Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Manual

Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software
Configuration Guide
Release 4.1.x
February 07, 2014
Cisco Systems, Inc.
www.cisco.com
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide.
Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers
are listed on the Cisco website at
www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Text Part Number: OL-30621-02

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this
URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
© 2013 - 2014 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

CONTENTS
About this Guide 1
Introduction 1
Document Revision History 2
Organization 3
Related Publications 5
Conventions 6
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request 7
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Cisco Service Control Overview 1-1
Introduction 1-1
Cisco Service Control Solution 1-2
Service Control for Broadband Service Providers 1-2
Cisco Service Control Capabilities 1-3
Cisco SCE Platform Description 1-4
Bandwidth Management of P2P Traffic 1-5
Management and Collection 1-6
Network Management 1-6
Subscriber Management 1-7
Service Configuration Management 1-7
Data Collection 1-7
IPv6 Support 1-8
2 Command-Line Interface 2-1
Introduction 2-1
Authorization and Command Mode Levels (Hierarchy) 2-2
CLI Authorization Levels 2-2
CLI Command Mode Hierarchy 2-3
Prompt Indications 2-6
Navigating Between Authorization Levels and Command Modes 2-6
The do Command: Executing Commands Without Exiting 2-7
OL-30621-02
CLI Help Features 2-9
Partial Help 2-9
Argument Help 2-9
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
iii

Contents
Navigational and Shortcut Features 2-11
Command History 2-11
Keyboard Shortcuts 2-11
Auto-Completion 2-12
FTP User Name and Password 2-13
Managing Command Output 2-14
Scrolling the Screen Display 2-14
Filtering Command Output 2-14
Redirecting Command Output to a File 2-15
Creating a CLI Script 2-16
CHAPTER
3 Basic Cisco SCE 8000 Platform Operations 3-1
Introduction 3-1
Starting the Cisco SCE 8000 Platform 3-2
Checking Conditions Prior to System Startup 3-2
Starting the System and Observing Initial Conditions 3-2
Final Tests 3-3
How to Verify Operational Status 3-3
How to View the User Log Counters 3-3
Managing Configurations 3-5
Viewing Configurations 3-5
How to Save or Change the Configuration Settings 3-6
Example for Saving or Changing the Configuration Settings 3-7
Restoring a Previous Configuration 3-8
Example for Restoring a Previous Configuration 3-8
How to Display the Cisco SCE Platform Version Information 3-10
Example for Displaying the Cisco SCE Platform Version Information 3-10
How to Display the Cisco SCE Platform Inventory 3-13
Examples for Displaying the Cisco SCE Platform Inventory 3-13
Displaying the Cisco SCE Platform Inventory: FRUs Only 3-13
Displaying the Complete Cisco SCE Platform Inventory 3-14
iv
How to Display the System Uptime 3-17
Example for Displaying the System Uptime 3-17
Configuring the System Mode 3-17
Configuring the IPv6 Prefix Length 3-18
Monitoring Control Processor CPU Utilization 3-20
CLI Commands for Monitoring Control Processor CPU Utilization 3-20
Example for Monitoring Control Processor CPU Utilization 3-21
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

Rebooting and Shutting Down the Cisco SCE Platform 3-23
Rebooting the Cisco SCE Platform 3-23
Examples for Rebooting the Cisco SCE Platform 3-23
How to Shut Down the Cisco SCE Platform 3-23
Example for Shutting Down the Cisco SCE Platform 3-24
Contents
CHAPTER
4 Utilities 4-1
Introduction 4-1
Working with Cisco SCE Platform Files 4-2
Working with Directories 4-2
Working with Files 4-4
The User Log 4-7
The Logging System 4-7
Generating a File for Technical Support 4-9
How to Create a Directory 4-2
How to Delete a Directory 4-2
How to Change Directories 4-3
How to Display your Working Directory 4-3
How to List the Files in a Directory 4-3
How to Rename a File 4-4
How to Delete a File 4-4
Copying Files 4-5
How to Display File Contents 4-6
How to Unzip a File 4-6
Copying the User Log 4-7
Enabling and Disabling the User Log 4-8
Viewing the User Log Counters 4-8
Viewing the User Log 4-9
Clearing the User Log 4-9
Generating a File for Technical Support: Example 4-9
OL-30621-02
Managing Syslog 4-10
Enabling and Disabling Syslog 4-10
Configuring Remote Syslog Hosts 4-10
How to Add a Remote Syslog Host 4-11
How to Remove a Remote Syslog Host 4-11
Configuring the Minimum Severity Level to be Logged to Syslog 4-11
How to Configure the Minimum Severity Level for Syslog Messages 4-12
How to Restore the Default Minimum Severity Level for Syslog Messages 4-12
Configuring the Syslog Facility 4-12
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
v

Contents
How to Configure the Syslog Facility 4-13
How to Restore the Default Syslog Facility 4-13
Configuring the Syslog Logging Rate Limit 4-13
How to Configure the Syslog Rate Limit 4-14
How to Restore the Default Syslog Rate Limit 4-14
Configuring the Syslog Time Stamp Format 4-14
How to Configure the Syslog Time Stamp Format 4-15
How to Restore the Default Syslog Time Stamp Format 4-15
Enabling and Disabling the Syslog Message Counter 4-15
Monitoring Syslog 4-15
How to Display the Syslog Configuration 4-16
How to Display the Syslog Counters 4-16
Flow Capture 4-17
Limitations 4-17
The Flow Capture Process 4-18
Configuring a Flow Capture Traffic Rule 4-18
Configuring the Flow Capture Settings 4-18
Performing the Flow Capture 4-20
Monitoring the Flow Capture 4-20
CHAPTER
5 Configuring the Management Interface and Security 5-1
Introduction 5-1
Management Interface and Security 5-2
Configuring the Management Ports 5-3
Entering the Management Interface Configuration Mode 5-3
Configuring the Management Port Physical Parameters 5-4
Setting the IP Address and Subnet Mask of the Management Interface 5-4
Configuring the Management Interface Speed and Duplex Parameters 5-5
Specifying the Active Management Port 5-7
Management Interface Redundancy 5-8
Configuring the Management Ports for Redundancy 5-8
Configuring the Fail-Over Mode 5-9
Monitoring the Management Interface 5-10
Configuring Management Interface VLANs 5-11
Monitoring Management VLANs 5-14
TACACS+ Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting 5-15
Information About TACACS+ Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting 5-15
Login Authentication 5-15
Accounting 5-16
vi
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

Privilege-Level Authorization 5-16
Command-Level Authorization 5-17
General AAA Fallback and Recovery Mechanism 5-17
About Configuring TACACS+ 5-18
Configuring the Cisco SCE Platform TACACS+ Client 5-19
Adding a New TACACS+ Server Host 5-19
Removing a TACACS+ Server Host 5-20
Configuring the Global Default Key 5-20
Configuring the Global Default Timeout 5-21
Managing the User Database 5-22
Adding a New User to the Local Database 5-22
Defining the User Privilege Level 5-24
Adding a New User with Privilege Level and Password 5-24
Deleting a User 5-26
Configuring AAA Login Authentication 5-26
Configuring Maximum Login Attempts 5-26
Configuring the AAA Login Authentication Methods 5-27
Configuring AAA Privilege-Level Authorization Methods 5-28
Configuring AAA Command-Level Authorization Methods 5-28
Configuring AAA Accounting 5-29
Monitoring TACACS+ 5-30
Displaying Statistics for TACACS+ Servers 5-30
Displaying Statistics, Keys, and Timeouts for TACACS+ Servers 5-30
Monitoring TACACS+ Users 5-31
Contents
OL-30621-02
Configuring Access Control Lists (ACLs) 5-32
Adding Entries to an ACL 5-33
Removing an ACL 5-33
Defining a Global ACL 5-34
Managing the Telnet Interface 5-35
Preventing Telnet Access 5-35
Assigning an ACL to the Telnet Interface 5-35
Removing ACL Assignment from the Telnet Interface 5-36
Configuring Telnet Timeout 5-36
Configuring the SSH Server 5-37
The SSH Server 5-37
Key Management 5-37
Managing the SSH Server 5-38
Generating a Set of SSH Keys 5-38
Enabling the SSH Server 5-38
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
vii

Contents
Disabling the SSH Server 5-38
Running Only SSHv2 5-39
Assigning an ACL to the SSH Server 5-39
Removing the ACL Assignment from the SSH Server 5-39
Deleting the Existing SSH Keys 5-39
Monitoring the Status of the SSH Server 5-40
Configuring and Managing the SNMP Interface 5-41
About the SNMP Interface 5-41
SNMP Protocol 5-41
Security Considerations 5-42
About CLI 5-43
About MIBs 5-44
Configuration via SNMP 5-44
Enabling the SNMP Interface 5-45
How to Enable the SNMP Interface 5-45
How to Disable the SNMP Interface 5-45
Configuring SNMP Community Strings 5-45
Defining a Community String 5-46
Removing a Community String 5-46
Displaying the Configured Community Strings 5-47
Configuring SNMP Notifications 5-47
Configuring SNMP Server Group 5-48
Configuring SNMP Server View 5-48
Configuring SNMP Server User 5-49
Defining SNMP Hosts 5-50
Configuring SNMP Traps 5-51
SNMP Walk Acceleration for linkServiceUsage Queries 5-53
How to Enable SNMP Query Acceleration 5-53
SNMPv3 Configuration Example 5-53
CHAPTER
viii
6 Global Configuration 6-1
Introduction 6-1
IP Routing Configuration 6-2
Configuring the IP Routing Table 6-2
How to Configure the Default Gateway 6-2
How to Add an Entry to the IP Routing Table 6-3
How to Display the IP Routing Table 6-3
IP Advertising 6-4
Configuring IP Advertising 6-4
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Display the Current IP Advertising Configuration 6-5
Configuring Time Clocks and Time Zone 6-6
Displaying the System Time 6-6
Displaying the System Time: Example 6-6
Displaying the Calendar Time 6-7
Displaying the Calendar Time: Example 6-7
Setting the System Clock 6-7
Options 6-7
Setting the System Clock: Example 6-7
Setting the Calendar 6-7
Options 6-8
Setting the Calendar: Example 6-8
Setting the Time Zone 6-8
Options 6-8
Setting the Time Zone: Example 6-9
Removing the Current Time Zone Setting 6-9
Configuring Daylight Saving Time 6-9
Options 6-9
Guidelines 6-10
How to Define Recurring Daylight Saving Time Transitions 6-11
How to Define Non-Recurring Daylight Saving Time Transitions 6-11
How to Cancel the Daylight Saving Time Configuration 6-11
How to Display the Current Daylight Saving Time Configuration 6-12
Contents
OL-30621-02
Configuring SNTP 6-13
How to Enable the SNTP Multicast Client 6-13
How to Disable the SNTP Multicast Client 6-14
How to Enable the SNTP Unicast Client 6-14
Options 6-14
Enabling SNTP Unicast Client: Example 6-14
Disabling the SNTP Unicast Client 6-14
How to Disable the SNTP Unicast Client and Remove All Servers 6-14
How to Remove One SNTP Server 6-15
How to Define the SNTP Unicast Update Interval 6-15
Options 6-15
How to Display SNTP Information 6-15
Domain Name Server (DNS) Settings 6-17
Configuring DNS Lookup 6-17
How to Enable DNS Lookup 6-17
How to Disable DNS Lookup 6-17
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
ix

Contents
Configuring Name Servers 6-18
Options 6-18
How to Define Domain Name Servers 6-18
How to Remove a Domain Name Server 6-18
How to Remove All Domain Name Servers 6-19
How to Add a Host to the Host Table 6-19
Options 6-19
Adding Hosts to Removing them from the Host Table: Example 6-19
How to Display Current DNS Settings 6-19
Displaying Current DNS Settings: Example 6-19
Configuring Cisco Discovery Protocol 6-20
Cisco Discovery Protocol 6-20
Cisco Discovery Protocol on the Cisco SCE 8000 Platform 6-21
CDP Operational Modes on the Cisco SCE 8000 6-21
CDP Limitations on the Cisco SCE 8000 6-22
Configuring CDP on the Cisco SCE 8000 Platform 6-22
Enabling CDP Globally 6-22
Setting CDP Mode 6-23
Enabling CDP on a Specific Traffic Interface 6-23
Setting the Hold Time 6-24
Setting the Timer 6-24
Monitoring and Maintaining CDP 6-25
CDP Configuration Examples 6-27
Example: Setting the CDP Mode 6-27
Example: Monitoring and Maintaining CDP 6-27
CHAPTER
x
Enabling the CLI Interface Warning Banner 6-29
OS Fingerprinting and NAT Detection 6-30
Restrictions and Limitations 6-30
Configuring OS Fingerprinting 6-31
Monitoring OS Fingerprinting 6-33
7 Configuring Line Interfaces 7-1
Introduction 7-1
Line Interfaces 7-2
Information About Line Interfaces 7-2
Flow Control and Bandwidth Considerations 7-2
Maximum Packet Size 7-2
How to Configure the Ten Gigabit Ethernet Line Interfaces 7-2
Changing the Traffic Direction on the Ten Gigabit Ethernet Line Interfaces 7-3
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Specify the Traffic Direction on Link 1 7-3
Tunneling Protocols 7-4
Tunneling IPv6 Traffic 7-6
Selecting the Tunneling Mode 7-7
Configuring the 6to4 Tunnels 7-8
Configuring DS-Lite Tunnels 7-9
Configuring L2TP Tunnels 7-10
Configuring GRE Tunneling 7-11
Configuring IPinIP Tunneling 7-13
Configuring DSCP Marking 7-14
Configuring the 6to4 Environment 7-15
Configuring the VLAN Environment 7-16
Configuring the MPLS Environment 7-17
Configuring the L2TP Environment 7-18
Asymmetric L2 Support 7-18
Displaying the Tunneling Configuration 7-19
How to Display the 6to4 Configuration 7-19
How to Display the DS-Lite Configuration 7-19
How to Display the IPinIP Configuration 7-20
How to Display the Logged-In VPNs 7-20
Options 7-20
How to Display the Asymmetric L2 Support Mode 7-21
Contents
Managed VPNs 7-22
Monitoring VPN Support 7-23
Displaying VPN-related Mappings 7-23
Configuring Traffic Rules and Counters 7-26
Traffic Rules and Counters 7-26
What are Traffic Rules and Counters? 7-26
Traffic Rules 7-27
Traffic Counters 7-27
Configuring Traffic Counters 7-28
How to Create a Traffic Counter 7-28
How to Delete a Traffic Counter 7-28
How to Delete all Existing Traffic Counters 7-28
Configuring Traffic Rules 7-29
How to Create a Traffic Rule for IPv4 Addresses 7-29
How to Create a Traffic Rule for IPv6 Addresses 7-32
How to Delete a Traffic Rule 7-33
How to Delete All Traffic Rules 7-33
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xi

Contents
How to Delete All Flow Control Traffic Rules 7-34
Managing Traffic Rules and Counters 7-34
How to View a Specified Traffic Rule 7-34
How to View All Traffic Rules 7-34
How to View a Specified Traffic Counter 7-34
How to View All Traffic Counters 7-35
How to Reset a Specified Traffic Counter 7-35
How to Reset All Traffic Counters 7-35
DSCP Marking 7-36
How to Display the DSCP Marking Configuration 7-36
Counting Dropped Packets 7-37
About Counting Dropped Packets 7-37
Disabling the Hardware Packet Drop 7-37
CHAPTER
8 Configuring the Connection 8-1
Introduction 8-1
Configuring the Connection Mode 8-2
Options 8-2
Configuring the Connection Mode Examples 8-3
Monitoring the Connection Mode and Related Parameters 8-4
Connection Mode Examples 8-4
Configuring the Link Mode 8-6
About the Link Mode 8-6
Options 8-6
External Optical Bypass 8-7
How to Activate the External Bypass 8-7
How to Deactivate the External Bypass 8-8
How to Set the External Bypass to the Default State 8-8
How to Display the State of the External Bypass 8-8
Hardware Bypass 8-9
How to Enable the Hardware Bypass Mode 8-9
How to Disable the Hardware Bypass Mode 8-10
How to Display the Status of the Hardware Bypass Mode 8-10
How to Set the Hardware Bypass Status for a Static Party 8-10
How to Reset the Hardware Bypass Staus of a static party 8-10
How to Display the Hardware Bypass Status of a Static Party 8-11
How to Display the Startup Configuration Party Database 8-11
How to Display the Currently Running Party Database Configuration 8-12
xii
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Copy the Running Configuration Party Database to the Startup Configuration Party
Database
How to Copy the Startup Configuration Party Database and Create a Backup File 8-12
Configuring the Static Subscribers 8-13
How to the Set the IP Address for a Static Subscriber 8-13
How to Set the IP Range for a Static Subscriber 8-13
How to Display All Mappings to Dual Stack Static Subscriber 8-13
How to Display IPv6 Mappings to Dual Stack Static Subscriber 8-14
How to Display Dual Stack Static Subscriber 8-14
Link Failure Reflection 8-15
How to Enable Link Failure Reflection 8-15
How to Disable Link Failure Reflection 8-15
Enabling and Disabling Link Failure Reflection on All Ports 8-15
Options 8-16
How to Enable Link Failure Reflection on All Ports 8-16
How to Disable Link Failure Reflection on All Ports 8-16
Configuring Link Failure Reflection in Linecard-Aware Mode 8-16
How to Enable Linecard-Aware Mode 8-17
How to Disable Linecard-Aware Mode 8-17
8-12
Contents
CHAPTER
Asymmetric Routing Topology 8-18
Asymmetric Routing and Other Service Control Capabilities 8-18
Enabling Asymmetric Routing 8-18
Monitoring Asymmetric Routing 8-19
Monitoring Asymmetric Routing: Example 8-19
Configuring a Forced Failure 8-20
Configuring the Failure Recovery Mode 8-21
Options 8-21
Configure the Failure Recovery Mode: Examples 8-21
Configuring the Cisco SCE Platform/SM Connection 8-22
Configuring the Behavior of the Cisco SCE Platform in Case of Failure of the SM 8-22
Options 8-22
Configuring the SM-SCE Platform Connection Timeout 8-22
Options 8-23
9 Raw Data Formatting: The RDR Formatter and NetFlow Exporting 9-1
Introduction 9-1
RDR Formatter and NetFlow Exporting Support 9-2
The RDR Formatter 9-2
NetFlow 9-2
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xiii

Contents
NetFlow Terminology 9-2
NetFlow Exporting Support 9-3
Data Destinations 9-4
Categories 9-5
Priority 9-5
Setting DSCP for NetFlow 9-6
Forwarding Modes 9-6
Protocol 9-6
Transport Type 9-6
Configuring Data Destinations and Categories 9-7
Configuring a Data Destination 9-7
Options 9-7
Configuring the Data Destinations: Examples 9-7
Configuring the Data Categories 9-8
Configuring the Buffer Size 9-9
Configuring a Destination and Assigning Categories 9-9
Configuring the Forwarding Mode 9-13
Options 9-13
Configuring the Forwarding Mode: Example 9-13
Configuring the RDR Formatter 9-14
Options 9-14
How to Configure the Size of the RDR Formatter History Buffer 9-14
Configuring NetFlow Exporting Support 9-15
Options 9-15
How to Configure a DSCP Value for NetFlow 9-15
Options 9-15
How to Configure the Template Refresh Interval 9-15
Options 9-15
Configuring Dynamic Mapping of RDRs to Categories 9-17
Configuring Mappings 9-17
Options 9-17
How to Restore the Default Mapping for a Specified RDR Tag 9-17
Displaying Data Destination Configuration and Statistics 9-18
How to the Display the Current RDR Formatter Configuration 9-18
Displaying the RDR Formatter Configuration: Example 9-19
How to the Display the Current RDR Formatter Statistics 9-19
Displaying the Current RDR Formatter Statistics: Example 9-19
xiv
Disabling the Linecard from Sending RDRs 9-21
Disabling RDR Aggregation 9-22
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

Contents
CHAPTER
10 Managing Subscribers 10-1
Introduction 10-1
Information About Subscribers 10-2
What is a Subscriber? 10-2
Subscriber Modes in Service Control Solutions 10-3
Subscriber Database: Capacity and Limits 10-4
Working with Large Numbers of Subscribers 10-5
Actual Maximum Number of Subscribers 10-5
Subscriber Mapping Limits 10-5
Rate of Creating Anonymous Subscribers 10-5
Aging Subscribers 10-5
VPN-Based Subscribers 10-6
Automatic VLAN VPNs 10-6
Synchronizing Subscriber Information in a Cascade System 10-6
Anonymous Groups and Subscriber Templates 10-7
Subscriber Files 10-8
Subscriber Default csv File Format 10-8
IPv6 Subscriber csv File Format 10-9
Here is an example of a subscriber csv file in the default format: 10-9
Subscriber Anonymous Groups csv File Format 10-9
Importing and Exporting Subscriber Information 10-10
Editing the subaware.pro File 10-10
Options 10-11
How to Import Subscriber Information 10-11
How to Export Subscriber Information 10-11
How to Import a Subscriber Template 10-12
How to Export a Subscriber Template 10-12
Removing Subscribers and Templates 10-13
How to Remove a Specific Subscriber 10-13
Options 10-13
How to Remove All Introduced Subscribers 10-14
How to Remove a Specific Anonymous Subscriber Group 10-14
Options 10-14
How to Remove All Anonymous Subscriber Groups 10-14
How to Remove All the Anonymous Subscribers 10-14
How to Remove All Subscriber Templates 10-15
Removing VPN-based Subscribers 10-15
How to Remove Subscribers by Device 10-15
How to Remove Subscribers from the SM 10-15
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xv

Contents
How to Remove Subscribers from a Specified SCMP Peer Device 10-17
Creating Anonymous Groups 10-18
Defining Anonymous Groups 10-18
How to Define an Anonymous Group 10-18
Importing and Exporting Anonymous Groups 10-19
How to Import Anonymous Groups 10-19
How to Export Anonymous Groups 10-19
Monitoring Subscribers 10-20
How to Monitor the Subscriber Database 10-20
How to Display the Subscriber Database Counters 10-21
Clearing the Subscriber Database Counters 10-22
Displaying Subscribers 10-22
Displaying Subscribers: All Current Subscriber Names 10-22
Displaying Subscribers: By Subscriber Property or Prefix 10-23
How to Display Subscribers: By Mapping (IP Address, VPN, or VLAN ID) 10-25
How to Display Subscriber Information 10-27
How to Display a Listing of Subscriber Properties 10-28
How to Display Complete Information for a Specified Subscriber 10-28
How to Display Values of Subscriber Properties for a Specified Subscriber 10-28
How to Display Mappings for a Specified Subscriber 10-28
How to Display OS Counters for a Specified Subscriber 10-29
Displaying Anonymous Subscriber Information 10-29
How to Display Currently Configured Anonymous Groups 10-29
How to Display Currently Configured Templates for Anonymous Groups 10-30
How to Display Current Configuration for a Specified Anonymous Group 10-30
How to Display Subscribers in a Specified Anonymous Group 10-30
How to Display All Subscribers Currently in Anonymous Groups 10-30
How to Display the Number of Subscribers in a Specified Anonymous Group 10-31
How to Display the Total Number of Subscribers in All Anonymous Groups 10-31
xvi
Configuring the Actual Maximum Number of Subscribers 10-32
How to Override the Configured Capacity Option 10-32
How to Override the Configured Capacity Option in a Cascade Setup 10-32
How to Restore the Configured Capacity Option 10-33
How to Monitor the Maximum Number of Subscribers 10-33
Configuring Subscriber Aging 10-34
How to Enable Aging for Anonymous Group Subscribers 10-34
How to Enable Aging for Introduced Subscribers 10-34
How to Disable Aging for Anonymous Group Subscribers 10-34
How to Disable Aging for Introduced Subscribers 10-35
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Set the Aging Timeout Period for Anonymous Group Subscribers 10-35
Options 10-35
How to Set the Aging Timeout Period for Introduced Subscribers 10-35
Options 10-35
How to Display Aging for Anonymous Group Subscribers 10-35
How to Display Aging for Introduced Subscribers 10-36
Managing VPNs and VPN Subscriber Mappings 10-37
How to Display VPN-Related Mappings 10-37
How to Clear Automatic VPNs 10-37
Configuring the Cisco SCE Platform/SM Connection 10-39
Configuring the Behavior of the Cisco SCE Platform in Case of Failure of the SM 10-39
Options 10-39
Configuring the SM-SCE Platform Connection Timeout 10-40
Options 10-40
Contents
CHAPTER
11 Redundancy and Failover 11-1
Introduction 11-1
Redundancy and Failover 11-2
Terminology and Definitions 11-2
Redundant Topologies 11-2
External Bypass 11-3
Hardware Bypass 11-3
In-line Dual Link Redundant Topology 11-3
Failure Detection 11-3
Link Failure Reflection 11-5
Hot Standby and Failover 11-6
Hot Standby 11-6
Failover 11-6
Hardware Crash Mode 11-8
Failure in the Cascade Connection 11-9
Installing a Cascaded System 11-9
Recovery 11-11
Replacing the Cisco SCE Platform (Manual Recovery) 11-11
Manual Steps 11-11
Automatic Steps (in parallel with the manual steps, requires no user intervention): 11-12
Reboot Only (Fully Automatic Recovery) 11-12
OL-30621-02
CLI Commands for Cascaded Systems 11-13
Topology-Related Parameters for Redundant Topologies 11-13
Configuring the Connection Mode 11-13
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xvii

Contents
Examples 11-14
Monitoring the System 11-14
How to View the Current Connection Mode 11-14
How to View the Cisco SCE-ID 11-15
How to View the Current Redundancy Status of the Cisco SCE Platform 11-15
How to View Information about the Peer Cisco SCE Platform 11-15
How to View Information about the Cascade Connections 11-16
How to View the Current Link to Port Mappings 11-16
How to View the Current Link Mode 11-17
Configuring Forced Failure 11-18
System Upgrades 11-19
Firmware Upgrade (package installation) 11-19
Application Upgrade 11-19
Simultaneous Upgrade of Firmware and Application 11-20
CHAPTER
12 Identifying and Preventing Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks 12-1
Introduction 12-1
Attack Filtering and Attack Detection 12-2
Attack Filtering 12-2
Specific Attack Filtering 12-2
Attack Detection 12-4
Attack Detection Thresholds 12-4
Attack Handling 12-5
Subscriber Notification 12-6
Hardware Filtering 12-6
Configuring Attack Detectors 12-8
Enabling Specific-IP Detection 12-10
Options 12-10
How to Enable Specific-IP Detection 12-10
How to Enable Specific-IP Detection for the TCP Protocol Only for all Attack Directions 12-11
How to Enable Specific-IP Detection for the TCP Protocol for Port-Based Detections Only for
Dual-Sided Attacks
12-11
How to Disable Specific-IP Detection for Protocols Other than TCP, UDP, and ICMP for all Attack
Directions
12-11
How to Disable Specific-IP Detection for ICMP for Single-Sided Attacks Defined by the Source
12-11
IP
Configuring the Default Attack Detector 12-11
Options 12-12
How to Define the Default Action and Optionally, the Default Thresholds 12-13
How to Reinstate the System Defaults for a Selected Set of Attack Types 12-13
xviii
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Reinstate the System Defaults for All Attack Types 12-14
Specific Attack Detectors 12-14
Options 12-14
How to Enable a Specific Attack Detector and Assign it an ACL 12-15
How to Define the Action and Optionally the Thresholds for a Specific Attack Detector 12-16
How to Define the Subscriber Notification Setting for a Specific Attack Detector 12-16
How to Define the SNMP Trap Setting for a Specific Attack Detector 12-16
How to Define the List of Destination Ports for TCP or UDP Protocols for a Specific Attack
Detector
How to Delete User-Defined Values 12-17
How to Disable a Specific Attack Detector 12-17
How to Disable All Non-default Attack Detectors 12-18
How to Disable All Attack Detectors 12-18
Sample Attack Detector Configuration 12-18
Subscriber Notifications 12-20
Configuring the Subscriber Notification Port 12-20
Options 12-20
How to Remove the Subscriber Notification Port 12-20
12-17
Contents
Preventing and Forcing Attack Detection 12-21
Options 12-21
Preventing Attack Filtering 12-21
How to Remove All dont-filter Settings 12-22
Forcing Attack Filtering 12-22
How to Remove All force-filter Settings 12-23
Monitoring Attack Filtering 12-24
Monitoring Attack Filtering Using SNMP Traps 12-24
Monitoring Attack Filtering Using CLI Commands 12-26
How to Display a Specified Attack Detector Configuration 12-26
How to Display the Default Attack Detector Configuration 12-28
How to Display All Attack Detector Configurations 12-28
How to Display Filter State (Enabled or Disabled) 12-29
How to Display Configured Threshold Values and Actions 12-29
How to Display the Current Counters 12-30
How to Display all Currently Handled Attacks 12-31
How to Display all Existing Force-Filter Settings 12-31
How to Display all Existing Don't-Filter Settings 12-31
How to Display the List of Ports Selected for Subscriber Notification 12-31
How to Find out Whether Hardware Attack Filtering has been Activated 12-32
Viewing the Attack Log 12-32
The Attack Log 12-32
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xix

Contents
How to View the Attack Log 12-33
How to Copy the Attack Log to a File 12-33
CHAPTER
13 Managing the SCMP 13-1
Introduction 13-1
About SCMP 13-2
SCMP Terminology 13-3
Deployment Scenarios 13-3
Single ISG Router with a Single Cisco SCE Platform (1xISG – 1xCisco SCE) 13-4
Single ISG Router with Two Cascaded Cisco SCE Platforms (1xISG – 2xCisco SCE) 13-4
Multiple ISG Routers with Two Cascaded Cisco SCE Platforms (NxISG – 2xCisco SCE) 13-5
Multiple ISG Routers with Multiple Cisco SCE Platforms via Load Balancing (NxISG – MxCisco
SCE)
13-6
SCMP Peer Devices 13-7
Connection Management 13-7
SCMP Subscriber Management 13-8
GUID and Subscriber ID 13-8
Configuring the SCMP 13-9
Configuring SCMP Parameters 13-9
How to Enable the SCMP 13-9
How to Disable the SCMP 13-10
How to Configure the SCMP Peer Device to Push Sessions 13-10
Configuring the SCMP Peer Device to Force Each Subscriber to Single Cisco SCE Platform 13-10
Defining the Keep-alive Interval Parameter 13-11
Defining the Reconnect Interval Parameter 13-11
Defining the Loss-of-Sync Timeout Parameter 13-12
Adding an SCMP Peer Device 13-12
How to Define an SCMP Peer Device 13-12
How to Assign the SCMP Peer Device to an Anonymous Group 13-13
Deleting Subscribers Managed by an SCMP Peer Device 13-14
Options 13-14
Deleting an SCMP Peer Device 13-14
Defining the Subscriber ID 13-14
Options 13-15
Configuring the RADIUS Client 13-15
Options 13-16
xx
Monitoring the SCMP Environment 13-17
How to Monitor the SCMP 13-17
Options 13-17
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to display the general SCMP configuration 13-17
How to display the configuration all currently defined SCMP peer devices 13-18
How to display the configuration for a specified SCMP peer device 13-18
How to display the statistics for all SCMP peer devices 13-18
How to display the statistics for a specified SCMP peer device 13-19
Monitoring the RADIUS Client 13-19
Contents
CHAPTER
14 Value-Added Services (VAS) Traffic Forwarding 14-1
Introduction 14-1
Information About VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-2
VAS Service Goals 14-2
How VAS Traffic Forwarding Works 14-3
Requirements for VAS Servers 14-4
VAS Traffic Forwarding and SCA BB 14-5
VLAN Tags for VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-5
Service Flow 14-5
Data Flow 14-6
Non-VAS Data Flow 14-7
VAS Data Flow 14-7
Load Balancing 14-8
Load Balancing and Subscribers 14-8
Load Balancing and Subscriber Mode 14-9
VAS Redundancy 14-10
VAS Server Failure 14-10
VAS Server Group Failure 14-10
Ethernet Switch Failure 14-11
Disabling a VAS Server 14-11
OL-30621-02
VAS Status and VAS Health Check 14-12
VAS Server States 14-13
VAS Traffic Forwarding Topologies 14-14
Single Cisco SCE Platform, Multiple VAS Servers 14-14
Data Flow 14-15
Multiple Cisco SCE Platforms, Multiple VAS Servers 14-15
SNMP Support for VAS 14-17
Interactions Between VAS Traffic Forwarding and Other Cisco SCE Platform Features 14-18
Incompatible Cisco SCE Platform Features 14-18
VAS Traffic Forwarding and DDoS Processing 14-18
Specific IP DDoS Attack Detection 14-18
Specific IP Attack Filter 14-18
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xxi

Contents
VAS Traffic Forwarding and Bandwidth Management 14-19
Global Controllers and VAS Flows 14-19
Configuring VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-20
Configuring VAS Traffic Forwarding from the SCA BB Console 14-21
Global Options 14-21
Enabling VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-21
Options 14-21
Disabling VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-22
Configuring the VAS Traffic Link 14-22
Options 14-23
How to Select the Link for VAS Traffic 14-23
How to Revert to the Default Link for VAS Traffic 14-23
Configuring a VAS Server 14-23
Options 14-24
How to Enable a VAS Server 14-24
How to Disable a VAS Server 14-24
How to Restore all VAS Server Properties to Default 14-24
Assigning a VLAN ID to a VAS Server 14-24
Options 14-25
How to Configure the VLAN Tag Number for a Specified VAS Server 14-25
How to Remove the VLAN Tag Number from a Specified VAS Server 14-25
Configuring the Health Check 14-25
How to Enable VAS Server Health Check 14-26
How to Disable VAS Server Health Check 14-27
How to Define the UDP Ports to be Used for Health Check 14-27
How to Remove the UDP Ports Configuration 14-27
Configuring Pseudo IP Addresses for the Health Check Packets 14-27
Configuring a VAS Server Group 14-28
Adding and Removing Servers 14-29
Configuring VAS Server Group Failure Parameters 14-29
VAS Configuration Example 14-31
xxii
Monitoring VAS Traffic Forwarding 14-32
How to Display Global VAS Status and Configuration 14-32
Example 14-32
How to Display Operational and Configuration Information for a Specific VAS Server Group 14-33
Example 14-33
How to Display Operational and Configuration Information for All VAS Server Groups 14-33
How to Display Operational and Configuration Information for a Specific VAS Server 14-33
Example 14-33
How to Display Operational and Configuration Information for All VAS Servers 14-34
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

How to Display the VAS Servers Used by a Specified Subscriber 14-34
How to Display Health Check Counters for a Specified VAS Server 14-34
Example 14-34
How to Display Health Check Counters for All VAS Servers 14-35
How to Clear the Health Check Counters for a Specified VAS Server 14-35
How to Clear the Health Check Counters for All VAS Servers 14-35
Intelligent Traffic Mirroring 14-36
Using Traffic Mirroring for Behavioral Targeting 14-36
How Traffic Mirroring Works 14-37
Traffic Mirroring and SCA BB 14-37
Mirroring Termination 14-38
Mirroring Exceptions 14-38
Mirroring the TCP-Segmented HTTP GET Packets 14-38
Cisco SCE Connectivity 14-39
Traffic Mirroring and Bandwidth Management 14-41
Configuring Traffic Mirroring 14-41
Monitoring Traffic Mirroring 14-42
Traffic Mirroring Sample Configuration 14-42
Contents
APPENDIX
A Cisco Service Control MIBs A-1
Introduction A-1
MIB Files A-2
Loading MIBs A-4
pcube to Cisco MIB Mapping A-5
Pcube Engage MIB (CISCO-SCAS-BB-MIB) A-6
pcube to Cisco MIB Mapping: Detailed OID Mappings A-7
Cisco SCE Platform-Specific MIB Information A-26
CISCO-ENTITY-ALARM-MIB A-26
MIB Updates A-27
Release 3.5.5 MIB Updates A-27
CISCO-SERVICE-CONTROL-TP-STATS-MIB A-27
Release 3.6.0 MIB Updates A-27
CISCO-PROCESSOR-MIB A-27
ENTITY-MIB A-27
Index Changes A-28
Release 3.6.5 MIB Updates A-29
Temperature Sensor Traps Updated A-29
Release 3.7.0 MIB Updates A-29
SNMP Support for Aggregative Global Controllers A-29
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
xxiii

Contents
linkUp and linkDown Notification Traps A-29
Release 4.1.0 MIB Updates A-30
SNMP TRAP for Global Attacks A-30
SNMP Walk Functionality for Temperature MIBs A-30
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
B Monitoring Cisco SCE Platform Utilization B-1
Introduction B-1
Cisco SCE Platform Utilization Indicators B-2
CPU Utilization B-2
Flows Capacity B-2
Subscribers Capacity B-2
Service Loss B-3
Monitoring Service Loss B-3
C Cisco SCE 8000 Licensing Information C-1
OpenSSH License C-1
NetSNMP License C-9
xxiv
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
OL-30621-02

Introduction
About this Guide
Revised: February 07, 2014, OL-30621-02
This preface describes who should read Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide, how it
is organized, and its document conventions.
This guide is for experienced network administrators who are responsible for configuring and
maintaining the Cisco SCE platform.
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
1
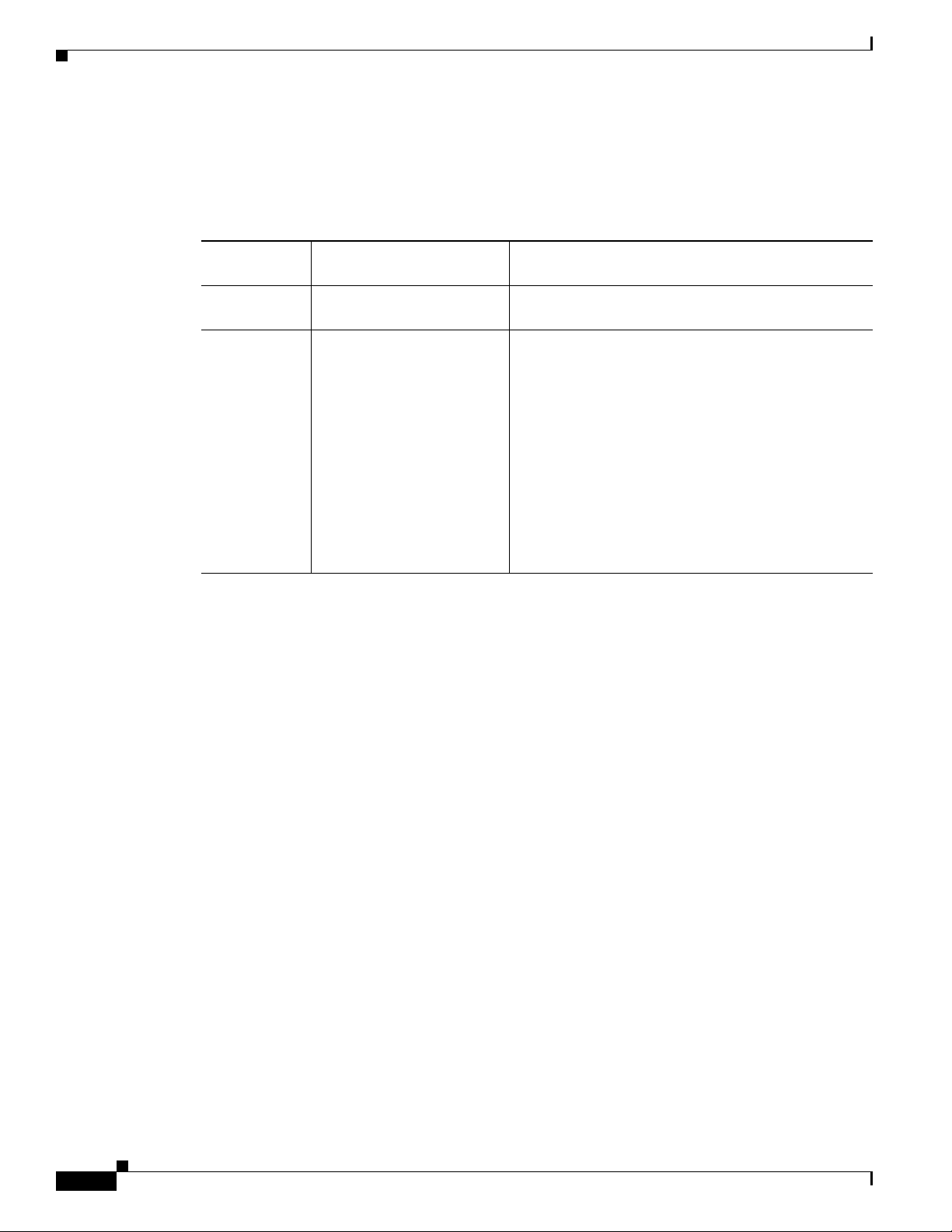
Document Revision History
The following Document Revision History records the changes made to this document.
Table 1 Document Revision History
Cisco Service Control
Revision
OL-30621-02 Release 4.1.x
OL-30621-01 Release 4.1.x
Release and Date Change Summary
February 07, 2014
December 23, 2013
Updated “MIB Updates” section on page A-27 with
limitations on linkUp/linkDown trap.
First version of this document (new for the Release
4.1.x train).
The following changes were made from the last release
of the 4.0.x train:
• Updated “Configuring and Managing the SNMP
Interface” section on page 5-41 with SNMPv3
details.
• Updated the “Tunneling Protocols” section on
page 7-4.
• Added “Release 4.1.0 MIB Updates” section on
page A-30.
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
2
OL-30621-02
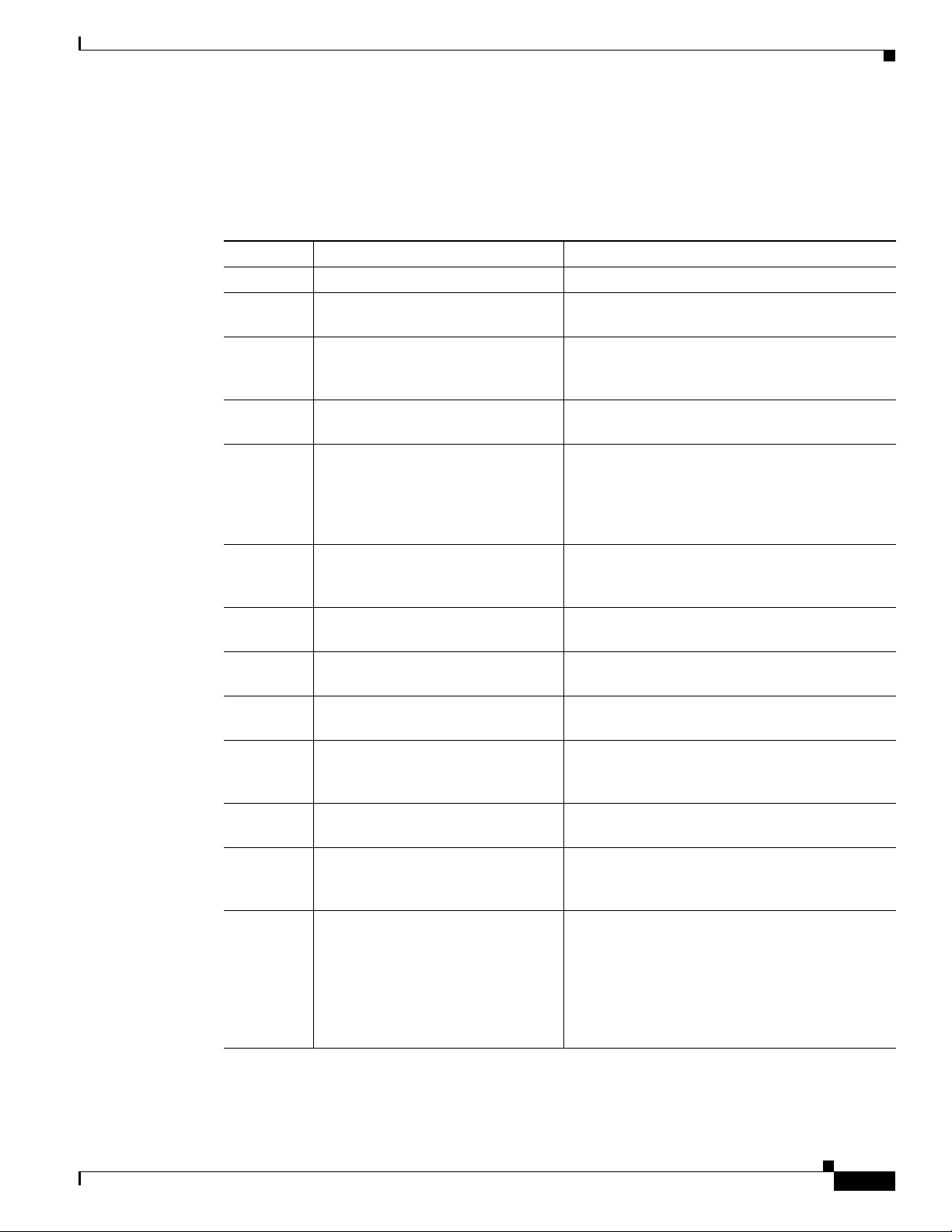
Organization
This guide contains the following sections.
Table 2 Document Organization
Section Title Description
Chapter 1 Cisco Service Control Overview Overview of Cisco SCE platform management.
Chapter 2 Command-Line Interface Detailed explanation of how to use the Cisco SCE
Chapter 3 Basic Cisco SCE 8000 Platform
Chapter 4 Utilities Explanation of the setup wizard and the user log,
Chapter 5 Configuring the Management
Chapter 6 Global Configuration Explanation of how to configure various global
Chapter 7 Configuring Line Interfaces Explanation of how to configure tunneling, TOS
Chapter 8 Configuring the Connection Explanation of how to configure the connection
Chapter 9 Raw Data Formatting: The RDR
Chapter 10 Managing Subscribers Explanation of how to import and export
Chapter 11 Redundancy and Failover Explanation of how to configure and manage a
Chapter 12 Identifying and Preventing
Chapter 13 Managing the SCMP Explanation of Service Control Management
Operations
Interface and Security
Formatter and NetFlow Exporting
Distributed Denial-of-Service
Attacks
Command-line Interface.
Explanation of how to manage configurations,
install applications and upgrade the system
software.
as well as of file operations.
Explanation of how to configure the various
management options: Telnet, SSH, and SNMP.
Also how to configure the system time, Domain
Name Settings, management IP address, and
passwords.
settings, such as system time, Domain Name
Settings, and IP routing.
marking, and traffic rules.
mode, link mode, and failure behaviors
Explanation of how to configure the connection
mode, link mode, and failure behaviors.
subscriber information and how to monitor
subscribers.
redundant system.
Explanation of how to configure attack filtering.
Protocol (SCMP), which is a protocol that
integrates the Cisco SCE platform and the ISG
(Intelligent Service Gateway) functionality of the
Cisco routers. It also explains how to configure
and manage SCMP, SCMP peer devices and the
RADIUS client.
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
3
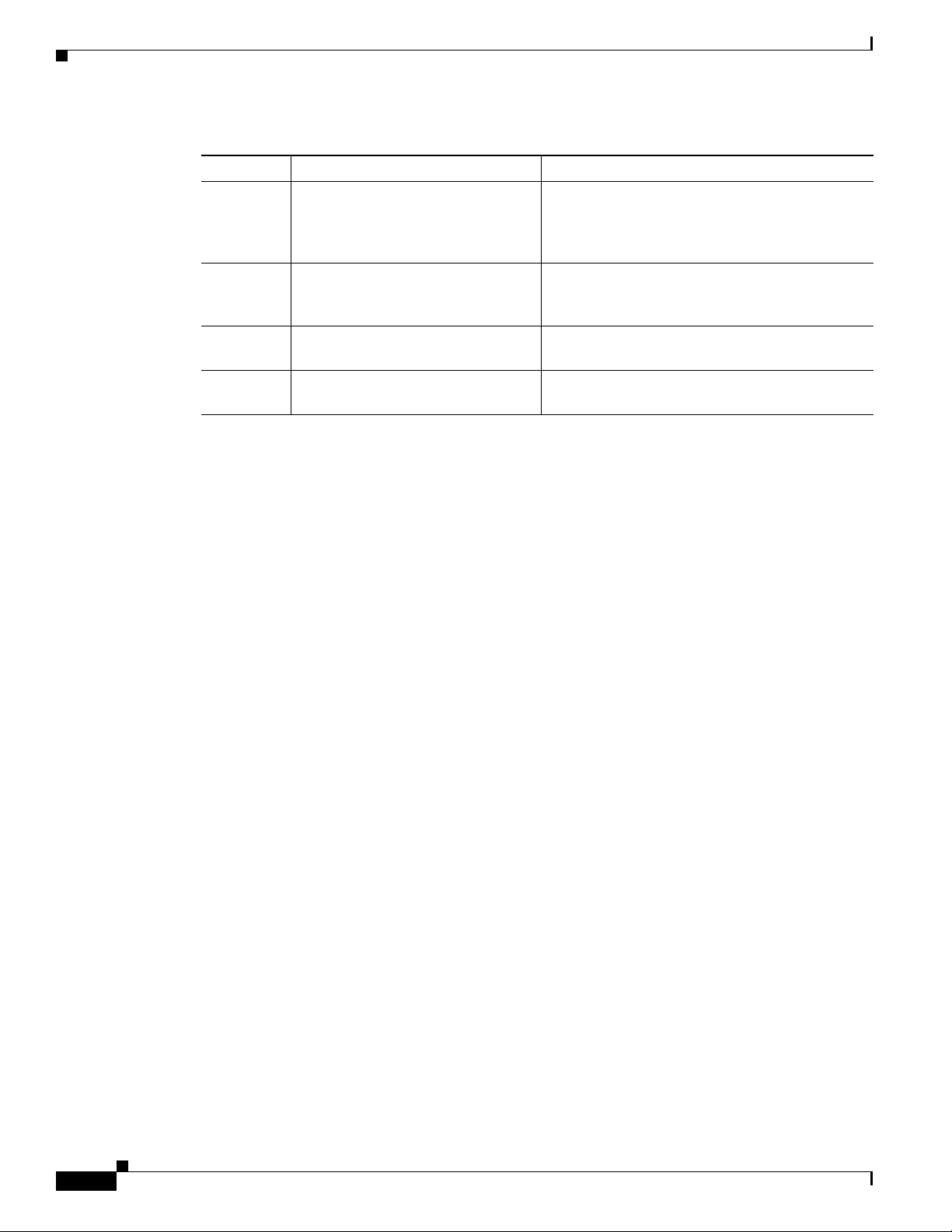
Table 2 Document Organization (continued)
Section Title Description
Chapter 14 Value-Added Services (VAS) Traffic
Forwarding
Appendix A Cisco Service Control MIBs Explanation of how to map the proprietary pcube
Appendix B Monitoring Cisco SCE Platform
Utilization
Appendix C Cisco SCE 8000 Licensing
Information
Explanation of Value Added Services (VAS)
traffic forwarding and how to configure it. Also
explains how the same capabilities are used for
traffic mirroring.
MIB supported in previous releases to the new
MIB structure.
Explanation of how to monitor Cisco SCE
platforms that are installed in real traffic.
Copy of Open SSH and NetSNMP license
information.
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
4
OL-30621-02

Related Publications
Your Cisco SCE platform and the software running on it contain extensive features and functionality,
which are documented in the following resources:
• For further information regarding the Service Control CLI and a complete listing of all CLI
commands, refer to the Cisco SCE8000 CLI Command Reference
• For initial installation and startup information, refer to the relevant installation guide:
–
Cisco SCE8000 10GBE Installation and Configuration Guide
• For international agency compliance, safety, and statutory information for wide-area network
(WAN) interfaces for the Cisco SCE 2000 platform, refer to the regulatory and safety information
document:
–
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco SCE8000
• For installation and configuration of the other components of the Service Control Management Suite
refer to:
–
Cisco SCMS Subscriber Management User Guide
–
Cisco SCMS Collection Manager User Guide
–
Cisco Service Control Application for Broadband User Guide
–
Cisco Insight User Guide
• To view Cisco documentation or obtain general information about the documentation, refer to the
following sources:
–
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page 7
–
The Cisco Information Packet that shipped with your Cisco SCE 8000 platform.
OL-30621-02
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
5

Conventions
This document uses the following conventions.
Table 3 Conventions
Convention Indication
bold font Commands and keywords and user-entered text appear in bold font.
italic font Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and arguments for which you supply
values are in italic font.
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{x | y | z} Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars.
[x | y | z] Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars.
string A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or
the string will include the quotation marks.
courier font Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in courier font.
< > Nonprinting characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.
[ ] Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.
!, # An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code
indicates a comment line.
Note Means reader take note.
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Timesaver Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in
the paragraph.
Warning
Means reader be warned. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in
bodily injury.
Cisco SCE 8000 10GBE Software Configuration Guide
6
OL-30621-02
 Loading...
Loading...