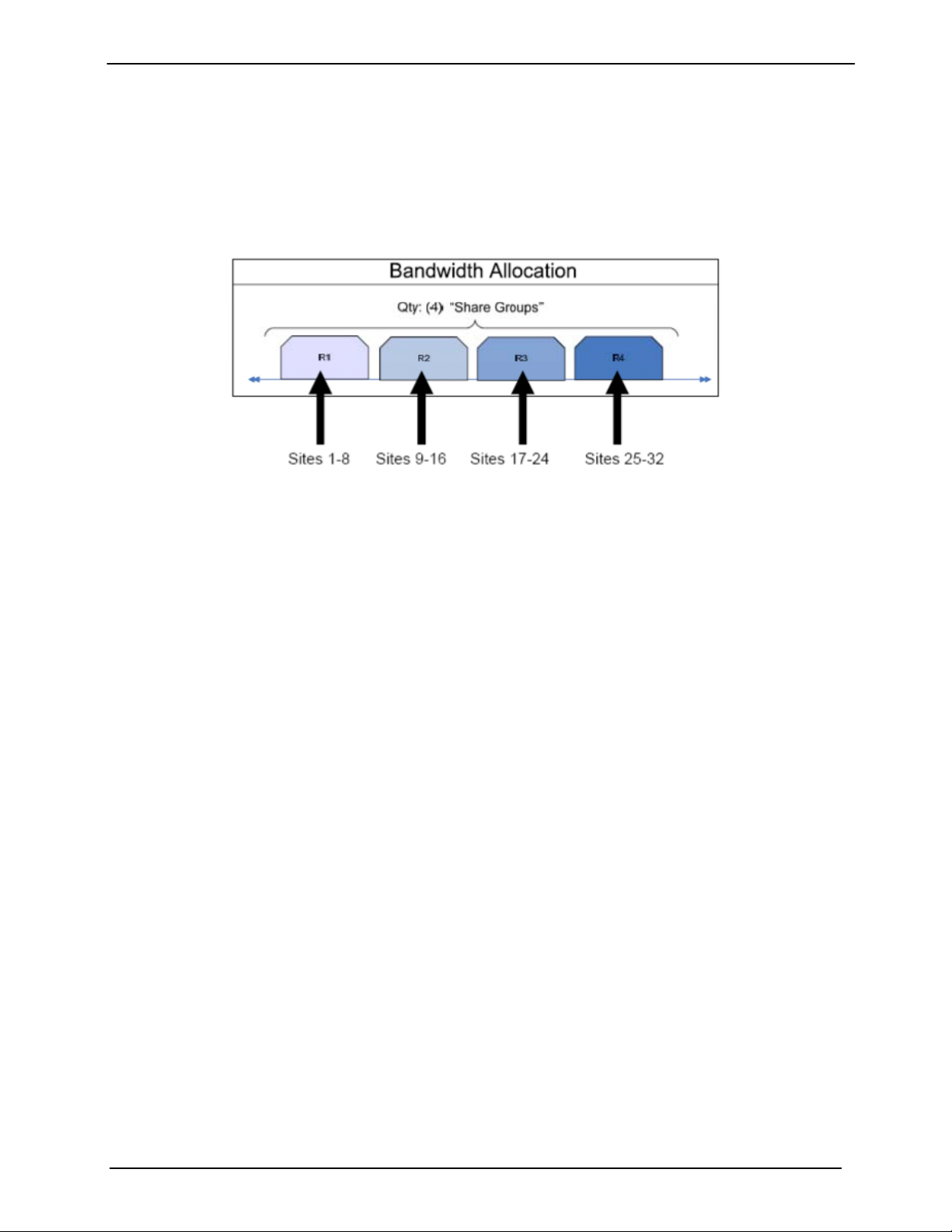
1.4.1 SkyWire Network Share Group
The MDX420 can support up to four burst demodulators. Each burst demodulator receives a single
carrier or “share group” supporting up to 8 gateways. With two burst demodulators installed into an
MDX420, a mesh network can now support up to 16 gateways with a single satellite hop con nectivity.
Since the MDX420 can have up to 4 burst demodulators installed, a gateway can receive 4 share groups
supporting up to 32 gateways in a mesh network using only 1 burst modulator.
Figure 1-4 SkyWire RX System with Four Share Groups
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–5
Page 22
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
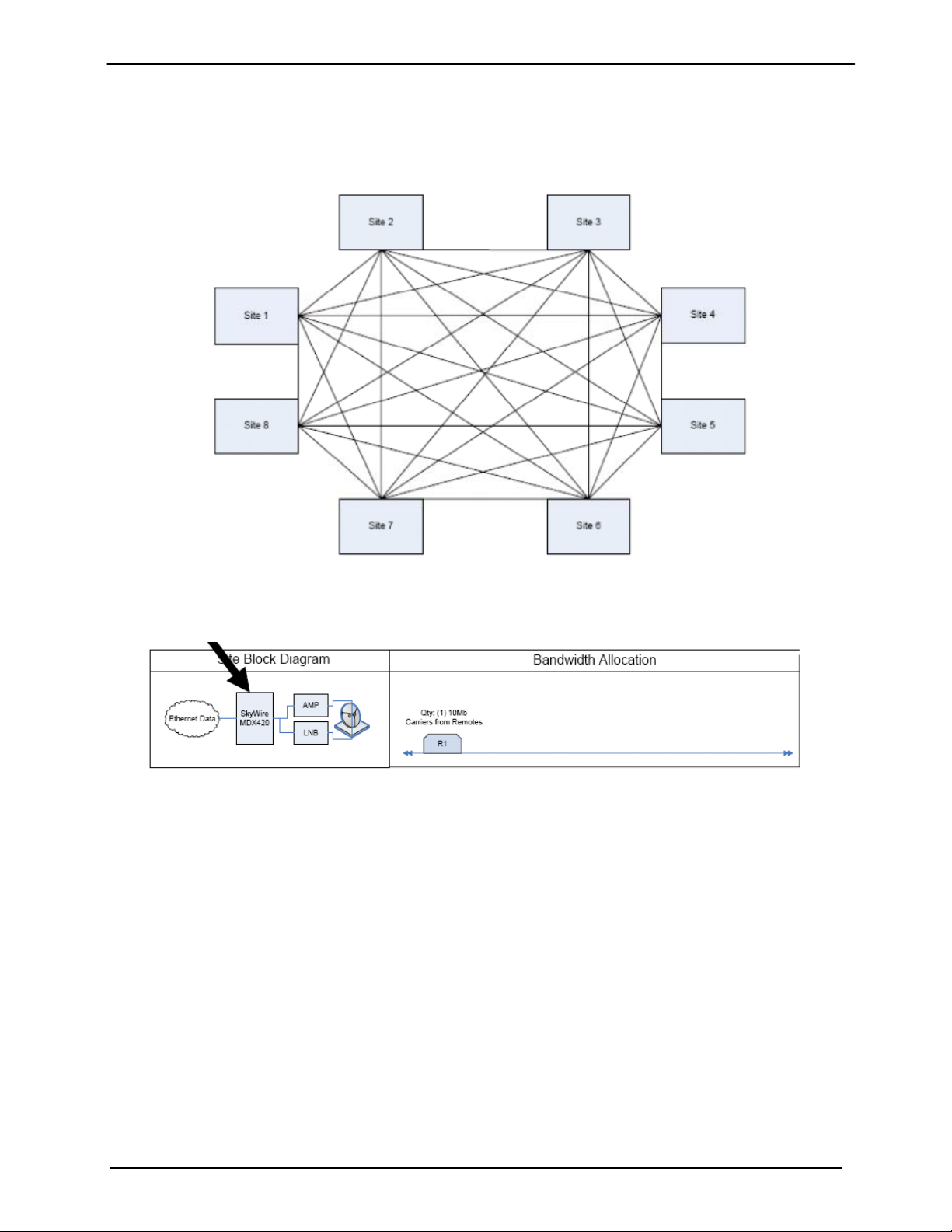
1.4.2 SkyWire Eight Site Mesh Network Example
The example below shows one share group consisting of 8 sites. Each site has a single MDX420 with 1
burst demodulator installed.
One MDX420 per site
Figure 1-5 Eight site Full Mesh Network Diagram
Figure 1-6 Eight Site Full Mesa Network Plan
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–6
Page 23
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
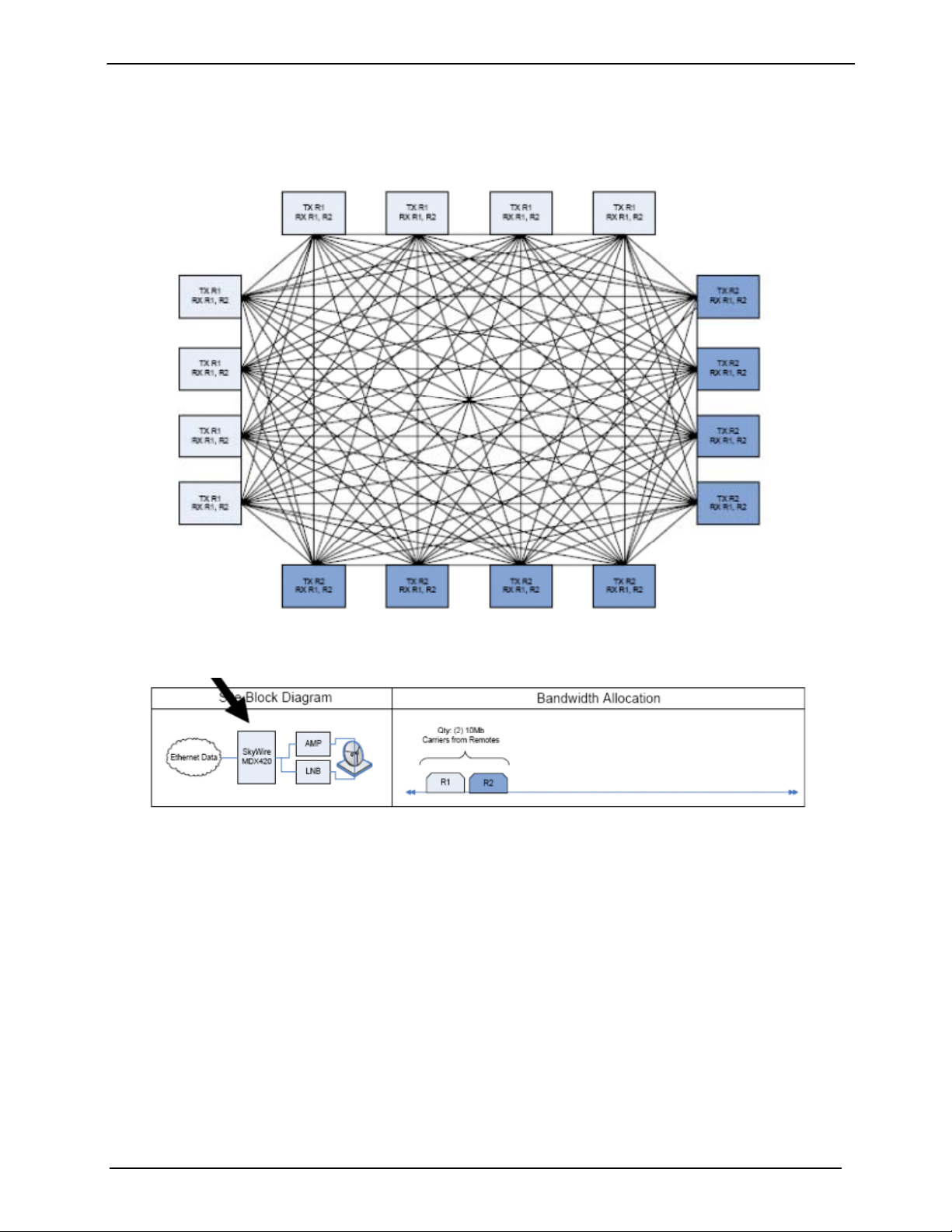
1.4.3 SkyWire Sixteen Site Mesh Network Example
The example below (Figures 1-7 and 1-8) shows two share groups consisting of 16 gateways. Each
gateway has a single MDX420 consisting of a single burst modulator and two burst demodulators. The
addition of a second burst demodulator allows the network to support 16 gateways with a single hop.
One MDX420 per site
Figure 1-7 Sixteen Site Full Mesh Network Diagram
Figure 1-8 Sixteen Site Full Mesh Network Plan
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–7
Page 24
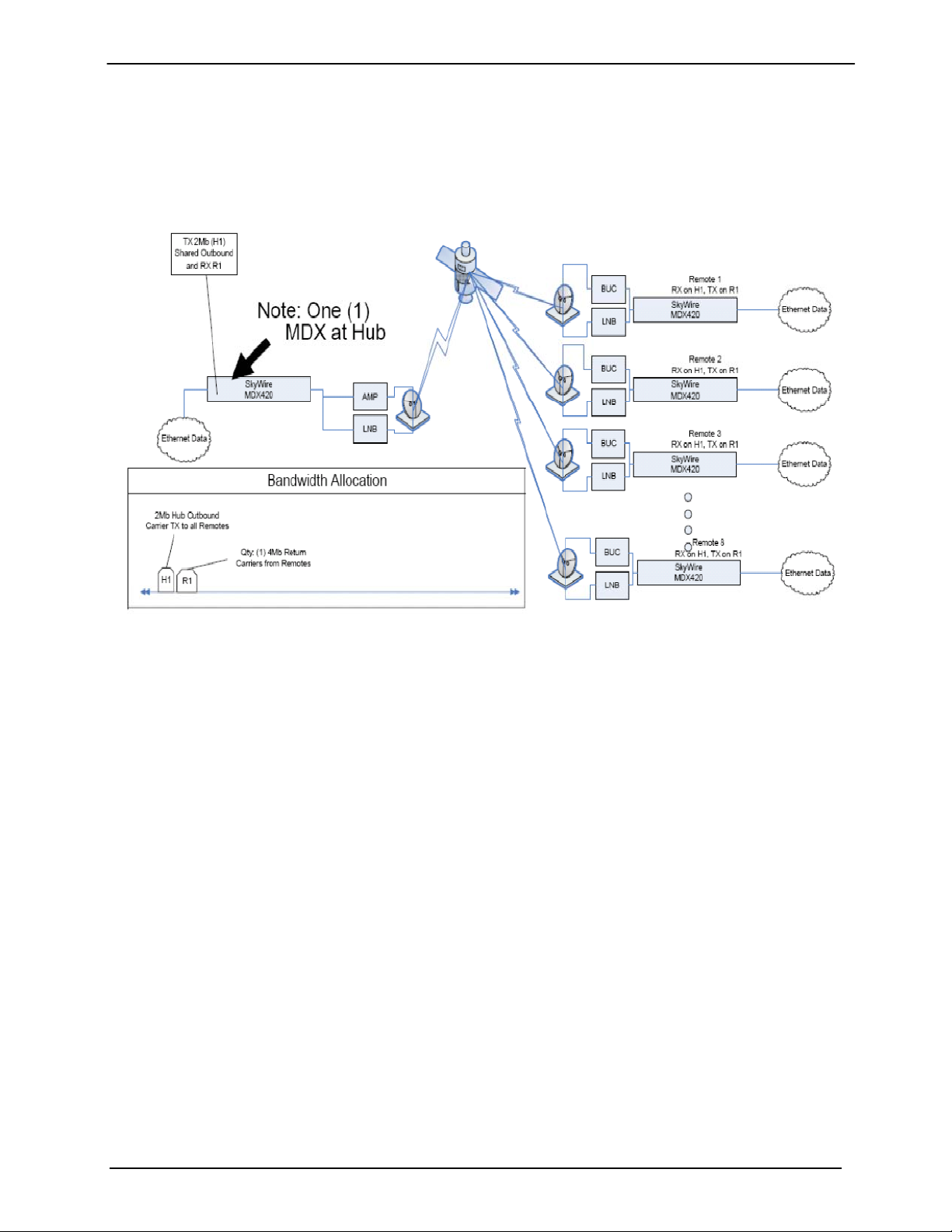
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
1.4.4 SkyWire Eight Site Hub / Spoke (Star) Network Example
The example below (Figure 1-9) shows an eight site Hub / Spoke network with a 2Mbps outbound shared
carrier and a 4Mbit/s inbound shared carrier. Each gateway has a single MDX420 con sisting of a single
burst modulator and two burst demodulators. Remotes have a 256kbps CIR with burstable through-put
up to 4Mbps.
Figure 1-9 Network Diagram of a HUB / SPOKE (Star) Network
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–8
Page 25

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
1.5 IP Ethernet Data Port
The IP data interface on the MDX420 is a dual port 10/100/1000 Ethernet bridge operating at the data link
layer (layer 2). Refer to Appendix C for technical overview of the Gigabit Ethernet Bridge interface.
IP Data Ethernet interface supports:
Automatic learning & aging (stores forwarding database)
Auto Crossover
Auto Polarity
Auto Negotiation (Flow control)
Embedded Quality of Service
CRC Control
For the Ethernet Bridge interface to operate in a normal condition, there is nothing to configure, simply
connect to one of the ports on the back panel.
The Ethernet Bridge interface allows all higher level protocols like IPv4, IPv6, DHCP, UDP, TCP, HTTP,
and FTP to pass transparently.
1.5.1 Quality of Service (QoS)
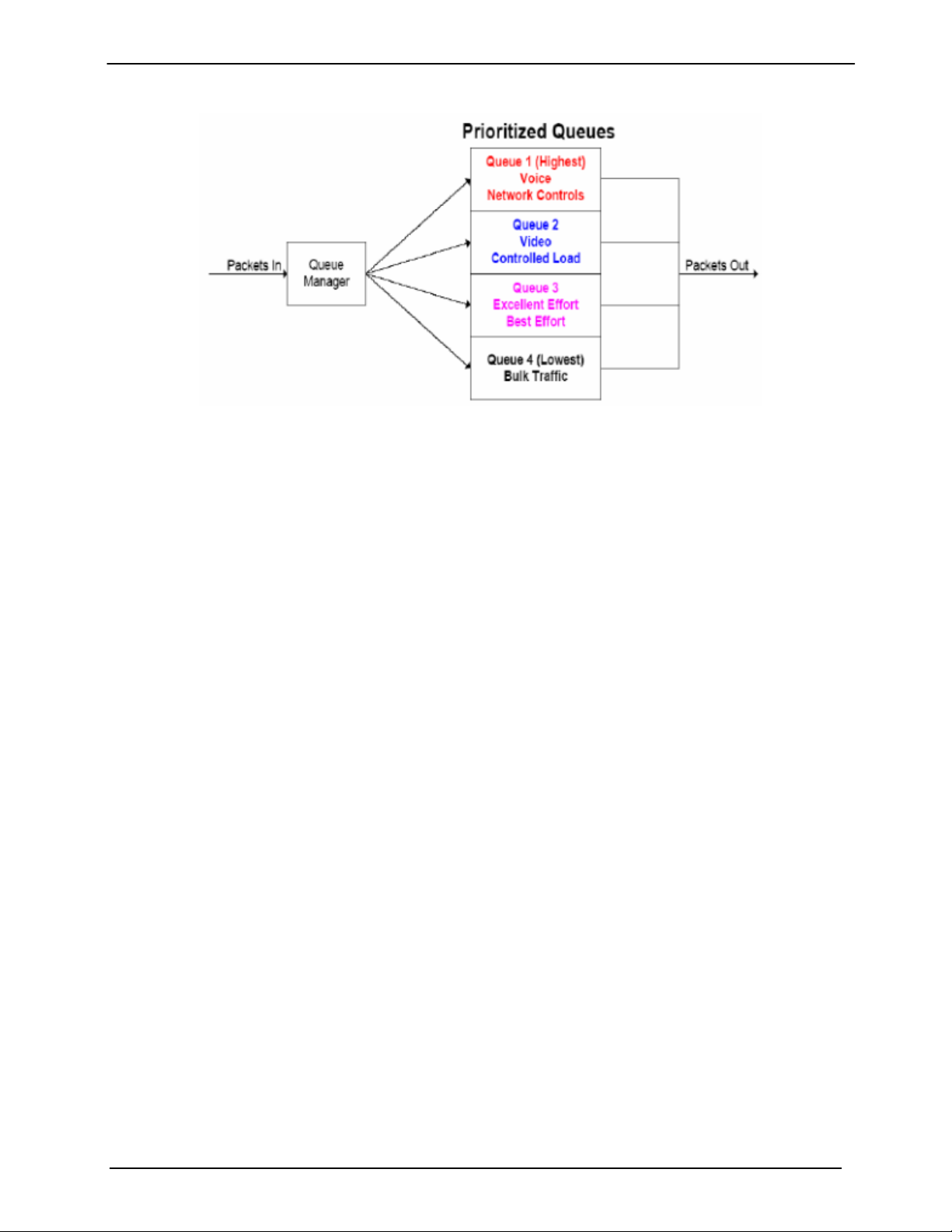
Most networks are comprised of various types of real time and non real time services. SkyWire offers
basic layer 2/3 QoS control, allowing the user to prioritize data queues ensuring that higher priority traffic,
like voice and network control, are not backed up behind lower priority traffic. SkyWire also supports
queuing features that allow the user to prioritize queuing in different ways.
SkyWire Quality of Service (QoS) features includes:
Normal - Uses the following formats (IEEE 803.3ac Tag containing IEEE 802.1p priority
information provided by an external device, Type of Service field (RFC 791) or Differentiated
Services field (RFC 2474) contained in an IPv4 header and Traffic Class field (RFC 2460)
contained in an IPv6 header.
Port Based - In this mode, physical port (J3) has the highest priority and physical port (J4)
has the lowest priority. The Port Based priority overrides any other priority
SkyWire QoS QUEUE features include:
Fair Weighted - Selects the queue weighting of 8,4,2,1 allowing higher priority traffic to pass
through more quickly and insures even the lowest priority traffic gets some bandwidth.
Packets are processed in a weighted round robin manner with 8 having the highest priority.
Strict Priority - Ensures that the higher priority traffic will always be transmitted before any
lower priority traffic. With this setting, higher priority traffic will be immediately transmitted
until the buffer is empty starving all lower priority traffic until upper priority traffic is cleared.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–9
Page 26
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Introduction
Figure 1-10 QoS Priority Queuing
In certain circumstances it may be desirable to have the Ethernet Interface to operate in a FIFO like mode
with no reordering of packets. This can be done by using a single port and setting the Ethernet QoS type
to Port Base and the Ethernet QoS Queue to strict priority. This will allow packets to be transmitted in the
exact order in which they are received.
1.5.2 CRC Control Satellite Packet Error Checking
Packet error checking is a standard part of any terrestrial Ethernet system and is performed using the
CRC contained in the layer 2 Ethernet wrapper. The CRC is used as a checksum to detect alteration of
data during transmission. When a CRC error is encountered, the packet is typically discarded by the
router, switch, or hub in which the error was detected.
A similar methodology is utilized over the satellite link where bit errors result in a corrupted packet with a
bad CRC. For most situations, the standard process of discarding these packets when they are
encountered is the preferred methodology as the packet can simply be retransmitted.
However, there are some cases where the end device would rather receive the erred packet than no
packet at all. Scenarios involving cryptography or where the end device has additional error correction
capability are examples of two such situations. For these customers, the gateway provides the ability to
turn off the satellite packet error checking and packets with bit errors will be output with a valid CRC so
that they will properly pass to the connecting router or switch. Checking the CRC Control box in the
Sattelite Demod Configuration GUI (normal operation) will look for a valid CRC and if not found will drop
the Ethernet datagram. Unchecking the CRC control box will append a valid CRC to a potentially corrupt
Ethernet datagram and pass the datagram to the next device in the chain. Note: CRC control only
functions from the flow of satellite to the Ethernet LAN. Ethernet LAN to satellite flow will always drop bad
CRC datagrams regardless of selection.
Regardless of the configuration of the CRC Control function, enabled or disabled, SkyWire maintains and
reports satellite link statistics on total packets, erred packets, and packet error rate (PER).
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 1–10
Page 27
MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Hardware & Software Configurations
Chapter 2. SkyWire Hardware &
Software Configurations
2.1 SkyWire Features and Options
Hardware and software options are available at time of order. Some options are field
upgradeable.
2.2 Standard Configuration
The MDX420 comes standard with the following features:
AC Power
QPSK modulation with .710 and .793 FEC selection
Standard or Enhanced Eb/No operation
1Mbps maximum transmit data rate
1 Burst Modulator installed
1 Burst Demodulator installed
2.3 Hardware Options
The items below identify specific hardware options and the availability of field upgrade (FLD) or
only at time of order (TOR). Refer to Section 7.3.5, for information on how to view these features
on the MDX420 GUI interface.
DC Input Prime Power (TOR)- Allows for an optional 48 Volt DC Input Power Source.
This is a factory upgrade only.
BUC Power via the IF Output Connector (TOR)- Optional power supply can be added
supporting 24 or 48 Volts to the BUC. This is a factory upgrade only
Additional Burst Demodulators (FLD)- MDX420 comes equipped with 1 burst
demodulator and can be upgraded to add an additional 3 burst demodulator for a
total of 4.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 2–1
Page 28

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Hardware & Software Configurations
2.4 Software Options
Software upgrades are a simple and quick way of adding new features to an installed gateway.
Software upgrades can be easily installed via the GUI interface. Refer to Appendix A, for
information on how upgrade features are enabled.
Maximum transmit data rate can be upgraded to 5Mbps, 10Mbps, or 20Mbps
8PSK modulation
2.5 Hardware Field Upgrades
Hardware options are purchased parts that can be installed by the customer. Please contact the
Comtech Corporation Sales Department for information on price, availability, and shipping costs.
Plug-In Burst Demodulator Cards: MDX420 can support up to 4 Burst Demodulators
Cards.
CAUTION
Always make sure that power is removed from the unit before any optional modules are
installed. Failure to do so may damage the equipment.
IMPORTANT
Make sure that only authorized service personnel handle and install hardware options.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 2–2
Page 29

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Unpacking and Installation
Chapter 3. Unpacking and Installation
This section provides unpacking and installation instructions.
3.1 Installation Requirements
The gateway is designed to be installed within any standard 19-inch (48.26 cm) wide equipment cabinet
or rack. It requires one rack unit (RU) of installation space (1.75 inches/4.45 cm) vertically and 13.0
inches (33.0 cm) of depth. Including cabling, a minimum of 16.0 inches (40.64 cm) of rack depth is
required. The rear panel of the gateway has power entering from the left and IF Cabling entering from the
right (as viewed from the rear of the gateway). Data and Control Cabling can enter from either side.
Please refer to Section 4 for rear panel connector descriptions and pinouts. The gateway can be placed
on a table or suitable surface if required.
WARNING
PROPER GROUNDING PROTECTION
During installation and setup, make sure that the gateway is properly
grounded. The equipment shall be connected to the protective earth
connection through the end user protective earth protection.
Also, make sure that the IF input and output coax cable shielding are correctly
terminated to the Chassis ground.
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
There are no user-serviceable parts or configuration settings inside the
Chassis. A shock hazard exists internally at the power supply module.
DO NOT open the Chassis under any circumstances.
IMPORTANT
When installing the gateway in an equipment rack or any other method,
adequate ventilation must be provided.
The ambient temperature inside the rack must be between 0
held constant for best equipment operation.
The air available to the rack must be clean and relatively dry.
The gateways must not be placed immediately above a high-heat or EMF
Generator to ensure the output signal integrity and proper receive operation.
DO NOT install the gateway in an unprotected location where there is direct
contact with moisture, rain, snow, wind or sun.
and 50C, and
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 3–1
Page 30

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Unpacking and Installation
3.2 Unpacking
The gateway was carefully packaged to avoid damage and should arrive complete with the following
items for proper installation:
MDX420 Gateway Unit
Power Cord
Installation and Operation Manual
(GUI) Configuration Software CD
Documentation Package
The gateway is shipped fully assembled. It does not require removal of the covers for any purpose in
installation.
3.3 AC Power Requirements
The power supply is designed for universal AC application. If the available AC mains power at the
installation site requires a different cord set from the one included in the package, then a suitable and
approved cord set (for the country where the equipment is to be installed) will be required before
proceeding with the installation.
Prime Power: 100 to 240VAC, 50 to 60 Hz Auto Sensing
Wattage: Base unit: less than 40 watts; Base unit with BUC Power: less than 200 Watts.
CAUTION
Before applying power to the gateway initially, disconnect the transmit output from the
operating ground station equipment. If the current configuration settings are unknown
when power is applied, incorrect settings could disrupt existing communications traffic.
3.4 Installation Considerations
The only tools required for rack installation are four (4) customer-supplied rack installation screws and the
appropriate screwdriver. Rack installation brackets are an integral part of the front bezel of the gateway
and are not removable.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 3–2
Page 31

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
Chapter 4. Front & Rear Panel
Interfaces
This section discusses the front panel and rear panel electrical interfaces available on the MDX420.
4.1 Front Panel
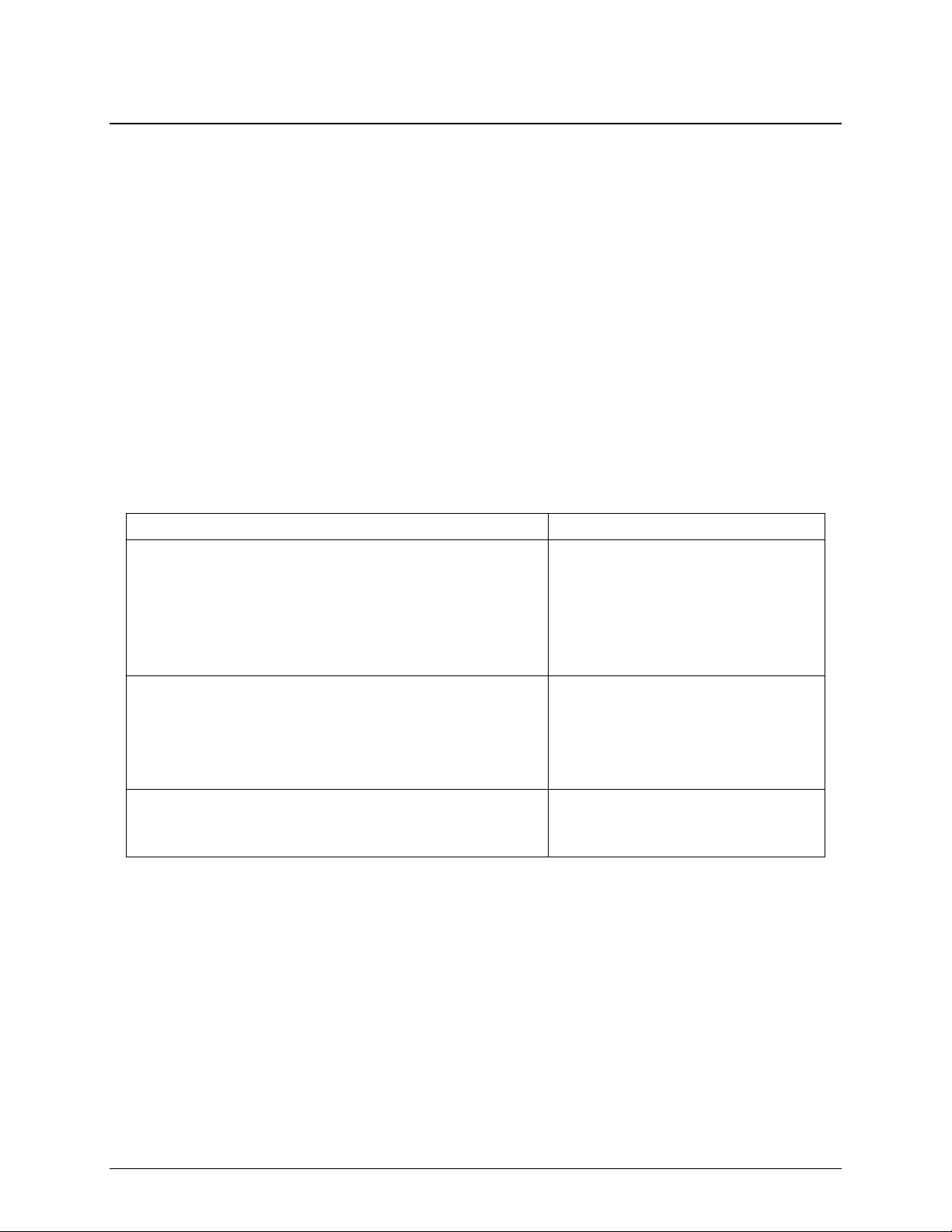
4.1.1 Front Panel Status Indicators
The Front Panel status LEDs allows for quick visual status of the gateway.
The front panel layout is shown in Figure 4-1 and illustrates the location of the front panel status LED’s.
The front panel status LED’s are: Demodulator 1 through 4, Modulator, Common, Test, and Event. The
LED descriptions are shown in Table 4-1.
Figure 4-1 Front Panel
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–1
Page 32

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
4.2 Front Panel LED Status Indicators
Eight LEDs on the Front Panel (Refer to Table 4-1) indicate the status of operation. The LED colors
maintain a consistent meaning.
Table 4-1
LED Color Function
Demodulators LED Indicators 1 - 4
Off Indicates that the burst demodulator in this position is not
present in the gateway.
Signal Lock Green
(normal)
Major Alarm Red Indicates that the burst demodulator is in an alarmed
Minor Alarm Yellow Indicates that a burst demodulator warning condition exists.
Transmit On Green
(normal)
Major Alarm Red Indicates that the burst modulator is an alarmed condition
Minor Alarm Yellow Indicates that a burst modulator warning condition exists.
Off Indicates that the common alarm is not present.
Fault Red Indicates a problem in the gateway’s common circuitry, e.g.
Indicates that the burst demodulator is locked to an incoming
carrier, including FEC synchronization.
condition and not locked to any carrier.
Modulator LED Indicator
Indicates that the burst modulator is ON and transmitting
without fault.
and the gateway is not transmitting.
Common LED Indicator
the power supply or processor.
Test LED Indicator
Off Indicates a none test mode condition.
On Yellow Indicates there is a test mode running in the gateway.
Event LED Indicator
Off Indicates that the event is not present in the system
On Yellow Indicates one or more events have occurred in the gateway
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–2
Page 33

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
4.3 Rear Panel Connections
All connections are made on the rear panel of the gateway (refer to Figure 4-2). Any connection to the
gateway must be made with the appropriate mating connector.
Figure 4-2 MDX420 Satellite Gateway Rear Panel
4.3.1 Compact Flash (J5)
The compact flash slot is located on the back panel of the MDX420. The compact flash card store s all the
operational data and must be present when the gateway is operating.
4.3.2 Power Input Modules
4.3.2.1 AC Power Input Module
AC Input Module (Figure 4-2) is located on the left side of the gateway. Power applied to the port with the
supplied power cable is 100 – 240 VAC, 50 – 60 Hz. Integrated into the power input module is the power
ON/OFF rocker switch. Power consumption for the gateway is less than 40 watts for the base
configuration. Base unit with BUC Power: less than 200 Watts. A chassis ground connection (#10 -32
threaded stud), is located to the lower right of the module.
4.3.2.2 DC Power Input (Optional)
The Optional DC Power Input and Switch (Figure 4-3) is available for the gateway. The gateway may be
powered from a 48v ± 5vdc VDC source with a power consumption of 1 A for the base configuration.
Refer to Table 4-2 for pinouts.
Table 4-2. DC Power
A –
B Ground
C +
Figure 4-3 DC Power Connector
4.3.3 Chassis Connections (Standard)
4.3.3.1 TX IF (J9)
The transmit IF output port is a 50-Ohm N-Type female connector. The power level is programmable from
0 to -25 dBm, in 0.1 dBm steps. The IF frequency can be programmed to 950 – 1750 MHz in 1 Hz step s.
This interface has an optional capability of supporting BUC voltages and 10 MHz reference. A TX DC
Voltage LED indicator (below the J9 connector) is illuminated when DC power is being supplied to the
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–3
Page 34

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
BUC. In addition, the gateway supports monitoring features that provide verification of system status.
The gateway monitors both the current and the voltage at the output of the transmit port, thus allowing the
user to monitor the status of both the indoor gateways and outdoor equipment.
4.3.3.2 RX IF (J8)
The receive IF input port is a 75 Ohm F-Type female connector. The IF frequency can be programmed
from 950 to 2050 MHz in 1 Hz Steps.
This interface supports LNB voltages and the capability of supporting an optional 10 MHz reference. . A
RX DC Voltage LED indicator (below the J8 connector) is illuminated when DC power is being supplied to
the LNB. In addition, the gateway supports monitoring features that provide verification of system status.
The gateway monitors both the current and the voltage at the input of the receive port, thus allowing the
user to monitor the status of both the indoor gateways and outdoor equipment.
4.3.3.3 Alarm (J6)
The Alarm Port is a 9-Pin Female “D” Connector. Refer to Table 4-3 for pinouts.
Table 4-3. ALARM Port 9-Pin Female “D” Connector (J6)
Pin No. Connection Direction
1 Summary Fault - NO No Direction
2 Summary Fault – C No Direction
3 Summary Fault – NC No Direction
4 Ground Ground
5 Mod Fault (open collector) Output
6 Demod 1 Fault (open collector) Output
7 Demod 2 Fault (open collector) Output
8 Demod 3 Fault (open collector) Output
9 Demod 4 Fault (open collector) Output
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–4
Page 35

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
4.3.3.4 Service Port (J7)
The Service port is a 9-Pin female “D” connector. The service port allows access to the MDX420
Terminal screens. The Terminal screens allow the use of an external terminal for basic monitor and
control of the MDX420. No external software is required other than a VT100 terminal emulation software
(e.g. HyperTerminal or ProComm) when a computer is used as a terminal.
Please Note: The Service port offers a limited set of monitor and control functions and is not intended to
be a full service monitor and control port. Full monitor and control of the SkyWire gateway is supported
via the SNMP Control interface.
The electrical interface of the service port is RS232. The terminal control mode supports VT100 terminal
emulation mode, 19.2 kbaud rate, and must be set for 8 data bit, 1 stop bit and no parity (8, N, 1). .
Available Menus: Refer to section 6 for description of the Terminal screens
Demodulator Controls
Demodulator Alarms
Modulator Controls
Modulator Alarms
System Controls
System Alarms
TCP/IP/FTP
SNMP v1, v2 & v3
Event Log
Test and Diagnostic
Logout
Refer to Table 4-4 for connector pinouts.
Table 4-4. Service Port (RS-232) 9-Pin Female “D” Connector (J7)
Pin No. Signal Name Signal Direction
1 No Connect
2 Receive Data RS-232 RXD-232 Input
3 Transmit Data RS-232 TXD-232 Output
4 No Connect NC
5 Ground GND
6 No Connect
7 No Connect
8 No Connect
9 No Connect
4.3.3.5 Control Port, Ethernet 10/100 (J1 & J2)
The control port (J1 & J2) is used for the Monitor & Control (M&C) of the gateway. The physical interface
is a standard female RJ-45, Auto-Crossover and Auto-Sensing, 10/100 Connector. Connecting to either
control port is a valid connection for M&C of a single gateway.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–5
Page 36

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Front & Rear Panel Interfaces
4.3.3.6 Data Port, Ethernet 10/100/1000 (J3 & J4)
The Ethernet data interface provides two RJ-45, Auto-Crossover and Auto-Sensing, 10/100/1000
Ethernet data ports.
J3 is Port 1
J4 is Port 2
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 4–6
Page 37

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Configuring the MDX420 SkyWire
Chapter 5. Configuring the
MDX420 SkyWire
5.1 Initial Setup of the MDX420 SkyWire
This section describes the initial setup and configuration of the MDX420.
You must have a thorough understanding of the overall system requirements and future expansion needs
before you configure the unit.
5.2 Function Accessibility
All of the configuration parameters of the gateway are available through the 10/100 Ethernet control port
using SNMP V1, V2, or V3 protocol The service port offers limited access to the gateway’s parameters
through menu-driven terminal screens. TCP/IP setting and Passwords for the control port are established
through service port terminal screens. Refer to Chapter 6 for terminal screens and Chapter 7 for the
Comtech-supplied GUI Configuration Controller information.
The gateway supports these M&C interfaces:
Control Port - 10/100 Ethernet - Configuration Controller GUI, SNMP v1&v2 or v3, MIB Browser ,or
user-supplied NMS
Service Port - RS232 - VT100 terminal screens (limited functions)
5.3 Initial Configuration Check
The MDX420 is shipped from the factory with preset factory defaults. At initial power-up, do a user check
to verify the shipped gateway configuration.
You can reset the modem to its original factory defaults. Log in to the modem and enter the command
“DNV” on the top-level screen of the serial terminal interface.
To save user configuration settings, enter the “SNV” command. To load the saved user configuration,
enter the “LNV” command. Saving a user configuration creates a “USER.NV” file in the “Archive” folder
on the compact flash. See section 7.4.5 to understand how this can also be done from the GUI.
IMPORTANT
DO NOT EDIT the “DEFAULT.NV” file. Doing so can corrupt the default non vol settings and make the
product unstable.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 5–1
Page 38

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Configuring the MDX420 SkyWire
5.3.1 Standard Factory Configuration Settings
Modulator: Demodulator
Data Rate: 1.0 Mbps
FEC: 0.793 Rate Turbo
Modulation: QPSK
Frequency: 950 MHz
Modulator Output Power: -25 dBm
Modulator: Enabled
BUC Power: OFF (when installed)
10 MHz Reference: OFF (when installed)
Data Rate: 1.0 Mbps
FEC: 0.793 Rate Turbo
Modulation: QPSK
Frequency: 950 MHz
LNB Power: OFF
10 MHz Reference: OFF
5.4 Initial Power-Up
CAUTION
Before initial power up of the gateway, disconnect the transmit output from the operating
ground station equipment. If the current Burst Modulator Configuration Settings are unknown,
incorrect settings can disrupt existing communications traffic.
New gateways from the factory are normally shipped in a default configuration that includes setting the
transmit carrier OFF. To power on the gateway, set the rear panel switch (near the power entry
connector) to ON. At every power-up, the unit will test itself, several of its components, and front panel
LEDs before operation. If a failure is detected, the Common Fault LED glows.
You can do the initial field checkout of the gateway from the Comtech-supplied Gateway Configuration
Controller GUI, or use an external device with the supplied SNMP MIB.
5.5 Monitor and Control
Monitor and Control of the MDX420 occurs through Ethernet and terminal communications. The
administrator must use the service port to set up and configure the control port. Use the control port to
configure the gateway and the network. The gateway control port is configured with factory defaults.
5.5.1 Ethernet Control Port Factory Defaults:
Boot Mode: NON-VOL
IP Mask: 255.255.255.0
Modem IP Addr: 192.168.0.236
SNMP V2
Read Community public
Read/Write Community public
5.5.2 Control Port (J1 & J2)
You must set up the Control port interface parameters (TCP/IP & SNMP) through the Service port before
you can use the Control port. See Appendix B for information on setting up the Control port. The Control
port is dedicated to 10/100 Ethernet using SNMP protocol for Monitor and Control of the gateway. The
administrator uses the Control port to control all parameters of the satellite gateway. Comtech supplies a
GUI application, Configurator Controller Software, to use for setting up and monitoring the gateway.
5.5.3 Service Port (J7)
The Service port is dedicated to menu-driven terminal communications. The Service port gives access to
the MDX420 terminal screens. The terminal screens give limited access to monitor and control the
MDX420 using an external terminal or computer. The terminal screens give access to the unit's
parameters and TCP/IP settings. The Service port does not allow setup of the network configuration
parameters. Refer to Chapter 6 for more about configuration using the Service port.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 5–2
Page 39

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
Chapter 6. Terminal Screens
6.1 Service Port User Interface
This section contains information pertaining to the terminal screens accessible via the service
port interface.
Please Note: The service port offers a limited set of monitor and control functions and is not
intended to be a full service monitor and control port. Full monitor and control of the SkyWire
gateway is supported via the SNMP control interface.
6.2 Description of the Service Port (J7)
The Service port is a 9-Pin Female “D” Connector. The service port allows access to the
MDX420 Terminal Screens. The service port uses a RS232 Connection to the terminal device.
Refer to section 6.1.4 for available Menus.
6.2.1 Terminal Screens
The Terminal screens allow the user with an external terminal limited access for monitor and
control of the gateway. No external software is required other than Terminal Emulation Software
(e.g. "Hyperterminal" or “Procomm” for a computer when used as a terminal.
Terminal screens allow for two modes of access, Administrative and Viewer.
Administrator - requires user to login thus allowing the user full control of the unit parameters.
Viewer - user can view most menus and cannot change any parameters.
NOTE: The default Logon password is “password”.
Administrative Passwords for the SkyWire Configuration Controller software (SkyWire Controller)
can only be modified in the Terminal screens. SNMP V1, V2 and V3 are supported. When V3 is
used, three contexts are supported: VIEWER, OPERATOR, and ADMINISTRATOR, Context,
Authentication and Privacy are a portion of each SNMPV3 message.
Password for the Terminal screen can only be modified in the SkyWire Controller System menu
(See Section 7.3.5 “Service Port Admin Password”). The System menu displays the option to
change the Terminal Passwords.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–1
Page 40

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.2 Reserved
6.2.3 Connecting to the Service Port (J7)
Connect the terminal to the Service port (J7) on the rear of the gateway using the RS-232 Cable.
Verify that your terminal emulation software is set to the following:
Emulation Type: VT-100
Baud Rate: 19.2 K
Data Bits: 8
Parity: No Parity (Fixed)
Stop Bits: 1 Stop Bit
Table 6-1. Service Port (RS-232) 9-Pin Female “D” Connector (J7)
Pin No. Signal Name Signal Direction
1 No Connect
2 Receive Data RS-232 RXD-232 Input
3 Transmit Data RS-232 TXD-232 Output
4 No Connect NC
5 Ground GND
6 No Connect
7 No Connect
8 No Connect
9 No Connect
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–2
Page 41

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4 Terminal Screens
6.2.4.1 Main Menu
Available Menus include:
Demodulator Controls (1-4)
Modulator Controls
System Controls
Demodulator Alarms (1-4)
Modulator Alarms
System Alarms
TCP/IP/FTP
SNMP V1, V2 & V3
Event Log
Test & Diagnostics
LOGON
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–3
Page 42

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.2 Demodulator Menu Options and Parameters
(Common to all installed Burst Demodulators)
DEMODULATOR MENU 1 THROUGH 4
NETWORK SPEC {RAD MESH}
Allows the user to enter the Network specs.
IF FREQUENCY
(MHz)
RF FREQUENCY
(MHz)
LO FREQUENCY
(MHz)
SIDE BAND {LOW SIDEBAND, HIGH SIDEBAND}
LNB 10MHz Ref {ENABLED, DISABLED}
LNB DC SUPPLY {ENABLED, DISABLED}
CHANNEL
CONTROL
{950 - 2050 MHz}
Allows the user to enter the Burst Modulator IF Output Frequency of the gateway in
1 Hz increments.
Displays the input frequency to the LNB also referred to as Satellite downlink
frequency. The user must enter the LNB LO and OSC SIDE BAND before using
this menu. The DOWNLINK FREQUENCY is a calculated measurement of both
the LNB LO and OSC SIDE BAND. Once the menus are entered correctly, the
user can control the uplink Frequency from this menu.
Allows the user to enter the Local Oscillator frequency of the LNB LO in order for
the uplink frequency to be displayed correctly (refer to the LNB manufacturer’s
specifications).
Allows the user to select the location of the LNB LO. The user must enter the
location of the LNB LO in order for the DOWNLINK FREQUENCY to be displayed
correctly. The LNB LO can be either higher or lower in frequency than the LNB
INPUT frequency. If the LNB LO is higher in frequency then the user must enter
HIGH SIDEBAND.
Allows the user to enable or disable the 10 MHz LNB reference clock.
Allows the user to enable or disable the LNB supply voltage.
{ENABLED, DISABLED}
Allows the user to enable or disable the burst demodulator.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–4
Page 43

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
DATA RATE (bps) {Refer to Technical Specs for Data Rates}
Allows the user to set the Data Rate in bps steps via the Terminal Screen
SYMB RATE (sps) {256000 - 10000000}
Allows the user to set and or view the Symbol Rate.
INNER FEC Turbo{.710, .793}
Allows the user to select the RX Code Rate
DEMODULATION {QPSK, 8PSK}
Allows the user to select the demodulation type.
RESET REMOTES
CAUTION: Resetting the remote will disable the burst demodulator and erase the
entire configuration table associated with that burst demodulator. This selection
should only be used to reset the burst demodulator to a known starting point or to
erase a previous configuration.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–5
Page 44

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.3 Modulator Menu Options and Parameters
MODULATOR MENU
NETWORK
SPEC
IF FREQ (MHz) {950 - 1750 MHz}
RF FREQ (MHz)
LO FREQ (MHz)
SIDE BAND {LOW SIDEBAND, HIGH SIDEBAND}
BUC 10 MHz
Ref
BUC DC
SUPPLY
CARRIER CTL {ON, OFF}
POWER LEVEL
(dBm)
{RAD MESH}
Allows the user to enter the desired Network specs.
Allows the user to enter the Burst Modulator IF Output Frequency of the gateway in 1
Hz increments.
Displays the output frequency of the BUC also referred to as Satellite uplink
frequency. The user must enter the BUC LO and OSC SIDE BAND before using this
menu. The UPLINK FREQUENCY is a calculated measurement of both the BUC LO
and OSC SIDE BAND. Once the menus are entered correctly, the user can control
the uplink Frequency from this menu.
Allows the user to enter the Local Oscillator frequency of the BUC LO in order for the
uplink frequency to be displayed correctly (refer to the BUC manufacturer’s
specifications).
Allows the user to select the location of the BUC LO. The user must enter the location
of the BUC LO in order for the UPLINK FREQUENCY to be displayed correctly. The
BUC LO can be either higher or lower in frequency than the BUC output frequency. If
the BUC LO is higher in frequency then the user must enter HIGH SIDEBAND.
{ENABLED, DISABLED}
Allows the user to enable or disable the 10 MHz BUC reference clock.
{ENABLED, DISABLED}
Allows the user to enable or disable the BUC supply voltage.
Allows the user to enable and disable the carrier.
{0 to -25 dBm}
Allows the user to enter the Transmitter Power Level.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–6
Page 45

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
DATA RATE
(bps)
SYMBOL RATE
(sps)
{Refer to Technical Specs for Data Rates}
Allows the user to set the Data Rate in bps steps via the Terminal Screen.
{256000 - 10000000}
Allows the user to set and or view the Symbol Rate.
INNER FEC Turbo {.710, .793}
Allows the user to select the TX Code Rate
MODULATION {QPSK, 8PSK}
Allows the user to select the modulation type.
SPECTRUM {NORMAL, INVERTED}
Allows the user to invert the direction of rotation for PSK Modulation.
Spectral inversion may be required if the BUC LO is higher in frequency than the BUC
output frequency. When BUC LO is higher than the BUC output frequency, this
creates a spectral inversion and the IF Spectrum must be again inverted to
compensate.
DEMOD {1-4}
User can select which burst demodulator will be associated with the unit’s modulator.
A value of 0 indicates the device is in RX only and is not using it’s modulator. When
using the modulator a demod MUST be used to demodulate the uplink signal for
timing purposes regardless if there is only one site transmitting into the share group.
REMOTE {1-8}
Identifies the remote location of the network as referenced in the Network
Configurator. Refer to the Network Configurator.
AUTO START {ON, OFF}
Enables the gateway to automatically initiate the start of a new network. The gateway
will initiate the starting process within 2 minutes of not detecting the assigned shared
carrier. It will continue to attempt initialization every minute until the gateway detects
the assigned shared carrier. The initialization process requires one gateway within
the shared group to initialize the link. As other remote gateways are configured and
set to receive the shared carrier signal, the distributed intelligence of the SkyWire
network will provide access to the remotes and they will be asked to join the network.
START
NETWORK
This allows the user to manually initialize the network for the first time. Once all the
remotes in the SkyWire Network have been configured and the satellite parameters
are set, the network can be started. The initialization process requires one gateway
within the shared group to initialize the link (either in auto start mode or manually). As
other remote gateways are configured and set to receive the shared carrier signal, the
distributed intelligence of the SkyWire network will provide access to the remotes and
they will be asked to join the network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–7
Page 46

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.4 System Controls
SYSTEM CONTROLS
FEATURE ID 1234.1234.1234
This displays the current Feature ID. This feature code is used to define available
feature within the Gateway. This code is also used for purchased feature
upgrades. Feature code is different for every unit. (Refer to Appendix A).
Contact the Comtech Sales Department for hardware and software upgrades.
GATEWAY ID Fixed ID
This is the unique ID that each MDX420 shipps with. This unique ID will be
required by the SkyWire Configuration Controller and should be recorded by the
network administrator.
MODE {FACTORY DEMO, NORMAL}
Identifies the features ID mode options. Factory Demo mode is used when a 30
day demo key is requested through a sales person and will enable all software
features for 30 operational days. After 30 operational days the unit will remove all
un-purchased options and revert back to Normal mode.
CANCEL DEMO
Allows user to cancel Factory Demo Mode.
Once Demo Mode has been cancelled, the Demo ID will no longer be valid.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–8
Page 47

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.5 Demodulator Alarms
(Common to all installed Burst Demodulators)
DEMODULATOR ALARM STATUS 1 THROUGH 4
DEMOD FPGA {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates a receive FPGA hardware failure.
DECODER FPGA {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates a decoder failure.
TUNER PLL {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the Rx L-Band Synthesizer is not locked. This alarm will flash on
during certain gateway parameter changes. A solid indication points toward a
configuration problem within the gateway.
SIGNAL LOCK {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the burst demodulator is unable to lock to a signal.
IFEC LOCK {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
FRAME LOCK {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the Framing Unit is unable to find the expected framing pattern.
ESNO Fault {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates Rx signal quality fallen below input threshold.
CARRIER LEVEL {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates Rx signal level has fallen below input threshold.
TESTPRN SYNC {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates Rx pattern is synchronized to the data pattern
CLEAR LATCHED
Allows the user to reset the latched alarms by selecting
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–9
Page 48

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.6 Modulator Alarms
The Alarms menu description:
CURR - Current alarm status (PASS, FAIL)
LTCH - Latched alarm status - (PASS, FAIL) displays a fault that used to exist.
Unmasked - Displays all alarms and follows standard alarm protocol
Masked - Hides the specified alarm and allows to unit function as if no alarm existed.
MODULATOR ALARM STATUS
MOD FPGA {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates a transmit FPGA configuration failure.
ENCODER
FPGA
IF LO
SYNTH
OUTPUT
LEVEL
BUC
VOLTAGE
BUC
CURRENT
CLEAR
LATCHED
MESH
AUTH
{Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates a transmit encoder configuration failure.
{Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the Tx L-Band Synthesizer is not locked. This alarm will flash on during
certain gateway parameter changes. A solid indication points toward a configuration
problem within the gateway.
{Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the Output Level is out of specification.
{Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the BUC voltage is out of specification
{Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates that the BUC Current is out of specification.
Allows the user to reset the latched alarms by selecting
Indicates the Gateway/Authorization ID number cannot be detected on the mesh network.
This alarm is active as soon as the modulator is enabled when there is a corresponding
non “0” demod associated with the modulator (see section 6.1.4.2). This alarm will clear
only when the unit has successfully joined a share group and is part of the network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–10
Page 49

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.7 System Alarms
TERR FPGA CFG {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates an Interface Card FPGA configuration failure.
GLUE FPGA {Pass/Fail, Unmasked/Masked}
Indicates Glue FPGA configuration failure.
+1.2V RX SUPPLY
+1.8V TX SUPPLY
+3.3V SUPPLY
+5V SUPPLY
+12V SUPPLY
+24V SUPPLY
CLEAR LATCHED
Displays the measured voltage of the 1.2 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Displays the measured voltage of the 1.8 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Displays the measured voltage of the +3.3 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Displays the measured voltage of the +5 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Displays the measured voltage of the +12 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Displays the measured voltage of the +24 Volt power bus located inside the
gateway.
Allows the user to reset the latched alarms by selecting
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–11
Page 50

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.8 TCP/IP/FTP Controls
TCP/IP (menu)
BOOT
MODE
BOOTp
SERVER
LOCAL
HOST NAME
{DEFAULT, NON-VOL, BOOTP, IP TEST}
DEFAULT: During initialization (boot up), the gateway will restore the web setting to the
standard IP Mask and addresses supplied by the gateway. The gateway will be taken off
the network and will not be accessible. The Default settings are:
IP Address Mask: 255.000.000.000 (FF.00.00.00 hex)
Gateway IP Address: 010.000.000.001 (C0.A8.00.EE hex)
Server IP Address: 010.001.001.001 (0A.01.01.01 hex)
Router IP Address: 010.000.001.001 (0A.00.01.01 hex)
BOOTP: During initialization (boot up), the gateway will get the names, masks, and IP
Addresses of the gateway, router, and server.
NON-VOL: Stores and uses IP Mask and addresses as provided by the user.
IP TEST: Stores and uses IP Mask and addresses to fixed settings as listed below.
Bootp Server Tag: 206
IP Address Mask: 255.255.255.000 (FF.FF.FF.00 hex)
Gateway IP Address: 192.168.0.238 (C0.A8.00.EE)
Server IP Address: 192.168.000.101 (C0.A8.00.65)
{128 – 257, default is 206}
Only used if Bootp is selected in Boot Mode. Should be consistent with the tag expected
by the users Bootp Server.
The Local Host Name for the network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–12
Page 51

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
IP MASK {ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Mask
The IP Address Mask of the local network. The mask is expressed in a hexadecimal
format, and must be a valid TCP/IP Mask. This field should be set before changes are
made to the Gateway or Router Address.
MODEM IP
ADDR
{ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Mask
The IP Address of the gateway. This address should be consistent for the mask defined.
This address is expressed in hexadecimal format. Broadcast and loop back addresses
will not be allowed. These are addresses with all subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
SERVER IP
ADDR
{ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Address
The IP Address of the Boot Server and the address of the SNMP Trap Server when
SNMP is active. If a server is used and there is no local router, this address must be
consistent with the gateway address. If a router has been specified, the address is
presumed to be reachable via the router. Broadcast and loop back addresses will not be
allowed. These are addresses with all subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
ROUTER IP
ADDR
{ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Address
The IP Address of the Local Network Router. If a router is present on the local network,
this address must be consistent with the IP Mask and the subnet of the gateway. If no
router is present, then the address should be set to a foreign address. This address is
expressed in hexadecimal format.
Broadcast and loop back addresses will not be allowed. These a re addresses with all
subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
Modem
Ether Addr
{hhhhhhhhhhhh}
Displays the Ethernet address of the device. Set at the factory and is a unique identifier
for the Ethernet physical interface.
ETHER
RATE
{10/100 MBPS/Auto Negotiate}
The data rate for the local Ethernet Interface. 10/100 Mbps/Auto Sensing – for 10 or 100
Base-T in either half-duplex or full duplex.
FTP User ID {XXXXXXXXXXXXXX}
The FTP USER ID and Password will be shared by all sites transmitting into the same
share group regardless of what is entered here. This setting is only used by the first site
that starts the share group. Once in a share group any changes to the User ID or
Password will be communicated to all sites in that share group automatically. The default
User ID is: user
FTP
Password
{XXXXXXXXXXXXXX}
The FTP USER ID and Password will be shared by all sites transmitting into the same
share group regardless of what is entered here. This setting is only used by the first site
that starts the share group. Once in a share group any changes to the User ID or
Password will be communicated to all sites in that share group automatically. The default
Password is: password
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–13
Page 52

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.9 SNMP V1 & V2 Controls
SNMP VERSION {V1 & V2, V3}
This selection controls the SNMP Version that will be used in messaging between
the equipment and its host.
When V1 & V2 is used, RD COMMUNITY and RDWR COMMUNITY are used to
determine the authorization of an incoming message.
TRAP VERSION {V1, V2}
This controls the type of message format used when a message trap is generated
by the equipment and bound for a SNMP Host. Messages will only be sent if the
gateway has been authorized to do so.
TRAP
AUTHORIZATION
V1&2 RD
COMMUNITY
V1&2 RDWR
COMMUNITY
PRIMARY TRAP
HOST
{TRAPS OFF, TRAPS ON}
This controls the type of message format used when a message trap is generated
by the equipment and bound for a SNMP host. Messages will only be sent if the
gateway has been authorized to do so.
{16 characters of name}
This menu is only displayed when SNMP VERSION is set to V1 & V2. This is the
community that a host must be acting within when an OID variable is requested
by a V1/V2 SNMP message. The defaulted setting is “Public”.
{16 characters of name}
This menu is only displayed when SNMP VERSION is set to V1 & V2.
This is the community that a host must be acting within when an OID variable is
being changed by a V1/V2 SNMP message. The defaulted setting is “public”.
{xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx}
This specifies the IP address of the "public" SNMP host. Trap messages are sent
to this address when a trap is generated by the equipment.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–14
Page 53

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.10 SNMP V3 Controls
SNMP VERSION {V1 & V2, V3}
This selection controls the SNMP Version that will be used in messaging between
the equipment and its host.
When V3 is used, three contexts are supported: VIEWER, OPER, and ADMIN.
Context, Authentication and Privacy are a portion of each SNMPV3 message.
The VIEWER context will only allow the user with appropriate authentication to
see the local gateway settings. This is the most restricted access possible.
The OPER context allows a user with appropriate authentication to access and
control the local gateway parameters.
The ADMIN context allows a user with appropriate authentication to access and
control all network parameters. These OIDs are used to control the devices,
satellite link and operation.
TRAP VERSION {V1, V2}
This controls the type of message format used when a message trap is generated
by the equipment and bound for a SNMP Host. Messages will only be sent if the
gateway has been authorized to do so.
TRAP
AUTHORIZATION
PRIMARY TRAP
HOST
USER #
{TRAPS OFF, TRAPS ON}
This controls the type of message format used when a message trap is generated
by the equipment and bound for a SNMP host. Messages will only be sent if the
gateway has been authorized to do so.
{xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx}
This specifies the IP address of the "public" SNMP host. Trap messages are sent
to this address when a trap is generated by the equipment.
NOTE: The following selections are common to all users. These settings will
be used as access parameters for the Configurator Controller. The gateway
allows for 4 distinct users that are identified in this menu.
Sets user display name. User default names are administrator, operator and
viewer. This is also referred to as the Security User Name in the User Profile
Configuration.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–15
Page 54

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
GROUP {ADMIN, OPER, VIEWER, NO GROUP}
Sets the group access level for the user. This is also referred to as the Context
Name in the User Profile Configuration.
AUTHP
Sets the Authentication Password for the user. Password must match the
Authentication Password in the User Profile Configuration
PRIVP
Sets the Privacy Password for the user. Password must match the Privacy
Password in the User Profile Configuration
AUTHM {MD5, SHA, NONE}
Sets the Authentication mode for the user. Mode must match the Authentication
Protocol in the User Profile Configuration
PRIVM {DES, NONE}
Sets the Privacy mode for the user. Mode must match the Privacy Protocol in the
User Profile Configuration
USER RESET Resets the User defaults.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–16
Page 55

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.11 Event Log
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–17
Page 56

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Terminal Screens
6.2.4.12 Test Diagnostics
Carrier TYPE {NORMAL, CW, DUAL, OFFSET, POS FIR, NEG FIR, CNT MOD}
Allows the user to set the type of carrier.
NORMAL: Causes the Burst Modulator to output normal modulation.
CW: Causes the Burst Modulator to output a pure carrier.
DUAL: Causes a double sideband output.
OFFSET: Causes a single sideband output.
POS FIR: For manufacturer’s use only.
NEG FIR: For manufacturers use only.
CNT MOD: Transmits a continuously modulated carrier. This mode is used to
verify the proper bandwidth and noise level margin of the carrier within the
satellite transponder. This is may also be used for antenna alignment. The
test mode does not allow any data to be transmitted.
CNT BST: Continuous Burst mode tells the modulator to send a burst at every
time slot regardless of burst slot assignment. This type of operation is very
useful when installing the first site of a share group or for debugging a network
issue. CNT BST will look like an SCPC carrier on a spectrum analyzer
(virtually always on) and it will satisfy any demodulator who is properly
configured to lock to the signal. CNT BST can be used to verify frequency,
Spectral Inversion and Symbol rates are properly set and to verify the uplink
and downlink chain are in good working order.
LOOPBACK {NONE} This is not available in the MDX420
MOD TEST PATTERN {NONE} This is not available in the MDX420
DEMOD1-4 {NONE} This is not available in the MDX420
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 6–18
Page 57

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Chapter 7. SkyWire Controller GUI
7.1 SkyWire Controller Graphical User Interface (GUI)
At the time of this publication, the GUI version is 1.8.5(H). The SkyWire Controller is also referred
to in this manual as SkyWire GUI or GUI. Using the Comtech supplied SkyWire Controller
software requires the user to install the SkyWire Controller software onto a PC. The GUI gives
the user access to the menus for setting up the gateway and network parameters. The GUI is
included with the purchase of the MDX420.
PC System Requirements are:
Java 7 or greater
Windows 7 or 8
13.7 MB free space (HDD)
128 MB free memory (RAM)
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–1
Page 58

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.2 Installing the SkyWire Controller GUI
The SkyWire Controller installation CD is shipped with the SkyWire Gateway. Alternatively the
latest SkyWire Controller software can also be found on Comtech’s customer support FTP site for
download. Please contact your customer service or sales representative to get access to the
FTP site.
The following steps describe the installation procedure for installing the SkyWire Controller on
your computer.
Step 1: Place the SkyWire Controller CD-ROM in the CD-ROM Drive and double-click on the
SkyWireControllerInstaller jar file.
Read the Comtech license agreement carefully. Click the “I Agree” to proceed with the
installation.
Step 2: Select the installation options and click “Next”.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–2
Page 59

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Step 3: The default installation subdirectory window will appear. To use the default installation
subdirectory click “Install” or click “B rowse” to modify the directory for installation. Press “Install”
to begin the installation.
Step 4: stand by until the installation shows “Completed”. Click “Close” to exit.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–3
Page 60

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.3 Connect and Login
In order to activate the SkyWire Controller, the MDX420 must be turned ON and connected to the
computer via the 10/100 Ethernet Control port.
Set up the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties of the computer LAN port to be on the same
subnet as the Control port on the MDX420. In Windows, this is done through the Network
Connections category. The factory default subnet is 192.168.0.x, where x is an address between
1 and 255 except for 236. If the IP address of the MDX420 has been changed from the factory
default address, the subnet may be different. Consult your Network Administrator for the proper
subnet setting for the computer.
Connect an Ethernet RJ45 cable between the computer and Control Port J1 or J2 of the
MDX420. The gateway’s IP address is automatically detected by the SkyWire Controller.
On the Login screen (Figure 7.3) click the button to the right of the Destination name to configure
the SkyWire Controller interface parameters.
Figure 7.3 Login Screen for SNMPv2
7.3.1 Destination Configuration Screen
The Destination Configuration screen is displayed in Figure 7.3.1. This screen allows the user to
provide a Destination Name for the gateway, enter the gateway IP Address, set the SNMP
protocol version, and select the desired polling interval.
NOTE: The IP Address and SNMP Version parameters in the Destination Configuration screen
must match the parameters set by the Service port
(refer to section 6.1.4.8, 6.1.4.9, and 6.1.4.10)
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–4
Page 61

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.3.1 Destination Configuration Screen
Destination Configuration setup parameters (Sections 7.3.1.1 through 7.3.1.4):
7.3.1.1 Destination Name
The current IP Address is the default name and can be changed by the user. The first time the
Destination Configuration menu appears, the administrator can create an appropriate name for
the gateway, for example, Phoenix (Figure 7.3.1.1). Upon selecting a desired name it will appear
in the Destination pull down menu on the Log-In screen and also in the title bar on the
Configuration Controller window (Figure 7.3.1.4).
Figure 7.3.1.1 Destination Configuration
NOTE: Changing the Destination Name is not a requirement but is provided as a simple way to
identify the different gateways by the physical location in the network.
7.3.1.2 IP Address
192.168.0.236 is a factory default and can be changed by user to match what is set by the
Service port (refer to section 6.2.4.11)
7.3.1.3 SNMP Version
SNMPv2 is the factory default version and can be changed by the user to match what is set by
the Service port (refer to section 6.2.4.9 or 6.2.4.10). The gateway utilizes either SNMPv2 or v3
protocols as the means of exchanging monitor and control information. It is suggested that
SNMPv2 be used for the initial setup of the gateway.
7.3.1.3.1 SNMPV2
When selecting SNMPv2, the unit allows public access to all menus. SNMPv2 allows any user to
access and control all parameters of the gateway. On the SNMPv2 Login screen, the Read and
Read/Write communities default to “public”. The Read Community and Rd/WR Community
configuration must be set to match the configuration as set by the Service port (refer to section
6.2.4.9).
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–5
Page 62

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.3.1.3.2 SNMPV3
When selecting SNMPv3, the gateway enables administrative controls and allows limited access
to all other users. In this mode, the administrator retains access to all parameters but can limit
access to certain users by assigning them as Viewers, Operators, or Administrators and must be
set to match the configuration as set by the Service port (refer to section 6.2.4.10). Configuring
SNMP Version 3 will be described later in this chapter.
7.3.1.4 Polling Interval
The SkyWire Controller will poll the gateway based on the setting of the Polling Internal (in
seconds). The default setting is 2 seconds and an be changed by the user to the desired polling
interval
Click on the Save button to store the destination profile for easy future access.
Once the user is authenticated, a quick summary (Figure 7.3.1.4) of the burst demodulators and
network status, event logs, and summary faults is displayed.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–6
Page 63

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4 SkyWire Controller Configure Tab
After successfully logging into the configuration controller, the user must first configure the
MDX420 satellite link parameters to the desired setting. Satellite Link menus include but are not
limited to:
Figure 7.4 SkyWire Configuration Controller
RF Frequency
IF Frequency
Modulation
Inner FEC (Forward Error Correction)
Standard or Enhanced Performance
Data Rate
Symbol Rate
Block Up Converter (BUC)
Low Noise Block (LNB) converter
NOTE: The MDX420 allows the user to determine if the frequency control for the burst
modulator and burst demodulator are either IF or RF and if the information rate control is
to be entered as symbol rate or data rate. Refer to Section 7.4 for control options settings.
Using the SkyWire top-level menu system, select the Configure / Satellite Link / Modulator menu
(Figure 7.4-1).
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–7
Page 64

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.4-1. Satellite Link Menu Selection
The satellite link configuration window (Figure 7.4.1.1) provides access to all gateway satellite
configuration parameters through the use of tabs. Select a tab for the section of the gateway
where satellite link parameters are to be changed. that you want to configure.
7.4.1 Configure Satellite Link
7.4.1.1 Modulator Configuration
To setup the burst modulator, select the Modulator tab in the Satellite Link Configuration screen.
Press the Edit button to make changes and once satisfied with the new settings, click on the
Apply button to have them take effect.
Figure 7.4.1.1 Modulator Tab Edit Mode
TX Enable: Tx Enable should be selected when the MDX-420 is transmitting into the network.
Regardless of any other setting, if TX Enable is not selected the MDX-420 will not TX into the
network. Un-select this box if the MDX-420 is used in a receive only capacity.
Auto Start: The Auto Start function allows a share group to automatically recover from a complete
outage. It is primarily intended for use in unattended networks. The Auto Start function can be
enabled by placing a Check in the Auto Start check box on the Modulator tab in the Satellite Link
Configuration screen (Figure 7.4.1.1).
Beginning two minutes after power-up, the MDX-420 operation with regard to Auto Start is as
follows:
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–8
Page 65

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
If the Auto Start function is enabled, the MDX-420 determines if it can receive the designated
share group’s channel.
If there is no share group carrier to receive, the MDX-420 attempts to start the network.
Wait one minute
Go to step 1.
NOTE: It is NOT recommended that Auto Start be enabled on more than one MDX-420 within a
share group.
The decision as to which, if any, MDX-420 has the Auto Start function enabled should include the
following two considerations:
Likelihood of a signal outage at that site – If possible, select an MDX-420 at a site that
has the least chance of an outage.
Access to the MDX-420 – If possible, select an MDX-420 to which the network
administrator has either direct or non-over-the-air access.
Network Spec: Network spec is set to RADYNE MESH and is not changeable at this time.
Performance: The Performance selection can be set to Standard or Enhanced. This setting must
be the same for all units that are transmitting into the same share group. The performance
setting is a trade-off of Eb/No required to close the link and bandwidth efficiency. See the below
table to understand how this setting will affect network performance:
Modulation and Coding Threshold Eb/No Typical Eb/No Efficiency
1) Enhanced - QPSK.710 2.9 3.5 90%
2) Enhanced - QPSK.793 3.3 3.8 90%
3) Standard - QPSK.793 3.4 4.4 93%
4) Enhanced - 8PSK.793 6.5 7.6 88%
5) Standard - 8PSK.793 7.8 9.0 91%
Selected Demod: The Selected Demod is the demod that is associated with the modulated signal.
Every MDX-420 that is transmitting into a share group must be locally demodulated in order to
meet timing and BW sharing algorithm criteria. The Selected Demod is the physical demod slot
that is associated with the modulator’s share group. By default this is demod slot 1 as this demod
is always populated from the factory. The demod can be set to any populated demod slot if more
than one demod is purchased and installed in the MDX-420. A Selected Demod setting of “0”
means that the MDX-420 is in a listen only mode and can not transmit into any share group.
Selected Remote: The Selected Remote is automatically assigned by the network and can not
be changed. This number correlates to the physical location on the GUI interface. A number of 2
for example would indicate that this site is in position 2 of the bar graph of a multiple site share
group. Note: each share group will re-start the count so the number of the remote will always be
between 1-8 for a particular share group. Alternatively, when viewing the GUI interface, the
“yellow” bar is another way to know what MDX-420 device you have the SNMP session with.
Gateway ID: This is the unique ID that each MDX420 shipps with. This unique ID will be
required by the SkyWire Configuration Controller and should be recorded by the network
administrator. NOTE: The Gateway ID will be needed to configure the network (see section 7.6).
All other configurable items in the modulator configuration screen should be treated as if
configuring any other satellite modem.
7.4.1.2 Demodulator Configuration
There are up to four burst demodulators that may be installed in the SkyWire Gateway. To
configure any of the installed burst demodulators, select the corresponding demod tab. Press the
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–9
Page 66

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Edit button (Figure 7.4.1.2) to make changes and once satisfied with the new settings, cli ck on
the Apply button to have them take effect.
Repeat the above process for all installed burst demodulators.
Figure 7.4.1.2 Demodulator 1 Tab Edit Mode
RX Enable: Rx Enable should be checked if you wish to demodulate and receive traffic from a
share group on this demodulator. Unchecking this box will disable the demodulator regardless of
any other settings.
CRC Control: The gateway allows users to enable or disable CRC Control. When CRC Control is
checked, the gateway automatically performs Ethernet packet error checking on the receive
Satellite Link. When an Ethernet packet with a bad CRC is encountered, the packet is discarded
by the gateway.When CRC Control is unchecked, the gateway will remove the invalid CRC and
append a valid CRC to the Ethernet datagram and pass the packet to the LAN network. Enabling
CRC Control may be suitable for users that need all packets to pass based on their application.
Regardless of the configuration of the CRC Control function, enabled or disabled, the gateway
maintains and reports satellite link statistics on total packets, erred packets, and packet error rate
(PER). Note: CRC Control is only used on the RX satellite link. If an invalid CRC is seen by the
10/100/1000 Interface the packet will be disgarded and will not be transmitted to the satellite
regardless of the CRC Control check box selection.
Performance: See section 7.4.1.1
All other configurable items in the demodulator configuration screen should be treated as if
configuring any other satellite modem.
7.4.1.3 BUC and LNB Configuration
To setup the BUC (Figure 7.4.1.3-1) and/or LNB (Figure 7.4.1.3-2), select the corresponding tab
on the satellite link configuration window. Enter the LO frequency and LO Mix (Hi side or Low
side). Click on the Enable button to activate the DC Supply and or 10MHz Frequency Reference
to the BUC or LNB. They are individually controlled with a checked box meaning that they are
enabled, unchecked box meaning that they are disabled.
Once satisfied with the new settings, click on the Apply button to have them take effect.
Warning: Care must be taken to insure that the DC Supply Enable is Disabled when
connecting the SkyWire Gateway to external equipment that cannot accept a DC voltage
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–10
Page 67

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
input, such as a Spectrum Analyzer. Failure to do so may result in damage to the external
equipment.
Figure 7.4.1.3-1 BUC Tab Edit Mode
Figure 7.4.1.3-2 LNB Tab Edit Mode
7.4.1.4 AUPC Configuration
AUPC or “Automatic Uplink Control” operation is an OPTIONAL setting and does not need to be
configured to enable SkyWire to function. AUPC operation is designed to compensate for
UPLINK fade conditions. By default AUPC is not enabled. If a user wants to mitigate the effects
of uplink fade the SkyWire modem can be configured to do so. Note: Improper use of AUPC
can take a network down and may damage ground equipment or use excessive power on
the satellite. Read below carefully.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–11
Page 68

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.4.1.4 AUPC Configuration
Theory of operation: Fade conditions can happen for numerous reasons such as uplink rain
fade, downlink rain fade, antenna mispointing, LNB failure, BUC failure, cable run issues,
temperature etc. The purpose of SkyWire’s AUPC is to try and mitigate the effects of UPLINK
fade ONLY. The reason we do not want to mitigate the effects of downlink fade is due to the fact
that SkyWIre is designed to work in a MESH environment so compensating for one site’s
downlink fade will overdrive the uplink power and the system will be using more of the satellite
power resources than the satellite operator would typically allow. Further to this point increasing
the uplink power to compensate for one site’s downlink rain fade would negatively impact all sites
that did NOT have downlink fade. The purpose of SkyWire’s AUPC is to attempt to illuminate the
satellite
with a constant or near constant power and to overcome uplink rain fade. The use of
AUPC is a site by site selection, some units in the share may use this while others in the same
share group may not. AUPC only effects the TX power of the device being configured to use
AUPC and the demodulator RX level is only reading the level of it’s own burst not the RX level of
other sites or an average of all sites in the share group.
Operation: Once the network is up and running in a stable environment and all carrier levels
and Eb/No levels are within the operational range desired (see section 7.6.1 Demodulator
Status Screen) AND the site in which AUPC is to be turned on is in CLEAR SKY
CONDITIONS the user should follow these instructions in this exact order:
1) Click on the “Set Ideal Conditions” button. When this button is clicked, the “Ideal TX
Power Level (dBm)” and “Ideal RX Power Level (dBm)” fields will populate with the
present values of the modulator’s TX power setting and the demodulators Carrier Level
reading. NOTE: If the actual values of the demodulator and modulator are NOT set
when doing this or if the values stay at their default (0.0 dBm TX and -45 dBm RX) this
means that the present conditions of the demod are NOT within SkyWire’s specification
and AUPC SHOULD NOT BE USED. You will also see an event in the event log stating
“INVALID AupcIdealRXCarrierLeveldBm”. If you get this message in the Event Log DO
NOT USE AUPC.
2) Set the TX % Fade figure to a number between 50 and 90 (more on this below).
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–12
Page 69

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
3) Set a Max TX Power Level (dBm) (any figure from 0 to -25). Note: Do NOT set an
excessively large Max TX Power level unless there is a reason to believe all of the
excess power could actually be used strictly for uplink rain fade.
4) Enable AUPC by checking the box
5) Click Apply
TX % Fade: The demodulator carrier level used in AUPC is a measurement of it’s own burst as
seen by the demod from the satellite. Unfortunately if there is a fade condition at the site, what
the demod is seeing is both the uplink fade and the downlink fade. We want to compensate for
the uplink fade only for reasons mentioned above, so we need to determine what percentage of
the fade is due to the uplink and what percentage of the fade is due to the downlink. Generally
speaking uplink frequencies are higher than downlink frequencies and because of this there is
generally more fade on the uplink (this is a good thing because this is what we can compensate
for). The TX fade percentage can be calculated using the following math:
TX% Fade = TX Fade /(TX Fade + RX Fade)
Example: Ku Band link with with 4.4dB of total fade. Due to the frequencies used, 2.4 dB is due
to the uplink and 2.0dB is due to the downlink. This site has a TX% Fade of 55%.
Below is a table of common TX Fade % Figures using the center of each Band as the metric for
fade %
Downlink (GHz) Uplink (GHz) TX Fade %
Band f
f
low
f
high
f
mid
f
low
f
high
TX Fade / (TX + RX Fade)
mid
C-band 3.4 4.2 3.8 5.85 6.65 6.25 72%
X-band 7.25 7.75 7.5 7.9 8.4 8.15 54%
Ku-band 11.7 12.2 11.95 14 14.5 14.25 58%
Ka-band 20.2 21.2 20.7 30 31 30.5 63%
Max TX Power Level (dBm): Take care in setting the Max TX Power level. Although tempting
to simply allow the modem to TX up to it’s maximum capability in doing so you are taking far more
risk than is necessary and can seriously damage equipment or take down the network. As
mentioned above, fade comes in many forms and if for example cables on the RX chain were
slowly deteriorating or the antenna was slightly pointed incorrectly, the demod will see all of this
as fade and try to compensate by changing the uplink power. In a clear sky condition with bad
RX cables a demod seeing a fade will increase the power to try to compensate for this fade up to
the maximum power set in this parameter. For this reason it is best to take some time and
determine how much total rain and thus how much total UPLINK fade the site could actually see
and to calculate the maximum amount of uplink power needed to illuminate the satellite in worst
fade conditions. In doing so you will reduce the impact of other fade conditions.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–13
Page 70

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.2 Configure Terrestrial Interface
The Terrestrial Interface window allows access to setup Control port and Data port parameter s.
Ethernet controls like flow control and Quality of Service are supported. QoS offers the ability to
provide different priority to different applications, users, or data flows to guarantee a certain level
of performance to a data flow. Refer to Figure 7.4.2-1.
Figure 7.4.2-1 Terrestrial Interface
In Band Control: When In-Band Control is checked, the MDX-420 will allow itself to be monitored
and controlled locally through Control Ports J1 & J2 or by a remote gateway over the satellite link
without an external connection between the control port and the data port. When unchecked, a
SNMP session can only occur locally through Control Ports J1 or J2.
FLOW CONTROL: When checked it auto-negotiates rate of data transmission with the device
connected to the MDX420. When unchecked no back pressure is applied to connecting routers
or switches for flow control.
DAISY CHAIN MODE: Daisy Chain Mode can be used whenever a single site is demodulating
more than 4 share groups as is commonly seen in Hub and Spoke applications or in larger MESH
networks with 5 or more share groups. This mode is used where one (1) MDX-420 is transmitting
into a share group and demodulating 1-4 share groups and there are additional MDX-42 0 units
that are only used to demodulate additional share groups (not transmitting). Looking at Figure
7.4.2-2, the proper way to eliminate layer 2 issues such as spanning tree or endless loop when
multiple MDX420 units are used is to connect the devices in the following manner. When Daisy
Chain Mode is selected on a unit, traffic entering Port J4 will be forwarded to Port J3 and MAC
learning and aging will be disabled on Port J4. By doing this none of the destination MAC
address that come in on Port 4 will be associated to either the LAN or WAN side of the link.
The MDX-420 that is being used to transmit traffic must have “Daisy Chain Mode” checked (we
will call this MDX-T). The MDX-420 that is being used as a demod only (we will call this MDX-R1)
must connect MDX-R1 Port J3 to MDX-T Port J4. It is a good idea to also check “Daisy Chain
Mode” on MDX-R1 in case future share groups are added. It would then be possible to connect
future MDX-420s being used in a demod only configuration (MDX-R2) by again connecting MDXR2 Port J3 to MDX-R1 Port J4.
QUALITY of SERVICE (QoS): Two types supported NORMAL and PORT BASED.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–14
Page 71

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
NORMAL - Uses the following formats (IEEE 803.3ac Tag containing IEEE 802.1p priority
information provided by an external device, Type of Service field (RFC 791) or Differentiated
Services field (RFC 2474) contained in an IPv4 header and Traffic Class field (RFC 2460)
contained in an IPv6 header.
PORT BASED - In this mode, (J3) has the highest priority and (J4) has the lowest priority. The
Port Based overrides any standard priority
QoS QUEUE (FAIR WEIGHTED, STRICT PRIORITY)
FAIR WEIGHTED: - Selects the queue weighting of 8,4,2,1 that insures even the lowest priority
traffic gets some bandwidth (packets are processed in a weighted round robin manner).
STRICT PRIORITY: - insures that the higher priority traffic will always be transmitted before any
lower priority traffic. With this setting, the lower priority traffic can starve.
First In First Out (FIFO): - In certain circumstances it may be desirable to have the Ethernet
Interface to operate in a FIFO like mode with no reordering of packets. This can be done by
using a single port and setting the Ethernet QoS type to Port Base and the Ethernet QoS Queue
to strict priority. This will allow packets to be transmitted in the exact order in which they are
received.
Default settings for the terrestrial interface are:
M&C Control Port:
In-Band Control: Disabled
Ethernet Data Port:
Flow Control: Enabled
Daisy Chain: Disabled
Quality of Service:
Type: Normal
Queuing: Fair Weighted
Figure 7.4.2-2 Daisy Chain Set up for Data Ports
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–15
Page 72

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.3 Configure Network Configuration
Once the SkyWire gateway satellite parameters have been configured the next step is to
configure the network settings. A SkyWire gateway can be configured with up to 4 burst
demodulators. From the Configure menu, select Network Configuration and click on the demod
associated with the modulator (see section 7.4.1.1 “Selected Demod”). If only one burst
demodulator is installed, the tabs for Demod 2, Demod 3, and Demod 4 will be grayed out.
The Network configuration screen is divided into two sections. The upper section is the Channel
section that shows the basic configuration of the selected burst demodulator. The lower sectio n
is the Remotes configuration section. The Remotes configuration section provides the
mechanism to assign the parameters for each gateway within the network share group.
Configuring a SkyWire network requires a thorough understanding of the overall network
requirements prior to creating, adding, or deleting gateways in the network.
Channel Configuration: With few exceptions, the “Channel” section of the Network Configuration
screen is a brief representation of what was configured and can be seen in the demod
configuration (see section 7.3.1.2). Other items only available on this screen include the
following:
Start Network: Clicking on this box will manually tell the MDX-420 to start a new share group if
the unit is not already participating in an existing share group. The Start Network control button
allows the user to initialize the network for the first time. Once one or more of the remotes in the
SkyWire Network have been configured and the satellite parameters are set, the network can be
started. The initialization process requires one gateway within the shared group to initialize the
link. As other remote gateways are configured and set to receive the shared carrier signal, the
distributed intelligence of the SkyWire network will provide access to the remotes and they will be
asked to join the network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–16
Page 73

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Reboot Network: Clicking on this box will manually tell all MDX-420 devices in the share-group to
shut down and perform a soft re-boot. This is useful when updating firmware on all sites in a
share group so that all sites shut down and start-up with the same FW revision. You will be
prompted to enter your SNMP V2 or SNMP V3 password to complete this action.
Share Group Access Code: This is a field that can optionally be used to provide a unique name
for a share group. This is used primarily to prevent demodulators without the proper access cod e
from listening to the share group in a listen-only manner. Click the Edit button, create a unique
name and hit enter. Once entered on any site in a share group all other sites in the share group
will be given the new unique name. NOTE: This name will need to be manually changed on any
MDX-420 units listening to but not transmitting into (participating in) this share group. Any MDX420 that is participating in this share group will NOT require this name to be entered in order to
join the share group. If the name is not present or incorrectly entered the site will still join the
network if it is being requested to join and will automatically re-program the proper Share Group
Access Code into it’s table.
The Remotes configuration section provides the mechanism to assign the sharing parameters for
each gateway that will be part of the selected share group. The setup of this table is done at a
single location for the share group and is distributed to all other sites participating in the sh are
group. Maintenance, additions, and deletions of gateways from the share group can be
performed from any active gateway location.
The upper portion of the screen indicates the minimum configurable step-size of the BW
parameters. This mimimum step size is automatically calculated by the MDX-420 based on
criteria such as Data Rate, Modulation, Performance and FEC that were all established in the
Modulator Configuration section of the GUI (see section 7.3.1). A multiple of this step size MUST
be used in setting all BW parameters.
The table has eight positions representing eight potential gateways in the share group. The
decision as to which position applies to a specific gateway is at the discretion of the network
administrator. Position in the table has no bearing on the bandwidth sharing priorities withi n the
share group.
For each position of the Remotes table three settings are used to determine how the carrier
bandwidth will be shared.
Dedicated Information Rate (DIR) – Data Rate in Kbits per second that cannot be used by anyone
except the assigned gateway.
Committed Information Rate (CIR) – Data Rate in Kbits per second that are available to the
assigned gateway when ever requested, but is pooled when not in use by the assigned gateway.
Maximum Information Rate (MIR) – The maximum Data Rate in Kbits per second the site can
use. An entry of “0” in this field means that you are not restricting the maximum Data Rate and
the site can use all available BW in the pool if allotted. A setting of “0” is the most common entry.
Elevation Angle - Antenna elevation angle at the site of the transmitting gateway identified in the
Access Code. An elevation angle of “270” is to be used for laboratory testing without any satellite
delay. An elevation angle of “180” can be used for sites that have an unknown elevation angle or
sites that may be in a mobile environment where the elevation angle is not known or changing but
can not be used in the lab environment.
Access Code - Enter the unique Gateway ID of the SkyWire gateway (refer to Section 7.4.1.1
“Gateway ID”). This is a hardware identification number and must be entered for the gateway to
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–17
Page 74

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
properly join the share group. NOTE: If entered incorrectly the remote site will not join the
network.
Circuit Name – Text name to help identify the circuit. The circuit name is not a required field but if
entered, the circuit name will appear as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over a remote’s
graphics bar on the Demodulator Summary Status screen.
Assigning a SkyWire gateway to the network as Remote 1 is a simple three step process (Figures
7.4.3-1 through 7.4.3-3).
1 Click on the Create control button on the left of the first position in the Remotes table.
2 Click on the Edit control button to begin entering the network parameters:
set the appropriate CIR, DIR, MIR
antenna elevation angle,
enter the Access Code,
circuit name (if desired)
check the Enable button
3 Click Apply to enter the new settings.
Repeat the process for all SkyWire Gateways that need to join this network. This process is also
used when a new gateway is being added to an existing share group.
Figure 7.4.3-1
Figure 7.4.3-2
Figure 7.4.3-3
Figure 7.4.3-4
To temporarily remove a remote from the network after it has been created, encheck the
“Enabled” box. To permanently remove a remote from the network after it has been created, click
the “Destroy” button. Clicking the Destroy button (Figure 7.4.3-4) disables the gateway assigned
to that position, clears the position in the table and permanently removes all user entered data for
that site. NOTE: Disabling or destroying a site you are locally connected to will terminate any
access to other sites in the network from this device.
Network Configuration Notes:
1 The Step Size value is based on the symbol rate, modulation and coding of the shared carrier.
2 The settings for DIR and CIR must be equal to or multiples of the Step Size.
3 Also when configuring the settings of DIR, CIR and MIR, the relationship must be as follows:
DIR <= CIR <= MIR.
4 The sum of all CIRs in the share group must be less than the Data Rate shown in the Channel
section of the screen.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–18
Page 75

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
5 Entering a value of zero (0) for the MIR disables the MIR function and allows a remote to burst up to
the available data rate of the shared carrier.
6 An elevation angle of 270 must be used when performing tests in the laboratory or when no satellite
delay is present in the set-up.
7 An elevation angle of 180 can be used for mobile sites or sites with unknown locations.
7.4.4 Configure Test and Diagnostics
Access to the Test & Diagnostics screen is via the SkyWire Controller top-level menu system.
Select the Configure / Test & Diagnostics / Mod menu (Figure 7.4.4-1).
Figure 7.4.4-1 Test & Diagnostics Menu Selection
Test and Diagnostics provides specific information about the available gateway test modes for the
gateway burst modulator. The available internal test functions are used for setting the burst
modulator carrier to a test mode. Test modes under Carrier TYPE
Figure 7.4.4-2 Burst Modulator Internal Test Functions
Normal: Causes the burst modulator to output normal modulation.
CW: Causes the burst modulator to output a pure carrier.
Dual: Causes a double sideband output.
Offset: Causes a single sideband output.
Positive FIR: For manufacturer’s use only.
Negative FIR: For manufacturers use only.
CNT MOD: Transmits a continuously modulated carrier. This mode is used to verify the proper
bandwidth and noise level margin of the carrier within the satellite transponder. This is may also
be used for antenna alignment. The test mode does not allow any data to be transmitted.
Note: There are currently no available test modes for the burst demodulato rs. The screen
tab is available for future use.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–19
Page 76

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.5 Configure System Configuration
Figure 7.4.5 System Configuration Screen
The system configuration screen (Figure 7.4.5) provides specific information about the gateway that
is accessible by the administrator. In addition, it provides the administrator the option to secure the
gateway from unauthorized use.
Firmware Version: Displays the current gateway Firmware Version
Secure Modem Enable: Enabling the Secure mode hides the Gateway ID (requires SNMP
v.3)
Service Port Admin Password: Allows the user to edit or change the password used by the
serial service port J7. If this password is lost or forgotten, a user may restore the factory
default passwords by clicking on “Load Defaults” shown on this screen. NOTE: If a user
clicks the Load Defaults button it is highly suggested that they do this locally as loading the
default factory settings will likely cause the unit to drop out of the network.Feature Mode:
Displays the Feature mode (Normal, Demo). Note: When Demo mode is shown here there
may be features of the MDX-420 that are running but not purchased. When the demo mode
runs out of time, these features will be disabled and the unit may revert to an unknown state.
Feature ID: Displays the Feature ID needed by the Comtech factory to supply field upgrades.
When purchasing a filed upgrade please have this number ready.
Gateway ID: Displays the unique Gateway ID of the MDX-420 when not in Secure Mode
Time Format:: Shows the format for entering the real time date and time
Time: Displays the real time clock
Installed Features: Displays installed features that are active in “Normal” Feature Mode
On the bottom of the screen there are three buttons to save and load different configurations.
These three buttons have the same capability as the “LNV”, “SNV” and “DNV” commands
discussed in section 5.3 Initial Configuration Check.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–20
Page 77

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Load Config: Will load all the user settings from the “USER.NV” file located on the compact flash
(CF) card located in the Archive folder. Use the Load Config tool when a known USER.NF file
contains the settings desired to operate the modem, bring the modem back to a known state, or
partially configure a modem by bringing it into a known state.
Save Config: Will save all present configuration settings to a file called “USER.NV” located on
the compact flash (CF) card under the ARCHIVE folder. This tool can be used to save a known
state in case the modem looses it’s configuration or to create a file that can be loaded onto other
SkyWire CF cards so that they can load the known configuration.
Load Defaults: Will load the “DEFAULT.NV” file from the compact flash under the ARCHIVE
folder. This will have the effect of resetting the modem to the factory default state. All user
settings and passwords will be reset to the default settings by doing this.
Shown below is an example of files located on the Compact Flash (J5) under the ARCHIVE
directory. This is where the “USER.NV” and “DEFAULT.NV” files are located under normal
operation. The “DEFAULT.NV” file SHOULD NOT BE EDITED. Doing so may corrupt the
default non vol settings and may make the product unstable.
Figure 7.4.5 MC Archive
Note: A user with SNMPv3 administrative privileges can secure the Gateway ID by checking
the Secure Modem Enable. Securing the Gateway ID can only be done by the administrator.
Warning: Do not lose administrative passwords. Once the gateway is secured, Gateway IDs
are hidden. The Gateway ID cannot be recovered if administrative passwords for the SkyWire
Controller and Terminal are lost. Unit must be returned to factory and reworked at the
expense of the customer.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–21
Page 78

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.6 Configure Alarms
Demod Alarms: To view the detailed alarms of the burst demodulator(s), select the tab for the
Demod 1-4. The Detailed Alarms screen for the selected burst demodulator (Figure 7.4.6-1) will
be displayed.
Figure 7.4.6-1 Detailed Alarams
Major Alarms:
o Demod FPGA Indicates a receive FPGA hardware failure.
o Decoder FPGA Indicates a decoder failure.
o Tuner PLL Indicates that the Rx L-Band Synthesizer is not locked. This alarm will
flash on during certain gateway parameter changes. A solid indication points toward a
configuration problem within the gateway.
o Signal Lock Indicates that the burst demodulator is unable to lock to a signal.
Minor Alarms:
o IFEC Lock Reserved for future use.
o Frame Lock Indicates that the Framing Unit is unable to find the expected framing
pattern.
o EsNo Indicates Rx signal quality fallen below input threshold.
o Carrier Level Indicates Rx signal level has fallen below input threshold.
o Test Pattern Sync Reserved for future use
o Carrier Level Cal The gateway has not been properly calibrated.
Modulator Alarms: To view the detailed alarms of the modulator, select the Mod tab. The
Detailed Alarms screen for the modulator (Figure 7.4.6-2) will be displayed.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–22
Page 79

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.4.6-2
Major Alarms:
o Mod FPGA Indicates a transmit FPGA configuration failure.
o Encoder FPGA Indicates a transmit encoder configuration failure.
o LO Synthesizer Indicates that the Tx L-Band Synthesizer is not locked. This alarm
will flash on during certain gateway parameter changes. A solid indication points
toward a configuration problem within the gateway.
o Share Group Config The burst modulator and that active listener burst demodulator
satellite configuration parameters do not match
Minor Alarms:
o Output Level Indicates that the Output Level is out of specification.
o BUC Voltage Indicates that the BUC voltage is out of specification
o BUC Current Indicates that the BUC Current is out of specification.
o Mesh Authorization Indicates the Gateway/Authorization ID number cannot be detected
on the mesh network.
o Carrier Level Cal The gateway has not been properly calibrated
o DC Offset Cal The gateway has not been properly calibrated
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–23
Page 80

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
To view the detailed alarms of the gateway common hardware, select the Common tab. The
Detailed Alarms screen for the gateway common equipment (Figure 7.4.6-3) is shown.
Figure 7.4.6-3
Major Alarms:
Glue FPGA Indicates Glue FPGA configuration failure.
Terr. Interface FPGA Indicates an Interface Card FPGA configuration failure.
Minor Alarms:
+1.2V Displays the measured voltage of the 1.2 Volt power bus located inside
the gateway.
+1.8V Displays the measured voltage of the 1.8 Volt power bus located inside
the gateway.
+3.3V Displays the measured voltage of the +3.3 Volt power bus located inside
the gateway.
+5V Displays the measured voltage of the +5 Volt power bus located inside
the gateway.
+12V Displays the measured vol t age of the +12 Volt powe r bus located inside
the gateway.
+24V Displays the measured vol t age of the +24 Volt powe r bus located inside
the gateway.
LNB Voltage Indicates that the LNB voltage is out of specification
LNB Current Indicates that the LNB Current is out of specification.
Terr. Ethernet Link Indicates lack of activity on the gateway Ethernet Data port.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–24
Page 81

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.7 Configure Share Group
Configuring the “Share Group” is an effective way of making a global change to all or multiple sites that
are participating (transmitting) into a share group. This is a simple way to make global changes to the
IF/RF parameters of the share group without having to change parameters on a site by site basis.
Common reasons to make such a change would be to increase the carrier size to accommodate more
users or traffic, moving the share group from one frequency to another or changes to modulation and
coding when moving the carrier to a new transponder.
Share Group changes will impact the modulator IF parameters and associated demod parameters of all
sites that are transmitting into this share group. Note: Sites that are not participating in the share group
but that have demodulators tuned to the share group being changed (ie. passive receivers) will NOT
receive new IF/RF parameters and will need to be manually changed to match the new RF parameters.
Current Settings: These are the current IF/RF settings of the MDX-420 and all other MDX-420
units that are participating in this share group.
Desired Settings: Enter the desired settings of the new share group. Parameters such as TX RF,
RX RF, Modulation, FEC, Symbol Rate / Data Rate and Performance should be entered as the
new characteristics of the share group. For assistance on any of these items please refer to
section 7.4.1.1.
Once the desired settings are entered and you are ready to make a share group configuration
change click the “Next” button.
The user is then prompted to select which sites in the current share group that will be making this change.
Click the “Include” box for those sites that are to execute the new RF change command. Selecting all the
sites will change the characteristics of the entire share group.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–25
Page 82

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Share Group Configuration Rules:
It is a requirement that all sites be “Enabled” (See section 7.4.3) in the share group; are active
and show an active green light on the GUI at the time a share group command is entered for
processing. All active sites in the share group need to be informed that a share group change is
being requested.
If a site is not presently available and not in the network it must be “Disabled” by unchecking the
“Enabled: box (See section 7.4.3) before a share group command will be accepted.
If you select the site the GUI is currently controlling, all other sites in the share group will
automatically be selected.
When a sub-set of the total sites in the share group are selected (not all sites) the sub-set is
assumed to be moving to an EXISTING alternative share group. You can not move a sub-set of
sites to a new frequency location in order to creat a new share group.
Once the share group configuration changes have been made, select “Next”. At this time parameters of
the change are sent to each MDX-420 but are NOT EXECUTED. Each device that will be affected by the
change must first check that the change is executable and reply with an acceptace or rejection of the
change. The “Status” color of each site that is requested to change will then turn either green (accepted)
or red (rejected).
By doing this the MDX-420 devices affected ensure that they have the proper options and configuration to
execute the command. For example, asking all sites to change to a 5Mb data rate to add capacity would
require that all sites have the 5Mb data rate option installed. If an “included” site is unable to execute a
command or if any of the configuration rules above are not met the user will get a Configuration Error
message as seen below:
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–26
Page 83

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
If all sites affected accept the change the user can click on “Next” to goto the authentication
screen:
Depending on the version of SNMP (2 or 3) being run, the user will then be asked for the
appropriate community or password to proceed to execution. Once the password is entered click
“Next” to execute the command.
Upon execution, the network will allow the sites to either create a new share group (all sites only)
or move selected sites to another share group (sub-set of sites). WHEN MOVING ALL SITES: If,
after roughly 10 minutes, all sites have not properly moved, ALL sites will revert back to their
original state. This includes the settings of “Auto Start” (See Section 7.4.1.1 “Auto Start”) again it
is HIGHLY suggested that one site and only one site in a share group have Auto Start selected.
If no sites in the share group have Auto Start selected and if the Share Group change reverts
back to the original settings the network will not automatically re-form. WHEN MOVING A SUBSET OF SITES: individual sites that properly entered into the new share group will stay and sites
that had difficulty will revert to the original share group.
If there are sites that for any reason have difficulty with the share group command, sites can
always be individually moved as needed without using the Share Group Channel Config.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–27
Page 84

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.4.8 Configure TCP/IP Settings
TCP/IP Settings are all READ ONLY settings from the GUI. These settings are only configurable from
the service port J7 serial interface ONLY.
Boot Mode: Determines what IP addresses, gateways and masks will be used by the modem. Under
normal operation this should be NONVOL. Other selections typically used in test or in the factory are:
DEFAULT, BOOTP, IP TEST. See section 6.2.4.8 for more on this.
BootP Server Tag: Only used in BootP Boot Mode and the tag must match the sever’s expected tag.
Local Host Name: Local Host Name for the Network
IP MASK {ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Mask The IP Address Mask of the local network. The mask is
expressed in a hexadecimal format, and must be a valid TCP/IP Mask. This field should be set before
changes are made to the Gateway or Router Address.
MODEM IP ADDR {ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Mask The IP Address of the gateway. This address
should be consistent for the mask defined. This address is expressed in hexadecimal format. Broadcast
and loop back addresses will not be allowed. These are addresses with all subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
SERVER IP ADDR {ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Address The IP Address of the Boot Server and the
address of the SNMP Trap Server when SNMP is active. If a server is used and there is no local router,
this address must be consistent with the gateway address. If a router has been specified, the address is
presumed to be reachable via the router. Broadcast and loop back addresses will not be allowed. These
are addresses with all subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
ROUTER IP ADDR {ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd} Decimal Address The IP Address of the Local Network Router.
If a router is present on the local network, this address must be consistent with the IP Mask and the
subnet of the gateway. If no router is present, then the address should be set to a foreign address. This
address is expressed in hexadecimal format. Broadcast and loop back addresses will not be allowed.
These are addresses with all subnet bits set to 0’s or 1’s.
Modem Ether Addr {hhhhhhhhhhhh} Displays the Ethernet address of the device. Set at the factory
and is a unique identifier for the Ethernet physical interface.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–28
Page 85

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
ETHER RATE {10/100 MBPS/Auto Negotiate} The data rate for the local Ethernet Interface. 10/100
Mbps/Auto Sensing – for 10 or 100 Base-T in either half-duplex or full duplex.
FTP User ID {XXXXXXXXXXXXXX} The user ID for creating a FTP session. FTP sessions are used to
update a unit’s Firmware. Note: It is strongly suggested to use the same FTP User ID for all MDX-420
units in a network. The default user ID is: user
FTP Password {XXXXXXXXXXXXXX} The Password for enabling a FTP session. FTP sessions are
used to update a unit’s Firmware. Note: It is strongly suggested to use the same FTP Password for all
MDX-420 units in a network.The default Password is: password
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–29
Page 86

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.5 Tools Tab
The tools tab allows the user to set certertain criteria for ease of use and to update and check the
status of the firmware running on the MDX-420 sites in the current share group.
7.5.1 Options
Options (Figure 7.5.1) allows for the user to determine if the Carrier Frequency and Throughput
control for the burst modulator and burst demodulator.
Carrier Frequency Control: IF or RF. IF indicates L-Band control and RF indicates control
using the Satellite uplink and downlink frequencies. This selection will change t he way
frequencies are displayed and entered in the modulator and demodulator configuration screens.
Statistics Averaging Period (secs): Enter the number of seconds used for the averaging period
for all of the display statics.
Throughput Control: Data Rate or Symbol Rate. Selecting the Data Rate control allows the
user to set the data throughput for the SkyWire gateway based on the user data rate. Selecting
the Symbol Rate control allows the user to set the data throughput for the SkyWire gateway
based on the symbol rate of the modulated carrier.
FTP Control: Used to update MDX-420 Firmware (See Section 6.2.4.8 “FTP User ID” and “FTP
Password”
Figure 7.5.1 Options Control Screen
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–30
Page 87

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.5.2 Firmware Status
The Firmware Status page gives a brief overview of the Firmware that is available to each MDX420 in the share group.
NOTE: The proper FTP User ID and Password must be entered into the Options control
screen (see Figure 7.5.1) in order to see the firmware status for each MDX420.
This information tells the user what firmare versions are in the “archive” and “accepted” folders of
the MDX-420. This doe NOT tell you what version of firmware is actually running on the MDX420, only what is available. To know what version is currently running click on the main tab
“Configure” and “System” (see section 7.4.5). For more information on how to update firmware
over satellite or boot from a specific firmware version please read the white paper:
AN/SKYWIRE_FTP Rev. –“SKYWIRE™ GATEWAY M&C UPDATE PROCEDURE USING FTP
UTILITY PROGRAM”
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–31
Page 88

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.6 Main Screen / Home Screen
The main screen (Figure 7.6), or home screen once logged into a SkyWire MDX-420 contains 4
main sections.
1) Demodulator Status
2) Network Status
3) Event Logs
4) Alarms
Figure 7.6 Main screen
7.6.1 Demodulator Status Screen
The Demodulator Status screen that is the upper left portion of the Main Screen, (Figure 7.6) is
used to monitor carrier status of the burst demodulators located in the gateway which the
SkyWire Controller is logged into. Individual remote data is normalized for relative performance.
Carrier composite information is displayed numerically based on the use r define d Polling Interval
(Section 7.3.1).
By using the Graph drop down menu, information about individual sites in the share group can be
seen. This information is displayed on a per MDX-420 basis. In this example there are three (3)
MDX-420 sites in a single share group. Information per MDX-420 is available as:
% Total IR – Normalized percent of total throughput
% CIR – Normalized percent of assigned committed information rate
% Max IR – Normalized percent of assigned maximum information rate
Total Packets – Total packets received
Packet Errors – Total packet errors
Carrier Level (dBm) – Receive Carrier level of the burst demodulator
Eb/No (dB) – Signal quality of the shared carrier received by the burst demodulator
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–32
Page 89

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
PER – Packet error rate
Some of these drop down graphs, such as the Carrier Level and Eb/No have indicators in red and
green on the “Y” axis of the graph to help operators understand if the products are being used in a
suggested range (see figures 7.6.1-a and 7.6.1b). These ranges change depending on the d ata rate,
performance, modulation and coding being used.
Figure 7.6.1-a Figure 7.6.1-b
Composite status (located on the right side of each Demod section) does not change regardless of
the Graph drop-down and includes information on the carrier as a whole (all sites that are members of
a share group treated as a single composite carrier):
Carrier (min) – Carrier level of the active burst demodulator in the share group with the lowest
receive carrier level
Eb/No (min) – Signal quality indicator of the active burst demodulator in the share group with the
lowest Eb/No
PPS – packets per second – Statistically averaged snapshot of the total packet per second rate
received by the share group.
% Total IR – composite throughput
PER – composite packet error rate
Packet errors – composite packet errors
Total packets – composite packets
Figure 7.6.1-c Demodulator Status
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–33
Page 90

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.6.2 Network Status Screen
The Network Status display (Figure 7.6.2) is divided into two sections. The TX section is specific to the
MDX-420 the operator is currently logged into and shows graphical and numerical status about the
information transmitted to the shared carrier. The Demod ”X” Composite section shows the graphical and
numeric composite status of all sites on the shared carrier that is associataed with the modulator (see
section 7.4.1.1 “Selected Demod”). By using the Graph pull down menu various statistics can be viewed:
TX Information:
Kbps – Transmitted information rate in Kilobits per second from the MDX-420
pps – Transmitted packets per second from the MDX-420
%CIR - Information rate as a % of configured CIR for the currently logged in MDX-420
% Total IR - Information rate as a % of the total share group total information rate
Total packets – Total packets transmitted by the MDX-420
Demod X Composite:
Kbps – Received information rate in Kilobits from all units in the share group
pps – Received packets per second from all units in the share group
%CIR - Information rate as a % of configured CIR for the currently logged in MDX-420
% Total IR - Information rate as a % of the total share group total information rate
Total packets – Total packets transmitted by the MDX-420
Figure 7.6.2. Network Status
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–34
Page 91

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.6.3 Alarm Status Screen
Alarm summary (Figure 7.6.3) provides the top level view of both current and latched alarms on
the gateway which the SkyWire Controller is logged into.
Figure 7.6.3 Alarms (Summary)
To view the details of the individual alarms, double click on either the current or latched alarm and
the details will be displayed. Detailed alarms are described in section (7.4.6)
7.6.4 Events Log Screen
Event logs (Figure 7.6.4) provides a historical listing of captured events that may be of interest to
the user for the gateway since power up or the last clearing of the events for:
Modem – Gateway specific
SNMP – Interface related
Application – SkyWire Controller program related
Figure 7.6.4 Event Log
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–35
Page 92

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.7 Defining User Ac c es s C ontrols (SNMPv3)
Once the SkyWire gateway parameters have been established, the administrator can determine
user access controls. Defining and establishing access controls allows the administrator to limit
user access to the gateway and the network. Limiting access ensures that network parameters
are not arbitrarily placed into unauthorized users. When SNMPv3 is selected, the administrator
can assign access privileges to users. They may be configured as Viewers, Operators or Users
with administrative access.
Note: Setting up SNMP V3 administrative controls can be done during initial setup of the Network.
7.7.1 Setup Terminal Access parameters
Prior to configuring the User Access Control on the SkyWire Configuration Controller software
(SkyWire Controller), the administrator must configure the Group Access setting in the SNM P
Terminal screens. Refer to Figure 7.7.1. The SNMP Version 3 Terminal screen parameters must
be set up first in order to allow access to the gateway with the SkyWire Controller. SNMP
Terminal parameters and SkyWire Controller parameters must match. Refer to Section 6 for
additional information on accessing the Service port terminal screens.
The gateway is shipped with SNMP Control factory default parameters per Table 7.7.1.
There are three user "Groups" that determine access type for each user. These groups include
ADMIN, OPER or VIEWER. Administrator must configure parameters for each group.
VIEWER: Allows the user to view the gateway status. There is no access to Gateway ID or
network data.
OPERA: Allows the user to view the link status and limited parameter controls. No access to
Gateway ID.
ADMIN: Full access and control to all menus within the Network.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–36
Page 93

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.7.1 SNMP Version 3 Terminal Screen
USER1 USER2 USER3 USER4
ID administrator operator viewer
Group ADMIN OPER VIEWER NO GROUP
AuthP password password password
PrivP password password password
AuthM MD5 MD5 MD5 NONE
PrivM DES DES DES NONE
User Reset
Table 7.7.1 SNMP Version 3 Terminal Default Parameters
Administrator Settings for SNMP Terminal Screens:
ID 1-4: Default names are administrator, operator and viewer. Names can change.
Group: ADMIN, OPER, OR VIEWER
AuthP: Defined by the administrator and at least 8 characters in length.
PrivP: Defined by the administrator and at least 8 characters in length.
AuthM: None, MD5 or SHA
PrivM: None, DES
Reset: Resets the user parameters to the defaulted names listed
Note: Parameters assigned in the Terminal must be the parameters used when logging in with
the SkyWire Controller.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–37
Page 94

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
7.7.2 Setup SkyWire Controller Access Parameters
If the user is currently logged into a SkyWire gateway with the SkyWire Controller, the user must
log out and log back in to activate the SNMPv3 controls set in the Terminal menu. In the Login
screen, click the button to the right of the Destination Name to configure the SkyWire Controll er
interface parameters. The Destination Configuration menu will be displayed as shown in Figure
7.7.2-1. Select the originally saved Destination Name in the pull down menu or create a new
Destination Name for the gateway. By selecting SNMPv3 for this gateway, the login screen will
require SNMPv3 log-in passwords and allow access to the SNMPv3 menus.
WARNING: When SNMPv3 is selected, the unit secures the mesh network by requiring
authentication privacy. This verifies that the contents of the messages have not been altered as
that the source is authenticated. It also protect against disclosure as ease dropping.
Figure 7.7.2-1 Login Screen – Select SNMPv3
Figure 7.7.2-2 Login Screen for SNMPv3
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–38
Page 95

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Terminal (SNMP) SkyWire Controller
ID# Security Name
Group Context Name
AuthP Authentication Password
PrivP Privacy Password
AuthM Authentication Protocol
PrivM Privacy Protocol
Table 7.7.2 Login Screen Names between Terminal and SkyWire Controller
7.7.3 The SNMPv3 Login Menus
The SNMPv3 menus allow the user to begin the user access configuration process. Use the
factory defaults to access the User Profile Configuration Menus and begin configuring profiles for
the administrator and all other users within this gateway.
The MDX420 is shipped from factory with the following Login Screen defaults:
Menu Names Factory Defaults
User profile Name: Viewer, Operator, Administrator
Authentication Password: password
Privacy Password: password
User Profile Name: The default user names are preassigned to allow the administrator initial
access to the configuration menus. When user names are created in the next section of the
configuration menus, that name will be displayed in the drop down menus. User Profile can have
as many profile names as needed. Once user names are created, they will only need to login
using the assigned name and passwords given. Password must be a least 8 cha racte rs in length.
Authentication Password: Use the password created in the SNMP Terminal screen. The
password settings between the SkyWire Controller and the Terminal screens have to match in
order to work correctly. Refer to the SNMP Terminal Screens in section 6. Password must be a
least 8 characters in length.
Privacy Password: Use the password created in the SNMP Terminal screen. The password
settings between the SkyWire Controller and the Terminal screens have to match in order to work
correctly. Refer to the SNMP Terminal Screens in section 6. Password must be a least 8
characters in length.
7.7.4 SNMPv3 User Profile Configuration
Select the user profile type in the SNMPv3 Menu and click on the button at the bottom of the
Login screen to display the User Profile Configuration screen (Figure 7.7.4-1). In this screen the
administrator can create and configure all the users.
User Profile Configuration Menus and the factory defaults are listed below:
Menu Names Factory Defaults
User profile Name: Viewer/Operator/Administrator
Security User Name: Viewer/Operator/Administrator
Context Name: Viewer/Operator/Administrator
Authentication Protocol: None
Privacy Protocol: None
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–39
Page 96

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Steps to Creating User Gateway Access:
1. Ensure the SNMP and SkyWire Controller parameters are identical
2. Identify all the operators, viewers and administrators within the gateway network
3. Determine their access level
4. Assign names to each user, ex. New York1, London1, Jakarta
5. Select the security name for the specific user.
6. Select user Context/Group Name (Administrator, Operator, or Viewer)
7. Select Authentication Protocol (None, MD5, SHA)
8. Select Privacy Protocol (None, DES)
9. Click on the Save button to store the destination profile for easy future access
Detailed Steps to Setting up a User:
User Profile Name: The User Profile Name defaults are Viewer, Operator and Administrator
(Figure 7.7.4-1). The Administrator can create as many profiles needed. There is no limit to the
number of user profile names. Once the User Profile name is created it will be displayed on the
Login drop down screen.
Security User Name: Security User Name is shipped with defaulted names. Security name is the
User name assigned in the Terminal Screens. The Administrator can change the Security names
in the SNMP Terminal menu. Once the Security name is created the Terminal menu, it will be
display in the User Profile Configuration menu.
Figure 7.7.4-1 User Profile Name Menus
Context Name: Administrator must enter the Context/Group Name of each user (Figure 7.7.4-2).
Selection should be in the same group as the security user name. Context Name is limited to
three selections, Viewer, Operator and Administrator.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–40
Page 97

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.7.4-2 Context Name Menus
Authentication Protocol: Authentication Protocol provides data integrity and data origin
authentication (Figure 7.7.4-3). Hash function MD5 or SHA-1 are supported. Selection must be
in the same as selected in the SNMP Terminal screens.
None: Allows the operator to assign the applicable user Access Level group.
MD5: Allows the operator to assign the applicable user Access Level group
SHA: Allows the operator to assign the applicable user Access Level group
Figure 7.7.4-3 Authentication Protocol Menus
Privacy Protocol: DES is used for encryption providing protection against disclosure of message
payload (Figure 7.7.4-4). Selection should be in the same as selected in the SNMP Terminal
screens.
None: Allows the operator to assign the applicable user Access Level group
DES: Allows the operator to assign the applicable user Access Level group
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–41
Page 98

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway SkyWire Controller (GUI)
Figure 7.7.4-4 Privacy Protocol Menus
Click on the Save button to store the User in the User Profile Configuration Menu
User name and setting will be available on the Login Screen.
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 7–42
Page 99

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Technical Specifications
Chapter 8. Technical
Specifications
SkyWire™ MDX420 Performance
Acquisition Modulation User Data Network Typical
Performance & TPC FEC Rate Range Threshold BER 1E-8
Enhanced QPSK .710 328k - 12.7m 2.9dB 3.5dB
Enhanced QPSK .793 366k - 14.2m 3.3dB 3.8dB
Standard QPSK .793 378k - 14.7m 3.4dB 4.4dB
Enhanced 8PSK .793 537k - 20.9m 6.5dB 7.6dB
Standard 8PSK .793 555k - 21.6m 7.8dB 9.0dB
Modulator
Modulation: QPSK (8PSK Optional)
L-Band Tuning Range: 950 to 1750 MHz in 1 Hz Steps
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Connector: N-Type (50 Ohm)
Return Loss: 10 dB Minimum
Output Power: 0 to -25 dBm
Output Accuracy: ±1.0 dB Over Frequency and Temperature
Spurious: -55 dBc In-Band
-45 dBc Out-of-Band
Harmonics: -45 dBc
On/Off Power Ratio: >60 dB
Symbol Rate Range .256 to 10 Msps in 1 sps steps
FEC: Turbo Product Code .710, .793
Internal Stability: ±280 ppB
±50 ppB (Optional)
Optional BUC Power: 3.3 Amps @ 24 V Maximum
2.8 Amps @ 48 V Maximum
BUC Reference: 10 MHz, +3 dBm ± 3 dB
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 8–1
Page 100

MDX420 SkyWire™ Satellite Network Gateway Technical Specifications
Demodulator
Demodulation: QPSK (8PSK Optional)
L-Band Tuning Range: 950 to 2050 MHz in 1 Hz Steps
Impedance: 75 Ohm
Connector: F-Type (75 Ohm) Female
Return Loss: 10 dB Minimum
Input Level: 10 x Log (Symbol Rate) -122 +
12 dB
Total Input Power: -10 dBm or +40 dBc (the lesser)
Symbol Rate Range .256 to 10 Msps in 1 sps steps
FEC: Turbo Product Code .710, .793
Carrier Acquisition Range: ± 5% of the Symbol Rate
LNB DC Power: 500 mA @ 24 VDC Maximum
LNB Reference: 10 MHz, +3 dBm ± 3 dB
Monitor and Control
Ethernet 10/100 Base-T
SNMP V1, V2, and V3
MIB Browser
Radyne Network Configuration GUI
Service Port
Terminal RS-232
Terrestrial Interface
Ethernet 10/100/1000 Base-T
Alarms
One Form-C Relay
Five Open Collector
Environmental
Prime Power: 100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz, Auto-sensing
40 Watts Max, Gateway only
200 Watts Max, BUC & LNB Powered
Operating Temperature: 0 to 50° C, 95% Humidity, Non-Condensing
Storage Temperature: -20 to 70° C, 99% Humidity, Non-Condensing
Physical
Size: 19”W x 13”D x 1.75”H
(48.26 x 33.0 x 4.45 cm)
Weight: 7 pounds (3.17 kg)
MN-MDX420 Revision 6 8–2
 Loading...
Loading...