Page 1

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB
Gateway Administration Guide
Version 12.1
Last Updated May 31, 2012
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-25069-03
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED
WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED
WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to
part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a res idential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own
expense.
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain
version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL
FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE
OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE
PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING ,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR
ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and ot her countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at
www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company.
Any I nternet P rotocol (IP) addresses and phone nu mbers used in this doc ument are not inte nded to be ac tual addresses and pho n e numbers. Any examples, command d ispla y
output, network topology diagra ms, a nd other figures included in the docume nt ar e shown for illust rative purposes only. Any use o f ac tual IP ad dresses or phone numbe rs in
illustrative content is unintent ional and coincide ntal.
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
© 2012 Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliated entities. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
iii
CONTENTS
About this Guide ................................................................................................ ix
Conventions Used .................................................................................................................................... x
Contacting Customer Support ................................................................................................................. xii
Additional Information ............................................................................................................................. xiii
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network ................................................................. 15
Product Description ................................................................................................................................ 16
HNB Access Network Elements ......................................................................................................... 17
Home NodeB ................................................................................................................................. 17
Security Gateway (SeGW) ............................................................................................................. 18
HNB Gateway (HNB-GW) .............................................................................................................. 18
HNB Management System (HMS) ................................................................................................. 18
Licenses ............................................................................................................................................. 18
Platform Requirements....................................................................................................................... 19
Network Deployment and Interfaces ...................................................................................................... 20
HNB Gateway in 3G UMTS Network ................................................................................................. 20
Supported Logical Interfaces ............................................................................................................. 20
Features and Functionality - Base Software .......................................................................................... 22
AAA Server Group Support ................................................................................................................ 22
AAL2 Establish and Release Support ................................................................................................ 23
Access Control List Support ............................................................................................................... 23
ANSI T1.276 Compliance ................................................................................................................... 24
ATM VC Management Support .......................................................................................................... 24
Congestion Control and Management Support .................................................................................. 24
Emergency Call Handling ................................................................................................................... 25
GTP-U Tunnels Management Support............................................................................................... 26
HNB-UE Access Control .................................................................................................................... 26
HNB Management Function ............................................................................................................... 26
Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex.............................................................................................. 27
Intra-Domain Multiple CN Support Through Iu-Flex ........................................................................... 27
Iu Signalling Link Management Support ............................................................................................ 28
IuH User-Plane Transport Bearer Handling Support ......................................................................... 28
Network Access Control Functions through SeGW ........................................................................... 28
Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) ..................................................................................... 29
3GPP AAA Server Support ............................................................................................................ 29
X.509 Certificate-based Authentication Support ............................................................................ 29
Open Access Mode Support .............................................................................................................. 29
QoS Management with DSCP Marking .............................................................................................. 30
RADIUS Support ................................................................................................................................ 31
UE Management Function for Pre-Rel-8 UEs .................................................................................... 31
System Management Features .......................................................................................................... 32
Management System Overview ..................................................................................................... 32
Bulk Statistics Support ................................................................................................................... 33
Threshold Crossing Alerts (TCA) Support ..................................................................................... 34
ANSI T1.276 Compliance .............................................................................................................. 35
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software ...................................................... 37
Page 4

▀ Contents
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
iv
OL-25069-03
Dynamic RADIUS Extensions (Change of Authorization) .................................................................. 37
IP Security (IPSec) ............................................................................................................................. 38
Session Recovery ............................................................................................................................... 38
Web Element Management System ................................................................................................... 39
How HNB-GW Works ............................................................................................................................. 40
HNB Provisioning and Registration Procedure .................................................................................. 40
UE Registration Procedure ................................................................................................................. 42
UE Registration Procedure of Non-CSG UEs or Non-CSG HNBs ................................................ 42
Iu Connection Procedures .................................................................................................................. 44
Iu Connection Establishment Procedure ........................................................................................ 44
Network Initiated Iu Connection Release Procedure ..................................................................... 46
Paging and Serving RNS Relocation Procedures .............................................................................. 48
Paging Procedure .......................................................................................................................... 48
SRNS Relocation Procedure.......................................................................................................... 48
RANAP Reset Procedures ................................................................................................................. 49
HNB Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure ........................................................................................ 49
CN Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure ........................................................................................... 49
HNB-GW Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure ................................................................................. 49
Supported Standards .............................................................................................................................. 51
3GPP References ............................................................................................................................... 51
IETF References ................................................................................................................................ 52
ITU-T Recommendations ................................................................................................................... 54
Object Management Group (OMG) Standards .................................................................................. 55
Understanding the Service Operation ............................................................ 57
Terminology ............................................................................................................................................ 58
Contexts ............................................................................................................................................. 58
Logical Interfaces ............................................................................................................................... 58
Bindings .............................................................................................................................................. 60
Services and Networks ....................................................................................................................... 60
HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures ................................................. 63
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW ............................................................ 64
Required Local Context Configuration Information ............................................................................ 64
Required System-Level Configuration Information ............................................................................ 65
Required Source Context Configuration Information ......................................................................... 67
Required Destination Context Configuration Information ................................................................... 69
RTP Pool Configuration .......................................................................................................................... 71
IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over IuCS ................................................................................................... 71
IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over Iuh ...................................................................................................... 72
RTP IP Pool Configuration Verification .............................................................................................. 73
HNB-GW Service Configuration ............................................................................................................. 74
Hashing Algorithm Configuration ........................................................................................................ 75
Iuh Interface Configuration ................................................................................................................. 76
SS7 Routing Domain Configuration ................................................................................................... 76
Peer Server Id Configuration for PS Core Network ............................................................................ 76
Peer Server Id Configuration for CS Core Network ........................................................................... 77
SCCP Network Instance Configuration .............................................................................................. 78
HNB-PS Network Configuration ......................................................................................................... 78
HNB-CS Network Configuration ......................................................................................................... 79
HNB-GW Service Configuration ......................................................................................................... 80
GTP-U Service Configuration ............................................................................................................. 81
x.509 Certificate Configuration ........................................................................................................... 82
Security Gateway and Crypto map Template Configuration .............................................................. 83
Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex Configuration ....................................................................... 84
Page 5

Contents ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
v
Open Access Mode Configuration ..................................................................................................... 84
Verifying HNB-GW Configuration ....................................................................................................... 85
IuCS over ATM Configuration ................................................................................................................ 86
Configuring the SONET Card ............................................................................................................. 86
Configuring Linkset Id and ATM Parameters ..................................................................................... 86
Configuring ALCAP Service and AAL2 Node .................................................................................... 87
Configuring the ATM Port ................................................................................................................... 88
Associating ALCAP Service with HNB-CS Network Service ............................................................. 88
Iu-Flex Configuration .............................................................................................................................. 90
Iu-Flex over IuCS Interface Configuration .......................................................................................... 90
Iu-Flex over IuPS Interface Configuration .......................................................................................... 91
Logging Facility Configuration ................................................................................................................ 92
Displaying Logging Facility ................................................................................................................. 92
Congestion Control Configuration .......................................................................................................... 94
Configuring the Congestion Control Threshold .................................................................................. 94
Configuring Service Congestion Policies ........................................................................................... 94
Configuring New Call Policy ............................................................................................................... 95
Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration ........................................................................................................ 96
SNMP-MIB Traps for HNB-GW Service ................................................................................................. 97
Event IDs for HNB-GW Service .............................................................................................................. 98
Monitoring the Service ..................................................................................... 99
Monitoring System Status and Performance ........................................................................................ 100
Monitoring Logging Facility ................................................................................................................... 103
Clearing Statistics and Counters .......................................................................................................... 104
Troubleshooting the Service ......................................................................... 105
Test Commands ................................................................................................................................... 106
Using the GTPU Test Echo Command ............................................................................................ 106
Using the GTPv0 Test Echo Command ........................................................................................... 106
Using the IPsec Tunnel Test Command .......................................................................................... 107
Performance Improvement Commands ............................................................................................... 108
Turning off IPC Message Aggregation To Reduce Latency Towards Core Network ...................... 108
Engineering Rules........................................................................................... 109
DHCP Service Engineering Rules ........................................................................................................ 110
HNB-GW Engineering Rules ................................................................................................................ 111
Interface and Port Engineering Rules .................................................................................................. 112
IuCS Interface Rules ........................................................................................................................ 112
IuPS Interface Rules ........................................................................................................................ 112
Service Engineering Rules ................................................................................................................... 113
CoA, RADIUS DM, and Session Redirection (Hotlining) ............................. 115
RADIUS Change of Authorization and Disconnect Message............................................................... 116
CoA Overview .................................................................................................................................. 116
DM Overview .................................................................................................................................... 116
License Requirements...................................................................................................................... 116
Enabling CoA and DM ...................................................................................................................... 116
Enabling CoA and DM ................................................................................................................. 117
CoA and DM Attributes ................................................................................................................ 117
CoA and DM Error-Cause Attribute ............................................................................................. 118
Viewing CoA and DM Statistics ................................................................................................... 119
Session Redirection (Hotlining) ............................................................................................................ 122
Overview .......................................................................................................................................... 122
License Requirements ................................................................................................................. 122
Operation .......................................................................................................................................... 122
Page 6

▀ Contents
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
vi
OL-25069-03
ACL Rule ...................................................................................................................................... 122
Redirecting Subscriber Sessions ................................................................................................. 122
Session Limits On Redirection ..................................................................................................... 123
Stopping Redirection .................................................................................................................... 123
Handling IP Fragments ................................................................................................................ 123
Recovery ...................................................................................................................................... 123
AAA Accounting ........................................................................................................................... 123
Viewing the Redirected Session Entries for a Subscriber ................................................................ 123
IP Security ........................................................................................................ 129
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 131
Applicable Products and Relevant Sections .................................................................................... 132
IPSec Terminology ............................................................................................................................... 135
Crypto Access Control List (ACL) ..................................................................................................... 135
Transform Set ................................................................................................................................... 135
ISAKMP Policy ................................................................................................................................. 135
Crypto Map ....................................................................................................................................... 135
Manual Crypto Maps .................................................................................................................... 136
ISAKMP Crypto Maps .................................................................................................................. 136
Dynamic Crypto Maps .................................................................................................................. 136
Implementing IPSec for PDN Access Applications............................................................................... 137
How the IPSec-based PDN Access Configuration Works ................................................................ 137
Configuring IPSec Support for PDN Access .................................................................................... 138
Implementing IPSec for Mobile IP Applications .................................................................................... 140
How the IPSec-based Mobile IP Configuration Works ..................................................................... 140
Configuring IPSec Support for Mobile IP.......................................................................................... 143
Implementing IPSec for L2TP Applications .......................................................................................... 145
How IPSec is Used for Attribute-based L2TP Configurations .......................................................... 145
Configuring Support for L2TP Attribute-based Tunneling with IPSec .............................................. 147
How IPSec is Used for PDSN Compulsory L2TP Configurations .................................................... 148
Configuring Support for L2TP PDSN Compulsory Tunneling with IPSec ........................................ 149
How IPSec is Used for L2TP Configurations on the GGSN ............................................................. 150
Configuring GGSN Support for L2TP Tunneling with IPSec ............................................................ 151
Transform Set Configuration ................................................................................................................. 152
Configuring Transform Set ............................................................................................................... 152
Verifying the Crypto Transform Set Configuration ........................................................................... 152
ISAKMP Policy Configuration ............................................................................................................... 154
Configuring ISAKMP Policy .............................................................................................................. 154
Verifying the ISAKMP Policy Configuration ...................................................................................... 155
ISAKMP Crypto Map Configuration ...................................................................................................... 156
Configuring ISAKMP Crypto Maps ................................................................................................... 156
Verifying the ISAKMP Crypto Map Configuration ............................................................................. 157
Dynamic Crypto Map Configuration ...................................................................................................... 159
Configuring Dynamic Crypto Maps ................................................................................................... 159
Verifying the Dynamic Crypto Map Configuration ............................................................................ 159
Manual Crypto Map Configuration ........................................................................................................ 161
Configuring Manual Crypto Maps ..................................................................................................... 161
Verifying the Manual Crypto Map Configuration .............................................................................. 162
Crypto Map and Interface Association .................................................................................................. 164
Applying Crypto Map to an Interface ................................................................................................ 164
Verifying the Interface Configuration with Crypto Map ..................................................................... 164
FA Services Configuration to Support IPSec ........................................................................................ 166
Modifying FA service to Support IPSec ............................................................................................ 166
Verifying the FA Service Configuration with IPSec .......................................................................... 167
HA Service Configuration to Support IPSec ......................................................................................... 168
Page 7

Contents ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
vii
Modifying HA service to Support IPSec ........................................................................................... 168
Verifying the HA Service Configuration with IPSec .......................................................................... 169
RADIUS Attributes for IPSec-based Mobile IP Applications ................................................................ 170
LAC Service Configuration to Support IPSec ....................................................................................... 171
Modifying LAC service to Support IPSec ......................................................................................... 171
Verifying the LAC Service Configuration with IPSec ........................................................................ 172
Subscriber Attributes for L2TP Application IPSec Support .................................................................. 173
PDSN Service Configuration for L2TP Support.................................................................................... 174
Modifying PDSN service to Support Attribute-based L2TP Tunneling ............................................. 174
Modifying PDSN service to Support Compulsory L2TP Tunneling .................................................. 175
Verifying the PDSN Service Configuration for L2TP ........................................................................ 175
Redundant IPSec Tunnel Fail-Over ..................................................................................................... 176
Supported Standards ....................................................................................................................... 176
Redundant IPSec Tunnel Fail-over Configuration ................................................................................ 177
Configuring Crypto Group ................................................................................................................ 177
Modify ISAKMP Crypto Map Configuration to Match Crypto Group ................................................ 178
Verifying the Crypto Group Configuration ........................................................................................ 178
Dead Peer Detection (DPD) Configuration........................................................................................... 180
Configuring Crypto Group ................................................................................................................ 180
Verifying the DPD Configuration ...................................................................................................... 181
APN Template Configuration to Support L2TP .................................................................................... 182
Modifying APN Template to Support L2TP ...................................................................................... 182
Verifying the APN Configuration for L2TP........................................................................................ 183
IPSec for LTE/SAE Networks ............................................................................................................... 184
Encryption Algorithms ...................................................................................................................... 184
HMAC Functions .............................................................................................................................. 184
Diffie-Hellman Groups ...................................................................................................................... 184
Dynamic Node-to-Node IPSec Tunnels ........................................................................................... 185
ACL-based Node-to-Node IPSec Tunnels ....................................................................................... 185
Traffic Selectors ............................................................................................................................... 185
Authentication Methods .................................................................................................................... 186
X.509 Certificate-based Peer Authentication ................................................................................... 186
Certificate Revocation Lists .............................................................................................................. 188
Child SA Rekey Support .................................................................................................................. 188
IKEv2 Keep-Alive Messages (Dead Peer Detection) ....................................................................... 189
E-UTRAN/EPC Logical Network Interfaces Supporting IPSec Tunnels .......................................... 189
IPSec Tunnel Termination ................................................................................................................ 190
Page 8

Page 9

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
ix
About this Guide
This document pertains to the features and functionality that run on and/or that are related to the Cisco® ASR 5000
Chassis.
This preface includes the following sections:
Conventions Used
Contacting Customer Support
Additional Information
Page 10
About this Guide
▀ Conventions Used
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
x
OL-25069-03
Conventions Used
Icon
Notice Type
Description
Information Note
Provides information about important features or instructions.
Caution
Alerts you of potential damage to a program, device, or system.
Warning
Alerts you of potential personal injury or fatality. May also alert you of potential
electrical hazards.
Electrostatic Discharge
(ESD)
Warns you to take proper grounding precautions before handling ESD sensitive
components or devices.
Typeface Conventions
Description
Text represented as a screen
display
This typeface represents text that appears on your terminal screen, for example:
Login:
Text represented as commands
This typeface represents commands that you enter at the CLI, for example:
show ip access-list
This document always gives the full form of a command in lowercase letters. Commands
are not case sensitive.
Text represented as a command
variable
This typeface represents a variable that is part of a command, for example:
show card slot_number
slot_number is a variable representing the desired chassis slot number.
Text represented as menu or submenu names
This typeface represents menus and sub-menus that you access within a software
application, for example:
Click the File menu, then click New.
Command Syntax
Conventions
Description
{ keyword or
variable }
Required keywords and variables are surrounded by braces. They must be entered as part of the
command syntax.
[ keyword or
variable ]
Optional keywords or variables that may or may not be used are surrounded by brackets.
The following tables describe the conventions used throughout this documentation.
Page 11

About this Guide
Conventions Used ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
xi
Command Syntax
Conventions
Description
|
Some commands support alternative variables. These “options” are documented within braces or
brackets by separating each variable with a vertical bar.
These variables can be used in conjunction with required or optional keywords or variables. For
example:
{ nonce | timestamp }
OR
[ count number_of_packets | size number_of_bytes ]
Page 12

About this Guide
▀ Contacting Customer Support
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
xii
OL-25069-03
Contacting Customer Support
Go to http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/support/ to submit a service request. A valid Cisco account (username and
password) is required to access this site. Please contact your Cisco account representative for additional information.
Page 13

About this Guide
Additional Information ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
xiii
Additional Information
Refer to the following guides for supplemental information about the system:
Command Line Interface Reference
Statistics and Counters Reference
Thresholding Configuration Guide
SNMP MIB Reference
Web Element Manager Installation and Administration Guide
Product-specific and feature-specific administration guides
Release notes that accompany updates and upgrades to StarOS
Page 14

Page 15

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
15
Chapter 1
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
The Cisco® provides 3GPP wireless carriers with a flexible solution that functions as a Home NodeB Gateway (HNBGW) in HNB Access Network to connect UEs with existing UMTS networks.
The Home NodeB Gateway works as a gateway for Home NodeBs (HNBs) to access the core networks. The HNB-GW
concentrates connections from a large amount of HNBs through IuH interface and terminates the connection to existing
Core Networks (CS or PS) using standard Iu (IuCS or IuPS) interface.
This overview provides general information about the HNB Gateway including:
Product Description
Network Deployment and Interfaces
Features and Functionality - Base Software
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software
How HNB-GW Works
Supported Standards
Page 16
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
16
OL-25069-03
Product Description
The Home NodeB Gateway is the HNB network access concentrator used to connect the Home NodeBs (HNBs)/Femto
Access Point (FAP) to access the UMTS network through HNB Access Network. It aggregates Home Node-B or Femto
Access Points to a single network element and then integrates them into the Mobile Operators Voice, Data and
Multimedia networks.
Femtocell is an important technology and service offering that enables new Home and Enterprise service capabilities for
Mobile Operators and Converged Mobile Operators (xDSL/Cable/FFTH plus Wireless). The Femtocell network consists
of a plug-n-play customer premise device generically called a Home NodeB (HNB) with limited range radio access in
home or Enterprise. The HNB will auto-configure itself with the Operators network and the user can start making voice,
data and multimedia calls.
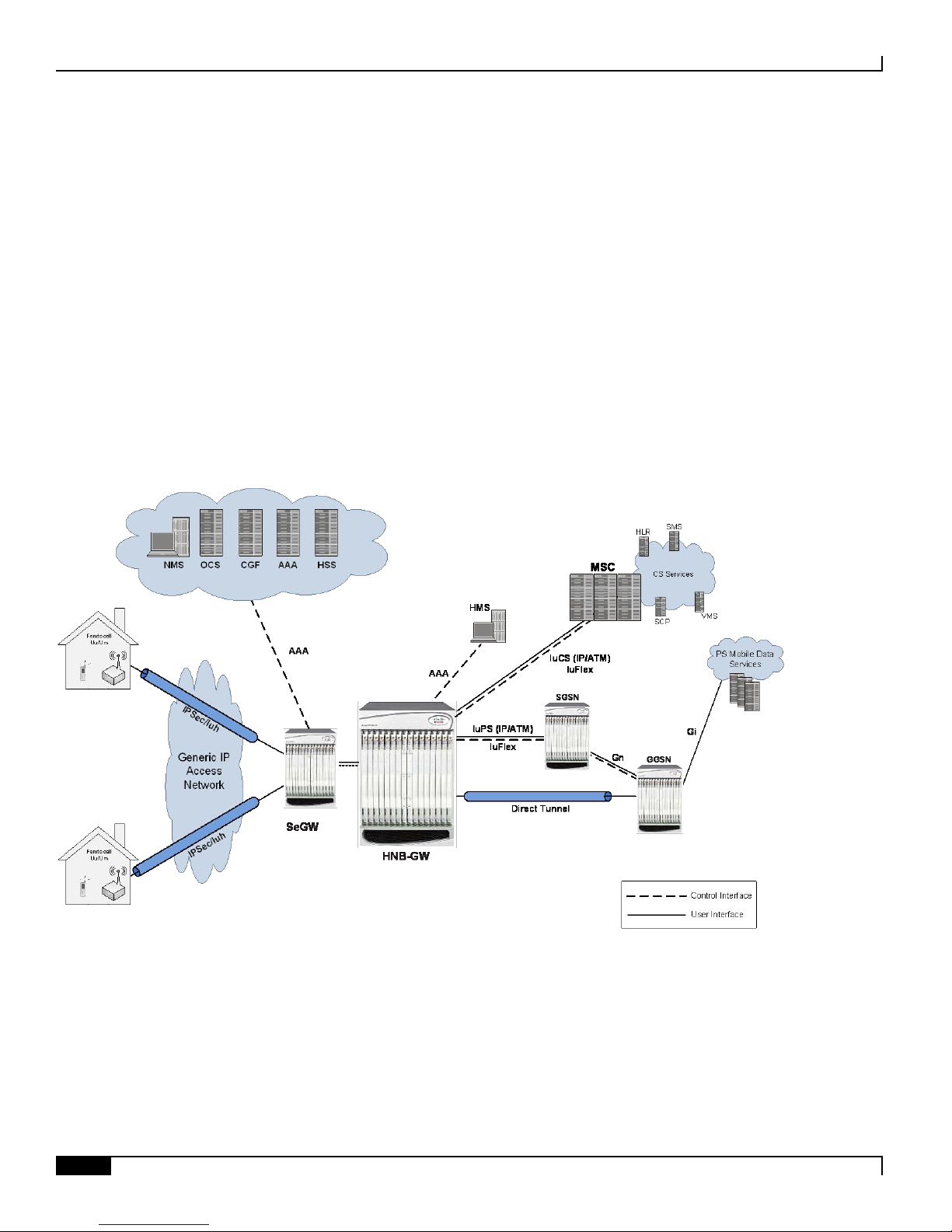
The figure given describes a high level view of UMTS network with Femtocell and HNB-GW.
Figure 1. HNB-GW Deployment in 3G UMTS Network
Once a secure tunnel has been established between the HNB and the SeGW and the HNB has been configured by the
HMS, the Operator has to connect the Femtocell network to their Core Network and services. There are several
interworking approaches to Circuit Switch (CS) and Packet Switch (PS) domains. One approach is to make the
Femtocell network appear as a standard Radio Access Network (RAN) to the Core Network. In addition to the HNB,
SeGW and HMS the RAN approach requires a network element generically called a Femto Gateway (FGW/HNB-GW).
The HNB-GW provides interworking and aggregation of large amount of Femtocell sessions toward standard CN
interfaces (IuPS/IuCS). In this approach services and mobility are completely transparent to CN elements (e.g. MSC,
xGSN).
Page 17
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
17
The other approach is to connect the Femtocell to an IMS Network to provide CS services to subscribers when on the
Femtocell and deploy a new network element generically called a Convergence Server to provide service continuity and
mobility over standard interfaces at the MSC layer (e.g GSM-MAP, IS-41). These two approaches are clearly different
in how CS based services and mobility are achieved.
In accordance with 3GPP standard, the HNB-GW provides following functions and procedures in UMTS core network:
HNB Registration/De-registration Function
UE Registration/De-registration Function for HNB
IuH User-plane Management Functions
IuH User-plan Transport Bearer Handling
Iu Link Management Functions
Important: Some of the features may not be available in this release. Kindly contact your local Cisco
representative for more information on supported features.
HNB Access Network Elements
This section provides the brief description and functionality of various network elements involved in the UMTS Femto
access network. The HNB access network includes the following functional entities:
Home NodeB
Security Gateway (SeGW)
HNB Gateway (HNB-GW)
HNB Management System (HMS)
Home NodeB
A Home NodeB (HNB) is the a customer premise equipment that offers Uu interface to UE and IuH over IPSec tunnel
to HNB-GW for accessing UMTS Core Network (PS or CS) in Femtocell access network.
It also provides the support to HNB registration and UE registration over IuH with HNB-GW. Apart from these
functions HNB also supports some RNC like functions as given below:
RAB management functions
Radio Resource Management functions
Iu Signalling Link management
GTP-U Tunnels management
Buffer Management
Iu U-plane frame protocol initialization
Mobility management functions
Security Functions
Service and Network Access functions
Paging co-ordination functions
UE Registration for HNB
Page 18

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Product Description
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
18
OL-25069-03
IuH user-plane Management functions
Security Gateway (SeGW)
Security Gateway is a logical entity in Cisco HNB-GW.
Basic function of this entity are:
Authentication of HNB
Providing access to HMS and HNB-GW
This entity terminates the secure tunnelling for IuH and TR-069 between HNB and HNB-GW and HMS respectively.
In this implementation it is an optional element which is situated on HNB-GW.
HNB Gateway (HNB-GW)
The HNB-GW provides the access to Femto user to UMTS core network. It acts as an access gateway to HNB and
concentrates connections from a large amount of HNBs. The IuH interface is used between HNB and HNB-GW and
HNB-GW connects with the Core Networks (CS or PS) using the generic Iu (IuCS or IuPS) or Gn interface.
It also terminates Gn and other interfaces from UMTS core networks to provide mobile data services to HNB and to
interact with HMS to perform HNB authentication and authorization.
HNB Management System (HMS)
It is a network element management system for HNB access. Management interface between HNB and HMS is based
on TR-069 family of standards.
It performs following functions while managing HNB access network:
Facilitates HNB-GW discovery for HNB
Provision of configuration data to the HNB
Performs location verification of HNB and assigns appropriate serving elements (HMS, Security Gateway and
HNB-GW)
The HNB Management System (HMS) comprises of the following functional entities:
File Server: used for file upload or download, as instructed by TR-069 manager
TR-069 Manager: Performs CM, FM and PM functionality to the HNB through Auto-configuration server
(HMS)
Licenses
The HNB-GW is a licensed Cisco product. Separate session and feature licenses may be required. Contact your Cisco
account representative for detailed information on specific licensing requirements. For information on installing and
verifying licenses, refer to the Managing License Keys section of the Software Management Operations chapter in the
System Administration Guide.
Page 19

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
19
Platform Requirements
The HNB-GW service runs on a Cisco® ASR 5x00 chassis running StarOS Rel. 10 or later. The chassis can be
configured with a variety of components to meet specific network deployment requirements. For additional information,
refer to the Installation Guide for the chassis and/or contact your Cisco account representative.
Page 20
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Network Deployment and Interfaces
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
20
OL-25069-03
HNB-GW
IPsec
Gateway
CS Service
PS Service
HNB-GW AP
In-line Services
HPLMN/VPLMN
AAA
TR-069/196
SSL/ORBEM
Direct Tunnel
GGSN
SGSN
Iu-PS/Iu-Flex
Iu-CS/Iu-Flex
MSC
HLR
Optional Services
Optional
Element
Iuh
IPsec IKEv2
RNS
Uu
RADIUS
HNB
EMS
HMS
Network Deployment and Interfaces
This section describes the supported interfaces and deployment scenario of HNB-GW in 3G Femto access network.
The following information is provided in this section:
HNB Gateway in 3G UMTS Network
Supported Logical Interfaces
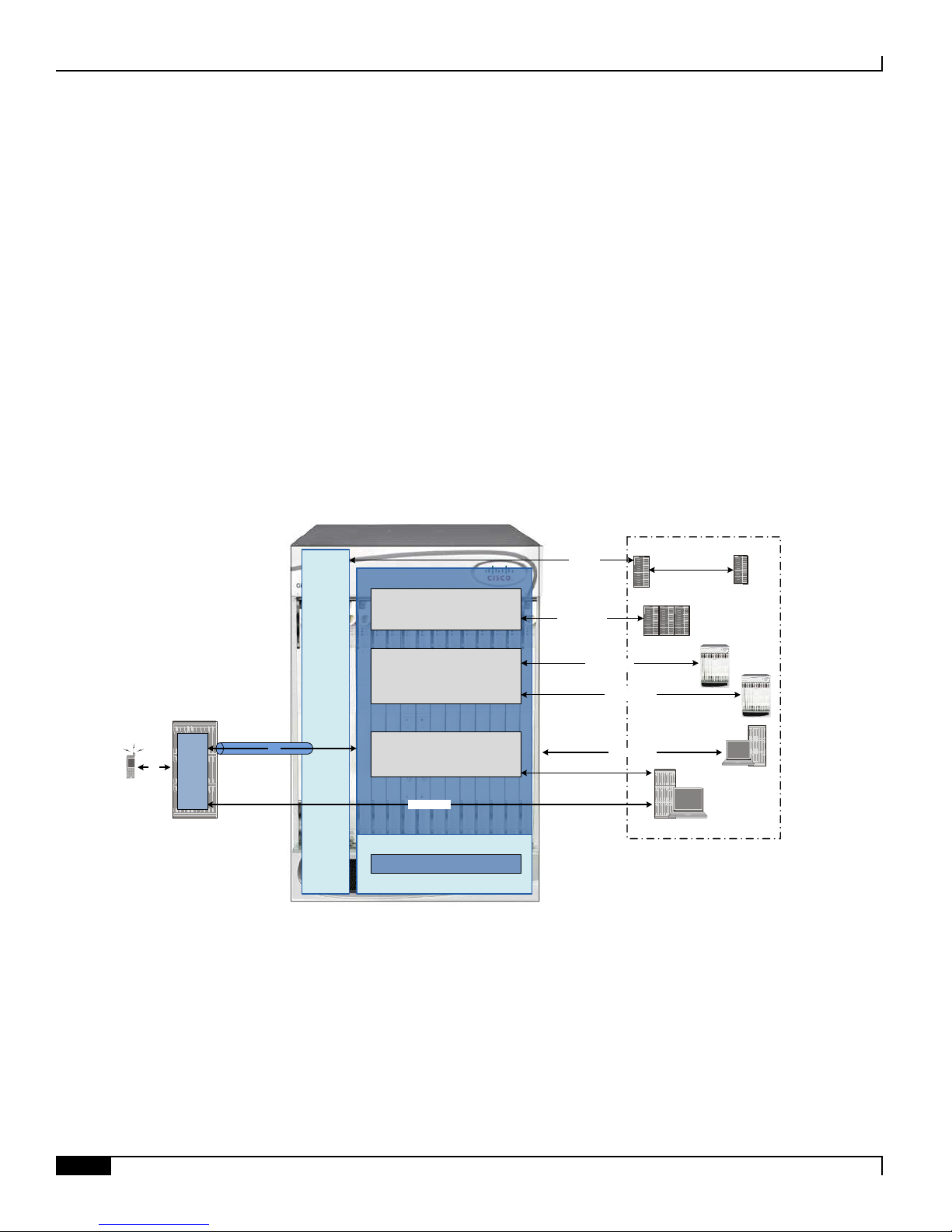
HNB Gateway in 3G UMTS Network
The following figure displays simplified network views of the HNB-GW in an Femto access network accessing UMTS
PS or CS Core Network.
Figure 2. HNB-GW in UMTS Network and Interfaces
Supported Logical Interfaces
This section provides the brief information on supported interfaces on HNB-GW node.
In support of both mobile and network originated subscriber UE contexts, the HNB-GW provides the following network
interface support:
IuH Interface: This interface is the reference point for the control plane protocol between Home NodeB and
HNB-GW. IuH uses SCTP over IPSec IKEv2 tunnel as the transport layer protocol for guaranteed delivery of
signaling messages between HNB-GW and Home NodeB.
Page 21

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Network Deployment and Interfaces ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
21
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with HNB on the same Femtocell Access Network.
This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining subscriber UE contexts.
One or more IuH interfaces can be configured per system context.
IuCS: This interface is the reference point in UMTS which links the HNB-GW, which acts as an RNC (Radio
Network Controller), with a Mobile Switching Centre (3G MSC) in the 3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network.
This interface provides an IuCS over IP or IuCS over ATM (IP over AAL5 over ATM) interface between the
MSC and the RNC (HNB-GW) in the 3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network. RAN Application Part (RANAP)
is the control protocol that sets up the data plane (GTP-U) between these nodes. SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP) or
QSAAL (MTP3B/QSAAL) handle IuCS (control) for the HNB-GW.
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with 3G MSC on the same Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN). This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining the CS access for Femtocell
UE to circuit switched UMTS core networks
One or more IuCS interfaces can be configured per system context.
IuPS: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and SGSN. This interface provides an IuPS over
IP or IuPS over ATM (IP over AAL5 over ATM) interface between the SGSN and the RNC (HNB-GW) in the
3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network. RAN Application Part (RANAP) is the control protocol that sets up the
data plane (GTP-U) between these nodes. SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP) or QSAAL (MTP3B/QSAAL) handle
IuPS-C (control) for the HNB-GW.
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with SGSN on the same Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN). This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining the PS access for Femtocell
UE to packet switched UMTS core networks.
One or more IuPS interfaces can be configured per system context.
Gi: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and IP Offload Gateway. It is used by the HNB-GW
to communicate with Packet Data Networks (PDNs) through IP Offload Gateway in the H-PLMN/V-PLMN.
Examples of PDNs are the Internet or corporate intranets.
One or more Gi interfaces can be configured per system context.
Gn: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and GGSN. It is used by the HNB-GW to
communicate with GGSNs on the same GPRS/UMTS Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN).
One or more Gn interfaces can be configured per system context.
RADIUS: This interface is the reference point between a Security Gateway (SeGW) and a 3GPP AAA Server or
3GPP AAA proxy (OCS/CGF/AAA/HSS) over RADIUS protocol for AAA procedures for Femto user.
In the roaming case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy can act as a stateful proxy between the SeGW and 3GPP AAA
Server.
The AAA server is responsible for transfer of subscription and authentication data for
authenticating/authorizing user access and UE authentication. The SeGW communicates with the AAA on the
PLMN using RADIUS protocol.
One or more RADIUS interfaces can be configured per system context.
TR-069: This interface is an application layer protocol which is used for remote configuration of terminal
devices, such as DSL modems, HNBs and STBs. TR-069 provides an auto configuration mechanism between
the HNB and a remote node in the service provider network termed the Auto Configuration Server. The
standard also uses a combination of security measures including IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange v2) and IPsec
(IP Security) protocols to authenticate the operator and subscriber and then guarantee the privacy of the data
exchanged.
One TR-069 interface can be configured per HNB node.
Page 22

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
22
OL-25069-03
Features and Functionality - Base Software
This section describes the features and functions supported by default in base software on HNB-GW service and do not
require any additional license to implement the functionality with the HNB-GW service.
Following features and supports are discussed in this section:
AAA Server Group Support
AAL2 Establish and Release Support
Access Control List Support
ANSI T1.276 Compliance
ATM VC Management Support
Congestion Control and Management Support
Emergency Call Handling
GTP-U Tunnels Management Support
HNB-UE Access Control
HNB Management Function
Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex
Intra-Domain Multiple CN Support Through Iu-Flex
Iu Signalling Link Management Support
IuH User-Plane Transport Bearer Handling Support
Network Access Control Functions through SeGW
Open Access Mode Support
QoS Management with DSCP Marking
RADIUS Support
System Management Features
UE Management Function for Pre-Rel-8 UEs
AAA Server Group Support
Value-added feature to enable VPN service provisioning for enterprise or MVNO customers. Enables each corporate
customer to maintain its own AAA servers with its own unique configurable parameters and custom dictionaries.
This feature provides support for up to 800 AAA (RADIUS and Diameter) server groups and 800 NAS IP addresses that
can be provisioned within a single context or across the entire chassis. A total of 128 servers can be assigned to an
individual server group. Up to 1,600 accounting, authentication and/or mediation servers are supported per chassis and
may be distributed across a maximum of 1,000 nodes. This feature also enables the AAA servers to be distributed across
multiple nodes within the same context.
Page 23
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
23
Important: In 12.3 and earlier releases, refer to the AAA and GTPP Interface Administration and Reference for
more information on AAA Server Group configuration.
AAL2 Establish and Release Support
Support to establish and release of ATM adaptation layer 2 (AAL2) channel within an ATM virtual connection by the
HNB-GW in complete or partial compliance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 25.414 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface data transport and transport signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.415 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface user plane protocols (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.467 V8.0.0. (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home NodeB; Stage 2 (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.1.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
ITU-T Recommendation Q.2630.1: AAL type2 signalling protocol (Capability Set 1)
ITU-T Recommendation Q.2630.2: AAL type2 signalling protocol (Capability Set 2)
ITU-T Recommendation I.363.2 B: ISDN ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) Specification: Type 2 AAL
ITU-T Recommendation I.366.1: Segmentation and Reassembly Service Specific Convergence Sublayer for
the AAL type 2
The HNB-GW connects to core network elements like MSC and SGSN over IuCS and IuPS interfaces respectively. The
Iu interface towards core network elements could either by IP based or ATM based. To provide ATM based interface
support, Cisco HNB-GW provides AAL2 support on system in order to establish a voice bearer with MSC.
Access Control List Support
Access Control Lists provide a mechanism for controlling (i.e permitting, denying, redirecting, etc.) packets in and out
of the system.
IP access lists, or Access Control Lists (ACLs) as they are commonly referred to, are used to control the flow of packets
into and out of the system. They are configured on a per-context basis and consist of “rules” (ACL rules) or filters that
control the action taken on packets that match the filter criteria
Once configured, an ACL can be applied to any of the following:
An individual interface
All traffic facilitated by a context (known as a policy ACL)
An individual subscriber
All subscriber sessions facilitated by a specific context
There are two primary components of an ACL:
Rule: A single ACL consists of one or more ACL rules. As discussed earlier, the rule is a filter configured to
take a specific action on packets matching specific criteria. Up to 128 rules can be configured per ACL.
Page 24
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
24
OL-25069-03
Each rule specifies the action to take when a packet matches the specifies criteria. This section discusses the
rule actions and criteria supported by the system.
Rule Order: A single ACL can consist of multiple rules. Each packet is compared against each of the ACL rules,
in the order in which they were entered, until a match is found. Once a match is identified, all subsequent rules
are ignored.
Important: For more information on Access Control List configuration, refer IP Access Control List chapter in
System Administration Guide.
ANSI T1.276 Compliance
ANSI T1.276 specifies security measures for Network Elements (NE). In particular it specifies guidelines for password
strength, storage, and maintenance security measures.
ANSI T1.276 specifies several measures for password security.
These measures include:
Password strength guidelines
Password storage guidelines for network elements
Password maintenance, e.g. periodic forced password changes
These measures are applicable to the systems and the Web Element Manager since both require password
authentication. A subset of these guidelines where applicable to each platform will be implemented. A known subset of
guidelines, such as certificate authentication, are not applicable to either product. Furthermore, the platforms support a
variety of authentication methods such as RADIUS and SSH which are dependent on external elements. ANSI T1.276
compliance in such cases will be the domain of the external element. ANSI T1.276 guidelines will only be implemented
for locally configured operators.
ATM VC Management Support
Support for Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) virtual circuits (VC) management function of AAL2 and AAL5
protocol by the HNB-GW in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TR 29.814 V7.1.0 (2007-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Networks and Terminals Feasibility Study on Bandwidth Savings at Nb Interface with IP transport (Release 7)
HNBGW supports PVC (permanent virtual circuits) connections with CN nodes for AAL2 and AAL5 type of traffic.
The Common Part Sublayer (CPS) payload which is carried out by the AAL2 protocol over ATM is also configurable
with this feature. It provides the dynamic Common Part Sublayer (CPS) payload configuration for AAL2 protocol
traffic over ATM for negotiation between HNB-GW and MSC during call. Default size for payload is 45 but values may
range from 1 to 64 Bytes. This feature makes the operator to choose the CPS payload size dynamically.
Congestion Control and Management Support
Congestion Control monitors the system for conditions that could potentially degrade performance when the system is
under heavy load. Typically, these conditions are temporary (for example, high CPU or memory utilization) and are
quickly resolved. However, continuous or large numbers of these conditions within a specific time interval may have an
Page 25
HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
25
impact the system’s ability to service subscriber sessions. Congestion control helps identify such conditions and invokes
policies for addressing the situation.
Congestion control operation is based on configuring the following:
Congestion Condition Thresholds: Thresholds dictate the conditions for which congestion control is enabled
and establishes limits for defining the state of the system (congested or clear). These thresholds function in a
way similar to operation thresholds that are configured for the system as described in the Thresholding
Configuration Guide. The primary difference is that when congestion thresholds are reached, a service
congestion policy and an SNMP trap, starCongestion, are generated.
A threshold tolerance dictates the percentage under the configured threshold that must be reached in order for
the condition to be cleared. An SNMP trap, starCongestionClear, is then triggered.
Port Utilization Thresholds: If you set a port utilization threshold, when the average utilization of all
ports in the system reaches the specified threshold, congestion control is enabled.
Port-specific Thresholds: If you set port-specific thresholds, when any individual port-specific
threshold is reached, congestion control is enabled system-wide.
Service Congestion Policies: Congestion policies are configurable for each service. These policies dictate how
services respond when the system detects that a congestion condition threshold has been crossed.
Important: For more information on Congestion Control support, refer Congestion Control chapter in System
Administration Guide.
Emergency Call Handling
The HNB-GW supports the handling of Emergency call in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.3.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
3GPP TS 33.102 V9.1.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services
and System Aspects; 3G Security; Security architecture Release 9)
The HNB-GW provides access for all UE/HNB when emergency call initiated. In case of non CSG UEs or non CSG
HNBs, after Emergency call is finished, the context established between the HNB and operator’s core network entities
for UEs who can not get access over the HNB is released to prevent the UE from accessing non-emergency services.
HNB-GW handles the emergency call in following way:
Authentication: In case of emergency call, HNB sends a UE REGISTRATION REQUEST message with
“Registration cause” as emergency call and excludes the “UE Permanent identity” (i.e IMSI) and HNBGW
does not perform access control for emergency call case.
Single Iu and Single RAB: In case of emergency call, HNBGW does not allow multiple RABs for UE. This
means that UE must have only one Iu connection, either CS or PS, and have only one RAB on that Iu
connection. HNB-GW implements “Single IU, Single RAB policy” when UE registration comes with
Emergency.
The RUA-CONNECT has an IE called “establishment cause” which can take values as “Normal” or
“Emergency”. If UE-registration was due to emergency then RUA-CONNECT must contain “Emergency”. If
RUA-CONNECT contains “normal” then HNB-GW rejects it.
While rejecting RUA connection or RAB connection the HNB-GW uses following reject cause:
RUA - Misc: unspecified
Page 26

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
26
OL-25069-03
RAB - Misc: unspecified
If UE-registration is normal then both (normal and emergency) RUA-CONNECT is allowed.
GTP-U Tunnels Management Support
Support to manage the GTP-U tunnels between HNB-GW and GSNs by in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.1.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 29.060 V9.0.0 (2009-09): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Network and Terminals; General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) across the
Gn and Gp interface (Release 9)
HNB-GW supports establishment of GTPU tunnels for each RAB over the IuPS interface. HNB-GW terminates the
GTP-U teunnels coming from CN (SGSN) and initiates seperate GTP-U tunnel towards HNB.
HNB-UE Access Control
UE/HNB access control support in 3G UMTS HNB Access Network is provided on HNB-GW through IMSI White list
database and AAA attribute processing. This feature is in accordance with following standards:
3GPP TS 23.003 V8.9.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Network and Terminals; Numbering, addressing and identification (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.3.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B (HNB) Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release
9)
IETF RFC-2865, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS), June 2000
The HNB-GW provides UE registration and de-registration procedure for the HNB to convey Rel-8 UE identification
data to the HNB-GW in order to perform access control for the UE in the HNB-GW. The UE Registration also
establishes a UE specific context identifier to be used between HNB and HNB-GW. The procedure triggered when the
UE attempts to access the HNB via an initial NAS message and there is no context in the HNB allocated for that UE.
For pre-Release 8 UEs, which do not support CSG and does not listen for CSG-ID, the HNB-GW ensures that a UE is
authorized to access a particular Femtocell. To perform access control check for pre-Release 8 UE, HNB-GW maintains
a per-HNB Whitelist. This whitelist consists of IMSIs which are allowed to access that particular HNB. The whitelist is
stored in the HMS and is downloaded to HNB-GW when HNB-REGISTRATION procedure happens.
HNB Management Function
Support for HNB registration and de-registration in 3G UMTS HNB Access Network accordance with the following
standards:
Page 27

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
27
3GPP TS 25.469 V8.1.0 (2009-03): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release 8)
IETF RFC 4960, Stream Control Transmission Protocol, December 2007
The HNB-GW provides HNB registration and de-registration procedure to register the HNB with the HNB-GW. This
procedure enables the HNB-GW to provide service and core network connectivity for the HNB. On HNB-GW node this
procedure is the first HNBAP procedure triggered after the SCTP association has become operational between HNB and
HNB-GW.
HNB management function processes the HNB/UE access control procedure through White-List processing on HNBGW node. Dynamic update of White-List gives the dynamic HNB management ability to HNB-GW.
Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex
Support for multiple MSC selection in a CS core network is provided with this feature support.
HNBGW can connect to multiple MSC and SGSN through Iu-Flex or LAC mapping. This feature implements the
multiple MSC selection using LAC.
For this support the HNB-GW uses HNB's LAC, received during registration procedure in
HNB_REGISTER_REQUEST message, to distribute RANAP-Initial UE message to an MSC. It maps the LAC with
MSC point code and a set of LACs configured for each MSC, connected to the HNB-GW.
In the HNBGW, to select an MSC based on the LAC the following algorithm is used:
If both Iu-Flex and LACs are configured for a MSC, then Iu-Flex is used to select a MSC.
If only Iu-Flex is configured then Iu-Flex is used for selecting MSC.
If only LACs are configured then MSC is selected using LAC from HNB.
If both Iu-Flex and LACs are not configured in the HNBGW, it selects default MSC.
Intra-Domain Multiple CN Support Through Iu-Flex
Iu-Flex is the routing functionality for intra domain connection of HNB-GW nodes to multiple CN nodes (MSC/SGSN).
It provides a routing mechanism and related functionality on HNB-GW to enable it to route information of different
Core Network (CN) nodes with in the CS or PS domain. It is implemented in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 23.236 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services
and System Aspects; Intra-domain connection of Radio Access Network (RAN) nodes to multiple Core
Network (CN) nodes (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
HNBGW supports Iu-Flex routing mechanism and other applications like many-to-many relation and load-sharing
between CN nodes with HNB-GW and CN node pooling. This mechanism provides following benefits to network
operator:
Eliminates the single point of failure between an RNC/HNB-GW and a CN Node.
Ensures geographical redundancy, as a pool can be distributed across sites.
Minimizes subscriber impact during service, maintenance, or node additions or replacements.
Increases overall capacity via load sharing across the MSCs/SGSNs in a pool.
Page 28

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
28
OL-25069-03
Reduces the need/frequency for inter-CN node RAUs. This substantially reduces signaling load and data transfer
delays.
Supports load redistribution with the MSC/SGSN offloading procedure.
To incorporate the concept of multiple CN nodes, Iu-Flex introduces the concept of “pool-areas” which is enabled by
the routing mechanism in HNB GW. A pool-area is served by multiple CN nodes (MSCs or SGSNs) in parallel which
share the traffic of this area between each other. Furthermore, pool-areas may overlap. From a RAN perspective a poolarea comprises all LA(s)/RA(s) of one or more RNC/BSC or HNBGW that are served by a certain group of CN nodes in
parallel. One or more of the CN nodes in this group may in addition serve LAs/RAs outside this pool-area or may also
serve other pool-areas. This group of CN nodes is also referred to as MSC pool or SGSN pool respectively.
The Iu-Flex enables a few different application scenarios with certain characteristics. The service provision by multiple
CN nodes within a pool-area enlarges the served area compared to the service area of one CN node. This results in
reduced inter CN node updates, handovers and relocations and it reduces the HLR/HSS update traffic. The configuration
of overlapping pool-areas allows to separate the overall traffic into different UE moving pattern, e.g. pool-areas where
each covers a separate residential area and all the same city centre. Other advantages of multiple CN nodes in a poolarea are the possibility of capacity upgrades by additional CN nodes in the pool-area or the increased service availability
as other CN nodes may provide services in case one CN node in the pool-area fails.
Iu Signalling Link Management Support
Support for Iu signal link management function for HNB-GW in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 25.412 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface signalling transport (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.413 V7.9.0 (2008-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface RANAP signalling (Release 7)
3GPP TS 25.414 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface data transport and transport signalling (Release 9)
HNBGW supports RANAP protocol for management of IuPS/IuCS connections. The IU connection on the IuPS/IuCS
interface is realized using an SCCP connection towards SGSN/MSC. The SCCP could be over SIGTRAN or ATM.
IuH User-Plane Transport Bearer Handling Support
Support for transfer of CS as well as PS data over IP on the IuH interface:
3GPP TS 25.467 V8.0.0. (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home NodeB; Stage 2 (Release 8)
HNB-GW supports GTP-U v1 for PS traffic transport and RTP/RTCP for CS traffic transport on IuH interface. HNBGW terminates the GTPU tunnels and RTP sessions at itself for each tunnel/session between CN and HNB.
Network Access Control Functions through SeGW
These functions enable secure user and device level authentication between the authenticator component of the HNBGW and a 3GPP HSS/AuC and RADIUS-based AAA interface support.
This section describes following features:
Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA)
Page 29

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
29
3GPP AAA Server Support
X.509 Certificate-based Authentication Support
Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA)
HNB-GW provides Authentication and Key Agreement mechanism for user authentication procedure over the HNB
Access Network. The Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) mechanism performs authentication and session key
distribution in networks. AKA is a challenge- response based mechanism that uses symmetric cryptography.
The AKA is the procedure that take between the user and network to authenticate themselves towards each other and to
provide other security features such as integrity and confidentiality protection.
In a logical order this follows the following procedure:
1. Authentication: Performs authentication by, identifying the user to the network; and identifying the network to
the user.
2. Key agreement: Performs key agreement by, generating the cipher key; and generating the integrity key.
3. Protection: When the AKA procedure is performed it protects, the integrity of messages; confidentiality of
signalling data; and confidentiality of user data
3GPP AAA Server Support
This interface between the SeGW and AAA Server provides a secure connection carrying authentication, authorization,
and related information. in accordance with the following standards:
3GPP TS 33.320 V9.1.0 (2010-03): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services
and System Aspects; Security of Home Node B (HNB) / Home evolved Node B (HeNB) (Release 9)
This reference point is located between 3GPP AAA Server/Proxy and HNB-GW. The functionality of this reference
point is to enable following requirements on SeGW:
The SeGW shall be authenticated by the HNB using a SeGW certificate.
The SeGW shall authenticate the HNB based on HNB certificate.
The SeGW authenticates the hosting party of the HNB in cooperation with the AAA server using EAP-AKA.
The SeGW shall allow the HNB access to the core network only after successful completion of all required
authentications.
Any unauthenticated traffic from the HNB shall be filtered out at the SeGW
X.509 Certificate-based Authentication Support
HNB-GW supports X.509 Certificate-based authentication to HNB/UE for a public key infrastructure (PKI) for single
sign-on (SSO) and Privilege Management Infrastructure (PMI). X.509 specifies the standard formats for public key
certificates, certificate revocation lists, attribute certificates, and a certification path validation algorithm.
Open Access Mode Support
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) marking over IuH interface support in 3G UMTS HNB Access Network is
provided on HNB-GW for traffic quality management in accordance with following standards:
3GPP TS 25.414 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface data transport and transport signalling (Release 9)
Page 30

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
30
OL-25069-03
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B (HNB) Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release
9)
IETF RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
IETF RFC 4594, Configuration Guidelines for DiffServ Service Classes
IETF RFC 4960, Stream Control Transmission Protocol
In a fixed line-mobile convergence scenario, the user data and signaling traffic from a UE is forwarded by an HNB to
HNB-GW over IuH interface. IP is used as network layer for IuH. RTP/ RTCP or GTP over UDP/IP form transport for
user data. SCTP/IP is used for control signaling over IuH.
These data and control packets traverse public Internet before reaching HNB-GW and vice-a-versa for the downlink
traffic. RTP typically carries jitter-sensitive real-time media data such as voice and video. RTCP carries media
reception/ transmit feedback that is not delay sensitive. GTP carries generic, non-media data. These various traffic
types, each, deserve different QoS handling by the IP nodes they traverse between HNB and HNB-GW. Thus DSCP
codes are assigned in the IP headers of the traffic such that intermediate IP nodes can provide differentiated QoS
treatment to the traffic for an acceptable end-user experience.
HNB-GW supports DSCP marking of the traffic on IuH for downlink traffic towards HNB and for uplink traffic
towards MSC when IP transport is used for IuCS or IuPS.
QoS Management with DSCP Marking
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) marking over IuH interface support in 3G UMTS HNB Access Network is
provided on HNB-GW for traffic quality management in accordance with following standards:
3GPP TS 25.414 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface data transport and transport signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B (HNB) Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release
9)
IETF RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
IETF RFC 4594, Configuration Guidelines for DiffServ Service Classes
IETF RFC 4960, Stream Control Transmission Protocol
In a fixed line-mobile convergence scenario, the user data and signaling traffic from a UE is forwarded by an HNB to
HNB-GW over IuH interface. IP is used as network layer for IuH. RTP/ RTCP or GTP over UDP/IP form transport for
user data. SCTP/IP is used for control signaling over IuH.
These data and control packets traverse public Internet before reaching HNB-GW and vice-a-versa for the downlink
traffic. RTP typically carries jitter-sensitive real-time media data such as voice and video. RTCP carries media
reception/ transmit feedback that is not delay sensitive. GTP carries generic, non-media data. These various traffic
types, each, deserve different QoS handling by the IP nodes they traverse between HNB and HNB-GW. Thus DSCP
codes are assigned in the IP headers of the traffic such that intermediate IP nodes can provide differentiated QoS
treatment to the traffic for an acceptable end-user experience.
Page 31

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
31
HNB-GW supports DSCP marking of the traffic on IuH for downlink traffic towards HNB and for uplink traffic
towards MSC when IP transport is used for IuCS or IuPS.
RADIUS Support
In HNB-GW the RADIUS support provides a mechanism for performing authorization and authentication for subscriber
sessions based on the following standards:
RFC-2618, RADIUS Authentication Client MIB, June 1999
RFC-2620, RADIUS Accounting Client MIB, June 1999
RFC-2865, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS), June 2000
RFC-2866, RADIUS Accounting, June 2000
RFC-2867, RADIUS Accounting Modifications for Tunnel Protocol Support, June 2000
RFC-2868, RADIUS Attributes for Tunnel Protocol Support, June 2000
RFC-2869, RADIUS Extensions, June 2000
Within context configured on the system, there are AAA and RADIUS protocol-specific parameters that can be
configured. The RADIUS protocol-specific parameters are further differentiated between RADIUS Authentication
server RADIUS Accounting server interaction.
Among the RADIUS parameters that can be configured are:
Priority: Dictates the order in which the servers are used allowing for multiple servers to be configured in a
single context.
Routing Algorithm: Dictate the method for selecting among configured servers. The specified algorithm
dictates how the system distributes AAA messages across the configured AAA servers for new sessions. Once
a session is established and an AAA server has been selected, all subsequent AAA messages for the session
will be delivered to the same server.
In the event that a single server becomes unreachable, the system attempts to communicate with the other servers that
are configured. The system also provides configurable parameters that specify how it should behave should all of the
RADIUS AAA servers become unreachable.
Important: In 12.3 and earlier releases, refer to the AAA and GTPP Interface Administration and Reference for
more information on RADIUS AAA configuration.
UE Management Function for Pre-Rel-8 UEs
Support for Pre-Rel-8 UE registration and de-registration in 3G UMTS HNB Access Network in accordance with the
following standards:
3GPP TS 25.467 V8.0.0. (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home NodeB; Stage 2 (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.469 V8.1.0 (2009-03): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release 8)
IETF RFC 4960, Stream Control Transmission Protocol, December 2007
Page 32

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
32
OL-25069-03
The HNB-GW provides UE registration and de-registration procedure for the HNB to convey pre-Rel-8 UE
identification data to the HNB-GW in order to perform access control for the UE in the HNB-GW. The UE Registration
also establishes a UE specific context identifier to be used between HNB and HNB-GW. The procedure triggered when
the UE attempts to access the HNB via an initial NAS message and there is no context in the HNB allocated for that UE.
System Management Features
This section describes following features:
Management System Overview
Bulk Statistics Support
Threshold Crossing Alerts (TCA) Support
ANSI T1.276 Compliance
Management System Overview
The system's management capabilities are designed around the Telecommunications Management Network (TMN)
model for management - focusing on providing superior quality network element (NE) and element management system
(Web Element Manager) functions. The system provides element management applications that can easily be integrated,
using standards-based protocols (CORBA and SNMPv1, v2), into higher-level management systems - giving wireless
operators the ability to integrate the system into their overall network, service, and business management systems. In
addition, all management is performed out-of-band for security and to maintain system performance.
Operation and Maintenance module of chassis offers comprehensive management capabilities to the operators and
enables them to operate the system more efficiently. There are multiple ways to manage the system either locally or
remotely using its out-of-band management interfaces. These include:
Using the command line interface (CLI)
Remote login using Telnet, and Secure Shell (SSH) access to CLI through SPIO card's Ethernet management
interfaces
Local login through the Console port on SPIO card using an RS-232 serial connection
Using the Web Element Manager application
Supports communications through 10 Base-T, 100 Base-TX, 1000 Base-TX, or 1000
Base-SX (optical gigabit Ethernet) Ethernet management interfaces on the SPIO
Client-Server model supports any browser (i.e. Microsoft Internet Explorer v5.0 and above or Netscape v4.7 or
above, and others)
Supports Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) protocol and Simple Network Management
Protocol version 1 (SNMPv1) for fault management
Provides complete Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security (FCAPS) capabilities
Can be easily integrated with higher-level network, service, and business layer applications using the Object
Management Group's (OMG’s) Interface Definition Language (IDL)
The following figure demonstrates these various element management options and how they can be utilized within the
wireless carrier network.
Page 33

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
33
Figure 3. Element Management System
Important: HNB-GW management functionality is enabled for console-based access by default. For
GUI-based management support, refer WEM Installation and Administration Guide.
Important: For more information on command line interface based management, refer Command Line
Interface Reference.
Bulk Statistics Support
The system's support for bulk statistics allows operators to choose to view not only statistics that are of importance to
them, but also to configure the format in which it is presented. This simplifies the post-processing of statistical data
since it can be formatted to be parsed by external, back-end processors.
When used in conjunction with the Web Element Manager, the data can be parsed, archived, and graphed.
Page 34

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
34
OL-25069-03
The system can be configured to collect bulk statistics (performance data) and send them to a collection server (called a
receiver). Bulk statistics are statistics that are collected in a group. The individual statistics are grouped by schema.
Following is a partial list of supported schemas:
System: Provides system-level statistics
Card: Provides card-level statistics
Port: Provides port-level statistics
GTP-U: Provides GPRS Tunneling Protocol - User message statistics
HNB-AAL2: Provides ATM adaptation layer 2 (AAL2) protocol level-statistics
HNB-ALCAP: Provides Access Link Control Application Part (ALCAP) service-level statistics
CS-Network-RANAP: Provides RANAP-level statistics for HNB-CS network
CS-Network-RTP: Provides RTP protocol-level statistics for HNB-CS network
HNB-GW-HNBAP: Provides HNBAP-level statistics for HNB-GW service
HNB-GW-RANAP: Provides RANAP-level statistics for HNB-GW service
HNB-GW-RTP: Provides RTP protocol-level statistics for HNB-GW service
HNB-GW-RUA: Provides RUA protocol-level statistics for HNB-GW service
HNB-GW-SCTP: Provides HNB -SCTP protocol-level statistics
PS-Network--RANAP: Provides RANAP-level statistics for HNB-PS network
SCCP: Provides SCCP service-level statistics at system-level
SS7Link: Provides SS7 link configuration related statistics at system-level
SS7 Routing Domain: Provides SS7 Routing domain configuration related statistics at system level
The system supports the configuration of up to 4 sets (primary/secondary) of receivers. Each set can be configured with
to collect specific sets of statistics from the various schemas. Statistics can be pulled manually from the IMG or sent at
configured intervals. The bulk statistics are stored on the receiver(s) in files.
The format of the bulk statistic data files can be configured by the user. Users can specify the format of the file name,
file headers, and/or footers to include information such as the date, IMG host name, IMG uptime, the IP address of the
system generating the statistics (available for only for headers and footers), and/or the time that the file was generated.
When the Web Element Manager is used as the receiver, it is capable of further processing the statistics data through
XML parsing, archiving, and graphing.
The Bulk Statistics Server component of the Web Element Manager parses collected statistics and stores the information
in the PostgreSQL database. If XML file generation and transfer is required, this element generates the XML output and
can send it to a Northbound NMS or an alternate bulk statistics server for further processing.
Additionally, if archiving of the collected statistics is desired, the Bulk Statistics server writes the files to an alternative
directory on the server. A specific directory can be configured by the administrative user or the default directory can be
used. Regardless, the directory can be on a local file system or on an NFS-mounted file system on the Web Element
Manager server.
Threshold Crossing Alerts (TCA) Support
Thresholding on the system is used to monitor the system for conditions that could potentially cause errors or outage.
Typically, these conditions are temporary (i.e high CPU utilization, or packet collisions on a network) and are quickly
resolved. However, continuous or large numbers of these error conditions within a specific time interval may be
Page 35

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Base Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
35
indicative of larger, more severe issues. The purpose of thresholding is to help identify potentially severe conditions so
that immediate action can be taken to minimize and/or avoid system downtime.
The system supports Threshold Crossing Alerts for certain key resources such as CPU, memory, number of sessions etc.
With this capability, the operator can configure threshold on these resources whereby, should the resource depletion
cross the configured threshold, a SNMP Trap would be sent.
The following thresholding models are supported by the system:
Alert: A value is monitored and an alert condition occurs when the value reaches or exceeds the configured high
threshold within the specified polling interval. The alert is generated then generated and/or sent at the end of
the polling interval.
Alarm: Both high and low threshold are defined for a value. An alarm condition occurs when the value reaches
or exceeds the configured high threshold within the specified polling interval. The alert is generated then
generated and/or sent at the end of the polling interval.
Thresholding reports conditions using one of the following mechanisms:
SNMP traps: SNMP traps have been created that indicate the condition (high threshold crossing and/or clear) of
each of the monitored values.
Generation of specific traps can be enabled or disabled on the chassis. Ensuring that only important faults get
displayed. SNMP traps are supported in both Alert and Alarm modes.
Logs: The system provides a facility called threshold for which active and event logs can be generated. As with
other system facilities, logs are generated Log messages pertaining to the condition of a monitored value are
generated with a severity level of WARNING.
Logs are supported in both the Alert and the Alarm models.
Alarm System: High threshold alarms generated within the specified polling interval are considered
“outstanding” until a the condition no longer exists or a condition clear alarm is generated. “Outstanding”
alarms are reported to the system's alarm subsystem and are viewable through the Alarm Management menu in
the Web Element Manager.
The Alarm System is used only in conjunction with the Alarm model.
Important: For more information on threshold crossing alert configuration, refer Thresholding
Configuration Guide.
ANSI T1.276 Compliance
ANSI T1.276 specifies security measures for Network Elements (NE). In particular it specifies guidelines for password
strength, storage, and maintenance security measures.
ANSI T1.276 specifies several measures for password security. These measures include:
Password strength guidelines
Password storage guidelines for network elements
Password maintenance, e.g. periodic forced password changes
These measures are applicable to the systems and the Web Element Manager since both require password
authentication. A subset of these guidelines where applicable to each platform will be implemented. A known subset of
guidelines, such as certificate authentication, are not applicable to either product. Furthermore, the platforms support a
variety of authentication methods such as RADIUS and SSH which are dependent on external elements. ANSI T1.276
Page 36

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Base Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
36
OL-25069-03
compliance in such cases will be the domain of the external element. ANSI T1.276 guidelines will only be implemented
for locally configured operators.
Page 37

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
37
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature
Software
This section describes the optional enhanced features and functions support with HNB-GW service.
Important: Some of the following features may require the purchase of an additional license to implement the
functionality with the HNB-GW service.
This section describes following features:
Dynamic RADIUS Extensions (Change of Authorization)
IP Security (IPSec)
Session Recovery
Web Element Management System
Dynamic RADIUS Extensions (Change of Authorization)
Dynamic RADIUS extension support provide operators with greater control over subscriber PDP contexts by providing
the ability to dynamically redirect data traffic, and or disconnect the PDP context.
This functionality is based on the RFC 3576, Dynamic Authorization Extensions to Remote Authentication Dial In User
Service (RADIUS), July 2003 standard.
The system supports the configuration and use of the following dynamic RADIUS extensions:
Change of Authorization: The system supports CoA messages from the AAA server to change data filters
associated with a subscriber session. The CoA request message from the AAA server must contain attributes to
identify NAS and the subscriber session and a data filter ID for the data filter to apply to the subscriber session.
Disconnect Message: The DM message is used to disconnect subscriber sessions in the system from a RADIUS
server. The DM request message should contain necessary attributes to identify the subscriber session.
The above extensions can be used to dynamically re-direct subscriber PDP contexts to an alternate address for
performing functions such as provisioning and/or account set up. This functionality is referred to as Session Redirection,
or Hotlining.
Session redirection provides a means to redirect subscriber traffic to an external server by applying ACL rules to the
traffic of an existing or a new subscriber session. The destination address and optionally the destination port of TCP/IP
or UDP/IP packets from the subscriber are rewritten so the packet is forwarded to the designated redirected address.
Return traffic to the subscriber has the source address and port rewritten to the original values. The redirect ACL may be
applied dynamically by means of the Radius Change of Authorization (CoA) extension.
Important: For more information on dynamic RADIUS extensions support, refer CoA, RADIUS, And Session
Redirection (Hotlining) in this guide.
Page 38

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
38
OL-25069-03
IP Security (IPSec)
IP Security provides a mechanism for establishing secure tunnels from mobile subscribers to pre-defined endpoints (i.e.
enterprise or home networks) in accordance with the following standards:
RFC 2401, Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol
RFC 2402, IP Authentication Header (AH)
RFC 2406, IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
RFC 2409, The Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
RFC-3193, Securing L2TP using IPSEC, November 2001
IP Security (IPSec) is a suite of protocols that interact with one another to provide secure private communications across
IP networks. These protocols allow the system to establish and maintain secure tunnels with peer security gateways.
IPSec tunnel supports AAA and DHCP address overlapping. Address overlapping is meant for multiple customers using
the same IP address for AAA/DHCP servers. The AAA and DHCP control messages are sent over IPSec tunnels and
AAA/DHCP packets required to be encrypted are decided as per the ACL configuration done for specific session.
Important: For more information on IPSec configuration, refer HNB-GW Service Configuration section.
Session Recovery
The Session Recovery feature provides seamless failover and reconstruction of subscriber session information in the
event of a hardware or software fault within the system preventing a fully connected user session from being
disconnected.
Session recovery is performed by mirroring key software processes (e.g. session manager and AAA manager) within the
system. These mirrored processes remain in an idle state (in standby-mode), wherein they perform no processing, until
they may be needed in the case of a software failure (e.g. a session manager task aborts). The system spawns new
instances of “standby mode” session and AAA managers for each active Control Processor (CP) being used.
Additionally, other key system-level software tasks, such as VPN manager, are performed on a physically separate
packet processing card to ensure that a double software fault (e.g. session manager and VPN manager fails at same time
on same card) cannot occur. The packet processing card used to host the VPN manager process is in active mode and is
reserved by the operating system for this sole use when session recovery is enabled.
The additional hardware resources required for session recovery include a standby System Processor Card (SPC) and a
standby packet processing card.
There are two modes for Session Recovery.
Task recovery mode: Wherein one or more session manager failures occur and are recovered without the need
to use resources on a standby packet processing card. In this mode, recovery is performed by using the
mirrored “standby-mode” session manager task(s) running on active packet processing cards. The “standbymode” task is renamed, made active, and is then populated using information from other tasks such as AAA
manager.
Full packet processing card recovery mode: Used when a packet processing card hardware failure occurs, or
when a packet processing card migration failure happens. In this mode, the standby packet processing card is
made active and the “standby-mode” session manager and AAA manager tasks on the newly activated packet
processing card perform session recovery.
Page 39

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Features and Functionality - Optional Enhanced Feature Software ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
39
Session/Call state information is saved in the peer AAA manager task because each AAA manager and session manager
task is paired together. These pairs are started on physically different packet processing cards to ensure task recovery.
Important: For more information on this feature, refer Session Recovery chapter in System Administration
Guide.
Web Element Management System
Provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) for performing Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security
(FCAPS) management of the system.
The Web Element Manager is a Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)-based application that
provides complete Fault, Configuration, Accounting, Performance, and Security (FCAPS) management capability for
the system.
For maximum flexibility and scalability, the Web Element Manager application implements a client-server architecture.
This architecture allows remote clients with Java-enabled web browsers to manage one or more systems via the server
component which implements the CORBA interfaces. The server component is fully compatible with the fault -tolerant
Sun® Solaris® operating system.
The following figure demonstrates various interfaces between the Cisco Web Element Manager and other network
components.
Figure 4. Web Element Manager Network Interfaces
Important: For more information on WEM support, refer WEM Installation and Administration Guide.
Page 40

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
40
OL-25069-03
How HNB-GW Works
This section provides information on the function and procedures of the HNB-GW in a wireless network and presents
message flows for different stages of session setup.
The following procedures are supported in this release:
HNB Provisioning and Registration Procedure
UE Registration Procedure
Iu Connection Procedures
Paging and Serving RNS Relocation Procedures
RANAP Reset Procedures
HNB Provisioning and Registration Procedure
This section describes the call flow for HNB provisioning and registration procedure.
The following figure and the text that follows describe the message flow for HNB provisioning and registration with
HNB-GW procedure.
Page 41

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
How HNB-GW Works ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
41
Figure 5. HNB Provisioning and Registration Setup Call Flow
1. HNB initialization is performed to obtain HNB configuration from the HNB Management System (HMS).
Similarly, HNB-GW discovery is performed to obtain the initial serving HNB-GW information.
2. A secure tunnel is established from the HNB to the Security Gateway.
3. Location verification shall be performed by the HMS based on information sent by the HNB (e.g. macro
neighbor cell scans, global navigational satellite system type of information etc.). HMS determines the serving
elements and provides the HNB-GW, HMS and Security Gateway to the HNB. The HMS also provisions
configuration parameters to the HNB only after successful location verification in the HMS.
4. Reliable transport setup (SCTP) completed and the HNB sets up a SCTP transport session to a well-defined port
on the serving HNB-GW. HNB Registration procedure started.
5. The HNB attempts to register with the serving HNB-GW using a HNB-REGISTER-REQUEST message. This
message may contains:
HNB Location Information: The HNB provides location information via use of one or more of the
following mechanisms:
detected macro coverage information (e.g. GERAN and/or UMTS cell information)
geographical co-ordinates (e.g. via use of GPS, etc)
Page 42

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
42
OL-25069-03
Internet connectivity information (e.g. IP address).
HNB Identity: the HNB has a globally unique and permanent identity.
HNB Operating Parameters: Such as the selected LAC, RAC, SAC, etc.
6. The HNB-GW uses the information from the HNB-REGISTER-REQUEST message to perform access control
of the HNB (e.g. whether a particular HNB is allowed to operate in a given location, etc). If the HNB-GW
accepts the registration attempt the PLMN-ID received in the request shall be used to lookup the PLMN to
RNC id mapping table and corresponding RNC-ID shall be returned in the HNB-REGISTER-ACCEPT
message else the HNB-GW may reject the registration request (e.g. due to network congestion, blacklisted
HNB, unauthorized HNB location, etc). In reject case, the HNB-GW shall respond with a HNB-REGISTERREJECT indicating the reject cause.
Important: The HNB shall start broadcasting only after successful registration with the HNB-GW.
UE Registration Procedure
This section describes the UE registration procedures for HNB provides means for the HNB to convey UE identification
data to the HNB-GW in order to perform access control for the UE in the HNB GW. The UE Registration also informs
the HNB-GW of the specific HNB where the UE is located.
The UE registration procedure generally triggers when the UE attempts to access the HNB through an initial NAS
message and there is no context id in the HNB for specific UE.
UE Registration procedure is described for following scenarios:
UE Registration Procedure of Non-CSG UEs or Non-CSG HNBs
UE Registration Procedure of Non-CSG UEs or Non-CSG HNBs
This procedure is applicable for non-CSG UEs or HNBs.
The following figure and the text that follows describe the message flow for UE registration procedure of Non-CSG
UEs or Non-CSG HNBs:
Page 43

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
How HNB-GW Works ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
43
Figure 6. UE Registration Call Flow for Non-CSG UEs or Non-CSG HNBs
1. Upon camping on the HNB, the UE initiates an initial NAS procedure (e.g. LU Procedure) by establishing an
RRC connection with the HNB. UE capabilities are reported to the HNB as part of the RRC Connection
establishment procedure.
Page 44

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
44
OL-25069-03
2. The UE then transmits a RRC Initial Direct Transfer message carrying the initial NAS message (e.g. Location
Updating Request message) with identity (IMSI or TMSI).
3. The HNB checks UE capabilities provided in step 1, if these indicate that CSG is not supported and if the
identity of the UE (provided during RRC Connection Establishment) is unknown at the HNB being accessed,
i.e. no Context id exists for the UE, the HNB initiates UE registration towards HNB-GW (step 6-8).
4. Before starting the UE Registration procedure, HNB optionally triggers the Identification procedure asking for
the UE IMSI, if such identity is not provided during the RRC Connection Establishment. If the HNB has a
context id for the UE, the UE registration procedure is not performed nor the Identification procedure.
5. The HNB may optionally perform access control based on IMSI and provided access control list.
6. The HNB attempts to register the UE on the HNB-GW by transmitting the UE-REGISTER-REQUEST. The
message contains at a minimum:
UE Identity: IMSI of the (U)SIM associated with the UE and the indication about UE capabilities
provided in step 1.
Important: The UE IMSI provided in the UE-REGISTER message is unauthenticated.
7. The HNB-GW checks UE capabilities and if these indicate that CSG is not supported the HNB-GW shall
perform access control for the particular UE attempting to utilize the specific HNB.
8. If the HNB-GW accepts the UE registration attempt it shall allocate a context-id for the UE and respond with a
UE-REGISTER-ACCEPT message, including the context-id, to the HNB. If the HNB-GW chooses to not
accept the incoming UE registration request then the HNB-GW shall respond with a UE-REGISTRATIONREJECT message.
9. The HNB then sends a RUA (RANAP User Adaptation) CONNECT message containing the RANAP Initial UE
message to HNB-GW.
10. The reception of the RUA CONNECT message at the HNB-GW triggers the setup of SCCP connection by the
HNB-GW towards the CN. HNB-GW forwards the Initial UE Message to CN.
11. The CN response with a SCCP Connection Confirm message to HNB-GW.
12. The UE then continue with the NAS procedure (e.g. Location Updating procedure) towards the CN, via HNB
and the HNB-GW.
Iu Connection Procedures
This section describes call flow for Iu connection procedures on HNB-GW.
Following procedure call flows are described for Iu connection procedures between HNB, HNB-GW, and SGSN/MSC
in core network:
Iu Connection Establishment Procedure
Network Initiated Iu Connection Release Procedure
Iu Connection Establishment Procedure
This procedure is applicable for establishment of IuH and IuPS/IuCS connection between HNB to HNB-GW and HNBGW to SGSN/MSC in core network.
The following figure and the text that follows describe the message flow for an Iu connection establishment procedure.
Page 45

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
How HNB-GW Works ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
45
Figure 7. Iu Connection Establishment Call Flow
1. Upon receiving of UE-REGISTER-ACCEPT message from HNB-GW, the HNB then sends a RUA CONNECT
message to HNB-GW containing the RANAP Initial UE message.
2. The reception of the RUA CONNECT message at the HNB-GW triggers the setup of SCCP connection by the
HNB-GW towards the CN (SGSN/MSC). HNB-GW forwards the Initial UE Message.
3. The CN responses with a SCCP Connection Confirm message.
4. The UE then continue with the authentication and security procedures towards the CN, via HNB and the HNB-
GW.
5. The SGSN/MSC performs Direct Transfer procedure with HNB-GW and sends SCCP-DATA-FORM1 REQ to
HNB-GW.
Page 46

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
46
OL-25069-03
6. The HNB-GW uses the information received in Direct Transfer procedure from CN and forwards the same to
HNB through RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER message.
7. On successful acceptance of RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER message the HNB responds to HNB-GW and sends
RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER Response message to HNB-GW.
8. On reception of successful acceptance of RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER message from HNB, the HNB-GW sends
SCCP-DATA-FORM1 (Direct Transfer) Response message to CN (SGSN/MSC). This completes the
establishment of IuH and IuPS/IuCS connection through HNB, HNB-GW, and SGSN/MSC in core network.
Network Initiated Iu Connection Release Procedure
This procedure is applicable for release of IuH and IuPS/IuCS connection between HNB to HNB-GW and HNB-GW to
SGSN/MSC in core network.
The following figure and the text that follows describe the message flow for an Iu connection release procedure initiated
by CN (SGSN/MSC).
Page 47

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
How HNB-GW Works ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
47
Figure 8. Network Initiated Iu Connection Release Call Flow
1. User session is established between UE and CN via HNB and HNB-GW over Iu interface and CN (SGSN/MSC)
starts RANAP Iu Release procedure with HNB-GW and sends SCCP-DATA-FORM1 REQ with RANAP Iu
Release command to HNB-GW.
2. The HNB-GW uses the information received in SCCP-DATA-FORM1 REQ with RANAP Iu Release procedure
from CN and forwards the same to HNB through RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER message with RANAP Iu
Release command.
3. On reception of RANAP Iu Release command in RUA-DIRECT-TRANSFER message the HNB triggers the
RCC Connection Release procedure and responds to HNB-GW with RANAP Iu Release Complete command
in RUA-DISCONNECT Response message.
4. On reception of successful RANAP Iu Release Complete command in RUA-DISCONNECT Response message
from HNB, the HNB-GW sends RANAP Iu Release Complete command in SCCP-DATA-FORM1 Response
message to CN (SGSN/MSC).
Page 48

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
48
OL-25069-03
5. On reception of RANAP Iu Release Complete command in SCCP-DATA-FORM1 Response message from
HNB-GW, CN sends SCCP-RELEASED message to HNB-GW and triggers the associated SCCP connection.
On reception of SCCP-RELEASED message from CN, the HNB-GW sends RUA-DISCONNECT message to
HNB and disconnect the IuH connection with HNB.
6. After successful completion of RUA-DISCONNECT procedure and IuH connection release, HNB-GW sends
SCCP-RELEASE-COMPLETE message to CN and HNB-GW confirms the IuPS/IuCS connection released
between HNB-GW and CN.
Paging and Serving RNS Relocation Procedures
This section describes the call flow for network-initiated paging and SRNS relocation procedures on HNB-GW.
Following procedure call flows are described for Paging and SRNS relocation procedures between HNB, HNB -GW,
and SGSN/MSC in core network:
Paging Procedure
SRNS Relocation Procedure
Paging Procedure
This procedure is applicable for establishment of IuH and IuPS/IuCS connection between HNB to HNB-GW and HNBGW to SGSN/MSC in core network.
The following text describes the call flow for Paging procedure on HNB-GW:
1. HNB-GW receives Paging from SGSN/MSC. HNB-GW finds out if any UE is registered with that IMSI.
2. If a UE is registered then HNB-GW sends the Paging message to the HNB through which the UE is registered.
3. If no registered UE is found then HNB-GW finds out the list of HNBs which have IMSI received in the message
in their respective Whitelist.
4. If one or more HNBs were found, and Paging message contained LAI, then HNB -GW compares the HNB’s
PLMN-ID and LAC values against LAI received in the Paging. The HNB which do not have matching values
is dropped from this list.
5. If one or more HNBs were found, and Paging message contained RAI, then HNB -GW compares the HNB’s
PLMN-ID, LAC and RAC values against RAI received in the Paging. The HNB which do not have matching
values is dropped from this list.
6. If Paging message did not have Paging-area then list of HNBs is same as what was found in step 1 otherwise list
of HNBs is as found in step 2 or step 3.
If this list is empty then Paging message is dropped. Otherwise HNB-GW sends Paging message to these
HNBs.
SRNS Relocation Procedure
This procedure is applicable for intra-CN or inter-CN handover procedure between HNB to HNB-GW and HNB-GW to
SGSN/MSC in core network.
The following text describes the call flow for SRNS relocation procedure on HNB-GW:
1. HNB-GW receives Relocation-Request from SGSN/MSC in case subscriber moves from Macrocell to Femtocell
in a connected mode.
2. If the request does not contain IMSI (i.e. for an emergency call), HNB-GW sends Relocation-Request-Reject
with an appropriate cause.
3. . If the request contains IMSI, HNB-GW finds the list of registered HNBs which have this IMSI in their white-
list. If there is no such HNB found, HNB-GW sends Relocation-Request-Reject with appropriate cause.
Page 49

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
How HNB-GW Works ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
49
4. If there is only one such HNB found which has this IMSI in its white-list, HNB-GW sends Relocation-Request
to this HNB.
5. If there are more than one such HNBs found which have this IMSI in their whitelist, then HNBGW looks for
Home-HNB for this IMSI. If there are more than one Home-HNB found then HNB-GW sends RelocationRequest-Reject with appropriate cause.
6. If there are multiple HNBs registered which have this IMSI in their whitelist but only one Home-HNB found,
HNBGW sends Relocation-Request to this HNB.
RANAP Reset Procedures
This section describes the call flow for various RANAP Reset procedures supported in HNB-GW.
Following procedure call flows are described for RANAP Reset procedures between HNB, HNB-GW, and SGSN/MSC
in core network:
HNB Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
CN Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
HNB-GW Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
HNB Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
This procedure is applicable for HNB-initiated RANAP Reset procedure between HNB, HNB-GW, and SGSN/MSC in
core network.
The following text describes the call flow for HNB-initiated RANAP Reset procedure:
1. HNB sends RANAP-RESET command message to HNB-GW for a session.
2. HNB-GW identifies the all affected Iu connection for particular HNB and sends RESET-ACK message to HNB.
3. HNB-GW sends SCCP_Released (SCCP-RLSD) message to CN to release the SCCP connection for each
affected Iu connection for particular HNB.
4. CN (SGSN/MSC) sends the SCCP_Release_Complete (SCCP-RLC) message to HNB-GW and release the
SCCP connection for requested HNB.
CN Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
This procedure is applicable for HNB-initiated RANAP Reset procedure between HNB, HNB-GW, and SGSN/MSC in
core network.
The following text describes the call flow for HNB-initiated RANAP Reset procedure:
1. CN (SGSN/MSC) sends RANAP-RESET command message to HNB-GW for a session.
2. On receiving RANAP-RESET from CN, the HNB-GW starts Guard timer for configured timeout duration.
3. HNB-GW identifies the all affected Iu connections and sends RUA-DISCONNECT message to HNB.
4. On expiry of Guard timer the HNB-GW sends the RESET-ACK message to CN.
HNB-GW Initiated RANAP Reset Procedure
This procedure is applicable for HNB-GW-initiated RANAP Reset procedure between HNB, HNB-GW, and
SGSN/MSC in core network.
The HNB-GW initiates RESET towards CN node in following scenarios:
Page 50

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ How HNB-GW Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
50
OL-25069-03
The HNB-GW is reloaded or service restarted and SCCP Subsystem Number (SSN) allowed from CN
(SGSN/MSC) node is received.
The received SSN Prohibited or Point-code Address Inaccessible indication comes for a CN node, HNB-GW
start a configurable timer.
If SSN allowed indication comes before timer expires, the timer is stopped.
On timer expiry HNB-GW deletes all SCCP connections towards the CN node.
If SSN Allowed indication comes after timer expiry, HNB-GW sends RANAP-RESET command
message to the CN node.
The RANAP-RESET from HNB-GW is sent only if HNB-GW-initiated RANAP-RESET is configured in HNB-GW
service.
Page 51

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Supported Standards ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
51
Supported Standards
The HNB-GW complies with the following standards for 3G UMTS Femto wireless data services.
3GPP References
IETF References
ITU-T Recommendations
Object Management Group (OMG) Standards
3GPP References
3GPP TS 23.003 V8.9.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Network and Terminals; Numbering, addressing and identification (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.412 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface signalling transport (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.413 V7.9.0 (2008-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface RANAP signalling (Release 7)
3GPP TS 25.414 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface data transport and transport signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.415 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iu interface user plane protocols (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.467 V8.0.0. (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home NodeB; Stage 2 (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.1.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.467 V9.3.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN architecture for 3G Home Node B (HNB); Stage 2 (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.468 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN IuH Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.468 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh Interface RANAP User Adaptation (RUA) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V8.1.0 (2009-03): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release 8)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.0.0 (2009-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release 9)
3GPP TS 25.469 V9.2.0 (2010-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Radio
Access Network; UTRAN Iuh interface Home Node B (HNB) Application Part (HNBAP) signalling (Release
9)
Page 52

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Supported Standards
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
52
OL-25069-03
3GPP TS 29.060 V9.0.0 (2009-09): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Network and Terminals; General Packet Radio Service (GPRS); GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) across the
Gn and Gp interface (Release 9)
3GPP TR 29.814 V7.1.0 (2007-06): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Core
Networks and Terminals Feasibility Study on Bandwidth Savings at Nb Interface with IP transport (Release 7)
3GPP TS 33.320 V9.1.0 (2010-13): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services
and System Aspects; Security of Home Node B (HNB) / Home evolved Node B (HeNB) (Release 9)
3GPP TS 23.236 V8.0.0 (2008-12): 3rd Generation Partnership Project; Technical Specification Group Services
and System Aspects; Intra-domain connection of Radio Access Network(RAN) nodes to multiple Core
Network(CN) nodes (Release 8)
IETF References
RFC-768, User Datagram Protocol (UPD), August 1980
RFC-791, Internet Protocol (IP), September 1982
RFC-793, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), September 1981
RFC-894, A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Ethernet Networks, April 1984
RFC-1089, SNMP over Ethernet, February 1989
RFC-1144, Compressing TCP/IP headers for low-speed serial links, February 1990
RFC-1155, Structure & identification of management information for TCP/IP-based internets, May 1990
RFC-1157, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Version 1, May 1990
RFC-1212, Concise MIB Definitions, March 1991
RFC-1213, Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based Internets: MIB-II, March
1991
RFC-1215, A Convention for Defining Traps for use with the SNMP, March 1991
RFC-1224, Techniques for managing asynchronously generated alerts, May 1991
RFC-1256, ICMP Router Discovery Messages, September 1991
RFC-1305, Network Time Protocol (Version 3) Specification, Implementation and Analysis, March 1992
RFC-1398, Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-Like Interface Types, January 1993
RFC-1418, SNMP over OSI, March 1993
RFC-1570, PPP LCP Extensions, January 1994
RFC-1643, Definitions of Managed Objects for the Ethernet-like Interface Types, July 1994
RFC-1701, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE), October 1994
RFC-1850, OSPF Version 2 Management Information Base, November 1995
RFC-1901, Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2, January 1996
RFC-1902, Structure of Management Information for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMPv2), January 1996
RFC-1903, Textual Conventions for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2),
January 1996
Page 53

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Supported Standards ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
53
RFC-1904, Conformance Statements for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2),
January 1996
RFC-1905, Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2), January
1996
RFC-1906, Transport Mappings for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2), January
1996
RFC-1907, Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMPv2), January 1996
RFC-1908, Coexistence between Version 1 and Version 2 of the Internet-standard Network Management
Framework, January 1996
RFC-1918, Address Allocation for Private Internets, February 1996
RFC-1919, Classical versus Transparent IP Proxies, March 1996
RFC-2002, IP Mobility Support, May 1995
RFC-2003, IP Encapsulation within IP, October 1996
RFC-2004, Minimal Encapsulation within IP, October 1996
RFC-2005, Applicability Statement for IP Mobility Support, October 1996
RFC-2118, Microsoft Point-to-Point Compression (MPPC) Protocol, March 1997
RFC 2131, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
RFC-2136, Dynamic Updates in the Domain Name System (DNS UPDATE)
RFC-2211, Specification of the Controlled-Load Network Element Service
RFC-2246, The Transport Layer Security (TLS) Protocol Version 1.0, January 1999
RFC-2328, OSPF Version 2, April 1998
RFC-2344, Reverse Tunneling for Mobile IP, May 1998
RFC-2394, IP Payload Compression Using DEFLATE, December 1998
RFC 2401, Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol
RFC 2402, IP Authentication Header (AH)
RFC 2406, IP Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
RFC 2409, The Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
RFC-2460, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)
RFC-2461, Neighbor Discovery for IPv6
RFC-2462, IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
RFC-2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
RFC-2486, The Network Access Identifier (NAI), January 1999
RFC-2571, An Architecture for Describing SNMP Management Frameworks, April 1999
RFC-2572, Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), April
1999
RFC-2573, SNMP Applications, April 1999
RFC-2574, User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMPv3), April 1999
Page 54

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
▀ Supported Standards
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
54
OL-25069-03
RFC-4594, Configuration Guidelines for DiffServ Service Classes
RFC-2597, Assured Forwarding PHB Group, June 1999
RFC-2598, Expedited Forwarding PHB, June 1999
RFC-2618, RADIUS Authentication Client MIB, June 1999
RFC-2620, RADIUS Accounting Client MIB, June 1999
RFC-2661, Layer Two Tunneling Protocol “L2TP”, August 1999
RFC-2697, A Single Rate Three Color Marker, September 1999
RFC-2698, A Two Rate Three Color Marker, September 1999
RFC-2784, Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) - March 2000, IETF
RFC-2794, Mobile IP Network Access Identifier Extension for IPv4, March 2000
RFC-2809, Implementation of L2TP Compulsory Tunneling via RADIUS, April 2000
RFC-2845, Secret Key Transaction Authentication for DNS (TSIG), May 2000
RFC-2865, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS), June 2000
RFC-2866, RADIUS Accounting, June 2000
RFC-2867, RADIUS Accounting Modifications for Tunnel Protocol Support, June 2000
RFC-2868, RADIUS Attributes for Tunnel Protocol Support, June 2000
RFC-2869, RADIUS Extensions, June 2000
RFC-4960, Stream Control Transmission Protocol
RFC-3007, Secure Domain Name System (DNS) Dynamic Update, November 2000
RFC-3012, Mobile IPv4 Challenge/Response Extensions, November 2000
RFC-3056, Connection of IPv6 Domains via IPv4 Clouds, February 2001
RFC-3101 OSPF-NSSA Option, January 2003
RFC-3143, Known HTTP Proxy/Caching Problems, June 2001
RFC-3193, Securing L2TP using IPSEC, November 2001
RFC-3314, Recommendations for IPv6 in Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Standards, September
2002
RFC-3316, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) for Some Second and Third Generation Cellular Hosts, April 2003
RFC-3706, A Traffic-Based Method of Detecting Dead Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Peers, February 2004
RFC-3543, Registration Revocation in Mobile IPv4, August 2003
RFC 3588, Diameter Base Protocol, September 2003
RFC 4006, Diameter Credit-Control Application, August 2005
RFC-4306, Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol, December 2005
ITU-T Recommendations
ITU-T Recommendation Q.2630.1 - AAL type2 signalling protocol (Capability Set 1)
ITU-T Recommendation Q.2630.2 - AAL type2 signalling protocol (Capability Set 2)
Page 55

HNB Gateway in Wireless Network
Supported Standards ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
55
ITU-T Recommendation I.361 B-ISDN ATM layer specification
ITU-T Recommendation I.363.2 B-ISDN ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL) Specification: Type 2 AAL
ITU-T Recommendation I.366.1 Segmentation and Reassembly Service Specific Convergence Sublayer for the
AAL type 2
ITU-T Recommendation Q.2150.1 AAL type 2 signaling transport converter on broadband MTP
ITU-T Recommendation E.164 - The international public telecommunication numbering plan
ITU-T Recommendation E.191 - B-ISDN addressing
Object Management Group (OMG) Standards
CORBA 2.6 Specification 01-09-35,Object Management Group
Page 56

Page 57

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
57
Chapter 2
Understanding the Service Operation
The system provides wireless carriers with a flexible solution for providing Security Gateway (SeGW) and HomeNodeB Gateway (HNB-GW) functionality for 3G UMTS networks.
The system functioning as an HNB-GW is capable of supporting the following types of subscriber sessions:
CS Session over IuCS: The subscriber is provided voice, video, and CS data service on circuit switch session
through MSC in CS network.
PS Session over IuPS: The subscriber is provided packet switch connection with different traffic class on PS
session with GSN in PS.
Network-initiated Sessions: Network-initiated session procedures include Paging, RANAP-Reset, Service RNS
Relocation etc. from CN side on HNB-GW for a specific subscriber session and in turn HNB-GW initiates the
required procedures with HNBs and CNs.
Prior to connecting to the command line interface (CLI) and beginning the system's configuration, there are important
things to understand about how the system supports these applications. This chapter provides terminology and
background information that must be considered before attempting to configure the system.
Page 58

Understanding the Service Operation
▀ Terminology
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
58
OL-25069-03
Terminology
This section defines some of the terms used in the chapters that follow.
Contexts
A context is a logical grouping or mapping of configuration parameters that pertain to various physical ports, logical IP
interfaces, and services. A context can be thought of as a virtual private network (VPN).
The system supports the configuration of multiple contexts. Each is configured and operates independently from the
others. Once a context has been created, administrative users can then configure services, logical IP interfaces,
subscribers, etc.for that context. Administrative users would then bind the logical interfaces to physical ports.
Contexts can also be assigned domain aliases, wherein if a subscriber’s domain name matches one of the configured
alias names for that context, then that context is used.
Contexts on the system can be categorized as follows:
Source context: Also referred to as the “ingress” context, this context provides the subscriber’s point-of-entry in
the system. It is also the context in which services are configured. For example, in a 3G UMTS network, the
HNB access radio network containing the Home-NodeBs (HNBs) would communicate with the system via IuH
interfaces configured within the source context as part of the HNB-GW service.
Destination context: Also referred to as the “egress” context, this context is where a subscriber is provided
connectivity to core network (such as access to the MSC, SGSN, GGSN etc.) as configured on HNB-GW
service and related services. For example, the system’s destination context would be configured with the IuCS,
IuPS, Gn, Gi or IP offload interfaces facilitating subscriber data traffic to/from the core network (MSC, SGSN,
GGSN) or other PDN (Mobile Data Service or Internet.
AAA context: This context provides AAA functionality for subscriber bearer contexts and/or administrative user
sessions and contains the policies and logical interfaces for communication between Security Gateway (SeGW)
and a 3GPP AAA Server or 3GPP AAA proxy (OCS/CGF/AAA/HSS) over AAA interface for authentication
and authorization procedures for Femto user.
In the roaming case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy can act as a stateful proxy between SeGW and 3GPP AAA Server.
The AAA server is responsible for transfer of subscription and authentication data for
authenticating/authorizing user access and UE authentication. The SeGW communicates with the AAA on the
PLMN using AAA interface.
Important: To ensure scalability, authentication functionality for subscriber sessions should
not be configured in the local context.
For administrative users, authentication functionality can either be configured in the local context or be
authenticated in the same context as subscribers.
Local context: This is the default context on the system used to provide out-of-band management functionality.
Logical Interfaces
This section describes the logical interface supported on HNB-GW.
Page 59

Understanding the Service Operation
Terminology ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
59
Prior to allowing the flow of user data, the port must be associated with a virtual circuit or tunnel called a logical
interface. A logical interface within the system is defined as the logical assignment of a virtual router instance that
provides higher-layer protocol transport, such as Layer 3 IP addressing. Interfaces are configured as part of the VPN
context and are independent from the physical port that will be used to bridge the virtual interfaces to the network.
Logical interfaces are assigned to IP addresses and are bound to a specific port during the configuration process. Logical
interfaces are also associated with services through bindings. Services are bound to an IP address that is configured for a
particular logical interface. When associated, the interface takes on the characteristics of the functions enabled by the
service. For example, if an interface is bound to an HNB-GW service, it will function as an IuH interface between the
SeGW (HNB-GW) service and the HNB. Services are defined later in this section.
In support of both mobile and network originated subscriber UE contexts, the HNB-GW provides the following network
interface support:
IuH Interface: This interface is the reference point for the control plane protocol between Home NodeB and
HNB-GW. IuH uses SCTP over IPSec IKEv2 tunnel as the transport layer protocol for guaranteed delivery of
signaling messages between HNB-GW and Home NodeB.
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with HNB on the same Femtocell Access Network.
This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining subscriber UE contexts.
One or more IuH interfaces can be configured per system context.
IuCS: This interface is the reference point in UMTS which links the HNB-GW, which acts as an RNC (Radio
Network Controller), with a Mobile Switching Centre (3G MSC) in the 3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network.
This interface provides an IuCS over IP or IuCS over ATM (IP over AAL5 over ATM) interface between the
MSC and the RNC (HNB-GW) in the 3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network. RAN Application Part (RANAP)
is the control protocol that sets up the data plane (GTP-U) between these nodes. SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP) or
QSAAL (MTP3B/QSAAL) handle IuCS (control) for the HNB-GW.
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with 3G MSC on the same Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN). This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining the CS access for Femtocell
UE to circuit switched UMTS core networks
One or more IuCS interfaces can be configured per system context.
IuPS: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and SGSN. This interface provides an IuPS over
IP or IuPS over ATM (IP over AAL5 over ATM) interface between the SGSN and the RNC (HNB-GW) in the
3G UMTS Femtocell Access Network. RAN Application Part (RANAP) is the control protocol that sets up the
data plane (GTP-U) between these nodes. SIGTRAN (M3UA/SCTP) or QSAAL (MTP3B/QSAAL) handle
IuPS-C (control) for the HNB-GW.
This is the interface used by the HNB-GW to communicate with SGSN on the same Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN). This interface serves as path for establishing and maintaining the PS access for Femtocell
UE to packet switched UMTS core networks.
One or more IuPS interfaces can be configured per system context.
Gi: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and IP Offload Gateway. It is used by the HNB-GW
to communicate with Packet Data Networks (PDNs) through IP Offload Gateway in the H-PLMN/V-PLMN.
Examples of PDNs are the Internet or corporate intranets.
One or more Gi interfaces can be configured per system context.
Gn: This interface is the reference point between HNB-GW and GGSN. It is used by the HNB-GW to
communicate with GGSNs on the same GPRS/UMTS Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN).
One or more Gn interfaces can be configured per system context.
RADIUS: This interface is the reference point between a Security Gateway (SeGW) and a 3GPP AAA Server or
3GPP AAA proxy (OCS/CGF/AAA/HSS) over RADIUS protocol for AAA procedures for Femto user.
Page 60

Understanding the Service Operation
▀ Terminology
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
60
OL-25069-03
Bindings
A binding is an association between “elements” within the system. There are two types of bindings: static and dynamic.
Static binding is accomplished through the configuration of the system. Static bindings are used to associate:
In the roaming case, the 3GPP AAA Proxy can act as a stateful proxy between the SeGW and 3GPP AAA
Server.
The AAA server is responsible for transfer of subscription and authentication data for
authenticating/authorizing user access and UE authentication. The SeGW communicates with the AAA on the
PLMN using RADIUS protocol.
One or more RADIUS interfaces can be configured per system context.
TR-069: This interface is an application layer protocol which is used for remote configuration of terminal
devices, such as DSL modems, HNBs and STBs. TR-069 provides an auto configuration mechanism between
the HNB and a remote node in the service provider network termed the Auto Configuration Server. The
standard also uses a combination of security measures including IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange v2) and IPsec
(IP Security) protocols to authenticate the operator and subscriber and then guarantee the privacy of the data
exchanged.
One TR-069 interface can be configured per HNB node.
A specific logical interface (configured within a particular context) to a physical port. Once the interface is
bound to the physical port, traffic can flow through the context just as if it were any physically defined circuit.
Static bindings support any encapsulation method over any interface and port type.
A service to an IP address assigned to a logical interface within the same context. This allows the interface to
take on the characteristics (i.e., support the protocols) required by the service. For example, a GGSN service
bound to a logical interface will cause the logical interface to take on the characteristics of a Gn interface
within a GPRS/UMTS network.
Dynamic binding associates a subscriber to a specific egress context based on the configuration of their profile or
system parameters. This provides a higher degree of deployment flexibility as it allows a wireless carrier to support
multiple services and facilitates seamless connections to multiple networks.
Services and Networks
This section describes the services configured on HNB-GW to support various functionality.
Services are configured within a context and enable certain functionality. The following services can be configured on
the system:
HNB-GW services: HNB-GW services are configured in Context configuration mode to support both mobile-
initiated and network-requested user contexts. The HNB-GW service must be bound to a logical interface
within the same context. Once bound, the interface takes on the characteristics of an IuH interface. Multiple
services can be bound to the same logical interface. Therefore, a single physical port can facilitate multiple IuH
interfaces.
Radio Network PLMN: The Radio Network PLMN is configured in HNB-GW service is required to associate
PLMNs with HNB-GW. The PLMN specific configuration e.g. RNC id and association of CS or PS network
shall be configured under this configuration mode.
Page 61

Understanding the Service Operation
Terminology ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
61
HNB-GW/SeGW
Configuration
Interface
Service or
Configuration (Cfg.)
Context (Ctx.)
Source
Ctx .
HNB-GW
Service
SeGW Cfg.
.
Iuh
AAA
Dest. Ctx.
CS
Cfg.
Iu-CS
PS
Cfg.
Iu-PS
To GGSN
Gn
To SGSN(s)
Iu-Flex
To MSC(s)
Iu-Flex
To SGSN(s)
To MSC(s)
To HNB(s)
To AAA(s)
CS Network: CS Network is a context independent configuration to define circuit switched networks. This
circuit switched network configuration provides parameters for one or more MSCs where CS-domain Iuconnections shall be routed. In a typical deployment HNB-GW is connected to only one MSC.
CS network configured at the system level need to be associated with a Radio Network PLMN configured
within HNB-GW service with desired granularity; PLMN level or location-area in that PLMN.
PS Network: PS Network is a context independent configuration to define packet switched networks. This
packet switched network configuration provides parameters for one or more SGSN where PS-domain Iuconnections shall be routed. In a typical deployment HNB-GW is connected to only one SGSN.
PS network configured at the system level need to be associated with a Radio Network PLMN configured
within HNB-GW service with desired granularity.
GTP-U services: GTP-U services are configured in Context configuration mode in pair of two services; one for
GTP-U tunnel support towards HNB on IuH interface and another for GTP-U tunnel support towards the core
network on IuPS interface to communicate with SGSN respectively.
The system supports multiple GTP-U interface connections over this service. Although this service can be
configured in any independent context, but for IuH interface it must be configured in the same context as HNBGW; i.e. source context.
Following figure illustrates the relationship between services, interfaces, and contexts within the HNB-GW system for
HNB access 3G UMTS networks.
Figure 9. Service, Interface, and Context Relationship Within the System
The source context used to service a subscriber session is the same as the context in which the HNB-GW service is
configured. Each HNB-GW service is bound to an IP address in a source context. The HNBs select which IP ad dress to
use, typically by using DNS. Once a UE has established a bearer context with an HNB-GW, the HNBs continue to use
the same context as the subscriber anchored to that HNB-GW.
Page 62

Understanding the Service Operation
▀ Terminology
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
62
OL-25069-03
The destination contexts used to service a subscriber session to connect with CN.
The system determines the configuration used in destination context based on the parameter contained within the
information received from HNB and also the configuration in HNB-GW service.
The AAA context or AAA configuration in source context uses that context for subscriber authentication.
Page 63

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
63
Chapter 3
HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
This chapter is meant to be used in conjunction with the other chapters that describes the information needed to
configure the system to support HNB-GW functionality for use in HNB access networks.
It is recommended that you identify the options from the previous chapters that are required for your specific
deployment. You can then use the procedures in this chapter to configure those options.
This chapter describes following:
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
RTP Pool Configuration
HNB GW Service Configuration
IuCS over ATM Configuration
Logging Facility Configuration
Configuring Congestion Control
SNMP-MIB Traps for HNB-GW Service
Event IDs for HNB-GW Service
Important: At least one packet card must be made active prior to service configuration. Information and
instructions for configuring the packet cards to be active can be found in the Configuring System Settings chapter of the
System Administration Guide.
Caution: While configuring any base-service or enhanced feature, it is highly recommended to take care of
conflicting or blocked IP addresses and port numbers for binding or assigning. In association with some service steering
or access control features, like Access Control List configuration, use of inappropriate port number may result in
communication loss. Refer respective feature configuration document carefully before assigning any port number or IP
address for communication with internal or external network.
Page 64

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
64
OL-25069-03
Required
Information
Description
Management Interface Configuration
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface will be
recognized by the system.
Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number
where the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example, port
17/1 identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17.
A single physical port can facilitate multiple interfaces.
Gateway IP address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
Security
administrator name
The name or names of the security administrator with full rights to the system.
Security
administrator
password
Open or encrypted passwords can be used.
Remote access
type(s)
The type of remote access that will be used to access the system such as telnetd, sshd, and/or ftpd.
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
This section provides a high-level series of steps and the associated configuration file examples for configuring the
system to perform as an HNB-GW node in a test environment. Information provided in this section includes the
following:
Required Local Context Configuration Information
Required System-Level Configuration Information
Required Source Context Configuration Information
Required Destination Context Configuration Information
Required Local Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the local context on an HNB-GW.
Table 1. Required Information for Local Context Configuration
Page 65

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
65
Required Information
Description
SS7 Routing Domain Configuration
SS7 Routing
Domain id and
variant
An identification for SS7 routing domain and must be an integer between 1 and 12 by which the SS7
routing domain will be identified and configured.
A variant can be configured for the SS7 routing domain. some of them are:
ansi: American National Standards Institute (U.S.A.)
bici: Broadband Intercarrier Interface standard
china: Chinese standard
itu: International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T) Telecommunication Standardization Sector
ntt: Japanese standard
ttc: Japanese standard
Sub Service Field
(SSF)
A network indicator in the subservice field for SS7 message signal units (MSUs).
It can be configured with any of the following indicators:
International
National
Reserved
Spare
Application Server
Process (ASP)
instance
An M3UA Application Server Process (ASP) instance identified from 1 through 4.
This instance need to configure end point address as well.
Peer server id
Specifies a peer server instance to setup a SIGTRAN peer for sending and receiving M3UA traffic. Up to
49 peer servers can be defined.
A peer server id configuration may contain:
Routing context for peer server to use
Self point code in SS7 type address
Operational Mode
Peer Server Process (PSP) instance
Required System-Level Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure at the system-level Global configuration mode
(context independent) to support 3G UMTS Femto support.
Table 2. Required Information for System Configuration
Page 66

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
66
OL-25069-03
Required Information
Description
Peer Server Process
(PSP) instance
Specifies the peer server process instance in peer server id. The instance must be an integer from 1 to 4.
A PSP instance configuration need to define:
PSP mode: client or server
Exchange mode: double ended or single ended
End point address in SS7 address format
Association of ASP instance
Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) Network Instance Configuration
SCCP Network
Instance and variant
An identification for SCCP network instance and must be an integer between 1 and 12 by which the SCCP
network instance will be identified and configured.
A variant can be configured for the SS7 routing domain. some of them are:
ansi: American National Standards Institute (U.S.A.)
china: Chinese standard
itu: International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T) Telecommunication Standardization Sector
ntt: Japanese standard
ttc: Japanese standard
SS7 Routing
Domain id and
variant
An identification for SS7 routing domain and must be an integer between 1 and 12 by which the SS7
routing domain will be identified and associated with this SCCP network instance.
Destination point
code
Specifies the destination point code (DPC) in SS7 address format along with SSN and SCCP version.
Circuit Switched Network Configuration
Circuit Switched
Network instance
An identification string between 1 and 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Circuit Switched
Core Networks instance which needs to be associated with HNB Radio Network PLMN id.
An HNB-CS network instance is required for Femto UMTS access over IuCS/Iu-Flex interface between
HNB-GW service and CS networks elements; i.e. MSC/VLR.
Multiple CS network instances (maximum 8) can be configured on a system.
SCCP Network id
Specifies a predefined Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) network id in at system level in Global
configuration mode to be associated with the CS network instance in order to route the messages towards
MSC/VLR over IuCS interface.
RTP IP Pool name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the RTP pool is
configured and associated with CS network configuration to allocate RTP IP address ot session managers
in HNB-GW service over IuCS towards CS core networks.
Default MSC point
code
Specifies the default MSC point-code with HNB-CS network instance. This MSC point code (SS7 address)
is used when HNB-GW is to be connected to only one MSC with in a CS network or as default MSC for
all HNBs connected through specific HNB-CS network instance.
Packet Switched Network Configuration
Page 67

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
67
Required Information
Description
Packet Switched
Network instance
An identification string between 1 and 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Packet Switched
Core Networks instance which needs to be associated with HNB Radio Network PLMN id.
An HNB-CS network instance is required for Femto UMTS access over IuPS/Iu-Flex interface between
HNB-GW service and PS networks elements; i.e. SGSN.
Multiple PS network instances (maximum 8) can be configured on a system.
SCCP Network id
Specifies a predefined Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP) network id in at system level in Global
configuration mode to be associated with the PS network instance in order to route the messages towards
SGSN over IuPS interface.
GTP-U service
name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the GTP-U service can be
associated with HNB-GW system in PS network instance for GTP-U tunnel towards core network. It is
pre-configured in destination context.
Multiple names are needed if multiple GTP services is used.
Important: One GTP-U service can be associated in PS network instance to provide
GTP-U tunnel over IuPS interface towards PS core network and another GTP-U service needs to
be associated in HNB-GW service instance for GTP-U tunnel over Iuh interface towards HNB.
Default SGSN point
code
Specifies the default SGSN point-code with HNB-CS network instance. This SGSN point code (SS7
address) is used when HNB-GW is to be connected to only one SGSN with in a PS network or as default
SGSN for all HNBs connected through specific HNB-PS network instance.
Required Information
Description
Source context name
An identification string from 1 to 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the Source context is
recognized by the system.Generally it is identified as source context.
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface is
recognized by the system.
Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number
where the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example,
port 17/1 identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17. A single physical port can facilitate multiple
interfaces.
Gateway IP address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
Iuh Interface Configuration (To/from Home-NodeB)
Required Source Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the Source context on an HNB-GW.
Table 3. Required Information for Source Context Configuration
Page 68

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
68
OL-25069-03
Required Information
Description
HNB-GW service
Name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the HNB-GW service can
be identified on the system. It is configured in Context configuration mode.Multiple names are needed if
multiple HNB-GW services will be configured.
HNB-GW Service Configuration
Iuh interface IP
address
IPv4 addresses assigned to the Iuh interface as SCTP bond address.
This address will be used for binding the SCTP (local bind address(es)) to communicate with the HNBs
using GTP-U.The HNB-GW passes this IP address during setting up the SCTP association with the HNB.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Iuh SCTP Port
The physical port to which the Iuh interface will be bound. The local SCTP port used to communicate with
the HNBs over Iuh interface.
RTP IP address
This is the IP address of HNB-GW which is configured as RTP address and sent to HNB to map the RTP
streams with this IP address on HNB-GW. This configuration is required at HNB-GW to communicate
with MSC/VLR over IuCS-over-IP tunnel.
RTP IP Pool name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the RTP pool is
configured and associated with HNB-GW service to allocate RTP IP address to Session Manager instances
over Iuh towards HNB.
Optional Security Gateway Configuration
Security Gateway IP
address
This is the IP Address where the SeGW service is bound and shall be provided to HNB during SeGWDiscovery.
Only one SeGW IP address can be configured.
IPsec Crypto-map Template Configuration
EAP profile
This is the profile to be used to provide authenticator modes for incoming packets on Security Gateway.
Only one EAP profile can be configured.
IP Pool for IPsec
Tunnel
Specifies the IP pool to assign IP address for IPsec traffic to use.
IKEv2 Transform
set
IKEv2 transform set for IKE security association.
IPsec Crypto-map
Template
Specifies the Crypto-map template to be used for IPsec IKEv2 tunneling for the interface configured as an
Iuh.
This crypto-map template is to be associated with HNB-GW service if SeGW is enabled and bind with
HNB-GW service.
Only one IPsec Crypto-map Template can be configured.
AAA Server Group
Context name
Specifies the name of the context in which a AAA server group is configured for association with SeGW
for AAA parameters during subscriber authentication phases.
AAA Server Group
name
Specifies the AAA server group already configured in a context and is to be used for first/second phase of
authentication of subscriber while using SeGW functionality in an HNB-GW service.
RTP Pool Configuration
RTP IP Pool name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the RTP pool can be
identified on the system to allocate RTP IP address to session manager instances over Iuh towards HNB. It
is to be associated with HNB-GW service.
Radio Network PLMN Configuration
Page 69

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
69
Required Information
Description
Public Land Mobile
Network (PLMN)
Identifiers
Mobile Country Code (MCC): The MCC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Mobile Network Code (MNC): The MNC can be configured to any integer value from 0 to 999.
Radio Network
Controller (RNC)
identifier
Specify the RNC id which shall be provided to HNB during HNB-REGISTRATION procedure.
Depending upon the requirement the RNC-ID can be provided at the desired granularity as given below
follows:
LAC id: Location Area identifier
RAC id: Routing Area identifier
Cell id: Cell identifier
GTP-U service name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the GTP-U service can be
associated with HNB-GW system in HNB-GW service for GTP-U tunnel towards HNB access network
(HNB). It is pre-configured in Context configuration mode.
Multiple names are needed if multiple GTP-U services is used.
Important: One GTP-U service can be associated with HNB-GW service instance to
provide GTP-U tunnel over Iuh interface towards HNB access network (HNB) and another
GTP-U service needs to be associated with PS network instance for GTP-U tunnel over IuPS
interface towards PS core network to GSNs.
GTP-U Tunnel Innerves Configuration
GTP-U service name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the GTP-U service can be
associated with HNB-GW system for GTP-U tunnel towards HNB access network (HNB). Various control
parameters can be configured for GTP-U packet transmission.
Multiple names are needed if multiple GTP services is used.
GTP-U Tunnel
interface IP address
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface as GTP-U bond address.
This address will be used for binding the GTP-U service (local bind address(es)) for sending/receiving
GTP-U packets from/to HNB using GTP-U tunnel.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
GTP-U Tunnel
interface Port
The physical port to which the Iuh interface will be bound. The local GTP-U port used to communicate
with the HNB over GTP-U tunnel interface.
Required
Information
Description
Required Destination Context Configuration Information
The following table lists the information that is required to configure the destination context.
Table 4. Required Information for Destination Context Configuration
Page 70

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Information Required to Configure the System as an HNB-GW
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
70
OL-25069-03
Required
Information
Description
Destination
context name
An identification string from 1 to 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the destination context will
be recognized by the system.
Interface name
An identification string between 1 and 79 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the interface is
recognized by the system.
Multiple names are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
IP address and
subnet
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
Physical port
number
The physical port to which the interface will be bound. Ports are identified by the chassis slot number where
the line card resides followed by the number of the physical connector on the card. For example, port 17/1
identifies connector number 1 on the card in slot 17. A single physical port can facilitate multiple interfaces.
Gateway IP
address
Used when configuring static IP routes from the management interface(s) to a specific network.
GTP-U Tunnel Interface Configuration
GTP-U service
name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the GTP-U service can be
associated with HNB-GW system in PS network instance for GTP-U tunnel towards core network. Various
control parameters can be configured for GTP-U packet transmission.
Multiple names are needed if multiple GTP services is used.
GTP-U Tunnel
interface IP
address
IPv4 addresses assigned to the interface as GTP-U bond address.
This address will be used for binding the GTP-U service (local bind address(es)) for sending/receiving GTPU packets from/to PS core network using GTP-U tunnel.
Multiple addresses and subnets are needed if multiple interfaces will be configured.
GTP-U Tunnel
interface Port
The physical port to which the Iuh interface will be bound. The local GTP-U port used to communicate with
the PS core network over GTP-U tunnel interface.
RTP Pool Configuration
RTP IP Pool name
An identification string from 1 to 63 characters (alpha and/or numeric) by which the RTP pool can be
identified on the system to allocate RTP IP address to session amanager instances over IuCS towards CS core
networks. It is to be associated with PS network configuration.
Page 71

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
RTP Pool Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
71
RTP Pool Configuration
This configuration sets the IP pools for assigning IP addresses per session manager. The session manager acts as a
mediator between HNB and MSC, shielding the IP address details of either end-point from the other one. It works on
both way of connection in establishing a RTP session between the HNB and HNB-GW over Iuh and between HNB-GW
and the core network over IuCSoIP. Upon successful authentication, the session manager instances are assigned an RTP
IP address during HNB-GW service bringing up and similarly for CS-network connectivity in case of IuCSoIP.
IP addresses can be dynamically assigned from a single pool/a group of IP pools/a group of IP pool groups. The
addresses/IP pools/ IP pool groups are placed into a queue in each pool or pool group. An address is assigned from the
head of the queue and, when released, returned to the end. This method is known as least recently used (LRU).
When a group of pools have the same priority, an algorithm is used to determine a probability for each pool based on the
number of available addresses, then a pool is chosen based on the probability. This method, over time, allocates
addresses evenly from the group of pools.
Important: Note that setting different priorities on each individual pool can cause addresses in some pools to be
used more frequently.
To configure the RTP IP pool:
Step 1 Create the RTP IP pool for IPv4 addresses in source context for RTP pool allocation over Iuh interface by applying the
example configuration in the IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over IuCS section.
Step 2 Create the RTP IP pool for IPv4 addresses in destination context for RTP pool allocation over IuCS interface by
applying the example configuration in the IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over Iuh section.
Step 3 Verify your RTP IP pool configuration by applying the example configuration in the RTP IP Pool Configuration
Verification section.
Step 4 Save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location using the Exec mode
command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save configuration files, refer to the
System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over IuCS
Use the following example to create the IPv4 address RTP pool for RTP address allocation over IuCS
interface towards CS core network.
configure
context <dest_ctxt_name>
ip pool <cs_ip_pool_name> <ip_address/mask>
end
Notes:
Page 72

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ RTP Pool Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
72
OL-25069-03
<cs_ip_pool_name> is name of the IP pool configured in destination context named <dest_ctxt_name> and
to be associated with CS Network Configuration to allocate RTP end point address towards CS network over
IuCS interface.
IP pool size needs to be determined on the number of subscriber session on HNB-GW. It uses one IP address for
each session manager instance of user.
To ensure proper operation with CS network configuration, RTP IP pools should be configured within a
destination context.
Each address in the pool requires approximately 24 bytes of memory. Therefore, in order to conserve available
memory, the number of pools may need to be limited depending on the number of addresses to be configured
and the number of PSCs/PSC2s installed.
Each PSC card requires a minimum of 10 RTP pools to be configured.
Each PSC2 card requires a minimum of 16 RTP pools to be configured.
Setting different priorities on individual pools can cause addresses in some pools to be used more frequently.
For more information on commands/keywords that configure additional parameters and options, refer ip pool
command section in Context Configuration Mode Commands chapter of Command Line Interface Reference.
IPv4 RTP Pool Creation Over Iuh
Use the following example to create the IPv4 address RTP pool for RTP address allocation over Iuh interface
towards HNB.
configure
context <dest_ctxt_name>
ip pool <ip_pool_name> <ip_address/mask>
end
Notes:
<ip_pool_name> is name of the IP pool configured in destination context named <dest_ctxt_name> and
associated with HNB-GW service to allocate the RTP end point address in HNB-GW service over Iuh
interface.
To ensure proper operation with HNB-GW configuration, RTP IP pools must be configured within the same
context as HNB-GW.
IP pool size needs to be determined on the number of subscriber session on HNB-GW. It uses one IP address for
each session manager instance of user.
Each address in the pool requires approximately 24 bytes of memory. Therefore, in order to conserve available
memory, the number of pools may need to be limited depending on the number of addresses to be configured
and the number of PSCs/PSC2s installed.
Each PSC card requires 10 RTP pools to be configured.
Each PSC2 card requires 16 RTP pools to be configured.
Setting different priorities on individual pools can cause addresses in some pools to be used more frequently.
Page 73

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
RTP Pool Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
73
For more information on commands/keywords that configure additional parameters and options, refer ip pool
command section in Context Configuration Mode Commands chapter of Command Line Interface Reference.
RTP IP Pool Configuration Verification
Step 1 Verify that your IPv4 address pool configured properly by entering the following command in Exec Mode:
show ip pool
The output from this command will look similar to the sample shown below. In this example all IP pools
were configured in the isp1 context.
context : isp1:
+-----Type: (P) - Public (R) - Private
| (S) - Static (E) - Resource
|
|+----State: (G) - Good (D) - Pending Delete (R)-Resizing
||
||++--Priority: 0..10 (Highest (0) .. Lowest (10))
||||
||||+-Busyout: (B) - Busyout configured
|||||
|||||
vvvvv Pool Name Start Address Mask/End Address Used Avail
----- --------- --------------- --------------- ------ ------
PG00 ipsec 12.12.12.0 255.255.255.0 0 254
RG00 pool3 30.30.0.0 255.255.0.0 0 65534
SG00 pool2 20.20.0.0 255.255.0.0 10 65524
PG00 pool1 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 0 65534
SG00 vpnpool 192.168.1.250 192.168.1.254 0 5
Total Pool Count: 5
Page 74

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
74
OL-25069-03
HNB-GW Service Configuration
HNB-GW services are configured within source contexts and allow the system to function as an HNB-GW in the 3G
UMTS wireless data network.
Important: This section provides the minimum instruction set for configuring an HNB-GW service
that allows the system to process bearer contexts with IPsec authentication on SeGW. Commands that
configure additional HNB-GW service properties are provided in the different chapters of Command Line
Interface Reference.
These instructions assume that you have already configured the system level configuration as described in System
Administration Guide.
To configure the system to work as HNB-GW service with SeGW enabled:
Step 1 Optional. Configure threshold parameters by applying the example configuration in the Total HNB-GW Session
Thresholds chapter in Thresholding Configuration Guide.
Step 2 Optional. Configure system to enable logging facilities for HNB-GW service session subscriber and protocols by
applying the example configuration in the Logging Facility Configuration section.
Step 3 Optional. Configure congestion control parameters for HNB-GW service instance on system by applying the example
configuration in the Congestion Control Policy Configuration section.
Step 4 Optional. Enable and configure the SNMP Traps to generate alarms and alerts from system for various events and
thresholds for HNB-GW service instance by applying the example configuration in the Alarm and Alert Trap
Configuration section.
Step 5 Configure system to use source Boxer Internal address (SBIA) in hashing function for ECMP-LAG distribution of RTP
traffic over IuCS interface for by applying the example configuration in the Hashing Algorithm Configuration section.
Step 6 Create an interface in source context for Iuh interface by applying the example configuration in the Iuh Interface
Configuration section.
Step 7 Configure SS7 routing domain by applying the example configuration in the SS7 Routing Domain Configuration
section.
Step 8 Configure Peer Server identity for Circuit Switched (CS) core network in SS7 routing domain by applying the example
configuration in the Peer Server Id Configuration for CS Core Network section.
Step 9 Configure Peer Server identity for Packet Switched (PS) core network in SS7 routing domain by applying the example
configuration in the Peer Server Id Configuration for PS Core Network section.
Step 10 Configure SCCP network id with national variant by applying the example configuration in the SCCP Network Instance
Configuration section.
Step 11 Configure CS network parameters by applying the example configuration in the HNB-CS Network Configuration
section.
Step 12 Configure PS network parameters by applying the example configuration in the HNB-PS Network Configuration
section.
Page 75

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
75
Step 13 Configure GTP-U service parameters by applying the example configuration in the GTP-U Service Configuration
section.
Step 14 Configure RTP pool parameters by applying the example configuration in the RTP Pool Configuration section.
Step 15 Create and configure the HNB-GW service and associate related parameters with HNB-GW by applying the example
configuration in the HNB-GW Service Configuration section.
Step 16 Optional. Configure Security Gateway parameters with Crypto-template and enable SeGW by associating it with HNB-
GW to enabling SeGW by applying the example configuration in the Security Gateway and Crypto Template
Configuration section.
Step 17 Optional. Configure x.509 security certificate for FAP with Crypto-template by applying the example configuration in
the x.509 Certificate Configuration section.
Step 18 Optional. Modify the HNB-CS Network configuration to support multiple MSC selection without Iu-Flex by applying
the example configuration in the Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex Configuration section.
Step 19 Optional. Modify the HNB-GW service configuration to support the Open Access mode support for open HNBs and
paging parameters by applying the example configuration in the Open Access Mode Configuration section.
Step 20 Verify your HNB-GW configuration by following the steps in the HNB-GW Service Configuration Verification section.
Step 21 Save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location using the Exec mode
command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save configuration files, refer to the
System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
Hashing Algorithm Configuration
Use the following example to configure the system to use SBIA for hashing algorithm in ECMP-LAG for even
distribution of RTP packets over IuCS interface:
Caution: This configuration is mandatory for standalone HNB-GW deployment and highly
recommended in other deployment scenarios where HNB-GW is used in combination with other services.
configure
ecmp-lag hash use-sbia-only
end
Notes:
This is a global configuration level command and will apply to all services configured on chassis.
This configuration provides the even distribution of RTP traffic seen over IuCS interface.
If this option is not chosen, system uses IP Source Address, IP Destination Address, IP Protocol and Source
Boxer Internal Address as inputs to the hashing algorithm for ECMP-LAG distribution.
Page 76

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
76
OL-25069-03
Iuh Interface Configuration
Use the following example to configure the Iuh interfaces in source context:
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name> -noconfirm
interface <intf_name>
ip address <ip_address>
end
Notes:
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is to configure.
<intf_name> is name of the interface which is to be used for Iuh reference between HNB-GW and HNB.
SS7 Routing Domain Configuration
Use the following example to configure the SS7 routing domain id for HNB-GW service on system:
configure
ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id> variant <v_type> -noconfirm
ssf {international | national | reserved | spare}
asp instance <asp_instance>
end-point address <end_point_address> context <end_ctxt_name>
end-point bind
end
Notes:
<end_point_address> is IP address of the end point associated with application server process for M3UA
end-point parameters in a specific SS7 routing domain instance.
<end_ctxt_name> is name of the context which is associated with end point IP address for application server
process for M3UA end-point parameters in a specific SS7 routing domain instance.
Peer Server Id Configuration for PS Core Network
Use the following example to configure the Peer Server Id in SS7 routing domain for PS core network on system:
configure
ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id> variant <v_type>
Page 77

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
77
peer-server id <peer_server_id>
name <sgsn_name>
mode {loadshare | standby}
routing-context <routing_ctxt_id>
self-point-code <sgsn_pointcode>
psp instance <psp_instance_id>
psp-mode {client | server}
exchange-mode [double-ended | single-ended]
end-point address <end_point_address>
associate asp instance<asp_instance>
end
Notes:
<ss7rd_id> is SS7 Routing domain identity number already configured for SS7 routing domain instance.
<sgsn_pointcode> is the address of SGSN configured in HNB-PS Network Configuration section and to be
used for SCCP network instance.
Peer Server Id Configuration for CS Core Network
Use the following example to configure the Peer Server Id in SS7 routing domain for CS core network on system:
configure
ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id> variant <v_type>
peer-server id <peer_server_id>
name <msc_name>
mode {loadshare | standby}
routing-context <routing_ctxt_id>
self-point-code <msc_pointcode>
psp instance <psp_instance_id>
psp-mode {client | server}
exchange-mode [double-ended | single-ended]
end-point address <end_point_address>
Page 78

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
78
OL-25069-03
associate asp instance <asp_instance>
end
Notes:
<ss7rd_id> is SS7 Routing domain identity number already configured for SS7 routing domain instance.
<msc_pointcode> is the address of MSC configured in HNB-CS Network Configuration section and to be used
for SCCP network instance.
SCCP Network Instance Configuration
Use the following example to configure the SCCP network instance to be associated with HNB-GW service on system:
configure
sccp-network <sccp_id> variant <v_type> -noconfirm
self-point-code <ss7_pointcode>
associate ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id>
destination dpc <sgsn_pointcode> name <dpc_route_name>
destination dpc <sgsn_pointcode> version <sccp_variant>
destination dpc <sgsn_pointcode> ssn <dest_subsystem_num>
destination dpc <msc_pointcode> name <dpc_route_name>
destination dpc <msc_pointcode> version <sccp_variant>
destination dpc <msc_pointcode> ssn <dest_subsystem_num>
end
Notes:
<sccp_id> is SCCP network identifier to be associated with HNB-GW.
<v_type> is type of variant to be used for SCCP network instance.
<sgsn_pointcode> is the address of SGSN configured in HNB-PS Network Configuration section and to be
used for SCCP network instance.
<msc_pointcode> is the address of MSC configured in HNB-CS Network Configuration section and to be used
for SCCP network instance.
HNB-PS Network Configuration
Use the following example to configure the packet switched network parameters to be associated with HNB-GW service
on system:
configure
Page 79

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
79
ps-network <ps_network_name> -noconfirm
associate sccp-network <sccp_network_id>
associate gtpu-service <gtpu_ps_svc_name> context <dest_ctxt_name>
sgsn point-code <sgsn_point_code>
no sgsn deadtime
map core-network-id cn_id point-code <sgsn_point_code>
end
Notes:
<ps_network_name> is name of the packet switched network to be associated with HNB-GW for IuPS session.
<sgsn_point_code> is address of the SGSN in SS7 point code format to be used for packet switched traffic
through HNB-GW.
<gtpu_svc_name> is name of the GTP-U service configured in <gtpu_ctxt_name> to provide GTP-U tunnel
over IuPS interface for packet switched traffic towards PS-CN.
HNB-CS Network Configuration
Use the following example to configure the circuit switched network parameters to be associated with HNB-GW service
on system:
configure
cs-network <cs_network_name> -noconfirm
associate rtp-pool <cs_ip_pool_name> context <dest_ctxt_name>
associate sccp-network <sccp_network_id>
msc point-code <msc_point_code>
no msc deadtime
map core-network-id cn_id point-code <msc_point_code>
end
Notes:
<cs_network_name> is name of the HNB-CS Network service to be associated with HNB-GW for IuCS
session.
<msc_point_code> is address of the MSC in SS7 point code format to be used for circuit switched call
through HNB-GW.
<cs_ip_pool_name> is name of the IP pool configured in destination context named <dest_ctxt_name> to
allocate RTP end point address in this CS network over IuCS interface.
Page 80

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
80
OL-25069-03
HNB-GW Service Configuration
Use the following example to configure the HNB-GW service on system in source context to provide access to HNBs
towards core networks:
configure
sgsn-global
aggregate-ipc-msg { linkmgr | sessmgr } { flush-frequency frequency | num-msgs
number_msgs }
exit
context <vpn_ctxt_name>
hnbgw-service <hnbgw_svc_name> -noconfirm
sctp bind address <ip_address>
sctp bind port <sctp_port>
ranap reset hnbgw-initiated
ranap reset max-retransmissions <max_retrans>
ranap reset guard-timeout <timeout_dur>
rtp mux
rtcp report interval <dur>
associate rtp-pool <ip_pool_name>
associate gtpu-service <gtpu_iuh_svc_name>
no handin cn-domain cs
ip iuh-qos-dscp protocol { sctp | udp } payload { all | gtpu | rtcp | rtp }
<dscp_marking>
ip iu-qos-dscp protocol { sctp | udp } payload { all | gtpu | rtcp | rtp }
<dscp_marking>
radio-network-plmn mcc <mcc> mnc <mnc_code>
rnc-id <rnc_id>
associate ps-network <ps_network_name>
associate cs-network <cs_network_name>
end
Page 81

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
81
Notes:
aggregate-ipc-msg is an optional command supplied through SGSN Global Configuration mode and used to
reduce the latency of IPC messages in SessMgr or LinkMgr towards CN. For more information, refer
Performance Improvement Commands section in Troubleshooting the Service chapter of this guide.
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is configured.
<hnbgw_svc_name> is name of the HNB-GW service which is to be configured for used for Iuh reference
between HNB-GW and HNB.
<ip_address> is the SCTP IP address on which is HNB will communicate with HNB-GW and has
characteristics of Iuh interface.
<gtpu_iuh_svc_name> is name of the GTP-U service configured in <vpn_ctxt_name> to provide GTP-U
tunnel over Iuh interface towards HNB.
<ip_pool_name> is name of the IP pool configured in source context named <vpn_ctxt_name> to allocate
RTP end point address to session manager instance in HNB-GW service over Iuh interface.
rtcp report interval <dur> command configures the generation of RTCP packet/ report types on a per
HNB-GW service instance basis and sets the specified time interval <dur> in seconds between two
consecutive RTCP reports.
GTP-U Service Configuration
Use the following example to configure the GTP-U service parameters to provide GTP-U tunnel over Iuh and IuPS
interface. Separate instances of this service need to be configured for Iuh and IuPS interfaces.
configure
context <dest_ctxt_name> -noconfirm
gtpu-service <gtpu_ps_svc_name> -noconfirm
bind address {ipv4-address | ipv6-address} <ip_address>
path-failure detection-policy gtp echo
end
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name> -noconfirm
gtpu-service <gtpu_iuh_svc_name> -noconfirm
bind address {ipv4-address | ipv6-address} <ip_address>
path-failure detection-policy gtp echo
end
Notes:
<dest_ctxt_name> is name of the destination context in which GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U
tunnel over IuPS interface towards core network.
Page 82

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
82
OL-25069-03
<gtpu_ps_svc_name> is name of the GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U tunnel over IuPS interface
towards core network.
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is to be configured. The same
context must be used for GTP-U service configuration to provide GTP-U tunnel over Iuh interface towards
HNB.
<gtpu_iuh_svc_name> is name of the GTP-U service configured to provide GTP-U tunnel over Iuh interface
towards HNB.
x.509 Certificate Configuration
Use the following example to configure the x.509 certificates on the system to provide security certification between
FAP and SeGW on HNB-GW.
configure
certificate name <x.509_cert_name> pem { data <pem_data_string> | url <pem_data_url>}
private-key pem { [encrypted] data <PKI_pem_data_string> | url <PKI_pem_data_url>}
ca-certificate name <ca_root_cert_name> pem { data <pem_data_string> | url
<pem_data_url>}
exit
crypto template <segw_crypto_template> ikev2-dynamic
authentication local certificate
authentication remote certificate
keepalive interval <dur> timeout <dur_timeout>
certificate <x.509_cert_name>
ca-certificate list ca-cert-name <ca_root_cert_name>
payload <crypto_payload_name> match childsa [match {ipv4 | ipv6}]
ip-address-alloc dynamic
ipsec transform-setlist <ipsec_trans_set>
end
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name>
subscriber default
ip context-name <vpn_ctxt_name>
ip address pool name <ip_pool_name>
Page 83

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
83
end
Notes:
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is configured.
<x.509_cert_name> is name of the x.509 certificate where PEM data <pem_data_string> and PKI
<PKI_pem_data_string> is configured.
<ca_root_cert_name> is name of the CA root certificate where PEM data <pem_data_string> is
configured for CPE.
Security Gateway and Crypto map Template Configuration
Use the following example to configure the IPsec profile and Crypto map template enabling SeGW on HNB -GW for
IPsec tunneling.
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name>
eap-profile <eap_prof_name>
mode authentication-pass-through
exit
ip pool ipsec <ip_address> <subnetmask>
ipsec transform-set <ipsec_trans_set>
exit
ikev2 transform-set <ikev2_trans_set>
exit
crypto template <crypto_template>
authentication eap-profile <eap_prof_name>
exit
ikev2-ikesa transform-set list <ikev2_trans_set>
payload <crypto_payload_name> match childsa [match {ipv4 | ipv6}]
ip-address-alloc dynamic
ipsec transform-setlist <ipsec_trans_set>
exit
ikev2-ikesa keepalive-user-activity
end
Page 84

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ HNB-GW Service Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
84
OL-25069-03
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name>
hnbgw-service <hnbgw_svc_name>
security-gateway bind address <segw_ip_address> crypto-template <crypto_template>
context <segw_ctxt_name>
end
Notes:
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is configured.
<segw_ctxt_name> is name of the context in which Se-GW service is configured. By default it takes context
where HNB-GW service is configured.
<hnbgw_svc_name> is name of the HNB-GW service which is to be configured for used for Iuh reference
between HNB-GW and HNB.
Multiple MSC Selection without Iu-Flex Configuration
Use the following example to configure the multiple MSC selection over IuCS interface for MSC pooling and sharing.
configure
cs-network <cs_network_name>
associate sccp-network <sccp_network_id>
map lac range <lac_start> to <lac_end> point-code <msc_point_code>
end
Notes:
<cs_network_name> is name of the HNB-CS network which is already configured and associated with HNB-
GW service.
<sccp_network_id> is the identifier used for the SCCP network which is already configured and associated
with HNB-CS Network <cs_network_name>.
LAC value must be an integer between 0 and 65535.
Open Access Mode Configuration
Use the following example to configure the Open Access Mode for open HNBs in an HNB-GW service instance. It also
includes the paging optimization configuration for open HNBs.
configure
context <vpn_ctxt_name>
hnbgw-service <hnbgw_svc_name> -noconfirm
Page 85

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
HNB-GW Service Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
85
hnb-access-mode open max-registered-ue <reg_ue>
paging open-hnb [ hnb-where-ue-registered fallback ] {always | never | only-ifwith-paging-area}
end
Notes:
<vpn_ctxt_name> is name of the source context in which HNB-GW service is configured.
<hnbgw_svc_name> is name of the HNB-GW service in which Open Access mode support is to be configured.
<reg_ue> is number of the UEs allowed to be registered through open HNB in Open Access Mode support. By
default 16 UEs are allowed.
Verifying HNB-GW Configuration
This section shows the configuration parameters configured for HNB-GW service.
Step 1 Verify that your HNB-GW services were created and configured properly by entering the following command in Exec
Mode:
show hnbgw-service hnbgw-service <hnbgw_svc_name>}
The output of this command displays concise listing of HNB-GW service parameter settings as configured on
system.
Step 2 Verify configuration errors of your HNB-GW services by entering the following command in Exec Mode:
show configuration errors section hnbgw-service}
The output of this command displays current configuration errors and warning information for the target
configuration file as specified for HNB-GW service
Page 86

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ IuCS over ATM Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
86
OL-25069-03
IuCS over ATM Configuration
To configure IuCS-over-ATM on HNB-GW service:
Step 1 Configure and activate the SONET card by applying the example configuration in the Configuring the SONET Card
section.
Step 2 Modify the configured SS7 Routing Domain configuration with Linkset Id and ATM parameters by applying the
example configuration in the Configuring Linkset Id and ATM Parameters section.
Step 3 Configure ALCAP service and AAL2 node parameters by applying the example configuration in the Configuring
ALCAP Service and AAL2 Node section.
Step 4 Configure the ATM port and PVC for AAL2 and AAL5 type of PVC by applying the example configuration in the
Configuring the ATM Port section.
Step 5 Modify the configured HNB-CS Network service configuration to associate ALCAP service for IuCS-over-ATM
support by applying the example configuration in the Associating ALCAP Service with HNB-CS Network Service
section.
Step 6 Save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location using the Exec mode
command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save configuration files, refer to the
System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
Configuring the SONET Card
To configure a SONET card for IuCS-over-ATM facility, apply the following example configuration:
configure
card <sonet_card_num>
framing {sonet | SDH}
no shutdown
end
Notes:
For other configuration procedures of ATM card, refer Creating and Configuring ATM Interfaces and Ports
section in System Administration Guide.
For more commands and keyword options, refer Command Line Interface Reference.
Configuring Linkset Id and ATM Parameters
To configure the linkset id and ATM parameters you need to modify existing SS7 Routing domain configuration by
applying the following example:
Page 87

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
IuCS over ATM Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
87
configure
ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id> variant <v_type>
ssf {international | national | reserved | spare}
linkset id <linkset_id>
self-point-code <self_pointcode>
adjacent-point-code <adj_pointcode>
link id <link_id> link-type atm-broadband
priority <link_priority_value>
signaling-link-code <sig_link_code>
exit
exit
route destination-point-code <rd_pointcode> linkset-id <linkset_id>
end
Notes:
<ss7rd_id> is pre-configured SS7 Routing Domain instance for IuCS-over-ATM in HNB-GW service.
Configuring ALCAP Service and AAL2 Node
To configure the ALCAP service with AAL2 node a nd AAL2 path parameters apply the following example:
configure
context <alcap_ctxt_name>
alcap-service <alcap_svc_name> -noconfirm
associate ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id>
self-point-code <alcap_pointcode>
aal2-route endpoint <AESA_route_endpoint> aal2-node <aal2_node_name>
aal2-node <aal2_node_name>
point-code <aal2_pointcode>
aal2-path-id <aal2_path_id> [block]
end
Notes:
Page 88

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ IuCS over ATM Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
88
OL-25069-03
<alcap_ctxt_name> is name of the context in which ALCAP service is configured.
<alcap_svc_name> is name of the ALCAP service which is to be configured for IuCS-over-ATM between
HNB-GW and CS core network.
<ss7rd_id> is a pre-configured SS7 routing domain instance.
<alcap_pointcode> is address of the ALCAP node in SS7 point code notation.
Configuring the ATM Port
To configure ATM port for IuCS-over-ATM facility, apply the following example configuration:
configure
port atm <sonet_card_num>/<port_num>
no shutdown
pvc vpi <vpi_num> vci <aal5_vci_num> type aal5
no shutdown
bind link ss7-routing-domain <ss7rd_id> linkset-id <linkset_id> link-id <link_id>
exit
pvc vpi <vpi_num> vci <aal2_vci_num> type aal2 cps-payload-size <cps_paylod_size>
no shutdown
bind alcap-service <alcap_svc_name> context <alcap_ctxt_name> aal2-node
<aal2_node_name> aal2-path <aal2_path_id>
end
Notes:
<alcap_ctxt_name> is name of the context in which ALCAP service is configured.
<alcap_svc_name> is name of the pre-configured ALCAP service which is bound to ATM port for IuCS-over-
ATM between HNB-GW and CS core network.
<aal2_node_name> is a pre-configured AAL2 node in ALCAP Service Configuration mode.
<aal2_path_id> is a pre-configured identifier for AAL2 path in AAL2 Node Configuration mode.
Associating ALCAP Service with HNB-CS Network Service
To associate a pre-configured ALCAP service with HNB-CS Network Service for IuCS-over-ATM function, apply the
following example configuration:
configure
cs-network <cs_network_name>
Page 89

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
IuCS over ATM Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
89
associate alcap-service <alcap_svc_name> context <alcap_ctxt_name>
end
Notes:
<cs_network_name> is a pre-configured HNB-CS Network service associated with HNB-GW for CS session.
<alcap_svc_name> is name of the ALCAP service configured in destination context named
<alcap_ctxt_name> to provide IuCS over ATM support through this CS network.
Page 90

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Iu-Flex Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
90
OL-25069-03
Iu-Flex Configuration
To configure Iu-Flex support on HNB-GW service:
Step 1 Modify the configured HNB-CS Network configuration with Iu-Flex parameters by applying the example configuration
in the Iu-Flex over IuCS Interface Configuration section.
Step 2 Modify the configured HNB-PS Network configuration with Iu-Flex parameters by applying the example configuration
in the Iu-Flex over IuPS Interface Configuration section.
Step 3 Save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location using the Exec mode
command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save configuration files, refer to the
System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
Iu-Flex over IuCS Interface Configuration
Use the following example to configure the Iu-Flex feature over IuCS interface for MSC pooling and sharing.
configure
cs-network <cs_network_name>
map idnns range <idnns_start> to <idnns_end> point-code <msc_point_code> [ backup
point-code <bkup_msc_point_code>]
map nri range <nri_start> to <nri_end> point-code <msc_point_code>
nri length <nri_value>
null-nri <null_nri_value>
offload-msc point-code <msc_point_code>
end
Notes:
<cs_network_name> is name of the HNB-CS network which is already configured and associated with HNB-
GW service.
<nri_value> must be an integer between 1 and 10. A zero NRI length value disables the Iu-Flex feature on
HNB-GW service.
offload-msc point-code <msc_point_code> command enables the exclusion of specific primary MSC
during NAS Node Selection Function (NNSF) procedure when it needs to be off-loaded while using Iu-Flex
functionality on HNB-GW node.
Important: Offload check is only for the primary point code and NOT for the backup point code. This command
can be used for planned maintenance as well.
Page 91

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Iu-Flex Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
91
Iu-Flex over IuPS Interface Configuration
Use the following example to configure the Iu-Flex feature over IuPS interface for SGSN pooling and sharing.
configure
ps-network <ps_network_name>
map idnns range <idnns_start> to <idnns_end> point-code <sgsn_point_code> [ backup
point-code <bkup_sgsn_point_code>]
map nri range <nri_start> to <nri_end> point-code <sgsn_point_code>
nri length <nri_value>
null-nri <null_nri_value>
offload-sgsn point-code <sgsn_point_code>
end
Notes:
<sgsn_network_name> is name of the HNB-PS network which is already configured and associated with
HNB-GW service.
<nri_value> must be an integer between 1 and 10. A zero NRI length value disables the Iu-Flex feature on
HNB-GW service.
offload-sgsn point-code <sgsn_point_code> command enables the exclusion of specific primary
SGSN during NAS Node Selection Function (NNSF) procedure when it needs to be off-loaded while using IuFlex functionality on HNB-GW node.
Important: Offload check is only for the primary point code and NOT for the backup point code. This command
can be used for planned maintenance as well.
Page 92

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Logging Facility Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
92
OL-25069-03
Logging Facility Configuration
Use the following example to configure the HNB-GW system to enable the logging and debug facilities for HNB-GW
subscriber and related protocols.
Important: This section provides the minimum instruction set for configuring logging facilities for
system monitoring that allows the user to monitor the events and logging. Commands that configure
additional logging facilities are provided in the Exec Mode Command chapter of Command Line Interface
Reference.
configure
logging console
logging display event-verbosity {min | concise | full}
logging filter runtime facility aal2 { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility alcap { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility alcapmgr { critical | error | warning | unusual | info
| trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility diameter { critical | error | warning | unusual | info
| trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility hnb-gw { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility hnbmgr { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility sccp { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility sctp { critical | error | warning | unusual | info |
trace | debug }
logging filter runtime facility threshold { critical | error | warning | unusual | info
| trace | debug }
Important: Refer System Administration Guide for more information on logging facility configuration.
Displaying Logging Facility
This section shows the logging facility event logs for logging facilities enabled on HNB-GW node.
Page 93

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Logging Facility Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
93
Step 1 Verify the logging facilities configured on HNB-GW system node by entering the following command in Exec Mode:
show logging [ active | verbose]
The output of this command provides the display of event logs for configured logging facilities.
Page 94

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Congestion Control Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
94
OL-25069-03
Congestion Control Configuration
To configure Congestion Control functionality:
Step 1 Configure Congestion Control Threshold by applying the example configuration in the Configuring the Congestion
Control Threshold section.
Step 2 Configure Service Congestion Policies by applying the example configuration in the Configuring Service Congestion
Policies section.
Step 3 Optional. Operator can configure the system to reject all new incoming calls to specific or all HNB-GW service
instance in a busy-out or planned maintenance or for troubleshooting by applying the example configuration in the
Configuring New Call Policy section.
Step 4 Save your configuration to flash memory, an external memory device, and/or a network location using the Exec mode
command save configuration. For additional information on how to verify and save configuration files, refer to the
System Administration Guide and the Command Line Interface Reference.
Configuring the Congestion Control Threshold
To configure congestion control threshold, apply the following example configuration:
configure
congestion-control threshold max-sessions-per-service-utilization <percent>
congestion-control threshold tolerance <percent>
end
Notes:
There are several additional threshold parameters. See the Global Configuration Mode chapter of the Command
Line Interface Reference for more information.
The tolerance is the percentage under a configured threshold that dictates the point at which the condition is
cleared.
Repeat this configuration as needed for additional thresholds.
Configuring Service Congestion Policies
To create a congestion control policy, apply the following example configuration:
configure
congestion-control policy hnbgw-service action { drop | none | reject }
end
Notes:
Page 95

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
Congestion Control Configuration ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
95
For HNB-GW service sessions reject is the default action.
Configuring New Call Policy
To create a new call policy in a busy our or planned maintenance or other operator intervened scenario, apply the
following example configuration:
newcall policy hnbgw-service [all | name <hnbgw_svc_name>] reject
Notes:
For HNB-GW service sessions reject is the default action for all new calls coming on a specific or all HNB-
GW service instance.
Page 96

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
96
OL-25069-03
Alarm and Alert Trap Configuration
To enable and configure the SNMP Traps to generate alarms and alerts from system for various events and thresholds in
HNB-GW service, apply the following example configuration:
configure
snmp trap { enable | suppress} [congestion] {ThreshTotalHNBGWHnbSess |
ThreshTotalHNBGWIuSess | ThreshTotalHNBGWUeSess} [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} {ThreshTotalHNBGWHnbSess | ThreshTotalHNBGWIuSess |
ThreshTotalHNBGWUeSess} [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWALCAPNodeReset [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWALCAPPathBlock [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWALCAPPathReset [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWALCAPPathUnBlock [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWMSCRanapReset [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWSGSNRanapReset [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWServiceStart [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWServiceStop [ target <trap_collector>]
snmp trap { enable | suppress} HNBGWServiceStop [ target <trap_collector>]
end
Notes:
There are several additional SNMP Traps which can be configured. Refer Global Configuration Mode chapter of
the Command Line Interface Reference for more information.
For more information on SNMP Traps, refer System SNMP-MIB Reference.
Repeat this configuration as needed for additional traps.
Page 97

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
SNMP-MIB Traps for HNB-GW Service ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
97
Traps
Object Id
starThreshHNBGWHnbSess
starentTraps 484
starThreshClearHNBGWHnbSess
starentTraps 485
starThreshHNBGWUeSess
starentTraps 486
starThreshClearHNBGWUeSess
starentTraps 487
starThreshHNBGWIuSess
starentTraps 488
starThreshClearHNBGWIuSess
starentTraps 489
starHNBGWSGSNRanapReset
starentTraps 1155
starHNBGWMSCRanapReset
starentTraps 1156
starALCAPNodeReset
starentTraps 1157
starALCAPPathReset
starentTraps 1158
starALCAPBlock
starentTraps 1159
starALCAPUnBlock
starentTraps 1160
SNMP-MIB Traps for HNB-GW Service
SNMP traps are used to manage and monitor the service on HNB-GW node.
Supported SNMP traps and its id are indicated in the following table.
Table 5. SNMP Traps and Object Ids
Important: For more information on SNMP trap configuration and supported object ids, refer System SNMP-
MIB Reference.
Page 98

HNB-GW Service Configuration Procedures
▀ Event IDs for HNB-GW Service
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
98
OL-25069-03
Event IDs for HNB-GW Service
Facility
Event ID Range
HNB-GW Facility Events
151000-151999
HNB Manager Facility Events
158000-158199
ALCAP Manager Facility Events
160500-160899
ALCAP Protocol Facility Events
160900-161399
SCTP Protocol Facility Events
87300-87499
AAA Client Facility Events
6000-6999
Alarm Controller Facility Events
65000-65999
Card/Slot/Port (CSP) Facility Events
7000-7999
Command Line Interface Facility Events
30000-30999
Event Log Facility Events
2000-2999
Lawful Intercept Log Facility Events
69000-69999
Mobile IPv6 Facility Events
129000-129999
Network Access Signaling Facility Events
153000-153999
Statistics Facility Events
31000-31999
System Facility Events
1000-1999
System Initiation Task (SIT) Main Facility Events
4000-4999
Threshold Facility Events
61000-61999
Virtual Private Network Facility Events
5000-5999
Identification numbers (IDs) are used to reference events as they occur when logging is enabled on the system. Logs are
collected on a per facility basis.
Each facility possesses its own range of event IDs as indicated in the following table.
Important: Not all event IDs are used on all platforms. It depends on the platform type and the license(s)
running.
For more information on logging facility configuration and event id, refer Configuring and Viewing System Logs chapter
in System Administration Guide.
Table 6. System Event Facilities and ID Ranges
Page 99

Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide ▄
OL-25069-03
99
Chapter 4
Monitoring the Service
This chapter provides information for monitoring service status and performance using the show commands found in
the Command Line Interface (CLI). These command have many related keywords that allow them to provide useful
information on all aspects of the system ranging from current software configuration through call activity and status.
The selection of keywords described in this chapter is intended to provided the most useful and in-depth information for
monitoring the system. For additional information on these and other show command keywords, refer to the Command
Line Interface Reference.
In addition to the CLI, the system supports the sending of Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) traps that
indicate status and alarm conditions. Refer to the SNMP MIB Reference Guide for a detailed listing of these traps.
Page 100

Monitoring the Service
▀ Monitoring System Status and Performance
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series 3G Home NodeB Gateway Administration Guide
100
OL-25069-03
To do this:
Enter this command:
Monitor HNB-GW Service Information
Monitor HNB-GW subscribers by call identifier
monitor subscriber callid call_id
Monitor HNB-GW subscribers by user name identifier
monitor subscriber usernamesubscriber_name
Monitor HNB-GW subscribers by IMSI value
monitor subscriber imsiimsi
Monitor HNB-GW subscribers by IP address of UE
monitor subscriber ipaddripv4_address
Monitoring HNB and UE by Protocol Monitoring
Monitor HNB through Protocol Monitoring
monitor protocol
Use following protocol options for HNB monitoring:
SCTP
HNBAP
RUA
RADIUS-AUTH
RADIUS-COA
Monitor UE through Protocol Monitoring
monitor protocol
Use following protocol options for HNB monitoring:
HNBAP
RUA
RANAP
SCCP
ALCAP
AAL2
GTP-U
RTP
View Subscriber Information
Display Session Resource Status
View session resource status
show resources session
Monitoring System Status and Performance
This section contains commands used to monitor the status of tasks, managers, applications and other software
components in the system. Output descriptions for most of the commands are located in the Counters and Statistics
Reference.
Table 7. System Status and Performance Monitoring Commands
 Loading...
Loading...