
September 26, 2011
Product Overview
Technical Explanation
Periodical Service
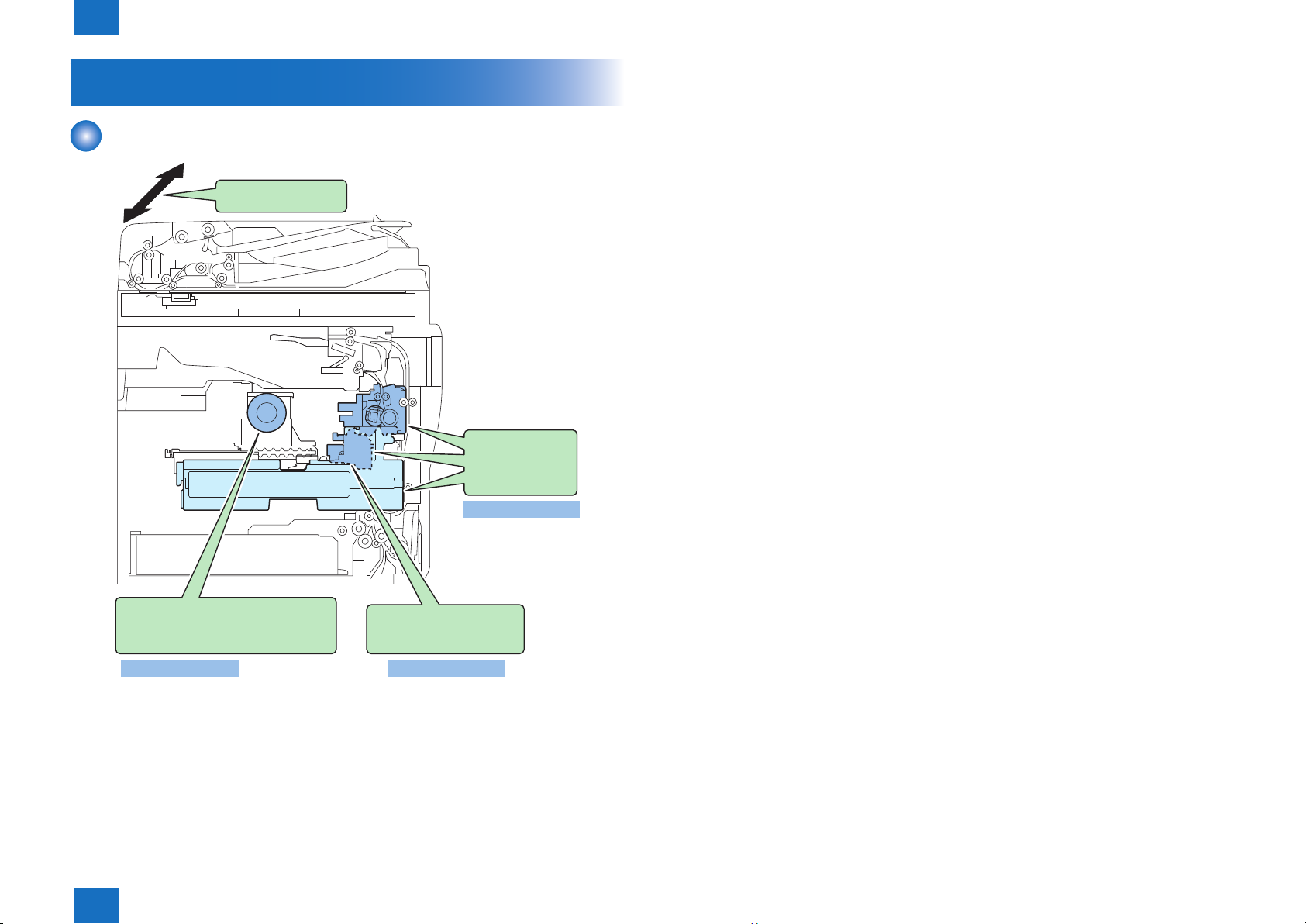
Disassembly/Assembly
Adjustment
Troubleshooting
Error Code
Service Mode
Installation
Appendix
imageRUNNER 1750/1740/1730 Series
Service Manual
Revision 1
987654321

Application
This manual has been issued by Canon Inc. for qualied persons to learn technical theory,
installation, maintenance, and repair of products. This manual covers all localities where the
products are sold. For this reason, there may be information in this manual that does not
apply to your locality.
Corrections
This manual may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors due to improvements
or changes in products. When changes occur in applicable products or in the contents of this
manual, Canon will release technical information as the need arises. In the event of major
changes in the contents of this manual over a long or short period, Canon will issue a new
edition of this manual.
The following paragraph does not apply to any countries where such provisions are
inconsistent with local law.
Trademarks
The product names and company names used in this manual are the registered trademarks
of the individual companies.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may
not be copied, reproduced or translated into another language, in whole or in part, without the
consent of Canon Inc.
© CANON INC. 2011
Caution
Use of this manual should be strictly supervised to avoid disclosure of condential
information.
Explanation of Symbols
The following symbols are used throughout this Service Manual.
Symbols Explanation Symbols Explanation
Check.
Check visually. Insert the claw.
Remove the claw.
The following rules apply throughout this Service Manual:
1. Each chapter contains sections explaining the purpose of specic functions and the
relationship between electrical and mechanical systems with reference to the timing of
operation.
In the diagrams,
name accompanies the symbol, the arrow
represents the path of mechanical drive; where a signal
indicates the direction of the
electric signal.
The expression "turn on the power" means ipping on the power switch, closing the
front door, and closing the delivery unit door, which results in supplying the machine with
power.
Check the noise. Use the bundled part.
Disconnect the connector. Push the part.
Connect the connector. Plug the power cable.
Remove the cable/wire
from the cable guide or wire
saddle.
Set the cable/wire to the
cable guide or wire saddle.
Remove the screw.
Turn on the power.
2. In the digital circuits, '1' is used to indicate that the voltage level of a given signal is
"High", while '0' is used to indicate "Low". (The voltage value, however, differs from
circuit to circuit.) In addition, the asterisk (*) as in "DRMD*" indicates that the DRMD
signal goes on when '0'.
In practically all cases, the internal mechanisms of a microprocessor cannot be checked
in the eld. Therefore, the operations of the microprocessors used in the machines
are not discussed: they are explained in terms of from sensors to the input of the DC
controller PCB and from the output of the DC controller PCB to the loads.
The descriptions in this Service Manual are subject to change without notice for product
improvement or other purposes, and major changes will be communicated in the form of
Service Information bulletins.
All service persons are expected to have a good understanding of the contents of this Service
Manual and all relevant Service Information bulletins and be able to identify and isolate faults
in the machine.
Tighten the screw.

Contents
0 Safety Precautions
CDRH Act -----------------------------------------------------------------------0-2
Laser Safety --------------------------------------------------------------------0-2
Handling of Laser System --------------------------------------------------0-2
Turn power switch ON -------------------------------------------------------0-3
Power Supply ------------------------------------------------------------------0-3
Safety of Toner -----------------------------------------------------------------0-4
About Toner ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0-4
Toner on Clothing or Skin -------------------------------------------------------- 0-4
Notes When Handling the Lithium and Ni-MH Batteries ------------0-4
Notes Before it Works Serving ---------------------------------------------0-4
Points to Note at Cleaning --------------------------------------------------0-4
Notes On Assembly/Disassembly -----------------------------------------0-4
1 Product Overview
Product Lineup -----------------------------------------------------------------1-2
Host machine ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-2
Host machine conguration -------------------------------------------------------------- 1-2
Model type ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1-2
Option --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-2
Pickup/Delivery / Image Reading System Options --------------------------------- 1-2
Function expansion system options --------------------------------------------------- 1-3
Features -------------------------------------------------------------------------1-4
Product Features ------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-4
Secured Print Jobs ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-5
Service Mode Disable of USB memory function ------------------------------------ 1-5
Setting “Auto-clear Time” to “short” ---------------------------------------------------- 1-5
Arabic support (In Europe only) --------------------------------------------------------- 1-5
Communication test function of E-RDS ----------------------------------------------- 1-5
Specications ------------------------------------------------------------------1-6
Specications ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-6
Weight and Size -------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-7
Productivity (Print speed) -------------------------------------------------------- 1-7
Paper type --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-7
Pickup ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-7
Parts Name ---------------------------------------------------------------------1-8
External View ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-8
Cross Sectional View ------------------------------------------------------------1-10
Operation --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1-11
Power Switch -------------------------------------------------------------------------------1-11
Description of Control Panel ------------------------------------------------------------ 1-11
2 Technical Explanation
Basic Conguration -----------------------------------------------------------2-2
Functional Conguration --------------------------------------------------------- 2-2
Basic sequence ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-2
Original Exposure and Feed System -------------------------------------2-3
Construction ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-3
Specications/controls/functions -------------------------------------------------------- 2-3
Major Components ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-4
Reader Controller PCB -------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-6
Basic Operation -------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-7
Basic Sequence ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-7
ADF Operation Mode ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-8
Controls ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-11
Controlling the Scanner Drive System -----------------------------------------------2-11
Contact Image Sensor (CIS) ------------------------------------------------------------2-12
Enlargement / Reduction ----------------------------------------------------------------2-13
Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors --------------------2-14
Dust Detection Control -------------------------------------------------------------------2-16
Dust Detection Preventive Process ---------------------------------------------------2-17
Dust Detection Correction Control-----------------------------------------------------2-18
Image Processing -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-18
Control of ADF ---------------------------------------------------------------------2-20
Original Size Detection by ADF --------------------------------------------------------2-20

Pickup and Feed Operations -----------------------------------------------------------2-22
Reversal Operation------------------------------------------------------------------------2-22
Delivery Operation-------------------------------------------------------------------------2-24
Jam Detection ------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-25
Work of Service -------------------------------------------------------------------2-26
Periodically Replaced Parts -------------------------------------------------------------2-26
Consumable Parts -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-26
Periodical Servicing -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-26
When replacing the parts ----------------------------------------------------------------2-26
Main Controller -------------------------------------------------------------- 2-27
Overview ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-27
Conguration/Function -------------------------------------------------------------------2-27
Controls -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-28
Image Data Flow ---------------------------------------------------------------------------2-28
Image Processing Module Conguration --------------------------------------------2-28
Reader Unit Input Image Processing -------------------------------------------------2-29
Compression/Expansion/Edit Processing Block -----------------------------------2-29
Printer Output Image Processing ------------------------------------------------------2-30
Image Data Flow of Copy Function ---------------------------------------------------2-30
Image Data Flow of SEND Function --------------------------------------------------2-31
Image Data Flow of FAX Transmission Function ----------------------------------2-31
Image Data Flow of FAX Reception Function --------------------------------------2-32
Image Data Flow of PDL Function ----------------------------------------------------2-32
Service Tasks ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-33
Periodically Replaced Parts -------------------------------------------------------------2-33
Consumable Parts -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-33
Periodical Servicing -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-33
Laser Exposure System --------------------------------------------------- 2-34
Construction ------------------------------------------------------------------------2-34
Specications/Controls/Functions -----------------------------------------------------2-34
Main Conguration Parts ----------------------------------------------------------------2-34
Control System Conguration ----------------------------------------------------------2-35
Basic Sequence -------------------------------------------------------------------2-36
Basic Sequence ----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-36
Various Controls -------------------------------------------------------------------2-37
Controlling the Laser Activation Timing ----------------------------------------------2-37
Controlling the Intensity of Laser Light -----------------------------------------------2-39
Controlling the Laser Scanner Motor -------------------------------------------------2-39
Controlling the Laser Shutter -----------------------------------------------------------2-39
Image Formation System ------------------------------------------------- 2-40
Basic Conguration ---------------------------------------------------------------2-40
List of Image Formation Specications ----------------------------------------------2-40
Major Components in image formation system ------------------------------------2-41
Image Formation Process ---------------------------------------------------------------2-42
Basic Sequence -------------------------------------------------------------------2-43
Initial rotation sequence ------------------------------------------------------------------2-43
Sequence at printing ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-43
Last rotation sequence -------------------------------------------------------------------2-43
Controls -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-44
Drum Unit ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-44
Developing Assembly ---------------------------------------------------------------------2-45
Toner Supply Area -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-46
Transfer Unit --------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-48
Chang in bias by user mode (Special Mode) ---------------------------------------2-49
Waste Toner Box ---------------------------------------------------------------------------2-49
Service Tasks ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-50
Periodically Replaced Parts -------------------------------------------------------------2-50
Consumable Parts -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-50
Periodical Servicing -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-50
Fixing System ---------------------------------------------------------------- 2-51
Overview ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-51
Features --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-51
Specications -------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-51
Major Components ------------------------------------------------------------------------2-52
Controls -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-53
Fixing Temperature Control (temperature control) --------------------------------2-53
Standby Temperature Controll ----------------------------------------------------------2-54
Print temperature control ----------------------------------------------------------------2-54
Down Sequence Control -----------------------------------------------------------------2-56
Change in xing performance by user mode (Special Mode) ------------------2-57
Pre-xing arch level control -------------------------------------------------------------2-58
Protection function-------------------------------------------------------------------------2-59
Service Tasks ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-59
Periodically Replaced Parts -------------------------------------------------------------2-59
Consumable Parts -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-59
Periodical Servicing -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-59

Pickup Feed System ------------------------------------------------------- 2-60
Overview ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-60
Specications -------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-60
Parts Conguration ------------------------------------------------------------------------2-60
Paper Path ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-62
Controls -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-63
Overview -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-63
Cassette Pickup Assembly --------------------------------------------------------------2-63
Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Assembly -------------------------------------------------2-67
Fixing/Registration Assembly -----------------------------------------------------------2-67
Delivery Assembly -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-68
Reverse/Duplex Assembly --------------------------------------------------------------2-69
Jam Detection ------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-70
Work of Service -------------------------------------------------------------------2-71
Periodical ServicePeriodical Service -------------------------------------------------2-71
Consumables -------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-71
Periodically Servicing ---------------------------------------------------------------------2-71
External Auxiliary System ------------------------------------------------- 2-72
Controls -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2-72
Software counter ---------------------------------------------------------------------------2-72
Fan --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-72
Power supply -------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-73
Service Tasks ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-75
Periodically Replaced Parts -------------------------------------------------------------2-75
Consumable Parts -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-75
Periodical Servicing -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-75
Embedded RDS ------------------------------------------------------------- 2-76
Product Overview -----------------------------------------------------------------2-76
Overview -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2-76
Features and benets --------------------------------------------------------------------2-76
Service cautions -------------------------------------------------------------------2-76
E-RDS Setup -----------------------------------------------------------------------2-77
Conrmation and preparation in advance -------------------------------------------2-77
E-RDS setting items ----------------------------------------------------------------------2-80
Steps to E-RDS settings -----------------------------------------------------------------2-80
Initializing E-RDS settings ---------------------------------------------------------------2-82
COM-LOG Report -------------------------------------------------------------------------2-82
FAQ ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-83
Troubleshooting ------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-84
Error code and strings ----------------------------------------------------------- 2-86
3 Periodical Service
List of periodically replacement parts, consumable parts and
locations for cleaning ---------------------------------------------------------3-2
periodically replacement parts -------------------------------------------------- 3-2
Consumable parts ----------------------------------------------------------------- 3-2
4 Disassembly/Assembly
Preface --------------------------------------------------------------------------4-2
Outline -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-2
List of Parts ---------------------------------------------------------------------4-3
External View ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-3
Front Side ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-3
Rear Side ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-4
Internal View --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-4
List of Main Unit -------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-5
Electrical Components ------------------------------------------------------------ 4-7
ADF Unit -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-7
Reader Unit ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-8
Printer Unit ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4-9
List of Connectors -----------------------------------------------------------4-15
External Cover/Internal System -----------------------------------------4-22
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-22
Front Side ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-22
Rear Side ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-23
Internal View --------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-23
Removing the Front Cover -----------------------------------------------------4-24
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-24
Removing the Rear Cover ------------------------------------------------------4-24
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-24
Removing the Right Front Cover ----------------------------------------------4-25
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-25
Removing the Right Rear Cover ---------------------------------------------- 4-26
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-26
Removing the Right Door Unit -------------------------------------------------4-26

Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-26
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-26
Removing the Left Cover -------------------------------------------------------4-27
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-27
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-27
Removing the Inner Rear Cover ----------------------------------------------4-28
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-28
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-28
Removing the Delivery Outer Cover -----------------------------------------4-29
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-29
Removing the Delivery Inner Cover ------------------------------------------4-29
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-29
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-29
Removing the Right Inner Cover ----------------------------------------------4-30
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-30
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-30
Removing the Left Inner Cover ------------------------------------------------4-32
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-32
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-32
Removing the Support Column Cover ---------------------------------------4-32
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-32
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-32
Removing the Reader Front Cover -------------------------------------------4-33
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-33
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-33
Removing the Reader Rear Cover -------------------------------------------4-34
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-34
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-34
Removing the Reader Bottom Cover ----------------------------------------4-36
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-36
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-36
Removing the Control Panel Unit ---------------------------------------------4-36
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-36
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-36
Original Exposure/Feed System ---------------------------------------- 4-39
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-39
Removing the Copyboard Glass ---------------------------------------------- 4-40
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-40
When Replacing the Copyboard Glass ----------------------------------------------4-41
Removing the ADF Reading Glass -------------------------------------------4-42
When Replacing the ADF Reading Glass -------------------------------------------4-43
Removing the ADF Unit --------------------------------------------------------- 4-43
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-43
Removing the Reader Unit -----------------------------------------------------4-44
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-44
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-44
Removing the Reader Controller PCB ---------------------------------------4-46
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-46
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-46
Removing the CIS Unit ---------------------------------------------------------- 4-47
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-47
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-47
When Replacing the CIS Unit ----------------------------------------------------------4-48
Removing the ADF Upper Cover Unit ---------------------------------------4-48
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-48
Removing the ADF Separation Pad ------------------------------------------4-50
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-50
Removing the ADF Pickup Roller Unit ---------------------------------------4-51
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-51
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-51
Removing the ADF Pickup Tray ----------------------------------------------- 4-52
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-52
Removing the ADF Pickup Unit -----------------------------------------------4-53
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-53
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-53
Controller System ----------------------------------------------------------- 4-57
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-57
Removing the DC Controller PCB -------------------------------------------- 4-57
Preparation before Replacement ------------------------------------------------------4-57
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-57
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-57
After Replacement/RAM Clearing -----------------------------------------------------4-58
Removing the Main Controller PCB ------------------------------------------4-58
Preparation before Replacement ------------------------------------------------------4-58
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-58
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-58

After Replacement-------------------------------------------------------------------------4-60
Removing the HVT PCB --------------------------------------------------------4-60
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-60
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-60
Removing the Power Supply PCB --------------------------------------------4-62
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-62
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-62
Laser Exposure System --------------------------------------------------- 4-63
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-63
Removing the Laser Scanner Unit --------------------------------------------4-63
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-63
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-63
After Replacing the Laser Scanner Unit ---------------------------------------------4-65
Image Formation System ------------------------------------------------- 4-66
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-66
Removing the Waste Toner Container ---------------------------------------4-67
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-67
Removing the Toner Cartridge -------------------------------------------------4-68
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-68
Removing the Drum Unit --------------------------------------------------------4-68
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-68
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-68
Removing the Developing Assembly -----------------------------------------4-69
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-69
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-69
Removing the Transfer Roller --------------------------------------------------4-71
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-71
Removing the Separation Static Eliminator --------------------------------4-72
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-72
Removing the Main Drive Unit -------------------------------------------------4-73
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-73
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-73
Removing the Hopper Unit -----------------------------------------------------4-75
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-75
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-75
Fixing System ---------------------------------------------------------------- 4-79
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-79
Removing the Fixing Assembly ------------------------------------------------4-79
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-79
Removing the Fixing Drive Unit -----------------------------------------------4-81
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-81
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-81
Pickup Feed System ------------------------------------------------------- 4-83
Location -----------------------------------------------------------------------------4-83
Removing the Cassette Feed Roller ----------------------------------------- 4-83
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-83
Removing the Cassette Separation Roller ---------------------------------4-85
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-85
Removing the Cassette Pickup Roller ---------------------------------------4-86
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-86
Removing the Cassette Pickup Idler Gear ---------------------------------4-87
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-87
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-87
Removing the Cassette Pickup Unit -----------------------------------------4-87
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-87
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-87
Removing the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller --------------------------4-88
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-88
Removing the Multi-purpose Tray Separation Pad -----------------------4-91
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-91
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-91
Removing the Delivery/Reverse Unit ----------------------------------------4-92
Preparation ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-92
Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4-92
5 Adjustment
Overview ------------------------------------------------------------------------5-2
Adjustment when replacing parts ---------------------------------------------- 5-2
Image Position Adjustment ------------------------------------------------------ 5-2
Adjustment when Replacing the Parts -----------------------------------5-3
Original Exposure and Feed System ----------------------------------------- 5-3
When Replacing the CIS Unit ----------------------------------------------------------- 5-3
When Replacing the Copyboard Glass ----------------------------------------------- 5-3
When Replacing the ADF Reading Glass -------------------------------------------- 5-4

Main Controller System ---------------------------------------------------------- 5-4
Before Replacing the Main Controller PCB ------------------------------------------ 5-4
After Replacing the Main Controller PCB --------------------------------------------- 5-4
Before Replacing the DC Controller PCB -------------------------------------------- 5-5
After Replacing the DC Controller PCB ----------------------------------------------- 5-5
When Replacing the RAM PCB --------------------------------------------------------- 5-5
Laser Exposure System ---------------------------------------------------------- 5-5
After Replacing the Laser Scanner Unit ---------------------------------------------- 5-5
Image Position Adjustment -------------------------------------------------5-6
Left Edge Margin Adjustment --------------------------------------------------- 5-6
Leading Edge Non-image Width Adjustment ------------------------------- 5-6
Left Edge Non-image Width Adjustment ------------------------------------- 5-7
Image Position Adjustment for ADF ------------------------------------------- 5-8
Creation of Adjusting Test Sheet -------------------------------------------------------- 5-8
Squareness Adjustment ------------------------------------------------------------------- 5-8
Adjustment of Image Magnication Factor for Sub Scanning Section -------- 5-9
Horizontal Registration Adjustment ---------------------------------------------------5-10
Leading Edge Registration Adjustment ----------------------------------------------5-10
6 Troubleshooting
Initial Check --------------------------------------------------------------------6-2
List of Initial Check Items -------------------------------------------------------- 6-2
Test Print ------------------------------------------------------------------------6-3
Overview ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-3
Steps to Select a Test Print Type ---------------------------------------------- 6-3
How to View the Test Print ------------------------------------------------------- 6-4
Grid (TYPE=01) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-4
Halftone (TYPE=02) ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-4
Solid black (TYPE=03) -------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-5
Solid white (TYPE=04) -------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-5
4dot-6space / dot-6space (TYPE=06 / 07) ------------------------------------------- 6-6
Troubleshooting items -------------------------------------------------------6-7
List of Troubleshooting Items --------------------------------------------------- 6-7
Image Failure ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-7
Toner soiling at the back side of paper ------------------------------------------------ 6-7
Soiling at the leading/trailing edge of paper ----------------------------------------- 6-7
Poor transfer of the image, hollow character ---------------------------------------- 6-8
Image smear/toner bleed/condensation ---------------------------------------------- 6-8
Large curl of paper ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-9
Paper jam in solid image when the leading edge margin is small (1 to 4mm) -6-9
Jam with thin paper (63g/cm2 or lighter) --------------------------------------------- 6-9
The toner bottle set lever cannot be operated or is hard to operate. ---------- 6-9
Abnormal noise at pickup from the Multi-purpose Tray -------------------------6-10
Software to Be Upgraded and Upgrading Method ------------------ 6-11
Overview ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6-11
Procedure ---------------------------------------------------------------------------6-12
7 Error Code
Overview ------------------------------------------------------------------------7-2
Outline -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 7-2
Error Code ----------------------------------------------------------------------7-3
Error Code Details ----------------------------------------------------------------- 7-3
Error codes related to Fax ------------------------------------------------------7-10
Overview -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------7-10
User error codes ---------------------------------------------------------------------------7-10
Service error codes -----------------------------------------------------------------------7-10
Jam Code --------------------------------------------------------------------- 7-12
Main Unit ----------------------------------------------------------------------------7-12
ADF -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------7-13
Staple Finisher-H1 ----------------------------------------------------------------7-14
Alarm Code ------------------------------------------------------------------- 7-15
Alarm Code Details ---------------------------------------------------------------7-15
8 Service Mode
Outline ---------------------------------------------------------------------------8-2
Outline of Service Mode ---------------------------------------------------------- 8-2
Using the Mode --------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-3
Setting of Bit Switch --------------------------------------------------------------- 8-3
Outline ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-3
Back-Up ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 8-4
Service Label ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-4
Details of Service Mode -----------------------------------------------------8-5

#SSSW ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-5
SSSW Composition ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 8-5
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-5
#MENU ------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-15
Menu Switch Composition ---------------------------------------------------------------8-15
Deatails ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-15
#NUMERIC -------------------------------------------------------------------------8-16
Numerical Parameter Composition----------------------------------------------------8-16
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-17
#SCAN -------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-22
Setting of Scanner Functions (SCANNER) -----------------------------------------8-22
SCAN SW -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-25
Numeric Parameter Settings (Numeric Prama.) -----------------------------------8-26
READER -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-27
#PRINT ------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-32
Numerin Parameter Settings (Numeric Prama). -----------------------------------8-32
Service Soft Switch Settings (PRINTER) --------------------------------------------8-33
List of Functions ----------------------------------------------------------------------------8-34
List of Functions(PRINT CST) ----------------------------------------------------------8-37
#NETWORK ------------------------------------------------------------------------8-38
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-38
Conrmation of contents of CA certicate -------------------------------------------8-39
#CODEC ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-39
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-39
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-39
#SYSTEM ---------------------------------------------------------------------------8-40
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-40
Details of Bit Switch -----------------------------------------------------------------------8-40
Details of System Numeric --------------------------------------------------------------8-41
#ACC ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-42
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-42
#COUNTER ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 8-42
Counters -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-42
Clearing Counters -------------------------------------------------------------------------8-43
#LMS ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-43
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-43
Outline ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-44
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-44
Method of conrming license option --------------------------------------------------8-44
Inactivity of the transmitted license----------------------------------------------------8-44
Erasing a License--------------------------------------------------------------------------8-46
#E-RDS ------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-47
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-47
#REPORT ---------------------------------------------------------------------------8-47
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-47
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-48
#DOWNLOAD ---------------------------------------------------------------------8-52
Download ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-52
#CLEAR -----------------------------------------------------------------------------8-52
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-52
#DISPLAY --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8-53
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-53
#ROM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-53
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-53
#TEST MODE ---------------------------------------------------------------------8-53
Outline ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-53
Conguration --------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-54
Details ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8-54
9 Installation
How to check this Installation Procedure -------------------------------9-2
When Using the parts included in the package ---------------------------- 9-2
Symbols in the Illustration ------------------------------------------------------- 9-2
Installation ----------------------------------------------------------------------9-2
Option Installation Sequence ----------------------------------------------9-2
Drum Heater-D1 ---------------------------------------------------------------9-3
Points to Note at Installation ---------------------------------------------------- 9-3
Checking the Contents ----------------------------------------------------------- 9-3
Check Items when Turning OFF the Power --------------------------------- 9-3
Installation Outline Drawing ----------------------------------------------------- 9-3
Installation Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------- 9-4
Removing the Covers---------------------------------------------------------------------- 9-4
Before Installing ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9-5
Installing the Environment Drum Heater ---------------------------------------------- 9-8
Copy Card Reader-F1 ----------------------------------------------------- 9-11

Check Item of the Contents ----------------------------------------------------9-11
Points to Note at Installation ---------------------------------------------------9-11
Checking the Contents ----------------------------------------------------------9-11
Copy Card Reader-F1 -------------------------------------------------------------------- 9-11
Copy Card Reader Attachment-C1 ----------------------------------------------------9-11
Check Items when Turning OFF the Power --------------------------------9-12
Installation Outline Drawing ---------------------------------------------------- 9-12
Installation Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------9-12
Assembling the Card Reader -----------------------------------------------------------9-12
Removing the Covers---------------------------------------------------------------------9-14
Installing the Card Reader Kit ----------------------------------------------------------9-16
Registering the Card IDs --------------------------------------------------------9-21
System Upgrade RAM-C1 ------------------------------------------------ 9-22
Checking the Contents ----------------------------------------------------------9-22
Check Items when Turning OFF the Power --------------------------------9-22
Installation Outline Drawing ---------------------------------------------------- 9-22
Installation Procedure ------------------------------------------------------------9-22
Removing the Covers---------------------------------------------------------------------9-22
Before Installing ----------------------------------------------------------------------------9-23
Installing the SO-DIMM ------------------------------------------------------------------9-24
Appendix
Service Tools --------------------------------------------------------------------- II
Special Tools --------------------------------------------------------------------------- II
Oils and Solvents --------------------------------------------------------------------- II
General Timing Chart ----------------------------------------------------------III
Basic sequence at printing (A4 single-sided print (2 sheets), cassette) III
Basic sequence at printing (A4 double-sided print (1 sheet), cassette) IV
General Circuit Diagram -------------------------------------------------------V
General Circuit Diagram (1/10) ----------------------------------------------------V
General Circuit Diagram (2/10) --------------------------------------------------- VI
General Circuit Diagram (3/10) -------------------------------------------------- VII
General Circuit Diagram (4/10) ------------------------------------------------- VIII
General Circuit Diagram (5/10) --------------------------------------------------- IX
General Circuit Diagram (6/10) ----------------------------------------------------X
General Circuit Diagram (7/10) --------------------------------------------------- XI
General Circuit Diagram (8/10) -------------------------------------------------- XII
General Circuit Diagram (9/10) ------------------------------------------------- XIII
General Circuit Diagram (10/10) ----------------------------------------------- XIV
List of User Mode ------------------------------------------------------------- XV
Common Settings -------------------------------------------------------------------XV
Timer Settings -----------------------------------------------------------------------XV
Adjustment/Cleaning -------------------------------------------------------------- XVI
Report Settings --------------------------------------------------------------------- XVI
Copy Settings ----------------------------------------------------------------------- XVI
Communications Settings ------------------------------------------------------- XVII
Printer Settings ------------------------------------------------------------------- XVIII
Settings Menu ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- XVIII
PCL Settings*1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- XVIII
PS Settings* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- XVIII
Other Settings ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- XVIII
Address Book Settings -----------------------------------------------------------XIX
Register Address ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- XIX
One-touch Buttons --------------------------------------------------------------------------XX
System Management Settings --------------------------------------------------XXI
System Manager Info.Setting ------------------------------------------------------------ XXI
Device Info. Settings -----------------------------------------------------------------------XXI
Dept. ID Management --------------------------------------------------------------------- XXI
User ID Management ----------------------------------------------------------------------XXI
Network Settings ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- XXI
Communications Settings -------------------------------------------------------------- XXIII
Forwarding Settings ---------------------------------------------------------------------- XXIV
Store/Print When Forwarding ---------------------------------------------------------- XXIV
Remote UI ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- XXIV
Restrict the Send Function ------------------------------------------------------------- XXIV
Auto Online/Ofine -----------------------------------------------------------------------XXIV
Register LDAP Server --------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Job Log Display ----------------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Memory Media Store Log ----------------------------------------------------------------XXV
License Registrastion ---------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
USB Device ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Dept. ID/User Name Display ------------------------------------------------------------XXV
PDL Selection (PnP) ----------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Memory Media Settings ------------------------------------------------------------------XXV

Update Firmware --------------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Volume Control --------------------------------------------------------------------XXV
Backup Data ----------------------------------------------------------------- XXVI

Safety Precautions
CDRH Act
■
Laser Safety
■
Handling of Laser System
■
Turn power switch ON
■
Power Supply
■
Safety of Toner
■
Notes When Handling
■
the Lithium and Ni-MH
Batteries
Notes Before it Works
■
Serving
Points to Note at Cleaning
■
Notes On Assembly/
■
Disassembly
imageRUNNER
1750/1740/1730 Series
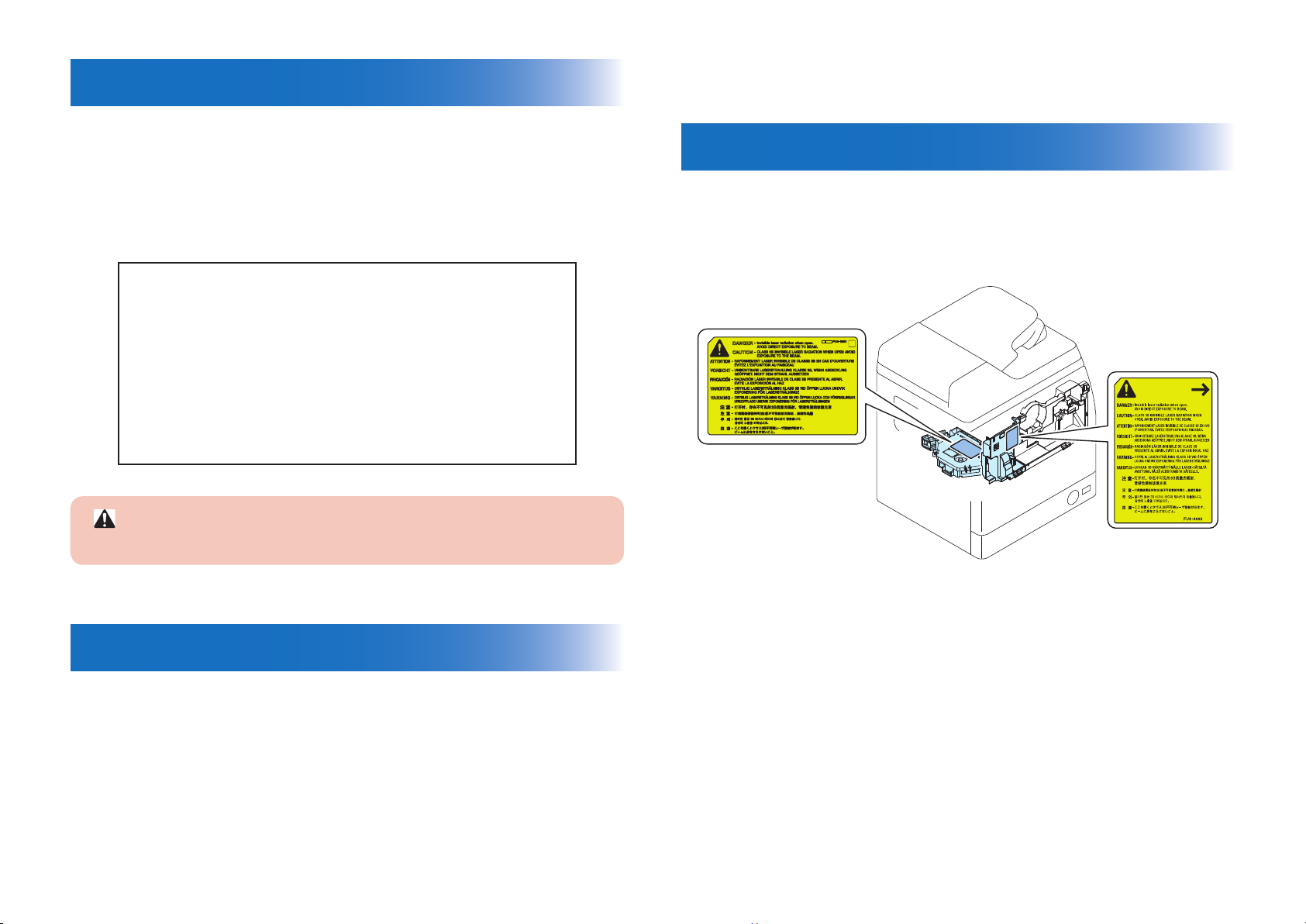
0-2
CDRH Act
The Center for Devices and Radiological Health of the US Food and Drug Administration put
into force regulations concerning laser products on August 2, 1976. These regulations apply
to laser products manufactured on and after August 1, 1976, and the sale of laser products
not certied under the regulations is banned within the Untied States. The label shown here
indicates compliance with the CDRH regulations, and its attachment is required on all laser
products that are sold in the United States.
CANON INC.
30-2,SHIMOMARUKO,3-CHOME,OHTA-KU,TOKYO,JAPAN
MANUFACTURED:
THIS PRODUCT CONFORMS WITH DHHS RADIATION
PERFORMANCE STANDARD 21CFR CHAPTER 1
SUBCHAPTER J.
F-0-1
This product is certicated as a Class 1 laser product under IEC60825-1:2007.
Handling of Laser System
When servicing the area around the laser assembly, be sure to turn off the main power.
The machine's covers that can reect laser light are identied by means of a warning label
(Figure). If you must detach a cover showing the label, be sure to take extra caution during
the work.
A different description may be used for a different product.
Laser Safety
When servicing the area around the laser assembly, be sure to turn off the main power.
The machine's covers that can reect laser light are identied by means of a warning label
(Figure). If you must detach a cover showing the label, be sure to take extra caution during
the work.
F-0-2
0-2
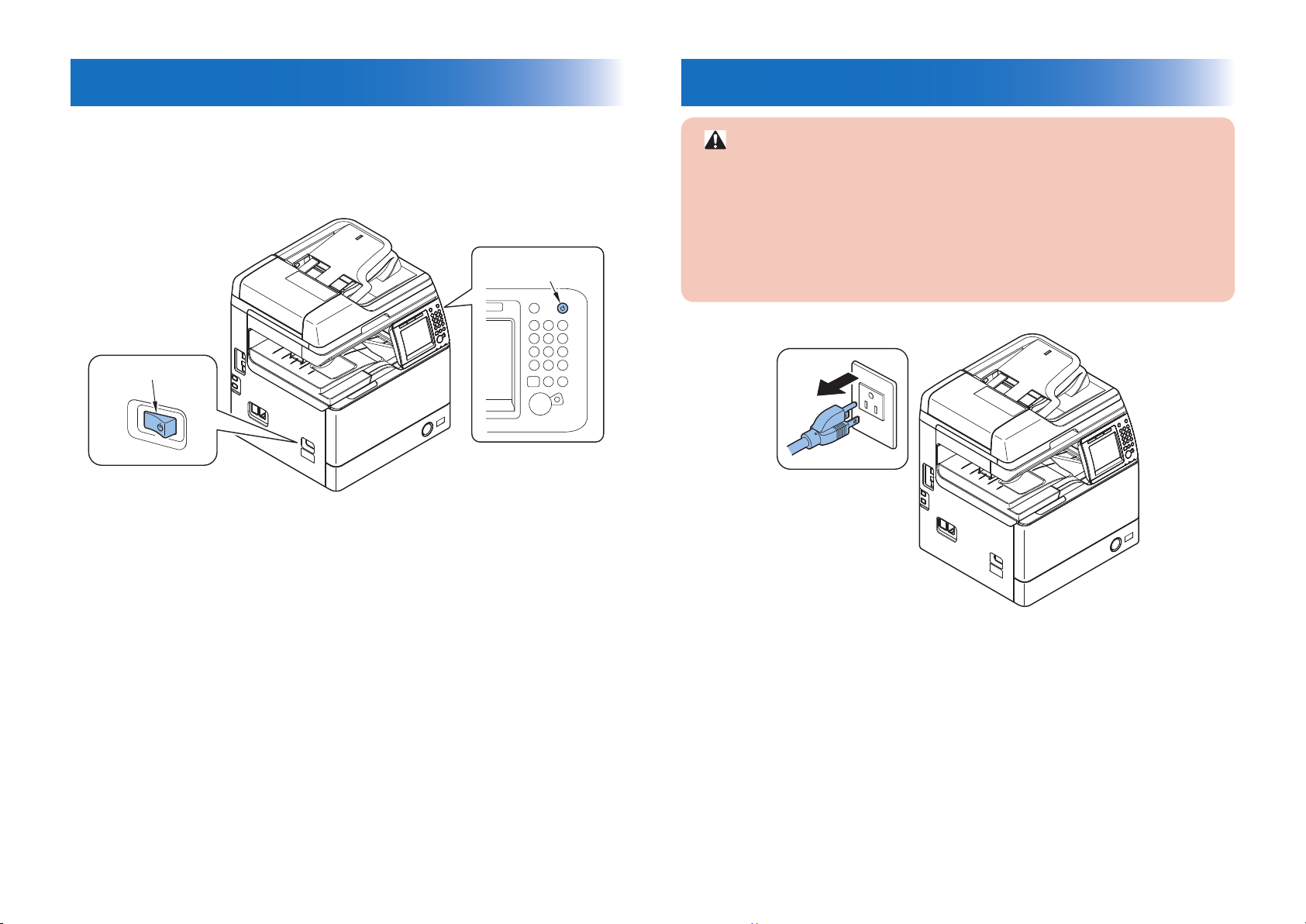
0-3
Turn power switch ON
The machine is equipped with 2 power switches: main power switch and control panel power
switch.
The machine goes on when the main power switch is turned on (i.e., other than in low power
mode, sleep mode).
Control Panel
Power Switch
Main Power Switch
F-0-3
Power Supply
1. As a general rule, do not use extension cords. Using an extension cord may result
in a re or electrical shock. If an extension cord must be used, however, use one
for local rated voltage and over, untie the cord binding, and insert the power plug
completely into the extension cord outlet to ensure a rm connection between the
power cord and the extension cord.
2. The socket-outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily
accessible.
F-0-4
0-3

0-4
Safety of Toner
About Toner
The machine's toner is a non-toxic material made of plastic, iron, and small amounts of dye.
Do not throw toner into re. It may cause explosion.
Toner on Clothing or Skin
• If your clothing or skin has come into contact with toner, wipe it off with tissue; then, wash it
off with water.
• Do not use warm water, which will cause the toner to jell and fuse permanently with the
bers of the cloth.
• Tonner is easy to react with plastic material, avoid contact with plastic.
Notes When Handling the Lithium and Ni-MH Batteries
RISK OF EXPLOSION IF BATTERY IS REPLACED BY AN INCORRECT TYPE.
DISPOSE OF USED BATTERIES ACCORDING TO THE INSTRUCTIONS.
The following warnings are given to comply with Safety Principles (EN60950).
Notes Before it Works Serving
At servicing, be sure to turn OFF the power source according to the specied steps and
disconnect the power plug.
Points to Note at Cleaning
When performing cleaning using organic solvent such as alcohol, be sure to check that
the component of solvent is vaporized completely before assembling.
Notes On Assembly/Disassembly
Follow the items below to assemble/disassemble the device.
1. Disconnect the power plug to avoid any potential dangers during assembling/disassembling
works.
2. If not specially instructed, reverse the order of disassembly to reinstall.
3. Ensure to use the right screw type (length, diameter, etc.) at the right position when
assembling.
4. To keep electric conduction, binding screws with washers are used to attach the grounding
wire and the varistor. Ensure to use the right screw type when assembling.
5. Unless it is specially needed, do not operate the device with some parts removed.
6. Never remove the paint-locked screws when disassembling.
Wenn mit dem falschen Typ ausgewechselt, besteht Explosionsgefahr.
Gebrauchte Batterien gemäß der Anleitung beseitigen.
F-0-5
0-4

Product Overview
1
Product Lineup
■
Features
■
Specications
■
Parts Name
■
Product Overview
1
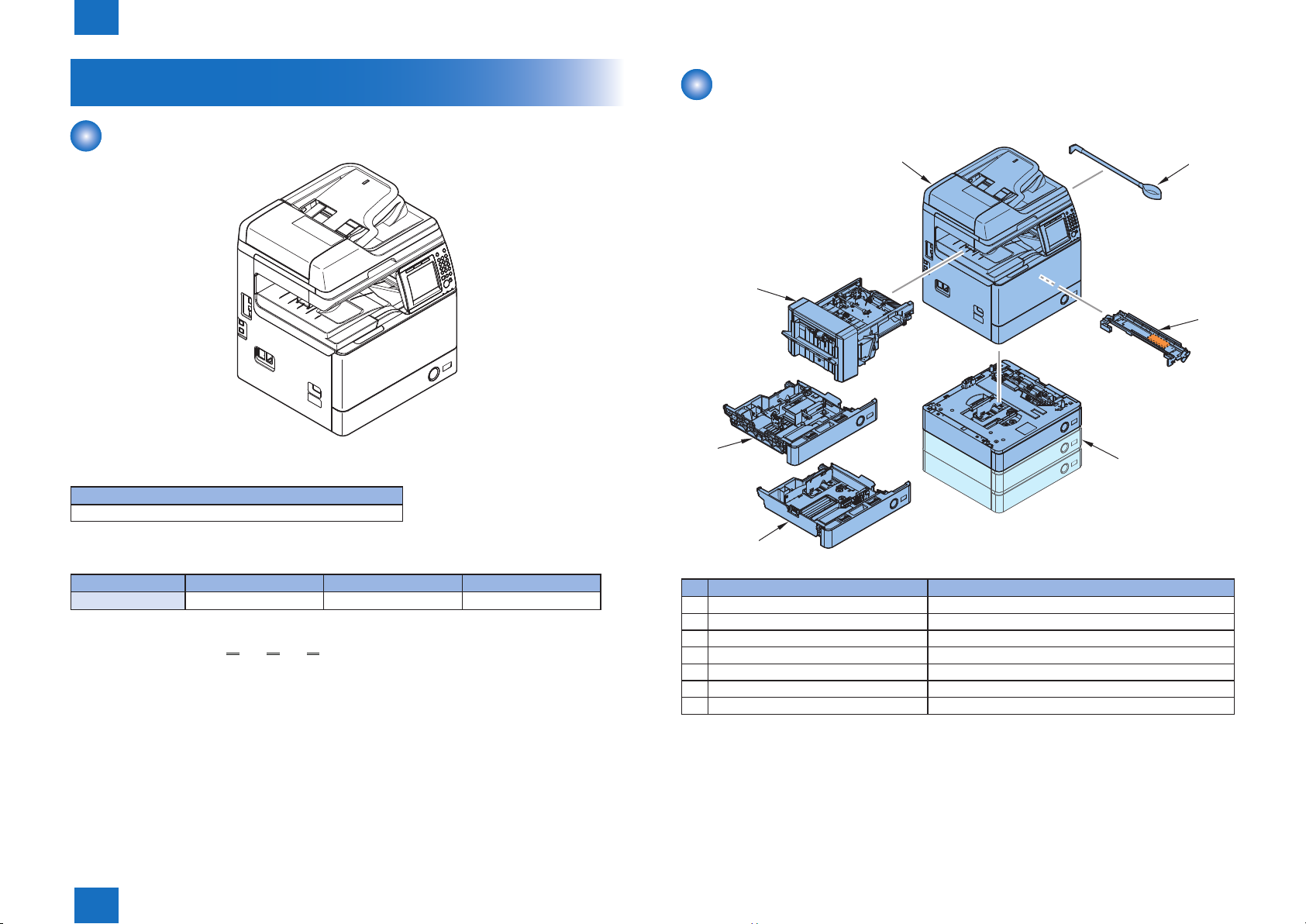
1
imageRUNNER 1750 / 1740 / 1730
Product Overview > Product Lineup > Option > Pickup/Delivery / Image Reading System Options
1-2
Product Lineup
Host machine
F-1-1
■Host machine conguration
Conguration
Reader+DADF+Printer
T-1-1
■Model type
imageRUNNER 1750 imageRUNNER 1740 imageRUNNER 1730
Print Speed
Underlined (2-digit) numeric figures indicate print speed (ppm: print per minute).
50ppm 40ppm 30ppm
F-1-2
T-1-2
Option
■Pickup/Delivery / Image Reading System Options
[1]
[3]
[6]
[5]
No. Product name Remarks and condition
1 imageRUNNER 1750/1740/1730
2 ADF Access Handle-A1
3 Staple Finisher-H1
4 Cassette Module-Y1 Up to 3 units can be installed
5 FL Cassette-AP1
6 Envelope Cassette-D1
7 Drum Heater-D1
[4]
[2]
[7]
F-1-3
T-1-3
Product Overview > Product Lineup > Option > Pickup/Delivery / Image Reading System Options
1
1-2

1
[1]
Product Overview > Product Lineup > Option > Function expansion system options
1-3
■Function expansion system options
[2]
[3]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
No. Product name Remarks and condition
1 Copy Card Reader-F1 Copy Card Reader Attachment-C1 is required.
2 Copy Card Reader Attachment-C1
3 USB Application 3-Port Interface Kit-B1
4 Super G3 Fax Board-AJ1
5 System Upgrade RAM-C1 512MB
6 PCL Printer Kit-AL1 512MB is required for RAM. When using 256MB RAM,
System Upgrade RAM-C1 is required.
7 PS Printer Kit-AL1 512MB is required for RAM. When using 256MB RAM,
System Upgrade RAM-C1 is required.
8 Barcode Printing Kit-B1 PCL Printer Kit-AF1 is required.
9 Color Send Kit-Z1 512MB is required for RAM. When using 256MB RAM,
System Upgrade RAM-C1 is required.
10 Color Send Searchable PDF Kit-E1 512MB is required for RAM. When using 256MB RAM,
System Upgrade RAM-C1 is required.
11 eM Controller-C1, 230V
T-1-4
[4]
Product Overview > Product Lineup > Option > Function expansion system options
1
F-1-4
1-3
1
Product Overview > Features > Product Features
1-4
Features
Product Features
Depth: 500mm or less.
• Canon's rst B&W MFP of toner supply-type which accommodates paper up to A4 size
Low running cost
• Improved maintainability
Fixing Assembly and Drum Unit can be replaced by the user.
Replacement time for consumable parts and options by the service technician has
been signicantly reduced.
• Performance
FCOT: 5 sec. or less
Recovery from sleep mode: 10 sec. or less
1W sleep mode
• Installability
Depth: 500mm or less.
Fixing Assembly
Drum Unit
Waste Toner Box
- User replaceable
Low running cost
Toner Cartridge
Canon's first B&W MFP of toner supply-type
which accommodates paper up to A4 size
Low running cost
Product Overview > Features > Product Features
1
Drum Unit
- Highly-durable OPC drum is
adopted
Low running cost
F-1-5
1-4
1
Product Overview > Features > Product Features > Communication test function of E-RDS
1-5
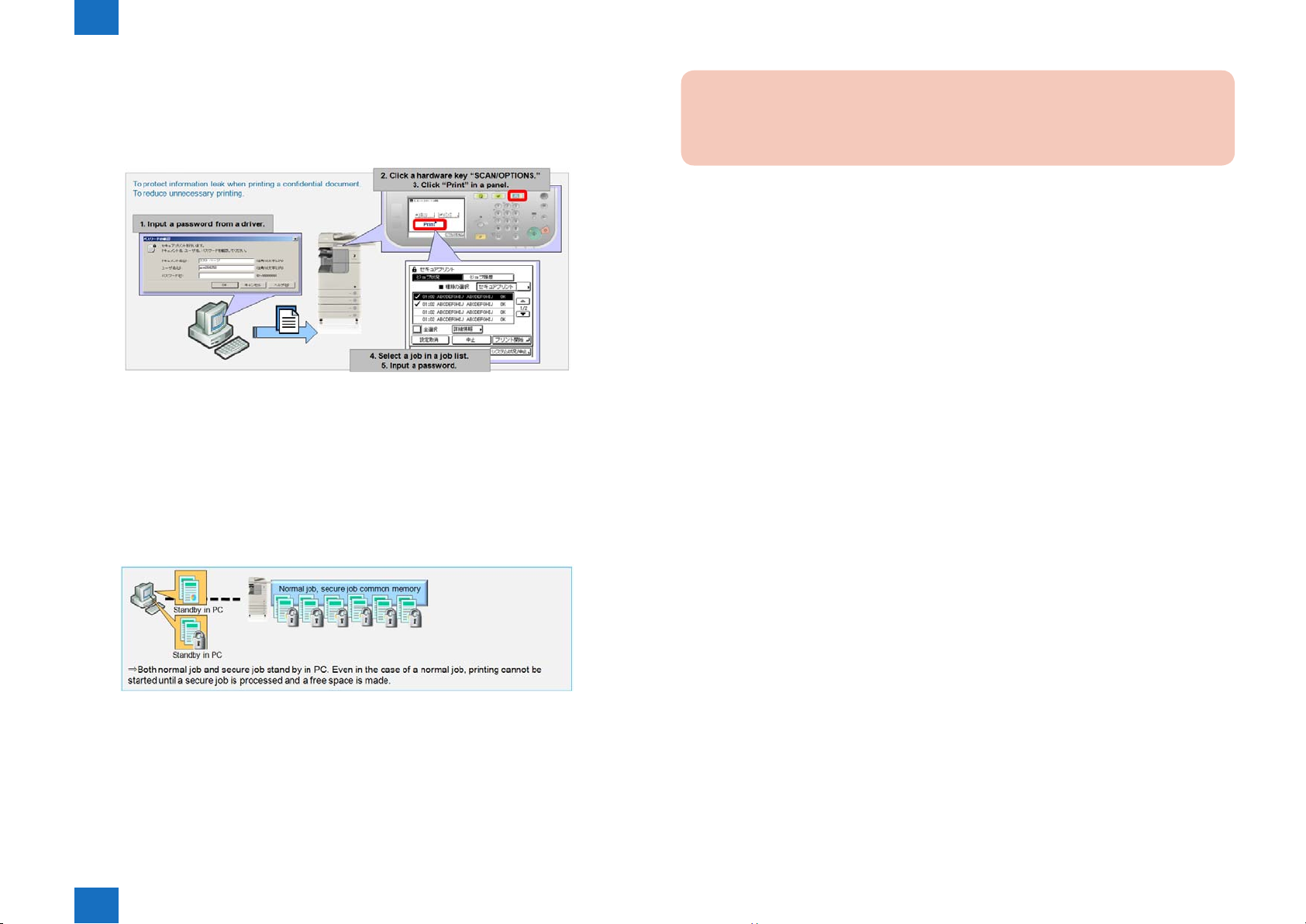
■Secured Print Jobs
Secured Print is the function that a password is provided to the PDL(UFR II and PCL, PS)
print job and it is sent to the device. Then, it is rasterized on the device side, saved in the
image server and output by entering the password from the device's panel.
F-1-6
●Process at full-memory
• Even in the case of a normal job, print cannot be started until a secure job is processed
and a free space is created. A print job can be submitted in both normal/ secure jobs. But, a
job enters a stand-by status in the PC’s Windows spool area. Then, after a memory area is
ensured on a main body side, the job is held in the main body.
• Print, copy and fax use a same memory area. So until the memory area has a free space,
only a copy function of; 1 to N, N to 1, 1-sided/1-sided is available and only a FAX send/
reception function of Direct send is available.
Caution:
• Job is erased by power OFF/ON.
• A secure print job can be submitted to a device up to 100 jobs.
■Service Mode Disable of USB memory function
Invalidating a USB memory function (Print From USB Memory & Scan To USB Memory) is
possible in Service Mode.
The details refer to "Details of Service Mode".
■Setting “Auto-clear Time” to “short”
Default: 2min. Selectable in 0 (not clearing automatically), 10sec, 20sec, 30sec, 40sec,
50sec, 1min., 2min., 3min. …9min.
Less than 1 minute settings are the new function.
The details refer to User Guide.
■Arabic support (In Europe only)
Arabic display support in Local UI message (Copy, FAX, Printer, system status, status, user
mode)
*Remote UI, report print and FEP/character input are not supported.
■Communication test function of E-RDS
F-1-7
●Restrictions
• Encryption secure pint is not supported.
• A device doesn’t enter Sleep when a secure print job is submitted.
• Not collaborated with device authentication. Job selection and password input are
necessary even after device authentication.
Product Overview > Features > Product Features > Communication test function of E-RDS
1
Communication test function of E-RDS is implemented to a counter screen.
The details refer to the chapter of E-RDS.
1-5
1
Product Overview > Specications > Specications
1-6
Specications
Specications
Item Specications
Copyboard
Machine installation method
Light source
Photosensitive medium
Image reading system
Copying method
Exposure method
Charging method
Developing method
Transfer method
Separation method
Pickup method
Fixing method
Delivery method
Magnication ratio
Drum cleaning method
Toner type
Toner supplying method
Toner level detection function
Leading edge image margin
Left edge image margin
Leading edge non-image width
Left edge non-image width
non-image width
Warm-up time
Image gradations
Resolution at reading
Resolution at writing
First print time
Paper type (Cassette)
Paper type (Multi-purpose Tray)
Original stream reading, original xed reading
Desktop
LED (RGB)
OPC
CIS
Indirect electrostatic method
Laser exposure
Roller charging
Dry, 1-component toner projection development
Roller transfer
Curvature separation
Cassette: Retard separation
Multi-purpose Tray: Pad separation
On-demand xing
Face-down (inner delivery)
25 to 400%
Cleaning Blade
Magnetic negative toner
Toner Container method
Yes
2.5 +/- 1.5mm
2.5 +/- 1.5mm
2.5 +/- 1.5mm
2.5 +/- 1.5mm
When the Feeder is used: 2.5 +/- 2.0mm
30 sec or less when the power is turned ON
256 gradations
600 x 600dpi
1200 x 1200dpi
5.0 sec or less
Plain paper (64 to 90g/m2), Recycled paper (64 to 90g/m2),
Heavy paper (91 to 105g/m2), 3-hole paper, 4-hole paper,
*Envelope (No. 10 (COM10), ISO-B5, Monarch, ISO-C5, DL)
*Only when the option Cassette Unit-Y1 is installed and the
option Envelope Cassette-D1 is installed in the 2nd cassette.
Plain paper (64 to 90g/m2), Recycled paper (64 to 90g/m2),
Heavy paper (91 to 128g/m2), 3-hole paper, 4-hole paper, Bond
paper (90g/m2), Transparency, Label paper, Envelope (No. 10
(COM10), ISO-B5, Monarch, ISO-C5, DL)
Item Specications
Paper size (Cassette)
Paper size (Multi-purpose Tray)
Pickup capacity
Duplexing method
Operation noise
Ozone volume
Rated power supply
Maximum power
consumption
Dimensions (WxDxH)
Weight
A4R, A5R, B5R, LTR-R, LGL, EXEC-R, STMTR-R, 16K-R
A4R, A5R, B5R, LTR-R, LGL, EXEC-R, STMTR-R, 16K-R,
Custom size (99 x 140mm to 216 x 356mm), Envelope (No. 10
(COM10), ISO-B5, Monarch, ISO-C5, DL)
Cassette: 550 sheets (80g/m2)
Multi-purpose Tray: 100 sheets (80g/m2)
Through-pass duplex
imageRUNNER 1750/1750i/1750iF:
During copy: 75.0dB or smaller *1/During standby: 53.00dB or
smaller *2
imageRUNNER 1740/1740i/1740iF:
During copy: 73.0dB or smaller *1/During standby: 53.00dB or
smaller *2
imageRUNNER 1730/1730i/1730iF:
During copy: 69.50dB or smaller/During standby: 43.00dB or
smaller *2
*1 Excluding the Chinese models Chinese models: 71.00dB or
smaller (During copy)
*2 Excluding the Chinese models Chinese models: 45.00dB or
smaller (During standby)
1.5mg/h or smaller
120 - 127 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 10.0 A
220 - 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 5.0 A
120 to 127 V model approx. 1283.4 W
220 to 240 V model approx. 1234.0 W
560mm x 500mm x 633mm
560mm x 500mm x 983mm with the 3 cassette
Approx. 43.3kg
T-1-5
Product Overview > Specications > Specications
1
1-6
1
Product Overview > Specications > Paper type > Pickup
1-7
Weight and Size
Product name
imageRUNNER 1750/1750i/1740/1740i
/1730/1730i
imageRUNNER 1750iF/1740iF/1730iF
(with FAX)
Staple Finisher-H1
Cassette Module-Y1
Copy Card Reader-F1
Productivity (Print speed)
Paper
Size Mode
A4-R 1-sided
2-sided
LTR-R 1-sided
2-sided
A5-R /
STMT-R
1-sided
2-sided
Paper
type
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
Plain
paper
Heavy
paper
basis
weight
(g/m2)
91-105 45 40 40 40 30 30
106-128 - 21 - 21 - 21
91-105 44 39 39 39 29 29
106-128 - - - - - -
91-105 45 40 42 40 32 30
106-128 - 21 - 21 - 21
91-105 42 37 39 37 30 28
106-128 - - - - - -
91-105 25 25 25 25 25 25
106-128 - 17 - 17 - 17
91-105 22 22 22 22 22 22
106-128 - - - - - -
Cassette
64-90 50 40 40 40 30 30
64-90 49 39 39 39 29 29
64-90 52 40 42 40 32 30
64-90 48 37 39 37 30 28
64-90 25 25 25 25 25 25
64-90 22 22 22 22 22 22
Width
(mm)
560 500 633 44.3
560 500 633 45.1
798 395 263 10.5
540 500 158 7.7
1750 1740 1730
Depth
(mm)
96 88 40 0.2
Multi-
purpose
Tray
Height
(mm)
imageRUNNER
Multi-
Cassette
purpose
Tray
Weight
Approx. (kg)
Cassette
T-1-6
Multi-
purpose
Tray
T-1-7
Paper type
See the table below for custom paper size..
Type Feeding direction (mm) Width direction (mm)
Custom size 140 to 356 99 to 216
■Pickup
Available paper types
Paper type
(g/m2)
- Plain paper
(64 to 90)
- Color paper
(64 to 90)
- Recycled paper
(64 to 90)
- Heavy paper
(91 to 105)
- Heavy paper
(106 to 128)
- Bond paper
(75 to 90)
- Label paper A4R, LTR-R
- Transparency A4R, LTR-R
- Envelope No.10 (COM10),
- Custom size
paper
Size
A4R, A5R,
B5R, LGL,
LTR-R, STMTR,
EXEC-R, 16K-R
A4R, A5R,
B5R, LGL,
LTR-R, STMTR,
EXEC-R, 16K-R
ISO-B5,
Monarch,
ISO-C5, DL
99 mm x 140
mm to 216 mm
x 356 mm
Multi-
purpose
Tray
Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes
Yes No No No No No
Yes No No No No No
Yes No No No No No
Yes No Yes No No No
Yes No No No No No
Cassette
1
Cassette 2
With
Envelope
Feeder
Without
Envelope
Feeder
T-1-8
Cassette 3Cassette
4
T-1-9
Product Overview > Specications > Paper type > Pickup
1
1-7

1
[5]
Product Overview > Parts Name > External View
Parts Name
External View
Front view, Left side
[2]
[3]
1-8
[4]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[1]
[14]
[13]
[1] ADF Left Cover [8] ADF Front Lower Cover
[2] ADF Rear Cover [9] Reader Front Cover
[3] ADF Upper Cover [10] Control Panel Unit
[4] Side Guides [11] Front Cover
[5] Original Feed Tray [12] Cassette
[6] ADF Front Upper Cover [13] Left Cover
[7] Original Delivery Tray [14] Reader Left Cover
[10]
[11]
[12]
F-1-8
Product Overview > Parts Name > External View
1
1-8

1
Product Overview > Parts Name > External View
1-9
Rear view, Right side
[10]
[9]
[8]
[7]
[6]
[1] Reader Rear Cover [7] Right Door Unit
[2] Reader Controller Cover [8] Right Rear Fan Cover
[3] Rear Cover [9] Right Front Fan Cover
[4] Right Rear Cover [10] Support Column Cover
[5] Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Unit [11] Reader Right Front Cover
[6] Right Front Cover [12] Reader Right Rear Cover
[11]
[5]
[12]
[4]
[3]
[1]
[2]
F-1-9
Delivery Assembly
[5]
[4]
[3]
[6]
[1] Reader Bottom Cover
[2] Delivery Inner Cover
[3] Delivery Outer Cover
[4] Delivery Stopper
[5] Inner Rear Cover
[6] Reverse Tray
[1]
[2]
F-1-10
Product Overview > Parts Name > External View
1
1-9

1
[10]
[1]
[2]
[3] [4]
[5]
[6] [7] [8]
[9]
Product Overview > Parts Name > Cross Sectional View
1-10
Cross Sectional View
[36]
[35]
[34]
[33]
[32]
[31]
[11]
[12]
[13]
[14]
[15]
[16]
[17]
[18]
[19]
[20]
[1] Lead Roller 1 [19] Transfer Roller
[2] Registration Roller [20] Duplex Feed Roller 2
[3] Lead Roller 2 [21] Registration Roller
[4] ADF Feed Roller [22] Multi-purpose Tray Pullout Roller
[5] ADF Delivery Reverse Roller [23] Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller
[6] ADF Pickup Roller [24] Multi-purpose Tray Separation Pad
[7] ADF Separation Pad [25] Vertical Path Roller
[8] ADF Delivery Roller [26] Separation Roller (Cassette)
[9] ADF Reverse Roller [27] Feed Roller (Cassette)
[10] Drum Unit [28] Pickup Roller (Cassette)
[11] Reverse Roller [29] Primary Charging Roller
[12] Expansion Delivery Kit [30] Developing Assembly
[13] Delivery Roller [31] Laser Scanner Unit
[14] Fixing Outlet Roller [32] Toner Container
[15] Duplex Feed Roller 1 [33] Hopper
[16] Pressure Roller [34] Copyboard Glass
[17] Fixing Film Unit [35] CIS Unit
[18] Photosensitive Drum [36] ADF Reading Glass
[30]
Product Overview > Parts Name > Cross Sectional View
1
[29]
[28]
[27]
[26]
[21]
[22]
[23]
[24]
[25]
F-1-11
1-10
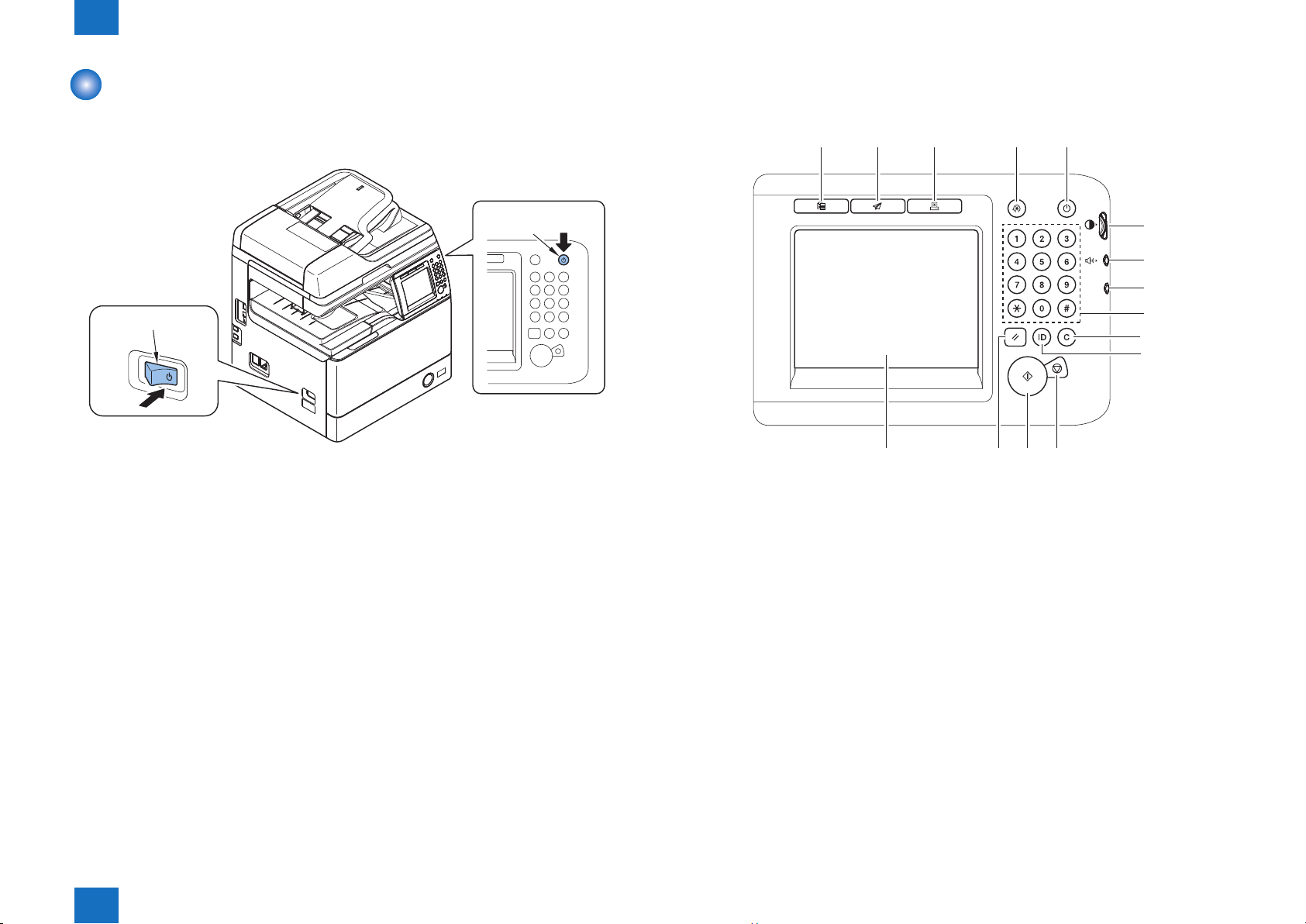
1
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5]
Product Overview > Parts Name > Operation > Description of Control Panel
1-11
Operation
■Power Switch
●Types of Power Switches
Control Panel
Power Switch
Main Power Switch
This machine has the Main Power Switch and the Control Panel Power Switch.
[1] Main Power Switch
This switch is used to turn OFF / ON the power of host machine.
[2] Control Panel Power Switch
This switch is used to enter the energy saver mode or recover to the normal mode.
●Points to Note on Turning ON/OFF the Power Switch
- Be sure to turn OFF the main power switch when turning OFF the power. (The
conventional shut-down sequence process is not needed.)
- After turning OFF the power (after turning OFF the Main Power Switch), do not turn ON
the main power switch again unless the screen disappears.
- Do not turn OFF the power during downloading
F-1-12
■Description of Control Panel
●Control Panel
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12][13][14][15]
F-1-13
[1] Copy Key [9] Numeric Key
[2] Send Key [10] Clear Key
[3] Remote Scanner/Expansion Key [11] ID (Authentication) Key
[4] Initial Settings/Registration Key [12] Stop Key
[5] Control Panel Power Switch [13] Start Key
[6] Screen Contrast Dial [14] Reset Key
[7] Volume Adjustment Key [15] Touch Panel Display
[8] Counter Check Key
Product Overview > Parts Name > Operation > Description of Control Panel
1
1-11
1
Product Overview > Parts Name > Operation > Description of Control Panel
●Main Menu
Functions Key Location
Copy Copy Key
Control PanelSend*1 or FAX*2 Send Key
Scan or Direct Print Scan/Option Key
System Monitor [System Monitor] Touch Panel Display
*1 To enable SEND function, Simple Send Expansion Kit-Y1 is required .
*2 To enable FAX function, Super G3 Fax Board-AG1 is required..
●Settings/Registration Menu
[1] Common Settings [6] Copy Settings
[2] Timer Settings [7] Communications Settings
[3] Adjustment/Cleaning [8] Printer Settings
[4] Report output [9] Address Book Settings
[5] System Manager Settings
1-12
T-1-10
Product Overview > Parts Name > Operation > Description of Control Panel
1
1-12

Technical Explanation
2
Basic Conguration
■
Original Exposure and Feed System
■
Main Controller
■
Laser Exposure System
■
Image Formation System
■
Fixing System
■
Pickup Feed System
■
External Auxiliary System
■
Embedded RDS
■
Technical Explanation
2
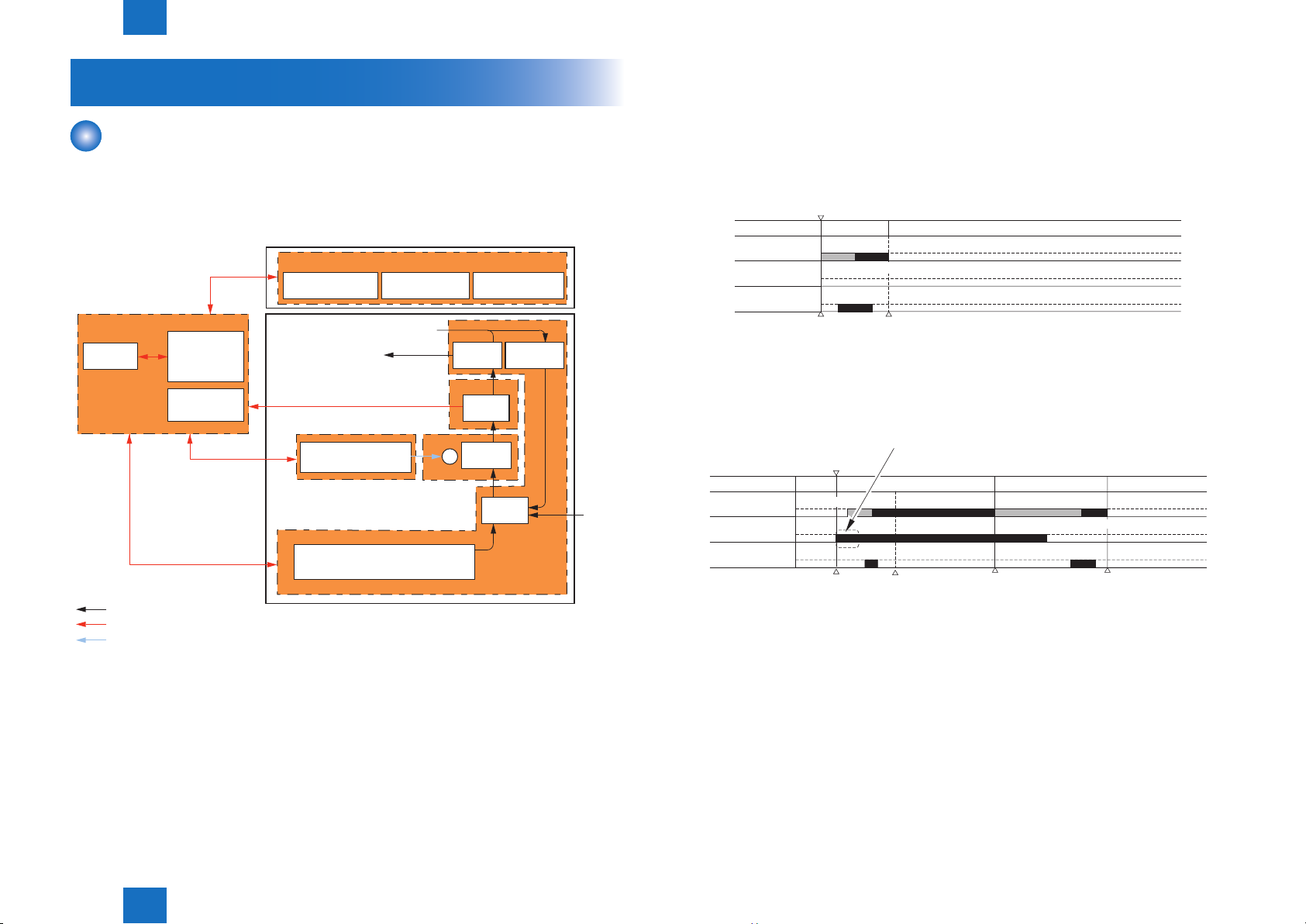
2
Technical Explanation > Basic Conguration > Functional Conguration > Basic sequence
Basic Conguration
2-2
■Basic sequence
Functional Conguration
This machine consists of 6 major blocks: Original Exposure System, Controller System,
Laser Exposure System, Image Formation System, Fixing System, and Pickup/Delivery
System.
Document Exposure System
Controller System
Option
Board
Flow of Paper
Flow of Signal
Laser beam
Main
Controller
DC
Controller
Reader
Controller PCB
Laser Exposure System
Laser Scanner Unit
Cassette
CIS
Delivery
Fixing
System
Image
Formation
System
LED
Duplexing
Feed
Fixing
Transfer
Pickup
Pickup/Feed
System
●Sequence at Power-On
• Reader
Main power switch
ON
Shading
position
STBY
Scanner motor
LED
CIS HP sensor
Backwarding
Shading
position
SREADY
Forwarding
●Print sequence
• Reader (in book mode, 1-sheet original)
Black shading/White shading
ForwardingBackwarding
Light-ON
ON ON
Leading edge
of original
Scanner motor
LED
CIS HP sensor
Start key
ON
Shading
position
Trailing edge
of original
SCRWSCFWSTBY STBY
Backwarding
Forwarding
Shading
position
F-2-2
F-2-3
Technical Explanation > Basic Conguration > Functional Conguration > Basic sequence
2
F-2-1
2-2

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Specications/controls/functions
2-3
Original Exposure and Feed System
Construction
■Specications/controls/functions
The major specications, controls and functions of the original exposure and feed system are
described below.
Item Specication/function
Original exposure LED
Original scan In book mode Original scan is performed by moving the contact image sensor
(CIS).
In ADF mode Original stream reading is performed with the contact image
sensor (CIS) xed.
Read resolution B/W: 600 dpi (main scanning) x 600 dpi (sub scanning)
(Color SEND: 300 dpi (main scanning) x 600 dpi (sub scanning))
Gradation 256 gradation
Carriage position detection CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Magnication 25% to 400%
Main scanning
direction
Sub scanning
direction
Lens Rod lens array
Original reading sensor Number of lens: 1
CIS drive control Drive control by Reader motor (M10)
Original size
detection
ADF original pickup method Auto pickup/delivery method
ADF setting direction of original Original tray pickup: face-up stacking
ADF setting position of original Original tray pickup: center reference
ADF separation method of original Upper separation by separation pad
ADF scanning method of original Stream reading
ADF weight of
original
In book mode Main scanning direction: by reection sensor (AB/Inch)
In ADF mode Main scanning direction: by photo interrupter on ADF
1-sided AB: 42 to 128 g/m2
2-sided 50 to 128 g/m2
Color original 64 to 128 g/m2
B/W or Color
mixed original
Original longer
than 432mm
Image is processed on main controller PCB.
Image is processed on main controller PCB.
Number of pixels: Total 5148 (incl. 5104 effective pixels)
Maximum original scan width: 216mm
Sub scanning direction: by reection sensor (AB/Inch)
Sub scanning direction: by photo interrupter on ADF
Inch: 50 to 128 g/m2
50 to 128 g/m2 (Color: 64 to 128 g/m2)
60 to 90 g/m2 (1-sided, 1-sheet feeding)
Item Specication/function
ADF original size A4R, B5R, A5, A5R, LGL, LTRR, STMTR, STMT, 16K-R (For
STMT, horizontal scanning only)
Original width direction: 139.7 to 219 mm
Original feed direction: 128 to 356 mm (In banner paper printing
mode: maximum 630 mm)
ADF original tray capacity 100 sheets (80 g/m2 paper, original height: 10mm or less)
ADF original processing mode 1-sided original processing
2-sided original processing
ADF original size detection
function
ADF mixed
original mode
function
Book original Yes (The thickness of the book original must not exceed 30
ADF done stamp function No
Mix of same
conguration
mode
Mix of different
conguration
mode
Yes (standard size)
Yes (weight of original same as continuous feed mode)
Assured combination for mix with same conguration
A5/A4R, STMT/LTRR/LGL
No
mm.)
T-2-1
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Specications/controls/functions
2
2-3

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Major Components
2-4
■Major Components
●Reader Unit
Following shows major components of reader unit.
Reader motor (M10)
Reader controller PCB (PCB3)
ADF open/closed
detection sensor (PS23)
CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Contact image sensor (CIS)
Item Notation Specication/function
Reader motor M10 Stepping motor: controls the carriage drive.
CIS HP sensor PS24 Photo interrupter: detects the home position of CIS
unit.
ADF open/closed detection
sensor
Original size detection sensor 1 PS22 Detects the original size. (AB/Inch)
Original size detection sensor 2 PS21 Detects the original size. (AB/Inch)
Contact image sensor - Reads the original. (LED + Light guide + CIS unit)
Reader controller PCB PCB3 Controls the reader unit and ADF unit.
PS23 Photo interrupter: detects the opening or closing of
ADF. (detects the opening or closing of the ADF at
approximate 18 degrees.)
Original size detection
sensor 1 (PS22)
Original size detection
sensor 2 (PS21)
F-2-4
T-2-2
●ADF unit
Following shows major components of ADF unit.
1) Cross Section
Delivery reversal roller (upper)
Delivery reversal flapper 2
Delivery roller
Reversal roller
Original pickup tray
Original delivery tray
Lead roller 2
Registration roller
Lead roller 1
Platen guide
Feed roller
Separation pad
Delivery reversal flapper 1
Pickup roller
Delivery reversal roller
Item Specication/function
Pickup roller Picks up the original.
Feed roller Separates and feeds the original.
Separation pad Separates the original.
Registration roller Feeds the original and forms a skew feed correction loop.
Lead roller 1 Feeds the original before reading.
Lead roller 2 Feeds the original after reading.
Delivery reversal roller Delivers the original and performs upstream reversal feed of
the original.
Delivery reversal roller (upper) Separated from the mating delivery reversal roller by the roller
release solenoid during reverse feed of the original.
Delivery roller Delivers the original.
Reversal roller Performs downstream reversal feed of the original.
Platen guide Original read section.
Delivery reversal apper 1 Switches between the upstream reversal path and the
downstream reversal path.
Delivery reversal apper 2 Switches between the upstream reversal path and the delivery
path.
Original pickup tray Allows you to load an original.
Original delivery tray Stacks the delivered originals.
F-2-5
T-2-3
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Major Components
2
2-4

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Major Components
2) Sensor Layout
PS26
PS25
PS29
PS27
3) Drive Conguration
M11
SL4
M12
PS30
SL5
PS28
SL8
PS31
PS32
F-2-6
Item Notation Specication/function
Feed motor M11 Stepping motor: Feeds the original.
Delivery reversal motor M12 Stepping motor: Feeds, reverses, and delivers the
original.
Registration solenoid SL4 Transmits the driving force of the feed motor to the
registration roller.
Pickup solenoid SL5 Transmits the driving force of the delivery reversal
motor to the pickup roller and feed roller.
Flapper solenoid 2 SL6 Drives the delivery reversal apper 2.
Flapper solenoid 1 SL7 Drives the delivery reversal apper 1.
Roller release solenoid SL8 Separates the delivery reversal roller from the mating
delivery reversal roller during upstream reversal feed
of the original.
Lead sensor PS25 Photo interrupter: Detects the original read timing.
Registration sensor PS26 Photo interrupter: Detects the original leading edge
looping timing.
Stay sensor PS27 Photo interrupter: Detects the original reversal timing
during downstream reversal feed.
Reversal sensor PS28 Photo interrupter: Detects the original feed during
downstream reversal feed.
Timing sensor PS29 Photo interrupter: Detects feed of the original.
Original set sensor PS30 Photo interrupter: Detects presence/absence of the
original on the original pickup tray.
Original width detection
sensor
Original length detection
sensor
PS31 Photo interrupter: Detects the width of the original on
the original pickup tray.
PS32 Photo interrupter: Detects the length of the original on
the original pickup tray.
T-2-4
2-5
SL7
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Major Components
SL6
F-2-7
2
2-5

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Reader Controller PCB
■Reader Controller PCB
The function conguration of reader controller PCB is described below.
2-6
J907
J911
Notation Description
IC1 Image processing, control of contact image sensor, control of motors and
solenoids drive, control of sensors detection
J902 Connector for contact image sensor
J903 Connector for power supply from host machine (power supply unit)
J904 Connector for original size detection sensor 1 and 2
J905 Connector for reader motor
J906 Connector for feed motor and delivery reversal motor of ADF
J907 Connector for communication with main controller PCB of host machine
J908 Connector for registration solenoid and pickup solenoid and apper
solenoid 1 and 2
J909 Connector for timing sensor and original set sensor and original width
detection sensor and original length detection sensor
J910 Connector for lead sensor and registration sensor and stay sensor and
reversal sensor
J911 Connector for CIS HP sensor and ADF open/closed detection sensor
J912 Connector for roller release solenoid
J909
J910 J903 J908 J912
IC1
J906
J905
J904J902
F-2-8
T-2-5
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Construction > Reader Controller PCB
2
2-6

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > Basic Sequence
2-7
Basic Operation
■Basic Sequence
●Basic Sequence at Power-On
Main power switch
ON
Reader motor (M10)
LED
CIS HP sensor (PS24)
1. CIS position check
SREADY STBY
Shading
position
CIS HP sensor
Shading
position
HP
Shading
position
Leading edge
of original
:Forward
:Reverse
F-2-9
●Basic Sequence at Start Key ON (Book mode/1 original)
Start key
ON
Reader motor (M10)
LED
CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Shading
position
Copyboard glass reading
start position
1. Moves to the start position
after black shading and
white shading
2. Original scan
3. Moves to the standby
position
Black shading and White shading
Leading edge
of original
CIS HP sensor
HP
Trailing edge
Shading
position
SCRWSCFWSTBY STBY
of original
Leading edge
of original
Shading
position
:Forward
:Reverse
F-2-11
Trailing edge
of original
F-2-10
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > Basic Sequence
2
F-2-12
2-7

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2-8
●Basic Sequence at Start Key ON (ADF mode/1 original)
Start key
ON
Reader motor (M10)
LED
CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Shading
position
Stream reading
start position
1. Black shading and
White shading and
Original scan
Black shading and White shading
Stream reading
position
Copyboard glass
reading start
position
Trailing edge
of original
CIS HP sensor
HP
SCFWSCRWSTBY STBY
Shading
position
Shading
position
:Forward
:Reverse
F-2-13
■ADF Operation Mode
ADF has four operation modes.
Operation mode names and outline of operations and associated print modes are given in the
following table:
Operation mode name Outline of operation Associated print mode
Forward pickup/delivery Picks up, reads, and then delivers
an original.
Forward pickup/reversal
delivery
Picks up, reads, and then reverses
and delivers an original
Single-sided original → Singlesided print
Single-sided original → Doublesided print
Double-sided original →
Double-sided print
Double-sided original → Singlesided print
T-2-6
F-2-14
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2
2-8

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2-9
●Forward Pickup/Delivery (Single-sided original → Single-sided print)
Operation
The original ows as shown below.
Note:
This operation is performed for all single-sided originals irrespective of whether original
width are the same or different.
• Operation of single-sided original reading (2 originals)
- 1st original: Pickup
- 1st original: Delivery
- 2nd original: Reading
●Forward Pickup/Reversal Delivery (Double-sided original → Doublesided print) Operation
The original ows as shown below.
Note:
This operation is performed for all single-sided originals irrespective of whether original
width are the same or different.
• Operation of double-sided original reading (2 originals)
- 1st original: Pickup
- 1st original: Reversal and
Formation of loop
- 1st original: Formation of loop
- 1st original: Formation of loop
- 1st original: Reading
- 2nd original: Pickup and
Formation of loop
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2
- 2nd original: Delivery
- End of job
F-2-15
- 1st original: Reading of
reverse side
- 2nd original: Pickup
- 1st original: Reading
- 1st original: Feeding to
downstream reversal path
- 2nd original: Formation of loop
Next
- 1st original: Feeding to
upstream reversal path
F-2-16
2-9

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2-10
- 1st original: Reversal
- 2nd original: Reading
- 1st original: Delivery
- 2nd original: Feeding to
upstream reversal path
- 2nd original: Reversal and
Formation of loop
- 2nd original: Reading of
reverse side
- 2nd original: Feeding to
downstream reversal path
- 2nd original: Delivery
- End of job
F-2-17
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Basic Operation > ADF Operation Mode
2
2-10

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Controlling the Scanner Drive System
2-11
Controls
■Controlling the Scanner Drive System
●Overview
Parts conguration of scanner drive is described below.
Reader motor (M10)
Reader controller PCB (PCB3)
ADF open/closed
detection sensor (PS23)
Sensor light-blocking plate
Reverse
Carriage drive belt
Forward
●Reader Motor Control
Reader motor driver (IC15) turns on/off the reader motor (M10) and controls its direction and
speed of rotation according to the signals from ASIC (IC1).
Reader controller PCB
3.3V +24V
1.8V
OM_RTPA
OM_RTPAN
IC1
ASIC
Note:
The scan speed is 160 mm/sec.
OM_RTPB
OM_RTPBN
OM_PS
OM_CURRENT
+5V
IC15
Motor
driver
J905
1
2
3
4
B*
B
A
A*
M10
F-2-19
CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Contact image sensor (CIS)
Carriage rail
• Reader motor (M10) drive signal
Controls the rotation and its direction and speed of motor.
• CIS HP sensor (PS24)
Detects that the contact image sensor (CIS) is at the home position.
• ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23)
Detects the open or close status of the ADF.
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Controlling the Scanner Drive System
2
Carriage
F-2-18
2-11

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Contact Image Sensor (CIS)
2-12
1) Forward Movement during Image Scan
During image scanning, the reader controller PCB controls the reader motor (M10) to
control the contact image sensor (CIS) operation.
Start
position
Acceleration
Movement
speed
[1] Acceleration area: The motor accelerates to the speed specified
for each mode.
[2] Runup area: A margin to stabilize the speed.
[3] Image read area: The image is read at a constant speed.
[4] Deceleration area: Upon detection of the trailing edge,
the motor decelerates rapidly and stops.
2) Backward Movement after Image Scan
After image scan, the carriage moves back to the contact image sensor (CIS) shading
position at the constant speed (160 mm/sec).
Leading edge
of original
Constant speed
[1] [2] [3] [4]
Movement distance
Trailing edge
of original
Deceleration
Stop
F-2-20
■Contact Image Sensor (CIS)
●Outline
The original is exposed to light and read using the contact image sensor (CIS) to read the
image on a line-by-line basis.
Image reading line
Copyboard glass
Rod lens array
LED (R/G/B)
Original reading
sensor array
Light guide
Light guide
Scan direction
Rod lens array
Light guide
LED (R/G/B)
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Contact Image Sensor (CIS)
2
LED
CCD
F-2-21
Component Function
LED Illuminates the original.
Light guide Illuminates the entire image line with the LED light.
Rod lens array Collects the light reected by the original.
Original reading sensor array Receives the light that passed through the rod lens array.
T-2-7
2-12

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Enlargement / Reduction
2-13
●Analog Control Performed by the CIS
The ow of analog image processing performed by the contact image sensor (CIS) is as
follows:
a. The light reected by the original is collected by the rod lens array.
b. The light is received by the original scan sensor array.
c. The original scan sensor array converts the received light to an electric signal and outputs
it.
The original scan sensor array consists of eleven channels (units).
Each channel is provided with an output correction table to output an image signal after
performing gain correction for the input brightness signal.
5148 pixels
Original scan sensor
channel x11
468 pixels
Driver circuit
3 2 1
■Enlargement / Reduction
●Magnication Change in Main Scanning Direction
In book mode or ADF mode
In the main scanning direction, image is read at 100%; thereafter, the data is subjected to
processing by the main controller PCB to suit the selected reproduction ratio.
●Magnication Change in Sub Scanning Direction
The magnication in sub scanning direction is changed as follows:
1) In book mode
Image is read at original scan speed kept at 160 mm/sec; thereafter, the data is subjected
to processing by the main controller PCB to suit the selected reproduction ratio.
2) In ADF mode
Image is read at original scan feeding speed kept at 320 mm/sec; thereafter, the data is
subjected to processing by the main controller PCB to suit the selected reproduction ratio.
11
F-2-22
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Enlargement / Reduction
2
2-13

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors
2-14
■Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors
●Overview
Presence or absence of an original on the copyboard glass is detected as follows according
to the combination of the output levels of reective photo sensors:
• Absence of original: The level of the reected light from the reective photo sensor, which
is detected when the ADF is open, changes when the ADF is closed.
• Presence of original: The level of the reected light from the reective photo sensor, which
is detected when the ADF is open, does not change when the ADF is closed.
Sensor mounting locations are shown below.
• Main and sub scanning direction: Reective photo sensor (2 locations)
Sub scanning direction
Upper left corner
of original
Main scanning
direction
STMTR
A5R
Size plate
A4R
LTRR/LGL
Size plate
●Outline of Original Size Detection
When the ADF is closed at 18 degrees, the ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23) turns
on. The output levels of the original size detection sensor 1 (PS22) and original size detection
sensor 2 (PS21) are read for 2 seconds after the ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23)
turns on or until the Start key is pressed. If the output levels change, the machine judges that
no original is present. If they do not change, the machine judges that an original is present.
1) ADF opens (ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23): OFF)
Original size detection sensor 1 (PS22)/Original size detection sensor 2 (PS21): OFF
ADF
PS23: OFF
2) ADF is closed to an angle of approximate 18 degrees. (ADF open/closed detection
sensor (PS23): ON)
Original size detection sensor 1 (PS22)/Original size detection sensor 2 (PS21): ON or
OFF
ADF
Original
F-2-24
Original size detection sensor 1
(PS22)
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors
Original size detection sensor 2
(PS21)
F-2-23
PS23: ON
Original size detection sensor 1
(PS22)
2
Approx. 18°
Original
Original size detection sensor 2
(PS21)
F-2-25
2-14

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors
2-15
3) ADF is closed. (ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23): ON)
Original size detection sensor 1 (PS22)/Original size detection sensor 2 (PS21): ON
ADF
PS23: ON
Original size detection sensor 1
(PS22): No change in level
• Note that a wrong original size may be identied because the sensor output level does not
change in the following cases:
• When the black original
• When the original is a book (its thickness does not allow the ADF to close fully, making it
difcult to detect the sensor level change.)
• When the ADF is not closed fully (the sensor level change is not detected after lapse of the
above time-out time (2 seconds).)
Original
Original size detection sensor 2
(PS21): Change in level
F-2-26
Original sizes are detected as follows according to the combination of sensor output levels:
●AB size
Original
size
A5R or
undefined size
A4R
●Inch size
Original
size
STMTR or
undefined size
LTRR
LGL
Original size
detection sensor 1
(PS22)
Original size
detection sensor 1
(PS22)
Original size
detection sensor 2
(PS21)
Original size
detection sensor 2
(PS21)
:No changed
:Changed
F-2-27
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Original Size Detection by Original Size Detection Sensors
2
2-15

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Dust Detection Control
2-16
Related Service Mode:
• Select the following service mode to determine whether to detect the original size:
SCAN > READER > OPTION > USER > SIZE-DET
<Setting value>
0: The original size is not detected.
1: The original size is detected.
• Select the following service mode to switch between AB and inch sizes:
SCAN > READER > OPTION > BODY > SENS-CNF
<Setting value>
0: AB size
1: Inch size
• When both the original size detection sensor 1 (PS22) and the original size detection
sensor 2 (PS21) detect no original (sensor output levels do not change), select the
following service mode to change the original size to be detected:
SCAN > READER > OPTION > BODY > UNK-A5R
<Setting value>
0: Undened size
1: A5R or STMTR
■Dust Detection Control
●Overview
In ADF mode, the machine changes the original read position or corrects the read image
depending on the presence/absence of dust on the ADF reading glass or platen guide, thus
preventing dust from showing up in the image.
The control of dust detection is as follows:
1) Dust detection preventive process
2) Dust detection correction control
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Dust Detection Control
2
2-16

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Dust Detection Preventive Process
■Dust Detection Preventive Process
The contact image sensor (CIS) detects the reected light from the ADF reading glass and
platen guide surface (at the read position) to judge presence or absence of dust.
This process is performed when the power is turned on or each time a job is completed.
The dust detection process is performed at three positions (A, B, and C) as follows regardless
of whether there is dust:
1) The dust detection process is performed at position A.
2) The dust detection position moves to position B to perform the dust detection process
there.
3) The dust detection position moves to position C to perform the dust detection process
there.
4-a) The dust-free position is determined as the original read position in the order of priority (A
> B > C).
4-b) If dust is detected at all of positions A, B, and C, position A is determined as the original
read position.
ADF reading glass
A B C
Lens
2-17
0.5mm0.5mm
Platen guide
Contact image sensor unit
F-2-28
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Dust Detection Preventive Process
2
Position Description
A Reference position for read
B About 0.5 mm to the right of the reference position A
C About 1.0 mm to the right of the reference position A
T-2-8
Note:
When dust has been detected at all of positions A, B, and C, setting an original on the
ADF will show a message that prompts the user to clean the glass surface.
2-17

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Image Processing
2-18
■Dust Detection Correction Control
Whenever the original from the ADF is read, presence or absence of duct is detected at the
original read position determined in the dust detection preventive process. If presence of dust
is detected, the image correction process is performed to prevent dust from appearing in the
output image.
Main power
switch ON
Start key ON
STBYWMUPR
Dust detection correction control
1st
SCAN
Dust detection
correction control
2nd
SCAN
Dust detection
correction control
F-2-29
■Image Processing
●Overview
Major specications and functions of the image processing system are as follows:
• Original reading sensor array Number of lines: 1
Number of pixels: Total 5148 (incl. 5104 effective pixels)
• Shading correction Shading correction: Performed for each job.
Shading adjustment: Performed in the Service mode.
Contact image
sensor (CIS)
Original reading
sensor
About image processing, the function of the reader controller PCB is as follows:
• Original reading sensor drive
• Original reading sensor output gain correction and offset correction
• Original reading sensor output A/D conversion
• Shading correction
• LED intensity adjustment
Analog image processor Digital image processor
Analog
image
processing
Reader controller PCB
A/D
conversion
Shading
processing
controller
Main
PCB
F-2-30
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Image Processing
2
2-18

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Image Processing
2-19
●Original Reading Sensor Drive
The original reading sensor is a 1-line linear image sensor consisting of 5147 photocells.
After completion of photoelectric conversion in the lightreceiving block, the signals are output
to the reader controller PCB in parallel for each channel (total eleven channels) of the original
reading sensor array.
Original reading
sensor 11
Light receiving block
Original reading
senor 10
HL L HH L HL H H L
Original reading
sensor 1
output
………
F-2-31
●Original Reading Sensor Output Gain Correction and Offset
Correction
The analog video signals output from the original reading sensor are corrected so that they
will have a specic gain level (gain correction), and the output voltages generated in the
absense of incident light are also corrected so that they will have a specic offset level (offset
correction).
●Outline of Shading Correction
The original reading sensor outputs are necessary even for the following reasons even when
the density of the original is uniform:
(1) Variation in sensitivity among original reading sensor pixels
(2) Variation in light intensity of rod lens array
The machine performs shading correction to even out the original reading sensor output.
There are two types of shading correction: shading adjustment performed in the service mode
and shading correction performed for each job.
●Shading Adjustment
The machine measures the density of the standard white plate, and stores the measured
density data. It then processes the stored data to use it as the target value for shading
correction.
●Shading Correction
The machine performs shading correction for each scan. It measures the density of the
standard white plate, and compares the measured value with the target value stored in the
shading correction circuit to use the difference between the two as the shading correction
value. The machine uses this shading correction value to correct the variation among the
original reading sensor pixels when scanning the originals, thus evening out the image
density level.
Original reading
sensor output
Target value
Characteristics after correction
Characteristics before correction
●Original Reading Sensor Output A/D Conversion
After completion of the gain correction and offset correction, the analog video signals are
converted to digital signals corresponding to individual pixel voltage levels by the A/D
converter.
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Controls > Image Processing
2
Measurement value
Standard
white plate
White
Original density
F-2-32
2-19

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Original Size Detection by ADF
2-20
●LED Intensity Adjustment
The machine adjusts the length of time during which the LED turns on for each scan so that
the image scan level of the original reading sensor will be specic level.
Related Service Mode:
• CIS gain and offset correction
SCAN > READER > FUNCTION > CCD > CCD-ADJ
• DF white level adjustment
SCAN > READER > FUNCTION > CCD > DF-WLVL1 (Original glass scan)
SCAN > READER > FUNCTION > CCD > DF-WLVL2 (Stream reading scan)
SCAN > READER > FUNCTION > CCD > DF-WLVL3 (Original glass scan)
SCAN > READER > FUNCTION > CCD > DF-WLVL4 (Stream reading scan)
Control of ADF
■Original Size Detection by ADF
The size of the original set on the ADF is detected by the following two methods:
1) Initial detection of document size
2) Final detection of document size
Original length detection sensor (PS32)
Original width detection sensor (PS31)
Feeding direction
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Original Size Detection by ADF
2
Lead sensor (PS25)
Original
F-2-33
2-20

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Original Size Detection by ADF
2-21
●Initial Detection of Original Size
The length (feed-directional size) of the original set in the original pickup tray is detected by
the original length detection sensor (PS32), and its width (cross-directional size) is detected
by the original width detection sensor (PS31).
The original size is judged as follows according to the combination of the states of these two
sensors:
• AB size
Original size
A4R ON OFF
A5R or undened size OFF OFF
• Inch size
Original size
LGL ON ON
LTRR ON OFF
STMTR or undened size OFF OFF
LGL OFF ON
When both the original width detection sensor (PS31) and the original length detection sensor
(PS32) detect no original, select the following service mode to change the original size to be
detected:
• SCAN > FEEDER > OPTION > UNK-A5R
<Setting value>
0: Undened size
1: A5R or STMTR
Original width detection sensor
(PS31)
Original width detection sensor
(PS31)
Original length detection sensor
(PS32)
T-2-9
Original length detection sensor
(PS32)
T-2-10
Related Service Mode:
• Select the following service mode to switch between AB and inch sizes of the original
fed by the ADF:
SCAN > SW > 005 > Bit 1 and Bit 2
<Setting value>
Size setting Bit 1 Bit 2
AB size
Inch size
1 0
0 1
T-2-11
●Final Detection of Original Size
The original length is judged by the distance the original runs from the moment the lead
sensor (PS25) turns on (the leading edge of the original is detected) to the moment it turns off
(the trailing edge of the original is detected).
The original size is nally determined according to the width detected by the original width
detection sensor (PS31) and the length detected by the lead sensor (PS25).
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Original Size Detection by ADF
2
2-21

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Reversal Operation
2-22
■Pickup and Feed Operations
The pickup unit consists of two rollers, a pickup roller and a feed roller.
When the Start key is turned on (the original pickup signal is input), the delivery reversal
motor (M12) turns in the normal direction, the pickup solenoid (SL5) turns off to lower the
pickup unit, and then the pickup roller and feed roller turn to pick up and feed the original.
A shutter and a separation pad are provided to prevent double feed of originals during pickup
operation. The separation pad is used to separate the original.
When the original arriving at the registration roller loops, the pickup solenoid (SL5) turns on to
raise the pickup unit.
Then, the registration solenoid (SL4) turns on and the feed motor (M11) turns to rotate the
registration roller, feeding the original.
Pickup roller
Original
Shutter
■Reversal Operation
Reversal operation is performed in the duplex printing mode or various sized originals printing
mode.
There are two types of reversal operations: upstream reversal feed operation and
downstream reversal feed operation.
Either type of reversal feed operation is selected according to the following conditions:
1) Upstream reversal feed operation
• When the front side is read in the duplex printing mode
• When the front side is read in the various sized originals printing mode
2) Downstream reversal feed operation
• When the back side is read in the duplex printing mode
• When the back side is read in the various sized originals printing mode
Pickup solenoid (SL5)
Delivery reversal motor (M12)
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Reversal Operation
2
Feed roller
Separation pad
Shutter
F-2-34
2-22

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Reversal Operation
2-23
●Upstream Reversal Feed Operation
After the front of the original is read, the apper solenoid 1 (SL7) turns off and the apper
solenoid 2 (SL6) turns on to feed the original to the upstream reversal path with the delivery
reversal apper 1 and delivery reversal apper 2.
When the original is fed by the registration roller, the roller release solenoid (SL8) turns on
to raise the delivery reversal roller, thus preventing the delivery reversal roller from applying
pressure to the paper.
1) The apper solenoid 1 turns off and the apper solenoid 2 turns on to feed the original to
the upstream reversal path.
Delivery reversal flapper 2
Flapper solenoid 2: ON
SL6
SL7
Delivery reversal flapper 1
Flapper solenoid 1: OFF
F-2-35
3) The delivery reversal roller turns in the reverse direction to feed the original for back
side read. After the original arrives at the registration roller, the roller release solenoid
(SL8) turns on to raise the delivery reversal roller.
Delivery reversal roller (upper)
SL8
Roller release solenoid: ON
Registration roller
Delivery reversal flapper 2
Flapper solenoid 2: ON
SL6
F-2-37
2) After being fed by the specied distance in the upstream reversal path, the original
stops.
Delivery reversal roller
Delivery reversal flapper 2
Flapper solenoid 2: ON
SL6
F-2-36
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Reversal Operation
2
2-23

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Delivery Operation
2-24
●Downstream Reversal Feed Operation
After the back side of the original is read, the apper solenoid 1 (SL7) turns on to feed the
original to the downstream reversal path using the delivery reversal apper 1. Then, the
original is delivered with the reversal roller and delivery roller.
1) The apper solenoid 1 turns on to feed the original to the downstream reversal path.
Delivery reversal flapper 1
Flapper solenoid 1: ON
SL7
F-2-38
2) After being fed by the specied distance in the downstream reversal path, the original
stops.
Reversal roller
■Delivery Operation
After being read, the original is delivered to the original delivery tray using the delivery
reversal roller and delivery roller.
1) The apper solenoid 1 turns off and the apper solenoid 2 turns off to feed the original.
Delivery reversal flapper 2
Flapper solenoid 2: OFF
SL6
SL7
Delivery reversal flapper 1
Flapper solenoid 1: OFF
F-2-41
2) The original is delivered to the original delivery tray.
F-2-39
3) The reversal roller turns in the reverse direction to deliver the original.
Delivery roller
F-2-40
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Delivery Operation
2
Original delivery tray
F-2-42
2-24

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Jam Detection
2-25
■Jam Detection
Whether jam is occured or not, determined by whether there is paper or not in the sensor
area by the timing check that memorized in advance by the reader controller PCB.
When the reader controller PCB detected jam, it will stop feeding operation and display the
message in the operation panel about the jam occurrence.
As the machine stores the jam codes, it can be checked by outputting a jam error log report
in the service mode.
PS30
PS25
PS23
The jam is detected by the following sensors.
• ADF open/closed detection sensor (PS23)
• Lead sensor (PS25)
• Registration sensor (PS26)
• Stay sensor (PS27)
• Reversal sensor (PS28)
• Original set sensor (PS30)
PS27
PS28
PS26
F-2-43
Jam type Sensor Jam description
Registration sensor delay jam PS26 When the registration sensor cannot detect an
original within the specied time.
Registration sensor stationary
jam
Lead sensor delay jam PS25 When the lead sensor cannot detect the original
Lead sensor stationary jam PS25 When the trailing edge of the original cannot be
Stay sensor delay jam PS27 When the stay sensor cannot detect the original
Stay sensor stationary jam PS27 When the trailing edge of the original cannot be
Reversal sensor delay jam PS28 When the reversal sensor cannot detect the original
Reversal sensor stationary jam PS28 When the trailing edge of the original cannot be
ADF open jam PS23 When the ADF is opened during its operation.
Initial stationary jam PS25/
Pickup NG jam PS30 When original pickup operation starts with no original
Timing error jam - When the original feed sequence is not completed
PS26 When the trailing edge of the original cannot be
detected after lapse of the specied time after the
original was detected by the registration sensor.
within the specied time.
detected after lapse of the specied time after the
original was detected by the lead sensor.
within the specied time.
detected after lapse of the specied time after the
original was detected by the stay sensor.
within the specied time.
detected after lapse of the specied time after the
original was detected by the reversal sensor.
When an original is detected in the feed path during
PS26/
PS27/
PS28
pickup of the rst original.
set on the original pickup tray.
during the specied time.
T-2-12
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Control of ADF > Jam Detection
2
2-25

2
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Work of Service > When replacing the parts
Work of Service
■Periodically Replaced Parts
None
■Consumable Parts
No. Parts name Parts number Q'ty Estimated life
1 ADF Pickup Roller Unit FM4-7732 1 80,000 sheets
2 ADF Separation Pad FL3-5538 1 80,000 sheets
■Periodical Servicing
None
Perform as needed.
■When replacing the parts
Part name Operation Reference
Contact image sensor (CIS)
Copyboard glass
ADF reading glass
• CIS gain and offset correction
• DF white level adjustment
• Input the value of label on the copyboard
glass
• DF white level adjustment
• DF white level adjustment Refer to page 5-4
Refer to page 5-3
Refer to page 5-3
2-26
T-2-13
T-2-14
Technical Explanation > Original Exposure and Feed System > Work of Service > When replacing the parts
2
2-26

2
J8109
J8202 J8115
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Overview > Conguration/Function
2-27
Main Controller
Overview
■Conguration/Function
SO-DIMM
Main Controller PCB
Secondary Battery
Item Function
Main Controller PCB
Image memory (SO-DIMM)
Flash ROM
SRAM
USB port
Ethernet port
SD Card slot
Secondary Battery
F-2-44
System Control/Memory Control/Printer Output Image
Processing Control, Reader Image Input Processing, Card
Reader Connection I/F, Image Processing for FAX, USB
Expansion HUB Connection I/F
Temporarily saving image data
Capacity 256MB (Max. 512MB)
For FAX or SEND-equipped model; standard: 512MB
Storing System Software
Boot ROM: 16MB
Program ROM: 128MB
Keeping user data/service data information
USB2.0 Device I/F, USB2.0 Host I/F
Ethernet I/F
SD I/F
Models with FAX or SEND function only
Secondary Battery for image backup at power failure (to backup
for 1 hour by 2-hour charging)
T-2-15
●Main controller PCB
J8106
J8114
BAT1
J8102
J8124
J8134
J8142
SW3
J8143 J8112 J8125 J8116 J8119
J8200 J8201
J8117
Jack Function Jack Function
J8104 USB port J8134 Connector to connect to FAX
J8106 Slot to connect to SO-DIMM J8142 Connector to connect to Laser Scanner
J8109 For debug J8143 Connector to connect to Laser Scanner
J8111 Connector to connect to LAN J8150 USB port
Connector to connect to DC
J8112
Controller PCB
Connector to connect to Control
J8114
Panel
Connector to connect to Control
J8117
Card
Connector to connect to Card
J8119
Reader
Connector to connect to Control
J8124
Panel
Connector to connect to Control
J8125
Card
J8200 Connector to connect to FAX
J8201 Connector to connect to FAX
J8202 Connector to connect to Reader
Lithium Battery for RTC
Life: approx. 10 years
BAT1
Replacement of a single battery is not available
in the service eld.
Switch to shut power supply when replacing
SW3
SO-DIMM
J8111
J8104
J8150
F-2-45
T-2-16
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Overview > Conguration/Function
2
2-27

2
Other iR machine
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Processing Module Conguration
2-28
Controls
■Image Data Flow
Copy
A
Print output
Original
A
Scan
A
Image data
- SEND
- FAX
- PullScan
- E-Mail
- PDL Print
PC
F-2-46
■Image Processing Module Conguration
Reader Controller PCB
DC Controller PCB
SO-DIMM
Reader unit input
image processing block
Processes the image data
read by the reader unit.
Main Controller PCB
Printer unit output image
processing block
Processes image data for
output to the printer unit.
F-2-47
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Processing Module Conguration
2
2-28

2
Main controller PCB
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Compression/Expansion/Edit Processing Block
2-29
■Reader Unit Input Image Processing
Reader unit
Enlargement/reduction
Edge emphasis
-intensify-to-density conversion
-density adjustment (F adjustment)
-gamma correction
Binary processing (error diffusion)
To compression/expansion/editing block
Main controller PCB
■Compression/Expansion/Edit Processing Block
Reader image
processing block
Enlargement/
reduction
Rotation
Integration
to printer unit output image processing block
PDL image
processing block
Compression
Expansion
SO-DIMM
F-2-49
F-2-48
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Compression/Expansion/Edit Processing Block
2
2-29

2
Main controller PCB
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of Copy Function
2-30
■Printer Output Image Processing
Compression/expansion/editing block
Binary density conversion
Enlargement/reduction
Smoothing
To DC controller PCB
■Image Data Flow of Copy Function
Reader unit
Main controller PCB
Image processing block for reader unit
SO-DIMM
Data rotation
Data compression
Data expansion
F-2-50
Image processing block for printer unit
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of Copy Function
2
DC controller PCB
F-2-51
2-30

2
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of FAX Transmission Function
2-31
■Image Data Flow of SEND Function
Reader unit
Main controller PCB
Image processing block for reader unit
Data expansion
Data rotation
Resolution conversion
Ethernet port
(compression data)
SO-DIMM
USB2.0
■Image Data Flow of FAX Transmission Function
Reader unit
Main controller PCB
Image processing block for reader unit
SO-DIMM
Data compression
Data rotation
Data expansion
Image processing block for FAX
To network
F-2-52
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of FAX Transmission Function
2
Super G3 Fax Board
F-2-53
2-31

2
Ethernet
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of PDL Function
2-32
■Image Data Flow of FAX Reception Function
Super G3 Fax Board
Main controller PCB
Image processing block for fax
Data rotation
Data compression
Data expansion
Image processing block for printer unit
SO-DIMM
■Image Data Flow of PDL Function
PDL
Rendering processing block
Compression/expansion
/editing block
Processing block for printer unit
DC controller PCB
Main controller PCB
SO-DIMM
F-2-55
2
DC controller PCB
F-2-54
2-32
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Controls > Image Data Flow of PDL Function

2
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
Service Tasks
■Periodically Replaced Parts
None.
■Consumable Parts
None.
■Periodical Servicing
None.
2-33
Technical Explanation > Main Controller > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
2
2-33

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Construction > Main Conguration Parts
2-34
Laser Exposure System
Construction
■Specications/Controls/Functions
●Laser light
The number of laser light
Output
Wave length
●Scanner motor
Motor type
The number of rotation
Type of bearing
●Polygon mirror
The number of facet
●Controls
Synchronous control
Laser intensity control
Others
4
10mW
775nm to 799nm (Infrared laser)
DC brushless motor
Approx 36732 rpm / 31715 rpm (2-speed control)
Oil
6 (Φ40)
Main scanning direction synchronous control
APC control
Laser ON/OFF control
Laser scanner motor control
Laser shutter control
T-2-17
T-2-18
T-2-19
T-2-20
■Main Conguration Parts
[1]
[1] Laser Unit
[2] Polygon mirror
[3] BD mirror
[4] BD PCB
[3]
[2] [4]
Name Function
F-2-56
Emits laser
Scans the laser light in the main scanning direction
Reects the laser light in the BD PCB direction
Generates the BD signa
T-2-21
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Construction > Main Conguration Parts
2
2-34

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Construction > Control System Conguration
2-35
■Control System Conguration
Controls for the laser exposure system are mainly performed by the Main Controller PCB and
Image PCB.
Laser driver PCB
J602
J2
J601
Image signal
Laser control signal
J1
Scanner motor control signal
Scanner motor PCB
J208
DC Controller PCB
BD PCB
BD signal
Signal name Function
Image signal
DATA C+ C laser image data signal entry
DATA C- C laser image data signal entry
DATA B- B laser image data signal entry
DATA B+ B laser image data signal entry
DATA A- A laser image data signal entry
DATA A+ A laser image data signal entry
DATA D+ D laser image data signal entry
DATA D- D laser image data signal entry
Laser control signal
CTRL0-0 A/B laser control signal
CTRL0-1 A/B laser control signal
CTRL0-2 A/B laser control signal
CTRL1-0 C/D laser control signal
CTRL1-1 C/D laser control signal
CTRL1-2 C/D laser control signal
Scanner motor control signal
POLYGON_M_FG* FG output signal
POLYGON_M_ACC* Motor speed-up signal
POLYGON_M_DEC* Motor speed-down signal
BD signal
BD BD signal
T-2-22
Main Controller PCB
J8143
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Construction > Control System Conguration
J8142
F-2-57
2
2-35

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Basic Sequence > Basic Sequence
Basic Sequence
■Basic Sequence
Initial rotation (INTR): After the control panel key is ON, the machine starts the scanner
motor and rotates the laser scanner motor until it reaches the number of target rotation while
keepingall laser OFF. Once it reaches the target, the machine enters stand-by mode. (FG
control)
If pressing the start key before the control panel key is ON*, standby time gets shorter after
the scanner motor reaches the target.
Print (PRINT): When copy start key is ON, the machine drives D laser. After BD PCB detects
D laser, the machine performs the APC (laser intensity) control of each laser. Oncethe BD
signal reaches the specied cycle, the machine is ready to print. Image data is output from
the main controller based on the synchronous signal and laser isemitted corresponding to it.
<In the case of A4, 1 sheet>
Control panel key ON
Laser scanner
motor
PVREQ signal
(Start key ON 1 )
Waiting in FG control
Speed up
Start key ON
PRINT STBYSTBY INTR
BD control
Speed down
2-36
Laser
BD 1
Laser D
Laser C
Laser B
Laser A
1: BD signal is generated based on A laser light. Only A laser light reaches BD sensor
on BD PCB and B/C/D laser does not reach.
BD 1
Laser D
Laser C
Laser B
Laser A
ight on
L
Light offLight offLight off
: BD detection/APC control
: AP control
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Basic Sequence > Basic Sequence
2
Image per 1 line
F-2-58
2-36

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Activation Timing
Various Controls
■Controlling the Laser Activation Timing
●Laser ON/OFF Control
Laser ON/OFF control is dependent on the combination of the laser control signal (A/B laser:
CNT0-0/0-1/0-2, C/D laser: CNT1-0/1-1/1-2) from the image PCB.
2-37
<A laser/B laser>
Laser control signal Laser status
CNT0-0 CNT0-1 CNT0-2 A Laser B Laser
1 1 1 Image data output Image data output
0 1 1 Forcible output OFF
1 0 1 OFF Forcible output
0 0 1 Forcible output Forcible output
1 1 0 Forcible output OFF Forcible output OFF
0 1 0 ON (For APC control) OFF
1 0 0 OFF ON (For APC control)
0 0 0 Discharge: APC reset
(Fixed when laser is not used)
<C laser/D laser>
Laser control signal Laser status
CNT1-0 CNT1-1 CNT1-2 C Laser D Laser
1 1 1 Image data output Image data output
0 1 1 Forcible output OFF
1 0 1 OFF Forcible output
0 0 1 Forcible output Forcible output
1 1 0 Forcible output OFF Forcible output OFF
0 1 0 ON (For APC control) OFF
1 0 0 OFF ON (For APC control)
0 0 0 Discharge: APC reset
(Fixed when laser is not used)
Discharge: APC reset
(Fixed when laser is not used)
Discharge: APC reset
(Fixed when laser is not used)
T-2-23
T-2-24
CTRL_1-2
CTRL_1-1
CTRL_1-0
CTRL_0-2
CTRL_0-1
CTRL_0-0
J8142
Main Controller PCB
F-2-59
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Activation Timing
2
2-37

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Activation Timing
2-38
●Main Scanning Synchronous Control
Main scanning synchronous control is operated at synchronous PCB based on BD
synchronous signal.
Based on BD signal that is formed from A laser light detected by BD PCB, BD synchronous
signal for each laser is formed inside image PCB.
Image data written in the line memory is read out by the readable signal (RE_A, RE_B, RE_
C, RE_D) according to the 4 phase differences formed inside the delayPCB based on the BD
synchronous signal (BD_SYNCH) and is sent to the laser driver.
[6]
BD signal
J8143
J8142
[1] Synchronous PCB [4] VDO
[2] Delay PCB [5] VDO signal process unit
[3] Line memory [6] Laser driver PCB
BD_SYNCH: BD synchronous signal
RE_A/B/C/D: Readable signal
NOTE:
Regarding BD signal formation
Not B laser but A laser only reaches BD sensor on BD PCB. BD signal is formed based
on A laser light.
[5]
Main Controller PCB
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Activation Timing
2
[1]
BD_SYNCH
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
RE_A
RE_B
RE_C
RE_D
[3]
[3]
[4]
[3]
[3]
F-2-60
2-38

2
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Shutter
2-39
■Controlling the Intensity of Laser Light
●APC Control
The machine monitors the laser light that is emitted to the built-in photo diode of laser diode
and adjusts the laser to appropriate intensity.
■Controlling the Laser Scanner Motor
●Controlling the Laser Scanner Motor
From when the laser scanner motor starts and the laser scanner motor reaches the number
of target rotation to before image formation starts, the machine controlsthe rotation speed by
referring to the laser scanner motor rotation speed signal (FG signal).
During image formation, it controls the laser scanner motor rotationspeed based on BD
signal.
Laser scanner motor rotation speed is controlled by speed-up signal (ACC signal) and speeddown signal (DEC signal).
■Controlling the Laser Shutter
●Laser Shutter Control
When the right door opens, laser shutter will be closed by laser shutter link that works in
conjunction with the right door and the laser light is blocked. Also, whenthe front door or right
door open is detected, laser scanner motor and the laser emission will be turned OFF.
[1]
[2]
DOOR CLOSED
[1][3] [3] [1]
DOOR OPEN
ACC
DEC
FG
J208
DC Controller PCB
F-2-61
Technical Explanation > Laser Exposure System > Various Controls > Controlling the Laser Shutter
2
[2] [2]
1] Laser shutter
[
[2] Laser shutter link (works in conjunction with the right door)
[3] Laser unit
F-2-62
2-39

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > List of Image Formation Specications
Image Formation System
Basic Conguration
■List of Image Formation Specications
Item Specications/Function/Method
Photosensitive
Drum
Primary
Charging
Developing Developing method
Transfer Transfer method
Separation Separation method
Waste Toner
Type
Cleaning mechanism
Processing speed
Charging method
Roller diameter
Cleaning mechanism
Developing Cylinder
OD
Toner
Toner level detection
mechanism
Roller diameter
Cleaning mechanism
Organic Photo Conductor High Durable Drum (E Drum)
Cleaning Blade
311mm/sec (at pickup from Cassette)
134mm/sec (at pickup from Multi-purpose Tray)
Roller charging
AC bias constant voltage control: approx. 550 to 2600Vp-p
DC bias constant voltage control: approx. -400 to -800V
DC bias switch control (variable by Environment Sensor
Detection)
Diameter: 12
Brush Roller (Diameter: 10)
Dry, 1-component toner projection development
AC bias constant voltage control: approx. 800Vp-p
DC bias control: approx. -250 to -650V
DC bias switch control (Variable by density setting and
Environment Sensor Detection)
Diameter: 20
Magnetic negative toner
Toner detection by Toner Level Detection Sensor (in Sub
Hopper and Developing Assembly)
Roller charging
DC constant current control: approx. 25 to 30 micro A
Cleaning bias control: -1650V (DC constant voltage control)
DC current level control (variable by Environment Sensor
Detection, paper type, paper width and pickup location)
Diameter: 16
Cleaning bias application
Electrostatic separation (Static Eliminator) + curvature
separation
DC constant voltage control: -2600V (strong bias), -2200
(weak bias)
To collect into Waste Toner Box
Waste Toner Box capacity: approx. 750g
2-40
T-2-25
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > List of Image Formation Specications
2
2-40

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > Major Components in image formation system
■Major Components in image formation system
The following shows major component parts in image formation system:
[3]
[4]
[14]
[13]
[1]
[2]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
Name Function
[1] Drum Unit
[2] Brush Roller
[3] Primary Charging Roller
[4] Cleaning Blade
[5] Waste Toner Feed Screw
[6] Photosensitive Drum
[7] Static Eliminator
[8] Transfer Roller
[9] Developing Cylinder
[10] Developing Assembly
[11] oner Feed Screw
(Inside Developing
Assembly)
[12] Toner Feed Screw
(Inside Hopper)
[13] Hopper Assembly
[14] Toner Container
2-41
A unit consists of the Photosensitive Drum, Primary
Charging Roller, etc.
To rotate by engaging with the Primary Charging Roller
to clean the Primary Charging Roller.
To rotate by engaging with the Photosensitive Drum to
make the surface of Photosensitive Drum negativelycharged.
To remove residual toner on the surface of
Photosensitive Drum.
To feed toner that was collected by the Cleaning Blade
into the Waste Toner Box.
To create image on the surface of Photosensitive Drum.
To make the back side of paper negatively-charged to
separate the paper from the Photosensitive Drum.
To make the back side of paper positively-charged to
transfer toner on the paper.
To transfer toner in the Developing Assembly on the
Photosensitive Drum.
A unit consists of the Developing Cylinder, Developing
Blade, etc.
To ll toner that was supplied from the Sub Hopper into
the Developing Assembly
To feed toner that was supplied from the Toner Bottle
into the Developing Assembly.
To accumulate toner supplied from the Toner Bottle.
A toner-lled container for toner supply
T-2-26
[12]
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > Major Components in image formation system
[11]
[10]
[9]
F-2-63
2
2-41

■Image Formation Process
Primary charging roller
The image formation system of this machine consists of the Photosensitive Drum, Primary
Charging Roller, Developing Cylinder, Transfer Charging Roller, Static Eliminator and
Cleaning Blade, and the image formation process around the Drum Unit mainly consists of
the 6 blocks.
[2]
[1]
2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > Image Formation Process
Cleaning Blade
[6]
Photosensitive drum
Paper
[5]
Static eliminator
Image formation block Description
[1] Primary charging block
[2] Laser exposure block
[3] Developing block
[4] Transfer block
[5] Separation block
[6] Drum cleaning block
To evenly make the surface of the Photosensitive
Drum negatively-charged.
To neutralize electric charge by scanning laser beam
on the drum surface to create latent image.
To create visible image by attaching toner that has
been negatively charged from the Developing Cylinder
to the latent static latent image on the surface of the
Photosensitive Drum.
To apply positively-charged potential from the back
side of paper to transfer toner on the drum to the
paper.
To separate paper from the Photosensitive Drum by
elastic force of paper and make the paper easy to be
separated by applying negatively-charged potential
from the back side of paper.
To remove residual toner on the surface of the drum
by the Cleaning Blade to be collected into the Waste
Toner Box.
2-42
T-2-27
[3]
Transfer charging roller
[4]
Developing cylinder
F-2-64
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Conguration > Image Formation Process
2
2-42

2
Pickup
Registration
Registration
Registration
Image write
Image write
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Sequence > Last rotation sequence
2-43
Basic Sequence
The following shows the basic sequence of this machine:
■Initial rotation sequence
• At pickup from Cassette and pickup from Multi-purpose Tray
ON
Main Motor (M2)
Primary Charging AC Bias
Primary Charging DC Bias
Laser
Developing AC Bias
Developing DC Bias
Developing Cylinder Clutch (CL2)
Transfer Bias
Static Eliminator Bias
ON
F-2-65
■Sequence at printing
ON
Image formation sequence
(1st sheet)
Main Motor (M2)
Primary Charging
AC Bias
Primary Charging
DC Bias
Laser
Developing AC Bias
Developing DC Bias
Developing Cylinder
Clutch (CL2)
Transfer Bias
Static Eliminator Bias
■Last rotation sequence
end
end
Sheet-to-sheet
sequence
ON
Image formation sequence
(2nd sheet and later)
F-2-66
2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Basic Sequence > Last rotation sequence
Main Motor (M2)
Primary Charging AC Bias
Primary Charging DC Bias
Laser
Developing AC Bias
Developing DC Bias
Developing Cylinder Clutch (CL2)
Transfer Bias
Static Eliminator Bias
Cleaning bias (-2700V) is applied at [1] as shown above.
[1]
F-2-67
2-43

2
Waste Toner Feed Screw
Primary charging roller
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Drum Unit
2-44
Controls
■Drum Unit
The Drum Unit mainly consists of the Photosensitive Drum, Primary Charging Roller, Brush
Roller, Cleaning Blade and Waste Toner Feed Screw, and is driven by the Main Motor (M2).
The Cleaning Blade is in contact with the surface of the Photosensitive Drum to remove
residual toner on the surface of the Photosensitive Drum that was not transferred to the
paper. Residual toner collected by the Cleaning Blade is sent from the Toner Ejection Mouth
to Waste Toner Box by the Waste Toner Feed Screw. The Brush Roller is also in contact with
the Primary Charging Roller, and the Brush Roller cleans the Primary Charging Roller.
Cleaning Blade
Brush Roller
Primary
Charging Roller
M 2
Toner Ejection Part
Photosensitive Drum
M2 Main Motor
[1] Main Motor drive signal
DC Controller PCB
[1]
F-2-68
●Primary Charging Bias Control
This machine performs direct charging by the Charging Roller. AC bias is applied to the
Primary Charging Roller to make steady DC bias and charging.
Photosensitive drum
HVT PCB
Environment sensor
[2]
Primary AC bias
[1] Primary charging bias control signal
[2] Environment sensor detection signal
[1]
control circuit
Primary DC bias
control circuit
DC Controller PCB
F-2-69
●DC/AC bias constant voltage control
The DC bias control circuit and AC bias control circuit in the DC Controller PCB control DC
bias and AC bias, which are applied to the Primary Charging Roller, to make constant voltage.
●Drum Unit Detection
Charging AC bias is applied at Power-on, recovery from sleep state, or opening/closing the
door to detect the Drum Unit by the return value.
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Drum Unit
2
●DC bias switch control
DC bias changes output value of DC bias according to the environment detected by the
Environment Sensor (THU1).
2-44

2
Photosensitive drum
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Developing Assembly
2-45
■Developing Assembly
The Developing Assembly mainly consists of the Developing Cylinder, Developing Blade,
Toner Stirring Plate, and Toner Feed Screw, and is driven by the Main Motor (M2) and Sleeve
Clutch (CL2).
The Toner Feed Screw and Toner Stirring Plate feed the toner, which was sent from the Toner
Container, to ll in the Developing Assembly. Toner in the Developing Assembly is detected
by the Developing Assembly Toner Sensor (TS2), which is a magnetic sensor.
Toner Agitation Plate
Toner Feed Screw
TS2
Developing Blade
Developing Cylinder
CL 2
M 2
[1][2][3]
DC Controller PCB
●Developing Bias Control
DC bias and AC bias are applied to the Developing Cylinder.
Density Setting
Main Controller PCB
Environment sensor
[3]
Developing AC bias
control circuit
[2]
[1] Developing bias control signal
[2] Environment sensor detection signal
[3] Density setting signal
HVT PCB
[1]
DC Controller PCB
Developing cylinder
Developing DC bias
control circuit
F-2-71
F-2-70
TS2 Developing Assembly Toner Sensor
CL2 Sleeve Clutch
M2 Main Motor
[1] Sleeve Clutch drive signal
[2] Main Motor drive signal
[3] Developing Assembly Toner Sensor detection signal
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Developing Assembly
2
●DC/AC bias constant voltage control
The DC bias control circuit and AC bias control circuit in the DC Controller PCB control DC
bias and AC bias, which are applied to the Developing Cylinder, to make constant voltage.
●DC bias switch control
DC bias changes output value of DC bias according to the environment and density settings
detected by the Environment Sensor (THU1).
2-45

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Toner Supply Area
2-46
■Toner Supply Area
●Toner Supply Control
Route of Toner Supply
Toner Cartridge
TS2
TS1 Hopper Toner Sensor
M2 Main Motor
M6 Hopper Motor
M5 Bottle Motor
[1] Hopper Toner Sensor detection signal
[2] Bottle Motor drive signal
[3] Main Motor drive signal
[4] Hopper Motor drive signal
TS1
Sub Hopper
Toner Feed Screw
Toner Feed Screw
Developing Assembly
M 2M 5 M 6
DC Controller PCB
[1][2][3][4][5]
F-2-72
Title Description Supply timing
Supply to the
Sub Hopper
Supply to the
Developing
Assembly
To supply developer
in the Toner Container
into the Sub Hopper
To supply developer
from the Sub Hopper
to the Developing
Assembly.
When output result of Hopper
Toner Sensor (TS1) changes from
H to L.
The Developing Clutch is turned
On and the Main Motor (M2) is
driven.*1
When output result of Developing
Assembly Toner Sensor (TS2)
changes from H to L while the
above conditions are satised.
*1 The screw of Developing Assembly is driven by the Main Motor; therefore, supplying toner
Operation of the host
machine
To drive the
Bottle Motor (M5)
intermittently (to rotate
for 3 sec and stop for 2
sec).
To drive the
Hopper Motor (M6)
intermittently (to rotate
for 1 sec and stop for 1
sec)
T-2-28
while the Main Drive Motor is not driven causes toner leakage.
●Toner level detection
Message
(machine
operation)
Supply toner.
Supply toner.
T-2-29
Detection description Detection timing
Toner-out alert (when the
number of printable sheets
reaches 1000 (sheets)
based on 6% of image
ratio with A4 paper)
Toner-out (Level of toner in
the Developing Assembly
is approx. 0%.)
When output result of the
sensor changes from H to
L while there has been no
change in value of the sensor
despite a supply operation for
approx. 150 sec.
When the Developing
Assembly Toner Sensor (TS2)
detects toner-out and the
machine has printed 1000
sheets with 6% image ratio
with A4 paper.
Detecting to
(location)
Hopper Toner
Sensor
Developing count
by Developing
Assembly Toner
Sensor (TS2)
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Toner Supply Area
2
2-46

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Toner Supply Area
●Detection for replacing Toner Container
This machine does not have a sensor to detect replacement of a Toner Container. Therefore,
execute the toner supply sequence as follows to determine replacement of a Toner Container.
• Toner supply sequence
1. Make the Main Motor (M2), Developing Clutch, Hopper Motor (M6) and Bottle Motor (M5)
driven to supply toner.
2. When the Hopper Level Sensor detects presence of toner, the machine resumes normal
operation. When the Hopper Level Sensor failed to detect presence of toner for more than
60 sec, it is determined that there has been no replacement of a Toner Container.
• Replacement when the power is turned ON
When the Front Cover is opened/closed, the machine determines that a Toner Container has
been replaced and executes toner supply sequence.
• Replacement when the power is turned OFF or the machine is at sleep 2 state
The machine executes the toner supply sequence at power-on if there was a toner-out alert
or toner-out message when the power was turned OFF the last time.
2-47
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Toner Supply Area
2
2-47

2
Photosensitive drum
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Transfer Unit
2-48
■Transfer Unit
The Transfer Unit mainly consists of the Transfer Roller and Static Eliminator, and the
Transfer Roller rotates by engaging with the Drum Unit
Separation Static
Charge Eliminator
Transfer Roller
F-2-73
●Transfer bias/separation static eliminator bias control
DC bias is applied to the Transfer Roller and Static Eliminator.
[1] Separation static eliminator bias control signal
[2] Transfer bias control signal
[3] Environment sensor detection signal
●Transfer bias constant current controll
Transfer bias, which is applied to the Transfer Roller, is controlled by the Transfer Bias
Control Circuit in the DC Controller PCB to make constant current.
●Transfer bias level control
Transfer bias changes output value of transfer bias according to the environment detected by
the Environment Sensor (THU1), paper type, paper width, pickup position, etc.
●Cleaning bias control
This is a control to apply negatively-charged voltage at last rotation to bring the toner attached
on the Transfer Roller back to the Photosensitive Drum.
●Separation static eliminator bias control
Two types of negatively-charged voltages, weak and strong biases, are applied to the
Static Eliminator according to the print mode and sequence so that the paper is easy to be
separated from the Photosensitive Drum by reducing electrostatic absorption force.
Static eliminator
Environment sensor
HVT PCB
[3]
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Transfer Unit
Transfer charging roller
Transfer bias
control circuit
DC Controller PCB
[2]
Static eliminator bias
control circuit
2
[1]
F-2-74
2-48

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Waste Toner Box
2-49
■Chang in bias by user mode (Special Mode)
Special mode settings in user mode include a mode to change the density or improve the
separation performance by changing the bias. The following describes the mode which
executes bias control.
User mode Overview Setting value Control details
Special Mode M
(Density adjustment)
Special Mode O
(Separation priority
mode)
Special Mode E
(Background density
adjustment mode)
To change the density
by chancing the value of
transfer bias.
To control the separation
bias in the case of frequent
jams on the 2nd side when
using backside of printed
paper, etc.
To darken the density
of background such as
watermark.
Standard
(Default)
Low The density is lightened by
High The density is darkened by
Off
(Default)
On Separation bias at paper feed is
Off
(Default)
On The background density is
Normal control
weakening the bias.
strengthening the bias.
Normal control
strengthened. Also, the leading
edge margin is set to 4.5mm.
Normal control
darkened by strengthening the
transfer bias.
T-2-30
■Waste Toner Box
●Overview
The toner, which was not transferred to the paper but attached on the Photosensitive Drum, is
removed by the Cleaning Blade that is in contact with the Photosensitive Drum, and then fed
into the Waste Toner Box by the Waste Toner Feed Screw.
There is a screw for feeding toner in the Waste Toner Box. This screw is driven by the Waste
Toner Motor and engaged with movement of the Hopper Motor.
Note that there is no mechanism to detect presence of a Waste Toner Box with this machine.
The Front Cover cannot be closed unless the Waste Toner Box is mechanically installed;
therefore, the machine is not driven without having the Waste Toner Box installed
Waste Toner Box
Waste Toner Feed Screw
Waste Toner
Full Sensor (PS2)
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Controls > Waste Toner Box
2
Toner
F-2-75
PS2 Waste toner full level sensor
2-49

2
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
2-50
●Full Detection
Detection description Detection timing
Alert for full level of waste
toner (approx. 2000 sheets
left to reach the full level of
waste toner)
Full level of waste toner
(0% left to reach ful
When replacing a Waste Toner Box and the Waste Toner Full Sensor detects absence of
waste toner after the Waste Toner Full Sensor detected presence of a Waste Toner Box, the
counter of the Waste Toner Box is cleared. When replacing a Waste Toner Box before the
alert, be sure to clear the following in service mode: COUNTER > DRBL-1 > WST-TNR
Special full level detection
When attaching a Waste Toner Container that has been used by the other machine, or the
counter information is lost for some reason, it is necessary to notify full level before an alert
is given. (The counter shows less than 50,000 although the sensor detects full level of waste
toner) In such a case, it is determined as full level without an alert and the machine cannot
continue printing.
Explain the user that there will be no alert when any of the above is executed.
When output result of the
sensor changes from H to L
and the total counter value
exceeds 50,000 sheets.
fter approx. 2000 sheets have
been printed by starting the
Developing Assembly
Detecting to
(location)
Waste Toner
Full Sensor
Total counter
Total counter Replace the Waste
Message
(machine operation)
Prepare the Waste
Toner Case.
(Continuous printing
is enabled.)
Toner Case. (Host
machine is stopped.)
T-2-31
Service Tasks
■Periodically Replaced Parts
None
■Consumable Parts
No. Parts name Parts number Q'ty Estimated life
1 Waste Toner Container FM4-8035 1 100,000 sheets
2 Transfer Roller FM4-6522 1 180,000 sheets
3 Static Eliminator FL3-4857 1 90,000 sheets
T-2-32
■Periodical Servicing
None
Perform as needed.
Technical Explanation > Image Formation System > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
2
2-50

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Overview > Specications
2-51
Fixing System
Overview
■Features
This machine uses the on-demand xing method.
Separation Guide
Fixing Film
Fixing Heater
Fixing Inlet Guide
Fixing Delivery Roller
Fixing Inlet Guide
Pressure Roller
■Specications
Item Function/method
Fixing method
Fixing speed
Fixing Heater
Control temperature
Temperature Control
Cleaning mechanism
Edge temperature rising control
Fixing Arch Control
Protection function
*1. The gure varies depending on xing mode and xing temperature at the start of Startup
control.
On-demand xing
139mm/sec (1/1-speed high: 0.8% acceleration)
137mm/sec (1/1-speed)
133mm/sec (1/1-speed slow: 3.1% deceleration)
Ceramic Heater
208 deg C (plain paper) *1
Main Thermistor, Sub Thermistor
Cleaning Roller
Down sequence
Loop Sensor
Main Thermistor, Sub Thermistor,
Thermoswitch (Rated operational temperature: 250 deg C)
T-2-33
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Overview > Specications
2
F-2-76
2-51

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Overview > Major Components
2-52
■Major Components
Sub Thermistor (THM2)
Pressure Roller
Fixing Film Unit
Fixing Pressure
Release Sensor (PS18)
Fixing Paper
Sensor (PS19)
Part name Function / method
--- Film Unit
--- Pressure Roller
H1/H2 Fixing Heater
TH1 Main Thermistor
TH2 Sub Thermistor
TP1 Thermoswitch
Fixing Pressure
PS18
Release Sensor
PS19 Fixing Paper Sensor
A toner image on paper is xed by applying heat/pressure.
Ceramic Heater
Engaged with the heater
Temperature control and abnormal temperature rising detection
Engaged with the heater
Temperature control, abnormal temperature rising detection, edge
temperature-rising/cooling control
A kind not engaged with the heater.
AC power supply is blocked at detection of a failure.
Detection of pressure application/release to the Film Unit
Jam Detection
T-2-34
Fixing Thermistor (THM1)
Fixing Thermoswitch (TP1)
Fixing Heater (H1)
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Overview > Major Components
2
Sub Heater (H2)
F-2-77
2-52

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Fixing Temperature Control (temperature control)
2-53
Controls
■Fixing Temperature Control (temperature control)
●Standby Temperature Control
This is a control to pre-heat the Fixing Assembly to reduce time to start printing.
• Flying Startl
●Print Temperature Control
This is a control to increase xing temperature to the target level and keep it during printing.
• Startup (initial rotation) temperature control
• Print temperature control
• Paper interval temperature controll
●Down Sequence Control
This is a control to prevent xing failure due to temperature increase at the edge or
temperature decrease. Productivity (throughput) decreases.
• Down sequence when feeding small-size paper
• Down sequence when switching paper sizel
F-2-78
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Fixing Temperature Control (temperature control)
2
2-53

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Print temperature control
2-54
■Standby Temperature Controll
Max. 10 sec
●Flying Start
Purpose:
To reduce time to print the rst sheet (FCOT).
F-2-79
■Print temperature control
F-2-80
●Startup (initial rotation) temperature control
A xing temperature is increased to a printable temperature after receiving a command to
start printing.
Starting conditions:
• When opening the Copyboard Cover or ADF while the detected temperature of the
Main Thermistor is lower than 100 deg C.
• When setting the original on the ADF while the detected temperature of the Main
Thermistor is lower than 100 deg C.
• When the Main Power Switch is turned ON or the machine is recovered from sleep
mode to standby mode while the detected temperature of the Main Thermistor is lower
than 180 deg C
Control description:
The temperature control target is set at 177 deg C and the Fixing Motor is controlled
at half-speed to start operation. The control continues for 10 sec at most until the
machine receives a command to start printing.
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Print temperature control
2
●Print temperature control
To set optimal target temperature to prevent xing failure or offset, and keep the specied
target temperature during printing
A.Setting the target temperature
A target temperature is determined according to the paper type/size, time which
elapsed from when xing temperature control (including standby control) nished the
last time, and xing temperature when startup control started.
B.Temperature control during printing
When the paper passes through the Fixing Assembly, temperature is controlled to
keep the target temperature (see the next page) according to the detected temperature
of the Main Thermistor.
2-54

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Print temperature control
2-55
C.Paper interval temperature control
At paper interval where no paper is fed to the Fixing Assembly, the control temperature
is set lower than the print control temperature (-5 deg C *1) to prevent temperature
rising of the Fixing Assembly and save energy.
*1. -5 deg C for plain paper. The temperature is set at -15 deg C or -20 deg C
according to the paper type.
Target temperature during printing
The control temperature is determined according to the xing mode and xing temperature
at the start of Startup control. Eight xing modes are available according to the selected
pickup cassette and paper type.
The following shows an example of control temperature when the xing temperature at
the start of Startup control is 65 deg C or higher and lower than 70 deg C: (Temperature at
standby with 20 deg C room temperature)
Control temperature (deg C)
1-sided print/1st side
Fixing mode Setting
Plain paper (64 to 90g/m
Heavy paper 1 (91 to 105g/m2)
Heavy paper 2 (106 to 128g/m2)
Bond paper
Transparency
Envelope
Special Mode N (Medium)
Special Mode N (High)
*1 Special Mode N (Medium): -20 deg C of normal control temperature (at pickup from
cassette, when xing temperature at the start of Startup control is 100 deg C or higher)
*2 Special Mode N (High): -35 deg C of normal control temperature (at pickup from
cassette, when xing temperature at the start of Startup control is 100 deg C or higher)
2
)
Paper type
*1
*2
of 2-sided print
Normal
Speed
215 155 210 150
215 155 210 150
--- 175 --- 170
--- 175 --- 170
--- 150 --- ---
--- 180 --- 175
195 150 185 145
180 145 170 140
Low
Speed
2nd side of 2-sided
print
Normal
Speed
Low
Speed
T-2-35
Related Service Mode
Fixing control temperature offset (to increase/reduce control temperature)
PRINT > SW
> 62 (control temperature at the time of normal pickup)
> 63 (control temperature in heavy paper/heavy paper H/Bond Paper mode)
> 166 (control temperature at the time of low speed pickup)
> 173 (control temperature on the 2nd side of 2-sided print)
<Setting value>
0 to 2: +15 degrees C
3 to 11: +12 to -15 degrees C (increment by 3 degrees C) [Default: 7]
12 to 14: -15 degrees C
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Print temperature control
2
2-55

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Down Sequence Control
2-56
■Down Sequence Control
●Down sequence when feeding small-size paper
Purpose:
To prevent xing offset and deterioration of the Fixing Film by controlling temperature
increase at a non paper feed area at continuous printing of small-size paper (paper
that has smaller than A4R of width-direction length)
Starting conditions:
Down sequence is performed in a stepwise manner. This is a control to reduce
throughput on a step-by-step basis as the detected temperature of the Sub Thermistor
reaches the specied temperature or higher as shown in the table below for
consecutive 400msec during printing.
Stages Normal The 1st stage The 2nd stage The 3rd stage
A temperature to go
for the next stage
Operation:
Increasing paper interval (to make longer temperature control at a temperature lower
than that of normal print) to reduce xing temperature in 4 stages at most.
Fixing mode Stages LGL
Plain paper (64 to 90g/m2)
Heavy paper 1 (91to 105g/
m2)
Special Mode N (Medium)
Heavy paper 2 (106 to
128g/m2)
Bond paper Normal 13 22 17 17 ---
Transparency Normal --- 17 --- --- ---
Envelope Normal --- --- --- --- 12
235 degrees C 245 degrees C 255 degrees C 260 degrees C
T-2-36
A4R
LTRR
Normal 43/40/30 50/40/30 25 23 ---
1 25 25 20 20 --2 20 20 18 18 --3 15 15 15 15 ---
Normal 14 21 17 17 ---
1 10 17 14 10 --2 8 14 10 8 --3 6 6 6 6 ---
1 10 15 14 10 --2 8 14 10 8 --3 6 6 6 6 ---
1 --- 14 --- --- --2 --- 10 --- --- --3 --- 6 --- --- ---
1 --- --- --- --- 10
2 --- --- --- --- 8
3 --- --- --- --- 6
A5R/B5R
EXE-R/STMTR
Custom
size
Envelope
T-2-37
Termination condition:
When the machine detects 175 degrees C or lower for consecutive 400msec after
reaching the 3rd stage, the machine is recovered to move to the 1st stage.
Normal
245deg C,400msec
1st Step
255deg C,400msec
2st Step
260deg C,400msec
3st Step
Related Service Mode
Temperature settings to start down sequence
PRINT > SW > 64
<Setting value>
0: +20 deg C
1: +10 deg C
2: 0 deg C [default: 2]
3: -10 deg C
4: -20 deg C
Return
210deg C,400msec
F-2-81
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Down Sequence Control
2
2-56

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Change in xing performance by user mode (Special Mode)
2-57
●Down sequence when switching paper size
Purpose:
When feeding a sheet with a wider width than a preceding sheet during continuous
printing, temperature at the non paper-feed area of the preceding sheet increases,
and it can cause xing offset and wrinkles when feeding the succeeding sheet. This
down sequence controls temperature increase at the non paper feed area.
Non-feed area
Film
Non-feed area
Starting conditions:
When the paper is switched to a wider paper than the preceding sheet during printing,
the detected temperature of the Sub Thermistor is higher than 210 deg C (*1).
Operation:
This is a control to stop pickup of the succeeding sheet and power distribution to the
Fixing Heater to reduce xing temperature.
Termination condition:
When detected temperature of the Sub Thermistor is 170 deg C or lower (*1).
*1. The temperature differs according to the user mode settings (Special Mode S).
F-2-82
■Change in xing performance by user mode (Special Mode)
Changing the control temperature or throughput affects xing performance in some modes
of special mode settings in user mode. The following describes the mode which affects xing
performance.
User mode Overview Setting value Control temperature/throughput
Special Mode N
(to avoid curl/jam
at a high humidity
environment)
Special Mode P
(to avoid curl
of thin paper/
recycled paper)
Special Mode G
(to increase xing
performance of
This is a mode to set
temperature control
when any of plain
paper, recycled paper,
color paper or 3-hole
paper is selected on
the Control Panel. To
reduce productivity
to increase xing
performance.
This is a mode to set
temperature control
when any of plain
paper, recycled paper,
color paper or 3-hole
paper is selected on
the Control Panel. To
reduce productivity
to increase xing
performance.
To reduce productivity
to increase xing
performance.
heavy paper)
Special Mode S
(to ease
deceleration
of print speed
at temperature
rising at the edge)
To reduce wait time
for pickup permission
temperature when
the paper size is
changed to prioritize
productivity over xing
performance.
*1 Special Mode N (Medium): -20 deg C of normal control temperature (at pickup from
cassette, when xing temperature at the start of Startup control is 100 deg C or higher)
*2 Special Mode N (High): -35 deg C of normal control temperature (at pickup from cassette,
when xing temperature at the start of Startup control is 100 deg C or higher)
Off Normal temperature control
(temperature control for plain paper
Auto
(to increase xing
performance)
(Default)
Manual (Medium)
(to increase xing
performance)
Manual (High)
(to increase xing
performance)
Off
(Default)
Medium
(to increase xing
performance)
High
(to increase xing
performance)
Off
(Default)
On
(to increase xing
performance)
Off
(default)
On
(Priority on
productivity)
mode)
This is a mode to switch between the
normal temperature control and N1
mode (*1) according to the environment
(temperature/humidity).
Special Mode N (Medium) mode
temperature control
Special Mode N (High) mode (*2)
temperature control
Normal temperature control
(temperature control for plain paper
mode)
Thin paper mode temperature control
S-thin paper mode temperature control
Normal control
To reduce throughput by 4 or 5 sheets
This is a control to set the pickup
permission temperature at 210 deg C
and pickup recovery temperature at 170
deg C.
This is a control to set the pickup
permission temperature at 190 deg C
and pickup recovery temperature at 230
deg C.
T-2-38
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Change in xing performance by user mode (Special Mode)
2
2-57

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Pre-xing arch level control
2-58
■Pre-xing arch level control
Purpose:
Constantly creating an optimal arch between the transfer and xing areas prevents a
shock, which occurs when the paper's trailing edge passes through the Registration
Roller, and obtains an optimal image.
Fixing Film
Pressure Roller
Sensor: OFF
Photosensitive Drum
Starting conditions:
This control is performed every time the paper is fed.
Operation:
The Arch Sensor detects a paper arch between the transfer nip and xing nip to
change the drive speed of the Fixing Motor.
1) When the paper's leading edge goes over 35mm from the Transfer Roller, drive speed
of the Fixing Motor is reduced by 3.1% against the process speed. The reduced speed
is maintained until the paper creates an arch and the Arch Sensor is turned ON.
2) After the Arch Sensor has been detected ON for consecutive 50msec or longer,
drive speed of the Fixing Motor is increased by 0.8% against the process speed. The
increased speed is maintained until the paper arch disappears and the Arch Sensor is
turned OFF.
loop.
3) After the Arch Sensor has been detected OFF for consecutive 50msec or longer, drive
speed of the Fixing Motor is reduced by 3.1% against the process speed. The reduced
speed is maintained until the paper creates an arch and the Arch Sensor is turned ON.
4) Repeat steps 2) and 3). When the paper's trailing edge reaches at 10mm before
the Transfer Roller, drive speed of the Fixing Motor is increased by 0.8% against the
process speed.
Registration Roller
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Controls > Pre-xing arch level control
2
Arch Sensor (PS9)
Transfer Roller
5) Go back to step 1) in the case of continuous printing. The machine goes to the last
rotation operation in the case of 1 sheet print.
Sensor: ON
F-2-83
2-58

2
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
2-59
■Protection function
Code Description
E000
Error in xing temperature rising
0001 When the detected temperature of the Main Thermistor fails to reach the
E001
E002
E003
E004
E014
E261
specied temperature at temperature rising control.
Error in overheating of Fixing Assembly
0000 When the Main Thermistor detects 250 deg C or higher for consecutive
200msec or longer.
0001 When the hardware circuit detects overheating of the Main Thermistor or
Sub Thermistor for 30msec or longer.
0002 When the Sub Thermistor detects 295 deg C or higher for consecutive
200msec or longer.
Error in temperature rising of Fixing Assembly
0000 1. When the Main Thermistor detected a temperature lower than 115 deg C
for consecutive 400msec or longer after 6 seconds that the Main Thermistor
detected 100 deg C
2. When the Main Thermistor detected a temperature lower than 150
deg C for consecutive 400msec or longer after 6.0 seconds that the Main
Thermistor detected 140 deg C
Detection of low temperature
0000 When the Main Thermistor detects lower than 140 deg C for consecutive
400msec or longer.
Thermistor disconnection detection error
0000 When removal of the connector (J214) is detected for consecutive 30msec. Not
Error in rotation of Fixing Motor (M1)
0001 Detection is performed every 100msec since the start of drive and there has
been no lock detection signal in 2sec.
0002 Detection is performed every 100msec during the drive (after the lock
detection) and the lock signal has not detected for 5 times consecutively (in
500msec).
0003 When the Fixing Pressure Release Sensor never detected pressure release
during the 3 seconds while the xing pressure was released
0004 When the Fixing Pressure Release Sensor never detected pressure during
the 3 seconds while the xing pressure was applied
Error in zero cross signal
0000 When the relay is ON, the zero cross signal failed to be detected for
500msec or longer.
*When the same status is detected again despite an error retry.
Clearing
of error
Required
Required
Required
Required
Required
Required
required
Not
required
Not
required
Not
required
Not
required
Not
required
T-2-39
Service Tasks
■Periodically Replaced Parts
None.
■Consumable Parts
No. Parts name Parts number Q'ty Estimated life
Fixing Assembly (120V) FM4-6495 1 160,000 sheets
1
Fixing Assembly (230V) FM4-8050 1 160,000 sheets
■Periodical Servicing
None.
Perform as needed.
T-2-40
Related Service Mode
Error code clear
CLEAR > ENGIN > ERRCLR
Technical Explanation > Fixing System > Service Tasks > Periodical Servicing
2
2-59

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Parts Conguration
2-60
Pickup Feed System
Overview
■Specications
Item Description
Paper storage method
Pickup method Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Stacking capacity Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Paper feed reference
Paper size Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Paper weight Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Paper size
switching
Supported size for
2-sided print
2-sided print method
*1: "Setting method when the size detection patterns are overlapped"(page 2-64).
*2: Long length paper is supported.
To make a copy with long length paper, settings are required in service mode and
applicable mode.(Up to 620mm image supported.)
*3: Custom paper size is not supported.
Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Cassette
Multi-purpose Tray
Front-loading method
Retard separation
Pad separation
550 sheets (80g/m2), 650 sheets (64g/m2)
100 sheets (80g/m2), 110 sheets (64g/m2)
Center reference
A4-R, A5-R, B5-R, LGL, LTR-R, STMT-R, EXEC-R,
16K-R
special standard-size *1
Width: 99mm to 216mm
Length: 140mm to 356mm (Up to 630mm long length
paper can be supported. *2)
A4-R, A5-R, B5-R, LGL, LTR-R, STMT-R, EXEC-R,
16K-R, Envelopes (No.10 (COM10), ISO-B5, Monarch,
ISO-C5, DL)
64 to 105g/m
64 to 128g/m2
Auto switching
Manual switching
210mm to 356mm (105g/m2)
210mm to 356mm (105g/m2) *3
Through path
2
T-2-41
■Parts Conguration
●Rollers Layout drawing
[16]
[1] Reverse Roller [9] Duplex feed roller 2
[2] Delivery Roller [10] Registration Roller
[3] Fixing outlet roller [11] Vertical Path Roller
[4] Duplex feed roller 1 [12] Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller
[5] Pressure Roller [13] Multi-purpose Tray Pullout Roller
[6] Fixing Roller [14] Separation Roller
[7] Drum [15] Feed Roller
[8] Transfer Roller [16] Pickup Roller
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
[9]
[10]
[11]
[12][13][14][15]
F-2-84
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Parts Conguration
2
2-60

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Parts Conguration
2-61
●Sensors Layout Drawing
PS6
PS4
PS5
PS19
PS9
PS8
PS11
PS12
PS20
●Route of Drive
M2
M1
M4
SL2
M7
CL1
SL3
PS13 PS7PS14PS15PS16PS17SW2
F-2-85
PS4 Delivery Paper Full Sensor PS13 Cassette Pickup Sensor
PS5 Delivery Sensor PS14 Cassette Lifting Plate Detection Sensor
PS6 Reverse Paper Sensor PS15 Cassette Paper Sensor
PS7 Multi-purpose Tray Paper Sensor PS16 Cassette Paper Level Sensor A
PS8 Duplex Feed Sensor PS17 Cassette Paper Level Sensor B
PS9 Loop Sensor PS19 Fixing Paper Sensor
PS11 Registration Sensor PS20 Transparency Sensor
PS12 Pre-Registration Sensor SW2 Cassette Size Detection Switch
NOTE:
Transparency detection of this machine is performed by the Transparency Sensor (PS20)
which is a ag-type sensor.
Uneven speed at the time of transparency feed is detected to judge whether it is
transparency.
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Parts Conguration
2
M9
M1 Fixing Motor CL1 Registration Clutch
M2 Main Motor SL1 Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Solenoid
M4 Reverse Feed Motor SL2 Reverse Feed Solenoid
M7 Duplex Feed Motor SL3 Cassette Pickup Solenoid
M8 Pickup Motor
M9 Lifter Motor
M8
SL1
F-2-86
2-61

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Paper Path
■Paper Path
2-62
Reversing Point
Delivery Point
Pickup From Cassette
Pickup From
Manual Feeder
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Overview > Paper Path
2
F-2-87
2-62

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2-63
Controls
■Overview
Reverse/Duplex
Assembly
Delivery
Assembly
Fixing / Registration
Assembly
Multi-Purpose Pickup
Assembly
■Cassette Pickup Assembly
●Overview
Paper inside a cassette is lifted up by the Lifting Plate.
When pickup takes place, the Cassette Pickup Solenoid (SL1) is turned ON so that the
Pickup Roller is moved down. When the Pickup Roller comes in contact with the surface of
paper, the paper is picked up by rotation of the roller.
Only a single paper picked up is moved to the feed path by the Feed Roller and the
Separation Roller, and moved as far as the Registration Roller by the Vertical Path Roller.
If the Cassette Pickup Sensor (PS13) is ON when starting pickup (in the case that the
succeeding paper is also picked up when a paper is picked up and fed), the feed speed is
decreased.
The Vertical Path Roller, Pickup Roller, Feed Roller, and Separation Roller are driven by the
Cassette Pickup Motor (M8).
[1]
SL1
PS13
[4]
[2]
[3]
Cassette Pickup
Assembly
Area Detection/Control
Cassette Pickup Assembly
Multi-purpose Tray
Pickup Assembly
Fixing/Registration
Assembly
Delivery Assembly Delivery Acceleration Control Delivery Full Detection
Reverse/Duplex
Assembly
Jam Detection List of Jam Codes Forcible Paper Feed Control
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
Paper Level Detection Control Pickup Retry Control
Paper Detection Control Paper Size Detection Control
Lifter Control Paper Detection Pickup Retry Control
Paper Size Detection Registration Control Size Mismatch Detection Control
Reverse Flapper Operation Duplex Re-pickup Control
Duplex Reverse Control Duplex Circulation
2
T-2-42
F-2-88
[5]
[1] Pickup Roller [4] Vertical Path Roller
[2] Feed Roller [5] Lifting Plate
[3] Separation Roller
M9
M8
F-2-89
●Pickup Retry Control
Pre-Registration Sensor
If the
the start of pickup operation, operation of the Pickup Motor (M8) and the Cassette Pickup
Solenoid (SL3) is suspended once, and the pickup operation is executed again. If the
Registration Sensor
(PS12) is not turned ON after re-pickup operation, a delay jam is notied.
(PS12) is not turned ON within a specied period of time after
Pre-
2-63

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2-64
●Paper Size Detection Control
Paper size in a cassette is automatically detected by the "Cassette Size Switch". Paper size
in a cassette is automatically detected by adjusting the Guide Plate position.
By shifting the Guide Plate, concavo-convex area of the Cassette Size Dial is switched
and the Cassette Size Switch at the printer side is switched. The switch consists of 4
microswitches, and length and width are detected in accordance with the combination of
ON/OFF. As long as standard size paper, it can be used for both AB conguration and inch
conguration. However, distinction between A5-R and STMT-R and between EXEC-R and
16K-R should be specied manually on the check screen.
SW2
F-2-90
Length Detection
Size Length 1 2 3 4
A5-R 210.0 - - ON ON
STMT-R 215.9 - - ON ON
B5-R 257.0 ON - - EXEC-R 267.0 ON ON - 16K-R 270.0 ON ON - LTR-R 279.4 - ON ON A4-R 297.0 ON - ON ON
LGL 355.6 - - ON (No cassette) - - - - -
T-2-43
In addition, presence of the cassette is detected when the size switch is pushed. (If no switch
is pushed, it is judged as no cassette.)
Rear Guide Plate
Cassette Size
Switch (SW2)
Rear
Detection
Rink
F-2-91
Setting method when the size detection patterns are overlapped
Method to distinguish between A5-R and STMT-R and between EXEC-R and 16K-R is
specied by the user settings.
Method to distinguish the special paper is specied by the user settings.
Setting sizes are as follows.
Related service mode
PRINT> CST> CASX> CASX-UY> Setting number (Cassette paper size group special,
standard-size paper entry)
X indicates the cassette number, and Y indicates size category. (X, Y is one of the number
1/2/3/4.)
U sizes Settings
U1 26: OFI, 37: M-OFI, 24: FLSP, 25: A-FLSP,
42: FA4, 34: G-LGL 0: Default
U2 32: G-LTR-R, 23: K-LGL-R, 0: Default
U3 Not used
U4 28: B-OFI, 0: Default
T-2-44
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2
2-64

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2-65
●Paper Level Detection Control
Paper level inside the cassette is detected by the sensors shown in the following table.
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor A
(PS16)
OFF OFF OFF 100% to 50%
ON OFF OFF
ON ON OFF Approx. 50 sheets or less
- - ON No papers
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor B (PS17)
Tray
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor B
(PS17)
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor A (PS16)
Cassette Paper
Sensor
(PS15)
Cassette Paper
Sensor (PS15)
Paper level
Approx. 50% to approx. 50
sheets
Paper Flag
Display on
the Control
Panel
T-2-45
If the paper is full
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor B
OFFOFF
If the paper is approx.half
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor B
OFFONON
If the paper is a little
Cassette Paper
Level Sensor B
Cassette Paper Level Sensor A
Cassette Paper Level Sensor A
Cassette Paper Level Sensor A
Paper
Paper
Paper
Paper Level Flag
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2
Lifter Gear
F-2-92
ON
If the paper is absent
Cassette Paper Sensor
Flag
Paper Tray
F-2-93
2-65

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2-66
●Paper Detection Control
After the Cassette Lifting Plate Detection Sensor (PS14) is turned ON, the Cassette Paper
Sensor (PS15) detects presence/absence of paper. When the Cassette Paper Sensor (PS15)
is ON, absence of paper is notied.
In addition, if the Cassette Lifting Plate Detection Sensor (PS14) is not turned ON even
raising the Lifter for 3 seconds, absence of paper is notied.
Paper Flag
PS15
M9
Lifting Plate
Lifting Plate Flag
PS14
Lifter
●Lifter Control
When Cassette is set
The Lifting Plate is raised until the Cassette Lifting Plate Detection Sensor (PS14) is turned
ON.
During pickup
The behavior is determined in accordance with the detection when the Cassette Pickup
Solenoid (SL3) is turned ON and the detection by the Cassette Lifting Plate Detection Sensor
(PS14) executed 100msec. later.
100msec. later after Cassette Pickup Solenoid (SL3) is turned ON
ON OFF
When the Cassette
Pickup Solenoid (SL3)
is turned ON
Lifting Plate
ON - If the same detection continues for 5 consecutive
sheets, the Lifting Plate is raised until the Cassette
Lifting Plate Detection Sensor (PS14) is turned ON.
OFF - Raising the Lifting Plate immediately until the Cassette
Lifting Plate Detection Sensor (PS14) is turned ON.
SL3
M9
Lifting Plate Flag
PS14
Lifter
T-2-46
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Cassette Pickup Assembly
2
F-2-94
F-2-95
2-66

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Fixing/Registration Assembly
2-67
■Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Assembly
●Overview
Paper on the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Tray of the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Unit is pushed
against the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller by the Lifting Plate, and only a single sheet
of paper is separated and fed by the work of the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller and the
Separation Pad.
M8
Multi-purpose
Tray Pickup Roller
Multi-purpose Tray
Separation Pad
Pressure Spring
Manual Feeder
Paper Sensor (PS7)
Paper Detection
Lever
●Pickup Retry Control
If the Pre-Registration Sensor (PS12) is not turned ON within the specied period of time
after the start of pickup operation, detection by the Multi-purpose Tray Paper Sensor (PS7) is
referred.
• When Multi-purpose Tray Paper Sensor (PS7) is ON:
Execute the pickup operation again. If the Pre-Registration Sensor (PS12) is not turned ON
after the start of re-pickup operation, a delay jam is notied.
• When Multi-purpose Tray Paper Sensor (PS7) is OFF:
Terminate the pickup operation.
SL1
Side Guide
Pickup Guide Plate
Multi-purpose Tray
F-2-96
■Fixing/Registration Assembly
●Registration Control
The Registration Roller is driven by the Main Motor (M2). There is the Registration Clutch
(CL1) between the Registration Roller and the Main Motor, and it controls ON/OFF of the
Registration Roller to align the paper with the image on the drum at the specied registration.
In addition, the speed is decreased right before a paper hits the Registration Roller so that
hitting sound is alleviated (speed is not decreased when picking up from the Cassette 1 of
imageRUNNER 1730/1740).
M2
CL1
Registration Roller
F-2-97
●Paper Detection
Presence/absence of paper is detected by the Multi-purpose Tray Paper Sensor (PS7).
When absence of paper is detected but the same size and same type of papers exist in
another paper source, auto cassette change is executed.
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Fixing/Registration Assembly
2
2-67

2
PS19
Pressure Roller
Delivery Speed
Increased Position
Fixing Outlet Roller
Delivery Roller
Bond Paper
M1
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Delivery Assembly
2-68
●Size Mismatch Detection Control
Whether the size is mismatched is determined by paper length.
The time a paper passes through the Registration Sensor (PS11) is converted into distance.
Compared with the paper size (specied by the user in case of the Multi-purpose Tray Pickup
Tray) detected by the Cassette Size Detection Switch (SW1), if the measured distance is
shorter than the specied distance (16mm), it is judged that the size is mismatched.
Priority of the size mismatch detection control is lower than other controls. In addition, due to
the behavioral error of paper, the measured distance has a margin of error of approx. +6mm.
Paper size mismatch cannot be detected with the following combinations because the
difference in paper size is small.
• A4-R, LTR-R
• A5-R, STATEMENT-R
• B5-R, EXEC-R, 16K-R
In case of envelope, paper size mismatch is not detected (because detection by the
Registration Sensor (PS11) is not stable when feeding the envelope).
■Delivery Assembly
●Delivery Acceleration Control
Since elasticity of bond paper is low, delivery speed is increased when feeding the bond
paper to improve the stackability.
Condition for acceleration: When the Finisher is not installed, and the bond paper is set
Timing for acceleration: When the trailing edge of paper passes through the Fixing Paper
Sensor (PS19)
Timing to return the speed: When the Registration Clutch (CL1) is turned ON for the
succeeding paper
F-2-98
●Delivery Full Detection
If the Delivery Paper Full Sensor (PS4) is ON for a specied period of time, it is notied to the
Main Controller PCB. After the notication, printing stops by the Controller's decision.
2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Delivery Assembly
Detection Lever
PS4
Delivery Point
F-2-99
2-68

2
Reverse Flapper
SL2
PS6
M4
Reverse Roller
Duplex Reverse Stop Position
25 mm
Duplex feed roller 1
PS8
58 mm
Duplex feed roller 2
Duplex Standby Position
M7
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Reverse/Duplex Assembly
2-69
■Reverse/Duplex Assembly
●Reverse Flapper Operation
The Reverse Flapper behaves in accordance with the Reverse Feed Solenoid (SL2).
• When Reverse Feed Solenoid (SL2) is OFF: Feed to the Delivery Outlet
• When Reverse Feed Solenoid (SL2) is ON: Feed to the Reverse Mouth
F-2-100
●Duplex Reverse Control
Paper is reversed outside the machine using the Reverse Mouth.
The paper is fed to the duplex reverse stop position (it stops at 25mm from the trailing edge
of paper) by using the Reverse Sensor (PS6) as a reference. Then, reverse operation starts.
●Duplex Re-pickup Control
If it is possible to secure necessary paper interval by estimating the paper interval with the
preceding paper when the Duplex Feed Sensor (PS8) is ON, the paper is re-picked up to the
pre-registration.
If the necessary paper interval cannot be secured, the paper stays at the duplex standby
position (58mm downstream from the Duplex Lower Roller). After recalculated standby time
has passed, re-pickup is executed.
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Reverse/Duplex Assembly
2
F-2-102
●Duplex Circulation
The following shows the number of circulating sheets at the 2-sided print.
Length in paper feed direction Number of circulating sheets
320mm or less 3
321mm or more 2
T-2-47
F-2-101
2-69

2
PS6
M4
Reverse Roller
100 mm
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Jam Detection
2-70
■Jam Detection
●List of Jam Codes
A jam code consists of 4 alphanumeric characters.
The upper 2 digits indicate the jam type, and the lower 2 digits indicate the sensor that
detected a jam.
ACC ID Jam Code Type Sensor Name Sensor ID
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
0101 Delay Pre-Registration Sensor PS12
0201 Stationary Pre-Registration Sensor PS12
0A01 Power-on Pre-Registration Sensor PS12
0102 Delay Cassette 2 Retry Sensor (Option) PS103
0202 Stationary Cassette 2 Retry Sensor (Option) PS103
0A02 Power-on Cassette 2 Retry Sensor (Option) PS103
0103 Delay Cassette 3 Retry Sensor (Option) PS203
0203 Stationary Cassette 3 Retry Sensor (Option) PS203
0A03 Power-on Cassette 3 Retry Sensor (Option) PS203
0104 Delay Cassette 4 Retry Sensor (Option) PS303
0204 Stationary Cassette 4 Retry Sensor (Option) PS303
0A04 Power-on Cassette 4 Retry Sensor (Option) PS303
0105 Delay Registration Sensor PS11
0205 Stationary Registration Sensor PS11
0A05 Power-on Registration Sensor PS11
0107 Delay Fixing Paper Sensor PS19
0207 Stationary Fixing Paper Sensor PS19
0A07 Power-on Fixing Paper Sensor PS19
0108 Delay Delivery Sensor PS5
0208 Stationary Delivery Sensor PS5
0A08 Power-on Delivery Sensor PS5
010A Delay Reverse Sensor PS6
020A Stationary Reverse Sensor PS6
0A0A Power-on Reverse Sensor PS6
010B Delay Transparency Sensor PS20
020B Stationary Transparency Sensor PS20
0A0B Power-on Transparency Sensor PS20
010D Delay Duplex Feed Sensor PS8
020D Stationary Duplex Feed Sensor PS8
0A0D Power-on Duplex Feed Sensor PS8
0B00 Door open - 0CA0 Sequence jam*2- 0CF1 Error
0D91 Size Error - 9901 Sequence jam*2- 9902 Sequence jam*2- -
*1
- -
ACC ID Jam Code Type Sensor Name Sensor ID
3
3
3
3
3
*1: The state is recovered by opening and closing the Door, or turning OFF and then ON the
power supply.
If the same jam is detected regardless of the operation above, the error code is displayed.
*2: The state is recovered by opening and closing the Door, or turning OFF and then ON the
power supply.
9903 Sequence jam*2- 9904 Sequence jam*2- 9905 Sequence jam*2- 9906 Sequence jam*2- 9907 Sequence jam*2- -
T-2-48
●Forcible Paper Feed Control
If the Finisher is installed when a jam occurs at the Reverse Assembly, jammed papers are
forcibly fed because they cannot be seen. If the Reverse Paper Sensor (PS6) is ON, the
Reverse Motor (M4) is driven for 100mm when opening/closing the door.
F-2-103
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Controls > Jam Detection
2
2-70

2
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Work of Service > Periodically Servicing
Work of Service
■Periodical ServicePeriodical Service
None
■Consumables
No. Item Parts No. Q'ty Life Remarks
1 Multi-purpose Tray Pickup Roller FL2-3897 1 150,000 sheets
2 Multi-purpose Tray Separation Pad FL3-4890 1 150,000 sheets
3 Cassette Pickup Roller FB6-3405 1 500,000 sheets Same as estimated
4 Cassette Feed Roller FC6-7083 1 80,000 sheets Replace with Cassette
5 Cassette Separation Roller FC6-6661 1 80,000 sheets Replace with Cassette
■Periodically Servicing
None
product life.
Separation Roller.
Feed Roller.
2-71
T-2-49
Technical Explanation > Pickup Feed System > Work of Service > Periodically Servicing
2
2-71

2
FM2
Technical Explanation > External Auxiliary System > Controls > Fan
2-72
External Auxiliary System
Controls
■Software counter
Count-up timing differs depending on the following conditions:
• Print mode (1-sided/2nd side of 2-sided print, 1st side of 2-sided print)
• Differs depending on the delivery position (Staple Finisher)
Print mode
Delivery position
Host machine Delivery Tray Delivery Sensor (PS5) Duplex Feed Sensor (PS8)
Staple Finisher Delivery Sensor (S2)
1-sided print/2nd side of
2-sided print
Count-up timing
1st side of 2-sided print
T-2-50
■Fan
●Overview
Location of Fans
FM6
FM1
FM5
FM4
FM8
FM7
No. Name Function Error codes
Delivery Cooling Fan (Rear) To cool the Delivery Assembly E822-0004,E822-0005
FAN1
Delivery Cooling Fan (Center) To cool the Delivery Assembly E822-0002,E822-0003
FAN
2
Delivery Cooling Fan (Front) To cool the Delivery Assembly E822-0000,E822-0001
FAN3
Power Supply Cooling Fan To cool power supply E804-0000,E804-0001
FAN4
Heat Exhaust Fan (Front) To exhaust heat in the machine E805-0002,E805-0003
FAN5
Heat Exhaust Fan (Rear) To exhaust heat in the machine E805-0000,E805-0001
FAN6
Developing Cooling Fan (Front) To cool the Developing
FAN7
Developing Cooling Fan (Rear) To cool the Developing
FAN8
Assembly and laser
Assembly and laser
FM3
F-2-104
E820-0000,E820-0001
E820-0002,E820-0003
T-2-51
Technical Explanation > External Auxiliary System > Controls > Fan
2
2-72
 Loading...
Loading...