Page 1

TITAN 250
Turbomachinery Package Specification
Oil & Gas an d P o w e r G e n e r a t i o n Ap p l i c a t i o n s
Generator Set
Page 2

TURBOMACHINERY PACKAGE
SPECIFICATION
TM
Titan
Solar Turbines Incorporated
P.O. Box 85376
San Diego, CA 92186-5376
250 Generator Set
Caterpillar is a trademark of Caterpillar Inc. Solar, Titan, SoLoNOx, and Turbotronic are trademarks of Solar Turbines
Incorporated. All other trademarks, service marks, or registered trademarks appearing in this specification are the
intellectual property of their respective companies. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Direct customers of Solar Turbines Incorporated that receive this Turbomachinery Package Specification directly from
Solar Turbines Incorporated may make limited copies of parts of this specification for use in the creation of their own
specification documents. However, such customers shall not distribute any part of this Turbomachinery Package
Specification outside their own organizations for any other purpose. Any other use without the permission of Solar
Turbines Incorporated is strictly prohibited.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
Page 3

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table of Contents
1 INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................5
1.1 General Description ..........................................................................................................5
1.2 Overview ...........................................................................................................................5
2 TITAN 250 GAS TURBINE GENERATOR SET .......................................................................6
2.1 General Description ..........................................................................................................6
2.2 Package Description.........................................................................................................6
2.3 Major Components and Systems......................................................................................6
3 TITAN 250 GAS TURBINE......................................................................................................10
3.1 General Description ........................................................................................................10
4 REDUCTION-DRIVE GEARBOX ............................................................................................13
4.1 General Description ........................................................................................................13
5 GENERATOR AND ASSOCIATED EQUIPMENT..................................................................14
5.1 General Description ........................................................................................................14
5.2 Functional Description ....................................................................................................14
6 START SYSTEM .....................................................................................................................17
6.1 General Description ........................................................................................................17
6.2 Functional Description ....................................................................................................17
6.3 Backup Slow Rotation System........................................................................................18
7 FUEL SYSTEM........................................................................................................................21
7.1 General Description ........................................................................................................21
8 LUBRICATION SYSTEM.........................................................................................................24
8.1 General Description ........................................................................................................24
9 TURBOTRONIC 4 CONTROL SYSTEM.................................................................................29
9.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................29
9.2 System Architecture........................................................................................................29
9.3 Component Descriptions.................................................................................................31
9.4 System Monitoring and Control Functions......................................................................32
9.5 TT4000 Display and Monitoring System.........................................................................34
10 GENERATOR CONTROL AND MONITORING......................................................................40
10.1 General Description ........................................................................................................40
10.2 Generator Control ...........................................................................................................41
11 ENCLOSURE...........................................................................................................................45
11.1 General Description ........................................................................................................45
11.2 Standard Features ..........................................................................................................46
11.3 Optional Features ...........................................................................................................46
12 AIR INLET SYSTEM................................................................................................................52
12.1 General Description ........................................................................................................52
13 EXHAUST SYSTEM................................................................................................................55
13.1 General Description ........................................................................................................55
13.2 Turbine Exhaust Heat Recovery System........................................................................55
14 ACCESSORY EQUIPMENT....................................................................................................57
14.1 DC Power Supply and Battery Charger System.............................................................57
14.2 Turbine Cleaning System................................................................................................57
14.3 Package Lifting Kit ..........................................................................................................59
14.4 Engine Removal Equipment ...........................................................................................59
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
2
Page 4

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
15 MARINIZATION.......................................................................................................................61
15.1 General Description ........................................................................................................61
16 QUALITY ASSURANCE AND TESTING................................................................................63
16.1 Quality Assurance...........................................................................................................63
16.2 Testing ............................................................................................................................63
17 PRESERVATION, INSTALLATION, AND DOCUMENTATION.............................................66
17.1 General Description ........................................................................................................66
17.2 Preservation....................................................................................................................66
17.3 Site Requirements ..........................................................................................................66
17.4 Mechanical Installation Requirements............................................................................66
17.5 Documentation................................................................................................................67
18 CERTIFICATION .....................................................................................................................70
18.1 General Description ........................................................................................................70
18.2 National Electrical Code..................................................................................................70
18.3 Canadian Electrical Code ...............................................................................................70
18.4 Conformité Européenne Mark.........................................................................................71
18.5 International Electrotechnical Commission Safety Assessment.....................................72
18.6 Offshore Marine Applications..........................................................................................72
18.7 Summary.........................................................................................................................73
19 SUPPORT SERVICES.............................................................................................................74
19.1 Construction Services .....................................................................................................74
19.2 Customer Services..........................................................................................................74
19.3 Contract Power and Leasing Services............................................................................75
19.4 Solar’s Worldwide Locations...........................................................................................75
CONVERSION CHART..................................................................................................................76
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS...........................................................................................................77
LIST OF SOLAR’S ENGINEERING SPECIFICATIONS...............................................................80
LIST OF SOLAR’S PRODUCT INFORMATION LETTERS..........................................................80
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
3
Page 5

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table of Figures
Figure 1. Typical Titan 250 Gas Turbine Generator Set.............................................................6
Figure 2. Typical Titan 250 Generator Set Service Connections (Driver Skid) ..........................8
Figure 3. Titan 250 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine Cutaway ..............................................................10
Figure 4. Typical Combustion Process .....................................................................................11
Figure 5. Typical Reduction Gearbox for the Titan 250 Generator Set....................................13
Figure 6. Typical Open Drip-Proof Generator with Permanent Magnet Exciter System ..........14
Figure 7. Direct-Drive AC Starter Motor and VFD Cabinet.......................................................17
Figure 8. Typical Direct-Drive AC Start System........................................................................18
Figure 9. Turning Gear Assembly.............................................................................................18
Figure 10. Typical Fuel System Schematic ................................................................................21
Figure 11. Typical Lube Oil System............................................................................................26
Figure 12. Typical Onskid Control System..................................................................................30
Figure 13. Typical Offskid Control System..................................................................................30
Figure 14. Turbotronic 4 System Architecture ............................................................................31
Figure 15. Typical TT4000 Operation Summary Display Screen ...............................................35
Figure 16. Typical TT4000 Strip Chart Display...........................................................................35
Figure 17. Typical TT4000S Engine Summary Screen ..............................................................36
Figure 18. Typical TT4000S Generator Summary Screen .........................................................36
Figure 19. Typical Generator, Exciter, and Generator Control Module Arrangement ................41
Figure 20. Typical Generator Metering Panel.............................................................................44
Figure 21. Typical Complete Package Enclosure.......................................................................45
Figure 22. Typical Fire and Gas System.....................................................................................48
Figure 23. Typical CO2 Fire Suppression Cylinders and Cabinets .............................................49
Figure 24. Typical Water Mist Fire Suppression Cylinders and Cabinet ....................................49
Figure 25. Typical Titan 250 Turbine Air Inlet and Exhaust Systems.........................................52
Figure 26. Typical Battery Charger.............................................................................................57
Figure 27. Turbine Cleaning System ..........................................................................................58
Figure 28. Turbine Cleaning Cart................................................................................................58
Figure 29. Separation of Engine Sections ..................................................................................59
Figure 30. Rails and Fixtures for Axial Separation of Engine Sections ......................................59
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
4
Page 6

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
1 Introduction
1.1 General Description
Solar Turbines Incorporated is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture, and
installation of industrial gas turbines. Solar's 40 years of experience integrating high
technology with fluid compression, liquid pumping, power generation, and cogeneration
applications has resulted in more than 12,500 gas turbine installations in 92 countries
around the world. Solar gas turbine packages have logged more than 1.3 billion operating
hours around the world in a wide range of applications. Solar gas turbine packages are
complete operational systems that require a minimum of site preparation prior to
installation.
The Titan 250 generator sets represent years of intensive engineering and manufacturing
design. Solar gas turbines are manufactured to rigid industrial standards and are
thoroughly tested in modern facilities. Solar's operations are certified by Det Norske
Veritas (DNV) to conform to International Standardization Organization (ISO) 9001:2000
Standard for Quality Management Systems.
1.2 Overview
This document describes product features and provides product specification information
for the Titan 250 generator sets. Included are basic package configurations, ancillary
descriptions, installation requirements, and a list of customer support services available
at the time of publication. Please note that changes in equipment, service descriptions,
and specifications may occur without prior notice.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
5
Page 7
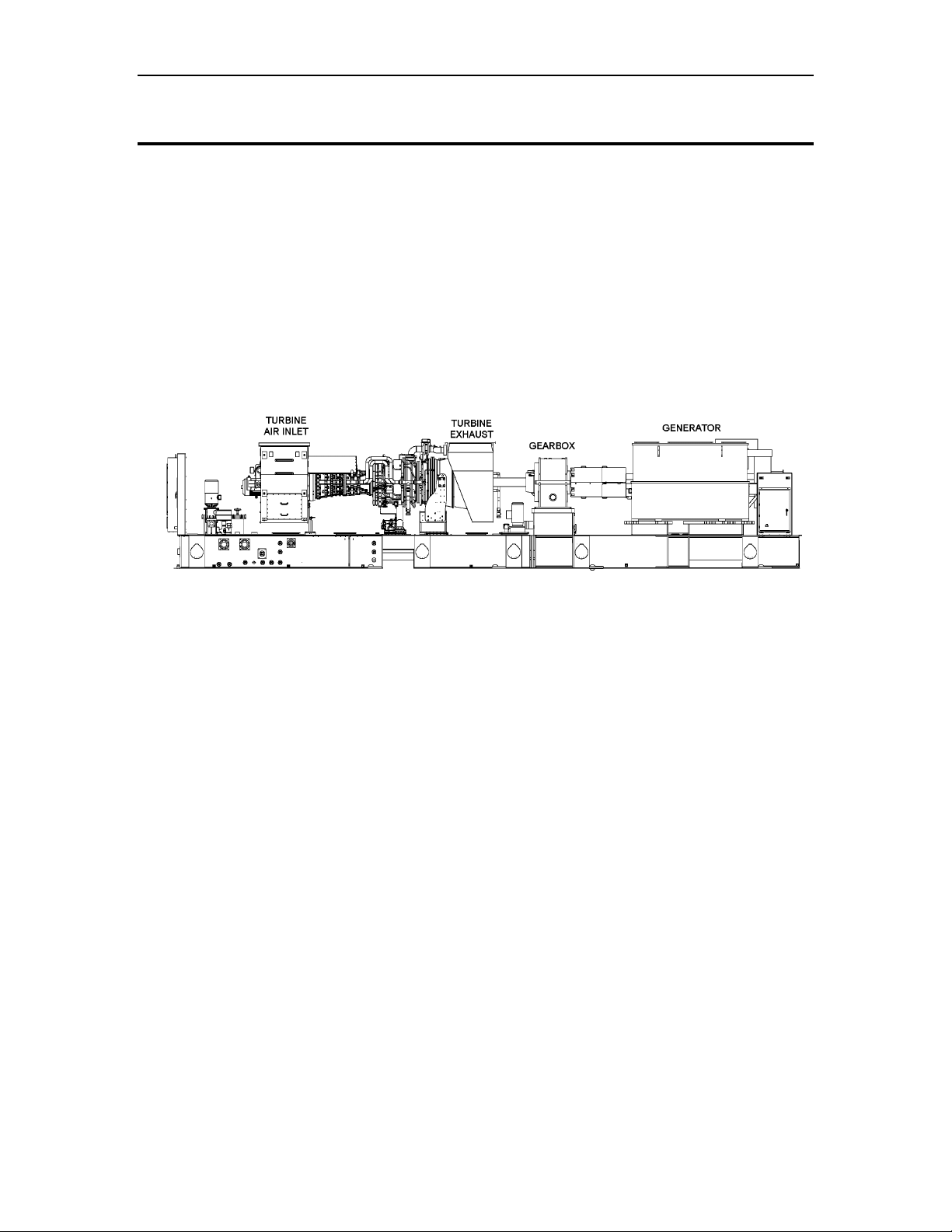
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
2 Titan 250 Gas Turbine Generator Set
2.1 General Description
The Titan 250 gas turbine generator set (Figure 1) is a completely integrated and fully
operational package equipped with all accessories and auxiliary systems required for
operation. In addition to the standard package features, a wide array of optional
equipment is available to meet the customer’s installation and operation requirements.
Designed specifically for industrial service, Solar’s gas turbine generator sets are
compact, lightweight, and require minimal floor space for installation. Proven packaging
designs greatly reduce installation costs, time, materials, and labor.
The package features a radial exhaust resulting in a short overall package length that
conserves valuable mounting space.
Figure 1. Typical Titan 250 Gas Turbine Generator Set
2.2 Package Description
The gas turbine generator set consists of an axial-flow gas turbine engine, generator, and
reduction-drive gearbox. These components are installed in-line on a two-piece heavysteel base frame referred to as the skid. The skid is a structural steel assembly with
beam sections and cross members welded together. The two sections of the skid can be
separated to facilitate handling and shipment but when bolted together they form a rigid
structure suitable for three-point mounting. Drip pans are included to collect any potential
liquid leakage. Package connection points for fuel, lube oil, air, and water are located on
the outer edge of the skid.
Electrical connections are made in onskid junction boxes. Machined mounting surfaces
on the skid facilitate component alignment. The gearbox is bolted directly to the engine
and coupled by means of a splined interconnecting drive shaft that eliminates the need
for field alignment. The gearbox and generator are connected by means of a flexible
dry-disk, shear-type coupling enclosed in a coupling guard. Jacking points are provided
to facilitate alignment of the generator to the gearbox.
2.3 Major Components and Systems
Major components and systems of the gas turbine generator set typically include:
• Gas turbine
• Reduction-drive gearbox
• Generator
• Start system
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
6
Page 8

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
• Fuel system
• Lubricating oil system
• Turbotronic™ 4 Control System
• Onskid electrical wiring
• Skid with drip pans
• Piping and manifolds
• Ancillary air inlet system
• Ancillary exhaust system
• Package enclosure (if specified) with:
− Ventilation system
− Fire detection and suppression system
− Combustible gas detection system
2.3.1 Package Electrical System
The onskid package electrical system can be furnished to meet the following certification
requirements:
• National Electrical Code (NEC)
• Canadian Electrical Code (CEC)
• Conformité Européenne (CE) Mark
• European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC)
When supplied, the offskid control console, variable frequency drives, batteries, and
battery charger are not approved for hazardous duty areas and must be installed in a
nonhazardous area.
Three-Phase Motor Voltage
All three-phase motors and three-phase electrical components have the same voltage
rating. Motor starters and contactors are not provided.
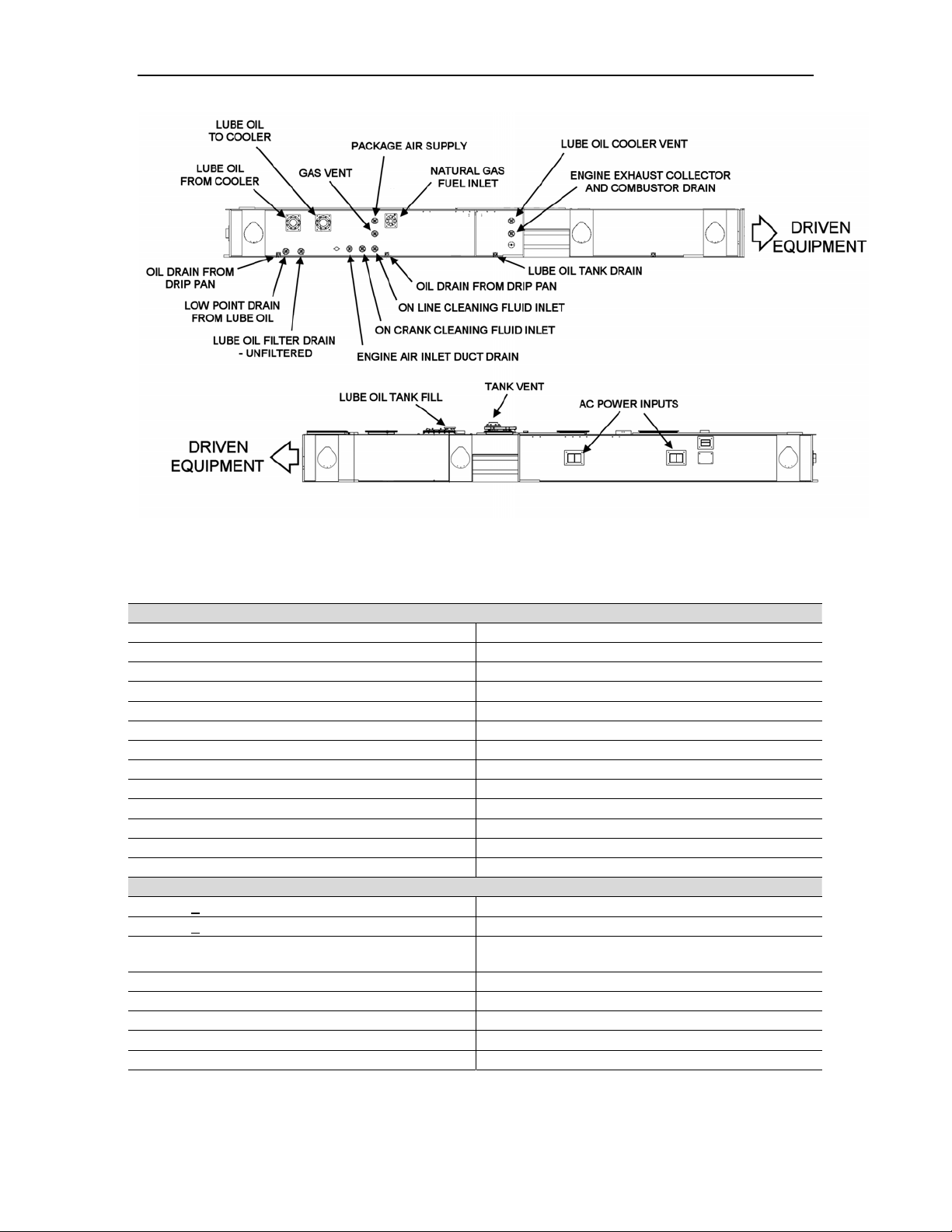
2.3.2 Service Connections
The Titan 250 generator set is supplied with self-contained systems for starting, fuel, lube
oil, and control. All service connections (Figure 2) are conveniently located on the outer
edges of the skid.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
7
Page 9
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 2. Typical Titan 250 Generator Set Service Connections (Driver Skid)
Table 1. Package Specifications
Dimensions
Approximate Package Measurements
Height, Unenclosed 3.89 m (12 ft 9 in.)
Height, Enclosed 4.12 m (13 ft. 6 in.)
Width (to skid edges) 3.37 m (11 ft 1 in.)
Width (including lifting bollards) 3.60 m (11 ft 10 in.)
Length, Engine Skid 10.29 m (33 ft 9 in.)
Length, Generator Skid
Approximate Package Weights
AC Start Motor Assembly 450 kg (990 lb)
Gas Turbine Assembly 19 050 kg (42,000 lb)
Total Driver (unenclosed package, without oil) 49 900 kg (110,000 lb)
Total Driver (enclosed package, without oil) 57 600 kg (127,000 lb)
Generator (unenclosed)
Piping and Tubing Thickness
Piping > 76.2 mm (3 in.) Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) Schedule 40 (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Piping < 50.8 mm (2 in.) NPS Schedule 80 (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Tubing 3.175 mm (0.125 in.) Nominal Tubing Size
(NTS)
Tubing 6.35 mm (0.25 in.) NTS 1.245 mm (0.049 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
Tubing 12.7 mm (0.50 in.) NTS 1.651 mm (0.065 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
Tubing 19.05 mm (0.75 in.) NTS 1.651 mm (0.065 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
Tubing 25.40 mm (1.00 in.) NTS 2.108 mm (0.083 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
Tubing 31.75 mm (1.25 in.) NTS 2.768 mm (0.109 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
0.889 mm (0.035 in.) Minimum Wall Thickness
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
8
Page 10
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Construction Materials
Piping, Manifolds, and Tubing < 10.2 cm (4 in.)
Note (a)
Piping, Manifolds, and Tubing > 10.2 cm (4 in.)
Note (a)
Piping Interface Connections 316L Stainless Steel (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Flange Assembly Hardware 316L Stainless Steel
Pipe Support Brackets
Pipe Flexible Couplings
Tubing Dual Ferrule Compression Fittings 316L Stainless Steel
Sliding Lube Oil Drain Couplings and Plates
Lube Oil Vent Flame Arrestor Aluminum
Electrical System Certifications
NEC Class 1, Group D, Division 1 or 2
CENELEC Zone 1 or 2, Group II
CE, ATEX Zone 2, Group II
Three-Phase Package Motors
Optional Motor Voltage Ratings
Single-Phase Battery Charger
Optional Battery Charger Voltage Ratings
Single-Phase Lighting and Space Heater Voltage
Optional Package Lighting and Space Heater
Voltage Ratings
316L Stainless Steel (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Carbon Steel (Unless Otherwise Specified)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
380, 400, or 415 VAC, 50 Hz
460 VAC 60 Hz
220, 230, 240, 380, 400, 415, 440, 460, or 480
VAC, 50 Hz or 60 Hz
120, 220, 230, or 240 VAC, 50 Hz or 60 Hz
Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
Onskid Junction Boxes IP56 to IP66
Control Console IP50
Battery Charger, NEC IP22
Battery Charger, CE IP31
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 9-56 Fusion Welding
ES 9-58 Standard Paint Program – Turbomachinery
ES 1593
ES 1762
ES 2201 Auxiliary Air
ES 2231
Solar’s Applicable Product Information Letters
PIL 127 Product Certification
Notes:
(a) All package piping is fabricated from 316L stainless steel with the exception of lube oil vent
lines and any piping welded directly to a carbon steel lube oil tank or tank cover.
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar’s Product Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1
and Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems for Gas Turbine Packages Installed In
Hazardous Areas (CENELEC/IEC Standards – European ATEX Directive 94/9/EC)
Standards and Practices for The Design and Installation of Cable Channels and TC
Rated Cables Installed In Class 1, Division 2 Hazardous Areas
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
9
Page 11
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
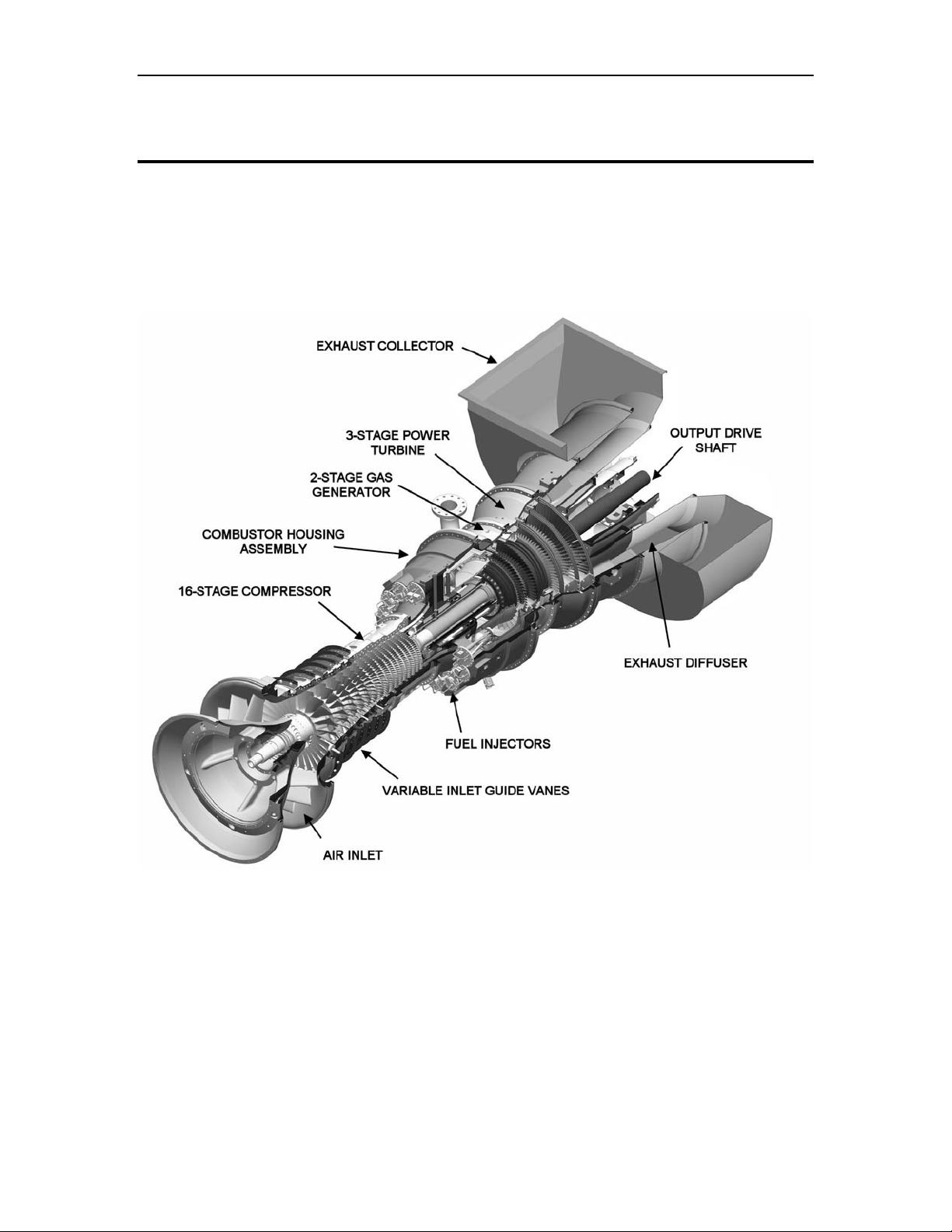
3 Titan 250 Gas Turbine
3.1 General Description
The two-shaft Titan 250 gas turbine (Figure 3) is a completely integrated and selfcontained prime mover. The Titan 250 gas turbine combines high performance operation
with rugged industrial construction. This design philosophy allows for high efficiency, low
maintenance, and a long service life. The Titan 250 gas turbine is designed for a high
degree of compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) requirements.
Figure 3. Titan 250 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine Cutaway
3.1.1 Principles of Operation
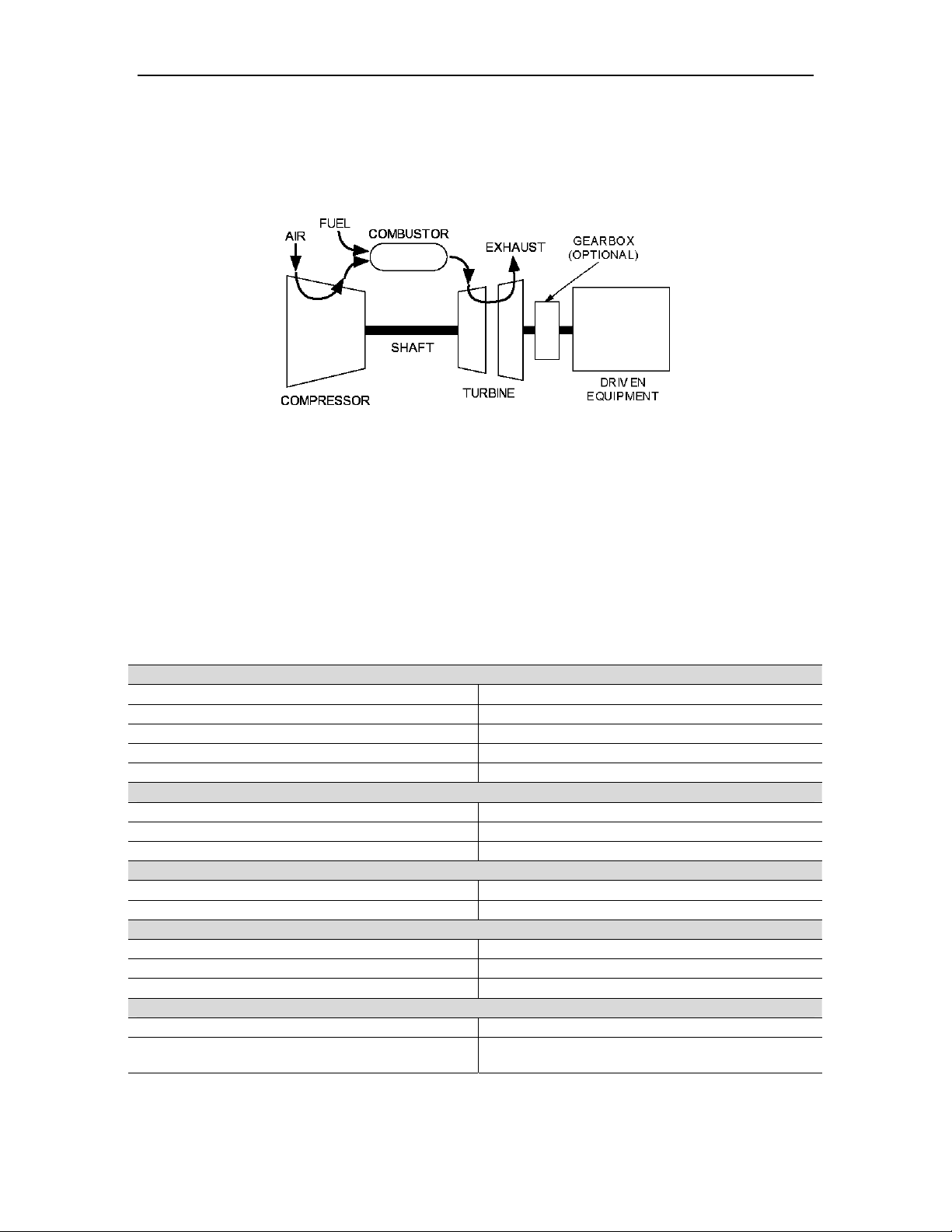
During the typical combustion process (Figure 4), air is drawn into the gas turbine air inlet
and is compressed by the multi-stage, axial-flow engine compressor. The compressed air
is directed into the annular combustion chamber at a steady flow. Fuel is injected and
mixed with the compressed air and ignited during the start cycle. Continuous combustion
will be maintained as long as there is an adequate flow of pressurized air and fuel. Hotpressurized gas from the combustor expands through and drives the turbine, dropping in
pressure and temperature as it exits the turbine. This combustion cycle converts the
energy in the fuel into kinetic rotating power at the turbine output shaft.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
10
Page 12
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
For combustion, the gas turbine requires approximately one-fourth of the total air it
compresses. The excess air is mixed with the combustion products to reduce the gas
temperature at the turbine first stage-inlet. The cooling air also keeps metal temperatures
in the combustor and turbine assembly relatively low to ensure a long service life.
Figure 4. Typical Combustion Process
3.1.2 SoLoNOx Combustion System
The Titan 250 incorporates Solar’s proprietary SoLoNOx dry emissions system that
reduces pollution by limiting the formation of nitrous oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide
(CO), and unburned hydrocarbons (UHC). This system uses lean premix combustion to
lower the maximum flame temperature and reduce pollution formation. Solar’s
engineering staff will work with the customer to meet local permitting emission
requirements.
Table 1. Titan 250 Gas Turbine Specifications
Compressor
Type Axial Flow
Number of Stages 16
Compression Ratio 24:1
Flow (Nominal) 67.3 kg/sec (148 lb/sec)
Speed, Maximum 10,500 rpm
Combustion Chamber
Type Annular
Ignition Torch
Number of Fuel Injectors 14 (SoLoNOx, Low Emissions)
Gas Generator
Type Axial
Number of Stages 3
Power Turbine
Type Axial
Number of Stages 2
Speed 7000 rpm
Bearings
Radial 5 Tilt Pad with Proximity Probes
Thrust
2 Tilt Pad with Resistance Temperature Device
Probes
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
11
Page 13
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Construction Materials
Compressor Case
- Forward Section Nodular Iron
- Aft Section WC6 Alloy Steel
Combustor Case 410 Stainless Steel
Exhaust Diffuser Nodular Iron
Accessory Gear Housing Ductile Iron
Protective Coatings
Compressor Rotor and Stator Blades Inorganic Aluminum
Nozzles, First and Second Stage Precious Metal Diffusion Aluminide
Blades, First and Second Stage Precious Metal Diffusion Aluminide
Approximate Weight
Gas Turbine Assembly 19 050 kg (42,000 lb)
Performance
Output Power Note (a)
22 370 kW (30,000 hp)
Heat Rate 9000 kJ/ kW-hr (6360 Btu/ kW-hr)
Exhaust Flow 245 660 kg/hr (541,590 lb/hr)
Exhaust Temperature 465°C (865°F)
Temperature Monitoring
Turbine T5 (12) Thermocouples
Vibration Monitoring
Turbine Bearing #1 Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Turbine Bearing #2 Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Turbine Bearing #3 Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Turbine Bearing #4 Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Turbine Bearing #5 Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Gas Producer Rotor Shaft Displacement Probe, Axial Position
Power Turbine Rotor Shaft Displacement Probe, Axial Position
Gas Producer Rotor Shaft Keyphasor
Power Turbine Rotor Shaft Keyphasor
Accessory Gearbox Velocity Pickup
Notes:
(b) Performance is calculated under the following conditions:
Nominal Rating - ISO at 15°C (59°F), Sea Level
No Inlet/Exhaust Losses
Relative Humidity at 60%
LHV = 31.5 to 43.3 MJ/nm
3
(800 to 1,100 Btu/scf)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
12
Page 14
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
4 Reduction-Drive Gearbox
4.1 General Description
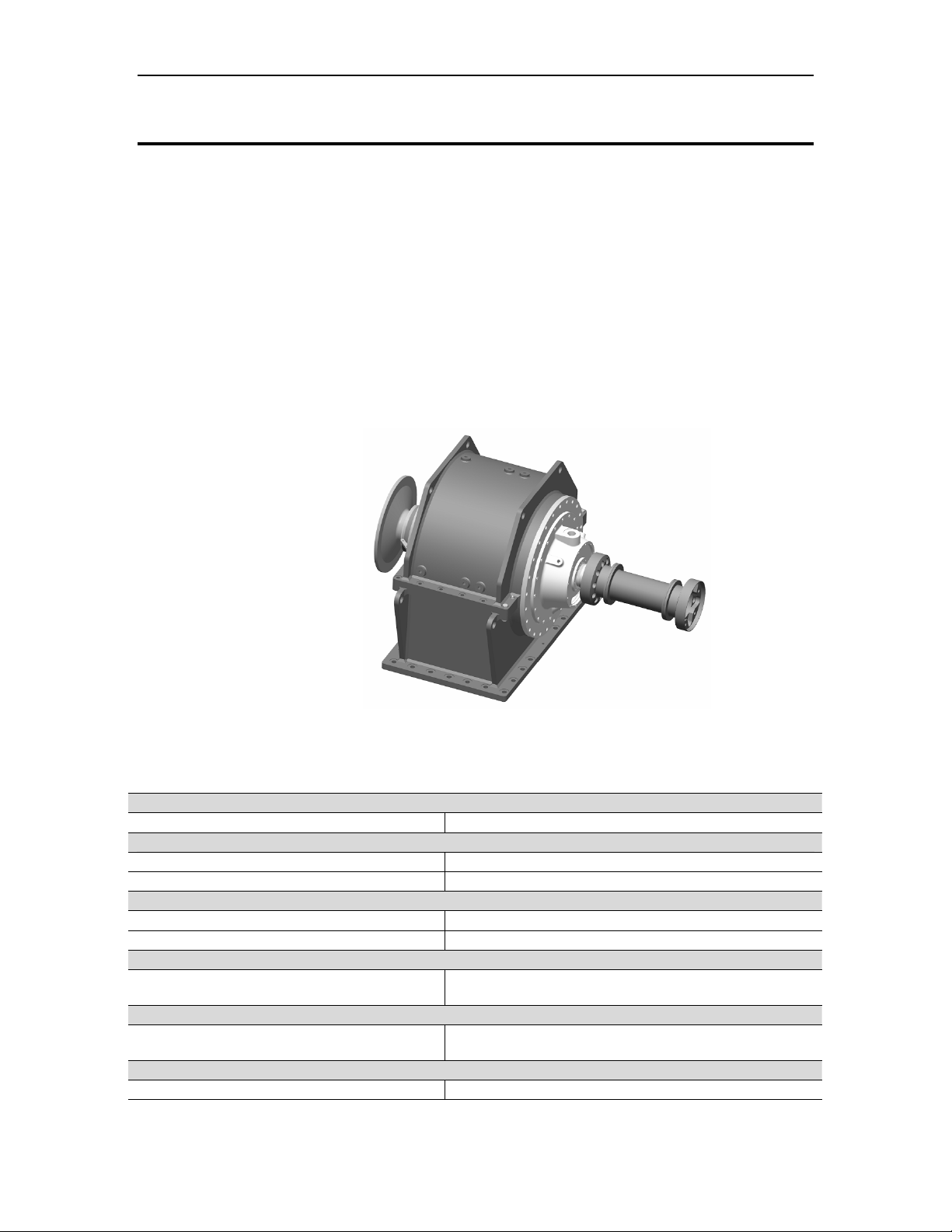
The reduction-drive gearbox (Figure 5) is an industrial, epicyclic, star-gear design
selected specifically for generator set applications. The gearbox uses few moving parts,
which provides high reliability and ease of assembly and disassembly. The reduction
gearbox is designed for continuous-duty operation and reduces the output speed of the
turbine to the required operating speed of the generator. The gearbox is coupled to the
gas turbine through a balanced high-speed shaft, splined at both ends. The output shaft
is coupled to the generator through a flexible disk-type dry coupling enclosed in a
coupling guard. The design of the gearbox facilitates straight-through shafting, avoiding
offset problems and permitting engine, gear, and generator alignment from a common
base. Gear lubrication is provided by the package lube oil system.
The gearbox is designed to provide 99% reliability between major inspections and
overhauls.
Figure 5. Typical Reduction Gearbox for the Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 2. Reduction-Drive Gearbox Specifications
Approximate Weight
Gearbox 7300 kg (16,100 lb)
Output Speed
50 Hz Service 1500 rpm
60 Hz Service 1800 rpm
Inspection and Overhaul Intervals
Major Inspection Interval 30,000 hours
Overhaul Interval 100,000 hours
Compliance
American Petroleum Institute (API)
Ratings
American Gear Manufacturers Association
(AGMA)
Vibration Monitoring
Gearbox Acceleration Probe
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
613 Compliant With Exceptions, Refer to Solar’s
Standard List of Exceptions
In Excess of 1.10 for Generator Applications
13
Page 15
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
5 Generator and Associated Equipment
5.1 General Description
For maximum flexibility, the gas turbine package can be provided with several different
generator types and voltage outputs to accommodate a broad range of application
requirements. The generator, exciter, and control system are integrated to provide
optimal performance.
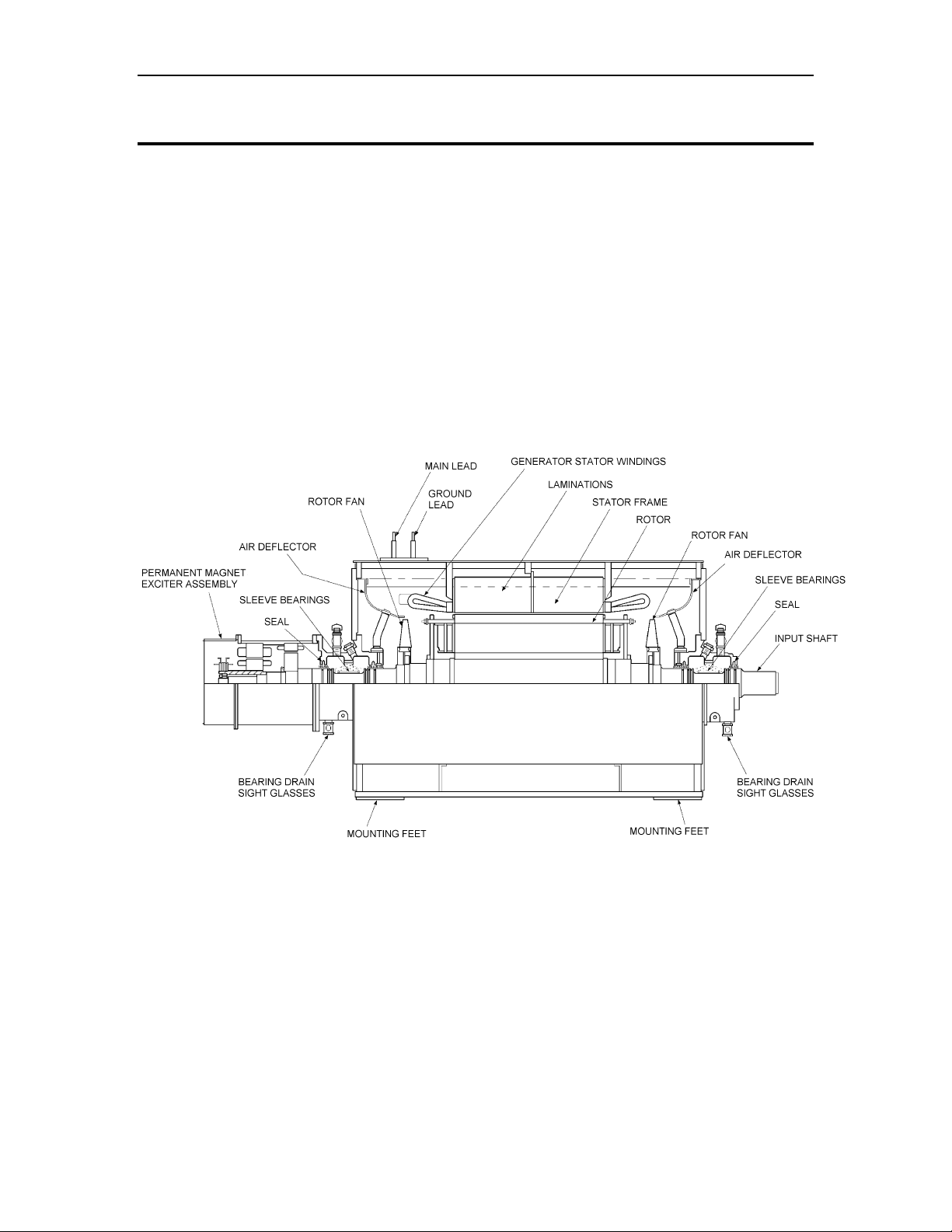
The standard generator type supplied is open drip-proof (ODP) (Figure 6). However the
following other enclosure types are available to meet a variety of environmental
conditions and cooling requirements:
• Closed air circuit air cooled (CACA)
• Closed air circuit water-to-air cooled (CACW)
• Totally enclosed air-to-air cooled (TEAAC)
• Totally enclosed water-to-air cooled (TEWAC)
Figure 6. Typical Open Drip-Proof Generator with Permanent Magnet Exciter System
5.2 Functional Description
During generator operation, three-phase AC power generated by the exciter armature is
converted to DC power by a rectifier. The DC output from the rectifier is applied as field
excitation current to the generator rotor windings to create magnetic flux. The generator
voltage output is controlled by the generator field current and the generator field current
is controlled by a brushless exciter. The amount of DC current applied to the exciter field
determines the exciter output voltage. A potential transformer senses the bus potential
and provides a signal to the combined generator control module (CGCM) for excitation
control.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
14
Page 16

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Any variations in bus potential will also be sensed and corrected by this circuit. After
voltage builds, the generator accelerates to 100% speed and excitation and voltage
control is assumed by the CGCM. A crosscurrent-compensating transformer provides the
signal to the CGCM for reactive loadsharing between multiple paralleled units.
It should be noted that the generator rotor windings rotate and the generator armature is
stationary. The exciter field coils are also stationary and the exciter armature rotates with
the main generator rotor shaft. As a result, a single rotating assembly consisting of the
exciter armature, exciter rectifier, and the generator rotor windings is formed. This single
rotating assembly greatly simplifies all electrical connections within the generator.
5.2.1 Standard Features
Generators include the following standard features:
• Sleeve bearings with pressure fed sumps
• Terminal box
• Form wound stator windings
• Amortisseur windings
• Rotor balance to 125% rated speed
• Anti-condensation space heaters
• Permanent magnet generator (PMG)
• Rotating armature-type VAC exciter
• Full-wave rectifier assembly
Special order generators are available to meet unique customer requirements including
non-U.S. specifications.
5.2.2 Rotor
The salient, four-pole, forged rotor is dynamically balanced to minimize vibration. Motor
fans move cooling air through the generator and around the rotor. The rotors have
layer-wound field windings cemented with a high-strength resin and are baked to cure the
resin. The rotor is in electrical and mechanical balance at all speeds up to 125% of rated
speed.
5.2.3 Stator
The stator is built with high-grade silicon steel laminations that are precision-punched and
individually insulated. Windings are typically form-wound and treated with thermosetting
synthetic varnish or vacuum pressure impregnated (VPI) epoxy for maximum moisture
resistance, high dielectric strength, and high bonding qualities. The windings are braced
to withstand shock loads such as motor starting and short circuits. Space heaters can be
supplied to minimize condensation during shutdowns.
5.2.4 Shaft
The shaft diameter provides the necessary stiffness to avoid torsional vibration. The
turbine-driven generator set is given a complete torsional analysis.
5.2.5 Frame
The frame is heavy-duty steel and is fabricated with deep welds and internal reinforcing
for extra rigidity and strength. The frame also includes lifting lugs.
5.2.6 Exciter
Excitation current for the generator field coils is provided by a brushless rotating exciter
with a PMG pilot exciter. The exciter is mounted directly on the generator rotor shaft. The
exciter consists of two basic parts, a small three-phase, AC generator with rotating
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
15
Page 17
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
armature and a three-phase, full-wave, diode-type bridge rectifier that rotates with the
armature. The pilot exciter is a PMG that rotates with the main generator rotor shaft. It
feeds the exciter field windings with excitation current and is controlled by the CGCM.
5.2.7 Bearing Lubrication System
The generator is supplied with a force-fed bearing lubrication system consisting of onskid
piping and a filter strainer. Oil is supplied from the package lube oil system.
Table 3. Generator and Associated Equipment Specifications
Approximate Weight
Generator (Typical Open Drip Proof) 45 000 kg (99,200 lb)
Construction Types
Open Drip Proof (OPD), Air Cooled Standard
Closed Air Circuit Water-to-Air Cooled (CACW) Optional
Closed Air Circuit, Air Cooled (CACA) Optional
Totally Enclosed Air-to-Air Cooled (TEAAC) Optional
Totally Enclosed Water Air Cooled (TEWAC) Optional
Generator
Optional Voltage Ratings See Note (a)
Frequency Ratings 50 or 60 Hz
Number of Poles 4
Number of Leads 6
Connection Wye
Stator Windings Form Wound
Insulation
Temperature Rise See Note (b)
Overload Capacity
Overload Compliance NEMA
Short Circuit Capability 300% For 10 seconds
Rotor Balance To 125% of Rated Speed
Maximum Wave Form Deviation 10%
Maximum Harmonic Content 3%
Telephone Influence Factor (TIF)
Balanced 100
Residual 75
Efficiency
Space Heater
Voltage 120, 220, 230, or 240 VAC
Frequency 50 or 60 Hz
Phase 1 Phase
Vibration Monitoring
Generator Bearing Driven End Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Generator Bearing Exciter End Displacement Probes, X and Y axis
Notes:
(a) Other voltages can be provided to meet specific customer requirements.
(b) A 80°C (144°F) temperature rise is based on the generator nameplate rating at 40°C (104°F)
and a power factor of 0.8 for continuous duty service.
11,000, 12,470, or 13,800 VAC,
National Electrical Manufacturers Association
(NEMA) Class F
NEMA Class B,
-150% Rated Current for One Minute
-110% Rated Current for Two Hours
The combined generator, exciter, and regulator
efficiency at full load is nominally 97%.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
16
Page 18
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
6 Start System
6.1 General Description
The start system includes a direct-drive AC starter motor driven by a solid-state variable
frequency drive (VFD). The start system provides torque to initiate engine rotation and to
assist the engine in reaching a self-sustaining speed. The starter motor is mounted
directly on the gas turbine accessory drive gearbox. The VFD regulates voltage and
frequency to the starter motor for engine rotation as commanded by the Turbotronic 4
control system.
6.2 Functional Description
To begin gas turbine rotation, the VFD initially provides low-frequency AC power to the
starter motor. The VFD gradually increases the speed of the starter motor until the gas
turbine reaches purging speed. When purging is completed, the control system activates
the fuel system. The speed of the starter motor is gradually increased until the gas
turbine reaches starter dropout speed. The VFD then deenergizes the starter motor and
the motor clutch assembly is disengaged.
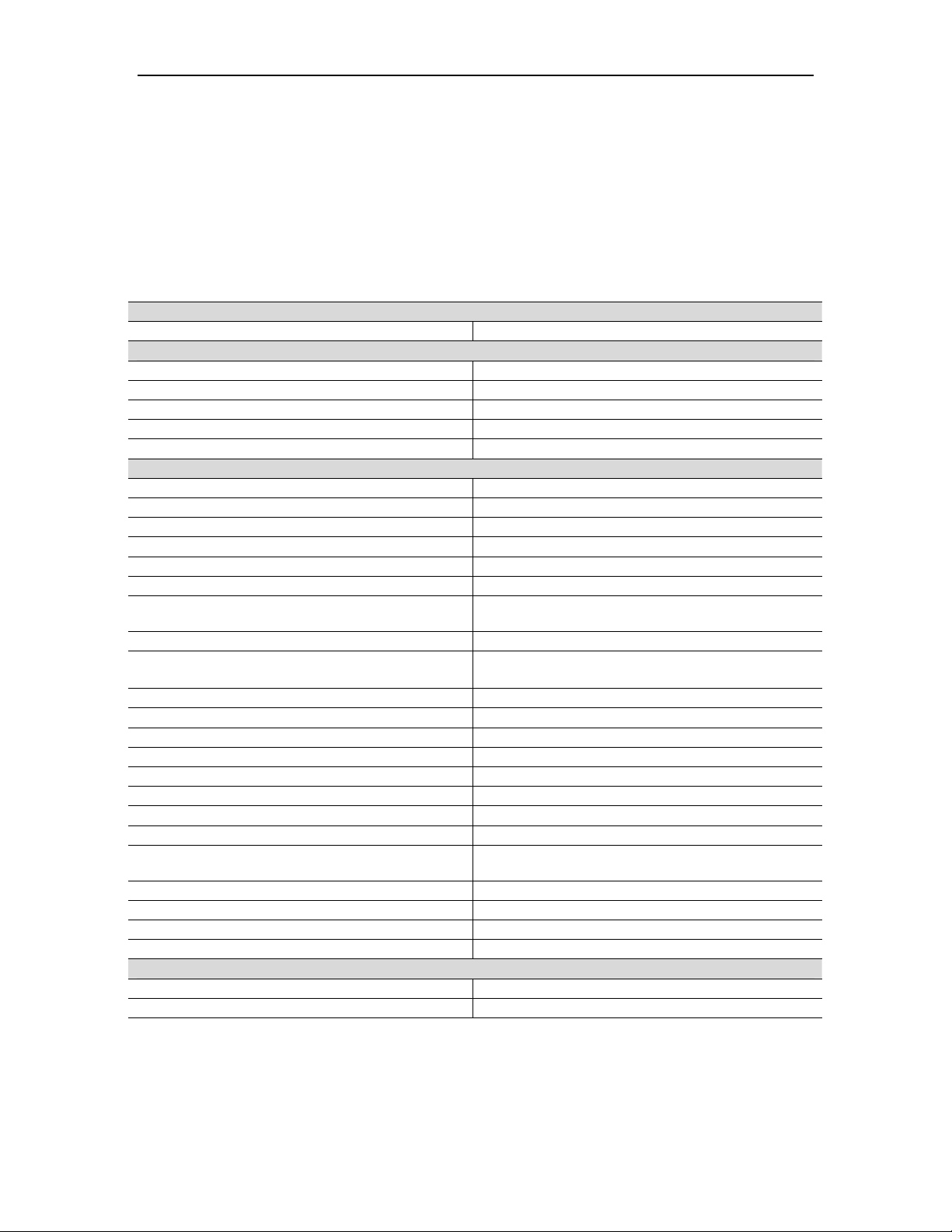
6.2.1 Starter Motor
The starter motor (Figure 7) provides high breakaway starting torque and acceleration
from standstill to starter dropout speed. The motor is standard frame size and is
constructed to be explosion proof and flameproof. The motor includes an integral
over-temperature protection thermostat connected to the Turbotronic 4 control system for
hazardous area motor certification and protection. Separate cable entry points are
provided for power connections, thermal protection wiring, and the space heater wiring.
Starting power is transferred to the gas turbine via the reduction-drive gearbox and overrunning clutch and shaft assembly. After a shutdown, the starter motor rotates the turbine
at low speed to prevent deformation of the rotor during cool down.
Figure 7. Direct-Drive AC Starter Motor and VFD Cabinet
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
17
Page 19
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
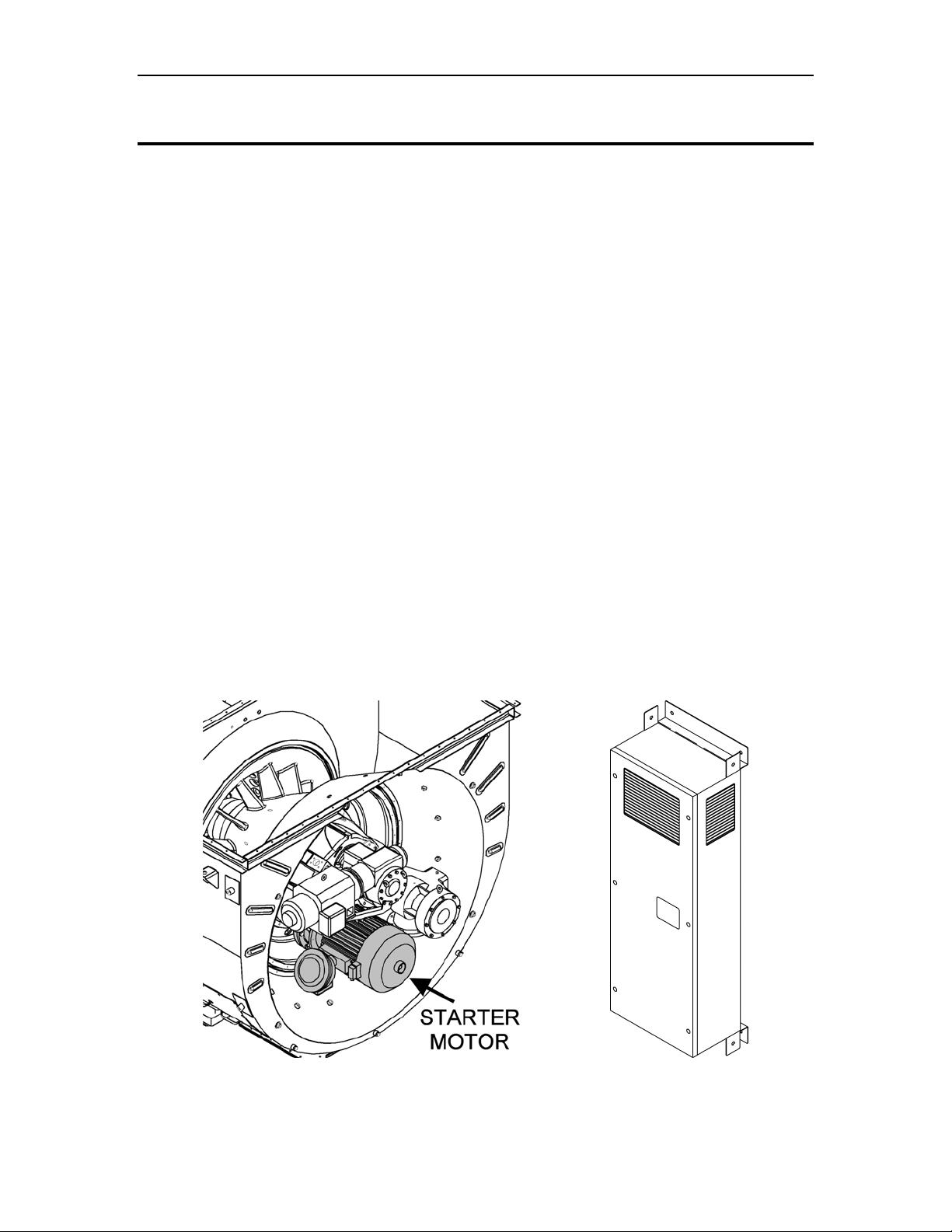
6.2.2 Variable Frequency Drive
The VFD (Figure 7) is a motor speed controller that provides pulse-width modulated
power with variable frequency and voltage to the starter motor. Controlled by the
Turbotronic 4 control system, the VFD regulates voltage and frequency to the starter
motor to control engine speed from standstill to starter dropout speed. The system is
capable of performing up to six start attempts per hour, as well as extended purge cycles
for heat recovery unit applications and engine wash cycles. The VFD cabinet is designed
for installation in a non-hazardous location. Electrical disconnects and overcurrent
protection devices are not provided.
6.2.3 Power Wiring
The start system (Figure 8) requires customer-furnished, three-phase AC input.
Additional three-phase AC power wiring is required to connect the VFD to the starter
motors. A start contactor is not required for VFD operation. A customer-furnished fused
disconnect at the VFD input is recommended. Optional motor space heater wiring is
available.
Figure 8. Typical Direct-Drive AC Start System
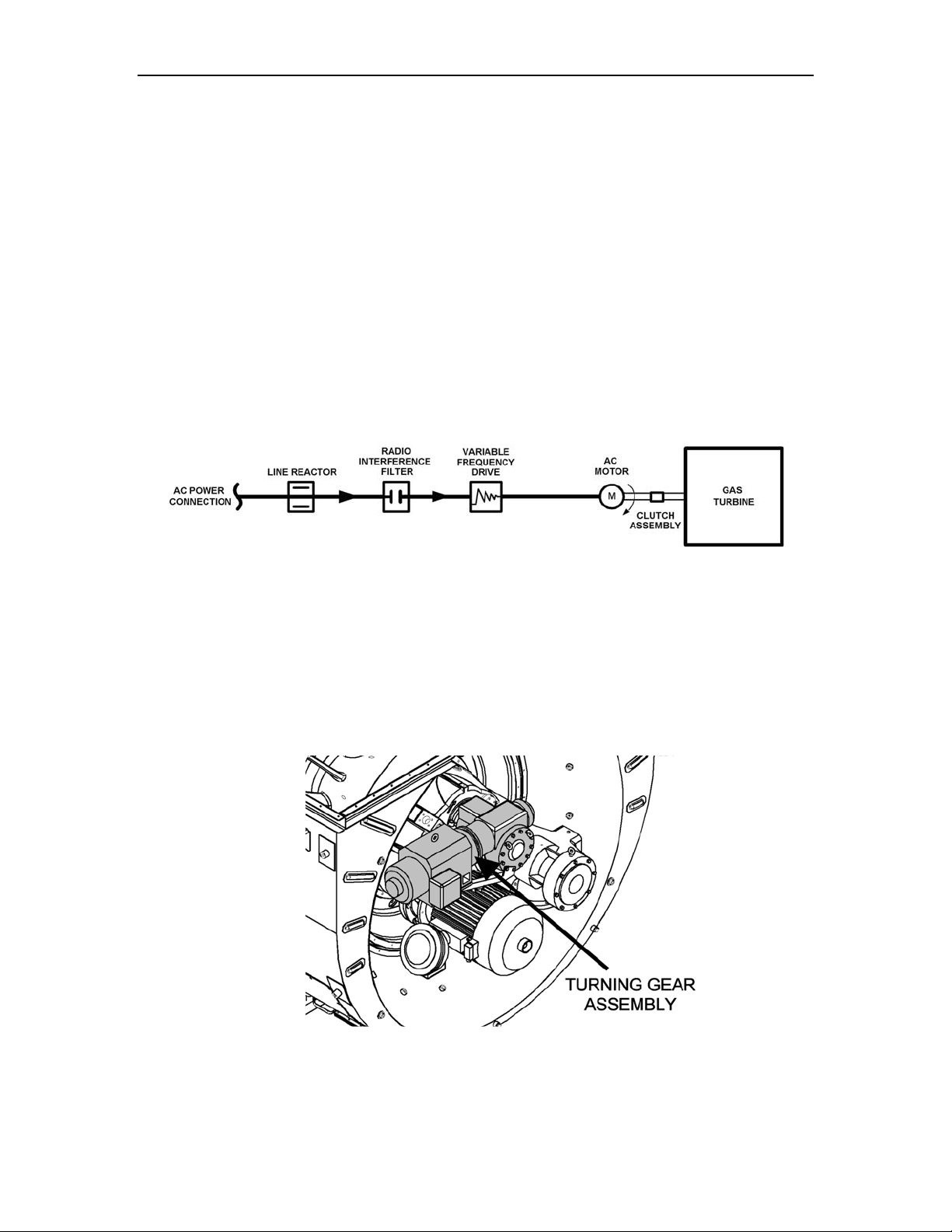
6.3 Backup Slow Rotation System
The Titan 250 package is equipped with a DC powered turning gear system (Figure 9) to
ensure low speed rotation of the turbine as backup for the DAC starter motor in the event
of loss of AC power to the package. The system engages the decelerating turbine at low
speed and maintains rotation for a specified time.
Figure 9. Turning Gear Assembly
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
18
Page 20
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 4. Start System Specifications
Variable Frequency Drive
Optional Voltage Input Ranges See Note (a)
Minimum Input Current
- 380 to 460 VAC Input 525 amps
- 500 to 600 VAC Input 342 amps
Voltage Output Range 0 to 460 VAC, (0 to 240 Hz)
Maximum Line Distribution Capacity 1000 kVa
Maximum Fault Current Capacity See Note (b)
Maximum Breakaway Amperage 383 amps
Maximum Breakaway Torque 918 N-m (677 ft-lb)
Power Factor 0.96
Efficiency 98%
Minimum/Maximum Operating Temperature
Heat Rejection
- 380 to 460 VAC Input 7350 watts
- 500 to 600 VAC Input 9485 watts
Input Fuse Rating 600 amp
Approximate Measurements
- Height 220 cm (87 in.)
- Width 69 cm (24 in.)
- Depth 60 cm (28 in.)
Approximate Weight 28 831 kg (850 lb)
- Length 73 cm (29 in.)
- Diameter 46 cm (18 in.)
Starter Motor
Motor Type Squirrel-cage Induction
Motor Voltage Rating 380 AC, (0 to 133 Hz)
Power 93 kW (125 hp)
Operating Speed 0 to 7000 rpm
Maximum Breakaway Amperage 659 amps
Maximum Breakaway Torque 488 N-m (360 ft-lb)
Minimum/Maximum Operating Temperature
Space Heater Voltage 115 VAC, 60 Hz
Approximate Measurements
- Length 66 cm (26 in.)
- Diameter 45.7 cm (18 in.)
Approximate Weight
- AC Starter Motor Assembly 450 kg (990 lb)
Power Wiring
VFD to Starter Motors Power Cable Length
Turning Gear Motor
Motor Type Squirrel-cage Induction
Motor Voltage Rating 240 VDC
Power 3.73 kW (5 hp)
Operating Speed 2500 rpm
Turbine Rotation Speed 300 rpm
380 to 460 VAC, (48 to 62 Hz)
500 to 600 VAC, (48 to 62 Hz)
30 000 amps
-10 to 40°C (14 to 104°F)
-40 to 60°C (-40 to 140°F)
38 m (123 ft), See Note (c)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
19
Page 21
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Applicable Engineering Specifications
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1593
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1762
Applicable Product Information Letters
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 149 Direct-drive AC Start Systems
Notes:
(a) If the customer-furnished input voltage is greater than 600 VAC ±5%, a step-down
transformer is recommended.
(b) Feeder circuits exceeding this limit require the use of an isolation transformer, line reactor, or
other means of adding similar impedance to limit fault current.
(c) Longer cable runs may require an onskid marshalling box and/or output line reactor.
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product
Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1 and Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems For
Gas Turbine Packages Installed in Hazardous Areas
(CENELEC Standards)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
20
Page 22
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
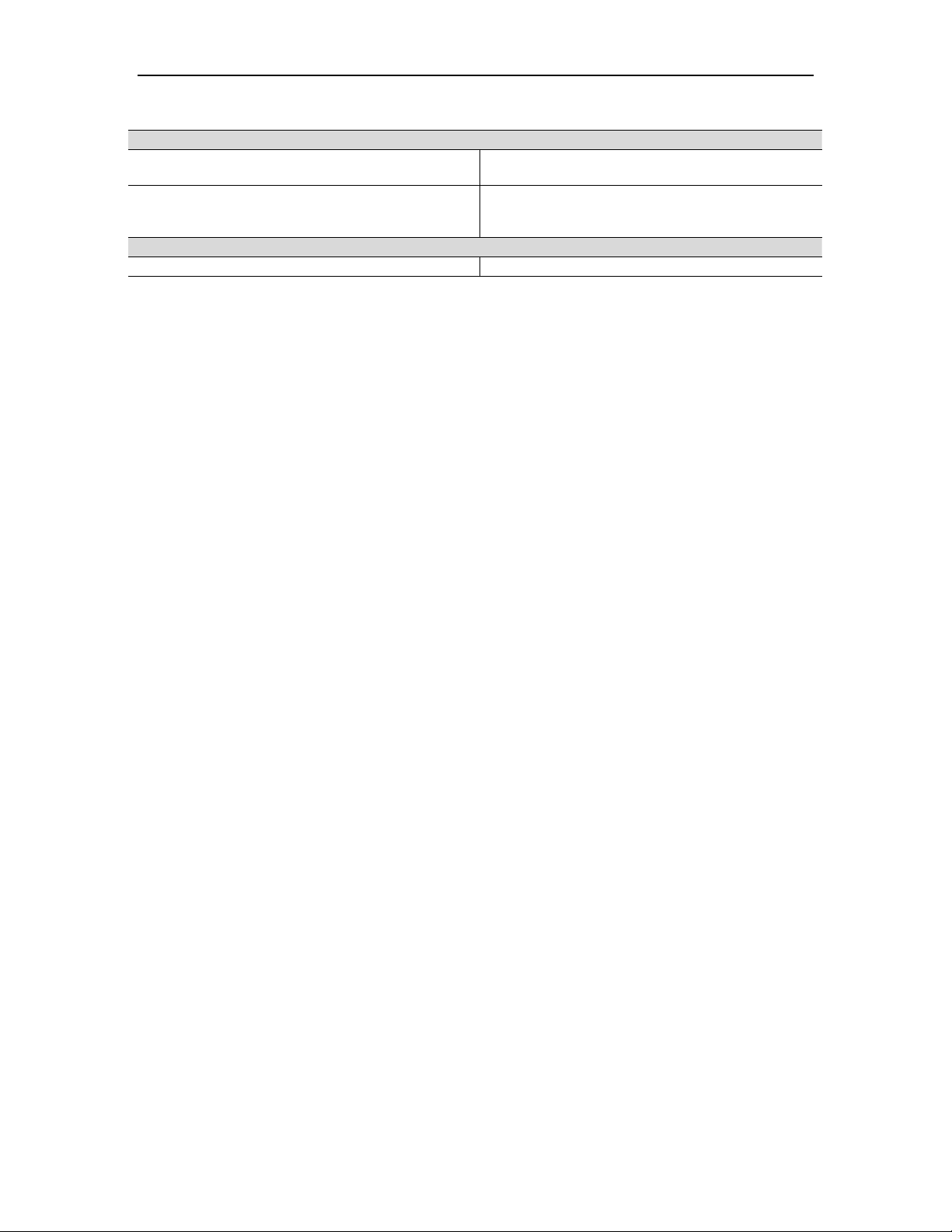
7 Fuel System
7.1 General Description
The fuel system (Figure 10), in conjunction with the control system, includes all
necessary components to control ignition and fuel flow during all modes of operation.
TP
LEGEND
TP = PRESSURE TRANSMITTER
RT = RTD (TEMPERATURE)
VS = VALVE SOLENOID
PILOT
FUEL
CONTROL
VALVE
TP
PILOT FUEL
MANIFOLD
TO FUEL
INJECTORS
GAS VENT
VENT
VALVE
TP
SECONDARY
SHUT OFF
VALVE
V
S
FUEL
AIR
TP
V
S
PRIMARY
SHUT OFF
VALVE
VS VS
Figure 10. Typical Fuel System Schematic
7.1.1 SoLoNOx Combustion System
The SoLoNOx combustion system uses special fuel injectors with main and pilot fuel
ports. The fuel injected through these ports is controlled during starting and steady-state
operation to maintain stable combustion and minimize the formation of nitrous oxides
(NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and unburned hydrocarbon (UHC) emissions. To further
regulate emission levels, combustion airflow is regulated using a bleed valve mounted on
the combustor case. The SoLoNOx combustion system also includes an additional inlet
gas filter/coalescer for mounting offskid.
TORCH
REGULATOR
TORCH SHUT
OFF VALVE
TP
MAIN
FUEL
CONTROL
VALVE #1
TPRT
MAIN
FUEL
CONTROL
VALVE #2
TP
TORCH
REGULATOR
TP
TP
TP
MAIN FUEL
MANIFOLD
#1
MAIN FUEL
MANIFOLD
#2
TO FUEL
INJECTORS
TO FUEL
INJECTORS
TO TORCH
7.1.2 Fuel System
The SoLoNOx fuel system includes:
• Supply pressure transmitter
• Pilot air operated primary gas fuel shutoff valve
• Pilot air operated secondary gas fuel shutoff valve
• Pilot air operated gas vent valve
• Electrically operated fuel control valves (2)
• Torch with shutoff valve and pressure regulators
• Main fuel manifold
• Fuel injectors
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
21
Page 23
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
• Fuel pilot control valve
• Fuel pilot manifold
• Inlet gas filter/coalescer loose shipped for field installation
Component Operation
The gas fuel pressure supplied to the turbine skid must meet minimum and maximum
pressure and flow requirements. If the gas fuel pressure is too high or too low, the control
system will prevent turbine operation. Pneumatically actuated primary and secondary gas
fuel shutoff valves are controlled using pilot air pressure. For each valve, pilot air
pressure is admitted to and exhausted from a pneumatic actuator through a solenoid
valve. Fail-safe operation ensures both valves will close in case pilot air pressure is lost.
The gas fuel control valves and the SoLoNOx fuel pilot control valve, are powered by
integrated DC motor-driven actuators. Integrated actuator electronics provide precise
closed-loop valve control based on position command inputs versus position feedback
outputs. The three valves are fast acting and provide fuel metering for light-off,
acceleration, full load, and load transient conditions. Fail-safe operation ensures both
valves will close in case the command signal or control power is lost. During the start
sequence prior to ignition, the control system will verify gas pressure and perform a gas
valve check to verify proper operation of all gas fuel valves.
Table 5. Fuel System Specifications
Gas Fuel System
Acceptable Gas Fuels See Note (a)
Fuel Quality Refer to Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 9-98
Compliance
Minimum/Maximum Gas Fuel Supply Pressure
Minimum Flow Rate 3513 to 5480 kg/hr (7746 to 12086 lbm/hr), See
Minimum/Maximum Fuel Supply Temperature
Primary Gas Fuel Shutoff Valve Pneumatically Actuated Spring-Closed Ball Valve
Secondary Gas Fuel Shutoff Valve Pneumatically Actuated Vane Type Valve
Gas Fuel Control Valve and SoLoNOx Fuel Pilot
Control Valve
Actuator Voltage 120 VDC
Valve Discrete Signals 0 to 24 VDC
Valve Analog Signals 4 to 20 mA
Maximum Operating Pressure 4137 kPag (600 psig)
Maximum Operating Temperature 93°C (200°F)
Response Time Less Than 100 msec From 10-to-90% Stroke
Valve Body
Gas Fuel Filter (Conventional Units Only) 10 Micron
Offskid Coalescing Filter Module (SoLoNOx Units
Only)
Maximum Operating Pressure 3447 kPag (500 psig)
Maximum Flow 122 m3/min (4300 ft3/min)
Minimum/Maximum Operating
Temperatures
Filtration Efficiency β0.3 > 200 per ISO 4572
Natural Gas
Propane
Butane
National Association of Corrosion Engineers
(NACE) Compliant
2240 to 3447 kPag (325 to 500 psig), See Note (b)
Note (b)
-40 to 93°C (-40 to 200°F), See Note (c)
Actuator Valve
Aluminum (Standard)
Stainless Steel (Optional)
-29 to 100°C (-20 to 212°F)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
22
Page 24
Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Customer-Furnished Pilot Air System
Fluid Clean-Dry Air
Air Quality
Minimum/Maximum Regulated Pressure Range 689 to 1379 kPag (100 to 200 psig)
Pilot Air Filter 10 micron
Construction Materials
Piping, Manifolds, and Tubing 316L Stainless Steel
Applicable Engineering Specifications
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 9-98
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1593
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1762
Applicable Product Information Letters
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 148 LPG and NGL Fuels
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 162
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 176 Siloxanes in Gas Fuel
Notes:
(a) The gas fuel system is designed to operate with fuels that comply with Solar’s Engineering
Specification ES 9-98. Most commercially available natural gas fuels comply with ES 9-98.
The gas fuel system can be modified to operate with fuels that do not comply with ES 9-98.
Solar gas turbines can operate on low Btu fuels. Please contact Solar Turbines for
assistance in evaluating fuel characteristics and gas turbine requirements.
(b) Fuel pressure and flow requirements can be affected by several factors such as; fuel
temperature, fuel lower heating value, air inlet temperature, fuel composition, fuel specific
gravity, engine injector type, inlet duct loss, relative humidity, site elevation, and piping length
and diameter. Based on site conditions, minimum fuel pressure and flow requirements may
be less than stated values. Please contact Solar Turbines for site-specific fuel pressure and
flow requirements.
(c) Fuel must have a differential temperature (ΔT) of at least 27°C (50°F) above fuel dew point
temperature.
(d) The particle size in the air stream should not exceed 10μ. Since it is impractical to remove
100% of all particles larger than 10μ, this is defined as ß10 > 100, or 99% efficient. Oil or
hydrocarbon content should not exceed 1 ppm. The dew point at line pressure shall be at
least 6°C (10°F) below the minimum temperature to which any part of the air system is
exposed or between -29°C and 93°C (-20°F and 200°F). Air should be free of all corrosive
contaminants, hazardous gases, flammables, and toxics.
See Note (d)
Fuel, Air, and Water (or Steam) for Solar Gas
Turbine Engines
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product
Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1 and Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems for
Gas Turbine Packages Installed In Hazardous
Areas (CENELEC/IEC Standards – European
ATEX Directive 94/9/EC)
Recommendations for the Sourcing, Handling,
Storage and Treatment of Fuels for Solar Gas
Turbines
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
23
Page 25

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
8 Lubrication System
8.1 General Description
The lubrication system, (Figure 11) circulates oil under pressure to the gas turbine and
driven equipment. Lube oil is supplied from the lube oil tank located in the driver frame.
Oil temperature is maintained at optimal levels by a thermostatic control valve, oil tank
heater, and optional oil cooler.
The lubrication system incorporates the following components:
• Oil tank
• Oil tank heater
• Lube oil (customer furnished)
• Gas turbine driven main lube oil pump
• AC Motor-driven pre/post lube oil pump
• DC Motor-driven backup lube oil pump
• Duplex lube oil filter system with replaceable elements
• Oil level, pressure, and temperature indications
• Pressure and temperature regulators
• Strainers
• Oil tank vent separator
• Oil tank vent flame trap
Optional features include:
• Offskid oil cooler
• Stainless steel oil tank and tank covers
• Stainless steel filter system
8.1.1 Lube Oil
Lube oil is customer furnished. Petroleum base or synthetic oil with a viscosity grade of
C32 or C46 may be used. Synthesized hydrocarbon oils are recommended due to lower
pour point, higher viscosity index, better heat transfer, and lower oxidation rate. Lube oil
must conform to Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 9-224.
8.1.2 Gas Turbine-Driven Main Lube Oil Pump
The main lube oil pump is mounted on an integral accessory drive gearbox. This
positive-displacement pump provides lube oil pressure for normal operation.
8.1.3 AC Motor-Driven Pre/Post Lube Oil Pump
The pre/post lube oil pump provides lube oil pressure during package starting and for
post-lube cooling of the gas turbine and driven equipment bearings. The pre/post lube oil
pump provides lube oil pressure during a gas turbine roll down in the event the main lube
oil pump has failed.
8.1.4 DC Motor-Driven Backup Lube Oil Pump
The backup lube oil pump provides lube oil pressure for post lube cooling of the gas
turbine and driven equipment bearings in the event the pre/post lube oil pump fails. The
backup lube oil pump provides lube oil pressure during a gas turbine roll down in the
event the main lube oil pump and pre/post lube oil pump have both failed. The backup
lube oil pump also provides lube oil pressure during an emergency condition such as a
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
24
Page 26

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
fire, control system failure, emergency stop, or if a turbine over-speed is detected by the
backup system.
8.1.5 Duplex Lube Oil Filter System
The duplex lube oil filter system is supplied with a filter transfer valve and filter differential
pressure indication with alarm. The transfer valve allows a filter transfer to be performed
while the gas turbine is running. The lube oil filter system is contained completely within
the skid. The interconnect piping between the skid edge and the offskid oil cooler, if
applicable, is not provided.
8.1.6 Lube Oil Vent Coalescer
An offskid lube oil vent coalescer is provided to remove oil vapor from the lube oil tank
vent airflow. The coalescer drains trapped oil vapor back to the lube oil tank and allows
the remaining vent airflow to exhaust to the atmosphere. A tank overpressure alarm and
shutdown are also included. The lube oil vent coalescer is loose shipped for offskid
installation by others.
PT
THRUST
BEARING
GENERATOR COUPLING GEARBOX
FG FG FG
FLAME
ARRESTER
VENT
DEMISTER
PT
BACKUP
LT
PUMP
GAS PRODUCER SHAFT
RT
RT
SCAVENGE LUBE OIL PUMP
(MARINE APPLICATIONS)
PRE/POST
PUMP
FG
LUBE OIL
COOLER
LUBE OIL TANK
DPT
COOLER
CONTROL VALVE
MAIN LUBE
OIL PUMP
DUPLEX
LUBE OIL
FILTER
SYSTEM
RT
LEGEND
DPT DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE TRANSMITTER FG FLOW GAUGE (SIGHT GLASS)
LT LEVEL TRANSMITTER RT TEMPERATURE DEVICE (RTD)
PT PRESSURE TRANSMITTER FILTER
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
25
Page 27

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 11. Typical Lube Oil System
8.1.7 Lube Oil Vent Flame Arrestor
The lube oil vent flame arrestor prevents an ignition source from entering the lube oil
tank. The flame arrestor is loose shipped for offskid installation by others.
8.1.8 Lube Oil System Options Lube Oil Cooler
An air-to-oil type cooler is available to provide oil cooling for the gas turbine and the
driven equipment. The cooler is sized for specified heat loads and ambient temperatures
and is designed for a 4.4°C (40°F) approach temperature. The cooler is loose shipped for
offskid installation by others.
Lube Oil Immersion Tank Heater
The lube oil tank immersion heater ensures the lube oil tank temperature is adequate for
starting in cold conditions. The tank heater also facilitates a short lube oil temperature
warm up period after a cold start. Electrical supply contactors are not included.
Table 6. Lubrication System Spe cifications
Main Lube Oil Pump
Pump Type Engine-Driven Rotary Screw
Flow 1999 lpm (528 gpm)
Discharge Pressure
Pre/Post Lube Oil Pump
Pump Type AC Motor-Driven Centrifugal
Optional Motor Voltage Ratings
Motor, Power 7.45 kW (10 hp)
Backup Lube Oil Pump
Pump Type DC Motor-Driven Centrifugal
Motor Voltage Rating 120 VDC
Motor, Power 7.45 kW (10 hp)
Lube Oil Cooler
Lube Cooler Oil Volume (Per Cooler) Project Specific
Design Heat Load (Per Cooler) Project Specific
Design Oil Flow Rate (Per Cooler) Project Specific
Air Flow Rate
Maximum Ambient Temperature 43°C (110°F)
Maximum Design Lube Oil Cooler Outlet
Temperature
Maximum Lube Oil Cooler Design Pressure Drop
Minimum Lube Oil Cooler Design Pressure 1 035 kPag (150 psig)
Optional Motor Voltage Ratings
Optional Motor, Power
Lube Oil Tank Immersion Heater, See Notes (d) and (e)
Optional Voltage Ratings
Power 3-Phase VAC, 40 kW
Minimum/Maximum Regulated Supply Pressure 100 to 225 psig (689 to 1551 kPag)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
690 kPag (100 psig), See Note (a)
380 VAC, 400 VAC, and 415 VAC (50 Hz)
460 VAC and 575 VAC (60 Hz)
Project Specific, See Note (b)
66°C (150°F)
173 kPag (25 psig), See Note (c)
380 VAC, 400 VAC, and 415 VAC (50 Hz)
460 VAC and 575 AC (60 Hz)
7.5 kW (10 hp), 15 kW (20 hp), or 2 x 15 kW (20
hp)
380 VAC, 400 VAC, and 415 VAC (50 Hz)
460 VAC and 575 VAC (60 Hz)
26
Page 28

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Maximum Flow Demand Rate 4.67 nm3/min. (165 scfm)
Main Lube Oil Duplex Filters
Type Self-Supporting Pedestal
Duplex Filters 10 Micron
Certification ASME, Section VIII, Division 1
Backup Lube Oil Pump Filter
Type Bowl Filter
Minimum/Maximum Operating Temperatures -54 to 135°C (-65 to 275°°F)
Simplex Filter β X > 75 Micron
Lube Oil Vent Coalescer
Type Air/Oil Mist Eliminator
Maximum Working Temperature 93°C (200°F)
Orientation Vertical
Performance
100% removal of all droplets greater than 3
microns and 99.5% removal of all droplets less
than 3 microns.
Certification ASME, Division 1
Approximate Dimensions (Height x Diameter) 198.1cm x 121.9 cm (77.9 in. x 48 in.)
Approximate Weight 1093 kg (2,410 lb)
Lube Oil Vent Flame Arrestor
Orientation
Approximate Dimensions (Height x Width x
Diameter)
Vertical, See Note (f)
32 cm x 23 cm x 22 cm
(13 in. x 9 in. x 9 in.)
Approximate Weight 11 kg (25 lb)
Strainers
Tank Fill 20 mesh
Gearbox Breather Vent (If Applicable) 40 mesh
Gas Producer Start-Up Strainer
Gearbox Start-Up Strainer (If Applicable)
Compressor Driven End Start-Up Strainer
Compressor Exciter End Start-Up Strainer
70 Micron, See Note (g)
70 Micron, See Note (g)
70 Micron, See Note (g)
70 Micron, See Note (g)
Lube Oil
Viscosity Grade ISO VG 32 (C32) Use When Ambient Temperature is < 110°F
Viscosity Grade ISO VG 46 (C46) Use When Ambient Temperature is > 110°F
Pour Point
Must Be At Least 6°C (11°F) Below The Lowest
Ambient Temperature)
Lube Oil Tank Capacity
11 450 L (3025 gal), See Note (h)
Weight 1995 kg (4,400 lb)
Construction Materials
Piping, Manifolds, and Tubing 316L Stainless Steel
Lube Oil Tank and Tank Covers
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Construction Materials (Cont’d)
Main Lube Oil Duplex Filter Housing and Transfer
Valve
Backup Lube Oil Pump Filter Housing
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Lube Oil Vent Coalescer
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Lube Oil Vent Flame Arrestor Aluminum
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
27
Page 29

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Applicable Engineering Specifications
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 9-224
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1593
Solar’s Engineering Specification ES 1762
Applicable Product Information Letters
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 058 Package Sound Levels
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 161 Lube Oil System Cleanliness
Fuel, Air, and Water (or Steam) for Solar Gas
Turbine Engines
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product
Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1 and Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems for
Gas Turbine Packages Installed In Hazardous
Areas (CENELEC/IEC Standards – European
ATEX Directive 94/9/EC)
Notes:
(a) A pressure control valve regulates main lube oil supply pressure to 241 kPag (35 psig) when
unit is at normal operating temperature.
(b) Prevailing winds must be considered to prevent the lube oil cooler from exhausting into the
engine air inlet system or to take air in from the engine exhaust system. No airflow
backpressure is allowed at the lube oil cooler face.
(c) The maximum total design pressure drop of the off skid oil cooler loop including supply and
return lines shall not exceed 50 psid (345 kpad) at the design flow rate and an oil viscosity of
60 ssu (10.5 centistokes). No check valves are allowed in the oil cooler loop. This is
recommended for all applications (but mandatory for units in cold climates), oil cooler supply,
return and optional vent lines must slope from the oil cooler to the turbine package to
facilitate draining when the unit is not operating.
(d) The heater is mandatory if unit ambient temperature is less than 10°C (50°F).
(e) The lube oil tank immersion heater ensures the lube oil tank temperature remains above
10°C (50°F) for starting in cold temperatures.
(f) The flame arrestor must be installed vertically at the end of the lube tank vent piping.
(g) Start-up strainers must be inspected after 100 hours of operation.
(h) An additional 246 L (65 gal) is required for package filters and piping. Additional oil will also
be required to fill any offskid oil piping and vessels (if applicable).
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
28
Page 30

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
9 Turbotronic 4 Control System
9.1 Overview
The Turbotronic 4 control system controls and monitors the turbomachinery package
including the gas turbine and driven equipment. The system scope can be expanded to
include monitoring and/or control of balance of plant equipment that is directly package
related. The system architecture is based on a Rockwell Automation/Allen-Bradley
hardware and software platform and includes fully integrated generator, vibration and,
when required, fire and gas monitoring and control subsystems.
In the standard onskid configuration (Figure 12) the primary control system components
are mounted on the package skid with a local operator interface. An auxiliary display and
monitoring system is available, mounted either in an optional console or desktop
computer, and connected to the package by redundant network cables. In the standard
offskid configuration, the entire control system is mounted in an offskid console with a full
set of hardwired cables connecting to the package as illustrated in (Figure 13).
An independent backup shutdown system provides additional protection. This shuts the
package down in a safe and orderly manner in the event of malfunction of the primary
control system.
9.2 System Architecture
Key system components include:
• ControlLogix controller (Allen-Bradley)
• RSLogix 5000 programming software (Rockwell Automation)
• 1794 Flex I/O input/output modules (Allen-Bradley)
• Combination generator control module (Allen-Bradley/Basler Electric)
• 1701 FieldMonitor vibration monitoring system (Bently Nevada)
• ControlNet network (ControlNet International)
• TT4000 offskid display and monitoring system (Solar Turbines)
• Offskid operator control panel (Solar Turbines)
• TT4000S onskid local operator interface (Solar Turbines)
• Onskid operator control panel (Solar Turbines)
• Fire and gas monitoring and control system (Det-tronics)
• Independent backup shutdown system (Solar Turbines)
Figure 14 provides an overview of the principle control system elements. The ControlNet
network provides primary communications between components. Hardwire backup is
provided for critical circuits. The TT4000S and onskid operator panel are located on the
package skid. The TT4000 and offskid operator panel are located in a non-hazardous
area such as a control room. The variable speed frequency drive (VFD) for the starter
motor is typically located in a motor control center. All other components are rated NEC
Class 1, Division 2 or CENELEC Zone 2 for hazardous area duty and are located on the
package skid for the onskid controls configuration or in an auxiliary console for the offskid
configuration.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
29
Page 31

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
AUXILIARY
CONSOLE
y METERING PANEL
PACKAGE SKID
y TURBINE CONTROL PANEL
y TT4000
y TT4000S
y OPERATOR PANEL
CONTROLNET ETHERNET
y CONTROL PROCESSOR
y I/O MODULES
y BACKUP SHUTDOWN SYSTEM
y FIRE & GAS SYSTEM
y VIBRATION MONITOR
y GENERATOR CONTROL MODULE
Figure 12. Typical Onskid Control System
AUXILIARY CONSOLE
AUXILIARY DESKTOP
COMPUTER
y TT4000
REMOTE DESKTOP
COMPUTER
y TT4000
y METERING PANEL
y TURBINE CONTROL PANEL
PACKAGE SKID
y TT4000
REMOTE DESKTOP
COMPUTER
CONTROLNET ETHERNET
y TT4000
y TT4000S
y OPERATOR PANEL
y CONTROL PROCESSOR
y I/O MODULES
y BACKUP SHUTDOWN SYSTEM
y FIRE & GAS SYSTEM
y VIBRATION MONITOR
y GENERATOR CONTROL MODULE
Figure 13. Typical Offskid Control System
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
30
Page 32

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
SAFE AREA OPERATOR
MOTOR CONTROL
CENTER
VARIABLE
FREQUENCY
DRIVES
ONSKID OPERATOR
INTERFACE
TT4000S
PRIMARY CONTROL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
CONTROLLOGIX
CONTROLLER
SERIAL LINK TO
SUPERVISORY
CONTROL
INTERFACE
TT4000
TURBINE
CONTROL
PANEL
OPERATOR
PANEL
I/O
MODULES
CONNECTIONS TO PACKAGE AND FIELD INSTRUMENTATION
BACKUP
SHUTDOWN
SYSTEM
Figure 14. Turbotronic 4 System Architecture
9.3 Component Descriptions
9.3.1 Controller
The ControlLogix controller, running RSLogix 5000 software, provides primary control.
Project-specific programs are created in a Windows-based system and uploaded to the
controller. The RSLogix 5000 software supports ladder and function block programming
and complies with the International Electrical Code (IEC) 61131-3 standard for
programmable controllers.
9.3.2 ControlNet 1.5
Operating at 5 Mbps, the network is repeatable and deterministic. Cabling is redundant
with two separate channels carrying the same information. The maximum total length of
the network is 1000 meters without the use of repeaters. However, this length decreases
based on the number of nodes on the network. A practical design limit is 800 meters.
CONTROLNET
FIRE & GAS
SYSTEM
VIBRATION
MONITOR
GENERATOR
CONTROL
MODULE
9.3.3 Input/Output Modules
Flex I/O modules provide an interface between the package instrumentation and the
processor. Specific modules handle discrete inputs, analog inputs, temperature inputs,
speed inputs, discrete outputs and analog outputs.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
31
Page 33

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
9.3.4 Vibration Monitoring System
The system uses 1701 FieldMonitors and associated sensing devices from Bently
Nevada. The capacity of each monitor is eight vibration channels plus a keyphasor input.
The system is configurable from the control processor. It detects preprogrammed alarm
and shutdown levels. See the specification tables for a list of monitored channels.
9.3.5 Backup Shutdown System
The backup shutdown system shuts the package down in a safe and orderly manner
without damage to the equipment in the event of a failure in the primary system. The
control processor is monitored by both an internal watchdog circuit and by an external
watchdog device. If either circuit detects a processor failure, the backup system takes
control. It opens the generator circuit breaker, closes the fuel valves, and initiates a post
lube cycle to protect the turbine bearings. Once a backup shutdown is initiated, operation
can only be restored manually from the control panel after all faults have been cleared.
The emergency stop push-button switches are wired to both the primary and backup
systems.
9.3.6 Fire and Gas System
Enclosed packages require fire and gas control protection. The Eagle Quantum Premier
system from Det-Tronics detects gas and/or fire inside the enclosure based on inputs
from gas, thermal, and optical flame detectors. If fire is detected, the system releases an
extinguishing agent into the enclosure. If a fire or an unacceptable gas level is detected,
the system instructs the Turbotronic control processor to initiate a package shutdown.
The system is also wired directly to the backup shutdown system. See Enclosure Section
11 for a more complete description.
9.3.7 Combination Generator Control Module
The combination generator control module (CGCM) provides voltage regulation,
automatic breaker synchronization, excitation control, power metering, load sharing, and
protective relay functions. For a more detailed description of the CGCM capabilities, refer
to Section 10, Generator Control and Monitoring.
9.3.8 Control System Power Supplies
The control system operates on 24 VDC power. The standard battery charge system
provides 120 VDC power to the control system. The control system includes a 120 to 24
volt DC-to-DC converter to supply 24 VDC power to the control system. For a more
detailed description of the battery charger system, refer to Section 14, Accessory
Equipment.
9.4 System Monitoring and Control Functions
The control system provides sequencing control during gas turbine startup, steady state
operation, and shutdown. Protective functions are provided during all stages of operation.
9.4.1 Starting and Loading
The Start command initiates the sequence. Prior to rotation, the lube oil pump undergoes
a test cycle, the enclosure fans (if applicable) are started, and the fuel valves undergo a
test cycle with fuel pressure verification.
The starter then rotates the gas turbine and the compressor develops airflow to purge
any accumulated gas in the gas turbine, air inlet, and exhaust duct. The purge cycle is
tailored to the exhaust duct volume.
When the engine has reached the required speed and temperature, a small amount of
fuel is introduced into the combustor from the gas torch and ignited by the ignitor plug.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
32
Page 34

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
The fuel control valve gradually opens and admits fuel into the combustor through the
injectors. The inlet guide vanes open and the bleed valve gradually closes. Fuel flow,
engine temperature, and turbine speed all increase. Once starter dropout speed is
exceeded, the starter freewheels and is de-energized. The engine continues to
accelerate under its own power.
The generator is loaded by closing the generator circuit breaker. The circuit breaker can
be closed to a dead (de-energized) or a hot (energized) bus. If a dead bus is detected,
the circuit breaker may be closed without synchronization. If a hot bus is detected, the
system must synchronize the generator output to the bus before the circuit breaker is
closed. Typically, synchronization and closing of the breaker are done automatically.
Manual synchronization is available as an option.
9.4.2 Steady-State Control
During steady-state operation, the control system keeps the equipment within specified
operating conditions. The maximum power limit is determined by engine temperature and
speed.
Temperature control is based on the third-stage nozzle temperature (T5). A set of
thermocouples arranged circumferentially around the turbine are used and the values
averaged. If one thermocouple has a value that deviates from the average by more than
a preset amount, an alarm is generated by the control system. If two thermocouples
deviate, the package is shut down.
Special sensors continuously monitor the gas turbine speed and the control system
makes adjustments to meet operating requirements and to keep the speed within
specified limits. A separate backup overspeed detection system provides additional
protection by automatically shutting the engine down if a preset overspeed limit is
reached.
9.4.3 Stopping
The gas turbine may be shutdown either manually or automatically.
The Normal Stop command initiates a cooldown stop. The generator circuit breaker is
opened and the gas producer runs at idle speed for a preset time to allow the gas turbine
and driven equipment to cool, then the fuel valves close. The Emergency Stop
command results in the immediate opening of the generator circuit breaker and closure of
the fuel valves without a cooldown period.
In the event of a hazardous condition or equipment malfunction, the control system will
shut the package down automatically. These shutdowns are divided into four categories:
• Cooldown stop nonlockout (CN)
• Cooldown stop lockout (CL)
• Fast stop nonlockout (FN)
• Fast stop lockout (FL)
Cooldown and fast stops correspond to the manual normal and emergency stops
respectively. Lockout stops inhibit operation of the control system and prevent restarting
until the malfunction is reset. Lockout stops result from serious malfunctions that require
corrective action before the system can be restarted. Nonlockout stops result from an
operational disruption or abnormal condition and can be reset when conditions return to
normal.
To protect the rotor from deformation and to enable a prompt restart of the package, the
turbine does not come to a complete stop unless the shutdown is the result of fire being
detected. The starter motor, or the DC backup turning gear mechanism in the case of
loss of AC power, engages the turbine at low speed and maintains rotation until the
cooldown cycle is complete. At the same time, the control system initiates and supervises
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
33
Page 35

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
a post-lube cycle to protect the gas turbine and driven equipment bearings from thermal
damage.
If the shutdown is the result of fire being detected, the turbine is brought to a complete
stop and the start of the post lube cycle is delayed for 10 minutes, unless an operator
intervenes.
9.4.4 Vibration and Temperature Monitoring
In addition to the T5 thermocouples, the system provides continuous monitoring of
temperature and vibration levels at key package locations. Refer to the Specification
Table for details.
9.5 TT4000 Display and Monitoring System
The TT4000 display and monitoring system provides extensive data collection and
display capabilities. On a typical project, two standard versions of the product are used.
TT4000 is the fully featured version with extensive data collection and display capability.
It is installed in a high performance industrial grade personal computer (PC), in either a
desktop or a console panel mounted version. It runs on the Windows 2000 operating
system. The hardware is not rated for hazardous areas and must be installed in a nonhazardous area, typically a control room. Note: this full TT4000 version is required for the
engine performance map option.
TT4000S is a reduced version of the product specifically designed for the onskid
interface. It is installed in a special industrial grade PC that is approved for use in both
NEC Division 2 and CENELEC/ATEX Zone 2 areas. It runs on the embedded Windows
XP operating system. Due to the environment, it uses no moving media such as disk
drives, so data storage is limited. It displays data but without the graphics features of the
full TT4000 version.
9.5.1 TT4000 Display Screens
A menu bar at the left of each screen allows navigation to any other screen. A status bar
at the top of every screen displays up to four alarm conditions. Standard display screens
include:
• Operation Summary (complete package data, Figure 15)
• Generator Summary (generator operating data)
• Temperature Summary (all monitored temperature values)
• Vibration Summary (all monitored vibration values)
• Alarm Summary
• Discrete Event Log
• Strip Chart Display (real time data, Figure 16)
• Historical Data Display (strip chart format)
• Program Constants
Optional Display Screens:
• Gas Turbine Performance
Customized screens can be provided to display other product specific information.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
34
Page 36

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 15. Typical TT4000 Operation Summary Display Screen
Figure 16. Typical TT4000 Strip Chart Display
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
35
Page 37

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 17. Typical TT4000S Engine Summary Screen
Figure 18. Typical TT4000S Generator Summary Screen
9.5.2 TT4000S Display Screens
The TT4000S displays a comparable set of screens to the full TT4000 except that the
data are in numerical form and graphics are limited (Figures 17 and 18).
9.5.3 TT4000 Data Collection and Display
The Discrete Event Log records changes in status for all defined discrete inputs,
including operator commands, alarms and shutdown annunciations, and key sequencing
and status signals. Up to 5000 events are stored and can be viewed and sorted by
heading.
Analog Data are collected and saved to disk. The standard data files are:
Hourly Log - data are read at hourly intervals for 2 years. Each year’s data are stored in
a separate file. Data is recorded whether or not the equipment is operating.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
36
Page 38

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Minute Log - data are read and stored at one-minute intervals for the previous 62 days,
one file for each day.
10 Second Log - data are read at 10-second intervals for the previous 31 days, one file
for each day.
Trigger Log - data are read at one-second intervals for 6 minutes before a “trigger” event
that is defined in the software. The standard trigger is a shutdown. Six minutes before the
trigger of data are written to a file. Up to 50 trigger logs files can be stored.
9.5.4 TT4000 Display Language
In addition to English, dual language screens are available with English and Spanish
(Latin America), Portuguese (Brazil), French, German or Chinese (simplified). Other
languages can be provided as custom features.
9.5.5 TT4000 Operating Modes
There are two operating modes for the TT4000 software: Design Time and Run Time.
Design Time is used to create or modify a project’s working files. Run Time uses those
files in the normal equipment operation.
9.5.6 Supervisory Control Interfaces
The Turbotronic 4 control system can transmit data to, and receive control instructions
from, a supervisory control system. All analog data and the status of all discrete values
are available for transmittal. Interface modules mount in the controller rack and connect
through the rack’s backplane. Available connections are:
• ControlLogix 1.5
• Ethernet
• Data Highway Plus
• Modbus
9.5.7 System Programmability
The Turbotronic 4 system is fully programmable in the field. Programming requires a
licensed copy of Rockwell Automation’s RSLogix 5000 software installed on a suitable
computer with the corresponding interface card installed. Solar offers two standard
options:
Software, instruction manual, interface card and connecting cable.
Fully configured portable computer with the software, instruction manual, interface card and
connecting cable
9.5.8 Engineering Units
The following engineering unit options are available for the screen displays:
Pressure
Temperature
Metric 1 Metric 2 Metric 3 English
kPa bar kg/cm
°C °C °C °F
3
psig
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
37
Page 39

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 7. Turbotronic 4 Control System Specifications
Control System Components
Control Processor Allen-Bradley ControlLogix controller
Input/Output Modules Allen-Bradley Flex I/O modules
Generator Control
Vibration Monitoring System Bently Nevada 1701 FieldMonitor
Internal Control System Network ControlNet 1.5
Human Machine Interface (HMI) Solar’s TT4000 Display & Monitoring System
Fire & Gas Monitoring System (Enclosed
Packages)
Temperature & Vibration Monitoring
Gas Turbine Refer to Section 3
Gearbox Refer to Section 4
Generator Refer to Section 5
Offskid Control Console Dimensions
One-Bay Control Console
Height 2286 mm (90 in.)
Width 914 mm (36 in.)
Depth 800 mm (31.5 in.)
Approximate Weight 570 kg (1250 lb)
Two-Bay Control Console
Height 2286 mm (90 in.)
Width 1448 mm (57 in.)
Depth 800 mm (31.5 in.)
Approximate Weight 680 kg (1500 lb)
Supervisory Interface Modules
ControlNet 1.5
Cables RG-6U Coaxial
Maximum Cable Length 1000 m (3300 ft)
Transmission Protocol Common Industrial Protocol (CIP)
Transmission Speed 5 Mbps
Ethernet
Cables 10BaseT
Network Length 100 m (330 ft) To Nearest Hub
Transmission Protocol CIP Protocol with TCP/IP
Transmission Speed 10 Mbps
Data Highway Plus
Cables DH+ Twisted Pair
Maximum Cable Length 3000 m (10,000 ft)
Transmission Protocol CIP or DF1 Protocol
Transmission Speed 57.6 bps
Modbus
Cables RS232C, RS422, or RS485
Cable Length
Transmission Protocol Subset of Modbus RTU Protocol
Allen-Bradley/Basler Electric Combination
Generator Control Module
Det-Tronics Eagle Quantum Premier System
RS232C: 15 m (50 ft)
RS422 and RS485: 1200 m (4000 ft)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
38
Page 40

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Package End Devices
Transmitters 4-20 mA
Switches 0-24VDC
Thermocouples Type N
Resistance Temperature Devices (RTDs) 100 ohm Platinum
Proximiters 3300XL
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 9-56 Fusion Welding
ES 1593
ES 2231
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1
and Division 2
Standards and Practices for The Design and Installation of Cable Channels and TC
Rated Cables Installed In Class 1, Division 2 Hazardous Areas
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
39
Page 41

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
10 Generator Control and Monitoring
10.1 General Description
For generator control and monitoring, the Turbotronic 4 control system incorporates a
Rockwell Automation/Allen-Bradley combination generator control module (CGCM). The
CGCM provides generator control, protection, and monitoring. Three excitation control
modes are available:
• Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) - A constant generator output voltage is
maintained
• Power factor (PF) control - A constant power factor is maintained when operating
in parallel with a large power source
• Reactive power control - A constant reactive load is maintained when operating
in parallel with a large power source
The following excitation control features are available:
• Under frequency limiting
• Over and under excitation limiting
• Reactive droop compensation
• Cross-current compensation
• Line-drop compensation
Protection features for the driver and driven equipment include:
• Field current limit
• Generator overcurrent
• Generator overvoltage
• Generator undervoltage
• Loss of excitation current
• Loss of operating power
• Loss of sensing
• Over excitation voltage
• Overfrequency
• Underfrequency
• Phase rotation error
• Reverse power
• Reverse volt amp reactive (VAR)
• Exciter (rotating) diode monitor
The protection features provided typically do not meet the requirements of power utility
companies for the general protection of power distribution systems. This can only be
done through the use of appropriately certified protective relay components with settings
approved by qualified personnel based on a comprehensive analysis of the complete
system.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
40
Page 42

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
10.2 Generator Control
10.2.1 Functional Description
The Turbotronic 4 control system working in conjunction with the generator’s excitation
system provides control, monitoring, and protection of the generator and its output. The
key components are:
• Permanent magnet generator (PMG)
• Rotating armature-type AC exciter
• Full-wave rectifier assembly
• CGCM
Figure 19 provides a simplified layout of these components. The exciter armature is
mounted on the main generator rotor and generates an AC voltage as it revolves in the
magnetic flux produced by the stationary field. The stationary field is wound on salient
poles supported by the stator core or frame. The PMG consists of permanent magnets on
the generator rotor and a stationary armature, also supported by the generator frame.
The rotating rectifier assembly rectifies the exciter armature AC output to DC. In turn, the
DC power is applied to the main generator rotating field windings. The complete exciter is
enclosed and protected by a removable cover. When the rotor operates at synchronous
speed, the PMG provides power to the CGCM. The CGCM provides the appropriate
exciter field current to control the exciter armature output, which is rectified to provide DC
power to the main generator rotating field winding.
GENERATOR
GENERATOR CIRCUIT
BREAKER
BUS
GENERATOR
ARMATURE
(Stationary)
GENERATOR
FIELD
RECTIFIER
ASSEMBLY
EXCITER
ARMATURE
EXCITER FIELD
(Stationary)
PERMANT
MAGNET
GENERATOR
ROTATING PORTION
GENERATOR
POTENTIAL
TRANSFORMERS
EXCITATION POWER
EXCITATION OUTPUT
CONTROLNETTo Turbotronic 4 Control Processor
COMBINED GENERATOR CONTROL MODULE
GENERATOR
CURRENT
TRANSFORMERS
CROSS CURRENT
COMPENSATION
TRANSFORMER
LOAD SHARE LINES
(To other Combined Generator Control
Module or Load Share Module)
POTENTIAL
TRANSFORMERS
BUS
Figure 19. Typical Generator, Exciter, and Generator Control Module Arrangement
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
41
Page 43

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
During initial turbine generator acceleration, the excitation power is switched off. At
approximately 80% speed, the PMG output is connected to the excitation power contacts
and voltage begins to build. The CGCM then provides controlled exciter field current at a
level to maintain the generator terminal voltage at a predetermined value established by
the operator. A potential transformer (usually supplied with the switchgear) provides a
voltage level signal to the CGCM. By sensing the generator output voltage and controlling
the power to the brushless exciter, the CGCM automatically maintains the generator
output voltage at a constant level at all load conditions.
Since the PMG output power is independent of the main generator line voltage and
current levels, there is no need for additional auxiliary equipment to provide power to the
CGCM during transient conditions. The PMG provides sufficient generator terminal
voltage during conditions of high generator line current to allow for selective tripping
during a short-circuit condition. Current, potential, and cross current transformers
required for input to the CGCM are not included. A cross-current compensating circuit is
included to accommodate reactive load sharing between multiple turbine generators
operating in parallel. Instrumentation transformers are usually supplied with the
switchgear.
10.2.2 Control Modes
In addition to voltage regulation, the following generator control modes are also available:
• Speed/Load Control
− Isochronous (Isoch) Speed Control
− Droop Speed Control
− Kilowatt Import Control
• Reactive Compensation
− Droop Voltage Control
• Power Factor Control
• Reactive Load Volt Amp Reactive Control
− Differential Cross Current Control
10.2.3 Breaker Synchronization
The control system provides automatic generator breaker synchronization control when
paralleling to the bus. Automatic synchronization can be initiated by the operator or by a
remote signal received from a supervisory control system. If manual synchronization is
required, an optional generator metering panel must be included. Synchronization control
is provided by the CGCM.
10.2.4 Auto Start and Synchronizing System
When the generator set is in standby mode, the control system will automatically start the
generator set, accelerate the engine to loading speed, and synchronize the generator
breaker to the bus upon receipt of a supervisory command. If the control system detects
a hot bus, it will synchronize the generator to the bus and close the breaker. If the control
system detects a dead bus, it will close the generator breaker without synchronization.
10.2.5 Kilowatt Import Control
The kW import control system controls the real load (kW) when the generator set is in
parallel with a large power source. When kW import control is enabled, the control
system monitors the load imported from the utility and adjusts the turbine generator set
fuel flow to maintain a preset amount of imported power. When it is not desirable to
export power to the utility, kW import control is normally selected. While in parallel with a
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
42
Page 44

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
large power source, protection against excessive kW load is provided by turbine T5
temperature control.
10.2.6 Generator Metering Panel (Optional)
Mounted on the front of an optional control console, the generator metering panel (Figure
20) provides meters to monitor generator output and switches to manually adjust
generator voltage and to synchronize the generator breaker to the bus. The metering
panel typically includes the following analog meters, lights, and switches:
• AC ammeter
• Frequency meter
• KW/kVAr meter
• AC voltmeter
• Power factor meter
• Synchroscope
• Exciter field ammeter
• Exciter field voltmeter
• Manual synchronizing lights
• Manual synchronizing switch
• Generator breaker Open/Close switch
• Generator breaker Open/Close status lights
• Automatic synchronization switch (optional)
• Automatic synchronization fail light (optional)
• Generator line-to-line voltmeter select switch
• Kilowatt (kW) and kilovolt amp reactive (kVAr) power meter select switch
• Generator phase current ammeter select switch
All data indicated by the metering panel is also indicated on the video display terminal.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
43
Page 45

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 20. Typical Generator Metering Panel
10.2.7 Generator Vibration and Temperature Monitoring
X and Y proximity probes are mounted in the generator exciter and driven-end bearings.
These probes are monitored continuously by the control system. Alarm and shutdown
levels are set to protect the generator from excessive vibration levels
Resistance temperature devices (RTDs) are mounted in the generator exciter and driven
end bearings. Two RTDs are also imbedded in each of the three stator-winding phases.
One RTD is connected to the control system and the other is provided as a spare. Alarm
and shutdown levels are set to protect the generator from excessive temperature levels.
10.2.8 Redundant Combined Generator Control Module (Optional)
A second CGCM can be provided to function as a hot backup to the primary CGCM. The
system is configured for automatic transfer to the second CGCM in the event the primary
CGCM fails. All control, protection, and monitoring features of the primary CGCM are
duplicated in the second CGCM. Control can also be manually transferred between the
CGCMs.
Table 8. Generator Specifications
Voltage Regulation
Voltage Regulator Solid State
Phase Sensing
Voltage Adjustment Range ±10% With a Voltage Resolution of 0.1%
Steady-State Voltage Regulation 0.25% From No Load to Rated kVA
Reactive Load Sharing Within 5% of Nameplate Rating
Cross-Current Compensation Optional
Voltage Drift See Note (a)
Generator Breaker Synchronization
Generator Voltage
Generator Phase
Generator Frequency
Generator Ready to Load
Notes:
(a) The change in voltage will not exceed 1.0% over a 30-minute period when the generator is
operating at rated voltage, power factor of 0.8 to 1.0, and with a constant load between no
load and full rated load.
Three Phase (Standard)
Single Phase Sensing (Optional)
To Close Breaker, Generator Voltage Must be
Within ± 1.0 Percent of Bus Voltage
To Close Breaker, Generator Phase Must be Within
± 10 Degrees of Bus Phase
To Close Breaker, Generator Frequency Must Be
Within ± 0.01 Hz of bus frequency
Twenty seconds after generator set attains 90
percent speed
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
44
Page 46

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
11 Enclosure
11.1 General Description
A driver-only or complete package enclosure can be provided as required. The enclosure
housing (Figure 21) is a completely self-contained, weatherproof, insulated, and soundattenuated system. The enclosure is mounted on the package skid and supported by a
heavy-duty frame. The enclosure sides include removable panels and/or doors to allow
access to major components for inspection and maintenance and to permit removal of
components by forklift or overhead crane. The engine area is furnished with bi-fold type
doors to facilitate engine removal from either side of the package. All enclosure doors
include a three-point heavy-duty door locking mechanism, handles, hinges, latching
mechanism, internal lock override release, restraining device, and attaching hardware.
The enclosure panels are treated with fiberglass material for sound attenuation and
thermal insulation. Weather stripping is installed between all panels for sealing and sound
attenuation. The enclosure is normally factory assembled on the package skid prior to
shipment, but can be drop shipped pre-assembled for site installation or shipped as a kit
for site assembly and installation. The following standard features are included with the
basic enclosure:
• Inlet and exhaust ventilation silencers
• Single fan ventilation system
• Pressurization system
• AC lighting
• Equipment handling system
• Stainless steel door hardware
Figure 21. Typical Complete Package Enclosure
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
45
Page 47

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
11.2 Standard Features
11.2.1 Inlet and Exhaust Ventilation Silencers
The enclosure ventilation openings are equipped with silencers with weather louvers.
11.2.2 Single-Fan Ventilation
A single high efficiency motor-driven fan provides enclosure ventilation. The ventilation
fan provides airflow to ensure the enclosure internal air temperature remains within
acceptable limits. Fan size can vary depending on the ventilation system filtration
configuration. Fan motor wiring is terminated at the motor junction box. Enclosure
ventilation openings are provided to facilitate airflow circulation. For additional ventilation
or certification requirements, a dual fan ventilation system may be selected as an option.
11.2.3 Enclosure High Temperature Alarm
A heat sensor, completely separate from the fire system thermal detectors, is mounted in
the enclosure. The sensor is set to activate an alarm if enclosure temperature is
abnormally high.
11.2.4 Pressurization System
The ventilation airflow through the enclosure can be controlled to provide either positive
or negative pressure relative to the outside pressure. Hazardous area classifications and
the applicable codes and regulations will determine the pressurization requirements for
specific projects.
11.2.5 Lighting
Fluorescent lighting is provided to illuminate the enclosure interior. Lighting on/off
switches are provided on the enclosure exterior.
11.2.6 Sound Attenuation
The sound-attenuated enclosure is intended for use with suitable gas turbine air inlet and
exhaust silencing systems in environments where low noise levels are required.
Enclosure ventilation openings are equipped with silencers to achieve maximum sound
attenuation. The actual achievable noise reduction is a function of the noise source,
installation considerations, other equipment in close proximity, and the acoustical
characteristics of existing buildings and barriers.
The intent of the enclosure design is to comply with U.S. Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA) standards for eight-hour employee exposure. Transmission loss
of the panels in decibels is available upon request. Further information is available in
Solar’s publication SPNP, “Noise Prediction Guidelines for Industrial Gas Turbines.”
11.3 Optional Features
11.3.1 Enclosure Configuration
An enclosure can be selected to house both the gas turbine and generator or only the
gas turbine.
11.3.2 Dual Fan Ventilation
The enclosure can be ventilated with a dual AC motor-driven fan system. The fan motor
wiring is terminated at the motor junction box. Openings are provided to ensure adequate
airflow is circulated through the enclosure. For Conformité Européenne (CE) Mark
certification, the second or backup ventilation fan is mandatory and must be powered by
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
46
Page 48

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
an AC source independent from the package power system. This independent power
source is not provided by Solar.
11.3.3 Dust Protection System
The enclosure ventilation inlets are equipped with a single-stage, disposable, barrier-type
filter unit equipped with a differential pressure alarm switch. The ventilation exhaust
openings are equipped with back-draft dampers to prevent the entry of dust when the unit
is not running.
11.3.4 Dust and Moisture Protection System
The enclosure ventilation inlet can be equipped with a two-stage filter unit consisting of a
first-stage vane separator and a second-stage filter. The moisture eliminator section is
hinged for filter access. The unit is equipped with a differential pressure alarm switch and
gauge. The ventilation exhaust opening is equipped with back-draft dampers to prevent
the entry of dust and water when the unit is not running.
11.3.5 Standby Lighting
Standby lights provide emergency, automatic, and backup lighting inside the enclosure in
the event of an AC power loss. Power is supplied from the package battery system. To
avoid battery system drainage, the circuitry includes a shutoff timer.
11.3.6 Marinization
Increased stiffening of enclosure structural components and additional flexibility of
enclosure and flexible joints between the gas turbine and enclosure can be provided.
11.3.7 Door Open Alarm
The enclosure doors can be equipped with a door position switch that will initiate an
alarm when any enclosure door is not closed securely.
11.3.8 Fire and Gas System
Enclosed packages must include a fire and gas control system. The typical fire and gas
system shown in Figure 22 provides gas monitoring, fire detection, and extinguishing
agent release using an advanced distributed architecture to monitor gas, heat, and
optical flame detectors. The system communicates with the Turbotronic 4 control system
to initiate a shutdown if a fire or a high gas level is detected. On the package exterior,
indicator lights, strobe lights, and an alarm horn provide system status. A keyswitch is
provided to inhibit the system and a push button switch is provided to manually release
the fire-extinguishing agent.
The primary fire detection system uses multi-spectrum IR (MIR) flame detectors. The
system includes an automatic optical integrity feature to provide a continuous check of
the optical surfaces, detector sensitivity, electronic circuitry of the detector-controller
system, and automatic fault identification with digital display of system status in numerical
code. The secondary detection system consists of rate-compensated thermal detectors.
The two detection systems act independently in detecting and reporting a fire. The
number of detectors may vary depending on the enclosure configuration.
The fire system control panel provides system supervision (for open circuit, ground fault,
or loss of integrity), initiates alarm and release of fire suppression agent, and visual
display of system status. The suppression system agent release is activated
automatically with release solenoids located on the fire suppression skid. The optional
or water mist suppression system can also be activated manually by switches
CO
2
mounted on the gas turbine enclosure or at the suppression skid. If a fire is detected, the
fire detectors transmit an electrical signal to the fire system control panel to activate the
fire alarm and suppression system.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
47
Page 49

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
The enclosure is also equipped with two gas detectors: one at the gas turbine enclosure
ventilation air inlet and the other at the ventilation exhaust to provide continuous
monitoring of combustible gases. The detectors consist of IR hydrocarbon sensors that
provide input to the logical operating network (LON) module. The gas turbine start signal
is interlocked with the combustible gas monitoring system to ensure the atmosphere is
safe prior to initiating a turbine engine start. An alarm is initiated if the gas monitor fails.
To / From Customer
Supervisory System
ControlNet
Turbotronic 4
Control
Processor
Turbotronic 4
Back-up
Shutdown
System
EQP
DCIO
DCIO
Figure 22. Typical Fire and Gas System
Turbomachinery Package
MIR MIR
IR IR
STROBES / HORN
OPERATOR PANEL
AUTO
INHIBIT
DISCHARGED
AUTO / INHIBIT
MANUAL RELEASE
LON
TD TD
TDTD
SUPPRESSION
MIR = Multi-spectrum IR Flame Detector
TD = Thermal Detector
IR = IR Gas Detector
LON = Local Operating Network
MIRMIR
FIRE
SYSTEM
11.3.9 CO
Fire Suppression System
2
The enclosure can be equipped with a CO
fire suppression system consisting of a
2
primary total flooding distribution system and a secondary metered distribution system to
extend the design concentration of 37% CO
for 20 minutes.
2
On fire detection by the optional fire and gas detection system, the detectors transmit an
electrical signal via the fire control panel to activate the fire suppression system release
solenoids located in the CO
this signal, the solenoid actuated control heads activate the CO
fire suppression cylinder cabinets (Figure 23). On receipt of
2
cylinders, releasing CO
2
into the enclosure. CO2 pressure actuates the pressure trip operated dampers that close
all vent openings. CO
release control heads are also provided with manual release
2
levers.
11.3.10 Water Mist Fire Suppression System
The enclosure can be equipped with a water mist (fine water spray) fire suppression
system consisting of a high-pressure distribution system to provide approximately 10
minutes continuous water discharge. The typical water mist fire suppression cylinder
cabinet (Figure 24) consists of two high-pressure nitrogen cylinders used as a propellant
and five water bottles.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
48
2
Page 50

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
On detection of a fire by the optional fire and gas detection system, the fire control panel
activates the fire suppression system release solenoids located on the water mist
suppression skid. On receipt of this signal, the solenoid actuated control heads activate
the discharge valves on the water cylinders, releasing a water mist into the enclosure. A
pressure switch in the water mist discharge piping transmits an electrical signal to the fire
control panel to activate a release solenoid to close pressure-operated dampers on all
vent openings. The water mist nitrogen actuator valve is also provided with a manual
release lever.
11.3.11 Fire Cylinder Cabinets
When installed outdoors, weatherproof fire cylinder cabinets are available to house the
extinguishing agent. The cabinets are equipped with service doors. The manual pull
levers are routed by cable to the exterior wall of the cabinet.
Figure 23. Typical CO
Fire Suppression Cylinders and Cabinets
2
Figure 24. Typical Water Mist Fire Suppression Cylinders and Cabinet
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
49
Page 51

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 9. Enclosure S pecifications
Enclosure
Optional Ventilation Fan Motor Voltage
Ratings
Primary Enclosure Lighting Voltage 220 VAC (50 Hz) or 110 VAC (60 Hz)
Standby Enclosure Lighting Voltage 120 VDC
Sound Pressure Level
Enclosure Roof Load 244 kg/m2 (50 lb/ft2)
Enclosure Wind Load 193 kph (120 mph)
Approximate Measurements
Height 4 m (13 ft), Does Not Include Ventilation Ducting
Width
Length 15 m (49 ft)
Approximate Weights
Gas Turbine Enclosure 8618 kg (19,000 lb)
Generator Enclosure 5670 kg (12,500 lb)
Fire Suppression System Compliance
CO2 Fire Suppression System
Water Mist Fire Suppression System
Water Mist Fire Suppression System
Minimum Operating Temperature 4°C (40°F), Optional Heater Available
CO2 Fire Cylinder Cabinets
Fire Cylinder Cabinet, Main
Height 198 cm (78 in.)
Width 214 cm (84 in.)
Depth 46 cm (18 in.)
Approximate Cabinet Weight 429 kg (946 lb), Without Cylinders
Approximate Cylinder Weight 45 kg (100 lb)
Fire Cylinder Cabinet, Extended Release
Height 198 cm (78 in.)
Width 122 cm (48 in.)
Depth 46 cm (18 in.)
Approximate Cabinet Weight 269 kg (592 lb), Without Cylinders
Approximate Cylinder Weight 45 kg (100 lb)
Water Mist Fire Cylinder Cabinet
Fire Cylinder Cabinet
Height 226 cm (89 in.)
Width 165 cm (65 in.)
Depth 91 cm (36 in.)
Approximate Cabinet Weight 1297 kg (2859 lb), Without Cylinders
Approximate Cylinder Weight 1697 kg (3741 lb)
Construction Materials
Enclosure Housing Carbon Steel
Enclosure Door Hardware 316L Stainless Steel
Fire Cylinder Cabinets
Dust and Moisture Protection System
380 VAC, 400 VAC, and 415 VAC (50 Hz)
460 VAC (60 Hz)
See Note (a)
7 m (23 ft), With Enclosure Doors Open and Engine
Removal Hoist Attached
U.S. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 12
United States Coast Guard (USCG) CFR 46
U.S. NFPA Code 750
USCG CFR 46
Carbon Steel
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
50
Page 52

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 1593
ES 1762
Solar’s Applicable Product Information Letters
PIL 054 OSHA Noise Requirements
PIL 058 Package Sound Levels
PIL 150 Fire and Gas Detection and Control System
Notes:
(a) The estimated A-weighted sound pressure level is 85 dBA at a distance of 1 m (3 ft) from the
enclosure wall and a height of 1.5 m (5 ft). This value is based on an average of multiple
readings taken around the perimeter of the package. This level applies only to the enclosed
equipment and is exclusive of sound generated by piping, unenclosed driven equipment (if
applicable), other equipment, reflected sound, or contributing site conditions. Sound levels at
a specific site will depend on existing walls, barriers, equipment in close proximity, multiple
units, and other installation considerations.
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1
and Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems for Gas Turbine Packages Installed
In Hazardous Areas (CENELEC/IEC Standards – European ATEX Directive
94/9/EC)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
51
Page 53

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
12 Air Inlet System
12.1 General Description
The gas turbine combustion process requires a steady and consistent flow of clean air.
Proper gas turbine inlet air filtration is critical to gas turbine life. Careful consideration
should be given to selecting the appropriate air filtration system. Solar offers several air
filtration systems that conform to a broad range of operating requirements. For
unenclosed packages, the turbine air inlet can be mounted on the right-hand or left-hand
side of the package in a vertical or 45-degree angle to vertical position. For enclosed
packages, the air inlet must be in the vertical position. Figure 25 shows typical Titan 250
air inlet and exhaust systems.
Figure 25. Typical Titan 250 Turbine Air Inlet and Exhaust Systems
12.1.1 Prefilter and Barrier Inlet Air Filter
The prefilter and barrier inlet air filter system is suitable for moderate environments. This
system features vertical moisture eliminators, direct-contact prefilter elements, and high
efficiency barrier filter elements. Access doors are provided in the filter housing for
servicing. A weather hood and insect screens are available as options.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
52
Page 54

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
12.1.2 Insect Screens
Optional insect screens can be installed on each side of the air inlet filters (except for
self-cleaning filters). This option is used with the air filter when large numbers of insects
are present. The insect screen design reduces the velocity of the air stream sufficiently to
allow most insects to fly away. Use of the screen helps to avoid clogging and premature
filter replacement. During cold weather operation, the insect screens should be removed
and stored due to a potential for ice or snow to clog the screens.
12.1.3 Self-Cleaning Barrier Type Air Filter (Updraft Type)
The self-cleaning barrier type air filter system is suitable for extreme environments where
dust loading or cold-weather operation is a concern. This system requires a suitable
supply of cleaning air. Cleaning air can be provided by the customer or supplied using
turbine compressor discharge pressure (Pcd) bleed air. If bleed air is used, an air heat
exchanger is provided for mounting in the air inlet ducting between the air inlet filter and
the turbine air inlet. Access to change filter elements from below must be provided
Standard features include:
• Support leg kit
• Dual differential pressure alarm and shutdown switch
• Filter elements
• Differential pressure gauge
• Electrical connections prewired to a common junction box
12.1.4 Marine-Type
The marine-type air filter system is suitable for use in coastal, offshore, and tropical
locations. This system provides high efficiency removal of salt, water, and particulates.
This system consists of:
• First stage marine vane separator/moisture eliminator
• Second stage prefilter
• Third stage high efficiency bag filters
• Fourth stage marine vane separator/moisture eliminator
Access doors are provided in the first stage marine vane separator/moisture eliminator
for filter removal. Standard features include:
• High performance drainage system
• Transition outlet flange
• Lifting lugs
• Instrumentation panel
• Differential pressure gauge
• Electrical connections prewired to a common junction box
• High differential pressure alarm and shutdown switches
12.1.5 Air Inlet Silencer
Optional air inlet silencers can be incorporated into the air inlet ducting to reduce noise
levels. Typical installations include one air inlet silencer..
12.1.6 Air Inlet Ducting and Support
An optional support structure and ducting can be provided for offskid support of the air
inlet filter and silencer assembly. Attaching hardware and a tube of sealant are provided
for one flange per duct.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
53
Page 55

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 10. Air Inlet System Specifications
Air Inlet System
Pressure Drop Less Than 102 mm (4 in.) H2O with a Clean Air Filter
Ducting Loads Should Not Be Applied In Any Direction
Prefilter and Barrier Inlet Air Filter
Pressure Drop
Clean 44 mm (1.75 in.) water
Fouled 127 mm (5 in.) water
Self-Cleaning Barrier Type Air Filter
Fluid Clean-Dry Air
Air Quality
Minimum/Maximum Regulated Pressure Range 552 to 758 kPag (80 to 100 psig)
Intermittent Flow Rate 0.5 nm3/min (18 scfm)
Pressure Drop (Clean) 25 mm (1.0 in.) water
Marine-Type Air Filter
Pressure Drop (Clean) 53 mm (2.1 in.) water
Construction Materials
Prefilter/Barrier
Insect Screen
Self Cleaning Barriers
Marine-Type Air Filter 316L Stainless Steel (Standard)
Air Inlet Silencer
Air Inlet Ducting
Air Inlet Support Structure Carbon Steel (Standard)
Applicable Product Information Letters
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 054 OSHA Noise Requirements
Solar’s Product Information Letter PIL 178 Salt Ingress Protection for Gas Turbines
Notes:
(a) The particle size in the air stream should not exceed 10μm. Since it is impractical to remove
100% of all particles larger than 10μm, this is defined as ß10 > 100, or 99% efficient. Oil or
hydrocarbon content should not exceed 1 ppm. The dew point at line pressure shall be at
least 6°C (10°F) below the minimum temperature to which any part of the air system is
exposed or between 1.6°C and 60°C (35°F and 140°F). Air should be free of all corrosive
contaminants, hazardous gases, flammables, and toxics.
See Note (a)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel (Standard)
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
54
Page 56

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
13 Exhaust System
13.1 General Description
The exhaust system (Figure 25) typically consists of all components installed
downstream of the engine exhaust bellows expansion joint, including silencers and
ducting, that are necessary to ensure a smooth flow of exhaust gas from the engine. The
exhaust duct system must be terminated in a manner that precludes recirculation of
exhaust products through the engine air inlet or oil cooler. Exhaust considerations include
the relative height of the exhaust duct above the air inlet, building roof design, direction of
prevailing winds, and the proximity of adjacent structures. The importance of having an
exhaust system properly designed cannot be overemphasized. A poorly designed
exhaust system can cause loss of power capability and impose severe mechanical
strains on the gas turbine. Exhaust systems should be designed to meet the following
requirements:
• Where two or more units exhaust into a common header, such as used for heat
recovery equipment, provisions must be made to prevent hot gas from flowing
into the non-operating unit (common exhaust ducting is not recommended).
• Final termination of ducting must not allow exhaust gas to be drawn into the gas
turbine inlet.
• Capability to purge the complete exhaust system prior to gas turbine lightoff. For
short simple exhaust systems, purging should be designed to accomplish three
air volume changes. For large complex exhaust systems, purging should be
designed to accomplish five air volume changes either through gas turbine
cranking or supplementary exhaust blowers.
When exhaust silencing is required, provisions must be made to adequately mount and
support the equipment and limit the exhaust silencer pressure loss.
13.1.1 Exhaust Silencer
Solar can provide a silencer with support structure and ducting suitable for connection to
the radial exhaust of the Titan 250 generator set. Brackets are available for mounting the
silencer in a vertical or horizontal position.
13.2 Turbine Exhaust Heat Recovery System
High thermal efficiencies can be obtained by using the gas turbine exhaust heat energy.
There are several methods for using the exhaust heat and attaining greater than 80% fuel
utilization. The methods used and the efficiencies achieved are primarily dependent on
the type of application. The most common uses are:
1. Producing steam with a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG) or heating a
process fluid with a heat recovery fluid heater.
2. Using the gas turbine exhaust as a source of preheated combustion air in a
boiler or furnace (the gas turbine exhaust contains 15-18% oxygen).
3. Using the gas turbine exhaust directly for a drying or heating process in which
high temperature air is necessary. A mixture of gas turbine exhaust and fresh air
can be used in a reduced air temperature process. An air-to-air heat exchanger
is required when the process involves any products in the human food chain.
Solar can design and provide a complete exhaust heat recovery system to meet specific
application requirements. The system must be designed to minimize the backpressure
imposed on the gas turbine exhaust and provide a smooth flow transition into the exhaust
heat recovery device.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
55
Page 57

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 11. Exhaust System Specifications
Exhaust System
Temperature Class T2
Total System Pressure Loss Should Not Exceed 152 mm (6 In.) of Water
Exhaust Temperature 465°C (865°F)
Nominal System Back Pressure
Construction Materials
Exhaust Silencers
Exhaust Ducting
Exhaust Bellows Expansion Joint
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 1632 Exhaust Silencers for Solar Turbine Engines
Notes:
(a) Higher backpressures can be accommodated. The exhaust backpressure should be less
than 25.4 mm (1 in.) water column during gas turbine starting.
203 mm (8 in.) of water, See Note (a)
Carbon Steel
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
Carbon Steel
316L Stainless Steel (Optional)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
56
Page 58

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
14 Accessory Equipment
14.1 DC Power Supply and Battery Charger System
This system provides 120 VDC power for the following devices:
• The electric actuators that drive the fuel valves, bleed valve and variable guide
vanes.
• The 120 to 24 volt DC-to-DC converter in the control system that provides the 24
VDC control power.
• The DC backup lube oil pump and DC back-up engine turning gear motors.
• The DC backup lube oil scavenging pump motor (when applicable for offshore
installations).
The system includes a 3-phase charger (Figure 26) and a set of batteries configured for
120VDC output, mounted on a freestanding rack. The batteries are sized to provide
sufficient power to allow the package to shut down and cool down in an orderly manner in
the event of loss of external AC power. The system is designed for indoor installation in a
nonhazardous area. The batteries are shipped fully charged and ready for use. Two
battery types are available:
• Valve-regulated, sealed gas-recombination, lead-acid
• Nickel Cadmium
Figure 26. Typical Battery Charger
14.2 Turbine Cleaning System
The optional turbine compressor cleaning system (Figure 27) facilitates periodic cleaning
of the turbine compressor. The cleaning system is designed for use in salt-laden or dusty
environments or where compressor contamination from hydrocarbon vapors is possible.
The turbine compressor cleaning system is composed of the following systems:
• On-crank cleaning system
• On-line cleaning system
Both cleaning systems are independent of each other and include a separate distribution
manifold with pressure atomizing spray nozzles in the engine air inlet collector, onskid
piping, strainer, and solenoid shutoff valves to deliver water or approved cleaning fluid to
the manifold. Both systems require an external source of clean-filtered air to pressurize
the cleaning solutions.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
57
Page 59

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Figure 27. Turbine Cleaning System
14.2.1 On-Crank Cleaning System
The on-crank cleaning system only operates at gas turbine cranking speed with the fuel
system and ignition system deactivated. The gas turbine cranking and cleaning solution
activation can be initiated from the control console or turbine control junction box.
14.2.2 On-Line Cleaning System
The on-line cleaning system only operates when the gas turbine speed is between 90
and 100% gas producer speed and with or without load. Cleaning solution activation can
be initiated from the control console or turbine control junction box. This system is
intended to supplement the on-crank system by increasing the time intervals between
periodic on-crank cleaning.
14.2.3 Turbine Cleaning Cart
A portable offskid cleaning tank (Figure 28) can be provided to supply cleaning fluid to
the skid edge cleaning system connection. The cleaning tank can be used to mix, hold,
and pressurize the turbine cleaning solution. The tank comes with wheels that are
removable for stationary installation.
Figure 28. Turbine Cleaning Cart
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
58
Page 60

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
14.3 Package Lifting Kit
A package lifting kit can be shipped separately that contains slings, spreader bars, and
assorted hardware to facilitate separate lifting of the driver and driven equipment
modules with or without an export crate.
14.4 Engine Removal Equipment
The Titan 250 package is equipped with an innovative system to remove the gas turbine
as a complete entity or in sections (Figure 29). The compressor, combustor, gas
producer turbine and the power turbine can be separated axially using fixtures that attach
to longitudinal rails (Figure 30). The rails are an integral part of the package frame. When
service is scheduled, the fixtures are mounted on the rails and attached to the turbine. A
screw-thread mechanism is then used to separate the sections. This arrangement allows
easy access to the different sections of the engine for in-situ service. It also allows the
individual sections, or the entire engine, to be removed laterally using a separate external
rail-based handling system.
Figure 29. Separation of Engine Sections
Figure 30. Rails and Fixtures for Axial Separation of Engine Sections
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
59
Page 61

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Table 12. Accessory Equipment Specifications
120 VDC Battery and Charger System
Charger Type Floor Mount
Supply Voltage
Operating Temperature
Approximate Measurements (Charger)
Height 1.21 m (47.5 in.)
Width 0.98 m (38.5 in.)
Depth 0.65 m (25.5 in.)
Approximate Measurements (Lead Acid Batteries)
Height 1.78 m (5.8 ft)
Width 3.05 m (10.0 ft)
Depth 0.76 m (2.5 ft)
Approximate Measurements (NiCd Batteries)
Height 1.65 m (5.4 ft)
Width 4.83 m (15.8 ft)
Depth 1.02 m (3.3 ft)
Turbine Cleaning System
Water/Solvent Supply Pressure 85 to 100 psig (586 to 689 kPag)
Water/Solvent Supply Min. Temperature Ambient (Except In Extreme Cold)
On-Line Water/Solvent Flow Rate 2.3 – 4.5 L/min (0.6 – 1.2 gpm)
On-Line Propulsion Air Flow Rate 0.026 nm3/min (0.98 SCFM)
Package On-Line Triple Stage Strainer 300/200/100 Micron
On-Crank Water/Solvent Flow Rate 9.1 – 12.9 L/min (2.4 – 3.4 gpm)
On-Crank Propulsion Air Flow Rate 0.080 nm3/min (3.0 SCFM)
Package On-Crank Triple Stage Strainer 300/200/100 Micron
External Air Supply Clean Filtered Air
Air Supply Pressure 586 to 690 kPag (85 to 100 psig)
Turbine Cleaning Cart
Capacity 98 L (26 gal)
Tank Discharge Strainer 100 Micron
External Air Supply Clean Filtered Air
Air Supply Pressure 586 to 690 kPag (85 to 100 psig)
Approximate Measurements
Height 102 cm (40.2 in.)
Width 55 cm (21.7 in.)
Length 121.6 cm (47.87 in.)
Approximate Weight 86 kg (190 lb)
Tank Material 316L Stainless Steel
Certification
Electrical Certifications
CSA LR 77954
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 9-62 Ingestive Cleaning Solar Gas Turbine Engines
ES 2416 DC Supply Systems
380, 400, or 415 VAC, 50 Hz, 3 phase
460 VAC 60 Hz, 3 phase
-10 to 50°C (14 to 122°F)
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
(ASME) or Pressure Equipment Directive (PED)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
60
Page 62

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
15 Marinization
15.1 General Description
The Titan 250 generator sets may be operated in offshore oil and gas applications.
Depending upon operating conditions and movement of the underlying support structure,
optional package modifications may be required. Solar turbomachinery packages operate
successfully on the following types of offshore installations:
• Fixed platform (FP)
• Tension leg platform (TLP)
• Compliant tower (CT)
• Spar platform (SP)
• Semi-submersible platform (SSP)
• Floating production systems (FPS)
• Floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO)
• Mini-tension leg platform (Mini-TLP)
Applications are evaluated based on the expected motion severity and the degree of
package mounting surface flexing. Solar offers the following package modifications to
achieve successful long-term operation.
15.1.1 Package Sub-base
As a standard, the Titan 250 package is suitable for three-point mounting. In severe
cases, a substructure may be required to provide additional package rigidity to protect
equipment and to maintain proper alignment of the driver and driven equipment.
15.1.2 Gimbals
Gimbals provide protection against G-forces generated by vessel pitch and roll
movements and against deflection, twisting, and thermal growth of the mounting deck.
Gimbals may be used for three-point package mounting.
15.1.3 Anti-Vibration Mounts
Anti-vibration mounts (AVMs) are used to isolate the mounting surface from packagegenerated vibrations. AVMs do not provide the same level of motion protection as
gimbals. AVMs may be used for three-point package mounting.
15.1.4 Internal Package Modifications
Moderate or severe package motion can potentially interfere with lube oil system
operation. To prevent interference, modifications may be made to the lube oil system to
ensure proper lube oil circulation.
15.1.5 Inclinometers
For moderate and severe duty applications, an inclinometer is furnished to provide alarm
annunciation and equipment shutdown inputs when maximum allowable angular
displacements are exceeded. Alarm levels are typically set 2 degrees below shutdown
levels.
15.1.6 Flexible Ducting
Flexible ducting can be provided for the turbine air inlet duct, turbine exhaust duct, and,
enclosure ventilation duct.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
61
Page 63

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
15.1.7 Certification
Certification is typically required to demonstrate offshore turbomachinery compliance with
applicable rules for a fixed or mobile offshore installation. Solar can provide the
necessary certification or assist the customer in obtaining certification. Involvement of
one of the following certifying authorities is usually required:
• Det Norske Veritas (DNV)
• Bureau Veritas (BV)
• Lloyd’s Register (LR)
• American Bureau of Shipping (ABS)
15.1.8 Deck Deflection Limits
The package supporting deck structure must have sufficient stiffness to maintain
alignment of the turbine and driven equipment under dynamic vessel motion. Table 13,
lists the maximum allowable deflections measured between the furthest mounting points.
With analysis, these limits may be extended through the use of gimbals or AVMs.
15.1.9 Angular Displacement and Acceleration
Table 15, Marinization Specifications, lists the maximum allowable angular displacement
and acceleration limits for marine applications. The Basic Duty category is met by the
standard package without any additional modification. Moderate Duty and Severe Duty
categories require modification.
15.1.10 Main and Auxiliary Service
The information provided in this section does not apply to equipment used in “Main and
Auxiliary Service”. If equipment is intended for this type of service, please contact Solar
Turbines Incorporated for guidance to ensure the correct application and certification
requirements are met.
Table 13. Marinization Specifications
Supporting Deck Deflection Limits
Hogging and Sagging 0.3833 mm/m (0.0046 in/ft)
Deck Twist 0.0198°/m (0.006°/ft)
Angular Displacement and Acceleration Limits
Maximum Permissible Angular Displacements
Dynamic:
Static:
Maximum Permissible Accelerations
Operating:
Survival:
Pitch / Period 2° / 13 sec 7.5° / 9 sec 10° / 9 sec 7.5° / 9 sec
Roll / Period 2° / 13 sec 7.5° / 13 sec 22.5° / 13 sec 10° / 13 sec
Trim 2° 5° 5° 5°
List 2° 5° 15° 5°
Basic Duty
± 0.1 g ± 0.5 g ± 1.0 g ± 1.0 g
± 0.5 g ± 1.0 g ± 1.5 g ± 1.5 g
Moderate
Duty
Severe Duty
Parallel Perpendicular
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
62
Page 64

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
16 Quality Assurance and Testing
16.1 Quality Assurance
Solar is an International Organization for Standards (ISO) 9000 company with ISO
9001:2000 and 9002 certification. Several Solar gas turbine models and manufacturing
processes have been "type" certified. In recognition of Solar’s commitment to quality,
Solar has received Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) II Class “A” certification and
the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. Solar has developed a comprehensive set
of specifications to address areas such as engineering requirements, manufacturing and
assembly standards, and test procedures and acceptance criteria.
Upon request, Solar will evaluate customer-required standards to assess Solar’s ability to
comply. Project inspection, testing, and quality assurance (QA) documentation, along
with customer or third-party involvement in the QA process, is defined in the inspection
and test plan (ITP). The ITP is the controlling quality assurance document for a project.
Since advance procurement is involved in Solar's production process, special inspection
and documentation milestones may be missed if these requirements are not defined at
the project outset.
All testing operations are conducted under the direct control of Solar's QA department,
which ensures compliance with specified test procedures. In addition to in-plant testing of
the finished package, quality control engineers survey the manufacture of all purchased
parts and subassemblies and are responsible for functional testing of incoming
components. The same rigid standards apply to parts manufactured both in and outside
of Solar.
16.2 Testing
Factory testing is in accordance with Solar's engine test specifications and as outlined
below. The customer or customer's designated representative can observe factory
production tests listed in the production and testing schedules. However, production tests
will not be delayed due to the unavailability of the customer or customer's representative.
The production test facilities provide a comprehensive test program using simulators to
perform static testing of package systems to verify control, system operation, and
component calibration. Calibrated engine test cells feature a computerized real-time data
acquisition system that collects digital and analog data from the engine during
acceptance testing to facilitate a comprehensive test report.
16.2.1 Test Phases
Solar's production test facilities provide a three-phase test program. The first phase uses
simulation equipment to perform static testing of the control console and package
systems to verify electrical and fluid system continuity and calibration. The second phase
consists of interconnecting the package and control console (if applicable) to undergo
additional simulated systems testing of the total package. In the final phase, the package
is controlled and monitored by its own control console and the computerized test facility.
16.2.2 Generator Package Acceptance Testing
The basic package assembly, which includes the gas turbine, reduction-drive gearbox,
generator, package-mounted accessories, and control console, are tested as a complete
system to ensure proper integration and function in accordance with Solar's package test
specifications. Results are recorded and maintained by Solar. The acceptance test
generally includes the following:
• Starting and combustion cycles
• Lubricating oil system temperature and pressure measurements
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
63
Page 65

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
• Vibration measurements
• Power and heat rate measurements at partial and full load under ambient
conditions with a unity power factor of 1.0
• Turbine and generator temperature measurement
• Variable guide vane adjustment
• Generator and engine tuning
• Fuel transfers (for dual fuel units)
• Load/speed transient testing
• Malfunction and safety devices testing
• AC metering and control circuitry testing (if AC metering is supplied), calibration
of AC metering circuits is performed by bench testing
The package is usually tested with the generator. When this is not practical due to
schedule availability or test cell limitations, the package may be tested with a slave
generator. Prior to shipment, the contract generator will be mounted and aligned on the
package. Items excluded from standard package testing are inlet and exhaust systems,
ancillary equipment such as filters, silencers, ducting, battery systems, oil coolers,
ancillary skid, switchgear, and any customer-furnished hardware.
16.2.3 Generator Testing
The generator is tested in accordance with the Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Engineers (IEEE) standard specifications and Solar's specifications at the manufacturer's
plant. These tests satisfy both Solar and National Electrical Manufacturers Association
(NEMA) requirements. Supplier testing is performed under periodic quality control review
by Solar to ensure conformity.
16.2.4 Acceptance Test Data
Acceptance test data are reviewed and approved by Test Engineering, Quality
Engineering, and the project manager prior to submittal to the customer. With this review
and approval cycle, the test data are furnished approximately four weeks after completion
of acceptance testing. The test data includes test result comparisons to Solar's
acceptance test specifications using calculations, graphs, strip charts, and descriptions.
Data are provided for each turbine generator set. The acceptance test data generally
includes the following:
• Turbine fuel consumption rates – a comparison of measured fuel consumption
versus specified fuel consumption that shows a correlation between fuel
consumption, power output, and turbine gas temperature at full load.
• Voltage and frequency transients – strip chart traces are provided that show
voltage and frequency deviations during load transitions.
• Operating values – a chart that includes the following operating parameters at
each step load from no load to full load:
− Lubricating oil pressure, temperature, and flow
− Package temperatures
− Generator power
− Generator voltage, amperage, and frequency
− Engine compressor discharge pressure
− Package vibration levels
16.2.5 Additional Testing
As an option, additional testing can include a four hour full-load test using gas and/or
liquid fuel, factory emissions testing, and field performance testing.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
64
Page 66

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
16.2.6 Source Inspection
As an option, Solar can conduct a final product inspection at the supplier facility for the
following contract-specific items:
• Inlet system filter
• Inlet system silencer
• Exhaust system silencer
• Lube oil cooler
• Generator, including rotor balancing and standard generator testing
16.2.7 Customer Participation
As an option, the customer may witness specified tests on a noninterference basis and/or
hold point basis.
16.2.8 Weld Radiography
As an option, radiographic welding inspections can be performed on a percentage of the
gas fuel and/or lube oil system piping and manifolds.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
65
Page 67

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
17 Preservation, Installation, and Documentation
17.1 General Description
This chapter describes preservation, general installation requirements, and project
documentation.
17.2 Preservation
Long term and short term preservation can be provided for the engine and package. The
type of preservation required dependents upon the following:
• Type of transportation (sea, air, or truck)
• Climatic conditions during transport and storage
• Storage period
• Storage facilities
• Static and dynamic loads imposed during shipment
Long-term preservation is required if:
• Equipment will be stored in an unimproved storage area for greater than 90 days
before installation
• Transportation is by ship
• Transportation includes transshipment (package will go from truck to barge to
truck, etc., e.g., rigorous loads will be encountered during shipment)
• Package will be exposed to severe weather conditions during transport
Short-term preservation is required if:
• Equipment will be stored in an improved storage area for less than 90 days
before installation
• Transportation is not by ship
• Transportation does not include transshipment (package will not go from truck to
barge to truck, etc., e.g., rigorous loads will not be encountered during shipment)
• Package will not be exposed to severe weather conditions during transport
17.3 Site Requirements
Solar's gas turbine generator sets require minimal site preparation. The Titan 250
generator set is supplied with self-contained systems for starting, fuel, lube oil, and
control, minimum piping and wiring connections are required for installation. All service
connections are conveniently located on the outer edge of the skid.
17.4 Mechanical Installation Requirements
17.4.1 Mounting
Correct mounting of the gas turbine package is vital to successful package installation
and requires adequate preparation by the user. The site pad thickness is governed by
soil condition and the weight of the gas turbine package, air inlet system, and exhaust
system. Mounting pad locations and weights will differ with each package, depending
upon selected options, and will be clearly shown on the installation drawings. The
equipment layout should provide adequate floor space for major components with
sufficient room around the package for routine maintenance access.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
66
Page 68

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
17.4.2 Alignment Tooling
As an option, alignment tooling can be provided to align the reduction gearbox output
shaft hub to the generator input shaft hub. The alignment tooling includes a dial indicator
kit, gearbox-to-generator alignment tool, axial distance gauge, and custom storage
container.
17.4.3 Lube Oil Cooler(s)
The lube oil cooler(s) is/are not integral with the package and must be located and
installed separately.
17.4.4 Gas Turbine Air Inlet System
The gas turbine air inlet should be located so that entry of gas turbine exhaust, oil tank
vent vapor, or other contaminants is minimized. The air inlet duct must be free of
accumulated water prior to starting the gas turbine.
17.4.5 Gas Turbine Exhaust System
The importance of having an exhaust system properly installed cannot be
overemphasized. A poorly installed exhaust system can cause a loss of power and
impose severe mechanical strains on the gas turbine. The exhaust duct system must be
terminated in a manner that precludes recirculation of exhaust products through the gas
turbine air inlet or oil cooler. Exhaust installation considerations include the relative height
of the exhaust duct above the air inlet, building roof design, direction of prevailing winds,
and the proximity of adjacent structures. When exhaust silencing is required, provisions
must be made to adequately mount and support the equipment and limit the exhaust
silencer pressure loss.
17.5 Documentation
Four copies of the Operation and Maintenance Instruction (OMI) manuals and Quality
Control (QC) data books are provided on CD-ROM. Additional copies and alternative
formats can be ordered at additional cost. Project specific drawings are provided in
electronic format and include:
• Electrical schematic
• Wiring diagram
• Electrical interface/Interconnect diagram
• Turbotronic software documentation
• Cause and effect drawing
• Mechanical interface drawing
• Start, Fuel, Lube, Air/Drain, and Enclosure system schematics
Solar’s Product Information Letter 184 “Documentation for New Equipment” provides a
complete list of all the documentation supplied on a typical project.
17.5.1 Quality Control Data Book
The QC data book typically includes the following:
• Inspection and test plan (ITP)
− Describes the quality assurance requirements for each product on a project
basis.
− Lists the primary controlling and verifying documents, codes and standards
used to define the quality requirements, and identifies inspection points.
• Package certified test report
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
67
Page 69

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
• Generator acceptance test report
• American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) data reports, as applicable
• Solar’s Certificate of Compliance
If specified on the final project ITP, the QC data book may also include the following
documents at additional cost and increased delivery time:
• Engine rotor balance record
• Engine casing leak test record
• Documentation from suppliers of major package components such as oil coolers,
oil filters, gearboxes and driven equipment
• Optional electrical device list when applicable
• Third-Party Certificates and Declarations of Conformity when applicable
17.5.2 Torsional Analysis Report (Optional)
A torsional analysis can be performed on the entire drive train to determine if there are
any significant torsional resonance conditions within ±10% of the operating speed range.
If a resonance condition (interference) is found, then a fatigue analysis is performed to
confirm the resonance will not cause fatigue failure in the shafting.
17.5.3 Lateral Analysis Report (Optional)
A lateral forced response analysis of the driven equipment can be performed to confirm
that any lateral critical speeds aren’t close enough to the operating speed range to cause
lateral vibration problems.
17.5.4 Operation and Maintenance Instruction Manual
The Operation and Maintenance Instruction Manual (OMI) provides descriptive and
instructional data for operating and servicing the turbomachinery package. General,
functional, and component descriptions of the turbine engine and associated package
systems with supporting illustrations are included in four volumes:
• Systems Operator's Guide - Intended for the equipment operator, the systems
operator’s guide provides familiarization with controls and indicators, operating
procedures, and safety precautions to ensure safe equipment operation.
• Maintenance Instructions - Intended for maintenance and field service
personnel, the maintenance instructions include preventive and corrective
procedures, including periodic inspection requirements, alignment procedures,
cleaning procedures, removal and installation procedures, adjustment
procedures, and tolerances.
• Supplementary Data - Provided in the form of supplier manuals and data
sheets, the supplementary data provides descriptions of components and
assemblies not covered or fully discussed in the Maintenance Instructions
volume. Due to copyright restrictions, supplementary data from suppliers is
available in English only.
• Illustrated Parts List - Provides part numbers, part names, quantities, reference
designators, and illustrations for locating and ordering parts.
• Language - The OMI is provided in English. Other languages are available as an
option.
The OMI manual typically includes the following features:
• Electronic viewing of data in a Windows environment
• All volumes of the manual set on one CD-ROM
• Search feature including full text search for supplier data
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
68
Page 70

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
• Graphics in a separate window for simultaneous viewing of text with associated
illustration
• PDF version for printing
17.5.5 Service Parts List
Identifies operational service parts and tooling. Once engineering has been finalized and
manufacturing bills are available, Solar's Service Parts department creates a detailed
listing of service parts from the actual equipment manufacturing bills of material.
Table 14. Preservation, Installation, and Documentation Specifications
Mechanical Installation Requirements
Mounting
Space Between Units In Multiple-Unit
Installations
Lube Oil Cooler(s)
Top of The Lube Oil Cooler(s)
Total oil volume of “Outgoing and Return”
Lines
Total Combined Pressure Drop of The
Supply and Return Lines and Lube Oil
Cooler(s)
Start, Fuel, Lube, Air/Drain System Schematics
Compliance American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Y32.10
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 9-4 Interpretation of Drawing Requirements
ES 9-76 Traceability Requirements Critical Parts, Engine and Related Systems
ES 2231
Solar’s Applicable Product Information Letters
PIL 184 Documentation for New Equipment
PIL 097 Package Preservation and Preparation for Shipment
Notes:
(a) This is to prevent oil tank flooding in the event of a drain back.
Standards and Practices for The Design and Installation of Cable Channels and TC
Rated Cables Installed In Class 1, Division 2 Hazardous Areas
A Minimum of 2.5 m (8 ft)
Not Be More Than 9 m (30 ft) Above The Bottom of
The Package Frame, See Note (a)
1282 L (340 gal)
Should Not Exceed 345 kPag (50 psig)
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
69
Page 71

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
18 Certification
18.1 General Description
Solar’s leadership in the gas turbine industry is supported by its ability to comply with
regulations, codes, and standards required by industry and/or regional authorities around
the world. Solar continually evaluates compliance requirements to ensure conformance to
the following standards:
• National Electrical Code (NEC)
• Canadian Electrical Code (CEC)
• Conformité Européenne (CE) Mark
• International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Safety Assessment
• Australian/New Zealand Standard (AS/NZS) 3000 Wiring Rules
• Offshore Marine Applications
18.2 National Electrical Code
For installations that require National Electrical Code (NEC) certification, Solar complies
with the NEC codes and standards adopted by local authorities and government entities.
Sources for these codes and standards include:
• Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
• National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
• Underwriters Laboratories Incorporated (UL)
• American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
• National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE)
The following OSHA approved Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories (NRTLs)
provide approval for codes and standards:
• Underwriters Laboratories Incorporated (UL)
• Factory Mutual (FM)
• Canadian Standards Association (CSA), when certifying to U.S. standards
• Entela Incorporated (ENTELA)
(CSA and UL also develop and promulgate standards).
The NEC establishes classification of hazardous sites in terms of Classes, Divisions,
Zones, and material Groups. Class I covers locations where flammable gases may be
present in quantities sufficient to ignite. Division 1 covers situations where flammable
gases may be present as part of a process, while Division 2 covers locations where
flammable gas is less likely to be present. Generator packages are designed for use in
Class I, Division 2 hazardous locations.
18.3 Canadian Electrical Code
For installations that require Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) certification, Solar complies
with the CEC codes and standards adopted by local authorities and government entities.
Sources for these codes and standards include:
• Canadian Standards Association (CSA), electrical requirements only
• Entela Inc. (ENTELA), when certifying to Canadian standards
• Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL), when certifying to Canadian standards
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
70
Page 72

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
18.4 Conformité Européenne Mark
For installations that require Conformité Européenne (CE) Mark certification, Solar
complies with the CE Mark codes and standards adopted by local authorities and
government entities. Sources for these codes and standards include the following
European Union (EU) directives:
• Explosive Atmospheres (ATEX) Directive 94/9//EC
• Pressure Equipment Directive 97/23/EC
• Machinery Safety Directive 98/37/EC
• Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 89/336/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
18.4.1 Methods of Establishing Conformity
To ensure compliance with applicable directives, Det Norske Veritas (DNV), an approved
Notified Body, supports Solar’s efforts to comply with directives by providing consultation
and, where applicable, certification. Solar has received from DNV “type certification” for
standard turbomachinery packages for ATEX and PED directives. As a result, Solar selfcertifies for CE Mark requirements on standard packages. This self-certification process
includes the following:
• The package is designed and manufactured to European Committee for
Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Committee for
Standardization (CEN) standards.
• A hazard analysis is performed to define any and all conceivable hazards.
• Tests are performed to verify proper operation and functionality of components
and systems.
• Operation and Maintenance Instruction (OMI) manuals, package labels, and
control system display screens are produced in the operator’s native language.
• Prior to application of the Conformité Européenne (CE) Mark, the Test Facilities,
Production, Quality, and a Compliance Engineer perform an audit of the
completed package.
• A Declaration of Conformity is then issued for each CE Marked package.
18.4.2 Solar Compliance
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) / Electrotechnical Standardization
(CENELEC) (60079-10) categorizes hazardous areas in terms of Zones shown in Table
15.
Table 15. Zone Classifications
Zone Definition
0 Explosive atmosphere continuously present
1 Explosive atmosphere often present
2 Explosive atmosphere may be present under fault conditions
While electrical systems can be provided to meet Zone 1 or Zone 2, under ATEX,
generator sets can only be certified for Zone 2 due to the hot surface temperature of the
gas turbine.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
71
Page 73

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
18.5 International Electrotechnical Commission Safety Assessment
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 61508 is an international standard that
describes a standardized approach to Asses the functional safety of electric, electronic,
and programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard is based on a lifecycle evaluation of system reliability and safety level determination. Safety integrity levels
are categorized as SIL1, SIL2, SIL3, and SIL4. Levels are established by assessing the
potential for personnel injury, equipment damage, and environmental damage. The
installation site design and operating requirements will determine the applicable SIL level.
Solar can provide reliability data on its equipment to assist customers in their overall
safety assessments.
18.6 Offshore Marine Applications
For installations that require offshore marine certification, Solar conforms to the rules and
standards established by certification authorities and/or customer specifications.
Certification can be performed by one of the following authorities:
• Det Norske Veritas (DNV)
• American Bureau of Shipping (ABS)
• Lloyd’s Register (LR) of Shipping
• Bureau Veritas (BV)
Solar can provide certification or provide supporting information to permit certification by
another party.
18.6.1 Det Norske Veritas Certification
Det Norske Veritas (DNV) certification includes design verification and a manufacturing
survey. DNV witnesses the fabrication and testing of engines and packages. Operations
witnessed by DNV are defined in the inspection and test plan (ITP) that is prepared by
Solar’s Quality department and approved by DNV at the beginning of a project.
To eliminate redundant inspections, Solar has established a manufacturing survey
arrangement (MSA) with DNV for a specific group of products. This MSA is based on a
DNV audit of Solar's Quality System. The MSA authorizes Solar to carry out a specific
level of inspections and tests without the presence of a DNV representative.
18.6.2 American Bureau of Shipping
The American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) performs design appraisals and inspections.
Typically, ABS certification is performed according to ABS “Guide for Building and
Classing Facilities on Offshore Installations,” 1991. ABS certification of Solar's gas
turbines is based on compliance with the American Petroleum Institute (API) Standard
616, with standard exceptions.
18.6.3 Lloyd’s Register of Shipping
Typically, Lloyd’s Register (LR) of Shipping performs design appraisals and
manufacturing surveys. LR recognizes engine type approvals provided by DNV. LR’s test
and inspection witness points are defined in the project Inspection and Test Plan (ITP).
18.6.4 Bureau Veritas
Bureau Veritas (BV) performs design appraisals and manufacturing surveys. Typically,
BV certification is performed according to BV publication “Floating Production, Storage
and Offloading Units Ch 10 NR456 April 1998.” Certification of Solar's gas turbines is
based on compliance with the American Petroleum Institute (API) Standard 616, with
specified exceptions.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
72
Page 74

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
18.7 Summary
Solar has a continuing program to support customers in ensuring that Solar’s products
conform to applicable codes and regulations. Solar also has the resources to provide
customer guidance and assistance in this process.
Table 16. Certification Specifications
Solar’s Applicable Engineering Specifications
ES 1593
ES 2231
Solar’s Applicable Product Information Letters
PIL 127 Product Certification
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1
and Division 2
Standards and Practices for The Design and Installation of Cable Channels and TC
Rated Cables Installed In Class 1, Division 2 Hazardous Areas
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
73
Page 75

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
19 Support Services
19.1 Construction Services
Solar’s Construction Services organization offers a comprehensive range of equipment
and services to successfully meet power system expectations and needs. Our experience
takes us to many parts of the world, onshore and offshore, managing various types of
power configurations. Our services are based on years of experience and expertise in
power system engineering and complete project management that include:
• Feasibility studies
• Proposal preparation
• Design and engineering
• Material procurement
• Fabrication
• Onsite construction
• Quality control
• Scheduling
• Budget control
• Shipping
• Installation, testing, and commissioning
Material procurement, for example, can include prime movers, driven equipment,
associated mechanical process equipment, and electric power generation equipment.
Construction Services is uniquely qualified worldwide to provide complete fluid
compression, liquid pumping, and power generation systems, with single-source
responsibility, engineering expertise, optimal economic designs, and real attention to
quality and safety to ensure complete power system satisfaction
19.2 Customer Services
Solar’s Customer Services organization is dedicated to the support of Solar’s equipment
worldwide. Customer Services support includes technical training, field service personnel,
service parts, overhaul and repair services, and customized operation and maintenance
programs. Customer Services also offers gas turbine uprates and updates, retrofit
conversions to low emission SoLoNOx turbine configurations, and complete package
refurbishments, all of which provide cost-effective life-cycle solutions.
Solar’s Customer Services organization is known for its excellent service and support that
no other gas turbine service company can compare in:
• Product knowledge and experience with more than 11,500 units in 90 nations
• In-depth technical support via Solar’s global Customer Information Network
• Factory-qualified repair and overhaul procedures
• Genuine Solar Certified Parts
• Worldwide field service personnel and service facilities
• Around-the-clock response
• Exchange engine program to minimize your downtime
Solar stands behind each of our customers with uncompromising commitment to the
success of their turbomachinery installations throughout the equipment's life cycle.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
74
Page 76

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
19.3 Contract Power and Leasing Services
Solar offers numerous financing options. All or part of a project can be financed, offered
under a lease agreement, or installed on a service tariff with a performance contract.
Financing or leasing terms can extend from short-term rentals to long-term leases of 10
years or more. Financing can be structured as full-payout financing instruments that lead
to ownership or as off-balance sheet operating leases that can allow for the return of the
equipment at the end of the lease.
Under a performance contract, Solar may supply, install, operate, maintain, and own the
equipment, as well as auxiliary components required to provide the service, such as
electric power, steam, or compressed gas. The tariff charged by Solar is based on the
amount of service delivered. Solar has extensive worldwide background in financing and
in providing power contracts to assist you in determining the best financial option to
optimize your economic return from the turbomachinery project.
19.4 Solar’s Worldwide Locations
Solar maintains sales and service facilities throughout the world. For a list of the current
locations please visit Solar on the internet at www.solarturbines.com.
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
75
Page 77

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Conversion Chart
Conversion Factors
To Convert From
English
To S.I. Metric Multiply By
Btu kJ 1.0551 kcal 0.252
Btu/h W 0.2931 kcal/h 0.252
Btu/scf kJ/nm
3
39.3694 kcal/nm
cfm m3/min 0.028317 m3/min 0.028317
cfm m3/s 0.00047195 m3/s 0.00047195
cu ft m
3
0.028317 m
°F °C (°F-32) 5/9 °C (°F-32) 5/9
°F (Interval) °C (Interval) 5/9 °C (Interval) 5/9
ft m 0.3048 m 0.3048
ft-lbf/lb
m
mJ/kg 0.0029891 kJ/kg 0.002989
ft/s m/s 0.3048 m/s 0.3048
gal. (U.S.) L 3.7854 L 3.7854
hp kW 0.7457 kW 0.7457
in. mm 25.400 cm 2.540
in. Hg kPa 3.3769 cm Hg 2.540
in. H2O kPa 0.2488 cm H2O 2.540
kcal kJ 4.1868
lb kg 0.4536 kg 0.4536
lb/cu ft kg/m
lbf-in.
3
16.0185 kg/m
Nm 0.1129848
MMSCFD Nm3/min 18.62 Nm3/h 1117
mph km/h 1.6093 km/h 1.6093
psi kPa 6.8948 kg/cm
psia kPa (a) 6.8948 bars Abs 0.068948
psig KPa (g) 6.8948 Ata 0.070
scfm Nm3/min 0.0268 Nm3/h 1.61
sq in. mm
sq ft m
2
2
645.16 cm
0.0929 m
yd m 0.914 m 0.914
To Convert From
Old Metric
To S.I. Metric Multiply By
Atm kPa 101.325
Bar kPa 100.0
cm mm 10
cm Hg kPa 1.3332
cm H2O kPa 0.09807
kcal/h W 1.16279
2
kg/cm
kPa 98.0665
Nm3/h Nm3/min 0.0167
To Convert To
Old Metric
3
3
Multiply By
9.382
0.028317
3
16.0185
2
2
2
0.070
6.4516
0.0929
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
76
Page 78

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
List of Abbreviations
Abbreviations
ABS
1
ABS
2
AGMA American Gear Manufacturers Association
API American Petroleum Institute
AS/NZS Australian/New Zealand Standard
ASME American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Ata Atmosphere Absolute
ATEX Atmosphere Explosive
AVM Anti-Vibration Mount
AVR Automatic Voltage Regulation
Btu British Thermal Unit
Btu/h British Thermal Units/Hour
BV Bureau Veritas
CACA Closed Air Circuit Air Cooled
CACW Closed Air Circuit Water-To-Air Cooled
CE Conformité Européene
CEC Canadian Electrical Code
CEN European Committee for Standardization
CENELEC Comité Européen de Normalisation Électrotechnique
cfm Cubic Feet/Minute
CGCM Combination Generator Control Module
cm Centimeter
2
cm
3
cm
CO Carbon Monoxide
CO
2
CSA Canadian Standards Association
CT Compliant Tower
Cu ft Cubic Feet
°C Degrees Celsius
dBA Decibels (Acoustic)
DNV Det Norske Veritas
ENTELA Entela Incorporated
ES Engineering Specification
EU European Union
FM Factory Mutual
FP Fixed Platform
fps
1
FPS
2
FPSO Floating Production, Storage and Offloading
ft-lb Foot-Pound
ft-lbf/lb
m
ft/s Feet/Second
°F Degrees Fahrenheit
gal. Gallon
hp Horsepower
American Bureau of Shipping
Absolute
Square Centimeter
Cubic Centimeter
Carbon Dioxide
Feet Per Second
Floating Production Systems
Foot-Pound Force/Pound Mass
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
77
Page 79

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Abbreviations (Cont.)
HRSG Heat Recovery Steam Generator
IEC International Electrotechnical Commission
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
in. Inch
in. Hg Inches of Mercury
in. H2O Inches of Water
IP Ingress Protections
IR Infrared
IS Intrinsically Safe
ISO International Standards Organization
Isoch Isochronous
ITP Inspection and Test Plan
kcal Kilocalorie
kg Kilogram
kJ Kilojoule
kPa Kilopascal
ksi 1000 pounds/square inch
kw Kilowatt
L Liter
LR Lloyd’s Register
m Meter
mm Millimeter
MMSCFD Millions of Standard* Cubic Feet/Day
MPa Mega Pascal
Mph Miles per Hour
MRP Manufacturing Resource Planning
MSA Manufacturing Survey Arrangement
2
m
3
m
m3/min Cubic Meters/Minute
N Newton
2
N/m
NACE National Association of Corrosion Engineers
NEC National Electrical Code
NEMA National Electrical Manufacturers Association
NFPA U.S. National Fire Protection Agency
Ngp Speed, Gas Producer
Nm3/h Normal** Cubic Meters/Hour
Npt Speed, Power Turbine
NOx Nitrogen Oxides
NRTL Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory
ODP Open Drip Proof
OMI Operation and Maintenance Instruction
OSHA U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration
QA Quality Assurance
QC Quality Control
Pcd Pressure, Compressor Discharge
PED Pressure Equipment Directive
Square Meter
Cubic Meter
Pascal
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
78
Page 80

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
Abbreviations (Cont’d)
PF Power Factor
PIL Product Information Letter
PMG Permanent Magnet Generator
psi Pounds/Square Inch
psia Pounds/Square Inch Absolute
psig Pounds/Square Inch Gauge
rpm Revolutions Per Minute
RTD Resistance Temperature Device
scf Standard* Cubic Foot
scfd Standard* Cubic Feet/Day
scfm Standard* Cubic Feet/Minute
3
sm
/h Standard*** Cubic Meters/Hour
SoLoNOx
Solar Proprietary Low Emissions System
SP Spar Platform
sq Square
TEAAC Totally Enclosed Air-To-Air Cooled
TEWAC Totally Enclosed Water-To-Air Cooled
TLP Tension Leg Platform
UHC Unburned Hydrocarbon
UL Underwriters Laboratories Incorporated
UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply
USCG United States Coast Guard
UV Ultraviolet
VAC Voltage, Alternating Current
VAR Volt Amp Reactive
VDC Voltage, Direct Current
VFD Variable Frequency Drive
VPI Vacuum Pressure Impregnated
* “Standard” = 60°F, 14.7 psia
** “Normal” = 0°C, 1.01325 x 105 Pascals
*** “Standard” = 15°C, 760 mm Hg
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
79
Page 81

Turbomachinery Package Specification Titan 250 Generator Set
List of Solar’s Engineering Specifications
Solar’s Engineering Specifications
ES 9-4 Interpretation of Drawing Requirements
ES 9-56 Fusion Welding
ES 9-62 Ingestive Cleaning Solar Gas Turbine Engines
ES 9-76 Traceability Requirements Critical Parts, Engine and Related Systems
ES 9-98 Fuel, Air, and Water (or Steam) for Solar Gas Turbine Engines
ES 9-224 Lubricating Oils for Use In Solar Gas Turbine Engines
ES 1593
ES 1762
ES 2231
ES 2416 DC Supply Systems
Note:
Engineering specifications can be made available upon request in accordance with Caterpillar
and Solar Turbines Incorporated confidentially guidelines.
Guidelines for NEC Compliance of Solar Product Lines: Class I, Group D, Division 1 and
Division 2
Standards and Practices for Electrical Systems For Gas Turbine Packages Installed in
Hazardous Areas (CENELEC Standards)
Standards and Practices for The Design and Installation of Cable Channels and TC Rated
Cables Installed In Class 1, Division 2 Hazardous Areas
List of Solar’s Product Information Letters
Solar’s Product Information Letters
PIL 012-OG Customer Drawings - Oil and Gas
PIL 054 OSHA Noise Requirements
PIL 058 Package Sound Levels
PIL 097 Package Preservation and Preparation for Shipment
PIL 127 Product Certification
PIL 148 LPG and NGL Fuels
PIL 149 Direct-drive AC Start Systems
PIL 150 Direct-drive AC Start Systems
PIL 161 Lube Oil System Cleanliness
PIL 162
PIL 176 Siloxanes in Gas Fuel
PIL 178 Salt Ingress Protection for Gas Turbines
Recommendations for the Sourcing, Handling, Storage and Treatment of Fuels for
Solar Gas Turbines
© 2008 Solar Turbines Incorporated. All rights reserved. TPS250GS/908 - Preliminary
80
 Loading...
Loading...