Page 1
fx-9860G AU
User’s Guide
E
http://edu.casio.com
Page 2
Important!
Please keep your manual and all information handy for
future reference.
Page 3

BEFORE USING THE CALCULATOR
2
FOR THE FIRST TIME...
This calculator does not contain any main batteries when you purchase it. Be sure to
perform the following procedure to load batteries, reset the calculator, and adjust the
contrast before trying to use the calculator for the first time.
1. Making sure that you do not accidently press the o key, slide the case onto the
calculator and then turn the calculator over. Remove the back cover from the calculator
by pulling with your finger at the point marked
2. Load the four batteries that come with the calculator.
• Make sure that the positive (+) and negative (–) ends of the batteries are facing
correctly.
1.
1
3. Remove the insulating sheet at the location marked “BACK UP” by pulling in the
direction indicated by the arrow.
4. Replace the back cover, making sure that its tabs enter the holes marked 2 and turn
the calculator front side up. The calculator will turn on automatically and the MAIN
MENU will appear on the display.
20060601
Page 4

• If the Main Menu shown to the right is not on the display,
open the back cover and press the P button located
inside of the battery compartment.
P button
5. Use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to select the SYSTEM icon and press
w, then press 1(
) to display the contrast adjustment screen.
6. Adjust the contrast.
• The e cursor key makes display contrast darker.
• The d cursor key makes display contrast lighter.
• 1(INIT) returns display contrast to its initial default.
7. To exit display contrast adjustment, press m.
20060601
Page 5
Quick-Start
TURNING POWER ON AND OFF
USING MODES
BASIC CALCULATIONS
REPLAY FEATURE
FRACTION CALCULATIONS
EXPONENTS
GRAPH FUNCTIONS
DUAL GRAPH
DYNAMIC GRAPH
TABLE FUNCTION
20050401
Page 6

1
Quick-Start
Quick-Start
Welcome to the world of graphing calculators.
Quick-Start is not a complete tutorial, but it takes you through many of the most common
functions, from turning the power on, and on to graphing complex equations. When
you’re done, you’ll have mastered the basic operation of this calculator and will be ready
to proceed with the rest of this user’s guide to learn the entire spectrum of functions
available.
Each step of the examples in Quick-Start is shown graphically to help you follow along
quickly and easily. When you need to enter the number 57, for example, we’ve indicated it as follows:
fh.
Press
Whenever necessary, we’ve included samples of what your screen should look like.
If you find that your screen doesn’t match the sample, you can restart from the beginning by pressing the “All Clear” button
TURNING POWER ON AND OFF
o
.
To turn power on, press o.
To turn power off, press
Calculator power turns off automatically if you do not perform any operation within the
Auto Power Off trigger time you specify. You can specify either six minutes or 60
minutes as the trigger time.
!
OFF
o
.
USING MODES
This calculator makes it easy to perform a wide range of calculations by simply
selecting the appropriate mode. Before getting into actual calculations and operation
examples, let’s take a look at how to navigate around the modes.
To s elect the RUN
1. Press m to display the Main Menu.
•
MAT mode
20050401
Page 7
2
Quick-Start
2. Use defc to highlight RUN
and then press w.
This is the initial screen of the RUN
where you can perform manual calculations,
matrix calculations, and run programs.
•
MAT mode,
•
MAT
BASIC CALCULATIONS
With manual calculations, you input formulas from left to right, just as they are written
on paper. With formulas that include mixed arithmetic operators and parentheses, the
calculator automatically applies true algebraic logic to calculate the result.
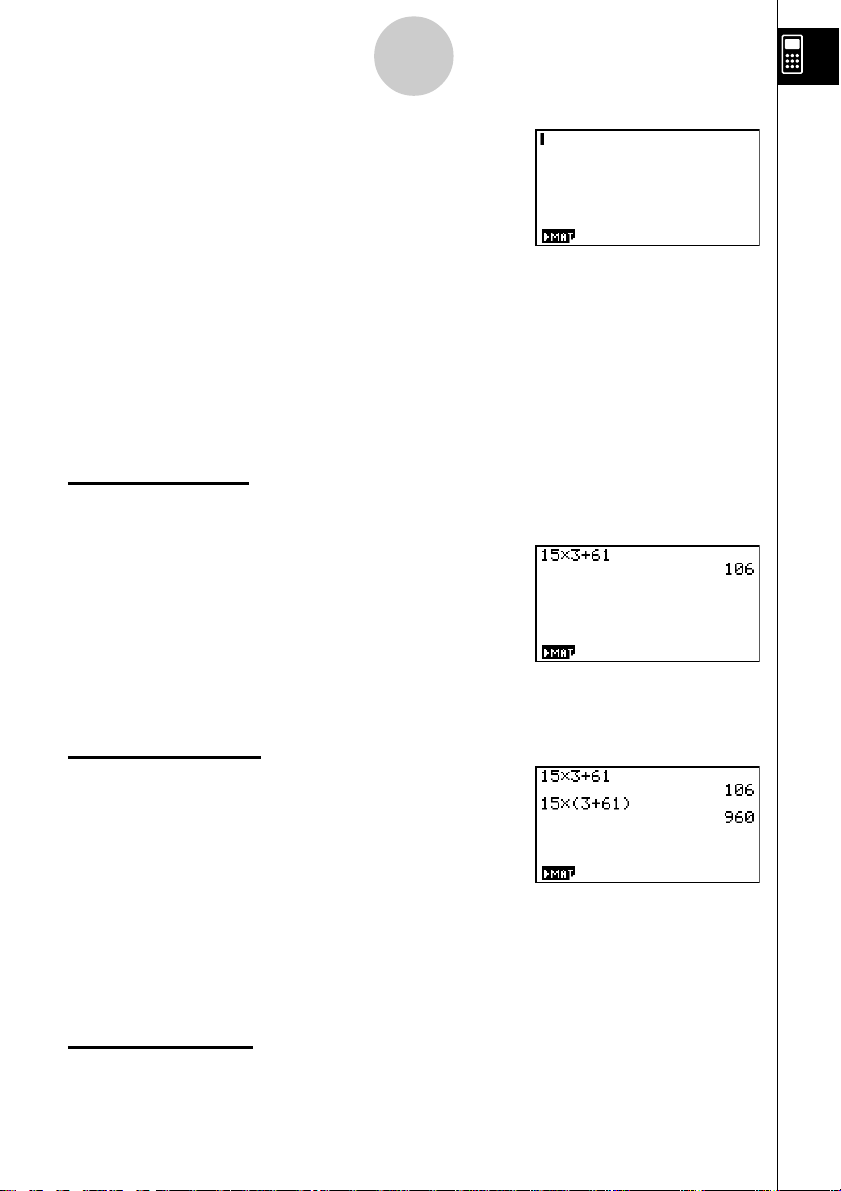
Example:
1. Press
2. Press bf*d+gb w.
Parentheses Calculations
Example:
15 × 3 + 61
o to clear the calculator.
15 × (3 + 61)
1. Press bf*(d
+gb)w.
Built-In Functions
This calculator includes a number of built-in scientific functions, including trigonometric
and logarithmic functions.
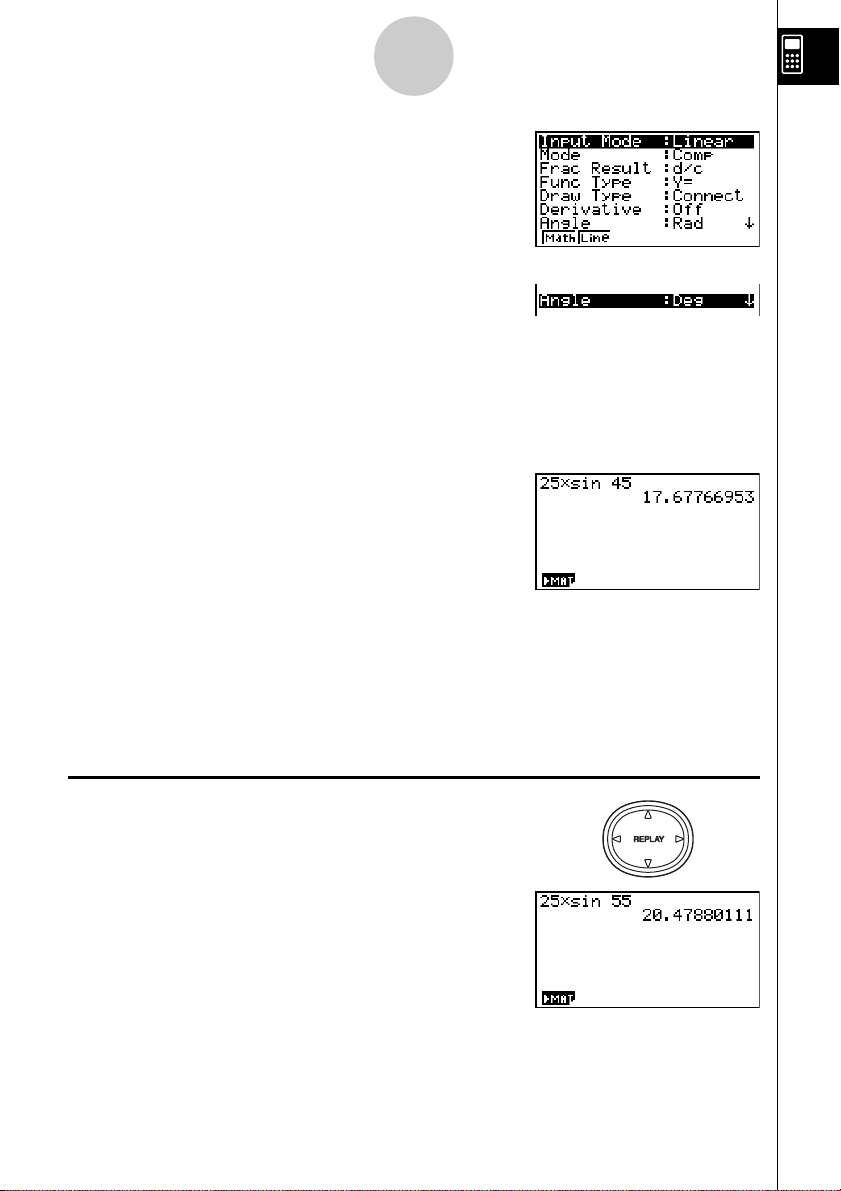
Example:
Important!
Be sure that you specify Deg (degrees) as the angle unit before you try this
example.
25 × sin 45˚
20050401
Page 8
3
Quick-Start
SET UP
1. Press!m to display the Setup screen.
2. Press cccccc1(Deg)
to specify degrees as the angle unit.
3. Press J to clear the menu.
4. Press o to clear the unit.
5. Press cf* sefw.
REPLAY FEATURE
With the replay feature, simply press d or e to recall the last calculation that
was performed so you can make changes or re-execute it as it is.
Example:
1. Press d to display the last calculation.
2. Press
3. Press D to delete 4.
4. Press f.
5. Press w to execute the calculation again.
To change the calculation in the last example from (25 × sin 45˚) to
(25 × sin 55˚)
d to move the cursor (
I
) to the right side of 4.
20050401
Page 9
4
Quick-Start
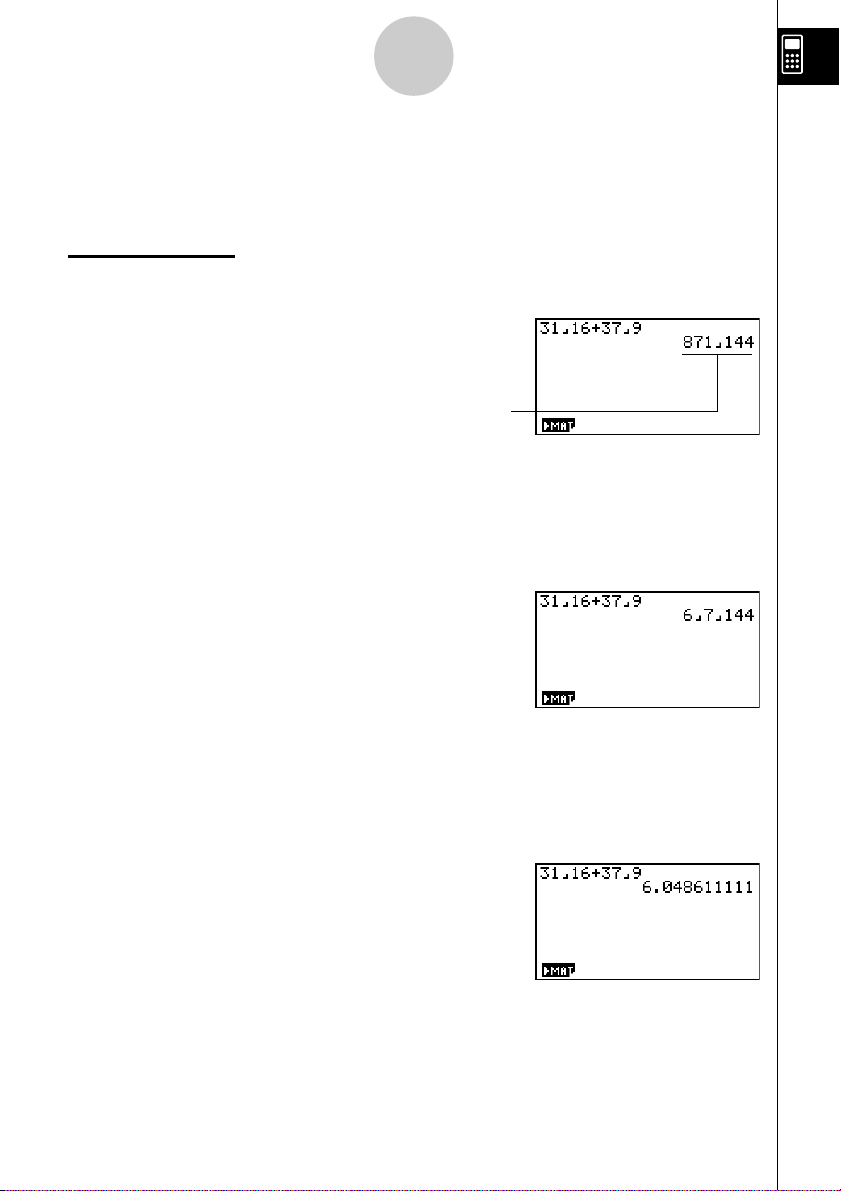
FRACTION CALCULATIONS
You can use the $ key to input fractions into calculations. The symbol “ { ” is used
to separate the various parts of a fraction.
Example:
31
/16 + 37/
9
1. Press o.
2. Press db$bg+
dh$jw.
Indicates
Converting an Improper Fraction to a Mixed Fraction
While an improper fraction is shown on the display, press !Mto convert it to a
mixed fraction.
<
Press !M again to convert back to an improper fraction.
Converting a Fraction to Its Decimal Equivalent
While a fraction is shown on the display, press M to convert it to its decimal
equivalent.
871
/
144
<
Press M again to convert back to a fraction.
20050401
Page 10
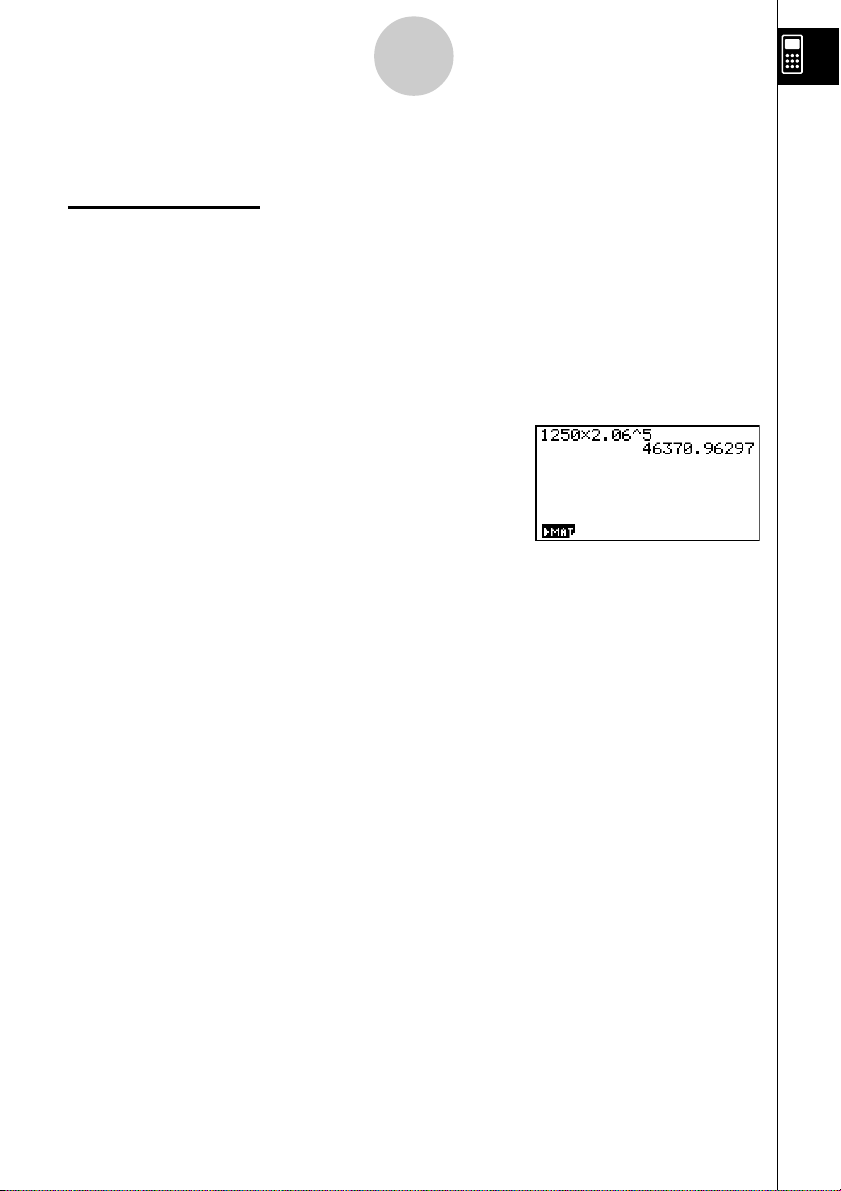
EXPONENTS
5
Quick-Start
Example:
1. Press o.
2. Press bcfa*c.ag.
3. Press
4. Press f. The ^5 on the display indicates that 5 is an exponent.
5. Press w.
1250 × 2.06
M and the ^ indicator appears on the display.
5
20050401
Page 11
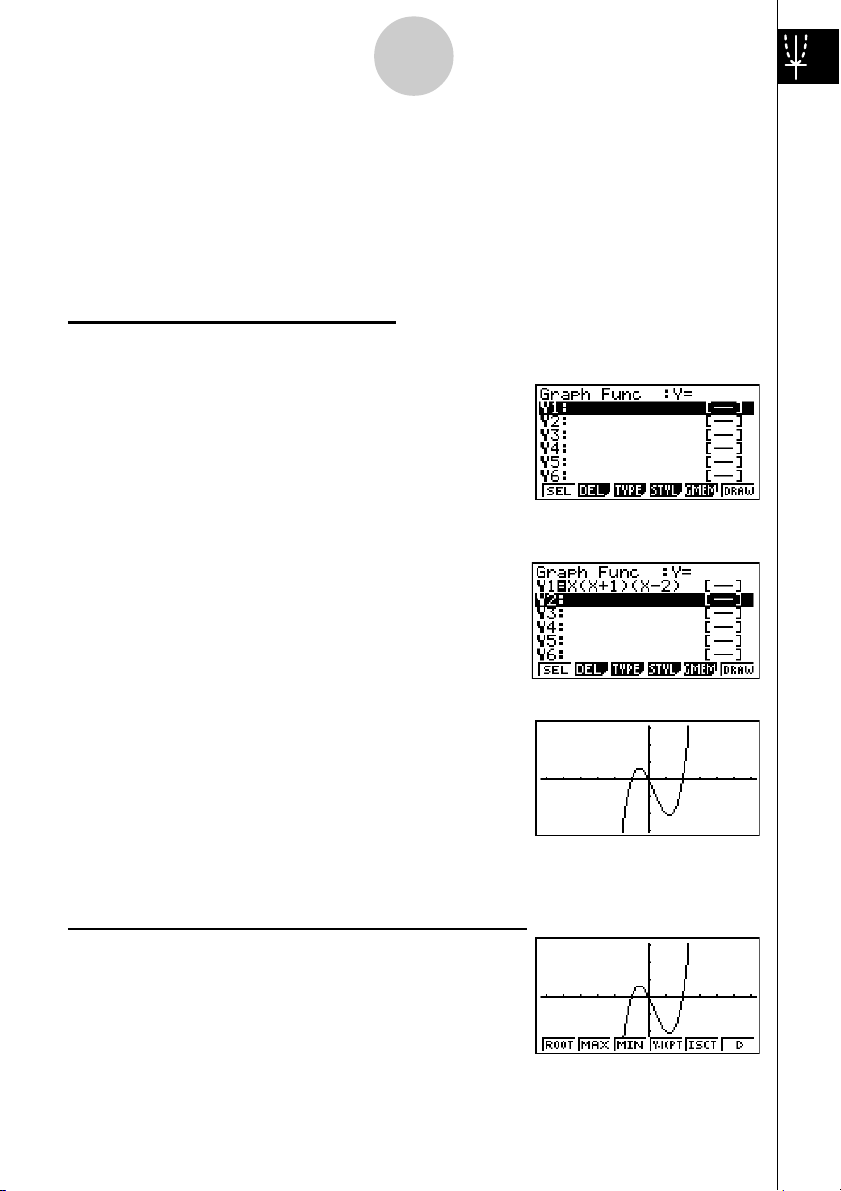
6
Quick-Start
GRAPH FUNCTIONS
The graphing capabilities of this calculator makes it possible to draw complex graphs
using either rectangular coordinates (horizontal axis: x ; vertical axis: y) or polar
θ
coordinates (angle:
All of the following graphing examples are performed starting from the calculator setup
in effect immediately following a reset operation.
; distance from origin: r).
Example
1. Press
2. Use defc to highlight
3. Input the formula.
1: To graph Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
m.
GRAPH, and then press w.
v(v+b)
(v-c)w
4. Press 6(DRAW) or w to draw the graph.
Example
1. Press !5(G-SLV).
2: To determine the roots of Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
20050401
Page 12
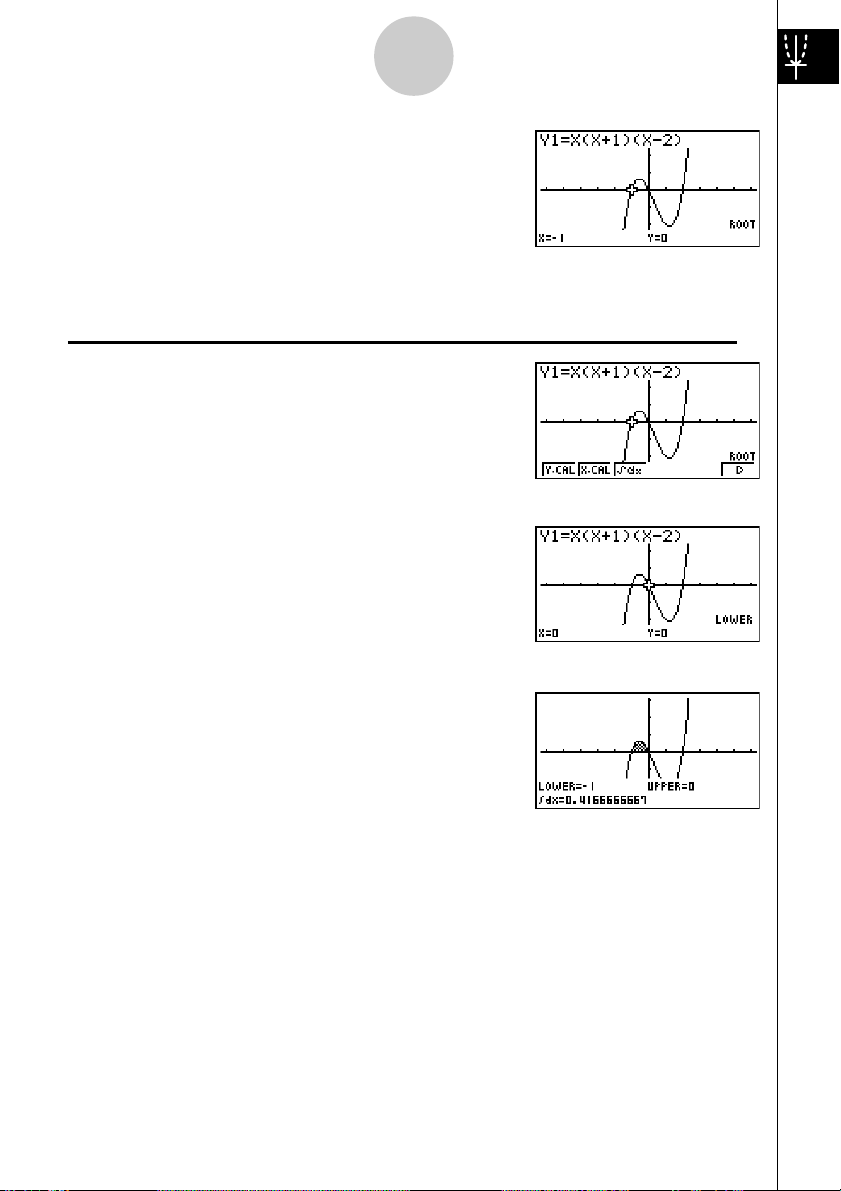
2. Press 1(ROOT).
Press e for other roots.
7
Quick-Start
Example
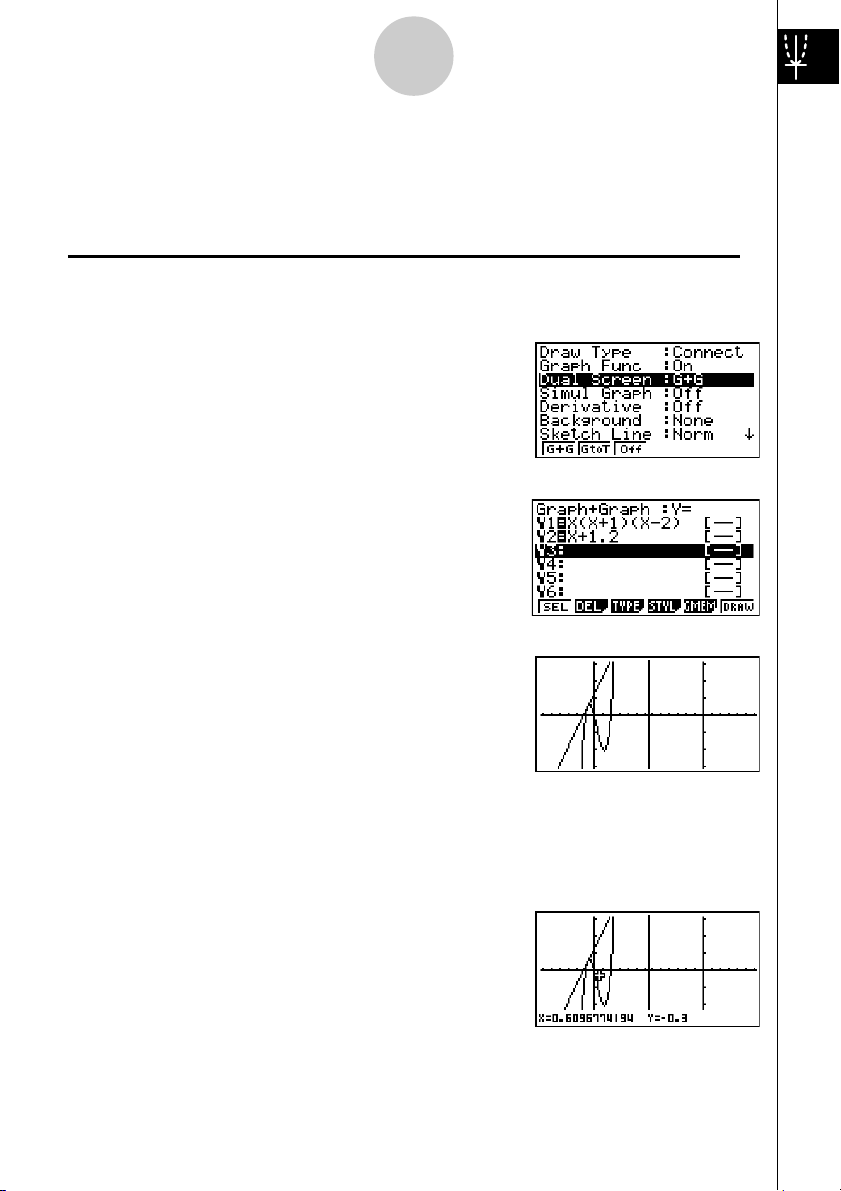
1. Press
2. Press 3(∫dx).
3. Use d to move the pointer to the location where
3: Determine the area bounded by the origin and the X = –1 root obtained
for Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
!5(G-SLV)6(g).
X = –1, and then press w. Next, use e to
move the pointer to the location where X = 0, and
then press
which becomes shaded on the display.
to input the integration range,
w
20050401
Page 13
8
Quick-Start
DUAL GRAPH
With this function you can split the display between two areas and display two graph
windows.
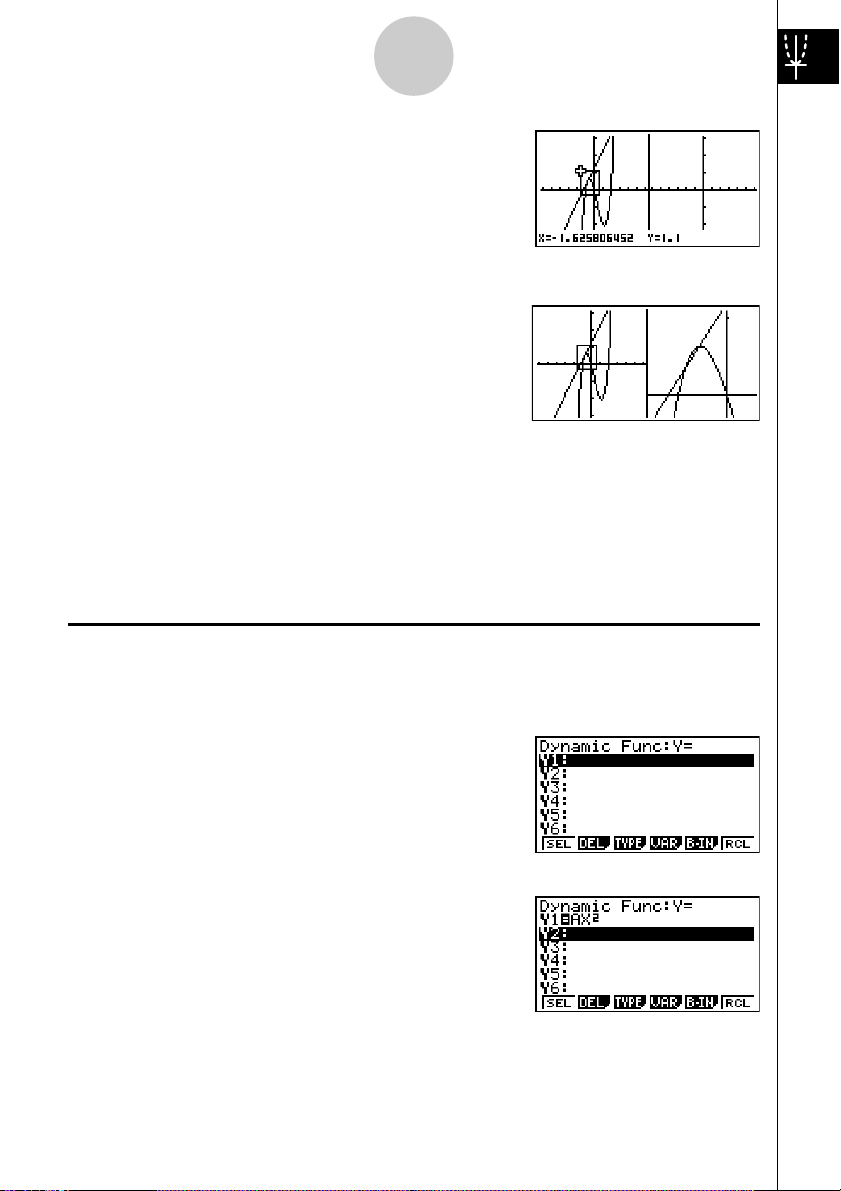
Example:
1. Press !mcc1(G+G)
to specify “G+G” for the Dual Screen setting.
2. Press
To draw the following two graphs and determine the points of intersection
Y1 = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
Y2 = X + 1.2
SET UP
J, and then input the two functions.
v(v+b)
(v-c)w
v+b.cw
3. Press 6(DRAW) or w to draw the graphs.
Box Zoom
Use the Box Zoom function to specify areas of a graph for enlargement.
1. Press !2(ZOOM) 1(BOX).
2. Use
d e f c to move the pointer
to one corner of the area you want to specify and
then press
w
.
20050401
Page 14
9
Quick-Start
3. Use d e f c to move the pointer
again. As you do, a box appears on the display.
Move the pointer so the box encloses the area
you want to enlarge.
4. Press w, and the enlarged area appears in the
inactive (right side) screen.
DYNAMIC GRAPH
Dynamic Graph lets you see how the shape of a graph is affected as the value
assigned to one of the coefficients of its function changes.
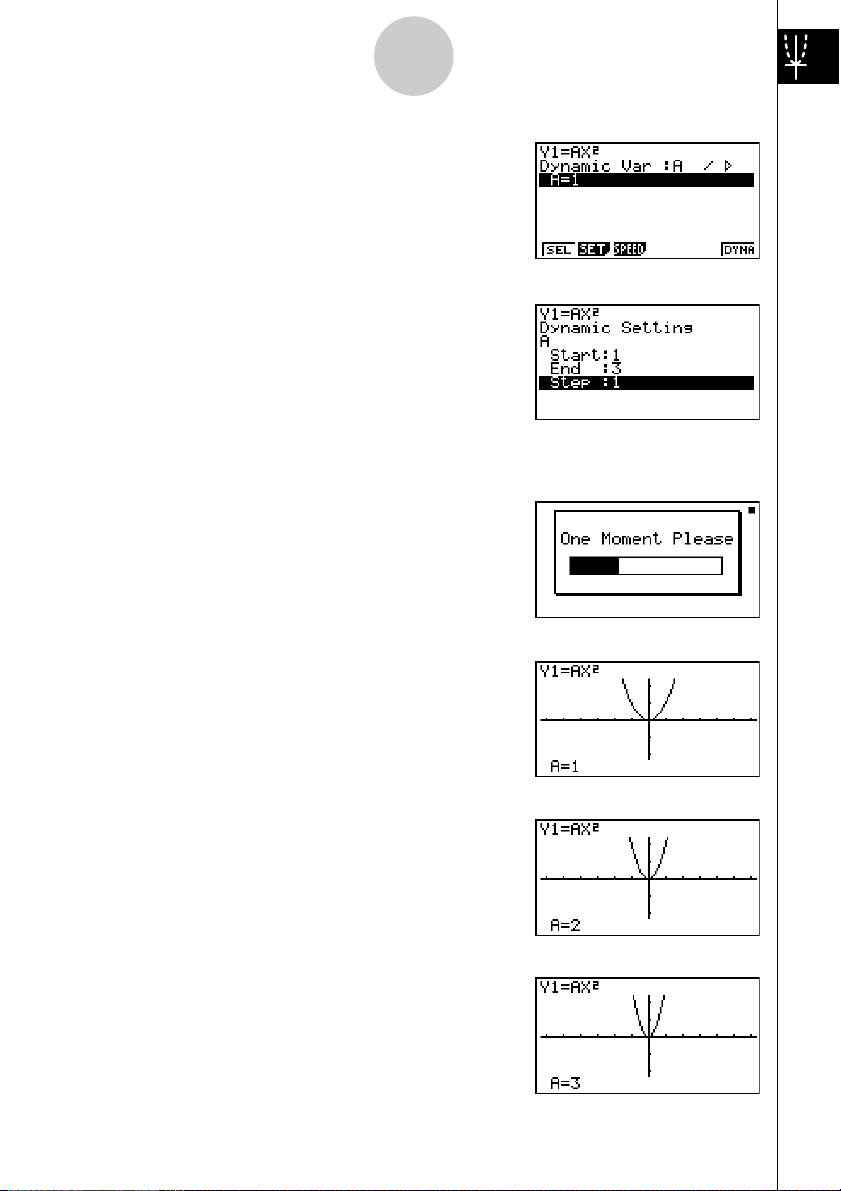
Example:
1. Press m.
2. Use d e f c to highlight DYNA,
and then press w.
3. Input the formula.
a
To draw graphs as the value of coefficient A in the following function changes
from 1 to 3
Y = AX
v
2
A
vxw
20050401
12356
Page 15
10
Quick-Start
4. Press 4(VAR) bw to assign an initial value
of 1 to coefficient A.
5. Press 2(SET) bwdwb
wto specify the range and increment of change
in coefficient A.
6. Press
7. Press 6(DYNA) to start Dynamic Graph drawing.
J.
The graphs are drawn 10 times.
•To interrupt an ongoing Dynamic Graph drawing
operation, press
o.
↓
↓↑
↓↑
20050401
Page 16
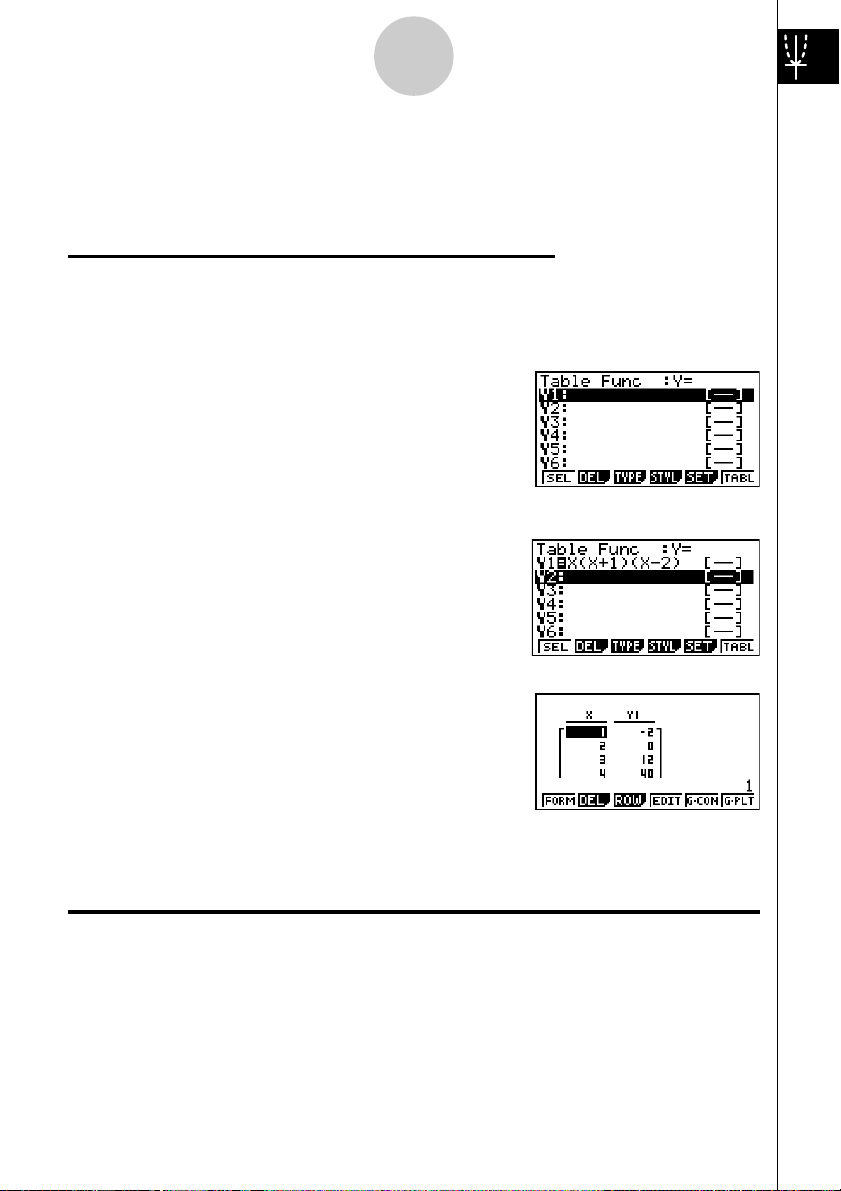
11
Quick-Start
TABLE FUNCTION
The Table Function makes it possible to generate a table of solutions as different
values are assigned to the variables of a function.
Example:
To create a number table for the following function
Y = X (X+1) (X–2)
1. Press m.
2. Use defc to highlight
TABLE, and then press w.
3. Input the formula.
v(v+b)
(v-c)w
4. Press 6(TABL) to generate the number
table.
To learn all about the many powerful features of this calculator, read on and explore!
20050401
Page 17
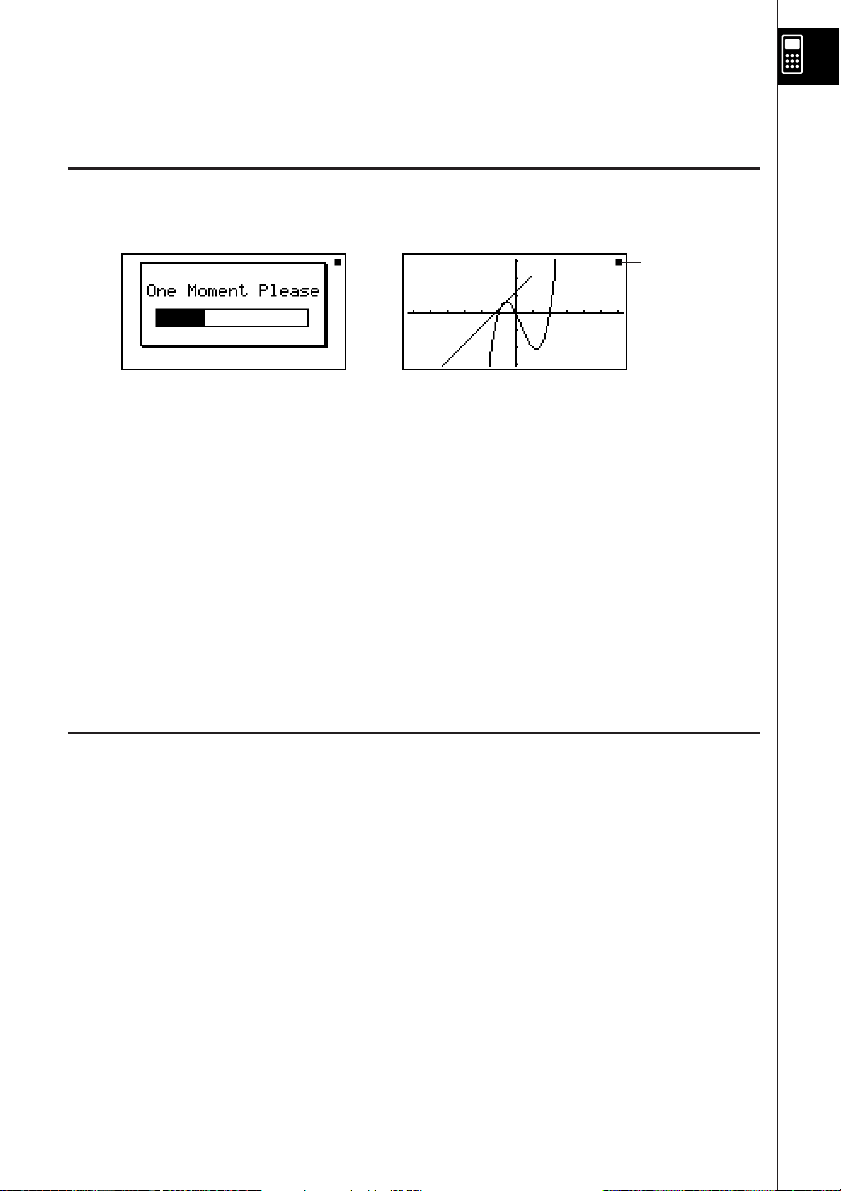
Precautions when Using this Product
A progress bar and/or a busy indicator appear on the display whenever the calculator is
performing a calculation, writing to memory (including Flash memory), or reading from
memory (including Flash memory).
Busy indicator
Progress bar
Never press the P button or remove the batteries from the calculator when the progress bar
or busy indicator is on the display. Doing so can cause memory contents to be lost and can
cause malfunction of the calculator.
This calculator is equipped with Flash memory for data storage. It is recommended that you
always backup your data to Flash memory. For details about the backup procedure, see
“12-7 MEMORY Mode” in the User’s Guide.
You can also transfer data to a computer using the Program-Link software (FA-124) that
comes bundled with the calculator. The Program-Link software can also be used to backup
data to a computer.
Precautions when Connecting to a Computer
A special USB driver must be installed on your computer in order to connect to the calculator.
The driver is installed along with the Program-Link software (FA-124) that comes bundled
with the calculator. Be sure to install the Program-Link software (FA-124) on your computer
before trying to connect the calculator. Attempting to connect the calculator to a computer
that does not have the Program-Link software installed can cause malfunction. For
information about how to install the Program-Link software, see the User’s Guide on the
bundled CD-ROM.
20050401
Page 18

Handling Precautions
•Your calculator is made up of precision components. Never try to take it apart.
•Avoid dropping your calculator and subjecting it to strong impact.
•Do not store the calculator or leave it in areas exposed to high temperatures or humidity, or
large amounts of dust. When exposed to low temperatures, the calculator may require more
time to display results and may even fail to operate. Correct operation will resume once the
calculator is brought back to normal temperature.
• The display will go blank and keys will not operate during calculations. When you are operating
the keyboard, be sure to watch the display to make sure that all your key operations are being
performed correctly.
•Replace the main batteries once every one year regardless of how much the calculator is used
during that period. Never leave dead batteries in the battery compartment. They can leak and
damage the unit.
•Keep batteries out of the reach of small children. If swallowed, consult a physician immediately.
•Avoid using volatile liquids such as thinner or benzine to clean the unit. Wipe it with a soft, dry
cloth, or with a cloth that has been moistened with a solution of water and a neutral detergent
and wrung out.
•Always be gentle when wiping dust off the display to avoid scratching it.
• In no event will the manufacturer and its suppliers be liable to you or any other person for any
damages, expenses, lost profits, lost savings or any other damages arising out of loss of data
and/or formulas arising out of malfunction, repairs, or battery replacement. It is up to you to
prepare physical records of data to protect against such data loss.
•Never dispose of batteries, the liquid crystal panel, or other components by burning them.
•Be sure that the power switch is set to OFF when replacing batteries.
• If the calculator is exposed to a strong electrostatic charge, its memory contents may be
damaged or the keys may stop working. In such a case, perform the Reset operation to clear
the memory and restore normal key operation.
• If the calculator stops operating correctly for some reason, use a thin, pointed object to press
the P button on the back of the calculator. Note, however, that this clears all the data in
calculator memory.
•Note that strong vibration or impact during program execution can cause execution to stop or
can damage the calculator’s memory contents.
•Using the calculator near a television or radio can cause interference with TV or radio reception.
•Before assuming malfunction of the unit, be sure to carefully reread this user’s guide and ensure
that the problem is not due to insufficient battery power, programming or operational errors.
20050401
Page 19

Be sure to keep physical records of all important data!
Low battery power or incorrect replacement of the batteries that power the unit can cause the
data stored in memory to be corrupted or even lost entirely. Stored data can also be affected by
strong electrostatic charge or strong impact. It is up to you to keep back up copies of data to
protect against its loss.
In no event shall CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. be liable to anyone for special, collateral, incidental,
or consequential damages in connection with or arising out of the purchase or use of these
materials. Moreover, CASIO Computer Co., Ltd. shall not be liable for any claim of any kind
whatsoever against the use of these materials by any other party.
• The contents of this user’s guide are subject to change without notice.
•No part of this user’s guide may be reproduced in any form without the express written
consent of the manufacturer.
• The options described in Chapter 12 of this user’s guide may not be available in certain
geographic areas. For full details on availability in your area, contact your nearest CASIO
dealer or distributor.
20050401
Page 20

1
Contents
Contents
Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
Chapter 1 Basic Operation
1-1 Keys ................................................................................................. 1-1-1
1-2 Display .............................................................................................. 1-2-1
1-3 Inputting and Editing Calculations .................................................... 1-3-1
1-4 Option (OPTN) Menu ....................................................................... 1-4-1
1-5 Variable Data (VARS) Menu ............................................................. 1-5-1
1-6 Program (PRGM) Menu ................................................................... 1-6-1
1-7 Using the Setup Screen ................................................................... 1-7-1
1-8 Using Screen Capture ...................................................................... 1-8-1
1-9 When you keep having problems… ................................................. 1-9-1
Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
2-1 Basic Calculations ............................................................................ 2-1-1
2-2 Special Functions ............................................................................. 2-2-1
2-3 Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format ................................. 2-3-1
2-4 Function Calculations ....................................................................... 2-4-1
2-5 Numerical Calculations ..................................................................... 2-5-1
2-6 Complex Number Calculations ......................................................... 2-6-1
2-7 Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations
with Integers ..................................................................................... 2-7-1
2-8 Matrix Calculations ........................................................................... 2-8-1
Chapter 3 List Function
3-1 Inputting and Editing a List ............................................................... 3-1-1
3-2 Manipulating List Data ...................................................................... 3-2-1
3-3 Arithmetic Calculations Using Lists .................................................. 3-3-1
3-4 Switching Between List Files ............................................................ 3-4-1
Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
4-1 Simultaneous Linear Equations ........................................................ 4-1-1
4-2 Quadratic and Cubic Equations ........................................................ 4-2-1
4-3 Solve Calculations ............................................................................ 4-3-1
4-4 What to Do When an Error Occurs ................................................... 4-4-1
20050401
Page 21

2
Contents
Chapter 5 Graphing
5-1 Sample Graphs ................................................................................ 5-1-1
5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen ................................. 5-2-1
5-3 Drawing a Graph .............................................................................. 5-3-1
5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory .................................................. 5-4-1
5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen ...................................... 5-5-1
5-6 Manual Graphing .............................................................................. 5-6-1
5-7 Using Tables ..................................................................................... 5-7-1
5-8 Dynamic Graphing ............................................................................ 5-8-1
5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula ........................................................ 5-9-1
5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph ............................................ 5-10-1
5-11 Function Analysis ........................................................................... 5-11-1
Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
6-1 Before Performing Statistical Calculations ....................................... 6-1-1
6-2 Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data ............... 6-2-1
6-3 Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data .............. 6-3-1
6-4 Performing Statistical Calculations ................................................... 6-4-1
6-5 Tests ................................................................................................. 6-5-1
6-6 Confidence Interval .......................................................................... 6-6-1
6-7 Distribution ....................................................................................... 6-7-1
Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
7-1 Before Performing Financial Calculations ........................................ 7-1-1
7-2 Simple Interest ................................................................................. 7-2-1
7-3 Compound Interest ........................................................................... 7-3-1
7-4 Cash Flow (Investment Appraisal).................................................... 7-4-1
7-5 Amortization ..................................................................................... 7-5-1
7-6 Interest Rate Conversion .................................................................. 7-6-1
7-7 Cost, Selling Price, Margin ............................................................... 7-7-1
7-8 Day/Date Calculations ...................................................................... 7-8-1
20050401
Page 22

Chapter 8 Programming
8-1 Basic Programming Steps ................................................................ 8-1-1
8-2 PRGM Mode Function Keys ............................................................. 8-2-1
8-3 Editing Program Contents ................................................................ 8-3-1
8-4 File Management .............................................................................. 8-4-1
8-5 Command Reference ....................................................................... 8-5-1
8-6 Using Calculator Functions in Programs .......................................... 8-6-1
8-7 PRGM Mode Command List ............................................................ 8-7-1
8-8 Program Library ................................................................................ 8-8-1
Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
9-1 Spreadsheet Overview ..................................................................... 9-1-1
9-2 File Operations and Re-calculation .................................................. 9-2-1
9-3 Basic Spreadsheet Screen Operations ............................................ 9-3-1
9-4 Inputting and Editing Cell Data ......................................................... 9-4-1
• SHT Mode Commands ................................................................ 9-5-1
9-5 S
9-6 Statistical Graphs ............................................................................. 9-6-1
9-7 Using the CALC Function ................................................................. 9-7-1
9-8 Using Memory in the S
Chapter 10 eActivity
10-1 eActivity Overview ........................................................................ 10-1-1
10-2 Working with eActivity Files .......................................................... 10-2-1
10-3 Inputting and Editing eActivity File Data....................................... 10-3-1
10-4 Using Matrix Editor and List Editor ............................................... 10-4-1
10-5 eActivity File Memory Usage Screen ........................................... 10-5-1
3
Contents
• SHT Mode ................................................. 9-8-1
Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
11-1 Using the System Settings Menu ................................................. 11-1-1
11-2 System Settings ........................................................................... 11-2-1
11-3 Version List................................................................................... 11-3-1
11-4 Reset ............................................................................................ 11-4-1
Chapter 12 Data Communications
12-1 Connecting Two Units .................................................................. 12-1-1
12-2 Connecting the Unit to a Personal Computer............................... 12-2-1
12-3 Performing a Data Communication Operation ............................. 12-3-1
12-4 Data Communications Precautions .............................................. 12-4-1
12-5 Image Transfer ............................................................................. 12-5-1
12-6 Add-ins ......................................................................................... 12-6-1
12-7 MEMORY Mode ........................................................................... 12-7-1
20050401
20060601
Page 23

Appendix
1 Error Message Table ...........................................................................α-1-1
2Input Ranges .......................................................................................
3 Specifications .......................................................................................
4 Key Index .............................................................................................α-4-1
5P Button (In case of hang up) .............................................................
6 Power Supply .......................................................................................
4
Contents
α
α
α
α
-2-1
-3-1
-5-1
-6-1
20050401
Page 24

Getting Acquainted
— Read This First!
About this User’s Guide
u! x( )
The above indicates you should press ! and then x, which will input a symbol. All
multiple-key input operations are indicated like this. Key cap markings are shown, followed
by the input character or command in parentheses.
u m EQUA
This indicates you should first press m, use the cursor keys (f, c, d, e) to select
the EQUA mode, and then press w. Operations you need to perform to enter a mode from
the Main Menu are indicated like this.
0
uFunction Keys and Menus
•Many of the operations performed by this calculator can be executed by pressing function
keys 1 through 6. The operation assigned to each function key changes according to
the mode the calculator is in, and current operation assignments are indicated by function
menus that appear at the bottom of the display.
• This user’s guide shows the current operation assigned to a function key in parentheses
following the key cap for that key. 1(Comp), for example, indicates that pressing 1
selects {Comp}, which is also indicated in the function menu.
•When (g) is indicated in the function menu for key 6, it means that pressing 6 displays
the next page or previous page of menu options.
uu
uMenu Titles
uu
•Menu titles in this user’s guide include the key operation required to display the menu
being explained. The key operation for a menu that is displayed by pressing K and then
{MAT} would be shown as: [OPTN]-[MAT].
• 6(g) key operations to change to another menu page are not shown in menu title key
operations.
20050401
Page 25
0-1-1
20050401
1-2-2
Display
Icon Mode Name Description
S•SHT Use this mode to perform spreadsheet calculations. Each file
(Spreadsheet) contains a 26-column ⋅ 999-line spreadsheet. In addition to
the calculator’s built-in commands and S
•
SHT mode
commands, you can also perform statistical calculations and
graph statistical data using the same procedures that you use
in the STATmode.
GRAPH Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw graphs
using the functions.
DYNA Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw multiple
(Dynamic Graph) versions of a graph by changing the values assigned to the
variables in a function.
TABLE Use this mode to store functions, to generate a numeric
table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
RECUR Use this mode to store recursion formulas, to generate a
(Recursion) numeric table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
CONICS Use this mode to draw graphs of conic sections.
EQUA Use this mode to solve linear equations with two through six
(Equation) unknowns, quadratic equations, and cubic equations.
PRGM Use this mode to store programs in the program area and to
(Program) run programs.
TVM Use this mode to perform financial calculations and to draw
(Financial) cash flow and other types of gra phs. to make
LINK Use this mode to transfer memory contents or back-up data
to another unit or PC.
MEMORY Use this mode to manage data stored in memory.
SYSTEM Use this mode to initialize memory, adjust contrast, and to
make other system settings.
20050401
kk
kk
kAbout the Function Menu
Use the function keys (1 to 6) to access the menus and commands in the menu bar
along the bottom of the display screen. You can tell whether a menu bar item is a menu or a
command by its appearance.
• Next Menu
Example:
Selecting displays a menu of hyperbolic functions.
• Command Input
Example:
Selecting inputs the sinh command.
• Direct Command Execution
Example:
Selecting executes the DRAW command.
kk
kk
kAbout Display Screens
This calculator uses two types of display screens: a text screen and a graph screen. The text
screen can show 21 columns and 8 lines of characters, with the bottom line used for the
function key menu. The graph screen uses an area that measures 127 (W) ⋅ 63 (H) dots.
Text Screen Graph Screen
The contents of each type of screen are stored in independent memory areas.
Press!6(G T) to switch between the graph screen and text screen.
1-2-3
Display
1-2-2
Display
1-2-3
Display
5-1-1
Sample Graphs
5-1-2
Sample Graphs
20050301
Example To graph y = 3
x
2
Procedure
1m GRAPH
2dvxw
36(DRAW) (or w)
Result Screen
#Pressing Awhile a graph is on the display
will return to the screen in step 2.
Getting Acquainted
uGraphs
As a general rule, graph operations are shown on
facing pages, with actual graph examples on the right
hand page. You can produce the same graph on your
calculator by performing the steps under the Procedure
above the graph.
Look for the type of graph you want on the right hand
page, and then go to the page indicated for that graph.
The steps under “Procedure” always use initial RESET
settings.
The step numbers in the “Set Up” and “Execution” sections on the left hand page
correspond to the “Procedure” step numbers on the right hand page.
Example:
Left hand page Right hand page
3. Draw the graph. 3 5(DRAW)(or w)
uu
uCommand List
uu
The PRGM Mode Command List (page 8-7) provides a graphic flowchart of the various
function key menus and shows how to maneuver to the menu of commands you need.
Example: The following operation displays Xfct: [VARS]-[FACT]-[Xfct]
5-1 Sample Graphs
kkkkkHow to draw a simple graph (1)
Description
Todraw a graph, simply input the applicable function.
Set Up
1. From the Main Menu, enter the GRAPH Mode.
Execution
2.Input the function you want to graph.
Here you would use the V-Window to specify the range and other parameters of the
graph. See 5-2-1.
3.Draw the graph.
20050301
uu
uPage Contents
uu
Three-part page numbers are centered at the top of
each page. The page number “1-2-3”, for example,
indicates Chapter 1, Section 2, page 3.
uu
uSupplementary Information
uu
Supplementary information is shown at the bottom of each page in a “ (Notes)” block.
indicates a note about a term that appears in the same page as the note.
*
# indicates a note that provides general information about topic covered in the same section
as the note.
20050401
Page 26

Chapter
Basic Operation
1-1 Keys
1-2 Display
1-3 Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-4 Option (OPTN) Menu
1-5 Variable Data (VARS) Menu
1-6 Program (PRGM) Menu
1-7 Using the Setup Screen
1-8 Using Screen Capture
1-9 When you keep having problems…
1
20050401
Page 27

1-1 Keys
1-1-1
Keys
20050401
Page 28
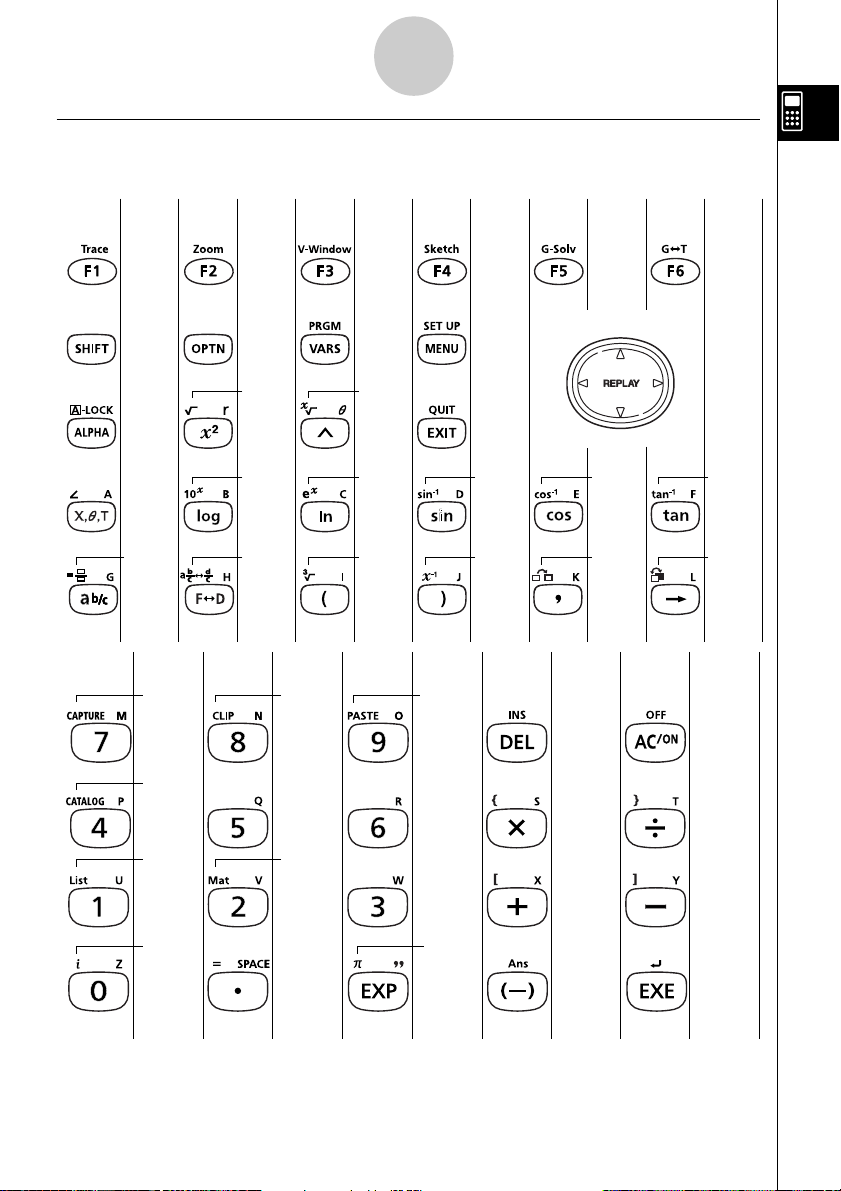
kk
k Key Table
kk
Page Page Page Page Page Page
1-1-2
Keys
5-11-1
5-2-7 5-2-1
1-6-1
5-10-1 5-11-9
1-7-1
1-1-3 1-4-1 1-5-1 1-2-1
2-4-7 2-4-5
1-1-3 2-4-7 2-4-5
2-4-10
2-4-10
2-4-5 2-4-5
2-4-5 2-4-5
2-4-12
2-4-11
2-4-7
2-1-1
2-4-4 2-4-4
2-4-4 2-4-4
2-4-7
10-3 -13 10 -3 -12
2-1-1
Page Page Page Page Page
1-8-1
1-3-5
1-3-7
1-3-2
1-3-1
1-3-7
2-1-1
1-2-3
2-4-4
2-4-4
2-2-1
2-1-1
3-1-2
2-8-11
2-6-2 2-4-4
20050401
2-1-1
2-2-5
2-1-12-1-1
2-1-1
Page 29
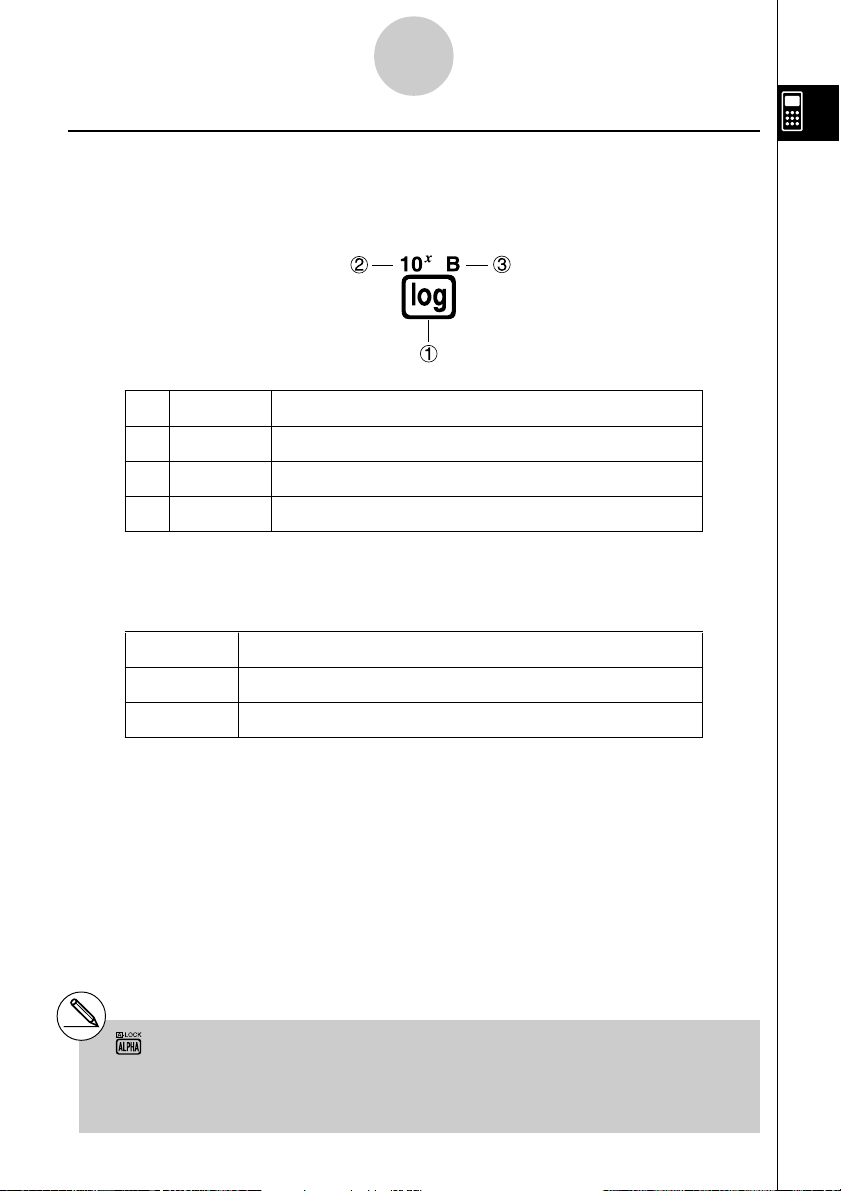
1-1-3
Keys
kk
k Key Markings
kk
Many of the calculator’s keys are used to perform more than one function. The functions
marked on the keyboard are color coded to help you find the one you need quickly and
easily.
Function Key Operation
1 log l
2 10
x
!l
3 B al
The following describes the color coding used for key markings.
Color Key Operation
Orange Press ! and then the key to perform the marked function.
Red Press a and then the key to perform the marked function.
# Alpha Lock
Normally, once you press a and then a key
to input an alphabetic character, the keyboard
reverts to its primary functions immediately.
If you press ! and then a, the keyboard
locks in alpha input until you press a again.
20050401
Page 30
1-2-1
Display
1-2 Display
k Selecting Icons
This section describes how to select an icon in the Main Menu to enter the mode you want.
uu
u To select an icon
uu
1. Press m to display the Main Menu.
2. Use the cursor keys (d, e, f, c) to move the highlighting to the icon you want.
Currently selected icon
3. Press w to display the initial screen of the mode whose icon you selected.
Here we will enter the STAT mode.
•You can also enter a mode without highlighting an icon in the Main Menu by inputting the
number or letter marked in the lower right corner of the icon.
The following explains the meaning of each icon.
Icon Mode Name Description
•
RUN
MAT Use this mode for arithmetic calculations and function
•
(Run
Matrix) calculations, and for calculations involving binary, octal,
STAT Use this mode to perform single-variable (standard deviation)
(Statistics) and paired-variable (regression) statistical calculations, to
•
e
ACT eActivity lets you input text, math expressions, and other data
(eActivity) in a notebook-like interface. Use this mode when you want to
decimal, and hexadecimal values and matrices.
perform tests, to analyze data and to draw statistical graphs.
store text or formulas, or built-in application data in a file.
20050401
Page 31

1-2-2
Display
Icon Mode Name Description
•
S
SHT Use this mode to perform spreadsheet calculations. Each file
(Spreadsheet) contains a 26-column × 999-line spreadsheet. In addition to
the calculator’s built-in commands and S
commands, you can also perform statistical calculations and
graph statistical data using the same procedures that you use
in the STAT mode.
GRAPH Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw graphs
using the functions.
DYNA Use this mode to store graph functions and to draw multiple
(Dynamic Graph) versions of a graph by changing the values assigned to the
variables in a function.
TABLE Use this mode to store functions, to generate a numeric
table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
RECUR Use this mode to store recursion formulas, to generate a
(Recursion) numeric table of different solutions as the values assigned to
variables in a function change, and to draw graphs.
CONICS Use this mode to draw graphs of conic sections.
EQUA Use this mode to solve linear equations with two through six
(Equation) unknowns, quadratic equations, and cubic equations.
PRGM Use this mode to store programs in the program area and to
(Program) run programs.
•
SHT mode
TVM Use this mode to perform financial calculations and to draw
(Financial) cash flow and other types of graphs. to make
LINK Use this mode to transfer memory contents or back-up data
to another unit or PC.
MEMORY Use this mode to manage data stored in memory.
SYSTEM Use this mode to initialize memory, adjust contrast, and to
make other system settings.
20050401
Page 32

1-2-3
Display
kk
k About the Function Menu
kk
Use the function keys (1 to 6) to access the menus and commands in the menu bar
along the bottom of the display screen. You can tell whether a menu bar item is a menu or a
command by its appearance.
• Next Menu
Example:
Selecting displays a menu of hyperbolic functions.
• Command Input
Example:
Selecting inputs the sinh command.
• Direct Command Execution
Example:
Selecting executes the DRAW command.
kk
k About Display Screens
kk
This calculator uses two types of display screens: a text screen and a graph screen. The text
screen can show 21 columns and 8 lines of characters, with the bottom line used for the
function key menu. The graph screen uses an area that measures 127 (W) × 63 (H) dots.
Text Screen Graph Screen
The contents of each type of screen are stored in independent memory areas.
Press !6(G↔T) to switch between the graph screen and text screen.
20050401
Page 33

1-2-4
Display
kk
k Normal Display
kk
The calculator normally displays values up to 10 digits long. Values that exceed this limit are
automatically converted to and displayed in exponential format.
u How to interpret exponential format
1.2E+12 indicates that the result is equivalent to 1.2 × 1012. This means that you should move
the decimal point in 1.2 twelve places to the right, because the exponent is positive. This
results in the value 1,200,000,000,000.
1.2E–03 indicates that the result is equivalent to 1.2 × 10–3. This means that you should move
the decimal point in 1.2 three places to the left, because the exponent is negative. This
results in the value 0.0012.
You can specify one of two different ranges for automatic changeover to normal display.
Norm 1 .................. 10–2 (0.01) > |x|, |x| > 10
Norm 2 .................. 10–9 (0.000000001) > |x|, |x| > 10
10
10
All of the examples in this manual show calculation results using Norm 1.
See page 2-3-2 for details on switching between Norm 1 and Norm 2.
20050401
Page 34

1-2-5
Display
kk
k Special Display Formats
kk
This calculator uses special display formats to indicate fractions, hexadecimal values, and
degrees/minutes/seconds values.
u Fractions
................. Indicates: 456
u Hexadecimal Values
................. Indicates: 0ABCDEF1(16), which
equals 180150001(10)
u Degrees/Minutes/Seconds
................. Indicates: 12° 34’ 56.78”
• In addition to the above, this calculator also uses other indicators or symbols, which are
described in each applicable section of this manual as they come up.
kk
k Calculation Execution Indicator
kk
Whenever the calculator is busy drawing a graph or executing a long, complex calculation or
program, a black box “k” flashes in the upper right corner of the display. This black box tells
you that the calculator is performing an internal operation.
12
––––
23
20050401
Page 35

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-1
1-3 Inputting and Editing Calculations
Note
•Unless specifically noted otherwise, all of the operations in this section are explained using the
Linear input mode.
kk
k Inputting Calculations
kk
When you are ready to input a calculation, first press A to clear the display. Next, input
your calculation formulas exactly as they are written, from left to right, and press w to
obtain the result.
○○○○○
Example 1 2 + 3 – 4 + 10 =
Ac+d-e+baw
○○○○○
Example 2 2(5 + 4) ÷ (23 × 5) =
Ac(f+e)/
(cd*f)w
k Editing Calculations
Use the d and e keys to move the cursor to the position you want to change, and then
perform one of the operations described below. After you edit the calculation, you can
execute it by pressing w. Or you can use e to move to the end of the calculation and
input more.
u To change a step
○○○○○
Example To change cos60 to sin60
Acga
ddd
D
s
20050401
Page 36

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-2
In the Linear input mode, pressing !D(INS) changes the cursor to ‘‘ ’’.
The next function or value you input is overwritten at the location of ‘‘ ’’.
Acga
ddd!D(INS)
s
To abort this operation, press !D(INS) again.
u To delete a step
○○○○○
Example To change 369 × × 2 to 369 × 2
Adgj**c
dD
In the insert mode, the D key operates as a backspace key.
#The cursor is a vertical flashing line (I) when
the insert mode is selected. The cursor is a
horizontal flashing line (
mode is selected.
) when the overwrite
# The initial default for Linear input mode is the
insert mode. You can switch to the overwrite
mode by pressing 1Y(INS).
20050401
Page 37

Inputting and Editing Calculations
u To insert a step
○○○○○
Example To change 2.362 to sin2.36
Ac.dgx
ddddd
s
u To change the last step you input
○○○○○
Example To change 369 × 3 to 369 × 2
Adgj*d
D
c
1-3-3
2
20050401
Page 38

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-4
kk
k Using Replay Memory
kk
The last calculation performed is always stored into replay memory. You can recall the
contents of the replay memory by pressing d or e.
If you press e, the calculation appears with the cursor at the beginning. Pressing d
causes the calculation to appear with the cursor at the end. You can make changes in the
calculation as you wish and then execute it again.
○○○○○
Example 1 To perform the following two calculations
4.12 × 6.4 = 26.368
4.12 × 7.1 = 29.252
Ae.bc*g.ew
dddd
!D(INS)
h.b
w
After you press A, you can press f or c to recall previous calculations, in sequence
from the newest to the oldest (Multi-Replay Function). Once you recall a calculation, you can
use e and d to move the cursor around the calculation and make changes in it to create
a new calculation.
○○○○○
Example 2
Abcd+efgw
cde-fghw
A
f (One calculation back)
f (Two calculations back)
#A calculation remains stored in replay memory
until you perform another calculation.
# The contents of replay memory are not
cleared when you press the A key, so you
can recall a calculation and execute it even
after pressing the A key.
# Replay memory is enabled in the Linear input
mode only. In the Math input mode, the history
function is used in place of the replay memory.
For details, see “History Function” (page 2-2-6).
20050901
20050401
Page 39

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-5
k Making Corrections in the Original Calculation
○○○○○
Example 14 ÷ 0 × 2.3 entered by mistake for 14 ÷ 10 × 2.3
Abe/a*c.d
w
Press J.
Cursor is positioned automatically at the
location of the cause of the error.
Make necessary changes.
db
Execute again.
w
kk
k Using the Clipboard for Copy and Paste
kk
You can copy (or cut) a function, command, or other input to the clipboard, and then paste
the clipboard contents at another location.
u To specify the copy range
Linear input mode
1. Move the cursor (I) to the beginning or end of the range of text you want to copy and
then press !i(CLIP).This changes the cursor to “ ”.
2. Use the cursor keys to move the cursor and highlight the range of text you want to
copy.
# The copy range of text you can specify
depends on the current “Input Mode” setting.
Linear input mode: 1 character
1 line
Multiple lines
Math input mode: 1 line only
20050401
Page 40

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-6
3. Press 1(COPY) to copy the highlighted text to the clipboard, and exit the copy range
specification mode.
The selected characters are not changed
when you copy them.
To cancel text highlighting without performing a copy operation, press J.
Math input mode
1. Use the cursor keys to move the cursor to the line you want to copy.
2. Press !i(CLIP) . The cursor will change to “ ”.
3. Press 1(CPY
•
L) to copy the highlighted text to the clipboard.
u To cut the text
1. Move the cursor (I) to the beginning or end of the range of text you want to cut and
then press !i(CLIP). This changes the cursor to “ ”.
2. Use the cursor keys to move the cursor and highlight the range of text you want to cut.
3. Press 2(CUT) to cut the highlighted text to the clipboard.
Cutting causes the original characters
to be deleted.
The CUT operation is supported for the Linear input mode only. It is not supported for the Math
input mode.
20050401
Page 41

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-7
u Pasting Text
Move the cursor to the location where you want to paste the text, and then press !
j(PASTE). The contents of the clipboard are pasted at the cursor position.
A
!j(PASTE)
kk
k Catalog Function
kk
The Catalog is an alphabetic list of all the commands available on this calculator. You can
input a command by calling up the Catalog and then selecting the command you want.
u To use the Catalog to input a command
1. Press !e(CATALOG) to display an alphabetic Catalog list of commands.
2. Input the first letter of the command you want to input. This will display the first
command that starts with that letter.
3. Use the cursor keys (f, c) to highlight the command you want to input, and then
press w.
○○○○○
Example To use the Catalog to input the ClrGraph command
A!e(CATALOG)I(C)c~cw
Pressing J or !J(QUIT) closes the Catalog.
20050401
Page 42

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-8
k Input Operations in the Math Input Mode
Selecting “Math” for the “Input Mode” setting on the Setup screen (page 1-7-1) turns on the
Math input mode, which allows natural input and display of certain functions, just as they
appear in your textbook.
Note
• The initial default “Input Mode” setting is “Linear” (Linear input mode). Before trying to
perform any of the operations explained in this section, be sure to change the “Input Mode”
setting to “Math”.
• In the Math input mode, all input is insert mode (not overwrite mode) input. Note that the
!D(INS) operation (page 1-3-2) you use in the Linear input mode to switch to insert
mode input performs a completely different function in the Math input mode. For more
information, see “Inserting a Function into an Existing Expression” (page 1-3-13).
•Unless specifically stated otherwise, all operations in this section are performed in the
•
RUN
MAT mode.
20050401
Page 43

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-9
u Math Input Mode Functions and Symbols
The functions and symbols listed below can be used for natural input in the Math input
mode. The “Bytes” column shows the number of bytes of memory that are used up by input
in the Math input mode.
Function/Symbol Key Operation Bytes
Fraction (Improper) $ 9
Mixed Fraction*
Power M 4
Square x 4
Negative Power (Reciprocal) !)(x
Cube Root !((3
Power Root !M(x)9
x
e
x
10
log(a,b) (Input from MATH menu*2)7
Abs (Absolute Value) (Input from MATH menu*2)6
Linear Differential*
Quadratic Differential*
Integral*
Σ Calculation*
Matrix (Input from MATH menu*2) 14*
Parentheses ( and ) 1
Braces (Used during list input.) !*( { ) and !/( } ) 1
Brackets (Used during matrix input.) !+( [ ) and !-( ] ) 1
1
!$(&)14
–1
)5
!x( )6
)9
!I(ex)6
!l(10x)6
3
3
3
4
(Input from MATH menu*2)7
(Input from MATH menu*2)7
(Input from MATH menu*2)8
(Input from MATH menu*2)11
5
*1Mixed fraction is supported in the Math input
mode only.
2
*
For information about function input from the
MATH function menu, see “Using the MATH
Menu” on page 1-3-10.
3
To lerance cannot be specified in the Math input
*
mode. If you want to specify tolerance, use the
Linear input mode.
4
*
For Σ calculation in the Math input mode, the
pitch is always 1. If you want to specify a
different pitch, use the Linear input mode.
5
*
This is the number of bytes for a 2 × 2 matrix.
20050401
Page 44

f(x)
x=α
β
α
Σ
Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-10
u Using the MATH Menu
In the RUN
You can use this menu for natural input of matrices, differentials, integrals, etc.
•
MAT mode, pressing 4(MATH) displays the MATH menu.
•{MAT} ... {displays the MAT submenu, for natural input of matrices}
•{2×2} ... {inputs a 2 × 2 matrix}
•{3×3} ... {inputs a 3 × 3 matrix}
•{m×n} ... {inputs a matrix with m lines and n columns (up to 6 × 6)}
•{logab} ... {starts natural input of logarithm log ab}
•{Abs} ... {starts natural input of absolute value |X|}
d
•{d/dx} ... {starts natural input of linear differential
•{d2/dx2} ... {starts natural input of quadratic differential
•{∫dx} … {starts natural input of integral
b
f(x)dx
a
•{Σ(} … {starts natural input of Σ calculation
f(x)
}
x = a
dx
2
d
f(x)
x = a
2
dx
}
}
}
u Math Input Mode Input Examples
This section provides a number of different examples showing how the MATH function
menu and other keys can be used during Math input mode natural input. Be sure to pay
attention to the input cursor position as you input values and data.
○○○○○
Example 1 To input 23 + 1
AcM
d
e
+b
w
20050401
Page 45

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-11
○○○○○
Example 2 To input
A(b+
$
cc
f
e
)x
w
J
○○○○○
Example 3 To input
Ab+4(MATH)6(g)1(∫dx)
2
2
1+
(
)
5
1
1+ x + 1dx
0
a+(X)+b
ea
fb
e
w
J
20050401
Page 46

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-12
○○○○○
Example 4 To input
2 ×
1
2
2
1
2
2
Ac*4(MATH)1(MAT)1(2×2)
$bcc
ee
!x( )ce
e!x( )cee$bcc
w
u When the calculation does not fit within the display window
Arrows appear at the left, right, top, or bottom edge of the display to let you know when
there is more of the calculation off the screen in the corresponding direction.
When you see an arrow, you can use the cursor keys to scroll the screen contents and
view the part you want.
20050401
Page 47

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-13
u Inserting a Function into an Existing Expression
In the Math input mode, you can make insert a natural input function into an existing
expression. Doing so will cause the value or parenthetical expression to the right of the
cursor to become the argument of the inserted function. Use !D(INS) to insert a
function into an existing expression.
u To insert a function into an existing expression
○○○○○
Example To insert the function into the expression 1 + (2 + 3) + 4 so the
1. Move the cursor so it is located directly to the left of the part of the expression that
2. Press !D(INS).
3. Press !x( ) to insert the function.
parenthetical expression becomes the argument of the function
you want to become the argument of the function you will insert.
• This changes the cursor to an insert cursor (').
• This inserts the function and makes the parenthetical expression its argument.
u Function Insert Rules
The following are the basic rules that govern how a value or expressions becomes the
argument of an inserted function.
• If the insert cursor is located immediately to the left of an open parenthesis, everything
from the open parenthesis to the following closing parenthesis will be the argument of the
inserted function.
• If the input cursor is located immediately to the left of a value or fraction, that value or
fraction will be the argument of the inserted function.
#In the Linear input mode, pressing
!D(INS) will change to the insert mode.
See page 1-3-2 for more information.
20050401
Page 48

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-14
u Functions that Support Insertion
The following lists the functions that can be inserted using the procedure under “To insert a
function into an existing expression” (page 1-3-13). It also provides information about how
insertion affects the existing calculation.
Function Key Operation
Improper Fraction $
Powe r M
!x( )
3
Cube Root !((
Power Root !M(
x
e
10
x
!I(
!l(10x)
)
x
)
e
x
)
log(a,b) 4(MATH)2(logab)
Absolute Value 4(MATH)3(Abs)
Linear Differential 4(MATH)4(
Quadratic Differential 4(MATH)5(
Integral
Σ Calculation
4(MATH)6(g)
1(
∫dx
4(MATH)6(g)
Σ
( )
2(
d/dx
2
d
/
dx
)
)
2
)
Original
Expression
Expression After
Insertion
u Editing Calculations in the Math Input Mode
The procedures for editing calculations in the Math input mode are basically the same as
those for the Linear input mode. For more information, see “Editing Calculations” (page
1-3-1).
Note however, that the following points are different between the Math input mode and the
Linear input mode.
•Overwrite mode input that is available in the Linear input mode is not supported by the
Math input mode. In the Math input mode, input is always
location.
• In the Math input mode, pressing the D key always performs a backspace operation.
20050401
inserted
at the current cursor
Page 49

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-15
•Note the following cursor operations you can use while inputting a calculation with natural
display format.
To do this: Press this key:
Move the cursor from the end of the calculation to the beginning e
Move the cursor from the beginning of the calculation to the end d
u Math Input Mode Calculation Result Display
Fractions, matrices, and lists produced by Math input mode calculations are displayed in
natural format, just as they appear in your textbook.
Sample Calculation Result Displays
#Fractions are displayed either as improper
fractions or mixed fractions, depending on the
“Frac Result” setting on the Setup screen. For
details, see “1-7 Using the Setup Screen”.
# Matrices are displayed in natural format, up
to 6 × 6. A matrix that has more than six rows
or columns will be displayed on a MatAns
screen, which is the same screen used in the
Linear input mode.
#Lists are displayed in natural format for up to
20 elements. A list that has more than 20
elements will be displayed on a ListAns
screen, which is the same screen used in the
Linear input mode.
#Arrows appear at the left, right, top, or bottom
edge of the display to let you know when
there is more data off the screen in the
corresponding direction.
You can use the cursor keys to scroll the screen
and view the data you want.
# Pressing 2(DEL)1(DEL
• L) while a
calculation result is selected will delete both the
result and the calculation that produced it.
# The multiplication sign cannot be omitted
immediately before an improper fraction or
mixed fraction. Be sure to always input a
multiplication sign in this case.
Example: 2 × —
# A M, x, or !)(
be followed immediately by another M, x, or
!)(
2
5
c*$ccf
–1
x
) key operation. In this case, use
–1
x
) key operation cannot
parentheses to keep the key operations
separate.
Example: (3
2)–1
(dx)!)(x–1)
20050401
20060601
Page 50

Inputting and Editing Calculations
1-3-16
u Math Input Mode Input Restrictions
Note the following restrictions that apply during input of the Math input mode.
•Certain types of expressions can cause the vertical width of a calculation formula to be
greater than one display line. The maximum allowable vertical width of a calculation
formula is about two display screens (120 dots). You cannot input any expression that
exceeds this limitation.
20050401
20060601
Page 51

1-4-1
Option (OPTN) Menu
1-4 Option (OPTN) Menu
The option menu gives you access to scientific functions and features that are not marked on
the calculator’s keyboard. The contents of the option menu differ according to the mode you
are in when you press the K key.
See “8-7 PRGM Mode Command List” for details on the option (OPTN) menu.
u Option menu in the RUN
•
MAT or PRGM mode
•{LIST} ... {list function menu}
•{MAT} ... {matrix operation menu}
•{CPLX} ... {complex number calculation menu}
•{CALC} ... {functional analysis menu}
•{STAT} ... {paired-variable statistical estimated value menu}
•{HYP} ... {hyperbolic calculation menu}
•{PROB} ... {probability/distribution calculation menu}
•{NUM} ... {numeric calculation menu}
•{ANGL} ... {menu for angle/coordinate conversion, DMS input/conversion}
•{ESYM} ... {engineering symbol menu}
•{PICT} ... {picture memory menu}*
•{FMEM} ... {function memory menu}*
1
1
•{LOGIC} ... {logic operator menu}
•{CAPT} ... {screen capture menu}
# The option (OPTN) menu does not appear
during binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal
calculations.
1
*
The PICT, FMEM and CAPT items are not
displayed when “Math” is selected as the
Input Mode.
20050401
Page 52

1-4-2
Option (OPTN) Menu
u Option menu during numeric data input in the STAT, TABLE, RECUR, EQUA
•
and S
• {LIST}/{CPLX}/{CALC}/{HYP}/{PROB}/{NUM}/{ANGL}/{ESYM}/{FMEM}/{LOGIC}
uu
u Option menu during formula input in the GRAPH, DYNA, TABLE, RECUR
uu
SHT modes
and EQUA modes
• {List}/{CALC}/{HYP}/{PROB}/{NUM}/{FMEM}/{LOGIC}
The following shows the function menus that appear under other conditions.
u Option menu when a number table value is displayed in the TABLE or
RECUR mode
•{LMEM} … {list memory menu}
•{
}/{ENG}/{ENG}
° ’ ”
The meanings of the option menu items are described in the sections that cover each mode.
20050401
Page 53

Variable Data (VARS) Menu
1-5-1
1-5 Variable Data (VARS) Menu
To recall variable data, press J to display the variable data menu.
{V-W IN}/{FACT}/{STAT}/{GRPH}/{DYNA}/
{TABL}/{RECR}/{EQUA*1}/{TVM*1}
See “8-7 PRGM Mode Command List” for details on the variable data (VARS) menu.
u V-WIN — Recalling V-Window values
• {X}/{Y}/{T,
• {R-X}/{R-Y}/{R-T,
• {min}/{max}/{scal}/{dot}/{ptch}
u FACT — Recalling zoom factors
•{Xfact}/{Yfact}
θ
}
... {x-axis menu}/{y-axis menu}/{T,
θ
{x-axis menu}/{y-axis menu}/{T,θ menu} for right side of Dual Graph
...
}
θ
menu}
... {minimum value}/{maximum value}/{scale}/{dot value*2}/{pitch}
... {x-axis factor}/{y-axis factor}
*1The EQUA and TVM items appear only when
you access the variable data menu from the
RUN
•
MAT, PRGM or e
# The variable data menu does not appear if
you press J while binary, octal, decimal, or
hexadecimal is set as the default number
system.
•
ACT mode.
2
*
The dot value indicates the display range (Xmax
value – Xmin value) divided by the screen dot
pitch (126).
The dot value is normally calculated automatically from the minimum and maximum values.
Changing the dot value causes the maximum to
be calculated automatically.
20050401
Page 54

Variable Data (VARS) Menu
1-5-2
u STAT — Recalling statistical data
• {X} … {single-variable, paired-variable x-data}
•{n}/{
oo
o}/{Σ x}/{Σx
oo
2
}/{x
σ
n}/{xσn–1}/{minX}/{maxX}
…{number of data}/{mean}/{sum}/{sum of squares}/{population standard
deviation}/{sample standard deviation}/{minimum value}/{maximum value}
• {Y} ... {paired-variable y-data}
•{
pp
p
}/{Σ
pp
2
y}/{Σ y
}/{Σ
xy}/{ y
σ
n}/{
y
σ
n–1}/{minY}/{maxY}
…{mean}/{sum}/{sum of squares}/{sum of products of x-data and y-data}/
{population standard deviation}/{sample standard deviation}/{minimum value}/
{maximum value}
•{GRPH} ... {graph data menu}
•{a}/{b}/{c}/{d}/{e}
... {regression coefficient and polynomial coefficients}
•{r}/{r2} ... {correlation coefficient}/{coefficient of determination}
•{MSe} ... {mean square error}
•{Q1}/{Q3}
... {first quartile}/{third quartile}
•{Med}/{Mod}
... {median}/{mode} of input data
•{Strt}/{Pitch}
... histogram {start division}/{pitch}
•{PTS} ... {summary point data menu}
•{x1}/{y1}/{x2}/{y2}/{x3}/{y3} ... {coordinates of summary points}
20050401
Page 55

Variable Data (VARS) Menu
1-5-3
u GRPH — Recalling Graph Functions
•{Y}/{r} ... {rectangular coordinate or inequality function}/{polar coordinate function}
•{Xt}/{Yt}
... parametric graph function {Xt}/{Yt}
•{X} ... {X=constant graph function}
(Press these keys before inputting a value to specify a storage memory.)
u DYNA — Recalling Dynamic Graph Set Up Data
•{Strt}/{End} /{Pitch}
... {coefficient range start value}/{coefficient range end value}/{coefficient value
increment}
u TABL — Recalling Table Set Up and Content Data
•{Strt}/{End} /{Pitch}
... {table range start value}/{table range end value}/{table value increment}
•{Reslt*1}
... {matrix of table contents}
1
*
The Reslt item appears only when the TABL
menu is displayed in the RUN
e
•
ACT mode.
•
MAT, PRGM or
20050401
Page 56

Variable Data (VARS) Menu
1-5-4
u RECR — Recalling Recursion Formula*
• {FORM}
... {recursion formula data menu}
1
, Table Range, and Table Content Data
• {an}/{an+1}/{an+2}/{bn}/{bn+1}/{bn+2}/{cn}/{cn+1}/{cn+2}
... {an}/{an+1}/{an+2}/{bn}/{bn+1}/{bn+2}/{cn}/{cn+1}/{cn+2} expressions
• {RANG} ... {table range data menu}
• {Strt}/{End}
... table range {start value}/{end value}
• {a0}/{a1}/{a2}/{b0}/{b1}/{b2}/{c0}/{c1}/{c2}
... {a0}/{a1}/{a2}/{b0}/{b1}/{b2}/{c0 }/{c1}/{c2} value
• {anSt}/{bnSt}/{cnSt}
... origin of {an }/{bn}/{cn} recursion formula convergence/divergence graph (WEB
graph)
• {Reslt*2} ... {matrix of table contents*
3
}
u EQUA — Recalling Equation Coefficients and Solutions*
• {S-Rlt}/{S-Cof}
... matrix of {solutions}/{coefficients} for linear equations with two through six
unknowns*
6
• {P-Rlt}/{P-Cof}
... matrix of {solution}/{coefficients} for a quadratic or cubic equation
u TVM — Recalling Financial Calculation Data
•{n}/{I%}/{PV}/{PMT}/{FV}
... {payment periods (installments)}/{interest (%)}/{principal}/{payment amount}/
{account balance or principal plus interest following the final installment}
•{P/Y}/{C/Y}
... {number of installment periods per year}/{number of compounding periods
per year}
4
5
*
*1An error occurs when there is no function or
recursion formula numeric table in memory.
2
*
“Reslt” is available only in the RUN
PRGM and e
*3Table contents are stored automatically in
Matrix Answer Memory (MatAns).
4
*
Coefficients and solutions are stored
automatically in Matrix Answer Memory
(MatAns).
•
ACT modes.
•
MAT,
5
*
The following conditions cause an error.
-When there are no coefficients input for the
equation
-When there are no solutions obtained for the
equation
6
*
Coefficient and solution memory data for a
linear equation cannot be recalled at the same
time.
20050401
Page 57

Program (PRGM) Menu
1-6-1
1-6 Program (PRGM) Menu
To display the program (PRGM) menu, first enter the RUN
•
MAT or PRGM mode from the
Main Menu and then press !J(PRGM). The following are the selections available in the
program (PRGM) menu.
• {COM} ...... {program command menu}
• {CTL} ........ {program control command menu}
• {JUMP} .... {jump command menu}
• {? } ............ {input prompt}
• {^} ........... {output command}
• {CLR} ....... {clear command menu}
• {DISP } ...... {display command menu}
• {REL} ....... {conditional jump relational operator menu}
• {I/O} .......... {I/O control/transfer command menu}
• {:} ............. {multistatement connector}
The following function key menu appears if you press !J(PRGM) in the RUN
•
MAT
mode or the PRGM mode while binary, octal, decimal, or hexadecimal is set as the default
number system.
• {Prog} ...... {program recall}
• {JUMP}/{?} /{^}/{REL}/{:}
The functions assigned to the function keys are the same as those in the Comp mode.
For details on the commands that are available in the various menus you can access from
the program menu, see “8. Programming”.
20050401
Page 58

Using the Setup Screen
1-7-1
1-7 Using the Setup Screen
The mode’s Setup screen shows the current status of mode settings and lets you make any
changes you want. The following procedure shows how to change a setup.
u To change a mode setup
1. Select the icon you want and press w to enter a mode and display its initial screen.
Here we will enter the RUN
2. Press !m(SET UP) to display the mode’s
Setup screen.
•This Setup screen is just one possible example.
Actual Setup screen contents will differ
according to the mode you are in and that mode’s
current settings.
•
MAT mode.
...
3. Use the f and c cursor keys to move the highlighting to the item whose setting you
want to change.
4. Press the function key (1 to 6) that is marked with the setting you want to make.
5. After you are finished making any changes you want, press J to exit the Setup
screen.
k Setup Screen Function Key Menus
This section details the settings you can make using the function keys in the Setup screen.
indicates default setting.
u Input Mode
•{Math}/{Line}... {Math}/{Linear} input mode
20050401
Page 59

Using the Setup Screen
1-7-2
u Mode (calculation/binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal mode)
•{Comp} ... {arithmetic calculation mode}
•{Dec}/{Hex}/{Bin}/{Oct}
... {decimal}/{hexadecimal}/{binary}/{octal}
u Frac Result (fraction result display format)
•{d/c}/{ab/c}... {improper}/{mixed} fraction
u Func Type (graph function type)
Pressing one of the following function keys also switches the function of the v key.
•{Y=}/{r=}/{Parm}/{X=c}
... {rectangular coordinate}/{polar coordinate}/{parametric coordinate}/
{X = constant} graph
•{Y>}/{Y<}/{Yt}/{Ys}
... {y>f(x)}/{y<f(x)}/{y≥f(x)}/{y≤f(x)} inequality graph
u Draw Type (graph drawing method)
•{Con}/{Plot}
... {connected points}/{unconnected points}
u Derivative (derivative value display)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off} while Graph-to-Table, Table & Graph, and Trace are
being used
u Angle (default angle unit)
•{Deg}/{Rad}/{Gra}
... {degrees}/{radians}/{grads}
u Complex Mode
•{Real} ... {calculation in real number range only}
•{a + bi}/{r ∠θ}
... {rectangular format}/{polar format} display of a complex calculation
u Coord (graph pointer coordinate display)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Grid (graph gridline display)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
20050401
Page 60

Using the Setup Screen
1-7-3
u Axes (graph axis display)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Label (graph axis label display)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Display (display format)
•{Fix}/{Sci}/{Norm}/{Eng}
... {fixed number of decimal places specification}/{number of significant digits
specification}/{normal display setting}/{engineering mode}
u Stat Wind (statistical graph V-Window setting method)
•{Auto}/{Man}
... {automatic}/{manual}
u Resid List (residual calculation)
•{None}/{LIST}
... {no calculation}/{list specification for the calculated residual data}
u List File (list file display settings)
•{FILE} ... {settings of list file on the display}
u Sub Name (list naming)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Graph Func (function display during graph drawing and trace)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Dual Screen (dual screen mode status)
•{G+G}/{GtoT}/{Off}
... {graphing on both sides of dual screen}/{graph on one side and numeric table
on the other side of dual screen}/{dual screen off}
u Simul Graph (simultaneous graphing mode)
•{On}/{Off}
... {simultaneous graphing on (all graphs drawn simultaneously)}/{simultaneous
graphing off (graphs drawn in area numeric sequence)}
20050401
Page 61

Using the Setup Screen
1-7-4
u Background (graph display background)
•{None}/{PICT}
... {no background}/{graph background picture specification}
u Sketch Line (overlaid line type)
•{ }/{ }{ }/{ }
... {normal}/{thick}/{broken}/{dot}
u Dynamic Type (dynamic graph type)
•{Cnt}/{Stop}
... {non-stop (continuous)}/{automatic stop after 10 draws}
u Locus (dynamic graph locus mode)
•{On}/{Off}
... {locus drawn}/{locus not drawn}
u Y=Draw Speed (dynamic graph draw speed)
•{Norm}/{High}
... {normal}/{high-speed}
u Variable (table generation and graph draw settings)
•{RANG}/{LIST}
... {use table range}/{use list data}
u Σ Display (Σ value display in recursion table)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Slope (display of derivative at current pointer location in conic section
graph)
•{On}/{Off}
... {display on}/{display off}
u Payment (payment period setting)
•{BGN}/{END}
... {beginning}/{end} setting of payment period
20050401
Page 62

Using the Setup Screen
1-7-5
u Date Mode (number of days per year setting)
•{365}/{360}
... interest calculations using {365}*1/{360} days per year
u Auto Calc (spreadsheet auto calc)
•{On}/{Off}
... {execute}/{not execute} the formulas automatically
u Show Cell (spreadsheet cell display mode)
•{Form}/{Val} ... {formula}*2/{value}
u Move (spreadsheet cell cursor direction)*
•{Low}/{Right} ... {move down}/{move right}
3
*1The 365-day year must be used for date
calculations in the TVM mode.
Otherwise, an error occurs.
2
*
Selecting “Form” (formula) causes a formula in
the cell to be displayed as a formula. The
“Form” does not affect any non-formula data in
the cell.
3
*
Specifies the direction the cell cursor moves when
you press the w key to register cell input, when
the Sequence command generates a number
table, and when you recall data from List memory.
20050401
Page 63

1-8-1
Using Screen Capture
1-8 Using Screen Capture
Any time while operating the calculator, you can capture an image of the current screen and
save it in capture memory.
u To capture a screen image
1. Operate the calculator and display the screen you want to capture.
2. Press !h(CAPTURE).
•This displays a memory area selection dialog box.
3. Input a value from 1 to 20 and then press w.
•This will capture the screen image and save it in capture memory area named
“Capt n” (n = the value you input).
•You cannot capture the screen image of a message indicating that an operation or data
communication is in progress.
•A memory error will occur if there is not enough room in main memory to store the screen
capture.
u To recall a screen image from capture memory
1. In the RUN
1(RCL).
2. Enter a capture memory number in the range of 1 to 20, and then press w.
•You can also use the RclCapt command in a program to recall a screen image from
capture memory.
•
MAT mode (Linear input mode), press K6(g)6(g)5(CAPT)
20050401
Page 64

When you keep having problems…
1-9-1
1-9 When you keep having problems…
If you keep having problems when you are trying to perform operations, try the following
before assuming that there is something wrong with the calculator.
kk
k Getting the Calculator Back to its Original Mode Settings
kk
1. From the Main Menu, enter the SYSTEM mode.
2. Press 5(RSET).
3. Press 1(STUP), and then press 1(Yes).
4. Press Jm to return to the Main Menu.
Now enter the correct mode and perform your calculation again, monitoring the results on
the display.
kk
k In Case of Hang Up
kk
•Should the unit hang up and stop responding to input from the keyboard, press the P button
on the back of the calculator to reset the calculator to its initial defaults (see page α-5-1).
Note, however, that this may clear all the data in calculator memory.
20050401
Page 65

When you keep having problems…
1-9-2
kk
k Low Battery Message
kk
If either of the following messages appears on the display, immediately turn off the calculator
and replace main batteries as instructed.
If you continue using the calculator without replacing main batteries, power will automatically
turn off to protect memory contents. Once this happens, you will not be able to turn power
back on, and there is the danger that memory contents will be corrupted or lost entirely.
#You will not be able to perform data
communications operations after the low
battery message appears.
20050401
Page 66

Chapter
Manual Calculations
2-1 Basic Calculations
2-2 Special Functions
2-3 Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
2-4 Function Calculations
2-5 Numerical Calculations
2-6 Complex Number Calculations
2-7 Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations
with Integers
2-8 Matrix Calculations
2
Linear/Math input mode (page 1-3-8)
•Unless specifically noted otherwise, all of the operations in this chapter are
explained using the Linear input mode.
•When necessary, the input mode is indicated by the following symbols.
<Math> .... Math input mode
<Line> ..... Linear input mode
20050401
Page 67

2-1-1
Basic Calculations
2-1 Basic Calculations
kk
k Arithmetic Calculations
kk
•Enter arithmetic calculations as they are written, from left to right.
•Use the - key to input the minus sign before a negative value.
•Calculations are performed internally with a 15-digit mantissa. The result is rounded to a
10-digit mantissa before it is displayed.
• For mixed arithmetic calculations, multiplication and division are given priority over
addition and subtraction.
Example Operation
23 + 4.5 – 53 = –25.5 23+4.5-53w
56 × (–12) ÷ (–2.5) = 268.8 56*-12/-2.5w
(2 + 3) × 102 = 500 (2+3)*1E2w*
1
1 + 2 – 3 × 4 ÷ 5 + 6 = 6.6 1+2-3*4/5+6w
100 – (2 + 3) × 4 = 80 100-(2+3)*4w
2 + 3 × (4 + 5) = 29 2+3*(4+5w*
(7 – 2) × (8 + 5) = 65 (7-2)(8+5)w*
6
= 0.3
4 ×510
3
<Line>
6 /(4*5)w*
<Math>
2
3
4
$6c4*5w
(1 + 2i) + (2 + 3i) = 3 + 5i (b+c!a(i))+(c+
d!a(i))w
(2 + i) × (2 – i) = 5 (c+!a(i))*(c-!a(i)
)w
3
*1(2+3)E2 does not produce the correct
result. Be sure to enter this calculation as shown.
2
*
Final closed parentheses (immediately before
operation of the w key) may be omitted, no
matter how many are required.
*
A multiplication sign immediately before an open
parenthesis may be omitted.
4
*
This is identical to 6 / 4 / 5 w.
20050401
Page 68

2-1-2
Basic Calculations
kk
k Number of Decimal Places, Number of Significant Digits, Normal
kk
Display Range
[SET UP]- [Display] -[Fix] / [Sci] / [Norm]
•Even after you specify the number of decimal places or the number of significant digits,
internal calculations are still performed using a 15-digit mantissa, and displayed values
are stored with a 10-digit mantissa. Use Rnd of the Numeric Calculation Menu (NUM)
(page 2-4-1) to round the displayed value off to the number of decimal place and
significant digit settings.
•Number of decimal place (Fix) and significant digit (Sci) settings normally remain in effect
until you change them or until you change the normal display range (Norm) setting.
○○○○○
Example 100 ÷ 6 = 16.66666666...
Condition Operation Display
100/6w 16.66666667
4 decimal places !m(SET UP) f (or c 12 times)
1(Fix)ewJw 16.6667
5 significant digits !m(SET UP) f (or c 12 times)
2(Sci)fwJw 1.6667E+01
Cancels specification !m(SET UP) f (or c 12 times)
3(Norm)Jw 16.66666667
*1Displayed values are rounded off to the place
you specify.
1
*
1
*
20050401
Page 69

2-1-3
Basic Calculations
○○○○○
Example 200 ÷ 7 × 14 = 400
Condition Operation Display
200/7*14w 400
3 decimal places !m(SET UP) f (or c 12 times)
1(Fix)dwJw 400.000
Calculation continues using 200/7w 28.571
display capacity of 10 digits * Ans ×
14w 400.000
• If the same calculation is performed using the specified number of digits:
200/7w 28.571
The value stored internally K6(g)4(NUM)4(Rnd)w 28.571
is rounded off to the number * Ans ×
of decimal places specified 14w 399.994
on the Setup screen.
200/7w 28.571
You can also specify the
number of decimal places for 6(RndFi)!-(Ans),2) RndFix(Ans,2)
rounding of internal values w 28.570
for a specific calculation.*
1
* Ans ×
(Example: To specify 14w 399.980
rounding to two decimal
places)
kk
k Calculation Priority Sequence
kk
This calculator employs true algebraic logic to calculate the parts of a formula in the following
order:
1 Type A functions
Coordinate transformation Pol (x, y), Rec (r, θ)
Derivatives, second derivatives, integrations, Σ calculations
2
d/dx, d
/dx2, ∫dx, Σ, Mat, Solve, FMin, FMax, List→ Mat, Seq, Min, Max, Median, Mean,
Augment, Mat→List, P(, Q(, R(, t(, List, RndFix, log ab
Composite functions*2 fn, Yn, rn, Xtn, Ytn, Xn
*1To turn off rounding, specify 10 for the
significant number of digits.
2
*
You can combine the contents of multiple
function memory (fn) locations or graph
memory (Yn, rn, Xtn, Ytn, Xn) locations into
composite functions. Specifying fn1(fn2),
for example, results in the composite function
fn1°fn2 (see page 5-3-3).
A composite function can consist of up to five
functions.
#You cannot use a differential, quadratic differential,
integration, Σ, maximum/minimum
value, Solve, RndFix or log ab calculation
expression inside of a RndFix calculation term.
20050401
20070101
Page 70

2-1-4
Basic Calculations
2 Type B functions
With these functions, the value is entered and then the function key is pressed.
2
x
, x–1, x!, ° ’ ”, ENG symbols, angle unit °, r,
3 Power/root ^(xy),
4 Fractions a
x
b
/c
g
5 Abbreviated multiplication format in front of π, memory name, or variable name.
2π, 5A, etc.
6 Type C functions
With these functions, the function key is pressed and then the value is entered.
, 3, log, In, ex, 10x, sin, cos, tan, sin–1, cos–1, tan–1, sinh, cosh, tanh, sinh–1, cosh–1,
tanh–1, (–), d, h, b, o, Neg, Not, Det, Trn, Dim, Identity, Sum, Prod, Cuml, Percent, AList,
Abs, Int, Frac, Intg, Arg, Conjg, ReP, ImP
7 Abbreviated multiplication format in front of Type A functions, Type C functions, and
parenthesis
2 , A log2, etc.
3
8 Permutation, combination nPr, nCr, ∠
9 ×, ÷
0 +, –
! Relational operators =, , >, <, ≥, ≤
G
@ And (logical operator), and (bitwise operator)
# Or (logical operator), or, xor, xnor (bitwise operator)
○○○○○
Example 2 + 3 × (log sin2π2 + 6.8) = 22.07101691 (angle unit = Rad)
6
# When functions with the same priority are used
in series, execution is performed from right to
left.
x
e
In → ex{In( )}
120 120
Otherwise, execution is from left to right.
1
2
3
4
5
# Compound functions are executed from right to
left.
#Anything contained within parentheses receives
highest priority.
20050401
20070101
Page 71

2-1-5
Basic Calculations
k Multiplication Operations without a Multiplication Sign
You can omit the multiplication sign (×) in any of the following operations.
• Before Type A functions (1 on page 2-1-3) and Type C functions (6 on page 2-1-4), except
for negative signs.
○○○○○
Example 2sin30, 10log1.2, 2 3, 2Pol(5, 12), etc.
• Before constants, variable names, memory names
○○○○○
Example 2π, 2AB, 3Ans, 3Y1, etc.
• Before an open parenthesis
○○○○○
Example 3(5 + 6), (A + 1)(B – 1), etc.
k Overflow and Errors
Exceeding a specified input or calculation range, or attempting an illegal input causes an
error message to appear on the display. Further operation of the calculator is impossible
while an error message is displayed. The following events cause an error message to appear
on the display.
• When any result, whether intermediate or final, or any value in memory exceeds
±9.999999999 × 1099 (Ma ERROR).
• When an attempt is made to perform a function calculation that exceeds the input range
(Ma ERROR).
• When an illegal operation is attempted during statistical calculations (Ma ERROR). For
example, attempting to obtain 1VAR without data input.
• When an improper data type is specified for the argument of a function calculation
(Ma ERROR).
• When the capacity of the numeric value stack or command stack is exceeded (Stack
ERROR). For example, entering 25 successive ( followed by 2 + 3 * 4 w.
• When an attempt is made to perform a calculation using an illegal formula (Syntax
ERROR). For example, 5 ** 3 w.
# Most of the calculator’s keys are
inoperative while an error message is
displayed.
Press J to clear the error and display
the error position (see page 1-3-5).
# See the “Error Message Table” on page α-1-1 for
information on other errors.
20050401
20070101
Page 72

2-1-6
Basic Calculations
•When you try to perform a calculation that causes memory capacity to be exceeded
(Memory ERROR).
•When you use a command that requires an argument, without providing a valid argument
(Argument ERROR).
•When an attempt is made to use an illegal dimension during matrix calculations (Dimension
ERROR).
• When you are in the real mode and an attempt is made to perform a calculation that
produces a complex number solution. Note that “Real” is selected for the Complex Mode
setting on the Setup screen (Non-Real ERROR).
k Memory Capacity
In the Linear input mode, each time you press a key, either one byte or two bytes is used.
Some of the functions that require one byte are: b, c, d, sin, cos, tan, log, In, , and π.
Some of the functions that take up two bytes are d/dx(, Mat, Xmin, If, For, Return, DrawGraph,
SortA(, PxIOn, Sum, and an+1.
For details about the number of bytes required for each function in the Math input mode, see
page 1-3-9.
#As you input numeric values or commands,
they appear flush left on the display.
Calculation results, on the other hand, are
displayed flush right.
# The allowable range for both input and output
values is 15 digits for the mantissa and two
digits for the exponent. Internal calculations are
also performed using a 15-digit mantissa and
two-digit exponent.
20050401
Page 73

2-2-1
Special Functions
2-2 Special Functions
kk
k Calculations Using Variables
kk
Example Operation Display
193.2aav(A)w 193.2
193.2 ÷ 23 = 8.4 av(A)/23w 8.4
193.2 ÷ 28 = 6.9 av(A)/28w 6.9
kk
k Memory
kk
uVariables (Alpha Memory)
This calculator comes with 28 variables as standard. You can use variables to store values
you want to use inside of calculations. Variables are identified by single-letter names, which
are made up of the 26 letters of the alphabet, plus r and θ. The maximum size of values that
you can assign to variables is 15 digits for the mantissa and 2 digits for the exponent.
u To assign a value to a variable
[value] a [variable name] w
○○○○○
Example To assign 123 to variable A
Abcdaav(A)w
○○○○○
Example To add 456 to variable A and store the result in variable B
Aav(A)+efgaa
l(B)w
# Variable contents are retained even when
you turn power off.
20050401
Page 74

2-2-2
Special Functions
u To display the contents of a variable
○○○○○
Example To display the contents of variable A
Aav(A)w
u To clear a variable
○○○○○
Example To clear variable A
Aaaav(A)w
u To assign the same value to more than one variable
[value]a [first variable name*1]a3(~) [last variable name*1]w
○○○○○
Example To assign a value of 10 to variables A through F
Abaaav(A)
a3(~)at(F)w
uFunction Memory [OPTN]-[FMEM]
Function memory (f1~f20) is convenient for temporary storage of often-used expressions. For
longer term storage, we recommend that you use the GRAPH mode for expressions and the
PRGM mode for programs.
•{STO}/{RCL}/{fn}/{SEE} ... {function store}/{function recall}/{function area specification
as a variable name inside an expression}/{function list}
*1 You cannot use “r” or “θ” as a variable name.
20050401
Page 75

2-2-3
Special Functions
u To store a function
○○○○○
Example To store the function (A+B) (A–B) as function memory number 1
(av(A)+al(B))
(av(A)-al(B))
K6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)
1(STO)bw
JJJ
u To recall a function
○○○○○
Example To recall the contents of function memory number 1
K6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)
2(RCL)bw
u To recall a function as a variable
daav(A)w
baal(B)w
K6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)3(fn)
b+cw
u To display a list of available functions
K6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)
4(SEE)
# If the function memory number to which you
store a function already contains a function, the
previous function is replaced with the new one.
20050401
# The recalled function appears at the current
location of the cursor on the display.
Page 76

2-2-4
Special Functions
u To delete a function
○○○○○
Example To delete the contents of function memory number 1
AK6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)
1(STO)bw
•Executing the store operation while the display is blank deletes the function in the
function memory you specify.
u To use stored functions
○○○○○
Example To store x3 + 1, x2 + x into function memory, and then graph:
!m(SET UP)ccc1(Y=)J
AvMd+bK6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)1(STO)bw(stores (x3 + 1))
JAvx+v1(STO)cw(stores (x2 + x))
3
y = x
+ x2 + x + 1
Use the following V-Window settings.
Xmin = – 4, Xmax = 4, Xscale = 1
Ymin = –10, Ymax = 10, Yscale = 1
JA!4(SKTCH)1(Cls)w
5(GRPH)1(Y=)
K6(g)6(g)3(FMEM)3(fn)b+
3(fn)cw
• For full details about graphing, see “5. Graphing”.
#You can also use a to store a function in
function memory in a program.
In this case, you must enclose the function
inside of double quotation marks.
20050401
Page 77

2-2-5
Special Functions
kk
k Answer Function
kk
The Answer Function automatically stores the last result you calculated by pressing
w(unless the w key operation results in an error). The result is stored in the answer
memory.
u To use the contents of the answer memory in a calculation
○○○○○
Example 123 + 456 = 579
789 – 579 = 210
Abcd+efgw
hij-!-(Ans)w
In the Math input mode, the answer memory is refreshed with each calculation. Note,
however, that the answer memory content recall operation is different from that used in
the Linear input mode. For details, see “History Function” (page 2-2-6).
kk
k Performing Continuous Calculations
kk
Answer memory also lets you use the result of one calculation as one of the arguments in
the next calculation.
○○○○○
Example 1 ÷ 3 =
1 ÷ 3 × 3 =
Ab/dw
(Continuing)*dw
Continuous calculations can also be used with Type B functions (x2, x-1, x!, page 2-1-4), +,
–, ^(xy), x, ° ’ ”, etc.
# The largest value that the answer memory
can hold is 15 digits for the mantissa and 2
digits for the exponent.
# Only numeric values and calculation results
can be stored in answer memory.
# Answer memory contents are not cleared when
you press the A key or when you switch power
off.
# When “Linear” is selected as the Input Mode,
answer memory contents are not changed by an
operation that assigns values to Alpha memory
(such as: faav(A)w).
20050401
2005090120070101
Page 78

2-2-6
Special Functions
kk
k History Function
kk
The history function maintains a history of calculation expressions and results in the Math
input mode. Up to 30 sets of calculation expressions and results are maintained.
b+cw
*cw
You can also edit the calculation expressions that are maintained by the history function
and recalculate. This will recalculate all of the expressions starting from the edited
expression.
○○○○○
Example To change “1+2” to “1+3” and recalculate
Perform the following operation following the sample shown above.
ffffdDdw
# The value stored in the answer memory is
always dependent on the result produced by
the last calculation performed. If history
contents include operations that use the
answer memory, editing a calculation may
affect the answer memory value used in
subsequent calculations.
- If you have a series of calculations that use the
answer memory to include the result of the
previous calculation in the next calculation,
editing a calculation will affect the results of all
the other calculations that come after it.
-When the first calculation of the history includes
the answer memory contents, the answer
memory value is “0” because there is no
calculation before the first one in history.
20050401
20050901
Page 79

2-2-7
Special Functions
k Stacks
The unit employs memory blocks, called
commands. There is a 10-level
level
program subroutine stack
it exceeds the capacity of available numeric value stack or command stack space, or if
execution of a program subroutine exceeds the capacity of the subroutine stack.
○○○○○
Example
Numeric Value Stack Command Stack
numeric value stack
. An error occurs if you perform a calculation so complex that
stacks
, for storage of low priority values and
, a 26-level
command stack
, and a 10-
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
4
...
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
×
(
(
+
×
(
+
...
# Calculations are performed according to the
priority sequence. Once a calculation is
executed, it is cleared from the stack.
#Storing a complex number takes up two numeric
value stack levels.
#Storing a two-byte function takes up two
command stack levels.
20050401
20050901
Page 80

2-2-8
Special Functions
k Using Multistatements
Multistatements are formed by connecting a number of individual statements for sequential
execution. You can use multistatements in manual calculations and in programmed
calculations. There are two different ways that you can use to connect statements to form
multistatements.
•Colon (:)
Statements that are connected with colons are executed from left to right, without stopping.
•Display Result Command (
^^
^)
^^
When execution reaches the end of a statement followed by a display result command,
execution stops and the result up to that point appears on the display. You can resume
execution by pressing the w key.
○○○○○
Example 6.9 × 123 = 848.7
123 ÷ 3.2 = 38.4375
Abcdaav(A)
!J(PRGM)6(g)5(:)g.j
*av(A)!J(PRGM)5(^)
av(A)/d.cw
w
#You cannot construct a multistatement in
which one statement directly uses the result of
the previous statement.
Example: 123 × 456: × 5
Invalid
20050401
20050901
Page 81

Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
2-3-1
2-3 Specifying the Angle Unit and Display
Format
Before performing a calculation for the first time, you should use the Setup screen to specify
the angle unit and display format.
kk
k Setting the Angle Unit [SET UP]- [Angle]
kk
1. On the Setup screen, highlight “Angle”.
2. Press the function key for the angle unit you want to specify, then press J.
•{Deg}/{Rad}/{Gra} ... {degrees}/{radians}/{grads}
• The relationship between degrees, grads, and radians is shown below.
360° = 2π radians = 400 grads
90° = π/2 radians = 100 grads
kk
k Setting the Display Format [SET UP]- [Display]
kk
1. On the Setup screen, highlight “Display”.
2. Press the function key for the item you want to set, then press J.
•{Fix}/{Sci}/{Norm}/{Eng} ... {fixed number of decimal places specification}/
{number of significant digits specification}/{normal display}/{Engineering mode}
u To specify the number of decimal places (Fix)
○○○○○
Example To specify two decimal places
1(Fix) cw
Press the number key that corresponds to the
number of decimal places you want to specify
n
= 0 to 9).
(
#Displayed values are rounded off to the
number of decimal places you specify.
20050401
Page 82

Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
2-3-2
u To specify the number of significant digits (Sci)
○○○○○
Example To specify three significant digits
2(Sci) dw
Press the number key that corresponds
to the number of significant digits you
want to specify (
Specifying 0 makes the number of
significant digits 10.
n
= 0 to 9).
u To specify the normal display (Norm 1/Norm 2)
Press 3(Norm) to switch between Norm 1 and Norm 2.
Norm 1: 10
Norm 2: 10
–2
(0.01)>|x|, |x| >10
–9
(0.000000001)>|x|, |x| >10
Ab/caaw (Norm 1)
10
10
(Norm 2)
u To specify the engineering notation display (Eng mode)
Press 4(Eng) to switch between engineering notation and standard notation. The
indicator “/E” is on the display while engineering notation is in effect.
You can use the following symbols to convert values to engineering notation, such as
2,000 (= 2 × 103) → 2k.
E (Exa) × 10
P (Peta) × 10
T (Tera) × 10
G (Giga) × 10
M (Mega) × 10
k (kilo) × 10
18
15
12
9
6
3
#Displayed values are rounded off to the number
of significant digits you specify.
m (milli) × 10
µ (micro) × 10
n (nano) × 10
p (pico) × 10
f (femto) × 10
# The engineering symbol that makes the
mantissa a value from 1 to 1000 is automatically
selected by the calculator when engineering
notation is in effect.
20050401
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
Page 83

2-4-1
Function Calculations
2-4 Function Calculations
k Function Menus
This calculator includes five function menus that give you access to scientific functions not
printed on the key panel.
• The contents of the function menu differ according to the mode you entered from the Main
Menu before you pressed the K key. The following examples show function menus that
appear in the RUN
uu
u Hyperbolic Calculations (HYP) [OPTN]-[HYP]
uu
•{sinh}/{cosh}/{tanh} ... hyperbolic {sine}/{cosine}/{tangent}
•{sinh–1}/{cosh–1}/{tanh–1} ... inverse hyperbolic {sine}/{cosine}/{tangent}
uu
u Probability/Distribution Calculations (PROB) [OPTN]-[PROB]
uu
•{x!} ... {press after inputting a value to obtain the factorial of the value.}
•{nPr}/{nCr} ... {permutation}/{combination}
•{Ran#}... {pseudo random number generation (0 to 1)}
•{P(}/{Q(}/{R(} ... normal distribution probability {P(t)}/{Q(t)}/{R(t)}
•{t(} ... {value of normalized variate t(x)}
•
MAT mode.
uu
u Numeric Calculations (NUM) [OPTN]-[NUM]
uu
•{Abs} ... {select this item and input a value to obtain the absolute value of the value.}
•{Int}/{Frac} ... select the item and input a value to extract the {integer}/{fraction} part.
•{Rnd} ... {rounds off the value used for internal calculations to 10 significant digits
(to match the value in the Answer Memory), or to the number of decimal places (Fix)
and number of significant digits (Sci) specified by you.}
•{Intg} ... {select this item and input a value to obtain the largest integer that is not greater
than the value.}
•{RndFi} ... {rounds off the value used for internal calculations to specified digits (0~9)
(see page 2-1-3).}
20050401
Page 84

2-4-2
Function Calculations
uu
u Angle Units, Coordinate Conversion, Sexagesimal Operations (ANGL)
uu
[OPTN]-[ANGL]
•{°}/{r}/{g} ... {degrees}/{radians}/{grads} for a specific input value
•{° ’ ”} ... {specifies degrees (hours), minutes, seconds when inputting a degrees/minutes/
seconds value}
•{
} ... {converts decimal value to degrees/minutes/seconds value}*
° ’ ”
1
•{Pol(}/{Rec(} ... {rectangular-to-polar}/{polar-to-rectangular} coordinate conversion
•{'DMS} ... {converts decimal value to sexagesimal value}
uu
u Engineering Symbol (ESYM) [OPTN]-[ESYM]
uu
•{m}/{µ}/{n}/{p}/{f} ... {milli (10–3)}/{micro (10–6)}/{nano (10–9)}/{pico (10
{femto (10
–15
)}
–12
)}/
•{k}/{M}/{G}/{T}/{P}/{E} ... {kilo (103)}/{mega (106)}/{giga (109)}/{tera (1012)}/{peta (1015)}/
{exa (1018)}
•{ENG}/{ENG} ... shifts the decimal place of the displayed value three digits to
the {left}/{right} and {decreases}/{increases} the exponent by three.*
2
When you are using engineering notation, the engineering symbol is also changed
accordingly.
*1The {
2
*
} menu operation is available only
° ’ ”
when there is a calculation result on the
display.
The {ENG} and {ENG} menu operations are
available only when there is a calculation
result on the display.
# ENG/ENG switching is disabled for the following
types of calculation results.
- Result of matrix calculation input in the Math
input mode
- Result of list calculation input in the Math input
mode
20050401
Page 85

2-4-3
Function Calculations
kk
k Angle Units
kk
To change the angle unit of an input value, first press K6(g)5(ANGL). On the
function key menu that appears, select “°”, “r”, or “g”.
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
To convert 4.25 rad to degrees:
!m(SET UP)cccccc1(Deg)J
243.5070629 4.25K6(g)5(ANGL)2(r)w
47.3° + 82.5rad = 4774.20181°
2°20⬘30⬙ + 39⬘30⬙ = 3°00⬘ 00⬙
2.255° = 2°15⬘18⬙
47.3+82.5K6(g)5(ANGL)2(r)w
2K6(g)5(ANGL)4(° ’ ”) 204(° ’ ”) 30
4(° ’ ”)+04(° ’ ”)394(° ’ ”)304(° ’ ”)w
5(
)
° ’ ”
2.255K6(g)5(ANGL)6(g)3('DMS)w
# Once you specify an angle unit, it remains in
effect until you specify a different one. The
specification is retained even if you turn
power off.
20050401
Page 86

2-4-4
Function Calculations
kk
k Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions
kk
•Be sure to set the angle unit before performing trigonometric function and inverse
trigonometric function calculations.
π
(90° = ––– radians = 100 grads)
2
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
sin 63° = 0.8910065242 !m(SET UP)cccccc
1(Deg)J
s63w
π
cos (–– rad) = 0.5 !m(SET UP)cccccc
3
2(Rad)J
<Line>
c(!E(π)/3)w
<Math>
c$!E(π)c3w
tan (– 35gra) = – 0.6128007881 !m(SET UP)cccccc
3(Gra)J
t-35w
2 • sin 45° × cos 65° = 0.5976724775 !m(SET UP)cccccc
cosec 30° =
1(Deg)J
2*s45*c65w*
1
= 2
sin30° 1(Deg)J
!m(SET UP)cccccc
1
<Line>
1/s30w
<Math>
$1cs30w
sin-10.5 = 30° !m(SET UP)cccccc
(x when sinx = 0.5) 1(Deg)J
!s(sin–1)0.5*2w
*1* can be omitted. *2Input of leading zero is not necessary.
20050401
Page 87

2-4-5
Function Calculations
k Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
log 1.23 (log101.23) = 0.08990511144 l1.23w
log2 8 = 3 <Line>
K4(CALC)6(g)4(logab)2,8)w
<Math>
4(MATH)2(logab) 2e8w
In 90 (loge90) = 4.49980967 I90w
1.23
10
= 16.98243652 !l(10x)1.23w
(To obtain the antilogarithm of common
logarithm 1.23)
4.5
e
= 90.0171313 !I(ex)4.5w
(To obtain the antilogarithm of natural
logarithm 4.5)
(–3)4 = (–3) × (–3) × (–3) × (–3) = 81 (-3)M4w
–34 = –(3 × 3 × 3 × 3) = –81 -3M4w
7
123
1
(= 1237) = 1.988647795
<Line>
7!M(x )123w
<Math>
!M(x )7e123w
<Line>
2 + 3 × 3 – 4 = 10 2+3*3!M(x )64-4w*
64
<Math>
2+3*!M(x )3e64e-4w
1
*1^ (xy) and x take precedence over
multiplication and division.
# You cannot use a differential, quadratic
differential, integration, Σ, maximum/minimum
value, Solve, RndFix or log ab calculation
expression inside of a log ab calculation term.
# The Linear input mode and Math input mode
produce different results when two or more
powers are input in series, like: 2M3M2.
Linear input mode: 2^3^2 = 64
Math input mode:
This is because the Math input mode internally
treats the above input as: 2^(3^(2)).
20050401
= 512
Page 88

2-4-6
Function Calculations
k Hyperbolic and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
sinh 3.6 = 18.28545536 K6(g)2(HYP)1(sinh)3.6w
cosh 1.5 – sinh 1.5 K6(g)2(HYP)2(cosh)1.5-
= 0.2231301601 1(sinh)1.5w
–1.5
= e
(Display: –1.5) I!-(Ans)w
(Proof of cosh x ± sinh x = e±x)
20
cosh–1
= 0.7953654612
15
Determine the value of x
when tanh 4 x = 0.88
–1
tanh
0.88 <Line>
=
x
4
= 0.3439419141
<Line>
K6(g)2(HYP)5(cosh–1)(20/15)w
<Math>
K6(g)2(HYP)5(cosh–1)$20c15w
K6(g)2(HYP)6(tanh–1)0.88/4w
<Math>
$K6(g)2(HYP)6(tanh–1)0.88c4w
20050401
Page 89

2-4-7
Function Calculations
k Other Functions
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
+ =
25
(3 + i)
(–3)2 = (–3) × (–3) = 9 (-3)xw
–32 = –(3 × 3) = –9 -3xw
3.65028154 !x( )2+!x( )5w
= 1.755317302 <Line>
+0.2848487846i !x( )(d+!a(i))w
<Math>
!x( )d+!a(i)w
1
–––––– = 12
11
–– – ––
34
<Line>
(3!)(x
<Math>
–1
)-4!)(x–1))!)(x–1)w
$1c$1c3e-$1c4w
8! (= 1 × 2 × 3 × .... × 8) 8K6(g)3(PROB)1(x!)w
= 40320
3
What is the absolute value of
the common logarithm of
3
log | = 0.1249387366
|
4
= 42 <Line>36 × 42 × 49
3
?
4
!((
<Math>
!((
3
)(36*42*49)w
3
)36*42*49w
<Line>
K6(g)4(NUM)1(Abs)l(3/4)w
<Math>
4(MATH)3(Abs)l$3c4w
What is the integer part of K6(g)4(NUM)2(Int)-3.5w
– 3.5? – 3
What is the decimal part of K6(g)4(NUM)3(Frac)-3.5w
– 3.5? – 0.5
What is the nearest integer K6(g)4(NUM)5(Intg)-3.5w
not exceeding – 3.5? – 4
20050401
Page 90

2-4-8
Function Calculations
k Random Number Generation (Ran#)
This function generates a 10-digit truly random or sequentially random number that is greater
than zero and less than 1.
•A truly random number is generated if you do not specify anything for the argument.
Example Operation
Ran# (Generates a random number.) K6(g)3(PROB)4(Ran#)w
(Each press of w generates a new random w
number.) w
•Specifying an argument from 1 to 9 generates random numbers based on that sequence.
•Specifying an argument of 0 initializes the sequence.*
Example Operation
Ran# 1 (Generates the first random number in sequence 1.) K6(g)3(PROB)
(Generates the second random number in sequence 1.) w
Ran# 0 (Initializes the sequence.) 4(Ran#)aw
Ran# 1 (Generates the first random number in sequence 1.) 4(Ran#)bw
1
4(Ran#)bw
*1Changing to a different sequence or
generating a totally random number (without
an argument) initializes the sequence.
20050401
Page 91

2-4-9
Function Calculations
k Coordinate Conversion
uu
u Rectangular Coordinates
uu
•With polar coordinates, θ can be calculated and displayed within a range of
–180°< θ < 180° (radians and grads have same range).
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
Calculate r and θ° when x = 14 and y = 20.7 !m(SET UP)cccccc
1 24.989 → 24.98979792 (r)
2 55.928 → 55.92839019 (θ)
Calculate x and y when r = 25 and θ = 56° 2(Rec()25,56)w
1 13.979 → 13.97982259 (x)
2 20.725 → 20.72593931 (y)
uu
u Polar Coordinates
uu
1(Deg)J
K6(g)5(ANGL)6(g)1(Pol()
14,20.7)wJ
20050401
Page 92

2-4-10
Function Calculations
k Permutation and Combination
uu
u Permutation
uu
n! n!
nPr = ––––– nCr = –––––––
(n – r)! r! (n – r)!
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
○○○○○
Example To calculate the possible number of different arrangements using 4
items selected from among 10 items
Formula Operation
10P4 = 5040 10K6(g)3(PROB)2(nPr)4w
○○○○○
Example To calculate the possible number of different combinations of 4 items
that can be selected from among 10 items
Formula Operation
10C4 = 210 10K6(g)3(PROB)3(nCr)4w
uu
u Combination
uu
kk
k Fractions
kk
How you should input fractions depends on the input mode that is currently selected.
Improper Fraction Mixed Fraction
Math input mode
7
3
($7c3)(1$(()2e1c3)
1
2
3
7 { 32 { 1 { 3
Linear input mode
Numerator Denominator
(7$3)(2$1$3)
Integer Part
Numerator
• For information about the Math input mode, see “Input Operations in the Math Input Mode”
on page 1-3-8.
• Fraction calculation results are always reduced before being displayed.
20050401
Denominator
Page 93

2-4-11
Function Calculations
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
2173
–– + 3 –– = –––
5420
<Math>
$2c5e+!$(&)3e1c4 w
<Line>
2$5+3$1$4w
11
––––– + –––––
2578 4572
1
–– × 0.5 = 0.25*
2
1.5 + 2.3i = –– + –– i
112
–––––– =
11 7
–– + ––
34
= 6.066202547 × 10–4*
2
323
210
––
Display:
3{2
+23{10i
<Math>
1
$1c2578e+$1c4572w
<Line>
1$2578+1$4572w
<Math>
$1c2e*.5w
<Line>
1$2*.5w
1.5+2.3!a(i)w
3
MM*
<Math>
$1c$1c3e+$1c4w
<Line>
1$(1$3+1$4)w
*1When the total number of characters,
including integer, numerator, denominator
and delimiter marks exceeds 10, the fraction
is automatically displayed in decimal format.
2
*
Calculations containing both fractions and
decimals are calculated in decimal format.
3
*
Pressing M once when converting the decimal
part of a complex number to a fraction first
displays the real part and imaginary part on
separate lines.
20050401
Page 94

2-4-12
Function Calculations
Switching between improper fraction and mixed fraction format
Pressing the !M(
improper fraction format.
) key toggles the display fraction between mixed fraction and
<
Switching between fraction and decimal format
⇒
M
⇐
• If the calculation result includes a fraction, the display format (improper fraction or mixed
fraction) is in accordance with the “Frac Result” setting of the Setup screen. For details,
see “1-7 Using the Setup Screen”.
•You cannot switch from decimal format to mixed fraction format if the total number of digits
used in the mixed fraction (including integer, numerator, denominator, and separator
symbols) is greater than 10.
k Engineering Notation Calculations
Input engineering symbols using the engineering notation menu.
•Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example Operation
!m(SET UP) f (or c 12 times)
999k (kilo) + 25k (kilo) 999K6(g)6(g)1(EYSM)6(g)1(k)+
= 1.024M (mega) 251(k)w
4(Eng)J
9 ÷ 10 = 0.9 = 900m (milli) 9/10w
= 0.9 K6(g)6(g)1(EYSM)6(g)6(g)3(ENG)*
= 0.0009k (kilo) 3(ENG)*
= 0.9 2(ENG)*
= 900m 2(ENG)*
*1Converts the displayed value to the next higher
engineering unit, by shifting the decimal point
three places to the right.
1
2
2
*2Converts the displayed value to the next lower
engineering unit, by shifting the decimal point
three places to the left.
20050401
1
Page 95

Numerical Calculations
2-5-1
2-5 Numerical Calculations
The following describes the items that are available in the menus you use when performing
differential/quadratic differential, integration, Σ, maximum/minimum value, and Solve
calculations.
When the option menu is on the display, press 4(CALC) to display the function analysis
menu. The items of this menu are used when performing specific types of calculations.
•{Solve}/{d/dx}/{d2/dx2}/{∫dx}/{FMin}/{FMax}/{Σ(} ... {solve}/{differential}/
{quadratic differential}/{integration}/{minimum value}/{maximum value}/{Σ (sigma)}
calculations
k Solve Calculations
The following is the syntax for using the Solve function in a program.
Solve( f(x), n, a, b) (a: lower limit, b: upper limit, n: initial estimated value)
There are two different input methods that can be used for Solve calculations: direct
assignment and variable table input.
With the direct assignment method (the one described here), you assign values directly to
variables. This type of input is identical to that used with the Solve command used in the
PRGM mode.
Var iable table input is used with the Solve function in the EQUA mode. This input method is
recommended for most normal Solve function input.
An error (Time Out) occurs when there is no convergence of the solution.
For information about Solve calculations, see page 4-3-1.
#You cannot use a differential, quadratic
differential, integration, Σ, maximum/minimum
value, Solve, RndFix or log ab calculation
expression inside of a Solve calculation term.
# Pressing A during calculation of Solve (while
the cursor is not shown on the display) interrupts
the calculation.
20050401
20070101
Page 96

Numerical Calculations
2-5-2
k Differential Calculations [OPTN]-[CALC]-[d
To perform differential calculations, first display the function analysis menu, and then input
the values using the syntax below.
K4(CALC)2(
d/dx ( f (x), a) ⇒ ––– f (a)
The differentiation for this type of calculation is defined as:
f '(a) = lim –––––––––––––
Ax→0
In this definition,
infinitesimal
neighborhood of f ' (a) calculated as:
f (a + Ax) – f (a)
f '(a) –––––––––––––
In order to provide the best precision possible, this unit employs central difference to perform
differential calculations.
Using Differential Calculation in a Graph Function
• Omitting the tolerance (tol) value when using the differential command inside of a graph
function simplifies the calculation for drawing the graph. In such a case, precision is
sacrificed for the sake of faster drawing. The tolerance value is specified, the graph is
drawn with the same precision obtained when you normally perform a differential
calculation.
• You can also omit input of the derivative point by using the following format for the
differential graph: Y2=d/dx(Y1). In this case, the value of the X variable is used as the
derivative point.
d/dx) f(x),a,tol)
d
dx
f (a + Ax) – f (a)
Ax
is replaced by a
Ax
(a: point for which you want to determine the
derivative, tol: tolerance)
sufficiently small
Ax, with the value in the
/dx]
20050401
Page 97

Numerical Calculations
2-5-3
○○○○○
Example To determine the derivative at point x = 3 for the function
3
y = x
+ 4x2 + x – 6, with a tolerance of “tol” = 1E – 5
Input the function f(x).
AK4(CALC)2(d/dx)vMd+evx+v-g,
Input point x = a for which you want to determine the derivative.
d,
Input the tolerance value.
bE-f)
w
<Math>
A4(MATH)4(d/dx)vMde
+evx+v-ged
w
# In the function f(x), only X can be used as a
variable in expressions. Other variables (A
through Z excluding X, r,
constants, and the value currently assigned to
that variable is applied during the calculation.
# Input of the tolerance (tol) value and the
closing parenthesis can be omitted. If you omit
tolerance (tol) value, the calculator automatically uses a value for tol as 1
# Specify a tolerance (tol) value of 1E-14 or
greater. An error (Time Out) occurs whenever
no solution that satisfies the tolerance value
can be obtained.
θ
) are treated as
E-10.
# In the Math input mode, the tolerance value is
fixed at 1
E-10 and cannot be changed.
# Inaccurate results and errors can be caused by
the following:
- discontinuous points in
- extreme changes in
- inclusion of the local maximum point and local
minimum point in
- inclusion of the inflection point in
- inclusion of undifferentiable points in
- differential calculation results approaching zero
20050401
20070101
x values
x values
x values
x values
x values
Page 98

Numerical Calculations
2-5-4
u Applications of Differential Calculations
•Differentials can be added, subtracted, multiplied or divided with each other.
dd
––– f (a) = f '(a), ––– g (a) = g'(a)
dx dx
Therefore:
f '(a) + g'(a), f '(a) × g'(a), etc.
•Differential results can be used in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, and in
functions.
2 × f '(a), log ( f '(a)), etc.
• Functions can be used in any of the terms ( f (x), a, tol) of a differential.
d
––– (sinx + cosx, sin0.5, 1E - 8), etc.
dx
#You cannot use a differential, quadratic
differential, integration, Σ, maximum/minimum
value, Solve, RndFix or log ab calculation
expression inside a differential calculation
term.
#Pressing A during calculation of a differential
(while the cursor is not shown on the display)
interrupts the calculation.
#Always use radians (Rad mode) as the angle
unit when performing trigonometric differentials.
20050401
Page 99

Numerical Calculations
2-5-5
kk
k Quadratic Differential Calculations [OPTN]-[CALC]-[d
kk
2
/dx2]
After displaying the function analysis menu, you can input quadratic differentials using the
following syntax.
K4(CALC)3(d
2
/dx2) f(x),a,tol)
(a: differential coefficient point, tol: tolerance)
2
d
––– (f (x), a) ⇒ ––– f (a)
2
dx
2
d
2
dx
Quadratic differential calculations produce an approximate differential value using the
following second order differential formula, which is based on Newton’s polynomial
interpretation.
2 f (a + 3h) – 27 f(a + 2h) + 270 f(a + h) – 490 f (a)+270 f (a – h) – 27 f (a – 2h) +2 f (a – 3h)
f''(a) = –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
180h
2
In this expression, values for “sufficiently small increments of h” are used to obtain a value
that approximates f ”(a).
○○○○○
Example To determine the quadratic differential coefficient at the point where
x = 3 for the function y = x
3
+ 4x2 + x – 6
Here we will use a tolerance tol = 1E – 5
Input the function f(x).
AK4(CALC)3(d
2
/dx2) vMd+
evx+v-g,
Input 3 as point a, which is the differential coefficient point.
d,
Input the tolerance value.
bE-f)
w
# In the function f(x), only X can be used as a
variable in expressions. Other variables (A
through Z excluding X, r,
constants, and the value currently assigned to
that variable is applied during the calculation.
θ
) are treated as
# Input of the tolerance (tol) value and the closing
parenthesis can be omitted.
# Specify a tolerance (tol) value of 1
An error (Time Out) occurs whenever no solution
that satisfies the tolerance value can be obtained.
20050401
20070101
E-14 or greater.
Page 100

Numerical Calculations
2-5-6
<Math>
A4(MATH)5(d
2
/dx2)vMde
+evx+v-gedw
u Quadratic Differential Applications
•Arithmetic operations can be performed using two quadratic differentials.
2
d
––– f (a) = f ''(a), ––– g (a) = g''(a)
2
dx
2
d
2
dx
Therefore:
f ''(a) + g''(a), f ''(a) × g''(a), etc.
• The result of a quadratic differential calculation can be used in a subsequent arithmetic
or function calculation.
2 × f ''(a), log ( f ''(a) ), etc.
• Functions can be used within the terms ( f(x), a, tol ) of a quadratic differential expression.
2
d
––– (sin x + cos x, sin 0.5, 1E - 8), etc.
2
dx
# In the Math input mode, the tolerance value is
fixed at 1
E-10 and cannot be changed.
# The rules that apply for linear differential also
apply when using a quadratic differential
calculation for the graph formula (see page 25-2).
# Inaccurate results and errors can be caused
by the following:
- discontinuous points in
- extreme changes in
- inclusion of the local maximum point and
local minimum point in
- inclusion of the inflection point in
- inclusion of undifferentiable points in
values
- differential calculation results approaching
zero
x values
x values
x values
x values
x
#You can interrupt an ongoing quadratic differential
calculation by pressing the A key.
# Always use radians (Rad mode) as the angle unit
when performing trigonometric quadratic
differentials.
# You cannot use a differential, quadratic differen-
tial, integration, Σ, maximum/minimum value,
Solve, RndFix or log ab calculation expression
inside of a quadratic differential calculation term.
# With quadratic differential calculation, calculation
precision is up to five digits for the mantissa.
20050401
20070101
 Loading...
Loading...