Page 1

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway
Administration Guide
Version 15.0
Last Updated September 30, 2013
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED
WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED
WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain
version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL
FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE
OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE
PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR
ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phon e numbers. Any examples, co mmand display
output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any u se of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in
illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
© 2013 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
iii
CONTENTS
About this Guide ................................................................................................ v
Conventions Used ................................................................................................................................... vi
Contacting Customer Support ................................................................................................................. vii
Additional Information ............................................................................................................................. viii
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network ........................................................ 9
Product Description ................................................................................................................................ 10
Protocol Architecture .......................................................................................................................... 11
Deployment Scenarios for HeNB Access Network ............................................................................ 13
HeNB Access Network Elements ....................................................................................................... 15
Home eNodeB ............................................................................................................................... 15
Security Gateway (SeGW) ............................................................................................................. 16
HeNB Gateway (HeNB-GW) .......................................................................................................... 16
HeNB Management System (HeMS) ............................................................................................. 17
CSG List Server ............................................................................................................................. 17
Licenses ............................................................................................................................................. 17
Platform Requirements ...................................................................................................................... 17
Network Deployment and Interfaces ...................................................................................................... 18
Supported Logical Interfaces ............................................................................................................. 18
Features and Functionality - Base Software .......................................................................................... 21
AAA Server Group Support ................................................................................................................ 21
Access Control List Support ............................................................................................................... 21
Bulk Statistics Support ....................................................................................................................... 22
DSCP Marking on S1-U Relay ........................................................................................................... 23
Fault Reporting Support ..................................................................................................................... 23
Location Reporting Support ............................................................................................................... 23
QoS Support ....................................................................................................................................... 23
Redundancy Support.......................................................................................................................... 23
Troubleshooting Features Support ..................................................................................................... 24
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software ...................................................... 25
Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR) Support ..................................................................................... 25
CSG-ID Based Paging Optimization Support .................................................................................... 25
License-based Control for No. of HeNB Connections ........................................................................ 26
License-based Control for No. of Subscribers Allowed ...................................................................... 26
Understanding the Service Operation ........................................................... 27
Terminology ............................................................................................................................................ 28
Contexts ............................................................................................................................................. 28
Logical Interfaces ............................................................................................................................... 28
Bindings .............................................................................................................................................. 29
Services and Networks ...................................................................................................................... 29
HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures ............................................... 31
Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW .......................................................... 32
Required Local Context Configuration Information ............................................................................ 32
Required Source Context Configuration Information ......................................................................... 32
Page 4

▀ Contents
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
iv
Required Destination Context Configuration Information ................................................................... 33
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ........................................................................................................... 37
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ....................................................................................................... 38
IPSec Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 40
GTP-U Service Configuration ............................................................................................................. 41
LTE Policy Configuration .................................................................................................................... 42
Verifying HeNB-GW Configuration ..................................................................................................... 43
Logging Facility Configuration ................................................................................................................ 44
Displaying Logging Facility ................................................................................................................. 45
Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration ........................................................................................................ 46
SNMP MIB Traps for HeNB-GW Service ............................................................................................... 47
Event IDs for HeNB-GW Service ............................................................................................................ 48
Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service .................................................................. 49
Monitoring System Status and Performance .......................................................................................... 50
Monitoring Logging Facility ..................................................................................................................... 53
Clearing Statistics and Counters ............................................................................................................ 54
HeNB-GW Service Thresholds ....................................................................... 55
Saving Your Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 56
System-Level HeNB-GW Service Thresholds ........................................................................................ 57
Configuring System-level HeNB-GW Service Thresholds ................................................................. 57
Troubleshooting the Service .......................................................................... 59
Test Commands ..................................................................................................................................... 60
Using the GTPU Test Echo Command .............................................................................................. 60
Using the IPsec Tunnel Test Command ............................................................................................. 60
Using the SNMP TRAP command for debugging .............................................................................. 61
Using the RESOURCES SESSION command for debugging ........................................................... 61
Page 5

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
v
About this Guide
This document pertains to the features and functionality that run on and/or that are related to the Cisco® ASR 5000
Chassis.
Page 6
About this Guide
▀ Conventions Used
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
vi
Conventions Used
Icon
Notice Type
Description
Information Note
Provides information about important features or instructions.
Caution
Alerts you of potential damage to a program, device, or system.
Warning
Alerts you of potential personal injury or fatality. May also alert you of potential electrical hazards.
Typeface Conventions
Description
Text represented as a screen
display
This typeface represents displays that appear on your terminal screen, for example:
Login:
Text represented as commands
This typeface represents commands that you enter, for example:
show ip access-list
This document always gives the full form of a command in lowercase letters. Commands
are not case sensitive.
Text represented as a command
variable
This typeface represents a variable that is part of a command, for example:
show card slot_number
slot_number is a variable representing the desired chassis slot number.
Text represented as menu or submenu names
This typeface represents menus and sub-menus that you access within a software
application, for example:
Click the File menu, then click New
The following tables describe the conventions used throughout this documentation.
Page 7

About this Guide
Contacting Customer Support ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
vii
Contacting Customer Support
Use the information in this section to contact customer support.
Refer to the support area of http://www.cisco.com for up-to-date product documentation or to submit a service request.
A valid username and password are required to access this site. Please contact your Cisco sales or service representative
for additional information.
Page 8

About this Guide
▀ Additional Information
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
viii
Additional Information
Refer to the following guides for supplemental information about the system:
Cisco ASR 5000 Installation Guide
Cisco ASR 5000 System Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Command Line Interface Reference
Cisco ASR 5x00 Thresholding Configuration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 SNMP MIB Reference
Web Element Manager Installation and Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 AAA Interface Administration and Reference
Cisco ASR 5x00 GTPP Interface Administration and Reference
Cisco ASR 5x00 Release Change Reference
Cisco ASR 5x00 Statistics and Counters Reference
Cisco ASR 5x00 Gateway GPRS Support Node Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 HRPD Serving Gateway Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5000 IP Services Gateway Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Mobility Management Entity Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Packet Data Network Gateway Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Packet Data Serving Node Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 System Architecture Evolution Gateway Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Serving GPRS Support Node Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5x00 Serving Gateway Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5000 Session Control Manager Administration Guide
Cisco ASR 5000 Packet Data Gateway/Tunnel Termination Gateway Administration Guide
Release notes that accompany updates and upgrades to the StarOS for your service and platform
Page 9

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
9
Chapter 1
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
eNode B is the node with radio access capabilities in LTE radio access network (RAN) that is responsible for radio
transmission and reception from UEs in one or more in absence of Radio Network Controller (RNC) in LTE. The
functionality of eNode B is enhanced to handle the tasks which were handled by the RNC in the 3G network. The Home
eNode B (HeNB) provides LTE radio coverage for LTE devices/handsets within a home residential coverage area. An
HeNB incorporates the capabilities of a standard eNode B.
The Cisco® ASR5x00 provides LTE wireless carriers with a flexible solution that functions as a Home eNode B
Gateway (HeNB-GW) in HeNB Access Network to connect UEs with existing LTE networks.
The Home eNodeB Gateway works as a gateway for HeNBs to access the core networks. The HeNB-GW concentrates
connections from a large amount of HeNBs through S1 interface and terminates the connection to existing Core
Networks using standard interface.
This overview provides general information about the HeNB Gateway including:
Product Description
Network Deployment and Interfaces
Features and Functionality - Base Software
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software
Page 10
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
10
Product Description
The Home eNodeB Gateway (HeNB-GW) or Femtocell Gateway (F-GW) is the HeNB network access concentrator
used to control capabilities necessary to manage large clusters of femtocells. It aggregates HeNBs or Femto Access
Points (FAPs) to a single network element and then integrates them into the Mobile Operators Voice, Data and
Multimedia networks. The primary function of HeNB-GW is to enable simple, seamless, and highly secure access to
subscribers as they roam between trusted/secure mobile networks and untrusted/unsecure public networks.
Femtocell is an important technology and service offering that enables new Home and Enterprise service capabilities for
Mobile Operators and Converged Mobile Operators. The Femtocell network consists of a plug-n-play customer premise
device generically called a Home eNodeB (HeNB) with limited range radio access in home or Enterprise. Femtocells’
biggest advantage is their capability to offload traffic from the macrocell networkand enable new applications, for
example: location based services.
The figure given describes a high level view of LTE network with Femtocell and HeNB-GW.
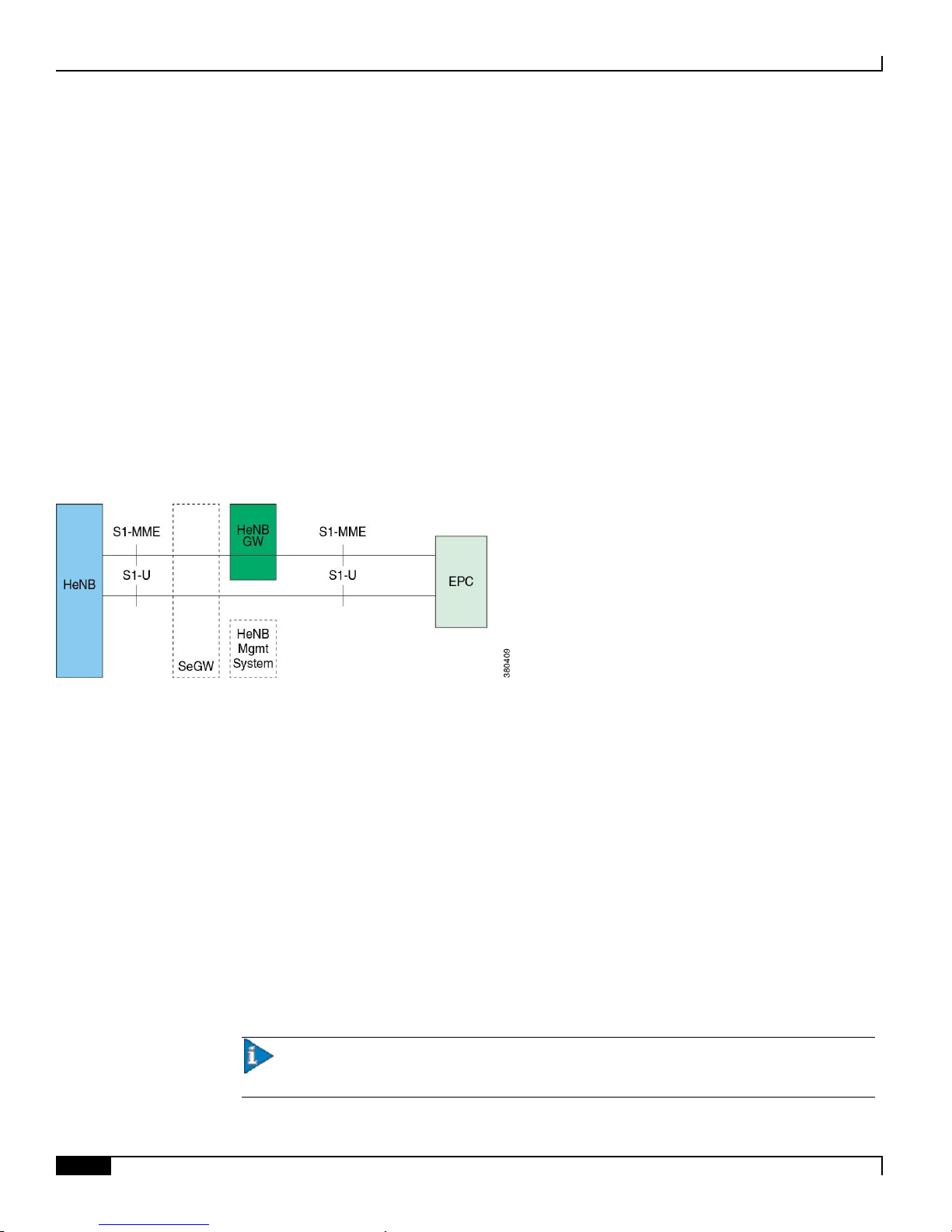
Figure 1. Home eNodeB Network Architecture
In the above figure, the S1 interface has been defined as an interface between
HeNB-GW and the Core Network (CN)/EPC
HeNB and the HeNB-GW
HeNB and the CN
An HeNB-GW provides standards-based S1-MME and S1-U network interfaces. As shown in the above high level LTE
Femto network architecture diagram, The HeNB-GW appears to the MME as an eNodeB. The HeNB-GW appears to
the HeNB as an MME. The S1 interface between HeNB and EPC whether the HeNB is connected to the CN/EPC via an
HeNB-GW or not. The HeNB-GW connects to the EPC in a way that inbound and outbound mobility to cells served by
the HeNB-GW does not necessarily require inter MME handovers.
In accordance with 3GPP LTE standards, the HeNB-GW hosts the following functions and procedures in LTE core
network:
Relaying UE-associated S1 application part messages between the MME serving the UE and the HeNB serving
the UE.
Terminating non-UE associated S1 application part procedures towards the HeNB and towards the MME.
Important: When an HeNB-GW is deployed, non-UE associated procedures shall be run
between HeNBs and the HeNB-GW and between the HeNB-GW and MME.
Page 11
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
11
Optionally terminating S1-U interface with the HeNB and with the S-GW.
Supporting tracking area code (TAC) and PLMN ID used by the HeNB.
Allowing no X2 interface establishment between the HeNB-GW and other nodes.
Optionally performing paging optimization in case the Allowed closed subscriber group (CSG) List of the paged
UE is included in the PAGING message.
At the same time, the MME hosts the following functions to support HeNB-GW:
CSG reporting to S-GW/P-GW
Access control for UEs that are members of CSG
Optionally performing paging optimization
Important: Some of the features may not be available in this release. Kindly contact your local Cisco
representative for more information on supported features.
Protocol Architecture
This section provides a brief description and pictorial representation of protocol stacks for User as well as Control
planes in context to HeNB-GW.
Protocol Stacks for S1 User Plane
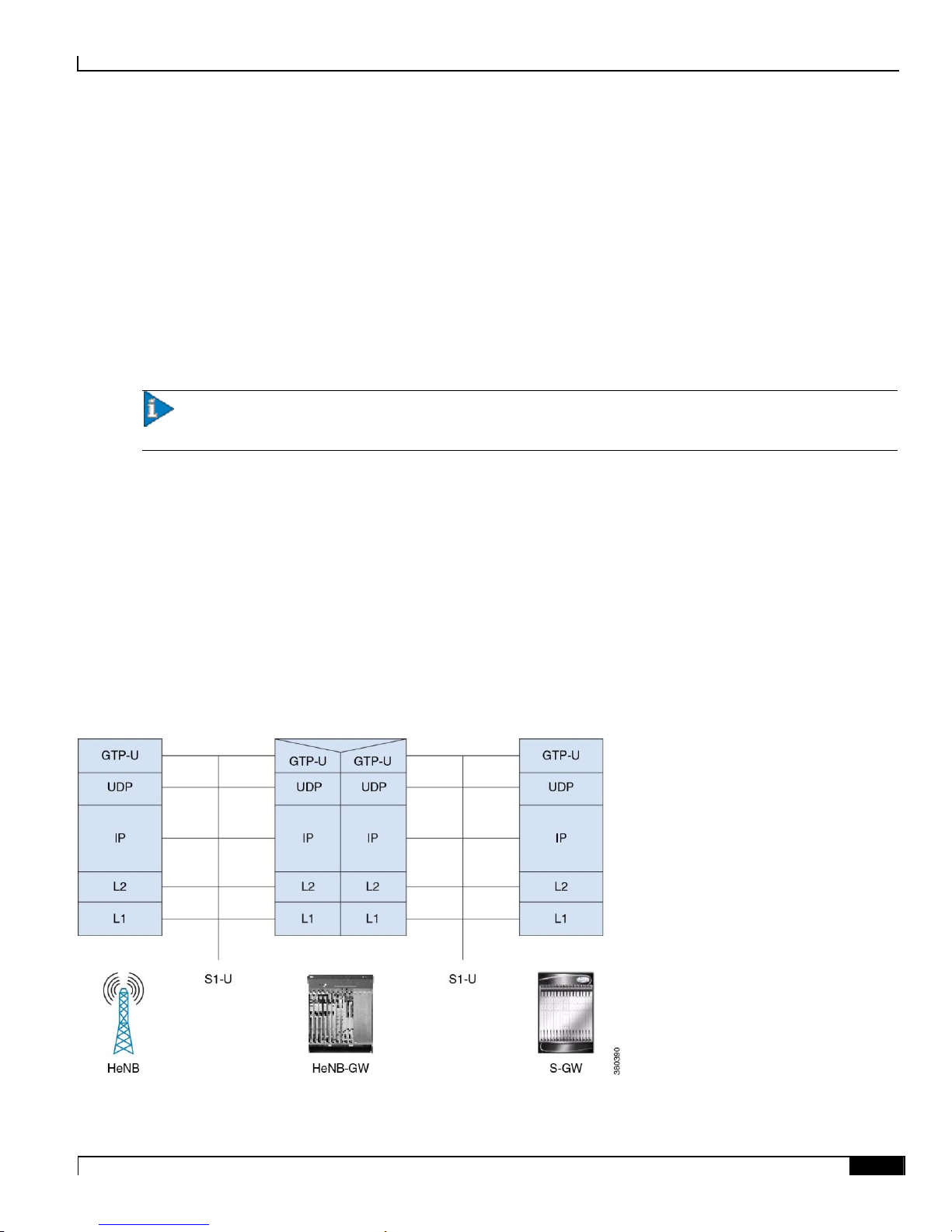
The S1-U data plane is defined between the HeNB, HeNB-GW and the S-GW. The figures below show the S1-U
protocol stack with and without the HeNB-GW.
Figure 2. User plane for S1-U interface for HeNB with HeNB-GW
Page 12
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
12
The HeNB-GW may optionally terminate the user plane towards the HeNB and towards the S-GW, and provide a relay
function for relaying User Plane data between the HeNB and the S-GW.
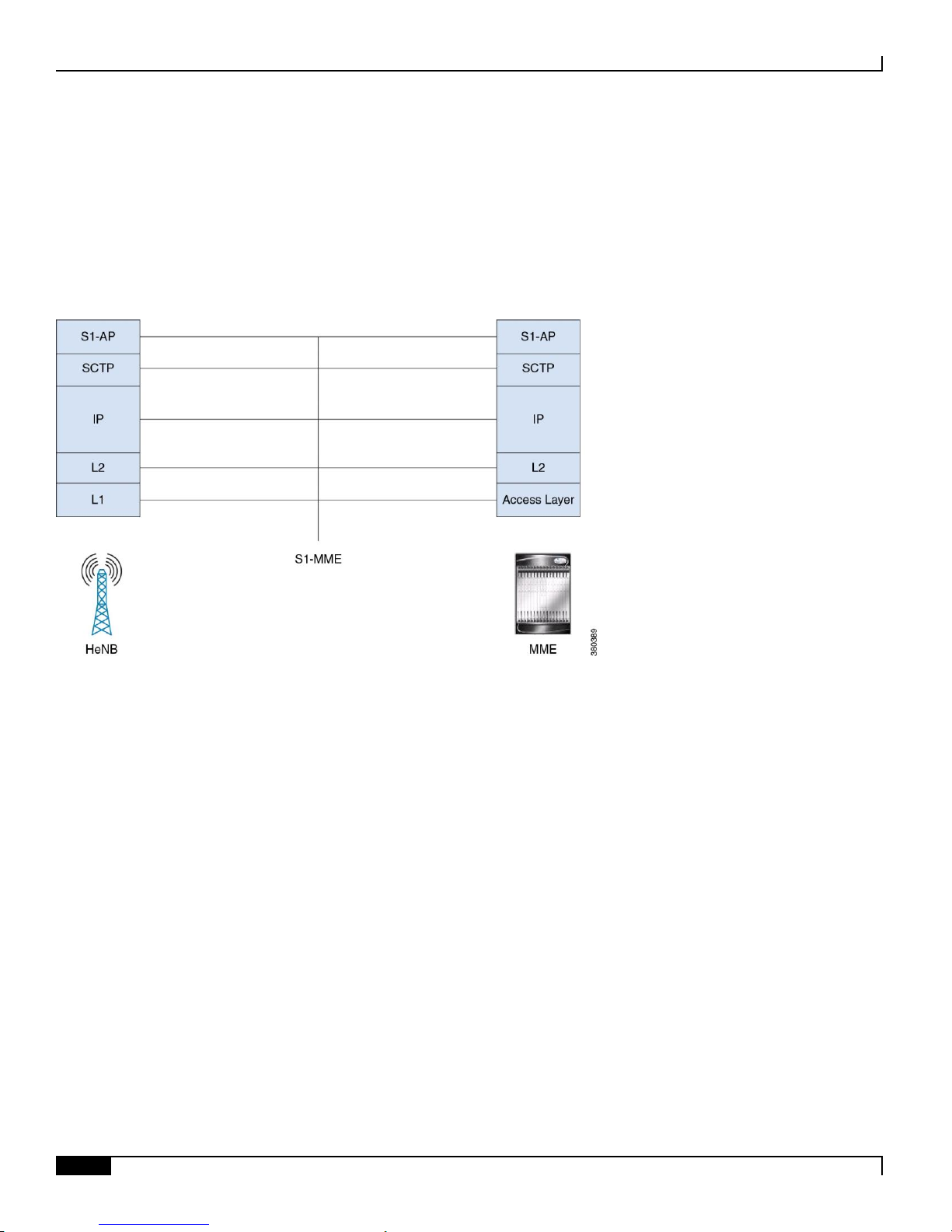
Protocol Stacks for S1 Control Plane
The two figures below show the S1-MME protocol stacks with and without the HeNB-GW. When the HeNB-GW is not
present, all the S1 procedures are terminated at the HeNB and the MME.
Figure 3. Control plane for S1-MME Interface for HeNB to MME without the HeNB-GW
The HeNB-GW terminates the non-UE-dedicated procedures: both with the HeNB, and with the MME. The HeNB-GW
provides a relay function for relaying Control Plane data between the HeNB and the MME. The scope of any protocol
function associated to a non-UE-dedicated procedure lies between HeNB and HeNB-GW, and/or between HeNB-GW
and MME.
Page 13
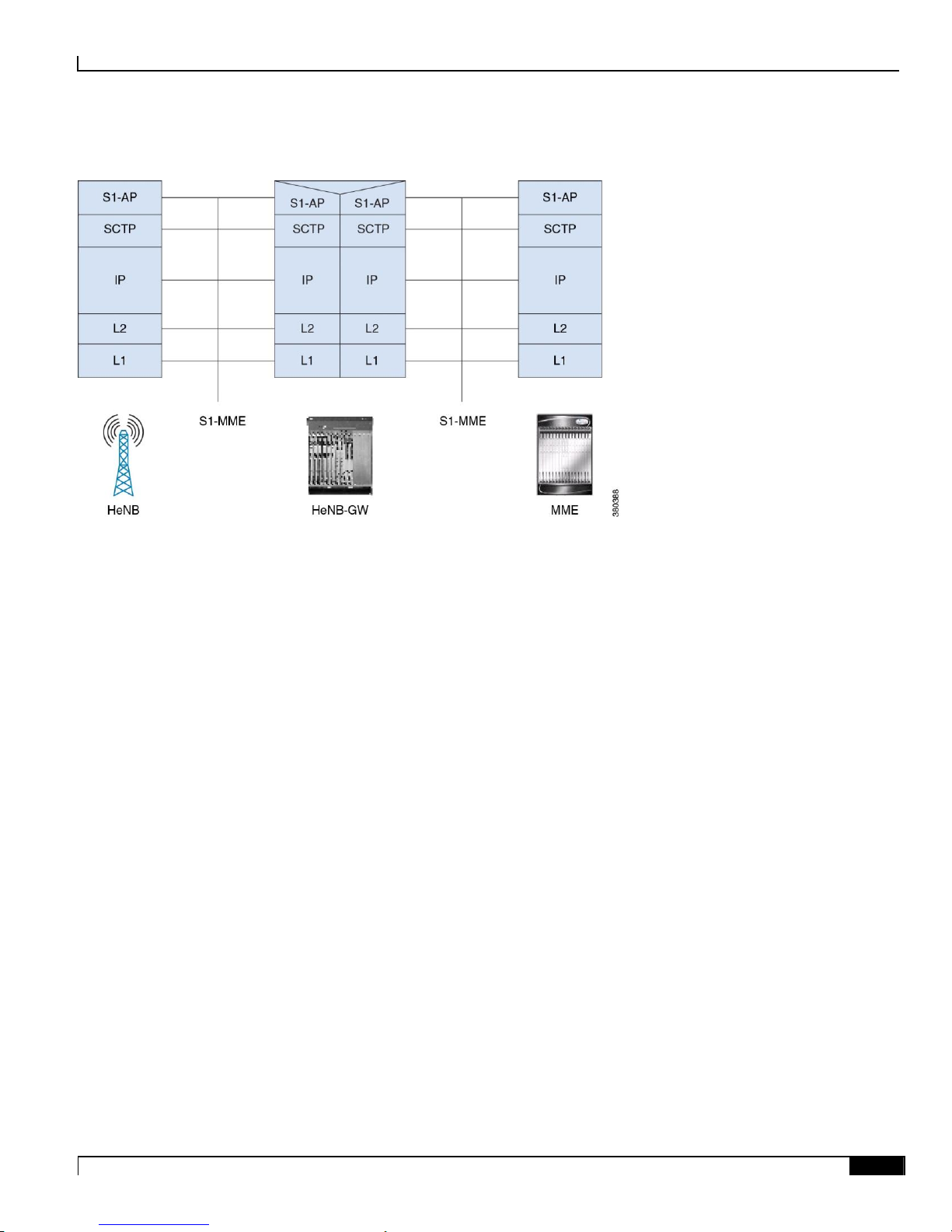
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
13
Figure 4. Control plane for S1-MME Interface for HeNB to MME with the HeNB-GW
Any protocol function associated to a UE-dedicated-procedure resides within the HeNB and the MME only.
Deployment Scenarios for HeNB Access Network
An HeNB-GW can be deployed to provide an alternate path for the data traffic. It holds capabilities to divert the data
traffic away from core and directly onto the Internet thus reducing the load on the core network.
There are following two variants of deploying an LTE Femtocell Gateway (HeNB-GW) solution according to the TR
23.830:
Variant I: With dedicated HeNB-GW where HeNBs connect via HeNB-GW for control and data aggregation.
This deplyment scenario is displayed in the following figure:
Page 14
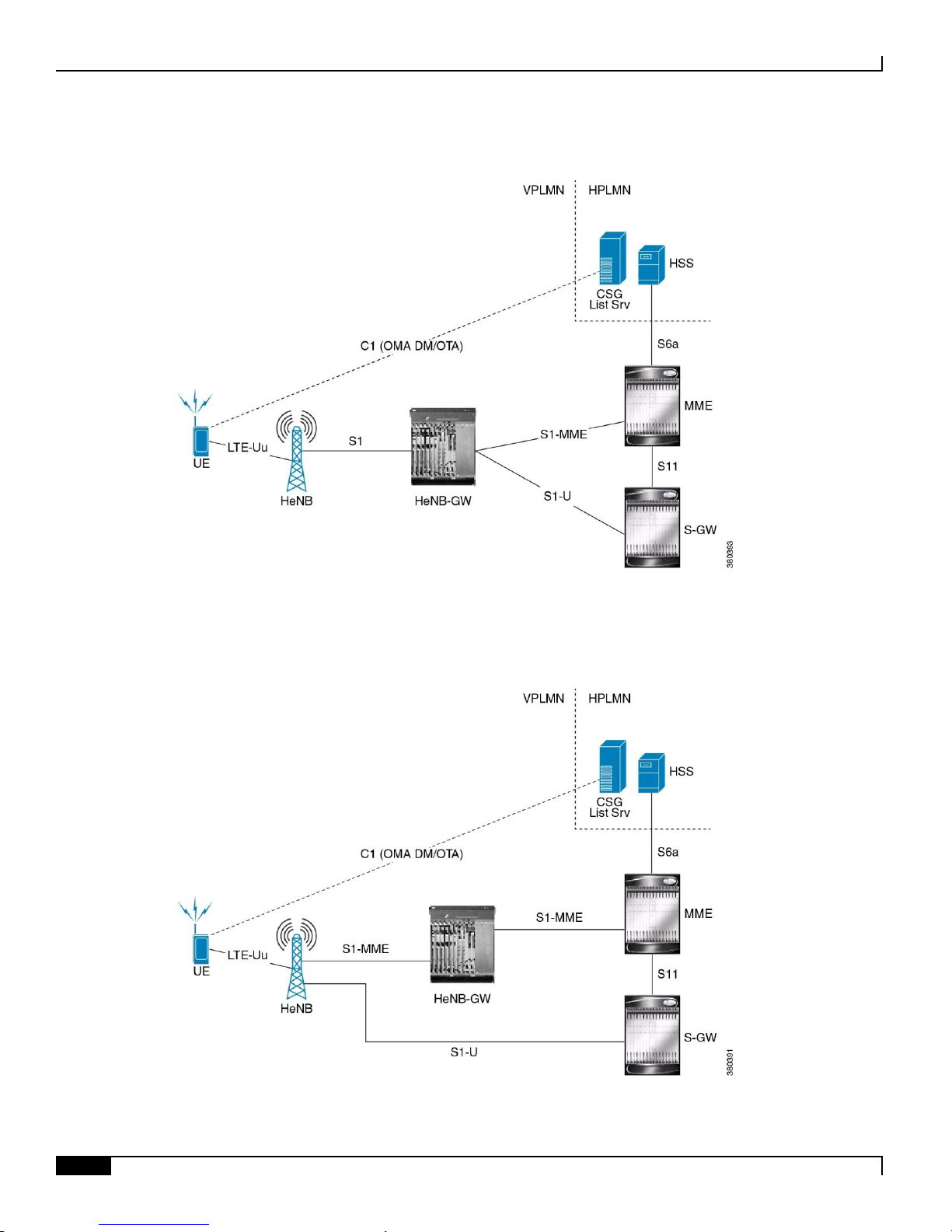
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
14
1. With Dedicated HeNB-GW
Variant II:With HeNB-GW for conrol plane aggregation only and directly connect to SGW for data plane. This
deplyment scenario is displayed in the following figure:
2. With HeNB-GW for Control Plane
Page 15
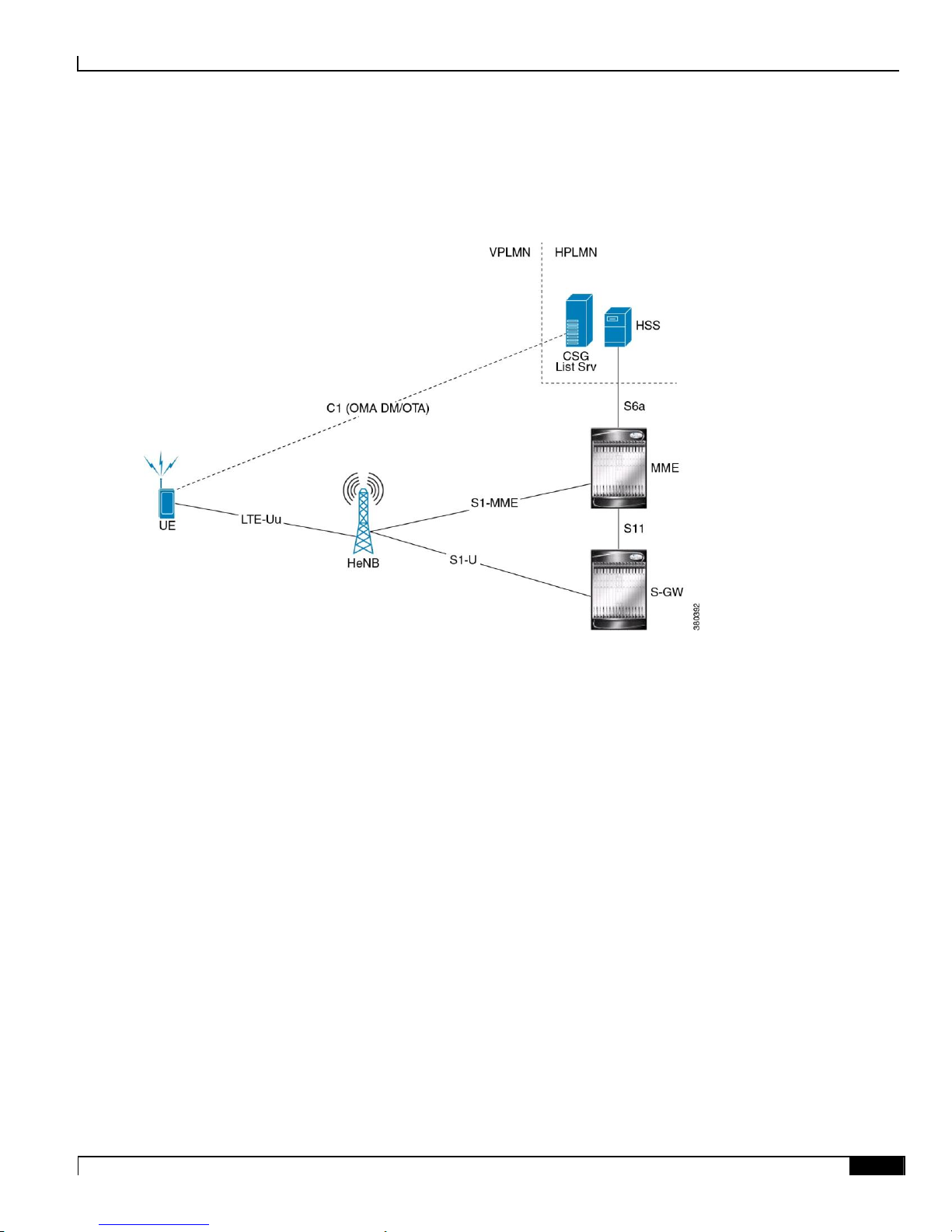
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
15
There is another deployment scenario for HeNBs where HeNB-GW is absent. In this deplyment, HeNBs connect
directly to highly scalable MMEs. This deplyment scenario is displayed in the following figure:
Figure 5. Without HeNB-GW
Cisco’s LTE Femtocell network solution focuses on Variant 1 where HeNB-GW is mandatory for HeNBs to connect.
Communication between the HeNB and the HeNB GW is secured by a security Gateway (SeGW) function. The SeGW
function is optionally collocated or else offloaded to external security function node.
HeNB Access Network Elements
This section provides the brief description and functionality of various network elements involved in the LTE Femtocell
access network. The HeNB access network includes the following functional entities:
Home eNodeB
Security Gateway (SeGW)
HeNB Gateway (HeNB-GW)
HeNB Management System (HeMS)
CSG List Server
Home eNodeB
A Home eNodeB (HeNB) is the a customer premise equipment that offers Uu interface to UE and S1 interface over
IPSec tunnel to HeNB-GW for accessing LTE Core Network in Femtocell access network.
It also provides the support to HeNB registration and UE registration over S1 interface with the HeNB-GW. Apart from
these functions HeNB also supports functions as given below:
Page 16
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
16
e-RAB management functions
Radio resource management functions
GTP-U tunnels management
Mobility management functions
Security functions
Service and Network access functions
Paging co-ordination functions
UE registration for HeNB
User-plane management functions including ciphering
Apart from the above listed basic functionalities, the HeNB is also involved in Mobility Management Entity (MME)
selection when no routing to an MME can be determined from the information provided by the UE. HeNB enforces the
UL (uplink) bearer level rate based on UE-AMBR and MBR via means of uplink scheduling; and does DL (downlink)
bearer level rate enforcement based on UE-AMBR (aggregate maximum bit rate).
Security Gateway (SeGW)
The Security Gateway is an logical function on HeNB-GW in the LTE femtocell network deployment, however it is
specified as a requirement in the Femtocell LTE network architecture. It may be implemented either as a separate
physical entity or co-located with an existing entity. The SeGW secures the communication from/to the HeNBs.
Basic function of this entity are:
Authentication of HeNBs
Termination of encrypted IPsec data connection from the femtocells
Providing access to HeMS and HeNB-GW
The SeGW holds capability of implementing a Denial of Service (DoS) shield to protect the EPC (S-GW and MME) by
detecting and then filtering out the attack traffic while maintaining the QoS (Quality of Service) of useful traffic. In our
implementation, it is an optional element which is situated on HeNB-GW.
HeNB Gateway (HeNB-GW)
The HeNB-GW provides the access to Femto user to LTE core network. It acts as an access gateway to HeNB and
concentrates connections from a large amount of HeNBs. HeNB-GW serves as a control plane (C-Plane) concentrator,s
pecifically the S1-MME interface.
The HeNB-GW may optionally terminate the user plane towards the HeNB and towards the S-GW, and may provide a
relay function for relaying User Plane data between the HeNB and the S-GW. The HeNB-GW supports NAS Node
Selection Function (NNSF).
Important: NAS Node Selection Function (NNSF)supports S1-Flex or multiple S1-MME connections
towards the EPC from any one HeNB.
Page 17

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
17
HeNB Management System (HeMS)
It is a network element management system for HeNB access. Management interface between HeNB and HMS is based
on TR-069 family of standards. Femto access point extensions are based on standards as defined in TR-196.
It performs following functions while managing HeNB access network:
Facilitates HeNB-GW discovery for HeNB(s)
Provision of configuration data to the HeNB
Performs location verification of HeNB(s) and assigns appropriate serving elements (HeMS, SeGW, and HeNB-
GW)
The HeNB Management System (HMS) comprises of the following functional entities:
File Server: used for file upload or download, as instructed by TR-069 manager
TR-069 Manager: Performs CM, FM and PM functionality to the HeNB through Auto-configuration server
(HMS)
CSG List Server
The Closed Subscriber Group (CSG) List Server is an optional function which allows the EPC network to update the
allowed CSG lists on CSG-capable UEs.
The CSG List Server hosts functions used by a subscriber to manage membership to multiple as well as different CSGs.
For example, the CSG List Server includes the UE CSG provisioning functions which are responsible to manage the
Allowed CSG List and the Operator CSG list stored on the UE.
Licenses
The HeNB-GW is a licensed Cisco product. Separate session and feature licenses may be required. Each HeNB-GW
session corresponds to one IKEv2 session from an HeNB node when SeGW is integrated and enabled. The license is
based on the number of sessions and enables all HeNB-GW functionality, including the following:
IKEv2 support, including all IKEv2 and IPSEC encryption/authentication
HeNB-GW service
GTP-U service for S1-U data plane
Contact your Cisco account representative for detailed information on specific licensing requirements. For information
on installing and verifying licenses, refer to the Managing License Keys section of the Software Management
Operations chapter in the System Administration Guide.
Platform Requirements
The HeNB-GW service runs on a Cisco® ASR 5x00 chassis running StarOS Rel. 15.0 or later. The chassis can be
configured with a variety of components to meet specific network deployment requirements. For additional information,
refer to the Installation Guide for the chassis and/or contact your Cisco account representative.
Page 18

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Network Deployment and Interfaces
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
18
Network Deployment and Interfaces
This section describes the supported interfaces and Cisco supported deployment scenario of HeNB-GW in LTE access
network.
As mentioned above in the section “Deployment Scenarios for HeNB Access Network”, Cisco’s LTE Femtocell
network solution focuses on Variant 1 where HeNB-GW is mandatory for HeNBs to connect. HeNB-GW may also be
frequently deployed or co-located together with MME and/or S-GW/P-GW in the same system.
These collocations are not yet supported in the Cisco ASR5x00 chassis and are planned for future releases.
Supported Logical Interfaces
This section provides the brief information on supported interfaces on HeNB-GW node.
In support of both mobile and network originated subscriber UE contexts, the HeNB-GW provides the following
network interface support:
E-UTRAN Uu Interface: The LTE Uu interface is responsible for all sort of signalling between UE and
eNodeB. It carries all signalling message between the eNodeB and the MME along with the user traffic
between the eNodeB and S-GW. This way the Uu interface works over both the Control as well as User planes.
The protocols of the LTE Uu interface include:
Radio Resource Control (RRC): This protocol governs the signalling between the UE and MME.
Technically, the RRC governing lies between the UE and eNodeB. It terminates on the RAN access
equipment and then signalling is forwarded to MME.
Non-Access Stratum (NAS): This protocol also governs the signalling between UE and MME
Other than the above protocols, both the control planes (Control and User) of the Uu interface are supported by
the same set of interface functions. These interface functions include Security and Header Compression. All of
these functions are carried by the physical layer over the air as shown in the following figure:
Page 19
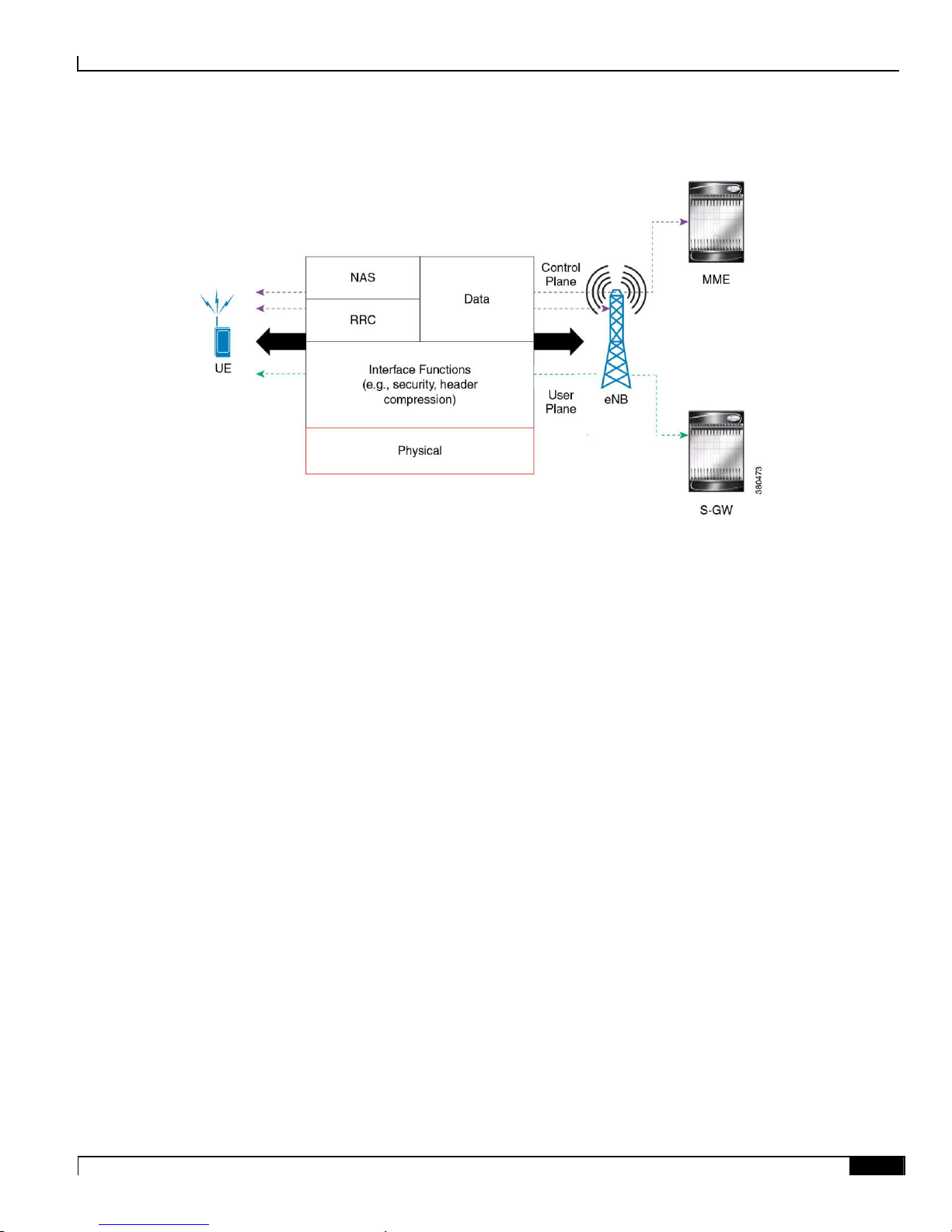
HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Network Deployment and Interfaces ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
19
1. e-UTRAN Uu Interface Logical Representation
The physical layer in LTE is based upon the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) using
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) in the downlink and variant of this Single Carrier
Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA) in the uplink.
S1 Interface: The communication between the E-UTRAN and the EPC has been designated to the S1 interface.
The S1 interface has been separated by the Control plane signalling and User plane traffic:
S1-MME: The S1 variant used for Control plane signalling is referred to as S1-MME interface.
S1-U: The S1 variant used for User plane traffic is referred to as S1-U interface.
The S1-MME interface is governed by the S1-AP protocol, whose functions include:
E-RAB Management Function: This functionality is responsible for setting up, modifying and
releasing evolved Radio Access Bearers (E-RABs), which are triggered by the MME. The release of
E-RABs may be triggered by the eNodeB as well.
Initial Context Transfer Function: This functionality is used to establish an S1-UE context in the
eNodeB. It is also used to setup the default IP connectivity, to setup one or more E-RAB(s) if
requested by the MME, and to transfer NAS signalling related information to the eNodeB if needed.
UE Capability Information Indication Function: This functionality is used to provide the UE
Capability Information when received from the UE to the MME.
Paging: This functionality provides the EPC with the capability to page the UE.
S1 Interface Management Functions: These functions comprise the following:
Reset functionality for ensuring a well defined initialization on the S1 interface.
Error Indication functionality for allowing a proper error reporting/handling in cases where no
failure messages are defined.
Overload function for indicating the load situation in the control plane of the S1 interface.
Load balancing function for ensuring equally loaded MMEs within an MME pool area.
S1 Setup functionality for initial S1 interface setup for providing configuration information.
Page 20

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Network Deployment and Interfaces
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
20
eNodeB and MME Configuration Update functions are to update application level
configuration data needed for the eNodeB and MME to inter operate correctly on the S1
interface.
S1 UE context Release Function: This functionality is responsible to manage the release of UE
specific context in the eNodeB and the MME.
UE Context Modification Function: This functionality allows to modify the established UE Context
partly.
Status Transfer: This functionality transfers Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) SN Status
information from source eNodeB to target eNodeB in support of in-sequence delivery and duplication
avoidance for intra LTE handover.
Trace Function: This functionality is to control a trace session recording for a UE in
ECM_CONNECTED or to control an MDT (Minimization of Derive Tests) session transferring MDT
measurements collected by the UE.
Location Reporting: This functionality allows MME to be aware of the UE’s current location.
Warning Message Transmission Function: This functionality provides the means to start and
overwrite the broadcasting of warning message.
RAN Information Management (RIM) Function: This functionality allows the request and transfer
of RAN information (For example, GERAN system information) between two RAN nodes via the
core network.
Configuration Transfer Function: This functionality allows the request and transfer of RAN
configuration information (For example, SON information) between two RAN nodes via the core
network
Page 21

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
21
Features and Functionality - Base Software
This section describes the features and functions supported by default in base software on HeNB-GW service and do not
require any additional license to implement the functionality with the HeNB-GW service.
Following features and supports are discussed in this section:
AAA Server Group Support
Access Control List Support
DSCP Marking on S1-U Relay
Fault Reporting Support
Location Reporting Support
QoS Support
Redundancy Support
Troubleshooting Features Support
AAA Server Group Support
It is a value-added feature to enable VPN service provisioning for enterprise or MVNO customers, however integrated
SeGW is required to be enabled for this feature. It enables each corporate customer to maintain its own AAA servers
with its own unique configurable parameters and custom dictionaries.
This feature provides support for up to 800 AAA (RADIUS and Diameter) server groups and 800 NAS IP addresses that
can be provisioned within a single context or across the entire chassis. A total of 128 servers can be assigned to an
individual server group. Up to 1,600 accounting, authentication and/or mediation servers are supported per chassis and
may be distributed across a maximum of 1,000 nodes. This feature also enables the AAA servers to be distributed across
multiple nodes within the same context.
Important: For more information on AAA Server Group configuration, if you are using StarOS 12.3 or an earlier
release, refer to the AAA and GTPP Interface Administration and Reference. If you are using StarOS 14.0 or a later
release, refer to the AAA Interface Administration and Reference.
Access Control List Support
Access Control Lists provide a mechanism for controlling (i.e. permitting, denying, redirecting, etc.) packets in and out
of the system.
IP access lists, or Access Control Lists (ACLs) as they are commonly referred to, are used to control the flow of packets
into and out of the system. They are configured on a per-context basis and consist of “rules” (ACL rules) or filters that
control the action taken on packets that match the filter criteria
Once configured, an ACL can be applied to any of the following:
An individual interface
All traffic facilitated by a context (known as a policy ACL)
Page 22

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
22
An individual subscriber
All subscriber sessions facilitated by a specific context
There are two primary components of an ACL:
Rule: A single ACL consists of one or more ACL rules. As discussed earlier, the rule is a filter configured to
take a specific action on packets matching specific criteria. Up to 128 rules can be configured per ACL.
Each rule specifies the action to take when a packet matches the specifies criteria. This section discusses the
rule actions and criteria supported by the system.
Rule Order: A single ACL can consist of multiple rules. Each packet is compared against each of the ACL rules,
in the order in which they were entered, until a match is found. Once a match is identified, all subsequent rules
are ignored.
Important: For more information on Access Control List configuration, refer IP Access Control List chapter in
System Administration Guide.
Bulk Statistics Support
The system's support for bulk statistics allows operators to choose to view not only statistics that are of importance to
them, but also to configure the format in which it is presented. This simplifies the post-processing of statistical data
since it can be formatted to be parsed by external, back-end processors.
When used in conjunction with the Web Element Manager, the data can be parsed, archived, and graphed.
The system can be configured to collect bulk statistics (performance data) and send them to a collection server (called a
receiver). Bulk statistics are statistics that are collected in a group. The individual statistics are grouped by schema.
Following is a partial list of supported schemas:
System: Provides system-level statistics
Card: Provides card-level statistics
Port: Provides port-level statistics
MME: Provides MME service statistics
GTP-U: Provides GPRS Tunneling Protocol - User message statistics
HENBGW-ACCESS: Provides HeNB-GW access side statistics
HENBGW-NETWORK: Provides HeNB-GW network side statistics
The system supports the configuration of up to 4 sets (primary/secondary) of receivers. Each set can be configured with
to collect specific sets of statistics from the various schemas. Statistics can be pulled manually from the chassis or sent
at configured intervals. The bulk statistics are stored on the receiver(s) in files.
The format of the bulk statistic data files can be configured by the user. Users can specify the format of the file name,
file headers, and/or footers to include information such as the date, chassis host name, chassis uptime, the IP address of
the system generating the statistics (available for only for headers and footers), and/or the time that the file was
generated.
When the Web Element Manager is used as the receiver, it is capable of further processing the statistics data through
XML parsing, archiving, and graphing.
The Bulk Statistics Server component of the Web Element Manager parses collected statistics and stores the information
in the PostgreSQL database. If XML file generation and transfer is required, this element generates the XML output and
can send it to a Northbound NMS or an alternate bulk statistics server for further processing.
Page 23

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
23
Additionally, if archiving of the collected statistics is desired, the Bulk Statistics server writes the files to an alternative
directory on the server. A specific directory can be configured by the administrative user or the default directory can be
used. Regardless, the directory can be on a local file system or on an NFS-mounted file system on the Web Element
Manager server.
DSCP Marking on S1-U Relay
Cisco supports the DSCP marking of S1-U traffic traversing the HeNB-GW. This functionality on HeNB-GW is
supported through command line interface (CLI). CLI configuration capability has been enabled for DSCP marking for
both Access and Network service.
CLIs are used for the dscp marking configuration for IP packets sent out on the S1-U interface, from the HeNB-GW to
the Access/Network side. Default value used for dscp marking is the dscp value for the incoming packet.
Important: For more information on the supported CLIs for this feature, refer the CLI Reference Guide.
Fault Reporting Support
SNMP traps are used for faults and fault reporting in the system for network side S1-MME and S1-U interfaces. For
these traps on the network side, some other mechanism is required, as the SCTP/S1-MME associations do not generate
SNMP traps.
Location Reporting Support
Cisco HeNB-GW supports the location reporting feature for the subscribers/UE movements.
Location Reporting is the procedure by which the serving MME keeps in the track of the UE change in location within
the allowed tracking area list of the eNodeB.
With the HeNBGW deployed in the Femtocell LTE network, MME does not direct connect to HeNBs, and therefore
any location report message is forwarded by the HeNB-GW to and fro. When HeNB-GW receives location reporting
control message with local eNodeB ID and remote MMEUE S1AP id, HeNB-GW forwards the same to the appropriate
HeNB by replacing it with remove ENB ID and local MME UE s1AP ID.
QoS Support
Cisco HeNB-GW along with the SeGW supports QoS handling based on the DSCP mapping configuration.
QoS support provides a foundation for contributing towards improved Quality of User Experience (QoE) by enabling
deterministic end-to-end forwarding and scheduling treatments for different services or classes of applications pursuant
to their requirements for committed bandwidth resources, jitter and delay. In this way, each application receives the
service treatment that users expect.
Redundancy Support
To support redundancy, the HeNB-GW tasks should be started based on the following guidelines:
Page 24

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
24
HENBGW DEMUX - The HENBGW DEMUX task recovers and updates the relevant information regarding
HeNB/UE connections by querying all the session managers (SMGRs) in the system. This task should not be
started on a PSC in which SMGRs are started. Regardless of whether session recovery is enabled or not, the
HENBGW DEMUX task should always be started on the Demux PSC.
As of now, there is no full support of Session Recovery on HeNB-GW for UEs. ONly the IPSec tunnel is
preserved in the HeNB-GW. Upon recovery, the IPsec tunnel being preserved, the HeNB re-connects and the
UE is paged via network initiated service request or transition to ECM ACTIVE state on the MME by sending
uplink packets itself, but only after the HeNB has successfully re-established its association with the HeNBGW.
SMGR – The SMGRs follow the standard guidelines used for other services and recover HeNB association and
UE state from its AAAMGR pair.
HENBGWMGR – The HENBGWMGRs use the henbgw-network-service information to restart the SCTP
connections towards MME(s). HENBGWMGRs are demux tasks and are started on the Demux PSC. Any state
information required for recovery is fetched from the HENBGW DEMUX task.
GTPUMGR – GTPUMGR task(s) are started in the demux PSC. Any required state information after a task
restart is fetched from the SMGR(s).
A minimum of 3 ACTIVE PSCs and 1 STANDBY PSC is required to support session recovery. One of the active PSCs
works as the DEMUX PSC and runs the demux tasks.
Troubleshooting Features Support
HeNB-GW provides monitor protocol support for S1AP, SCTP and GTP-U. Monitor subscriber feature has been
extended to include HeNB-GW calls also. Subscriber monitoring has been supported based on 'callid'.
The following logging facilities can be used for troubleshooting HENBGW:
henb-gw
henbgwdemux
henbgwmgr
gtpumgr
egtpu
ipsecmgr
sessmgr
The above listed in addition to the existing facilities can be enabled to capture logs at different levels, for example:
information, trace, debug etc.
Important: For more information on troubleshooting, refer the Troubleshooting the Service chapter of this guide.
Page 25

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
25
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature
Software
This section describes the optional enhanced features and functions support with HeNB-GW service.
Important: Some of the following features may require the purchase of an additional license to implement the
functionality with the HeNB-GW service.
This section describes following features:
Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR) Support
CSG-ID Based Paging Optimization Support
License-based Control for No. of HeNB Connections
License-based Control for No. of Subscribers Allowed
Automatic Neighbor Relation (ANR) Support
Automatic Neighbour Relation (ANR) functionality is nothing but relieving the operator from the complexity of
manually managing Neighbor Relations (NRs). In LTE deployments, the manual management of NRs becomes even
more challenging, as in addition of defining intra LTE neighbour relations for eNodeBs, operator has to provision
neighboring 2G, 3G, CDMA2000 cells as well.
The ANR function resides in the eNodeB and manages the conceptual Neighbour Relation Table (NRT). Located within
ANR, the Neighbour Detection Function (NDF) finds new neighbours and adds them to the NRT. ANR also contains
the Neighbour Removal Function (NRF) which removes outdated NRs. The NDF and the NRF functions are specific to
the implementation by operator.
An existing Neighbour cell Relation (NR) from a source cell to a target cell means that eNodeB controlling the source
cell knows the ECGI/CGI and Physical Cell Identifier (PCI) of the target cell and has an entry in the NRT for the source
cell identifying the target cell.
For each cell that the eNodeB has, the eNodeB keeps an NRT. For each NR, the NRT contains the Target Cell Identifier
(TCI), which identifies the target cell. For E-UTRAN, the TCI corresponds to the E-UTRAN Cell Global Identifier
(ECGI) and Physical Cell Identifier (PCI) of the target cell.
The ANR function relies on cells broadcasting their identity on global level, ECGI and allows O&M to manage the
NRT
CSG-ID Based Paging Optimization Support
Due to the high volume and small-sized femtocell deployment, it is well-known that paging messages is a big burden for
the femtocell system.In order to optimize the paging procedure by the HeNB-GW, the HeNB-GW is made aware of the
CSGs supported by the connected HeNBs. This allows the HeNB-GW to identify the appropriate HeNBs supporting
certain CSGs. This is known through the S1-Setup request sent by HeNBs.
In order to have a complete paging optimization solution, the allowed CSG list of the paged UE is included in the
paging message. The paging message is then sent with the allowed CSG list of the paged UE to the HeNB-GW by
MME.
Page 26

HeNB Gateway in Wireless LTE Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
26
With the help of the ACL, the HeNB filtering is done by the HeNB-GW. Finally, the paging message is only sent to the
HeNBs with the allowed CSG ID.
Important: This feature makes dependency on MME to initiate Paging messages containing CSG list.
License-based Control for No. of HeNB Connections
Number of HeNBs connecting to the HeNB-GW are controlled/limited based on the license configuration.
Important: SNMP traps are generated during Over/Under License capacity situation.
There are two scenarios for HeNBs connecting to the HeNB-GW: Through IPSec and Direcly HeNB-GW.
With IPSec (Integrated HeNB-GW and SeGW)
In case, IPSec is implemented or the Security Gateway is co-located with the HeNB-GW, IPSec Tunnel setup requests
are dropped once the number of tunnels exceed the configured license limit of the number of HeNBs.
Non-IPSec (Stanalone HeNB-GW)
HeNB-GW rejects the extra HeNB connection attempts with SCTP Abort once the license control is configured for
maximum number of HeNBs to connect to the HeNB-GW.
License-based Control for No. of Subscribers Allowed
Number of subscribers/UEs connecting to the HeNB-GW are also controlled/limited based on the license configuration.
Important: SNMP traps are generated during Over/Under License capacity situation. For more information on
SNMP Traps, refer the Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration section of the HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
chapter of this guide.
There are two scenarios for HeNBs connecting to the HeNB-GW: Through IPSec and Direcly HeNB-GW.
With IPSec (Integrated HeNB-GW and SeGW)
In case, IPSec is implemented or the Security Gateway is co-located with the HeNB-GW, IPSec Tunnel setup requests
are dropped once the number of tunnels exceed the configured license limit of the number of UEs. UEs limit is based on
configured UE license limit and are rejected with Error Indication message and cause code.
Non-IPSec (Stanalone HeNB-GW)
HeNB-GW rejects the extra UE connection attempts with Error Indocation message with proper cause code once the
license control is configured for maximum number of HeNBs to connect to the HeNB-GW.
Important: For troubleshooting License related issues, refer the Troubleshooting the Service chapter of this
guide.
Page 27

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
27
Chapter 2
Understanding the Service Operation
The system provides wireless carriers with a flexible solution for providing Security Gateway (SeGW) and HomeeNodeB Gateway (HeNB-GW) functionality for LTE Femtocell networks.
The system functioning as an HeNB-GW is capable of supporting the following types of subscriber sessions:
PS Session over S1AP: The subscriber is provided packet switch connection with different traffic class on PS
session with P-GW in PS.
Network-initiated Sessions: Network-initiated session procedures include Paging, Dedicated Bearers, UE
disconnections etc. from CN side on HeNB-GW for a specific subscriber session and in turn HeNB-GW
initiates the required procedures with HeNBs and CNs.
Prior to connecting to the command line interface (CLI) and beginning the system's configuration, there are important
things to understand about how the system supports these applications. This chapter provides terminology and
background information that must be considered before attempting to configure the system.
Page 28

Understanding the Service Operation
▀ Terminology
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
28
Terminology
This section defines some of the terms used in the chapters that follow.
Contexts
A context is a logical grouping or mapping of configuration parameters that pertain to various physical ports, logical IP
interfaces, and services. A context can be thought of as a virtual private network (VPN).
The system supports the configuration of multiple contexts. Each is configured and operates independently from the
others. Once a context has been created, administrative users can then configure services, logical IP interfaces,
subscribers, etc.for that context. Administrative users would then bind the logical interfaces to physical ports.
Contexts can also be assigned domain aliases, wherein if a subscriber’s domain name matches one of the configured
alias names for that context, then that context is used.
In HeNB-GW service implementation, the contexts can not be classified into source or destination contexts. This is
because GTP-U tunnels as well as HeNB-GW Access and Network services can be created over a single context.
The IP addresses as well as interfaces can also under the defined under the same context. These IP addresses are later
used to bind with different services including GTP-U, MME and Interfaces including S1-MME for HeNB-GW Access
service and Network service.
Logical Interfaces
This section describes the logical interface supported on HeNB-GW.
Prior to allowing the flow of user data, the port must be associated with a virtual circuit or tunnel called a logical
interface. A logical interface within the system is defined as the logical assignment of a virtual router instance that
provides higher-layer protocol transport, such as Layer 3 IP addressing. Interfaces are configured as part of the VPN
context and are independent from the physical port that will be used to bridge the virtual interfaces to the network.
Logical interfaces are assigned to IP addresses and are bound to a specific port during the configuration process. Logical
interfaces are also associated with services through bindings. Services are bound to an IP address that is configured for a
particular logical interface. When associated, the interface takes on the characteristics of the functions enabled by the
service. For example, if an interface is bound to an HeNB-GW service, it will function as an S1-MME interface between
the HeNB-GW/SeGW service and MME. Services are defined later in this section.
In support of both mobile and network originated subscriber UE contexts, the HeNB-GW provides the following
network interface support:
S1 Interface: This interface is the reference point for the control plane protocol between Home eNodeB and
HeNB-GW. This interface sets up S1AP association over SCTP as the transport layer protocol for guaranteed
delivery of signaling messages between HeNB-GW and Home eNodeB.
This is the interface used by the HeNB-GW to communicate with HeNBs on the same Femtocell Access
Network. This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining subscriber UE contexts.
S1-MME Interface: This interface is the reference point for the control plane protocol between E-UTRAN and
MME in the LTE Femtocell network.
Protocol stack architecture for the S1-MME interface has been described in the Protocol Architecture section
of the Overview chapter of this guide.
Page 29

Understanding the Service Operation
Terminology ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
29
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) guarantees the delivery of signalling messages between
MME and eNodeB via HeNB-GW.
S1-U: This interface is the reference point between E-UTRAN and Serving Gateway (S-GW). This interface is
responsible for the per bearer user plane tunnelling and inter eNodeB path switching during handover.
The HeNB-GW functions as a user-plane concentrator along with the control-plane concentration function.
This allows the S-GW to view the cluster of femtocells as a single entity. The user-plane aggregation
functionality provides support for both GTP-U and PMIP traffic.
One or more IuPS interfaces can be configured per system context.
RADIUS: This interface is the reference point between a Security Gateway (SeGW) and a 3GPP AAA Server or
3GPP AAA proxy (OCS/CGF/AAA/HSS) over RADIUS protocol for AAA procedures for Femto user.
In the roaming case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy can act as a stateful proxy between the SeGW and 3GPP AAA
Server.
The AAA server is responsible for transfer of subscription and authentication data for
authenticating/authorizing user access and UE authentication. The SeGW communicates with the AAA on the
PLMN using DIAMETER protocol.
One or more RADIUS interfaces can be configured per system context.
TR-069: This interface is an application layer protocol which is used for remote configuration of terminal
devices, such as DSL modems, HeNBs and STBs. TR-069 provides an auto configuration mechanism between
the HeNB and a remote node in the service provider network termed the Auto Configuration Server. The
standard also uses a combination of security measures including IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange v2) and IPsec
(IP Security) protocols to authenticate the operator and subscriber and then guarantee the privacy of the data
exchanged.
One TR-069 interface can be configured per HeNB node.
Bindings
A binding is an association between “elements” within the system. There are two types of bindings: static and dynamic.
Static binding is accomplished through the configuration of the system. Static bindings are used to associate:
A specific logical interface (configured within a particular context) to a physical port. Once the interface is
bound to the physical port, traffic can flow through the context just as if it were any physically defined circuit.
Static bindings support any encapsulation method over any interface and port type.
A service to an IP address assigned to a logical interface within the same context. This allows the interface to
take on the characteristics (i.e., support the protocols) required by the service. For example, a GTP-U service
bound to a logical interface will cause the logical interface to take on the characteristics of a GTP interface
within an LTE Femtocell network.
Dynamic binding associates a subscriber to a specific egress context based on the configuration of their profile or
system parameters. This provides a higher degree of deployment flexibility as it allows a wireless carrier to support
multiple services and facilitates seamless connections to multiple networks.
Services and Networks
This section describes the services configured on HeNB-GW to support various functionality.
Page 30

Understanding the Service Operation
▀ Terminology
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
30
Services are configured within a context and enable certain functionality. The following services can be configured on
the system:
HeNB-GW services: HeNB-GW services are configured in Context configuration mode to support both mobile-
initiated and network-requested user contexts. The HeNB-GW services must be bound to a logical interface
within the same context. There are two HeNB-GW services:
HeNB-GW Access Service: This service is configured under the Context configuration mode in order
to initialize the HeNB-GW functionality. The configuration of this service controls the functionality of
S1-MME interface from HeNB-GW to the HeNBs.
This service is bound to a local SCTP end-point address (IP address) to listen the incoming SCTP
associations from HeNBs.
HeNB-GW Network Service: This service is also configured in the Context configuration mode to
support the HeNB-GW functionalities. The configuration of this service controls the functionality of
S1-MME interface from HeNB-GW to MME. One-to-one mapping is maintained between the HeNBGW Access service and HeNB-GW Network service.
It is the HeNB-GW Network service where enabling of logical eNodeBs is configured within the
HeNB-GW. The Logical eNodeB configuration can be used to support load balancing within a pool of
TAIs. Each Logical eNodeB can connect up to 8 MMEs from the MME pool and therefore 64
connections are possible to be established between HeNB-GW and MME.
Important: At least one logical eNodeB configuration is required to start the HeNB-
GW Network service. Up to 8 logical eNodeBs can be configured per HeNB-GW Network
service.
Radio Network PLMN: The Radio Network PLMN is configured in HeNB-GW Access service to associate
PLMNs with HeNB-GW.
PLMN configuration is also required at the time of configuring Logical eNodeBs for the HeNB-GW Network
service.
GTP-U services: GTP-U services are configured in Context configuration mode in pair of two services; one for
GTP-U tunnel support towards HeNB on S1 interface and another for GTP-U tunnel support towards the core
network on S1-U interface to communicate with the S-GW respectively. These two GTP-U services are called
Access GTP-U service and Network GTP-U service.
GTP-U service comes in picture specially when the S1-U Relay option is enabled. S1-U relay activation
actually allows the data to flow through the GTP-U tunnel via HeNB-GW, otherwise it directly travels from
HeNBs to S-GW.
When S1-U relay is enabled, the HeNB-GW Access service has to be associated with the Network GTP-U
service and Access GTP-U service. Also the HeNB-GW Access service has to be associated with the HeNBGW Network service.
Important: S1-U Relay is disabled by default. Also when S1-U relay is enabled, both Access
and Network GTP-U services need to be in STARTED state for the HeNB-GW access service to be
STARTED.
Page 31

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
31
Chapter 3
HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
This chapter is meant to be used in conjunction with the other chapters that describes the information needed to
configure the system to support HeNB-GW functionality for use in HeNB access networks.
It is recommended that you identify the options from the previous chapters that are required for your specific
deployment. You can then use the procedures in this chapter to configure those options.
This chapter describes following :
Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW
HeNB-GW Service Configuration
Logging Facility Configuration
Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration
SNMP MIB Traps for HeNB-GW Service
Event IDs for HeNB-GW Service
Important: At least one packet card must be made active prior to service configuration. Information and
instructions for configuring the packet cards to be active can be found in the Configuring System Settings chapter of the
System Administration Guide.
Caution: While configuring any base-service or enhanced feature, it is highly recommended to take care of
conflicting or blocked IP addresses and port numbers for binding or assigning. In association with some service steering
or access control features, like Access Control List configuration, use of inappropriate port number may result in
communication loss. Refer respective feature configuration document carefully before assigning any port number or IP
address for communication with internal or external network.
Page 32

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
32
Required
Information
Description
Management Interface Configuration
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface will be
recognized by the system.
Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number
where the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example, port
17/1 identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17.
A single physical port can facilitate multiple interfaces.
Gateway IP address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
Security
administrator name
The name or names of the security administrator with full rights to the system.
Security
administrator
password
Open or encrypted passwords can be used.
Remote access
type(s)
The type of remote access that will be used to access the system such as telnetd, sshd, and/or ftpd.
Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW
This section provides a high-level series of steps and the associated configuration file examples for configuring the
system to perform as an HeNB-GW node in a test environment. Information provided in this section includes the
following:
Required Local Context Configuration Information
Required Source Context Configuration Information
Required Destination Context Configuration Information
Required Local Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the local context on an HeNB-GW.
Table 1. Required Information for Local Context Configuration
Required Source Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the Source context on an HeNB-GW.
Page 33

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
33
Table 2. Required Information for Source Context Configuration
Required
Information
Description
Source context
name
An identification string from 1 to 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Source context is
recognized by the system.Generally it is identified as source context.
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface is
recognized by the system.
Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number where
the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example, port 17/1
identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17. A single physical port can facilitate multiple interfaces.
Gateway IP
address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
Ingress and Egress GTP-U Services
Ingress GTP-U
service Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Ingress GTP-U service
can be identified on the system. It is configured in Context Configuration Mode. When S1-U Relay is enabled,
the Ingress GTP-U service configuration is critical as it has to be associated with the HeNB-GW Access
Service. It is also called access-side GTP-U service for the HeNB-GW ACCESS service.
Egress GTP-U
service Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Engress GTP-U service
can be identified on the system. It is configured in Context Configuration Mode. When S1-U Relay is enabled,
the Engress GTP-U service configuration is critical as it has to be associated with the HeNB-GW Access
Service. It is also called network-side GTP-U service for the HeNB-GW ACCESS service.
GTP-U Tunnel
interface IP
address
IP addresses assigned to the interface as GTP-U bond address.
This address will be used for binding the GTP-U service (local bind address(es)) for sending/receiving GTP-U
packets from/to HeNB using GTP-U tunnel.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
S1-AP Configuration (To/from Home-eNodeB)
HeNB-GW
access service
Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the HeNB-GW Access
service can be identified on the system. It is configured in Context Configuration Mode. At a time, only one
HeNB-GW Access Service can be configured per system.
HeNB-GW
Network service
Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the HeNB-GW Network
service can be identified on the system. It is also configured in Context Configuration Mode. At a time, only
one HeNB-GW Network Service can be configured per system and therefore there is 1:1 mapping between
HeNB-GW Access and Network services..
Required Destination Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the destination context.
Page 34

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
34
Table 3. Required Information for Destination Context Configuration
Required
Information
Description
Destination context
name
An identification string from 1 to 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the destination context will
be recognized by the system.
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface is
recognized by the system.Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number where
the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example, port 17/1
identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17. A single physical port can facilitate multiple interfaces.
Gateway IP address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
HeNB-GW Access Service Configuration
S1-MME interface
IP address
IPv4 addresses assigned to the S1-MME interface as SCTP bond address.This address will be used for
binding the SCTP (local bind address(es)) to communicate with the MME using eGTP. The HeNB-GW
passes this IP address during setting up the association with the MME.Multiple addresses and subnets are
needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Public Land
Mobile Network
(PLMN) Identifiers
Mobile Country Code (MCC): The MCC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Mobile Network Code (MNC): The MNC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
S1-MME SCTP
Port
The physical port to which is used to communicate with the HeNBs over S1-MME interface. It is usually an
integer value ranging from 1 to 65535.
MME ID Group ID
MME Group ID to be configured for the HeNB-GW Access Service. This is a required parameter since the
HeNB-GW acts as an MME to the HeNB(s) and this ID is filled in the S1-SETUP response sent to the
HeNB(s). It is an integer ranging from 32768..65535.
MME Code
MME Code is also part of the MME ID configuration. MME Group ID and MME Code both are required
for MME Identifier configuration for the HeNB-GW Access service. It is an integer which ranges from
0..255.
S1-U Relay
Enables the S1-U relay functionality for the HeNB-GW Access Service. Once S1-U Relay is enabled, the
association to Ingress and Egress GTP-U services is considered as critical configuration for the HeNB-GW
Access service.
Associate
HeNBGW Network
Service
A preconfigured HeNB-GW Network Service is requird to be associated to the HeNB-GW Access Service.
User can enter a desired HeNB-GW Network service name even if it is not pre-configured, but it will be
required to be configured in later course for this HeNB-GW Access service to come up.
Optional Security Gateway Configuration
Security Gateway
IP address
This is the IP Address where the SeGW service is bound and shall be provided to HeNB during SeGWDiscovery. This security gateway is associated with the HeNB-GW Access Service.
Only one SeGW IP address can be configured.
Diameter Endpoint
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Diameter endpoint
configuration is recognized by the system. This Diameter Endpoint is required by the SeGW to
communicate with the AAA server.
Page 35

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
35
Required
Information
Description
Diameter Endpoint Configuration
Endpoint Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Diameter endpoint
configuration is recognized by the system. This Diameter Endpoint is required by the SeGW to
communicate with the AAA server.
Origin realm name
An identification string between 1 through 127 characters. The realm is the Diameter identity. The
originator.s realm is present in all Diameter messages and is typically the company or service name.
Origin host name
An identification string from 1 to 255 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the origin host is
recognized by the system.
Origin host address
The IP address of the interface.
Peer name
The endpoint name described above.
Peer realm name
The interface origin realm name described above.
Peer address and
port number
The IP address and port number of the OCS.
IPsec Crypto-map Template Configuration
EAP profile
This is the profile to be used to provide authenticator modes for incoming packets on Security Gateway.
Only one EAP profile can be configured.
IP Pool for IPsec
Tunnel
Specifies the IP pool to assign IP address for IPsec traffic to use.
IKEv2 Transform
set
IKEv2 transform set for IKE security association.
IPsec Crypto-map
Template
Specifies the Crypto-map template to be used for IPsec IKEv2 tunneling for the interface configured.
This crypto-map template is to be associated with HeNB-GW Access service if SeGW is enabled and bind
with this HeNB-GW Access service.
HeNB-GW Access Service can run with or without the IPSec configuration. Since only one HeNB-GW
Access Service can be configured per system, either IPSec can be configured or not.
Only one IPsec Crypto-map Template can be configured.
AAA Server Group
Context name
Specifies the name of the context in which a AAA server group is configured for association with SeGW for
AAA parameters during subscriber authentication phases.
AAA Server Group
name
Specifies the AAA server group already configured in a context and is to be used for first/second phase of
authentication of subscriber while using SeGW functionality in an HeNB-GW service.
HeNB-GW Network Service Configuration
Logical eNodeB
The Logical eNodeB configuration option enables the configuration of one or more logical eNodeBs within
the HeNB-GW. The Logical eNodeB configuration is usually used to support load balancing within a pool
of TAIs. At least one logical eNodeB configuration is required to START an HeNB-GW Network service. 8
Logical eNodeBs are supported per HeNB-GW Network service.
Caution: Deleting or modifying any of the parameters for a fully configured logical
eNodeB results in the termination of SCTP connections to MMEs from that logical eNodeb.
Page 36

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HeNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
36
Required
Information
Description
Public Land
Mobile Network
(PLMN) Identifiers
Mobile Country Code (MCC): The MCC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Mobile Network Code (MNC): The MNC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Macro eNodeB ID
Macro eNodeB identifier, required as a parameter for the Logical eNodeB configuration. It is an option to
the Home eNodeB identifier.
Home eNodeB ID
Home eNodeB identifier, required as a parameter for the Logical eNodeB configuration. It is an option to
the Macro eNodeB identifier.
S1-MME interface
IP address
IPv4 addresses assigned to the S1-MME interface as SCTP bond address. This address will be used for
binding the SCTP (local bind address(es)) to communicate with the MME using eGTP. The HeNB-GW
passes this IP address during setting up the association with the MME.Multiple addresses and subnets are
needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
S1-MME SCTP
Port
The physical port to which is used to communicate with the HeNBs over S1-MME interface. It is usually an
integer value ranging from 1 to 65535.
Logical eNodeB Configuration
MME Pool
A pre-configured MME pool to be associated with the Logical eNodeB. An MME pool is configured in the
LTE Policy Configuration Mode. Only one MME Pool instance can be associated with a Logical eNodeB
instance. All MMEs in the pool are assumed to support all TAIs in the associated TAI List DB object. One
Logical eNodeB can connect up to 8 MMEs and therefore a max of 64 associations can be established
between HeNB-GW and MME
TAI List DB
A pre-configured list of tracking area identity (TAIs) pool to be associated with the Logical eNodeB. A TAI
List database is configured in the LTE Policy Configuration Mode. Only one TAI list DB can be associated
with the Logical eNodeB instance. The tai-list-db contains a list of TAIs. These are sent in the S1 Setup
message to the MME to indicate the list of TAIs supported by the eNodeB. The TAI database which can be
associated to each logical EnodeB can accommodate 256 configuration of TACs.
TAI List DB Configuration
MCC
Mobile Country Code (MCC): The MCC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
MNC
Mobile Network Code (MNC): The MNC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Tracking Area
Code (TAC)
TAC is an integer value rainging from 0..65535. The HeNB-GW Network service searches these TACs for
establishing UE connections.
Page 37

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
37
HeNB-GW Service Configuration
HeNB-GW services are configured within source contexts and allow the system to function as an HeNB-GW in the 4G
LTE wireless data network.
Important: This section provides the minimum instruction set for configuring an HeNB-GW service
that allows the system to process bearer contexts with IPsec authentication on SeGW. Commands that
configure additional HeNB-GW service properties are provided in the different chapters of Command Line
Interface Reference.
These instructions assume that you have already configured the system level configuration as described in System
Administration Guide.
To configure the system to work as HeNB-GW service with SeGW enabled:
Step 1 Configure a system context in the Global Configuration Mode, as shown in the Context Configuration section of the
HeNB-GW Service Configuration example. Using this step, the user enters in the Context Configuration Mode.
Step 2 Create an interface and enter the interface configuration mode for newly created interface to add IP addresses along
with the subnet mask for this interface, as shown in the Interface and IP Address Configuration section of the HeNB-
GW Service Configuration example. These IP addresses are used to bind to different services including GTP-U Access
and Network services and even interfaces like S1-MME.
Step 3 Configure the Access and Network GTP-U services, as shown in the Access and Network GTP-U Services
Configuration section of the HeNB-GW Service Configuration example. These services are bound individually to the IP
addresses configured in the Step 2.
Step 4 Configure the HeNB-GW Network service, as shown in the HeNB-GW Network Service Configuration section of the
HeNB-GW Service Configuration example. Using this step, the user enters in the HeNB-GW Network Service
Configuration Mode.
Step 5 Configure the logical eNodeB for the HeNB-GW Network service created in step4, as shown in the Logical eNodeB
Configuration section of the HeNB-GW Service Configuration example.
Step 6 Bind the S1-MME using IP address of this interface to the Logical eNodeB created in Step 5. Enter the IP address in
dotted decimal notation.
Step 7 Specify the SCTP port for the S1-MME interface bound in step 6.
Step 8 Associate the MME pool name to the Logical eNodeB. This MME pool can be created in the LTE Policy configuration
mode, as shown in the LTE Policy Configuration example.
Step 9 Associate the TAI List database to the Logical eNodeB. This TAI List database can e configured in the LTE Policy
configuration mode, as shown in the LTE Policy Configuration example.
Step 10 Configure the HeNB-GW Access service, as shown in the HeNB-GW Access Service Configuration section of the
HeNB-GW Service Configuration example. Using this step, the user enters in the HeNB-GW Access Service
Configuration Mode.
Step 11 Bind the S1-MME using IP address of this interface to the HeNB-GW service created in Step 10. Enter the IP address in
dotted decimal notation.
Page 38

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HeNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
38
Step 12 Specify the SCTP port for the S1-MME interface bound in Step 11.
Step 13 Configure the MME Group Identifier for the HeNB-GW Access service. As part of this configuration, group ID as well
as the MME code has to be configured. MME ID is used as part of S1 setup procedure during HeNB association. It is an
integer value ranging from 0 to 255.
Step 14 Associate the HeNB-GW Network service configured in the step 4 to this HeNB-GW Access Service.
Step 15 Configure the Public Land Mobile Network Identifiers MMC and MNC for this HeNB-GW Access Service.
Step 16 Enable the S1-U Relay for this HeNB-GW Access service. Using this step, the user enters in the S1-U Relay
Configuration Mode. This is an optional step.
Step 17 Associate the Access and Network GTP-U services created in the Step 3 to this HeNB-GW Access service. Association
of the GTP-U services is mandatory in case S1-U Relay is enabled.
HeNB-GW Service Configuration
Use the following example to configure the HeNB-GW service on system in source context to provide access to HeNBs
towards core networks:
configure
------------------ Context Configuration --------------------
context <ingress_ctxt_name>
----------- Interface and IP addresses Configuration -----------
interface <interface_name>
ip address <ipv4_addr> 255.255.255.0
ip address <ipv4_addr> 255.255.255.0 secondary
exit
-------- Access and Network GTP-U Services Configuration ------
gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_access> -noconfirm
bind ipv4-address <secondary1_ipv4_addr>
exit
gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_network> -noconfirm
bind ipv4-address <secondary2_ipv4_addr>
exit
------------- HeNB-GW Network Service Configuration -----------
henbgw-network-service <henb_network_svc_name> -noconfirm
Page 39

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
39
------------ Logical eNodeB Configuration ----------------------
logical-enb global-enb-id plmn id mcc <mcc_id> mnc <mnc_id> macro-enb-id
<macro_enodeb_id> -n
bind s1-mme ipv4-address <secondary3_ipv4_addr>
s1-mme sctp port <sctp_port_no>
associate mme-pool <mme_pool_name>
associate tai-list-db <lte_policy_tai_db>
exit
exit
-------------- HeNB-GW Access Service Configuration --------------------
henbgw-access-service <henb_access_svc_name> -n
bind s1-mme ipv4-address <primary_ipv4_addr>
s1-mme sctp port <sctp_port_no>
mme-id group-id <mme_id> mme-code <mme_code>
associate henbgw-network-service <henb_network_svc_name>
plmn id mcc <mcc_id> mnc <mnc_id>
-------------- S1-U Relay Configuration --------------------
s1u-relay
associate access-gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_access> context ingress
associate network-gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_network> context ingress
exit
exit
Notes:
<ingress_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HeNB-GW service is configured.
<interface_name> is the name of the interface under which primary and secondary IP addreses are to be
defined for different services to bind including GTP-U and HeNB-GW Access and Network services.
<gtpu_svc_access> is the name of the GTP-U service configured in the <ingress_ctxt_name> context
mode to provide GTP-U tunnel for HeNBGW Access service. This GTP-U service will be used as Access
GTP-U service and will be associated with the HeNB-GW Access Service in case s1-U relay is enabled.
<gtpu_svc_network> is the name of the second GTP-U service configured in the <ingress_ctxt_name>
context mode to provide GTP-U tunnel for HeNBGW Network service. This GTP-U service will be used as
Page 40

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HeNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
40
Network GTP-U service and will be associated with the HeNB-GW Access Service in case s1-U relay is
enabled.
<secondary1_ipv4_addr> is the IPV4 type address defined under the <interface_name> interface and
being binded to the <gtpu_svc_name1> GTP-U service.
<secondary2_ipv4_addr> is the IPV4 type address defined under the <interface_name> interface and
being binded to the <gtpu_svc_name2> GTP-U service.
<henb_network_svc_name> is the HeNB-GW Network service name
<secondary3_ipv4_addr> is the IPv4 type address used to bind with the S1-MME interface.
<mme_pool_name> is the MME pool name as defined while the LTE policy configuration.
Important: This MME pool is associated with the HeNB-GW network service.
<lte_policy_tai_db> is the tracking area information database name as defined while the LTE policy
configuration.
Important: This tracking area information database is associated with the HeNB-GW
network service.
<henb_access_svc_name> is the name of the HeNB-GW Access service name.
<primary_ipv4_addr> is the IPv4 type primary address used to bind with the S1-MME interface for this
HeNB-GW access service.
s1u-relay enables the S1-U relay functionality by the HeNB-GW service. When configured, user enters into
S1-U relay configuration mode. In this mode user has to configure associations to the Access and Network
GTP-U services for S1-U relay. When s1-u relay is enabled, the association to ingress and egress GTP-U
services is considered as a critical configuration for the HeNB-GW Access service. When S1-U relay is
enabled, both Access and Network GTP-Uu services need to be in STARTED state for the HeNB-GW Access
service to START.
Service is re-started.
IPSec Configuration
Use the following example to configure the IPSec configuration which goes with the Security Gateway (SeGW)
configuration on the HeNB-GW Access Service.
Configure
context <ctxt_name>
Important: Changing the S1-U Relay configuration is a disruptive operation. The HeNB-GW
eap-profile <eap_profile_name>
mode authenticator-pass-through
exit
Page 41

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
41
ipsec transform-set <ipsec_transform_set_name>
exit
ikev2-ikesa transform-set <ikesa_transform_set_name>
exit
crypto template <crypto_template_name> ikev2-dynamic
authentication remote eap-profile <eap_profile_name>
ikev2-ikesa transform-set list <ikesa_transform_set_name>
payload <crypto_template_payload_name> match childsa match ipv4
ip-address-allocation dynamic
Notes:
<ctxt_name> is the context name on which unique EAP name is to configured.
<eap_profile_name> is a string of size 1 to 128 which configure the context level unique Extensible
Authentication Profile (EAP) Name.
<ipsec_transform_set_name> configures the context level name to be used for the IKEv2 IKE Security
Association Transform Set. It is a string of size 1 to 127.
<crypto_template_name> configures the name of the Crypto Template. It is a string of size 1 to 104.
<crypto_template_payload_name> is the name of the Crypto Template Payload being configured. This
name is unique to the Crypto Template. It is a string of size 1 to 127.
GTP-U Service Configuration
Use the following example to configure the GTP-U service parameters to provide GTP-U tunnel over S1-U interface.
The two GTP-U
configure
context <dest_ctxt_name> -noconfirm
gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_access> -noconfirm
bind address { ipv4-address | ipv6-address } <ip_address>
end
configure
context <dest_ctxt_name> -noconfirm
gtpu-service <gtpu_svc_network> -noconfirm
bind address ipv4-address <ip_address>
Page 42

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HeNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
42
end
Notes:
<dest_ctxt_name> is name of the destination context in which GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U
tunnel over IuPS interface towards core network.
<gtpu_svc_access> is name of the GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U tunnel over S1-U interface
towards S-GW or core network. This service has to be associated with the HeNB-GW Access Service in case
S1-U Relay is enabled.
<gtpu_svc_network> is name of the GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U tunnel over towards HeNB.
This service has to be associated with the HeNB-GW Access Service in case S1-U Relay is enabled.
LTE Policy Configuration
Use the following example to configure the LTE Policy. Othe rconfigurations done under this config include MME pool
and tracking area information list (TAI list) database.
configure
lte-policy
mme-pool <mme_pool_name> -noconfirm
mme <mme-name> ipv4-address <ipv4_addr> sctp port <sctp_port_no>
exit
tai-list-db <lte_policy_tai_db>
tai mcc <mcc_id> mnc <mnc_id> tac <tac_code1> <tac_code2> <tac_code3>
exit
end
Notes:
<mme_pool_name> is a string of size 1 to 63, which configures a specified MME pool.
<mme-name> is a string of size 1 to 63, which configures a specific MME.
<ipv4_addr> is the remote SCTP IP address for S1 association to configured MME.
<sctp_port_no> is the SCTP port which is an integer ranging from 1 to 65535.
<lte_policy_tai_db> is the tracking area information list database, which must be a string of size 1 to 64.
<mcc_id> is a three digit number between 100 to 999.
<mnc_id> is two/three digit number between 00 to 999
<tac_code1> is the tracking area code value ranging as a integer from 0 ... 65535. Up to 256 can be defined on
one line.
Page 43

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HeNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
43
Verifying HeNB-GW Configuration
This section shows the configuration parameters configured for HeNB-GW service.
Step 1 Verify that your HeNB-GW services were created and configured properly by entering the following commands in Exec
Mode:
show henbgw-access-service <henbgw_access_svc_name>}
show henbgw-network-service <henbgw_network_svc_name>}
The output of these command display concise listing of HeNB-GW Access and Network service parameter
settings as configured on sym.
Step 2 Verify configuration errors of your HeNB-GW services by entering the following command in Exec Mode:
show configuration errors section henbgw-network-service}
The output of this command displays current configuration errors and warning information for the target
configuration file as specified for HNeB-GW Network service
Page 44

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Logging Facility Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
44
Logging Facility Configuration
Use the following example to configure the HeNB-GW system to enable the logging and debug facilities for HeNB-GW
subscriber and related protocols.
Important: This section provides the minimum instruction set for configuring logging facilities for
system monitoring that allows the user to monitor the events and logging. commands that configure
additional logging facilities are provided in the Exec Mode Command chapter of Command Line Interface
Reference.
logging filter active facility henbapp level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
logging filter active facility henbgw level { critical | error | warning | unusual | info
| trace | debug }
logging filter active facility henbgwdemux level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
logging filter active facility henbgwmgr level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
configure
logging console
logging display event-verbosity {min | concise | full}
logging filter runtime facility henb-gw level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility henbapp level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility henbgwdemux level { critical | error | warning |
unusual | info | trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility hnbmgr level { critical | error | warning | unusual |
info | trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility sctp { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility threshold { critical | error | warning | unusual | info
| trace | debug }
Important: Refer System Administration Guide for more information on logging facility configuration.
Page 45

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Logging Facility Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
45
Displaying Logging Facility
This section shows the logging facility event logs for logging facilities enabled on HeNB-GW node.
Step 1 Verify the logging facilities configured on HeNB-GW system node by entering the following command in Exec Mode:
show logging [ active | verbose]
The output of this command provides the display of event logs for all configured logging facilities.
Page 46

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
46
Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration
To enable and configure the SNMP Traps to generate alarms and alerts from system for various events and thresholds in
HeNB-GW service, apply the following example configuration:
configure
snmp trap enable ThreshHENBGWHenbSessions target [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap enable ThreshHENBGWPagingMessages target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap enable ThreshHENBGWUeSessions target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwAccessServiceStart [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwAccessServiceStop [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwMMESCTPAllAssocDown [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwMMESCTPAllAssocDownClear [ target
<trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwMMESCTPAssocDown [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwMMESCTPAssocUp [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwNetworkServiceStart [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HenbgwNetworkServiceStop [ target <trap_collector>]
Notes:
<trap_collector> is then ame of the 1st trap target. It is a string of size 1 to 31.
There are several additional SNMP Traps which can be configured. Refer Global Configuration Mode chapter of
the Command Line Interface Reference for more information.
For more information on SNMP Traps, refer System SNMP-MIB Reference.
Repeat this configuration as needed for additional traps.
Page 47

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
SNMP MIB Traps for HeNB-GW Service ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
47
Traps
Object Id
starThreshHENBGWHenbSessions
starentTraps 513
starThreshClearHENBGWHenbSessions
starentTraps 514
starThreshHENBGWUeSessions
starentTraps 515
starThreshClearHENBGWUeSessions
starentTraps 516
starThreshHENBGWPagingMessages
starentTraps 517
starThreshClearHENBGWPagingMessages
starentTraps 518
starHenbgwAccessServiceStart
starentTraps 1193
starHenbgwAccessServiceStop
starentTraps 1194
starHenbgwNetworkServiceStart
starentTraps 1195
starHenbgwNetworkServiceStop
starentTraps 1196
SNMP MIB Traps for HeNB-GW Service
SNMP traps are used to manage and monitor the service on HeNB-GW node.
Supported SNMP traps and its id are indicated in the following table.
Table 4. SNMP Traps and Object Ids
Important: For more information on SNMP trap configuration and supported object ids, refer System SNMP-
MIB Reference.
Page 48

HeNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Event IDs for HeNB-GW Service
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
48
Event IDs for HeNB-GW Service
Facility
Event ID Range
HeNB-GW Manager Facility Events
193000-193999
HeNB-GW Facility Events
195000-195999
HeNB-GW DEMUX Facility Events
194000-194999
SCTP Protocol Facility Events
87300-87499
AAA Client Facility Events
6000-6999
Alarm Controller Facility Events
65000-65999
Card/Slot/Port (CSP) Facility Events
7000-7999
Command Line Interface Facility Events
30000-30999
Event Log Facility Events
2000-2999
Threshold Facility Events
61000-61999
Identification numbers (IDs) are used to reference events as they occur when logging is enabled on the system. Logs are
collected on a per facility basis.
Each facility possesses its own range of event IDs as indicated in the following table. Following table lists HeNB-Gw
specific and other required facilities and corresponding Event ID Ranges:
Important: Not all event IDs are used on all platforms. It depends on the platform type and the license(s)
running.
For more information on logging facility configuration and event id, refer Configuring and Viewing System Logs chapter
in System Administration Guide.
Table 5. System Event Facilities and ID Ranges
Page 49

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
49
Chapter 4
Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
This chapter provides information for monitoring service status and performance using the show commands found in
the Command Line Interface (CLI). These commands have many related keywords that allow them to provide useful
information on all aspects of the system ranging from current software configuration through call activity and status.
The selection of keywords described in this chapter is intended to provided the most useful and in-depth information for
monitoring the system. For additional information on these and other show command keywords, refer to the Command
Line Interface Reference.
In addition to the CLI, the system supports the sending of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) traps that
indicate status and alarm conditions. Refer to the SNMP MIB Reference Guide for a detailed listing of these traps.
Page 50

Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
▀ Monitoring System Status and Performance
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
50
To do this:
Enter this command:
View HeNB-GW Service Information
View HeNB-GW services running on chassis
show henbgw session all
View summary of HeNB-GW sessions running on
chassis
show henbgw session summary
View detailed information of HeNB-GW sessions
show henbgw session full
View HeNB-GW session information specific to an
S1 peer
show henbgw session s1-peer ipv4-addr
Monitor HeNB-GW Subscriber Session Information
Monitor HeNB-GW subscribers by call identifier
monitor subscriber callid call_id
Monitor HeNB-GW subscribers by user name
identifier
monitor subscriber usernamesubscriber_name
Monitor HeNB-GW subscribers by IMSI value
monitor subscriber imsiimsi
Monitor HeNB-GW subscribers by IP address of UE
monitor subscriber ipaddripv4_address
Monitoring HeNB and UE by Protocol Monitoring
Monitor HeNB through Protocol Monitoring
monitor protocol
Use following protocol options for HeNB monitoring:
S1-AP
SCTP
GTP-U
Monitor UE through Protocol Monitoring
monitor protocol
Use following protocol options for HeNB monitoring:
S1-AP
SCTP
GTP-U
View Subscriber Information
Display Session Resource Status
Monitoring System Status and Performance
This section contains commands used to monitor the status of tasks, managers, applications and other software
components in the system. Output descriptions for most of the commands are located in the Counters and Statistics
Reference.
Table 6. System Status and Performance Monitoring Commands
Page 51

Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
Monitoring System Status and Performance ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
51
To do this:
Enter this command:
View session resource status
show resources session
Display Subscriber Configuration Information
View locally configured subscriber profile settings
(must be in context where subscriber resides)
show subscribers configuration username subscriber_name
View remotely configured subscriber profile settings
show subscribers aaa-configuration username
subscriber_name
View Subscribers Currently Accessing the System
View a listing of subscribers currently accessing the
system
show subscribers henbgw-only all
View information for a specific subscriber
show subscribers henbgw-only full username username
View Subscriber Counters
View counters for a specific subscriber
show subscribers counters username subscriber_name
View Recovered Session Information
View session state information and session recovery
status
show subscriber debug-info { callid | msid | username }
View Session Statistics and Information
Display Historical Session Counter Information
View all historical information for all sample
intervals
show session counters historical
Display Session Duration Statistics
View session duration statistics
show session duration
Display Session State Statistics
View session state statistics
show session progress
Display Session Subsystem and Task Statistics
Refer to the System Software Task and Subsystem Descriptions appendix of the System Administration Guide for additional
information on the Session subsystem and its various manager tasks.
View GTPU Manager statistics
show session subsystem facility gtpumgr all
View HeNB-GW Manager statistics
show session subsystem facility henbgwmgr all
View HeNB-GW Demux Manager statistics
show session subsystem facility henbgwdemux all
View Session Manager statistics
show session subsystem facility sessmgr all
View HeNB-GW Manager facility statistics
show logs facility henbgw
View HeNB Manager facility statistics
show logs facility henbgwmgr
View HeNB App facility statistics
show logs facility henbapp
View HeNB-GW Demux facility statistics
show logs facility henbgwdemux
Page 52

Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
▀ Monitoring System Status and Performance
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
52
To do this:
Enter this command:
View GTPU Manager Instance statistics
show gtpu statistics gtpumgr-instance gtpu_instance
Display Session Disconnect Reasons
View session disconnect reasons with verbose
output
show session disconnect-reasons
View HeNB-GW Access Service Configuration
Display an HeNB-GW Access Service Status
View all configured HeNB-GW access services
configuration in detail
show henbgw-access-service all
View HeNB-GW Network Service Configuration
Display an HeNB-GW Network Service Status
View all configured HeNB-GW Network services
configuration in detail
show henbgw-network-service all
View configuration errors in HeNB-GW Network
Service section in detail
show configuration errors section henbgw-networkservice verbose
View HeNB-GW Access Service Related Statistics
View HeNB-GW Access service statistics filtered on
an HeNB-GW Access service
show henbgw-access-service statistics henbgw-accessservice henbgw_access-svc_name verbose
View HeNB-GW Access service statistics filtered by
a peer id
show henbgw-access-service statistics peer-id
peer_identifier
View HeNB-GW Access service S1AP statistics
show henbgw-access-service statistics s1ap verbose
View HeNB-GW Access service SCTP statistics
show henbgw-access-service statistics sctp [ buffer |
verbose ]
View HeNB-GW Network Service Related Statistics
View HeNB-GW Network service statistics filtered
on an HeNB-GW Network service
show henbgw-network-service statistics henbgw-networkservice henbgw_network-svc_name verbose
View HeNB-GW Network service statistics filtered
by a peer id
show henbgw-network-service statistics peer-id
peer_identifier
View HeNB-GW Network service S1AP statistics
show henbgw-network-service statistics s1ap verbose
View HeNB-GW Network service SCTP statistics
show henbgw-network-service statistics sctp [ buffer |
verbose ]
View GTP-U Service Statistics
View GTP-U peer information
show gtpu statistics peer-address ip_address
View GTP-U Service information
show gtpu statistics gtpu-service gtpu_svc_name
Page 53

Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
Monitoring Logging Facility ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
53
Monitoring Logging Facility
To do this:
Enter this command:
Monitor logging facility for specific
session based on Call-id on system
logging trace callid call_id
Monitor logging facility based on IP
address used in session on system
logging trace ipaddr ip_address
Monitor logging facility based on MS
Identity used in session on system
logging trace msid ms_identifier
Monitor logging facility based on user
name used in session on system
logging trace username name
Monitor HeNB App logging facility on
HeNB-GW system
logging filter active facility henbapp level { critical | error
| warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor HeNB-GW logging facility on
HeNB-GW system
logging filter active facility henbgw level { critical | error |
warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor HeNB-GW Demux logging
facility on HeNB-GW system
logging filter active facility henbgwdemux level { critical |
error | warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor HeNB Manager logging facility
on HeNB-GW system
logging filter active facility henbgwmgr level { critical |
error | warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor S1AP logging facility on HeNBGW system
logging filter active facility s1ap level { critical | error |
warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor SCTP logging facility on HeNBGW system
logging filter active facility sctp level { critical | error |
warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
Monitor threshold logging facility on
HeNB-GW system
logging filter active facility threshold level { critical |
error | warning | unusual | info | trace | debug }
This section contains commands used to monitor the logging facility active for specific tasks, managers, applications
and other software components in the system.
Table 7. Logging Facility Monitoring Commands
Page 54

Monitoring the HeNB-GW Service
▀ Clearing Statistics and Counters
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
54
Clearing Statistics and Counters
It may be necessary to periodically clear statistics and counters in order to gather new information. The system provides
the ability to clear statistics and counters based on their grouping (HeNBGW-Access-Service, HeNBGW-NetworkService, GTP-U, etc.).
Statistics and counters can be cleared using the CLI clear command. Refer to Command Line Interface Reference for
detailed information on using this command.
Page 55

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
55
Chapter 5
HeNB-GW Service Thresholds
HeNB-GW Service thresholds generate alerts or alarms for the average number of calls setup. A threshold can be
configured to report this information on entire system for HeNB-GW service. Thresholds can also be configured for
session registration response failures, discarded interface registration requests, discarded network entry registration
acknowledgments for HeNB-GW services.
Threshold counter limits are configured for HeNB-GW HeNB SCTP association, HeNB-GW UE sessions, and HeNBGW Paging messages with poll interval value.
On reaching the threshold limits in the configured interval, if threshold monitoring is enabled for the HeNB-GW
service(s), threshold notifications get generated as SNMP traps. If threshold monitoring is disabled for the HeNB-GW
service(s), even on reaching the threshold limits, no notification gets generated.
Alerts or alarms are triggered for these HeNB-GW thresholds based on the following rules:
Enter condition: When the actual average of call setups or actual number of failures or discards passes, or is
equal to, the configured Threshold value an alert or alarm is set.
Clear condition: When the actual average of call setups or actual number of failures or discards passes below
the Threshold value the alert or alarm is cleared.
If a trigger condition occurs within the polling interval, the alert or alarm is not generated until the end of the polling
interval.
Page 56

HeNB-GW Service Thresholds
▀ Saving Your Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
56
Saving Your Configuration
When you configure thresholds they are not permanent unless you save the changes. When you have completed
configuring thresholds, save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location
using the Exec mode command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save
configuration files, refer to the System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
Page 57

HeNB-GW Service Thresholds
System-Level HeNB-GW Service Thresholds ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
57
System-Level HeNB-GW Service Thresholds
The system-level thresholds for HeNB-GW Service-Level can be configured to monitor thresholds for HeNB-GW
Paging messages.
Following thresholds can be configured for the HeNB-GW service-level:
Number of HeNB-GW Paging Messages
Total number of subscribers threshold for HeNB-GW HeNB sessions
Total number of subscribers threshold for HeNB-GW UE sessions
Configuring System-level HeNB-GW Service Thresholds
Use the following example to configure and enable these thresholds:
configuration
threshold henbgw-paging-messages <high_thresh> [ clear <low_thresh>]
threshold total-henbgw-henb-sessions <high_thresh> [ clear <low_thresh>]
threshold total-henbgw-ue-sessions <high_thresh> [ clear <low_thresh>]
threshold poll henbgw-paging-messages interval <dur>
threshold poll total-henbgw-henb-sessions interval <dur>
threshold poll total-henbgw-ue-sessions interval <dur>
threshold monitoring henbgw-service
end
Page 58

Page 59

Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
59
Chapter 6
Troubleshooting the Service
This chapter provides information and instructions for using the system command line interface (CLI) for
troubleshooting issues that may arise during service operation.
Page 60

Troubleshooting the Service
▀ Test Commands
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
60
Test Commands
Keyword/Variable
Description
gtpu-service
gtpu_svc_name
Specifies the GTP-U service configured on the system and associated with the HeNB-GW Network
service.
peer-address ip_addr
Specifies the IP address of the HeNB node.
NOTE: The IP address of the system’s interface must be bound to a configured HeNB-GW service
prior to executing this command.
all
Specifies that GTP-U echo requests will be sent to all Nodes that currently have sessions with the
HeNB-GW service.
gtpu-version { 0 | 1
}
Specifies the the GTPU version of peer node. This is optional; if provided and the peer version is not
known, the user supplied version is used while sending echo.
In the event that an issue was discovered with an installed application or line card, depending on the severity, it may be
necessary to take corrective action.
The system provides several redundancy and fail-over mechanisms to address issues with application and line cards in
order to minimize system downtime and data loss. These mechanisms are described in the sections that follow.
Using the GTPU Test Echo Command
This command tests the HeNB-GW’s ability to exchange GPRS Tunneling Protocol user plane (GTP-U) packets with
the specified peer nodes which can be useful in troubleshooting and/or monitoring.
The test is performed by the system sending GTP-U echo request messages to the specified node(s) and waiting for a
response.
Important: This command must be executed from within the context in which at least one HeNB-GW
service is configured.
The command has the following syntax:
gtpu test echo gtpu-service gtpu_svc_name { all | peer-address ip_addr } gtpuversion { 0 | 1 }
Using the IPsec Tunnel Test Command
This command tests the system’s ability to communicate through an IPsec Tunnel. This functionality is useful for
troubleshooting and/or monitoring.
The command has the following syntax:
test ipsec tunnel ip-pool ip_pool_name destination-ip des_ip_address source-ip
src_ip_address
Page 61

Troubleshooting the Service
Test Commands ▀
Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
61
Keyword/Variable
Description
ip_pool_name
The name of the IP pool configured for IPsec Tunnel. ip_pool_name can be from 1 to 63 alpha and/or
numeric characters in length and is case sensitive.
des_ip_address
The IP address of destination node of IPsec tunnel.
src_ip_address
The IP address of source node of IPsec tunnel.
Keyword/Variable
Description
ThreshHENBGWHenbSessions
Enables the threshold configuration for HeNB-GW HeNB sessions.
ThreshHENBGWPagingMessages
Enables the threshold configuration for HeNB-GW paging messages.
ThreshHENBGWUeSessions
Enables the threshold configuration for HeNB-GW UE sessions.
trap_target
Specifies that these trap(s) should be sent to this trap target.
Using the SNMP TRAP command for debugging
Once the thresholds are configured, then notifications get generated on reaching the limit in the configured interval and
are then shown in the SNMP trap.
The SNMP traps for HeNB-GE service can be configured using the following command syntax:
snmp trap enable { ThreshHENBGWHenbSessions | ThreshHENBGWPagingMessages |
ThreshHENBGWUeSessions } target trap_target
Using the RESOURCES SESSION command for debugging
The show resources session command is ideal for debugging the license-controlled number of HeNBs and
subscribers/UEsconnecting to the HeNB-GW.
The license status for all sort of resources can be viewed using the following command syntax:
show resources session
In case, the number of sessions are within the acceptable limits, the output of the above command looks as the following
sample (only HeNB-GW related sessions have been shown):
HENBGW Service:
In Use : 1161
Max Used : 1161 ( Monday May 06 05:22:00 IST 2013 )
Limit : 2000
License Status : Within Acceptable Limits
HENBGW UE Service:
Page 62

Troubleshooting the Service
▀ Test Commands
▄ Cisco ASR 5x00 Home eNodeB Gateway Administration Guide
62
In Use : 1700
Max Used : 1700 ( Monday May 06 05:20:10 IST 2013 )
Limit : 2000
License Status : Within Acceptable Limits
In case, the number of sessions are over the license capacity, the output of this command looks as the following sample
(only HeNB-GW related sessions have been shown):
HENBGW Service:
In Use : 2000
Max Used : 2000 ( Monday May 06 05:22:00 IST 2013 )
Limit : 2000
License Status : Over License Capacity (Rejecting Excess Calls)
HENBGW UE Service:
In Use : 2000
Max Used : 2000 ( Monday May 06 05:20:10 IST 2013 )
Limit : 2000
License Status : Over License Capacity (Rejecting Excess Calls)
 Loading...
Loading...